- 1Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Zigong First People's Hospital, Zigong, Sichuan, China
- 2College of Education, Chengdu College of Arts and Sciences, Chengdu, China
- 3Nursing Department, Zhangjiajie People's Hospital, Zhangjiajie, Hunan, China
- 4Medical School, Jishou University, Jishou, Hunan, China
Objective: This study aims to explore the interactions between social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors among elderly residents in nursing homes in the Xiangxi region of China.
Methods: A random cluster sampling method was employed to select elderly individuals from 27 nursing homes in the Xiangxi area. Data were collected using the general information questionnaire, the Social Capital Scale, the Positive Psychological Capital Scale, and the Health-Promoting Behaviors Scale. The mediating role of positive psychological capital between social capital and health-promoting behaviors was analyzed.
Results: A total of 341 questionnaires were collected from 27 nursing homes. The data reveals mean scores of 46.83 ± 10.26 for social capital, 72.48 ± 6.39 for positive psychological capital, and 68.25 ± 10.85 for health-promoting behaviors. Mediation analysis shows that the total effect of social capital on health-promoting behaviors was 0.800 (95% CI: 0.726, 0.873), with a direct effect of 0.478 (95% CI: 0.379, 0.577), accounting for 59.75% of the total effect. The indirect effect, mediated by positive psychological capital, was 0.321 (95% CI: 0.233, 0.409), contributing to 40.13% of the total effect.
Conclusion: Positive psychological capital acts as a mediating variable between social capital and health-promoting behaviors. Future interventions designed to enhance health-promoting behaviors must consider both social and psychological capitals to fully leverage their interplay and further promote healthy aging.
1 Introduction
The trend of global aging is intensifying. According to predictions by the World Health Organization (WHO), the global population aged 60 and over is expected to increase from 1 billion in 2020 to 1.4 billion by 2030 (Rui, 2023). By 2050, this number is projected to double, reaching 2.1 billion (Rui, 2023). As the most populous country in the world, China has also fully entered an aging society (Hong et al., 2023). Based on the latest statistics, the population aged 60 and above now accounts for 19.8% of the total population in China (NBS, 2022). Furthermore, this proportion is expected to continue rising in the coming years. These demographic trends pose significant challenges for public health policies and social service systems, particularly in promoting the health and welfare of the elderly.
As individuals age, there is an inevitable decline in the function of various systems and organs, which naturally increases the risk of chronic diseases and can lead to significant deterioration in overall health (Liberale et al., 2020; Ou et al., 2022; Rohrmann, 2020). Specifically, the elderly population is commonly afflicted with chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and osteoporosis (Kardas et al., 2021; Kim, 2021; Liberale et al., 2020). These illnesses not only directly impact their daily functional abilities but also significantly reduce their quality of life (Pretto et al., 2020; Tinoco et al., 2021). Moreover, the management and treatment of these health issues not only place a financial burden on individuals and their families but also exert pressure on the entire healthcare system (Giovanni et al., 2020; Zare et al., 2020). Crucially, elderly individuals residing in nursing homes represent a group with a high incidence of chronic diseases, highlighting the need for focused attention on this population (Zhu et al., 2023). However, in most nursing homes in China, while basic medical and living support can be provided, there is often insufficient attention to promoting the overall well-being of the elderly—including physical, psychological, and social dimensions (Gordon et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2018). Existing research indicates that healthy aging requires more than just the treatment of diseases; it is crucial to adopt preventive measures, including enhancing the social and positive psychological capital of the elderly to support their health-promoting behaviors (Xu and Zhao, 2022; Afrashteh et al., 2024; Ye et al., 2024; Jeste et al., 2022). In this context, the impact of social capital and positive psychological capital on elderly health behaviors is particularly significant (Xu and Zhao, 2022; Afrashteh et al., 2024). Social capital can enhance social networks and community participation, providing the necessary support systems that help the elderly access health information and resources, thereby facilitating positive health behaviors (Xu and Zhao, 2022; Afrashteh et al., 2024). Additionally, positive psychological capital, characterized by hope, resilience, optimism, and self-efficacy, can motivate elderly individuals to face health challenges, maintaining a positive outlook and active lifestyle (Xu et al., 2024).
In the context of healthy aging, the concept of social capital has increasingly been incorporated into strategies for health promotion and disease prevention (Lu et al., 2023). Social capital is typically defined as the resources an individual can mobilize through their social networks, which not only facilitate personal actions but also form part of the social structure (Lu et al., 2023; Xu, 2018). Individual social capital is manifested in six dimensions: social participation, social connections, social support, reciprocity, trust, and a sense of belonging (Lu et al., 2023; Xu, 2018). Specifically, social participation refers to the frequency and extent to which elderly individuals engage in various activities and organizations within and outside nursing homes or communities (Jiang and Liu, 2023; Yuying and Jing, 2022). Social connections refer to the frequency and quality of interactions that elderly individuals have with family, friends, and other people both inside and outside the institution (Sullivan et al., 2021; Htun et al., 2024). Social support refers to the types and extent of assistance that elderly individuals can receive from their social networks when they need help, including emotional support, informational support, and material aid (Paudel and Tiwari, 2022; Liu et al., 2023). Reciprocity involves mutual assistance behaviors between elderly individuals and others. Trust refers to the level of trust that elderly individuals have in those around them, such as family members, friends, neighbors, and caregivers, as well as their trust in social institutions like the healthcare system and government agencies (Chen and Zhu, 2021; Shie et al., 2022). A sense of belonging describes the elderly individuals' feelings of affiliation and identity with their community or nursing home, which can enhance their social identity and life satisfaction (Chu et al., 2022; Park et al., 2020).
Extensive research has robustly confirmed that social capital and its various dimensions play a crucial role in the psychological and physiological health of the elderly, effectively preventing chronic diseases and reducing mortality rates (Gontijo et al., 2019; Liang et al., 2020). The mechanisms through which social capital promotes health behaviors can be specifically summarized as follows: First, robust social networks provide crucial information about healthy lifestyles, encouraging individuals to adopt habits such as healthy eating and regular exercise (Hong et al., 2018; Alexandre et al., 2021). Second, social support reduces psychological stress and feelings of loneliness, maintains mental health, and encourages active social participation, which is especially important for the elderly (Choi et al., 2021; Hosseingholizadeh et al., 2019; Dakua et al., 2023; Mieziene et al., 2022). Lastly, reciprocal social behaviors increase the social rewards of participating in group activities, such as joining community health programs or group sports, thereby motivating continued engagement in these activities (Brennan-Ing et al., 2023; Emmering et al., 2018). Through these mechanisms, social capital not only supports the cultivation of individual health behaviors but also directly enhances the quality of life related to health. However, despite current research revealing a positive correlation between social capital and health behaviors, the deeper mechanisms of action require further empirical research, particularly in how enhancing social capital in nursing homes can promote elderly health behaviors and psychological well-being.
