- 1Animal Sciences Division, Nuclear Institute for Agriculture and Biology College (NIAB-C), Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences (PIEAS), Faisalabad, Pakistan
- 2School of Zoology, Minhaj University Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
Melatonin, a pleiotropic hormone plays a vital role in enhancing livestock performance not only by regulating circadian rhythms but also by exhibiting antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and metabolic regulatory effects that collectively improve resilience, fertility, and productivity. Melatonin’s synthesis is predominantly influenced by light exposure, with increased production in darkness; however, factors such as diet and health status further modulate its levels. By helping animals adapt to environmental stressors, melatonin boosts immune responses, mitigates chronic illnesses, and optimizes production efficiency. Its regulatory influence extends to the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, enhancing hormone secretion, synchronizing estrous cycles, and improving embryo viability. This results in improved reproductive outcomes through the protection of gametes, increased sperm motility, and enhanced oocyte quality, all of which benefit the fertilization process. Additionally, melatonin positively impacts productive performance, promoting muscle growth, development, and optimizing milk yield and composition through its interaction with metabolic and endocrine systems. As ongoing research continues to uncover its broader physiological effects, melatonin supplementation emerges as a promising approach to improving livestock welfare, productivity, and sustainability in modern animal husbandry.
1 Introduction
Melatonin, a versatile hormone mainly synthesized by the pineal gland, has a unique lipophilic structure that enables it to cross biological membranes, including the blood-brain barrier. This characteristic facilitates its widespread distribution throughout the body, allowing melatonin to interact with both endocrine and non-endocrine tissues (Kopustinskiene and Bernatoniene, 2021). However, melatonin synthesis is not confined to the pineal gland; tissues like the retina, gastrointestinal tract (GIT), and immune cells also produce extra-pineal melatonin, reinforcing its systemic influence (Markus et al., 2021). In livestock, melatonin has gained prominence due to its extensive role in improving health, reproductive efficiency, and productive performance (Al-Hamedawi and Hatif, 2020; Yang et al., 2021; Abulaiti et al., 2023; Leyva-Corona et al., 2023). While traditionally recognized for regulating circadian rhythms, melatonin exerts broader physiological effects by enhancing immune function, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting overall wellbeing in livestock species (Deng et al., 2020; Yin et al., 2020).
The antioxidant action of melatonin is key to its positive health impacts on livestock (Jaworek et al., 2021). It neutralizes free radicals, reduces lipid peroxidation (LPO), and activates antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), mitigating oxidative stress commonly encountered in high-production environments. These effects help prevent cellular damage, and lower the incidence of diseases such as mastitis and salmonellosis, thereby contributing to increase longevity and productivity in livestock (Li et al., 2020; Yao et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2022; Al-Jebory et al., 2024).
Melatonin’s impact on the immune system extends beyond its antioxidant properties. Through receptor mediated (RM) and non-receptor mediated (NRM) pathways, it influences inflammatory responses by regulating the release of cytokines, including interleukins (IL)-2, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (Ferreira et al., 2021; Muñoz-Jurado et al., 2022). This regulation is particularly valuable in managing immune-related conditions in livestock animals.
In reproductive physiology, melatonin is essential for managing the HGP axis, improving the production of key reproductive hormones like gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and progesterone (P4) (Wassem et al., 2022). In seasonal breeders melatonin influences estrous cycles, ovulation, and luteal activity, improving fertility outcomes (de Carvalho et al., 2021; Abulaiti et al., 2023; Yesilkaya and Erdem, 2024). Further, melatonin’s protective effects on ovarian tissues, through its antioxidant action, reduce oxidative stress and apoptosis, supporting higher pregnancy rates (Sun et al., 2020; Hashem et al., 2023). In male animals, melatonin modulates testicular function, improving semen quality and bolstering artificial insemination (AI) programs (Samir et al., 2020; Akar et al., 2024). Its impact on energy metabolism and mitochondrial function further promotes reproductive and productive efficiency, particularly under stress-inducing environments.
The role of melatonin also extends to enhance the productive performance of livestock by fostering growth, muscle development, and feed efficiency (Viola et al., 2023). By modulating fat deposition and muscle growth through key myogenic regulatory factors, melatonin improves feed conversion ratios. This results in greater weight gain and improved milk yield. Furthermore, its interaction with the intestinal microflora enhances nutrient absorption and immune responses, augmenting growth and overall performance in poultry and ruminants (Al-Samrai et al., 2023; Kanyar and Karadaş, 2023).
This study aims to deliver a thorough review of recent research and new insights into the impact of melatonin on livestock. By reviewing the latest scientific research, it aims to present current knowledge on how melatonin impacts livestock health, reproductive outcomes, and productive performance. Potential strategies for optimizing melatonin supplementation in livestock will also be discussed, alongside highlighting key opportunities for further investigation, aiding to the ongoing discussion on sustainable animal husbandry practices amid modern agricultural challenges.
2 Factors influencing melatonin synthesis
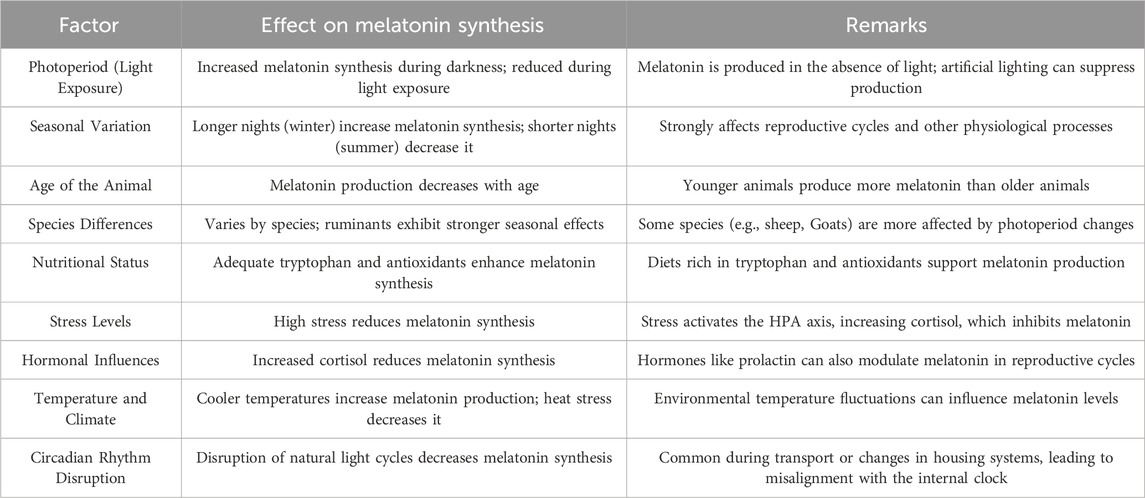
The synthesis of melatonin in livestock is influenced by a range of environmental, physiological, and management factors, each affecting production levels in unique ways. This complex regulation of melatonin synthesis is essential for aligning various physiological processes, such as reproductive cycles, immune responses, and stress resilience, with the environment. The factors detailed in Table 1 play significant roles in either enhancing or inhibiting melatonin production, depending on circumstances such as light exposure, seasonal changes, and stress (Hyder et al., 2017; Misztal et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2019; Li H. et al., 2021).
3 Sources of melatonin
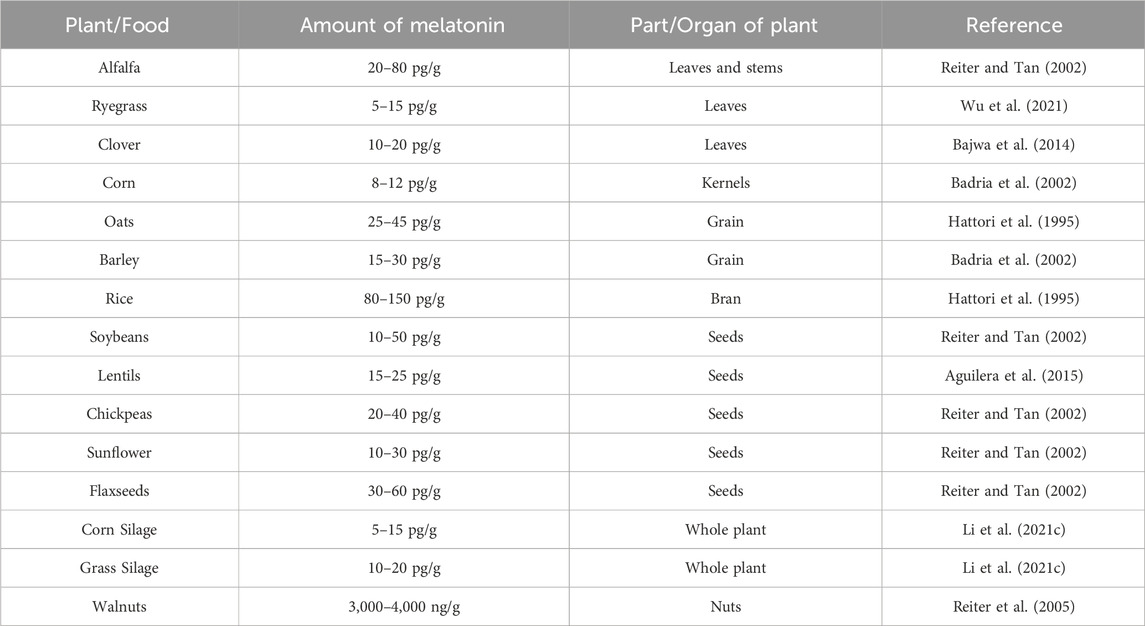
Melatonin occurs naturally in various edible plants and plant-based products, making it an advantageous component in livestock diets. These plants not only contain melatonin but also its precursors, with varying concentrations significantly depending on the specific plant tissue (Table 2) (Tan et al., 2012). These edible sources of melatonin are prevalent across common forage crops and grains used in livestock production. Forages such as alfalfa, clover, and ryegrass, frequently consumed by ruminants, naturally supply melatonin that aids in reducing stress and fostering relaxation in animals, leading to improved health and productivity.
4 Melatonin mechanism of action (RM and NRM)
Melatonin exerts its multifaceted effects on livestock through a combination of RM and NRM mechanisms, influencing various physiological processes. Its primary mode of action is through endocrine, autocrine, and paracrine pathways, largely facilitated by its binding to plasma membrane receptors and interactions with intracellular proteins (Samec et al., 2021). The distribution of melatonin receptors across different tissues and organs in livestock varies significantly. In mammals, including livestock animals, melatonin primarily engages with G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), such as melatonin receptor (MT) 1, MT2, and MT3, which are crucial for regulating processes like circadian rhythms, cardiovascular function, and immune responses (Boiko et al., 2022; Cecon et al., 2023). MT1 and MT2 receptors, in particular, play significant roles in livestock, where they regulate circadian rhythms and cardiovascular activity through inhibition of adenylate cyclase and modulation of phospholipase C signaling (Li M. et al., 2021; Samanta, 2022). MT3 receptors, which belong to the quinone reductase family, contribute to detoxification processes and oxidative stress reduction (Shabajee-Alibay et al., 2022).
Besides its effects through receptor interactions, melatonin also demonstrates important NRM effects, particularly in its role as a potent antioxidant. Melatonin’s ability to directly scavenge free radicals and activate antioxidant enzyme pathways underscores its protective capacity within cells. These actions help livestock combat oxidative stress, a common challenge in high-stress production environments (Purushothaman et al., 2020; Ikram et al., 2021). Melatonin also binds to transition metals, preventing the formation of harmful hydroxyl radicals, further supporting its antioxidant function (Galano et al., 2021). In livestock animals, melatonin is highly concentrated in mitochondria, where it protects vital cellular components—proteins, lipids, and DNA—from oxidative damage induced by free radicals during cellular respiration (Esteban-Zubero et al., 2023; Kennaway, 2023).
5 Health effects of melatonin in livestock
5.1 Source of circulating amino acids
Melatonin, synthesized from tryptophan, has garnered increasing interest due to its potential impact on circulating amino acids. Melatonin alleviated the impact of nutrient restriction on the levels of total amino acids and branched-chain amino acids during gestation in both small and large ruminants (Trotta et al., 2021; Swanson et al., 2022). Additionally, in these animals, melatonin exhibited a rescuing effect on nutrient restriction in various transport systems, including System A, System N, and anion amino acids (Swanson et al., 2022). This dual action of melatonin underscores its potential to modulate amino acid availability and transport systems, highlighting its significance in maintaining metabolic balance during gestation.
Research on melatonin as a therapeutic has expanded beyond gestational issues. In mammary glands cancer, melatonin diminished the impact of cancer on the levels of circulating amino acids. Specifically, aspartate, leucine, lysine, proline, serine, and valine concentrations were influenced by melatonin (Junior et al., 2022). This exhibits that melatonin effectively regulates amino acids in cancer, potentially inhibiting tumor growth by reducing the fuel source for cancer cells.
5.2 Endocrine modulations
The secretion patterns of melatonin are intricately linked to the metabolism of steroids and prostaglandins (PG) in livestock. In particular, luteal cells exposed to melatonin demonstrate a stimulatory effect on P4 hormone production (Bouroutzika et al., 2020; Pool et al., 2020). Melatonin supplementation has been shown to reduce PGF2 and estrogen (E2) levels in endometrial and hypothalamic cells, accompanied by a simultaneous decrease in the uterine contractile response to oxytocin (Wang et al., 2021a; Duan et al., 2022; Kacar et al., 2023). The interaction between melatonin and E2 receptors mirrors that of a selective E2 receptor modulator, potentially inhibiting E2 synthesis in steroidogenic tissues (Cos et al., 2014). Furthermore, melatonin has been linked to reduced activity and expression of aromatase, the enzyme involved in E2 production, as well as sulfatase, which affects E2 availability. This reduction might result in higher activity of E2 sulfotransferase, which produces E2 sulfate—a variant with diminished biological activity but a longer duration in the body (Jin et al., 2021).
Dietary supplementation of melatonin during the later stages of gestation has been linked to a reduction in both estradiol-17β and P4 concentrations (McCarty et al., 2018). This effect is attributed to the possible enhancement of cytochrome P450 1A enzymatic activity (Hwang et al., 2020; Singh M. et al., 2020; Hwang et al., 2021). A deficiency in estradiol production has been connected to traits resembling pre-eclampsia, suggesting that changes in estradiol metabolism due to melatonin exposure may influence utero-placental development during pregnancy (Sljivancanin Jakovljevic et al., 2020).
Exposure of bovine endometrial epithelial cells to estradiol results in decreased expression of melatonin receptor 1, whereas P4 treatment leads to an increase in this receptor’s expression (Brockus et al., 2016a). These findings underscore the complex relationship between the synthesis and metabolism of utero-placental steroids and PG and their influence on nutrient transport and uterine blood flow (Harman et al., 2023). Additionally, E2 is known to suppress adrenergic tone in the uterine arteries. Increased melatonin levels might lower E2 levels or sensitivity, potentially influencing the regulation of uterine blood flow, especially in problematic pregnancies (Edwards et al., 2020; Gaur and Purohit, 2020; Piotrowska-Tomala et al., 2022).
5.3 Impact on microbiome
The intricate interplay between immune system modulation and microbial fluctuations across the body has recently gained considerable attention in various livestock species. Harnessing the correlation between microbial presence and immune status has become an exciting frontier in livestock research. Melatonin exerts a profound influence on microbial populations of different systems in the body of animals, highlighting the vast scope of its biological impact. (Figure 1).
