- 1College of Agriculture, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China
- 2Guizhou Institute of Oil Crops, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, China
- 3Hunan University of Humanities, Science and Technology, College of Agriculture and Biotechnology, Loudi, China
Introduction: Brassica juncea is a major oilseed crop of Brassica. The seed weight is one of yield components in oilseed Brassica crops. Research on the genetic mechanism of seed weight is not only directly related to the yield and economic value of Brassica juncea but also can provide a theory foundation for studying other Brassica crops.
Methods: To map the genes for seed weight, the parental and F2 extreme bulks derived were constructed from the cross between the heavy-seeded accession 7981 and the light-seeded one Sichuan yellow (SY) of B. juncea, and used in bulk segregant sequencing (BSA-seq). Meanwhile, RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) was performed for both parents at six seed development stages.
Results: Our results showed that a total of thirty five SNPs were identified in thirty two genes located on chromosomes A02 and A10, while fifty eight InDels in fifty one genes located on A01, A03, A05, A07, A09, A10, B01, B02 and B04. The 7,679 differentially expressed genes were identified in developing seeds between the parents. Furthermore, integrated analysis of BSA-seq and RNA-seq data revealed a cluster of nine genes on chromosome A10 and one gene on chromosome A05 that are putative candidate genes controlling seed weight in B. juncea.
Discussion: This study provides a new reference for research on Brassica seed weight and lays a solid foundation for the examination of seed in other Brassica crops.
1 Introduction
Brassica juncea is widely grown as an oilseed in China, India, Bangladesh, Ukraine, Canada and Australia (Carruthers et al., 2017; Kaur et al., 2020; Pal et al., 2021). Furthermore, this species is an important vegetable in China and is used as a condiment. B. juncea plants exhibit resistance to drought, poor soil, disease and insects and are adapted to hot, dry regions (Tian et al., 2017).
Seed weight, measured by thousand seed weight (TSW), is one of yield components in oilseed Brassica crops. Therefore, enhanced TSW is the direct way to increase yield (Gegas et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2022). Seed weight is reminiscent of seed size and seed fullness. Cytologically, seed development is regulated mainly by a combination of cell proliferation and cell enlargement (Sundaresan, 2005) and requires the synergistic growth of the embryo, endosperm and seed coat (Baud et al., 2008; Borisjuk et al., 2013). The maternal tissue can influence seed size through the regulation of transcription factor, ubiquitination, G protein and hormone signaling pathways, among others (Li and Li, 2016; Li et al., 2019). Seed weight is a quantitative trait controlled by multiple genes and influenced by genotype and environmental conditions (Yadava et al., 2012). The emergence of molecular markers, single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) chips and other technologies has greatly promoted the mapping of complex quantitative traits such as TSW (Dhaka et al., 2017; Li et al., 2014). The three QTLs (Quantitative Trait Loci) for TSW were identified on chromosome A07, C07 and C09 in B. napus, respectively (Quijada et al., 2006). The thirty four QTLs for TSW were also identified using DH populations, and SSR and AFLP markers (Basunanda et al., 2010). In addition, GWAS analysis identified the 320 SNPs linked with seed weight trait using 257 genotyped inbred rapeseed cultivars (Dong et al., 2018; Salami et al., 2024). However, the few loci for TSW have been cloned in Brassica species. Liu et al. successfully cloned the first TSW gene, ARF18, which controls both silique length and TSW (Liu et al., 2015). The gene ARF18 promotes silique elongation, increases pod wall photosynthetic area, and therefore enhances TSW in rapeseed (Liu et al., 2015). Shi et al. have isolated the gene BnaA9.CYP78A9D which encodes a P450 monooxygenase that regulates the silique length by promoting cell elongation (Shi et al., 2019).Bulk segregant sequencing (BSA-seq) has been used to detect the allele frequency (AF) of SNPs and insertion-deletions (InDels) by constructing DNA pools of both parents and their F2 progenies with extreme values and thus identifying the associated genes (Gao et al., 2022). Using BSA-seq, Meng et al (Meng et al., 2023). located the candidate region associated with trichome traits and identified the candidate gene in B. juncea. Transcriptomic analysis using RNA-seq involves the study of gene expression at the RNA level. It is an important tool for studying the correlation between cell phenotype and gene function. Dynamic transcriptome analysis of varieties with contrasting seed sizes was used to identify the candidate genes associated with seed growth in B. napus and B. rapa (Geng et al., 2018; Niu et al., 2020). Recently, Shikha et al. performed comparative transcriptome analysis between two lines of Brassica juncea, small-seeded EG-2 and large-seeded PJ, at the initial stages of seed development and identified candidate genes regulating the cell cycle, cell wall biogenesis/modification, solute/sugar transport, and hormone signaling (Mathur et al., 2022). Moreover, transcriptomic analysis revealed that cell cycle-related genes play a key role in determining the seed size of B. juncea (Dhaka et al., 2022). However, the molecular regulatory mechanism of seed weight in Brassica species has not been fully elucidated.
In this study, we used the heavy- and light- seed accessions 7981 and Sichuan Yellow as parents to construct an F2 segregating population of B. juncea. Both parents and the bulks of the F2 progenies with extreme values were subjected to BSA-seq to identify the candidate regions associated with TSW in B. juncea. Meanwhile, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified between the two parents via RNA-seq at different seed development stages. The combination of BSA-seq and RNA-seq identified candidate genes for determining seed weight in B. juncea.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant materials and phenotyping
Based on the preliminary examination of global oilseed mustard (Brassica juncea) accessions grown in Changsha (short-day autumn sowing), Guiyang (short-day autumn sowing), Kunming (long-day summer sowing), and Xinjiang (long-day spring sowing) in two consecutive years (2018 and 2019), two accessions, 7981 and Sichuan Yellow, which showed phenotypic differences in thousand seed weight (TSW) across regions in different years, were chosen as materials. In this study, we named 7981 and Sichuan Yellow as the large seed (LS) and the small seed (SS), respectively.
The F1 hybrids was obtained by crossing 7981 with Sichuan Yellow, and self-pollinated to get F2 progeny. About 3,000 F2 individual seedlings were grown in Guiyang. The young leaves were collected from each individual and stored at -80°C for use. At maturity, a total of 1000 seeds from each individual plant were counted by a seed count instrument (CONTADOR, Pfeuffer, Germany), and then weighed by an electronic scale (CONTADOR, Germany). The mean of three replicates was taken as the measured value of TSW.
ANOVA was used to compare significant differences between the two seed lines.
2.2 Library construction and BSA-seq
Thirty individuals with extreme heavy TSW and the same number of individuals with extreme light TSW were selected from F2 progeny and used for construction of F2 extreme bulks. Ten individual plants from each parent were used for construction of the parental bulks. The genomic DNA was extracted from each bulk using the modified cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) method (Clarke, 2009). The purity and integrity of the DNA were detected using a NanoDrop instrument (NanoDrop, DE) and agarose gel electrophoresis, respectively. The DNA was quantified by a Qubit Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher, MA). The libraries were prepared according to the standard protocol of Illumina and sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq2500 platform (Illumina, CA).
The clean reads obtained after removing the adapter from the raw reads were aligned to the B. juncea reference genome (Brassica juncea (L.) Czern & Coss, http://117.78.45.2:96/genomes/) using BWA (v. 0.7.15-r1140, Burrows−Wheeler-Aligner) (Li and Durbin, 2009). SAMtools (v. 1.3.1) was used to remove duplicates (Li et al., 2009). Then, the variant calling of SNPs and InDels was performed with GATK (McKenna et al., 2010). ANNOVAR was used to annotate the filtered SNP calls, and a high-quality SNP set was ultimately obtained (Wang et al., 2010).
2.3 Identification of candidate genes for TSW by analysis of allelic frequency difference
Based on genotyping results, SNPs with homozygous differences between two parents were screened. Then, the SNP-index (SNP frequency) of each F2 bulk was calculated in each screened SNPs using the parent as the reference. In order to reduce the impact of sequencing and mapping errors, the SNPs were filtered according to the SNP-index results, the filtration criteria are as follows: 1) the SNPs with SNP-index less than 0.3 and SNP depth less than 7 in both F2 individual pools, 2) a site where the SNP-index of F2 progenies is missing, filters it out. To directly reflect the distribution of SNP-index on chromosomes of each F2 individual, the distribution of SNP-index on chromosomes was mapped. The 1Mb is selected as the window and 1kb as the step size. The average SNP-index in each window is calculated to reflect the SNP-index distribution of the two F2 bulks. After calculating the SNP-index of each F2 individual in each SNP sites, the △(SNP-index) value of each variant was calculated via QTLseqr (R package). Then, the 1,000 permutation tests were performed and the 95% confidence interval (CI) selected as the threshold for screening the candidate region of TSW. The regions with △SNP-index) above the 95% CI were identified as candidate regions for TSW.
As above, based on genotyping results, the InDels of homozygous differences between two parents were screened. The missing sites of F2 bulks were filtered out to reduce the impact of sequencing and alignment errors. Then the InDel-index and △(InDel-index) were calculated using the above methods, and the regions with △(InDel-index) above the 95% CI were identified as candidate regions for TSW.
According to the annotation information of SNPs and InDels in candidate regions, sites causing stop loss or stop gain, non-synonymous mutations, variable splicing sites or frameshift mutations were preferentially selected, and the genes having these sites were selected as candidate genes.
2.4 RNA-seq library preparation and sequencing
The developing seeds were harvested for RNA-seq from both parents at 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40 days after pollination (DAP), referred to as stages S1, S2, S3, S4, S5 and S6, respectively. Three biological replicates were performed for each seed sample. The mRNA libraries were constructed from high-quality RNA samples using an NEBNext Ultra Directional RNA Library Prep Kit (NEB, UK) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and sequenced on a HiSeq 4000 (Illumina, San Diego) using a paired-end run (2 × 150 bp). The raw reads generated were filtered to remove adapter, poly-N and low-quality reads. Then, the clean paired-end reads were aligned to the above B. juncea reference genome using HISAT2 (v.2.1.0) with default parameters (Kim et al., 2015).
2.5 Identification and annotation of DEGs
The gene expression level was estimated by HTSeq (v.0.6.1), and an FPKM greater than 1 was used as a threshold for determining gene expression (Trapnell et al., 2012). Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between 7981 and Sichuan yellow at six seed developmental stages were identified using the DESeq2 package (Love et al., 2014). A DEG with a log2 ratio > 0 in the read count between two libraries was considered as upregulated expression, while a log2 ratio<0 was considered as downregulated expression. The DEGs were annotated by Gene Ontology (GO) functional enrichment using GOseq (v.2.12) (Young et al., 2010) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) functional enrichment using KOBAS (v. 2.0) (Kanehisa et al., 2008). DEGs were considered as significantly enriched if the adjusted P value was <0.05.
