- 1Xinjiang Clinical Medical Research Center of Mental Health, The Psychological Medicine Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, Xinjiang, China
- 2Department of Trauma Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, Xinjiang, China
- 3Child Mental Health Research Center, Nanjing Brain Hospital, Clinical Teaching Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
- 4The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Zhejiang, China
- 5Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Metabolic Disease, Clinical Medical Research Institute, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, China
Behavioral addictive disorders (BADs) have become a significant societal challenge over time. The central feature of BADs is the loss of control over engaging in and continuing behaviors, even when facing negative consequences. The neurobiological underpinnings of BADs primarily involve impairments in the reward circuitry, encompassing the ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens in the ventral striatum, and prefrontal cortex. These brain regions form networks that communicate through neurotransmitter signaling, leading to neurobiological changes in individuals with behavioral addictions. While dopamine has long been associated with the reward process, recent research highlights the role of other key neurotransmitters like serotonin, glutamate, and endorphins in BADs’ development. These neurotransmitters interact within the reward circuitry, creating potential targets for therapeutic intervention. This improved understanding of neurotransmitter systems provides a foundation for developing targeted treatments and helps clinicians select personalized therapeutic approaches.
1 Introduction
With social progress and technological development, significant shifts have occurred in people’s lifestyles and behavior patterns. Concurrently, the prevalence of behavioral addictive disorders (BADs) is increasing, presenting with a wide range of manifestations. This trend is particularly noticeable among younger demographics, where studies indicate that approximately 1.25% to 5% of minors meet the criteria for Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) (1). In the 11th Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11) (2) issued by the World Health Organization (WHO), gambling disorder (GD) and IGD have been classified as disorders caused by addictive behaviors, sparking widespread research interest. Research indicates that other non-substance addictive behaviors, such as compulsive sexual behavior disorder (CSBD) (3), buying-shopping disorder (4) and internet-use disorders (5), show similar clinical presentations and neurobiological mechanisms to gambling and gaming addictions. The defining feature of BADs is the repetitive engagement in rewarding behaviors, accompanied by weakened control despite negative consequences. Moreover, BADs may share clinical, genetic, neurobiological, and phenomenological similarities with substance addictions. Recent meta-analyses have revealed that (6) both conditions exhibit disrupted resting-state functional connectivity between the frontal network and other high-level cognitive networks (including default mode, affective, and salience networks). Therefore, studying the neurobiological basis of BADs and exploring their mechanisms and treatment approaches has significant theoretical and practical implications similar to substance addictions.
BADs and substance addictions share a common core feature: the loss of behavioral control (7). This significant overlap in their manifestations implies a shared neurobiological basis involving the disruption of the “reward system,” also known as the reward circuit. In contrast to previous perspectives, it is now acknowledged (8) that individuals suffering from addiction are not addicted to a specific substance or activity but rather to the corresponding brain responses elicited. The reward circuit encompasses an intricate network of neurons governing human reward and punishment responses through interconnected pathways. It encompasses multiple brain regions, including the ventral tegmental area (VTA), nucleus accumbens (NAc)in the ventral striatum (VS), basal ganglia, prefrontal cortex (PFC), amygdala (AMY), and hippocampus. Among these regions, the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in the midbrain serves as the ultimate common pathway for reinforcement and reward triggered by physiological stimulation or addictive behaviors (9). In the development and maintenance of BADs, specific brain regions establish connectivity via neurotransmitter-mediated signaling, resulting in intricate individualized neurobiological changes.
In the past few decades, dopamine (DA) has held a prominent position as the central factor in BADs, playing a pivotal role within the reward circuit. Nevertheless, recent studies have underscored the significance of other neurotransmitters and their intricate interplay within the reward circuit, including serotonin (i.e., 5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), endorphins, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate (Glu), and norepinephrine (NE) (10, 11). The coordinated interactions among these neurotransmitters, particularly the DA-glutamate-GABA circuit in the NAc and the serotonin-DA interactions in the VTA, form the neurochemical basis of the reward circuit (12, 13). Furthermore, the interactions between neurotransmitters can also affect the activity of the reward circuit and the development and maintenance of BADs through mechanisms such as synaptic plasticity, neuronal excitability, membrane potential, and receptor binding (12, 13). Recent neuroimaging and molecular studies (6, 14, 15) have revealed specific neural pathways in BADs’ reward circuit, establishing direct links between psychological symptoms and their neurobiological underpinnings.
This review explores the roles of neurotransmitters such as DA, serotonin, endorphins, GABA, Glu, and NE in the reward circuit, focusing on elucidating the intricate interactions between these neurotransmitters. Additionally, this study will analyze the impact of neurotransmitter interactions on reward circuitry activity and BADs, providing insights and references for the neurobiological research of BADs and theoretical support for developing novel treatment strategies targeting specific neurotransmitter interactions.
2 Neurotransmitter interactions in BADs
2.1 Dopamine
The neurobiological mechanisms associated with the reward circuit in BADs remain partially understood. DA has been identified as a pivotal factor in reward processing, motivation control, and behavioral activation in BADs (16). The dopaminergic system (17, 18) includes the mesolimbic system (from the VTA to the NAc, AMY, and hippocampus), the mesocortical system (from the VTA to the PFC), the nigrostriatal system (from the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) to the striatum), and the tuberoinfundibular system, with the mesolimbic system playing a major role in the reward circuit. The VTA, where dopaminergic neurons are located, informs the organism whether environmental stimuli (such as natural rewards, substance abuse, online gaming, stress, etc.) are aversive or beneficial. Nerve propagation takes place from the VTA which leads to DA release in the NAc, and this dopaminergic signaling contributes to feelings of pleasure and contentment. These sentiments enhance motivation to pursue rewards. Current literature indicates (19–22) that individuals with gambling addiction may display inaccurate reward predictions or heightened uncertainty concerning rewards, leading to phasic, peak DA signals within the NAc. Moreover, prolonged and excessive engagement with the internet and video games can swiftly elevate DA release in the NAc. The PFC, encompassing the dorsolateral PFC and orbitofrontal cortex, is another critical brain region linked to BADs. Following DA release in the NAc by VTA neurons, the PFC contributes to decision-making and emotional regulation. For instance, it may construe addictive behaviors as manifestations of pleasure (reward) (20). Simultaneously, exposure to visually stimulating reward cues or pleasurable experiences during gaming triggers an upsurge in DA release within the VS (23–25). In summary, with prolonged exposure to specific activities or stimuli, brain regions integral to the reward circuit interpret signals and provide responses. The pathological surge in DA signaling within regions like the PFC and VS areas constitutes one of the underlying mechanisms of BADs (26).
Elevated DA transmission is crucial in the pathology of BADs. Research findings (27–29) are converging despite lacking cellular-level consensus. In pathological gambling (30–34), the intensity of gambling symptoms shows a positive correlation with heightened DA release within the VS and dorsal striatum (DS). Linnet et al. (35) identified a direct correlation between DA release and subjective excitement. In GD (36), D1 receptor activation in the direct striatal pathway and D2 receptor inhibition in the indirect pathway increase NAc dopamine, affecting decision-making. Moreover, the binding of DA to inhibitory receptors D2 and D3 in the NAc or PFC is closely associated with the impulsive characteristics of GD (37, 38). In addition to binding with receptors in the NAc, DA has been found to increase the severity and impulsivity of GD when it binds with D3 receptors in the SNc (34, 39). Experiments in animal models have also revealed a relationship between D4 receptors and impulse control and gambling behavior (40–42). Furthermore, a study showed (43) that the dopamine transporter (DAT) plays a role in gambling addiction, as the impulsivity of elderly individuals with GD is positively correlated with DAT activity. The clinical manifestations of GD are complex and diverse. It is not only associated with increased synthesis and release capacity of DA in the reward circuitry but also closely linked to the abundance of presynaptic DAT and the availability of postsynaptic receptors. Studies (44–48) of IGD show similar patterns, with increased DA secretion relating to impulsivity and reward dependence. Additionally, both the density and availability of DA receptors in the striatum are decreased in IGD patients compared to healthy controls. It has also been found that longer durations of internet gaming addiction can lead to a more severe imbalance of D2 receptors. Furthermore, the severity of internet gaming addiction and depressive mood negatively correlate with DAT levels (49, 50). In summary, the prolonged use of internet gaming can dysregulate the DA system, exacerbating the severity of IGD and increasing susceptibility to impulsive behaviors.
In contrast, reduced release of DA induces cravings for DA, increasing their vulnerability to engage in impulsive and compulsive behaviors. Resulting in imbalanced decision-making, triggering subsequent releases of additional DA. For example, a study using positron emission tomography (PET) with the tracer [11C] raclopride (51) found that in healthy control subjects, there was a positive correlation between DA release in the VS and performance on the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) while individuals with GD exhibited an inverse correlation. This suggests that diminished DA release contribute to the imbalanced decision-making observed in GD individuals within rewarding scenarios. Other studies (52, 53) have supported this notion by demonstrating that reduced DA synthesis and release are associated not only with imbalanced decision-making but also with heightened craving and dependence in patients. The intensified craving seen in individuals with BADs is not only linked to reduced DA release but also to a decrease in the density of D2 receptors (54). Reduced binding of D2 and D3 receptors within the VS can lead to heightened craving in gambling addiction patients, accompanied by the emergence of negative emotions such as anxiety and depression. The availability of DA receptors is inversely correlated with emotional impulsivity (“urgency”) in the striatum (30, 37, 55). Moreover, prolonged internet use or video gaming (20, 45) can lead to a decline in DA receptor sensitivity and frontal lobe dysfunction, resulting in cravings for games and triggering negative emotions in individuals with internet gaming addictions. Studies of CSBD neurobiology, including dopaminergic pathways, represent an emerging field, requiring further investigation to establish specific mechanisms (56). Although some studies indicate no significant differences in DA release within the reward circuitry (34, 37, 38) and the availability of D2 and D3 receptors (32, 33) when compared to healthy individuals, the pivotal role of the DA system in BADs remains indisputable based on the existing literature.
In summary, BADs emergence involves DA synthesis, release, receptor availability, DAT, and enzymatic function. DA system disruption and heightened reward circuit activity underlie control loss and impulsivity in BADs. The DA system serves as both the neurobiological foundation of BADs and a significant target for their treatment. This establishes a theoretical framework for the utilization of pharmacological interventions in BADs from a neurobiological standpoint in clinical settings. Specifically, D2 receptors play a role in the interaction with DA release within the reward circuitry of BADs. Several studies have indicated that the use of dopaminergic drugs (such as levodopa) in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and restless leg syndrome may increase the likelihood of developing gambling problems or other potential impulsive or compulsive behaviors, such as shopping, sex, binge eating, etc. (57–61). Symptom severity in BADs patients also tends to decrease when dopaminergic medications are reduced. Furthermore, the heightened risk of BADs associated with levodopa is not solely attributed to its binding with D2 receptors but also to its inhibition of GABA release, a critical element (62). Some conflicting evidence exists regarding the effects of dopamine D2 receptor antagonists (such as haloperidol, olanzapine, etc.). While one study found (63) that haloperidol reduced the inclination of individuals with GD to place more aggressive bets after receiving a reward in a slot machine task, another study reported (64) that haloperidol heightened the rewarding effects and gambling desires reported by individuals with GD. Additionally, olanzapine has not demonstrated positive effects in the treatment of GD (65–67). These findings highlight the intricate connection between dopamine D2 receptor function and gambling-related motivations and behaviors. Another subset of DA receptors, the D3 receptors (68), are highly concentrated in regions like the NAc, olfactory bulb, and hypothalamus (HYP) and are involved in functions such as reward processing, craving, and aversive emotions. DA agonists like pramipexole and ropinirole, which selectively target D3 receptors, increase the susceptibility to developing GD (39, 69–72). An experimental study using the rat gambling task (rGT) found that buspirone (a 5-HT1A receptor agonist) at a low dose level (3mg/kg) exclusively occupied D3 receptors, while at a high dose level (10mg/kg) simultaneously occupied D2 and D3 receptors, resulting in a greater number of advantageous responses than disadvantageous responses in the rGT for rats (73). In addition, the D4 receptors are also associated with gambling behavior (74). Activation of D4 receptors by the D4 agonist PD168077, primarily in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), led to rats displaying incorrect reward expectations during a rodent slot machine task. Since D4 receptor activation promotes gambling-like behaviors, this discovery suggests that D4 receptor antagonists might be promising therapeutic agents for treating BADs. DAT is a crucial protein that regulates DA levels in the synaptic cleft and controls the duration of DA signaling (75). In normal conditions, DAT reuptakes DA from the synaptic gap into the cytoplasm of presynaptic neurons, and alterations in DAT function significantly influence both intracellular and extracellular DA concentrations. Amphetamine is a dopaminergic drug (76) that not only affects synaptic plasticity in dopaminergic neurons but also causes reversal of the direction of DAT and dopamine release in the striatum, which can increase the concentration of DA in the synaptic cleft and may promote adverse effects such as gambling thoughts and behaviors. Another central nervous system stimulant, methylphenidate, inhibits the degradation enzymes of both DA and NE, extending their presence in the synaptic cleft and augmenting their effects. An 8-week trial administering methylphenidate to children diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and internet gaming addiction demonstrated significant reductions in both internet addiction scores and usage time (77), suggesting a potential for methylphenidate to be utilized as a beneficial intervention for internet addiction in children with ADHD. Additionally, supplementation therapy addressing compromised DA function has shown promise in fostering sustained dopaminergic activation, effectively treating impulsive behaviors associated with BADs without adverse effects (78). In the clinical treatment of BADs, attention should also be given to D1 and D5 receptors and the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) enzyme. However, it is important to interpret the aforementioned findings cautiously, as further experimental investigations are required to comprehensively comprehend the role of DA in various BADs to identify more precise targets for prevention and treatment.
Current addiction theories maintain some unresolved viewpoints regarding DA’s role. Beyond DA research, exploring other neurotransmitters is crucial for understanding BADs reward circuitry. A previous study indicated (79) that systems involving serotonin, endorphins, Glu and GABA are associated with substance addictions to varying degrees. Furthermore, these systems (11) exert significant interference on BADs and may interact with DA and other neurotransmitter systems in complex ways.
2.2 Serotonin (5-HT)
In addition to the DA system, there is compelling evidence (80) implicating the serotonergic system (the 5-HT system), in the reward circuitry of BADs, playing a role in the initiation and cessation of addictive behaviors. The dorsal and median raphe nuclei (DRN/MRN), located in the brainstem, are the primary sources of serotonergic neurons. These neurons project widely throughout the brain, particularly to key reward-related regions including the NAc, and AMY, where they modulate dopaminergic transmission. The NAc, through its core and shell subdivisions, is a pivotal brain area associated with reward and pleasure processing, which has been shown to be regulated by serotonin through 5-HT1B and 5-HT2C receptors (81). Similarly, disruptions in serotonin levels within the AMY have been linked to decision-making, impulse control, and emotions such as anxiety and fear in the context of BADs (82, 83). Furthermore, serotonin produced by serotonergic neurons in the DRN/MRN projects to various brain regions, including the PFC (84, 85). In the PFC, 5-HT primarily exerts inhibitory effects on pyramidal neurons, thereby contributing to the prefrontal inhibition of potentially harmful behaviors (86, 87). Thus, it is evident that serotonin release in regions such as the NAc, AMY, and PFC influences decision-making, behavioral control, and emotional changes in BADs by modulating the DA system.
While serotonin is not a part of the subcortical dopaminergic regulatory system, it can exert influence over the DA system through direct or indirect modulation. Specifically, dysregulation of the serotonergic system may contribute to clinical manifestations such as behavioral inhibition and impulsivity in GD. One study found (88) a positive correlation between the severity of gambling problems in 10 males with GD and levels of 5-HT1B receptors in the VS and ACC. Furthermore, factors like increased anxiety and depression in individuals with GD suggest that 5-HT release in the serotonergic system may play a crucial role in alleviating negative emotions in patients (89). Previous research (90) investigated the availability of serotonin transporters (SERT) in individuals with GD compared to healthy controls and found no intergroup differences. However, a recent study (43) discovered a positive correlation between increased SERT activity in the PFC and impulsivity in elderly individuals with GD. Another study (91) further demonstrated that higher SERT binding potential in the prefrontal region was associated with imbalanced decision-making (leaning more towards habit-based control) in individuals with GD. These findings suggest that abnormal increases in SERT may also be one of the pathogenic mechanisms of BADs. Additionally, the levels of the serotonin metabolite 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) in cerebrospinal fluid and the decreased activity of platelet monoamine oxidase (MAO) in blood (considered as a peripheral marker of 5-HT activity) (92–94) provide additional support for serotonin dysfunction in male gambling. In addition to findings related to gambling addiction, scholars have also discussed the significance of the serotonin system in IGD. It has been reported that prolonged exposure to electronic devices can lead to insufficient levels of vitamin D3 and melatonin in the body, resulting in gradual dysregulation of DA and serotonin neurotransmitter pathways in the brain, leading to addictive behaviors (95–97). Decreased levels of 5-HT have been found to be associated with the severity of internet gaming addiction and depressive mood, while regular exercise can increase 5-HT levels in the blood, alleviating negative emotions in individuals with IGD. Furthermore, a study (47) reported a correlation between decreased availability of 5-HT2A receptors in the temporal cortex and decreased availability of dopamine D2 receptors in the striatum in individuals with IGD. In addition to directly regulating DA release, evidence suggests that serotonin may modulate endorphins release in the HYP, potentially affecting GABA inhibition in the SNc and VTA, which could influence DA release in the NAc (80). This pathway may represent one of several mechanisms contributing to BADs. However, caution should be exercised in interpreting the stability and generalizability of the above research findings.
