- 1Department of Community and Public Health Nursing, Graduate School of Biomedical and Health Sciences, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan
- 2Department of Physical Analysis and Therapeutic Sciences, Graduate School of Biomedical and Health Sciences, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan
Introduction: This study aimed to develop the Dementia Attitude Scale Focusing on well-being (DASFWB) and to verify its reliability and validity. This scale measures the factors that individuals without dementia would consider important for their well-being if they were to develop dementia. It is expected to serve as a useful indicator for intervention strategies aimed at achieving an inclusive society.
Methods: The draft DASFWB scale was developed by extracting stories from older adults with mild Alzheimer's disease. The questionnaire was distributed to 1,614 adults aged 65 and older who were able to complete the self-administered questionnaire. Data from 815 individuals who completed the questionnaire without help (58.8% valid response rate) were analyzed. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were performed to identify the factors underlying the scale. Reliability was tested using Cronbach's alpha. Validity was tested through sample, criterion-related, convergent, and discriminant validity.
Results: The development and validation of the DASFWB identified a three-factor, 12-item scale. Cronbach's alpha coefficients for the scale and its three factors were 0.857, 0.843, 0.723, and 0.644, respectively. The confirmatory factor analysis model indices were as follows: χ2 = 146.574, df = 51, p < 0.001, comparative goodness of fit index = 0.930, goodness of fit index = 0.945, Tucker-Lewis index = 0.909, and root mean square error of approximation = 0.068. The composite reliability value for convergent validity, which was >0.7, was higher than the average variance extracted value. The criterion-related validity showed a weak correlation (ρ = −0.245 to 0.341, p < 0.001).
Discussion: The DASFWB exhibits good reliability and validity, indicating its utility as a measuring instrument.
1 Introduction
The prevalence of dementia increases with age (Lopez and Kuller, 2019), and the estimated number of people with dementia worldwide was 55.2 million in 2019, rising to 78 million in 2030 and 139 million in 2050 [World Health Organization (WHO, 2021a)]. In this context, stigma and discrimination affecting people with dementia are widespread worldwide and represent significant challenges that need to be addressed (WHO, 2021b). According to Goffman (1963), stigma is defined as “an attribute that is deeply discrediting,” which reduces the bearer “from a whole and usual person to a tainted, discounted one.” Stigma related to mental illness, including dementia, is a negative and inaccurate attitude toward a target group, characterized by stereotyping (cognitive aspect), prejudice (attitudinal aspect), and discrimination (behavioral aspect) (Corrigan and Penn, 2015; Matsumoto et al., 2024). Among these aspects, the attitudinal aspect is the central construct of stigma and has been most frequently employed as an outcome of dementia-friendly programs (Matsumoto et al., 2023).
Additionally, stigma can be categorized into self-stigma, public stigma, and courtesy stigma (Alzheimer's Disease International, 2019). Individuals with dementia experience self-stigma, characterized by the internalization of negative attitudes and behaviors associated with dementia. Public stigma involves negative attitudes and behaviors directed toward people with dementia. Courtesy stigma refers to the negative behaviors directed toward the family, friends, or close associates of individuals with dementia.
To reduce stigma toward people with dementia, WHO (2021a) set a goal for 75% of member countries to develop a national policy on dementia by 2025. In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare initiated a comprehensive effort to establish dementia policies in 2013 (Nakanishi and Nakashima, 2014). In June 2023, the Basic Act on Dementia to Promote an Inclusive Society was promulgated. The act aims to promote a vibrant society in which each person, including those with dementia, can fully realize their individuality and abilities and live in an inclusive and mutually-supportive social environment with others while respecting each person's character and individuality (Japanese Law Translation, 2023).
Previous research has pointed out that the existing scales for evaluating stigma and attitudes related to dementia have limitations regarding their target populations and applications (O'Connor and McFadden, 2010; Piver et al., 2013) and are not sufficiently established (Herrmann et al., 2018). Noguchi et al. (2022) developed a scale that assesses multidimensional public stigma, focusing on a participant's response to a hypothetical dementia diagnosis as well as people's attitudes toward a person with dementia. Matsumoto et al. (2024) developed a shortened version of the scale, originally developed by Kim and Kuroda (2011), to measure both positive and negative attitudes toward people with dementia. This version was developed to facilitate large-scale community and local government surveys. Furthermore, Bhatt et al. (2023) developed the Discrimination and Stigma Scale Ultra Short for People Living with Dementia to enable WHO member countries to assess stigma toward people with dementia at a regional level.
Stigma can worsen the mental health of people with dementia (WHO, 2021b). Previous research has demonstrated that stigma toward individuals with dementia is negatively correlated with well-being (Noguchi et al., 2022). well-being refers to a positive psychological state in which individuals feel good about themselves, serving as an important indicator of mental health (Ryan and Deci, 2001). This topic has garnered significant international interest, with numerous studies on well-being conducted in various countries (Huang et al., 2022). It has been noted that the well-being of individuals with dementia can deteriorate due to a lack of “continuity of experience,” which is related to memory and identity (Clare et al., 2020). However, while some individuals are able to cope positively with their dementia, others may suffer from fear and anxiety (Xanthopoulou and McCabe, 2019; Huizenga et al., 2022). This difference is believed to be significantly influenced by understanding of dementia and societal attitudes toward it (Eriksen et al., 2016). Therefore, eliminating discrimination and prejudice against individuals with dementia is crucial for enhancing well-being (Phinney et al., 2023).
This study aims to develop the Dementia Attitude Scale Focusing on well-being (DASFWB) and to verify its reliability and validity. This scale measures the factors that people without dementia would consider important for well-being if they were to develop dementia. While scales have been developed to evaluate stigma and attitudes toward dementia and people with dementia in pursuit of an inclusive society (Kim et al., 2021; Noguchi et al., 2022; Bhatt et al., 2023), none of them focus on well-being in every item. We designed a scale to ask questions framed with the positive phrase “even if one develops dementia,” allowing individuals to reflect on attitudes that are important for well-being from the perspective of those affected. This scale is expected to serve as a useful indicator for intervention strategies aimed at achieving an inclusive society.
2 Definition of terms
In this study, based on the definition by Kim and Kuroda (2011), we define attitudes toward dementia as encompassing both positive and negative feelings, as well as accepting and rejecting behaviors.
3 Methods
3.1 Study design
This study employed a cross-sectional design and a self-administered questionnaire without identifiable markings.
