- College of Communication and Information Engineering, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’ an, China
Camera relocalization determines the position and orientation of a camera in a 3D space. Althouh methods based on scene coordinate regression yield highly accurate results in indoor scenes, they exhibit poor performance in outdoor scenarios due to their large scale and increased complexity. A visual localization method, Py-Net, is therefore proposed herein. Py-Net is based on voting segmentation and comprises a main encoder containing Py-layer and two branch decoders. The Py-layer comprises pyramid convolution and 1 × 1 convolution kernels for feature extraction across multiple levels, with fewer parameters to enhance the model’s ability to extract scene information. Coordinate attention was added at the end of the encoder for feature correction, which improved the model robustness to interference. To prevent the feature loss caused by repetitive structures and low-texture images in the scene, deep over-parameterized convolution modules were incorporated into the seg and vote decoders. Landmark segmentation and voting maps were used to establish the relation between images and landmarks in 3D space, reducing anomalies and achieving high precision with a small number of landmarks. The experimental results show that, in multiple outdoor scenes, Py-Net achieves lower distance and angle errors compared to existing methods. Additionally, compared to VS-Net, which also uses a voting segmentation structure, Py-Net reduces the number of parameters by 31.85% and decreases the model size from 236MB to 170 MB.
1 Introduction
Camera relocalization is a fundamental problem in computer vision tasks. It aims to infer a camera’s translation vector and rotation angle in the world coordinate system from RGB images, determining the camera’s precise position and orientation in a scene.Camera relocalization is the core of simultaneous localization and mapping as well as a key module in technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and autonomous driving (Chen et al., 2021). Traditional camera relocalization methods often employ structure-from-motion (SFM) techniques to achieve high-precision camera localization by preserving the geometric information of a scene using three-dimensional (3D) point clouds (Shavit and Ferens, 2019). However, these methods use feature point matching that causes relocalization failure when dealing with complex scenes. Absolute pose estimation using deep learning (Kendall A. et al., 2015) overcomes the limitations of large memory occupancy and hardware of traditional methods. Scene coordinate regression (SCR)-based (Li et al., 2018) camera relocalization is a deep learning method and regresses two-dimensional (2D) image pixels to obtain a relation between the 2D pixels and 3D scene coordinates. Further, it uses a random sampling consistency (RANSAC) algorithm to select the best poses, considerably improving the relocalization accuracy. Additionally, image retrieval–based camera relocalization methods require matching the query image with an image database to find the most similar image (Balntas et al., 2018; Arandjelovic et al., 2016) for calculating the relative position of a camera (Laskar et al., 2017). These methods yield good relocalization results in the absence of presented scenes but have low localization speed.
SCR-based camera relocalization methods perform well in indoor scenes. Networks with multiple viewpoint constraints converge more easily than single-viewpoint models. Cai et al. (Cai and Zhan, 2019) enhanced SCR networks using geometric constraints and self-supervision, allowing the networks to learn reliable 2D to 3D relations and improving the training efficiency. Hierarchical scene coordinate networks offer better performance. Li et al. (Li et al., 2020) proposed HSCNet, which accurately predicts pixel scene coordinates from a single RGB image through multiple output layers, with the final layer predicting the 3D coordinates. Yang et al. (Yang et al., 2019) proposed SANet, which decouples model parameters from the scene using hierarchical coding, enabling the localization of unknown scenes and estimation of camera poses.
Outdoor scene relocalization faces many challenges, such as differences between datasets and real environments and varying scene properties, which affect relocalization accuracy. In the presence of duplicate structures in a scene, an uncertainty is generated in the positional solution. Duong et al. (Duong et al., 2020) proposed an efficient multioutput scene coordinate (EMOSC) method that combines machine learning and geometric methods. It is a multioutput depth forest regression method based on sparse feature detection, which greatly reduces the algorithm running time and improves the prediction accuracy. Wald et al. (Wald et al., 2020) introduced RIO-10 and a new metric: dense correspondence reprojection error. Dong et al. (Dong et al., 2021) developed an outlier-aware neural tree for high-precision camera relocalization in dynamic indoor settings, featuring decision trees, neural routes, and dynamic point filtering. SCR-based methods balance accuracy and computation time. Turkoglu et al. (Turkoglu et al., 2021) combined graph neural networks with image retrieval using relative positional loss for training. Bui et al. (Bui et al., 2022) proposed a simpler SCR algorithm using perceptrons and sparse descriptors, resulting in a smaller model. PixLoc (Sarlin P. et al., 2021) is a scene-independent algorithm requiring only a query image, 3D model, and reference image with poses for camera relocalization. It uses metric learning for generalization across different scenes. KFNet (Zhou et al., 2020) combines a recursive network with Kalman filtering, extending SCR to the time domain for 2D to 3D correspondence. A system reported in a previous study (Brachmann E. and Rother C., 2021) estimated camera translation and orientation from RGB-D or RGB images. It was trained using a 3D environment model and required only RGB images and ground truth for training. Despite the strengths of SCR methods, their accuracy is limited by feature extraction, necessitating improvements in this regard.
Herein, the current research status of camera relocalization is reviewed. Existing deep learning–based camera relocalization methods can be categorized into three types: direct regression methods, image retrieval–based methods, and SCR methods. The specific principles of these methods are described as follows.
Direct regression methods: In these methods, the camera pose is directly estimated by inputting an image into a convolutional neural network and performing supervised learning. Although this approach is simple and requires only one neural network, its accuracy is generally low.
Image retrieval–based methods: These methods initially involve the feature encoding of input images. Then, they can directly find an image in the database that is the most similar to the query image and estimate the camera pose by matching their features. Alternatively, they can estimate their relative poses and more accurately estimate the camera pose. These methods demonstrate good generalization and adapt well to large-scale scenes. However, finding the most similar image from the image database is time-consuming. Additionally, differences between database and query images often make the retrieval of the most similar image challenging. Similar to traditional camera relocalization methods that establish sparse point clouds, optimizing the image-retrieval step helps narrow down the search space, facilitating faster estimation of the camera pose. The algorithm efficiency can be enhanced to some extent using global descriptors as the retrieval criterion.
