- 1College of Agriculture, Shanxi Agricultural University, Taigu, China
- 2Center for Agricultural Genetic Resources Research, Shanxi Agricultural University/Key Laboratory of Gene Resources and Germplasm Enhancement, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs/Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics and Molecular Improvement of Shanxi Province, Taiyuan, China
- 3National Agricultural Technology Extension Service Center of the Ministry, Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Beijing, China
- 4Dryland Farming Institute, Hebei Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences, Hengshui, China
- 5Wheat Research Institute, Dezhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Dezhou, China
- 6Institute of Forage and Grassland Sciences, Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Harbin, China
- 7Institute of Crop Sciences, National Wheat Improvement Centre, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), Beijing, China
Powdery mildew (PM) poses an extreme threat to wheat yields and quality. In this study, 262 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) of Doumai and Shi 4185 cross were used to map PM resistance genes across four environments. High-density genetic linkage map of the Doumai/Shi 4185 RIL population was constructed using the wheat Illumina iSelect 90K single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array. In total, four stable quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for PM resistance, QPm.caas-2AS, QPm.caas-4AS, QPm.caas-4BL, and QPm.caas-6BS, were detected and explained 5.6%–15.6% of the phenotypic variances. Doumai contributed all the resistance alleles of QPm.caas-2AS, QPm.caas-4AS, QPm.caas-4BL, and QPm.caas-6BS. Among these, QPm.caas-4AS and QPm.caas-6BS overlapped with the previously reported loci, whereas QPm.caas-2AS and QPm.caas-4BL are potentially novel. In addition, six high-confidence genes encoding the NBS-LRR-like resistance protein, disease resistance protein family, and calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine-kinase were selected as the candidate genes for PM resistance. Three kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) markers, Kasp_PMR_2AS for QPm.caas-2AS, Kasp_PMR_4BL for QPm.caas-4BL, and Kasp_PMR_6BS for QPm.caas-6BS, were developed, and their genetic effects were validated in a natural population including 100 cultivars. These findings will offer valuable QTLs and available KASP markers to enhance wheat marker-assisted breeding for PM resistance.
Highlights
● Four QTLs for powdery mildew resistance were identified in the Doumai/Shi 4185 wheat RIL population. KASP markers for QPm.caas-2AS and QPm.caas-6BS were validated in a panel of wheat cultivars.
Introduction
Common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is one of the most crucial food crops globally, and it provides nearly 20% of human caloric intake and fulfills 25% of protein requirements. However, its productivity suffers from various biotic and abiotic threats. Powdery mildew (PM), caused by the fungal pathogen Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici (Bgt), is a particularly devastating destroy affecting leaves, spikelets, and awns. Since the 1970s, PM has extensively spread across nearly all major wheat cropping areas in mainland China (Kang et al., 2020a; Wang et al., 2023). Annual losses due to PM have surpassed eight million hectares worldwide in 2020s (Jia et al., 2020; Kang et al., 2020b; Wang et al., 2023). Although PM can be controlled by fungicides, it incurs a huge cost and causes environmental pollution. Breeding and employing PM-resistant cultivars are the most economical, environmentally friendly, and effective approaches to decrease economic losses (Ma et al., 1994; Kang et al., 2020a).
PM resistance can be categorized into all-stage resistance (ASR) and adult-plant resistance (APR). Typically, ASR is governed by major genes and provides immune or highly resistant responses to specific pathogen races throughout the entire growth cycle. Conversely, APR, generally mediated by minor genes, is less durable and can be easily overcome by emerging pathogen races. However, APR is often effective against all races of Bgt. The integration of four to five APR genes can result in a durable and high level of resistance (Li et al., 2016; Jia et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2021; Bapela et al., 2023). Due to its race non-specificity and longevity, APR has gained increasing importance in wheat breeding programs. To date, nearly 100 PM resistance alleles have been identified at over 60 loci (Pm1 to Pm68), and over 150 PM resistance loci are distributed across all 21 wheat chromosomes (Shah et al., 2018; Kang et al., 2020a; Simeone et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Although a massive number of loci for powdery mildew resistance have been reported, some PM resistance genes have negative pleiotropic effects. For example, Pm8 caused wheat quality reduction, whereas Pm16 led to a 15% yield loss (Summers and Brown, 2013; Li et al., 2020). Although there is already a substantial amount of research on powdery mildew, some studies use traditional simple sequence repeat (SSR) or diversity array technology (DArT) markers, which are less suitable for the current breeding. Thus, novel PM resistance genes were needed to accelerate wheat PM resistance breeding.
With the development of genotyping techniques (Liu et al., 2016; Liu J. et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2019), unearthing quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for complex traits has been accelerated by utilizing the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array, such as grain quality, yield, and disease resistance-related traits (Liu J. et al., 2017; Jia et al., 2020; Kang et al., 2020a, 2020b; He et al., 2021). Tightly linked or significantly associated SNPs can be transformed into kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) markers and incorporated into marker-assisted selection (MAS) breeding (Rasheed et al., 2016; Kaur et al., 2020). Doumai is a landrace with APR to PM, whereas Shi 4185 is a widely grown higher-yield winter wheat cultivar with high susceptibility to PM. A total of 262 F2:6 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from Doumai/Shi 4185 were used for PM resistance evaluation and novel locus identification. The objectives of this study were to 1) identify PM resistance loci and tightly linked SNP markers, 2) excavate candidate genes for further study, and 3) develop available KASP markers for wheat PM resistance breeding.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and phenotyping of powdery mildew
The 262 F2:6 RILs derived from Doumai/Shi 4185 were used for evaluating PM reactions. Additionally, a diverse panel with 100 cultivars originating from the Yellow-Huai Wheat Region were used to validate the effectiveness of developed KASP markers. All 262 F2:6 RILs and their parents were evaluated for PM reaction in Dezhou of Shandong and Shijiazhuang of Hebei during the 2020–2021 and 2021–2022 cropping seasons. The 100 wheat cultivars were planted in Gaoyi and Shijiazhuang of Hebei and Beijing during the 2020–2021 cropping season.
All RILs and 100 cultivars were planted in a randomized complete block design with three replicates. Each plot consisted of a single 1-m row, spaced 30 cm apart, containing approximately 50 plants. The highly susceptible cultivar Jingshuang 16, inoculated with E20, was planted every 10th row as a control. Additionally, it was placed perpendicularly and adjacent to the test rows to ensure uniform infection spread. Disease severity (DS) for each line was assessed by averaging the percentage of leaf area covered by PM. The initial assessment was conducted approximately 6 weeks post-inoculation, when the susceptible control, Jingshuang 16, exhibited severe disease symptoms. The maximum disease severity (MDS) for each line was determined when the DS of the control reached its peak value. The field trials were maintained following standard local agronomic practices.