Psychological capital refers to the positive psychological state and resources an individual exhibits when facing challenges and stress (Shi, 2013; Youssef-Morgan and Luthans, 2015). This concept, introduced by Luthans and others, is designed to measure and enhance an individual's adaptability and efficacy in complex environments (Shi, 2013; Youssef-Morgan and Luthans, 2015). In the elderly population, psychological capital is particularly significant (Jurek and Niewiadomska, 2021; Leonti and Turliuc, 2024). Extensive research has confirmed its close association with psychological health and quality of life in this group. Psychological capital comprises four core dimensions: self-efficacy, hope, resilience, and optimism (Shi, 2013; Youssef-Morgan and Luthans, 2015). Self-efficacy refers to an individual's confidence in their ability to accomplish specific tasks (Yu et al., 2023; Kim et al., 2020). Hope refers to a positive sense of expectation and the motivation to achieve goals successfully (Sand and Bristle, 2024). Resilience refers to the ability to recover and adapt in the face of adversity (Lavretsky, 2021). Optimism is defined as the tendency to hold positive expectations for the future (Yue et al., 2022).
Research indicates that psychological capital plays a pivotal role in promoting the health and well-being of the elderly (Ahmadboukani et al., 2023). Specifically, psychological capital interacts with the health behaviors and physiological health of the elderly through multiple mechanisms (Ahmadboukani et al., 2023). Firstly, psychological capital enhances the psychological adaptability of the elderly, allowing them to maintain better emotional balance and mental states when facing chronic illnesses or life stressors (Sadeghi and Bavazin, 2019; Li et al., 2022). Additionally, a high level of psychological capital encourages elderly individuals to engage more actively in health-promoting behaviors, such as regular physical activity, balanced diets, and social interactions, which in turn improve their physiological health and psychological well-being (Yoo, 2020). In the context of nursing home environments, strengthening the psychological capital of the elderly is particularly important as these settings can often provoke feelings of loneliness and neglect (Afrashteh et al., 2024). Strategically enhancing the self-efficacy, hope, resilience, and optimism of elderly residents can not only improve their daily functioning and quality of life but also facilitate the broader goal of achieving healthy aging.
Health-promoting behaviors refer to any active actions taken by an individual to enhance, protect, or maintain their health (Xie et al., 2022). These behaviors encompass a wide range, including regular physical activity, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, conscious stress management, avoidance of harmful substances, and regular health check-ups (Xie et al., 2022). Health-promoting behaviors are not only concerned with disease prevention but also involve actively improving an individual's overall well-being and quality of life (Xie et al., 2022; Spring et al., 2019). For instance, Mo et al. found that individuals engaging in more health-promoting behaviors often experience higher quality of life and greater feelings of happiness (Mo et al., 2022). Therefore, in the elderly population, especially those residing in nursing homes, exploring the underlying mechanisms that form their health behaviors is crucial. This not only helps improve their quality of life but also provides a scientific basis for formulating effective health promotion strategies to facilitate the achievement of healthy aging.
In summary, while existing research has explored the individual effects of social capital and positive psychological capital on elderly health, few studies have examined how these two factors simultaneously influence health-promoting behaviors, particularly in nursing home residents. Furthermore, the potential mediating role of positive psychological capital in the relationship between social capital and health behaviors remains underexplored. This study aims to address these gaps by investigating the complex relationships among social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors. Specifically, we analyze the mediating effect of positive psychological capital between social capital and health-promoting behaviors, and propose a mediation model to better understand how these factors interact. By doing so, this research seeks to provide empirical insights that could inform interventions aimed at promoting positive health behaviors among elderly residents in nursing homes, ultimately contributing to the development of effective strategies for healthy aging in this population.
This study uses Nola J. Pender's Health Promotion Model to explore the relationships between social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors (Cardoso et al., 2021). Introduced in 1982, the model focuses on how individual health behaviors are influenced by factors such as personal history, biopsychosocial characteristics, perceived barriers and benefits, self-efficacy, and situational influences. It is widely used in elderly health research to understand the factors affecting health behaviors among older adults. To further clarify the relationships among the three variables, this study proposes the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1: There is a positive correlation between social capital and positive psychological capital.
Hypothesis 2: There is a positive correlation between social capital and health-promoting behaviors.
Hypothesis 3: There is a positive correlation between positive psychological capital and health-promoting behaviors.
Hypothesis 4: Positive psychological capital mediates the relationship between social capital and health-promoting behaviors.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study participants
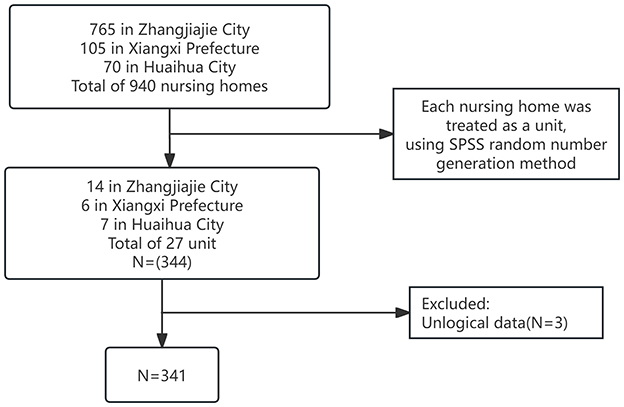
The study was conducted with elderly residents from nursing homes in the Xiangxi area, collected from June 2023 to April 2024. Due to the multivariate nature of the study, the sample size was set to 5–10 times the number of independent variables (Harrell, 2001). The study included six variables from general sociodemographic data, six dimensions of social capital, four dimensions of positive psychological capital, and six dimensions of health-promoting behaviors, totaling 22 independent variables. Calculations determined that the required sample size ranged from 110 to 220 participants, taking into account a 20% margin for invalid questionnaires, which necessitated distributing between 132 and 264 questionnaires. Additionally, considering the minimum sample size of 150 required for equation modeling, with an optimal sample size of over 200, the final sample included 341 participants. A random cluster sampling method was used, covering 940 nursing homes in the region including 765 in Zhangjiajie City, 105 in Xiangxi Prefecture, and 70 in Huaihua City. Each nursing home was treated as a unit; using the SPSS random number generation method, 27 units were randomly selected, from which elderly individuals meeting the inclusion criteria were chosen as the study participants (Figure 1).
Inclusion criteria for this study are as follows: (1) Age and nationality requirements: Participants must be Chinese citizens aged 60 years and older, residing in nursing homes. (2) Cognitive state: Participants must have a clear state of consciousness without any cognitive impairments, ensuring they can understand the questionnaire content and respond accurately. (3) Cooperation ability: Participants should be able to actively cooperate in the survey, including understanding questions and responding appropriately. (4) Self-care ability: Participants must possess basic daily living self-care skills. (5) Informed consent: Individuals must be capable of signing a consent form.
Exclusion criteria include: (1) Mental and cognitive health: Individuals with psychiatric disorders (such as depression or schizophrenia), dementia, or severe cognitive impairments are excluded. (2) Communication abilities: Individuals with communication barriers due to neurological diseases, hearing impairments, or speech disorders that prevent clear expression are also excluded.