SCR: Unlike traditional camera relocalization methods that rely on feature matching to establish the 2D–3D relation, SCR is more direct. By training a neural network, inputting an image, and obtaining the 3D positions of image pixels using the network, i.e., scene coordinates, the camera pose is calculated using the PnP-RANSAC algorithm based on the correspondence between 2D pixel points and 3D spatial coordinates. These methods considerably simplify the establishment of the 2D–3D relation. Unlike traditional camera relocalization and image retrieval–based methods, SCR does not directly store scene information in a database or 3D model. Instead, it implicitly expresses scene information using a neural network. A convolutional neural network is first trained to map 2D pixels to 3D spatial coordinates. Then, the spatial coordinates are input to the PnP-RANSAC algorithm for pose estimation. However, camera relocalization methods based on SCR may not perform as robustly in large-scale scenes as in small-scale scenes. In outdoor environments, the accuracy of camera relocalization may also be slightly influenced.
During camera relocalization in outdoor scenes, features extracted by an SCR network contain a large number of invalid scene coordinates, which can slightly affect the relocalization accuracy.To address this issue, herein, a voting segmentation network is adopted as the baseline model. However, using ResNet101 in the encoder of the voting segmentation network increases the model size and computational complexity; therefore, its immunity to external interference requires enhancement. To mitigate the impact of external noise on the encoder, pyramid convolution and 1 × 1 convolution kernels are used for constructing the main encoder. This design reduces the size of the network model and effectively enhances the feature extraction capability. Coordinate attention is also introduced to improve the resistance of the model to interference. Additionally, a more efficient feature extraction backbone network is developed using pyramid convolution to address object occlusion in outdoor scenes. Due to low texture and repetitive structures present in outdoor environments, the camera perceives the same scene from different poses, which in turn decreases the accuracy of camera relocalization. Furthermore, the spatial scene information of local features gradually diminishes as features propagate forward in the network. Thus, the output scene coordinates of a network do not provide usable scene information for estimating camera poses. To address these two issues, deep over-parameterized convolution modules are introduced into seg and vote decoders to improve the quality of scene image features while maintaining the original computational complexity.
This paper makes the following significant contributions.
(1) We propose a new network architecture, Py-layer, which is an encoding unit composed of stacked pyramid convolutions and 1 × 1 convolutions, with the addition of coordinate attention for feature correction. This simple and efficient network structure can extract multi-scale scene information, capture important features within the scene, and balance performance and efficiency.
(2) We use Py-layer to develop a camera relocalization solution based on a voting segmentation architecture. Deep over-parameterized convolution modules are integrated into the segmentation and voting decoders to address feature loss caused by repetitive structures and low-texture images in the scene.
(3) We conducted extensive experiments on the Cambridge Landmarks dataset to verify the effectiveness of our method in large-scale outdoor scenes. The experimental results show that, compared to VS-Net, which also uses a voting segmentation structure, our model improves average distance and angular accuracy by 29.41% and 33.33%, respectively, while reducing the number of parameters by 31.85%.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 overviews deep learning–based camera relocalization methods. Section 3 provides the details of the proposed Py-Net network and its components. Section 4 presents the experimental results, and Section 5 summarizes the study with concluding remarks.
2 Materials and methods
Herein, the proposed methodology as well as the hardware and software platforms and datasets required for experiments are discussed.
2.1 Network architecture
The Py-Net architecture is a simple yet powerful encoder–decoder network (Figure 1) comprising three main components: the image encoder, seg decoder, and vote decoder. This design enables the generation of accurate landmark segmentation maps and voting maps for 2D-to-3D correspondence modeling. During training, Py-Net uses a landmark segmentation method based on patch labeling to generate segmentation coordinates for all pixels that correspond to patches surrounding the landmarks. Additionally, each pixel within the landmark patch predicts a 2D directional vector pointing toward the landmark, thereby enabling reliable and precise coordinate voting.
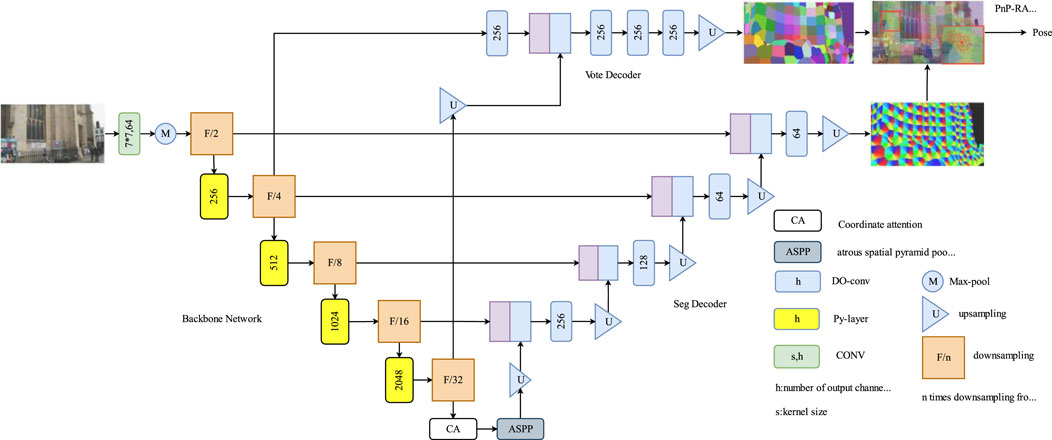
Figure 1. Py-Net network architecture. Py-Net architecture illustrates a encoder-decoder network, integrating an image encoder, segmentation decoder, and voting decoder, enabling accurate 2D-to-3D correspondence modeling.
The main encoder comprises stacked Py-layers of different sizes. The Py-layer is a coding layer composed of 1 × 1 and pyramid convolutions. 1 × 1 convolution kernels perform dimensionality reduction and expansion, whereas pyramid convolutions use convolutions of multiple sizes to process the input image. It contains multiple levels of feature extraction layers, each with convolutions of different sizes and depths. Thus, the ability of the network to extract scene information enhances. Coordinate attention is added at the end of the Py-layer for feature correction. The output of the encoder is then fed into atrous spatial pyramid pooling, where features are sampled in parallel using dilated convolutions with different sampling rates. Finally, seg decoder and vote decoder branches produce landmark segmentation and voting maps, respectively.