Molecular genotyping, map construction, and QTL analysis
The genomic DNA was extracted using the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method from young leaves of the mapping and validation populations. The RILs and parental lines were genotyped using the wheat Illumina 90K SNP array. SNPs with >20% missing data or minor allele frequency (MAF) <0.5 were excluded from further analysis. The filtered SNPs were grouped into bin markers using the BIN function of IciMapping v4.2 (Meng et al., 2015). The higher-density linkage map referenced by Wen et al. (2017) and Li et al. (2018) was constructed using the regression mapping algorithm in JoinMap v4.0. QTL mapping was analyzed using the inclusive composite interval mapping (ICIM) method in IciMapping v4.1 (Meng et al., 2015). A logarithm of odds (LOD) threshold of 2.6, determined by 1,000 permutations, was used to declare significant QTLs. The physical positions of the SNPs were according to the Chinese Spring reference genome sequence (IWGSC v1.0, https://urgi.versailles.inra.fr/blast_iwgsc/).
Statistical analysis
Phenotypic correlation coefficients, analysis of variance (ANOVA) based on the PROC GLM model, and t-tests were performed using SAS 9.4 software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Broad-sense heritabilities (H2) for PM response were calculated following the methodology described by Nyquist and Baker (1991).
KASP marker development and validation
SNPs flanking all four QTLs were converted into KASP markers (Rasheed et al., 2016) using PolyMarker. KASP assays were conducted in a 4-μL reaction volume consisting of 2 μL of 2× KASP Master Mix, 0.045 μL of KASP primer mix, and 2 μL of genomic DNA at a concentration of 30 ng/μL. The 384-well plates were read using the PHERAstar Plus SNP detection system (BMG Labtech GmbH, Ortenberg, Germany), and genotype analysis was performed using KlusterCaller software (LGC, Hoddesdon, UK). All the KASP markers were validated using a panel of 100 Chinese cultivars.
Identification of candidate genes for powdery mildew resistance
The selection of candidate genes was guided by the following methodologies. First, genes associated with disease resistance, pathogen response, and stress tolerance, along with SNPs located within or adjacent to the physical intervals of the QTLs, were identified using the IWGSC v1.1 reference. Second, variations within the initially screened candidate genes possessing significant mutations were selected, while those with non-significant changes were excluded. Third, genes exhibiting differential expression in leaves, stems, or spikes were selected based on data from the expVIP8 database (http://wheat-expression.com/).
Results
Phenotypic evaluation
The mean MDS for PM across all environments was 15.6% and 65.2% for Doumai and Shi 4185, respectively. The frequency distribution of MDS showed a continuous distribution, indicating polygenic inheritance and transgressive segregation. The MDS for PM in 262 RILs was continuously distributed at 5.6%–88.3% in Dezhou in 2021 (mean MDS 38.6%, standard error 21.1, and coefficient of variation 57.4%), 4.6%–92.3% in Dezhou in 2022 (mean MDS 38.3, standard error 22.0, and coefficient of variation 52.7%), 3.3%–83.6% in Shijiazhuang in 2021 (mean MDS 37.8%, standard error 20.0, and coefficient of variation 16.7%), and 4.3%–91.0% in Shijiazhuang in 2022 (mean MDS 38.9%, standard error 22.2, and coefficient of variation 57.0%). The MDS for the RIL population was significantly correlated (r = 0.55–0.76, p < 0.01) across all four environments. ANOVA showed that both line and line × environment interaction effects were significant for MDS (Supplementary Figure S1; Table S1). A high broad-sense heritability (Hb2 = 0.72) was obtained across all five environments.
Loci for powdery mildew resistance
Among the 80,587 SNP markers in the wheat Illumina assay 90K SNP array, 10,986 SNP markers were polymorphic between the two parental cultivars. A high-density linkage map spanning 2,156.07 cM was constructed for all 21 chromosomes using 2,840 representative bin markers (Wen et al., 2017; Li et al., 2018).
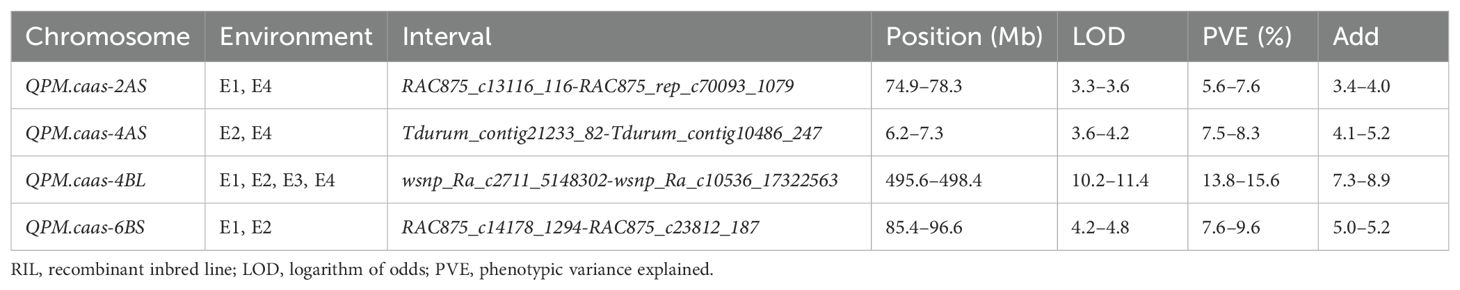
Four QTLs for PM resistance were identified in two or more environments and named QPm.caas-2AS (RAC875_c13116_116-RAC875_rep_c70093_1079, 74.9–78.3 Mb), QPm.caas-4AS (Tdurum_contig21233_82-Tdurum_contig10486_247, 6.2–7.3 Mb), QPm.caas-4BL (wsnp_Ra_c2711_5148302-wsnp_Ra_c10536_17322563, 495.6–498.4 Mb), and QPm.caas-6BS (RAC875_c14178_1294-RAC875_c23812_187, 85.4–96.6 Mb) (Table 1; Figure 1). Among these, QPm.caas-2AS was detected in Dezhou in 2021 and Shijiazhuang in 2022, explaining 5.6%–7.6% of the phenotypic variance explained (PVE), with additive effects ranging from 3.4% to 4.0%. QPm.caas-4AS was detected in Shijiazhuang in 2021 and Shijiazhuang in 2022 and contributed 7.5%–8.3% of the PVE with additive effects being 4.1%–5.2%. QPm.caas-4BL was detected in all environments and contributed 13.8%–15.6% of the PVE, with additive effects ranging from 7.3% to 8.9%. QPm.caas-6BS was detected in Dezhou in 2021 and Shijiazhuang in 2021, accounting for 7.6%–9.6% of the PVE, with additive effects ranging from 5.0% to 5.2%. All the resistance alleles of QPm.caas-2AS, QPm.caas-4AS, QPm.caas-4BL, and QPm.caas-6BS were derived from Doumai.