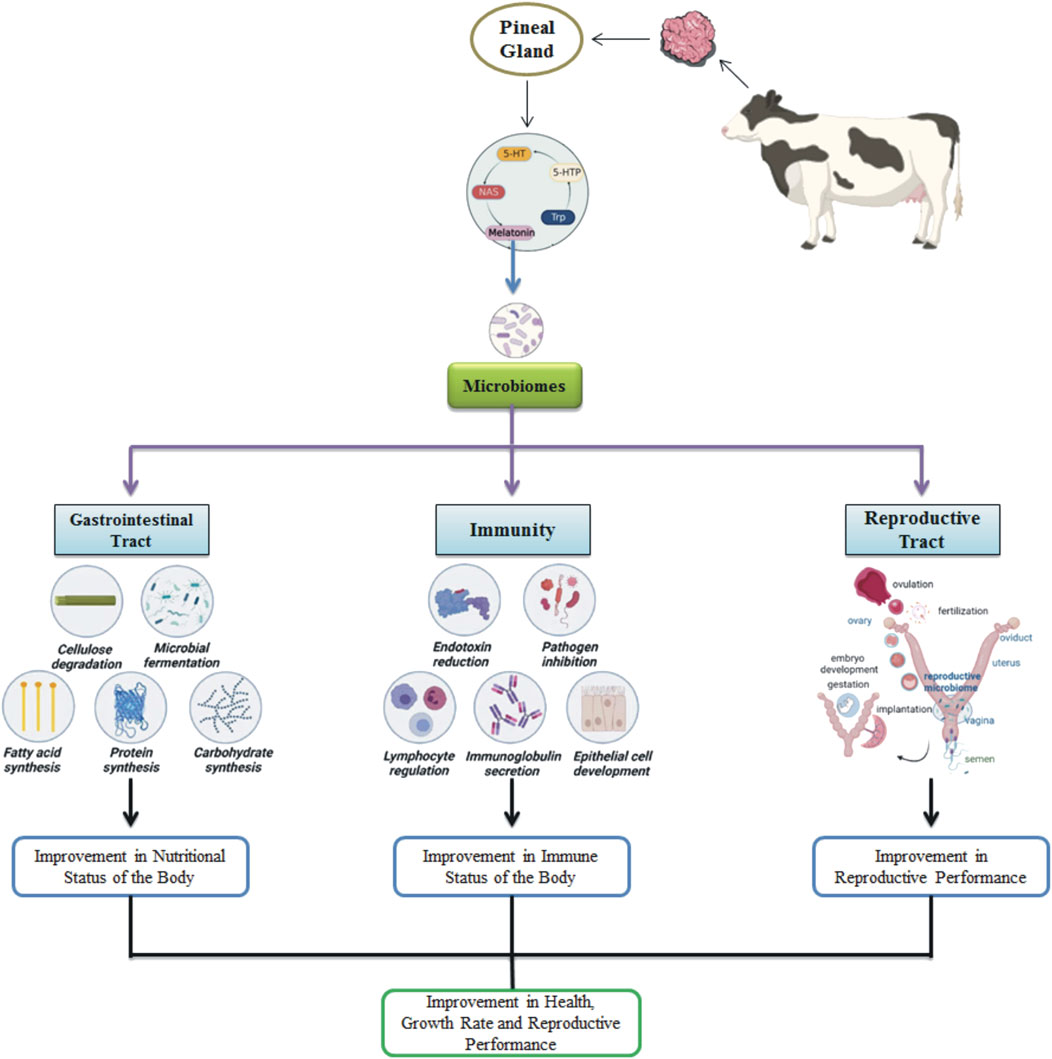
Figure 1. Melatonin effects on the microbiomes in the animal’s body, influencing gastrointestinal, immune, and reproductive functions.
5.3.1 GIT microbiome
Melatonin has significant potential in alleviating microbial dysbiosis (Gao et al., 2021). Its effects are mainly mediated through toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), which plays a crucial role in pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) signaling, especially in relation to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in Gram-negative bacteria (Kim et al., 2020). Melatonin’s presence within the GIT is remarkable, with concentrations exceeding those in the pineal gland by up to 400-fold, reflecting the abundance of melatonin receptors and the enzymes required for its production in the gut (Kennaway, 2023). Furthermore, gut microbes exhibit circadian rhythms that mirror those of the host, significantly influencing their metabolic functions (Zheng et al., 2024). Given melatonin’s critical role in regulating the biological clock, it becomes evident that the circadian rhythms of gut microbes and their functions are intricately tied to melatonin.
The identification of rhythmic patterns in the ruminant gut microbiome has prompted additional research, suggesting that melatonin’s effects might stem from its presence in saliva. Salivary melatonin, known for its role in regulating inflammation, promoting antioxidant responses, and accelerating the healing of oral wounds (Elsherbini and Ezzat, 2020), exhibits circadian rhythms similar to those found in ruminal fluid and muscularis (Ouyang et al., 2021). This implies that melatonin present in saliva might affect microbial communities across the GIT through circadian variations. Indeed, the rhythmic changes in rumen microbial populations correspond with fluctuations in melatonin levels, with elevated melatonin associated with a higher relative abundance of the families Preovotellaceae and Muribaculaceae, and a reduction in Succininivibrionaceae and Veillonellaceae (Fu et al., 2023). These findings exhibit melatonin’s capacity to impact Gram-negative bacteria through cytokine production and metabolic regulation (Xue et al., 2023). Fluctuations in melatonin levels within the GIT affect crucial metabolic pathways, thereby impacting the predominant phyla in the rumen, such as Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidetes (Fu et al., 2023).
5.3.2 Reproductive tract microbiome
Melatonin has recently emerged as a promising regulator of the reproductive tract microbiome in livestock. The reproductive microbiome plays a vital role in fertility and overall reproductive efficiency (Hussain et al., 2021). In cows, melatonin supplementation has been shown to modulate bacterial populations within the uterus and vagina, fostering a more favorable environment for reproduction. This effect is attributed to melatonin’s potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which may create optimal conditions for embryo development and implantation (Messman et al., 2021).
Beyond its influence on microbial composition, melatonin also impacts the immune response within the reproductive tract, which is intricately linked to the microbiome (Wang et al., 2021b). By enhancing immune function, melatonin indirectly supports a balanced microbiome, further promoting reproductive success. This dual role underscores the complex interplay between melatonin, the microbiome, and immune health, all of which are crucial for successful reproduction in livestock. Interestingly, melatonin’s effects on the reproductive tract microbiome vary across livestock species (Cosso et al., 2021). Factors such as physiological state, age, and environmental conditions likely contribute to these variations. Understanding these complexities is essential for developing tailored melatonin supplementation strategies that maximize reproductive health benefits across diverse livestock populations.
5.4 Immunomodulation
Melatonin, recognized for its immune-boosting and anti-apoptotic effects, is crucial in regulating immune responses, especially by boosting the T helper 1 immune pathway (Esquifino et al., 2004). While its primary function lies in regulating circadian rhythms, melatonin also exerts significant secondary effects on the immune system, including upregulating cytokine production, promoting T cell propagation, stimulating natural killer (NK) cell activity, amplifying antigen presentation, and maintaining a balanced cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) to CD8 immune cell ratio (Maestroni, 2001; Baltaci et al., 2018; Castellano and Molinier-Frenkel, 2020; Tune et al., 2020). Although studies on the use of melatonin supplements for livestock are still in the preliminary phase, it has shown promise in enhancing reproductive performance and mitigating stress or trauma-induced immunosuppression (Bouroutzika et al., 2021; Paulino et al., 2022).
Disruption of melatonin synthesis, whether through constant light exposure or the use of β-adrenergic blockers, results in a weakened immune response to antigens (Hanoun et al., 2015; Horodincu and Solcan, 2023). This immune suppression is characterized by an impaired primary antibody response, reduced immune cell populations in the thymus and spleen, and diminished lymphocyte proliferation. However, the administration of melatonin has been shown to reverse these immunosuppressive effects (Chang et al., 2020). Additionally, melatonin has been found to enhance vaccine efficacy, with animals receiving melatonin exhibiting a stronger antibody response post-vaccination, indicative of a more robust immune defense (Regodón et al., 2012; Cardinali et al., 2021; Wang S. et al., 2021). Further research into melatonin’s immune-stimulatory roles has revealed its complex interactions with cellular and cytokine profiles in both humoral and innate immune responses (Hosseini et al., 2021).
5.5 Impact on disease treatment
Melatonin treatment in Trypanosoma cruzi infections enhances the population of CD4+ CD28-negative T cells while simultaneously reducing CD28-negative cells within both the CD4+ and CD8+ subsets. This immunomodulatory effect is further reflected in the thymus, where melatonin decreases thyrotropin receptor antibody (TRAb) levels, aiding in the restoration of thymus size and thymocyte populations, essential for maintaining immune function (Brazao et al., 2020). Beyond its immune-boosting effects, melatonin’s potent anti-inflammatory properties offer significant protection against mastitis in dairy animals, helping to prevent the inflammatory damage commonly associated with this condition (Yao et al., 2020; Li and Sun, 2022).
In metabolic disorders like diabetes, melatonin demonstrates its antioxidant capabilities by normalizing malondialdehyde (MDA) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels while reducing cleaved caspase-3 expression, which signals its role in mitigating cellular damage (Abdulwahab et al., 2021). These protective effects extend to trauma-induced pulmonary issues, where melatonin improves total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and reduces organ damage, showcasing its broad therapeutic potential (Ates et al., 2022).
Melatonin’s influence is equally significant in the context of liver diseases, such as ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and cirrhosis, where it modulates the nitrogen oxide (NOx) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathways to alleviate oxidative damage and promote tissue recovery (Zhang C. et al., 2021; Esteban-Zubero et al., 2023). Similarly, in acute pancreatitis, melatonin effectively prevents LPO, while in kidney injury, it prevents cytotoxic impairment, highlighting its organ-protective role (Ahsen et al., 2014; Karabulut-Bulan et al., 2015). Moreover, its neuroprotective effects are evident in cases of brain damage, stroke, and ischemia, where melatonin mitigates inflammation, reduces edema, and promotes cell survival, further emphasizing its wide-ranging therapeutic applications across various systems (Mihardja et al., 2020; Wongchitrat et al., 2021).
5.6 Antioxidant properties
5.6.1 Mechanisms of oxidative stress reduction
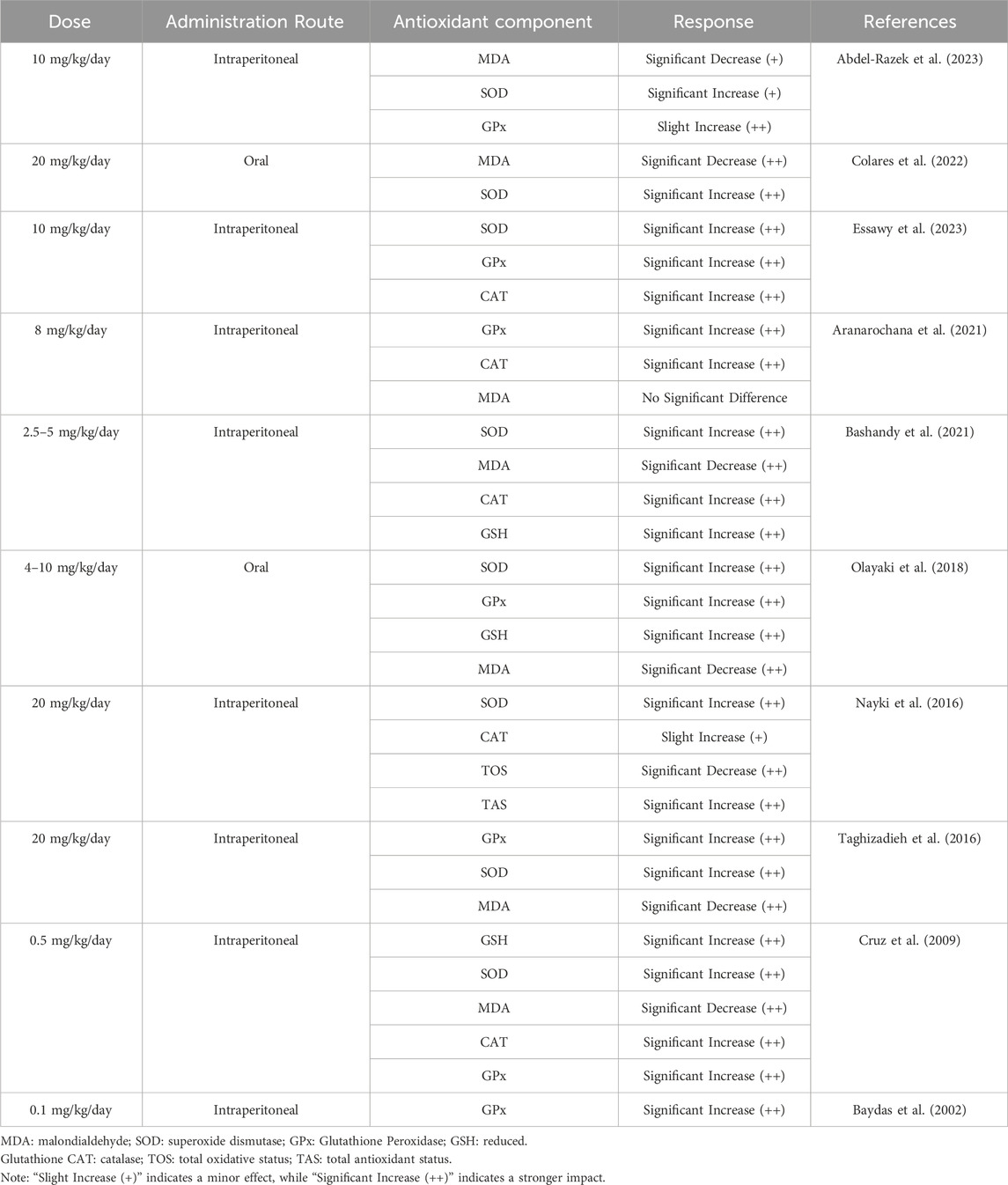
Melatonin is a potent antioxidant with the unique ability to dissolve in both water and fats, enabling it to function in various environments, such as within cell interiors, body fluids, membranes, and organelles (Zarezadeh et al., 2022). It outperforms conventional antioxidants like vitamins E and C in mitigating oxidative stress. Unlike typical antioxidants, which neutralize only one or a few reactive oxygen species (ROS), melatonin can neutralize up to 10 ROS molecules (Marchena et al., 2020). This remarkable capacity is attributed to its ability to stimulate key antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, CAT, GPx, and GSH, particularly when given in doses between 0.1 and 20 mg/kg per day (Table 3) (Baydas et al., 2002; Cruz et al., 2009; Nayki et al., 2016; Taghizadieh et al., 2016; Olayaki et al., 2018; Aranarochana et al., 2021; Bashandy et al., 2021; Colares et al., 2022; Abdel-Razek et al., 2023; Essawy et al., 2023).
Melatonin not only increases the mRNA levels of these antioxidant enzymes but also inhibits pro-oxidant enzymes such as nitric oxide synthase (Monteiro et al., 2024). By altering membrane fluidity, melatonin safeguards cell membranes from oxidative harm and eliminates free radicals before they damage lipids and proteins, all without promoting pro-oxidant effects (Kopustinskiene and Bernatoniene, 2021). It acts as an effective scavenger of free radicals and an electron donor, neutralizing various reactive species like hydroxyl radicals, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide (Ahmadi and Ashrafizadeh, 2020). When melatonin interacts with hydroxyl radicals, it produces 3-hydroxymelatonin, which is later excreted through urine. Its metabolites, such as AMK and AFMK, display even greater antioxidant potency (Galano and Reiter, 2018; Zarezadeh et al., 2022).
5.6.2 Initiation of antioxidant response components
Recent discoveries highlight melatonin’s pivotal role in activating the antioxidant response element (ARE) system, which triggers the transcription of numerous antioxidant proteins and enzymes to neutralize ROS and support essential protein transport (Vriend and Reiter, 2015). Central to this process is the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2 (Nrf2)-ARE signaling pathway, which significantly enhances the activity of key antioxidant enzymes. This pathway provides a protective mechanism that shields livestock from various diseases, helping to preserve their productive potential (Zhang W. et al., 2018; Dong et al., 2020).
Under oxidative stress, melatonin elevates cellular Nrf2 levels, which is crucial for its antioxidant function. Melatonin facilitates the nuclear translocation of the Nrf2 transcription factor and promotes its interaction with ARE, thereby amplifying the expression of antioxidant enzymes (Figure 2) (Deng et al., 2016). Further, melatonin has been demonstrated to reduce stress-related damage by safeguarding the hippocampus through the regulation of the Nrf2/Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathway. Although research is still expanding, melatonin is also thought to increase the concentration of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B (IκB) alpha, an inhibitor of NF-κB, suggesting an additional mechanism by which it regulates inflammatory responses (Rajput et al., 2017).
