Health
01 Jun 2017
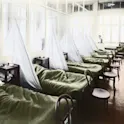
Pale Rider: the Spanish flu of 1918 and how it changed the world
This new book narrates a catastrophe that changed humanity for decades to come — and yet, is largely accounted as a footnote to World War I

Health
01 Jun 2017
This new book narrates a catastrophe that changed humanity for decades to come — and yet, is largely accounted as a footnote to World War I

Life sciences
30 Nov 2016
Predators eavesdrop on insect-plant interactions, while plants backstab the insects they attract, recent research shows

Life sciences
05 Oct 2016
A type of bacteria, which can cause diarrhea and inhibit growth in children in developing countries, is highly prevalent in a sample of children in an industrialized country.

Health
14 May 2016
What is Zika, what are its symptoms and how can you protect yourself? An infographic by Emily Maynard | Mphonline.org

Life sciences
27 Apr 2016
By Fernando Bolaños, Frontiers science writer The constant emergence of viral outbreaks has become a permanent threat to human health. Last year, Zika virus infected thousands of people in the Americas. It is also associated to several cases of neurological disorders and has raised worldwide public health alerts. Now due to the urgency, researchers are detailing the characteristics of the virus to find solutions. The study completed by a group of researchers from the Department of Biotechnology of the Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Tecnología Agraria y Alimentaria in Madrid, was published in the open-access journal Frontiers in Microbiology. It reveals the challenges humanity could face because of the increasingly frequent and devastating viral outbreaks. “Zika is spread by mosquitoes Aedes Ae. Aegypti, and Ae. Albopictus. They are considered the most invasive species in the world due to their adaptability to different climates. This has facilitated the rapid spread of the virus to five continents during the last 30 to 40 years. The virus was first detected in 1947 in Nigeria, but because it had a low affect on people´s health, not much was done until the recent huge outbreaks in the Americas,” explains researcher Juan Carlos Saiz. We already […]

Health
23 Feb 2016
This month’s Frontiers Staff Pick comes from Victor Kouassi. Victor is a Journal Operations Assistant and before joining us at Frontiers, was at the Francis Crick Institute in London where he conducted research on the immune responses of malaria. With his background in this field, he found the article “Major Histocompatibility Complex and Malaria: Focus on Plasmodium vivax Infection” interesting. It was published in Frontiers in Immunology late January 2016. Below is why he selected this article as his staff pick: There are over 100 species of Plasmodium, the parasite that causes malaria. These can infect many kinds of animals from monkeys, birds to lizards. This parasite has evolved an intricate life cycle by taking advantage of an invertebrate vector, the mosquito. A vertebrate host, like a human, is usually infected through a bite which transmits the parasite which goes straight to the liver. The parasite then divides into merozoites which are released into the blood. It is this form of the parasite that causes the symptoms of disease by entering red blood cells and eventually causing them to explode resulting in fevers, chills, headaches and, in worst case scenarios, coma, brain damage and miscarriages. Of the five species of Plasmodium that […]

Health
01 Dec 2015
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) causes HIV infection, which can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Since AIDS was clinically first observed in the USA in 1981, HIV infection has become one of the most important global health issues in the world. Held on 1st December annually since 1988, World AIDS Day gives people an opportunity to show support for people living with HIV and acknowledge those who have died. To support the global goal to stop the transmission of HIV, it is also a day to raise awareness about the prevention and control of AIDS. Although HIV infection was first detected in 1981, with the disease it causes being named AIDS in 1983 and the virus itself HIV in 1984, it is important to note that AIDS did not originate in 1981. There are two viruses associated with AIDS: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-2 is less pathogenic than HIV-1 and is mostly restricted to West Africa. HIV-2 is structurally similar to a simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) strain, SIVsm, which infects the sooty mangabey monkey. It is hypothesized that SIV crossed the species barrier to humans when contaminated animal blood entered cuts on the hands of people who were in […]

Health
25 May 2015
There are 200 million cases of malaria each year and 500,000 deaths, mostly among children under 5. Bednets, insecticides, and medication all help to control the disease, but complete eradication is a long way off.
Get the latest research updates, subscribe to our newsletter