
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Psychol. , 21 March 2025
Sec. Sport Psychology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1491262
This article is part of the Research Topic Psychological Factors in Physical Education and Sport - Volume V View all 24 articles
Purpose: This study aims to examine the inner relationship between children’s physical exercise, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and resilience, and explore effective ways to promote the improvement of children’s resilience.
Methods: Using measurement tools such as the Physical Activity Rating Scale (PARS-3), the General Self-Efficacy Scale (GSES), the Chinese version of the Emotional Intelligence Scale (EIS), and the Adolescents Resilience Scale, we conducted a questionnaire survey was conducted among 700 primary school students in 4 primary schools. The SPSS 22.0 software was used to process and analyze the data, including correlation analysis, regression analysis, and Bootstrap analysis, and AMOS 21.0 software was used to establish a structural equation model.
Results: (1) Physical exercise has a significant positive correlation with self-efficacy (r = 0.29, p < 0.001), emotional intelligence (r = 0.32, p < 0.001), and resilience (r = 0.37, p < 0.001), and there is also a significant positive correlation between emotional intelligence and resilience (r = 0.30, p < 0.001). (2) Physical exercise can directly and positively predict children’s resilience (β1 = 0.38) and its five sub-dimensions, that is, physical exercise can positively predict goal concentration (β = 0.35, p < 0.001), emotional control (β = 0.29, p < 0.001), positive cognition (β = 0.20, p < 0.01), family support (β = 0.33, p < 0.001), interpersonal assistance (β = 0.31, p < 0.001), respectively. (3) Self-efficacy (SE = 0.10) and emotional intelligence (SE = 0.08) have partial mediating effects, respectively, on the relationship between physical exercise and resilience, and the chain mediation effect of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence also reaches a significant level (SE = 0.02).
Conclusion: Physical exercise can have a positive impact on children’s resilience through self-efficacy and emotional intelligence, so schools or parents should attach importance to children’s physical activities, which is an effective way to improve their resilience.
Resilience, also known as psychological elasticity, psychological resilience, or ability to face adversity, is an individual’s ability or trait to cope with stress, setbacks, or trauma. It is an important positive psychological quality (Davydov et al., 2010; Windle, 2011). It is closely related to the mental health of children (senior primary school students) (Li et al., 2022). Typically, individuals with high resilience have richer psychological resources and the ability to flexibly mobilize internal and external resources to cope with difficulties. They are more likely to gain growth opportunities from negative events and turn adverse factors into motivation (Pietrzak et al., 2009; Troy and Mauss, 2011; Xi et al., 2011). Research has found that resilience is a protective factor for individual mental health and can reduce the negative impact of life events on mental health in a wide range (Ye et al., 2014; Han et al., 2019). Senior primary school students (9–12 years old) are in the critical period of transition from childhood to adolescence. They are facing major changes in physiology, psychology, and interpersonal relationships, and are more likely to develop negative emotions such as depression and anxiety (Yang, 2012). As one of the important psychological resources, an increase in resilience will allow individuals to gain more satisfaction and develop better life resources (Abolghasemia and Taklavi, 2010), thereby having more internal and external resources to cope with stressful events, have a stronger ability to deal with negative emotions, thereby improving life satisfaction (Tugade and Fredrickson, 2004). Therefore, examining the protective factors of children’s resilience and the relationship paths between variables from the perspective of positive psychology, and then finding effective ways to improve children’s resilience, is the key to promoting their mental health development.
With the development of exercise psychology, the positive relationship between physical exercise and individual resilience has received widespread attention. For example, researchers have found that children who regularly participate in physical activities have higher resilience, and high resilience can improve their adaptability and academic performance (Granizo et al., 2019). Individuals with high resilience are usually emotionally stable, have strong social adaptability and emotional management capabilities, and can better focus on goals when facing tasks. Even if they encounter negative events in study or life, they are more likely to respond with a positive attitude (Dong et al., 2023). Research shows that extracurricular physical exercise can promote children’s mental qualities of self-confidence and tenacity (Yan et al., 2019), and positively predict children’s resilience (Li et al., 2022). For example, football training has a significant effect on improving the resilience of senior primary school students (Liu, 2017). Meanwhile, the positive relationship between physical exercise and resilience has been effectively confirmed in college students (Liu, 2020) and children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (Liang et al., 2023). It can be explained as physical exercise is conducive to enhancing blood circulation and hormone secretion, promoting metabolism, effectively helping the body relax and divert attention, and thus has a positive effect on improving resilience (Deng et al., 2025; Li et al., 2024). It can be seen that the development of children’s resilience is important for healthy growth, but there are relatively few studies on the relationship between physical exercise and children’s resilience, and whether this relationship is affected by other variables is still unclear.
Self-efficacy refers to the subjective perception of an individual’s belief in whether he or she can complete a certain behavior or task at a certain level (Bandura, 1986). It is people’s evaluation of their abilities (Bandura, 1982), which is the psychological power of individuals’ continuous self-regulation, which can predict and explain corresponding behaviors (Bandura, 1997). Research shows that there is a significant correlation between physical exercise and self-efficacy (Tang, 2000). Among children and adolescents, the correlation between physical exercise and self-efficacy has been confirmed by some studies (Zhao et al., 2019), and the increase in physical activity, is more conducive to improving the performance of adolescents’ self-efficacy (Zhao et al., 2019). In other words, physical exercise plays an important role in improving an individual’s self-efficacy, and self-efficacy will undergo adaptive changes as the degree of exercise increases (Downs and Strachan, 2016). For example, an individual’s self-efficacy can be positively altered after an intense run or bike ride (McAuley et al., 1995). Meanwhile, children with high self-efficacy usually have a higher ability to cope with pressure, frustration, or trauma, that is, there is also a significant positive correlation between self-efficacy and children’s resilience (Liang, 2011). Children with high resilience have significantly higher scores on general self-efficacy than children with low resilience, indicating that the former have higher confidence in their ability to cope with pressure or challenges (Hamill, 2003; Xi et al., 2011). Research shows that individuals with high self-efficacy have higher behavioral motivations, can set practical goals for themselves, evaluate themselves more positively when facing difficulties, and are more able to use positive coping methods to solve the problems they face (Schwarzer and Warner, 2013), which helps individuals grow from difficulties and promotes the development of resilience (Feng et al., 2022). Further research found that self-efficacy has a mediating effect between physical exercise and mental health (Sheng et al., 2016). There is a mutual relationship between physical exercise, self-efficacy, and resilience among college students, and physical exercise can have a positive effect on resilience by promoting self-efficacy (Chen, 2023).