3.2 Creation of the draft scale
3.2.1 Conceptual structure and scale item creation
The scale was developed based on a semi-structured interview survey of seven older adults diagnosed with mild Alzheimer's disease (Ono and Nakatani, 2021). Two interviews were conducted: the first within 1 year of diagnosis and the second 1 year after the first interview. Having a role in life, a place to engage and participate with others, family and friends to confide in, support to accepting the diagnosis, and optimism for the future are all necessary for older adults with dementia to have a better life (Eriksen et al., 2016; Bronner et al., 2016; JDWG, 2018). With reference to previous studies, the interviews comprised discussions regarding (1) the individual's position within the household, participation in community activities, and daily struggles after being diagnosed with dementia; (2) their acceptance of the diagnosis; and (3) their hopes for future support with daily living. Focusing solely on the interview context, the study categorized 23 items and derived four categories: “distress toward knowing they have dementia,” “emotion of hope and despair toward their family,” “anxiety about socializing,” and “desire to live authentically in a familiar community.” Many items were related to the distress of having dementia and difficulties in daily life caused by the symptoms, which diminished the well-being of older adults. We also found that the participants maintained their well-being and wanted to live while interacting with people in the community, including persons with dementia. A draft of the DASFWB was developed based on the categories generated from the interview narratives.
3.2.2 Verification of content validity
To assess the validity of the 23-item scale, five certified nurses in dementia (Dementia Certified Nurses: DCN) and a university faculty member with dementia research experience were asked for their opinions on item modifications. DCNs are nursing professionals with advanced training and certification in dementia nursing. They provide advanced care to support patients with dementia and their families. Additionally, they offer guidance and consultation to other nursing professionals, leveraging their specialized knowledge and skills in dementia nursing. They also collaborate with other nursing and medical professionals to deliver care that respects the life, quality of life (QOL), and dignity of patients with dementia (Taneichi and Rokkaku, 2019). The DCN was asked to comment on: (1) whether the items were correctly worded; (2) whether they reflected well-being from the perspective of a person with dementia; (3) whether the items were similar in content; (4) whether the items were eligible to remain on the scale; and (5) which items should be added. Based on their feedback, five items were combined and two items were added. The Content Validity Index (CVI) was used to assess the content validity of the remaining 17 items; a CVI of 0.79 or higher indicates high content validity (Polit and Beck, 2006). Five DCNs rated each scale item on a 4-point scale from “adequate” to “not adequate.” As a result, all 17 items were adopted with a CVI of 0.80 or higher. Afterwards, the items were reviewed to see if they were easy for older adults to understand and not psychologically stressful and, finally, a CVI of 1 was achieved.
3.2.3 Validation of face validity
Face validity was tested in a pilot study with 10 older adults. The participants completed a questionnaire regarding whether the item meanings were clear and understandable, whether there was any ambiguity in the responses, and whether they experienced any difficulties when providing responses. No problems were identified related to ease of comprehension or burden in providing responses to the 17 items.
3.3 Participants and sample size
The participants were older adults living in a town with a population of 27,000, located in a rural area with a 40% aging rate. They were members of a community-based organization supported by national and local governments to promote enjoyable activities for older adults (Japan Federation of Senior Citizens Clubs, n.d.). The reason for selecting a single municipality was to avoid bias in public support for older adults. Participants were divided into two groups for exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). EFA required at least 10 participants per item (Carneiro, 2003) and CFA 200 participants (Anderson and Gerbing, 1984). Therefore, over 370 participants were required for EFA and CFA in the current study. The response rate we expected for the questionnaires was ~45% based on previous studies (Ozone et al., 2022). Furthermore, as some older adults who use long-term care insurance have cognitive decline (Ministry of Health, 2002), we excluded older adults with this type of insurance from the analysis, as their responses may not have been valid. In Japan, the certification rate for long-term care insurance is 18.4% (Cabinet Office, 2022). Based on the above, the questionnaire needed to be distributed to over 995 older adults; it was ultimately distributed to 1,614 older adults.
Following distribution, the questionnaires were collected by the club's senior officers. Participants were asked to hand in their sealed questionnaires to a senior club officer. Data were collected from November 2022 to January 2023.
3.4 Measures
The survey items included questions on basic characteristics, original draft of the DASFWB, and three different scales used to assess criterion-related validity.
3.4.1 Basic characteristics
Basic characteristics included questions on age, sex, marital status, sense of economic insecurity, living with family, use of long-term care insurance, presence of illness, and subjective symptoms of dementia (Ura et al., 2015; Miyamae et al., 2016; Kawamura et al., 2023).
3.4.2 Original draft of the DASFWB
The DASFWB was rated on a five-point scale as follows: 5 = agree, 4 = somewhat agree, 3 = undecided, 2 = not so much agree, and 1 = disagree. Higher scores indicated higher levels of well-being.
3.4.3 Criterion-related validity
The criterion-related validity measures included the 11-item revised Philadelphia Geriatric Center Morale Scale (PGC-MS) (Liang et al., 1992), the Japanese Lubben Social Network Scale (LSNS-6) short version (Kurimoto et al., 2011), and the revised Japanese version (Arimoto and Tadaka, 2019) of the University of California, Los Angeles Loneliness (UCLA-Loneliness) Scale.
3.4.4 The PGC-MS
The PGC-MS was developed and validated as a measure of subjective well-being among older adults and comprises three factors: psychological agitation, attitudes toward aging, and feelings of loneliness and dissatisfaction. The 11-item scale's short version total score scale ranged from 0 to 11, with one point for positive responses and zero for other responses; higher total scores indicated higher subjective well-being. This scale was chosen because it is believed that the psychological distress caused by stigma may affect well-being; it is expected to have a positive correlation with the DASFWB.
3.4.5 The LSNS-6
The reliability and validity of the LSNS-6 have been demonstrated (Lubben et al., 2006). This scale is implemented to determine the size of an individual's family, community, and network of friends. A higher score indicates a larger social network; indeed, social interactions are associated with quality of life and cognitive decline in older adults (Moreno et al., 2020; Evans et al., 2018). This scale considers reducing social networks due to stigma as an important factor for well-being, and it is assumed to have a positive correlation with the DASFWB.
3.4.6 The UCLA-loneliness
The UCLA-Loneliness scale quantifies an individual's loneliness level rather than measuring the extent of their social network. Higher scores on this scale indicate increased levels of perceived loneliness. Its reliability and validity have been empirically established (Saito et al., 2019). Loneliness has been linked to an increase in internalized stigma, leading individuals to accept societal labels, alienate themselves from others, and thus experience greater loneliness (Yildirim and Kavak Budak, 2020). Therefore, the choice of this scale is based on the hypothesis that it has a negative correlation with the DASFWB.
3.5 Data analysis
IBM SPSS Statistics standard Grand Pack 28.0 and IBM SPSS Amos version 29.0 were used for the data analysis.
3.5.1 Item analysis
To test the reliability and ceiling and floor effects, inter-item and item–total (I–T) correlations were examined. The ceiling effect was set to mean +5 standard deviation points, and the floor effect was set to mean −1 standard deviation point. As highly correlated coefficients may influence the results, inter-item correlation was set to r > 0.75 (Yusoff et al., 2021). For the I–T correlation, r < 0.3 was set as the criterion for exclusion (Yusoff et al., 2021).
