
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT article
Front. Psychol., 26 February 2025
Sec. Educational Psychology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1536951
This article is part of the Research TopicProtective vs Risk Factors for Stress and Psychological Well-being in Academic University ContextsView all 5 articles
Interpersonal Emotion Regulation (IER) may serve as a critical link between the established roles of social support and emotion regulation in mitigating academic burnout. This study explored the hypothesis that IER influences academic burnout through its impact on social support. 156 undergraduate students were involved in the study, with measures assessing academic burnout (Maslach Burnout Inventory—Student Survey), IER (Difficulties in Interpersonal Emotion Regulation), and social support (Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support). Results confirmed the protective role of social support and revealed distinct effects of different IER forms. Specifically, reassurance-seeking emerged as a protective factor, positively predicting social support and indirectly reducing burnout levels. Conversely, venting was found to exacerbate burnout both directly and indirectly, by diminishing social support.
While initially studied in the context of workplace stress (Freudenberger, 1974), the concept of burnout has been adapted to educational environments. “Academic Burnout” (AB) refers to a condition marked by exhaustion from study demands, a cynical or detached attitude toward university tasks, and a sense of ineffectiveness in relation to academic performance (Schaufeli et al., 2002; Zhang et al., 2006). AB has become a widespread phenomenon among university students, with overall prevalence of each dimension of the syndrome estimated at 55.4% for emotional exhaustion, 31.6% for cynicism, and 30.9% for academic efficacy (Rosales-Ricardo et al., 2021). Students experiencing burnout are more likely to have low academic performance, and increased levels of stress and anxiety, which can lead to more severe issues such as substance abuse and suicidal ideation (Deeb et al., 2018; Kadhum et al., 2022; Dyrbye et al., 2008). Moreover, AB correlates with a heightened risk of extended academic timelines, delayed graduation, and even dropout (Rahmati, 2015; Madigan and Curran, 2021).
Social Support (SS) is commonly defined as the perception or experience of being cared for, valued, and part of a network of mutual assistance and obligations (Cobb, 1976). According to the stress-buffering hypothesis (Cohen and Wills, 1985), SS protects individuals from the harmful effects of stress by either mitigating the perception of stress or providing resources to effectively cope with it. This hypothesis has been extensively validated through numerous studies, which consistently demonstrate that SS serves as both a predictive and protective factor against burnout (House, 1981; Viswesvaran et al., 1999; Halbesleben, 2006; Kim et al., 2018). In the context of AB, a recent meta-analysis highlights that SS not only buffers stress but also enhances students’ ability to manage academic and practical challenges effectively (Kim and Lee, 2022), especially individuals’ subjective belief or perception of the availability of support from their social network (‘perceived social support’) (Bahar et al., 2024). Additionally, SS significantly influences the relationship between burnout and subjective well-being (Rehman et al., 2020).
The university is considered a high-stress context for students due to academic pressure (e.g., tight deadlines and high expectations), financial strain, social adjustments, and future uncertainty regarding career prospects (Beiter et al., 2015). In academic settings, as in other high-stress contexts, emotion regulation plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of stress by shaping individuals’ emotional responses to challenging events (Chacón-Cuberos et al., 2019). Emotion regulation refers to the processes by which individuals influence the emotions they experience, when they experience them, and how they express and manage these emotions (Gross, 1998). A recent meta-analysis (Iuga and David, 2024) highlights emotion regulation as a significant factor in academic well-being, showing that adaptive strategies are negatively associated with AB, while maladaptive strategies can amplify the effects of stressful environments. Despite the importance of these previous findings, they neglect the role of interpersonal features of emotion regulation, that would be particularly relevant in association with SS. Interpersonal Emotion Regulation (IER) refers to efforts within social interactions in the pursuit of a regulatory goal, including all that ways by which individuals rely on others to regulate their emotion (Zaki and Williams, 2013). Previous contributions highlighted the relevance of IER as interconnection between SS and psychological suffering. For instance, Marroquín (2011) proposed a model built on substantial evidence highlighting the buffering role of SS in mitigating depression symptoms during adversity and suggested that IER strategies may mediate this protective effect. A recent study confirmed this hypothesis showing that the need to be soothed while regulating negative emotions may push people to seek SS, which can protect them from psychological distress (Gökdağ, 2021). Extending this hypothesis, we propose that IER may impact social support, which, in turn, could influence academic burnout. It is possible, however, that other forms of IER strategies may have different effects in the interplay between SS and AB. For instance, interpersonal venting and excessive reassurance-seeking are considered maladaptive IER strategies (Dixon-Gordon et al., 2018a; Messina et al., 2022), as they can lead to negative interpersonal outcomes, such as rejection, conflicts, or abandonment. These consequences may, in turn, reduce the availability of SS, exacerbating the risk of AB.