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to express, evaluate, and regulate one’s own and others’ emotions, as well as the ability to use emotions to solve practical problems, that is, a comprehensive ability to accurately perceive, evaluate, and express emotions (Salovey and Mayer, 1990; Mayer and Salovey, 1997). Research has found that emotional intelligence has an important impact on children’s interpersonal adaptation, academic achievement, and social adaptation (Zhang, 2014; Meng, 2018). Children with good emotional intelligence can express, manage, and reflect on their problems well. Emotions, thereby stimulating the ability to think positively, act positively, and coordinate interpersonal relationships (Yang, 2010). In recent years, the relationship between physical exercise and the emotional intelligence of students at different stages has received widespread attention from researchers. For example, Zhu (2020) found that moderate-intensity physical exercise at different times can improve the emotional intelligence level of primary school students, and especially has a significant improvement effect on primary school students’ self-emotion regulation and emotional perception. Ruiz-Ariza et al. (2019) found through research that cooperative high-intensity intermittent exercise has a significant impact on the creativity and emotional intelligence of middle school students, and can effectively improve the creativity, happiness, and social abilities of inactive middle school students. Wang et al. (2020) found through a cross-sectional survey that there is a positive correlation between physical exercise and emotional intelligence, and regular participation in physical exercise can promote the improvement of emotional intelligence among college students. Interestingly, the improvement of emotional intelligence can create conditions for the development of children’s resilience and can be used as a protective factor for resilience. For example, in stressful situations, emotion regulation ability and positive emotional experience serve as protective factors and are conducive to enhancing individual resilience (Olsson et al., 2003). A study on college students pointed out that emotional intelligence is positively related to resilience. Students with outstanding emotional intelligence tend to have higher levels of resilience, which is related to the ability to effectively regulate emotional information (Fa and Wang, 2021). The results suggest that physical exercise is related to the improvement of individual emotional intelligence (Ubago-Jimenez et al., 2019), and individuals with high emotional intelligence can better perceive, regulate, and control information about themselves and their surrounding environment (Higgs and Dulewicz, 2014), and good self-emotional assessment, emotional regulation, and emotional utilization can effectively predict resilience (Wen et al., 2014a).
Previous studies have shown that children’s physical exercise is related to self-efficacy (Huang et al., 2018; Isa et al., 2019; Xue et al., 2023), self-efficacy, and resilience (Hamill, 2003; Liang, 2011), and there is a significant correlation between physical exercise, self-efficacy and resilience (Chen, 2023). Meanwhile, physical exercise is related to emotional intelligence (Ruiz-Ariza et al., 2019; Zhu, 2020), emotional intelligence, and resilience (Liu et al., 2020), and there are different degrees of physical exercise, emotional intelligence, and resilience correlated (Wen et al., 2014a; Ubago-Jimenez et al., 2019). Interestingly, research has found that the general self-efficacy level of adolescents is related to their emotion regulation ability. The higher the self-efficacy level, the stronger their emotion regulation ability (Liu et al., 2011). Physical exercise can not only directly improve students’ negative emotional levels, but also indirectly improve students’ negative emotional levels by improving students’ self-efficacy (Liu, 2020).
To sum up, there are varying degrees of relationships between physical exercise, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and resilience. However, previous studies have mostly explored pairwise correlations between variables and lacked an overall perspective to examine the interrelationships between variables, thus limiting the generalizability and theoretical depth of the conclusions. In addition, psychological resilience is a comprehensive psychological index that involves many influencing factors. The path relationship between different factors has not been effectively verified through the model, and relevant research on children is rare. Therefore, this study intends to construct a chain mediation model between physical exercise, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and resilience, aiming to reveal the internal correlation between the variables and explain the protective factors of psychological resilience, to find ways to improve Effective paths for children’s resilience and mental health. Therefore, by constructing a chain mediation model among physical exercise, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and resilience, this study aims to reveal the internal correlation among various variables and explain the protective factors of resilience, to find an effective path to improve children’s resilience. Based on this, the following hypothesis was proposed in this study: H1: Physical exercise can positively predict children’s resilience. H2: Self-efficacy has a mediating effect between physical exercise and resilience. H3: Emotional intelligence has a mediating effect between physical exercise and resilience. H4: Self-efficacy and emotional intelligence have a chain mediating effect between physical exercise and children’s resilience.
This study adopted a cross-sectional survey research design and randomly selected 4 primary schools (Yubei District Airport Jiayuan Primary School, Yubei Central Park Primary School, Yubei Luozhi Primary School, and Yubei Bashu Primary School) in Yubei District, Chongqing, China to conduct a questionnaire survey. The samples involved students in the fourth, fifth, and sixth grades of primary school. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for sample selection: (1) No physical disability or movement disorder; (2) No mental illness or psychological disorder. In addition, based on previous research and to facilitate the establishment of a good structural equation model, we distributed a total of 700 questionnaires, recovered 655 questionnaires, eliminated 35 invalid questionnaires, and finally obtained 620 valid questionnaires. Among them, there are 277 boys and 343 girls. The average age of the participants is 9.99 ± 1.02 years old, the height is 1.48 ± 0.09 m, and the weight is 40.56 ± 12.30 kg. Questionnaire collection procedure: To ensure the quality and reliability of filling in the questionnaire, after explaining the precautions and requirements for filling out the questionnaire in detail to the students, participants should complete the filling in the questionnaire individually within 20 min according to their actual situation and collect it on the spot. In addition, to facilitate the participants to fill in the questionnaire, the distribution and filling of the questionnaire were carried out in the classroom during the break time. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants for this study. Meanwhile, since the survey targets a group of minors, we also obtained the approval of the parents of the participants in advance and signed the parent-informed consent form. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Southwest University, China (SWU-TY202105) and followed the Declaration of Helsinki, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
The “Physical Activity Rating Scale” (PARS-3) used was compiled and revised by Liang (1994), which evaluates subjects’ physical exercise from three aspects: exercise intensity, exercise frequency, and exercise time. It is quantified using a 5-point Likert type, with scores ranging from 1 to 5, based on which the level of participation in physical exercise is measured. Physical exercise score = exercise intensity score × (exercise time score - 1) × exercise frequency score. The score range is 0–100 points. The higher the score, the greater the amount of physical exercise. In this study, the test–retest reliability of this scale was high, with a correlation coefficient of r = 0.82. The factor loading is greater than 0.5, the AVE is greater than 0.6, and the combined reliability CR is greater than 0.6, indicating that this scale has good convergent validity. Meanwhile, the Cronbach alpha coefficient of this scale is 0.78. The measurement validity and reliability of this scale are shown in Table 1.
The emotional intelligence scale was revised by Wang and He (2002) was used. This scale has a total of 33 items, of which 5, 28, and 33 are reverse-scored. It contains four dimensions: emotion perception (11 items), self-emotion management (6 items), other people’s emotion management (10 items), and emotion application (6 items). A 5-point Likert scale is used for quantification. The items “very inconsistent, relatively inconsistent, unclear, relatively consistent, and very consistent” are scored as 1–5 points, respectively. The score range is 33–165 points. The higher the score, the higher the emotion. The stronger the intelligence. In this study, the test–retest reliability of this scale was high, with a correlation coefficient of r = 0.80. Each factor loading is greater than 0.7, the AVE is greater than 0.6, and the combined reliability CR is greater than 0.6, indicating that this scale has good convergent validity. The measurement validity and reliability of this scale are shown in Table 1.