Collectively, serotonin dysregulation is another pathogenic mechanism involved in BADs, as it influences key neural circuits related to reward processing, decision-making, and impulse control, primarily through its interactions with dopaminergic, glutamatergic, and GABAergic systems. Previous pharmacological studies offer a theoretical foundation for investigating the neurobiological aspects of BADs and identifying key therapeutic targets. One such target is the SERT, which plays a pivotal role in regulating 5-HT reuptake. SERT’s function is to reabsorb 5-HT from the synaptic cleft back into presynaptic neurons, thereby maintaining a stable 5-HT level and regulating serotonergic signaling strength (98). Dysregulation of SERT activity can lead to either excessive or insufficient serotonergic transmission, contributing to behavioral and emotional dysregulation in BADs. Previous studies have found that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as fluoxetine, paroxetine, and citalopram are effective in reducing symptom severity, craving, and maladaptive decision-making in GD (99–101), IGD (102–105), CSBD (106–108), and compulsive shopping disorder (109). The 5-HT1A receptors (110, 111) are inhibitory receptors that, when activated on glutamatergic pyramidal cells and/or GABAergic interneurons in the PFC, stimulate DA release in the frontal cortex. Research has shown (112–114) that 5-HT1A receptor agonists, such as buspirone, can ameliorate anxiety and depressive symptoms during withdrawal from substance addiction (e.g., cocaine, alcohol, nicotine). A study in rodents (73) has also demonstrated that buspirone can improve decision-making in the rGT. The 5-HT1B receptors are other inhibitory receptors primarily located in the SNc, where their activation inhibits the release of neurotransmitters such as GABA, acetylcholine (ACh), and Glu, thereby modulating neural excitability and reward processing (115–118). Preclinical and clinical studies (119–121) have highlighted the role of the 5-HT1B receptors in managing depression and anxiety and their association with aggression and impulse control. Meta-chlorophenyl piperazine (mCPP) (122, 123), a metabolite of trazodone, is a mixed agonist for 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 receptors, particularly 5-HT1B receptors. In individuals with GD, mCPP administration has been reported to elicit subjective feelings of ‘excitement’ or arousal, whereas control subjects typically report aversive reactions. The 5-HT1D receptors (124, 125) primarily distribute across regions, including the caudate putamen, NAc, olfactory cortex, DRN, and locus coeruleus (LC) in the brain of rats. A study (126) reported that individuals with GD exhibited a reduced response to the selective 5-HT1D receptor agonist sumatriptan in terms of growth hormone release, whereas in the control group, growth hormone release increased. Furthermore, the 5-HT2A receptors (127, 128) are excitatory receptors, with a significant concentration of binding sites in prefrontal brain areas, including the cortical and hippocampal regions, basal ganglia, and olfactory tubercle. These receptors are involved in modulating glutamate release, synaptic plasticity, and emotional regulation. Present research (129–132) showed that 5-HT acting on the 5-HT2A receptors can enhance Glu release in cortical pyramidal cells and GABAergic inhibition in the AMY. A study (133) on the treatment of GD with a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist (nefazodone) revealed that within eight weeks after treatment, the scores for Yale Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale adapted for Pathological Gambling (PG-YBOCS) and the Pathological Gambling Clinical Global Impression (PG-GCI) decreased by 37% compared to baseline levels. In a recent case report (134), researchers used a combination of fluoxetine and risperidone to treat GD patients and noted that three patients did not experience gambling thoughts and behaviors for a year and a half following treatment, suggesting that fluoxetine, as an SSRI medication, primarily acts on the SERT, while risperidone is an atypical antipsychotic medication that blocks the 5-HT2A receptors with high affinity and has limited selectivity for the 5-HT2C and DA receptors. Therefore, combining these two medications may be more effective in controlling addiction than using them individually, expanding the potential utility of 5-HT2A antagonists in managing addiction. The 5-HT2C receptors are primarily situated on postsynaptic serotonergic neurons that interact with GABAergic, glutamatergic, dopaminergic, and cholinergic neurons. For instance, stimulation of 5-HT2C receptors (135, 136) in the VTA increases the firing rate of GABAergic interneurons, leading to a decrease in the firing rate of dopaminergic neurons. Conversely, it has been reported (137) that 5-HT2C receptor antagonists can increase dopaminergic neurotransmission and DA levels in the NAc and PFC. Furthermore, studies (138–140) have found that when 5-HT from the MRN acts on the 5-HT2C receptors of GABAergic interneurons in the PFC, it enhances the inhibitory effects of these interneurons, thereby counteracting the inhibitory effects of GABA on pyramidal output neurons. This relief of inhibition leads to increased activity of pyramidal output neurons and increased excitability of glutamatergic neurons. An animal experiment (141) demonstrated that 5-HT2C receptor antagonists can disrupt maladaptive decision-making patterns in rats in the rGT, suggesting their potential role in modulating maladaptive behaviors, though the translational relevance to humans remains to be established. Similarly, a study (142) exploring the use of the antidepressant agomelatine (an M1/M2 agonist and 5-HT2C antagonist) in pathological gambling patients also indicated that the medication not only ameliorates anxiety and depressive symptoms in GD but also diminishes gambling thoughts and behaviors. Additionally, while the mechanisms of 5-HT2B receptors (143–146), 5-HT5A receptors (147) and 5-HT7 receptors (148, 149) in BADs remain unclear, prior research has demonstrated their involvement in substance addictions. For example, 5-HT2B receptors are implicated in regulating impulsivity and aggression, 5-HT5A receptors in circadian rhythm and mood regulation, and 5-HT7 receptors in cognitive flexibility and emotional processing, suggesting their potential as future pharmacological targets for BADs.
2.3 Endorphins
Endorphins play a pivotal role in the brain’s reward system, similar to the roles of DA and serotonin. In individuals with BADs, DA is believed to be associated (19, 22) with reward anticipation and prediction error signals, while serotonin (12, 150) is involved in impulse inhibition and behavioral control, particularly through its effects on the PFC and its modulation of subcortical structures such as the AMY and NAc. The endogenous opioid system (151–155) influences DA neurotransmission in the mesolimbic pathway extending from the VTA to the VS and is also involved in assigning hedonic value to rewards and integrating reward-related information to guide goal-directed decision-making and execution. Additionally, it contributes to the perception of pleasure and the experience of cravings while modulating responses to rewards and losses. The endogenous opioid peptide system (156, 157) consists of β-endorphins (highest content in the VTA, NAc and HYP) (158–160), enkephalins (highest content in the VTA, NAc, SNc, HYP, striatum and hippocampus) (161–163), dynorphins (highest content in the PFC, SNc, striatum and central AMY) (161, 164–166), and nociceptins (highest content in the PFC and VTA) (167, 168). These peptides exert their effects through μ-opioid receptors (MOR), δ-opioid receptors (DOR), κ-opioid receptors (KOR) and nociceptin opioid peptide receptors (NOPR). These receptor systems are typically expressed at elevated levels in brain regions responsible for processing emotions, rewards, and aversions, such as the VTA, NAc, ACC, HYP, AMY and insula. β-endorphins (169) can bind to MOR and DOR, with a higher affinity for MOR, while enkephalins (170) have a stronger affinity for DOR than MOR and KOR. Dynorphins (157, 171, 172) have the highest affinity for KOR but can also bind to MOR and DOR within physiological ranges. Nociceptins (173, 174) specifically bind to NOPR and have very low affinity for other opioid receptors.
The role of endorphins in addiction appears to vary depending on their binding to different receptors (175–177). Ligands targeting MOR and DOR receptors may be associated with rewarding effects and emotional regulation, while ligands for KOR receptors may be linked to aversive effects. The function of NOPR receptor ligands in BADs remains uncertain at present. However, preclinical studies suggest that (178) NOPR activation may play a role in stress modulation and the attenuation of reward-seeking behaviors, indicating potential therapeutic implications for BADs. Previous studies (80, 179–181) have found that gambling or gambling-like activities (i.e., horse racing, slot machines, etc.) can trigger the release of endorphins, particularly in the NAc and VTA, which are key regions in the brain’s reward circuitry. Simultaneously, the increased availability of MOR in the shell, caudate nucleus, and globus pallidus is associated with presynaptic DA synthesis capacity, implying that the release of endorphins not only directly augments DA release but also, through MOR activation, inhibits the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA in the VTA, thereby facilitating DA release in the NAc (182). Furthermore, it has been observed (183) that endorphins in the NAc increase in response to DA activation, suggesting a potential feedback loop between the dopaminergic and opioid systems. Conversely, excessive activity of the endorphin system can modulate dopaminergic function (184).
Up till now, researchers have investigated the effects of specific opioid receptor agonists and antagonists in the addiction process (185). On one hand, opioid agonists enhance DA release in the NAc, significantly increasing pleasure and leading to orgasmic-like cravings. On the other hand, opioid receptor antagonists inhibit DA release in the NAc and the ventral pallidum by disinhibiting GABAergic inputs to dopaminergic neurons in the VTA, suppressing the excitatory and craving-related effects associated with BADs. These findings may be important considerations for the future development of treatments for BADs, particularly in targeting the opioid-dopaminergic interactions that drive craving and reinforcement mechanisms. Opioid antagonists, such as naltrexone and nalmefene, primarily target MOR, DOR, and KOR (186), albeit with a lower affinity for DOR and KOR. By blocking MOR, these antagonists reduce the rewarding effects of addictive behaviors and substances, while their effects on DOR and KOR may contribute to mood stabilization and stress regulation. A recent meta-analysis of drug treatments for GD investigating the findings from four randomized controlled studies on naltrexone and nalmefene (187–190) found that opioid antagonists can improve the severity of GD in the short term. However, there is currently insufficient evidence to determine their efficacy in addressing the psychological symptoms of gambling, such as impulsivity and craving, or their long-term effectiveness in preventing relapse. In this regard, a study by Kim et al. (187) found that naltrexone was more effective in treating individuals reporting severe impulsive behaviors compared to those with low impulsive behaviors. Furthermore, concerning the dosage aspect of pharmacological treatment, Grant et al.’s research indicated that high doses of nalmefene (40mg/day) were significantly more effective than placebo in treating GD symptoms (188, 190). However, naltrexone (189) was found to be effective at lower doses (50mg/day) with fewer adverse effects. Additionally, despite the absence of large-scale randomized controlled trials, naltrexone (191, 192) has demonstrated preliminary efficacy in reducing CSBD symptoms and impulsive behaviors, while nalmefene (193, 194) has demonstrated positive effects on addiction symptoms and behaviors related to internet pornography addiction. Presently, the mechanism of action of NOPR in BADs is still unclear. Nevertheless, a human study (178) employing PET imaging to assess changes in NOPR binding using radiolabeled nociceptin identified increased NOPR levels in participants with cocaine use disorder, particularly in the midbrain, VS, and cerebellum, providing insights for further exploration of the role of NOPR in BADs.
2.4 Gamma-aminobutyric acid
GABA, a pivotal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system of mammals (195, 196), reduces neuronal excitability. It is primarily synthesized from Glu via the enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), with pyridoxal phosphate (the active form of vitamin B6) as a cofactor. Like endorphins, serotoninergic and glutamatergic neurons in the DRN can modulate GABA input to the SNc, consequently impacting DA release (197). Additionally, GABA (198–201) can also exert its effects by projecting from the ventral pallidum, VTA GABAergic interneurons and the medial spiny GABAergic neurons of the NAc, inhibiting DA release from the mesolimbic system through GABAA and GABAB receptors. It is important to recognize that although both Glu and GABA can influence DA release, their effects on DA are inversely related (202). Therefore, GABA plays a pivotal role in the reward process associated with BADs, acting as a critical intervention point and can directly impact DA release and indirectly modulate DA release by influencing Glu projections within the NAc.
In the past, research on GABA has primarily explored substance addiction, particularly its role in alcohol addiction (203, 204). Similar to substance addiction, there are some similarities in the neurobiology of BADs. With the advancement of experimental techniques, scholars have gradually started investigating the specific manifestations of GABA in BADs. For instance, a study (205) utilizing magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) technique found that in male individuals with GD, the discounting of small immediate rewards in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex was negatively correlated with GABA, while the discounting of larger delayed rewards was negatively correlated with the ratio of GABA/glutamate-glutamine (Glx) in the dorsolateral PFC. Mick et al. (206) used [11C]Ro15-4513 as a radioligand for GABAA receptors and detected increased GABA binding in the right hippocampus of individuals with GD. They also found a direct correlation between increased GABA binding to GABAA in the AMY and impulsivity (negative urgency) related to emotional factors in the GD group. Furthermore, Chowdhury et al. (207) found weaker GABAA receptor activity but higher Glu receptor activity in the primary motor cortex (M1) of problem gamblers compared to non-gamblers and high-risk gamblers, suggesting an imbalance in excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission in this region. Additionally, the compromised response inhibition ability of individuals with gambling addiction correlated with reduced GABAA receptor activity in M1, suggesting that decision-making and impulsive behaviors in those with gambling addiction are influenced not only by GABAA receptor activity within the reward circuitry but also by alterations in glutamate-mediated neurotransmission. In a study (208) investigating internet and smartphone addiction, it was observed that addiction severity, as well as symptoms of depression and anxiety, correlated with elevated GABA levels in the ACC. After nine weeks of cognitive-behavioral therapy, GABA levels tended to normalize. These findings contrast somewhat with research (209) on substance addiction, which may be related to elevated GABA levels leading to reduced ACC function (210). However, it is essential to note that the sample size of this study was small, and further validation of these findings is needed.
In summary, the dysregulation of the GABA system emerges as a potential target for pharmacological intervention in BADs, with a primary focus on GABAA and GABAB receptors. Previous animal studies (74, 211) showed that the intracerebral injection of a combination of GABAA receptor agonist (muscimol) and GABAB receptor agonist (baclofen hydrochloride) results in receptor inactivation in the PFC, ACC, and HYP regions. This inactivation weakens rodents’ ability to differentiate between winning and losing outcomes in a rGT, leading to a preference for disadvantageous options and reduced selection of optimal choices. Moreover, this combination’s effects have been observed to induce insular cortex inactivation in rats during a radial arm maze test, prompting risky decision-making behaviors (212). In clinical investigations, substance addictions such as alcohol addiction (213), nicotine addiction (214) and heroin addiction (215) have been found to be closely related to GABAA and GABAB receptors. In BADs, only one experimental study (62) indicated that compared to healthy volunteers, levodopa reduces the availability of GABAA receptors in the PFC and insular regions of problem gamblers seeking treatment, leading to decreased GABA release and a loss of inhibitory control, suggesting that dysfunctional DA regulation of GABA release may contribute to GD. While these findings are promising, caution is necessary due to limitations such as small sample sizes and insufficient control of confounding factors. Further rigorous research is required to confirm these results and establish their clinical relevance. Nonetheless, these findings offer new strategies for the treatment of BADs in the future.
2.5 Glutamate
In the reward circuitry of BADs, not only are DA projections from the VTA to the PFC (18, 216), serotonin projections from the MRN to the NAc (81), and GABA projections from the NAc to the ventral pallidum involved (198, 217), but Glu projections from the PFC to the NAc also play an important role (218, 219). Glu projections contribute to changes in cognitive functioning, especially cognitive flexibility, which is essential for adapting to new situations and modifying behavior. These projections enable individuals to consciously resist impulses and form new associations between stimuli (e.g., gaming) and behavioral responses, linking them to unconditioned responses such as reward or punishment. Glu is a naturally occurring amino acid and a fundamental component of proteins. It is the most widely distributed excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain (220). Glu and glutamine (Gln) can be interconverted through the action of glutamine synthetase, establishing a “Glu-Gln cycle” between glial cells and neurons. This cycle allows for the continuous recycling and regeneration of Glu (221). Maintaining the balance of Glu between synapses and glial cells is crucial for the PFC to effectively regulate the reward-sensitive NAc. This balance ensures proper excitatory signaling and prevents excessive Glu activity, which could dysregulate reward processing and decision-making. Insufficient Glu levels in glial cells can lead to increased Glu release at synapses, significantly enhancing DA release in the NAc (221). When the Glu pathway is compromised, individuals may become more motivated by short-term rewards at the expense of long-term objectives. This imbalance in decision-making is associated with impaired cognitive control and heightened impulsivity, which are characteristic of BADs.