2.6 qRT−PCR validation of the DEGs
Differentially expressed genes were subjected to qPCR analysis using the Bio-Rad CFX96 Real-Time PCR System with a two-step protocol after total RNA extraction, quantification, qualification, and first-strand cDNA synthesis. The primers used for the qRT−PCR analysis is shown in Supplementary Table S1. The reaction program included an initial denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 10 s and annealing and extension at 60°C for 30 s. Each sample was run with three biological replicates. The expression level of the actin gene was used as an internal control. The relative expression levels of each gene were calculated with the 2–ΔΔCt method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001).
3 Results
3.1 Seed phenotype of two B. juncea parental accessions
The seed phenotype of both parents 7981 and Sichuan yellow (SY) was shown in Figure 1. As shown in Figure 1B, TSW of 7981 grown at four sites was heavier than that of Sichuan Yellow at two consecutive years. The mean TSW of Sichuan Yellow is 1.8g whereas that of 7981 is 3.7g over four sites in two years (Figure 1C). In addition, the seed size also exhibited significant differences between the parents (Figure 1A). Figure 1D showed the distribution of F2 progeny in TSW.
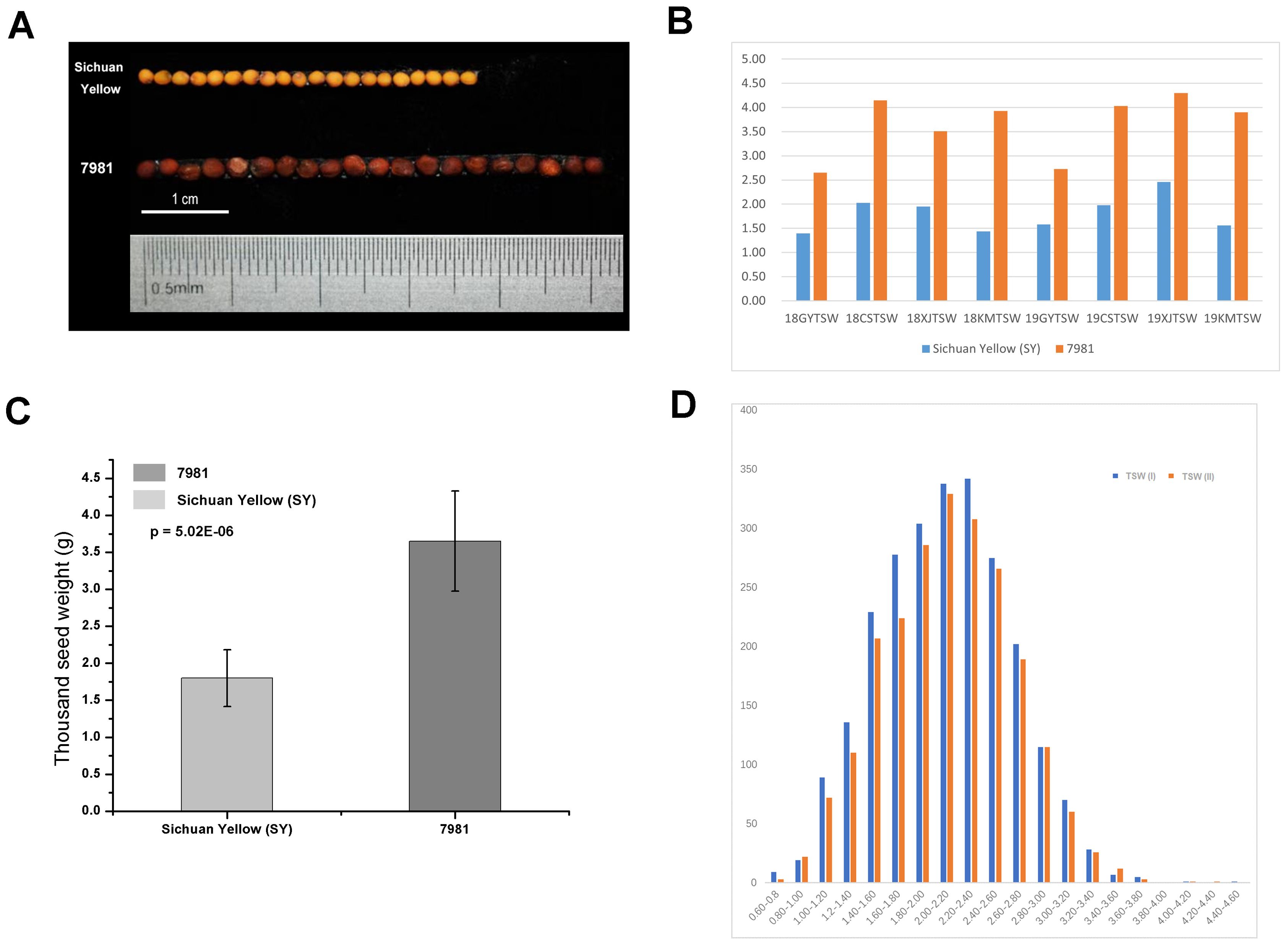
Figure 1. The phenotypic comparisons between the Brassica juncea accessions 7981 and Sichuan Yellow. (A) Comparisons in seed size and color in matured seeds of 7981 and Sichuan Yellow. (B) the TSW of two accessions grown in four geographical sites at two consecutive years (2018, 2019). e.g. the 18GYTSW in x axis means the seeds collected in Guiyang at 2018. (C) Comparison in TSW of matured seeds between 7981 and Sichuan Yellow. The measurement data are shown with standard error bars from four geographical sites at two years. The data are the means ± SE (n = 8). p value denotes a significant difference between two lines in TSW. (D) The frequency distribution in TSW of F2 individual plants.
3.2 Detection of SNPs and InDels by BSA-seq
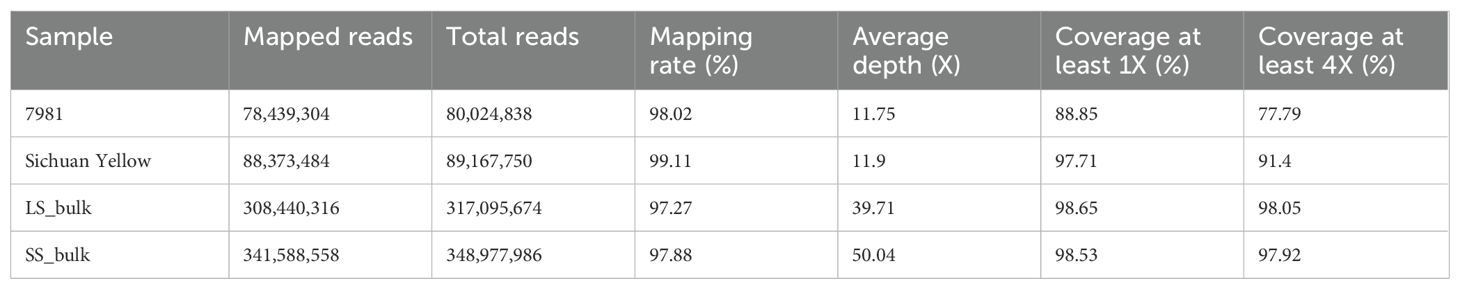
BSA-seq generated raw data of a total of 126,953,330,700 bp. After quality control, 125,289,937,200 bp of clean data were obtained. The guanine cytosine (GC) content of these clean reads ranged from 38.06% to 39.75%, and the quality of the sequencing data was high (Q20 ≥ 96.31%, Q30 ≥ 90.22%) (Supplementary Table S2). The clean reads were subsequently mapped against the reference genome, with a mapping rate ranging from 97.27% to 99.11% and an average coverage of 11× for both parents and approximately 40× for two F2 bulks. The degrees of coverage of 1× and 4× were 88.85% and 77.79%, respectively (Table 1).
A total of 4,801,126 SNPs and 1,063,911 InDels were called out using GATK 3.8 (Supplementary Table S3). Among them, 576,970 SNPs and 38,158 InDels were mapped to the exon regions using ANNOVAR, including 3,715 SNPs and 1,300 InDels in “Stop gain”, 842 SNPs and 144 InDels in “Stop loss”, 338,742 SNPs in “Synonymous”, 230,855 SNPs in “Nonsynonymous”, 11,159 InDels in “Frameshift deletion”, 10,136 InDels in “Frameshift insertion”, 7,868 InDels in “Nonframeshift deletion”, and 7,551 InDels in “Nonframeshift insertion” (Supplementary Table S3).
