- 1Department of Foreign Languages, Xinzhou Normal University, Xinzhou, China
- 2School of International Education, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
Recently, second-language learning success depends upon the students' interest and motivation by adopting innovations that require regulators' and new researchers' emphasis. Hence, this article explores the role of resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' interest on the students' demotivation. The article also examines the mediating role of students' demotivation among resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, lack of students' interest, and failure of the English education system in China. This study has gathered the data using survey questionnaires and analyzed the collected data using smart-PLS. The results exposed that the resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' interest have a significant and positive linkage with students' demotivation. The findings also indicated that students' demotivation significantly mediates among resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, lack of students' interest, and failure of the English education system in China. This study guides the policymakers to develop the policies related to improving the English education system in China using innovation that enhances students' interest and motivation.
JEL Classifications: O31, O32, H75.
Introduction
The rapid technological changes have closed the distances between different cultures of the world. As a result of this globalization, cultural exchange has taken the place. One of the common barriers reported as a result of this cultural exchange is communication. Every country has its own language. There is no common language in the world. The developing countries are in need to learn the developed countries' languages to commutate. With the passage of time, the language rated as common in the world is English. The phenomenon of English medium instruction (EMI) in higher education is now well-established and spreading rapidly over the world. Many academic fields are becoming more universal in their use of English, and much higher education (HE) institutions are implementing “Englishization” of their curricula to achieve internationalization. English has evolved from being taught as a foreign language alongside other disciplinary-focused courses to being an essential educational language used for studying and teaching non-language-related academic subjects as a result of this change in the medium of instruction. Literature proposed that English is narrated as an international language (McKay, 2018; Xu, 2018). The developing countries not having English as their native language pay special attention to English learning in order to get closer to the world. China is one of the fastest growing countries on the globe. Not only the world but China is also attracted to the world in terms of business, education, etc.
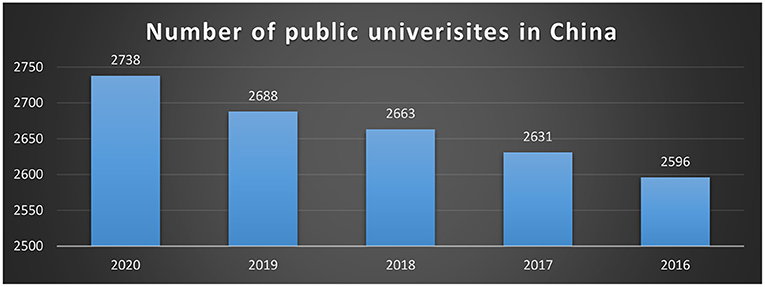
English language education has been a priority in China for the last quarter-century, and competence in English is widely recognized as a national as well as individual benefit. On a national level, the Chinese government sees English language education as playing an important role in national modernization and growth. Although the rationales articulated in a series of policy statements for expanding and strengthening English language teaching (ELT) in the education system have changed over time in response to perceived national development priorities, the importance and benefits of national proficiency in the language have never been questioned (Ma et al., 2021; Wang and Fan, 2021). On the individual level, English proficiency may lead to a plethora of economic, social, and educational prospects, that is, it can offer access to both material and “symbolic capital” for the improvement of one's wellbeing. It can be a passport to further education in the United States or overseas, lucrative work in the public or private sector, professional progress, and social status, for example. Because of the importance of English and the growing demand for English competence, enormous public and private efforts and resources have gone into English language instruction. The number of public universities in China is given in Figure 1.
This study addresses some gaps that exist in the literature like (1) being one of the important topics like English education system and capital and individual performance although researched although but still not reached its peak, (2) Fomenko et al. (2020) investigated the barrier of intercultural communication, whereas the present student has employed number of variables like resistance to innovation, students lack of interest, students demotivation and English language and check the model in Chinese educational institutions, (3) Badrkoohi (2018) investigated the association between demotivation and intercultural communication, whereas this study adds the variable and also checks the mediation effect in Chinese perspective, (4) Saeed et al. (2018) worked on the students interest factors, whereas this study adds the variables like resistance to innovation, students demotivation, students demotivation, and English language and checks the model with new data set; this study checks the model in Chinese perspective with new data set, (5) Kusdemir and Bulut (2018) worked on the student motivations, whereas this study takes the students' demotivation and tests the model in Chinese educational instructions, and (6) a study by (Schröer 2021) also examined the innovation role on the education system and suggested that the upcoming articles should add other factors to predict education system, and this article uses the resistant to innovation and lack of intercultural communication to predict the English education system. The significances of this study are as follows: (1) it highlights the importance of intercultural communication and education system in countries where the native language is not English like Chinese, (2) helps professional to revamp their policies for the betterment of linguistic education like English in China, and (3) helps the researchers to identify the linguistic importance for any country not having English as their mother language.
The study structure is divided into five phases. The first phase presents the introduction. In the second phase of the study, the pieces of evidence regarding resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, lack of student interest, student demotivation, and failure of the English education system are discussed in the light of past literature. The third phase of the study shines the spotlight on the methodology employed for the collection of data regarding resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, lack of student interest, student demotivation, and failure of the English education system and its validity is analyzed. In the fourth phase, the results of the study are compared with the pieces of evidence reviewed from the literature. In the last phase, the study implications along with the conclusion and future recommendations are presented, which concludes the article.