Current theories and empirical evidence suggest (219, 222, 223) that Glu from the PFC regulates DA levels through multiple pathways. While direct glutamatergic projections from the PFC to VTA are excitatory, the overall relationship between cortical Glu and DA transmission is complex and can involve inhibitory circuits. Glu from the PFC and/or AMY can modulate reward-driven behavior by affecting the responsiveness of DA cells in the VTA-NAc pathway, thus influencing DA’s reward-focused effects on decision-making. It has been reported (218) that compared to the ADHD group, the ADHD+IGD group showed decreased levels of Gln in the right PFC, which may be associated with the increased DA levels caused by excessive online gaming. Additionally, prolonged and excessive exposure to electronic games and other digital entertainment that provide immediate rewards can downregulate DA and Glu receptors in the NAc, resulting in symptoms such as tolerance, withdrawal and compulsive seeking of stimulation (48, 224). Furthermore, in a study of male samples with GD (205), the researchers reported a negative correlation between baseline Glx levels in the dorsal ACC and the severity of gambling. In another study (225), compared to 10 healthy males, 10 male pathological gamblers showed an increasing trend in Glu and aspartate levels in cerebrospinal fluid.
To summarize the contents described in this section, Glu can be considered as one of the essential elements for understanding the mechanisms underlying BAD’s formation from a psychopharmacological perspective. A number of pharmacologic studies (226) also provide evidence for abnormal Glu function in individuals with BADs, revealing that targeted interventions on Glu receptors can positively alleviate BAD’s symptoms. Glu exerts its effects through two different types of receptors (220), namely, metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) and ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPA, NMDA and Kainate). Specifically, N-acetylcysteine, which acts on inhibitory mGluR2/3 receptors, first increases extracellular Glu levels through the cystine-glutamate exchanger, which then stimulates mGluR2/3 receptors, thereby effectively reducing Glu synaptic release (227–229). When extracellular Glu levels are restored in the NAc, there is a certain inhibitory effect on cravings and impulsive behavior associated with addiction. Research (230) in rats has shown that N-acetylcysteine effectively reduces reward-seeking behavior. Clinical studies (231, 232) on GD have shown a significant reduction in gambling severity with active N-acetylcysteine treatment, a change that largely persists during the double-blind withdrawal phase. A recent case study involving a 19-year-old male with IGD (233) reported that after one month of N-acetylcysteine treatment at a dosage of 600mg twice daily, the patient experienced a significant decrease in cravings for gaming, consistent with findings from studies on GD and substance use disorders. Although all of the aforementioned clinical studies are preliminary and involved relatively small sample sizes, the consistent anti-addiction properties of N-acetylcysteine provide compelling evidence that this medication may be an effective adjunct in treating BADs. NMDA receptors have also been found to play a role in animal experiments (234). Blocking NMDA receptors (but not AMPA receptors) with the antagonist MK-801 hydrochloride reduces sensitivity to delayed reinforcement, uncertain reinforcement, and the amount of reinforcement in rats in operant conditioning chambers. In clinical trials, memantine, a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, has shown promise in reducing impulsive behaviors and improving cognitive flexibility in individuals with GD (235). Researchers have reported an average reduction of 35.1% in PG-YBOCS scores compared to baseline and significant improvement in cognitive flexibility during the intra-dimensional/extra-dimensional (ID/ED) set shift task. These findings may be attributed to memantine’s modulation of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the PFC, reducing impulsive behaviors. Additionally, bupropion, which also acts as a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, has been effective in reducing the severity of GD in patients and diminishing cravings for video games in individuals with IGD (103, 236). In addition to binding to NMDA receptors, bupropion can also interact with AMPA receptors, Kainate receptors, 5-HT3 receptors, and MOR, inhibiting DA and NE reuptake, thereby exhibiting a relatively complex mechanism of action in addiction. Case reports have shown that other NMDA receptor antagonists, such as acamprosate (237) and amantadine (238), may also have therapeutic effects on BADs. The AMPA receptor antagonist carbamazepine, as an antiepileptic drug, has been shown to effectively treat patients with GD by binding to AMPA receptors. By binding to AMPA receptors, carbamazepine reduces excitatory glutamatergic signaling, which may help regulate impulsive and compulsive behaviors associated with GD. In an open-label study by Black et al. (239), five individuals with GD received extended-release carbamazepine treatment for eight weeks, and the findings showed significant reductions in the participants’ PG-YBOCS scores and Gambling Severity Assessment Scale (GSAS) scores, consistent with previous case reports on the use of carbamazepine for GD (240). Topiramate, another antiepileptic drug, has multiple mechanisms of action (241), including the inhibition of AMPA receptors, mGluR5 receptors, and activation of GABAA receptors. In a case study from Brazil (242), a 57-year-old elderly woman with bipolar disorder and GD showed significant improvement in her gambling behavior when topiramate was added to her lithium carbonate treatment at a dose of 200mg/day and reported no cravings for gambling after two months of combination therapy. Moreover, topiramate has demonstrated positive effects in the treatment of CSBD (243) and compulsive buying disorder (244). Currently, studies have identified several glutamate transporters as key regulators of glutamatergic signaling in substance addictions. These include glutamate transporter-1 (GLT-1)) (245), which facilitates Glu reuptake into glial cells; excitatory amino acid transporters 1 and 3 (EAAT-1/3) (246, 247), which regulate synaptic Glu clearance; and vesicular glutamate transporters 1 and 2 (VGLUT-1/2), which mediate Glu storage and release from presynaptic neurons (248, 249).
2.6 Norepinephrine
NE, a catecholamine synthesized from DA by dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH), is primarily released under stress to enhance individual excitability (186, 250). Due to its comprehensive role in arousal and attention regulation, NE from the LC is increasingly associated with addiction through its projections to the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS)-NAc area (251). In individuals with GD, particularly male patients, excitement is often identified as a significant factor contributing to gambling. Previous studies (252, 253) have found that problem gamblers exhibit significantly higher levels of NE in their blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid during gambling compared to control groups. Additionally, a study investigating (179) psychological changes in players during a pachinko game revealed that NE, β-endorphin and DA levels were elevated during the initiation and winning phases compared to baseline levels and that gambling behavior was associated with increased heart rate and respiratory rate (254). These findings suggest a connection between gambling behavior and the autonomic arousal system targeted by NE. Recent research based on electroencephalography (EEG) has shown (255) that the enhancement of the P300 component during a two-choice gambling task called a two-armed bandit was dependent solely on the exploration phase, indicating that NE, rather than DA, plays a crucial role in triggering exploratory decisions. Interestingly, studies on IGD (256, 257) have found that compared to control groups, individuals with IGD had lower levels of NE during resting states. Furthermore, excessive playing of online games leads to decreased peripheral adrenaline and NE levels over time, altering autonomic regulation and increasing anxiety levels in adolescents. These findings contrast with the elevated levels of NE associated with GD (254), potentially due to the chronic stress stimulation caused by prolonged internet gaming (21, 258), which leads to adaptive responses such as receptor downregulation in the central nervous system. Chronic stress and prolonged gaming lead to a shift in behavioral control from goal-directed behavior, mediated by the PFC, to habitual control, which involves the dorsal striatum. This transition is driven by repetitive actions and changes in neurotransmitter regulation.
Interests in the role of NE in BADs are resurging. Early clinical and preclinical studies provide valuable insights for potential BAD treatments. DBH can convert DA to NE, and in a rodent experiment, it was found (259) that disulfiram, a DBH inhibitor, improved the performance of rats with disadvantageous strategies in the rGT, with a decrease in NE and an increase in DA observed in the striatum. Case reports have also suggested (260, 261) that disulfiram may reduce gambling cravings in individuals with GD. However, larger clinical trials are needed to confirm its efficacy and tolerability. Disulfiram’s effects may be mediated by its inhibition of DBH, which shifts the NE-DA balance in favor of DA. This mechanism could reduce stress-induced arousal and impulsivity, which are key drivers of gambling behavior. Further, the involvement of norepinephrine transporter (NET) in BADs has also been reported. Atomoxetine, as a NET blocker, has been shown to improve decision-making in male and female rats in the rGT by increasing synaptic NE levels (262). NE interacts with other neurotransmitters, such as DA and Glu, to regulate reward sensitivity and cognitive control. NE modulates DA release in the NAc, influencing the reward system’s sensitivity to stimuli. Additionally, in adolescents with comorbid ADHD and IGD, treatment with atomoxetine for 12 weeks resulted in a significant reduction in impulsivity and severity of internet gaming addiction (77). Other studies have revealed the important roles of α-2 adrenergic receptors in preclinical studies (262). Guanfacine, an α-2 adrenergic receptor agonist, which diminishes NE neuron firing by acting on autoreceptors, selectively enhanced decision-making abilities in risk-prone male rats and optimally performing female rats. In clinical research (263), the atypical stimulant modafinil was found to potentially reduce gambling cravings, impulsive behavior and risky decision-making in individuals with GD, which can be mediated through the stimulation of α-2 adrenergic receptors, inhibition of GABA release, elevation of extracellular Glu levels, weak inhibition of DAT or stimulation of HYP orexin neurons. Additionally, compared to healthy controls, male pathological gamblers showed an increased growth hormone response to the α-adrenergic receptor agonist clonidine (264). Furthermore, a study using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) (265) demonstrated differential activation in the AMY between individuals with GD and those without GD in response to yohimbine, an α-2 adrenergic antagonist. The β-adrenergic antagonist propranolol (266) has been shown to reduce compulsive gambling behavior in rodents in a slot machine task. Similarly, in a human gambling task (267), propranolol treatment did not result in significant changes in subjective state or mood compared to placebo. However, it did selectively alter decision-making in volunteers, specifically attenuating the processing of potential losses, indicating a reduced sensitivity to punishment cues.
2.7 Other neurotransmitters and neurotrophic factors
The neurobiological mechanisms underlying BADs involve the participation of multiple neurotransmitters. In addition to the neurotransmitters discussed above, such as DA, 5-HT and Glu, there are several other promising neurotransmitters and neurotrophic factors that may play a role in the pathogenesis of BADs, although current research in this area is still limited.
2.7.1 Corticotropin-releasing factor
It has been implicated in the research on rGT in rodents. The overexpression of CRF receptor 1 in the AMY of female rats has been found to be associated with increased risk-taking behavior (268). Additionally, compared to male rats, CRF receptor 1 antagonist (antalarmin) may be more effective in improving decision-making in female rats. A study involving Korean adolescent boys (269) also confirmed the association between polymorphisms in the CRF receptor gene and IGD, and it was found that individuals carrying the AA genotype and the A allele of rs28364027 (CRF1 gene) were more prone to IGD. Furthermore, several studies examining cortisol levels in BADs (270–275) indirectly suggest that abnormalities in the CRF system may underlie changes in decision-making patterns, cravings and stress responses associated with anxiety and emotional states.
2.7.2 ACh
Previous animal studies have reported (276) that muscarinic receptor antagonists (i.e., scopolamine) can improve decision-making patterns in the rGT task, increasing rats’ preference for advantageous options while reducing their selection of risky options. However, contradictory results have also been reported (277). Nicotinic receptor antagonists (such as mecamylamine) (276), while not affecting decision-making, were shown to be associated with reduced impulsive behavior in rats. On the other hand, another relevant study in mice (278) suggests that neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors may play a crucial role in the decision-making process. Studies by Montag et al. (279) and Jeong et al. (280) have both found an association between rs1044396 (CHRNA4 gene, encoding the α-4 subunit of the nicotinic ACh receptor) and IGD. ACh receptors also play a role in BADs by modulating the DA pathway, and increased cholinergic tone may be one of the factors affecting decision-making and impulse control in BADs.
2.7.3 Oxytocin
OXT has been found to primarily exert its effects through the oxytocin receptor (OXTR) in research related to addiction. Studies (281, 282) have indicated that rs2254295 and rs2268498 can modulate the function or expression of the OXTR gene, and individuals with the TT genotype have a lower risk propensity compared to participants with the CT and CC genotypes. Young male participants who inhaled intranasal OXT during the IGT exhibited a significant reduction in risk-taking behavior during the decision-making process under uncertainty. In regards to IGD, it has also been found (283) that male carriers of the TT genotype have lower levels of internet addiction. Furthermore, the level of plasma OXT was found to increase when individuals with CSBD, particularly those with problematic pornography use, were exposed to positive social stimuli (284). Therefore, the hypothesis that OXT may be a potential protective factor in BADs appears compelling.
2.7.4 Orexin
The role of the OX system (285) in regulating motivation and reward-seeking behavior in substance addiction has been well-established. Animal studies on BADs (286, 287) revealed that rats with a preference for high-reward outcomes exhibited increased orexin receptor 1 (OX1R) expression in the HYP and hippocampus. OX1R may be involved in impulsive behavior mediated by the HYP and hippocampus and in the selection of positively reinforced choices based on varying intensity and probability in the rGT task. Choi et al. confirmed (271) an increase in plasma OX levels in adolescents with IGD, indicating its potential involvement in IGD. OX may participate in the formation of BADs through its interaction with GABA and DA.
2.7.5 Leptin
Leptin has been suggested as a potential modulator of reward-related behaviors by regulating satiety and possibly influencing addictive behaviors through the mesolimbic reward pathway (288). Previous studies on patients with substance use disorders (alcohol, cocaine) (289, 290) have reported a positive correlation between leptin levels and craving. A recent study on healthy participants performing the IGT (291) demonstrated that individuals with higher leptin levels had worse performance on the IGT, while another study (292) revealed no relationship between leptin and craving in male IGD and GD. Overall, leptin is believed to be involved in the mechanisms underlying the formation of BADs through its interaction with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
2.7.6 Melatonin
It is a well-known regulator of various signaling pathways and biological rhythms (293). It has been reported that modulating melatonin can alter the behavior and physiological functions of individuals with substance addiction (294, 295). However, there is limited research on melatonin in regards to BADs, with only one study (142) indicating that individuals with GD showed improvements in addiction severity, anxiety and depression after treatment with agomelatine (a melatonin M1/M2 receptor agonist).
2.7.7 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
BDNF is highly expressed in limbic structures and the cerebral cortex and plays a crucial role in learning, memory, and reward-related processes (296). Several studies (297–300) have reported that BDNF levels positively correlate with the severity of GD or IGD in individuals. The increase in BDNF in BADs may be associated with alterations in DA transmission in the VTA and NAc. However, some studies (301, 302) have found no correlation between BDNF and BADs, suggesting the need for further investigation in longitudinal experiments.
2.7.8 Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor
GDNF is a neurotrophic factor involved in the development of dopaminergic neurons (303), and its role in reward mechanisms has been demonstrated in animal models of substance addiction (304). Current research (305) suggests that the GDNF gene variant rs2973033 is significantly associated with GD. Furthermore, it has been found (306) that plasma levels of GDNF in individuals with IGD are significantly lower compared to healthy controls and are negatively correlated with addiction severity.
Research on the mechanisms of neurotransmitters and neurotrophic factors in BADs remains limited, requiring validation through large-scale multicenter studies. However, there are promising indications that they may play a role in BADs by modulating DA, serotonin or GABA pathways in the reward circuitry. These mechanisms are integral to BADs and may present a new hope for the treatment of BADs for clinicians.
3 Emerging technologies: potential applications in BADs research
In recent years, emerging technologies have provided novel perspectives for research on BADs, particularly through the integration of CRISPR gene editing technology and neuroimaging, significantly advancing our understanding of neurotransmitter crosstalk mechanisms. CRISPR technology, through precise gene expression regulation, has revealed molecular mechanisms of dopaminergic neurons in the NAc (307). For instance, using CRISPRa and CRISPRi tools, researchers discovered that bidirectional regulation of Egr3 and Nab2 in D1-MSNs and D2-MSNs is crucial for reward processing and impulse control, while the innovatively developed light-sensitive Opto-CRISPR-KDM1a system not only achieved dynamic regulation of these genes but also revealed the key role of histone lysine demethylase in drug addiction (308). Through precise CRISPR-mediated regulation of COMT gene expression, researchers found that MB-COMT plays a crucial role in PFC dopamine metabolism, and this regulation directly influences cognitive control and reward processing through its balance with the GABAergic system (309). Neuroimaging studies further demonstrate significant dysfunction in emotion regulation networks among BADs patients, particularly abnormal activities in the PFC, striatum, and limbic system. Network-based fMRI analysis reveals that substance and BADs share functional alterations in prefrontal-striatal circuits, closely associated with dopaminergic system dysregulation (310). Recent studies have found that drug abuse “hijacks” the brain’s reward system, leading to enhanced dopaminergic neuronal ensemble activity in the NAc and disrupted responses to natural rewards (307). Complementary EEG studies have revealed characteristic changes in beta-band power and brain network connectivity in BADs patients, closely related to trait and behavioral impulsivity (311). Non-invasive neuromodulation techniques such as rTMS have shown promising results in treating GD, while the integration of neuroimaging markers enables more accurate prediction and monitoring of treatment responses (312). The integration of these emerging technologies has not only deepened our understanding of the neurobiological mechanisms of BADs but also established a solid scientific foundation for developing personalized treatment approaches and multi-target intervention strategies.