In both decoder branches, depth over-parameterized convolution (DOConv) module was used as the convolution module. This design over-parameterizes the decoder, increasing the number of learnable parameters while maintaining the original computational complexity and thus enhancing the quality of scene image features.
2.2 Pyramidal convolution layer
Compared with standard convolution, pyramidal convolution offers a more robust capability to process input images. It uses multiple convolution sizes containing multiple levels of feature extraction layers, each with convolutions of different sizes and depths; thus, it captures rich details of the scene. Standard convolution contains only one convolution size, and the convolutional depth us equal to the depth of the feature map. In contrast, the convolution size increases and depth decreases in pyramidal convolution with increasing feature extraction levels. In outdoor scenes, the occlusion of building parts may occur, making it difficult for a single type of convolution to effectively capture details in the scene image. However, pyramidal convolution can use convolution kernels with different receptive fields to capture fine features, thereby improving the camera relocalization accuracy.
Figure 2 shows that the number of residual blocks in the backbone network increases via pyramidal convolution, enabling the network to process images using multiple convolution sizes and multiple feature extraction levels. Thus, the ability of the network to extract scene information is enhanced. When optimizing the encoder of the voting segmentation network, the encoding function is mainly completed by 3 × 3 convolution kernels because 1 × 1 convolution kernels in each module serve to reduce and increase the dimensionality. Therefore, 3 × 3 convolutions are first improved in each module of the backbone encoder. Using pyramidal convolution, the network model can process input images using multiple sizes of convolution containing multiple levels of feature extraction layers, each with convolutions of different sizes and depths. Thus, the ability of the network model to extract scene information is slightly enhanced without introducing additional parameters and computational overhead.
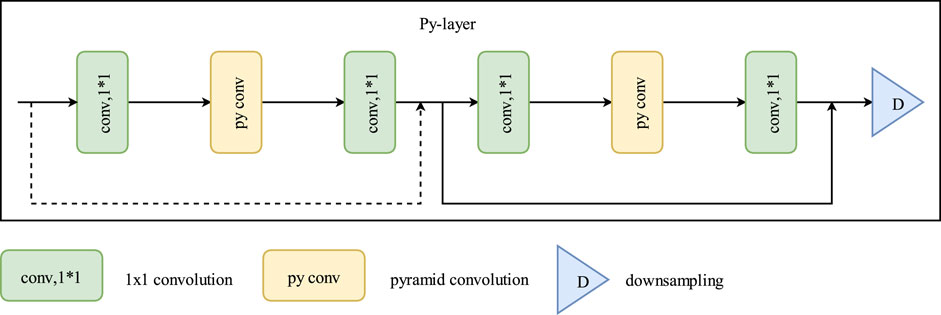
Figure 2. Py-layer network architecture. here pyramidal convolution increases the number of residual blocks. This allows the network to handle images with multiple convolution sizes and feature extraction levels, enhancing scene information extraction without increasing computational complexity.
For the input feature map
Here
The number of parameters of the pyramidal convolution is given by Equation 2:
Therefore, if the number of output feature maps is equal for each layer of the pyramidal convolution, then its parameters and computational costs will be evenly distributed across each level of the pyramid.
As shown in Figure 3, standard convolution can only have a single size convolution kernel, with the same kernel depth as the input features. Moreover, the number of computational parameters generated by a single convolution kernel is given by Equation 3:
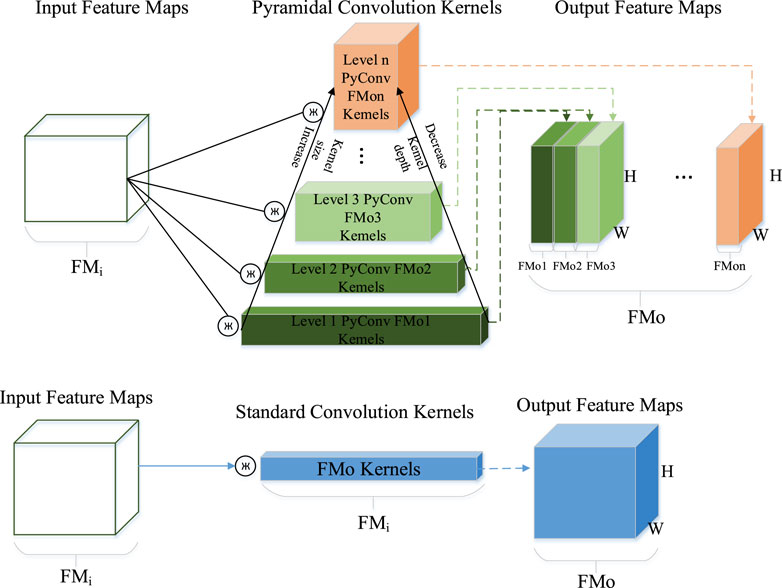
Figure 3. Comparative Analysis of pyramidal convolution and standard convolution in multi-level feature extraction and parameter count.
When multiple standard convolution kernels of different sizes are used to process input features, the as-generated computational and parameter quantities are greater than those generated via pyramidal convolution. This is because the input channels of these kernels must match the input features.