3.5.2 Reliability study
Cronbach's alpha coefficients were calculated for both the scale as a whole and each factor, to assess reliability. The criterion for the coefficient was set to > 0.7 (Yusoff et al., 2021).
3.5.3 EFA
The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) test and Bartlett's sphericity test were performed to determine the appropriateness of factor analysis. The typical range for KMO values is between 0.8 and 1.0, while the value produced by Bartlett's sphericity test is considered significant if it is < 0.05 (Williams et al., 2010). Factor analysis was performed using maximum likelihood and Promax rotation. We removed commonalities below 0.2 and factor loadings under 0.3 (Boateng et al., 2018). Subsequently, we verified the factor structure and assigned descriptive titles to each factor.
3.5.4 CFA
CFA was performed to test factor structure and the model's goodness of fit. The goodness of fit index, comparative fit index, and Tucker-Lewis index are within a range of 0–1. A good fit is generally declared if the value is >0.9, while root mean square error of approximation is seen as a good fit if the value is < 0.08 (Yusoff et al., 2021).
3.5.5 Convergent and discriminant validity
Composite reliability (CR) and average variance extracted (AVE) were used to assess convergent validity. A scale is considered to have good convergent validity when AVE > 0.5 and CR > 0.7; when 0.36 < AVE < 0.5, the scale is considered to have acceptable convergent validity (Shrestha, 2021). Discriminant validity is assessed by comparing the square root of the AVE with the correlation coefficient between factors. A scale has good discriminant validity if the correlation coefficient between factors is less than the corresponding square root of the AVE (Sahoo, 2019).
3.5.6 Criterion-related validity
To ensure criterion-related validity, the relationships between the developed scale, PGC-MS, LSNS-6, and UCLA-Loneliness were confirmed using Spearman's rank correlation coefficient.
3.6 Ethical considerations
This study involving human participants was approved by the ethics committee of epidemiology research at Hiroshima University (approval number E2022-0020). Participants were informed of the purpose and methods of the study and told that they were free to participate or withdraw from the study at any point without penalty or consequences. Furthermore, individuals would be unable to be identified based on their data. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards established by the Declaration of Helsinki.
4 Results
4.1 Participant characteristics
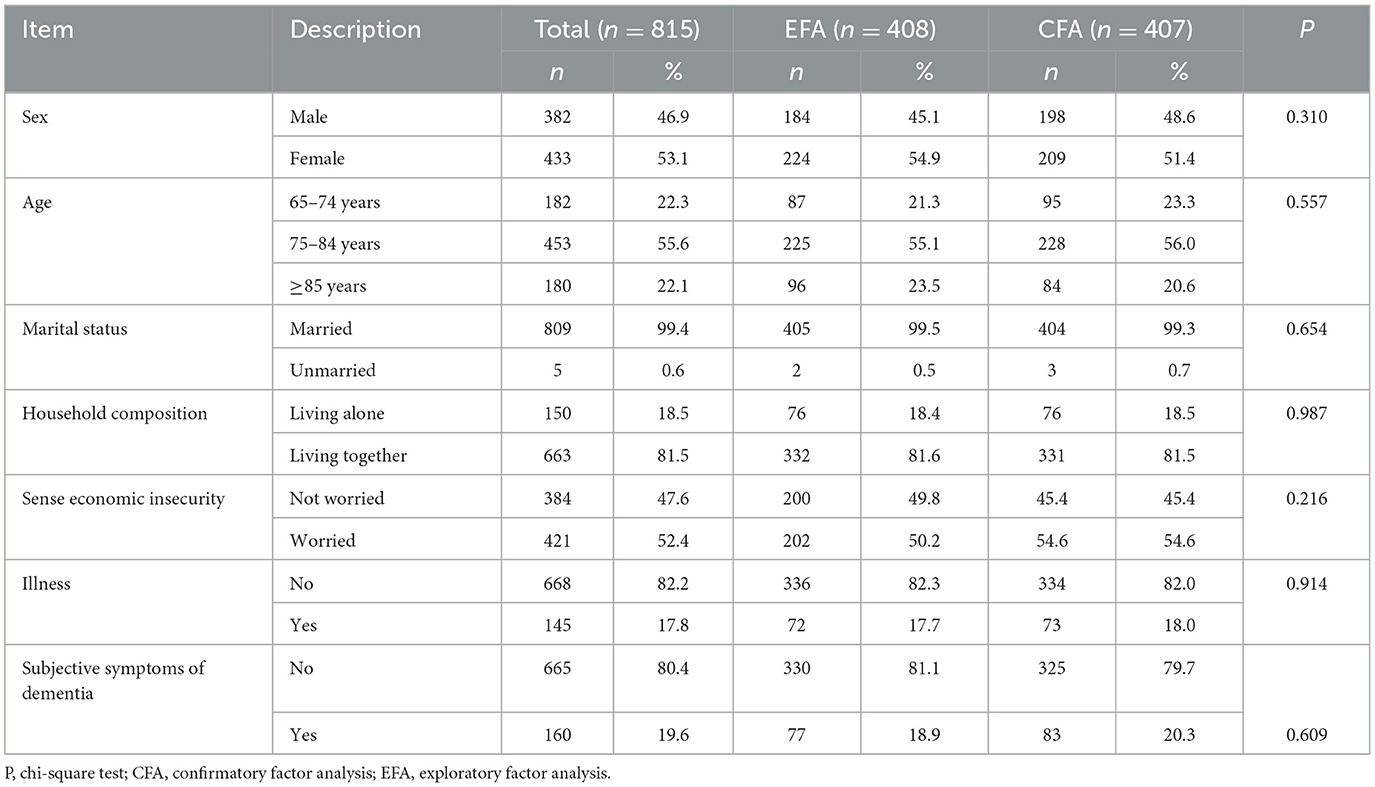
Of the 1,614 questionnaires distributed, responses from 815 individuals were analyzed (valid response rate: 50.5%). Participant characteristics are presented in Table 1. This study included 382 male (46.9%) and 433 female (53.1%) participants. The age group with the highest number of participants was 75–85 years, comprising 453 individuals (55.6%). Of the participants, 150 (18.5%) were living alone, 663 (81.5%) were living together, 668 (82.2%) reported having an illness under treatment, and 160 (19.6%) had subjective symptoms of dementia. No differences were found between the 408 EFA and 407 CFA participants.