3.3 Identification of candidate genes for TSW in B. juncea
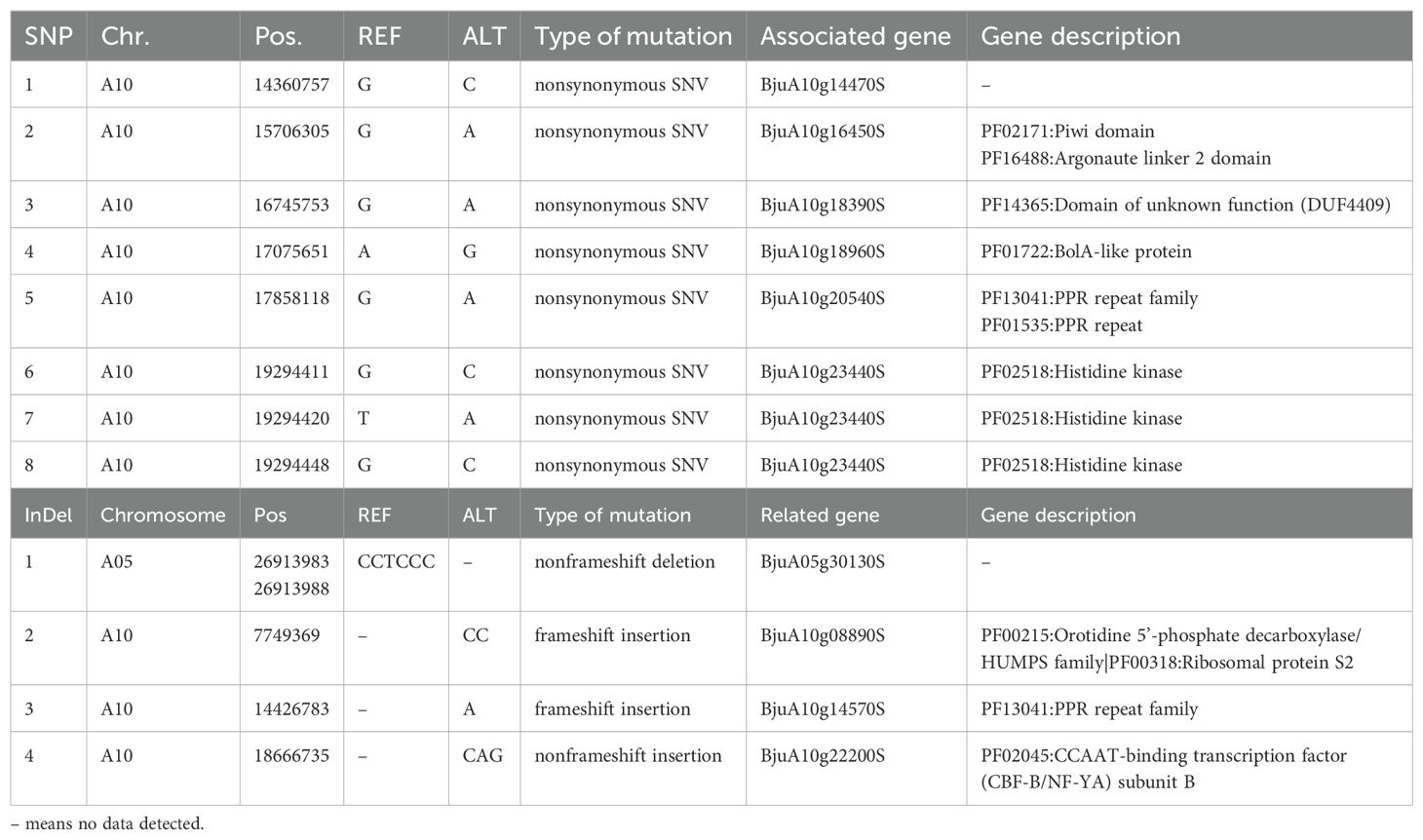
From the 822,583 SNPs with homozygous differences between two parents, we identified 817,134 SNPs with SNP-index values more than 0.3 and depths more than 7. The Manhattan map showed the distribution of SNP-index of each F2 bulk (Figure 2A). 120 SNPs on chromosomes A01, A02, A09, A10, B02 and B07 were identified with the △(SNP-index) value above the 95% CI (Supplementary Data Sheet S1). Annotation of these SNPs revealed that thirty-one SNPs were located in exons and these SNPs were distributed in chromosome A10, including eight synonymous mutations (Table 2, Supplementary Data Sheet S1). These eight nonsynonymous mutations were in six genes (BjuA10g14470S, BjuA10g16450S, BjuA10g18390S, BjuA10g18960S, BjuA10g20540S and BjuA10g23440S) (Table 1). Among these genes, BjuA10g16450S, BjuA10g18960S, BjuA10g20540S and BjuA10g23440S were annotated as a PIWI domain, a BolA-like protein, a PPR and a histidine kinase, respectively (Table 1). In addition, a total of 32 genes (30 genes in chromosome A10 and 2 genes in chromosome A02) harboring 35 significant SNPs were identified as candidate genes according to the annotation of candidate region of SNPs (Supplementary Data Sheet S2).
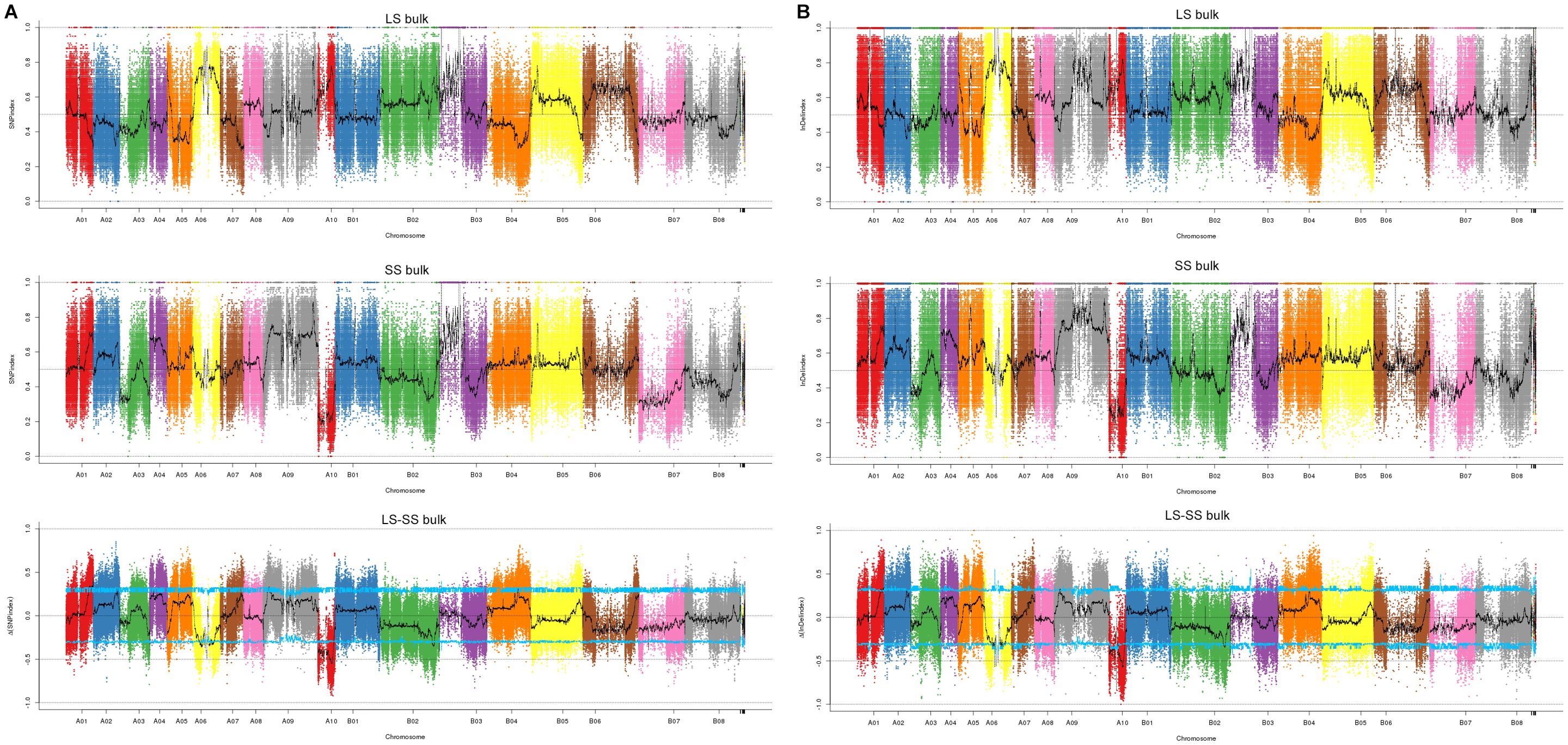
Figure 2. Distribution of SNP and InDel association values on chromosomes. (A) the distribution of SNPs. (B) the distribution of InDels. LS bulk means distribution of SNP- or InDel-index values of heaviest seed bulk on chromosomes, SS bulk means distribution of SNP- or InDel-index values of lightest seed bulk on chromosomes, LS-SS bulk means distribution of △ (SNP- or InDel-index) value on chromosomes, where the blue line represents the 95% CI threshold.
Similarly, 687,851 InDels were filtered out from 694,636 InDels. After calculating the InDel-index and △(InDel-index), the distribution of each bulk was presented in Manhattan map (Figure 2B). According to the △(InDel-index), 302 InDels were identified with the △(InDel-index) value above 95% CI (Supplementary Data Sheet S3). The annotation showed that four InDels were located within exons, including one frameshift insertion, one nonframeshift insertion and two nonframeshift deletions (Table 2, Supplementary Data Sheet S3). Among these InDels, three were located in three genes, namely, BjuA10g22200S (a CCAAT-binding transcription factor-encoding gene), BjuA10g14570S (a PPR repeat protein-encoding gene) and BjuA10g08890S (a ribosomal protein S2-encoding gene) (Table 2). The candidate gene analysis showed that fifty eight InDels significantly associated with TSW were distributed on chromosomes A01, A03, A05, A07, A09, A10, B01, B02, and B04, and located in 51 candidate genes (Supplementary Data Sheet S2).
3.4 Dynamic seed transcriptomic comparison between both B. juncea parents
To explore the seed weight-related genes in B. juncea, the seed transcriptomes were dynamically analyzed via RNA-seq. More than 1.66 ×109 raw reads were generated from thirty-six libraries, with an average of 6.79 Gb of clean reads for each sample and a Q30 of 92.7% across all samples (Supplementary Table S4). Mapping of the clean reads to the SY reference genome yielded a percentage of 90.89% (Supplementary Table S4).
3.5 Differentially expressed genes shared at various seed development stages between B. juncea parents
The genes that were differentially expressed were compared between both parents for each seed development stage. The highest number (44,176) and the lowest number (27,678) of DEGs were found between 7981 and SY at 15 and 30 DAP, respectively (Supplementary Table S5). 33,478, 29,078, 29,421 and 35,581 DEGs were detected at 20, 25, 35 and 40 DAP (Supplementary Table S5). The number of up- and down-regulated DEGs in the seeds at each stage between both parents is shown in Figure 3A.
