- 1Department of Social Medicine of School of Public Health and Department of Pharmacy of the First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Public Health Emergency Response, Zhejiang Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3Hangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 4Xiaoshan District Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 5Xihu District Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Introduction: Research on body appreciation has flourished globally in recent years. College students and adults, rather than adolescents have been mainly focused in China. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the current status of body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors among Chinese adolescents, and elucidate their multifaceted relationships.
Methods: A total of 487 students from two junior high schools were selected through stratified cluster sampling for this cross-sectional study conducted in Hangzhou city, China. Data were collected by using the questionnaire including the Body Appreciation Scale-2 (BAS-2), the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Adolescents (PAQ-A), and the self-designed Food Frequency Questions.
Results: The study showed current status of body appreciation among Chinese adolescents, with a majority categorized as physically inactive and having unhealthy dietary behaviors, leading to abnormal weight. Notably, this study provided novel evidence linking body appreciation with positive weight-related behavioral outcomes in both physical activity and dietary behaviors (such as sufficient fruit and vegetable consumption and reduced fried food intake) among Chinese adolescents. Besides, this study also revealed the impact of gender, mother's education, and household income on weight-related health behaviors among adolescents.
Discussion: This study emphasized the significant relationships between body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors among Chinese adolescents. These findings present empirical evidence for the development of intervention programs aimed at fostering body appreciation and promoting weight-related health behaviors in adolescents.
1 Introduction
Body image is a complex and multidimensional construct that can affect quality of life, as well as cognitive, affective, and behavioral functioning (Cash et al., 1991), but it can be simply described as one's positive or negative feelings toward their own body shape (McClain and Peebles, 2016). Previously, research in the field focused on the negative aspects of body image, particularly body dissatisfaction (Carvalho et al., 2020; Gualdi-Russo et al., 2022; Jiménez Flores et al., 2017). However, recent evidence suggests that positive body image has a greater impact on various life domains than negative body image (Cash and Fleming, 2002). Body appreciation is the core component of positive body image, defined as accepting, respecting, and thinking favorably of the body despite its deviation from media-portrayed ideals (Tylka and Wood-Barcalow, 2015b).
Body appreciation has been proven to be positively associated with numerous health-promoting behaviors, including sports participation (Riddervold et al., 2023), lower eating pathology (Linardon et al., 2022) and adaptive eating patterns (Linardon, 2021). Additionally, body appreciation is inversely associated with health-compromising behaviors, including alcohol and tobacco consumption (Nolen and Panisch, 2022). Given this evidence, it is of vital significance for adolescents to maintain body appreciation. However, China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS) in 2015 (Song et al., 2022) has shown that nearly three-fifths of Chinese children and adolescents aged 6–17 years held a negative attitude toward their bodies. Therefore, the development of body appreciation should be attached great importance to assist adolescents in achieving optimal well-being.
Over the past few decades, there has been an increased prevalence of overweight and obesity among children and adolescents (Abarca-Gómez et al., 2017), with weight-related behaviors playing significant roles in either increasing or reducing the risk. Only 14.2% and 3.1% of Chinese children and adolescents aged 6–17 meet the minimum daily recommendation for fruit and vegetable intake (Li et al., 2020). The statistics for physical activity present an equally bleak picture. Only 3.7% of children and adolescents meet physical activity guidelines (engaging in moderate to vigorous physical activity for at least 1 h daily) (Wang et al., 2021). Based on this situation, weight-related health behaviors among Chinese children and adolescents deserve more attention.
In previous work, researchers observed associations between body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors (especially physical activity and dietary behaviors). Piko et al. (2020) revealed that among female adolescents, body appreciation was positively associated with self-perceived health, sports participation and controlled diets. Kantanista et al. (2015) revealed that body image had a statistically significant positive correlation with moderate to vigorous physical activity among teenagers. Similarly, a few studies in China also uncovered analogous outcomes, but the participants in these studies were primarily college students and adults, rather than adolescents. However, adolescence is a formative period for developing the body appreciation and weight-related behaviors that often persist into adulthood (Daly et al., 2022; Gattario and Frisén, 2019), making adolescence the optimal time to encourage body appreciation and healthier behaviors. Understanding the relationship between body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors during this period is crucial for developing targeted health strategies for adolescents. Existing domestic studies have mainly concentrated on the separate relationship between body appreciation and either physical activity or dietary behaviors, but there is limited research exploring the relationship between body appreciation and these critical weight-related health behaviors.
This study aims to investigate the current status of body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors (particularly physical activity and dietary behaviors) among adolescents, and further elucidate their multifaceted relationships.
2 Method
2.1 Participants and procedures
This cross-sectional study was conducted between September and October 2022 in Hangzhou, China. A multi-stage cluster sampling was used to recruit participants. Firstly, Xihu District and Xiaoshan District located in central and suburb of Hangzhou, respectively, were purposively selected as the study area. Secondly, one junior high school was selected randomly from each of the two districts. Within the grades 7th and 8th of the target schools, a cluster sampling was employed, three classes were randomly selected from each grade. Participants were excluded according to the following criteria: (1) suffered from morbid obesity, metabolic disorders, neuroendocrine diseases or congenital genetic disease; (2) refused to sign the informed consent, or was unable to complete the questionnaire.
After obtaining permission from school principals, our research team visited selected class to recruit sufficient participants. The research assistants introduced the study and explained the caveats of the questionnaire, and then supervised participants filling out the questionnaire independently after obtaining the written consent. A total of eligible 487 students participated in the study. After excluding invalid questionnaires with incomplete information or logical errors, we involved 464 valid respondents in the final data analysis, giving a response rate of 95.3%.