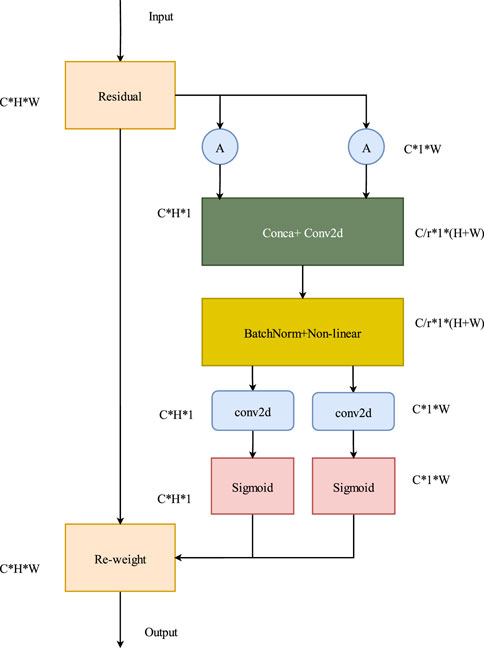
2.3 Coordinate attention
Attention mechanism is widely used in computer vision to enable network models to focus on relevant information. Some operations in convolutional neural networks, such as convolution, pooling, and fully connected layers, only consider nonself-desired clues. Contrarily, attention mechanism is purposeful and can explicitly model cues that align with its own intentions. As convolutions are conducted within local windows in the main encoder, their representation capability for global features is relatively weak. To address the issue of weak antiinterference capability in outdoor scenes with SCR networks, an attention mechanism is embedded in the encoder. This enables the network model to completely leverage global and local information. Consequently, the model can prioritize the areas of interest in an image, increase the corresponding weights of those areas, and ultimately highlight useful features while suppressing or ignoring irrelevant ones. These factors further enhance the localization accuracy.
Coordinate attention is a lightweight attention mechanism that considers channels and spaces in parallel (Figure 4). With the input of a feature X, X ∈
The output of width w and the cth channel can be expressed as Equation 5:
where
After the two pooling operations, the two embedding features
where
where
CA has higher computational efficiency and less computational overhead in the spatial dimension than other attention modules.
2.4 Depthwise over-parameterized convolution
In standard convolution, all kernels in a convolutional layer are convolved with the input image. Standard convolution emphasizes the spatial relation of pixels and considers it as channels but at the expense of relatively high computational complexity. In contrast, depthwise convolution assigns each kernel to a specific input channel. Each channel of the input image is convolved with a dedicated kernel. Depthwise convolution focuses more on the features represented in the depth of an image and has relatively lower computational complexity.
Deep over-parameterized convolution (Cao et al., 2022) is an extension of standard convolution, in which an additional depthwise convolution is incorporated. This additional convolutional structure increases the number of trainable model parameters and enhances the learning capacity of the model. The quality of scene features extracted by this model is also consequently improved.
The feature quality in the SCR network deteriorates due to the influence of repetitive structures and low-texture objects in scene images. To address this issue, standard convolutions must be substituted with deep over-parameterized convolutions. This replacement will enhance the quality of features extracted by the network and improve the overall nonlinear capability of the network, making it more robust. Figure 5 shows the structure of deep over-parameterized convolution.
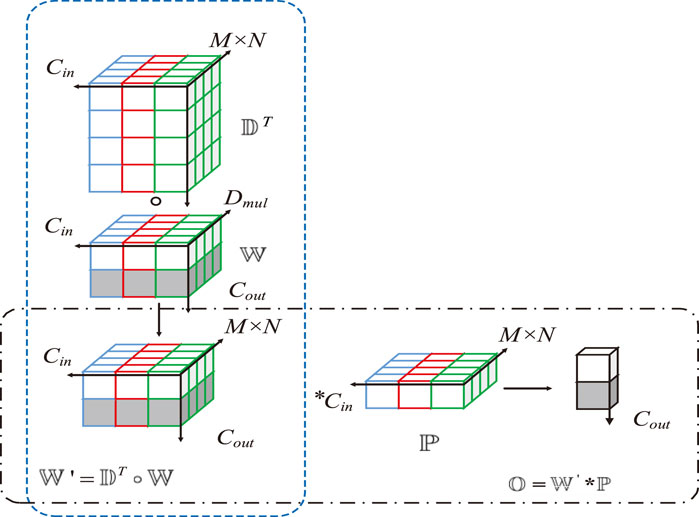
Figure 5. Depthwise over-parameterized convolution. By increasing the number of trainable model parameters, the learning capability of the model is enhanced. As a result, the quality of the extracted scene features is also improved.
Deep over-parameterized convolution comprises standard and depthwise convolutions. First, the convolutional kernel
As shown in Figure 6,
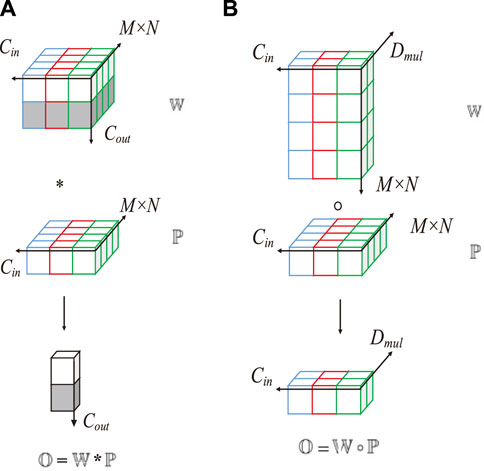
Figure 6. Computation methods of depthwise convolution and standard convolution. (A) Standard convolution, (B) DOConv.
The dimensions of
In depthwise convolution, each input channel of
where the depthwise convolutional kernel
DOConv and standard convolution have the same receptive field. For a feature input
2.5 Loss function
The scene is first reconstructed in 3D using Py-Net. The resulting 3D surface is divided into 3D image patches using the center point of each patch as a 3D landmark,
where K is the camera internal reference matrix and C is the camera pose parameter. Each pixel belonging to an image patch containing the coordinate
This vector is used to represent the orientation of the landmarks on the 2D plane. Supervised training of the voting segmentation network is possible by using the obtained segmentation map and voting map as training truths. This in turn establishes the relationship from 2D to 3D, thus enabling camera relocation.
The Vote Segmentation Network uses a prototype-based ternary loss function and a negative sample mining strategy to supervise the training of the network. Training the network in this way requires maintaining and updating a set of learnable class prototype embeddings P. Where each class prototype embedding represents a class and
Pixel embeddings can be obtained by voting on the segmentation branches of the segmentation network and the class of prototype embeddings P. Pixel embeddings can form a pixel-by-pixel embedding graph E. The prototype-based ternary loss function first first L2 normalizes each pixel embedding in the embedding graph E, and then minimizes the error between each pixel embedding
where
is used to measure the cosine similarity between the pixel embedding and prototype-like embedding.
