- 1Biomedical Sciences Department, College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, United States
- 2Department of Clinical Sciences, Ross University School of Veterinary Medicine, Basseterre, Saint Kitts and Nevis
- 3Laboratory of Ultrastructure and Tissue Biology, Anatomy Department, Biology Institute, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
- 4Department of Biomedical Sciences, Ross University School of Veterinary Medicine, Basseterre, Saint Kitts and Nevis
Diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disease in humans and cats. Cats share several features of human type-2 diabetes and can be considered an animal model for this disease. In the last decade, sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have been used successfully as a class of hypoglycemic drug that inhibits the reabsorption of glucose from the renal proximal tubules, consequently managing hyperglycemia through glycosuria. Furthermore, SGLT2i have been shown to have cardiac, renal, and other protective effects in diabetic humans acting as a pleiotropic drug. Currently, at least six SGLT2i are approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in humans with type-2 diabetes, and recently, two drugs were approved for use in diabetic cats. This narrative review focuses on the use of SGLT2i to treat diabetes mellitus in humans and cats. We summarize the human data that support the use of SGLT2i in controlling type-2 diabetes and protecting against cardiovascular and renal damage. We also review the available literature regarding other benefits of these drugs in humans as well as the effects of SGLT2i in cats. Adverse effects related to the use of these hypoglycemic drugs are also discussed.
1 Introduction
Glucose is an important energy source for cells and a substrate for many biochemical reactions. As a lipophobic substance, glucose cannot cross the membrane lipid bilayer to enter the cells throughout the body. Integral proteins located in the membrane of every cell called glucose transporters are responsible for glucose transport across the membrane. Glucose can be transported into the cell using facilitated diffusion (passive transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration with the help of a carrier protein) or using co-transport (active transport of two molecules in the same direction with the help of a transport protein called symporter). Symporters rely on the ion moving down the electrochemical gradient (e.g., sodium) to allow the other molecule to move against the concentration gradient (e.g., glucose) (Figures 1A,B).
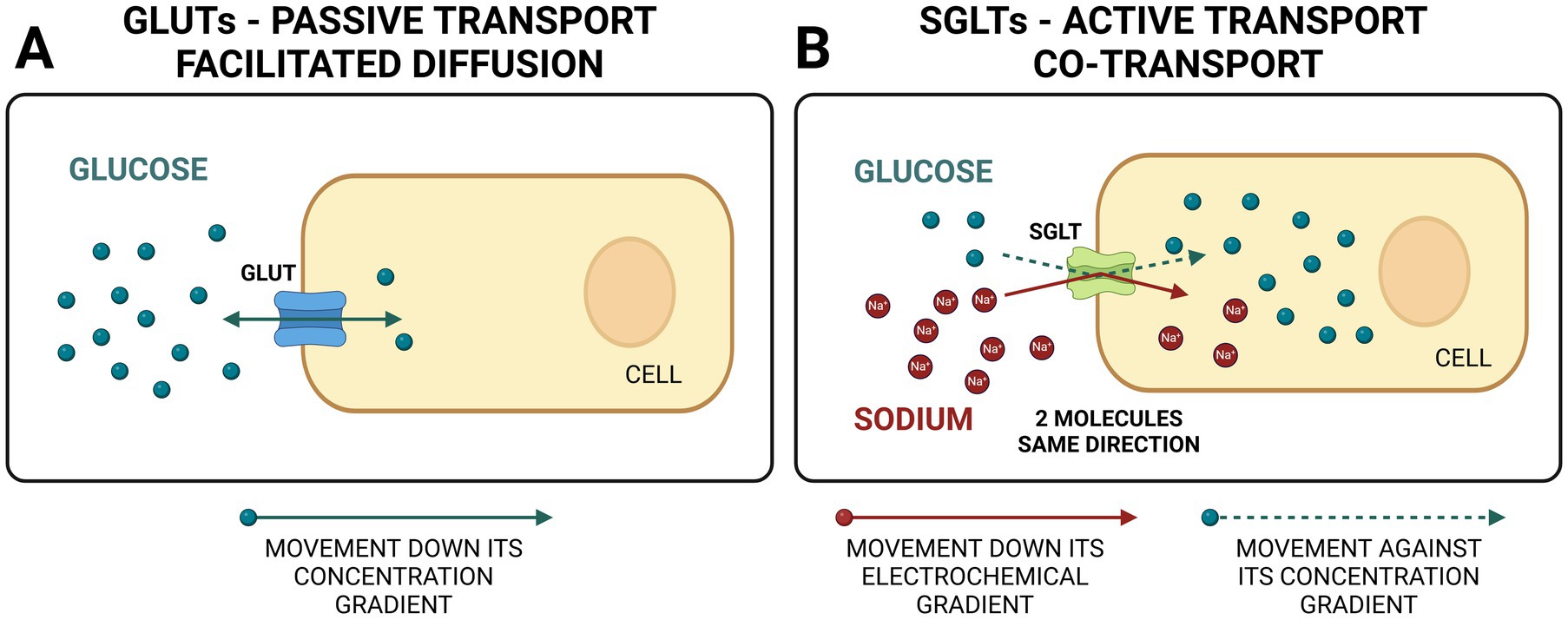
Figure 1. Comparison between GLUTs (glucose transporter facilitators) and SGLTs (sodium-glucose co-transporters). GLUTs use facilitated diffusion (passive transport) for bidirectional glucose transport. SGLTs use active transport to move two molecules in the same direction, one down and one against concentration gradient (co-transport). Created in BioRender. Ciambarella, B. (2025) https://BioRender.com/v21n984.
There are two main types of glucose transporters in the body. The first type is called GLUT (glucose transporter), and they use facilitated diffusion. GLUT proteins are encoded by the SLC2 genes and are members of the major facilitator superfamily of membrane transporters (Figure 1A). They are numbered according to their order of discovery. Currently, 14 GLUT proteins are expressed in humans and categorized into three classes based on sequence similarity: Class I (GLUTs 1–4, 14), Class II (GLUTs 5, 7, 9, and 11), and Class III (GLUTs 6,8,10,12 and 13 [H+ myo-inositol transporter or HMIT]). The second type is called SGLT (sodium-glucose linked transporter or sodium-glucose co-transporter) and relies on co-transport (1) (Figure 1B). SGLTs belong to the mammalian solute carrier family SLC5. This family includes 12 different members in humans that mediate the transport of sugars, vitamins, amino acids, or smaller organic ions such as choline. The SLC5 family belongs to the sodium symporter family (SSS), which encompasses transporters from all kingdoms of life. A summary of the main types of SGLTs present in the human body is presented in Table 1. Two SGLTs (1 and 2) are the most important ones affecting glucose transport in the kidneys (2–5).
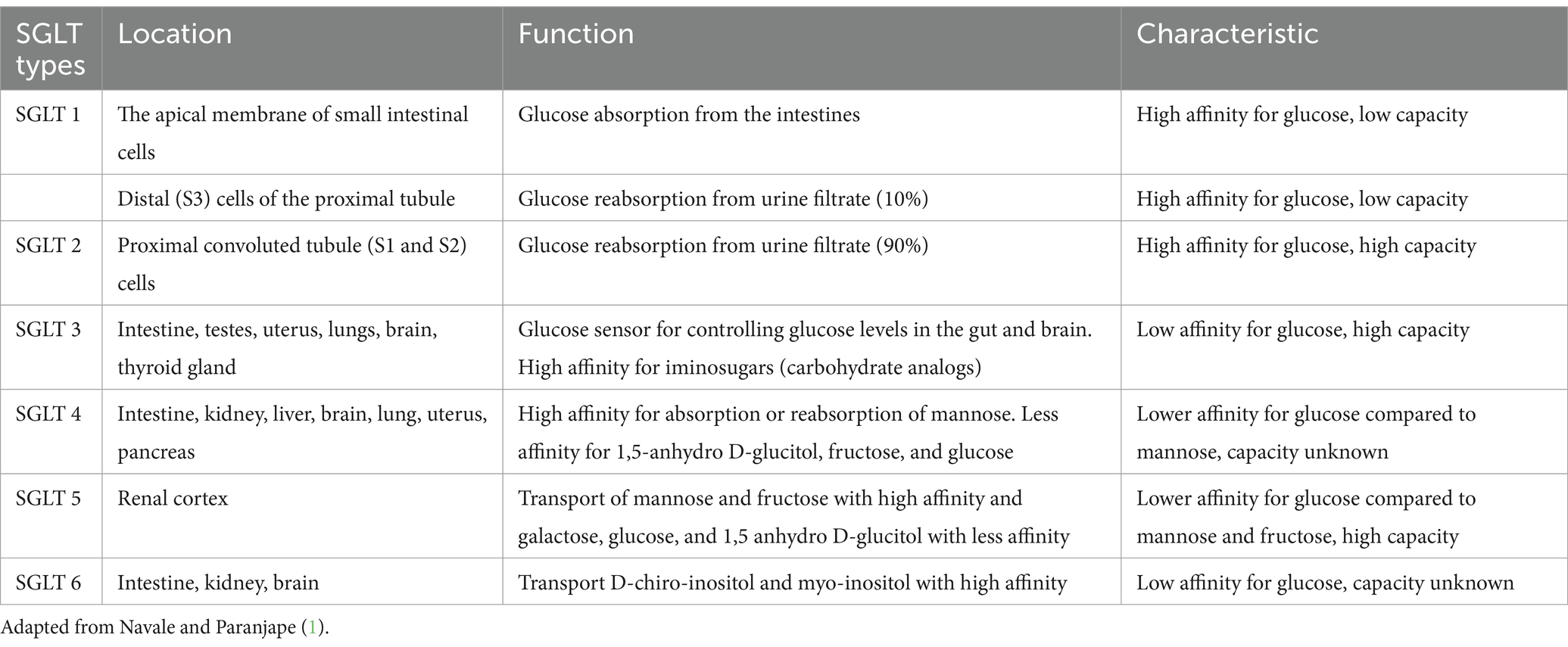
Table 1. Types, location, function, and characteristics of major sodium-glucose transporters (SGLT).