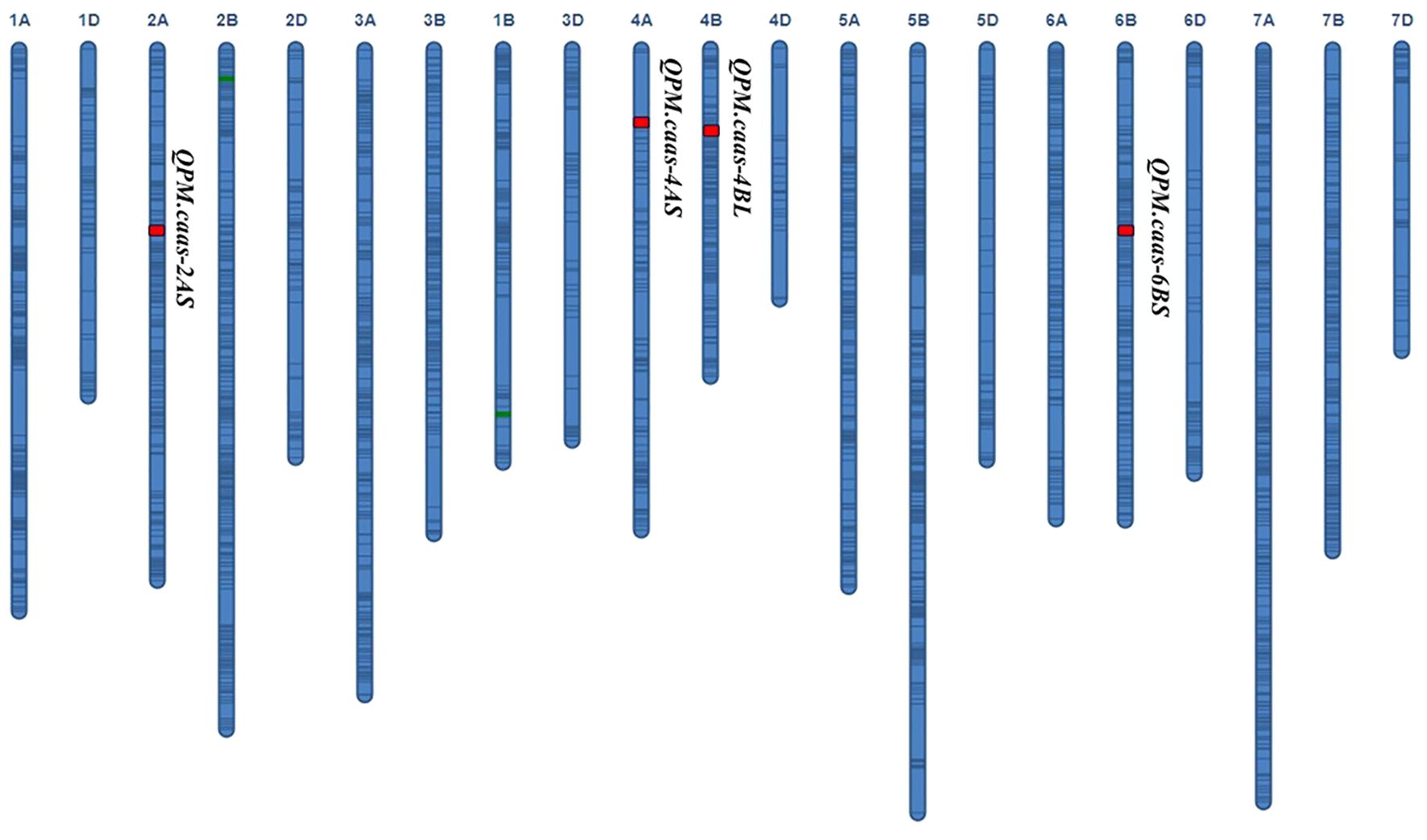
Figure 1. QTLs for the maximum disease severity of powdery mildew in the Doumai/Shi 4185 RIL population. QTLs, quantitative trait loci; RIL, recombinant inbred line.
Candidate gene identification
In total, six high-confidence genes were selected as the candidate genes for PM resistance. For QPm.caas-2AS, two candidate genes were detected. TraesCS2A01G125700 encodes the calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 2. The other is TraesCS2A01G129400, which encodes the disease resistance protein family. TraesCS4A01G010000 located in the genetic interval of QPm.caas-4AS encodes the kinase-like protein. TraesCS4B01G240500 at QPm.caas-4BL encodes the calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine-kinase. For QPm.caas-6BS, two candidate genes were identified, i.e., TraesCS6B01G107700 and TraesCS6B01G114200, which encode the NBS-LRR-like resistance protein and the disease resistance protein RPM1, respectively (Table 2; Figure 2).