4.2 Item analysis
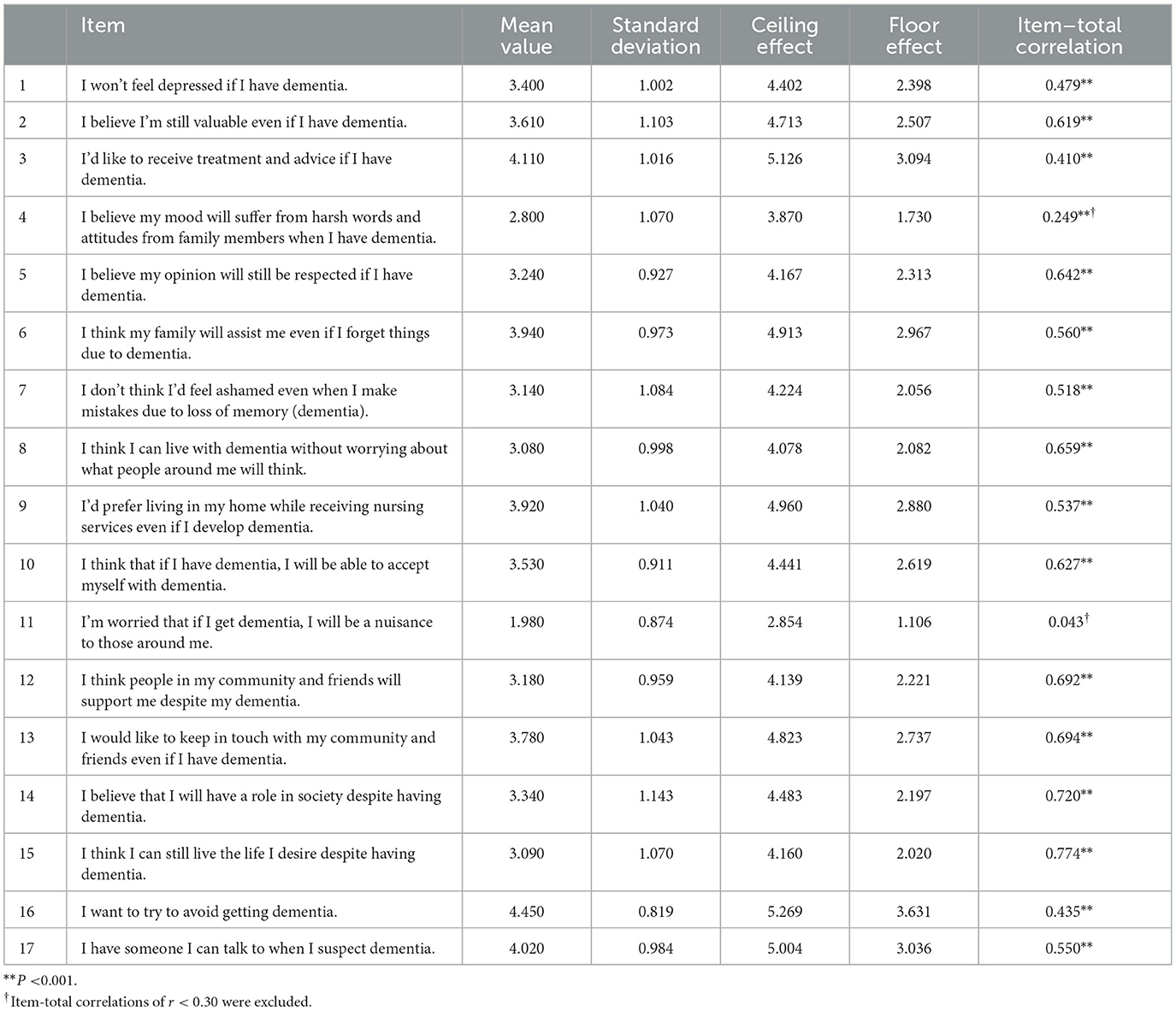
In this study, three out of the 17 total items exhibited ceiling effects (item 3: 4.11 ± 1.016, item 16: 4.450 ± 0.819, item 17: 4.020 ± 0.984). No floor effect items were present. The ceiling effect item was retained after careful consideration of its content by the experts. No item exhibited r > 0.75 in the inter-item correlations, and the I–T correlations with r < 0.30 (item 4: r = 0.249, item 11: r = 0.043) were deleted (Table 2).
4.3 EFA
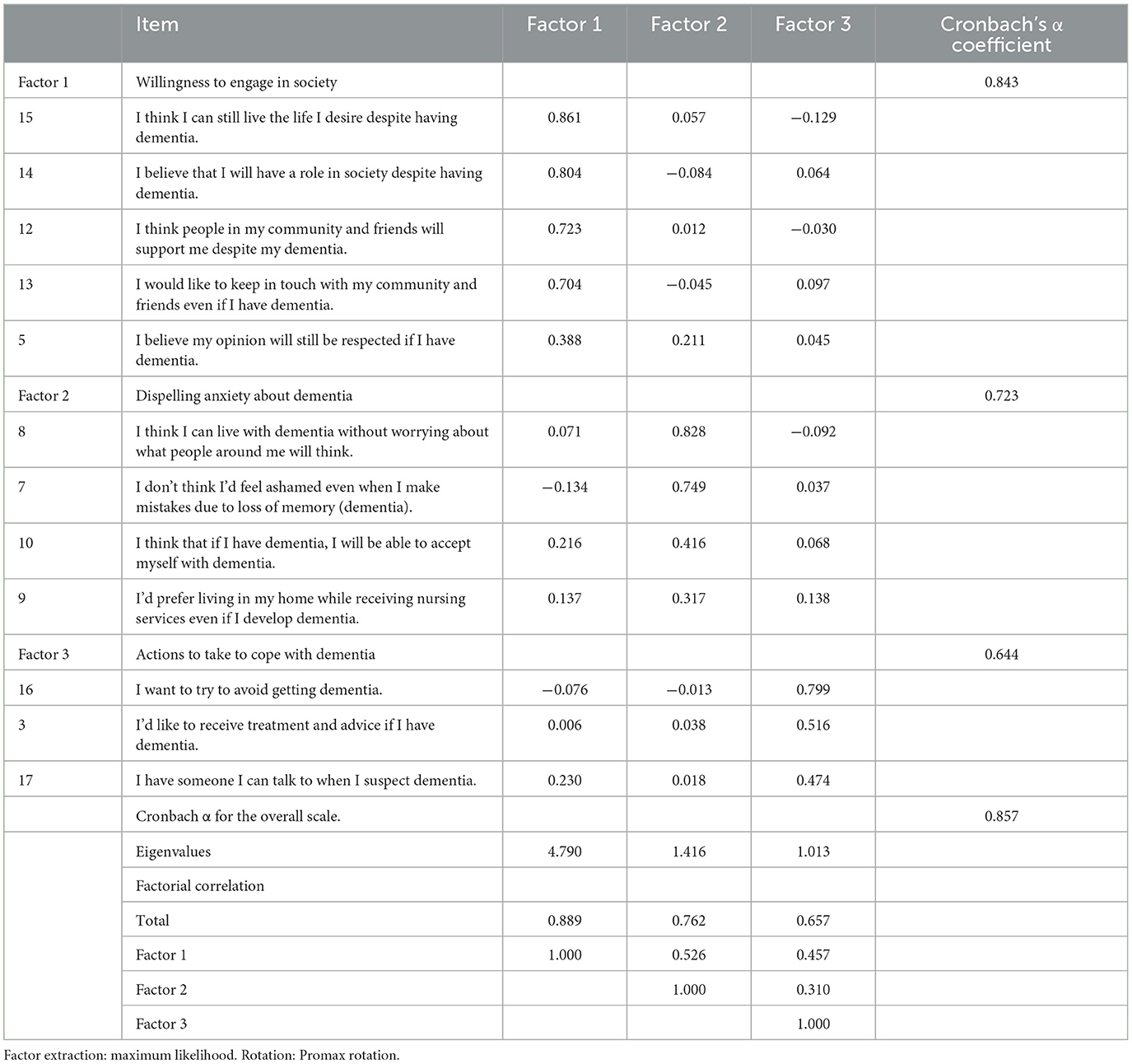
EFA was performed using maximum likelihood and Promax rotation, while the KMO and Bartlett's sphericity tests were conducted prior to EFA to determine the factor analysis' goodness of fit; the KMO value was 0.885, and Bartlett's sphericity test was p < 0.001, while EFA implementation was reasonable. The number of factors was extracted by adopting a three-factor structure that exhibited more than 1 in the eigenvalue analysis of the correlation matrix. Items with commonality < 0.20 or less, and factor loadings < 0.30, were deleted, resulting in a three-factor, 12-item scale (Table 3). The items deleted were item 1, “I won't feel depressed if I have dementia,” item 2, “I believe I'm still valuable even if I have dementia,” and item 6, “I think my family will assist me even if I forget things due to dementia.”