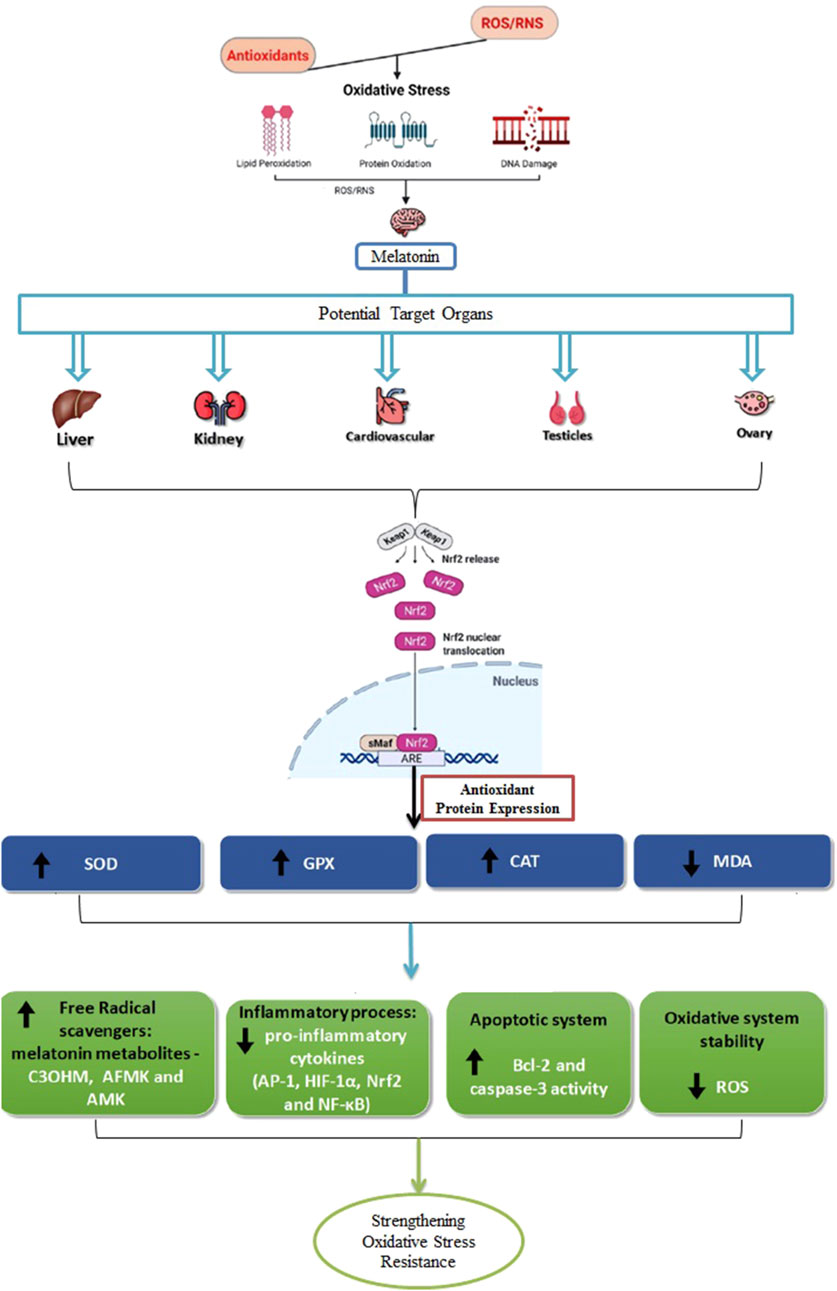
Figure 2. Antioxidant activity of melatonin across various tissues. It plays a role in receptor-independent pathways that result in the formation of metabolites like cyclic 3-hydroxymelatonin (C3OHM), N1-acetyl-N2-formyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AFMK), and N1-acetyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AMK). In addition to its antioxidant effects, melatonin modulates inflammatory responses by targeting key regulators, including activator protein 1 (AP-1), hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), Nrf2, and NF-κB. It also impacts apoptotic pathways by interacting with proteins such as B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and contributes to maintaining redox homeostasis by reducing the generation of ROS. This leads to an upregulation of antioxidant enzymes like SOD, GPx, and CAT, while decreasing MDA levels, an indicator of LPO. Due to its amphiphilic nature, melatonin can easily cross tissue barriers, enabling it to exert protective effects on organs such as the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system, as well as the reproductive organs like the testicles and ovaries.
Moreover, melatonin reduces the levels of nitrites, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and microsomal PG E synthase-1 (mPGES-1), while also preventing the translocation of NF-κB in peritoneal macrophages. By lowering pro-inflammatory mediators and enhancing HO-1 expression through NF-κB, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and Nrf2 signaling, melatonin shows significant potential as a therapeutic agent for conditions involving macrophage over-activation (Deng et al., 2020).
5.6.3 Protection from harmful impacts of chemical agents inducing oxidative stress
Melatonin acts as a safeguard against the detrimental effects of various chemical compounds that induce oxidative stress. For instance, dizocilpine maleate (MK-801), a compound known to induce oxidative damage in the prefrontal cortex, leads to psychotic symptoms, but melatonin can counteract these effects. Similarly, cadmium negatively impacts male reproductive health; however, melatonin alleviates this toxicity by lowering MDA levels, boosting SOD activity, increasing GSH, and elevating pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta (Venditti et al., 2021).
Melatonin also protects the cerebellum from damage caused by acrylamide by reducing LPO, boosting antioxidant enzyme activities, and lessening DNA damage (Ozturk et al., 2023). The cerebellum, which is highly susceptible to chemical insults, often undergoes neuron loss and organ shrinkage during development. Lead (Pb) is another toxicant that causes oxidative stress and neurotoxicity; however, melatonin (at 10 mg/kg) has been shown to reduce LPO and protect the cerebellum from Pb-induced toxicity (Bazrgar et al., 2015). Additionally, melatonin exhibits neuroprotective properties against ethanol toxicity in the cerebellum and lowers plasma homocysteine (Hcy) levels, further strengthening its role as a neuroprotective agent (Bagheri et al., 2024).
5.6.4 Shielding against radiation-induced damage
Animals are exposed to various forms of radiation, against which melatonin provides protection. For instance, tropical animals frequently encounter ultraviolet (UV) radiation. When these animals were treated with melatonin after UV exposure, there was a marked increase in the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, CAT, and GPx. This enhanced enzyme activity neutralized free radicals, reducing the damage caused by UV radiation. Although UV radiation can indirectly harm spleen tissue, melatonin treatment aided in restoring balance and preventing splenocyte apoptosis, thus maintaining organ function (Goswami and Haldar, 2014). Melatonin also functions as an antioxidant in testicles exposed to microwaves, helping to alleviate oxidative stress and reduce DNA fragmentation (Özgen et al., 2023).
5.7 Effects on physiological stress markers
Livestock animals are routinely exposed to a range of environmental, physiological, and psychological stressors, which can negatively impact their health, productivity, and overall welfare (Johnson, 2018; Chauhan et al., 2021). Elements like handling practices, environmental changes, shifts in herd dynamics, and illness can impair immune function, resulting in chronic diseases, weight loss, and reduced production, all of which have considerable economic impacts. In this regard, melatonin, known for its immune-stimulatory properties, plays a vital role in reducing stress by regulating both physiological and psychological responses in livestock (Figure 3).
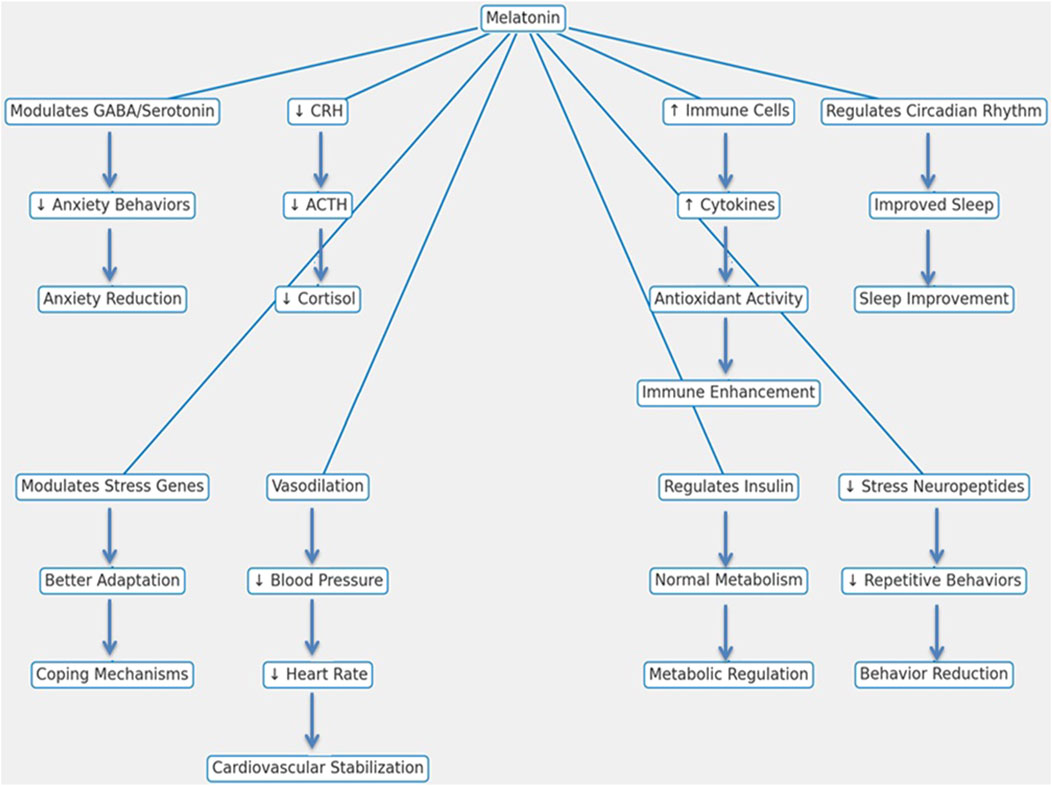
Figure 3. Mechanistic pathways of melatonin in reducing stress and enhancing physiological functions in livestock animals.
Melatonin primarily alleviates stress by modulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, an essential part of the body’s stress response system. It reduces the secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), leading to lower cortisol production, which is a major marker of physiological stress (Kumar and Singh, 2021). Further, melatonin affects the autonomic nervous system by encouraging vasodilation, lowering heart rate and blood pressure, and contributing to stable cardiovascular function (Imenshahidi et al., 2020; Zuo and Jiang, 2020).
Melatonin interacts with neurotransmitter systems, including gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and serotonin, to produce anxiolytic effects, reducing restlessness and aggression, especially during stressful events like transport and weaning (Xu et al., 2023). This reduction in anxiety enhances social behavior and improves interactions within the herd. Melatonin is also vital in managing the sleep-wake cycle and enhancing sleep quality, which is important for effective stress recovery. Better sleep enhances resilience against environmental stressors such as changes in housing and climate variations (Domple et al., 2017). Beyond its role in stress mitigation, melatonin contributes to metabolic regulation by interacting with insulin and other metabolic hormones, thereby stabilizing glucose and lipid metabolism and preventing stress-induced metabolic disorders (Samir et al., 2023). It also modulates gene expression in immune cells, boosting immune function, controlling inflammation, and supporting cell proliferation, all of which enhance the resilience of livestock animals (Wang et al., 2022). Levels of stress-related neuropeptides and hormones that are associated with abnormal behaviors such as pacing and excessive grooming are also reduced by melatonin in stressed animals (Zhang H. et al., 2021). By mitigating stress across multiple physiological systems, melatonin ultimately improves both welfare and productivity in livestock.
6 Reproductive performance
6.1 Mediation of reproduction
Melatonin regulates reproductive function by acting at both the hypothalamic and pituitary levels through highly expressed receptors (Wassem et al., 2022). Melatonin may affect reproduction by interacting with the hypothalamus through RM mechanisms and uptake. It reduces GnRH activity in the pituitary and lowers hypothalamic secretion by 45% by activating protein kinase (PK) A, PKC, and MAPK pathways. This suppression of gonadotropin release can help control the timing of puberty, as a drop in melatonin levels below a specific threshold prompts the hypothalamus to trigger reproductive changes (Rijal et al., 2020; Ding et al., 2021; Charif et al., 2022).
The pathway connecting the supra-chiasmatic nucleus (SCN) and the pituitary is crucial for reproduction in seasonally breeding mammals (Tolla and Stevenson, 2020). Information about light and dark cycles is relayed from the SCN to the pineal gland through a complex network of synapses, resulting in varying patterns of melatonin secretion that translate light cues into hormonal rhythms. Animals with SCN lesions or those that have had their pineal glands removed are unable to produce these photoperiodic responses, leading to disruptions in reproductive function (Carcangiu et al., 2014). Variations in day length serve as a “calendar” for many species, timing reproductive activity to coincide with periods of favorable energy availability and climatic conditions that enhance offspring survival. This conversion of environmental signals into the neuroendocrine system is facilitated by variations in nocturnal melatonin secretion (Giannetto et al., 2020).
Alterations in melatonin secretion resulting from changes in day length are consistent across different species but have varying impacts on reproductive function depending on the seasonal reproductive patterns. For short-day breeders like sheep and goats, elevated nocturnal melatonin levels stimulate the reproductive system, whereas in long-day breeders, these elevated levels suppress reproductive activity. Melatonin exerts its influence on reproduction both centrally, through its actions on the hypothalamus and pituitary, and directly in the gonads, which are not only targets of melatonin but also sites of its production (Singh P. et al., 2020; Tölü et al., 2022).
6.2 Influence of melatonin on ovarian activity
6.2.1 Granulosa cells (GC)
Follicular atresia significantly affects bovine reproductive performance, as it heavily depends on the health of GCs for ovarian follicle development. Disturbances in these cells, whether through apoptosis, autophagy, cell cycle arrest, or accumulation of ROS, can lead to follicular atresia (Wang H. et al., 2018; Ma et al., 2019; Wang Y.-X. et al., 2021). Additionally, alterations in steroid hormone synthesis further influence GC function. Melatonin, known for its ROS-scavenging properties and cellular regulatory abilities, plays a critical role in mitigating follicular atresia by reducing ROS levels and inhibiting apoptosis in GCs through various pathways (Xie et al., 2022).
In the initial phases of follicular atresia, apoptosis predominantly targets the inner layer of GCs, while the cumulus-oocyte complex and outer GCs remain largely unaffected, highlighting the selective nature of this process (Rajin et al., 2022). GCs are crucial for supporting and maintaining follicle growth, and their physiological condition greatly influences the fate of the follicle (Yuan et al., 2019). Mitochondria, as a primary source of ROS, contribute to mitochondrial swelling and apoptosis when ROS levels become excessive. Melatonin helps maintain antioxidant enzyme activity and neutralizes reactive oxygen by regulating ER oxidoreductin 1 (ERO1) and enhancing the activities of antioxidant enzymes (Fernández et al., 2015; Tamura et al., 2020).
Melatonin has been found to mitigate oxidative stress and apoptosis in bovine ovarian GCs caused by β-zearalenol (Yang et al., 2019). The protective effects of melatonin are modulated by its receptors, MT1 and MT2, as inhibition of these receptors can diminish melatonin’s benefits and interfere with cell cycle regulation (Gobbi and Comai, 2019). Melatonin’s influence also varies with environmental conditions such as temperature and oxygen concentration. For example, at 37.5°C and 5% O2, low concentrations of melatonin promote cell proliferation, while at 40°C, higher concentrations have the same effect (Zeebaree et al., 2018). This temperature-dependent response highlights melatonin’s potential in mitigating heat stress. Nonetheless, differences in physiological conditions and natural melatonin production make the reliable and effective use of supplemental melatonin challenging, highlighting the need for comprehensive data to guide evidence-based practices.