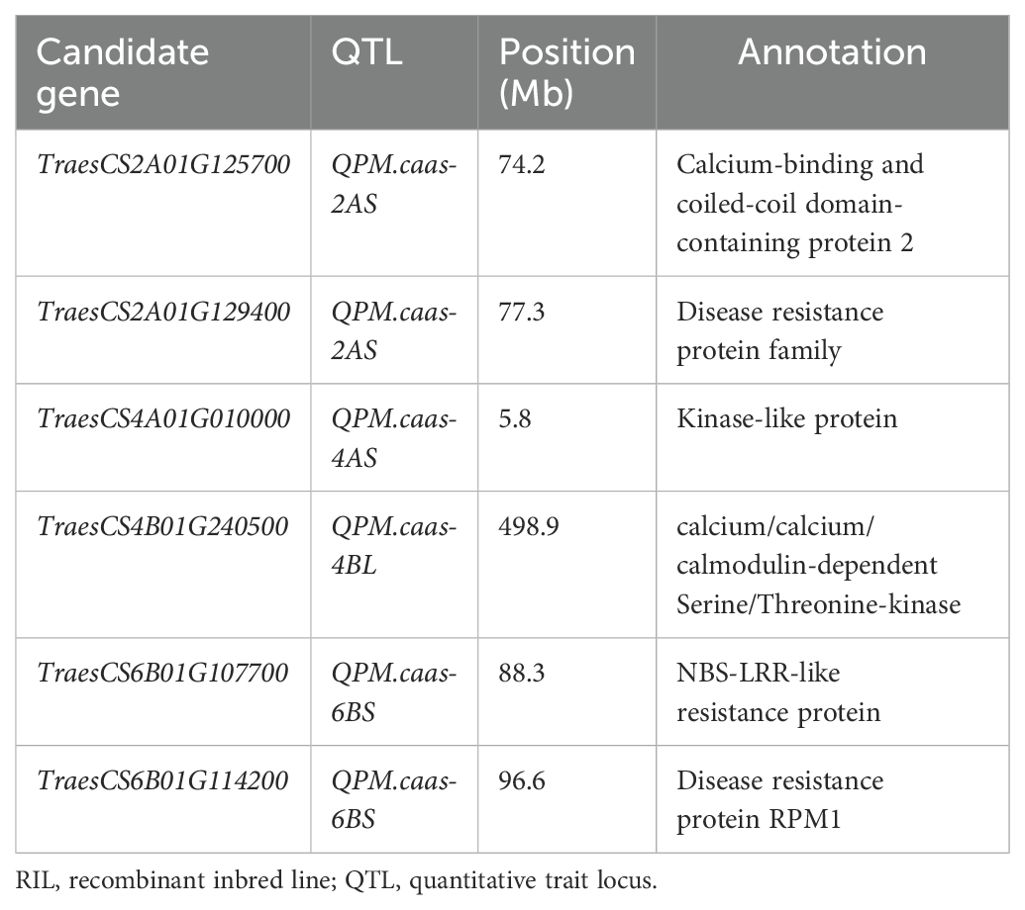
Table 2. The candidate gene list for the powdery mildew resistance identified in the Doumai/Shi 4185 RIL population.
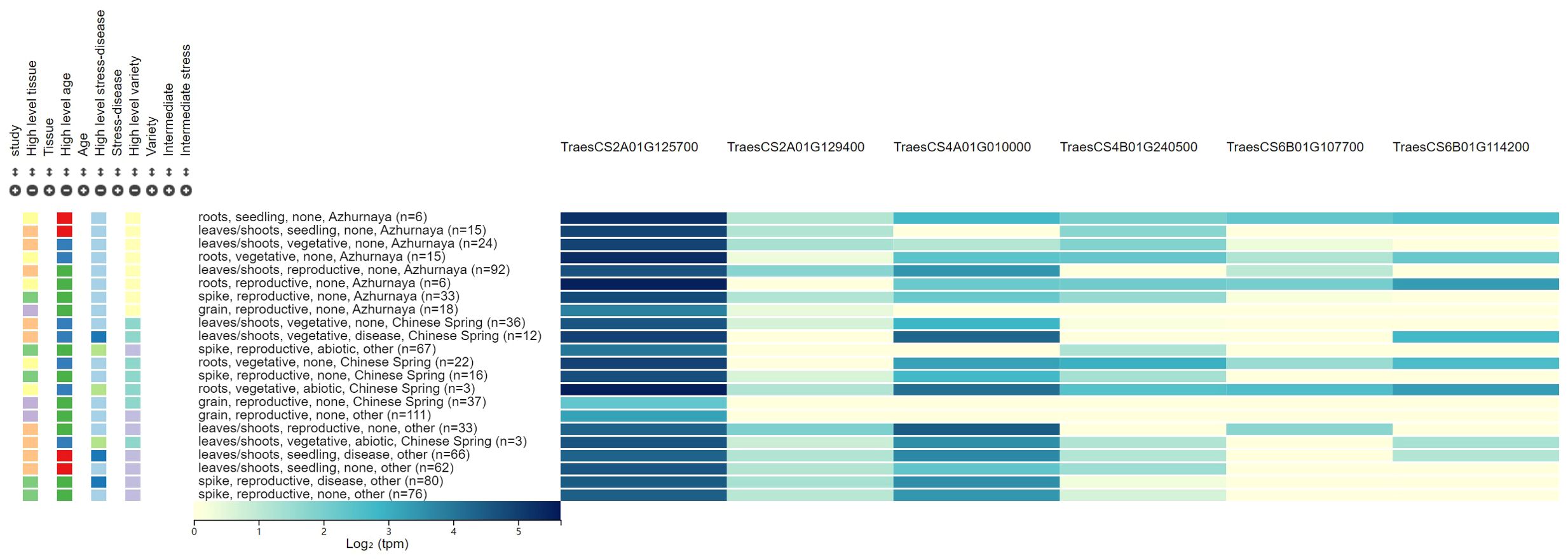
Figure 2. The expression patterns for the six candidate genes associated with powdery mildew resistance.
Validation of QTLs
All four QTLs (QPm.caas-2AS, QPm.caas-4AS, QPm.caas-4BL, and QPm.caas-6BS) were used to develop available KASP markers for wheat PM resistance breeding. Although attempts were made to develop KASP markers for QPm.caas-4AS (Tdurum_contig21233_82 and Tdurum_contig10486_247), it was non-chromosome specific or unable to be effectively distinguished between the two parental genotypes in the RIL population. Consequently, Kasp_PMR_2AS corresponding to BobWhite_rep_c62964_873 (594.2 Mb) located at the genetic interval of QPm.caas-2AS, Kasp_PMR_4BL corresponding to RFL_Contig2459_2314 (497.2 Mb) located at the genetic interval of QPm.caas-4BL, and Kasp_PMR_6BS corresponding to RAC875_rep_c116755_285 (77.4 Mb) for QPm.caas-6BS were successfully developed (Supplementary Tables S2, S3). Kasp_PMR_2AS, Kasp_PMR_4BL, and Kasp_PMR_6BS could distinguish two genotypes in the Doumai/Shi 4185 RIL population and were used to verify their effectiveness in the 100 diverse wheat cultivars. For Kasp_PMR_2AS, the favorable allele (GG, accounting for 21.0%, mean MDS 13.6%) exhibited higher resistance compared to the unfavorable allele (AA, accounting for 77.0%, mean MDS 19.5%) (p = 0.05). For Kasp_PMR_4BL, the favorable allele (AA, accounting for 39.0%, mean MDS 14.3%) showed higher resistance than the unfavorable allele (GG, accounting for 43.0%, mean MDS 20.1%) at p = 0.05 level. For Kasp_PMR_6BS, the favorable allele (AA, accounting for 78%, mean MDS 15.8%) showed higher resistance than the unfavorable allele (CC, accounting for 20.0%, mean MDS 27.4%) at p = 0.05 level. Unlike QPm.caas-6BS, the resistance alleles of QPm.caas-2AS (accounting for 21.0%) and QPm.caas-4BL (accounting for 39.0%) showed lower frequency distribution than their contrasting alleles, suggesting that these resistance alleles have great potential for selection in wheat breeding for PM resistance (Tables 2, 3).