2.2 Survey methodology
The data collection for this study was conducted with significant support and assistance from the Elderly Care Department of the Civil Affairs Bureau in the surveyed region. At the beginning of the research, we obtained a comprehensive list and basic information about the nursing institutions in the participating area from the Civil Affairs Bureau. After obtaining explicit consent from the directors of the nursing homes and the elderly residents, we arranged on-site, face-to-face surveys. The survey was conducted using the “Questionnaire Star” platform, a widely used online tool for data collection and management in China.
To minimize self-report bias, several measures were implemented throughout the survey process. Research team members carefully explained the purpose and content of the study to the elderly participants, ensuring that they fully understood the significance of their participation. In addition, informed consent was obtained from each participant, with particular attention paid to ensuring that they felt comfortable and free from any social pressure or expectations that might influence their responses. Furthermore, to further reduce potential social desirability bias, the research team read the survey items aloud and recorded the participants' responses verbatim. This approach ensured that the participants' answers accurately reflected their true opinions, rather than being influenced by a desire to please the interviewer or conform to social norms. Finally, to maintain the integrity of the data, researchers checked the accuracy and completeness of the questionnaires in real-time, verifying any errors or omissions immediately with the participants to ensure the collected data were accurate and complete.
2.3 Research instruments
2.3.1 General information
The general information includes gender, age, ethnicity, marital status, educational level, and personal monthly income.
2.3.2 Social capital scale
This scale, developed by Xu et al., consists of 22 items across six dimensions: social participation, social connections, social support, reciprocity, trust, and sense of belonging (Xu, 2018). The frequency of participation is rated on a scale from “never” to “often,” with “never” scoring 1 point, “seldom” 2 points, “sometimes” 3 points, “often” 4 points, and “always” 5 points. Higher scores in each dimension indicate a higher level of social capital. The scale was developed by Chinese scholars specifically for the elderly population, demonstrating strong cultural relevance and adaptation. The overall Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the scale is 0.919, with individual dimension alphas ranging from 0.652 to 0.940. In this study, the Cronbach's alpha for the scale was 0.91, indicating good internal consistency and suitability for the research purposes.
2.3.3 Positive psychological capital scale
This study used the Elderly Psychological Capital Scale developed for Older Adults developed by Shi Hui, a localized measurement tool specifically designed to assess the positive psychological states of Chinese older adults with good cultural adaptability (Shi, 2013). The scale comprises 20 items across four dimensions: self-efficacy, integrity and stability, resilience, and gratitude and dedication. It employs a 5-point Likert scale for scoring, with higher scores indicating a higher level of psychological capital among the elderly. The overall Cronbach's alpha coefficient of the scale is 0.876, with dimension-specific Cronbach's alpha coefficients ranging from 0.609 to 0.789, indicating good reliability and validity. In this study, the scale's Cronbach's alpha coefficient is 0.89, indicating strong internal consistency.
2.3.4 Health-promoting lifestyle profile II revised scale
In 2016, Wen and colleagues translated and revised the HPLP-II into a 40-item revised version that was tailored for the Chinese older adult population and is widely used as a tool to measure health-promoting behaviors in Chinese older individuals (Wenjun et al., 2016). The scale includes 40 items across six dimensions: interpersonal relations, nutrition, health responsibility, physical activity, stress management, and spiritual growth. It uses a 4-point Likert scale for scoring, with total scores ranging from 40 to 160: scores from 40 to 69 indicate poor health-promoting behavior, 70 to 99 are average, 100 to 129 are good, and 130 to 160 are excellent. The overall Cronbach's alpha coefficient of the scale is 0.920, with split-half reliability ranging from 0.64 to 0.78 and dimension-specific Cronbach's alpha coefficients ranging from 0.63 to 0.81. The test-retest reliability of the scale is 0.69, and in this study, the Cronbach's alpha is 0.93.
2.4 Ethical principles
This study was reviewed and approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of Jishou University, under the code JSDX-2024-0072. Prior to data collection, the purpose and content of the study were explained to the elderly participants, and they were informed that they could withdraw from the study at any time.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 25.0. Descriptive statistics were reported as percentages for categorical data and means ± standard deviations for continuous data. Differences in total scores of social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors across different sociodemographic groups were analyzed using t-tests and one-way ANOVA. The relationships among social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors were examined using two separate multivariate linear regression models. Mediation analysis was performed using the SPSS PROCESS plugin developed by Hayes, with social capital as the predictor variable, scores of positive psychological capital as the mediator, and total scores of health-promoting behaviors as the outcome variable. A bootstrapping procedure with 5,000 samples was used to test the estimated mediation effect (a*b). The theoretical model assessing the mediating role of positive psychological capital in the relationship between social capital and health-promoting behaviors is outlined as follows: “c′” represents the direct effect of social capital on health-promoting behaviors, the product of “a” and “b” (ab) represents the indirect effect of social capital on health-promoting behaviors through positive psychological capital, and “c” represents the total effect of social capital on health-promoting behaviors, which is the sum of “c′” and ab (Figure 2). In all analyses, sociodemographic characteristics (gender, age, ethnicity, marital status, educational level, and personal monthly income) were included as covariates to control for potential confounding effects.
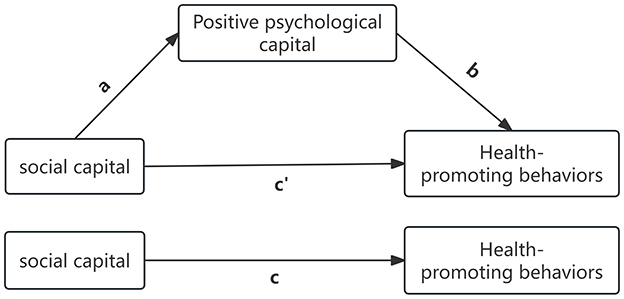
Figure 2. Conceptual mediation model of social capital, positive psychological capital, and health promoting behaviors.
3 Results
3.1 Sociodemographic characteristics
In this study, 344 questionnaires were initially distributed. After excluding questionnaires with illogical responses, 341 valid questionnaires were recovered, resulting in an effective response rate of 99.13%. The sample included 341 elderly individuals with an average age of 76.13 ± 9.58, ranging from 60 to 101 years. The sample comprised 234 males (68.62%) and 107 females (31.38%); 149 participants were Han Chinese (43.7%), and 192 were from minority ethnic groups (56.3%). Among the participants, 26 had spouses (7.62%), and 315 were without spouses (92.38%). Regarding educational levels, 278 had elementary school education or lower (81.52%), 30 had junior high school education (8.8%), 17 had high school or vocational school education (4.99%), 12 had some college education (3.52%), and 4 had a bachelor's degree or higher (1.17%). Personal monthly income levels were as follows: ≤ 1,000 RMB for 265 participants (77.71%), 1,001–3,000 RMB for 21 participants (6.16%), 3,001–5,000 RMB for 37 participants (10.85%), and ≥5,000 RMB for 18 participants (5.28%). Table 1 presents the sociodemographic characteristics of the participants.