The aim of this study was to investigate the interplay between SS, IER, and AB among university students. Specifically, we first examined the statistical associations among these variables, with the expectation of confirming previous evidence that SS is negatively associated with AB. Second, we aimed to explore the relatively underexamined relationship between IER and AB, hypothesizing that greater use of IER strategies might correlate with higher levels of AB. Finally, we tested the hypothesis that IER mediates the relationship between SS and AB. Specifically, we propose that IER may shape perceptions or availability of social support, which, in turn, influences levels of academic burnout.
The study was conducted at Mercatorum University, a private Italian online university. The study sample included 156 undergraduate students (80 males, 76 females), with mean age 36.46(±11.14). The demographic characteristics of our participants are summarized in Table 1. Potential participants were invited electronically via email to students’ listservs. Questionnaires were administered using Google Forms, with access links distributed to students through the university psychological counseling service email list. This study received approval from the Ethical Committee for Psychological Research at Mercatorum University. Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
The MBI-SS (Schaufeli et al., 1996) is a 15-item self-report questionnaire composed of three subscales: Exhaustion (e.g., “I feel used up at the end of a day at university”), Cynicism (e.g., “I doubt the significance of my studies”), and Professional Efficacy (e.g., “During class I feel confident that I am effective in getting things done”). We used the Italian version of MBI-SS from the study of Portoghese et al. (2018), in which reliability coefficients for each of the subscale scores were 0.86 for Exhaustion, 0.82 for Cynicism and 0.77 for Professional Efficacy.
The DIRE is a scenario-based measure (Dixon-Gordon et al., 2018a), in which participants are invited to indicate, for each scenario, the likelihood that they would respond in the way described in each item, using a Likert scale ranging from 1 (“very unlikely”) to 5 (“very likely”). The DIRE allows the assessment of two forms of difficulties in interpersonal emotion regulation: Vent (e.g., “Raise your voice or criticize your friends to express how you feel”) and Reassurance-seek (e.g., “Keep asking for reassurance”). In the validation study of the Italian version of the DIRE good internal consistencies have been reported for both the Vent (α = 76) and Reassurance- Seek (α = 0.87) subscales (Messina et al., 2022).
The MSPSS (Zimet et al., 1988) is a self-report questionnaire composed by 12-item scored by using a 7-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (“strongly disagree”) to 7 (“strongly agree”). The items are organized in three subscales assessing different SS contexts: Family Support (e.g., “My family really tries to help me”), Friend Support (e.g., “I can count on my friends when things go wrong”), and Significant Other Support (e.g., “There is a special person with whom I share joys and sorrows”). Coefficient α for the Italian version in a previous study was 0.87 (Fabio and Kenny, 2012).
Table 2 reports descriptive statistics for the selected variables. It can be noted that the asymmetry and kurtosis values were always comprised between 1 and − 1, suggesting that the distributions of all variables were approximately normal (Tabachnick and Fidell, 1989). To formally test this assumption, we computed Mardia’s multivariate skewness and kurtosis coefficients, using the calculator provided by Cain et al. (2017). According to Bollen (1989), if Mardia’s coefficients are lower than p(p + 2), where p is the number of observed variables involved in the analysis, then the combined distribution of the variables is multivariate normal. In the present study, these coefficients were 4.02 for skewness and 46.87 for kurtosis, which were both safely lower than the threshold value (48).