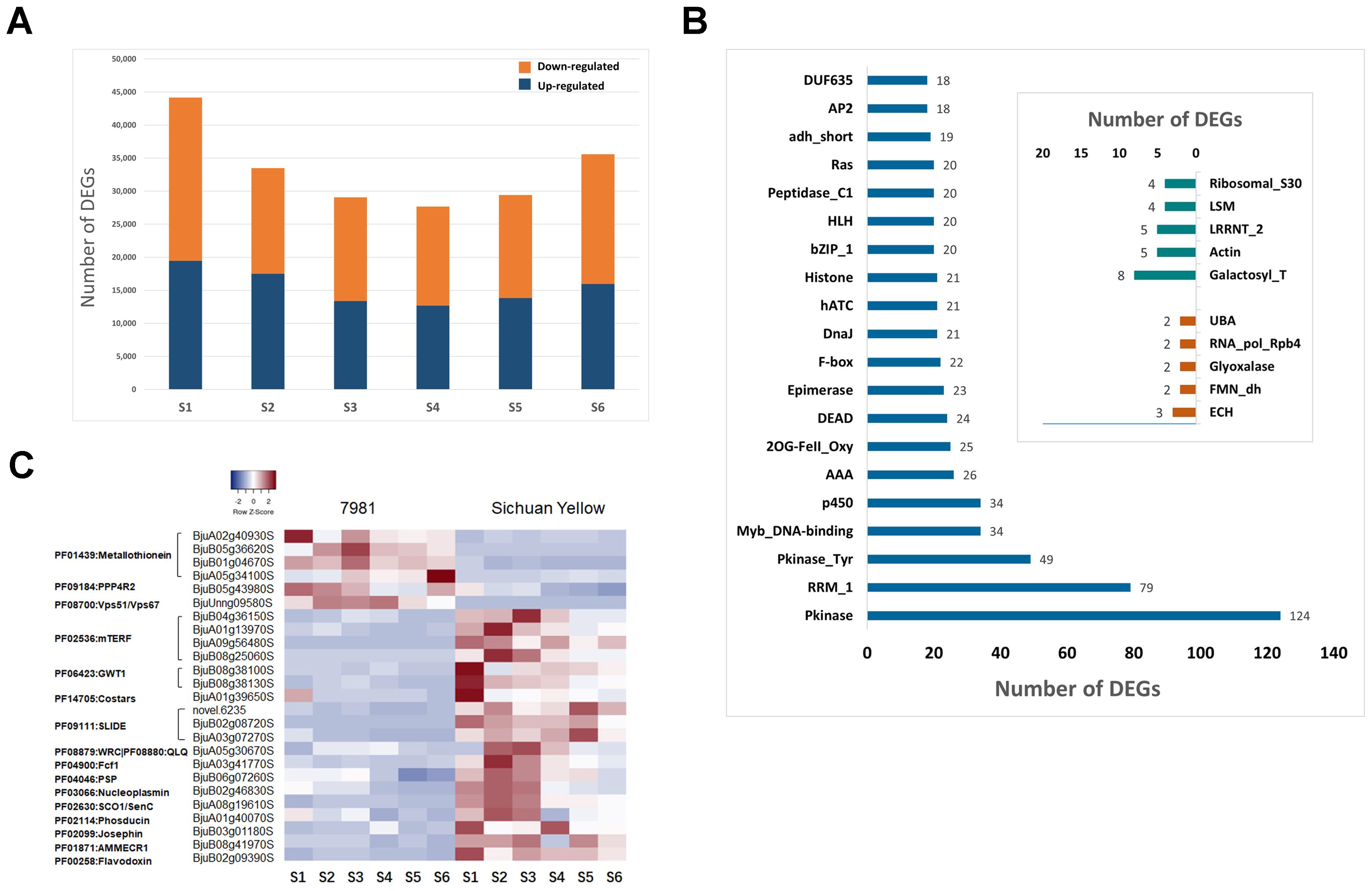
Figure 3. Analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) at six seed development stages. (A) The number of up- and down-regulated DEGs. (B) The Transcription factor gene family of the most DEG. (C) The heatmap of DEGs.
A total of 7,679 DEGs were shared with each seed developmental stage (Supplementary Data Sheet S4), among which 2,278 belonged to the transcription factor gene families, with the top 10 TFs being Pkinase, RRM_1, Pkinase Tyr, Myb_DNA-binding, p450, AAA, 2OG-FeII_Oxy, DEAD, Epimerase and F-box (Figure 3B). Except for these DEGs classified as TF family, the 2,792 of 7,679 DEGs were also annotated. Among these, there were 6 DEGs identified up-regulated and 19 DEGs down-regulated in accession 7981 at six development stages (Figure 3C). Gene annotation showed that the 6 DEGs were PF01439:Metallothionein and 2 DEGs annotated in PF09184:PPP4R2 and PF08700:Vps51/Vps67, and the 19 down-regulated DEGs were PF02536:mTERF, PF06423:GWT1, PF14705:Costars, PF09111:SLIDE, PF08879:WRC|PF08880:QLQ, PF08511:COQ9, PF04900:Fcf1, PF04046:PSP, PF03066:Nucleoplasmin, PF02630:SCO1/SenC, PF02114:Phosducin, PF02099:Josephin, PF01871:AMMECR1 and PF00258:Flavodoxin, respectively (Figure 3C).
To investigate the biological processes and pathways, these DEGs are involved in the Gene Ontology (GO) annotation and KEGG annotation were conducted (Figure 4). The top 5 most enriched GO and KEGG items by DEGs in six compared groups were further analyzed. A total of 61 GO items identified were classified into three categories of biological process, cellular component and molecular function (Figure 4A). In the biological process class, most of the DEGs were associated with ion transmembrane transport-, nucleotide-, purine-, pyridine- or ribosome-related processes. Among the cellular component terms, the GO terms “envelope”, “membrane coat”, “mitochondrial envelope”, “oxidoreductase complex”, “photosystem”, and “thylakoid” were most enriched. Among the molecular function terms, the significantly overrepresented items were protein heterodimerization activity, isomerase activity and motor activity (Figure 4A). KEGG annotation indicated that most of the DEGs were enriched in the ribosome, fatty acid biosynthesis, arginine biosynthesis and arginine and proline metabolism pathways 15~20 DAP, while the five pathways associated with the most enriched genes were photosynthesis, photosynthesis-antenna proteins, biosynthesis of amino acids, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, carbon metabolism, and carbon fixation 25-40 DAP (Figure 4B).
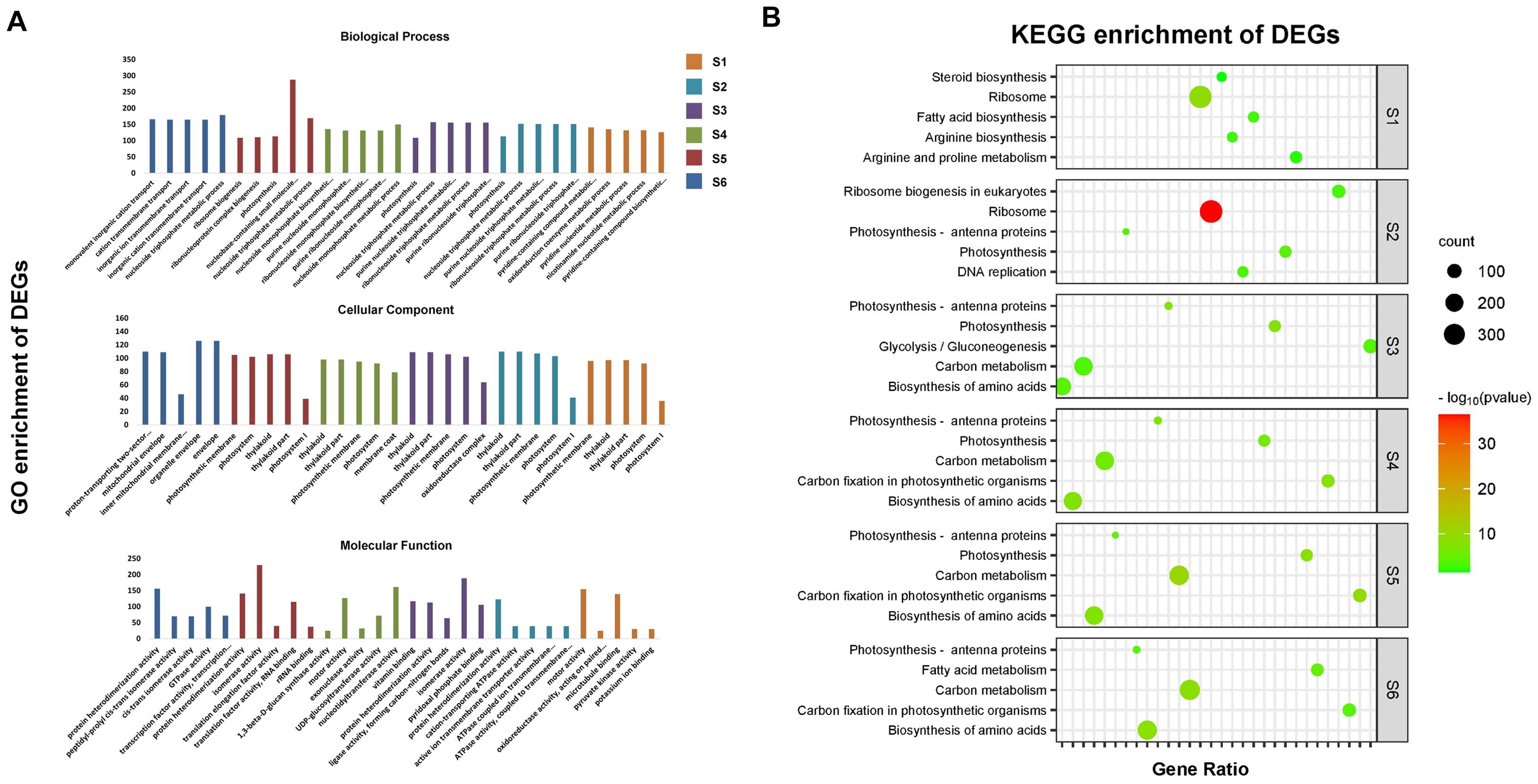
Figure 4. The Gene ontology classification and KEGG enrichment of DEGs. (A) The top 5 GO items most significantly enriched by DEGs at six seed development stages. (B) The top 5 KEGG items most significantly enriched by DEGs at six seed development stages.