All study participants and their parents (or guardians) provided written informed consent at study entry. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of School of Public Health of Zhejiang University (No. ZGL202201-5).
2.2 Measures
Data were collected by a self-administrated questionnaire including demographic characteristics, body appreciation, physical activity, and dietary behaviors.
2.2.1 Demographic characteristics
Participants self-reported their demographic information including gender, age, household registration, household income, and parents' education level. Weight and height were measured with an anthropometer, which were used to calculate body mass index (BMI) as kg/m2. BMI was categorized as underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obesity according to Screening standard for malnutrition of school-age children and adolescents (WS/T 456-2014) and the Screening for overweight and obesity among school-age children and adolescent (WS/T 586-2018) of China (Lei et al., 2019).
2.2.2 Body appreciation
The Chinese version of the Body Appreciation Scale-2 (BAS-2) (Swami et al., 2016), originally developed by Tylka and Wood-Barcalow (2015a), was applied to assess body appreciation. This scale consisted of ten items and was rated on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = Never, 5 = Always). The average score of the scale was computed by taking the mean of all the items. Consequently, the range of scores varied from 1 to 5, with higher scores indicating greater body appreciation. Previous research showed that the scale had good reliability (Cronbach's alpha = 0.90) and validity in the Chinese sample (He et al., 2023). Similarly, the Cronbach's alpha for our present study stood at 0.92.
2.2.3 Physical activity
We employed the Chinese version of the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Adolescents (PAQ-A) (Li et al., 2015) to assess the level of physical activity in the latest 7 days. The instrument comprised nine items. The first eight questions reflected the participation of physical activity at different times, such as during physical education class, at lunch, after school, during evenings and weekends, which were rated on a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (indicating low physical activity) to 5 (indicating high physical activity) (Wyszyńska et al., 2019). The ninth question informed us of the reasons preventing participants from engaging in physical activity during that week, as a basis for screening the valid questionnaires. The physical activity score was calculated from the average of the initial eight items. The higher the score, the greater the level of physical activity. Specifically, participants were categorized as active or inactive based on whether their scores were above or below 2.75, respectively (Benítez-Porres et al., 2016). This scale has been previously validated and employed in China (Li et al., 2019). In this study, the Cronbach's alpha was 0.89.
2.2.4 Dietary behaviors
Dietary behaviors were measured by the simplified Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) (Cheng et al., 2020) with culturally nuanced adaptations. All participants were required to report their average intake and consumption frequency for weight-related dietary categories (including fruit, vegetables, fried food, dessert, and sugary beverages) over the past month. These specific categories of food were chosen due to their prevalence in modern diets and their significant impact on health among adolescents. Fruit and vegetables are typically considered healthy, while fried food, dessert and sugary beverages are associated with unhealthy dietary patterns and obesity (Hong et al., 2023). The total intake of these foods was calculated by multiplying consumption frequency with average intake, subsequently converted to daily intake for further data analysis.
According to Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents (2022) (Chinese Nutrition Society, 2022), the recommended vegetable intake was 400–450 g/d for adolescents aged 11–17, and the recommended fruit intake was 200–300 g/d for adolescents aged 11–13, while 300–350 g/d for adolescents aged 14–17. In this study, sufficient fruit intake and sufficient vegetable intake were considered to meet the recommended standards of the Dietary Guidelines.