The general self-efficacy scale was revised by Wang et al. (2001) was used. This scale is a unidimensional scale with a total of 10 questions. A 5-point Likert scale was used for quantification. The items “disagree, disagree very much, generally, somewhat agree, strongly agree” were scored as 1–5 points, respectively. The score range was 10–50 points. The higher the score, the higher the score, the greater the sense of self-efficacy. The stronger. In this study, the test–retest reliability of this scale was high, with a correlation coefficient of r = 0.83. The factor loading is greater than 0.5, the AVE is greater than 0.5, and the combined reliability CR is greater than 0.7, indicating that this scale has good convergent validity. The measurement validity and reliability of this scale are shown in Table 1.
The “Adolescents Resilience Scale” compiled by Hu and Gan (2008) was used. This scale has a total of 27 items, including 5 dimensions: goal focus (5 items), emotional control (6 items), positive cognition (4 items), family support (6 items), and interpersonal assistance (6 items). The scale is quantified using a 5-point Likert scale. The items “completely inconsistent, somewhat inconsistent, unclear, somewhat consistent, completely consistent” are scored as 1–5 points respectively, with a score range of 27–135 points. The higher it is, the better the resilience is. In this study, the test–retest reliability of this scale was high, with a correlation coefficient of r = 0.85. Each factor loading is greater than 0.7, the AVE is greater than 0.7, and the combined reliability CR is greater than 0.6, indicating that this scale has good convergent validity. The measurement validity and reliability of this scale are shown in Table 1.
This study used SPSS25.0 to process and analyze the data, and used factor analysis, internal consistency testing, etc. to examine the reliability and validity of the scale; Pearson correlation analysis was used to examine the correlation coefficients between variables; Hierarchical regression analysis was used to examine the direct impact of physical exercise on emotional intelligence; Finally, Bootstrap analysis and AMOS21.0 software were used to establish a structural equation model to examine the relationship between variables and the mediating effect of self-efficacy and resilience. The significance level of all indicators was set at p < 0.05.
This study adopted a questionnaire survey method, and all questionnaire items were filled in by the subjects themselves, so there may be common method bias in the measurement. To minimize the impact of common method bias on the results, this study used anonymous questionnaire measurement, standardized testing, and other procedural control methods to control it accordingly. After the data collection was completed, this study also used Harman’s single-factor test to examine the problem of common method bias (Podsakoff et al., 2003). Put the measures of all variables together for unrotated factor analysis, the results show that there are 7 factors with characteristic roots greater than 1, and the variation explained by the first factor is 28.43%, which is less than the critical standard of 40%. As can be seen, common method bias did not pose a serious problem in this study.
Pearson correlation analysis showed (Table 2) that in this study, children’s physical exercise was related to self-efficacy (r = 0.29, p < 0.001), emotional intelligence (r = 0.32, p < 0.001), and resilience (r = 0.37, p < 0.001) all have significant positive correlations. Meanwhile, self-efficacy has a significant positive correlation with emotional intelligence (r = 0.31, p < 0.001) and resilience (r = 0.35, p < 0.001) respectively, and there is also a significant positive correlation between emotional intelligence and resilience (r = 0.30, p < 0.001). The correlation coefficients between the main research variables all reach significant levels, which provides a good basis for subsequent testing of mediating effects.
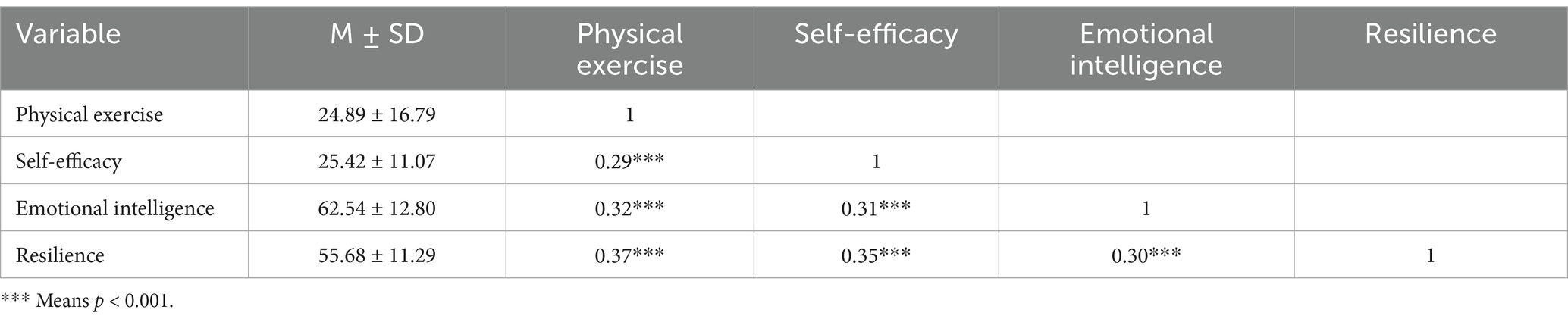
Table 2. Correlation between physical exercise, self-efficacy, resilience, and emotional intelligence.
After controlling for demographic variables (gender and age), physical exercise can significantly affect the five sub-dimensions of children’s psychological resilience, as shown that physical exercise can positively predict goal focus (β = 0.35, p < 0.001), emotion control (β = 0.29, p < 0.001), positive cognition (β = 0.20, p < 0.01), family support (β = 0.33, p < 0.001), and interpersonal assistance (β = 0.31, p < 0.001), explaining 12, 8, 4, 11, and 10% of the variance, respectively (See Table 3 for details).
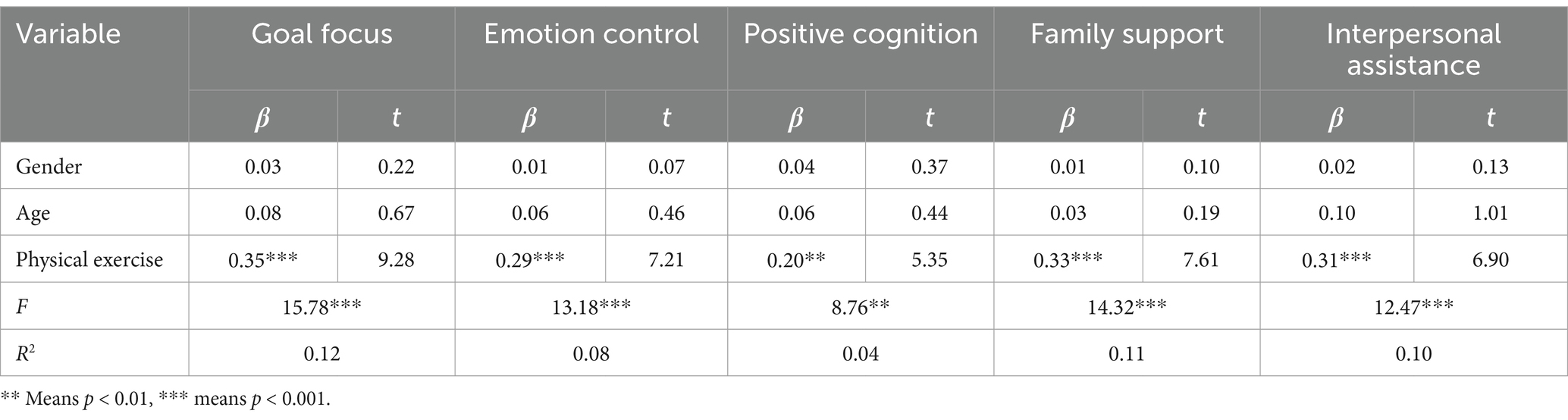
Table 3. Linear regression analysis of physical exercise on sub-dimensions of children’s psychological resilience.