Table 3 illustrates Pearson’s correlations. As can be noted: exhaustion and cynism were positively associated with Vent, but negatively associated with SS. Thus, as expected, students who used venting to a greater extent reported higher levels of exhaustion and cynism and lower levels of professional efficiency, whereas students who perceived greater SS reported lower levels of exhaustion and cynism and higher levels of professional efficiency. In addition, reassurance-seeking was positively associated with perceived social support, confirming that students who used this IER strategy to a greater extent were also more likely to perceive high social support. Lastly, reassurance-seeking and venting were positively correlated.
To determine which variables predicted AB, we performed a path analysis using the pathj module of Jamovi, which is based on the lavaan R package (Rosseel, 2012) and also allowed us to test indirect mediation effects. Reassurance-seeking and venting were considered as the exogenous variable, SS as the endogenous mediator, and exhaustion, cynism and professional efficiency as the endogenous output variables. We began from a fully-saturated model which included all the predicted paths and iteratively stripped away non-significant paths, until we were left with a parsimonious model which showed an acceptable fit to the data – χ2(4) = 5.97, p = 0.20, CFI = 0.98, adj.GFI = 0.99, RMSEA = 0.056 [95% CI: 0.000–0.143, p = 0.37]. The model explained 19.1% of the variance in social support, 12.8% of the variance in exhaustion, 10.6% of the variance in cynism, and 2.4% of the variance in professional efficiency. As illustrated in Figure 1, the following paths were significant: (a) SS was positively predicted by reassurance-seeking (β = 0.43, z = 5.91, p < 0.001) and negatively predicted by venting (β = −0.17, z = −2.35, p = 0.019); (b) exhaustion and cynism were negatively predicted by SS (β = −0.28, z = −3.76, p < 0.001 and β = −0.18, z = −2.40, p = 0.017, respectively) and positively predicted by venting (β = 0.19, z = 2.59, p = 0.010 and β = 0.25, z = 3.46, p < 0.001, respectively); and (c) professional efficiency was positively predicted by SS (β = 0.15, z = 1.97, p = 0.049).
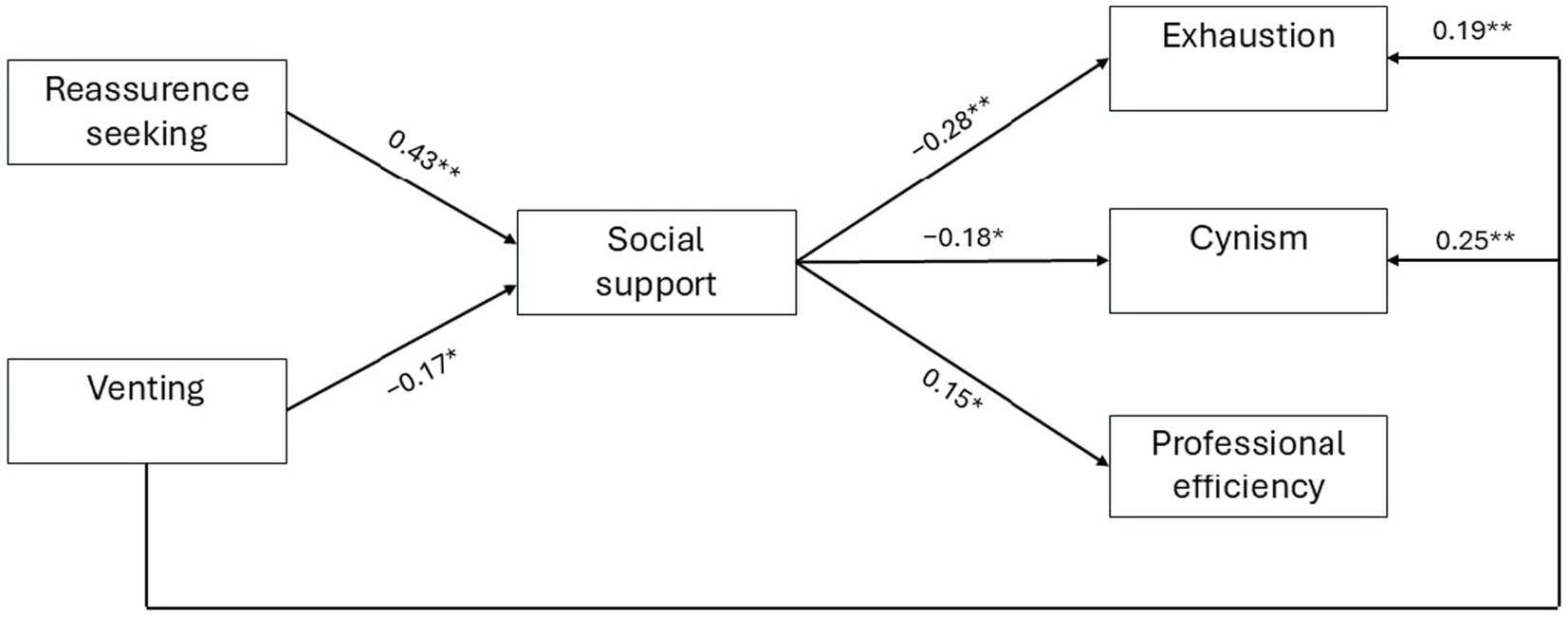
Figure 1. Final model of path analysis. Numbers refer to standardized paths (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
Most importantly, we also tested the significance of indirect effects via a bootstrapping procedure (5,000 iterations), using 95% confidence intervals. The consensus is that, if the confidence interval does not contain zero, then the indirect effect can be considered significant (Preacher and Hayes, 2004, 2008). The results (see Table 4) indicated that: (a) higher levels of reassurance-seeking predicted significant decreases in exhaustion and cynism by increasing SS (β = −0.12 [95%CI: −0.188, −0.041], z = −3.07, p = 0.002 and β = −0.07 [95%CI: −0.137, −0.002], z = −2.04, p = 0.040, respectively) and (b) higher levels of venting predicted significant increases in exhaustion by decreasing SS (β = 0.06 [95%CI: 0.000, 0.122], z = 1.97, p = 0.049). On the other hand, the