Factor 1 comprised five items denoting “willingness to engage with society,” as it revealed a distinct way of living and interacting with the community after dementia onset. Factor 2 comprised four items and was labeled “dispelling anxiety about dementia,” owing to its emphasis on accepting the disease and avoiding concerns about failure. Factor 3 comprised three items; it was named “actions to take to cope with dementia,” since it indicated efforts to prevent dementia and a willingness to promote health, such as seeking treatment and consultation, when symptoms of dementia were perceived. The Cronbach's alpha coefficients for the scale and individual factors were 0.843 for Factor 1, 0.723 for Factor 2, 0.644 for Factor 3, and 0.857 for the overall scale. The coefficient correlations ranged from ρ = 0.310–0.526, indicating a moderate to weak correlation.
4.4 CFA
CFA was conducted to test the goodness of fit of the three-factor structures obtained in the EFA. The results indicate that the 12 items of the three factors demonstrated a favorable goodness of fit, with χ2 = 146.574, df = 51, p < 0.001, Tucker-Lewis index = 0.909, comparative of fit index = 0.930, goodness of fit index = 0.945, and root mean square error of approximation = 0.068 (Figure 1).
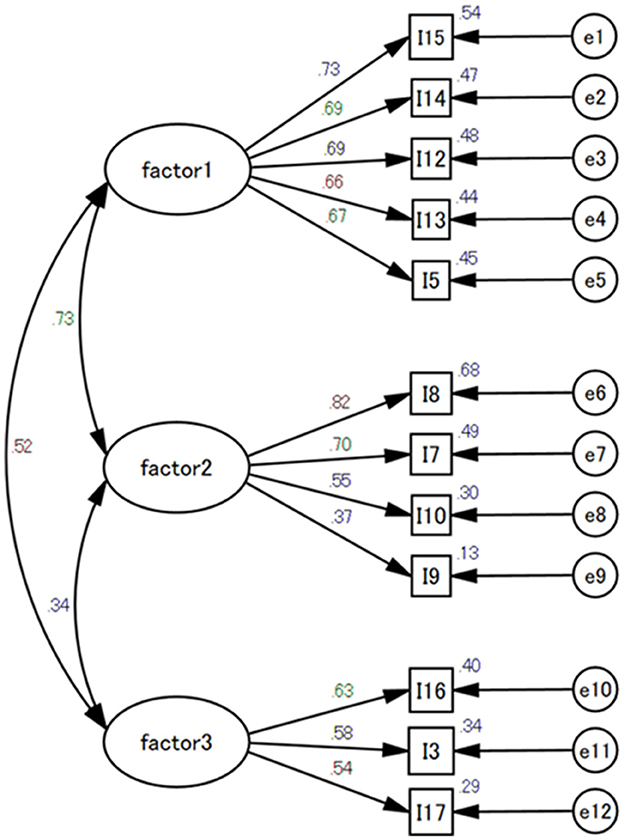
Figure 1. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Dementia Attitude Scale Focusing on well-being. CFI, comparative fit index; GFI, goodness fit index; TLI, Tucker-Lewis index; RMSEA, root mean square error of approximation. X2= 146.574; df= 51; CFI = 0.930; GFI= 0.945; TLI= 0.909; RMSEA = 0.068.
4.5 Convergent and discriminant validity
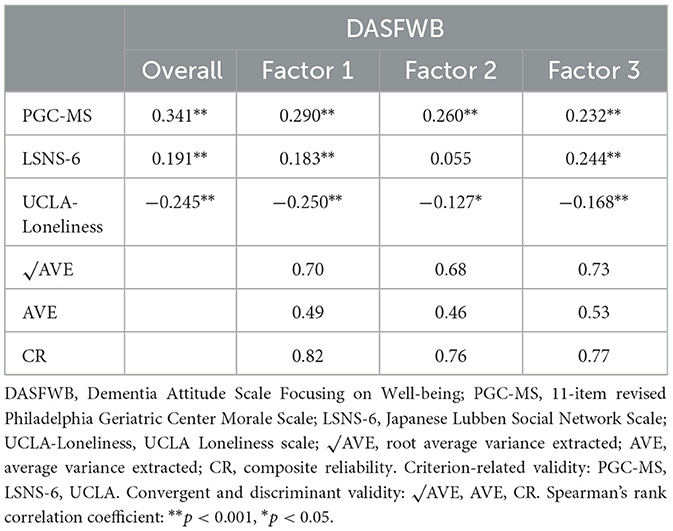
Convergent validity was assessed by analyzing the AVE and CR of the three factors. The AVE values for Factors 1, 2, and 3 were 0.49, 0.46, and 0.53, respectively, while the CR values were 0.82, 0.76, and 0.77, respectively. For Factors 1 and 2, the AVE ranged from 0.36 to 0.5, which was slightly below the criterion of 0.5. However, CR was over 0.7 for all factors (Table 4).