This study followed the mediation effect test process proposed by Wen et al. (2014b) to examine the path relationship between primary school students’ physical exercise, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and resilience (Figure 1). After controlling for gender and age, we first tested the total effect of physical exercise on resilience and then tested the model fit and the significance of each path coefficient after adding mediating variables (self-efficacy and emotional intelligence). In the total effect model, physical exercise could directly and significantly positively predict resilience (β1 = 0.38, p < 0.001). After adding the two mediating variables of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence, physical exercise can still positively predict resilience (β2 = 0.29, p < 0.001). All fit indices of the total effect and mediation effect models reached an acceptable level (Table 4).
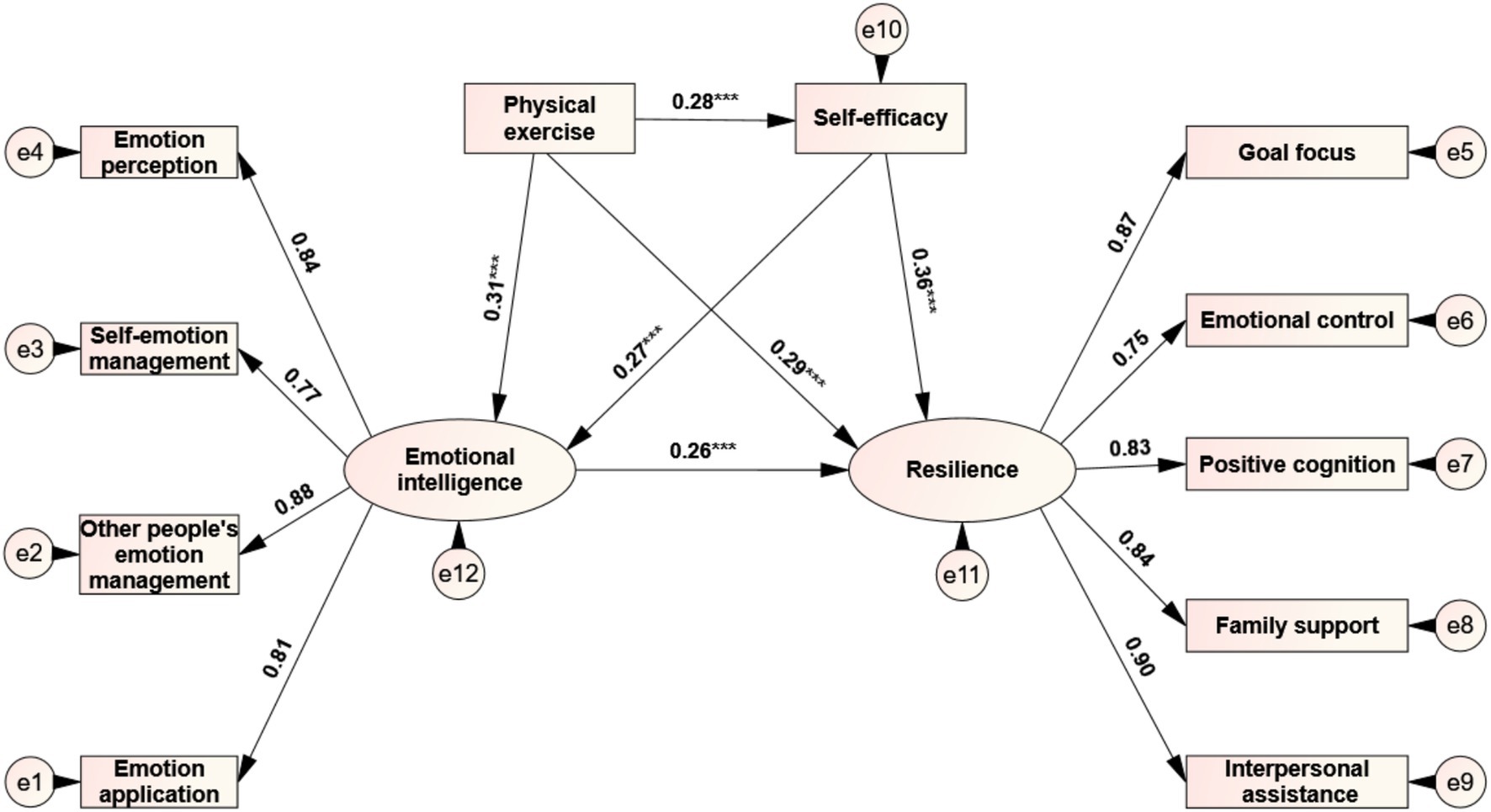
Figure 1. Chain mediation model between self-efficacy and emotional intelligence in physical exercise and resilience. Values in the figure are normalized regression weights.
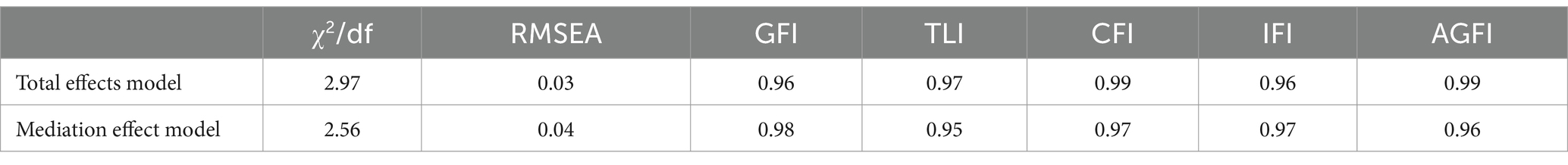
Table 4. List of fit indexes of total effect and mediating effect of physical exercise in predicting resilience.
The results of the mediation effect test show (Figure 1): (1) Physical exercise can significantly and positively predict self-efficacy (β = 0.28, p < 0.001), and self-efficacy can significantly and positively predict resilience (β = 0.36, p < 0.001), indicating that the mediating effect of the path of “physical exercise →self-efficacy →resilience” is significant, and its effect size is 0.28 × 0.36 = 0.10. (2) Physical exercise can significantly and positively predict emotional intelligence (β = 0.31, p < 0.001), and emotional intelligence can significantly and positively predict resilience (β = 0.26, p < 0.001), indicating that the mediating effect of the path of “physical exercise→emotional intelligence→resilience” is significant, with an effect size of 0.31 × 0.26 = 0.08. In addition, based on the research recommendations of Taylor et al. (2008) on the probability of type I error and statistical power when there is a “three-path mediation effect,” the joint significance method was used to test the chain mediation effect of “self-efficacy →emotional intelligence” between physical exercise and resilience. The results showed that: (3) self-efficacy could significantly and positively predict emotional intelligence (β = 0.27, p < 0.001), indicating that the mediating effect of the chain path of “physical exercise →self-efficacy →emotional intelligence →resilience” was significant, with an effect size of 0.28 × 0.27 × 0.26 = 0.02.