positive indirect effect of reassurance-seeking on professional efficiency via increases in SS (β = 0.03 [95%CI: −0.031, 0.100], z = 1.01, p = 0.308) and the positive indirect effect of venting on cynism via decreases in SS (β = 0.04 [95%CI: −0.008, 0.082], z = 1.59, p = 0.110) did not reach the standard significance level, as well as the negative indirect effect of venting on professional efficiency via decreases in SS (β = −0.01 [95%CI: −0.056, 0.019], z = −0.94, p = 0.34).
In line with prior research, our findings reaffirm the critical role of perceived SS in influencing students’ susceptibility to AB. SS emerged as a significant predictor across all dimensions of burnout, consistent with the well-established buffering hypothesis that emphasizes its protective role against stress-related outcomes (Cohen and Wills, 1985). Notably, the negative correlation between emotional exhaustion and total SS was stronger than the correlations observed for cynicism or professional efficacy. This suggests that emotional exhaustion - the most prominent and debilitating component of burnout—may be particularly sensitive to the availability and perception of social support, corroborating findings from earlier studies in work burnout (for a meta-analysis see Halbesleben, 2006) and AB (Rigg et al., 2013; Li et al., 2018).
Reassurance-seeking emerged as a protective factor, positively predicting SS and, through this increase, indirectly contributing to significant reductions in emotional exhaustion and cynicism while enhancing professional efficacy. As an interpersonal form of emotion regulation, reassurance-seeking involves actively seeking validation, comfort, or guidance from others during times of stress. This aligns with the hypothesis that IER strategies can strengthen social support, amplifying its protective effects against psychological distress (Marroquín, 2011; Gökdağ, 2021). Our findings are also in line with prior research demonstrating that reassurance-seeking fosters supportive relationships that provide both emotional sustenance and practical resources to navigate academic challenges (Kahn and Byosiere, 1992; Tripon, 2023). However, while reassurance-seeking appears beneficial in this context, caution is warranted given contrasting evidence highlighting potential risks if it becomes excessive or chronic. For example, the pursuit of constant validation from others, such as frequently asking for approval or reassurance about one’s appearance or performance, can undermine self-confidence and lead to emotional dependence (Dixon-Gordon et al., 2018b). Moreover, over time, excessive reassurance-seeking can strain relationships, lead to dependency (Joiner et al., 1999) and disrupt interpersonal networks for emotion regulation (Abe and Nakashima, 2022). These patterns can render reassurance-seeking interpersonally toxic and mark it as a potential behavioral indicator of risk for psychiatric concerns (Stewart and Harkness, 2015; Wakeling et al., 2020). Thus, while reassurance-seeking is valuable as an adaptive strategy, its long-term impacts and balance within relationships warrant careful consideration in future studies.