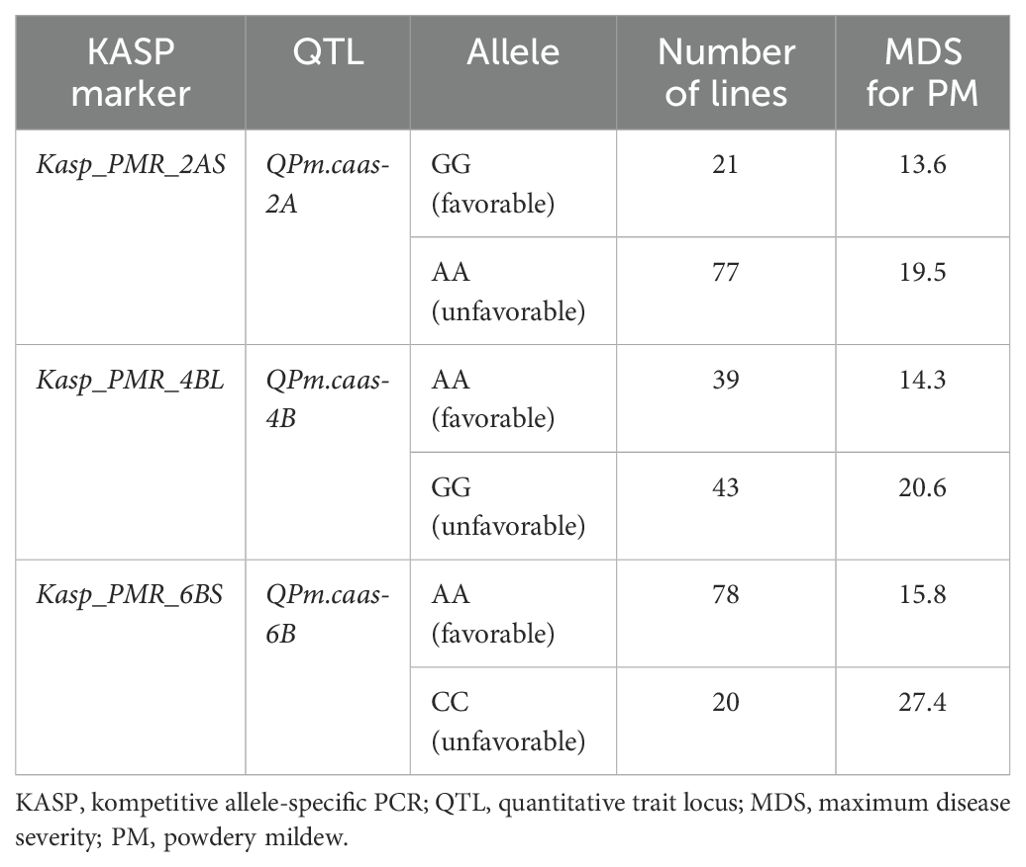
Table 3. The development and validation of the available KASP markers for wheat powdery mildew resistance.
Discussion
PM is a severe fungal disease that threatens wheat production and results in over 300,000 tons of yield loss annually (Qie et al., 2019; Kang et al., 2020a; Wang et al., 2023). Wheat PM resistance is a typical complex quantitative inherited trait (Marone et al., 2013; Sethi et al., 2021; Saini et al., 2022). Both environment and genotype have a great impact on the incidence of PM. Until now, over 200 wheat PM resistance QTLs or genes have been identified from wheat and related species (Ullah et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2019; He et al., 2021; Shi et al., 2021; He et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022; Nordestgaard et al., 2021; Wei et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2017). In this study, QPm.caas-2AS, QPm.caas-4AS, QPm.caas-4BL, and QPm.caas-6BS were identified for PM resistance.
Chromosome 2A is a gene-rich region for PM resistance. Seven permanently named Pm genes, including Pm4a-2AL, Pm4b-2AL, Pm4c-2AL, Pm4d-2AL, Pm50-2AL, Pm3k (112 Mb), and Pm52 (581.2–586.6 Mb), and 19 temporary genes or QTLs (such as QPm.sfr-2A, QPminra-2A-112, QPm.crag-2A, and QPm.ttu-2A) were reported previously (Li et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2019; Schmolke et al., 2012; Sánchez-Martín et al., 2021). The PM resistance QTL QPm.caas-2AS.1 identified in this study (74.9–78.3 Mb) was different from QPmbdt.nwafu-2AS, which originated from Baidatou (111.0–174.0 Mb) (Zhou et al., 2024). Thus, QPm.caas-2AS may be a novel QTL. Over 15 genes or loci for PM resistance were identified on chromosome 4A and mainly located on the long arm rather than the short arm (Sun et al., 2018; Janáková et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2021), such as Pm61, QPm.tut-4A (Janáková et al., 2019), QPm.sfr-4A.1 (Keller et al., 1999), QPm.sfr-4A.2 (Keller et al., 1999), Pm61 (Sun et al., 2018), and MITW30 (Liu et al., 2021). QPm.uga-4A from soft red winter wheat AGS2000 was presently located between markers tPt4753 and wPt3515 near the centromere on chromosome arm 4AS (Hao et al., 2015). Another PM resistance QTL located on chromosome 4AS (QPm.saas-4AS), contributed by CM104 (Liu et al., 2021), was detected on the distal chromosome arm 4AS (2.9–4.0 Mb). In this study, QPm.caas-4AS was identified at 6.2–7.4 Mb of chromosome 4AS and was adjacent to QPm.saas-4AS originating from CM104 (Liu et al., 2021).
On chromosome 4B, 12 PM resistance genes or QTLs were previously reported (Marone et al., 2013; Kang et al., 2020a). Most loci were distributed on the 4B centromere, such as QPm.ipk-4B and QPm.sfr-4B in W7984 and Swiss spelt cv. QPm.nuls-4BL in Avocet between XwPt1505 and Xgwm149; QPm.caas-4BL.1 was located at the interval of Xgwm149 and Xgwm495 in Libellula (Asad et al., 2014). In addition, five loci for PM resistance were identified at 512–583 Mb of chromosome 4B by meta-analysis (Marone et al., 2013; Sethi et al., 2021; Saini et al., 2022) and different from QPm.caas-4BL (495.6–498.4 Mb) identified in this study. Thus, QPm.caas-4BL may be a novel locus for PM resistance. Chromosome 6B is another gene-rich region for PM resistance, including Pm11 (6BS), Pm14 (6BS), Pm12 (6BS), Pm20 (6BS), and Pm54 (6BL) (Marone et al., 2013; Kang et al., 2020b; Sethi et al., 2021; Saini et al., 2022). In addition, over 12 loci (such as QPm.umb-6BS, QPm.caas-6BS, QPm.Bgt66-6BS, QPm.caas-6BL.1, and QPm.caas-6BL.2) for PM were identified on chromosome 6B. Meta-analyses (Marone et al., 2013; Kang et al., 2020a; Sethi et al., 2021; Saini et al., 2022) indicated that a cluster for PM resistance was identified on chromosome 6BS (67–88 Mb) and overlapped with the QPm.caas-6BS (85.4–96.6 Mb) identified in this study.