The voting decoder of the voting segmentation network is then used to determine the landmark’s cast position in the 2D image.The voting decoder is used to determine the casting position of landmarks in a two-dimensional image. Inputting an image, the voting decoder outputs a voting map d. For each pixel i in the input, it generates a two-dimensional direction vector
Where one denotes the indicator function and
where λ denotes the weight of voting loss.
3 Results
This section evaluates the performance of our method, Py-Net, on the Cambridge Landmark dataset. We compared our results with those of existing camera relocalization methods, and the experiments demonstrated that the proposed method achieved state-of-the-art accuracy. Finally, we conducted ablation studies to investigate the contributions of individual components.
3.1 Dataset
The improvement in the proposed model was validated using the Cambridge Landmarks (Kendall Alex et al., 2015) dataset containing five outdoor landmarks scenes: Great Court, Kings College, Old Hospital, Shop Facade, and St. Mary’s Church. The dataset was more complex than indoor scenes; therefore, it better demonstrated the robustness of the model, as exterior environments undergo drastic environmental changes. For instance, the outdoor camera moves faster than the indoor camera, which may result in blurry images.
3.2 Evaluation metrics
As the camera relocalization error in outdoor environments is significant than that in indoor settings, using the a 1-cm distance error and 1° angle error as well as 2-cm distance error and 2° angle error are the evaluation metrics is not ideal. Therefore, the median distance error within 5 cm and median angle error of 5° were used as the evaluation metrics instead. We also report the percentage of high-precision localization points with a distance error within 5 cm and an angle error within 5°
3.3 Results and analysis
The performance of Py-Net was compared with existing visual localization systems on the Cambridge Landmarks dataset. Detailed results are shown in Table 1, where the primary indicators for evaluating the accuracy of camera relocalization are compared: translation error (m) and rotation error (°). Experimental results indicate that Py-Net considerably outperforms the existing methods. The translation error decreased by 40% using the SCR method than DSAC. This indicates that the voting segmentation network can considerably reduce the number of outliers in the scene and improve the relocalization accuracy. Py-Net outperformed VS-Net, which also employs a voting segmentation architecture, in the majority of scenes, particularly in the Great Court scene, where the translation and rotation errors decreased by 14% and 50%, respectively. This suggests that using Py-layer to enhance the backbone encoder, the network can learn multiscale features. Thus, the ability of backbone encoder to extract scene information enhances, resulting in better performance.
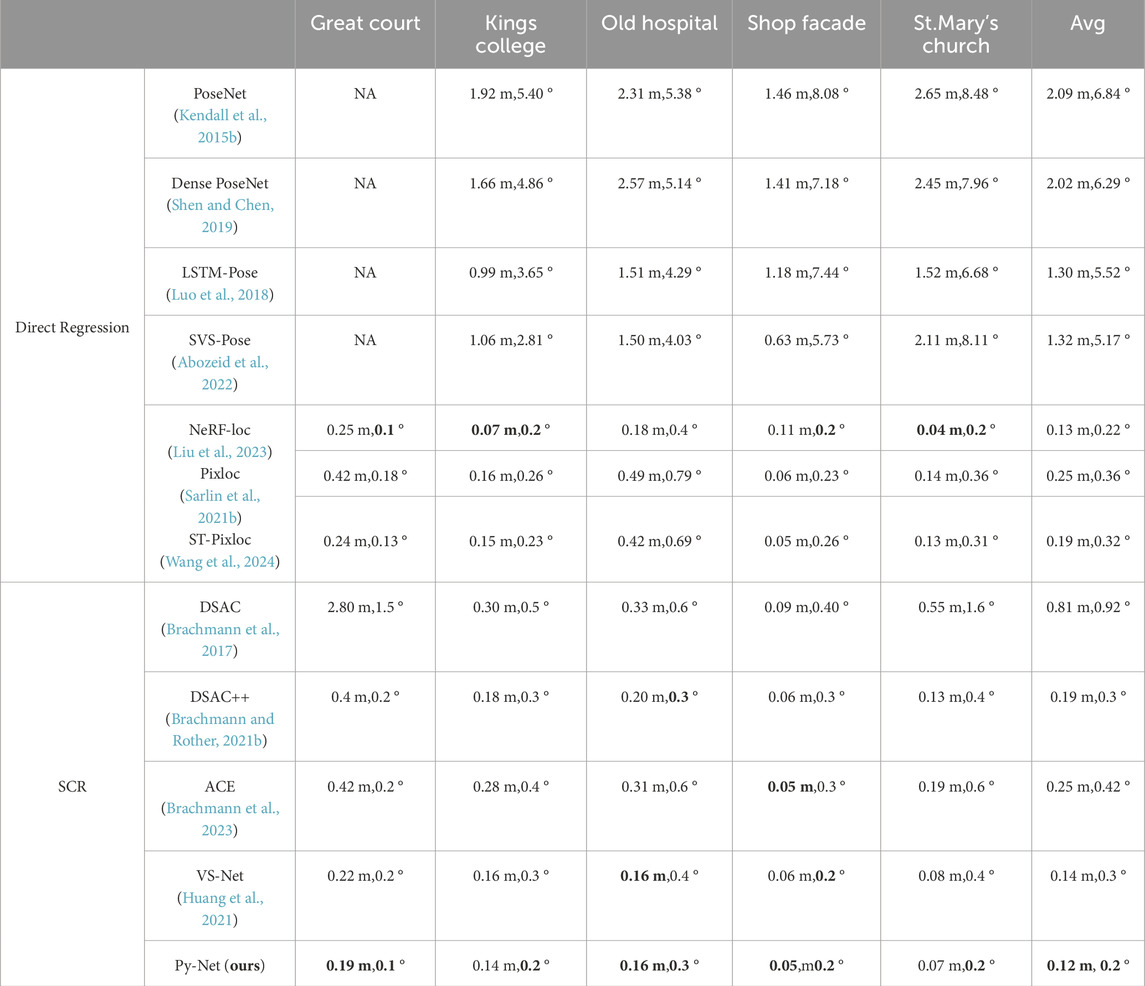
Table 1. Visual localization accuracy of state-of-the-art methods.We report the median translation error (m), rotation error (degrees), and localization precision, where the translation and rotation errors are within 5 cm and 5°, respectively. NA indicates no available values, Best results are in bold.