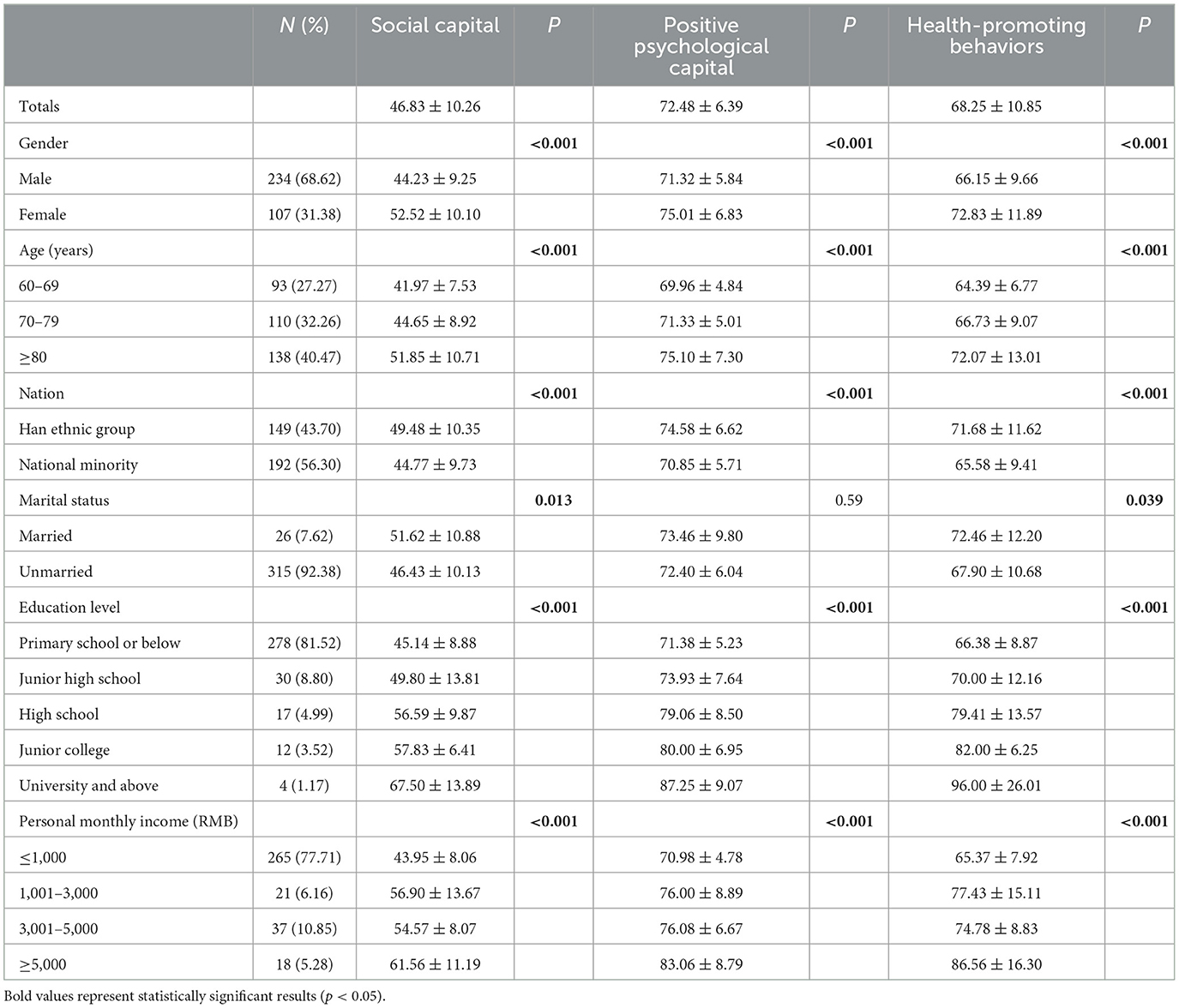
Table 1. Different socio-demographic characteristics of social capital, positive psychological capital, and health promotion behaviors (n = 341).
3.2 Sociodemographic characteristics and their impact on social capital, positive
Psychological Capital, and Health-Promoting Behaviors Statistical significance was found in the associations of social capital and health-promoting behaviors with sociodemographic characteristics such as gender, age, ethnicity, marital status, educational level, and personal monthly income (Table 1). However, for positive psychological capital, all characteristics except marital status showed statistical significance.
3.3 Relationships between social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors
The results of the multivariate linear regression models examining the relationships between social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors are as follows: After controlling for gender, age, ethnicity, marital status, educational level, and personal monthly income, Model 1 shows that social capital (B = 0.395, P < 0.001) is significantly related to positive psychological capital. Model 2 indicates that both social capital (B = 0.441, P < 0.001) and positive psychological capital (B = 0.627, P < 0.001) are related to health-promoting behaviors (Table 2).
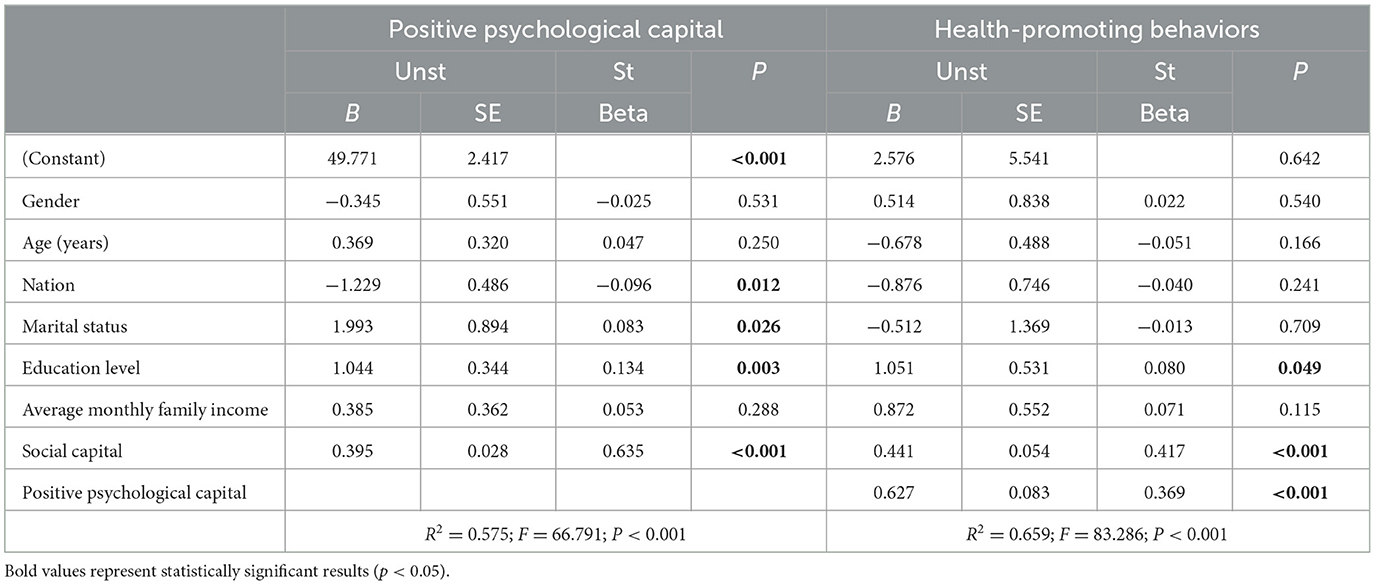
Table 2. Multiple linear regression of the relationship between social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors (n = 341).