Powdery mildew can affect wheat yield and agronomic traits, potentially causing linkage drag, as demonstrated by some studies involving genes like Pm8 and Pm16. We have previously conducted thorough multi-environment phenotypic assessments and genome-wide association analyses of agronomic traits, yield, and grain-related traits in the RIL populations of Doumai and Shi 4185 (Li et al., 2018). No co-localized associated loci were found near the four identified powdery mildew resistance QTLs, indicating that these genes do not cause linkage drag. This finding is consistent with our field observations. In the field, Doumai shows good resistance to powdery mildew and exhibits traits such as short plant height, robust stems, large grains, and large spikes.
Six candidate genes for PM resistance were identified
Six candidate genes for PM resistance were identified, which were involved in disease resistance, redox reaction, stress tolerance, and signal transduction. These candidate genes were screened according to the following criteria: 1) the genes are located in or adjacent to the physical intervals of QTLs identified, 2) they are related to the molecular processes in pathogen response, and 3) they may be differentially expressed in leaves, stems, and spikes. Six candidate genes involved in the biological metabolism of disease resistance protein family, kinase-like protein, and NBS-LRR-like resistance protein were identified. Two candidate genes (TraesCS2A01G125700 and TraesCS2A01G129400) for QPm.caas-2AS were identified. TraesCS2A01G125700 encodes the calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 2, which can recognize pathogen effectors delivered into plant cells during the infection process, and play a crucial role in the plant’s innate immune system (Liu N. et al., 2017). TraesCS2A01G129400 for QPm.caas-2AS and TraesCS6B01G114200 for QPm.caas-6BS encode the disease resistance protein family, which plays a crucial role in plant innate immune system and was associated with various diseases, such as stripe rust, leaf rust, and PM reaction (Nie and Ji, 2019; Chandran et al., 2021; Li et al., 2024). TraesCS4A01G010000 of QPm.caas-4AS encodes the kinase-like protein, a novel domain for wheat PM resistance gene, like Pm13 (Li et al., 2024). TraesCS4B01G240500 located at the genetic interval of QPm.caas-4BL encodes the calcium/-dependent serine/threonine-kinase, which plays important roles in a wide range of physiological functions, including plant hormone responses, metabolic regulation, and defense reactions against diseases (Chandran et al., 2021; Hu et al., 2021). TraesCS6B01G107700, the candidate gene for QPm.caas-6BS, encodes the NBS-LRR-like resistance protein, which is a crucial gene family in plant immune responses, mainly involved in the recognition and response to pathogens, and thus participates in the plant defense process (He et al., 2018, Pm21; Desiderio et al., 2021).
Applications in wheat breeding
Although traditional breeding methods have improved PM resistance, the process is often lengthy and inefficient. KASP is a genotyping technology used for identifying SNPs and insertions/deletions (InDels). It is highly regarded for its accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility in various applications, including genomic selection, MAS in plant breeding, and molecular marker development (Rasheed et al., 2017). In this research, the markers Kasp_PMR_2AS, Kasp_PMR_4BL, and Kasp_PMR_6BS were developed from closely linked SNP markers and validated as effective tools for MAS in breeding programs. Furthermore, varieties with favorable alleles, PM resistance, and desirable agronomic traits, such as Lumai14, Zhongmai895, Huaimai21, Lankao24, Lumai23, Wanmai38, Yumai47, and Zhou8425B, are recommended as parent lines to enhance PM resistance in wheat breeding.
Conclusions
In the present study, linkage analysis for PM resistance was conducted in the Doumai/Shi 4185 RIL population. Four loci on chromosomes 2A, 4A, 4B, and 6B were identified and explained 5.6%–15.6% of the phenotypic variations. Three available KASP markers (Kasp_PMR_2AS, Kasp_PMR_4BL, and Kasp_PMR_6BS) for PM resistance breeding were developed and validated in a natural population. The resistance loci, available KASP markers, and cultivars with more resistance alleles can be used to accelerate the progress of PM resistance breeding.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
We declare that these experiments complied with the ethical standards in China.
Author contributions
XL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XM: Resources, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. PL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. ML: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HJ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YW: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. GC: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. ZM: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. XJ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. JL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (YESS) (2020QNRC001), Wheat Seed Industry Innovation and Joint Breeding Project (NYGG26), Central Government-Guided Local Science and Technology Development Funds (YDZJSX20231C011), and Shanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation Youth Project (202203021212433), Scientific Research and Development Fund of Cotton Research Institute, Shanxi Agricultural University (SJJQN2023-06).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1443239/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Frequency distribution of the maximum disease severity of powdery mildew in the Doumai/Shi 4185 RIL population.