In the kidney, glucose is freely filtered from the blood at the glomerulus. To avoid losing significant amounts of the main body’s fuel into the urine, glucose reabsorption occurs in the renal tubules. Both SGLTs type 1 and 2 are proteins in the luminal border of the epithelial cells of the proximal convoluted tubules, reclaiming glucose from the kidney filtrate and returning it to the blood (Figure 2). Filtered glucose first encounters SGLT2 in the initial segment of the proximal renal tubules, where it co-transports one sodium ion with one molecule of glucose across the membrane (1, 6). Previously thought to be located in the early S1/S2 segment, new refined techniques have suggested that SGLT2 is solely located in the S1 segment of the proximal renal tubules, at least in rats (7). The SGLT2 is a high-capacity, low-affinity glucose transporter responsible for 90 percent of the total glucose absorption in the kidney (Figure 2). The SGLT1 is found in a later segment of the proximal tubule (S2 and S3), transporting one molecule of glucose or galactose with two sodium ions across the membrane (1, 6). SGLT1 is a lower-capacity, high-affinity transporter that accounts for 10% of glucose reabsorption (Figure 2). Because of their role in glucose reabsorption, SGLTs became a drug target for glycemic control.
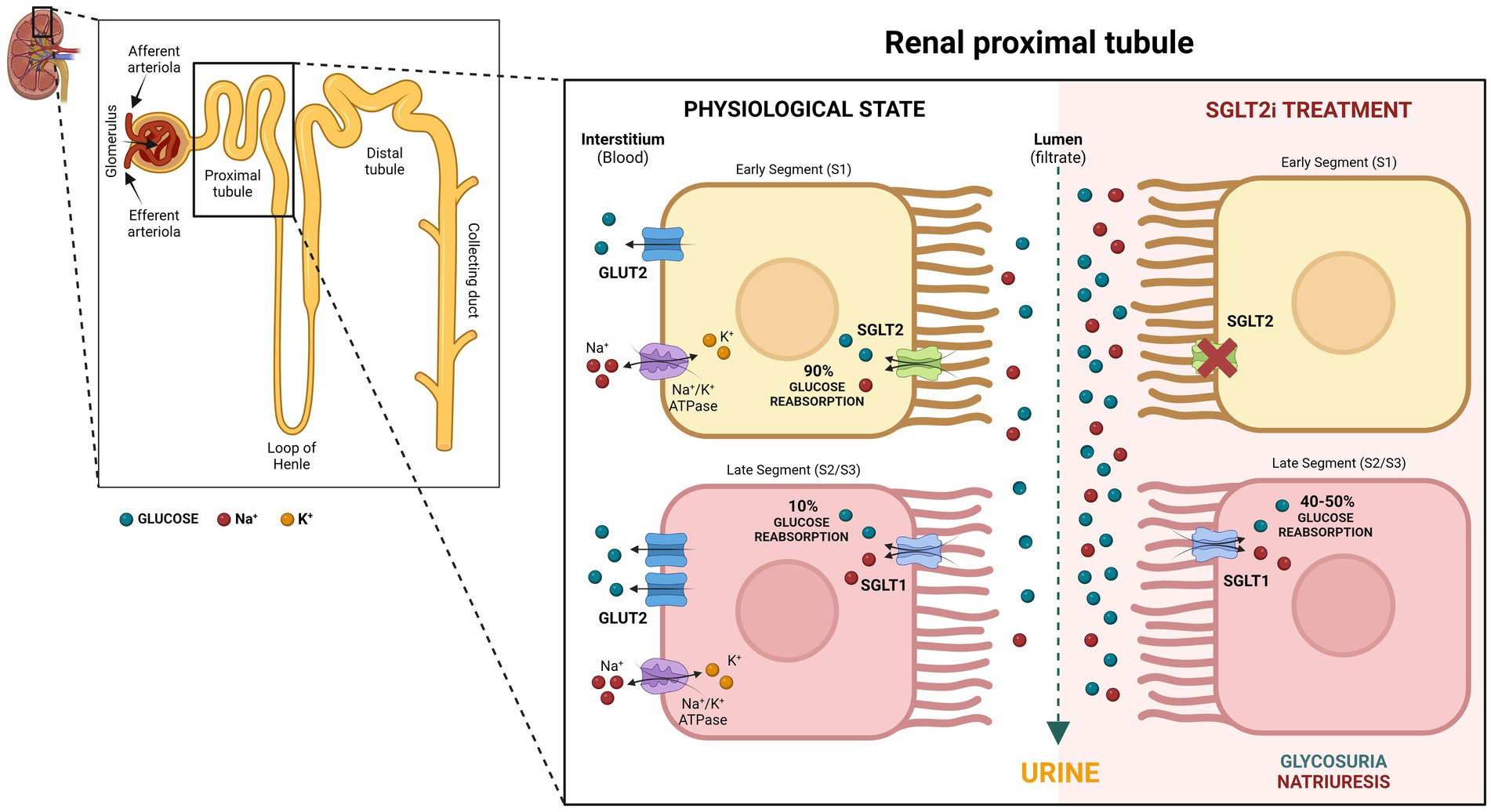
Figure 2. Role of SGLT2 and SGLT1 in glucose re-absorption within the proximal renal tubules with and without SGLT2 inhibition. Created in BioRender. Uerj, L. (2025) https://BioRender.com/v55m360.
This narrative review focuses on a recent Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved class of hypoglycemic drugs known as SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) to treat diabetes mellitus (DM) in cats. We summarize the human data that supports the use of SGLT2i in controlling human type-2 DM and protecting against the worsening of certain DM comorbidities. We also review the available literature regarding the effects of SGLT2i on cats.
2 Search strategy
One author (ABV) searched PubMed and Google Scholar for “SGLT inhibitors and diabetes mellitus,” “SGLT inhibitors and heart,” “SGLT inhibitors and kidney,” and “SGLT inhibitors and cognitive impairment.” Several combinations including the terms, “humans,” “cats,” “veterinary,” “SGLT1,” “SGLT2,” “review,” “cardioprotection,” “renal protection,” and “neuroprotection” were used to identify relevant publications up to June 2024. Manual scoping of results focused on original research articles, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and narrative reviews. The eligibility criteria included: all relevant literature on SGLTi in humans and cats, relevant supporting literature regarding the physiology of SGLTs and pharmacology of SGLT2i, peer-reviewed articles written in English, and full-text articles.
3 SGLTs as pharmacological targets
The first known substance with SGLT inhibitory activity, Phlorizin, is a glycoside phytocompound isolated from the root bark of an apple tree in 1835 (8). Phlorizin showed high affinity, specificity, and competitive inhibition capacity for SGLT1 and SGLT2 (9, 10). Since then, several phlorizin analogs (gliflozins) with different potency and selectivity against SGLT1 and SGLT2 have been developed and approved for human use worldwide.
Canagliflozin was the first SGLT2i approved in the United States (March 2013) for use in human adults with type 2 diabetes. Canagliflozin has 400-fold higher inhibitory activity for SGLT2 over SGLT1 (11). Currently, at least six high-potency gliflozins are approved for use in humans in the United States (Table 2). Recently, the FDA approved two gliflozins for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in cats: velagliflozin in December 2022 (Bexacat®; Elanco) and velagliflozin (12) in July 2023 (Senvelgo®; Boehringer Ingelheim) both with high affinity for SGLT2 inhibition. FDA-approved gliflozins for humans and cats are summarized in Table 2.