3.4 Mediating effect of positive psychological capital between social capital and health-promoting
The mediation analysis shows that positive psychological capital significantly mediates this relationship. Specifically, the indirect effect of positive psychological capital (path a*b) was found to be 0.321, with a 95% confidence interval (CI) ranging from 0.233 to 0.409, indicating that the mediating effect is statistically significant as the confidence interval does not include zero (Table 3 and Figure 3).

Table 3. Mediating effects of positive psychological capital between social capital and health promotion behaviors (n = 341).

Figure 3. The mediating effect of positive psychological capital between social capital and health promotion behavior.
Furthermore, the direct pathway from social capital to health-promoting behaviors (path c) is quantified with a total effect of 0.800 (95% CI: 0.726–0.873). After accounting for the mediator, the direct effect of social capital on health-promoting behaviors (path “c′”) is reduced to 0.321. Importantly, 40.13% of the total effect of social capital on health behaviors is mediated by positive psychological capital. This suggests that positive psychological capital does not merely enhance health-promoting behaviors independently but also amplifies the impact of social capital on these behaviors (Table 3 and Figure 3).
4 Discussion
This cross-sectional study among elderly populations in Chinese nursing homes highlights the significant roles of social capital and positive psychological capital in promoting health behaviors. The findings reveal that social capital directly fosters health behaviors in the elderly and that its impact is enhanced through the mediating role of positive psychological capital, which serves as a crucial bridge between social capital and health-promoting behaviors. Specifically, social capital, particularly through improved community connections and opportunities for participation in community organizations, not only provides psychological benefits but also offers greater access to support and resources, which can supplement formal healthcare services and positively affect the elderly's health and well-being (Ahmadboukani et al., 2023; Chang et al., 2023). Furthermore, positive psychological capital—comprising self-efficacy, hope, resilience, and optimism—demonstrates substantial benefits for psychological health by reducing loneliness and enhancing subjective well-being, which motivates the elderly to engage in health-promoting behaviors such as physical activity, healthy eating, and social interactions (Ahmadboukani et al., 2023). These findings validate the positive correlations among social capital, positive psychological capital, and health behaviors, confirming the pivotal role of these factors in promoting elderly health. This study not only highlights the direct roles of social and psychological capital in health promotion but also underscores their potential implications for public health policy and aged care service practices.
Our study found that the average health-promoting behavior score among elderly residents in Chinese nursing homes was 68.25 ± 10.85, indicating relatively low engagement in health-promoting behaviors. This score is significantly lower than that reported in other studies. For instance, a meta-analysis of 5,639 elderly individuals found that older adults generally engage in moderate health-promoting lifestyle behaviors (Yue et al., 2018). The low levels of health-promoting behaviors in Chinese nursing homes may stem from several factors, including limited institutional resources, a lack of health education, and insufficient personal health awareness, all of which hinder the adoption of proactive health behaviors (Fang et al., 2015; Li and Shi, 2022).
We found that the average social capital score of elderly residents in nursing homes in the Xiangxi region was 46.83 ± 10.26, significantly lower than the 75.41 ± 8.61 reported for elderly residents in Shenyang, Liaoning Province (Li, 2021). This difference likely reflects regional disparities in the development of social capital, influenced by socioeconomic status, healthcare access, and cultural factors. In economically underdeveloped regions like Xiangxi, where healthcare resources and social support are limited, elderly residents in nursing homes may experience greater social isolation, reducing their social capital. Previous studies highlight that social capital varies across different socioeconomic and cultural contexts, emphasizing the need to study it in developing and disadvantaged regions (Cain et al., 2018). In more developed areas, better community resources, economic stability, and social participation opportunities typically foster higher levels of social capital (Cain et al., 2018). Conversely, in regions like Xiangxi, limited resources hinder the formation of strong social networks and community ties, leading to lower individual social capital.
We found that elderly residents in nursing homes in the Xiangxi region scored 72.48 ± 6.39 in positive psychological capital, slightly lower than the 75.77 ± 5.82 reported by Han Jing et al. in Tangshan (Jing et al., 2021) and much lower than the 87.56 ± 8.07 observed in community-dwelling elderly individuals by Shi (2013). This trend suggests that nursing home residents generally exhibit lower psychological capital than their community-dwelling counterparts. Several factors may contribute to this difference, particularly the social and environmental conditions of nursing home life. Compared to community residents, nursing home residents typically have fewer social opportunities, with structured and repetitive activities that lack the stimulation and variety found in community settings (Moyle et al., 2015; Nygaard et al., 2020). This limited social participation may hinder social capital development and reduce psychological resilience, optimism, and overall psychological capital. Additionally, the transition to a nursing home represents a significant life change that can challenge elderly individuals' adaptability and lead to a loss of autonomy, negatively impacting self-efficacy and psychological capital (Yong et al., 2021). Furthermore, while many nursing homes provide basic care, they often lack sufficient psychological and emotional support, exacerbating unmet psychological needs and further lowering psychological capital (Clare et al., 2008; Nygaard et al., 2020).
This study further explored the mediating role of positive psychological capital between social capital and health-promoting behaviors, confirming Research Hypothesis 4. Mediation analysis indicated that the mediating effect of positive psychological capital accounted for 40.13% of the total effect, clearly demonstrating that social capital not only directly influences health-promoting behaviors but also indirectly promotes these behaviors by enhancing positive psychological capital. This finding underscores the necessity of not solely relying on single-dimensional social or psychological interventions when developing health promotion strategies for the elderly. To improve health-promoting behaviors and quality of life for the elderly, a multidimensional strategy is required (Aronson, 2020). Firstly, the strengthening of social capital, including enhancing social support networks, encouraging social participation among the elderly, and fostering a community culture of reciprocity, provides the elderly with necessary external resources and social opportunities, all of which are directly beneficial for the enactment of health-promoting behaviors (Chang et al., 2023). Additionally, social capital indirectly promotes health behaviors in the elderly by influencing positive psychological states such as self-efficacy, hope, resilience, and optimism (Ahmadboukani et al., 2023), such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and active participation in social activities.