Literature Review
The change is not accepted with a whole heart almost in aspects of society. Either it is business or educational institution, the employees or students usually express resistance to the adoption of the change. Resistance is one of the major causes of failure in innovation, and this resistance demotivated the students who want to make some innovations. In this context, Talwar et al. (2020) and Tang and Chen (2022) checked the relationship between resistance to innovation and student demotivation. In this article, we focused on digital innovation and mentioned that resistance occurs due to poor academic learning of students. Search protocols and research time period was 2002–2020. In this article, it is further added that the rate of failure is too high in 2009 in China. In conclusion, the article addresses the issue of failure such as consumer resistance, and this resistance loses the hope of students. Innovation launching is a process in which an uncertain outcome has been received. This outcome may be positive or negative, people avoid it due to the risk of a negative outcome, and this negative mindset demotivated the students who want to make or want to be part of innovation. In this context, Joachim et al. (2018) checked the relationship between restraining innovation and its effect on student hope. For this article, the method of AIR typology is used in Germany for conducting the result. This article is based on a study in the period of 1981–2018. In conclusion, the article addresses the problem related to innovation and called that resistance to innovation is a big reason for student demotivation. Investment in the education sector is considered a key element in human development. The World Bank has committed has innovation in the educational sector will reduce the poverty and provide political stability, But unfortunately, these innovations are resisted in Pakistan. Khushik and Diemer (2018) checked the relationship between innovation and students' demotivation. When the innovation does not bring in education, then students get demotivated to learn and explore the research. The main resistance is the spending of less amount of GDP in the education sector. Many rules have been made from 1971 to 2018, but nothing improved. In conclusion, the article addressed that, due to no innovation in the education sector, students become hopeless and have no chance other than to learn according to the older education system. Thus, the literature proposed that change in terms of innovation usually faced resistance (Choi et al., 2019; Senbeto et al., 2021). Thus, the following hypothesis is derived from the above debate:
H1: Resistance to innovation has a positive and significant impact on student demotivation in China.
The recent globalization brings the world closer. The people of developing countries are interested to approach developed countries with intentions for higher studies, business, etc. Cultural communication plays a vital role while cultural exchange in terms of education, business, etc. In this cultural exchange, one of the major barriers between developed and developing countries is communication. Literature witnessed that communication is the barrier (Apriyanti, 2018; Grujić and Krneta, 2018; Chien et al., 2021c). The students of developing countries who chose developed countries for education faced communication barriers. The developed nations communicate in their native language. Thus, the student approaches linguistic institutions to overcome it, but due to scarcity of resources like the less skilled coaching staff and lack of modern technology, the students get demotivated. In this context, Donnery (2022) checked the student demotivation factors in the English language and proposed that factors like overcrowded classes and the learning environment cause student demotivation. Thus, the international community requires their language for all sorts of communication, and students get demotivated as a result of different factors. In addition, a study by Badrkoohi (2018) also investigated the association among intercultural communication and student demotivation and revealed that the intercultural communication has a positive and significant impact on student demotivation. Thus, the following hypothesis is derived from the above debate:
H2: Lack of intercultural communication has a positive and significant impact on student demotivation in China.
There are number of factors faced by the students during their study, e.g., the student choice factor strongly affects the student results. Most of the times, the students lack interest in education due to multiple factors like the unskilled coaching staff, institution environment, force studies, etc. (Saeed et al., 2018; Indawati, 2021). Once the student lacks interest, it affects one's motivation. The literature proposed that there is an association between the student's interest and motivation or demotivation (Kusdemir and Bulut, 2018; Dingess II D. R., 2020; Chien et al., 2021a). In this context, (Dingess II D. R. 2020) explored the nexus between students' interest and motivation through a literature review. The study concluded that the student's interest strongly influences the student's motivation or demotivation. A student who studies with full interest results in getting motivation and produces good results otherwise vice versa. Similarly, Renninger et al. (2018) also explored whether there is any relationship between motivation and interest and are of the view that motivation and interest are significantly associated. Thus, the following hypothesis is derived from the above debate:
H3: Lack of student interest has a positive and significant impact on student demotivation in China.
One of the common differences between developed and developing countries is the education system, as well as quality. English is the world language. The developing countries having English not their native language faced a number of international communication barriers, which sometimes ruin their efforts. The education sector of any country is the backbone of the country's development, and the students are the blood of these institutions. Globalization urges the students to pursue higher studies in developed economies in order to learn advanced education tools to compete in the world. One of the common barriers faced by countries having not English as their native language is communication (Fomenko et al., 2020; Gardner, 2020). Thus, the students approach the local linguistic schools. Due to numerous factors, the students get demotivated, which results in poor results. The literature also proposed that demotivation leads to poor performance of students (Ghafournia and Farhadian, 2018; Pincay et al., 2019; Szabo et al., 2020). This poor performance of the students affects the collapse of the entire education system. Thus, there is an association between students' demotivation and the education system of any country. Thus, the following hypothesis is derived from the above debate:
H4: Student demotivation has a positive and significant impact on failure in English education system in China.
A motivated student leads to career success, but in the case of demotivation, it is vice versa. The students get motivated by a number of factors. Literature proposed that the student's motivation affect the students' performance. The students get motivated or demotivated due to a number of factors like educational institution factors, innovation, change factors, etc. One of the common and major factors, which affect the student's motivation, is change. The acceptance of change is one of the difficult factors as per psychological literature (Province, 2018; Chien et al., 2021b; Xu and Ma, 2021). In terms of education, this change can be in different forms like the introduction of technology in the education sector, the new curriculum, etc. The students resist the change, and as a result, they get demotivated. The association between motivation and resistance to innovation is proposed in the literature (Fischer et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2020). The student's demotivation affects the entire education system of the nations in terms of bad results. Thus, demotivation influences the nexus between innovation resistance and education system failure. Therefore, the student's demotivation can be employed as a mediator as supported by the literature (Zhang et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021). Thus, the following hypothesis is derived from the above debate:
H5: Student demotivation significantly mediates between resistance to innovation and failure of the English education system.