3.6 Putative candidate genes for TSW in B. juncea
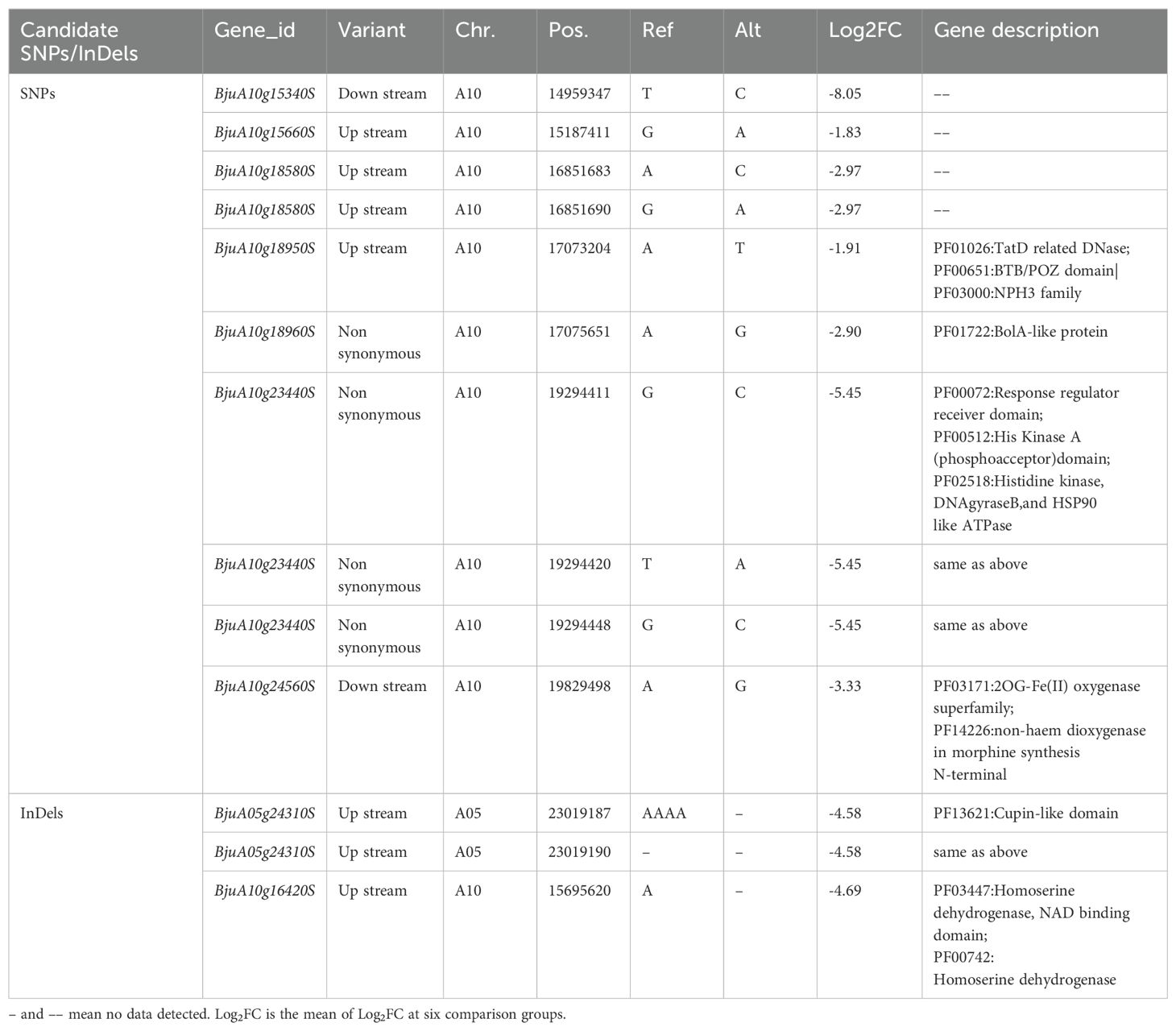
As mentioned above, the BSA-seq analysis reveals that thirty five significant SNPs located in thirty two genes and fifty eight significant InDels in fifty one genes were associated with TSW. Meanwhile, the transcriptome profiling showed that there were 7,679 DEGs between two accessions contrasting in seed weight. Integrated analysis of the above BSA-seq and RNA-seq data identified nine genes (BjuA10g15340S, BjuA10g15660S, BjuA10g18580S, BjuA10g18950S, BjuA10g18960S, BjuA10g23440S, BjuA10g24560S, BjuA05g24310S, BjuA10g16420S) which showed difference in structure and/or expression level (Table 3, Figure 4A). Among these genes, BjuA10g18960S and BjuA10g23440S harbored nonsynonymous SNPs. The former encodes the BolA-like protein, while the latter encodes the HSP90-like ATPase (Table 3, Figure 5A). Notably, the expression of BjuA10g18960S and BjuA10g23440S was significantly higher in Sichuan Yellow than in 7981 (Figure 5C), which was confirmed by qRT−PCR analysis (Figure 5B).
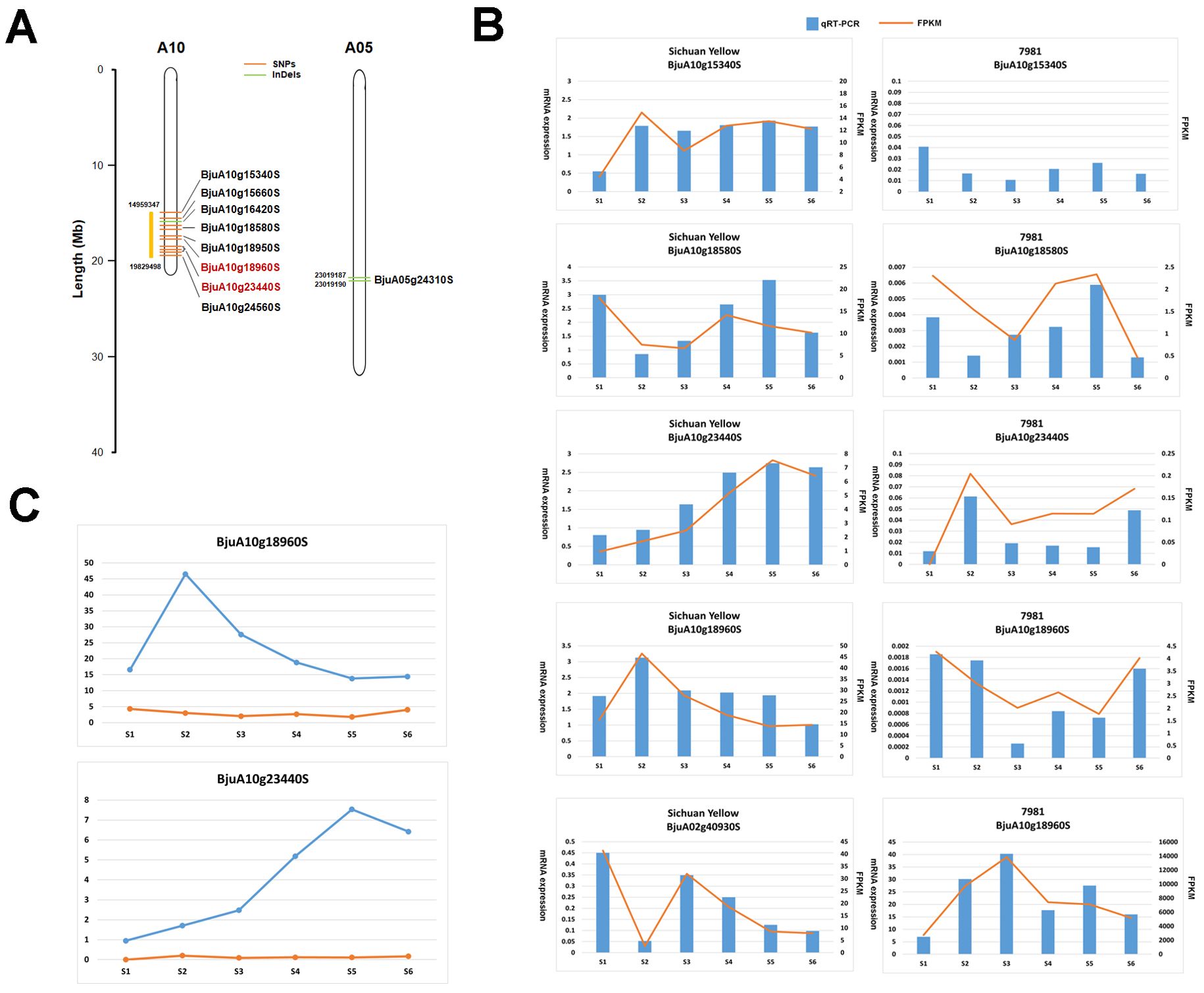
Figure 5. Candidate gens for thousand-seed weight (TSW) identified by BSA-seq and RNA-seq analysis. (A) The genomic location of candidate genes. (B) The expression level of candidate genes. (C) The expression of two most likely candidate genes for TSW.
4 Discussion
Seed weight is one of yield components in B. juncea. Development of seed weight and seed size is a precise and complex regulated process and controlled by cues from maternal and zygotic tissues with some environmental influence (Li and Li, 2016). A recombinant inbred line (RIL) population was used to decrease the environmental influence in mapping QTLs for thousand grain weight (TGW) in wheat (Tahmasebi et al., 2017; Heidari et al., 2011). Identification of QTLs related to seed weight and/or size will contribute to improvement in crop yield. At present, the genomic regions and/or candidate genes regulating seed size in B. juncea have been identified using marker-based bi-parental quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping or genome-wide association studies (Dhaka et al., 2017; Kang et al., 2021; Kumar and Bisht, 2020; Ramchiary et al., 2007; Sra et al., 2019). In addition, Namrata and his colleagues performed QTL analysis using B. juncea bi-parental doubled-haploid populations and identified 65 QTLs and numerous candidate genes influencing seed weight (Dhaka et al., 2017). However, more studies are needed to identify more genes for seed weight in B. juncea. In this study, we attempted to identify new candidate genes for TSW through BSA-seq of F2 progeny combined with transcriptome profiling of both parents 7981 and Sichuan Yellow.
BSA-seq is a method of constructing lineage populations containing extreme phenotypic traits, comparing their polymorphic loci by sequencing the parents and selected progeny with extreme trait values, and locating candidate intervals based on differences in allele frequencies (Zhang et al., 2018). We used this method in the present study and revealed chromosomes A01, A02, A03, A05, A07, A09, A10, B01, B02 and B04 probably carried the intervals for TSW in B. juncea. Consistent with the previous findings, the QTLs for TSW found by Namrata et al. were distributed on chromosomes A03, A07, A10 and B03 in B. juncea (Dhaka et al., 2017). The chromosomes A07, A08 and A09 contain highly significant QTLs for TSW in B. rapa (L.) (Alemu et al., 2024). In addition, the YLD-related QTLs were identified on chromosome A05 in B. napus (Ding et al., 2012). The candidate genes associated with seed yield in the candidate region of chromosome A02 were also identified in rapeseed (Pal et al., 2021). Therefore, the SNPs and Indels associated with TSW and corresponding chromosomal intervals detected in this study will provide a foundation for fine mapping for the genes involved in seed weight in B. juncea. Although the BSA method is commonly used for initial localization of genes with a relatively wide range and the bulked samples used in current study are not enough. The locations of TSW in B. juncea detected in current study also can further study for help breeding for TSW in Brassica combined with methods such as genetic mapping, molecular marker integration or amplified populations for further screening of genes within the range.