4 Conclusions and future perspectives
Advances in neuroscience have improved our understanding of how neurotransmitters contribute to the development of BADs. This work provides an overview of the neurobiology of BADs, focusing on the complex interplay of multiple neurotransmitters. The phenotypes of addiction arise from disruptions in neurotransmitter and neurotrophic factor expression and function. DA, a key neurotransmitter in the reward pathway, plays a central role in the mechanisms of BADs by modulating reward sensitivity, motivation, and reinforcement learning. DA interacts with other neurotransmitters, including serotonin, endorphins, GABA, Glu, NE, and neuropeptides such as CRF, ACh, OXT, and OX. Additionally, neurotrophic factors like BDNF and GDNF contribute to synaptic plasticity and neuroadaptations associated with BADs (see Figure 1). The interactions among these neurotransmitters influence biological behaviors such as reward processing, impulsiveness, and stress responses, which are closely linked to the onset and progression of BADs. Addiction is increasingly recognized as a chronic brain disorder, and evidence suggests it requires similar attention and treatment as other medical conditions. Neuroimaging and psychopharmacological investigations have identified anomalies in critical neurotransmitter targets among individuals with addiction. While these findings offer novel insights, further research is needed to validate their potential for treating BADs (see Figure 2). Despite substantial progress in the neurobiology of BADs and the preliminary efficacy and safety of pharmacological treatments for BADs, our understanding of the neurobiological mechanisms underlying their clinical features remains limited. To fully grasp the complexities of neurotransmitter actions in the brain, further research is needed to explore their interplay, regulation and how they ultimately drive behavior. Additionally, while there are some similarities in the neurobiology of different BADs, differences also exist. Therefore, future investigations should aim to delineate both the commonalities and unique neurobiological aspects inherent to various types of BADs, which could hold promise for identifying novel targets that could lead to more precise and personalized strategies for preventing and treating BADs. Finally, as neuroscientists and psychiatrists dedicated to addiction research, we advocate for the global scientific community to reconsider the prevailing dopamine-centric dedicated in BADs research. Leveraging advanced methodologies, such as genetic molecular localization, advanced imaging modalities, high-throughput single-cell analyses, and computational systems biology, offers an avenue for developing highly targeted therapies. By building upon existing research efforts, tailored “neurotransmitter therapies” may provide comprehensive therapeutic benefits for BADs while minimizing adverse impacts on the body’s physiological systems.
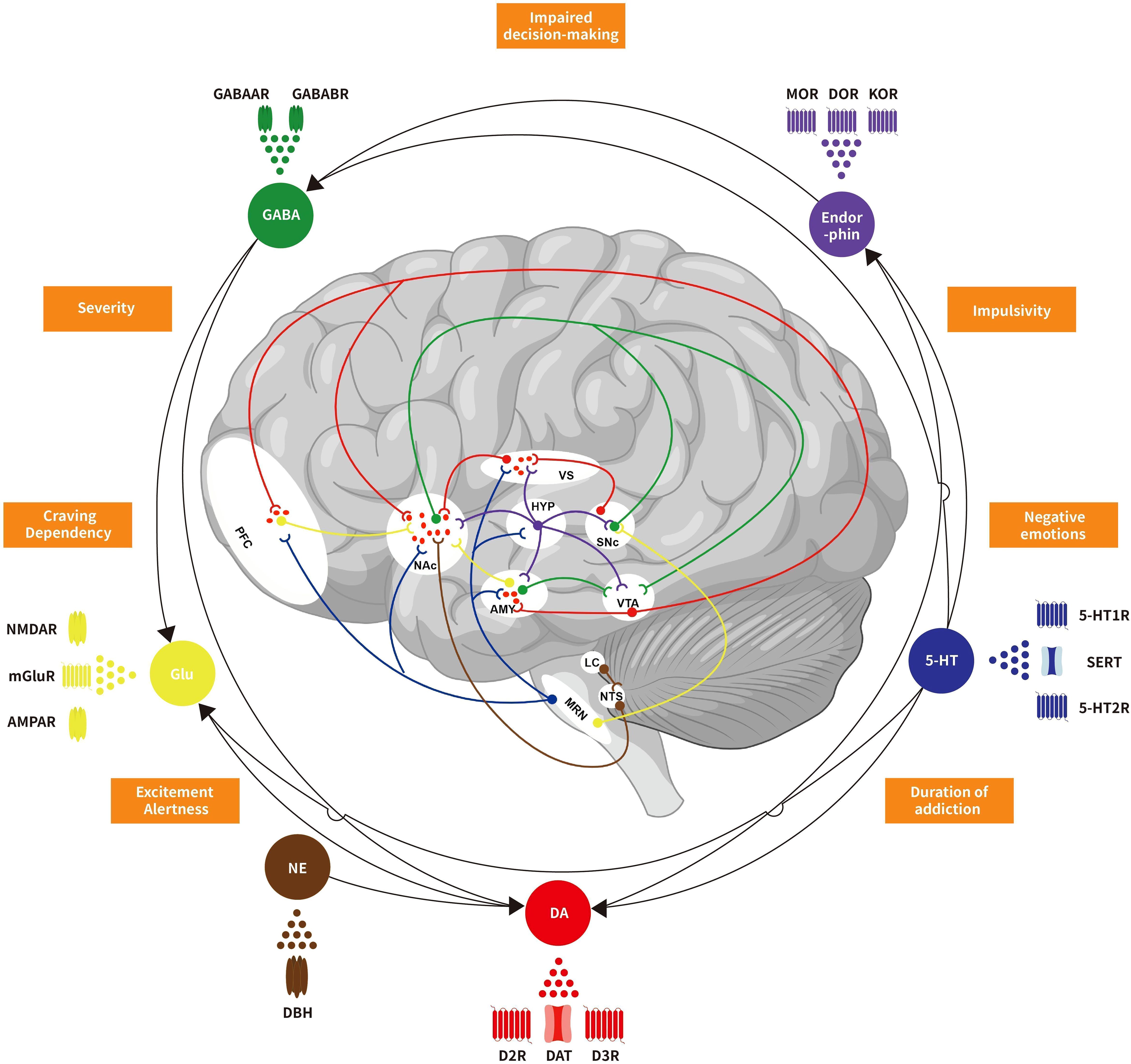
Figure 1. Schematic representation of neurotransmitters crosstalk and regulation in behavioral addiction reward circuit. Dopamine, serotonin, endorphins, GABA, glutamate, norepinephrine, and other neurotransmitters collectively form a complex regulatory network in the reward circuitry of behavioral addictive disorders. These neurotransmitters interact and interfere with each other, influencing not only biological behaviors but also closely associated with the occurrence and development of addiction. VTA, Ventral tegmental area; NAc, Nucleus accumbens; VS, Ventral striatum; PFC, Prefrontal cortex; AMY, Amygdala; SNc, Substantia nigra pars compacta; HYP, Hypothalamus; MRN, Median raphe nuclei; LC, Locus coeruleu; NTS, Nucleus tractus solitariu; DA, Dopamine; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; GABA, Gamma-aminobutyric acid; Glu, Glutamate; NE, Norepinephrine; D2R, Dopamine D2 receptors; D3R, Dopamine D3 receptors; DAT, Dopamine transporters; 5-HT1R, 5-HT1 receptors; 5-HT2R, 5-HT2 receptors; SERT, serotonin transporters; MOR, μ-opioid receptors; DOR, δ-opioid receptors; KOR, κ-opioid receptors; GABAAR, GABAA receptors; GABABR, GABAB receptors; mGluR, Metabotropic glutamate receptors; NMDAR, N-methyl D-aspartic acid receptors; AMPAR, Alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptors; DBH, Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase.
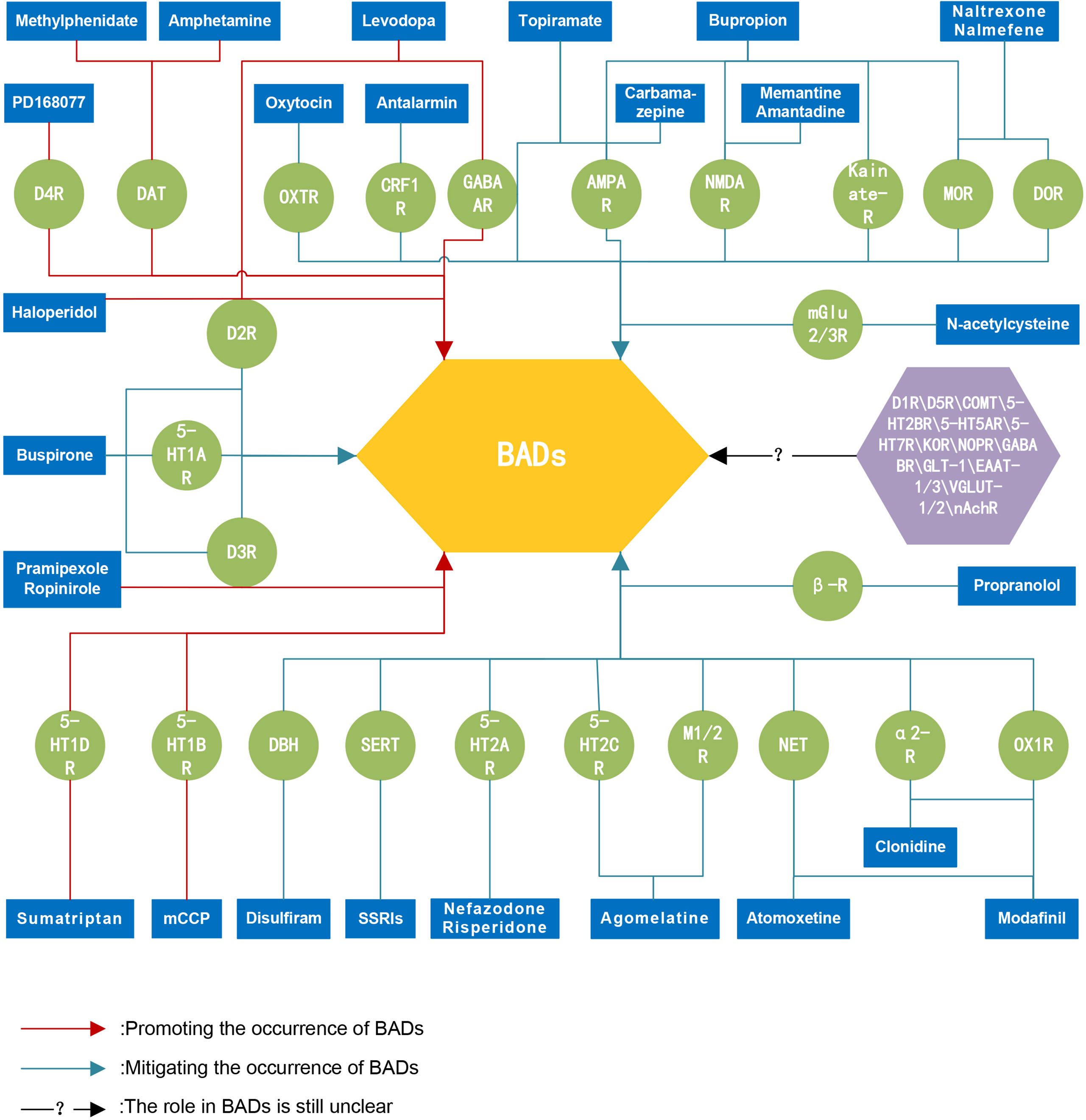
Figure 2. Schematic representation of potential pharmacological targets for the treatment of BADs. There are several important neurotransmitter targets involved in the occurrence and development of behavioral addictive disorders. These targets hold potential therapeutic prospects, and targeted "neurotransmitter therapies" may provide overall treatment benefits for individuals with behavioral addiction disorders without causing apparent damage to the body's physiological systems. BADs, behavioral addictive disorders; D1R, Dopamine D1 receptors; D2R, Dopamine D2 receptors; D3R, Dopamine D3 receptors; D4R, Dopamine D4 receptors; D5R, Dopamine D5 receptors; DAT, Dopamine transporters; COMT, catechol-O-methyltransferase enzyme; 5-HT1AR, 5-HT1A receptors; 5-HT1BR, 5-HT1B receptors; 5-HT1DR, 5-HT1D receptors; 5-HT2AR, 5-HT2A receptors; 5-HT2BR, 5-HT2B receptors; 5-HT2CR, 5-HT2C receptors; 5-HT5AR, 5-HT5A receptors; 5-HT7R, 5-HT7 receptors; SERT, serotonin transporters; MOR, μ-opioid receptors; DOR, δ-opioid receptors; KOR, κ-opioid receptors; NOPR, Nociceptin opioid peptide receptors; GABAAR, GABAA receptors; GABABR, GABAB receptors; mGlu2/3R, Metabotropic glutamate 2 and 3 receptors; NMDAR, N-methyl D-aspartic acid receptors; AMPAR, Alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptors; Kainate-R, Kainate receptors; GLT-1, Glutamate transporters-1; EAAT-1/3, Excitatory amino acid 1 and 3 transporters; VGLUT-1/2, Vesicular glutamate 1 and 2 transporters; DBH, Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase; NET, Norepinephrine transporters; α2-R, alpha-2 receptors; β-R, beta receptors; CRF1R, Corticotropin-releasing factor 1 receptors; M1/2R, Muscarinic acetylcholine 1 and 2 receptors; nAchR, Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; OXTR, Oxytocin receptors; OX1R, Orexin 1 receptors; SSRIs, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; mCCP, Meta-chlorophenyl piperazine.
Author contributions
ZP: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QJ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. JM: Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. XL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Writing – review & editing. SJ: Software, Writing – review & editing. QM: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. CM: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (grant number 2022D01D64), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81960258) and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Graduate Innovation Program (grant number XJ2024G149).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sugaya N, Shirasaka T, Takahashi K, Kanda H. Bio-psychosocial factors of children and adolescents with internet gaming disorder: a systematic review. Biopsychosoc Med. (2019) 13:3. doi: 10.1186/s13030-019-0144-5
2. World Health O. ICD-11: international statistical classification of diseases and related health problems, 10th revision. 2nd ed. Geneva: orld Health Organization (2019).
3. Mestre-Bach G, Potenza MN. Current understanding of compulsive sexual behavior disorder and co-occurring conditions: what clinicians should know about pharmacological options. CNS Drugs. (2024) 38:255–65. doi: 10.1007/s40263-024-01075-2
4. Muller A, Laskowski NM, Thomas TA, Antons S, Tahmassebi N, Steins-Loeber S, et al. Update on treatment studies for compulsive buying-shopping disorder: A systematic review. J Behav Addict. (2023) 12:631–51. doi: 10.1556/2006.2023.00033
5. Ma L, Tao Q, Dang J, Sun J, Niu X, Zhang M, et al. Altered local intrinsic neural activity and molecular architecture in internet use disorders. Brain Res Bull. (2024) 216:111052. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111052
6. Zeng X, Han X, Zheng D, Jiang P, Yuan Z. Similarity and difference in large-scale functional network alternations between the behavioral addictions and substance use disorder: A comparative meta-analysis - CORRIGENDUM. Psychol Med. (2024) 54:473–87. doi: 10.1017/S0033291723003434
7. Sussman S. Substance and Behavioral Addictions: Concepts, Causes and Cures. Substance and behavioral addictions concepts causes and cures | Health and clinical psychology. Cambridge: University Press (2017). Available at: https://www.cambridge.org/bv/universitypress/subjects/psychology/health-and-clinical-psychology/substance-and-behavioral-addictions-concepts-causes-and-cures?format=PB.