The education system of any country is the facilitator of the country's development in multiple terms. A better education system will produce good and skilled individuals who will support their nations to match the international standards. Thus, the failure or success of the country's education system decides the country's progress in the world. The world has become a global village, and cultural exchange is at its peak. In this global village, intercultural communication is acting as a bridge (Shvachkina and Rodionova, 2018; Lobanova et al., 2019). The countries not having English as their native language face hurdles in intercultural communication. In this study, the education system of the country plays a vital role. The countries not having good linguistic institutions results in a week of intercultural communication. The students approach these linguistic institutions and result in getting demotivated. Thus, the student's demotivation gets affected by intercultural communication and affects the country's education system due to weak performance (Badrkoohi, 2018; Kurosh and Kuhi, 2018). In the presence of literature, the student's demotivation can be employed as a mediator as supported by the literature (Zhang et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021). Thus, the following hypothesis is derived from the above debate:
H6: Student demotivation significantly mediates between the lack of intercultural communication and failure of the English education system.
We are living in a digital world. In this study, the countries that failed to meet the world standards are crushed by the rising competition, the only factor that enables the country to respond to the world. The success or failure of the country's education system is based on the student's performance. The student's performance is further based on their motivation as literature proposed that there is an association between students' performance and motivations (Mahler et al., 2018; Bosch et al., 2021). In contrast, the student's performance is based on the student's interest (Crouch et al., 2018; Lawner et al., 2019). Thus, the student's interest affects the education system of the country. Therefore, the student's demotivation affects the education system and is affected by the students' interests. Furthermore, in the presence of literature, the student's demotivation can be employed as a mediator as supported by the literature (Zhang et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021). Thus, the following hypothesis is derived from the above debate:
H7: Student demotivation significantly mediates between lack of student interest and failure of the English education system.
Methodology
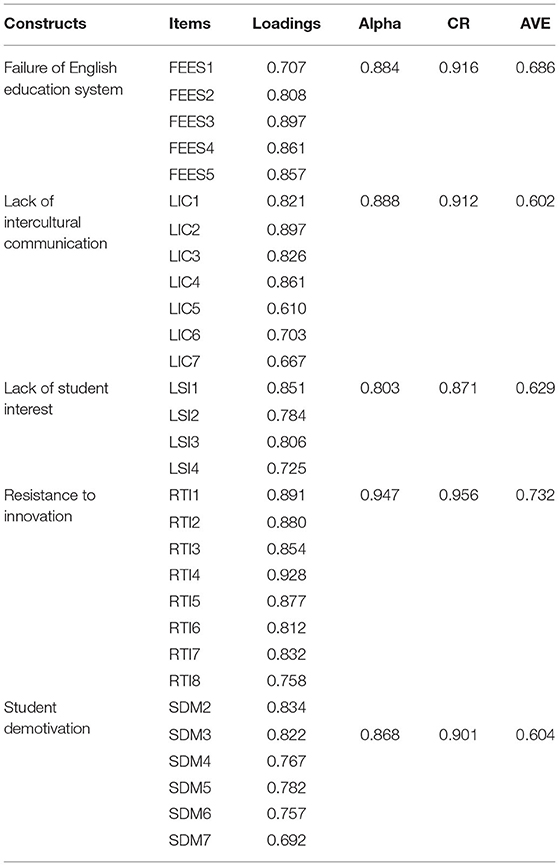
The article explores the role of resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' interest in the students' demotivation and also examines the mediating role of students' demotivation among resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, lack of students' interest, and failure of English education system in China. This study has gathered the data using survey questionnaires. The questionnaire is extracted from past studies; the lack of intercultural communication (LIC) has seven items extracted from Ay et al. (2018), resistance to innovation has eight items taken from Hosseini et al. (2016), lack of student' interest (LSI) has four items extracted from Zhoc et al. (2019), students' demotivation (SDM) has seven items taken from Afthanorhan et al. (2019), and failure of English education system (FEES) has five items taken from (Jääskeläinen et al. 2022). These items with sources are given in Table 1.