6.2.2 Follicles
Melatonin supports the development of bovine secondary follicles through membrane-bound receptors, whereas its antagonist, luzindole, inhibits these effects and decreases the expression of antioxidant enzymes in cultured follicles (Paulino et al., 2022). Additionally, melatonin stimulates follicular angiogenesis by increasing VEGF expression, which is crucial for follicular development (Tao et al., 2021). In theca cells, which exclusively express the MT2 receptor, melatonin inhibits androgen biosynthesis and slows ovarian atresia and aging by reducing apoptosis and regulating cell proliferation through the PI3K/Akt pathway (Wang S. et al., 2018; Ma et al., 2023). Abnormal melatonin levels in theca interna cells have also been linked to the development of follicular cysts in sows (Qin et al., 2022).
Beyond these roles, melatonin’s antioxidant properties support oocyte quality and enhance subsequent embryonic development, underscoring its potential in assisted reproduction. Studies have identified MT1 and MT2 mRNA in porcine cumulus-oocyte complexes, revealing that melatonin modulates GC function through MT2, which enhances cumulus expansion and embryonic development (He et al., 2016; Lee et al., 2018). Melatonin is critical for preventing age-related defects in germline-soma communication and aids in the transfer of antioxidant molecules from cumulus cells, preserving oocyte quality (Zhang H. et al., 2022).
Melatonin also shows promise as a pharmacological agent against endocrine disruptors such as Bisphenol A (BPA) and Bisphenol S (BPS), which impair follicular growth and steroidogenesis. It mitigates these harmful effects by increasing estradiol production, promoting GC proliferation, and protecting against mitochondrial apoptosis during oocyte maturation (Park et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2018; Berni et al., 2019). Its protective effects extend to other toxic substances, such as Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), which induces follicular atresia and oxidative stress. Melatonin’s antioxidant properties and ability to inhibit apoptosis provide effective protection against AFB1-induced toxicity (Cheng et al., 2019).
Furthermore, melatonin enhances results in ovarian tissue cryopreservation and is vital for reproductive processes and blastocyst implantation in various mammalian species. It achieves this by regulating apoptotic mechanisms, enhancing adhesion protein expression, and protecting against oxidative stress that compromises embryo quality and pregnancy success (Najafi et al., 2023). The detection of melatonin in follicular fluid, along with reduced levels in cases of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), further emphasizes its essential role in ovarian function and oocyte maturation (Shi et al., 2009).
6.2.3 Oocyte cells
The quality of oocytes is essential for reproductive success in female animals and is a key factor in ruminant embryo transfer. Fresh embryos generally lead to significantly higher live birth rates compared to those that have been cryopreserved (Insogna et al., 2021). Cryopreservation of oocytes has long been challenging due to issues with survival, fertilization, and developmental rates (Chen et al., 2003). To overcome these challenges, enhancing the quality of oocytes cultured in vitro before cryopreservation is crucial, and melatonin has proven to be a promising approach.
Studies show that melatonin can notably improve the developmental potential of oocytes, both in vitro and in vivo (Sananmuang et al., 2020). In cattle, melatonin improves oocyte developmental competence and embryonic growth by reducing ROS levels (Figure 4) (Gutiérrez-Añez et al., 2021). It also mitigates ROS in heat-stressed oocytes, increases maturation rates, boosts the proportion of embryos developing into blastocysts, and upregulates genes related to mitochondrial function (Yaacobi-Artzi et al., 2020). Melatonin also safeguards bovine oocytes from damage inflicted by harmful agents like paraquat, thus preserving their developmental potential (Pang et al., 2019).
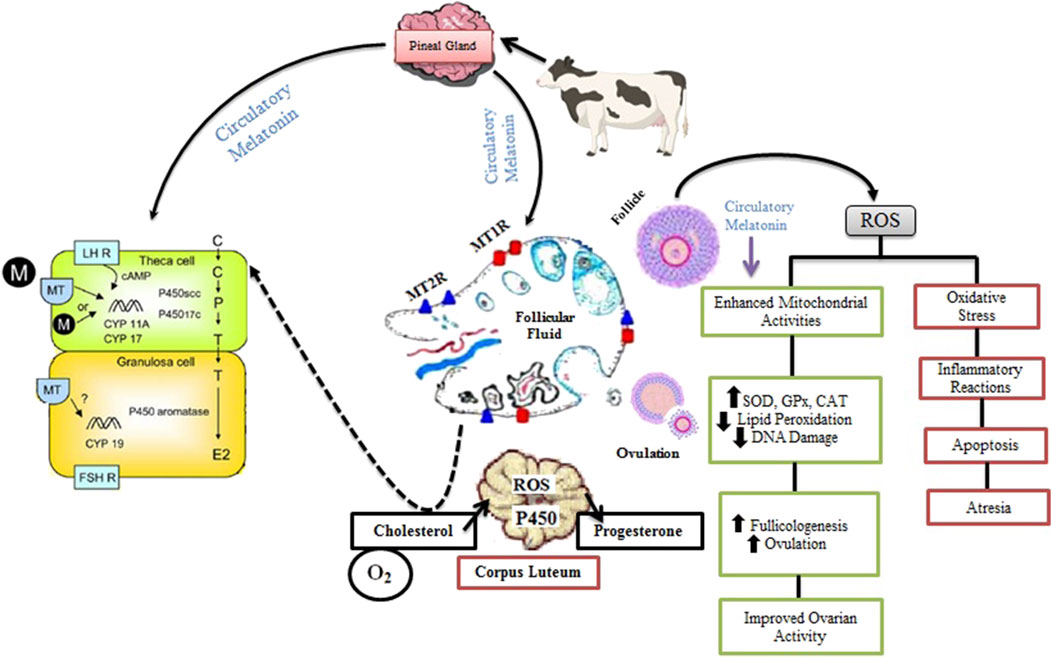
Figure 4. Role of Melatonin in Ovarian Function and Folliculogenesis in Livestock. Melatonin from circulation is taken up by the theca and granulosa cells of the follicle, where it interacts with its receptors, MT1R and MT2R, within the ovarian follicular fluid. This interaction stimulates the expression of LH and FSH mRNA, promoting hormone maturation and enhancing steroidogenic enzyme activities, such as those catalyzed by P450 aromatase, P450scc, and CYP17, which are responsible for synthesizing P4 and E2. During the process of follicular rupture, ROS are generated as a result of inflammatory reactions, leading to ovulation and further steroidogenesis, particularly the synthesis of P4 in the CL through monooxygenase reactions. Melatonin acts as a free radical scavenger, mitigating ROS-induced oxidative stress by boosting antioxidant enzymes like SOD, GPx, and CAT. This reduces LPO and DNA damage, while balancing ROS levels and antioxidative activity. By regulating mitochondrial function and minimizing oxidative damage, melatonin supports healthy follicle development, ovulation, and improved ovarian function, preventing detrimental effects such as apoptosis and follicular atresia. Ultimately, melatonin promotes the maturation of a healthy ovum, enhancing reproductive efficiency.
Substantial evidence underscores melatonin’s role in advancing oocyte development in bovines. It boosts the production of antioxidant enzymes via specific membrane and nuclear receptors, aiding in the removal of ROS. In cumulus-oocyte complexes, acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase (ASMT) may play a role in melatonin synthesis (El-Raey et al., 2011). By reducing oxidative stress via the MT1 membrane receptor, melatonin preserves spindle body function, a critical factor for oocyte development.
In cattle, administering melatonin from days 190–262 of gestation enhanced uterine blood flow, probably due to its impact on steroid metabolism (Brockus et al., 2016b). Melatonin also positively influenced estradiol metabolism, improving utero-placental development (Lemley and Vonnahme, 2017). During estrus synchronization and AI in cattle, external melatonin significantly elevated P4 levels, boosted antioxidant enzyme activity, and reduced MDA concentrations in the blood, resulting in a marked improvement in pregnancy rates (Guo et al., 2021).
6.2.4 Corpus luteum (CL)
A functional melatonergic system is essential for luteal function in mammals (Wang et al., 2021a). ROS, primarily generated from normal metabolic processes, are involved in both luteogenesis and luteolysis (Mierzejewski et al., 2023). During cholesterol transport for P4 synthesis and in the regression phase, LPO can damage the luteal plasma membrane, leading to impaired luteal function (Taketani et al., 2011; Cruz et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2021; Al-Shahat et al., 2022). Melatonin safeguards luteinizing GCs in the ovulatory follicle from ROS, boosts P4 production after ovulation, and helps prevent premature luteolysis in the newly developed CL. Elevated indolamine levels during the luteal phase underscore melatonin’s direct involvement in these processes. High concentrations of melatonin synthesis enzymes and receptor expression suggest that this site may serve as a key area for hormone synthesis and regulation (Xiao et al., 2018).
Melatonin deficiency in small ruminants disrupts follicular and luteal dynamics, resulting in decreased P4 synthesis (Kárpáti et al., 2023). In these animals, melatonin enhances P4 secretion by regulating autophagy through the AMPK/mTOR pathway (Duan et al., 2024). In equine corpus lutea, both MT1 receptor mRNA and protein are present. Melatonin reduces P4 production and P450scc expression in a dose-dependent manner. This inhibition can be reversed by luzindole, a non-selective melatonin receptor antagonist, indicating that functional melatonin receptors are present in luteal cells (Pedreros et al., 2011).
Melatonin’s role in luteal function has been evaluated during early pregnancy, given the endocrine organ’s importance in the initial stages of gestation (Verteramo et al., 2022). In heat-stressed cows, melatonin improves luteal hemodynamics (Abdelnaby and Abo El-Maaty, 2021). Local melatonin synthesis in the luteal cells of pregnant animals suggests a paracrine or autocrine role (Zhang et al., 2022b). In these animals, luteal cells during pregnancy show hormone receptor expression and increased P4 levels that correlate with melatonin concentration, mediated by upregulated P450scc and steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein (Zhang Y. et al., 2018). Moreover, melatonin stimulates GnRH and LH production in the luteal cells of pregnant animals, indicating a regulatory role through these hormones (Zhang et al., 2022c). Administering melatonin boosts the expression of genes related to pregnenolone synthesis, supports the development of the CL, aids in embryonic implantation, and enhances uterine receptivity during early pregnancy.
7 Melatonin influence on testicular function, spermatogenesis, and semen cryopreservation in livestock
Cryopreservation is vital for the long-term preservation of gametes in ruminants such as cattle and sheep, which is essential for genetic improvement and the conservation of endangered species. Although ROS are necessary for sperm capacitation, excessive ROS levels can cause damage to sperm morphology and DNA integrity through oxidative stress (Medrano et al., 2017; Ofosu et al., 2021). Melatonin by alleviating oxidative stress during sperm freezing, improves the quality of sperm after thawing (Appiah et al., 2019; Shahat et al., 2022).
Incorporating 1 mM melatonin into semen extenders improves sperm quality and mitigates the effects of heat stress. Additionally, melatonin implants significantly reduce the prevalence of morphologically abnormal sperm, increase motility, and boost total protein and cholesterol levels in seminal plasma (Inyawilert et al., 2021; Shahat et al., 2023). Optimal melatonin concentrations vary depending on the application: 10⁻³ M is recommended for semen cryopreservation, while 10⁻⁷ M is effective for enhancing oocyte maturation rates and increasing blastocyst numbers in in vitro fertilization (IVF). Medium concentrations of melatonin (0.25 mg/mL) yield the best results in terms of sperm motility and antioxidant indicators (Ramadan et al., 2019; Su et al., 2021).
Aside from influencing semen quality, melatonin is essential for spermatogenesis, as it regulates testicular function via the HPG axis. It delays puberty by decreasing levels of LH and prolactin, inhibiting GnRH-induced LH release, and lowering testosterone production—effects that can be reversed by the melatonin receptor MT1 blocker, luzindole (Frungieri et al., 2017). Throughout testicular growth and development, melatonin shields the testes from local inflammation and ROS, affecting hormone production and testicular cell growth via its receptors. Secreted by the pineal gland and absorbed by the testes, melatonin regulates testicular function, including testosterone secretion, apoptosis, and autophagy (El-Shalofy et al., 2021).
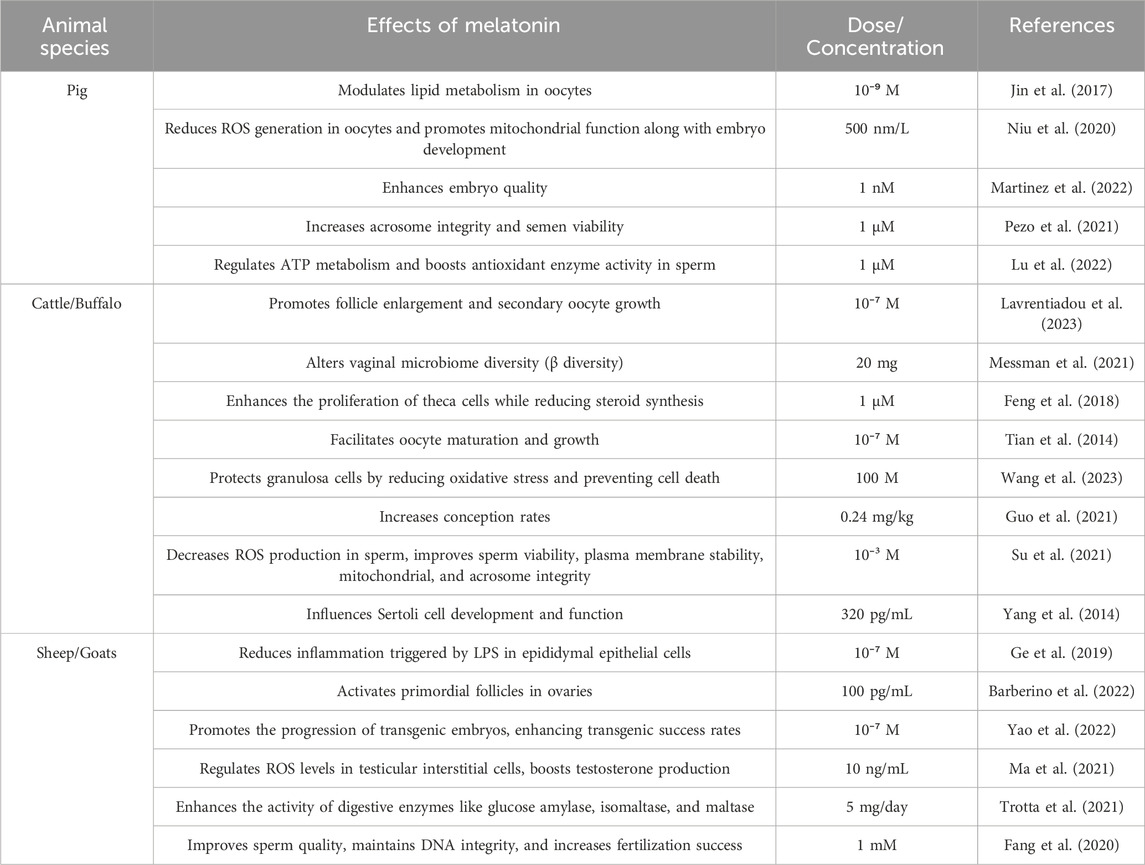
In vitro treatment of bovine sertoli cells with melatonin has been shown to increase the expression of spermatogenesis-related genes, such as Cyclin D1, Cyclin E, Platelet-derived growth factor subunit A (PDGFA), desert hedgehog (Dhh), Occludin, and Claudin (Xu et al., 2020). In healthy animals, 6 months of melatonin administration has been linked to alterations in semen characteristics, possibly due to melatonin’s inhibition of aromatase. Furthermore, in a model of testicular ischemia-reperfusion, melatonin notably decreased the incidence of morphologically abnormal sperm (Heidarizadi et al., 2022). The effects of melatonin on reproductive system functions across various livestock species are further detailed in Table 4.
8 Productive performance
8.1 Growth and development
Melatonin significantly influences muscle development, fat deposition, and meat quality in livestock animals, with recent research emphasizing its diverse effects. Supplementing with melatonin improves growth performance and feed efficiency across various species. For example, it enhances body weight and average daily gain in broiler chickens (Fathi et al., 2023; Al-Jebory et al., 2024), and similarly boosts growth rates and muscle development in pigs (Xia et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2023) and cattle (Abulaiti et al., 2023).