By decomposing the effect of physical exercise on children’s resilience (Table 5), it was found that the total effect of physical exercise on resilience was 0.49, the direct effect accounted for 59.18% of the total effect, and the mediating effect accounted for 40.82% of the total effect. Among them, the mediating effect of self-efficacy accounted for 20.41%, the mediating effect of emotional intelligence accounted for 16.33%, and the chain mediating effect of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence accounted for 4.08%. Each effect reached the significance level.
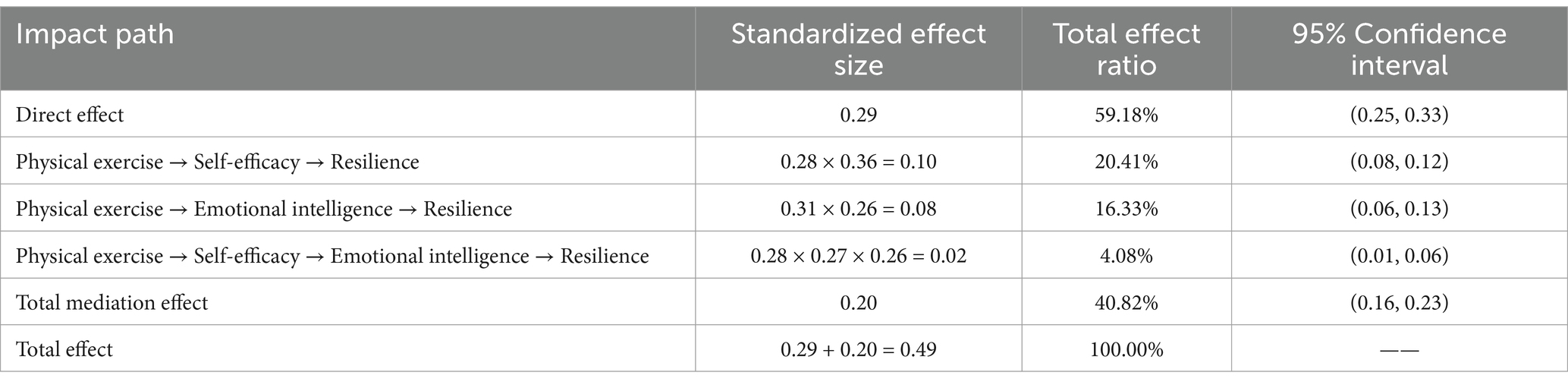
Table 5. Decomposition of the effect of physical exercise on primary school students’ emotional intelligence.
This study found that physical exercise has a significant positive correlation with children’s resilience (r = 0.37). Meanwhile, after controlling for demographic variables such as gender and age, physical exercise can directly and positively predict the five sub-dimensions of children’s resilience, and physical exercise also has a direct positive predictive effect on resilience (β1 = 0.38). This is consistent with previous studies, that is, physical exercise has a positive relationship with children’s resilience (Liu, 2017; Liang et al., 2023), and can positively predict children’s resilience (Li et al., 2022), which helps promote the development of psychological resilience. A review study also explained the relationship between children’s physical activity and cognitive emotions such as resilience (Cross et al., 2020). Similar conclusions have also been confirmed in the college student population, that is, physical exercise is positively correlated with the resilience of college students (Liu, 2020; Li et al., 2022). It should be pointed out that, based on previous studies, this study clarified the positive predictive effect of physical exercise on the five sub-dimensions of children’s resilience, namely goal focus (β = 0.35), emotional control (β = 0.29), positive cognition (β = 0.20), family support (β = 0.33) and interpersonal assistance (β = 0.31). This shows that the relationship between physical exercise and resilience is relatively complex, involving many factors such as attention, cognitive emotions, and environment. Studies have shown that physical exercise can provide an appropriate environment for improving psychological resilience (Xu et al., 2021) and that physical exercise can also benefit an individual’s psychological resilience by regulating stress perception (Arida and Teixeira-Machado, 2021). In other words, the relationship between physical exercise and resilience is diverse rather than single, and children’s active participation in physical exercise or physical activities is conducive to the overall improvement of multiple dimensions of resilience.
This study added children’s self-efficacy as a mediating variable to the mediation model between physical exercise and resilience. The results showed that self-efficacy has a partial mediating effect between physical exercise and resilience (standardized effect value SE = 0.10). The relationship between physical exercise and children’s resilience has been effectively explained above and is fully supported by previous studies (Yan et al., 2019; Granizo et al., 2019; Liang et al., 2023). Self-efficacy is an individual’s subjective evaluation of his or her ability to perform tasks (Bandura, 1982). It is closely related to behavioral choices, emotional response patterns, self-confidence, and thinking patterns. Positive self-efficacy can promote the development of abilities (Zhang et al., 1999). The amount of physical exercise is correlated with the self-efficacy of children (Huang et al., 2018) and adolescents (Zhao et al., 2019). Increasing the amount of physical exercise can help improve self-efficacy. Research shows that when individuals have strong confidence in completing tasks, they can mobilize all available resources, which will become guarantee factors for success (Tian et al., 2013) and may help improve resilience. Sabouripour et al. (2021) also believed that self-efficacy can promote the development of resilience and play a mediating role in the influence of other positive factors on resilience. Interestingly, self-efficacy plays a mediating role in the relationship between physical exercise and mental health (Jiang et al., 2018). Individuals with high self-efficacy are still able to adapt well to adversity or threats, and the goal focus, emotional control, and positive cognition of resilience play an important role (Xie et al., 2014). Meanwhile, self-efficacy also plays a mediating role between physical exercise and the mental health of middle school students. Students who participate more in sports have stronger self-efficacy, accompanied by higher subjective well-being and interpersonal adaptability (Sheng et al., 2016). Therefore, regular participation in physical exercise is closely related to the improvement of children’s self-efficacy and resilience, and physical exercise can also indirectly have a positive effect on children’s resilience through self-efficacy.