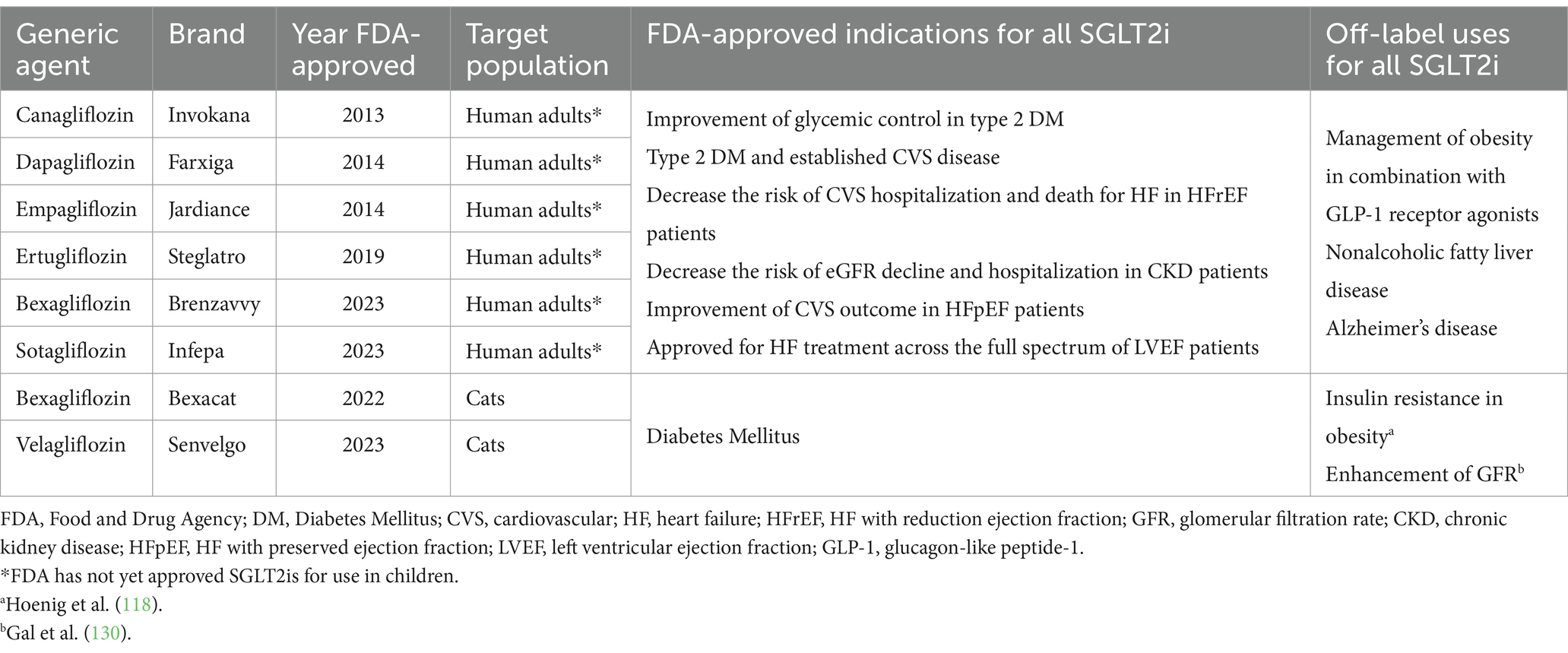
Table 2. Approved high-potency sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) for use in humans and cats in the United States.
The initial rationale behind gliflozins’ development was to manage hyperglycemia by inhibiting the glucose uptake from the proximal renal tubule, thereby allowing the kidneys to dispose of excess blood glucose in the urine (Figure 1). However, after years of clinical studies, there is strong evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors are more than hypoglycemic agents and act as pleiotropic drugs with significant metabolic, cardiovascular, renal, and possibly neuroprotective benefits in humans (13–18).
4 SGLT2i treatment in humans with DM and possible mechanism of action
Gliflozins act to improve diabetic hyperglycemia by inhibiting SGLT2, which is responsible for 90% of the glucose filtered at the glomerulus (19). However, physiological changes that occur in response to SGLT2i increase the resorptive capacity of SGLT1 and maintain filtered glucose reabsorption at around 50% (20) (Figure 2). This compensatory reabsorption may reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, which is a rare event in human patients using SGLT2i (21).
Soon after the inhibition of SGLT2, glycosuria will appear, and consequently, blood glucose concentration will decrease independent of insulin. An improvement in beta cell function is expected because of the reduction of glucotoxicity (22). Moreover, improvements in skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity, positively correlated with the improvement in daily plasma glucose fluctuations, were reported, possibly secondary to the improvement in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (23). Interestingly, the glucose-lowering effect of SGLT2i in humans is considered modest and probably insufficient to account for all clinical benefits demonstrated in patients using these drugs so far (15). The fall in glucose levels is less than might be expected because glucagon levels increase, contributing to an increase in hepatic glucose production (22). Chronic treatment with SGLT2i also increases lipolysis and a shift to fat oxidation, which results in weight loss. Nonetheless, this effect is presumably counteracted by the compensatory increase in food intake, and the weight loss is usually considered mild. Additionally, with time, glucose oxidation decreases, and lipid oxidation increases without affecting protein oxidation. These changes occur probably because of the low-glucose, low-insulin, and high-glucagon state and maintain energy balance in the long term (Figure 3) (22).
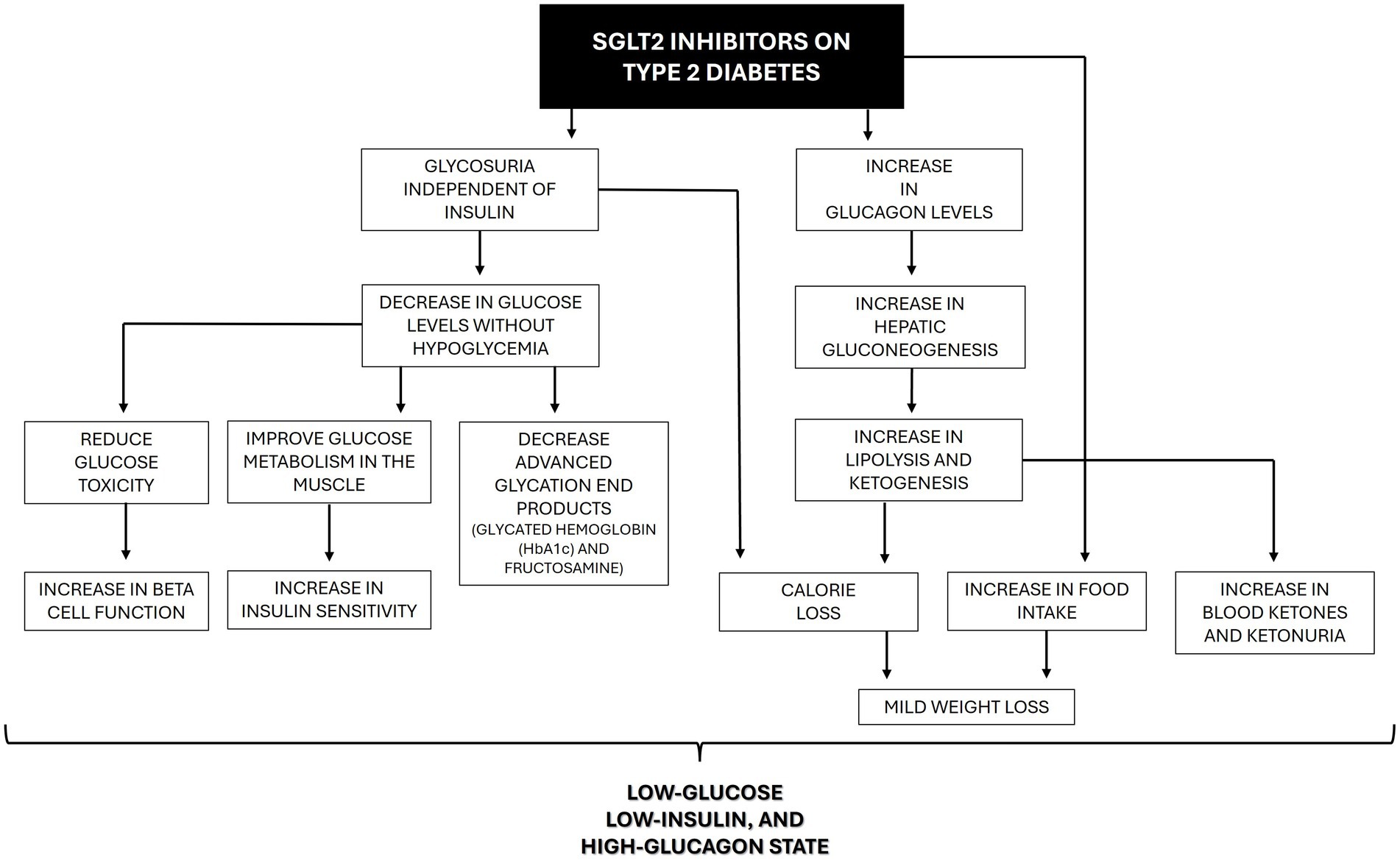
Figure 3. Beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes in humans.
Many of the benefits that are now recognized were not anticipated when SGLT2i was initially developed. Through different mechanisms, some still unknown, gliflozins produce a cascade of physiological benefits in major organ systems usually affected by DM (Figure 4).