Among these candidate SNPs and InDels, seven SNPs with nonsynonymous mutations and three InDels were located in exons of annotated genes (Table 3). The BjuA10g16450S, with a SNP of nonsynonymous mutation, encodes Argonaute (AGO) protein possessing the PIWI-domain. The AGO protein is the central component of plant development, and its PIWI domain is required for target mRNA cleavage and therefore regulate the major processes in plant development (Mallory and Vaucheret, 2006; Baumberger and Baulcombe, 2005; Qi et al., 2005; Mallory et al., 2009). The new gene BjuA10g22200S identified in this study, whose exon has an InDel, encodes a CCAAT-binding transcription factor. The CCAAT-binding transcription factor controls various aspects of embryo and post-embryo development, and seed development and maturation in Arabidopsis (Tang et al., 2021; Tian et al., 2020). Moreover, subunits A, B, and C of the CCAAT-binding transcription factor increase the grain yield of wheat (Qu et al., 2015). The grain yield is always closely associated with TKW, and the QTLs for TKW were frequently associated with QTLs for grain yield (GY) in wheat (Shariatipour et al., 2021).The PPR repeat protein encoding genes, BjuA10g20540S and BjuA10g14570S harbored one candidate SNP with a nonsynonymous mutation and one candidate InDel with a frameshift insertion, respectively, The PPR repeat protein known as the PPR motif localized to mitochondria and/or chloroplasts and mediates diverse aspects of plant organelles and seed development in plants (Small and Peeters, 2000; Barkan and Small, 2014; Li et al., 2021; Schmitz-Linneweber and Small, 2008).Loss of function of PPR proteins usually leads to defects in embryogenesis and/or endosperm development and inhibits seed development (Li et al., 2014; Sosso et al., 2012). Deficiency of the mitochondrial P-type PPR protein EMP10 severely disturbs embryo and endosperm development, resulting in an empty pericarp or papery seeds in maize (Cai et al., 2017). Moreover, the P-type protein PPR5 was recently identified as a regulator required for endosperm development in rice, and ppr5 mutants develop small starch grains (Zhang et al., 2019). These results showed that the PIWI domain, PPR repeat protein, and CCAAT-binding transcription factor-encoding genes related to the candidate SNPs/InDels identified in this study mostly participated in seed development, even in grain yield.
More than 7,000 DEGs were identified between the B. juncea accessions 7981 and the Sichuan Yellow at whole seed development stages. There are more DEGs at the S1 stage than at the other stages (Figure 3A). This is consistent with the study by Mathur and colleagues showing that more genes regulate seed development at the early seed stage in B. juncea (Mathur et al., 2022). Among the 7,679 DEGs common to the six comparison groups, 2,278 belonged to the 445 transcription factors (TF) family. Several DEGs were associated with the transcription factors Pkinase, RRM_1 and P450 (Figure 3B). The P450/CYP78A and P450/CYP79B1 had significantly higher expression in the high- than in low-yield rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and are known to regulate seed yield by affecting anther and pollen development, seed ripening, seed size, and seed weight regulation (Salami et al., 2024). The P450/CYP78A gene family such as AtCYP78A5, AtCYP78A6 and AtCYP78A9 has been proven to be highly related to seed size in Arabidopsis (Wang et al., 2015). Moreover, transcriptome profiling has shown that cytochrome P450 superfamily protein-encoding genes are candidate genes associated with increased seed size in peanut (Liu et al., 2022c). Protein kinases and phosphatases are responsible for several cellular events mediated by protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Among these events are cell growth and differentiation and cellular metabolism (MaChado et al., 2002). RRM is an RNA recognition motif and is abundant in RNA-binding proteins (RBPs). Gene Ontology enrichment analysis of barley RBPs indicated that these proteins were in all major cellular compartments and were associated with key biological processes, including translation, splicing, seed development and stress signaling (Mahalingam and Walling, 2020). In addition, disrupting the RNA binding activity of the RZ-1C protein, which contains RNA recognition motifs (RRMs), in Arabidopsis results in phenotypes that include delayed seed germination, reduced stature, and serrated leaves (Wu et al., 2016).
Yield is strongly correlated with biomass, which is mainly determined by photosynthetic efficiency (Heyneke and Fernie, 2018). The introduction of photorespiratory bypass agents into potato (Solanum tuberosum), Camelina sativa, and tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants was found to increase photosynthesis, biomass yield, and tuber/seed yield (Dalal et al., 2015; Nölke et al., 2014). The photorespiratory bypass (GOC) related gene OsGLO3 encoding glycolate oxidase 3 can significantly increases the photosynthesis efficiency and grain yield in rice (Shen et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020). Our study showed that the expression of the glycolate oxidase 3 (FMN_dh)-encoding gene (FMN_dh) was upregulated in 7981 at six seed development stages (Figure 3B). Similarly, the glyoxalase-encoding genes (BjuB03g21960S and BjuB04g27610S) were also upregulated in 7981. Glyoxalase I (GLYI) and glyoxalase II (GLYII) play a vital role in the chemical detoxification of methylglyoxal (MG) in biological systems (Liu et al., 2022a). Overexpression of the glyoxalase gene OsGlyI improved abiotic stress tolerance and grain yield in rice (Zeng et al., 2016). One study suggested that OsGLYI3 is specifically expressed in rice seeds and may be effective in promoting natural aging and longevity (Liu et al., 2022a). Metallothioneins (MTs) are polypeptide-encoded genes involved in plant growth, development, seed formation, and diverse stress responses (Liu et al., 2022b). One study revealed that the gene encoding metallothionein in maize may be regulated by abscisic acid (ABA) (Niu et al., 2022). During seed germination, storage proteins are decomposed to provide raw materials and energy for seedling growth. Metallothionein reduces the disulfide bond density of storage proteins, but increases their solubility and contribute to their mobilization (Aspart et al., 1984). The metallothionein-encoding genes (BjuA02g40930S, BjuA05g34100S, BjuB01g04670S, and BjuB05g36620S) were upregulated in 7981. From these results, we speculated that the genes encoding glyoxalate oxidase 3, glyoxalase and metallothionein may affect the difference in seed phenotype between the two B. juncea accessions investigated.
Nine genes were found to be both candidate SNP/InDel-located genes and differentially expressed genes between the two accessions at each seed development stages. The annotation showed that these genes encode the 2OG-Fe(II) oxygenase superfamily protein, BTB/POZ domain, cupin-like domain, homoserine dehydrogenase, BolA-like protein and histidine kinase. The 2OG-Fe (II) dioxygenase superfamily is the second largest protease family in plants and the genes encoding 2OG-Fe(II) dioxygenase GA2ox, GA3ox, and GA20ox are the key enzymes involved in gibberellin (GA) biosynthesis and play fundamental roles in plant growth and development (Ding et al., 2020; Hedden and Thomas, 2012; Han and Zhu, 2011). In addition, the gene AHT1 encoding ABA-HYPERSENSITIVE BTB/POZ PROTEIN 1, which contains a BTB/POZ domain, was upregulated more than 2.5 times by abscisic acid (ABA) in Arabidopsis, and the loss of AHT1 led to retardation of the germination process (Kim et al., 2016). Although few reports have demonstrated that the 2OG-Fe (II) oxygenase and BTB/POZ domain-containing genes directly affect seed weight and size, the regulation of these two genes during seed development deserves further study because of their important role in plant growth.
In the present study, the histidine kinase- and BolA-like protein encoding genes BjuA10g23440S and BjuA10g18960S were not only DEGs but also candidate SNP-related genes, and the SNPs in two genes were nonsynonymous (Table 3). The plant phytohormone cytokinin is a key growth regulator involved in the regulation of a wide range of developmental processes, including root and shoot growth, photomorphogenesis, flowering timing, senescence, seed development, and even crop yield (Kim et al., 2016). The histidine kinase is the key components of the phosphorelay in cytokinin signaling (Mok and Mok, 2001). Arabidopsis His-kinases (AHKs) were shown to play redundant or specific roles in the regulation of root and shoot growth, leaf aging and seed size (Riefler et al., 2006). QTL mapping found one major QTL for TSW, cqSW.A03-2 in B. napus. The histidine kinase gene (BnaA03G37960D) is likely to be a candidate gene for cqSW. A03-2 locus (Wang et al., 2020). Interestingly, consistent with the above study, the histidine kinase-encoding gene BjuA10g23440S identified in our study was also a candidate TSW gene in B. juncea. BolA-like proteins are ubiquitous and are present in numerous organisms, ranging from bacteria to higher eukaryotes (Qin et al., 2015). However, the physiological function of BolA proteins in plants has yet to be elucidated. The bola3 mutant does not exhibit any notable phenotype under normal growth conditions but rather grows better than the wild type under some stresses (Qin et al., 2015). The BolA-like protein-encoding gene BjuA10g18960S was also a putative candidate gene related to TSW as shown in this study. The regulatory effect of BolA-like proteins on seed weight is worthy of further study.
5 Conclusions
Ten regions associated with TSW were identified on chromosomes A01, A02, A03, A05, A07, A09, A10, B01, B02 and B04 by BSA-seq. Thirty five candidate SNPs and fifty eight candidate InDels were located in thirty two and fifty one genes, respectively. Candidate SNP/InDel-related genes containing the PIWI domain, the pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) protein and the CCAAT-binding transcription factor-encoding genes were identified and may participate in the regulation of seed development. The DEGs, including the Pkinase, RRM_1 and P450 TF families, were identified, while the genes encoding glyoxalate oxidase 3, glyoxalase and metallothionein were found to be significantly upregulated in the heavy-seed line 7981 at each seed development stages. Combined with RNA-seq and comparative transcriptome analysis of both parents contrasting in seed weight, nine candidate genes for TSW were identified, among which the histidine kinase- and the BolA-like protein-encoding genes BjuA10g18960S and BjuA10g23440S are most likely candidate genes for seed weight in B. juncea. Our study paves a way for cloning of genes for seed weight and marker-assisted selection for bold seed in B. juncea.
Data availability statement
The datasets of BSR and BSA transcriptome data generated during the current study are available in NCBI, Accession number: PRJNA1020652 and PRJNA1022584.