In contrast, venting appears to play a risk-enhancing role in students’ burnout. In our findings, venting had a dual negative impact on students’ burnout: one indirect, mediated by the loss of social support, and the other direct. Regarding the indirect influence, venting may erode the social networks that are crucial for buffering stress. Negative venting can lead to emotional contagion, where negative emotions are transferred to others, ultimately damaging relationships (Vijayalakshmi and Bhattacharyya, 2012; Niven et al., 2024). Indeed, venting may overwhelm the listeners, resulting in emotional fatigue and diminishing their capacity to offer supportive feedback. This weakening of SS further exacerbates burnout and emotional distress.
The direct effect of venting on emotional exhaustion and cynicism can be understood through the lens of cognitive neo-association theory (Berkowitz, 2012). According to this theory, venting may keep anger and frustration active in memory, reinforcing negative moods (Bushman, 2002). Previous research has linked the harmful effects of venting to a variety of mental health concerns, including depression (Malooly et al., 2017; Messina et al., 2023), borderline personality symptoms (Dixon-Gordon et al., 2018a, 2018b; Messina et al., 2022), and suicidal ideation (Chou et al., 2018). In the context of burnout, this mechanism may explain how venting exacerbates emotional exhaustion and cynicism in response to academic stressors, by perpetuating negative emotional states and hindering the recovery from stress.
This study has several limitations. First, due to the cross-sectional design of the current study, the temporal sequence of the independent variables, mediators, and dependent variables (causality) cannot be verified. This limitation is particularly relevant for reassurance-seeking, which emerged as a protective factor in this study, contrasting with previous evidence suggesting that excessive reassurance-seeking can have negative long-term consequences (Stewart and Harkness, 2015). To address this issue, future research could adopt a longitudinal design to better assess causal relationships and provide a more comprehensive understanding of how IER and SS influence AB among university students over time. Second, our sample was drawn from a single group of undergraduate students within one cultural context (Italy) and the specific setting of an online university, with students that may differ from those in traditional university environment (Pentina and Neeley, 2007). This unique composition may limit the generalizability of our findings to other student populations. Expanding research across diverse cultural and educational contexts is critical to enhancing the generalizability of findings. Future investigations into traditional versus online university settings or different cultural attitudes towards IER strategies can uncover nuanced insights. Finally, IER was assessed using a theory-driven instrument that focused exclusively on the dispositional use of reassurance-seeking and venting as emotion regulation strategies. This approach limits our ability to determine whether students employed other strategies to manage their emotions related to academic stress. Future studies using data-driven instruments or observational methods could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the range of strategies students use and identify which are most effective in mitigating AB.
This study enhances our understanding of the interplay between social support, interpersonal emotion regulation, and academic burnout among university students. Our findings confirm the protective role of SS and underscore the significant mediating function of IER. Specifically, reassurance-seeking emerged as a positive interpersonal strategy, bolstering SS and reducing burnout, while venting acted as a maladaptive strategy that eroded SS and exacerbated burnout symptoms. These results align with existing literature on the stress-buffering effects of SS and suggest that fostering adaptive IER, particularly through reassurance-seeking, while minimizing the use of venting, could be an effective strategy to reduce burnout and improve academic well-being. This study provides valuable insights for clinical practice aimed at reducing AB and promoting mental well-being among university students. Based on our results, and in line with previous contributions (Tang et al., 2021; Messina et al., 2021; Messina et al., 2024), group psychological interventions targeting IER could be promising to contrast AB.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by Commissione Etica Universitas Mercatorum. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
IM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TR: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. RM: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. CL: Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. PS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research received a grant from Mercatorum University (“Bandi competitivi di Ateneo, Grant No: 9-FIN/RIC”).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The authors declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. CHATGPT for editing.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abe, K., and Nakashima, K. (2022). Excessive reassurance-seeking and mental health: interpersonal networks for emotion regulation. Curr. Psychol. 41, 4711–4721. doi: 10.1007/s12144-020-00955-2
Bahar, Y., Murdiana, S., and Rifani, R. (2024). Academic burnout from various sources of social support in undergraduate psychology students. In ISPsy 2023: Proceedings of the 6th international seminar on psychology.