Melatonin achieves these benefits by accelerating myoblast proliferation, enhancing the transcription of myogenic regulatory factors, and modulating levels of myogenin and embryonic myosin heavy chain (Han et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2019; Lu et al., 2020). These mechanisms improve muscle physiology, resulting in increased carcass weight and dressing percentage. Melatonin also affects fat deposition patterns, often leading to reduced fat accumulation and leaner meat, which is advantageous from a health perspective.
Melatonin impacts various meat quality attributes. It may improve tenderness by aiding muscle maturation and reducing stress-related muscle proteins. However, its effect on meat color is less consistent, with some studies noting minimal changes while others report potential alterations (Wang et al., 2007; Duan et al., 2019). Furthermore, melatonin can enhance water-holding capacity, contributing to juicier and higher-quality meat (Carcangiu et al., 2018).
Consumer acceptance of melatonin-treated meat largely depends on perceived health benefits, such as leaner meat and improved tenderness. Despite these benefits, some consumers may be cautious about hormonal treatments. Transparent labeling and clear communication regarding melatonin’s benefits and safety are crucial for building consumer trust (Owino et al., 2019).
The market value of melatonin-treated meat could increase if the treatment results in significant quality improvements, such as enhanced tenderness and leanness, justifying higher prices and appealing to premium market segments. Regulatory approvals and adherence to food safety standards are essential for the market viability of melatonin-treated meat. Overall, melatonin’s effects on growth, muscle development, and meat quality highlight its potential to enhance livestock productivity while meeting consumer and market demands.
8.2 Milk production
Melatonin has significant potential for enhancing milk production in livestock through various mechanistic pathways. In dairy cattle, melatonin administration affects milk yield by synchronizing circadian rhythms, optimizing the timing and efficiency of lactation processes (Garcia-Ispierto et al., 2013; Şahin et al., 2021). This hormone regulates the pineal gland to align the cows’ internal clocks with external environmental cues, which is crucial for maintaining consistent milk production.
Melatonin also mitigates the adverse effects of seasonal variations in daylight and temperature. By influencing cows’ photoperiodic responses, melatonin helps maintain stable milk yields throughout different seasons (Boztepe et al., 2022; Elhadi et al., 2022). Additionally, melatonin reduces stress levels in dairy cattle, a key factor since stress is known to inhibit milk production. The hormone’s stress-reducing properties enhance overall wellbeing and, consequently, improve lactation performance (Yao et al., 2020; Cosso et al., 2021).
Through its regulation of circadian rhythms, stabilization of seasonal variations, and stress reduction, melatonin contributes to more consistent and increased milk production, thereby enhancing dairy farm productivity. The intricate interplay between melatonin’s physiological effects and milk production highlights its potential as a valuable tool in optimizing livestock management practices.
9 Conclusion
Melatonin plays a critical and multifaceted role in enhancing livestock health, reproductive efficiency, and productive potential through both RM and receptor-independent actions, such as its potent antioxidant and free radical scavenging properties. As research continues to clarify its mechanisms, melatonin is poised to become an essential tool in promoting health across domestic animals. It’s ability to directly influence ovarian physiology, including steroid hormone synthesis, oocyte maturation, ovulation, and CL formation, while simultaneously mitigating oxidative stress, positions it as a valuable therapeutic agent for enhancing livestock fertility and advancing artificial reproductive technologies. Additionally, its capacity to alter systemic metabolites, such as amino acids, offers novel insights into enhancing livestock growth and productive performance. Although its application in animal science is still emerging, melatonin holds significant potential to transform livestock management by promoting resilience to environmental stressors and supporting sustainable animal husbandry practices.
Author contributions
AA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges the assistance of “Chat GPT by Open AI (November 2024 version)” in improving the language and readability of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdelnaby E. A., Abo El-Maaty A. M. (2021). Melatonin and CIDR improved the follicular and luteal haemodynamics, uterine and ovarian arteries vascular perfusion, ovarian hormones and nitric oxide in cyclic cows. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 56, 498–510. doi:10.1111/rda.13888
Abdel-Razek H. A., Rizk M. S., Amer G. S., Kora M. A., Afifi A. M., Donia S. S. (2023). Impact of combined ischemic preconditioning and melatonin on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J. Basic Med. Sci. 26, 235–240. doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2022.67127.14722
Abdulwahab D. A., El-Missiry M. A., Shabana S., Othman A. I., Amer M. E. (2021). Melatonin protects the heart and pancreas by improving glucose homeostasis, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in T2DM-induced rats. Heliyon 7, e06474. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06474
Abulaiti A., Nawaz M., Naseer Z., Ahmed Z., Liu W., Abdelrahman M., et al. (2023). Administration of melatonin prior to modified synchronization protocol improves the productive and reproductive efficiency of Chinese crossbred buffaloes in low breeding season. Front. Vet. Sci. 10, 1118604. doi:10.3389/fvets.2023.1118604
Aguilera Y., Herrera T., Benítez V., Arribas S. M., de Pablo A. L. L., Esteban R. M., et al. (2015). Estimation of scavenging capacity of melatonin and other antioxidants: contribution and evaluation in germinated seeds. Food Chem. 170, 203–211. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.071
Ahmadi Z., Ashrafizadeh M. (2020). Melatonin as a potential modulator of Nrf2. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 34, 11–19. doi:10.1111/fcp.12498
Ahsen A., Gonul Y., Genc A., Ulu M. S., Yagmurca M., Kocogullari C. U., et al. (2014). Protective effect of melatonin on infrarenal aortic occlusion: this effect is related to anti-inflammatory effect and antioxidant effect. Inflammation 37, 1111–1119. doi:10.1007/s10753-014-9835-z
Akar M., Çevik M., Kocaman A., Kaya C., Esin B., Björkman S. (2024). Melatonin administration enhances testicular volume, testicular blood flow, semen parameters and antioxidant status during the non-breeding season in Bafra rams. Animals 14, 442. doi:10.3390/ani14030442
Al-Hamedawi T., Hatif S. (2020). Effect of melatonin and in combination with CIDR on reproductive performance in anestrus lactating Iraqi buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). Iraq. J. Vet. Med. 44, 99–102.
Al-Jebory H., Al-Saeedi M., Ajafar M., Ali N. (2024). Impact of melatonin on improving productive traits of broiler exposed to environmental stress. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 12, 775–781. doi:10.17582/journal.aavs/2024/12.4.775.781
Al-Samrai M. K., Al-Jumaily T. K., Taha A. T. (2023). Impact light regimen and melatonin on growth performance, welfare and physiological parameters of broiler chickens. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 117, 012004.
Al-Shahat A., Hulail M. A., Soliman N. M., Khamis T., Fericean L. M., Arisha A. H., et al. (2022). Melatonin mitigates cisplatin-induced ovarian dysfunction via altering steroidogenesis, inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative stress, and PTEN/PI3K/Akt/mTOR/AMPK signaling pathway in female rats. Pharmaceutics 14, 2769. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14122769
Appiah M. O., He B., Lu W., Wang J. (2019). Antioxidative effect of melatonin on cryopreserved chicken semen. Cryobiology 89, 90–95. doi:10.1016/j.cryobiol.2019.05.001
Aranarochana A., Sirichoat A., Pannangrong W., Wigmore P., Welbat J. U. (2021). Melatonin ameliorates valproic acid-induced neurogenesis impairment: the role of oxidative stress in adult rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 9997582. doi:10.1155/2021/9997582
Ates G., Tamer S., Yorulmaz H., Mutlu S., Olgac V., Aksu A., et al. (2022). Melatonin pretreatment modulates anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, YKL-40, and matrix metalloproteinases in endotoxemic rat lung tissue. Exp. Biol. Med. 247, 1080–1089. doi:10.1177/15353702221084933
Badria F. A., Abd El-Salam N. M., Abou-Salem F. M. (2002). Melatonin, serotonin, and tryptamine in some Egyptian food and medicinal plants. J. Med. Food 5, 153–157. doi:10.1089/10966200260398189
Bagheri F., Goudarzi I., Lashkarbolouki T., Elahdadi Salmani M., Goudarzi A., Morley-Fletcher S. (2024). Improving behavioral deficits induced by perinatal ethanol and stress exposure in adolescent male rat progeny via maternal melatonin treatment. Psychopharmacology 241, 153–169. doi:10.1007/s00213-023-06470-z
Bajwa V., Murch S. J., Saxena P. K. (2014). Melatonin-rich plants: production, significance in agriculture and human health. Prod. Biomass Bioact. Compd. Using Bioreact. Technol., 445–468. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9223-3_19
Baltaci S. B., Mogulkoc R., Baltaci A. K., Emsen A., Artac H. (2018). The effect of zinc and melatonin supplementation on immunity parameters in breast cancer induced by DMBA in rats. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 124, 247–252. doi:10.1080/13813455.2017.1392580
Barberino R. S., Macedo T. J., Lins T. L. B., Menezes V. G., Silva R. L., Monte A. P., et al. (2022). Immunolocalization of melatonin receptor type 1 in the sheep ovary and involvement of the PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a signaling pathway in the effects of melatonin on survival and in vitro activation of primordial follicles. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 89, 485–497. doi:10.1002/mrd.23639
Bashandy S. A., Ebaid H., Al-Tamimi J., Ahmed-Farid O. A.-H., Omara E. A., Alhazza I. M. (2021). Melatonin alleviated potassium dichromate-induced oxidative stress and reprotoxicity in male rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 1, 3565360. doi:10.1155/2021/3565360
Baydas G., Canatan H., Turkoglu A. (2002). Comparative analysis of the protective effects of melatonin and vitamin E on streptozocin-induced diabetes mellitus. J. Pineal Res. 32, 225–230. doi:10.1034/j.1600-079x.2002.01856.x
Bazrgar M., Goudarzi I., Lashkarbolouki T., Salmani M. E. (2015). Melatonin ameliorates oxidative damage induced by maternal lead exposure in rat pups. Physiol. Behav. 151, 178–188. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.06.040
Berni M., Gigante P., Bussolati S., Grasselli F., Grolli S., Ramoni R., et al. (2019). Bisphenol S, a bisphenol A alternative, impairs swine ovarian and adipose cell functions. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 66, 48–56. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2018.08.001
Boiko D. I., Shkodina A. D., Hasan M. M., Bardhan M., Kazmi S. K., Chopra H., et al. (2022). Melatonergic receptors (Mt1/Mt2) as a potential additional target of novel drugs for depression. Neurochem. Res. 47, 2909–2924. doi:10.1007/s11064-022-03646-5
Bouroutzika E., Ciliberti M. G., Caroprese M., Theodosiadou E., Papadopoulos S., Makri S., et al. (2021). Association of melatonin administration in pregnant ewes with growth, redox status and immunity of their offspring. Animals 11, 3161. doi:10.3390/ani11113161
Bouroutzika E., Kouretas D., Papadopoulos S., Veskoukis A. S., Theodosiadou E., Makri S., et al. (2020). Effects of melatonin administration to pregnant ewes under heat-stress conditions, in redox status and reproductive outcome. Antioxidants 9, 266. doi:10.3390/antiox9030266
Boztepe S., Keskin İ., Semacan A., Aytekin İ., Akyürek F., Şahin Ö. (2022). Melatonin differences between day and night milk in primiparous Holstein Friesian and Jersey dairy cattle. Selcuk J. Agric. Food Sci. 36, 27–30.
Brazao V., Santello F. H., Colato R. P., do Prado Jr J. C. (2020). T. cruzi infection among aged rats: melatonin as a promising therapeutic molecule. Exp. Gerontol. 135, 110922. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2020.110922
Brockus K., Hart C., Fleming B., Smith T., Ward S., Lemley C. (2016a). Effects of supplementing Holstein heifers with dietary melatonin during late gestation on growth and cardiovascular measurements of their offspring. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 51, 240–247. doi:10.1111/rda.12672
Brockus K., Hart C., Gilfeather C., Fleming B., Lemley C. (2016b). Dietary melatonin alters uterine artery hemodynamics in pregnant Holstein heifers. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 55, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2015.10.006
Carcangiu V., Giannetto C., Luridiana S., Piccione G. (2018). Features of the daily rhythms of blood melatonin and glucose in goats during different natural photoperiod. Chronobiol. Int. 35, 329–335. doi:10.1080/07420528.2017.1405968
Carcangiu V., Luridiana S., Mura M. C., Parmeggiani A., Giannetto C., Congiu F., et al. (2014). Melatonin circadian rhythm in three livestock species maintained in the same housed conditions. Biol. Rhythm Res. 45, 909–914. doi:10.1080/09291016.2014.929855
Cardinali D. P., Brown G. M., Pandi-Perumal S. R. (2021). An urgent proposal for the immediate use of melatonin as an adjuvant to anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. Melat. Res. 4, 206–212. doi:10.32794/mr11250091
Castellano F., Molinier-Frenkel V. (2020). Control of T-cell activation and signaling by amino-acid catabolizing enzymes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 613416. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.613416
Cecon E., Boutin J. A., Jockers R. (2023). Molecular characterization and pharmacology of melatonin receptors in animals. Receptors 2, 127–147. doi:10.3390/receptors2020008
Chang T., Niu C., Sun C., Ma Y., Guo R., Ruan Z., et al. (2020). Melatonin exerts immunoregulatory effects by balancing peripheral effector and regulatory T helper cells in myasthenia gravis. Aging (Albany NY) 12, 21147–21160. doi:10.18632/aging.103785
Charif S. E., Inserra P. I. F., Schmidt A. R., Cortasa S. A., Proietto S., Corso M. C., et al. (2022). Melatonin is involved in the modulation of the hypothalamic and pituitary activity in the South American plains vizcacha, Lagostomus maximus. J. Comp. Physiol. B 192, 141–159. doi:10.1007/s00360-021-01405-6
Chauhan S. S., Rashamol V., Bagath M., Sejian V., Dunshea F. R. (2021). Impacts of heat stress on immune responses and oxidative stress in farm animals and nutritional strategies for amelioration. Int. J. Biometeorol. 65, 1231–1244. doi:10.1007/s00484-021-02083-3
Chen B., You W., Shan T. (2019). Myomaker, and Myomixer-Myomerger-Minion modulate the efficiency of skeletal muscle development with melatonin supplementation through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 385, 111705. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111705
Chen S., Lien Y., Chao K., Ho H.-N., Yang Y., Lee T. (2003). Effects of cryopreservation on meiotic spindles of oocytes and its dynamics after thawing: clinical implications in oocyte freezing—a review article. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 202, 101–107. doi:10.1016/s0303-7207(03)00070-4
Chen W., Tu Y., Cai P., Wang L., Zhou Y., Liu S., et al. (2023). Melatonin supplementation promotes muscle fiber hypertrophy and regulates lipid metabolism of skeletal muscle in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 101, 256. doi:10.1093/jas/skad256
Chen Z., Wang K., Guo J., Zhou J., Loor J. J., Yang Z., et al. (2022). Melatonin maintains homeostasis and potentiates the anti-inflammatory response in Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis through microRNA-16b/YAP1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70, 15255–15270. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c05904
Cheng L., Qin Y., Hu X., Ren L., Zhang C., Wang X., et al. (2019). Melatonin protects in vitro matured porcine oocytes from toxicity of Aflatoxin B1. J. Pineal Res. 66, e12543. doi:10.1111/jpi.12543
Colares J. R., Hartmann R. M., Schemitt E. G., Fonseca S. R., Brasil M. S., Picada J. N., et al. (2022). Melatonin prevents oxidative stress, inflammatory activity, and DNA damage in cirrhotic rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 28, 348–364. doi:10.3748/wjg.v28.i3.348
Cos S., Álvarez-García V., González A., Alonso-González C., Martínez-Campa C. (2014). Melatonin modulation of crosstalk among malignant epithelial, endothelial and adipose cells in breast cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 8, 487–492. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2203
Cosso G., Mura M. C., Pulinas L., Curone G., Vigo D., Carcangiu V., et al. (2021). Effects of melatonin treatment on milk traits, reproductive performance, and immune response in Sarda dairy sheep. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 20, 632–639. doi:10.1080/1828051x.2021.1904796
Cruz A., Tasset I., Ramírez L., Arjona A., Segura J., Túnez I., et al. (2009). Effect of melatonin on myocardial oxidative stress induced by experimental obstructive jaundice. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 101, 460–463. doi:10.4321/s1130-01082009000700002
Cruz M. H. C., Leal C. L. V., Cruz J. F. d., Tan D.-X., Reiter R. J. (2014). Essential actions of melatonin in protecting the ovary from oxidative damage. Theriogenology 82, 925–932. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.07.011
de Carvalho N. A. T., de Carvalho J. G. S., de Souza D. C., Madureira E. H., de Sa Filho M. F., de Sousa Sales J. N., et al. (2021). Lack of effect of melatonin on ovarian function and response to estrous synchronization and fixed-time AI during the nonbreeding season in lactating dairy buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Anim. Reprod. Sci. 231, 106796. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2021.106796
Deng S.-L., Zhang B.-L., Reiter R. J., Liu Y.-X. (2020). Melatonin ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress by suppressing the p38MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-induced sheep orchitis. Antioxidants 9, 1277. doi:10.3390/antiox9121277
Deng W. S., Xu Q., Liu Y., Jiang C. H., Zhou H., Gu L. (2016). Effects of melatonin on liver function and lipid peroxidation in a rat model of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 11, 1955–1960. doi:10.3892/etm.2016.3160
Ding M., Jiang S., Miao J., Pan L. (2021). Possible roles of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and melatonin in the control of gonadal development of clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 262, 111059. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.111059
Domple V. D., Dangi S., Yadav V., Sarkar M., Singh G., Maurya V. (2017). Effect of melatonin supplementation on haematological parameters in buffalo calves under summer stress. Int. J. Livest. Res. 7, 266–274.