Author contributions
BY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LYa: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LK: Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LYo: Validation, Writing – review & editing. CH: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. HX: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. LQ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YR: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by grants from Guizhou Science and Technology Program Project Qiankehe Foundation-ZK (2023) General 186 and Guizhou Provincial Rapeseed Technology System CARS-12.
Acknowledgments
We thank the fund project for supporting this research. We also appreciate the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1458294/full#supplementary-material
References
Alemu, A., Sundaramoorthy, J., Abreha, K. B., Enyew, M., Geleta, M., Carlsson, A. S. (2024). Developing genomic tools to assist turnip rape [Brassica rapa (L.) subsp. oleifera (DC.) Metzg.] breeding. Front. Genet. 15. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1435474
Aspart, L., Meyer, Y., Laroche, M., Penon, P. (1984). Developmental regulation of the synthesis of proteins encoded by stored mRNA in radish embryos. Plant Physiol. 76, 664–673. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.664
Barkan, A., Small, I. (2014). Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 65, 415–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-040159
Basunanda, P., Radoev, M., Ecke, W., Friedt, W., Becker, H. C., Snowdon, R. J. (2010). Comparative mapping of quantitative trait loci involved in heterosis for seedling and yield traits in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). TAG. Theor. Appl. Genet. 120, 271–281. doi: 10.1007/s00122-009-1133-z
Baud, S., Dubreucq, B., Miquel, M., Rochat, C., Lepiniec, L. (2008). Storage reserve accumulation in Arabidopsis: metabolic and developmental control of seed filling. Arabidopsis book 6, e0113. doi: 10.1199/tab.0113
Baumberger, N., Baulcombe, D. C. (2005). Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1 is an RNA Slicer that selectively recruits microRNAs and short interfering RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 102, 11928–11933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505461102
Borisjuk, L., Neuberger, T., Schwender, J., Heinzel, N., Sunderhaus, S., Fuchs, J., et al. (2013). Seed architecture shapes embryo metabolism in oilseed rape. Plant Cell 25, 1625–1640. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.111740
Cai, M., Li, S., Sun, F., Sun, Q., Zhao, H., Ren, X., et al. (2017). Emp10 encodes a mitochondrial PPR protein that affects the cis-splicing of nad2 intron 1 and seed development in maize. Plant J. 91, 132–144. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13551
Carruthers, J. M., Cook, S. M., Wright, G. A., Osborne, J. L., Clark, S. J., Swain, J. L., et al. (2017). Oilseed rape (Brassica napus) as a resource for farmland insect pollinators: quantifying floral traits in conventional varieties and breeding systems. GCB Bioenergy: Bioproducts Sustain. Bioeconomy 9, 1370–1379. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12438
Clarke, J. D. (2009). Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) DNA miniprep for plant DNA isolation. Cold Spring Harbor Protoc. 2009, pdb.prot5177. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot5177
Dalal, J., Lopez, H., Vasani, N. B., Hu, Z., Swift, J. E., Yalamanchili, R., et al. (2015). A photorespiratory bypass increases plant growth and seed yield in biofuel crop Camelina sativa. Biotechnol. Biofuels 8, 175. doi: 10.1186/s13068-015-0357-1
Dhaka, N., Jain, R., Yadav, A., Yadav, P., Kumar, N., Sharma, M. K., et al. (2022). Transcriptome analysis reveals cell cycle-related transcripts as key determinants of varietal differences in seed size of Brassica juncea. Sci. Rep. 12, 11713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15938-5
Dhaka, N., Rout, K., Yadava, S. K., Sodhi, Y. S., Gupta, V., Pental, D., et al. (2017). Genetic dissection of seed weight by QTL analysis and detection of allelic variation in Indian and east European gene pool lines of Brassica juncea. Theor. Appl. Genet. 130, 293–307. doi: 10.1007/s00122-016-2811-2
Ding, G., Zhao, Z., Liao, Y., Hu, Y., Shi, L., Long, Y., et al. (2012). Quantitative trait loci for seed yield and yield-related traits, and their responses to reduced phosphorus supply in Brassica napus. Ann. Bot. 109, 747–759. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcr323
Ding, Q., Wang, F., Xue, J., Yang, X., Fan, J., Chen, H., et al. (2020). Identification and expression analysis of hormone biosynthetic and metabolism genes in the 2OGD family for identifying genes that may be involved in tomato fruit ripening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 5344. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155344
Dong, H., Tan, C., Li, Y., He, Y., Wei, S., Cui, Y., et al. (2018). Genome-wide association study reveals both overlapping and independent genetic loci to control seed weight and silique length in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00921
Gao, Y., Du, L., Ma, Q., Yuan, Y., Liu, J., Song, H., et al. (2022). Conjunctive analyses of bulk segregant analysis sequencing and bulk segregant rna sequencing to identify candidate genes controlling spikelet sterility of foxtail millet. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.842336
Gegas, V. C., Nazari, A., Griffiths, S., Simmonds, J., Fish, L., Orford, S., et al. (2010). A genetic framework for grain size and shape variation in wheat. Plant Cell 22, 1046–1056. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.074153
Geng, X., Dong, N., Wang, Y., Li, G., Wang, L., Guo, X., et al. (2018). RNA-seq transcriptome analysis of the immature seeds of two Brassica napus lines with extremely different thousand-seed weight to identify the candidate genes related to seed weight. PloS One 3, e0191297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191297
Han, F., Zhu, B. (2011). Evolutionary analysis of three gibberellin oxidase genes in rice, Arabidopsis, and soybean. Gene 473, 23–35. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2010.10.010
Hedden, P., Thomas, S. G. (2012). Gibberellin biosynthesis and its regulation. Biochem. J. 444, 11–25. doi: 10.1042/bj20120245
Heidari, B., Sayed-Tabatabaei, B. E., Saeidi, G., Kearsey, M., Suenaga, K. (2011). Mapping QTL for grain yield, yield components, and spike features in a doubled haploid population of bread wheat. Genome 54, 517–527. doi: 10.1139/g11-017
Heyneke, E., Fernie, A. R. (2018). Metabolic regulation of photosynthesis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 46, 321–328. doi: 10.1042/bst20170296
Kanehisa, M., Araki, M., Goto, S., Hattori, M., Hirakawa, M., Itoh, M., et al. (2008). KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D480–D484. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm882
Kang, L., Qian, L., Zheng, M., Chen, L., Chen, H., Yang, L., et al. (2021). Genomic insights into the origin, domestication and diversification of Brassica juncea. Nat. Genet. 53, 1392–1402. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00922-y
Kaur, H., Wang, L., Stawniak, N., Sloan, R., van Erp, H., Eastmond, P., et al. (2020). The impact of reducing fatty acid desaturation on the composition and thermal stability of rapeseed oil. Plant Biotechnol. J. 18, 983–991. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13263
Kim, H., Kim, S. H., Seo, D. H., Chung, S., Kim, S. W., Lee, J. S., et al. (2016). ABA-HYPERSENSITIVE BTB/POZ PROTEIN 1 functions as a negative regulator in ABA-mediated inhibition of germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 90, 303–315. doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0418-7
Kim, D., Langmead, B., Salzberg, S. L. (2015). HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12, 357–360. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317
Kumar, R., Bisht, N. C. (2020). Heterotrimeric Gα subunit regulates plant architecture, organ size and seed weight in the oilseed Brassica juncea. Plant Mol. Biol. 104, 549–560. doi: 10.1007/s11103-020-01060-5
Li, H., Durbin, R. (2009). Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinf. (Oxford England) 25, 1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li, H., Handsaker, B., Wysoker, A., Fennell, T., Ruan, J., Homer, N., et al. (2009). The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinf. (Oxford England) 25, 2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li, N., Li, Y. (2016). Signaling pathways of seed size control in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 33, 23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2016.05.008
Li, N., Shi, J., Wang, X., Liu, G., Wang, H. (2014). A combined linkage and regional association mapping validation and fine mapping of two major pleiotropic QTLs for seed weight and silique length in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 14, 114. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-114
Li, X., Sun, M., Liu, S., Teng, Q., Li, S., Jiang, Y. (2021). Functions of PPR proteins in plant growth and development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 11274. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011274
Li, N., Xu, R., Li, Y. (2019). Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 70, 435–463. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-095851
Li, X. J., Zhang, Y. F., Hou, M., Sun, F., Shen, Y., Xiu, Z. H., et al. (2014). Small kernel 1 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein required for mitochondrial nad7 transcript editing and seed development in maize (Zea mays) and rice (Oryza sativa). Plant J. 79, 797–809. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12584
Liu, J., Hua, W., Hu, Z., Yang, H., Zhang, L., Li, R., et al. (2015). Natural variation in ARF18 gene simultaneously affects seed weight and silique length in polyploid rapeseed. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 112, E5123–E5132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1502160112
Liu, S., Liu, W., Lai, J., Liu, Q., Zhang, W., Chen, Z., et al. (2022a). OsGLYI3, a glyoxalase gene expressed in rice seed, contributes to seed longevity and salt stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 183, 85–95. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.04.028
Liu, S., Liu, Y., Liu, C., Li, Y., Zhang, F., Ma, H. (2022b). Isolation and characterization of the gmmt-ii gene and its role in response to high temperature and humidity stress in Glycine max. Plants (Basel Switzerland) 11, 1503. doi: 10.3390/plants11111503
Liu, Y., Yi, C., Liu, Q., Wang, C., Wang, W., Han, F. (2022c). Multi-omics profiling identifies candidate genes controlling seed size in peanut. Plants (Basel Switzerland) 11, 3276. doi: 10.3390/plants11233276
Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods (San Diego Calif.) 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Love, M. I., Huber, W., Anders, S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15, 550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
MaChado, E. L., Chiesse da Silva, A., da Silva, M. J., Leite, A., Ottoboni, L. M. (2002). Endogenous protein phosphorylation and casein kinase activity during seed development in Araucaria angustifolia. Phytochemistry 61, 835–842. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(02)00429-6
Mahalingam, R., Walling, J. G. (2020). Genomic survey of RNA recognition motif (RRM) containing RNA binding proteins from barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. vulgare). Genomics 112, 1829–1839. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2019.10.016