References
Asad, M. A., Bai, B., Lan, C., Yan, J., Xia, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2014). Identification of QTL for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese wheat landrace Pingyuan 50. Crop J. 2, 308–314. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2014.04.009
Bapela, T., Shimelis, H., Terefe, T., Bourras, S., Sánchez-Martín, J., Douchkov, D., et al. (2023). Breeding wheat for powdery mildew resistance: genetic resources and methodologies-a review. Agronomy 13, 1173. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13041173
Chandran, N. K., Sriram, S., Prakash, T., Budhwar, R. (2021). Transcriptome changes in resistant and susceptible rose in response to powdery mildew. J. Phytopathol. 169, 556–569. doi: 10.1111/jph.v169.9
Desiderio, F., Bourras, S., Mazzucotelli, E., Rubiales, D., Keller, B., Cattivelli, L., et al. (2021). Characterization of the resistance to powdery mildew and leaf rust carried by the bread wheat cultivar Victo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 3109. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063109
Hao, Y., Parks, R., Cowger, C., Chen, Z., Wang, Y., Bland, D., et al. (2015). Molecular characterization of a new powdery mildew resistance gene Pm54 in soft red winter wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 128, 465–476. doi: 10.1007/s00122-014-2445-1
He, H., Guo, R., Gao, A., Chen, Z., Liu, R., Liu, T., et al. (2022). Large-scale mutational analysis of wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm21. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 988641. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.988641
He, H., Liu, R., Ma, P., Du, H., Zhang, H., Wu, Q., et al. (2021). Characterization of Pm68, a new powdery mildew resistance gene on chromosome 2BS of Greek durum wheat TRI 1796. Theor. Appl. Genet. 134, 53–62. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03681-2
He, H., Zhu, S., Zhao, R., Jiang, Z., Ji, Y., Ji, J., et al. (2018). Pm21, encoding a typical CC-NBS-LRR protein, confers broad-spectrum resistance to wheat powdery mildew disease. Mol. Plant 11, 879–882. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.03.004
Hu, Y., Cheng, Y., Yu, X., Liu, J., Yang, L., Gao, Y., et al. (2021). Overexpression of two CDPKs from wild Chinese grapevine enhances powdery mildew resistance in Vitis vinifera and Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 230, 2029–2046. doi: 10.1111/nph.v230.5
Janáková, E., Jakobson, I., Peusha, H., Abrouk, M., Škopová, M., Šimková, H., et al. (2019). Divergence between bread wheat and Triticum militinae in the powdery mildew resistance QPm.tut-4A locus and its implications for cloning of the resistance gene. Theor. Appl. Genet. 132, 1061–1072. doi: 10.1007/s00122-018-3259-3
Jia, M., Xu, H., Liu, C., Mao, R., Li, H., Liu, J., et al. (2020). Characterization of the powdery mildew resistance gene in the elite wheat cultivar Jimai 23 and its application in marker-assisted selection. Front. Genet. 11, 241. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00241
Kang, Y., Barry, K., Cao, F., Zhou, M. (2020a). Genome-wide association mapping for adult resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47, 1241–1256. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05225-4
Kang, Y., Zhou, M., Merry, A., Barry, K. (2020b). Mechanisms of powdery mildew resistance of wheat-a review of molecular breeding. Plant Pathol. 69, 601–617. doi: 10.1111/ppa.13166
Kaur, B., Mavi, G. S., Gill, M. S., Saini, D. K. (2020). Utilization of KASP technology for wheat improvement. Cereal Res. Commun. 48, 409–421. doi: 10.1007/s42976-020-00057-6
Keller, M., Keller, B., Schachermayr, G., Winzeler, M., Schmid, J. E., Stamp, P., et al. (1999). Quantitative trait loci for resistance against powdery mildew in a segregating wheat× spelt population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 98, 903–912. doi: 10.1007/s001220051149
Li, G., Cowger, C., Wang, X., Carver, B. F., Xu, X. (2019). Characterization of Pm65, a new powdery mildew resistance gene on chromosome 2AL of a facultative wheat cultivar. Theor Appl. Genet. 132, 2625–2632. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03377-2
Li, Y., Shi, X., Hu, J., Wu, P., Qiu, D., Qu, Y., et al. (2020). Identification of a recessive gene PmQ conferring resistance to powdery mildew in wheat landrace Qingxinmai using BSR-Seq analysis. Plant Dis. 104, 743–751. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-19-1745-RE
Li, F., Wen, W., He, Z., Liu, J., Jin, H., Cao, S., et al. (2018). Genome-wide linkage mapping of yield-related traits in three Chinese bread wheat populations using high-density SNP markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 131, 1903–1924. doi: 10.1007/s00122-018-3122-6
Li, G., Xu, X., Bai, G., Carver, B. F., Hunger, R., Bonman, J. M. (2016). Identification of novel powdery mildew resistance sources in wheat. Crop Sci. 56, 1817–1830. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2015.09.0551
Li, M., Zhang, H., Xiao, H., Zhu, K., Shi, W., Zhang, D., et al. (2024). A membrane associated tandem kinase from wild emmer wheat confers broad-spectrum resistance to powdery mildew. Nat. Commun. 15, 3124. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47497-w
Liu, N., Hake, K., Wang, W., Zhao, T., Romeis, T., Tang, D. (2017). CALCIUM-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE5 associates with the truncated NLR protein TIR-NBS2 to contribute to exo70B1-mediated immunity. Plant Cell 29, 746–759. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00822
Liu, J., He, Z., Rasheed, A., Wen, W., Yan, J., Zhang, P., et al. (2017). Genome-wide association mapping of black point reaction in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 17, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1167-3
Liu, J., He, Z., Wu, L., Bai, B., Wen, W., Xie, C., et al. (2016). Genome-wide linkage mapping of QTL for black point reaction in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 129, 2179–2190.
Liu, J., Rasheed, A., He, Z., Imtiza, M., Arif, A., Mahmood, T., et al. (2019). Genome-wide variation patterns between landraces and cultivars uncover divergent selection during modern wheat breeding (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 132, 2509–2523.
Liu, Z., Wang, Q., Wan, H., Yang, F., Wei, H., Xu, Z., et al. (2021). QTL mapping for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese elite common wheat Chuanmai104. Cereal Res. Commun. 49, 99–108. doi: 10.1007/s42976-020-00082-5
Ma, Z. Q., Sorrells, M. E., Tanksley, S. D. (1994). RFLP markers linked to powdery mildew resistance genes Pm1, Pm2, Pm3, and Pm4 in wheat. Genome 37, 871–875. doi: 10.1139/g94-123
Marone, D., Russo, M. A., Laidò, G., De Vita, P., Papa, R., Blanco, A., et al. (2013). Genetic basis of qualitative and quantitative resistance to powdery mildew in wheat: from consensus regions to candidate genes. BMC Genomics 14, 562. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-562
Meng, L., Li, H., Zhang, L., Wang, J. (2015). QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J. 3, 269–283. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2015.01.001
Nie, Y. B., Ji, W. Q. (2019). Cloning and characterization of disease resistance protein RPM1 genes against powdery mildew in wheat line N9134. Cereal Res. Commun. 47, 473–483. doi: 10.1556/0806.47.2019.27
Nordestgaard, N. V., Thach, T., Sarup, P., Rodriguez-Algaba, J., Andersen, J. R., Hovmøller, M. S., et al. (2021). Multi-parental populations suitable for identifying sources of resistance to powdery mildew in winter wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 570863. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.570863
Nyquist, W. E., Baker, R. J. (1991). Estimation of heritability and prediction of selection response in plant populations. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 10, 235–322. doi: 10.1080/07352689109382313
Qie, Y., Sheng, Y., Xu, H., Jin, Y., Ma, F., Li, L., et al. (2019). Identification of a new powdery mildew resistance gene pmDHT at or closely linked to the Pm5 locus in the Chinese wheat landrace Dahongtou. Plant Dis. 103, 2645–2651. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-02-19-0401-RE
Rasheed, A., Hao, Y., Xia, X., Khan, A., Xu, Y., Varshney, R. K., et al. (2017). Crop breeding chips and genotyping platforms: progress, challenges, and perspectives. Mol. Plant 10, 1047–1064. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.06.008
Rasheed, A., Wen, W., Gao, F., Zhai, S., Jin, H., Liu, J., et al. (2016). Development and validation of KASP assays for genes underpinning key economic traits in bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 129, 1843–1860. doi: 10.1007/s00122-016-2743-x
Saini, D. K., Chahal, A., Pal, N., Srivastava, P., Gupta, P. K. (2022). Meta-analysis reveals consensus genomic regions associated with multiple disease resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol. Breed. 42, 11. doi: 10.1007/s11032-022-01282-z
Sánchez-Martín, J., Widrig, V., Herren, G., Wicker, T., Zbinden, H., Gronnier, J., et al. (2021). Wheat Pm4 resistance to powdery mildew is controlled by alternative splice variants encoding chimeric proteins. Nat. Plants 7, 327–341. doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00869-2
Schmolke, M., Mohler, V., Hartl, L., Zeller, F. J., Hsam, S. L. K. (2012). A new powdery mildew resistance allele at the Pm4 wheat locus transferred from einkorn (Triticum monococcum). Mol. Breed. 29, 449–456. doi: 10.1007/s11032-011-9561-2
Sethi, A., Sharaff, M., Sahu, R. (2021). Deciphering common temporal transcriptional response during powdery mildew disease in plants using meta-analysis. Plant Gene. 27, 100307. doi: 10.1016/j.plgene.2021.100307
Shah, L., Rehman, S., Ali, A., Yahya, M., Riaz, M. W., Si, H., et al. (2018). Genes responsible for powdery mildew resistance and improvement in wheat using molecular marker-assisted selection. J. Plant Dis. Protect. 125, 145–158.