Beiter, R., Nash, R., McCrady, M., Rhoades, D., Linscomb, M., Clarahan, M., et al. (2015). The prevalence and correlates of depression, anxiety, and stress in a sample of college students. J. Affect. Disord. 173, 90–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.10.054
Berkowitz, L. (2012). A different view of anger: The cognitive‐neoassociation conception of the relation of anger to aggression. Aggress. Behav. 38, 322–333.
Bushman, B. J. (2002). Does venting anger feed or extinguish the flame? Catharsis, rumination, distraction, anger, and aggressive responding. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 28, 724–731. doi: 10.1177/0146167202289002
Cain, M. K., Zhang, Z., and Yuan, K. (2017). Univariate and multivariate skewness and kurtosis for measuring nonnormality: prevalence, influence and estimation. Behav. Res. Methods 49, 1716–1735. doi: 10.3758/s13428-016-0814-1
Chacón-Cuberos, R., Martínez-Martínez, A., García-Garnica, M., Pistón-Rodríguez, M. D., and Expósito-López, J. (2019). The relationship between emotional regulation and school burnout: structural equation model according to dedication to tutoring. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16:4703. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16234703
Chou, W. P., Yen, C. F., and Liu, T. L. (2018). Predicting effects of psychological inflexibility/experiential avoidance and stress coping strategies for internet addiction, significant depression, and suicidality in college students: a prospective study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15:788. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15040788
Cobb, S. (1976). Social support as a moderator of life stress. Psychosom. Med. 38, 300–314. doi: 10.1097/00006842-197609000-00003
Cohen, S., and Wills, T. A. (1985). Stress, social support, and the buffering hypothesis. Psychol. Bull. 98, 310–357. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.98.2.310
Deeb, G. R., Braun, S., Carrico, C., Kinser, P., Laskin, D., and Golob Deeb, J. (2018). Burnout, depression and suicidal ideation in dental and dental hygiene students. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 22, e70–e74. doi: 10.1111/eje.12259
Dixon-Gordon, K. L., Haliczer, L. A., Conkey, L. C., and Whalen, D. J. (2018a). Difficulties in IER: initial development and validation of a self-report measure. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 40, 528–549. doi: 10.1007/s10862-018-9647-9
Dixon-Gordon, K. L., Hollenbaugh, K. M., and Sullivan, A. L. (2018b). The role of reassurance seeking in borderline personality pathology. Personal. Disord. Theory Res. Treat. 9, 248–257.
Dyrbye, L. N., Thomas, M. R., Massie, F. S., Power, D. V., Eacker, A., Harper, W., et al. (2008). Burnout and suicidal ideation among U.S. medical students. Ann. Intern. Med. 149, 334–341. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-149-5-200809020-00008
Fabio, A. D., and Kenny, M. E. (2012). Emotional intelligence and perceived social support among Italian high school students. J. Career Dev. 39, 461–475. doi: 10.1177/0894845311421005
Gökdağ, C. (2021). How does IER explain psychological distress? The roles of attachment style and social support. Personal. Individ. Differ. 176:110763. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2021.110763
Gross, J. J. (1998). The emerging field of emotion regulation: An integrative review. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2, 271–299. doi: 10.1037/1089-2680.2.3.271
Halbesleben, J. R. (2006). Sources of social support and burnout: a meta-analytic test of the conservation of resources model. J. Appl. Psychol. 91, 1134–1145. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.91.5.1134
Iuga, I. A., and David, O. A. (2024). Emotion regulation and AB among youth: a quantitative meta-analysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 36:106. doi: 10.1007/s10648-024-09930-w
Joiner, T. E., Metalsky, G. I., Katz, J., and Beach, S. R. (1999). Depression and excessive reassurance-seeking. Psychol. Inq. 10, 269–278. doi: 10.1207/S15327965PLI1004_1
Kadhum, M., Ayinde, O. O., Wilkes, C., Chumakov, E., Dahanayake, D., Ashrafi, A., et al. (2022). Wellbeing, burnout and substance use amongst medical students: A summary of results from nine countries. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry., 68, 1218–1222.