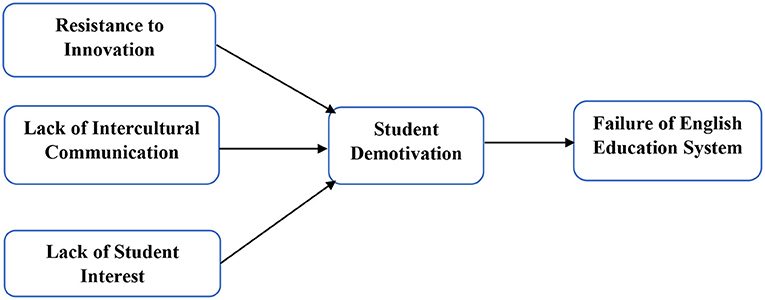
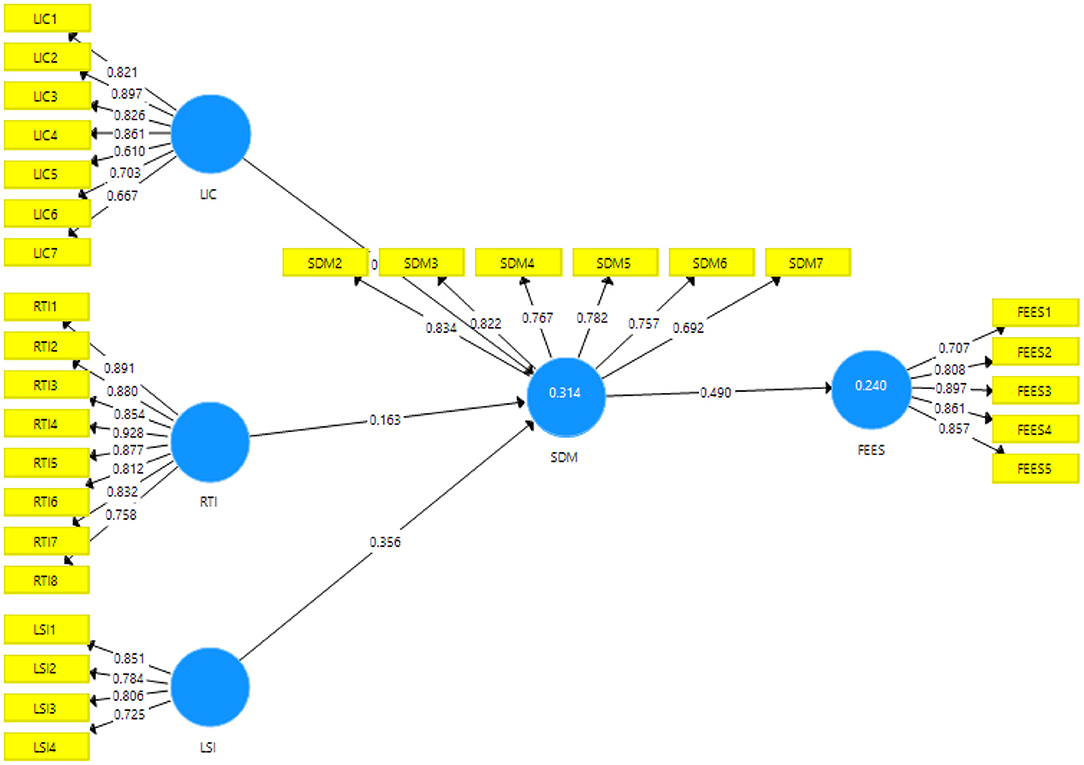
In this article, the resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and lack of students' interest have been used as independent variables, while students' demotivation has been taken as mediating variables, and the failure of the English education system has been used as a predictive variable. The questionnaires have been sent to the respondents using personal visits. The students who are learning English as the second language at educational institutions are the respondents of the study. They are selected based on purposive sampling. The researchers have sent around 623 surveys to the English learning students in the Beijing, China. This study has selected the education sector in Beijing, China, because most of the educational institutions exist there. In addition, researchers have received only 375 surveys after 1 months. These surveys have around 60.19% response rate. In addition, the smart-PLS was used to analyze the primary data. It is an effective statistical tool that effectively estimates the primary data, even in complex frameworks and large sample sizes (Hair Jr et al., 2021). This study has employed the innovation adoption theory that exposed that innovation brings the changes in the process and enhances the efficiency of the business and vice versa. This article also examines the resistance to innovation role on the failure of education system and exposes that if the institution resists to adopt innovation, then it fails to achieve their goals. Based on this theory, the framework has been developed and is illustrated in Figure 2.
Findings of the Study
This article's results have tested the reliability using composite reliability and alpha, and the statistics exposed that reliability is significant because the values are larger than 0.70. In addition, the results have also tested the content validity using factor loadings, and the statistics exposed that content validity is valid because the values are larger than 0.50. Finally, this article's results have also tested the convergent validity using average variance extracted (AVE), and the statistics exposed that convergent validity is valid because the values are larger than 0.50. Table 2 shows the convergent validity of the study.
This article's results have tested the discriminant validity using the Heterotrait Monotrait (HTMT) ratio. The statistics exposed that the discriminant validity is valid because the values are not larger than 0.90. Table 3 shows the results of the HTMT ratio.
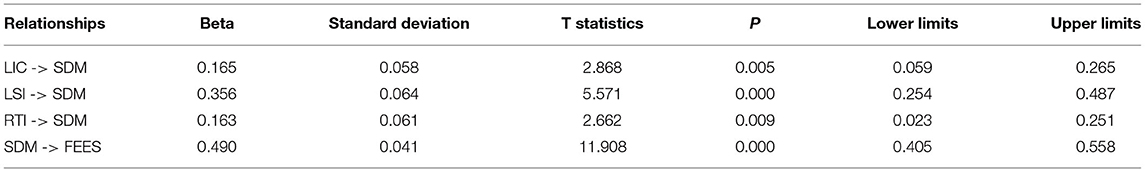
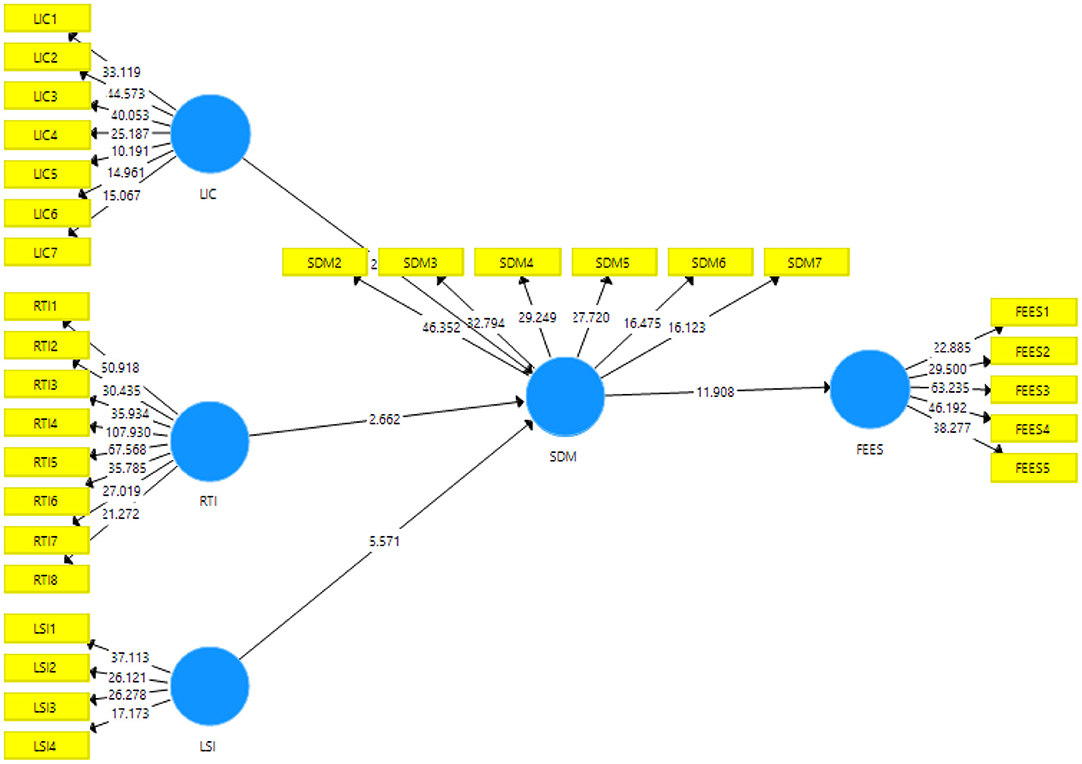
The results of the direct path exposed that the resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' interest have a significant and positive linkage with students' demotivation and accept H1, H2, and H3. Table 4 shows the direct association among variables. Figure 3 shows Measurement model assessment and Figure 4 shows Structural model assessment.