2.3 Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were performed to characterize the sample, concurrently testing for the normal distribution of continuous variables. Continuous data were presented as means and standard deviation (M ± SD) and median and interquartile [Median (IQR)], while categorical data were presented as frequencies (N) and percentages (%). The differences between groups were examined using the independent samples t-test or one-way ANOVA for parametric data, Mann-Whitney U-test or Kruskal-Wallis H-test for non-parametric data, and Pearson's chi-square test for categorical data.
The correlations between body appreciation, physical activity, and dietary behaviors were calculated using Pearson correlations or Spearman correlations. Hierarchical linear regression and logistic regression analyses were conducted to estimate the influence of body appreciation on physical activity and dietary behaviors, while controlling for covariates such as age, gender, household income, and parents' education level. Epidata 3.1 was used for data management and SPSS 26.0 for statistical analysis. Statistical significance was determined by a two-sided p < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristic of participants
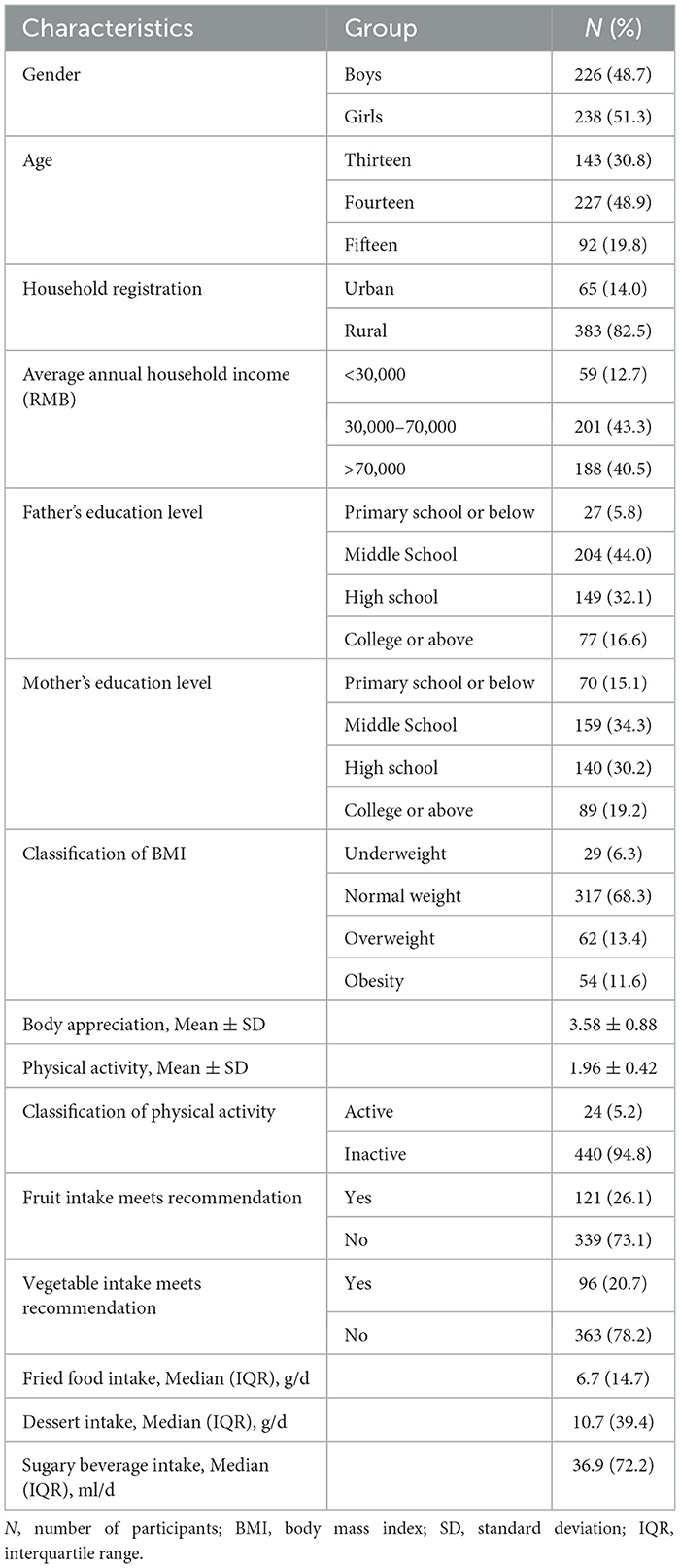
Participants' characteristics are presented in Table 1. In detail, 48.7% (n = 226) were boys, 48.9% (n = 227) were 14 years old and the majority (82.5%, n = 383) lived in rural areas. The education level of the father and mother was mainly middle or high school (76.1%, n = 353; 64.5%, n = 299, respectively). About 43.3% (n = 201) of participants reported that their average annual household income was 30,000–70,000 RMB. Approximately 70% of adolescents (n = 317) were of normal weight.
In this study, the body appreciation and physical activity scores of the participants were 3.58±0.88 and 1.96±0.42, respectively. Only 5.2% (n = 24) of the adolescents were categorized as active, while 94.8% (n = 440) of them were categorized as inactive. In terms of dietary behaviors, a significant number of participants did not meet the recommended intake of fruit (73.1%, n = 339) and vegetables (78.2%, n = 363) according to the Dietary Guidelines (Chinese Nutrition Society, 2022). Besides, the Median (IQR) of fried food intake was 6.7 (14.7) g/d, dessert intake was 10.7 (39.4) g/d, and sugary beverage intake was 36.9 (72.2) ml/d.
3.2 Univariate analysis of physical activity and dietary behaviors
The normality test showed that the scores of body appreciation and physical activity were normally distributed, whereas the scores of the intake of fruit, vegetables, fried food, dessert, and sugary beverages were non-normal distribution.
As shown in Table 2, there were significant gender differences and parents' education level differences in physical activity among the surveyed respondents. Boys were more likely to take part in physical activity than girls (2.03 ± 0.42 and 1.89 ± 0.41, respectively, p < 0.001). In addition, the participants whose fathers had high school education had a higher level of physical activity than those whose fathers had middle school education (2.06 ± 0.45 and 1.93 ± 0.39, respectively, p =0.010). Similarly, the participants whose mothers had high school education had a higher level of physical activity than those whose mothers had primary school education or below (2.02 ± 0.43 and 1.86 ± 0.38, respectively, p =0.016).
In the aspect of fruit intake, there were significant age differences and parents' education level differences in fruit intake. Thirteen-year-old participants were more likely to meet the recommended fruit intake (p = 0.001). The participants whose fathers had high school education level or above were more probable to meet the recommended fruit intake than those whose fathers' education level was middle school (p = 0.003). Compared with the participants whose mothers had high school education level or above, those whose mothers' education level was primary school or below were more challenging to meet the recommended fruit intake (p < 0.001). However, the differences in vegetable intake were not statistically significant across all demographic characteristics.
Regarding the fried food intake, participants with an average annual household income of > 70,000 RMB had higher intake of fried food compared to those with an average household income of < 30,000 RMB (p = 0.029). Likewise, there was a statistically significant difference in dessert intake based on the average annual household income (p = 0.043). However, there was no significant difference between the groups. Moreover, participants with an average annual household income of < 30,000 RMB had lower intake of sugary beverages than those with an average household income of > 30,000 RMB (p = 0.001). Compared to boys, girls were more likely to consume more dessert and fewer sugary beverages (p = 0.006 and p < 0.001, respectively).