Regarding discriminant validity, the square root of the AVE for all factors was greater than their corresponding correlation coefficients (Table 4).
4.6 Criterion-related validity
To evaluate the criterion-related validity, we calculated the correlation coefficients between the newly created scale and the PGC-MS, LSNS-6, and UCLA-Loneliness (Table 4). The correlation with PGC-MS was weak for the entire scale, ρ = 0.341 (p < 0.001), and for Factors 1–3, ranging from ρ = 0.232 to 0.290 (p < 0.001). For the LSNS-6, the overall score was ρ = 0.191 (p < 0.001), with Factors 1 and 3 having correlation coefficients of ρ = 0.183 (p < 0.001) and ρ = 0.244 (p < 0.001), respectively; Factor 2, however, was uncorrelated, with a coefficient of ρ = 0.055. UCLA-Loneliness had correlation coefficients of ρ = −0.245 (p < 0.001) for the entire scale, ρ = −0.250 (p < 0.001) for Factor 1, ρ = −0.127 (p < 0.05) for Factor 2, and ρ = −0.168 (p < 0.001) for Factor 3.
5 Discussion
5.1 Contents of the scale
The feelings of older adults with dementia used in the draft scale comprised four categories, whereas the DASFWB consisted of three factors and 12 items identified through the EFA. The DASFWB consists of three factors: “willingness to engage in society,” “dispelling anxiety about dementia,” and “actions to take to cope with dementia.” All items assume that a person without dementia has developed it. In addition, the focus on well-being is expected to foster positive attitudes toward dementia and help develop an inclusive society.
Factor 1, “willingness to engage in society,” which comprised one category of the conceptual construct, namely the “desire to live authentically in a familiar community,” and one item, the “emotion of hope and despair toward their family.” This factor represents an aspiration to reside in the community and interact with other community members. The “willingness to engage in society” factor in this scale reflects the view that social interactions play an important role in well-being. A sense of connection and belonging in a society where people's dignity is respected and are encouraged to engage in social networks is essential for their well-being and quality of life (Wiersma and Denton, 2016). However, the stigma associated with dementia can lead to social exclusion, abuse, and discrimination (WHO, 2021b), negatively affecting the well-being of people with dementia. Therefore, maintaining connections with the society is considered an important factor for well-being.
Factor 2, “dispelling anxiety about dementia,” includes an item in the construct category “anxiety about socializing.” This item is related to psychological well-being, such as being able to live one's life without worrying about what others think of one's dementia and being able to accept the illness. Despite the ongoing global efforts aimed at eliminating stigma toward people with dementia, inadequate awareness of dementia continues to subject those with dementia and their caregivers and families to prejudice and discrimination in their communities (WHO, 2021b). The stigma associated with dementia is negatively correlated with quality of life (Lion et al., 2020) and can lead to psychological distress, such as depression and anxiety (Sibley et al., 2021). Such psychological burdens can lead to a decline in well-being; “Dispelling anxiety about dementia” becomes an important factor for the well-being of individuals who hypothetically develop the condition.
Factor 3, “actions to take to cope with dementia,” assesses whether respondents can take actions on their own to prevent dementia and adopt countermeasures when they observe a decline in cognitive function. As everyone is at risk of developing dementia, it is vital to take measures to prevent and manage cognitive decline (Lisko et al., 2021). However, according to the report, ~20% of people with dementia wish to keep their diagnosis a secret (Alzheimer's Disease International, 2019). Shame may serve as an underlying mechanism through which stigma is enacted and perpetuated, resulting in delays in accessing diagnosis and support services (Lopez et al., 2020). The willingness to seek medical advice or consultation without hesitation when suspecting the onset of dementia is an important factor for well-being.
5.2 The reliability and validity of the scale
The reliability and validity of the DASFWB were tested using items, exploratory and confirmatory factors, constructs, and criterion-related analyses. After analyzing the items and conducting EFA, we identified a structure comprising 12 items and three factors from the draft of 17 items. Cronbach's alpha coefficients exceeded 0.7 overall for Factor 1, “willingness to engage in society,” and Factor 2, “dispelling anxiety about dementia.” However, Factor 3, “actions to take to cope with dementia,” yielded a lower alpha coefficient of 0.644, falling short of the established criterion of 0.7. Although an alpha coefficient of 0.60–0.74 is still deemed clinically significant (Cicchetti, 1994), the scale's reliability remained within an acceptable range.
CFA revealed that the model fit met statistical standards. The convergent validity results indicated that all factors had a CR > 0.7. Regarding Factor 1, “willingness to engage in society,” and Factor 2, “dispelling anxiety about dementia,” the AVE values were slightly below 0.5 but above 0.38. The square roots of the above AVE values were greater than the correlation coefficients, demonstrating good discriminant validity (Shrestha, 2021). Therefore, convergent and discriminant validity were considered to be acceptable.
Criterion-related validity demonstrated correlations between the newly developed scale and existing measures from the PGC-MG, LSNS-6, and UCLA-Loneliness. The LSNS-6 correlations indicated that an increased social network was associated with greater dementia-related well-being. Conversely, the UCLA-Loneliness correlations showed that increased loneliness was associated with decreased dementia-related well-being. However, only the subscale “dispelling anxiety about dementia” did not exhibit a correlation with LSNS-6. This may be because network size alone cannot explain psychological factors (Kino et al., 2023), as isolation does not necessarily affect physical or mental health. Based on these results, we consider that criterion-related validity is confirmed.
6 Limitations and future issues
This study examined the reliability and validity of the DASFWB. However, it has several limitations. First, participants were aged 65 years and older. Stigma toward individuals with dementia is a pervasive issue that needs to be addressed regardless of age. Therefore, future research should expand the age range of participants and verify the reliability and validity of the scale. Second, the survey was conducted in a single, highly aged local municipality, limiting the generalizability of the results. Consequently, extending the survey to regions with different lifestyles is necessary to further assess the accuracy of the scale. Third, the survey targeted individuals without dementia. To build an inclusive society, assessing attitudes toward people with and without dementia is essential. To this end, we believe it is necessary to consider a scale that includes the cooperation of people with dementia.
7 Conclusion
The DASFWB was developed based on content validity, surface validity, item analysis, EFA, CFA, and criterion-related validity. The DASFWB comprised 12 items with three factors “willingness to engage in society,” “dispelling anxiety about dementia,” and “actions to take to cope with dementia” and its reliability and validity were verified.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Epidemiology Research at Hiroshima University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
IO: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YI: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. XP: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. HH: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We express our deepest gratitude to the older adults who participated in the study. The authors would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alzheimer's Disease International (2019). World Alzheimer Report 2019: Attitudes to Dementia. Available at: https://www.alzint.org/u/WorldAlzheimer Report 2019.pdf (accessed October 8, 2024).