This study added children’s emotional intelligence as a mediating variable into the mediation model between physical exercise and resilience. The results showed that emotional intelligence has a partial mediating effect between physical exercise and resilience (SE = 0.08). Emotional intelligence is an individual’s ability to process emotional information (Mayer et al., 1999), which can guide individuals to regulate emotions reasonably (Huang and Dai, 1997) and will have a significant impact on emotional experience (Liang and Wang, 2018; Wang et al., 2020). Physical exercise plays an important role in suppressing negative emotions such as anxiety and depression in different populations and promoting the improvement of emotion regulation ability, which has been confirmed by many studies (Hayden and Allen, 1984; Xue and Zhao, 2018; Ruiz-Ariza et al., 2019; Zhu, 2020). Short-term aerobic exercise can significantly improve the executive function and emotion regulation ability of anxious students (Zhang et al., 2018). Individuals with high emotional intelligence can better perceive, regulate, and control information about themselves and their surroundings, thereby generating more positive emotional experiences (Higgs and Dulewicz, 2014). Self-emotional assessment, emotion regulation, and emotion application can better predict an individual’s psychological resilience (Wen et al., 2014a). Emotional intelligence can significantly predict individual psychological resilience (Wei et al., 2012). Emotional intelligence has a positive predictive effect on the personal strength and support of resilience (An and Pei, 2017), and is an important protective factor for resilience. On this basis, this study clarified the close relationship between physical exercise, emotional intelligence, and resilience, and revealed the partial mediating effect of emotional intelligence between physical exercise and children’s resilience.
To further reveal the intrinsic relationship between the variables, this study examined the chain-mediating effect of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence between physical exercise and resilience. The results showed that the chain-mediating effect of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence was significant (SE = 0.02), that is, physical exercise can affect resilience through the chain-mediation of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence. It is well known that physical exercise is one of the effective ways to improve mental health (Fu et al., 2006). On the one hand, the relationship between physical exercise, self-efficacy, and resilience has been confirmed by previous studies (Huang et al., 2018; Jiang et al., 2018; Cross et al., 2020; Sabouripour et al., 2021), and the results of this study also showed that self-efficacy played a mediating role between children’s physical exercise and resilience; On the other hand, the relationship between physical exercise, emotional intelligence and resilience has also been confirmed by previous studies (An and Pei, 2017; Zhang et al., 2018; Gong et al., 2019; Ruiz-Ariza et al., 2019), and the results of this study also showed that emotional intelligence plays a mediating role between children’s physical exercise and resilience. Interestingly, research has found that general self-efficacy is related to emotion regulation ability, and the higher the level of self-efficacy, the stronger the emotion regulation ability. Self-efficacy plays a mediating role between physical exercise and negative emotions (Wu et al., 2022). Physical exercise can significantly improve anxiety, depression, and emotion regulation self-efficacy of students at home during the epidemic. Self-efficacy plays a mediating role between physical exercise and students’ negative emotions (Liu et al., 2020). The results suggest that physical exercise can have a positive effect on children’s resilience through the chain mediation effect of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence. However, the mediating effect of emotional intelligence is lower than that of self-efficacy, which can be explained that in the indirect process of improving children’s resilience through physical exercise, self-efficacy may play a greater role and thus produce greater benefits for mental toughness, while emotional intelligence may be interfered by other factors in this process, and thus reduce the benefits for resilience.
This study aims to explore the relationship between children’s physical exercise, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and resilience from the perspective of exercise psychology and preliminarily clarifies the intrinsic relationship between the variables. However, since this study is a cross-sectional study and uses a questionnaire survey, the research method is relatively simple and the results are more subjective, which may have potential bias of self-reported data, and it is impossible to draw deeper relationships. Longitudinal empirical studies can be included in future studies to better explore the causal relationship between variables and to further reveal the impact of relevant potentially confounding variables such as socioeconomic status. Meanwhile, the survey subjects of this study were mainly children in Chongqing, China. Due to the small differences in the same region, the research scope was relatively limited. The samples of future studies can involve more regions, expand the scope and sample size of the samples, and improve the external validity of the research results. In addition, this study mainly examined the intrinsic relationship between physical exercise, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and resilience. In the future, more mediating or moderating variables can be explored to enrich the research results.
There is a significant positive correlation between children’s physical exercise, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, and resilience, and the relationship between variables can be further explored by comparing different physical exercises and gender in future investigations. Meanwhile, physical exercise can have a positive impact on children’s resilience through the chain mediation effect of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence. It should be noted that whether this mental health benefit continues with age and whether it is altered by other socio-demographic changes needs direct evidence from subsequent longitudinal or follow-up studies. In general, children’s resilience is a comprehensive variable that is easily affected by many factors, and regular physical exercise is an effective strategy to improve resilience, setting up longitudinal physical exercise intervention programs may be of great value in improving children’s resilience.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Southwest University, China (SWU-TY202105). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
CJ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. KW: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. HQ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project is funded by the Humanities and Social Sciences Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. 22SKGH508).
We would like to thank the informants for being part of this study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abolghasemia, A., and Taklavi, S. V. (2010). Resilience and perceived stress: predictors of life satisfaction in the students of success and failure. Procedia. Soc. Behav. Sci. 5, 748–752. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.07.178
An, R., and Pei, Y. Y. (2017, 2017). The mediating role of psychological resilience between emotional intelligence and academic stress in college students. Chin. J. School Health 38, 1092–1095. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2017.07.040
Arida, R. M., and Teixeira-Machado, L. (2021). The contribution of physical exercise to brain resilience. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 14:279. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.626769
Bandura, A. (1982). Self-efficacy mechanism in human agency. Am. Psychol. 37, 122–147. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.37.2.122
Bandura, A. (1986). The explanatory and predictive scope of self-efficacy theory. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 4, 359–373. doi: 10.1521/jscp.1986.4.3.359
Chen, K. (2023). Effects of physical exercise on academic burnout in college students: the mediating role of self-efficacy and resilience : Southwest University.
Cross, A., Howlett, N., and Sheffield, D. (2020). Social ecological interventions to increase physical activity in children and young people living with and beyond cancer: a systematic review. Psychol. Health 35, 1477–1496. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2020.1759601
Davydov, D. M., Stewart, R., Ritchie, K., and Chaudieu, I. (2010). Resilience and mental health. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 30, 479–495. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.03.003
Deng, D. L., Sun, Q. C., and Li, H. (2025). The influences of physical exercise on student burnout: based on the mediating role of psychological resilience. BMC Psychol. 13:114. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02394-9
Dong, Y. Q., Wu, J. T., Wang, C. S., Ge, Y. Y., Wu, Y. Z., Zhang, C. Y., et al. (2023). Cross-lag study on adolescents’ exercise atmosphere, psychological resilience and mobile phone dependence. China journal of health psychology 31, 298–303. doi: 10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2023.02.024
Downs, M., and Strachan, L. (2016). High school sport participation: does it have an impact on the physical activity self-efficacy of adolescent males? Int. J. Hum. Move. Sports Sci. 4, 6–11. doi: 10.13189/saj.2016.040102
Fa, J. J., and Wang, C. Y. (2021). Influence of emotional intelligence on exercise engagement and the mediation effect of mental toughness for undergraduates of sports specialty in Nanjing. J. Nanjing Norm. Univ. 44, 142–148.