3.3 Associations between physical activity, dietary behaviors, and body appreciation
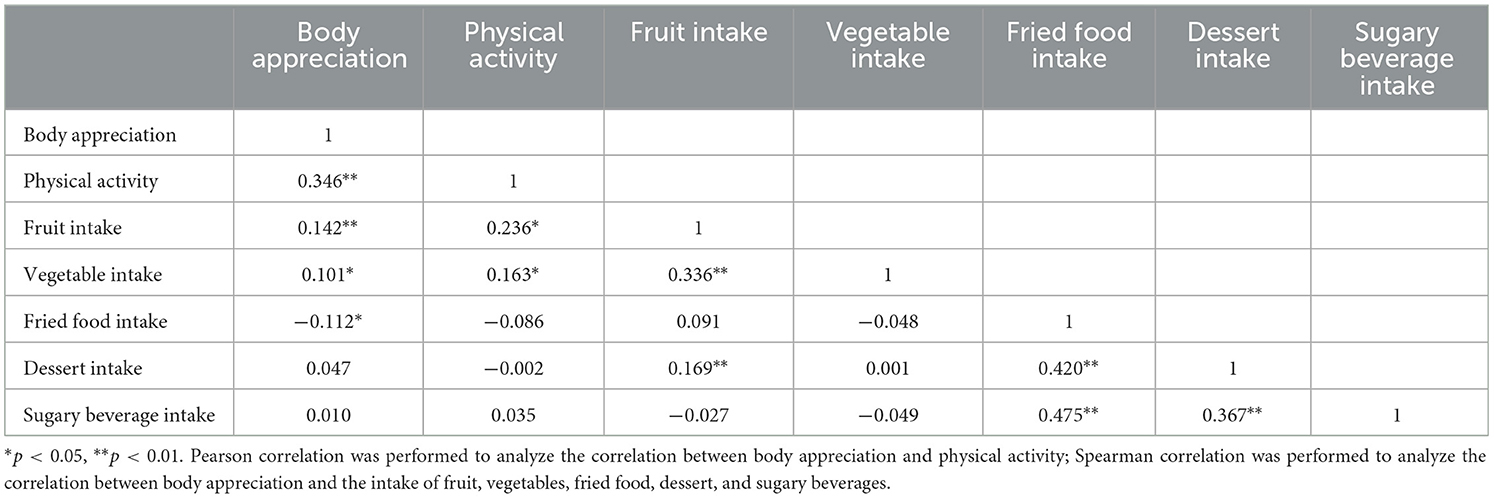
Correlation analysis (Table 3) showed that body appreciation was positively correlated with physical activity (r = 0.346, p < 0.01), sufficient fruit intake (r = 0.142, p < 0.01), and sufficient vegetable intake (r = 0.101, p < 0.05). Conversely, a significant negative correlation was observed between body appreciation and the intake of fried food (r = −0.112, p < 0.05).
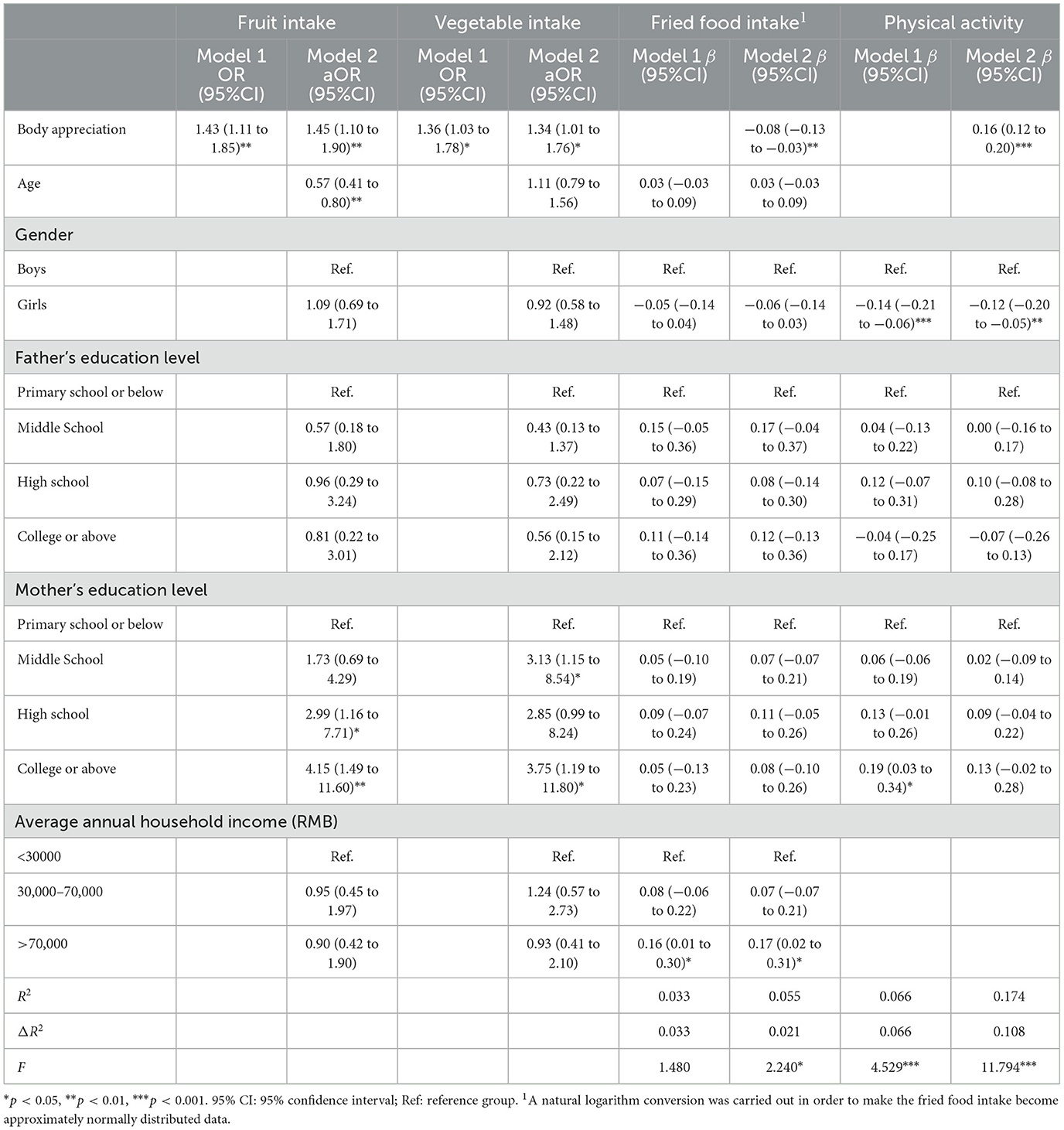
According to the results of univariate analysis, gender, age, parents' education level, average annual household income, and body appreciation were included in the logistic regression model of dietary behaviors (Table 4). There was a statistically significant trend for adequate fruit and vegetable consumption among adolescents with more educated mothers compared to those where mothers only had primary school or below education (both p < 0.05). Participants with higher body appreciation were more likely to meet the recommended fruit and vegetable intake [aOR = 1.45, 95%CI (1.10–1.90), p < 0.01; aOR = 1.34, 95%CI (1.01–1.76), p < 0.05, respectively].