Figure 7 compares the scene coordinate prediction between VS-Net and Py-Net. In outdoor scenes, the enlarged scene scale results in a substantial number of invalid scene coordinate points. This affects the prediction accuracy and limits the scene information available for camera relocation.
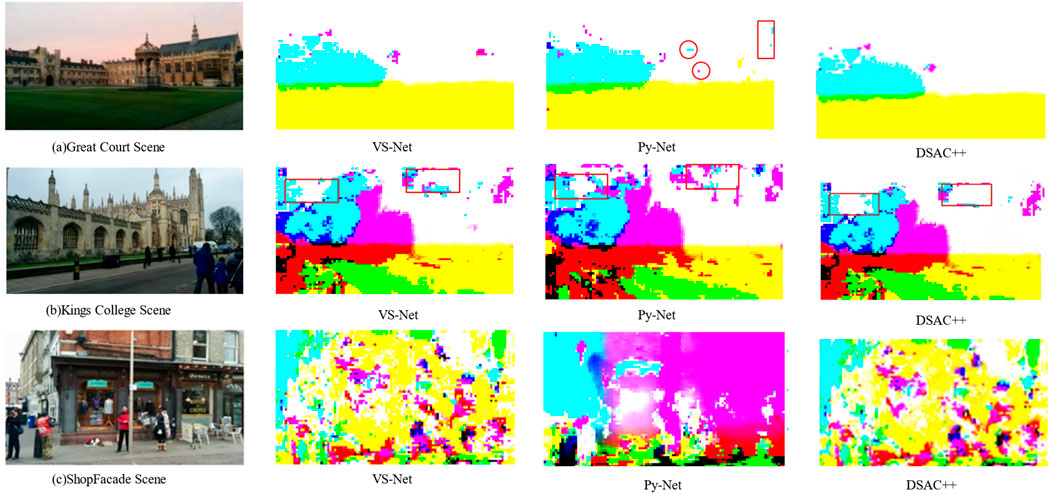
Figure 7. Comparison of scene coordinate predictions. (A) Great court snene; (B) Kings College Scene; (C) ShopFacade Scene. The network predicts the 2D-3D correspondences of the image, visualizing them as a scene coordinate map by rendering different coordinates in different colors. The richness of the scene information in the scene coordinate map significantly affects the accuracy of the PnP algorithm.
However, as shown in Figure 7A, Py-Net provides higher amounts of usable information within the predicted scene coordinate maps. In the Great Court scene, Py-Net generates a scene coordinate map with an increased level of scene information (Figure 7A). In the Kings College scene, the scene coordinate map predicted by Py-Net contains noticeably increased usable information (Figure 7B). The Shop Facade scene contains a substantial amount of usable scene information, with fewer background pixels representing the sky (Figure 7C). This indicates that incorporating depthwise separable convolutional modules into the scene coordinate decoder effectively enriches the amount of scene information, thereby enhancing the information representation capability of the network.
Figure 8 shows the positioning trajectories of the improved Py-Net on the Cambridge Landmark dataset. The figure compares the distance errors between VS-Net and Py-Net. Panels (a), (c), and (e) show the positioning trajectories of VS-Net, and panels (b), (d), and (f) show the positioning trajectories of the improved Py-Net. When zooming in on the positioning errors in the Great Court scene, a certain degree of reduction in distance errors can be observed. In the Kings College scene, Py-Net reduces the distance errors of marked points. As the test samples of the Shop Facade scene were limited, only a few positioning points with reduced errors are shown in the figure.
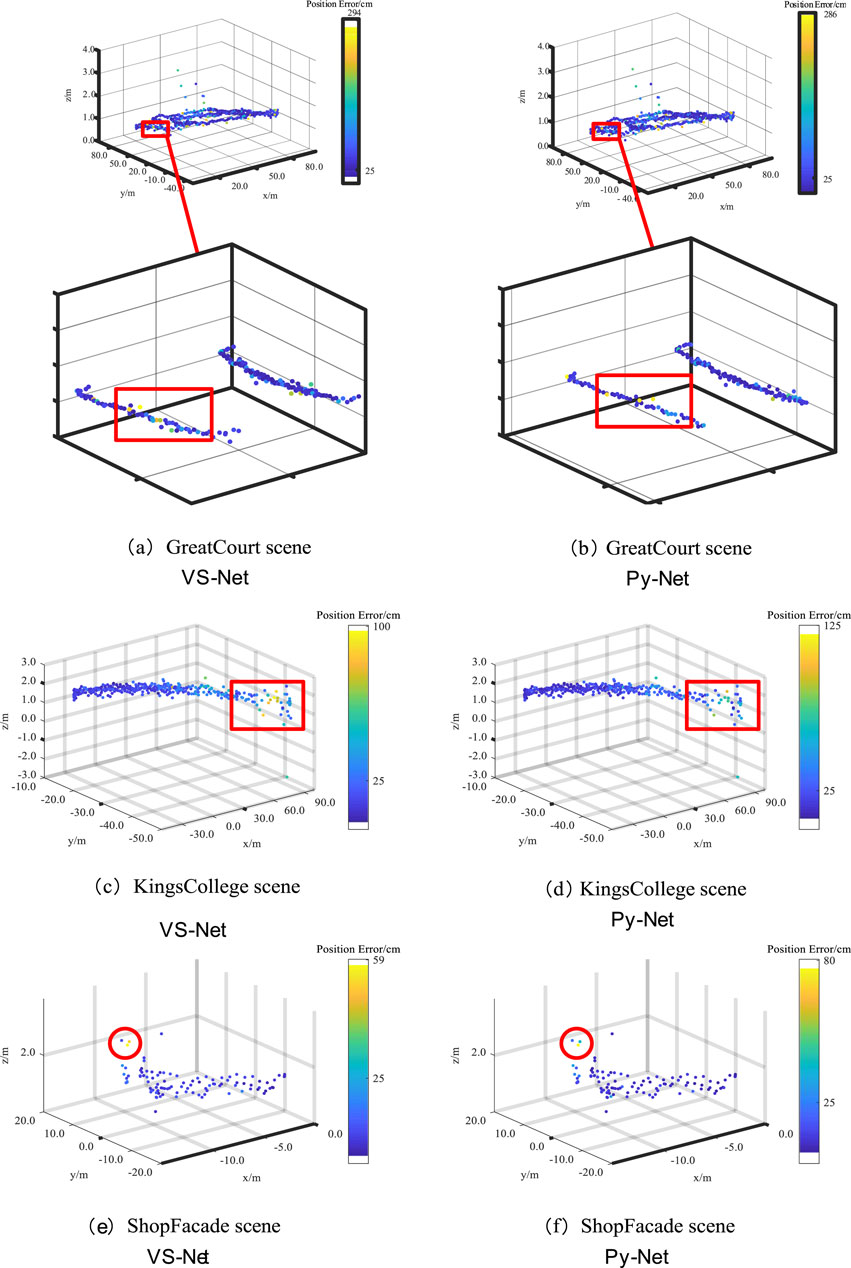
Figure 8. Comparison of Localization Trajectories on the Cambridge Landmark Dataset: VS-Net (A, C, E) vs. Improved Py-Net (B, D, F).