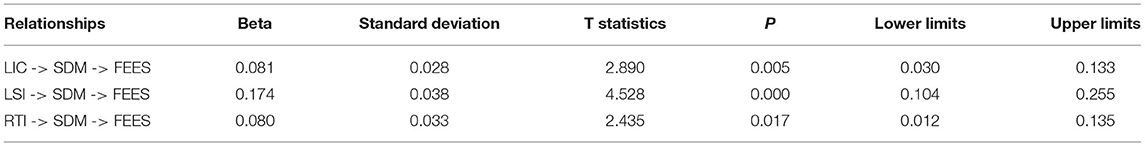
The findings of the indirect path indicated that students' demotivation significantly mediates among resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, lack of students' interest, and failure of the English education system in China and accepts H4, H5, and H6. Table 5 shows the indirect linkage among the variables.
Discussions
The results indicated that resistance to innovation has a positive relation to students' demotivation. These results agree with Moreno-Guerrero et al. (2020), which posits that just like in other fields of life, in education, innovation has great significance. The adoption of innovative sources of learning allows the students to keep in contact with their tutors all the time and make connections with their fellow students or seniors. These connections help them attain knowledge at any time and thus, create learning motivation in students. But, the students are not provided with innovative means of learning. These results are also supported by Chien (2019), which proclaims that the innovative means of learning used in the classrooms or outside help develop essential learning skills like organization, responsibility, independent work, initiative, collaboration, self-regulation, and self-confidence. But, in case the students are unable to benefit from learning innovation, there is a lack of learning skills, and they are demotivated to learn the subject. Hence, resistance to innovation causes student demotivation.
The results showed that lack of intercultural communication has a positive relation to students' demotivation. These results agree with Yunus (2018), which examines the role of lack of intercultural communication in students' demotivation. The study shows that when in a society, people of different cultures live together, and events are conducted where they may have the chance to meet, share their ideas, and develop common values; intercultural communication enhances the students' information and develops an interest in them to learn more about one's own and others' cultures. Moreover, the lack of intercultural communication reduces the student's motivation to learn more. These results are also in line with Chen (2018), which claims that when the students do not experience intercultural communication, they are unable to learn about one another's living styles. This does not allow developing the urge and stamina of the students to try to understand and learn more aspects of the living style of the party in front. So, the lack of intercultural communication leads to students' demotivation. The results revealed that students' lack of interest has a positive relation to students' demotivation and matched with those suggested by Cao and Meng (2020), which shows that it is the interest in the students which motivates them to follow a timeline, accomplishes the tasks assigned to them, focuses on the subject, develops understanding, solves learning problems, and attains comprehensive knowledge. But, when the students do not have enough interest, they are unable to act upon the syllabus and perform efficiently during classes. Thus, English education that is totally based on student interest and motivation is feared to meet with failures.
The results also stated that student demotivation is a mediator between resistance to innovation and failure of the English education system. These results are supported by Guan et al. (2020), which shows that when there is resistance to the adoption of innovation in education, as the lack of the use of different technologies, digital devices, software, and online learning portfolios, it restricts the scope of the knowledge, information, and different learning skills. This makes the student lose their confidence and learning motivation. When the students are a victim of demotivation, they can efficiently perform in the English learning classes, and the English education system becomes a failure. These results also agree with Adolphs et al. (2018), which highlights that when the students have to face resistance to the innovation adoption, they do not have the satisfaction that they can comprehensively understand the subject and reduce the problems in the way of learning. This reduces students' learning motivation. When the students do not take an interest in the learning processes, the English education system can be effectively run. Student demotivation mediates between resistance to innovation and the failure of the English education system.
The results indicated that students' demotivation is a mediator between the lack of intercultural communication and failure of the English education system. These results match with Gong et al. (2018), which shows that when people have no specific or appropriate communication network with people belonging to other cultures, they know a less about the way of living, their accent, behavior, and actions. Because of the lack of effective intercultural communication, they can share their ideas and attain others' knowledge. This reduces the motivation in the students about learning something belonging to another culture. When the students do not have the internal motivation to learn the English language with a particular accent because of the lack of intercultural communication, the number of students who are willing to learn the language decreases and causes failure of the English education system. These results are also in line with Kusumaningputri and Widodo (2018), which reveals that the student who lacks intercultural communication has little source of getting information regarding the second language. This shatters the learning motivation in the students, and the English learning education system cannot succeed whenever the majority of students are demotivated. The results also indicated that students' demotivation is a mediator between the lack of students' interest and failure of the English education system. These results agree with Liu (2020), students' personal interest in the subject they are going to learn affects their decisions regarding the learning resources, learning processes, tutors, hardworking, and discipline. When the students lack the interest to learn, they take ineffective decisions in learning processing and they lose their confidence and motivation, which are essential in language learning. With the presence of students without learning interest and motivation, the English education system fails.