Table 4 also showed that participants with an average annual household income of >70,000 RMB had significantly higher fried food intake than those with an annual household income of < 30,000 RMB [β = 0.17, 95%CI (0.02–0.31), p < 0.05]. Meanwhile, hierarchical linear analysis of fried food intake indicated that body appreciation explained an additional 2.1% of the variance in participants' fried food intake when controlling for demographic covariates (R2 = 0.055, F = 2.240, p < 0.05). More specifically, participants with higher body appreciation were less likely to consume fried food [β = −0.08, 95%CI (−0.13 to −0.03), p < 0.01].
The association between body appreciation and physical activity was also explored using hierarchical linear regressions. As shown in Table 4, demographic characteristics, including gender and parents' education level, were entered into Model 1, accounting for a variance of 6.6% (R2 = 0.066, F = 4.529, p < 0.001). In Model 2, body appreciation explained an additional 10.8% of the variance in physical activity when controlling for demographic characteristics (R2 = 0.174, F = 11.794, p < 0.001). In summary, girls [β = −0.12, 95%CI (−0.20 to −0.05), p < 0.01] were less likely to engage in physical activity and those with higher body appreciation [β = 0.16, 95%CI (0.12–0.20), p < 0.001] were more likely to engage in physical activity.
4 Discussion
This study investigated the current status of body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors among Chinese adolescents and contributed novel information about this group. The body appreciation measured by the BAS-2 in this study was lower than Canadian adolescents (Paquette et al., 2022), but higher than Lithuanian adolescents (Baceviciene and Jankauskiene, 2020). According to sociocultural theory (Cash, 2005), cultural attitudes toward body image and societal pressures unique in each country may explain the differences in body appreciation among adolescents from various cultural backgrounds. Within China, regional variations in body appreciation were also observed. Compared with adolescents in Wuhan (Chen et al., 2020) and Dandong (Gao et al., 2022), the adolescents in Hangzhou had a lower score of body appreciation. These differences may be influenced by regional disparities in lifestyle, socioeconomic status, and access to health education. Adolescents in urban areas of economically developed cities like Hangzhou may experience higher societal pressures related to body image due to greater exposure to media and social “ideal figure” expectations (Duan et al., 2022). Meanwhile, our participant adolescents' physical activity was lower than adolescents in Guilin (Lu et al., 2022) and Ethiopia (Andarge et al., 2021). Particularly, most of them were categorized as inactive, which indicated a poor level of physical activity. Likewise, unhealthy dietary behaviors were discovered in participants, such as insufficient intake of fruit and vegetables or excessive intake of fried food, dessert, and sugary beverages. Both insufficient physical activity and unhealthy eating habits among adolescents contribute to excessive weight gain, resulting in irreversible physiological and psychological harm to this age group.
Numerous studies have reported a positive correlation between body appreciation and physical activity (August et al., 2023; Shi et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024). Our findings also suggested that body appreciation was positively associated with physical activity in Chinese adolescents, which was consistent with Wang's study (Wang, 2022). Self-determination theory (Ryan and Deci, 2000) (SDT) could provide a theoretical mechanism for interpreting how body appreciation may influence physical activity, with its focus on the motivation underlying human behavior (Hurst et al., 2017). Specifically, Cox et al. (2019) linked body image variables to the intrinsic regulation of physical activity as defined within SDT, and discovered that body appreciation was a significant predictor of intrinsic motivation to be physically active. Therefore, individuals who maintain body appreciation are more likely to generate motivation to participate in physical activity.
Domestic scholars primarily investigated the relationship between body appreciation and intuitive eating (Luo et al., 2019) or eating disorders (Luo et al., 2021) among young women or adults, with little research exploring the relationship between body appreciation and daily dietary behaviors among adolescents. In this study, we found that body appreciation was positively associated with sufficient fruit and vegetable intake, while negatively associated with fried food intake. Consuming sufficient fruit and vegetables and reducing the intake of fried food epitomized healthy eating. In other words, body appreciation was associated with healthy dietary behaviors among adolescents, which has been confirmed in foreign studies (Jalali-Farahani et al., 2022; Neumark-Sztainer et al., 2006) as well. Individuals with low body appreciation may suffer from feelings of shame or self-criticism, based upon Heatherton and Baumeister's escape theory (Heatherton and Baumeister, 1991), they will turn to unhealthy eating behaviors, such as consuming high-fat, high-calorie foods to cope with those negative emotions, shifting from threatening stimuli to pleasurable ones. Consequently, it suggests that we can motivate adolescents to adopt healthy dietary behaviors by reinforcing the construction of body appreciation.