Dong Y., Zhao J., Zhu Q., Liu H., Wang J., Lu W. (2020). Melatonin inhibits the apoptosis of rooster Leydig cells by suppressing oxidative stress via AKT-Nrf2 pathway activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 160, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.06.024
Duan H., Hu J., Xiao L., Lv J., Zhang Y., Zhao X. (2022). β-Estradiol inhibits melatonin synthesis and melatonin receptor expression in sheep granulosa cells. Gene 814, 146128. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2021.146128
Duan H., Yang S., Xiao L., Yang S., Yan Z., Wang F., et al. (2024). Melatonin promotes progesterone secretion in sheep luteal cells by regulating autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Theriogenology 214, 342–351. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2023.11.010
Duan T., Wu Z., Zhang H., Liu Y., Li Y., Zhang W. (2019). Effects of melatonin implantation on carcass characteristics, meat quality and tissue levels of melatonin and prolactin in Inner Mongolian cashmere goats. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 10, 70–78. doi:10.1186/s40104-019-0377-y
Edwards A. K., McKnight S. M., Askelson K., McKnight J. R., Dunlap K. A., Satterfield M. C. (2020). Adaptive responses to maternal nutrient restriction alter placental transport in ewes. Placenta 96, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2020.05.002
Elhadi A., Salama A. A., Such X., Caja G. (2022). Responses to melatonin of 2 breeds of dairy ewes in early lactation under autumn photoperiod conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 105, 2587–2596. doi:10.3168/jds.2021-21270
El-Raey M., Geshi M., Somfai T., Kaneda M., Hirako M., Abdel-Ghaffar A. E., et al. (2011). Evidence of melatonin synthesis in the cumulus oocyte complexes and its role in enhancing oocyte maturation in vitro in cattle. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 78, 250–262. doi:10.1002/mrd.21295
El-Shalofy A., Hedia M., Kastelic J. (2021). Melatonin improves testicular haemodynamics, echotexture, and testosterone production in Ossimi rams during the breeding season. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 56, 1456–1463. doi:10.1111/rda.14010
Elsherbini A. M., Ezzat S. K. (2020). Effect of melatonin versus injectable platelet rich fibrin on critical wound healing in submandibular salivary glands of diabetic rats. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 10, 592–596. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2020.08.016
Esquifino A. I., Pandi-Perumal S., Cardinali D. P. (2004). Circadian organization of the immune response: a role for melatonin. Clin. Appl. Immunol. Rev. 4, 423–433. doi:10.1016/j.cair.2004.08.002
Essawy A. E., Mohamed A. I., Ali R. G., Ali A. M., Abdou H. M. (2023). Analysis of melatonin-modulating effects against tartrazine-induced neurotoxicity in male rats: biochemical, pathological and immunohistochemical markers. Neurochem. Res. 48, 131–141. doi:10.1007/s11064-022-03723-9
Esteban-Zubero E., López-Pingarrón L., Ramírez J. M., Reyes-Gonzales M. C., Azúa-Romeo F. J., Soria-Aznar M., et al. (2023). Melatonin preserves fluidity in cell and mitochondrial membranes against hepatic ischemia–reperfusion. Biomedicines 11, 1940. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11071940
Fang Y., Zhao C., Xiang H., Jia G., Zhong R. (2020). Melatonin improves cryopreservation of ram sperm by inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 55, 1240–1249. doi:10.1111/rda.13771
Fathi M., Saeedyan S., Kaoosi M. (2023). Effect of melatonin on oxidative stress, inflammation cytokines, biochemical parameters and growth performance in broiler chicken under induced stress by dexamethasone. Acta Agric. Scand. A Anim. Sci. 72, 149–157. doi:10.1080/09064702.2023.2222733
Feng T., Schutz L., Morrell B., Perego M., Spicer L. (2018). Effect of melatonin on bovine theca cells in vitro. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 30, 643–650. doi:10.1071/RD17203
Fernández A., Ordóñez R., Reiter R. J., González-Gallego J., Mauriz J. L. (2015). Melatonin and endoplasmic reticulum stress: relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J. Pineal Res. 59, 292–307. doi:10.1111/jpi.12264
Ferreira L. F., Garcia Neto P., Titon S. C., Titon Jr B., Muxel S. M., Gomes F. R., et al. (2021). Lipopolysaccharide regulates pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, corticosterone, and melatonin in toads. Integr. Org. Biol. 3, obab025. doi:10.1093/iob/obab025
Frungieri M. B., Calandra R. S., Rossi S. P. (2017). Local actions of melatonin in somatic cells of the testis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 1170. doi:10.3390/ijms18061170
Fu Y., Yao S., Wang T., Lu Y., Han H., Liu X., et al. (2023). Effects of melatonin on rumen microorganisms and methane production in dairy cow: results from in vitro and in vivo studies. Microbiome 11, 196. doi:10.1186/s40168-023-01620-z
Galano A., Guzmán-López E. G., Reiter R. J. (2021). Potentiating the benefits of melatonin through chemical functionalization: possible impact on multifactorial neurodegenerative disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 11584. doi:10.3390/ijms222111584
Galano A., Reiter R. J. (2018). Melatonin and its metabolites vs oxidative stress: from individual actions to collective protection. J. Pineal Res. 65, e12514. doi:10.1111/jpi.12514
Gao T., Wang Z., Cao J., Dong Y., Chen Y. (2021). Melatonin ameliorates corticosterone-mediated oxidative stress-induced colitis in sleep-deprived mice involving gut microbiota. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 9981480. doi:10.1155/2021/9981480
Garcia-Ispierto I., Abdelfatah A., López-Gatius F. (2013). Melatonin treatment at dry-off improves reproductive performance postpartum in high-producing dairy cows under heat stress conditions. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 48, 577–583. doi:10.1111/rda.12128
Gaur M., Purohit G. N. (2020). Changes in blood flow to the umbilicus, placentomes, and uterus in Surti buffaloes during complete gestation. Pharma Innov. J. 9, 460–466. doi:10.22271/tpi.2020.v9.i2i.4419
Ge W.-b., Xiao L.-f., Duan H.-w., Li Z.-s., Jiang Y.-t., Yang S.-s., et al. (2019). Melatonin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced epididymitis in sheep epididymal epithelial cells in vitro. Immunol. Lett. 214, 45–51. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2019.09.001
Giannetto C., Fazio F., Alberghina D., Giudice E., Piccione G. (2020). Clock genes expression in peripheral leukocytes and plasma melatonin daily rhythm in horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 84, 102856. doi:10.1016/j.jevs.2019.102856
Gobbi G., Comai S. (2019). Differential function of melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors in REM and NREM sleep. Front. Endocrinol. 10, 87. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00087
Goswami S., Haldar C. (2014). UVB irradiation severely induces systemic tissue injury by augmenting oxidative load in a tropical rodent: efficacy of melatonin as an antioxidant. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 141, 84–92. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.08.027
Guo L., Li M., Gao X., Yang Y., Zhao J., Wang J., et al. (2021). Two melatonin treatments improve the conception rate after fixed-time artificial insemination in beef heifers following synchronisation of oestrous cycles using the CoSynch-56 protocol. Aust. Vet. J. 99, 449–455. doi:10.1111/avj.13100
Gutiérrez-Añez J. C., Lucas-Hahn A., Hadeler K.-G., Aldag P., Niemann H. (2021). Melatonin enhances in vitro developmental competence of cumulus-oocyte complexes collected by ovum pick-up in prepubertal and adult dairy cattle. Theriogenology 161, 285–293. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.12.011
Han Y., Kim Y.-M., Kim H. S., Lee K. Y. (2017). Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation by regulating Osterix protein stability and expression. Sci. Rep. 7, 5716. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06304-x
Hanoun M., Maryanovich M., Arnal-Estapé A., Frenette P. S. (2015). Neural regulation of hematopoiesis, inflammation, and cancer. Neuron 86, 360–373. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.01.026
Harman A. R., Contreras-Correa Z. E., Messman R. D., Swanson R. M., Lemley C. O. (2023). Maternal nutrient restriction and dietary melatonin alter neurotransmitter pathways in placental and fetal tissues. Placenta 131, 13–22. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2022.11.008
Hashem N. M., El-Hawy A. S., El-Bassiony M. F., Saber A., Radwan M. A., Ghanem N. (2023). Melatonin administration during the first half of pregnancy improves the reproductive performance of rabbits: emphasis on ovarian and placental functions. Theriogenology 205, 40–49. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2023.04.006
Hattori A., Migitaka H., Iigo M., Itoh M., Yamamoto K., Ohtani-Kaneko R., et al. (1995). Identification of melatonin in plants and its effects on plasma melatonin levels and binding to melatonin receptors in vertebrates. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 35, 627–634.
He Y., Deng H., Jiang Z., Li Q., Shi M., Chen H., et al. (2016). Effects of melatonin on follicular atresia and granulosa cell apoptosis in the porcine. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 83, 692–700. doi:10.1002/mrd.22676
Heidarizadi S., Rashidi Z., Jalili C., Gholami M. (2022). Overview of biological effects of melatonin on testis: a review. Andrologia 54, e14597. doi:10.1111/and.14597
Horodincu L., Solcan C. (2023). Influence of different light spectra on melatonin synthesis by the pineal gland and influence on the immune system in chickens. Animals 13, 2095. doi:10.3390/ani13132095
Hosseini A., Ghaleh H. E. G., Aghamollaei H., Ramandi M. F., Alishiri G., Shahriary A., et al. (2021). Evaluation of Th1 and Th2 mediated cellular and humoral immunity in patients with COVID-19 following the use of melatonin as an adjunctive treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 904, 174193. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174193
Hussain T., Murtaza G., Kalhoro D. H., Kalhoro M. S., Metwally E., Chughtai M. I., et al. (2021). Relationship between gut microbiota and host-metabolism: emphasis on hormones related to reproductive function. Anim. Nutr. 7, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.aninu.2020.11.005
Hwang J.-C., Kim H.-D., Park B.-J., Jeon R.-H., Baek S.-M., Lee S.-W., et al. (2021). Immobilization stress increased cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) expression in the ovary of rat. J. Anim. Reprod. Biotechnol. 36, 9–16. doi:10.12750/jarb.36.1.9
Hwang J.-C., Park B.-J., Kim H.-D., Baek S.-M., Lee S.-W., Jeon R.-H., et al. (2020). Immunohistological expression of cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) in the ovarian follicles of prepubertal and pubertal rat. J. Anim. Reprod. Biotechnol. 35, 329–337. doi:10.12750/jarb.35.4.329
Hyder I., Sejian V., Bhatta R., Gaughan J. (2017). Biological role of melatonin during summer season related heat stress in livestock. Biol. Rhythm Res. 48, 297–314. doi:10.1080/09291016.2016.1262999
Ikram M., Park H. Y., Ali T., Kim M. O. (2021). Melatonin as a potential regulator of oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation: mechanisms and implications for the management of brain injury-induced neurodegeneration. J. Inflamm. Res. 14, 6251–6264. doi:10.2147/JIR.S334423
Imenshahidi M., Karimi G., Hosseinzadeh H. (2020). Effects of melatonin on cardiovascular risk factors and metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive review. Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 393, 521–536. doi:10.1007/s00210-020-01822-4
Insogna I. G., Lanes A., Lee M. S., Ginsburg E. S., Fox J. H. (2021). Association of fresh embryo transfers compared with cryopreserved-thawed embryo transfers with live birth rate among women undergoing assisted reproduction using freshly retrieved donor oocytes. JAMA 325, 156–163. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.23718
Inyawilert W., Rungruangsak J., Liao Y. J., Tang P. C., Paungsukpaibool V. (2021). Melatonin supplementation improved cryopreserved Thai swamp buffalo semen. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 56, 83–88. doi:10.1111/rda.13851
Jaworek A. K., Szepietowski J. C., Hałubiec P., Wojas-Pelc A., Jaworek J. (2021). Melatonin as an antioxidant and immunomodulator in atopic dermatitis—a new look on an old story: a review. Antioxidants 10, 1179. doi:10.3390/antiox10081179
Jin J. X., Lee S., Taweechaipaisankul A., Kim G. A., Lee B. C. (2017). Melatonin regulates lipid metabolism in porcine oocytes. J. Pineal Res. 62, e12388. doi:10.1111/jpi.12388
Jin Y., Choi Y. J., Heo K., Park S. J. (2021). Melatonin as an oncostatic molecule based on its anti-aromatase role in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 438. doi:10.3390/ijms22010438
Johnson J. S. (2018). Heat stress: impact on livestock well-being and productivity and mitigation strategies to alleviate the negative effects. Anim. Prod. Sci. 58, 1404–1413. doi:10.1071/an17725
Junior R. P., Chuffa L. G. d. A., Simão V. A., Sonehara N. M., Chammas R., Reiter R. J., et al. (2022). Melatonin regulates the daily levels of plasma amino acids, acylcarnitines, biogenic amines, sphingomyelins, and hexoses in a xenograft model of triple negative breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 9105. doi:10.3390/ijms23169105
Kacar E., Fatih T., Sahinturk S., Zorlu G., Serhatlioglu I., Bulmus O., et al. (2023). Modulation of melatonin receptors regulates reproductive physiology: the impact of agomelatine on the estrus cycle, gestation, offspring, and uterine contractions in rats. Physiol. Res. 72, 793–807. doi:10.33549/physiolres.935064
Kanyar I., Karadaş F. (2023). Effect of melatonin and vitamin E as antioxidants on body weight, carcass traits of Awassi lambs fed a high-energy and normal diet. Iraq. J. Agric. Sci. 54, 1339–1350.