Therefore, effective interventions for elderly residents in nursing homes should comprehensively consider the development of both social capital and psychological capital, as their synergistic effects can significantly enhance the health behaviors and quality of life of the elderly. First, nursing homes can regularly organize social activities and health education workshops, which not only provide a platform for social interaction but also enhance residents' awareness of health information and improve their psychological readiness to face health challenges. Through these activities, elderly individuals can strengthen their sense of social support while acquiring more health knowledge, which in turn can help modify unhealthy behaviors. Secondly, nursing homes should offer psychological counseling services and positive psychology training to help elderly residents improve their intrinsic motivation and psychological adaptation. Such interventions can enhance their psychological resilience, enabling them to maintain a positive mindset and adopt effective coping strategies when dealing with health issues. For example, psychological counseling can help alleviate negative emotions such as anxiety and depression, while mindfulness meditation training can improve emotional regulation skills. Additionally, policymakers should encourage nursing homes to integrate psychological health and social capital into resource allocation, ensuring the long-term sustainability of these interventions. The government can implement relevant policies to provide financial support for nursing homes, encouraging them to build social networks based on social capital, while also training caregivers in skills that promote psychological capital. Caregivers should regularly receive training to ensure the effective implementation of these comprehensive interventions.
4.1 Research strengths
This study employed a rigorous cluster sampling method, randomly selecting samples from multiple nursing homes, effectively ensuring the representativeness and statistical validity of the results. This approach not only increased the diversity of the sample but also enhanced the general applicability of the research findings, allowing the results to more accurately reflect the actual conditions of a broad elderly population. Additionally, another significant strength of this study lies in the uniqueness of its research focus. We delved into the relationships between social capital, psychological capital, and health behaviors among elderly residents in nursing homes, a relatively underexplored area in existing literature. These results reveal how social capital and psychological capital influence elderly health behaviors through various mechanisms, thus providing a theoretical basis for formulating effective intervention measures. Particularly within the specific social environment of nursing homes, these findings have important practical implications, offering scientific strategies for improving the quality of life and health status of the elderly.
4.2 Research limitations
Firstly, due to its cross-sectional design, this study can only highlight correlations, not causations, among social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors among elderly residents in nursing homes. Longitudinal or intervention studies are needed to establish the directionality and causality of these relationships. Secondly, the study's focus on the underdeveloped Xiangxi region limits the generalizability of the findings to broader elderly populations in other parts of China. The socioeconomic conditions of the Xiangxi region, including lower income levels, limited access to healthcare, and reduced social support, may influence both the social capital and health-promoting behaviors of elderly residents. These regional socioeconomic differences could potentially confound the observed relationships, making it difficult to generalize the results to regions with more developed economic and healthcare systems. Future research should compare different regions with varying socioeconomic conditions to verify these results across more diverse settings and assess how regional factors may shape the relationships between social capital, psychological capital, and health behaviors. Lastly, reliance on self-reported data may introduce biases, such as memory inaccuracies or social desirability effects. Future studies should incorporate objective measurements to validate the findings and reduce potential biases.
4.3 Conclusion
This study demonstrates a positive correlation among social capital, positive psychological capital, and health-promoting behaviors in elderly nursing home residents, with positive psychological capital mediating this relationship. For more effective health interventions, it is crucial to consider both social and psychological capitals. Future research should explore these relationships through longitudinal studies to better understand causality and direction. Additionally, comparing these dynamics in nursing home residents with community-dwelling elderly could enhance intervention strategies tailored to different living environments.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study has been approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of Jishou University: JSDX-2024-0072. It was performed per the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
LL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. FT: Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Supervision. JW: Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. TH: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study has received support from Zigong Municipal Health Commission's 2023 Health System Research Project [23yb070].
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the Civil Affairs Bureau's Elderly Care Department in the Xiangxi region, as well as all surveyed nursing homes, for their strong support in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Afrashteh, M. Y., Majzoobi, M. R., Janjani, P., and Forstmeier, S. (2024). The relationship between the meaning of life, psychological well-being, self-care, and social capital, with depression and death anxiety in the elderly living in nursing homes: the mediating role of loneliness. Heliyon 10:e30124. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30124
Ahmadboukani, S., Fathi, D., Karami, M., Bashirgonbadi, S., Mahmoudpour, A., and Molaei, B. (2023). Providing a health-promotion behaviors model in elderly: psychological capital, perceived social support, and attitudes toward death with mediating role of cognitive emotion regulation strategies. Health Sci. Rep. 6:e1020. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1020
Alexandre, K., Campbell, J., Bugnon, M., Henry, C., Schaub, C., Serex, M., et al. (2021). Factors influencing diabetes self-management in adults: an umbrella review of systematic reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 19, 1003–1118. doi: 10.11124/JBIES-20-00020
Aronson, L. (2020). Healthy aging across the stages of old age. Clin. Geriatric Med. 36, 549–558. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2020.06.001
Brennan-Ing, M., Wu, Y., Manalel, J. A., and Finkelstein, R. (2023). Taking charge: social support dynamics among older adults and their significant others in COVID-19 vaccination and mitigation efforts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20:4869. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20064869
Cain, C. L., Wallace, S. P., and Ponce, N. A. (2018). Helpfulness, trust, and safety of neighborhoods: social capital, household income, and self-reported health of older adults. Gerontologist 58, 4–14. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnx145
Cardoso, R. B., Caldas, C. P., Brandão, M. A. G., Souza, P. A. D., and Santana, R. F. (2021). Healthy aging promotion model referenced in Nola Pender's theory. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 75:e20200373. doi: 10.1590/0034-7167-2020-0373
Chang, H., Wang, X., and Wang, Z. (2023). Association between social capital and health-promoting lifestyle among empty nesters: the mediating role of sense of coherence. Geriatric Nurs. 53, 96–101. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2023.07.006
Chen, H., and Zhu, Z. (2021). Social trust and emotional health in rural older adults in China: the mediating and moderating role of subjective well-being and subjective social status. BMC Public Health 21, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10617-y