Anderson, J. C., and Gerbing, D. W. (1984). The effect of sampling error on convergence, improper solutions, and goodness-of-fit indices for maximum likelihood confirmatory factor analysis. Psychometrika 49, 155–173. doi: 10.1007/BF02294170
Arimoto, A., and Tadaka, E. (2019). Reliability and validity of Japanese versions of the UCLA loneliness scale version 3 for use among mothers with infants and toddlers: a cross-sectional study. BMC Womens Health 19:105. doi: 10.1186/s12905-019-0792-4
Bhatt, J., Brohan, E., Blasco, D., Oliveira, D., Bakolis, I., Comas-Herrera, A., et al. (2023). The development and validation of the Discrimination and Stigma Scale Ultra Short for People Living with Dementia (DISCUS-Dementia). BJPsych. Open 9:e164. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2023.551
Boateng, G. O., Neilands, T. B., Frongillo, E. A., Melgar-Quiñonez, H. R., and Young, S. L. (2018). Best practices for developing and validating scales for health, social, and behavioral research: a primer. Front. Public Health 6:149. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2018.00149
Bronner, K., Perneczky, R., McCabe, R., Kurz, A., and Hamann, J. (2016). Which medical and social decision topics are important after early diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease from the perspectives of people with Alzheimer's Disease, spouses and professionals? BMC Res. Notes 9:149. doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-1960-3
Cabinet Office. (2022). Chapter 1. Status of Aging Section 2 (in Japanese). Available at: https://www8.cao.go.jp/kourei/whitepaper/w-2022/html/zenbun/s1_2_2.html (accessed October 16, 2023).
Carneiro, A. V. (2003). Estimating sample size in clinical studies: basic methodological principles. Revista Portuguesa Cardiol. 22, 1513–1521.
Cicchetti, D. V. (1994). Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol. Assess. 6, 284–290. doi: 10.1037/1040-3590.6.4.284
Clare, L., Martyr, A., Morris, R. G., and Tippett, L. J. (2020). Discontinuity in the subjective experience of self among people with mild-to-moderate dementia is associated with poorer psychological health: Findings from the IDEAL cohort. J. Alzheimers Dis. 77, 127–138. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200407
Corrigan, P. W., and Penn, D. L. (2015). Lessons from social psychology on discrediting psychiatric stigma. Stigma Health 1, 2–17. doi: 10.1037/2376-6972.1.S.2
Eriksen, S., Helvik, A. S., Juvet, L. K., Skovdahl, K., Førsund, L. H., and Grov, E. K. (2016). The Experience of relations in persons with dementia: a systematic meta-synthesis. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 42, 342–368. doi: 10.1159/000452404
Evans, I. E. M., Llewellyn, D. J., Matthews, F. E., Woods, R. T., Brayne, C., Clare, L., et al. (2018). Social isolation, cognitive reserve, and cognition in healthy older people. PLoS ONE 13:e0201008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201008
Goffman, E. (1963). Stigma: Notes on the Management of Spoiled Identity. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Herrmann, L. K., Welter, E., Leverenz, J., Lerner, A. J., Udelson, N., Kanetsky, C., et al. (2018). A systematic review of dementia-related stigma research: can we move the stigma dial? Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 26, 316–331. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2017.09.006
Huang, D., Wang, J., Fang, H., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., and Cao, S. (2022). Global research trends in the subjective well-being of older adults from 2002 to 2021: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Psychol. 13:972515. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.972515
Huizenga, J., Scheffelaar, A., Fruijtier, A., Wilken, J. P., Bleijenberg, N., and Van Regenmortel, T. (2022). Everyday experiences of people living with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: a scoping review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:10828. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710828
Japan Federation of Senior Citizens Clubs (n.d.). Available at: http://www.zenrouren.com/about/index.html (accessed July 4, 2023).
Japanese Law Translation (2023). The Basic Act on Dementia to Promote an Inclusive Society (outline). Available at: https://www.japaneselawtranslation.go.jp/outline/92/905R510.pdf (accessed Mach 13, 2024).
JDWG (2018). Japan Dementia Working Group. Available at: http://www.jdwg.org/ (accessed July 4, 2023).
Kawamura, A., Kamide, N., Ando, M., Murakami, T., Shahzad, M. T., and Takahashi, K. (2023). The Combination of hearing impairment and frailty is associated with cognitive decline among community-dwelling elderly in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20:4437. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20054437
Kim, K., and Kuroda, K. (2011). Factors related to attitudes toward people with dementia: development of the attitude toward dementia scale and dementia knowledge scale (in Japanese). Bull. Soc. Med. 28, 43–56.
Kim, S., Eccleston, C., Klekociuk, S., Cook, P. S., and Doherty, K. (2021). Development and psychometric evaluation of the Dementia Public Stigma Scale. Int. J. Geratr. Psychiatry 37:5672. doi: 10.1002/gps.5672
Kino, S., Stickley, A., Arakawa, Y., Saito, M., Saito, T., and Kondo, N. (2023). Social isolation, loneliness, and their correlates in older Japanese adults. Psychogeriatrics 23, 475–486. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12957
Kurimoto, A., Awata, S., Ohkubo, T., Tsubota-Utsugi, M., Asayama, K., Takahashi, K., et al. (2011). Reliability and validity of the Japanese version of the abbreviated Lubben Social Network Scale (in Japanese). Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 48, 149–157. doi: 10.3143/geriatrics.48.149
Liang, J., Bennett, J., Akiyama, H., and Maeda, D. (1992). The structure of PGC Morale Scale in American and Japanese aged: a further note. J. Cross Cult. Gerontol. 7, 45–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00116576
Lion, K. M., Szcześniak, D., Bulińska, K., Evans, S. B., Evans, S. C., Saibene, F. L., et al. (2020). Do people with dementia and mild cognitive impairments experience stigma? A cross-cultural investigation between Italy, Poland and the UK. Aging Ment. Health 24, 947–955. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2019.1577799
Lisko, I., Kulmala, J., Annetorp, M., Ngandu, T., Mangialasche, F., and Kivipelto, M. (2021). How can dementia and disability be prevented in older adults: where are we today and where are we going? J. Int. Med. 289, 807–830. doi: 10.1111/joim.13227
Lopez, O. L., and Kuller, L. H. (2019). Epidemiology of aging and associated cognitive disorders: prevalence and incidence of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 167, 139–148. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-804766-8.00009-1
Lopez, R. P., Rose, K. M., Kenney, L., Sanborn, V., and Davis, J. D. (2020). Managing shame: a grounded theory of how stigma manifests in families living with dementia. J. Am. Psychiatr. Nurs. Assoc. 26, 181–188. doi: 10.1177/1078390319832965
Lubben, J., Blozik, E., Gillmann, G., Iliffe, S., von Renteln Kruse, W., Beck, J. C., et al. (2006). Performance of an abbreviated version of the Lubben Social Network Scale among three European Community-dwelling older adult populations. Gerontologist 46, 503–513. doi: 10.1093/geront/46.4.503
Matsumoto, H., Maeda, A., Igarashi, A., Weller, C., and Yamamoto-Mitani, N. (2023). Dementia education and training for the general public: a scoping review. Gerontol. Geriatr. Educ. 44, 154–184. doi: 10.1080/02701960.2021.1999938
Matsumoto, H., Takaoka, M., Yamamoto-Mitani, N., and Igarashi, A. (2024). Development of Four-Item Attitudes toward People Living with Dementia Scale for population surveys. Psychogeriatrics 24, 1120–1131. doi: 10.1111/psyg.13168
Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare. (2002). 2. The Long-Term Care Insurance System. Available at: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/topics/elderly/care/2.html (accessed August 4, 2023).