Karabulut-Bulan O., Bayrak B. B., Arda-Pirincci P., Sarikaya-Unal G., Us H., Yanardag R. (2015). Role of exogenous melatonin on cell proliferation and oxidant/antioxidant system in aluminum-induced renal toxicity. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 168, 141–149. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0320-9
Kárpáti E., Fürlinger D., Pleskó A. M., Gulyás L., Gáspárdy A., Becskei Z. (2023). Various approaches to influence melatonin level in sheep reproduction. Vet. Glas. 77, 16–34. doi:10.2298/vetgl220308007k
Kennaway D. J. (2023). The mammalian gastro-intestinal tract is a NOT a major extra-pineal source of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 75, e12906. doi:10.1111/jpi.12906
Kim S. W., Kim S., Son M., Cheon J. H., Park Y. S. (2020). Melatonin controls microbiota in colitis by goblet cell differentiation and antimicrobial peptide production through Toll-like receptor 4 signalling. Sci. Rep. 10, 2232. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-59314-7
Kopustinskiene D. M., Bernatoniene J. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of melatonin-mediated cell protection and signaling in health and disease. Pharmaceutics 13, 129. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13020129
Kumar P., Singh S. (2021). Growth rate, feed intake, physiological responses and hormonal profile of Murrah buffaloes implanted melatonin during summer season. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 91, 386–390. doi:10.56093/ijans.v91i5.115394
Lavrentiadou S. N., Sapanidou V., Tzekaki E. E., Margaritis I., Tsantarliotou M. P. (2023). Melatonin protects bovine spermatozoa by reinforcing their antioxidant defenses. Animals 13, 3219. doi:10.3390/ani13203219
Lee S., Jin J.-X., Taweechaipaisankul A., Kim G.-A., Lee B.-C. (2018). Stimulatory effects of melatonin on porcine in vitro maturation are mediated by MT2 receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1581. doi:10.3390/ijms19061581
Lemley C., Vonnahme K. (2017). Physiology and endocrinology symposium: alterations in uteroplacental hemodynamics during melatonin supplementation in sheep and cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 95, 2211–2221. doi:10.2527/jas.2016.1151
Leyva-Corona J. C., Angulo-Valenzuela N. I., Laborin-Escalante B. M., Gastelum-Delgado M. A., Silva-Avila N. J., Luna-Nevárez P., et al. (2023). Reproductive performance of hair ewes and rams implanted with melatonin previous to the anestrus season in Northwest Mexico. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 55, 174. doi:10.1007/s11250-023-03569-5
Li H., Li K., Zhang K., Li Y., Gu H., Liu H., et al. (2021a). The circadian physiology: implications in livestock health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 2111. doi:10.3390/ijms22042111
Li H., Sun P. (2022). Insight of melatonin: the potential of melatonin to treat bacteria-induced mastitis. Antioxidants 11, 1107. doi:10.3390/antiox11061107
Li M., Lv R., Zhang L., Zi X., Zhou H., Tang J. (2021b). Melatonin is a promising silage additive: evidence from microbiota and metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 12, 670764. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2021.670764
Li X., Zheng Z., Pan J., Jiang D., Tian Y., Huang Y. (2020). Influences of melatonin and endotoxin lipopolysaccharide on goose productive performance and gut microbiota. Brit. Poult. Sci. 61, 217–224. doi:10.1080/00071668.2019.1687851
Li Y., Lv Y., Bian C., You X., Shi Q. (2021c). Molecular evolution of melatonin receptor genes (mtnr) in vertebrates and its shedding light on mtnr1c. Gene 769, 145256. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2020.145256
Lu K.-H., Lin C.-W., Hsieh Y.-H., Su S.-C., Reiter R. J., Yang S.-F. (2020). New insights into antimetastatic signaling pathways of melatonin in skeletomuscular sarcoma of childhood and adolescence. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 39, 303–320. doi:10.1007/s10555-020-09845-2
Lu N., Jiang X., Zhang C., Li B., Tu W., Lei H., et al. (2022). Melatonin mediates via melatonin receptor 1 in a temperature-dependent manner regulating ATP metabolism and antioxidative enzyme activity of boar spermatozoa in vitro. Theriogenology 188, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.05.008
Ma J., Wang J., Hu S., Li Y., Zhang Y., Yang Y., et al. (2023). Effects of melatonin on development and hormone secretion of sheep theca cells in vitro. Theriogenology 198, 172–182. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.12.036
Ma J., Yang H., Liu L., Wan Y., Wang F. (2021). Melatonin alleviated oxidative stress induced by energy restriction on sheep Leydig cells through Sirt1/Sod2 pathway. Theriogenology 173, 83–92. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2021.07.011
Ma L., Zheng Y., Tang X., Gao H., Liu N., Gao Y., et al. (2019). miR-21-3p inhibits autophagy of bovine granulosa cells by targeting VEGFA via PI3K/AKT signaling. Reproduction 158, 441–452. doi:10.1530/REP-19-0285
Maestroni G. J. (2001). The immunotherapeutic potential of melatonin. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 10, 467–476. doi:10.1517/13543784.10.3.467
Marchena A. M., Franco L., Romero A. M., Barriga C., Rodríguez A. B. (2020). Lycopene and melatonin: antioxidant compounds in cosmetic formulations. Skin. Pharmacol. Physiol. 33, 237–243. doi:10.1159/000508673
Markus R. P., Sousa K. S., da Silveira Cruz-Machado S., Fernandes P. A., Ferreira Z. S. (2021). Possible role of pineal and extra-pineal melatonin in surveillance, immunity, and first-line defense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 12143. doi:10.3390/ijms222212143
Martinez C. A., Cuello C., Parrilla I., Maside C., Ramis G., Cambra J. M., et al. (2022). Exogenous melatonin in the culture medium does not affect the development of in vivo-derived pig embryos but substantially improves the quality of in vitro-produced embryos. Antioxidants 11, 1177. doi:10.3390/antiox11061177
McCarty K. J., Owen M. P., Hart C. G., Thompson R. C., Burnett D. D., King E. H., et al. (2018). Effect of chronic melatonin supplementation during mid to late gestation on maternal uterine artery blood flow and subsequent development of male offspring in beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 96 (12), 5100–5111. doi:10.1093/jas/sky363
Medrano A., Contreras C. F. B., Herrera F. M., Alcantar-Rodriguez A. M. (2017). Melatonin as an antioxidant preserving sperm from domestic animals. Asian Pac. J. Reprod. 6, 241–246. doi:10.4103/2305-0500.217317
Messman R. D., Contreras-Correa Z. E., Paz H. A., Lemley C. O. (2021). Melatonin-induced changes in the bovine vaginal microbiota during maternal nutrient restriction. J. Anim. Sci. 99, skab098. doi:10.1093/jas/skab098
Mierzejewski K., Kurzyńska A., Gerwel Z., Golubska M., Stryiński R., Bogacka I. (2023). Pparβ/δ ligands regulate oxidative status and inflammatory response in inflamed corpus luteum-an in vitro study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 4993. doi:10.3390/ijms24054993
Mihardja M., Roy J., Wong K. Y., Aquili L., Heng B. C., Chan Y. S., et al. (2020). Therapeutic potential of neurogenesis and melatonin regulation in Alzheimer's disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1478, 43–62. doi:10.1111/nyas.14436
Misztal T., Molik E., Nowakowski M., Marciniak E. (2018). Milk yield, lactation parameters and prolactin secretion characteristics in sheep treated with melatonin implants during pregnancy and lactation in long-day conditions. Livest. Sci. 218, 58–64. doi:10.1016/j.livsci.2018.10.018
Monteiro K. K. A. C., Shiroma M. E., Damous L. L., Simões M. d. J., Simões R. d. S., Cipolla-Neto J., et al. (2024). Antioxidant actions of melatonin: a systematic review of animal studies. Antioxidants 13, 439. doi:10.3390/antiox13040439
Muñoz-Jurado A., Escribano B. M., Caballero-Villarraso J., Galván A., Agüera E., Santamaría A., et al. (2022). Melatonin and multiple sclerosis: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulator mechanism of action. Inflammopharmacology 30, 1569–1596. doi:10.1007/s10787-022-01011-0
Najafi A., Asadi E., Benson J. D. (2023). Comparative effects of a calcium chelator (BAPTA-AM) and melatonin on cryopreservation-induced oxidative stress and damage in ovarian tissue. Sci. Rep. 13, 22911. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-49892-7
Nayki U., Onk D., Balci G., Nayki C., Onk A., Cankaya M., et al. (2016). The effect of melatonin on oxidative stress and apoptosis in experimental diabetes mellitus-related ovarian injury. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 32, 421–426. doi:10.3109/09513590.2015.1126819
Niu Y. J., Zhou W., Nie Z. W., Shin K. T., Cui X. S. (2020). Melatonin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and protects against rotenone-induced mitochondrial deficiency in early porcine embryos. J. Pineal Res. 68, e12627. doi:10.1111/jpi.12627
Ofosu J., Qazi I. H., Fang Y., Zhou G. (2021). Use of melatonin in sperm cryopreservation of farm animals: a brief review. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 233, 106850. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2021.106850
Olayaki L. A., Alagbonsi I. A., Abdulrahim A. H., Adeyemi W. J., Bakare M., Omeiza N. (2018). Melatonin prevents and ameliorates lead-induced gonadotoxicity through antioxidative and hormonal mechanisms. Toxicol. Ind. Health 34, 596–608. doi:10.1177/0748233718773508
Ouyang J., Wang M., Bu D., Ma L., Liu F., Xue C., et al. (2021). Ruminal microbes exhibit a robust circadian rhythm and are sensitive to melatonin. Front. Nutr. 8, 760578. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.760578
Owino S., Buonfiglio D. D., Tchio C., Tosini G. (2019). Melatonin signaling a key regulator of glucose homeostasis and energy metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. 10, 488. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00488
Özgen M., Take G., Kaplanoğlu İ., Erdoğan D., Seymen C. M. (2023). Therapeutic effects of melatonin in long-term exposure to 2100 MHz radiofrequency radiation on rat sperm characteristics. Rev. Int. Androl. 21, 100371. doi:10.1016/j.androl.2023.100371
Ozturk I., Elbe H., Bicer Y., Karayakali M., Onal M. O., Altinoz E. (2023). Therapeutic role of melatonin on acrylamide-induced hepatotoxicity in pinealectomized rats: effects on oxidative stress, NF-κB signaling pathway, and hepatocellular proliferation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 174, 113658. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2023.113658
Pang Y. W., Jiang X. L., Wang Y. C., Wang Y. Y., Hao H. S., Zhao S. J., et al. (2019). Melatonin protects against paraquat-induced damage during in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes. J. Pineal Res. 66, e12532. doi:10.1111/jpi.12532
Park H.-J., Park S.-Y., Kim J.-W., Yang S.-G., Kim M.-J., Jegal H.-G., et al. (2018). Melatonin improves oocyte maturation and mitochondrial functions by reducing bisphenol A-derived superoxide in porcine oocytes in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3422. doi:10.3390/ijms19113422
Paulino L., Barroso P., Silva B., Barroso L., Barbalho E., Bezerra F., et al. (2022). Immunolocalization of melatonin receptors in bovine ovarian follicles and in vitro effects of melatonin on growth, viability and gene expression in secondary follicles. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 81, 106750. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2022.106750
Pedreros M., Ratto M., Guerra M. (2011). Expression of functional melatonin MT1 receptors in equine luteal cells: in vitro effects of melatonin on progesterone secretion. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 23, 417–423. doi:10.1071/RD10137
Pezo F., Zambrano F., Uribe P., Moya C., de Andrade A. F. C., Risopatron J., et al. (2021). Oxidative and nitrosative stress in frozen-thawed pig spermatozoa. I: protective effect of melatonin and butylhydroxytoluene on sperm function. Res. Vet. Sci. 136, 143–150. doi:10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.02.006
Piotrowska-Tomala K. K., Jonczyk A. W., Szóstek-Mioduchowska A. Z., Żebrowska E., Ferreira-Dias G., Skarzynski D. J. (2022). The effects of prostaglandin E2 treatment on the secretory function of mare corpus luteum depends on the site of application: an in vivo study. Front. Vet. Sci. 8, 753796. doi:10.3389/fvets.2021.753796
Pool K., Rickard J., de Graaf S. (2020). Overcoming neuroendocrine and metabolic barriers to puberty: the role of melatonin in advancing puberty in Ewe lambs. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 72, 106457. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2020.106457
Purushothaman A., Sheeja A. A., Janardanan D. (2020). Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of melatonin and its related indolamines. Free Radic. Res. 54, 373–383. doi:10.1080/10715762.2020.1774575
Qin Y., Bai J., Dai J., Zhou J., Zhang T., Zhang S., et al. (2022). Alterations of cortisol and melatonin production by the theca interna cells of porcine cystic ovarian follicles. Anim 12, 357. doi:10.3390/ani12030357
Rajin T., Patra M., Sheikh P. A., Singh A. K., Mishra G. K., Karikalan M., et al. (2022). Expression of kisspeptin and its receptor in different functional classes of ovarian follicle in the buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Theriogenology 179, 87–96. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2021.11.017
Rajput P., Jangra A., Kwatra M., Mishra A., Lahkar M. (2017). Alcohol aggravates stress-induced cognitive deficits and hippocampal neurotoxicity: protective effect of melatonin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 91, 457–466. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.077
Ramadan T., Kumar D., Ghuman S., Singh I. (2019). Melatonin-improved buffalo semen quality during nonbreeding season under tropical condition. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 68, 119–125. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2019.01.010
Regodón S., Ramos A., Míguez M. P., Carrillo-Vico A., Rosado J. A., Jardín I. (2012). Vaccination prepartum enhances the beneficial effects of melatonin on the immune response and reduces platelet responsiveness in sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 8, 84–88. doi:10.1186/1746-6148-8-84
Reiter R. J., Manchester L., Tan D.-x. (2005). Melatonin in walnuts: influence on levels of melatonin and total antioxidant capacity of blood. Nutr. 21, 920–924. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2005.02.005
Reiter R. J., Tan D. X. (2002). Melatonin: an antioxidant in edible plants. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 957, 341–344. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb02938.x
Rijal S., Cho D. H., Park S.-A., Jang S. H., Ábrahám I. M., Han S. K. (2020). Melatonin suppresses the kainate receptor-mediated excitation on gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons in female and male prepubertal mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 5991. doi:10.3390/ijms21175991
Şahin Ö., Akyürek F., Aytekin İ., Boztepe S., Keskin I. (2021). Determination of melatonin differences between day and night milk in dairy cattle. J. Agric. Sci. 27, 449–453. doi:10.15832/ankutbd.687769
Samanta S. (2022). Physiological and pharmacological perspectives of melatonin. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 128, 1346–1367. doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1770799
Samec M., Liskova A., Koklesova L., Zhai K., Varghese E., Samuel S. M., et al. (2021). Metabolic anti-cancer effects of melatonin: clinically relevant prospects. Cancers 13, 3018. doi:10.3390/cancers13123018
Samir H., Mandour A. S., Radwan F., Ahmed A. E., Momenah M. A., Aldawood N. A., et al. (2023). Effect of acute melatonin injection on metabolomic and testicular artery hemodynamic changes and circulating hormones in Shiba goats under sub-tropical environmental conditions. Anim 13, 1794. doi:10.3390/ani13111794
Samir H., Nyametease P., Elbadawy M., Nagaoka K., Sasaki K., Watanabe G. (2020). Administration of melatonin improves testicular blood flow, circulating hormones, and semen quality in Shiba goats. Theriogenology 146, 111–119. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.01.053
Sananmuang T., Puthier D., Nguyen C., Chokeshaiusaha K. (2020). Novel classifier orthologs of bovine and human oocytes matured in different melatonin environments. Theriogenology 156, 82–89. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.06.029
Shabajee-Alibay P., Bonnaud A., Malpaux B., Delagrange P., Audinot V., Yous S., et al. (2022). A putative new melatonin binding site in sheep brain, MTx: preliminary observations and characteristics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 380, 76–89. doi:10.1124/jpet.121.000785
Shahat A. M., Thundathil J. C., Kastelic J. P. (2022). Melatonin or L-arginine in semen extender mitigate reductions in quality of frozen-thawed sperm from heat-stressed rams. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 238, 106934. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2022.106934
Shahat A. M., Thundathil J. C., Kastelic J. P. (2023). Melatonin improves post-thaw sperm quality after mild testicular heat stress in rams. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 58, 423–430. doi:10.1111/rda.14302