8. Adinoff B. Neurobiologic processes in drug reward and addiction. Harv Rev Psychiatry. (2004) 12:305–20. doi: 10.1080/10673220490910844
9. Gardner EL. Addiction and brain reward and antireward pathways. Adv Psychosom Med. (2011) 30:22–60. doi: 10.1159/000324065
10. Nair-Roberts RG, Chatelain-Badie SD, Benson E, White-Cooper H, Bolam JP, Ungless MA. Stereological estimates of dopaminergic, GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area, substantia nigra and retrorubral field in the rat. Neuroscience. (2008) 152:1024–31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.046
11. Antons S, Brand M, Potenza MN. Neurobiology of cue-reactivity, craving, and inhibitory control in non-substance addictive behaviors. J Neurol Sci. (2020) 415:116952. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.116952
12. Yau YH, Potenza MN. Gambling disorder and other behavioral addictions: recognition and treatment. Harv Rev Psychiatry. (2015) 23:134–46. doi: 10.1097/HRP.0000000000000051
13. Banz BC, Yip SW, Yau YH, Potenza MN. Behavioral addictions in addiction medicine: from mechanisms to practical considerations. Prog Brain Res. (2016) 223:311–28. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.08.003
14. von Deneen KM, Hussain H, Waheed J, Xinwen W, Yu D, Yuan K. Comparison of frontostriatal circuits in adolescent nicotine addiction and internet gaming disorder. J Behav Addict. (2022) 11:26–39. doi: 10.1556/2006.2021.00086
15. Wei L, Han X, Yu X, Sun Y, Ding M, Du Y, et al. Brain controllability and morphometry similarity of internet gaming addiction. Methods. (2021) 192:93–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.08.005
16. Potenza MN. Neurobiology of gambling behaviors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. (2013) 23:660–7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.03.004
17. Nicola SM. The flexible approach hypothesis: unification of effort and cue-responding hypotheses for the role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in the activation of reward-seeking behavior. J Neurosci. (2010) 30:16585–600. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3958-10.2010
18. Klein MO, Battagello DS, Cardoso AR, Hauser DN, Bittencourt JC, Correa RG. Dopamine: functions, signaling, and association with neurological diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2019) 39:31–59. doi: 10.1007/s10571-018-0632-3
19. Linnet J, Mouridsen K, Peterson E, Moller A, Doudet DJ, Gjedde A. Striatal dopamine release codes uncertainty in pathological gambling. Psychiatry Res. (2012) 204:55–60. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2012.04.012
20. Brand M, Young KS, Laier C. Prefrontal control and internet addiction: a theoretical model and review of neuropsychological and neuroimaging findings. Front Hum Neurosci. (2014) 8:375. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00375
21. Weinstein A, Lejoyeux M. New developments on the neurobiological and pharmaco-genetic mechanisms underlying internet and videogame addiction. Am J Addict. (2015) 24:117–25. doi: 10.1111/ajad.12110
22. Zack M, St George R, Clark L. Dopaminergic signaling of uncertainty and the aetiology of gambling addiction. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2020) 99:109853. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109853
23. O’Sullivan SS, Wu K, Politis M, Lawrence AD, Evans AH, Bose SK, et al. Cue-induced striatal dopamine release in Parkinson’s disease-associated impulsive-compulsive behaviours. Brain. (2011) 134:969–78. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr003
24. Wu K, Politis M, O’Sullivan SS, Lawrence AD, Warsi S, Bose S, et al. Single versus multiple impulse control disorders in Parkinson’s disease: an (1)(1)C-raclopride positron emission tomography study of reward cue-evoked striatal dopamine release. J Neurol. (2015) 262:1504–14. doi: 10.1007/s00415-015-7722-7
25. Greenfield DN. Treatment considerations in internet and video game addiction: A qualitative discussion. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. (2018) 27:327–44. doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2017.11.007
26. Hyman SE, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ. Neural mechanisms of addiction: the role of reward-related learning and memory. Annu Rev Neurosci. (2006) 29:565–98. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.113009
27. Elsinga PH, Hatano K, Ishiwata K. PET tracers for imaging of the dopaminergic system. Curr Med Chem. (2006) 13:2139–53. doi: 10.2174/092986706777935258
28. van Holst RJ, Sescousse G, Janssen LK, Janssen M, Berry AS, Jagust WJ, et al. Increased striatal dopamine synthesis capacity in gambling addiction. Biol Psychiatry. (2018) 83:1036–43. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.06.010
29. Akdemir UO, Bora Tokcaer A, Atay LO. Dopamine transporter SPECT imaging in Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonian disorders. Turk J Med Sci. (2021) 51:400–10. doi: 10.3906/sag-2008-253
30. Steeves TD, Miyasaki J, Zurowski M, Lang AE, Pellecchia G, Van Eimeren T, et al. Increased striatal dopamine release in Parkinsonian patients with pathological gambling: a [11C] raclopride PET study. Brain. (2009) 132:1376–85. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp054
31. Linnet J, Peterson E, Doudet DJ, Gjedde A, Moller A. Dopamine release in ventral striatum of pathological gamblers losing money. Acta Psychiatr Scand. (2010) 122:326–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2010.01591.x
32. Joutsa J, Johansson J, Niemela S, Ollikainen A, Hirvonen MM, Piepponen P, et al. Mesolimbic dopamine release is linked to symptom severity in pathological gambling. Neuroimage. (2012) 60:1992–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.02.006
33. Boileau I, Payer D, Chugani B, Lobo D, Behzadi A, Rusjan PM, et al. The D2/3 dopamine receptor in pathological gambling: a positron emission tomography study with [11C]-(+)-propyl-hexahydro-naphtho-oxazin and [11C]raclopride. Addiction. (2013) 108:953–63. doi: 10.1111/add.2013.108.issue-5
34. Boileau I, Payer D, Chugani B, Lobo DS, Houle S, Wilson AA, et al. In vivo evidence for greater amphetamine-induced dopamine release in pathological gambling: a positron emission tomography study with [(11)C]-(+)-PHNO. Mol Psychiatry. (2014) 19:1305–13. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.163
35. Linnet J, Moller A, Peterson E, Gjedde A, Doudet D. Dopamine release in ventral striatum during Iowa Gambling Task performance is associated with increased excitement levels in pathological gambling. Addiction. (2011) 106:383–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.03126.x
36. Heiden P, Heinz A, Romanczuk-Seiferth N. Pathological gambling in Parkinson’s disease: what are the risk factors and what is the role of impulsivity? Eur J Neurosci. (2017) 45:67–72. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13396
37. Clark L, Stokes PR, Wu K, Michalczuk R, Benecke A, Watson BJ, et al. Striatal dopamine D(2)/D(3) receptor binding in pathological gambling is correlated with mood-related impulsivity. Neuroimage. (2012) 63:40–6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.067
38. Joutsa J, Martikainen K, Niemela S, Johansson J, Forsback S, Rinne JO, et al. Increased medial orbitofrontal [18F]fluorodopa uptake in Parkinsonian impulse control disorders. Mov Disord. (2012) 27:778–82. doi: 10.1002/mds.24941
39. Seeman P. Parkinson’s disease treatment may cause impulse-control disorder via dopamine D3 receptors. Synapse. (2015) 69:183–9. doi: 10.1002/syn.21805
40. Eisenegger C, Knoch D, Ebstein RP, Gianotti LR, Sandor PS, Fehr E. Dopamine receptor D4 polymorphism predicts the effect of L-DOPA on gambling behavior. Biol Psychiatry. (2010) 67:702–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.09.021
41. Cocker PJ, Le Foll B, Rogers RD, Winstanley CA. A selective role for dopamine D(4) receptors in modulating reward expectancy in a rodent slot machine task. Biol Psychiatry. (2014) 75:817–24. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.08.026
42. Di Ciano P, Pushparaj A, Kim A, Hatch J, Masood T, Ramzi A, et al. The impact of selective dopamine D2, D3 and D4 ligands on the rat gambling task. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0136267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136267
43. Kaasinen V, Honkanen EA, Lindholm K, Jaakkola E, Majuri J, Parkkola R, et al. Serotonergic and dopaminergic control of impulsivity in gambling disorder. Addict Biol. (2023) 28:e13264. doi: 10.1111/adb.13264
44. Du YS, Jiang W, Vance A. Longer term effect of randomized, controlled group cognitive behavioural therapy for Internet addiction in adolescent students in Shanghai. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. (2010) 44:129–34. doi: 10.3109/00048670903282725
45. Kim SH, Baik SH, Park CS, Kim SJ, Choi SW, Kim SE. Reduced striatal dopamine D2 receptors in people with Internet addiction. Neuroreport. (2011) 22:407–11. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e328346e16e
46. Hahn T, Notebaert KH, Dresler T, Kowarsch L, Reif A, Fallgatter AJ. Linking online gaming and addictive behavior: converging evidence for a general reward deficiency in frequent online gamers. Front Behav Neurosci. (2014) 8:385. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00385
47. Tian M, Chen Q, Zhang Y, Du F, Hou H, Chao F, et al. PET imaging reveals brain functional changes in internet gaming disorder. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2014) 41:1388–97. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2708-8
48. Choi J, Cho H, Kim JY, Jung DJ, Ahn KJ, Kang HB, et al. Structural alterations in the prefrontal cortex mediate the relationship between Internet gaming disorder and depressed mood. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:1245. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01275-5
49. Hou H, Jia S, Hu S, Fan R, Sun W, Sun T, et al. Reduced striatal dopamine transporters in people with internet addiction disorder. J BioMed Biotechnol. (2012) 2012:854524. doi: 10.1155/2012/854524
50. Ariatama B, Effendy E, Amin MM. Relationship between internet gaming disorder with depressive syndrome and dopamine transporter condition in online games player. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. (2019) 7:2638–42. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.476
51. Linnet J, Moller A, Peterson E, Gjedde A, Doudet D. Inverse association between dopaminergic neurotransmission and Iowa Gambling Task performance in pathological gamblers and healthy controls. Scand J Psychol. (2011) 52:28–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9450.2010.00837.x
52. Potenza MN. How central is dopamine to pathological gambling or gambling disorder? Front Behav Neurosci. (2013) 7:206. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00206
53. Potenza MN. Searching for replicable dopamine-related findings in gambling disorder. Biol Psychiatry. (2018) 83:984–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.04.011
54. Noble EP, Blum K, Ritchie T, Montgomery A, Sheridan PJ. Allelic association of the D2 dopamine receptor gene with receptor-binding characteristics in alcoholism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (1991) 48:648–54. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810310066012
55. Payer DE, Guttman M, Kish SJ, Tong J, Strafella A, Zack M, et al. (1)(1)C]-(+)-PHNO PET imaging of dopamine D(2/3) receptors in Parkinson’s disease with impulse control disorders. Mov Disord. (2015) 30:160–6. doi: 10.1002/mds.26135
56. Kraus SW, Voon V, Potenza MN. Neurobiology of compulsive sexual behavior: emerging science. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2016) 41:385–6. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.300
57. Weintraub D, Koester J, Potenza MN, Siderowf AD, Stacy M, Voon V, et al. Impulse control disorders in Parkinson disease: a cross-sectional study of 3090 patients. Arch Neurol. (2010) 67:589–95. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.65
58. Sohtaoglu M, Demiray DY, Kenangil G, Ozekmekci S, Erginoz E. Long term follow-up of Parkinson’s disease patients with impulse control disorders. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. (2010) 16:334–7. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2010.02.006
59. Weintraub D, Nirenberg MJ. Impulse control and related disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener Dis. (2013) 11:63–71. doi: 10.1159/000341996
60. Grall-Bronnec M, Sauvaget A, Perrouin F, Leboucher J, Etcheverrigaray F, Challet-Bouju G, et al. Pathological gambling associated with aripiprazole or dopamine replacement therapy: do patients share the same features? A review. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2016) 36:63–70. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000444
61. Grall-Bronnec M, Victorri-Vigneau C, Donnio Y, Leboucher J, Rousselet M, Thiabaud E, et al. Dopamine agonists and impulse control disorders: A complex association. Drug Saf. (2018) 41:19–75. doi: 10.1007/s40264-017-0590-6
62. Moller A, Romer Thomsen K, Brooks DJ, Mouridsen K, Blicher JU, Hansen KV, et al. Attenuation of dopamine-induced GABA release in problem gamblers. Brain Behav. (2019) 9:e01239. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1239
63. Tremblay AM, Desmond RC, Poulos CX, Zack M. Haloperidol modifies instrumental aspects of slot machine gambling in pathological gamblers and healthy controls. Addict Biol. (2011) 16:467–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2010.00208.x
64. Zack M, Poulos CX. A D2 antagonist enhances the rewarding and priming effects of a gambling episode in pathological gamblers. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2007) 32:1678–86. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301295
65. McElroy SL, Nelson EB, Welge JA, Kaehler L, Keck PE Jr. Olanzapine in the treatment of pathological gambling: a negative randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. (2008) 69:433–40. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v69n0314
66. Fong T, Kalechstein A, Bernhard B, Rosenthal R, Rugle L. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of olanzapine for the treatment of video poker pathological gamblers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. (2008) 89:298–303. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.12.025
67. Sescousse G, Janssen LK, Hashemi MM, Timmer MH, Geurts DE, Ter Huurne NP, et al. Amplified striatal responses to near-miss outcomes in pathological gamblers. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2016) 41:2614–23. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.43
68. Sibley DR, Monsma FJ Jr. Molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (1992) 13:61–9. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90025-2
69. Piercey MF. Pharmacology of pramipexole, a dopamine D3-preferring agonist useful in treating Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol. (1998) 21:141–51.
70. Jost WH, Angersbach D. Ropinirole, a non-ergoline dopamine agonist. CNS Drug Rev. (2005) 11:253–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2005.tb00046.x
71. Pontone G, Williams JR, Bassett SS, Marsh L. Clinical features associated with impulse control disorders in Parkinson disease. Neurology. (2006) 67:1258–61. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000238401.76928.45
72. Zengin-Toktas Y, Authier N, Denizot H, Chassain C, Hafidi A, Llorca PM, et al. Motivational properties of D2 and D3 dopamine receptors agonists and cocaine, but not with D1 dopamine receptors agonist and L-dopa, in bilateral 6-OHDA-lesioned rat. Neuropharmacology. (2013) 70:74–82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.12.011
73. Di Ciano P, Cormick PM, Stefan C, Wong E, Kim A, Remington G, et al. The effects of buspirone on occupancy of dopamine receptors and the rat gambling task. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2017) 234:3309–20. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4715-5
74. Cocker PJ, Hosking JG, Murch WS, Clark L, Winstanley CA. Activation of dopamine D4 receptors within the anterior cingulate cortex enhances the erroneous expectation of reward on a rat slot machine task. Neuropharmacology. (2016) 105:186–95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.01.019
75. Kawarai T, Kawakami H, Yamamura Y, Nakamura S. Structure and organization of the gene encoding human dopamine transporter. Gene. (1997) 195:11–8. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00131-5
76. Zack M, Poulos CX. Amphetamine primes motivation to gamble and gambling-related semantic networks in problem gamblers. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2004) 29:195–207. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300333
77. Park JH, Lee YS, Sohn JH, Han DH. Effectiveness of atomoxetine and methylphenidate for problematic online gaming in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Hum Psychopharmacol. (2016) 31:427–32. doi: 10.1002/hup.v31.6
78. Blum K, Febo M, Badgaiyan RD. Fifty years in the development of a glutaminergic-dopaminergic optimization complex (KB220) to balance brain reward circuitry in reward deficiency syndrome: A pictorial. Austin Addict Sci. (2016) 1:1006.
79. Baler RD, Volkow ND. Drug addiction: the neurobiology of disrupted self-control. Trends Mol Med. (2006) 12:559–66. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2006.10.005
80. Blum K, Gondre-Lewis MC, Baron D, Thanos PK, Braverman ER, Neary J, et al. Introducing precision addiction management of reward deficiency syndrome, the construct that underpins all addictive behaviors. Front Psychiatry. (2018) 9:548. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00548
81. De Deurwaerdere P, Spampinato U. Role of serotonin(2A) and serotonin(2B/2C) receptor subtypes in the control of accumbal and striatal dopamine release elicited in vivo by dorsal raphe nucleus electrical stimulation. J Neurochem. (1999) 73:1033–42. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0731033.x
82. Wang L, Wu L, Wang Y, Li H, Liu X, Du X, et al. Altered brain activities associated with craving and cue reactivity in people with internet gaming disorder: evidence from the comparison with recreational internet game users. Front Psychol. (2017) 8:1150. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01150
83. Genauck A, Quester S, Wustenberg T, Morsen C, Heinz A, Romanczuk-Seiferth N. Reduced loss aversion in pathological gambling and alcohol dependence is associated with differential alterations in amygdala and prefrontal functioning. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:16306. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16433-y
84. Parent A, Descarries L, Beaudet A. Organization of ascending serotonin systems in the adult rat brain. A radioautographic study after intraventricular administration of [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuroscience. (1981) 6:115–38. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90050-6
85. Hornung JP. The human raphe nuclei and the serotonergic system. J Chem Neuroanat. (2003) 26:331–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2003.10.002
86. Kirby LG, Zeeb FD, Winstanley CA. Contributions of serotonin in addiction vulnerability. Neuropharmacology. (2011) 61:421–32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.03.022
87. Puig MV, Gulledge AT. Serotonin and prefrontal cortex function: neurons, networks, and circuits. Mol Neurobiol. (2011) 44:449–64. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8214-0
88. Potenza MN, Walderhaug E, Henry S, Gallezot JD, Planeta-Wilson B, Ropchan J, et al. Serotonin 1B receptor imaging in pathological gambling. World J Biol Psychiatry. (2013) 14:139–45. doi: 10.3109/15622975.2011.598559
89. Starcevic V, Khazaal Y. Relationships between behavioural addictions and psychiatric disorders: what is known and what is yet to be learned? Front Psychiatry. (2017) 8:53. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00053
90. Majuri J, Joutsa J, Johansson J, Voon V, Parkkola R, Alho H, et al. Serotonin transporter density in binge eating disorder and pathological gambling: A PET study with [(11)C]MADAM. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2017) 27:1281–8. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2017.09.007
91. Voon V, Joutsa J, Majuri J, Baek K, Nord CL, Arponen E, et al. The neurochemical substrates of habitual and goal-directed control. Transl Psychiatry. (2020) 10:84. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-0762-5
92. Nordin C, Eklundh T. Altered CSF 5-HIAA disposition in pathologic male gamblers. CNS Spectr. (1999) 4:25–33. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900006799
93. Ibañez IPdC A, Fernandez-Piqueras J. Pathological gambling and DNA polymorphic markers at MAO-A and MAO-B genes. Mol Psychiatry. (2000) 5:105–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000654
94. Perez de Castro I, Ibanez A, Saiz-Ruiz J, Fernandez-Piqueras J. Concurrent positive association between pathological gambling and functional DNA polymorphisms at the MAO-A and the 5-HT transporter genes. Mol Psychiatry. (2002) 7:927–8. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001148
95. Trinko JR, Land BB, Solecki WB, Wickham RJ, Tellez LA, Maldonado-Aviles J, et al. Vitamin D3: A role in dopamine circuit regulation, diet-induced obesity, and drug consumption. eNeuro. (2016) 3:ENEURO.0122-15.2016 1-16. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0122-15.2016
96. Kang S-H, So W-Y. Effect of competitive and non-competitive exercise on serotonin levels in adolescents with various levels of internet gaming addiction. ran J Public Health. (2018) 47:1047–9.