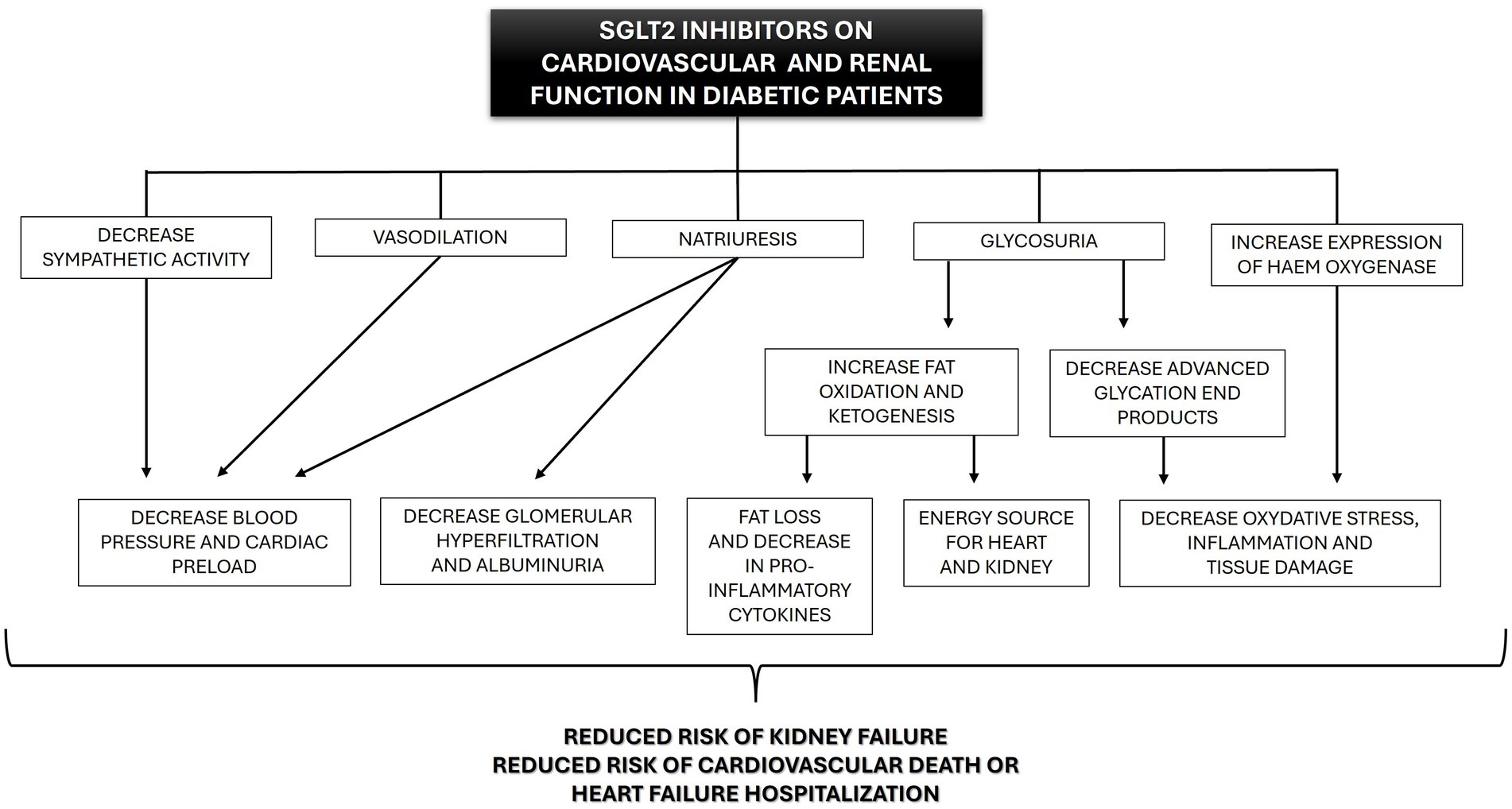
Figure 4. Beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) on cardiovascular and renal function in diabetic human patients.
In addition to the hypoglycemic effect, gliflozins act as proximal and osmotic diuretics, inducing natriuresis (21). This effect comes from the reduced activity of Na+/H+ exchanger 3 (NHE3), which, in normal conditions, reabsorbs 30% of the sodium in the proximal tubule. NHE3 is closely regulated by glucose metabolism and SGLT transporters, which makes it sensitive to SGLT2i (24). In diabetic patients, NHE3 activity is enhanced (hyper-reabsorption) and contributes to the decreased sodium availability at the macula densa, afferent arteriole vasodilation, increased intraglomerular pressure, and associated hyperfiltration (21). This glomerular hyperfiltration eventually leads to fibrosis within the glomerulus and tubulointerstitium and to proteinuria (25, 26). Under the action of SGLT2i, the unabsorbed sodium will be delivered to the macula densa cells in the distal nephron, normalizing afferent arteriole tone, intraglomerular pressure, and glomerular filtration, which probably decreases protein filtration and tubulointerstitial damage (21, 27, 28). In addition, previous research showed that natriuresis is likely responsible for the decrease in total sodium retention (21), tissue sodium content (29), and the reduced interstitial volume relative to blood volume (30). These effects may ameliorate fluid congestion with less impact on tissue perfusion compared to other diuretics (15). Furthermore, SGLT2i have electrolyte-sparing advantages compared to classical diuretics (thiazides and loop diuretics). Although the pathophysiological mechanisms remain poorly understood, in general, potassium, magnesium and sodium levels seem to be unaffected by SGLT2i treatment (31–34). These properties may provide greater flexibility regarding dose optimization for renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition drugs and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, which can be limited by hyperkalemia, particularly with kidney function decline (35).
Gliflozins also seem to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Antioxidant effects were related to the increased expression and activity of haem oxygenase, an enzyme involved not only in the degradation of haem but also in reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and thrombosis (36–39). The anti-inflammatory effects of SGLT2i might be the result of combined actions. First, SGLT2i reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6 and IL-8 (40–42). Second, these drugs increase β-oxidation of free fatty acids, increasing ketone production, especially in diabetic patients (43–45). Last, the ketone β-hydroxybutyrate can suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine release (e.g., IL1β and IL-18) by blocking the murine and human NLPR3 (NLR family pyrin domain containing 3), a protein expressed predominantly in macrophages and as a component of the inflammasome. Activated NLRP3 would trigger an immune response (46). Furthermore, patients using canagliflozin for over 2 years showed reduced levels of markers and mediators of fibrosis compared to patients receiving glimepiride (47). It is unclear if this anti-fibrotic action is mediated by antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms or independent anti-fibrotic mechanisms (48).
In addition to the above mechanisms, SGLT2i may reduce sympathetic hyperactivity (49–51), which is a common finding in patients with diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease, and can lead to vasoconstriction and increased risk of fatal arrhythmias (52, 53).
Finally, treatment with gliflozins also seems to induce vasodilation and reduce vascular resistance in animal models, probably secondary to an increase in the bioavailability of nitric oxide (54, 55). The effects induced by nitric oxide likely add to the vascular benefits of sympathetic inhibition and together could contribute to the favorable cardiac reverse remodeling (e.g., reduction in ventricular mass) reported with SGLT2i use (56).
5 Cardiovascular protective effects of SGLT2i in humans
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in people with DM. Currently, the FDA recommends cardiovascular (CV) outcomes trials (CVOTs) for all new hypoglycemic drugs to monitor the safety of these agents in people with either established CVD or at higher risk of development of CVD. Furthermore, clinical guidelines are frequently based on CVOTs results (57, 58). Some of the most convincing data about CV protective effects of SGLT2i came from early CVOTs using canagliflozin and empagliflozin (59, 60). These data showed that SGLT2i could reduce the risk of cardiovascular events (e.g., hospitalization for heart failure and cardiovascular death) in diabetic patients with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (60). Subsequent trials in patients with heart failure and reduced or preserved left ventricular ejection fraction demonstrated that SGLT2i also has beneficial effects on heart failure outcomes (15). At present, both the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2024 updates recommend the use of SGLT2i (dapagliflozin and empagliflozin) for patients with heart failure with or without diabetes mellitus (57, 58).
6 Renal protective effects of SGLT2i in humans
Diabetic nephropathy is a major complication of DM in humans, which results in chronic kidney disease (CKD) (61, 62). Humans with DM are 10 times more likely to develop end-stage kidney failure, and 40% of diabetic patients might develop the final stage of this disease (63). The nephroprotective effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in humans are well established and have been tested in randomized controlled trials in nearly 100,000 human adults (64). Research trials using empa-, cana- and dapagliflozin showed impressive results in renal outcomes for patients with DM (59, 60, 65). SGLT2i reduces the risk of kidney disease progression in people with or without diabetes and the risk of acute kidney injury. Furthermore, since SGLT2i do not affect serum potassium levels, there is a reduced risk of hyperkalemia compared to other drugs commonly used in diabetic nephropathy (e.g., angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) (18). Because SGLT2i significantly reduces or normalizes the glomerular hyperfiltration seen in diabetic patients, there is probably a decrease in the physical stress placed on glomerular capillaries. By decreasing the glomerular filtration of tubulo-toxic factors (e.g., albumin and advanced glycation end products), there is a decrease in hypoxia, oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis, and progression of CKD (66). Currently, empagliflozin and dapagliflozin are approved for the treatment of CKD with or without diabetes mellitus in human adults. No research or approval exists for the use of gliflozins in children with CKD (64).
7 Other benefits of SGLT2i treatment (blood pressure, weight loss, hepatic lipidosis, neuroprotection)
The benefits of SGLT2 in humans go beyond the hypoglycemic effect and cardiovascular and renal protection. Gliflozins can modestly decrease systolic and diastolic blood pressure without significantly increasing the risk of hypotensive episodes (67). Additionally, the glycosuric effect of SGLT2i results in calorie loss (elimination of 60–80 g of glucose per day in the urine), which consequently induces mild weight loss from the first weeks of treatment, which could be maintained for up to 4 years (19, 68–75). Furthermore, treatment with SGLT2 improves liver outcomes in people with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (43, 76–82). Moreover, since SGLT2i still have some affinity for SGLT1 receptors in the brain and can cross the blood–brain barrier, they have been studied for neuroprotective effects (83–85). Gliflozins demonstrate anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in the nervous system and inhibit acetylcholinesterase, which could contribute to cognitive improvement (16, 86).
8 Ketoacidosis, urogenital infection, and SGLT2i treatment in humans
Placebo-controlled trials and real-world cohort studies using gliflozins have reported favorable adverse effect profiles of these drugs in humans (15, 17, 87). Nevertheless, there is up to 0.3% increase in the risk of ketoacidosis development in people with diabetes using SGLT2i (18, 88). Although ketoacidosis is usually associated with hyperglycemia, glucose levels can be normal or modestly elevated in affected patients treated with SGLT2i, so-called euglycemic ketoacidosis (89, 90). The mechanisms by which gliflozins slightly increase the risk of DKA are probably related to reduced insulin secretion or increased insulin resistance and stimulation of glucagon secretion, increasing ketone body synthesis (91). In human medicine, this increased risk is mitigated by using several strategies, including withholding the agent when unwell and stopping therapy 3 days before any procedure that requires fasting, bowel preparation, or hospital admission (90).