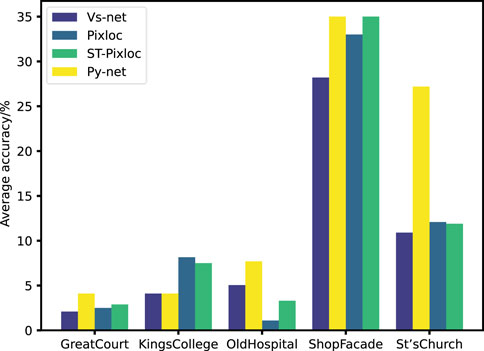
Figure 9 shows that in multiple scenes, Py-Net outperforms existing methods in the proportion of high-precision points with a distance error of less than 5 cm and an angle error of less than 5°. The increase in the proportion of high-precision localization points indicates that the number of invalid localization points in the scene has decreased, meaning that outliers have been filtered out.
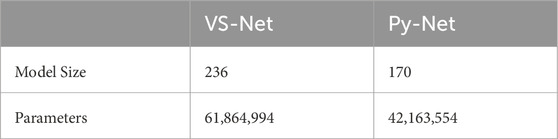
The Py-layer and depthwise separable convolution were introduced to enhance the performances of the main encoder and decoder, respectively. As a result, the size of Py-Net considerably compared with that of VS-Net (Table 2). Specifically, the model size decreased from 236 to 170 MB, and the parameter count was only 68.15% of the original. This improvement considerably enhanced the applicability of the model on devices with limited storage space.
Ablation experiments were conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the improvements proposed herein. By introducing the Py-layer and coordinated attention mechanism, Py-Net can effectively extract outdoor scene information and filter out invalid localization points in the scene. Thus, the model performance is improved across various scenes. In the Great Court scene, the distance error decreased by 16%, whereas in the Shop Facade and St. Mary’s Church scenes, the angle error decreased by 33%. As shown in Table 3, after incorporating the depthwise separable convolution module, the angle error of the network considerably increased across multiple scenes. This indicates that Py-Net can retain more scene information, thus achieving more accurate estimation results.
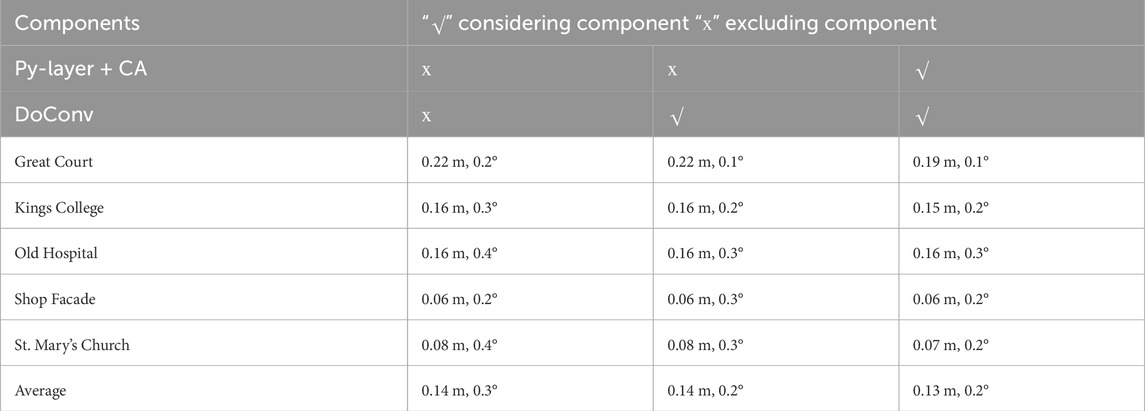
Table 3. Ablation experiment√ indicates the component is used, × indicates the component is not used.
4 Conclusion
This section summarizes the methods employed and the key findings of the study. The methods involved enhancing the performance of VS-Net for camera relocalization in outdoor scenes by optimizing its backbone network and improving feature extraction capability. The study resulted in a 14% increase in average translation accuracy on the Cambridge Landmark dataset, accompanied by a 30% reduction in model size.
Regarding potential real-time applicability, the optimized VS-Net model shows promise for real-time camera relocalization applications, particularly in outdoor environments. Future research directions may include further exploration of feature extraction techniques, investigating the model’s robustness in various environmental conditions, and integrating additional sensor modalities for improved performance and versatility.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Author contributions
JW: Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision. CG: Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Investigation. SH: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing. YW: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing. XF: Project administration, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (No. 62301414)Research on unconventional array beam synthesis method with limited excitation amplitude.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abozeid, A., Farouk, H., and Mashali, S. (2022). Depth-DensePose: an efficient densely connected deep learning model for camera-based localization. Int. J. Electr. and Comput. Eng. 12, 2792. doi:10.11591/ijece.v12i3.pp2792-2801
Arandjelovic, R., Gronat, P., and Torii, A. N. (2016). “CNN architecture for weakly supervised place recognition,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (USA: Las Vegas), 26–30.