Feng, B., Li, Z. L., Wang, K. X., and Cui, H. B. (2022). The relationship between purpose in life and resilience in college students: the multiple mediating roles of self-control and general self-efficacy. Psychol. Res. 15, 78–85. doi: 10.19988/j.cnki.issn.2095-1159.2022.01.010
Fu, Y., Yu, F., and Liu, D. Y. (2006). A correlation study between college Students' mental health level and physical exercise. China Sport Sci. Technol. 5:120-122+125.
Gong, Y. J., Zhang, Y. F., Yang, X. Y., Guan, Y., and Tang, D. H. (2019). Effectiveness of exercise intervention on sleep quality and negative emotion among female college students with anxiety. Chin. J. School Health 40, 542–545. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2019.04.018
Granizo, I. A. R., Vargas, J. M. A., and Mata, S. S. (2019). The role of resilience in the association between sports physical activity and academic aspects in schoolchildren. Sportis Scientific Tech. J. School Sport Physical Educ. Psychomotricity. 5, 513–531. doi: 10.17979/sportis.2019.5.3.5603
Hamill, S. K. (2003). Resilience and self-efficacy: the importance of efficacy beliefs and coping mechanisms in resilient adolescents. Colgate Univ. J. Sci. 115–146.
Han, L., Yuan, J. W., and Zhao, Q. Q. (2019). The impact of life events on mental health of rural left-behind children: the mediating role of peer attachment and psychological resilience and the moderating role of sense of security. Chin. J. Spec. Educ. 7, 55–62.
Hayden, R. M., and Allen, G. J. (1984). Relationship between aerobic exercise, anxiety, and depression: convergent validation by knowledgeable informants. J. Sports Med. 24, 69–74.
Higgs, M., and Dulewicz, V. (2014). Antecedents of well-being: a study to examine the extent to which personality and emotional intelligence contribute to well-being. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 25, 718–735. doi: 10.1080/09585192.2013.815253
Huang, M. E., and Dai, J. L. (1997). Emotional intelligence: the skills that promote mental health. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 5, 58–63.
Huang, C., Dannenberg, A. L., Haaland, W., and Mendoza, J. A. (2018). Changes in self-efficacy and outcome expectations from child participation in bicycle trains for commuting to and from school. Health Educ. Behav. 45, 748–755. doi: 10.1177/1090198118769346
Hu, Y. Q., and Gan, Y. Q. (2008). Development and psychometric validity of the resilience scale for Chinese adolescents. Acta Psychologica Sinica. 8, 902–912.
Isa, T., Ueda, Y., Nakamura, R., Misu, S., and Ono, R. (2019). Relationship between the intention-behavior gap and self-efficacy for physical activity during childhood. J. Child Health Care 23, 79–86. doi: 10.1177/1367493518777297
Jiang, Y., Zhang, L. W., and Mao, Z. X. (2018). Physical exercise and mental health: the effect of emotion regulation self-efficacy and emotion regulation strategy. Stud. Psychol. Behav. 16, 570–576.
Li, N., Fu, L., Yang, H., Zhao, W. T., Wang, X. B., Yan, Y. C., et al. (2024). The relationship between mobile phone dependence and academic burnout in Chinese college students: a moderated mediator model. Front. Psych. 15, 1382264. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1382264
Li, H. Y., Yan, J., Shen, B., Chen, A. G., and Huang, C. H. (2022). Effect of extracurricular physical exercise on life satisfaction of upper elementary students: the chain mediating role of self-confidence and resilience. China Sport Sci. Technol. 58, 51–56. doi: 10.16470/j.csst.2021148
Liang, H. (2011). Study on the relationship between mental resilience, general self-efficacy and attribution style of rural left-behind children : Qufu Normal University.
Liang, D. Q. (1994). Stress level of college students and its relationship with physical activity. Chinese Mental Health Journal. 1, 5–6.
Liang, X., Qiu, H., and Sit, C. H. P. (2023). The mediating role of resilience in the association between MVPA and psychological ill-being in children with ADHD. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 33, 485–494. doi: 10.1111/sms.14282
Liang, X. Y., and Wang, C. (2018). Impact of emotional intelligence on well-being of left-behind children. Chinese. J. Clin. Psychol. 26:387-390+386. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2018.02.038
Liu, X. Z. (2017). An experimental study on the effect of physical training on the resilience of the high-level graders in Priary school students : Hunan University of Science and Technology.
Liu, Z. H. (2020). Effects of physical exercise on negative emotion for universitystudents--the mediating and moderating effects of self-efficacy and mental resilience. J. Phys. Educ. 27, 102–108. doi: 10.16237/j.cnki.cn44-1404/g8.2020.05.014
Liu, Y., Li, X. N., Wang, X. S., Yang, N., Wang, B. J., and Shi, B. (2020). Mediating effect of exercise intervention on self-efficacy of negative emotion regulation of home schooled students during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Beijing Sport Univ. 43, 76–83. doi: 10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2020.03.009
Liu, Q. G., Zhou, L. Q., and Mei, S. L. (2011). The impact mechanism of self-efficacy on adolescents' emotion regulation. Chin. J. Spec. Educ. 12, 82–86.
Mayer, J. D., Caruso, D. R., and Salovey, P. (1999). Emotional intelligence meets traditional standards for an intelligence. Intelligence 27, 267–298. doi: 10.1016/S0160-2896(99)00016-1
Mayer, J. D., and Salovey, P. (1997). “What is emotional intelligence?” in Emotional development and emotional intelligence. eds. P. Salovey and J. D. Mayer (New York: Basic Books), 3–31.
McAuley, E., Bane, S. M., Rudolf, D. L., and LOX, C. L. (1995). Physique anxiety and exercise in middle - aged adults. J. Gerontol. 5, 229–235. doi: 10.1093/geronb/50B.5.P229
Meng, S. X. (2018). A study on the current situation and cultivation of primary school students' social emotional learning ability : Nanjing Normal University.
Olsson, C. A., Bond, L., Burns, J. M., Vella-Brodrick, D. A., and Sawyer, S. M. (2003). Adolescent resilience: a concept analysis. J. Adolesc. 26, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-1971(02)00118-5
Pietrzak, R. H., Johnson, D. C., Goldstein, M. B., Malley, J. C., and Southwick, S. M. (2009). Psychological resilience and postdeployment social support protect against traumatic stress and depressive symptoms in soldiers returning from operations enduring freedom and Iraqi freedom. Depress. Anxiety 26, 745–751. doi: 10.1002/da.20558
Podsakoff, P. M., Mackenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., and Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 88, 879–903. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Ruiz-Ariza, A., Suarez-Manzano, S., Lopez-Serrano, S., and Martinez-Lopez, E. J. (2019). The effect of cooperative high-intensity interval training on creativity and emotional intelligence in secondary school: a randomised controlled trial. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 25, 355–373. doi: 10.1177/1356336X17739271
Sabouripour, F., Roslan, S., Ghiami, Z., and Memon, M. A. (2021). Mediating role of self-efficacy in the relationship between optimism, psychological well-being, and resilience among Iranian students. Front. Psychol. 12:675645. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.675645
Salovey, P. J., and Mayer, D. (1990). Emotional Intelligence. Imaginat Cognit Persy. 9, 185–211. doi: 10.2190/DUGG-P24E-52WK-6CDG
Schwarzer, R., and Warner, L. M. (2013). “Perceived self-efficacy and its relationship to resilience” in Resilience in children, adolescents, and adults. eds. S. Prince-Embury and D. Saklofske (New York, NY: The Springer Series on Human Exceptionality. Springer), 139–150.