No increased risk of urinary tract infection has been reported in SGLT2 trials (92). On the other hand, humans with DM receiving therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors were associated with 2.3–6.4% increased risk of genital mycotic infections in major clinical trials (93–95). Studies reporting the same risk in people without DM who received SGLT2i have had conflicting results (96–99).
9 Current knowledge about SGLT2i treatment in cats with DM
Until recently, diabetic cats were primarily treated with insulin injections and a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet (100, 101). Although insulin is an effective treatment, it requires daily injections and personal commitments, which can impact the daily routine and quality of life of owners and cats (102–105). Several oral hypoglycemic drugs have been evaluated in healthy, experimentally hyperglycemic, obese, and diabetic cats in the past (106–111). Overall, only sulfonylurea glipizide is an acceptable treatment option in some cats (112, 113). Because of its mechanism of action stimulating insulin and amylin production, sulfonylureas can increase pancreatic amyloidosis and lead to beta-cell destruction (114–116). While both insulin and glipizide can induce hypoglycemia in cats, SGLT2i demonstrate an overall lower risk of hypoglycemia in humans when compared to other drugs (117).
In the last few years, studies have emerged highlighting the utility of SGLT2i in the treatment of feline DM. One study evaluated for the first time the effect of velagliflozin in obese cats (118). Placebo or velagliflozin (1 m/kg, PO, q24 h) was administered to two groups of six neutered obese cats matched by gender for 35 days. Authors documented an increase in urinary glucose excretion and suggested that velagliflozin could be beneficial for the treatment of diabetic cats (118). Using 252 newly diagnosed and insulin-treated cats, another study evaluated the effect of velagliflozin once daily as a standing-alone therapy compared to insulin injection therapy (119). Cats were administered velagliflozin (1 mg/kg, PO, q24 h) regardless of blood glucose level, and evaluated on days 2 or 3, and days 7 and 30 and then monthly. Of the 252 cats enrolled, only 198 were evaluated. From this population, 175 (88.4%) were considered a treatment success on day 30 based on improved glycemic control and clinical signs. The most common adverse effects were diarrhea and vomiting, and the most serious adverse event was DKA, which occurred in 5% of the naïve diabetic cats and 18% of cats previously treated with insulin (119).
Recently, a prospective, randomized, positive controlled, open-label, noninferiority field trial using client-owned diabetic cats (127 safety and 116 efficacy assessment) was published (120). Authors compared velagliflozin (1 mg/kg PO, q24 h) with porcine lent insulin (titrated Caninsulin, q12 h) and concluded that velagliflozin treatment was non-inferior to Caninsulin injections, and cats showed good quality of life and glycemic control without developing clinical hypoglycemia (120). Although porcine lent insulin can be used for cats, the author’s choice of insulin in cats is studies comparing SGLT2i and basal insulins like glargine will.
A second SGLT2i, called bexagliflozin, induced maximal renal glucose excretion at a dose of 15 mg/cat, PO, q24 h during pre-clinical research, according to the manufacturer (121). Not many studies have investigated this drug in cats so far (122, 123). One study evaluated the effect of bexagliflozin associated with insulin in five client-owned cats with poorly controlled DM (122). Cats were treated with bexagliflozin for 4 weeks, and all of them had a significant reduction in insulin dose requirement, and insulin was discontinued in two cats. Moreover, there was a significant decrease in blood glucose concentration obtained from blood glucose curves. No cats had any documented hypoglycemic episode, and adverse effects were considered mild (122). Another clinical trial evaluated the safety and effectiveness of bexagliflozin (15 mg/cat, PO, q24 h) as a monotherapy for newly diagnosed diabetic cats (123). In an open-label, historically controlled prospective clinical trial, authors evaluated the effect of bexagliflozin (15 mg/cat, PO, q24 h) in client-owned cats. Of the 84 cats enrolled, only 81 were evaluated on day 56. Eighty-four percent of these cats were considered treatment successes based on improvements in glycemic control and clinical signs. Commonly observed adverse events included emesis, diarrhea, anorexia, lethargy, and dehydration. The most important adverse event recorded was euglycemic DKA, diagnosed in three cats (3.6%) and presumed present in a fourth (123).
While the results of SGLT2i use in cats are promising, studies have not been conducted as independent clinical trials. Additionally, long-term oral medication can be challenging for some cats, even if it is taken once daily, and SGLT2i treatment could require the same life-long commitment as insulin usually does. Furthermore, bexagliflozin and velagliflozin are unavailable worldwide and may be cost-prohibitive for some cat owners. The dose recommendation is once daily, but not all diabetic cats are candidates for this monotherapy. The suggested criteria for use in newly diabetic cats can be found elsewhere (124, 125). When this review was published at the beginning of 2025, veterinary bexagliflozin was priced at around $ 120, and velagliflozin at around $ 280 per month per cat in the USA. For comparison, a bottle of human bexagliflozin (Brenzavvy®, 20 mg/30 tablets) is currently priced around $50, and a bottle of 10 mL of porcine lent insulin (Caninsulin®/Vetsulin®, Merck) costs around $70, which, according to the manufacturer, should be discarded after 42 days. Also, a 3 mL pen of glargine insulin costs around $100 and, in the author’s (ABV) experience, can be used safely for up to 3 months if stored in the fridge, considering that most cats receive 1–3 U/BID/daily.
Studies in diabetic cats using human SGLT2i, like dapagliflozin, are needed. This drug, for example, is one of the most popular in human medicine. The same brand (Farxiga® 10 mg/30 tablets) is widely available at lower costs in countries like Brazil ($38), Australia ($43), Canada ($76), and the United Kingdom ($90). Finally, SGLT2i treatment is compatible with most other glucose-lowering agents (126), and used in human patients with a wide range of comorbidities, but currently, its use in diabetic cats with concurrent illnesses is discouraged (124, 125).
10 Future perspectives for the use of SGLT2i in cats with other diseases
As in humans, cats commonly develop CV disease, CKD, obesity, hepatic lipidosis, and cognitive impairment as they age. Most of these diseases share similarities with human conditions, and some, like DM and cognitive dysfunction syndrome, were already considered a natural animal model for human studies (127–129). Currently, there is very limited knowledge regarding the effects of SGLT2i on other feline diseases.
A study evaluated the effect of velagliflozin (1 mg/kg/PO, q 24 h, for 35 days) or placebo in two groups of six neutered adult obese cats (118). Different parameters were evaluated before and after treatment. Significant changes after treatment with velagliflozin included a decrease in respiratory exchange ratio, an increase in cholesterol, a small increase in albumin, and a rise in beta-hydroxybutyrate and nonesterified fatty acids. Less insulin was secreted during an intravenous glucose tolerance test, suggesting improved insulin sensitivity. Treatment did not affect the intravenous insulin tolerance test, glucagon, leptin, or adiponectin. Water intake, urine output, urinary glucose excretion, and the glucose/creatinine ratio but not urinary electrolytes were significantly higher post-treatment (118). Currently, there are no studies regarding the long-term effects of SGLT2is in obese cats with or without DM.
A randomized 2-way controlled crossover study investigated the effect of dapagliflozin on glomerular filtration rate in eight adult castrated male healthy cats (130). Cats received or not 10 mg of SGLT2i per day for 5 days in each of the four trial periods, with washout periods of 7 days in between. Urine and blood were sampled on the first and fifth day of each trial to analyze serum urea, creatinine, symmetric dimethylarginine, and 24-h sodium and chloride urinary excretion. Glomerular filtration rate was accessed using iohexol clearance on the fifth day of each trial. Compared to controls, healthy cats treated with dapagliflozin significantly increased mean glomerular filtration rate. No significant changes were seen for other parameters. Authors believed that dapagliflozin-mediated delivery of sodium and glucose distal from the proximal convoluted tubule induced compensatory increased sodium absorption at the thick ascending loop of Henle that resulted in decreased sodium delivery to the distal tubule leading to tubuloglomerular feedback-mediated glomerular hyperfiltration (130). Currently, there are no studies on the effects of SGLT2i in cats with CKD or naturally occurring heart disease.
11 Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibitors have opened new possibilities for managing type-2 DM in both humans and cats. Cats share many similarities with human diseases and can develop obesity, heart failure, CKD, hepatic lipidosis, and cognitive dysfunction as they age. Future research in small animal medicine must address the benefits and adverse effects of SGLT2i treatment not only as a new hypoglycemic agent for feline DM but also as a pleiotropic drug with expected effects in many other physiological systems.