Shi J. M., Tian X. Z., Zhou G. B., Wang L., Gao C., Zhu S. E., et al. (2009). Melatonin exists in porcine follicular fluid and improves in vitro maturation and parthenogenetic development of porcine oocytes. J. Pineal Res. 47, 318–323. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00717.x
Singh M., Ghosh S., Prasad J., Katiyar R., Das G., Dhara S., et al. (2020a). Single melatonin treatment improves reproductive performance of Singharey goats during non-breeding season under sub-tropical condition of northeast India. Small Rumin. Res. 192, 106232. doi:10.1016/j.smallrumres.2020.106232
Singh P., Song C. Y., Dutta S. R., Gonzalez F. J., Malik K. U. (2020b). Central CYP1B1 (Cytochrome P450 1B1)-estradiol metabolite 2-methoxyestradiol protects from hypertension and neuroinflammation in female mice. Hypertension 75, 1054–1062. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14548
Sljivancanin Jakovljevic T., Kontic-Vucinic O., Nikolic N., Carkic J., Milasin J. (2020). VAL158MET catechol O-methyltransferase polymorphism contributes to the development of preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 39, 471–480. doi:10.1080/10641955.2020.1843663
Su G., Wu S., Wu M., Wang L., Yang L., Du M., et al. (2021). Melatonin improves the quality of frozen bull semen and influences gene expression related to embryo genome activation. Theriogenology 176, 54–62. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2021.09.014
Sun T. C., Liu X. C., Yang S. H., Song L. L., Zhou S. J., Deng S. L., et al. (2020). Melatonin inhibits oxidative stress and apoptosis in cryopreserved ovarian tissues via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Front. Mol. Biosci. 7, 163. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2020.00163
Swanson R., Contreras-Correa Z., Dinh T., King H., Sidelinger D., Burnett D., et al. (2022). Melatonin supplementation alters maternal and fetal amino acid concentrations and placental nutrient transporters in a nutrient restriction bovine model. Metabolites 12, 1208. doi:10.3390/metabo12121208
Taghizadieh M., Hajipour B., Asl N., Khodadadi A., Somi M., Banei M. (2016). Combination effect of melatonin and dexamethasone on liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Bratisl. Lekárske Listy 117, 47–53. doi:10.4149/bll_2016_010
Taketani T., Tamura H., Takasaki A., Lee L., Kizuka F., Tamura I., et al. (2011). Protective role of melatonin in progesterone production by human luteal cells. J. Pineal Res. 51, 207–213. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00878.x
Tamura H., Jozaki M., Tanabe M., Shirafuta Y., Mihara Y., Shinagawa M., et al. (2020). Importance of melatonin in assisted reproductive technology and ovarian aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1135. doi:10.3390/ijms21031135
Tan D.-X., Hardeland R., Manchester L. C., Korkmaz A., Ma S., Rosales-Corral S., et al. (2012). Functional roles of melatonin in plants, and perspectives in nutritional and agricultural science. J. Exp. Bot. 63, 577–597. doi:10.1093/jxb/err256
Tao J., Zhang L., Zhang X., Chen Y., Chen Q., Shen M., et al. (2021). Effect of exogenous melatonin on the development of mice ovarian follicles and follicular angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 11262. doi:10.3390/ijms222011262
Tian X., Wang F., He C., Zhang L., Tan D., Reiter R. J., et al. (2014). Beneficial effects of melatonin on bovine oocytes maturation: a mechanistic approach. J. Pineal Res. 57, 239–247. doi:10.1111/jpi.12163
Tolla E., Stevenson T. J. (2020). Sex differences and the neuroendocrine regulation of seasonal reproduction by supplementary environmental cues. Integr. Comp. Biol. 60, 1506–1516. doi:10.1093/icb/icaa096
Tölü C., Yazgan N., Akbağ H. I., Yurtman İ. Y., Savaş T. (2022). Effects of melatonin implants on reproductive performance of dairy sheep and dairy goats. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 57, 665–672. doi:10.1111/rda.14107
Trotta R., Lemley C., Vonnahme K., Swanson K. (2021). Effects of nutrient restriction and melatonin supplementation from mid-to-late gestation on maternal and fetal small intestinal carbohydrase activities in sheep. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 74, 106555. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2020.106555
Tune C., Meinhardt M., Kalies K., Pagel R., Schierloh L.-K., Hahn J., et al. (2020). Effects of sleep on the splenic milieu in mice and the T cell receptor repertoire recruited into a T cell dependent B cell response. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 5, 100082. doi:10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100082
Venditti M., Rhouma M. B., Romano M. Z., Messaoudi I., Reiter R. J., Minucci S. (2021). Evidence of melatonin ameliorative effects on the blood-testis barrier and sperm quality alterations induced by cadmium in the rat testis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 226, 112878. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112878
Verteramo R., Pierdomenico M., Greco P., Milano C. (2022). The role of melatonin in pregnancy and the health benefits for the newborn. Biomedicines 10, 3252. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10123252
Viola I., Canto F., Abecia J. A. (2023). Effects of melatonin implants on locomotor activity, body temperature, and growth of lambs fed a concentrate-based diet. J. Vet. Behav. 68, 24–31. doi:10.1016/j.jveb.2023.08.004
Vriend J., Reiter R. J. (2015). The Keap1-Nrf2-antioxidant response element pathway: a review of its regulation by melatonin and the proteasome. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 401, 213–220. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2014.12.013
Wang H., Pu Y., Luo L., Li Y., Zhang Y., Cao Z. (2018a). Membrane receptor-independent inhibitory effect of melatonin on androgen production in porcine theca cells. Theriogenology 118, 63–71. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.05.042
Wang J., Jia R., Gong H., Celi P., Zhuo Y., Ding X., et al. (2021a). The effect of oxidative stress on the chicken ovary: involvement of microbiota and melatonin interventions. Antioxidants 10, 1422. doi:10.3390/antiox10091422
Wang J., Zhu T., Ma X., Wang Y., Liu J., Li G., et al. (2021b). Melatonergic systems of AANAT, melatonin, and its receptor MT2 in the corpus luteum are essential for reproductive success in mammals. Biol. Reprod. 104, 430–444. doi:10.1093/biolre/ioaa190
Wang L., Lu D., Sun H., Zhao X., Shan D., Yang G., et al. (2007). Effects of photoperiod and melatonin on nitrogen partitioning and production performance of Inner Mongolia White Cashmere Goats. Front. Agr. China 1, 229–236. doi:10.1007/s11703-007-0040-9
Wang P., Sun L.-h., Wang X., Wu Q., Liu A. (2023). Effective protective agents against the organ toxicity of T-2 toxin and corresponding detoxification mechanisms: a narrative review. Anim. Nutr. 16, 251–266. doi:10.1016/j.aninu.2023.12.001
Wang S., Liu W., Pang X., Dai S., Liu G. (2018b). The mechanism of melatonin and its receptor MT2 involved in the development of bovine granulosa cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 2028. doi:10.3390/ijms19072028
Wang S., Liu W., Wen A., Yang B., Pang X. (2021c). Luzindole and 4P-PDOT block the effect of melatonin on bovine granulosa cell apoptosis and cell cycle depending on its concentration. Peer J. 9, e10627. doi:10.7717/peerj.10627
Wang Y.-q., Jiang Y.-j., Zou M.-s., Liu J., Zhao H.-q., Wang Y.-h. (2022). Antidepressant actions of melatonin and melatonin receptor agonist: focus on pathophysiology and treatment. Behav. Brain Res. 420, 113724. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113724
Wang Y.-X., Yang G.-H., Zhang L.-L., Wang J., Wang J.-F. (2021d). Melatonin as immune potentiator for enhancing subunit vaccine efficacy against bovine viral diarrhea virus. Vaccines 9, 1039. doi:10.3390/vaccines9091039
Wassem A., Sultan K., Abdul-Rahman S. (2022). Impact of melatonin and GnRH on puberty and some physiological parameters of local female goats. Pro-Environment Promediu 15.
Wongchitrat P., Shukla M., Sharma R., Govitrapong P., Reiter R. J. (2021). Role of melatonin on virus-induced neuropathogenesis—a concomitant therapeutic strategy to understand SARS-CoV-2 infection. Antioxidants 10, 47. doi:10.3390/antiox10010047
Wu G., Song D., Wei Q., Xing J., Shi X., Shi F. (2018). Melatonin mitigates bisphenol A-induced estradiol production and proliferation by porcine ovarian granulosa cells in vitro. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 192, 91–98. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2018.02.018
Wu X., Ren J., Huang X., Zheng X., Tian Y., Shi L., et al. (2021). Melatonin: biosynthesis, content, and function in horticultural plants and potential application. Sci. Hortic. 288, 110392. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110392
Xia S., Gao W., Li Y., Ma J., Gong S., Gao Z., et al. (2022). Effects of melatonin on intestinal function and bacterial compositions in sucking piglets. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 106, 1139–1148. doi:10.1111/jpn.13675
Xiao L., Hu J., Zhao X., Song L., Zhang Y., Dong W., et al. (2018). Expression of melatonin and its related synthase and membrane receptors in the oestrous corpus luteum and corpus luteum verum of sheep. Reprod. Dom. Anim. 53, 1142–1148. doi:10.1111/rda.13218
Xie S., Zhang R., Li Z., Liu C., Xiang W., Lu Q., et al. (2022). Indispensable role of melatonin, a scavenger of reactive oxygen species (ROS), in the protective effect of Akkermansia muciniphila in cadmium-induced intestinal mucosal damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 193, 447–458. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.10.316
Xu H., Mu X., Ding Y., Tan Q., Liu X., He J., et al. (2021). Melatonin alleviates benzo (a) pyrene-induced ovarian corpus luteum dysfunction by suppressing excessive oxidative stress and apoptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 207, 111561. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111561
Xu K., Wang J., Liu H., Zhao J., Lu W. (2020). Melatonin promotes the proliferation of chicken sertoli cells by activating the ERK/inhibin alpha subunit signaling pathway. Molecules 25, 1230. doi:10.3390/molecules25051230
Xu Z., Li W., Sun Y., Jin W., Yu L., Yang J., et al. (2023). Melatonin alleviates PTSD-like behaviors and restores serum GABA and cortisol levels in mice. Psychopharmacology 240, 259–269. doi:10.1007/s00213-023-06312-y
Xue C., Wang Y., He Z., Lu Z., Wu F., Wang Y., et al. (2023). Melatonin disturbed rumen microflora structure and metabolic pathways in vitro. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, 1–27. doi:10.1128/spectrum.00327-23
Yaacobi-Artzi S., Shimoni C., Kalo D., Hansen P. J., Roth Z. (2020). Melatonin slightly alleviates the effect of heat shock on bovine oocytes and resulting blastocysts. Theriogenology 158, 477–489. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.09.039
Yang F., Li L., Chen K., Li C., Wang Y., Wang G. (2019). Melatonin alleviates β-zearalenol and HT-2 toxin-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in bovine ovarian granulosa cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 68, 52–60. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2019.03.005
Yang M., Guan S., Tao J., Zhu K., Lv D., Wang J., et al. (2021). Melatonin promotes male reproductive performance and increases testosterone synthesis in mammalian Leydig cells. Biol. Reprod. 104, 1322–1336. doi:10.1093/biolre/ioab046
Yang W.-C., Tang K.-Q., Fu C.-Z., Riaz H., Zhang Q., Zan L.-S. (2014). Melatonin regulates the development and function of bovine Sertoli cells via its receptors MT1 and MT2. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 147, 10–16. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2014.03.017
Yao S., Wu H., Ma H., Fu Y., Wei W., Wang T., et al. (2020). Effects of rumen bypass melatonin feeding (RBMF) on milk quality and mastitis of Holstein cows. Peer J. 8, 9147. doi:10.7717/peerj.9147
Yao Y., Yang A., Li G., Wu H., Deng S., Yang H., et al. (2022). Melatonin promotes the development of sheep transgenic cloned embryos by protecting donor and recipient cells. Cell Cycle 21, 1360–1375. doi:10.1080/15384101.2022.2051122
Yesilkaya O. F., Erdem H. (2024). The effect of exogenous melatonin administration before superovulation on embryo yield in Assaf ewes. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 59, 14668. doi:10.1111/rda.14668
Yin X., Wei Y., Song W., Zhang H., Liu G., Chen Y., et al. (2020). Melatonin as an inducer of arecoline and their coordinated roles in anti-oxidative activity and immune responses. Food Funct. 11, 8788–8799. doi:10.1039/d0fo01841d
Yuan X. H., Yang C. R., Wang X. N., Zhang L. L., Gao X. R., Shi Z. Y. (2019). Progesterone maintains the status of granulosa cells and slows follicle development partly through PGRMC1. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 709–720. doi:10.1002/jcp.26869
Zarezadeh M., Barzegari M., Aghapour B., Adeli S., Khademi F., Musazadeh V., et al. (2022). Melatonin effectiveness in amelioration of oxidative stress and strengthening of antioxidant defense system: findings from a systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 48, 109–120. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.01.038
Zeebaree B. K., Kwong W. Y., Mann G. E., Gutierrez C. G., Sinclair K. D. (2018). Physiological responses of cultured bovine granulosa cells to elevated temperatures under low and high oxygen in the presence of different concentrations of melatonin. Theriogenology 105, 107–114. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2017.09.014
Zhang C., Clough S. J., Adamah-Biassi E. B., Sveinsson M. H., Hutchinson A. J., Miura I., et al. (2021a). Impact of endogenous melatonin on rhythmic behaviors, reproduction, and survival revealed in melatonin-proficient C57BL/6J congenic mice. J. Pineal Res. 71, e12748. doi:10.1111/jpi.12748
Zhang H., Li C., Wen D., Li R., Lu S., Xu R., et al. (2022a). Melatonin improves the quality of maternally aged oocytes by maintaining intercellular communication and antioxidant metabolite supply. Redox Biol. 49, 102215. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.102215
Zhang H., Yan Q., Wang X., Chen X., Chen Y., Du J., et al. (2021b). The role of mitochondria in liver ischemia-reperfusion injury: from aspects of mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial fission, mitochondrial membrane permeable transport pore formation, mitophagy, and mitochondria-related protective measures. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 1, 6670579. doi:10.1155/2021/6670579
Zhang W., Wang Z., Zhang L., Zhang Z., Chen J., Chen W., et al. (2018a). Melatonin stimulates the secretion of progesterone along with the expression of cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (P450scc) and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) in corpus luteum of pregnant sows. Theriogenology 108, 297–305. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2017.12.026
Zhang W., Zhang Z., Peng J., Yang S., Chen J., Wang C., et al. (2022b). Expression of arylalkylamine n-acetyltransferase (AANAT) and acetylserotonin o-methyltransferase (ASMT) in the corpus luteum of pregnant sows and synthesis of melatonin in luteal cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1-13.
Zhang W., Zhang Z., Peng J., Yang S., Tong D. (2022c). Effects of melatonin on the production of GnRH and LH in luteal cells of pregnant sows. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 68, 111–123. doi:10.1530/JME-21-0155
Zhang Y., Qiao B., Gao F., Wang H., Miao S., Zhao H. (2018b). Melatonin protects H9c2 cells against ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress via activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 18, 3497–3505. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.9315
Zhao D., Yu Y., Zhao Z., Sharma R., Reiter R. J. (2019). Melatonin synthesis and function: evolutionary history in animals and plants. Front. Endocrinol. 10, 441357.
Zheng J., Zhou Y., Zhang D., Ma K., Gong Y., Luo X., et al. (2024). Intestinal melatonin levels and gut microbiota homeostasis are independent of the pineal gland in pigs. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1352586. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2024.1352586
Keywords: melatonin, health, antioxidant status, animal performance, production potential
Citation: Afzal A (2024) Melatonin as a multifunctional modulator: emerging insights into its role in health, reproductive efficiency, and productive performance in livestock. Front. Physiol. 15:1501334. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1501334
Received: 24 September 2024; Accepted: 22 November 2024;
Published: 05 December 2024.
Edited by:
Stan Hileman, West Virginia University, United StatesReviewed by:
Rosa Pereira, National Institute for Agricultural and Veterinary Research (INIAV), PortugalFrancisco Acuña, National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET), Argentina
Copyright © 2024 Afzal. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ali Afzal, YWxpdWFmMTYzM0BnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Ali Afzal
Ali Afzal