Balntas, V., Li, S., and Prisacariu, V. R. (2018). “Continuous metric learning relocalisation using neural nets,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (Munich, Germany), 10–14.
Brachmann, E., Cavallari, T., and Prisacariu, V. A. (2023). Accelerated coordinate encoding: learning to relocalize in minutes using rgb and poses. CVPRdoi:10.1109/cvpr52729.2023.00488
Brachmann, E., Krull, A., Nowozin, S., Shotton, J., Michel, F., Gumhold, S., et al. (2017) “Dsac-differentiable ransac for camera localization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Brachmann, E., and Rother, C. (2021a). Visual camera Re-localization from RGB and RGB-D images using DSAC. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis Mach. Intell. 44, 5847–5865. doi:10.1109/tpami.2021.3070754
Brachmann, E., and Rother, C. (2021b). Visual camera re-localization from RGB and RGB-D images using DSAC. IEEE Trans. pattern analysis Mach. Intell. 44 (9), 5847–5865. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3070754
Bui, T., Tran, D., and Lee, J. (2022). Fast and lightweight scene regressor for camera relocalization. arXiv, 01830. arXiv:2212.
Cai, M., and Zhan, H. (2019). “Camera relocalization by exploiting multi-view constraints for scene coordinates regression,” in Proceed-ings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision workshops (Seoul, Korea), 27–18.
Cao, J., Li, Y., Sun, M., Chen, Y., Lischinski, D., Cohen-Or, D., et al. (2022). Do-conv: depthwise over-parameterized convolutional layer. IEEE Trans. Image Pro-cessing, 31, 3726, 3736. doi:10.1109/tip.2022.3175432
Chen, Z., Pei, H., and Wang, J. (2021). Survey of monocular camera-based visual relocalization. Robot 43, 373–384.
Dong, S., Fan, Q., and Wang, H. (2021). “Robust neural routing through space partitions for camera relocalization in dynamic indoor environments,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Nashville, TN: IEEE), 8540–8550. doi:10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00844
Duong, N., Soladie, C., Kacete, A., Richard, P. Y., and Royan, J. (2020). Efficient multi-output scene coordinate prediction for fast and accurate camera relocali-zation from a single RGB image. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 190, 102850. doi:10.1016/j.cviu.2019.102850
Huang, Z., Zhou, H., and Li, Y. (2021). “VS-net: voting with segmentation for visual localization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF con-ference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Nashville, TN: IEEE), 6097–6107. doi:10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00604
Kendall, A., Grimes, M., and Cipolla, R. (2015a). “Posenet: a convolutional network for real-time 6-DOF camera relocalization,” in Pro-ceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 11–17. Santiago, Chile.
Kendall, A., Grimes, M., and Cipolla, R. (2015b) “Posenet: a convolutional network for real-time 6-dof camera relocali-zation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision.
Laskar, Z., Melekhov, I., and Kalia, S. (2017). “Camera relocalization by computing pairwise relative poses using convolutional neural network,” in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops, 22–29. Venice,Italy.
Li, X., et al. (2018). “Scene coordinate regression with angle-based reprojection loss for camera relocalization,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) workshops.
Li, X., Wang, S., and Zhao, Y. (2020). “Hierarchical scene coordinate classification and regression for visual localization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Seattle, USA), 14–19.
Liu, J., Nie, Q., Liu, Y., and Wang, C. (2023). “Nerf-loc: visual localization ith conditional neural radiance field,” in Icra.
Luo, Y., et al. (2018) “Lstm pose machines,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Sarlin, P. E., Unagar, A., Larsson, M., Germain, H., Toft, C., Larsson, V., et al. (2021). “Back to the Feature: Learning Robust Camera Localization from Pixels to Pose,” in 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)(Nashville), 19–25.
Sarlin, P.-E., et al. (2021b) “Back to the feature: learning robust camera localization from pixels to pose,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Shavit, Y., and Ferens, R. (2019). Introduction to camera pose estimation with deep learning. arXiv, 05272. arXiv:1907.
Shen, Li, and Chen, Y. (2019) “Supervised high-dimension endecoder net: 3D end to end prediction network for mark-less human pose estimation from single depth map,” in 2019 5th international conference on control, automation and robotics (ICCAR). IEEE.
Turkoglu, M., Brachmann, E., and Schindler, K. (2021). “Visual camera Re-localization using graph neural networks and relative pose supervision,” in Proceedings of the international conference on 3D vision (Online), 1–3.
Wald, J., Sattler, T., and Golodetz, S. (2020). “Beyond controlled environments: 3D camera Re-localization in changing indoor scenes,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (Glasgow, UK), 23–28.
Wang, J., Wang, Y., Jin, Y., Guo, C., and Fan, X. (2024). ST-PixLoc: a scene-agnostic network for enhanced camera localization. IEEE Access 12, 105294–105308. doi:10.1109/access.2024.3435851
Yang, L., Bai, Z., and Tang, C. (2019). “SANet: scene agnostic network for camera localization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF interna-tional conference on computer vision (Seoul, Korea).
Keywords: camera relocalization, coordinate attention, pyramidal convolution, landmark segmentation map, landmark voting map
Citation: Wang J, Guo C, Hu S, Wang Y and Fan X (2024) Enhanced outdoor visual localization using Py-Net voting segmentation approach. Front. Robot. AI 11:1469588. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1469588
Received: 24 July 2024; Accepted: 10 September 2024;
Published: 09 October 2024.
Edited by:
Yinlong Liu, University of Macau, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Wang, Guo, Hu, Wang and Fan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Wang, YWppbmcyMDNAeHVzdC5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jing Wang*†
Jing Wang*† Cheng Guo
Cheng Guo