Author contributions
AV: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. SC: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. BC: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. MM: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Navale, AM, and Paranjape, AN. Glucose transporters: physiological and pathological roles. Biophys Rev. (2016) 8:5–9. doi: 10.1007/s12551-015-0186-2
2. Gyimesi, G, Pujol-Giménez, J, Kanai, Y, and Hediger, MA. Sodium-coupled glucose transport, the SLC5 family, and therapeutically relevant inhibitors: from molecular discovery to clinical application. Pflugers Archiv Eur J Physiol. (2020) 472:1177–206. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02433-x
3. Idris, I, and Donnelly, R. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors: an emerging new class of oral antidiabetic drug. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2009) 11:79–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00982.x
4. Kurosaki, E, and Ogasawara, H. Ipragliflozin and other sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: preclinical and clinical data. Pharmacol Ther. (2013) 139:51–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.04.003
5. Mueckler, M, and Thorens, B. The SLC2 (GLUT) family of membrane transporters. Mol Asp Med. (2013) 34:121–38. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.001
6. Pizzagalli, MD, Bensimon, A, and Superti-Furga, G. A guide to plasma membrane solute carrier proteins. FEBS J. (2021) 288:2784–835. doi: 10.1111/febs.15531
7. Limbutara, K, Chou, C-L, and Knepper, MA. Quantitative proteomics of all 14 renal tubule segments in rat. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2020) 31:1255–66. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020010071
8. De Koninck, L. Ueber Das Phloridzin (Phlorrhizin). Annalen Der Pharmacie. (1835) 15:75–7. doi: 10.1002/jlac.18350150105
9. Choi, C-I. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors from natural products: discovery of next-generation antihyperglycemic agents. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). (2016) 21:1136. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091136
10. Ghezzi, C, Loo, DDF, and Wright, EM. Physiology of renal glucose handling via SGLT1, SGLT2 and GLUT2. Diabetologia. (2018) 61:2087–97. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4656-5
11. Nomura, S, Sakamaki, S, Hongu, M, Kawanishi, E, Koga, Y, Sakamoto, T, et al. Discovery of canagliflozin, a novel C-glucoside with thiophene ring, as sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Chem. (2010) 53:6355–60. doi: 10.1021/jm100332n
12. Latli, B, Hrapchak, MJ, Chevliakov, M, and Shu, C. Carbon 14 and carbon 13 syntheses of velagliflozin. J Label Compound Radiopharm. (2024) 67:180–5. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.4091
13. El-Haggar, SM, Hafez, YM, El Sharkawy, AM, and Khalifa, M. Effect of Empagliflozin in peripheral diabetic neuropathy of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Clin. (2024) 163:53–61. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2024.01.027
14. Gunawan, PY, Gunawan, PA, and Hariyanto, TI. Risk of dementia in patients with diabetes using sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i): a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Diab Therapy Res Treat Educ Diab Relat Disord. (2024) 15:663–75. doi: 10.1007/s13300-024-01538-1
15. O’Hara, DV, Lam, CSP, McMurray, JJV, Yi, TW, Hocking, S, Dawson, J, et al. Applications of SGLT2 inhibitors beyond glycaemic control. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2024) 20:513–29. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00836-y
16. Pawlos, A, Broncel, M, Woźniak, E, and Gorzelak-Pabiś, P. Neuroprotective effect of SGLT2 inhibitors. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). (2021) 26:7213. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237213
17. Seidu, S, Alabraba, V, Davies, S, Newland-Jones, P, Fernando, K, Bain, SC, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors - the new standard of care for cardiovascular, renal and metabolic protection in type 2 diabetes: a narrative review. Diab Therapy Res Treat Educ Diab Relat Disord. (2024) 15:1099–124. doi: 10.1007/s13300-024-01550-5
18. Toyama, T, Neuen, BL, Jun, M, Ohkuma, T, Neal, B, Jardine, MJ, et al. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular, renal and safety outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2019) 21:1237–50. doi: 10.1111/dom.13648
19. Rajeev, SP, Cuthbertson, DJ, and Wilding, JPH. Energy balance and metabolic changes with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibition. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2016) 18:125–34. doi: 10.1111/dom.12578
20. DeFronzo, RA, Hompesch, M, Kasichayanula, S, Liu, X, Hong, Y, Pfister, M, et al. Characterization of renal glucose reabsorption in response to Dapagliflozin in healthy subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2013) 36:3169–76. doi: 10.2337/dc13-0387
21. Hou, Y-C, Zheng, C-M, Yen, T-H, and Kuo-Cheng, L. Molecular mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibitor on cardiorenal protection. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:7833. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217833
22. Ferrannini, E, Muscelli, E, Frascerra, S, Baldi, S, Mari, A, Heise, T, et al. Metabolic response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:499–508. doi: 10.1172/JCI72227
23. Goto, Y, Otsuka, Y, Ashida, K, Nagayama, A, Hasuzawa, N, Iwata, S, et al. Improvement of skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity by 1 week of SGLT2 inhibitor use. Endocr Connect. (2020) 9:599–606. doi: 10.1530/EC-20-0082
24. Pessoa, TD, Campos, LCG, Carraro-Lacroix, L, Girardi, ACC, and Malnic, G. Functional role of glucose metabolism, osmotic stress, and sodium-glucose cotransporter isoform-mediated transport on Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 activity in the renal proximal tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2014) 25:2028–39. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013060588
25. Maher, JF. Diabetic nephropathy: early detection, prevention and management. Am Fam Physician. (1992) 45:1661–8.
26. Simonson, MS. Phenotypic transitions and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. (2007) 71:846–54. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002180
27. Cravedi, P, and Remuzzi, G. Pathophysiology of proteinuria and its value as an outcome measure in chronic kidney disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2013) 76:516–23. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12104
28. Thomas, MC, and Cherney, DZI. The actions of SGLT2 inhibitors on metabolism, renal function and blood pressure. Diabetologia. (2018) 61:2098–107. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4669-0
29. Karg, MV, Bosch, A, Kannenkeril, D, Striepe, K, Ott, C, Schneider, MP, et al. SGLT-2-inhibition with Dapagliflozin reduces tissue sodium content: a randomised controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2018) 17:5. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0654-z
30. Hallow, KM, Helmlinger, G, Greasley, PJ, McMurray, JJV, and Boulton, DW. Why do SGLT2 inhibitors reduce heart failure hospitalization? A differential volume regulation hypothesis. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2018) 20:479–87. doi: 10.1111/dom.13126
31. Delanaye, P, and Scheen, AJ. The diuretic effects of SGLT2 inhibitors: a comprehensive review of their specificities and their role in renal protection. Diabetes Metab. (2021) 47:101285. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101285
32. Neuen, BL, Oshima, M, Perkovic, V, Agarwal, R, Arnott, C, Bakris, G, et al. Effects of canagliflozin on serum potassium in people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: the CREDENCE trial. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:4891–901. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab497
33. Ruiten, C Cv, Hesp, AC, and van Raalte, DH. Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors protect the cardiorenal axis: update on recent mechanistic insights related to kidney physiology. Eur J Intern Med. (2022) 100:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2022.03.031
34. Tang, J, Ye, L, Yan, Q, Zhang, X, and Wang, L. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on water and sodium metabolism. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:800490. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.800490
35. Neuen, BL, Oshima, M, Agarwal, R, Arnott, C, Cherney, DZ, Edwards, R, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and risk of hyperkalemia in people with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomized, controlled trials. Circulation. (2022) 145:1460–70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.057736
36. Campbell, NK, Fitzgerald, HK, and Dunne, A. Regulation of inflammation by the antioxidant Haem oxygenase 1. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) 21:411–25. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-00491-x
37. Consoli, V, Sorrenti, V, Grosso, S, and Vanella, L. Heme oxygenase-1 signaling and redox homeostasis in physiopathological conditions. Biomol Ther. (2021) 11:589. doi: 10.3390/biom11040589
38. Gager, GM, von Lewinski, D, Sourij, H, Jilma, B, Eyileten, C, Filipiak, K, et al. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on ion homeostasis and oxidative stress associated mechanisms in heart failure. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 143:112169. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112169
39. Peyton, KJ, Behnammanesh, G, Durante, GL, and Durante, W. Canagliflozin inhibits human endothelial cell inflammation through the induction of Heme oxygenase-1. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:8777. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158777
40. Abdollahi, E, Keyhanfar, F, Delbandi, A-A, Falak, R, Hajimiresmaiel, SJ, and Shafiei, M. Dapagliflozin exerts anti-inflammatory effects via inhibition of LPS-induced TLR-4 overexpression and NF-κB activation in human endothelial cells and differentiated macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. (2022) 918:174715. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174715
41. Niu, Y, Zhang, Y, Zhang, W, Jinghua, L, Chen, Y, Hao, W, et al. Canagliflozin ameliorates NLRP3 Inflammasome-mediated inflammation through inhibiting NF-κB signaling and upregulating Bif-1. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:820541. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.820541
42. Skrabic, R, Kumric, M, Vrdoljak, J, Rusic, D, Skrabic, I, Vilovic, M, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors in chronic kidney disease: from mechanisms to clinical practice. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:2458. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102458
43. Androutsakos, T, Nasiri-Ansari, N, Bakasis, A-D, Kyrou, I, Efstathopoulos, E, Randeva, HS, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors in NAFLD: expanding their role beyond diabetes and cardioprotection. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:3107. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063107
44. Ferrannini, E, Baldi, S, Frascerra, S, Astiarraga, B, Heise, T, Bizzotto, R, et al. Shift to fatty substrate utilization in response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in subjects without diabetes and patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. (2016) 65:1190–5. doi: 10.2337/db15-1356
45. Lupsa, BC, Kibbey, RG, and Inzucchi, SE. Ketones: the double-edged sword of SGLT2 inhibitors? Diabetologia. (2023) 66:23–32. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05815-1
46. Youm, Y-H, Nguyen, KY, Grant, RW, Goldberg, EL, Bodogai, M, Kim, D, et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. (2015) 21:263–9. doi: 10.1038/nm.3804
47. Heerspink, HJL, Perco, P, Mulder, S, Leierer, J, Hansen, MK, Heinzel, A, et al. Canagliflozin reduces inflammation and fibrosis biomarkers: a potential mechanism of action for beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia. (2019) 62:1154–66. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4859-4
48. Zhang, Y, Daisuke Nakano, Y, Guan, HH, Uemura, A, Masaki, T, Kobara, H, et al. A sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor attenuates renal capillary injury and fibrosis by a vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent pathway after renal injury in mice. Kidney Int. (2018) 94:524–35. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.05.002
49. Li, T, Chen, Y, Gua, C, and Baogang, W. Elevated oxidative stress and inflammation in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus are associated with sympathetic excitation and hypertension in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:840. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00840
50. Sano, M. Sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT)-2 inhibitors alleviate the renal stress responsible for sympathetic activation. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. (2020) 14:1753944720939383. doi: 10.1177/1753944720939383