Implications
This study's theoretical significance is because of its contributions to the literature on education. The main focus of the study is on the causes of failure in the English education system. The study examines the influences of resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest in students' demotivation. In the existing literature, one can find research on the impacts of resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest in students' demotivation, but there is no simultaneous study on the nexus between these factors and students' demotivation. So, this study presents distinctive literature. Moreover, this study initiates to explore mediating impacts of student motivation on the association between resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest and failure in the English education system. This study also has great empirical significance in almost all nations as it addresses a universal aspect, the education of English that is considered the mode of communication within and across the countries. This study guides the policymakers to develop the policies related to improving the English education system in China using innovation that enhances student interest and motivation. This study presents some serious causes of the student's demotivation and failure in the English education system, like resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest. This study suggests that to save the English education system from failure, policies must be formulated to reduce the resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, students' lack of interest, and students' demotivation. This study also guides the relevant authorities related to improve the English education system in China. In addition, this study also helps the new researchers in examining this area in future.
Conclusion
This study was conducted to estimate the contribution of resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest in students demotivation. One of its aims was to examine how the students' demotivation establishes a relation between resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest and failure in the English education system. A questionnaire-based empirical survey was conducted on English language schools in China, and data regarding resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, students' lack of interest, students' demotivation, and failure of the English language system. The resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest have a positive association with students' demotivation. The results indicated that the resistance to adopting the innovation in education resources and processes makes it difficult for the students to gain learning skills and get disengaged from the subject. As a result, student demotivation is caused by opposition to innovation. When pupils do not have the opportunity to engage in intercultural conversation, they are unable to get insight into one another's lifestyles. This makes it difficult for students to have the urge to learn. As a result, a lack of intercultural communication demotivates students. The students who lack the learning interest are weak learning skills and demotivation. The study suggests that resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest cause students' demotivation, which further takes the English education system toward failure.
Limitations and Future Directions
The study has many limitations that are expected to be fulfilled in future theoretical research by authors. This study throws light only on the impacts of resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, students' lack of interest in student demotivation, and the failure of the English education system. The institutional support, financial resources, and teachers' abilities have a crucial role in student demotivation and failure in the English education system. Future authors must also focus on these factors for protecting the English education system. In this study, students' demotivation has been addressed as a mediator between resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, and students' lack of interest and failure in the English education system. In the study, demotivation affects both the independent and dependent variables; thus, it must be used as a moderator in future research. This article has taken the mediating variable and ignored the moderating effect in the model and suggested that the future studies should add moderating variable in their studies.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author Contributions
JW contributed in introduction, literature review and methodology. LP contributed to conclusion. Both authors contributed equally to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by Xinzhou Science and Technology Bureau Soft Science Research Project (20210501).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adolphs, S., Clark, L., Dörnyei, Z., Glover, T., Henry, A., Muir, C., et al. (2018). Digital innovations in L2 motivation: harnessing the power of the ideal L2 self. System 78, 173–185. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2018.07.014
Afthanorhan, A., Awang, Z., Rashid, N., Foziah, H., and Ghazali, P. (2019). Assessing the effects of service quality on customer satisfaction. Manag. Sci. Lett. 9, 13–24. doi: 10.5267/j.msl.2018.11.004
Apriyanti, C. (2018). Communication barrier between local sellers and foreign tourists in pacitan. Pacitan 4, 98–102.
Ay, E., Kavuran, E., and Turkoglu, N. (2018). Intercultural Communication Apprehension Scale (PRICA): validity and reliability study in Turkish. Int. J. Caring Sci. 11, 1638–1644.
Badrkoohi, A. (2018). The relationship between demotivation and intercultural communicative competence. Cogent Educ. 5, 153–174. doi: 10.1080/2331186X.2018.1531741
Bosch, E., Seifried, E., and Spinath, B. (2021). What successful students do: evidence-based learning activities matter for students' performance in higher education beyond prior knowledge, motivation, and prior achievement. Learn. Individ. Differ. 91, 102–120. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2021.102056
Cao, C., and Meng, Q. (2020). Exploring personality traits as predictors of English achievement and global competence among Chinese university students: English learning motivation as the moderator. Learn. Individ. Differ. 77, 1018–1034. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2019.101814
Chen, C.-P. (2018). Understanding mobile English-learning gaming adopters in the self-learning market: the uses and gratification expectancy model. Comput. Educ. 126, 217–230. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2018.07.015
Chen, J., Su, Y.-S., de Jong, J. P. J., and von Hippel, E. (2020). Household sector innovation in China: impacts of income and motivation. Res. Policy 49, 103–125. doi: 10.1016/j.respol.2020.103931
Chien, C.-W. (2019). Pre-service teachers' innovation on English activity designs and materials for young learners. Teach. Educator 54, 4–21. doi: 10.1080/08878730.2018.1483456
Chien, F., Kamran, H. W., Nawaz, M. A., Thach, N. N., Long, P. D., and Baloch, Z. A. (2021b). Assessing the prioritization of barriers toward green innovation: small and medium enterprises Nexus. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 24, 1897–1927. doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01513-x
Chien, F., Pantamee, A. A., Hussain, M. S., Chupradit, S., Nawaz, M. A., and Mohsin, M. (2021a). Nexus between financial innovation and bankruptcy: evidence from information, communication and technology (ict) sector. Singapore Econ. Rev. 1–22. doi: 10.1142/S0217590821500181
Chien, F., Sadiq, M., Nawaz, M. A., Hussain, M. S., Tran, T. D., and Le Thanh, T. (2021c). A step toward reducing air pollution in top Asian economies: the role of green energy, eco-innovation, and environmental taxes. J. Environ. Manage. 297:113420. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113420
Choi, S. Y., Chung, G. H., and Choi, J. N. (2019). Why are we having this innovation? Employee attributions of innovation and implementation behavior. Soc. Behav. Pers. Int. J. 47, 1–13. doi: 10.2224/sbp.8124
Crouch, C. H., Wisittanawat, P., Cai, M., and Renninger, K. A. (2018). Life science students' attitudes, interest, and performance in introductory physics for life sciences: an exploratory study. Phys. Rev. Phys. Educ. Res. 14, 10–31. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevPhysEducRes.14.010111
Dingess II, D. R. (2020). Literature review: student interest and motivation in recorder studies. Corinthian 20, 1–23.