97. Zhao L, Li X, Yang Q, Peng Y, Jiang L, Jia P, et al. The longitudinal association between internet addiction and depressive and anxiety symptoms among Chinese adolescents before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:1096660. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1096660
98. Rudnick G, Clark J. From synapse to vesicle: the reuptake and storage of biogenic amine neurotransmitters. Biochim Biophys Acta. (1993) 1144:249–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90109-S
99. Dannon PN, Lowengrub K, Musin E, Gonopolski Y, Kotler M. Sustained-release bupropion versus naltrexone in the treatment of pathological gambling: a preliminary blind-rater study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2005) 25:593–6. doi: 10.1097/01.jcp.0000186867.90289.ed
100. Blanco C, Potenza MN, Kim SW, Ibanez A, Zaninelli R, Saiz-Ruiz J, et al. A pilot study of impulsivity and compulsivity in pathological gambling. Psychiatry Res. (2009) 167:161–8. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2008.04.023
101. Bellucci G, Munte TF, Park SQ. Influences of social uncertainty and serotonin on gambling decisions. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:10220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13778-x
102. Dell’Osso B, Hadley S, Allen A, Baker B, Chaplin WF, Hollander E. Escitalopram in the treatment of impulsive-compulsive internet usage disorder: an open-label trial followed by a double-blind discontinuation phase. J Clin Psychiatry. (2008) 69:452–6. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v69n0316
103. Han DH, Hwang JW, Renshaw PF. Bupropion sustained release treatment decreases craving for video games and cue-induced brain activity in patients with Internet video game addiction. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. (2010) 18:297–304. doi: 10.1037/a0020023
104. Han DH, Renshaw PF. Bupropion in the treatment of problematic online game play in patients with major depressive disorder. J Psychopharmacol. (2012) 26:689–96. doi: 10.1177/0269881111400647
105. Song J, Park JH, Han DH, Roh S, Son JH, Choi TY, et al. Comparative study of the effects of bupropion and escitalopram on Internet gaming disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2016) 70:527–35. doi: 10.1111/pcn.2016.70.issue-11
106. Kafka M. Psychopharmacologic treatments for nonparaphilic compulsive sexual behaviors. CNS Spectr. (2000) 5:49–59. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900012669
107. Wainberg ML, Muench F, Morgenstern J, Hollander E, Irwin TW, Parsons JT, et al. A double-blind study of citalopram versus placebo in the treatment of compulsive sexual behaviors in gay and bisexual men. J Clin Psychiatry. (2006) 67:1968–73. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v67n1218
108. Singh G, Singh H, Magny S, Virk I, Gill M. Use of fluoxetine in treating compulsive sexual behavior: A case report. Cureus. (2022) 14:e29245. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29245
109. Koran LM, Chuong HW, Bullock KD, Smith SC. Citalopram for compulsive shopping disorder: an open-label study followed by double-blind discontinuation. J Clin Psychiatry. (2003) 64:793–8. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v64n0709
110. Bortolozzi A, Masana M, Diaz-Mataix L, Cortes R, Scorza MC, Gingrich JA, et al. Dopamine release induced by atypical antipsychotics in prefrontal cortex requires 5-HT(1A) receptors but not 5-HT(2A) receptors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2010) 13:1299–314. doi: 10.1017/S146114571000009X
111. Santana N, Mengod G, Artigas F. Expression of alpha(1)-adrenergic receptors in rat prefrontal cortex: cellular co-localization with 5-HT(2A) receptors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2013) 16:1139–51. doi: 10.1017/S1461145712001083
112. de Oliveira Cito Mdo C, da Silva FC, Silva MI, Moura BA, Macedo DS, Woods DJ, et al. Reversal of cocaine withdrawal-induced anxiety by ondansetron, buspirone and propranolol. Behav Brain Res. (2012) 231:116–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.01.056
113. Elrashidi MY, Ebbert JO. Emerging drugs for the treatment of tobacco dependence: 2014 update. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. (2014) 19:243–60. doi: 10.1517/14728214.2014.899580
114. Gimeno C, Dorado ML, Roncero C, Szerman N, Vega P, Balanza-Martinez V, et al. Treatment of comorbid alcohol dependence and anxiety disorder: review of the scientific evidence and recommendations for treatment. Front Psychiatry. (2017) 8:173. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00173
115. Maura G, Raiteri M. Cholinergic terminals in rat hippocampus possess 5-HT1B receptors mediating inhibition of acetylcholine release. Eur J Pharmacol. (1986) 129:333–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90443-7
116. Johnson SW, Mercuri NB, North RA. 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptors block the GABAB synaptic potential in rat dopamine neurons. J Neurosci. (1992) 12:2000–6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-05-02000.1992
117. Singer JH, Bellingham MC, Berger AJ. Presynaptic inhibition of glutamatergic synaptic transmission to rat motoneurons by serotonin. J Neurophysiol. (1996) 76:799–807. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.2.799
118. Chadha A, Sur C, Atack J, Duty S. The 5HT(1B) receptor agonist, CP-93129, inhibits [(3)H]-GABA release from rat globus pallidus slices and reverses akinesia following intrapallidal injection in the reserpine-treated rat. Br J Pharmacol. (2000) 130:1927–32. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703526
119. Ruf BM, Bhagwagar Z. The 5-HT1B receptor: a novel target for the pathophysiology of depression. Curr Drug Targets. (2009) 10:1118–38. doi: 10.2174/138945009789735192
120. Nautiyal KM, Tanaka KF, Barr MM, Tritschler L, Le Dantec Y, David DJ, et al. Distinct circuits underlie the effects of 5-HT1B receptors on aggression and impulsivity. Neuron. (2015) 86:813–26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.041
121. Fakhoury M. Revisiting the serotonin hypothesis: implications for major depressive disorders. Mol Neurobiol. (2016) 53:2778–86. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9152-z
122. DeCaria CM BT, Hollander E. Serotonergic and noradrenergic function in pathological gambling. CNS Spectr. (1998) 3:38–45. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900006003
123. Pallanti S, Bernardi S, Quercioli L, DeCaria C, Hollander E. Serotonin dysfunction in pathological gamblers: increased prolactin response to oral m-CPP versus placebo. CNS Spectr. (2006) 11:956–64. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900015145
124. Bruinvels AT, Landwehrmeyer B, Gustafson EL, Durkin MM, Mengod G, Branchek TA, et al. Localization of 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D alpha, 5-HT1E and 5-HT1F receptor messenger RNA in rodent and primate brain. Neuropharmacology. (1994) 33:367–86. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90067-1
125. Mengod G CR, Vilaró MT, Hoyer D. Distribution of 5-HT receptors in the central nervous system. Handb Behav Neurosci. (2010) 21:123–38. doi: 10.1016/S1569-7339(10)70074-6
126. Pallanti S, Bernardi S, Allen A, Hollander E. Serotonin function in pathological gambling: blunted growth hormone response to sumatriptan. J Psychopharmacol. (2010) 24:1802–9. doi: 10.1177/0269881109106907
127. Pazos A, Probst A, Palacios JM. Serotonin receptors in the human brain–III. Autoradiographic mapping of serotonin-1 receptors. Neuroscience. (1987) 21:97–122. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90326-5
128. Lopez-Gimenez JF, Mengod G, Palacios JM, Vilaro MT. Selective visualization of rat brain 5-HT2A receptors by autoradiography with [3H]MDL 100,907. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (1997) 356:446–54. doi: 10.1007/PL00005075
129. Burnet PW, Eastwood SL, Lacey K, Harrison PJ. The distribution of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptor mRNA in human brain. Brain Res. (1995) 676:157–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00104-X
130. Jiang X, Xing G, Yang C, Verma A, Zhang L, Li H. Stress impairs 5-HT2A receptor-mediated serotonergic facilitation of GABA release in juvenile rat basolateral amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2009) 34:410–23. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.71
131. Mocci G, Jimenez-Sanchez L, Adell A, Cortes R, Artigas F. Expression of 5-HT2A receptors in prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons projecting to nucleus accumbens. Potential relevance for atypical antipsychotic action. Neuropharmacology. (2014) 79:49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.10.021
132. Bocchio M, Fucsina G, Oikonomidis L, McHugh SB, Bannerman DM, Sharp T, et al. Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2015) 40:3015–26. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.157
133. Pallanti S, Baldini Rossi N, Sood E, Hollander E. Nefazodone treatment of pathological gambling: a prospective open-label controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. (2002) 63:1034–9. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v63n1114
134. Bai M, Huang E, Du H, Yang L, Zhang X, Yang Y, et al. Fluoxetine combined with risperidone in treatment of online gambling disorder-case report. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e13772. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13772
135. Prisco S, Pagannone S, Esposito E. Serotonin-dopamine interaction in the rat ventral tegmental area: an electrophysiological study. vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (1994) 271:83–90. doi: 10.1016/1056-8719(94)90063-9
136. Di Giovanni G, Di Matteo V, La Grutta V, Esposito E. m-Chlor ophenylpiperazine excites non-dopaminergic neurons in the rat substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area by activating serotonin-2C receptors. Neuroscience. (2001) 103:111–6. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00561-3
137. Gobert A, Rivet JM, Lejeune F, Newman-Tancredi A, Adhumeau-Auclair A, Nicolas JP, et al. Serotonin(2C) receptors tonically suppress the activity of mesocortical dopaminergic and adrenergic, but not serotonergic, pathways: a combined dialysis and electrophysiological analysis in the rat. Synapse. (2000) 36:205–21. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(20000601)36:3<205::AID-SYN5>3.0.CO;2-D
138. Vysokanov A, Flores-Hernandez J, Surmeier DJ. mRNAs for clozapine-sensitive receptors co-localize in rat prefrontal cortex neurons. Neurosci Lett. (1998) 258:179–82. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(98)00882-9
139. Liu S, Bubar MJ, Lanfranco MF, Hillman GR, Cunningham KA. Serotonin2C receptor localization in GABA neurons of the rat medial prefrontal cortex: implications for understanding the neurobiology of addiction. Neuroscience. (2007) 146:1677–88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.02.064
140. Nocjar C, Alex KD, Sonneborn A, Abbas AI, Roth BL, Pehek EA. Serotonin-2C and -2a receptor co-expression on cells in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience. (2015) 297:22–37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.050
141. Adams WK, Barkus C, Ferland JN, Sharp T, Winstanley CA. Pharmacological evidence that 5-HT(2C) receptor blockade selectively improves decision making when rewards are paired with audiovisual cues in a rat gambling task. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2017) 234:3091–104. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4696-4
142. Egorov AY. The use of agomelatine (valdoxan) in gambling therapy: a pilot study. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. (2015) 115:28–31. doi: 10.17116/jnevro20151159128-31
143. Doly S, Valjent E, Setola V, Callebert J, Herve D, Launay JM, et al. Serotonin 5-HT2B receptors are required for 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion and 5-HT release in vivo and in vitro. J Neurosci. (2008) 28:2933–40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5723-07.2008
144. Bevilacqua L, Doly S, Kaprio J, Yuan Q, Tikkanen R, Paunio T, et al. A population-specific HTR2B stop codon predisposes to severe impulsivity. Nature. (2010) 468:1061–6. doi: 10.1038/nature09629
145. Pitychoutis PM, Belmer A, Moutkine I, Adrien J, Maroteaux L. Mice lacking the serotonin htr2B receptor gene present an antipsychotic-sensitive schizophrenic-like phenotype. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2015) 40:2764–73. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.126
146. Lacoste J, Lamy S, Ramoz N, Ballon N, Jehel L, Maroteaux L, et al. A positive association between a polymorphism in the HTR2B gene and cocaine-crack in a French Afro-Caribbean population. World J Biol Psychiatry. (2020) 21:784–9. doi: 10.1080/15622975.2018.1563721
147. Thomas DR. 5-ht5A receptors as a therapeutic target. Pharmacol Ther. (2006) 111:707–14. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.12.006
148. Kim JH, Park BL, Cheong HS, Bae JS, Kim LH, Kim JW, et al. Association between HTR7 genetic polymorphisms and alcohol dependence, using the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT). Alcohol Clin Exp Res. (2014) 38:2354–61. doi: 10.1111/acer.2014.38.issue-9
149. Hauser SR, Hedlund PB, Roberts AJ, Sari Y, Bell RL, Engleman EA. The 5-HT7 receptor as a potential target for treating drug and alcohol abuse. Front Neurosci. (2014) 8:448. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00448
150. Brewer JA, Potenza MN. The neurobiology and genetics of impulse control disorders: relationships to drug addictions. Biochem Pharmacol. (2008) 75:63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.06.043
151. Spanagel R, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Opposing tonically active endogenous opioid systems modulate the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (1992) 89:2046–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2046
152. Trigo JM, Martin-Garcia E, Berrendero F, Robledo P, Maldonado R. The endogenous opioid system: a common substrate in drug addiction. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2010) 108:183–94. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.10.011
153. Leeman RF, Potenza MN. A targeted review of the neurobiology and genetics of behavioural addictions: an emerging area of research. Can J Psychiatry. (2013) 58:260–73. doi: 10.1177/070674371305800503
154. Fields HL, Margolis EB. Understanding opioid reward. Trends Neurosci. (2015) 38:217–25. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2015.01.002
155. Laurent V, Morse AK, Balleine BW. The role of opioid processes in reward and decision-making. Br J Pharmacol. (2015) 172:449–59. doi: 10.1111/bph.2015.172.issue-2
156. Raynor K, Kong H, Chen Y, Yasuda K, Yu L, Bell GI, et al. Pharmacological characterization of the cloned kappa-, delta-, and mu-opioid receptors. Mol Pharmacol. (1994) 45:330–4.