Kahn, R. L., and Byosiere, P. (1992). “Stress in organizations” in Handbook of industrial and organizational psychology. eds. M. D. Dunnete and L. M. Hough (Palo Alto: Consulting Psychologists), 571–650.
Kim, B., Jee, S., Lee, J., An, S., and Lee, S. M. (2018). Relationships between SS and student burnout: a meta-analytic approach. Stress. Health 34, 127–134. doi: 10.1002/smi.2771
Kim, H. O., and Lee, I. (2022). The mediating effects of social support on the influencing relationship between grit and AB of the nursing students. Nurs. Open 9, 2314–2324. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1241
Li, J., Han, X., Wang, W., Sun, G., and Cheng, Z. (2018). How social support influences university students' academic achievement and emotional exhaustion: the mediating role of self-esteem. Learn. Individ. Differ. 61, 120–126. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2017.11.016
Madigan, D. J., and Curran, T. (2021). Does burnout affect academic achievement? A meta-analysis of over 100,000 students. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 33, 387–405. doi: 10.1007/s10648-020-09533-1
Malooly, A. M., Flannery, K. M., and Ohannessian, C. M. (2017). Coping mediates the association between gender and depressive symptomatology in adolescence. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 41, 185–197. doi: 10.1177/0165025415616202
Marroquín, B. (2011). Interpersonal emotion regulation as a mechanism of social support in depression. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 31, 1276–1290. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.09.005
Messina, I., Calvo, V., Masaro, C., Ghedin, S., and Marogna, C. (2021). Interpersonal emotion regulation: from research to group therapy. Front. Psychol. 12:636919. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.636919
Messina, I., Maniglio, R., and Spataro, P. (2023). Attachment insecurity and depression: the mediating role of interpersonal emotion regulation. Cogn. Ther. Res. 47, 637–647. doi: 10.1007/s10608-023-10386-5
Messina, I., Rossi, T., Bonaiuto, F., Granieri, G., Cardinali, P., Petruccelli, I., et al. (2024). Group psychological counseling to contrast academic burnout: a research protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Front. Psychol. 15:1400882. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1400882
Messina, I., Spataro, P., Grecucci, A., Marogna, C., and Dixon-Gordon, K. L. (2022). Difficulties in interpersonal regulation of emotions (DIRE) questionnaire: psychometric properties of the Italian version and associations with psychopathological symptoms. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 44, 1126–1134. doi: 10.1007/s10862-022-09992-6
Niven, K., Hughes, D. J., Tan, J. K., and Wickett, R. (2024). Individual differences in interpersonal emotion regulation: What makes some people more (or less) successful than others?. Soc. Personal Psychol. Compass. 18:e12951.
Pentina, I., and Neeley, C. (2007). Differences in characteristics of online versus traditional students: implications for target marketing. J. Mark. High. Educ. 17, 49–65. doi: 10.1300/J050v17n01_05
Portoghese, I., Leiter, M. P., Maslach, C., Galletta, M., Porru, F., D’Aloja, E., et al. (2018). Measuring burnout among university students: factorial validity, invariance, and latent profiles of the Italian version of the Maslach Burnout Inventory Student Survey (MBI-SS). Front. psychol., 9, 2105.
Preacher, K. J., and Hayes, A. F. (2004). SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 36, 717–731.
Preacher, K. J., and Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav. Res. Methods. 40, 879–891.