51. Ye, S, Zhong, H, Yanamadala, S, and Campese, VM. Oxidative stress mediates the stimulation of sympathetic nerve activity in the phenol renal injury model of hypertension. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979). (2006) 48:309–15. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000231307.69761.2e
52. Rahman, A, and Nishiyama, A. Inhibiting SGLTs diminishes sympathetic output by reducing rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) neuron activity. Hypertens Res. (2024) 47:571–2. doi: 10.1038/s41440-023-01522-5
53. Scheen, AJ. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on the sympathetic nervous system and blood pressure. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2019) 21:70. doi: 10.1007/s11886-019-1165-1
54. Durante, W, Behnammanesh, G, and Peyton, KJ. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on vascular cell function and arterial remodeling. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:8786. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168786
55. Lescano, CH, Leonardi, G, Torres, PHP, Amaral, TN, Henrique, L, Filho, d F, et al. The sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors synergize with nitric oxide and prostacyclin to reduce human platelet activation. Biochem Pharmacol. (2020) 182:114276. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114276
56. Dhingra, NK, Mistry, N, Puar, P, Verma, R, Stefan Anker, C, Mazer, D, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors and cardiac remodelling: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized cardiac magnetic resonance imaging trials. ESC Heart Fail. (2021) 8:4693–700. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13645
57. Beghini, A, Sammartino, AM, Papp, Z, Von Haehling, S, Biegus, J, Ponikowski, P, et al. 2024 update in heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. (2024). doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14857
58. Maddox, TM, Januzzi, JL, Allen, LA, Breathett, K, Brouse, S, Butler, J, et al. 2024 ACC expert consensus decision pathway for treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2024) 83:1444–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.12.024
59. Neal, B, Perkovic, V, and Matthews, DR. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:2097–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1712572
60. Zinman, B, Wanner, C, Lachin, JM, Fitchett, D, Bluhmki, E, Hantel, S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:2117–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504720
61. Schrijvers, BF, De Vriese, AS, and Flyvbjerg, A. From hyperglycemia to diabetic kidney disease: the role of metabolic, hemodynamic, intracellular factors and growth factors/cytokines. Endocr Rev. (2004) 25:971–1010. doi: 10.1210/er.2003-0018
62. Sulaiman, MK. Diabetic nephropathy: recent advances in pathophysiology and challenges in dietary management. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2019) 11:7. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0403-4
63. Hill, NR, Fatoba, ST, Oke, JL, Hirst, JA, O’Callaghan, CA, Lasserson, DS, et al. Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Plos One. (2016) 11:e0158765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158765
64. Gross, O, Haffner, D, Schaefer, F, and Weber, LT. SGLT2 inhibitors: approved for adults and cats but not for children with CKD. Nephrol Dial Transpl. (2024) 39:907–9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfae029
65. Wiviott, SD, Raz, I, Bonaca, MP, Mosenzon, O, Kato, ET, Cahn, A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:347–57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812389
66. Vallon, V, and Verma, S. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on kidney and cardiovascular function. Annu Rev Physiol. (2021) 83:503–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-095920
67. Rong, X, Li, X, Gou, Q, Liu, K, and Chen, X. Risk of orthostatic hypotension associated with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diab Vasc Dis Res. (2020) 17:1479164120953625. doi: 10.1177/1479164120953625
68. Alicic, RZ, Johnson, EJ, and Tuttle, KR. SGLT2 inhibition for the prevention and treatment of diabetic kidney disease: a review. Am J Kidney Dis. (2018) 72:267–77. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.03.022
69. Cai, X, Yang, W, Gao, X, Chen, Y, Zhou, L, Zhang, S, et al. The association between the dosage of SGLT2 inhibitor and weight reduction in type 2 diabetes patients: a meta-analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md). (2018) 26:70–80. doi: 10.1002/oby.22066
70. Cefalu, WT, Leiter, LA, Yoon, K-H, Arias, P, Niskanen, L, Xie, J, et al. Efficacy and safety of Canagliflozin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (CANTATA-SU): 52 week results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet (London, England). (2013) 382:941–50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60683-2
71. Cheong, AJ, Yang, YN, Teo, YH, Teo, NL, Syn, HT, Ong, AZH, et al. SGLT inhibitors on weight and body mass: a meta-analysis of 116 randomized-controlled trials. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md). (2022) 30:117–28. doi: 10.1002/oby.23331
72. Del Prato, S, Nauck, M, Durán-Garcia, S, Maffei, L, Rohwedder, K, Theuerkauf, A, et al. Long-term glycaemic response and tolerability of Dapagliflozin versus a Sulphonylurea as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: 4-year data. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2015) 17:581–90. doi: 10.1111/dom.12459
73. Inzucchi, SE, Davies, MJ, Khunti, K, Trivedi, P, George, JT, Zwiener, I, et al. Empagliflozin treatment effects across categories of baseline HbA1c, body weight and blood pressure as an add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2021) 23:425–33. doi: 10.1111/dom.14234
74. Pan, R, Zhang, Y, Wang, R, Yao, X, Ji, H, and Zhao, Y. Effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0279889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279889
75. Ridderstråle, M, Andersen, KR, Zeller, C, Kim, G, Woerle, HJ, Broedl, UC, et al. Comparison of empagliflozin and glimepiride as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 104-week randomised, active-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diab Endocrinol. (2014) 2:691–700. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70120-2
76. Shao, S-C, Kuo, L-T, Chien, R-N, Hung, M-J, and Lai, EC-C. SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes with non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases: an umbrella review of systematic reviews. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2020) 8:e001956. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001956
77. Sinha, B, Datta, D, and Ghosal, S. Meta-analysis of the effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients with type 2 diabetes. JGH Open Access J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 5:219–27. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12473
78. Taheri, H, Malek, M, Ismail-Beigi, F, Zamani, F, Sohrabi, M, Babaei, MR, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Adv Ther. (2020) 37:4697–708. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01498-5
79. Tobita, H, Yazaki, T, Kataoka, M, Kotani, S, Oka, A, Mishiro, T, et al. Comparison of Dapagliflozin and teneligliptin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients without type 2 diabetes mellitus: a prospective randomized study. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2021) 68:173–80. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.20-129
80. Wei, Q, Xinyue, X, Guo, L, Li, J, and Li, L. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on type 2 diabetes mellitus with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Endocrinol. (2021) 12:635556. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.635556
81. Wong, C, Leon, CY, Yaow, CH, Ng, YH, Chin, YF, Low, AY, et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:609135. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.609135
82. Xing, B, Zhao, Y, Dong, B, Zhou, Y, Lv, W, and Zhao, W. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Diab Invest. (2020) 11:1238–47. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13237
83. Heimke, M, Lenz, F, Rickert, U, Lucius, R, and Cossais, F. Anti-inflammatory properties of the SGLT2 inhibitor Empagliflozin in activated primary microglia. Cells. (2022) 11:3107. doi: 10.3390/cells11193107
84. Khedr, LH, Rahmo, RM, Eldemerdash, OM, Helmy, EM, Ramzy, FA, Lotfy, GH, et al. Implication of M2 macrophage on NLRP3 inflammasome signaling in mediating the neuroprotective effect of canagliflozin against methotrexate-induced cognitive impairment. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 130:111709. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111709
85. Ünal, İ, Cansız, D, Beler, M, Sezer, Z, Güzel, E, and Emekli-Alturfan, E. Sodium-dependent glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor empagliflozin exerts neuroprotective effects in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease model in zebrafish; mechanism involving ketogenesis and autophagy. Brain Res. (2023) 1820:148536. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2023.148536
86. Rizzo, MR, Di Meo, I, Polito, R, Auriemma, MC, Gambardella, A, di Mauro, G, et al. Cognitive impairment and type 2 diabetes mellitus: focus of SGLT2 inhibitors treatment. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 176:106062. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106062
87. Nelinson, DS, Sosa, JM, and Chilton, RJ. SGLT2 inhibitors: a narrative review of efficacy and safety. J Osteopathic Med. (2021) 121:229–39. doi: 10.1515/jom-2020-0153
88. Bhatt, DL, Michael Szarek, P, Steg, G, Cannon, CP, Leiter, LA, McGuire, DK, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening heart failure. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:117–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2030183
89. Qiu, H, Novikov, A, and Vallon, V. Ketosis and diabetic ketoacidosis in response to SGLT2 inhibitors: basic mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2017) 33. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2886
90. Thiruvenkatarajan, V, Inglis, JM, Meyer, E, Umapathysivam, MM, Nanjappa, N, Van Wijk, R, et al. Peri-colonoscopy implications of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor therapy: a mini-review of available evidence. Can J Diabetes. (2023) 47:287–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2022.12.003
91. Donnan, JR, Grandy, CA, Chibrikov, E, Marra, CA, Aubrey-Bassler, K, Johnston, K, et al. Comparative safety of the sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. (2019) 9:e022577. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022577
92. Liu, J, Li, L, Li, S, Jia, P, Deng, K, Chen, W, et al. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on UTIs and genital infections in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:2824. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02733-w
93. Nuffield Department of Population Health Renal Studies Group and SGLT2 inhibitor Meta-Analysis Cardio-Renal Trialists’ Consortium. Impact of diabetes on the effects of sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on kidney outcomes: collaborative meta-analysis of large placebo-controlled trials. Lancet (London, England). (2022) 400:1788–801. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02074-8
94. Perkovic, V, Jardine, MJ, Neal, B, Bompoint, S, Heerspink, HJL, Charytan, DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:2295–306. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1811744
95. Wanner, C, Inzucchi, SE, Lachin, JM, Fitchett, D, von Eynatten, M, Mattheus, M, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:323–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1515920
96. Anker, SD, Butler, J, and Packer, M. Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. Reply. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386:e57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2118470
97. Herrington, WG, Baigent, C, and Haynes, R. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. Reply. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388:2301–2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2301923
98. McMurray, JJV, Docherty, KF, and Jhund, PS. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. Reply. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:972–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1917241
99. Packer, M, Anker, SD, Butler, J, Filippatos, G, Pocock, SJ, Carson, P, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:1413–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190
100. Behrend, E, Holford, A, Lathan, P, Rucinsky, R, and Schulman, R. 2018 AAHA diabetes management guidelines for dogs and cats*. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. (2018) 54:1–21. doi: 10.5326/JAAHA-MS-6822
101. Vieira, Aline. Does diet matter when treating feline diabetes mellitus? Veterinary Practice News. (2019). Available at: https://www.veterinarypracticenews.com/diabetes-mellitus-november-2019/ (Accessed May 20, 2024).