Miyamae, F., Ura, C., Sakuma, N., Niikawa, H., Inagaki, H., Ijuin, M., et al. (2016). The development of a self-administered dementia checklist: the examination of concurrent validity and discriminant validity. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 53, 354–362. doi: 10.3143/geriatrics.53.354
Moreno, T. K, Manrique, E, B., Ramírez, G. E, and Sánchez, G, S. (2020). Social isolation undermines quality of life in older adults. Int. Psychogeriatr. 32, 1283–1292. doi: 10.1017/S1041610219000310
Nakanishi, M., and Nakashima, T. (2014). Features of the Japanese national dementia strategy in comparison with international dementia policies: how should a national dementia policy interact with the public health- and social-care systems? Alzheimers Dement. 10, 468–476.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.06.005
Noguchi, T., Shang, E., Nakagawa, T., Komatsu, A., Murata, C., and Saito, T. (2022). Establishment of the Japanese version of the dementia stigma assessment scale. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 22, 790–796. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14453
O'Connor, M. L., and McFadden, S. H. (2010). Development and psychometric validation of the Dementia Attitudes Scale. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010:454218. doi: 10.4061/2010/454218
Ono, I., and Nakatani, H. (2021). Feelings of elderly people living in the community after being diagnosed with mild Alzheimer's disease (in Japanese). J. Jpn Acad. Home Health Care 24, 60–66.
Ozone, S., Goto, R., Kawada, S., and Yokoya, S. (2022). Frailty and social participation in older citizens in Japan during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Gen. Fam. Med. 23, 255–260. doi: 10.1002/jgf2.539
Phinney, A., Becker, M., Burnside, L., Malcolm, P., and Puurveen, G. (2023). Dementia without borders: building community connections to reduce stigma and foster inclusion. Dementia 22, 550–560. doi: 10.1177/14713012231151723
Piver, L. C., Nubukpo, P., Faure, A., Dumoitier, N., Couratier, P., and Clément, J. P. (2013). Describing perceived stigma against Alzheimer's disease in a general population in France: the STIG-MA survey. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 28, 933–938. doi: 10.1002/gps.3903
Polit, D. F., and Beck, C. T. (2006). The content validity index: are you sure you know what's being reported? Critique and recommendations. Res. Nurs. Health. 29, 489–497. doi: 10.1002/nur.20147
Ryan, R. M., and Deci, E. L. (2001). On happiness and human potentials: a review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 52, 141–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.141
Sahoo, M. (2019). “Structural equation modeling: threshold criteria for assessing model fit,” in Methodological Issues in Management Research: Advances, Challenges, and the Way Ahead, eds. R. N. Subudhi, S. Mishra, and M. Sahoo (Bingley: Emerald Publishing Limited), 269–276.
Saito, T., Cable, N., Aida, J., Shirai, K., Saito, M., and Kondo, K. (2019). Validation study on a Japanese version of the three-item UCLA Loneliness Scale among community-dwelling older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 19, 1068–1069. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13758
Shrestha, N. (2021). Factor analysis as a tool for survey analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 9, 4–11. doi: 10.12691/ajams-9-1-2
Sibley, A. A., Shrestha, S., Lipovac-Dew, M., and Kunik, M. E. (2021). Examining depression symptoms with/without coexisting anxiety symptoms in community-dwelling persons with dementia. Am. J. Alzheimers. Dis. Other Demen. 36:1533317521990267. doi: 10.1177/1533317521990267
Taneichi, H., and Rokkaku, R. (2019). A qualitative focus group discussion study on the experiences of Certified Nurses in Dementia Nursing related to effective staff education. Nurs. Open 7, 547–555. doi: 10.1002/nop2.419
Ura, C., Miyamae, F., Sakuma, N., Niikawa, H., Inagaki, H., Ijuin, M., et al. (2015). Development of a self-administered dementia checklist (SDC) (1): examination of factorial validity and internal reliability. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 52, 243–253. doi: 10.3143/geriatrics.52.243
WHO (2021a). Global Status Report on the Public Health Response to Dementia. World Health Organization. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/344707/9789240034624-eng.pdf (accessed September 12, 2023).
WHO (2021b). Towards a Dementia Inclusive Society. World Health Organization. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240031531 (accessed September 10, 2024].
Wiersma, E. C., and Denton, A. (2016). From social network to safety net: Dementia-friendly communities in rural northern Ontario. Dementia 15, 51–68. doi: 10.1177/1471301213516118
Williams, B., Onsman, A., and Brown, T. (2010). Exploratory factor analysis: a five-step guide for novices. Aus. J. Paramed. 8, 1–13. doi: 10.33151/ajp.8.3.93
Xanthopoulou, P., and McCabe, R. (2019). Subjective experiences of cognitive decline and receiving a diagnosis of dementia: qualitative interviews with people recently diagnosed in memory clinics in the UK. BMJ Open 9:e026071. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026071
Yildirim, T., and Kavak Budak, F. (2020). The relationship between internalized stigma and loneliness in patients with schizophrenia. Perspect. Psychiatr. Care 56, 168–174. doi: 10.1111/ppc.12399
Keywords: dementia, attitude, scale development, well-being, Japan
Citation: Ono I, Nakatani H, Inoue Y, Peng X and Hamada H (2024) Development of the dementia attitude scale focusing on well-being. Front. Psychol. 15:1410048. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1410048
Received: 04 April 2024; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 28 November 2024.
Edited by:
Mario Bernardo-Filho, Rio de Janeiro State University, BrazilReviewed by:
José Alexandre Bachur, University of Franca, BrazilTakashi Amano, Rutgers University, Newark, United States
Copyright © 2024 Ono, Nakatani, Inoue, Peng and Hamada. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ichie Ono, b25vLWlAeWFzdWRhLXUuYWMuanA=
 Ichie Ono
Ichie Ono Hisae Nakatani1
Hisae Nakatani1 Yuriko Inoue
Yuriko Inoue Xuxin Peng
Xuxin Peng