Choi, E., Han, K.-M., Chang, J., Lee, Y. J., Choi, K. W., Han, C., et al. (2021). Social participation and depressive symptoms in community-dwelling older adults: emotional social support as a mediator. J. Psychiatric Res. 137, 589–596. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.10.043
Chu, M., Lee, C.-Y., Suona, L., Gao, M., Chen, T., Zhang, S., et al. (2022). Improving the sense of city belonging among migrant elderly following family from an elderly service perspective: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 22:2032. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14445-6
Clare, L., Rowlands, J., Bruce, E., Surr, C., and Downs, M. (2008). The experience of living with dementia in residential care: an interpretative phenomenological analysis. Gerontologist 48, 711–720. doi: 10.1093/geront/48.6.711
Dakua, M., Karmakar, R., and Lhungdim, H. (2023). Social capital and well-being of the elderly ‘left-behind' by their migrant children in India. BMC Public Health 23:2212. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-17012-9
Emmering, S. A., Astroth, K. S., Woith, W. M., Dyck, M. J., and Kim, M. (2018). Social capital, health, health behavior, and utilization of healthcare services among older adults: a conceptual framework. Nurs. Forum 53, 416–424. doi: 10.1111/nuf.12268
Fang, E. F., Scheibye-Knudsen, M., Jahn, H. J., Li, J., Ling, L., Guo, H., et al. (2015). A research agenda for aging in China in the 21st century. Ageing Res. Rev. 24, 197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2015.08.003
Giovanni, A., Enrico, A., Aime, B., Michael, B., Marianne, B., Jonathan, C., et al. (2020). Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 76, 2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010
Gontijo, C. F., Firmo, J. O. A., Lima-Costa, M. F., and Loyola Filho, A. I. D. (2019). A longitudinal study of the association between social capital and mortality in community-dwelling elderly Brazilians. Cad. Saude Publica 35:e00056418. doi: 10.1590/0102-311X00056418
Gordon, A. L., Goodman, C., Achterberg, W., Barker, R. O., Burns, E., Hanratty, B., et al. (2020). Commentary: COVID in care homes—challenges and dilemmas in healthcare delivery. Age Ageing 49, 701–705. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afaa113
Harrell, F. E. (2001). Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic Regression, and Survival Analysis. Cham: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-3462-1
Hong, C., Sun, L., Liu, G., Guan, B., Li, C., and Luo, Y. (2023). Response of global health towards the challenges presented by population aging. China CDC Weekly 5:884. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2023.168
Hong, M., De Gagne, J. C., and Shin, H. (2018). Social networks, health promoting-behavior, and health-related quality of life in older Korean adults. Nurs. Health Sci. 20, 79–88. doi: 10.1111/nhs.12390
Hosseingholizadeh, N., Sadeghi, R., Ardebili, H. E., Foroushani, A. R., and Taghdisi, M. H. (2019). The correlation of self-efficacy and social support with social participation: a cross sectional study among the elderly. J. Med. Life 12:239. doi: 10.25122/jml-2019-0010
Htun, H. L., Teshale, A. B., Ryan, J., Owen, A. J., Woods, R. L., Chong, T. T. J., et al. (2024). Gender-specific analysis of social connection patterns and risk of dementia in community-dwelling older people. Alzheimer. Dement. 20, 4879–4890. doi: 10.1002/alz.14055
Jeste, D. V., Koh, S., and Pender, V. B. (2022). Perspective: social determinants of mental health for the new decade of healthy aging. Am. J. Geriatric Psychiatry 30, 733–736. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2022.01.006
Jiang, H., and Liu, Z. (2023). Community home elderly care services, multidimensional health and social participation of chronically ill elderly—empirical analysis based on propensity score matching and multiple mediation analysis. Front. Public Health 11:1121909. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1121909
Jing, H., Huiju, H., Qiqun, T., and Jie, C. (2021). Analysis of the status quo and influencing fators of the mental capital of the elderly in pension institutions. Nurs. Prac. Res. 18, 3640–3644. doi: 10.1080/10410236.2022.2074779
Jurek, K., and Niewiadomska, I. (2021). Relationship between psychological capital and quality of life among seniors working after retirement: the mediating role of hope of success. PLoS ONE 16:e0259273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259273
Kardas, P., Lichwierowicz, A., Urbański, F., Chudzyńska, E., Czech, M., and Kardas, G. (2021). Prevalence of chronic polypharmacy in community-dwelling elderly people in Poland: analysis of national real-world database helps to identify high risk group. Front. Pharmacol. 12:739740. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.739740
Kim, A. S., Jang, M. H., Park, K. H., and Min, J. Y. (2020). Effects of self-efficacy, depression, and anger on health-promoting behaviors of Korean elderly women with hypertension. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:6296. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176296
Kim, H. C. (2021). Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in Korea. Glob. Health Med. 3, 134–141. doi: 10.35772/ghm.2021.01008
Lavretsky, H. (2021). Health, resilience, and successful aging in the older us veterans. Am. J. Geriatric Psychiatry 29, 257–259. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2020.08.018
Leonti, R. M., and Turliuc, M. N. (2024). Better and healthier together? The mediation effect of positive psychological capital on the relationship between perceived social support and health-related quality of life among older adults. Int. J. Aging Hum. Dev. doi: 10.1177/00914150241268178
Li, C., and Shi, C. (2022). Adverse events and risk management in residential aged care facilities: a cross-sectional study in Hunan, China. Risk Manage. Healthc. Policy 15, 529–542. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S351821
Li, S. (2021). A Study of the Correlation Between Cognitive Function, Depression and Social Capital Among the Elderly in Nursing Institutions. Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Available at: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27213/d.cnki.glnzc.2021.000552 (accessed October 13, 2024).
Li, W., Yang, S., Li, J., Li, Z., Yan, C., Gui, Z., et al. (2022). Social capital and self-rated health among Chinese rural empty nesters: a multiple mediation model through sleep quality and psychological distress. J. Affect. Disord. 298, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.11.016
Liang, H., Yue, Z., Liu, E., and Xiang, N. (2020). How does social capital affect individual health among the elderly in rural China?—mediating effect analysis of physical exercise and positive attitude. PLoS ONE 15:e0231318. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231318
Liberale, L., Montecucco, F., Tardif, J.-C., Libby, P., and Camici, G. G. (2020). Inflamm-ageing: the role of inflammation in age-dependent cardiovascular disease. Euro. Heart J. 41, 2974–2982. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz961
Liu, L., Yang, Y., Zhao, Y., and Zhang, T. (2023). Ethnic differences in social support for elderly individuals in rural southern China: a cross-sectional survey. Asia Pacific J. Public Health 35, 21–26. doi: 10.1177/10105395221141966
Lu, S., Chui, C., and Lum, T. (2023). Promoting social capital for healthy aging: towards an integrative framework. Gerontologist 63, 628–636. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnac062
Mieziene, B., Emeljanovas, A., Novak, D., and Kawachi, I. (2022). Social capital promotes a healthier diet among young adults by reducing psychological distress. Nutrients 14:5187. doi: 10.3390/nu14235187
Mo, P. K., Wong, E. L., Yeung, N. C., Wong, S. Y., Chung, R. Y., Tong, A. C., et al. (2022). Differential associations among social support, health promoting behaviors, health-related quality of life and subjective well-being in older and younger persons: a structural equation modelling approach. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 20:38. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-01931-z
Moyle, W., Fetherstonhaugh, D., Greben, M., and Beattie, E. (2015). Influencers on quality of life as reported by people living with dementia in long-term care: a descriptive exploratory approach. BMC Geriatr. 15:50. doi: 10.1186/s12877-015-0050-z
NBS, C. N. B. O. S. (2022). The National Economy Will Rise to a New Level in Spite of the Pressure. Available at: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202302/t20230203_1901709.html (accessed October 13, 2024).