Sheng, J. G., Gao, S. Q., and Tang, G. X. (2016). The influences of exercise on the mental health of middle school students: intermediary effect of self-efficacy. China Sport Sci. Technol. 52:98-103+135.
Tang, Z. Y. (2000). On the relationship between physical exercise and mental health. J. Psychol. Sci. 3, 370–369.
Tian, Y. H., Qin, L., Wang, D. D., and Wang, M. H. (2013). The effect of AIDS-affected Children’s resilience on their school adjustment and academic performance. Chin. J. Spec. Educ. 10, 39–45.
Troy, A. S., and Mauss, I. B. (2011). Resilience in the face of stress: emotion regulation as a protective factor. Resilience Mental Health 1, 30–44.
Tugade, M. M., and Fredrickson, B. L. (2004). Resilient individuals use positive emotions to bounce back from negative emotional experiences. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 86, 320–333. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.86.2.320
Taylor, A. B., Mackinnon, D. P., and Tein, J. Y. (2008). Tests of the three-path mediated effect. Organizational Research Methods. 11, 241–269.doi: 10.1177/1094428107300344
Ubago-Jimenez, J. L., Gonzalez-Valero, G., Puertas-Molero, P., and Garcia-Martinez, I. (2019). Development of emotional intelligence through physical activity and sport practice. Behav. Sci. 9, 1–10. doi: 10.3390/bs9040044
Wang, K., Yang, Y., Zhang, T. R., Ouyang, Y. Y., Liu, B., and Luo, J. (2020). The relationship between physical activity and emotional intelligence in college students: the mediating role of self-efficacy. Front. Psychol. 11:967. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00967
Wang, C. K., and He, Z. W. (2002). The relationship between parental rearing styles with general self-efficacy and emotional intelligence in middle school students. Chinese Ment. Health J. 16, 781–785.
Wang, C. K., Hu, Z. F., and Liu, Y. (2001). Evidences for reliability and validity of the Chinese version of general self-efficacy scale. Chinese J. Appl. Psychol. 7, 37–40.
Wei, L. Q., Gong, Q. H., and Gao, R. H. (2012). Correlation analysis between emotional intelligence and psychological resilience among female college students majoring in nursing. Chin. J. Nurs. 47, 74–76.
Wen, Y., and Liu, W. (2014a). On the relationship of postgraduate students psychological resilience and emotional intelligence. J. Graduate Educ. 5, 48–51.
Wen, Z. L., and Ye, B. J. (2014b). Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 22, 731–745. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
Windle, G. (2011). What is resilience? A review and concept analysis. Rev. Clin. Gerontol. 21, 152–169. doi: 10.1017/S0959259810000420
Wu, J. T., Zhao, X. J., Zhao, W. N., Chi, X. D., Ji, J. L., Hu, J., et al. (2022). Effect of physical exercise on negative emotions of college students: the mediating role of self-efficacy. Chin. J. Health Psychol. 30, 930–934. doi: 10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2022.06.027
Xi, J. Z., Sang, B., and Zuo, Z. H. (2011). Stress/adversity cognition in psychologically resilient children. J. Psychol. Sci. 34, 102–107. doi: 10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.2011.01.020
Xie, L. P., Wang, H. L., Zou, W. X., Zhang, X., and He, Z. (2014). Left-at-home lower secondary school students self-efficacy and social adaptation: the mediating effect of resilience. Chin. J. Spec. Educ. 7, 52–58.
Xu, S., Liu, Z., Tian, S., Ma, Z., Jia, C., and Sun, G. (2021). Physical activity and resilience among college students: the mediating effects of basic psychological needs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:3722. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073722
Xue, C. Y., Zhong, Y., Li, Y. X., Qin, X., and Wang, J. F. (2023). Effect of delayed sports services after class on academic burnout: The chain mediating effect of cognitive engagement and self-efficacy. China Journal of Health Psychology. 31, 571–577. doi: 10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2023.04.018
Xue, Y., and Zhao, L. R. (2018). The relationship between ability structures of emotional regulation and physical activity among university students. Journal of Guangzhou Sport University. 38, 112–115. doi: 10.13830/j.cnki.cn44-1129/g8.2018.04.028
Yan, J., Li, Q., and Zhang, Z. K. (2019). The influence of extracurricular physical exercise on the physical self-esteem and self-confidence of elementary students. Sports & Science. 40, 100–104. doi: 10.13598/j.issn1004-4590.2019.02.012
Yang, M. (2010). Current status of research on primary school students' emotional intelligence. J. Campus Life Mental Health. 8, 249–250.
Yang, D. H. (2012). A study of character strengths among senior primary students and the relationship between character strengths and life satisfaction for them. Master dissertation, Hunan Normal University.
Ye, Y., Fan, F., Chen, S. J., Zhang, Y., Long, K., Tang, K. Q., et al. (2014). The relationship between resilience, negative life events and depressive symptoms: steeling effect and sensitizing effect. J. Psychol. Sci. 37, 1502–1508. doi: 10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.2014.06.037
Zhang, C. (2014). The effect of primary and secondary school Students' emotional intelligence on their interpersonal adaptation. Chin. J. Spec. Educ. 11, 82–89.
Zhang, D. K., Fang, L. L., and Ling, W. Q. (1999). Theory and current research status of self-efficacy. Advances. Psychol. Sci. 1:39-43+11.
Zhang, Y. F., Gong, Y. J., Tang, D. H., and Guan, Y. (2018). Effects of acute aerobic exercise on emotion regulation ability in female college students with anxiety: Potential mechanism and influencing factors. J. Tianjin Univ. Sport. 33, 210–216. doi: 10.13297/j.cnki.issn1005-0000.2018.03.005
Zhao, G. R., Ju, D., and Ma, L. (2019). Study on physical exercise Amount's influences on self-efficacy, learning emotion and learning performance of high school students. Educ. Sci. Res. 7, 61–65.
Keywords: physical exercise, children, self-efficacy, emotional intelligence, resilience, chain mediating
Citation: Jiang C, Wang K and Qin H (2025) Physical exercise and children’s resilience: mediating roles of self-efficacy and emotional intelligence. Front. Psychol. 16:1491262. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1491262
Received: 04 September 2024; Accepted: 05 March 2025;
Published: 21 March 2025.
Edited by:
Giuseppe Battaglia, University of Palermo, ItalyReviewed by:
Samuel Honório, Polytechnic Institute of Castelo Branco, PortugalCopyright © 2025 Jiang, Wang and Qin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hao Qin, ODQ3Nzc4MDc5QHFxLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.