Donnery, E. (2022). “From demotivation to Intercultural Communicative Competence (ICC): Japanese university learner journeys in the International Virtual ExchangeProject (IVEProject),” in Second Language Teaching and Learning through Virtual Exchange (De Gruyter Mouton), 35–48. doi: 10.1515/9783110727364-003
Fischer, C., Malycha, C. P., and Schafmann, E. (2019). The influence of intrinsic motivation and synergistic extrinsic motivators on creativity and innovation. Front. Psychol. 10, 29–48. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00137
Fomenko, T., Bilotserkovets, M., Klochkova, T., Statsenko, O., Sbruieva, A., Kozlova, O., et al. (2020). Overcoming barriers in intercultural communication: a case study on agricultural idioms in English, Ukrainian and Chinese. Acad. J. Interdiscipl. Stud. 9, 157–170. doi: 10.36941/ajis-2020-0120
Gardner, D. (2020). Teaching English oral communication for China's English minor undergraduates: barriers, challenges and options. Asian J. Appl. Linguist. 7, 73–90.
Ghafournia, N., and Farhadian, Z. (2018). The relationship among demotivating factors, gender, educational fields, and reading proficiency: a study of Iranian EFL Learners. [ ]. IJREE 3, 36–49. doi: 10.29252/ijree.3.4.36
]. IJREE 3, 36–49. doi: 10.29252/ijree.3.4.36
Gong, Y., Hu, X., and Lai, C. (2018). Chinese as a second language teachers' cognition in teaching intercultural communicative competence. System 78, 224–233. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2018.09.009
Grujić, T., and Krneta, L. (2018). English Language as Education Barrier in Using Information Technology. eLearning Softw. Educ. 2, 463–470. doi: 10.12753/2066-026X-18-136
Guan, C., Mou, J., and Jiang, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence innovation in education: a twenty-year data-driven historical analysis. Int. J. Innov. Stud. 4, 134–147. doi: 10.1016/j.ijis.2020.09.001
Hair Jr, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., Danks, N. P., and Ray, S. (2021). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: a workbook: springer Nature. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-80519-7
Hosseini, M. H., Delaviz, M., Derakhshide, H., and Delaviz, M. (2016). Factors affecting consumer resistance to innovation in mobile phone industry. Int. J. Asian Soc. Sci. 6, 497–509. doi: 10.18488/journal.1/2016.6.9/1.9.497.509
Indawati, I. (2021). The Internal Factors That Cause of the Lack Students Interest on English Subject in MTS Nasyrul Ulum (A Case Study: Nine Students of MTS Nasyrul Ulum). Institut agama islam negeri madura. 70.
Jääskeläinen, T., López-Íñiguez, G., and Lehikoinen, K. (2022). Experienced workload, stress, and coping among professional students in higher music education: an explanatory mixed methods study in Finland and the United Kingdom. Psychol. Music 1–24. doi: 10.1177/03057356211070325
Joachim, V., Spieth, P., and Heidenreich, S. (2018). Active innovation resistance: an empirical study on functional and psychological barriers to innovation adoption in different contexts. Ind. Mark. Manag. 71, 95–107. doi: 10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.12.011
Khushik, F., and Diemer, A. (2018). Critical analysis of education policies in Pakistan: a sustainable development perspective. Soc. Sci. Learn. Educ. J. 3, 01–16. doi: 10.15520/sslej.v3i09.2282
Kurosh, S., and Kuhi, D. (2018). The role of intercultural communication competence in Iranian EFL Learners' Demotivation: an examination of the predicting causes. Theor. Pract. Lang. Stud. 8, 1230–1235. doi: 10.17507/tpls.0809.18
Kusdemir, Y., and Bulut, P. (2018). The relationship between elementary school students' reading comprehension and reading motivation. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 6, 97–110. doi: 10.11114/jets.v6i12.3595
Kusumaningputri, R., and Widodo, H. P. (2018). Promoting Indonesian university students' critical intercultural awareness in tertiary EAL classrooms: the use of digital photograph-mediated intercultural tasks. System 72, 49–61. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2017.10.003
Lawner, E. K., Quinn, D. M., Camacho, G., Johnson, B. T., and Pan-Weisz, B. (2019). Ingroup role models and underrepresented students' performance and interest in STEM: a meta-analysis of lab and field studies. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 22, 1169–1195. doi: 10.1007/s11218-019-09518-1
Liu, I.-F. (2020). The impact of extrinsic motivation, intrinsic motivation, and social self-efficacy on English competition participation intentions of pre-college learners: differences between high school and vocational students in Taiwan. Learn. Motiv. 72, 1016–1029. doi: 10.1016/j.lmot.2020.101675
Lobanova, E. I., Zenina, L. V., Iksanova, M. G., Medvedeva, I. V., and Kalabekova, L. U. (2019). The human factor in intercultural communications: solution methods and technologies. Amazonia Investiga 8, 328–336.