Nygaard, A., Halvorsrud, L., Grov, E. K., and Bergland, A. (2020). What matters to you when the nursing home is your home: a qualitative study on the views of residents with dementia living in nursing homes. BMC Geriatr. 20, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12877-020-01612-w
Ou, M.-Y., Zhang, H., Tan, P.-C., Zhou, S.-B., and Li, Q.-F. (2022). Adipose tissue aging: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cell Death Dis. 13:300. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04752-6
Park, I., Veliz, P. T., Ingersoll-Dayton, B., Struble, L. M., Gallagher, N. A., Hagerty, B. M., et al. (2020). Assisted living residents' sense of belonging and psychosocial outcomes. West. J. Nurs. Res. 42, 805–813. doi: 10.1177/0193945920906181
Paudel, K., and Tiwari, A. (2022). High social support system among elderly in a Hilly district: a descriptive cross-sectional study. J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 60:874. doi: 10.31729/jnma.7750
Pretto, C. R., Winkelmann, E. R., Hildebrandt, L. M., Barbosa, D. A., Colet, C. F., and Stumm, E. M. F. (2020). Quality of life of chronic kidney patients on hemodialysis and related factors. Rev. Lat. Am. Enferm. 28:e3327. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.3641.3327
Rohrmann, S. (2020). “Epidemiology of frailty in older people,” in Frailty and Cardiovascular Diseases: Research into an Elderly Population, Vol. 1216, ed. N. Veronese (Cham: Springer), 21–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-33330-0_3
Rui, J. R. (2023). Health information sharing via social network sites (SNSs): integrating social support and socioemotional selectivity theory. Health Commun. 38, 2430–2440. doi: 10.1080/10410236.2022.2074779
Sadeghi, M., and Bavazin, F. (2019). Loneliness in the elderly: prediction based on mental well-being, psychological capital and spiritual intelligence. Aging Psychol. 5, 41–51. doi: 10.22126/JAP.2019.1125
Sand, G., and Bristle, J. (2024). Motivating protective behavior against COVID-19: fear versus hope. J. Aging Health 36, 350–366. doi: 10.1177/08982643221089427
Shi, H. (2013). A Study of the Relationship Among Psychological Capital, Social Support and Life Satisfaction of the Elderly. China: Suzhou University.
Shie, A.-J., Huang, Y.-F., Li, G.-Y., Lyu, W.-Y., Yang, M., Dai, Y.-Y., et al. (2022). Exploring the relationship between hospital service quality, patient trust, and loyalty from a service encounter perspective in elderly with chronic diseases. Front. Public Health 10:876266. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.876266
Spring, B., Stump, T., Penedo, F., Pfammatter, A. F., and Robinson, J. K. (2019). Toward a health-promoting system for cancer survivors: patient and provider multiple behavior change. Health Psychol. 38:840. doi: 10.1037/hea0000760
Sullivan, J. L., Engle, R. L., Shin, M. H., Davila, H., Tayade, A., Bower, E. S., et al. (2021). Social connection and psychosocial adjustment among older male veterans who return to the community from VA nursing homes. Clin. Gerontol. 44, 450–459. doi: 10.1080/07317115.2020.1812141
Tinoco, J. D. M. V. P., Souza, B. P. E. S. D., Oliveira, S. X. D., Oliveira, J. A. D., Mesquita, E. T., and Cavalcanti, A. C. D. (2021). Association between depressive symptoms and quality of life in outpatients and inpatients with heart failure. Rev. Esc. Enferm. USP 55:e03686. doi: 10.1590/s1980-220x2019030903686
Wang, J., Wang, J., Cao, Y., Jia, S., and Wu, B. (2018). Perceived empowerment, social support, and quality of life among Chinese older residents in long-term care facilities. J. Aging Health 30, 1595–1619. doi: 10.1177/0898264318795724
Wenjun, C., Ying, G., Weiwei, P., and Jianzhong, Z. (2016). Development and psychometric tests of a Chinese version of the HPLP-II scales. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 20, 286–289. doi: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2016.03.018
Xie, L., Zhang, S., Xin, M., Zhu, M., Lu, W., and Mo, P. K.-H. (2022). Electronic health literacy and health-related outcomes among older adults: a systematic review. Prev. Med. 157:106997. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2022.106997
Xu, N., Li, R., Feng, L., and Liang, M.-Y. (2024). Path analysis of the effect of positive psychological capital on health-promoting lifestyle in patients with copd after pulmonary rehabilitation: an observational study. Medicine 103:e39204. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039204
Xu, X. (2018). Relationship of Social Capital and Multidimensional Health of the Elder –A Case Study of Anhui Province. Anhui Medical University.
Xu, X., and Zhao, L. (2022). Social capital and the realization of mutual assistance for the elderly in rural areas—based on the intermediary role of psychological capital. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20:415. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010415
Ye, C.-J., Liu, D., Chen, M.-L., Kong, L.-J., Dou, C., Wang, Y.-Y., et al. (2024). Mendelian randomization evidence for the causal effect of mental well-being on healthy aging. Nat. Hum. Behav. 8, 1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41562-024-01905-9
Yong, B., Lin, R., and Xiao, H. (2021). Factors associated with nursing home adjustment in older adults: a systematic review. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 113:103790. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103790
Yoo, H.-M. (2020). A phenomenological study on the continuing participation of the elderly in sports: focusing on positive psychological capital. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 20, 494–502. doi: 10.5392/JKCA.2020.20.09.494
Youssef-Morgan, C. M., and Luthans, F. (2015). Psychological capital and well-being. Stress Health J. Int. Soc. Investig. Stress 31, 180–188. doi: 10.1002/smi.2623
Yu, Y., Wu, Y., Huang, Z., and Sun, X. (2023). Associations between media use, self-efficacy, and health literacy among chinese rural and urban elderly: a moderated mediation model. Front. Public Health 11:1104904. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1104904
Yue, D., Baoquan, Z., and Wenchang, Z. (2018). Meta-analysis of the current status of health-promoting lifestyles among chinese older adults. Chin. J. Nurs. Educ. 15, 331–335.
Yue, Z., Liang, H., Qin, X., Ge, Y., Xiang, N., and Liu, E. (2022). Optimism and survival: health behaviors as a mediator—a ten-year follow-up study of Chinese elderly people. BMC Public Health 22:670. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13090-3
Yuying, Z., and Jing, C. (2022). Gender differences in the score and influencing factors of social participation among Chinese elderly. J. Women Aging 34, 537–550. doi: 10.1080/08952841.2021.1988313
Zare, F., Ameri, H., Madadizadeh, F., and Reza Aghaei, M. (2020). Health-related quality of life and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. SAGE Open Med. 8. doi: 10.1177/2050312120965314
Zhu, X., Jia, F., Kong, L., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Daily walking kinematic characteristics of the elderly in different residential settings: experimental study on Chinese community-living elderly and long-term nursing home residents. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 35, 2531–2542. doi: 10.1007/s40520-023-02532-6
Keywords: Xiangxi region, nursing homes, elderly, social capital, positive psychological capital, health-promoting behaviors, mediation effect
Citation: Liao L, Li Y, Tian F, Wu J, Zhong J, He T and Li J (2025) The mediating role of psychological capital in health behaviors among elderly nursing home residents. Front. Psychol. 16:1534124. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1534124
Received: 27 November 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 22 January 2025.
Edited by:
Anna Maria Berardi, Université de Lorraine, FranceCopyright © 2025 Liao, Li, Tian, Wu, Zhong, He and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinxiu Li, MjQwNzY3Nzk1OEBxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Liping Liao1†
Liping Liao1† Yunhua Li
Yunhua Li Jinxiu Li
Jinxiu Li