157. Conway SM, Mikati MO, Al-Hasani R. Challenges and new opportunities for detecting endogenous opioid peptides in reward. Addict Neurosci. (2022) 2:100016. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100016
158. Boyadjieva NI, Sarkar DK. Effects of ethanol on basal and prostaglandin E1-induced increases in beta-endorphin release and intracellular cAMP levels in hypothalamic cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. (1997) 21:1005–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1997.tb04245.x
159. Johansson P, Ray A, Zhou Q, Huang W, Karlsson K, Nyberg F. Anabolic androgenic steroids increase beta-endorphin levels in the ventral tegmental area in the male rat brain. Neurosci Res. (1997) 27:185–9. doi: 10.1016/S0168-0102(96)01141-8
160. Olive MF, Koenig HN, Nannini MA, Hodge CW. Stimulation of endorphin neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens by ethanol, cocaine, and amphetamine. J Neurosci. (2001) 21:RC184. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-23-j0002.2001
161. Christensson-Nylander I, Herrera-Marschitz M, Staines W, Hokfelt T, Terenius L, Ungerstedt U, et al. Striato-nigral dynorphin and substance P pathways in the rat. I. Biochemical and immunohistochemical studies. Exp Brain Res. (1986) 64:169–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00238213
162. Lugo JN Jr., Wilson MA, Kelly SJ. Perinatal ethanol exposure alters met-enkephalin levels of male and female rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol. (2006) 28:238–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2005.12.004
163. Abate P, Hernandez-Fonseca K, Reyes-Guzman AC, Barbosa-Luna IG, Mendez M. Prenatal ethanol exposure alters met-enkephalin expression in brain regions related with reinforcement: possible mechanism for ethanol consumption in offspring. Behav Brain Res. (2014) 274:194–204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.08.022
164. Wille-Bille A, Bellia F, Jimenez Garcia AM, Miranda-Morales RS, D’Addario C, Pautassi RM. Early exposure to environmental enrichment modulates the effects of prenatal ethanol exposure upon opioid gene expression and adolescent ethanol intake. Neuropharmacology. (2020) 165:107917. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107917
165. Wang H, Flores RJ, Yarur HE, Limoges A, Bravo-Rivera H, Casello SM, et al. Prefrontal cortical dynorphin peptidergic transmission constrains threat-driven behavioral and network states. bioRxiv. (2024) 112:2062–78.e7. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.08.574700
166. Roland AV, Harry Chao TH, Hon OJ, Machinski SN, Sides TR, Lee SI, et al. Acute and chronic alcohol modulation of extended amygdala calcium dynamics. Alcohol. (2024) 116:53–64. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2024.02.004
167. Carboni L, Romoli B, Romualdi P, Zoli M. Repeated nicotine exposure modulates prodynorphin and pronociceptin levels in the reward pathway. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2016) 166:150–8. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.07.002
168. Hernandez J, Perez L, Soto R, Le N, Gastelum C, Wagner EJ. Nociceptin/orphanin FQ neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus and Ventral Tegmental Area Act via Nociceptin Opioid Peptide Receptor Signaling to Inhibit Proopiomelanocortin and A(10) Dopamine Neurons and Thereby Modulate Ingestion of Palatable Food. Physiol Behav. (2021) 228:113183. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.113183
169. Casello SM, Flores RJ, Yarur HE, Wang H, Awanyai M, Arenivar MA, et al. Neuropeptide system regulation of prefrontal cortex circuitry: implications for neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Neural Circuits. (2022) 16:796443. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.796443
170. Devi L, Goldstein A. Conversion of leumorphin (dynorphin B-29) to dynorphin B and dynorphin B-14 by thiol protease activity. J Neurochem. (1986) 47:154–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb02843.x
171. Gomes I, Sierra S, Lueptow L, Gupta A, Gouty S, Margolis EB, et al. Biased signaling by endogenous opioid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2020) 117:11820–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000712117
172. Fricker LD, Margolis EB, Gomes I, Devi LA. Five decades of research on opioid peptides: current knowledge and unanswered questions. Mol Pharmacol. (2020) 98:96–108. doi: 10.1124/mol.120.119388
173. Reinscheid RK NH, Bourson A, Ardati A, Henningsen RA, Bunzow JR, Grandy DK, et al. Orphanin FQ: a neuropeptide that activates an opioidlike G protein-coupled receptor. Sci 1995. (1979) 270:792–4. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5237.792
174. Rossi GC, Leventhal L, Bolan E, Pasternak GW. Pharmacological characterization of orphanin FQ/nociceptin and its fragments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (1997) 282:858–65. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3565(24)36828-4
175. Herz A. Endogenous opioid systems and alcohol addiction. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (1997) 129:99–111. doi: 10.1007/s002130050169
176. Pan ZZ. mu-Opposing actions of the kappa-opioid receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (1998) 19:94–8. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(98)01169-9
177. Le Merrer J, Becker JA, Befort K, Kieffer BL. Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol Rev. (2009) 89:1379–412. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00005.2009
178. Narendran R, Tollefson S, Himes ML, Paris J, Lopresti B, Ciccocioppo R, et al. Nociceptin receptors upregulated in cocaine use disorder: A positron emission tomography imaging study using [(11)C]NOP-1A. Am J Psychiatry. (2019) 176:468–76. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18081007
179. Shinohara K, Yanagisawa A, Kagota Y, Gomi A, Nemoto K, Moriya E, et al. Physiological changes in Pachinko players; beta-endorphin, catecholamines, immune system substances and heart rate. Appl Hum Sci. (1999) 18:37–42. doi: 10.2114/jpa.18.37
181. Majuri J, Joutsa J, Arponen E, Forsback S, Kaasinen V. Dopamine synthesis capacity correlates with micro-opioid receptor availability in the human basal ganglia: A triple-tracer PET study. Neuroimage. (2018) 183:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.07.069
182. Bonci A, Williams JT. Increased probability of GABA release during withdrawal from morphine. J Neurosci. (1997) 17:796–803. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-02-00796.1997
183. Koob GF, Volkow ND. Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2010) 35:217–38. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.110
184. George SR, Van Loon GR. beta-Endorphin alters dopamine uptake by the dopamine neurons of the hypothalamus and striatum. Brain Res. (1982) 248:293–303. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90587-X
185. Ronken E, Mulder AH, Schffelmeer ANM. Interacting presynaptic k-opioid and GABAA receptors modulate dopamine release from rat striatal synaptosomes. J Neurochemistry. (1993) 61:1634–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb09797.x
186. Bullock SA, Potenza MN. Pathological gambling: neuropsychopharmacology and treatment. Curr Psychopharmacol. (2012) 1:10.2174/2211556011201010067. doi: 10.2174/2211557911201010067
187. Kim SW, Grant JE, Adson DE, Shin YC. Double-blind naltrexone and placebo comparison study in the treatment of pathological gambling. Biol Psychiatry. (2001) 49:914–21. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(01)01079-4
188. Grant JE, Potenza MN, Hollander E, Cunningham-Williams R, Nurminen T, Smits G, et al. Multicenter investigation of the opiod antagonist nalmefene in the treatment of pathological gambling. Am J Psychiatry. (2006) 63:303–12. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.163.2.303
189. Grant JE, Kim SW, Hartman BK. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the opiate antagonist naltrexone in the treatment of pathological gambling urges. J Clin Psychiatry. (2008) 69:783–9. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v69n0511
190. Grant JE, Odlaug BL, Potenza MN, Hollander E, Kim SW. Nalmefene in the treatment of pathological gambling: multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Psychiatry. (2010) 197:330–1. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.110.078105
191. Grant JE, Kim SW. A case of kleptomania and compulsive sexual behavior treated with naltrexone. Ann Clin Psychiatry. (2001) 13:229–31. doi: 10.3109/10401230109147386
192. Raymond NC, Grant JE, Coleman E. Augmentation with naltrexone to treat compulsive sexual behavior: a case series. Ann Clin Psychiatry. (2010) 22:56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.amp.2009.11.002
193. Bostwick JM, Bucci JA. Internet sex addiction treated with naltrexone. Mayo Clin Proc. (2008) 83:226–30. doi: 10.1016/S0025-6196(11)60846-X
194. Yazdi K, Fuchs-Leitner I, Gerstgrasser NW. Nalmefene in the treatment of internet pornography addiction - A case report and review of literature. J Addict Med. (2020) 14:348–51. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000602
195. Martin DL, Rimvall K. Regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in the brain. J Neurochem. (1993) 60:395–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03165.x
196. Oketch-Rabah HA, Madden EF, Roe AL, Betz JM. United states pharmacopeia (USP) safety review of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Nutrients. (2021) 13:2742. doi: 10.3390/nu13082742
197. Morales M, Root DH. Glutamate neurons within the midbrain dopamine regions. Neuroscience. (2014) 282:60–8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.032
198. Sugita S, Johnson SW, North RA. Synaptic inputs to GABAA and GABAB receptors originate from discrete afferent neurons. Neurosci Lett. (1992) 134:207–11. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90518-C
199. Kalivas PW. Neurotransmitter regulation of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. (1993) 18:75–113. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(93)90008-N
200. Ciliax BJ, Drash GW, Staley JK, Haber S, Mobley CJ, Miller GW, et al. Immunocytochemical localization of the dopamine transporter in human brain. J Comp Neurol. (1999) 409:38–56. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19990621)409:1<38::AID-CNE4>3.0.CO;2-1
201. Vlachou S, Markou A. GABAB receptors in reward processes. Adv Pharmacol. (2010) 58:315–71. doi: 10.1016/S1054-3589(10)58013-X
202. Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N. Topiramate in the new generation of drugs: efficacy in the treatment of alcoholic patients. Curr Pharm Des. (2010) 16:2103–12. doi: 10.2174/138161210791516404
203. Namkoong K, Cheon KA, Kim JW, Jun JY, Lee JY. Association study of dopamine D2, D4 receptor gene, GABAA receptor beta subunit gene, serotonin transporter gene polymorphism with children of alcoholics in Korea: a preliminary study. Alcohol. (2008) 42:77–81. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.01.004
204. Enoch MA, Baghal B, Yuan Q, Goldman D. A factor analysis of global GABAergic gene expression in human brain identifies specificity in response to chronic alcohol and cocaine exposure. PloS One. (2013) 8:e64014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064014
205. Weidacker K, Johnston SJ, Mullins PG, Boy F, Dymond S. Impulsive decision-making and gambling severity: The influence of gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA) and glutamate-glutamine (Glx). Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2020) 32:36–46. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2019.12.110
206. Mick I, Ramos AC, Myers J, Stokes PR, Chandrasekera S, Erritzoe D, et al. Evidence for GABA-A receptor dysregulation in gambling disorder: correlation with impulsivity. Addict Biol. (2017) 22:1601–9. doi: 10.1111/adb.2017.22.issue-6
207. Chowdhury NS, Livesey EJ, Blaszczynski A, Harris JA. Motor cortex dysfunction in problem gamblers. Addict Biol. (2021) 26:e12871. doi: 10.1111/adb.12871
208. Seo HS, Jeong EK, Choi S, Kwon Y, Park HJ, Kim I. Changes of neurotransmitters in youth with internet and smartphone addiction: A comparison with healthy controls and changes after cognitive behavioral therapy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. (2020) 41:1293–301. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6632
209. Lingford-Hughes A, Reid AG, Myers J, Feeney A, Hammers A, Taylor LG, et al. A [11C]Ro15 4513 PET study suggests that alcohol dependence in man is associated with reduced alpha5 benzodiazepine receptors in limbic regions. J Psychopharmacol. (2012) 26:273–81. doi: 10.1177/0269881110379509
210. Bush G, Luu P, Posner MI. Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cognit Sci. (2000) 4:215–22. doi: 10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01483-2
211. Zeeb FD, Baarendse PJ, Vanderschuren LJ, Winstanley CA. Inactivation of the prelimbic or infralimbic cortex impairs decision-making in the rat gambling task. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2015) 232:4481–91. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4075-y
212. Mizoguchi H, Katahira K, Inutsuka A, Fukumoto K, Nakamura A, Wang T, et al. Insular neural system controls decision-making in healthy and methamphetamine-treated rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:E3930–3939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1418014112
213. Maccioni P, Colombo G. Role of the GABA(B) receptor in alcohol-seeking and drinking behavior. Alcohol. (2009) 43:555–8. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.09.030
214. Fattore L, Spano MS, Cossu G, Scherma M, Fratta W, Fadda P. Baclofen prevents drug-induced reinstatement of extinguished nicotine-seeking behaviour and nicotine place preference in rodents. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2009) 19:487–98. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2009.01.007
215. Xi ZX, Stein EA. GABAergic mechanisms of opiate reinforcement. Alcohol Alcohol. (2002) 37:485–94. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/37.5.485
216. Hillarp NA, Fuxe K, Dahlstrom A. Demonstration and mapping of central neurons containing dopamine, noradrenaline, and 5-hydroxytryptamine and their reactions to psychopharmaca. Pharmacol Rev. (1966) 18:727–41. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015156
217. Yim CY, Mogenson GJ. Effect of picrotoxin and nipecotic acid on inhibitory response of dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area to stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. Brain Res. (1980) 199:466–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90705-2
218. Bae S, Han DH, Kim SM, Shi X, Renshaw PF. Neurochemical correlates of internet game play in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) study. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. (2016) 254:10–7. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2016.05.006
219. Mateo Y, Johnson KA, Covey DP, Atwood BK, Wang HL, Zhang S, et al. Endocannabinoid actions on cortical terminals orchestrate local modulation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Neuron. (2017) 96:1112–1126 e1115. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.012
220. Nussbaum D, Honarmand K, Govoni R, Kalahani-Bargis M, Bass S, Ni X, et al. An eight component decision-making model for problem gambling: a systems approach to stimulate integrative research. J Gambl Stud. (2011) 27:523–63. doi: 10.1007/s10899-010-9219-8
221. Stahl SM. Essential psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific basis and practical applications. 3rded. New York: Cambridge University Press (2008).