Shi, X., Wu, P., Hu, J., Qiu, D., Qu, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2021). Molecular characterization of all-stage and adult-plant resistance loci against powdery mildew in winter wheat cultivar Liangxing 99 using BSR-Seq technology. Plant Dis. 105, 3443–3450. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-03-21-0664-RE
Simeone, R., Piarulli, L., Nigro, D., Signorile, M. A., Blanco, E., Mangini, G., et al. (2020). Mapping Powdery Mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici) Resistance in wild and cultivated tetraploid wheats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 7910.
Summers, R. W., Brown, J. K. M. (2013). Constraints on breeding for disease resistance in commercially competitive wheat cultivars. Plant Pathol. 62, 115–121. doi: 10.1111/ppa.2013.62.issue-S1
Sun, H., Hu, J., Song, W., Qiu, D., Cui, L., Wu, P., et al. (2018). Pm61: a recessive gene for resistance to powdery mildew in wheat landrace Xuxusanyuehuang identified by comparative genomics analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 131, 2085–2097. doi: 10.1007/s00122-018-3135-1
Ullah, K. N., Li, N., Shen, T., Wang, P., Tang, W., Ma, S., et al. (2018). Fine mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm4e in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Planta 248, 1319–1328. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2990-y
Wang, Q., Guo, J., Jin, P., Guo, M., Guo, J., Cheng, P., et al. (2022). Glutathione S-transferase interactions enhance wheat resistance to powdery mildew but not wheat stripe rust. Plant Physiol. 190, 1418–1439. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac326
Wang, B., Meng, T., Xiao, B., Yu, T., Yue, T., Jin, Y., et al. (2023). Fighting wheat powdery mildew: from genes to fields. Theor. Appl. Genet. 136, 196. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04445-4
Wei, Z. Z., Klymiuk, V., Bocharova, V., Pozniak, C., Fahima, T. (2020). A post-haustorial defense mechanism is mediated by the powdery mildew resistance gene, PmG3M, derived from wild emmer wheat. Pathogens 9, 418. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9060418
Wen, W., He, Z., Gao, F., Liu, J., Jin, H., Zhai, S., et al. (2017). A high-density consensus map of common wheat integrating four mapping populations scanned by the 90K SNP Array. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 1389. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01389
Wu, X., Bian, Q., Gao, Y., Ni, X., Sun, Y., Xuan, Y., et al. (2021). Evaluation of resistance to powdery mildew and identification of resistance genes in wheat cultivars. Peer J. 9, e10425. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10425
Wu, P., Hu, J., Zou, J., Qiu, D., Qu, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2019). Fine mapping of the wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm52 using comparative genomics analysis and the Chinese Spring reference genomic sequence. Theor. Appl. Genet. 132, 1451–1461. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03291-7
Yang, L., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Luo, M., Yang, M., et al. (2017). Identification and evaluation of resistance to powdery mildew and yellow rust in a wheat mapping population. PloS One 12, e0177905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177905
Zhang, R., Xiong, C., Mu, H., Yao, R., Meng, X., Kong, L., et al. (2021). Pm67, a new powdery mildew resistance gene transferred from Dasypyrum villosum chromosome 1V to common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Crop J. 9, 882–888. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2020.09.012
Zhang, D., Zhu, K., Dong, L., Liang, Y., Li, G., Fang, T., et al. (2019). Wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm64 derived from wild emmer (Triticum turgidum var. dicoccoides) is tightly linked in repulsion with stripe rust resistance gene Yr5. Crop J. 7, 761–770. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2019.03.003
Keywords: 90K SNP array, KASP, powdery mildew, Triticum aestivum, resistance
Citation: Liu X, Zhang X, Meng X, Liu P, Lei M, Jin H, Wang Y, Jin Y, Cui G, Mu Z, Liu J and Jia X (2024) Identification of genetic loci for powdery mildew resistance in common wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1443239. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1443239
Received: 03 June 2024; Accepted: 02 September 2024;
Published: 09 October 2024.
Edited by:
Francis Chuks Ogbonnaya, Grains Research and Development Corporation, AustraliaReviewed by:
Alagu Manickavelu, Central University of Kerala, IndiaSatinder Kaur, Punjab Agricultural University, India
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Zhang, Meng, Liu, Lei, Jin, Wang, Jin, Cui, Mu, Liu and Jia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoyun Jia, amlheGlhb3l1bkBzeGF1LmVkdS5jbg==; Jindong Liu, TGl1amluZG9uZ0BjYWFzLmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xia Liu1,2†
Xia Liu1,2† Hui Jin
Hui Jin Yanzhen Wang
Yanzhen Wang Yirong Jin
Yirong Jin Jindong Liu
Jindong Liu Xiaoyun Jia
Xiaoyun Jia