EDITORIAL
Published on 23 Feb 2021
Editorial: Bacteriophages Isolation From the Environment and Their Antimicrobial Therapeutic Potential
doi 10.3389/fmicb.2021.649334
- 5,091 views
- 2 citations
33k
Total downloads
201k
Total views and downloads
EDITORIAL
Published on 23 Feb 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Jul 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Jul 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 24 Jun 2020

METHODS
Published on 05 Jun 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 03 Jun 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 13 May 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 May 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 08 Apr 2020

ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 17 Mar 2020
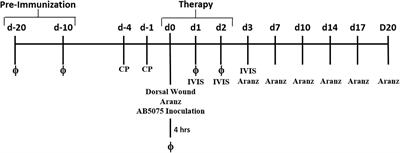
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 06 Mar 2020
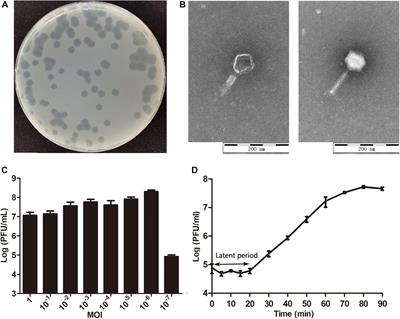
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Published on 21 Feb 2020