Apart from body appreciation, physical activity and dietary behaviors varied by adolescent sex and family socio-economic status (SES). In detail, girls participated in physical activity less frequently than boys, which was in keeping with those from the majority of similar surveys (Cairney et al., 2012). Also, maternal education level was found have a more prominent impact than body appreciation on teenagers adopting healthy dietary behaviors (including sufficient fruit and vegetable consumption). Compared to body appreciation, higher annual household income significantly affected the consumption of fried food among adolescents, likely because those from high-income families have greater access to fried food without financial constraints. Therefore, parent education is also important targets of interventions aimed at improving dietary behaviors of adolescents.
Physical activity and dietary behaviors are significant factors influencing weight management in adolescents. Therefore, this study focused on the relationship between body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors (including physical activity and dietary behaviors), a topic hitherto unexplored among Chinese adolescents. Our study revealed that adolescents with high body appreciation were more likely to engage in healthy eating and physical activity, developing and maintaining healthy lifestyles and weight management throughout the life cycle. Therefore, body appreciation during adolescence should be given special attention. Initially, adolescents should cultivate body appreciation and proper weight perceptions through targeted interventions, such as thematic educational programs. Then, the family and school environments wield substantial influence over adolescents' character development and cognitive formation (Sugiarti et al., 2022; Verhoeven et al., 2019). Parents should encourage open and honest communication about body image and emphasize the uniqueness and individuality of each person's body, helping adolescents develop correct and healthy aesthetics. Simultaneously, schools should expand their curriculum to include more courses and lectures on body image, nurturing adolescents' respectful outlook toward their own bodies and those of their peers. This multifaceted approach enhances their comprehension of body image dynamics and lays a robust foundation for cultivating genuine body appreciation.
There are several strengths and limitations in this study. This study provided novel information on the current status of body appreciation, physical activity, and dietary behaviors among Chinese adolescents. The study also explored the relationships between body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors in Chinese adolescents, which has received little attention in previous research. Some limitations still need to be addressed. Firstly, the cross-sectional design hinders conclusive inferences about causality, therefore, longitudinal and qualitative research could be conducted in the future (Wang and Cheng, 2020). Secondly, our findings are only confirmed for adolescents aged 13–15 living in Hangzhou, China, and thus generalizability is limited. Thirdly, for the convenience of the questionnaire, only fruit, vegetables, fried food, dessert, and sugary beverages were selected as indicators of adolescents' dietary behaviors. Twenty-four hours dietary recall method can be employed in further studies to investigate dietary consumption thoroughly among adolescents (Salvador Castell et al., 2015).
5 Conclusions
The study shows current status of body appreciation among Chinese adolescents, with a majority categorized as physically inactive and having unhealthy dietary behaviors, leading to abnormal weight. Notably, this study provides novel evidence linking body appreciation with positive weight-related behavioral outcomes in both physical activity and dietary behaviors (such as sufficient fruit and vegetable consumption and reduced fried food intake) among Chinese adolescents. Therefore, the impact of body appreciation should be taken into account when devising strategies to improve weight-related health behaviors in this population. Besides, this study also reveals the impact of gender, mother's education, and household income on weight-related health behaviors among adolescents. These findings present empirical evidence for the development of intervention programs aimed at fostering body appreciation and promoting weight-related health behaviors in adolescents.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of School of Public Health of Zhejiang University (No. ZGL202201-5). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
YZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation. YC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MW: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. BL: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. TS: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. JH: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. FJ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HW: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank our youth and their parents/guardians for participating and also own our deep thanks to those school coordinators, teachers and staff who supported the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abarca-Gómez, L., Abdeen, Z., Hamid, Z., Abu-Rmeileh, N., Acosta-Cazares, B., and Acuin, C (2017). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 390, 2627–2642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3
Andarge, E., Trevethan, R., and Fikadu, T (2021). Assessing the physical activity questionnaire for adolescents (PAQ-A): specific and general insights from an Ethiopian context. Biomed Res. Int. 2021:5511728. doi: 10.1155/2021/5511728
August, K. J., Malik, D., Markey, C. H., Woods, K., and Gerwitz, G. C. (2023). Additive and interactive associations among body appreciation, self-compassion, and gender in understanding college students' health behaviors. Body Image 47:101634. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2023.101634
Baceviciene, M., and Jankauskiene, R. (2020). Associations between body appreciation and disordered eating in a large sample of adolescents. Nutrients 12:752. doi: 10.3390/nu12030752
Benítez-Porres, J., Alvero-Cruz, J. R., Sardinha, L. B., López-Fernández, I., and Carnero, E. A. (2016). Cut-off values for classifying active children and adolescentes using the physical activity questionnaire: PAQ-C and PAQ-ACut-off values for classifying active children and adolescents using the physical activity questionnaire: PAQ-C and PAQ-A. Nutricion Hospitalaria 33:564. doi: 10.20960/nh.564
Cairney, J., Kwan, M. Y., Velduizen, S., Hay, J., Bray, S. R., and Faught, B. E. (2012). Gender, perceived competence and the enjoyment of physical education in children: a longitudinal examination. Int. J. Beha. Nutr. Phys. Act. 9:26. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-9-26
Carvalho, G. X., Nunes, A. P. N., Moraes, C. L., and Veiga, G. V. D. (2020). Body image dissatisfaction and associated factors in adolescents. Ciencia Saude Coletiva 25, 2769–2782. doi: 10.1590/1413-81232020257.27452018
Cash, T. F. (2005). The influence of sociocultural factors on body image: searching for constructs. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 12, 438–442. doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bpi055
Cash, T. F., and Fleming, E. C. (2002). The impact of body image experiences: development of the body image quality of life inventory. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 31, 455–460. doi: 10.1002/eat.10033
Cash, T. F., Pruzinsky, T., Grazer, F. M., and Sorensen, C. L. (1991). Body images: development, deviance, and change. Plastic Reconstruct. Surg. 88, 367. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199108000-00041
Chen, X., Luo, Y., and Chen, H. (2020). Friendship quality and adolescents' intuitive eating: a serial mediation model and the gender difference. Acta Psychologica Sinica 52, 485–496. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00485
Cheng, Z., Shuai, P., Qiao, Q., and Li, T. (2020). Validity and reliability of a simplified food frequency questionnaire: a cross sectional study among physical health examination adults in southwest region of China. Nutr. J. 19:114. doi: 10.1186/s12937-020-00630-z
Chinese Nutrition Society. (2022). Dietary Guidelines for Chinese School-Aged Children (2022). Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House.