Mallory, A. C., Hinze, A., Tucker, M. R., Bouché, N., Gasciolli, V., Elmayan, T., et al. (2009). Redundant and specific roles of the ARGONAUTE proteins AGO1 and ZLL in development and small RNA-directed gene silencing. PloS Genet. 5, e1000646. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000646
Mallory, A. C., Vaucheret, H. (2006). Functions of microRNAs and related small RNAs in plants. Nat. Genet. 38 Suppl, S31–S36. doi: 10.1038/ng1791
Mathur, S., Paritosh, K., Tandon, R., Pental, D., Pradhan, A. K. (2022). Comparative analysis of seed transcriptome and coexpression analysis reveal candidate genes for enhancing seed size/weight in Brassica juncea. Front. Genet. 13. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.814486
McKenna, A., Hanna, M., Banks, E., Sivachenko, A., Cibulskis, K., Kernytsky, A., et al. (2010). The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 20, 1297–1303. doi: 10.1101/gr.107524.110
Meng, Y., Lyu, X., Liu, J., Gao, W., Ma, Y., Liao, N., et al. (2023). Structural variation of GL1 gene determines the trichome formation in Brassica juncea. Theor. Appl. Genet. 136, 75. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04301-5
Mok, D. W., Mok, M. C. (2001). Cytokinin metabolism and action. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 52, 89–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.89
Niu, L., Du, C., Wang, W., Zhang, M., Wang, W., Liu, H., et al. (2022). Transcriptome and co-expression network analyses of key genes and pathways associated with differential abscisic acid accumulation during maize seed maturation. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 359. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03751-1
Niu, Y., Wu, L., Li, Y., Huang, H., Qian, M., Sun, W., et al. (2020). Deciphering the transcriptional regulatory networks that control size, color, and oil content in Brassica rapa seeds. Biotechnol. Biofuels 13, 90. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01728-6
Nölke, G., Houdelet, M., Kreuzaler, F., Peterhänsel, C., Schillberg, S. (2014). The expression of a recombinant glycolate dehydrogenase polyprotein in potato (Solanum tuberosum) plastids strongly enhances photosynthesis and tuber yield. Plant Biotechnol. J. 12, 734–742. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12178
Pal, L., Sandhu, S. K., Bhatia, D., Sethi, S. (2021). Genome-wide association study for candidate genes controlling seed yield and its components in rapeseed (Brassica napus subsp. napus). Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 27, 1933–1951. doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-01060-9
Qi, Y., Denli, A. M., Hannon, G. J. (2005). Biochemical specialization within Arabidopsis RNA silencing pathways. Mol. Cell 19, 421–428. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.014
Qin, L., Wang, M., Zuo, J., Feng, X., Liang, X., Wu, Z., et al. (2015). Cytosolic BolA plays a repressive role in the tolerance against excess iron and mv-induced oxidative stress in plants. PloS One 10, e0124887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124887
Qu, B., He, X., Wang, J., Zhao, Y., Teng, W., Shao, A., et al. (2015). A wheat CCAAT box-binding transcription factor increases the grain yield of wheat with less fertilizer input. Plant Physiol. 167, 411–423. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.246959
Quijada, P. A., Udall, J. A., Lambert, B., Osborn, T. C. (2006). Quantitative trait analysis of seed yield and other complex traits in hybrid spring rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): 1. Identification of genomic regions from winter germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 113, 549–561. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0323-1
Ramchiary, N., Padmaja, K. L., Sharma, S., Gupta, V., Sodhi, Y. S., Mukhopadhyay, A., et al. (2007). Mapping of yield influencing QTL in Brassica juncea: implications for breeding of a major oilseed crop of dryland areas. Theor. Appl. Genet. 115, 807–817. doi: 10.1007/s00122-007-0610-5
Riefler, M., Novak, O., Strnad, M., Schmülling, T. (2006). Arabidopsis cytokinin receptor mutants reveal functions in shoot growth, leaf senescence, seed size, germination, root development, and cytokinin metabolism. Plant Cell 18, 40–54. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.037796
Salami, M., Heidari, B., Alizadeh, B., Batley, J., Wang, J., Tan, X. L., et al. (2024). Dissection of quantitative trait nucleotides and candidate genes associated with agronomic and yield-related traits under drought stress in rapeseed varieties: integration of genome-wide association study and transcriptomic analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1342359
Schmitz-Linneweber, C., Small, I. (2008). Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins: a socket set for organelle gene expression. Trends Plant Sci. 13, 663–670. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.10.001
Shariatipour, N., Heidari, B., Tahmasebi, A., Richards, C. (2021). Comparative genomic analysis of quantitative trait loci associated with micronutrient contents, grain quality, and agronomic traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.709817
Shen, B. R., Wang, L. M., Lin, X. L., Yao, Z., Xu, H. W., Zhu, C. H., et al. (2019). Engineering a new chloroplastic photorespiratory bypass to increase photosynthetic efficiency and productivity in rice. Mol. Plant 12, 199–214. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.11.013
Shi, L., Song, J., Guo, C., Wang, B., Guan, Z., Yang, P., et al. (2019). A CACTA-like transposable element in the upstream region of BnaA9.CYP78A9 acts as an enhancer to increase silique length and seed weight in rapeseed. Plant J. 98, 524–539. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14236
Small, I. D., Peeters, N. (2000). The PPR motif - a TPR-related motif prevalent in plant organellar proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 46–47. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01520-0
Sosso, D., Canut, M., Gendrot, G., Dedieu, A., Chambrier, P., Barkan, A., et al. (2012). PPR8522 encodes a chloroplast-targeted pentatricopeptide repeat protein necessary for maize embryogenesis and vegetative development. J. Exp. Bot. 63, 5843–5857. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers232
Sra, S. K., Sharma, M., Kaur, G., Sharma, S., Akhatar, J., Sharma, A., et al. (2019). Evolutionary aspects of direct or indirect selection for seed size and seed metabolites in Brassica juncea and diploid progenitor species. Mol. Biol. Rep. 46, 1227–1238. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04591-3
Sundaresan, V. (2005). Control of seed size in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 102, 17887–17888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509021102
Tahmasebi, S., Heidari, B., Pakniyat, H., McIntyre, C. L. (2017). Mapping QTLs associated with agronomic and physiological traits under terminal drought and heat stress conditions in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 60, 26–45. doi: 10.1139/gen-2016-0017
Tang, G., Xu, P., Li, P., Zhu, J., Chen, G., Shan, L., et al. (2021). Cloning and functional characterization of seed-specific LEC1A promoter from peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). PloS One 16, e0242949. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242949
Tian, E., Liu, K., Ye, B., Luo, C., Lin, S. (2017). The genetic analysis of the Brassica juncea RIL population for important quality traits. Seed 36, 1–5. doi: 10.16590/j.cnki.1001-4705.2017.08.001
Tian, R., Wang, F., Zheng, Q., Niza, V., Downie, A. B. (2020). Direct and indirect targets of the arabidopsis seed transcription factor ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 3. Plant J. 103, 1679–1694. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14854
Trapnell, C., Roberts, A., Goff, L., Pertea, G., Kim, D., Kelley, D. R., et al. (2012). Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 7, 562–578. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.016
Wang, K., Li, M., Hakonarson, H. (2010). ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, e164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq603
Wang, X., Li, Y., Zhang, H., Sun, G., Zhang, W., Qiu, L. (2015). Evolution and association analysis of GmCYP78A10 gene with seed size/weight and pod number in soybean. Mol. Biol. Rep. 42, 489–496. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3792-3
Wang, L. M., Shen, B. R., Li, B. D., Zhang, C. L., Lin, M., Tong, P. P., et al. (2020). A synthetic photorespiratory shortcut enhances photosynthesis to boost biomass and grain yield in rice. Mol. Plant 13, 1802–1815. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.10.007
Wang, H., Yan, M., Xiong, M., Wang, P., Liu, Y., Xin, Q., et al. (2020). Genetic dissection of thousand-seed weight and fine mapping of cqSW.A03-2 via linkage and association analysis in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 133, 1321–1335. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03553-9
Wu, Z., Zhu, D., Lin, X., Miao, J., Gu, L., Deng, X., et al. (2016). RNA binding proteins rz-1b and rz-1c play critical roles in regulating pre-mrna splicing and gene expression during development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 28, 55–73. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00949
Yadava, S. K., Arumugam, N., Mukhopadhyay, A., Sodhi, Y. S., Gupta, V., Pental, D., et al. (2012). QTL mapping of yield-associated traits in Brassica juncea: meta-analysis and epistatic interactions using two different crosses between east European and Indian gene pool lines. Theor. Appl. Genet. 125, 1553–1564. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1934-3
Young, M. D., Wakefield, M. J., Smyth, G. K., Oshlack, A. (2010). Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 11, R14. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14
Zeng, Z., Xiong, F., Yu, X., Gong, X., Luo, J., Jiang, Y., et al. (2016). Overexpression of a glyoxalase gene, OsGly I, improves abiotic stress tolerance and grain yield in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 109, 62–71. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.09.006
Zhang, X., Li, R., Chen, L., Niu, S., Chen, L., Gao, J., et al. (2018). Fine-mapping and candidate gene analysis of the Brassica juncea white-flowered mutant Bjpc2 using the whole-genome resequencing. Mol. Genet. Genomics 293, 359–370. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1390-5
Zhang, L., Qi, Y., Wu, M. M., Zhao, L., Zhao, Z. H., Lei, C. L., et al. (2019). Mitochondrion-targeted PENTATRICOPEPTIDE REPEAT5 is required for cis -splicing of nad4 intron 3 and endosperm development in rice. Crop J. 9, 82–296. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2020.09.002
Zhang, C., Zhao, X., Pang, C., Pen, M., Wang, X., Chen, F., et al. (2021). Genome-wide association study of 1000-seed weight in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Acta Agronomica Sin. 47, 650–659. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04136
Keywords: Brassica juncea, seed weight, BSA-seq, RNA-seq, candidate genes
Citation: Yang B, Yang L, Kang L, You L, Chen H, Xiao H, Qian L, Rao Y and Liu Z (2024) Integrated analysis of BSA-seq and RNA-seq identified the candidate genes for seed weight in Brassica juncea. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1458294. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1458294
Received: 02 July 2024; Accepted: 13 November 2024;
Published: 03 December 2024.
Edited by:
Ryo Fujimoto, Kobe University, JapanReviewed by:
Puneet Walia, Lovely Professional University, IndiaBahram Heidari, Shiraz University, Iran
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Yang, Kang, You, Chen, Xiao, Qian, Rao and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhongsong Liu, enNsaXU0OEBodW5hdS5uZXQ=
 Bin Yang
Bin Yang Liu Yang1
Liu Yang1 Hao Chen
Hao Chen