Rahmati, Z. (2015). The study of academic burnout in students with high and low level of self-efficacy. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 171, 49–55. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.087
Rehman, A. U., Bhuttah, T. M., and You, X. (2020). Linking burnout to psychological well-being: the mediating role of social support and learning motivation. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 13, 545–554. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S250961
Rigg, J., Day, J., and Adler, H. (2013). Emotional exhaustion in graduate students: the role of engagement, self-efficacy and social support. J. Educ. Dev. Psychol. 3:138. doi: 10.5539/jedp.v3n2p138
Rosales-Ricardo, Y., Rizzo-Chunga, F., Mocha-Bonilla, J., and Ferreira, J. P. (2021). Prevalence of burnout syndrome in university students: a systematic review. Salud Mental 44, 91–102. doi: 10.17711/SM.0185-3325.2021.013
Rosseel, Y. (2012). Lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 48, 1–36. doi: 10.18637/jss.v048.i02
Schaufeli, W. B., Leiter, M. P., Maslach, C., and Jackson, S. E. (1996). “The MBIgeneral survey” in Maslach burnout inventory manual. eds. C. Maslach, S. E. Jackson, and M. P. Leiter (Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press).
Schaufeli, W. B., Martínez, I. M., Pinto, A. M., Salanova, M., and Bakker, A. B. (2002). Burnout and engagement in university students: a cross-national study. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 33, 464–481. doi: 10.1177/0022022102033005003
Stewart, J. G., and Harkness, K. L. (2015). The interpersonal toxicity of excessive reassurance-seeking: evidence from a longitudinal study of romantic relationships. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 34, 392–410. doi: 10.1521/jscp.2015.34.5.392
Tabachnick, B. G., and Fidell, L. S. (1989). Using multivariate statistics. 2nd Edn. Philadelphia: Harper and Row.
Tang, C., Wang, T., Luo, Y., and He, J. (2021). The effectiveness of online counseling in managing academic burnout. J. Educ. Psychol. 113, 302–316.
Tripon, C. (2023). Navigating the STEM jungle of professionals: unlocking critical competencies through emotional intelligence. J. Educ. Sci. Psychol. 13, 34–47. doi: 10.51865/JESP.2023.1.05
Vijayalakshmi, V., and Bhattacharyya, S. (2012). Emotional contagion and its relevance to individual behavior and organizational processes: a position paper. J. Bus. Psychol. 27, 363–374. doi: 10.1007/s10869-011-9243-4
Viswesvaran, C., Sanchez, J. I., and Fisher, J. (1999). The role of social support in the process of work stress: a meta-analysis. J. Vocat. Behav. 54, 314–334. doi: 10.1006/jvbe.1998.1661
Wakeling, S., Stukas, A. A., Wright, B. J., and Evans, L. (2020). Negative feedback seeking and excessive reassurance seeking behavior and depression: a meta-analytic review. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 39, 788–823. doi: 10.1521/jscp.2020.39.9.788
Zaki, J., and Williams, W. C. (2013). Interpersonal emotion regulation IER. Emotion 13, 803–810. doi: 10.1037/a0033839
Zhang, Y., Gan, Y., and Cham, H. (2006). Perfectionism, academic burnout, and academic engagement among Chinese college students. Psychol. Rep. 99, 813–823.
Keywords: interpersonal-emotion-regulation, social-support, venting, reassurance-seeking, academic-burnout, students-mental-health
Citation: Messina I, Rossi T, Maniglio R, Loconsole C and Spataro P (2025) Risk and protective factors in academic burnout: exploring the mediating role of interpersonal emotion regulation in the link with social support. Front. Psychol. 16:1536951. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1536951
Received: 29 November 2024; Accepted: 13 February 2025;
Published: 26 February 2025.
Edited by:
Jose Manuel Martinez-Vicente, University of Almeria, SpainReviewed by:
Cristina Tripon, Polytechnic University of Bucharest, RomaniaCopyright © 2025 Messina, Rossi, Maniglio, Loconsole and Spataro. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Irene Messina, aXJlbmUubWVzc2luYUB1bmltZXJjYXRvcnVtLml0
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.