Cox, A. E., Ullrich-French, S., Tylka, T. L., and McMahon, A. K. (2019). The roles of self-compassion, body surveillance, and body appreciation in predicting intrinsic motivation for physical activity: cross-sectional associations, and prospective changes within a yoga context. Body Image 29, 110–117. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2019.03.002
Daly, A. N., O'Sullivan, E. J., and Kearney, J. M. (2022). Considerations for health and food choice in adolescents. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 81, 75–86. doi: 10.1017/S0029665121003827
Duan, C., Lian, S., Yu, L., Niu, G., and Sun, X. (2022). Photo activity on social networking sites and body dissatisfaction: the roles of thin-ideal internalization and body appreciation. Behav. Sci. 12:280. doi: 10.3390/bs12080280
Gao, Y., Liu, S., Yu, X., Huang, W., Zhao, L., Teng, J., et al. (2022). Sociocultural attitudes towards appearance on unhealthy weight controlbehaviors: the mediating effects of body appreciation and lntuitive eating. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 30, 554–560. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2022.03.012
Gattario, K. H., and Frisén, A. (2019). From negative to positive body image: Men's and women's journeys from early adolescence to emerging adulthood. Body Image 28, 53–65. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2018.12.002
Gualdi-Russo, E., Rinaldo, N., and Zaccagni, L. (2022). Physical activity and body image perception in adolescents: a systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:13190. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013190
He, J., Cui, T., Barnhart, W. R., and Chen, G. (2023). The Chinese version of the functionality appreciation scale: psychometric properties and measurement invariance across gender and age. J. Eat. Disord. 11:99. doi: 10.1186/s40337-023-00826-8
Heatherton, T. F., and Baumeister, R. F. (1991). Binge eating as escape from self-awareness. Psychol. Bull. 110, 86–108. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.110.1.86
Hong, J., Gong, Q., Gao, H., Wang, J., Guo, Y., Jiang, D., et al. (2023). Association between dietary behavior and overweight and obesity among Chinese students: a cross-sectional study. Children 10:1617. doi: 10.3390/children10101617
Hurst, M., Dittmar, H., Banerjee, R., and Bond, R. (2017). “I just feel so guilty”: the role of introjected regulation in linking appearance goals for exercise with women's body image. Body Image 20, 120–129. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2016.12.002
Jalali-Farahani, S., Zayeri, F., Zarani, F., Azizi, F., and Amiri, P. (2022). Network associations among body image, lifestyle, body mass index, and quality of life in adolescents. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metabol. 20:e123237. doi: 10.5812/ijem-123237
Jiménez Flores, P., Jiménez Cruz, A., and Bacardi Gascón, M. (2017). Body-image dissatisfaction in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Nutricion Hospitalaria 34, 479–489. doi: 10.20960/nh.455
Kantanista, A., Osiński, W., Borowiec, J., Tomczak, M., and Król-Zielińska, M. (2015). Body image, BMI, and physical activity in girls and boys aged 14-16 years. Body Image 15, 40–43. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2015.05.001
Lei, Y. T., Ma, J., Hu, P. J., Dong, B., Zhang, B., and Song, Y. (2019). [The status of spermarche, menarche and corresponding relationships with nutritional status among students of 13 ethnic minorities in Southwest China in 2014]. Chin. J. Prevent. Med. 53, 492–496. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.05.011
Li, L., Ouyang, Y., Wang, H., Huang, F., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., et al. (2020). Status of fruit and vegetable intake among children and adolescents in 15 provinces of China. Chin. J. Health Educ. 36, 3–7.
Li, X., Wang, Y., Li, X., Li, D., Sun, C., Xie, M., et al. (2015). Reliability and Validity of Physical Activity Questionnaire for Adolescents(PAQ-A) in Chinese Version. J. Beijing Sport Univ. 38, 63–67.
Li, Z., Wu, H., and Liangwu, Q. (2019). Assessment of physical activity level, health status and perceptual impairment in adolescent students. J. Kunming Med. Univ. 40, 39–43.
Linardon, J. (2021). Positive body image, intuitive eating, and self-compassion protect against the onset of the core symptoms of eating disorders: a prospective study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 54, 1967–1977. doi: 10.1002/eat.23623
Linardon, J., McClure, Z., Tylka, T. L., and Fuller-Tyszkiewicz, M. (2022). Body appreciation and its psychological correlates: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Body Image 42, 287–296. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2022.07.003
Lu, H., Wang, H., Chen, Q., and Wei, H. (2022). Analysis of the current situation and influencing factors of physical activity among secondary school students in Guilin. Sci. Technol. Station. Sport. Goods 24, 127–129.