102. Aptekmann, KP, Armstrong, J, Coradini, M, and Rand, J. Owner experiences in treating dogs and cats diagnosed with diabetes mellitus in the United States. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. (2014) 50:247–53. doi: 10.5326/JAAHA-MS-6101
103. Niessen, SJM, Powney, S, Guitian, J, Niessen, APM, Pion, PD, Shaw, J a M, et al. Evaluation of a quality-of-life tool for cats with diabetes mellitus. J Vet Intern Med. (2010) 24:1098–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.2010.0579.x
104. Niessen, SJM, Hazuchova, K, Powney, SL, Guitian, J, Niessen, APM, Pion, PD, et al. The big pet diabetes survey: perceived frequency and triggers for euthanasia. Vet Sci. (2017) 4:27. doi: 10.3390/vetsci4020027
105. Re, M, Del Baldo, F, Tardo, AM, and Fracassi, F. Monitoring of diabetes mellitus using the flash glucose monitoring system: the owners’ point of view. Vet Sci. (2023) 10:203. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10030203
106. Mori, A, Ueda, K, Lee, P, Oda, H, Ishioka, K, Arai, T, et al. Effect of acarbose, sitagliptin and combination therapy on blood glucose, insulin, and incretin hormone concentrations in experimentally induced postprandial hyperglycemia of healthy cats. Res Vet Sci. (2016) 106:131–4. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2016.04.001
107. Nelson, R, Spann, D, Elliott, D, Brondos, A, and Vulliet, R. Evaluation of the oral antihyperglycemic drug metformin in normal and diabetic cats. J Vet Intern Med. (2004) 18:18–24. doi: 10.1892/0891-6640(2004)18<18:eotoad>2.0.co;2
108. Nishii, N, Takashima, S, Iguchi, A, Murahata, Y, Matsuu, A, Hikasa, Y, et al. Effects of sitagliptin on plasma incretin concentrations after glucose administration through an esophagostomy tube or feeding in healthy cats. Domest Anim Endocrinol. (2014) 49:14–9. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2014.04.006
109. Padrutt, I, Lutz, TA, Reusch, CE, and Zini, E. Effects of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues exenatide, exenatide extended-release, and of the dipeptidylpeptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor sitagliptin on glucose metabolism in healthy cats. Res Vet Sci. (2015) 99:23–9. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2014.12.001
110. Clark, MH, Hoenig, M, Ferguson, DC, and Dirikolu, L. Pharmacokinetics of pioglitazone in lean and obese cats. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. (2012) 35:428–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2011.01341.x
111. Clark, M, Thomaseth, K, Dirikolu, L, Ferguson, DC, and Hoenig, M. Effects of pioglitazone on insulin sensitivity and serum lipids in obese cats. J Vet Intern Med. (2014) 28:166–74. doi: 10.1111/jvim.12255
112. Feldman, EC, Nelson, RW, and Feldman, MS. Intensive 50-week evaluation of glipizide administration in 50 cats with previously untreated diabetes mellitus. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (1997) 210:772–7. doi: 10.2460/javma.1997.210.06.772
113. Nelson, RW, Feldman, EC, Ford, SL, and Roemer, OP. Effect of an orally administered sulfonylurea, glipizide, for treatment of diabetes mellitus in cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (1993) 203:821–7. doi: 10.2460/javma.1993.203.06.0821
114. Ford, SL. NIDDM in the cat: treatment with the Oral hypoglycemic medication, glipizide. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. (1995) 25:599–615. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(95)50056-7
115. Jotha-Mattos, L, Vieira, AB, Castelo, M d SM, Queiroz, AS d M, de Souza, HJM, de Alencar, NX, et al. Amyloidogenesis of feline amylin and plasma levels in cats with diabetes mellitus or pancreatitis. Domest Anim Endocrinol. (2021) 74:106532. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2020.106532
116. Miller, AB, Nelson, RW, Kirk, CA, Neal, L, and Feldman, EC. Effect of glipizide on serum insulin and glucose concentrations in healthy cats. Res Vet Sci. (1992) 52:177–81. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(92)90007-o
117. Halimi, S, and Vergès, B. Adverse effects and safety of SGLT-2 inhibitors. Diabetes Metab. (2014) 40:S28–34. doi: 10.1016/S1262-3636(14)72693-X
118. Hoenig, M, Clark, M, Schaeffer, DJ, and Reiche, D. Effects of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor Velagliflozin, a new drug with therapeutic potential to treat diabetes in cats. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. (2018) 41:266–73. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12467
119. Behrend, E, Ward, C, Chukwu, V, Cook, A, Kroh, C, Lathan, P, et al. Velagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, as once-daily, Oral solution, stand-alone therapy for feline diabetes mellitus. J Vet Internal Med. (2023) 37:2638–60. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16902
120. Niessen, SJM, Kooistra, HS, Forcada, Y, Bjørnvad, CR, Albrecht, B, Roessner, F, et al. Efficacy and safety of once daily oral administration of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor velagliflozin compared with twice daily insulin injection in diabetic cats. J Vet Intern Med. (2024) 38:2099–119. doi: 10.1111/jvim.17124
121. Bloom, CA, and Rand, JS. Diabetes and the kidney in human and veterinary medicine. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. (2013) 43:351–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cvsm.2012.11.002
122. Benedict, SL, Mahony, OM, McKee, TS, and Bergman, PJ. Evaluation of Bexagliflozin in cats with poorly regulated diabetes mellitus. Can J Vet Res. (2022) 86:52–8.
123. Hadd, MJ, Bienhoff, SE, Little, SE, Geller, S, Ogne-Stevenson, J, Dupree, TJ, et al. Safety and effectiveness of the sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor Bexagliflozin in cats newly diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. J Vet Intern Med. (2023) 37:915–24. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16730
124. Cook, AK, and Behrend, E. SGLT2 inhibitor use in the management of feline diabetes mellitus. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. (2025) 48:19–30. doi: 10.1111/jvp.13466
125. Scott-Moncrieff, C. The role of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in feline diabetes mellitus management. Today’s Vet Pract. (2024)
126. Hill, J. CANVAS and EMPA-REG findings support cardiovascular safety of SGLT2 inhibitors. J Diabetes Nurs. (2017) 21:193–4.
127. Henson, MS, and O’Brien, TD. Feline models of type 2 diabetes mellitus. ILAR J. (2006) 47:234–42. doi: 10.1093/ilar.47.3.234
128. Sordo, L, and Gunn-Moore, DA. Cognitive dysfunction in cats: update on neuropathological and behavioural changes plus clinical management. Vet Rec. (2021) 188:e3. doi: 10.1002/vetr.3
129. Hoenig, M. The cat as a model for human obesity and diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. (2012) 6:525–33. doi: 10.1177/193229681200600306
Keywords: feline diabetes mellitus, type-2 diabetes mellitus, bexagliflozin, velagliflozin, kidney disease, heart disease, cognitive dysfunction, glucose transporters
Citation: Vieira AB, Cavanaugh SM, Ciambarella BT and Machado MV (2025) Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: a pleiotropic drug in humans with promising results in cats. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1480977. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1480977
Edited by:
Isaac Karimi, Razi University, IranReviewed by:
Blythe D. Shepard, Georgetown University Medical Center, United StatesÁlan Pöppl, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Vieira, Cavanaugh, Ciambarella and Machado. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Aline B. Vieira, YWJ2MzhAY29ybmVsbC5lZHU=; YWxpbmVidmllaXJhQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Aline B. Vieira
Aline B. Vieira Sarah M. Cavanaugh
Sarah M. Cavanaugh Bianca T. Ciambarella
Bianca T. Ciambarella Marcus V. Machado
Marcus V. Machado