222. Kalivas PW, Volkow ND. The neural basis of addiction: a pathology of motivation and choice. Am J Psychiatry. (2005) 162:1403–13. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.162.8.1403
223. Perlov E, Philipsen A, Matthies S, Drieling T, Maier S, Bubl E, et al. Spectroscopic findings in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: review and meta-analysis. World J Biol Psychiatry. (2009) 10:355–65. doi: 10.1080/15622970802176032
224. Kuss DJ. Internet gaming addiction: current perspectives. Psychol Res Behav Manag. (2013) 6:125–37. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S39476
225. Nordin C, Gupta RC, Sjodin I. Cerebrospinal fluid amino acids in pathological gamblers and healthy controls. Neuropsychobiology. (2007) 56:152–8. doi: 10.1159/000115782
226. Olive MF, Cleva RM, Kalivas PW, Malcolm RJ. Glutamatergic medications for the treatment of drug and behavioral addictions. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. (2012) 100:801–10. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.04.015
227. Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND. Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry. (2002) 159:1642–52. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.10.1642
228. Moran MM, McFarland K, Melendez RI, Kalivas PW, Seamans JK. Cystine/glutamate exchange regulates metabotropic glutamate receptor presynaptic inhibition of excitatory transmission and vulnerability to cocaine seeking. J Neurosci. (2005) 25:6389–93. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1007-05.2005
229. Barker JM, Taylor JR, De Vries TJ, Peters J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and addiction: Pathological versus therapeutic effects on drug seeking. Brain Res. (2015) 1628:68–81. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.058
230. Baker DA, McFarland K, Lake RW, Shen H, Toda S, Kalivas PW. N-acetyl cysteine-induced blockade of cocaine-induced reinstatement. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2003) 1003:349–51. doi: 10.1196/annals.1300.023
231. Grant JE, Kim SW, Odlaug BL. N-acetyl cysteine, a glutamate-modulating agent, in the treatment of pathological gambling: a pilot study. Biol Psychiatry. (2007) 62:652–7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.11.021
232. Knackstedt LA, LaRowe S, Mardikian P, Malcolm R, Upadhyaya H, Hedden S, et al. The role of cystine-glutamate exchange in nicotine dependence in rats and humans. Biol Psychiatry. (2009) 65:841–5. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.040
233. Singh A, Singh G, Singh S, Kazi SE, Gill M. N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of internet gaming disorder. Cureus. (2022) 14:e28662. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28662
234. Yates JR, Batten SR, Bardo MT, Beckmann JS. Role of ionotropic glutamate receptors in delay and probability discounting in the rat. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2015) 232:1187–96. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3747-3
235. Grant JE, Chamberlain SR, Odlaug BL, Potenza MN, Kim SW. Memantine shows promise in reducing gambling severity and cognitive inflexibility in pathological gambling: a pilot study. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2010) 212:603–12. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-1994-5
236. Black DW. An open-label trial of bupropion in the treatment of pathologic gambling.24(1), 108–110. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2004) 24:108–10. doi: 10.1097/01.jcp.0000114844.58996.4a
237. Raj YP. Gambling on acamprosate: a case report. J Clin Psychiatry. (2010) 71:1245–6. doi: 10.4088/JCP.10l06059ecr
238. Pettorruso M, Martinotti G, Di Nicola M, Onofrj M, Di Giannantonio M, Conte G, et al. Amantadine in the treatment of pathological gambling: a case report. Front Psychiatry. (2012) 3:102. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00102
239. Black DW, Shaw MC, Allen J. Extended release carbamazepine in the treatment of pathological gambling: an open-label study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2008) 32:1191–4. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.02.013
240. Haller R, Hinterhuber H. Treatment of pathological gambling with carbamazepine. Pharmacopsychiatry. (1994) 27:129. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1014292
241. Kaminski RM, Banerjee M, Rogawski MA. Topiramate selectively protects against seizures induced by ATPA, a GluR5 kainate receptor agonist. Neuropharmacology. (2004) 46:1097–104. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.02.010
242. Nicolato R, Romano-Silva MA, Correa H, Salgado JV, Teixeira AL. Lithium and topiramate association in the treatment of comorbid pathological gambling and bipolar disorder. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. (2007) 41:628. doi: 10.1080/00048670701400040
243. Khazaal Y, Zullino DF. Topiramate in the treatment of compulsive sexual behavior: case report. BMC Psychiatry. (2006) 6:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-6-22
244. Nicoli de Mattos C, Kim HS, Marasaldi RF, Requiao MG, de Oliveira EC, Zambrano Filomensky T, et al. A 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of topiramate for the treatment of compulsive buying disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2020) 40:186–90. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000001183
245. Kryger R, Wilce PA. The effects of alcoholism on the human basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience. (2010) 167:361–71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.061
246. Kim JH, Do SH, Kim YL, Zuo Z. Effects of chronic exposure to ethanol on glutamate transporter EAAT3 expressed in Xenopus oocytes: evidence for protein kinase C involvement. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. (2005) 29:2046–52. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000187594.92476.07
247. Flatscher-Bader T, Wilce PA. Impact of alcohol abuse on protein expression of midkine and excitatory amino acid transporter 1 in the human prefrontal cortex. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. (2008) 32:1849–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00754.x
248. Zhou FC, Sahr RN, Sari Y, Behbahani K. Glutamate and dopamine synaptic terminals in extended amygdala after 14-week chronic alcohol drinking in inbred alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol. (2006) 39:39–49. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2006.06.013
249. Mark KA, Quinton MS, Russek SJ, Yamamoto BK. Dynamic changes in vesicular glutamate transporter 1 function and expression related to methamphetamine-induced glutamate release. J Neurosci. (2007) 27:6823–31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0013-07.2007
250. Kuo HI, Paulus W, Batsikadze G, Jamil A, Kuo MF, Nitsche MA. Acute and chronic noradrenergic effects on cortical excitability in healthy humans. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2017) 20:634–43. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx026
251. Kerfoot EC, Chattillion EA, Williams CL. Functional interactions between the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) and nucleus accumbens shell in modulating memory for arousing experiences. Neurobiol Learn Mem. (2008) 89:47–60. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2007.09.005
252. Blaszczynski AP, Winter SW, McConaghy N. Plasma endorphin levels in pathological gambling. J Gambling Behav. (1986) 2:3–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01019930
253. Roy A, Adinoff B, Roehrich L, Lamparski D, Custer R, Lorenz V, et al. Pathological gambling: A psychobiological study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (1988) 45:369–73. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800280085011
254. Meyer G, Schwertfeger J, Exton MS, Janssen OE, Knapp W, Stadler MA, et al. Neuroendocrine response to casino gambling in problem gamblers. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2004) 29:1272–80. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2004.03.005
255. Hassall CD, McDonald CG, Krigolson OE. Ready, set, explore! Event-related potentials reveal the time-course of exploratory decisions. Brain Res. (2019) 1719:183–93. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.05.039
256. Zhang HX, Jiang WQ, Lin ZG, Du YS, Vance A. Comparison of psychological symptoms and serum levels of neurotransmitters in Shanghai adolescents with and without internet addiction disorder: a case-control study. PloS One. (2013) 8:e63089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063089
257. Kim N, Kim MJ, Hughes TL, Kwak H, Kong ID. Relationships of internet gaming reasons to biological indicators and risk of internet gaming addiction in Korean adolescent male game users. BMC Psychiatry. (2020) 20:341. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02714-w
258. Wiers RW, Bartholow BD, van den Wildenberg E, Thush C, Engels RC, Sher KJ, et al. Automatic and controlled processes and the development of addictive behaviors in adolescents: a review and a model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. (2007) 86:263–83. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2006.09.021
259. Di Ciano P, Manvich DF, Pushparaj A, Gappasov A, Hess EJ, Weinshenker D, et al. Effects of disulfiram on choice behavior in a rodent gambling task: association with catecholamine levels. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2018) 235:23–35. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4744-0
260. Mutschler J, Buhler M, Diehl A, Mann K, Kiefer F. Disulfiram, an old drug with new potential in the treatment of pathological gambling? Med Hypotheses. (2010) 74:209–10. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.07.007
261. Muller CA, Banas R, Heinz A, Hein J. Treatment of pathological gambling with disulfiram: a report of 2 cases. Pharmacopsychiatry. (2011) 44:81–3. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1271683
262. Chernoff CS, Hynes TJ, Winstanley CA. Noradrenergic contributions to cue-driven risk-taking and impulsivity. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2021) 238:1765–79. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05806-x
263. Zack M, Poulos CX. Effects of the atypical stimulant modafinil on a brief gambling episode in pathological gamblers with high vs. low impulsivity. J Psychopharmacol. (2009) 23:660–71. doi: 10.1177/0269881108091072
264. Pallanti S, Bernardi S, Allen A, Chaplin W, Watner D, DeCaria CM, et al. Noradrenergic function in pathological gambling: blunted growth hormone response to clonidine. J Psychopharmacol. (2010) 24:847–53. doi: 10.1177/0269881108099419
265. Elman I, Becerra L, Tschibelu E, Yamamoto R, George E, Borsook D. Yohimbine-induced amygdala activation in pathological gamblers: a pilot study. PloS One. (2012) 7:e31118. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031118
266. Cocker PJ, Lin MY, Tremblay M, Kaur S, Winstanley CA. The beta-adrenoceptor blocker propranolol ameliorates compulsive-like gambling behaviour in a rodent slot machine task: implications for iatrogenic gambling disorder. Eur J Neurosci. (2019) 50:2401–14. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14070
267. Rogers RD, Lancaster M, Wakeley J, Bhagwagar Z. Effects of beta-adrenoceptor blockade on components of human decision-making. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2004) 172:157–64. doi: 10.1007/s00213-003-1641-5
268. Georgiou P, Zanos P, Bhat S, Tracy JK, Merchenthaler IJ, McCarthy MM, et al. Dopamine and stress system modulation of sex differences in decision making. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2018) 43:313–24. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.161
269. Park J, Sung JY, Kim DK, Kong ID, Hughes TL, Kim N. Genetic association of human Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor 1 (CRHR1) with Internet gaming addiction in Korean male adolescents. BMC Psychiatry. (2018) 18:396. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1974-6
270. Chatzittofis A, Arver S, Oberg K, Hallberg J, Nordstrom P, Jokinen J. HPA axis dysregulation in men with hypersexual disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2016) 63:247–53. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.10.002
271. Choi MR, Cho H, Chun JW, Yoo JH, Kim DJ. Increase of orexin A in the peripheral blood of adolescents with Internet gaming disorder. J Behav Addict. (2020) 9:93–104. doi: 10.1556/2006.8.2019.65
272. Wyckmans F, Banerjee N, Saeremans M, Otto R, Kornreich C, Vanderijst L, et al. The modulation of acute stress on model-free and model-based reinforcement learning in gambling disorder. J Behav Addict. (2022) 11:831–44. doi: 10.1556/2006.2022.00059
273. Tsumura H, Fukuda M, Kanda H. Blunted cortisol and normal sympathetic nervous system responses to an acute psychosocial stressor in internet addiction. Heliyon. (2022) 8:e12142. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12142
274. Balaganesh S, Balasubramaniam A, Indiran MA, Rathinavelu PK, Kumar MPS. Determination of salivary cortisol and salivary pH level in gaming teenagers - A cross-sectional study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. (2022) 12:838–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2022.09.005
275. van Timmeren T, Piray P, Goudriaan AE, van Holst RJ. Goal-directed and habitual decision making under stress in gambling disorder: An fMRI study. Addict Behav. (2023) 140:107628. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2023.107628
276. Betts GD, Hynes TJ, Winstanley CA. Pharmacological evidence of a cholinergic contribution to elevated impulsivity and risky decision-making caused by adding win-paired cues to a rat gambling task. J Psychopharmacol. (2021) 35:701–12. doi: 10.1177/0269881120972421
277. Silveira MM, Malcolm E, Shoaib M, Winstanley CA. Scopolamine and amphetamine produce similar decision-making deficits on a rat gambling task via independent pathways. Behav Brain Res. (2015) 281:86–95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.12.029
278. Pittaras EC, Faure A, Leray X, Moraitopoulou E, Cressant A, Rabat AA, et al. Neuronal nicotinic receptors are crucial for tuning of E/I balance in prelimbic cortex and for decision-making processes. Front Psychiatry. (2016) 7:171. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00171
279. Montag C, Kirsch P, Sauer C, Markett S, Reuter M. The role of the CHRNA4 gene in Internet addiction: a case-control study. J Addict Med. (2012) 6:191–5. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0b013e31825ba7e7
280. Jeong JE, Rhee JK, Kim TM, Kwak SM, Bang SH, Cho H, et al. The association between the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha4 subunit gene (CHRNA4) rs1044396 and Internet gaming disorder in Korean male adults. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0188358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188358
281. Bozorgmehr A, Alizadeh F, Sadeghi B, Shahbazi A, Norouzi Ofogh S, Joghataei MT, et al. Oxytocin moderates risky decision-making during the Iowa Gambling Task: A new insight based on the role of oxytocin receptor gene polymorphisms and interventional cognitive study. Neurosci Lett. (2019) 708:134328. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134328
282. Zebhauser PT, Macchia A, Gold E, Salcedo S, Burum B, Alonso-Alonso M, et al. Intranasal oxytocin modulates decision-making depending on outcome predictability-A randomized within-subject controlled trial in healthy males. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:3230. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123230
283. Sariyska BL R, Reuter M, Cheng C, Gnisci A, Kaliszewska-Czeremska K, Laconi S, et al. Internet use: Molecular influences of a functional variant on the OXTR gene, the motivation behind using the Internet, and cross-cultural specifics. Pers Individ Dif. (2016) 100:512. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2016.05.286
284. Kor A, Djalovski A, Potenza MN, Zagoory-Sharon O, Feldman R. Alterations in oxytocin and vasopressin in men with problematic pornography use: The role of empathy. J Behav Addict. (2022) 11:116–27. doi: 10.1556/2006.2021.00089
285. Matzeu A, Martin-Fardon R. Targeting the orexin system for prescription opioid use disorder. Brain Sci. (2020) 10:226. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10040226
286. Fadel J, Deutch AY. Anatomical substrates of orexin-dopamine interactions: lateral hypothalamic projections to the ventral tegmental area. Neuroscience. (2002) 111:379–87. doi: 10.1016/S0306-4522(02)00017-9
287. Sekste EA, Lebedev AA, Bychkov ER, Airapetov MI, Gramota KE, Thyssen IY, et al. Increase in the level of orexin receptor 1 (OX1R) mRNA in the brain structures of rats prone to impulsivity in behavior. BioMed Khim. (2021) 67:411–7. doi: 10.18097/PBMC
288. Hommel JD, Trinko R, Sears RM, Georgescu D, Liu ZW, Gao XB, et al. Leptin receptor signaling in midbrain dopamine neurons regulates feeding. Neuron. (2006) 51:801–10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.023
289. Kiefer F, Jahn H, Otte C, Demiralay C, Wolf K, Wiedemann K. Increasing leptin precedes craving and relapse during pharmacological abstinence maintenance treatment of alcoholism. J Psychiatr Res. (2005) 39:545–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2004.11.005
290. von der Goltz C, Koopmann A, Dinter C, Richter A, Rockenbach C, Grosshans M, et al. Orexin and leptin are associated with nicotine craving: a link between smoking, appetite and reward. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2010) 35:570–7. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.09.005
291. Chang DC, Piaggi P, Burkholder JE, Votruba SB, Krakoff J, Gluck ME. Higher insulin and higher body fat via leptin are associated with disadvantageous decisions in the Iowa gambling task. Physiol Behav. (2016) 167:392–8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.10.009
292. Geisel O, Hellweg R, Wiedemann K, Muller CA. Plasma levels of leptin in patients with pathological gambling, internet gaming disorder and alcohol use disorder. Psychiatry Res. (2018) 268:193–7. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.06.042
293. Onaolapo OJ, Onaolapo AY. Melatonin in drug addiction and addiction management: Exploring an evolving multidimensional relationship. World J Psychiatry. (2018) 8:64–74. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v8.i2.64
294. Vengeliene V, Noori HR, Spanagel R. Activation of melatonin receptors reduces relapse-like alcohol consumption. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2015) 40:2897–906. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.143
295. Takahashi TT, Vengeliene V, Spanagel R. Melatonin reduces motivation for cocaine self-administration and prevents relapse-like behavior in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl). (2017) 234:1741–8. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4576-y
296. Boulle F, van den Hove DL, Jakob SB, Rutten BP, Hamon M, van Os J, et al. Epigenetic regulation of the BDNF gene: implications for psychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. (2012) 17:584–96. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.107
297. Geisel O, Banas R, Hellweg R, Muller CA. Altered serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with pathological gambling. Eur Addict Res. (2012) 18:297–301. doi: 10.1159/000338281
298. Angelucci F, Martinotti G, Gelfo F, Righino E, Conte G, Caltagirone C, et al. Enhanced BDNF serum levels in patients with severe pathological gambling. Addict Biol. (2013) 18:749–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00411.x
299. Choi SW, Shin YC, Mok JY, Kim DJ, Choi JS, Suk-Hyun Hwang S. Serum BDNF levels in patients with gambling disorder are associated with the severity of gambling disorder and Iowa Gambling Task indices. J Behav Addict. (2016) 5:135–9. doi: 10.1556/2006.5.2016.010
300. Kibitov AO, Trusova AV, Chuprova NA, Solovieva MG, Grechaniy SV, Soldatkin VA, et al. An associations of possible genetic risk markers for Internet addiction with childhood trauma experience and personality traits in young adults: preliminary results. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. (2021) 121:77–83. doi: 10.17116/jnevro202112107177
301. Kim KM, Choi SW, Lee J, Kim JW. EEG correlates associated with the severity of gambling disorder and serum BDNF levels in patients with gambling disorder. J Behav Addict. (2018) 7:331–8. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.43
302. Geisel O, Banas R, Schneider M, Hellweg R, Muller CA. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with internet use disorder. Psychiatry Res. (2013) 209:525–8. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.12.020
303. Yoshimura T, Usui H, Takahashi N, Yoshimi A, Saito S, Aleksic B, et al. Association analysis of the GDNF gene with methamphetamine use disorder in a Japanese population. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2011) 35:1268–72. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2011.04.003
304. Ghitza UE, Zhai H, Wu P, Airavaara M, Shaham Y, Lu L. Role of BDNF and GDNF in drug reward and relapse: a review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2010) 35:157–71. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.11.009
305. Das A, Pagliaroli L, Vereczkei A, Kotyuk E, Langstieh B, Demetrovics Z, et al. Association of GDNF and CNTNAP2 gene variants with gambling. J Behav Addict. (2019) 8:471–8. doi: 10.1556/2006.8.2019.40
306. Jeong JE, Paik SH, Choi MR, Cho H, Choi JS, Choi SW, et al. Altered plasma levels of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with internet gaming disorder: A case-control, pilot study. Psychiatry Investig. (2019) 16:469–74. doi: 10.30773/pi.2019.04.02.2
307. Tan B, Browne CJ, Nobauer T, Vaziri A, Friedman JM, Nestler EJ. Drugs of abuse hijack a mesolimbic pathway that processes homeostatic need. bioRxiv. (2023) 384:eadk6742. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.03.556059
308. Choi EY, Franco D, Stapf CA, Gordin M, Chow A, Cover KK, et al. Inducible CRISPR epigenome systems mimic cocaine induced bidirectional regulation of nab2 and egr3. J Neurosci. (2023) 43:2242–59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1802-22.2022
309. Su Y, DePasquale M, Liao G, Buchler I, Zhang G, Byers S, et al. Membrane bound catechol-O-methytransferase is the dominant isoform for dopamine metabolism in PC12 cells and rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. (2021) 896:173909. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173909
310. Pico-Perez M, Costumero V, Verdejo-Roman J, Albein-Urios N, Martinez-Gonzalez JM, Soriano-Mas C, et al. Brain networks alterations in cocaine use and gambling disorders during emotion regulation. J Behav Addict. (2022) 11:373–85. doi: 10.1556/2006.2022.00018
311. Yin Q, Chen T, Long Y, Zhai J, Liu X, Liu W, et al. Neurophysiological correlates of trait and behavioral impulsivity across methamphetamine and gambling Addiction. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e40212. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40212
312. Pettorruso M, Martinotti G, Montemitro C, De Risio L, Spagnolo PA, Gallimberti L, et al. Multiple sessions of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation as a potential treatment for gambling addiction: A 3-month, feasibility study. Eur Addict Res. (2020) 26:52–6. doi: 10.1159/000504169
Keywords: behavioral addictive disorders, reward circuit, neurotransmitters, dopamine, crosstalk
Citation: Peng Z, Jia Q, Mao J, Luo X, Huang A, Zheng H, Jiang S, Ma Q, Ma C and Yi Q (2025) Neurotransmitters crosstalk and regulation in the reward circuit of subjects with behavioral addiction. Front. Psychiatry 15:1439727. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1439727
Received: 28 May 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 14 January 2025.
Edited by:
Giovanni Martinotti, University of Studies G. d’Annunzio Chieti and Pescara, ItalyReviewed by:
Kabirullah Lutfy, Western University of Health Sciences, United StatesValerio Ricci, San Luigi Gonzaga University Hospital, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Jia, Mao, Luo, Huang, Zheng, Jiang, Ma, Ma and Yi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qizhong Yi, cWl6aG9uZ3lpQDEyNi5jb20=; Chuang Ma, MTUxNjE3NTkxOUBxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhenlei Peng
Zhenlei Peng Qiyu Jia
Qiyu Jia Junxiong Mao1
Junxiong Mao1 Hao Zheng
Hao Zheng Qi Ma
Qi Ma Chuang Ma
Chuang Ma