Luo, Y. J., Jackson, T., Stice, E., and Chen, H. (2021). Effectiveness of an internet dissonance-based eating disorder prevention intervention among body-dissatisfied young Chinese women. Behav. Ther. 52, 221–233. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2020.04.007
Luo, Y. J., Niu, G. F., Kong, F. C., and Chen, H. (2019). Online interpersonal sexual objectification experiences and Chinese adolescent girls' intuitive eating: the role of broad conceptualization of beauty and body appreciation. Eat. Behav. 33, 55–60. doi: 10.1016/j.eatbeh.2019.03.004
McClain, Z., and Peebles, R. (2016). Body image and eating disorders among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 63, 1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2016.07.008
Neumark-Sztainer, D., Paxton, S. J., Hannan, P. J., Haines, J., and Story, M. (2006). Does body satisfaction matter? Five-year longitudinal associations between body satisfaction and health behaviors in adolescent females and males. J. Adolesc. Health 39, 244–251. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2005.12.001
Nolen, E., and Panisch, L. S. (2022). The relationship between body appreciation and health behaviors among women and adolescent girls: a scoping review. Health Soc. Work 47, 113–122. doi: 10.1093/hsw/hlac006
Paquette, M. M., Dion, J., Bothe, B., and Bergeron, S. (2022). Validation of the body appreciation scale-2 in cisgender, heterosexual and sexual and gender minority adolescents and sexuality-related correlates. Body Image 43, 193–204. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2022.09.001
Piko, B. F., Obál, A., and Mellor, D. (2020). Body appreciation in light of psychological, health- and weight-related variables among female adolescents. Europe's J. Psychol. 16, 676–687. doi: 10.5964/ejop.v16i4.2183
Riddervold, S., Haug, E., and Kristensen, S. M. (2023). Sports participation, body appreciation and life satisfaction in Norwegian adolescents: a moderated mediation analysis. Scand. J. Public Health 52, 704–710. doi: 10.1177/14034948231184525
Ryan, R. M., and Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am. Psychol. 55, 68–78. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.55.1.68
Salvador Castell, G., Serra-Majem, L., and Ribas-Barba, L. (2015). What and how much do we eat? 24-hour dietary recall method. Nutricion Hospitalaria 31, 46–48. doi: 10.3305/nh.2015.31.sup3.8750
Shi, L., Jiang, L., Zhou, S., Zhou, W., and Yang, H. (2024). Self-appreciation is not enough: exercise identity mediates body appreciation and physical activity and the role of perceived stress. Front. Psychol. 15:1377772. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1377772
Song, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, T., Maitusong, P., and Lian, X. (2022). Association of body perception and dietary weight management behaviours among children and adolescents aged 6–17 years in China: cross-sectional study using CHNS (2015). BMC Public Health 22:175. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-12574-6
Sugiarti, R., Erlangga, E., Suhariadi, F., Winta, M. V. I., and Pribadi, A. S. (2022). The influence of parenting on building character in adolescents. Heliyon 8:e09349. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09349
Swami, V., Ng, S. K., and Barron, D. (2016). Translation and psychometric evaluation of a Standard Chinese version of the body appreciation scale-2. Body Image 18, 23–26. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2016.04.005
Tylka, T. L., and Wood-Barcalow, N. L. (2015a). The body appreciation scale-2: item refinement and psychometric evaluation. Body Image 12, 53–67. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2014.09.006
Tylka, T. L., and Wood-Barcalow, N. L. (2015b). What is and what is not positive body image? Conceptual foundations and construct definition. Body Image 14, 118–129. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2015.04.001
Verhoeven, M., Poorthuis, A., and Volman, M. (2019). The role of school in adolescents' identity development. a literature review. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 31, 35–63. doi: 10.1007/s10648-018-9457-3
Wang, X., and Cheng, Z. (2020). Cross-sectional studies: strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations. Chest 158, S65–S71. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.012
Wang, F., Li, Y., and Feng, Q. (2021). Status quo and characteristics of physical activities of children and adolescents. Afterschool Educ. China 22, 86–107.
Wang, G. (2022). Influence of body image on physical exercise of adolescents of different genders. Shandong Sports Sci. Technol. 44, 51–57. doi: 10.14105/j.cnki.1009-9840.2022.03.004
Wyszyńska, J., Matłosz, P., Podgórska-Bednarz, J., Herbert, J., Przednowek, K., Baran, J., et al. (2019). Adaptation and validation of the physical activity questionnaire for adolescents (PAQ-A) among Polish adolescents: cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 9:e030567. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-030567
Keywords: body appreciation, weight-related health behaviors, physical activity, dietary behaviors, Chinese adolescents
Citation: Zhong Y, Chen Y, Wang M, Lu B, Shen T, Hu J, Jiang F and Wang H (2025) The relationship between body appreciation and weight-related health behaviors among Chinese adolescents. Front. Psychol. 16:1484077. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1484077
Received: 23 August 2024; Accepted: 06 January 2025;
Published: 29 January 2025.
Edited by:
Daniel Rodriguez, La Salle University, United StatesReviewed by:
Jaime Camacho Ruiz, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México, MexicoAncah Caesarina Novi Marchianti, University of Jember, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Zhong, Chen, Wang, Lu, Shen, Hu, Jiang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongmei Wang, cm9zYUB6anUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors share first authorship
 Yuyuan Zhong
Yuyuan Zhong Ying Chen1,2†
Ying Chen1,2† Hongmei Wang
Hongmei Wang