Ma, L., Xiao, L., and Liu, J. (2021). Motivational beliefs of urban and rural students in English as a foreign language learning: the case of China. J. Multilingual Multicult. Dev. 7, 1–14. doi: 10.1080/01434632.2021.1991933
Mahler, D., Grossschedl, J., and Harms, U. (2018). Does motivation matter?–The relationship between teachers' self-efficacy and enthusiasm and students' performance. PLoS ONE 13, 207–230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207252
McKay, S. L. (2018). English As an international language: what it is and what it means for pedagogy. RELC J. 49, 9–23. doi: 10.1177/0033688217738817
Moreno-Guerrero, A.-J., Romero-Rodriguez, J.-M., Lopez-Belmonte, J., and Alonso-Garcia, S. (2020). Flipped learning approach as educational innovation in water literacy. Water 12, 574–589. doi: 10.3390/w12020574
Pincay, H. J. J. V., Pincay, M. d. R. V, Pincay, M. L. V., and Perez, A. V. (2019). Demotivation and academic performance on first year in university. Int. Res. J. Manag. IT Soc. Sci. 6, 19–26. doi: 10.21744/irjmis.v6n1.433
Province, Y. (2018). The Influence of Campus Environment on College Students' Innovation and Entrepreneurship Thinking from the Perspective of Psychology. Francis Academic Press, UK 4, 286–289.
Renninger, K. A., Ren, Y., and Kern, H. M. (2018). Motivation, engagement, and interest:“In the end, it came down to you and how you think of the problem” International handbook of the learning sciences (Vol. 2, pp. 116-126): Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781315617572-12
Saeed, I., Khan, N. F., Bari, A., and Khan, R. A. (2018). Factors contributing to the lack of interest in research activities among postgraduate medical students. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 34, 913–917. doi: 10.12669/pjms.344.15411
Schröer, A. (2021). Social innovation in education and social service organizations. Challenges, actors, and approaches to foster social innovation. Front. Educ. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2020.555624
Senbeto, D. L., Hon, A. H. Y., and Law, R. (2021). Organizational cultures determine employee innovation in response to seasonality: regulatory processes of openness and resistance. J. Hospitality Tourism Res. 6, 69–85. doi: 10.1177/10963480211011629
Shvachkina, L. A., and Rodionova, V. I. (2018). Intercultural communications as a tool of formation of the global axiological system in the conditions of establishment of the entrepreneurial type of thinking of the Russian society. J. Hist. Cult. Art Res. 7, 452–459. doi: 10.7596/taksad.v7i3.1750
Sun, Y., Zhang, Y., and Shen, X.-L. (2021). Will extrinsic motivation motivate or demotivate knowledge contributors? A moderated mediation analysis. J. Knowledge Manag. 3, 1–29.
Szabo, S., Mihalčová, B., Lukáč, J., Gallo, P., Cabinová, V., and Vajdová, I. (2020). Demotivation of medical staff in the selected health facility in Slovakia. Ekon. Manag. 7, 245–269. doi: 10.15240/tul/001/2020-2-006
Talwar, S., Talwar, M., Kaur, P., and Dhir, A. (2020). Consumers' resistance to digital innovations: a systematic review and framework development. Australas. Mark. J. 28, 286–299. doi: 10.1016/j.ausmj.2020.06.014
Tang, Z., and Chen, L. (2022). Understanding seller resistance to digital device recycling platform: an innovation resistance perspective. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 51, 101–114. doi: 10.1016/j.elerap.2021.101114
Wang, L., and Fan, J., (2021). Core Issues in Business English Education in China. In L. Wang and J. Fan (Eds.), Working Towards a Proficiency Scale of Business English Writing: A Mixed-Methods Approach (Vol. 3, pp. 1-8). Singapore: Springer Singapore. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-5449-7_1
Xu, X., and Ma, M. (2021). The innovation of enterprise human resource management mode from the perspective of behavioral psychology. Psychiatr. Danub. 33, 168–172.
Xu, Z. (2018). Exploring english as an international language – Curriculum, materials and pedagogical strategies. RELC J. 49, 102–118. doi: 10.1177/0033688217753848
Yunus, M. M. (2018). Innovation in education and language learning in 21st century. J. Sustain. Dev. Educ. Res. 2, 33–34. doi: 10.17509/jsder.v2i1.12355
Zhang, X., Dai, S., and Ardasheva, Y. (2020). Contributions of (de)motivation, engagement, and anxiety to English listening and speaking. Learn. Individ. Differ. 79, 101–125. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2020.101856
Keywords: resistance to innovation, lack of intercultural communication, students' interest, students' demotivation, English education system
Citation: Wang J and Pan L (2022) Role of Resistance to Innovation, Lack of Intercultural Communication, and Student Interest on the Student Demotivation Results Towards the English Education System. Front. Psychol. 13:922402. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.922402
Received: 17 April 2022; Accepted: 19 May 2022;
Published: 01 July 2022.
Edited by:
Shahid Nawaz, Islamia University of Bahawalpur, PakistanReviewed by:
Mivumbi Michel, The Open University of Tanzania, TanzaniaHamid Mahmood, Foundation University, Islamabad, Pakistan
Copyright © 2022 Wang and Pan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Pan, ZGlya3N0aW5nQDE2My5jb20uY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jin Wang
Jin Wang Lei Pan
Lei Pan