- Department of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Despite the fact that the text image-based optical character recognition (OCR) methods have been applied to a wide range of applications, they do suffer from performance degradation when the image is contaminated with moiré patterns for the sake of interference between the display screen and the camera. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel network for text image demoiréing. Specifically, to encourage our study on text images, we collected a dataset including a number of pairs of images with/without moiré patterns, which is specific for text image demoiréing. In addition, due to the statistical differences among various channels on moiré patterns, a multi-channel strategy is proposed, which roughly extracts the information associated with moiré patterns and subsequently contributes to moiré removal. In addition, our purpose on the text image is to increase the OCR accuracy, while other background pixels are insignificant. Instead of restoring all pixels like those in natural images, a character attention module is conducted, allowing the network to pay more attention on the optical character-associated pixels and also achieving a consistent image style. As a result from this method, characters can be more easily detected and more accurately recognized. Dramatic experimental results on our conducted dataset demonstrate the significance of our study and the superiority of our proposed method compared with state-of-the-art image restoration approaches. Specifically, the metrics of recall and F1-measure on recognition are increased from 56.32%/70.18% to 85.34%/89.36%.
1 Introduction
Due to the huge number of text images, the automatic text recognition from a given image is quite necessary in recent years. Thanks to the techniques of optical character recognition (OCR) [1–3], image-based text detection [4, 5] and recognition [6] have been effectively improved and are widely applied to many applications, such as ID card recognition [7], table recognition [8], and license plate recognition [9, 10]. Despite the fact that these methods have achieved satisfactory performances, they are sensitively influenced by the quality of images. As displayed in Figure 1, it is a general and inevitable phenomenon that the captured image is corrupted with diverse moiré patterns due to interference between the display screen and the camera, resulting in significant performance degradation in both character detection and recognition. Thus, in this paper, we focus on the moiré pattern removal from the text images for OCR.

Figure 1. OCR on the images with (A) or without (B) moiré patterns. Characters in green denote the accurate recognition, and characters in red denote the inaccurate recognition. Making a comparison between (A) and (B), recognition accuracy on the text image is significantly influenced by the moiré patterns.
It is particularly challenging to remove moiré patterns from photographs. Different from other corruptions, such as noise [11, 12], rain [13, 14], and haze [15, 16], the moiré pattern exhibits a diverse range of characteristics. Specifically, as shown in Figure 1B, colors, thickness, and shapes (stripes or ripples) are even diverse across different areas in a photograph, and the frequency domain, as analyzed in [17], further demonstrates its complexity.
To restore the image, [18] proposed a convolutional neural network (CNN), in which a multi-resolution strategy is adopted to remove the moiré patterns from a wide range of frequencies. Inspired by this work, other studies [17, 19–22] have been proposed for image demoiréing. Despite the fact that these aforementioned works effectively obtain a moiré-free image from the input, they are only adaptive for natural images, as the structures between text images and natural images differ significantly. Compared with natural images, the key information in text images is the optical characters. In other words, the purpose of text image demoiréing is to improve the accuracy of text recognition after restoration, which encourages us to pay more attention on the optical character-associated pixels. Thus, not only the moiré patterns should be removed from the raw image but also the semantic structures of optical characters should be enhanced.
To achieve this goal, we propose the text image demoiréing network (TIDNet). Considering that the moiré pattern in the G (green) channel is statistically weaker than that in the R (red) and B (blue) channels [17], its edge patterns are roughly but adaptively extracted by our presented rough moiré pattern extraction module, regardless of whether the scales of values in the R, G, and B channels are different or similar. Furthermore, we also propose a character attention module, allowing the network to particularly pay much more attention on the optical characters for our OCR application. In detail, as shown in Figure 2, it is obvious that under different viewpoints and capturing distances, colors of moiré-contaminated images captured from the same image differ significantly, making complete recovery more difficult. In addition, if an image is covered by watermarks (Figure 2A), it seems impossible to restore it from the contaminated images due to the missing information in image collection (Figures 2B–D). Subsequently, the inaccurate background pixel estimation may even inversely result in the degradation of performance. In fact, we need to improve the recognition accuracy. The greater the difference between the foreground and background, the easier it is to detect and recognize the text. Thus, apart from image demoiréing, we further transform diverse image styles to a consistent version, where the background pixels are white, while the foreground characters are black. Thanks to this strategy, not only the estimation for the complex background is avoided but also the difference between the characters and background pixels is enlarged, contributing to both character detection and recognition. In addition, a mask strategy and a semantic measurement are jointly introduced, allowing our model to pay much more attention on the character-associated pixels.

Figure 2. (A) Image without moiré patterns. (B–D) Images with moiré patterns, which are captured under different viewpoints and distances.
In order to achieve moiré pattern removal, a dataset is necessary. In addition, we create a text image dataset named HITSZ-TID, which is composed of 3,739 pairs of images. For each pair, it consists of an image contaminated with moiré patterns, as well as its associated reference image without moiré patterns. Particularly, we extract the contaminated image under multiple devices, viewpoints, and distances, ensuring the diversity and generalization of our collected dataset.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
• A text image demoiréing network (TIDNet) is particularly designed for text image demoiréing. Thanks to our proposed method, the recognition accuracy on text images contaminated with moiré patterns is greatly improved. Values of Recall and F1-measure on recognition increased from 56.32%/70.18% to 85.34%/89.36%.
• The rough moiré pattern extraction module and character attention module are jointly introduced into our TIDNet. Due to the differences in different channels on the moiré patterns, the moiré is first removed roughly. Furthermore, the textural and semantic characters are also exploited, which are specifically adaptive for text image moiré removal.
• A dataset HITSZ-TID which is for text image demoiréing is created. It consists of 3,739 image pairs, where each pair contains an image contaminated with moiré patterns and its corresponding reference image free from the moiré patterns. This dataset fills the gap between the OCR and image demoiréing, contributing to the research study on these two fields.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, some related works about image demoiréing and text image processing are briefly described. Our created dataset and proposed TIDNet are then introduced in Section 3 and Section 4, respectively. To demonstrate the significance of text image demoiréing for OCR and the effectiveness of our proposed method, we conducted experiments in Section 5, followed by conclusion in Section 6.
2 Related works
In this section, we briefly introduce the related works on image demoiréing and text image processing.
2.1 Image demoiréing
Due to the interference of different repetitive patterns, the image contaminated with moiré patterns is an inevitable phenomenon. In recent years, various methods have been proposed for moiré pattern removal. By exploiting the prior assumption that moiré patterns are dissimilar on textures, a low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition method [23] was developed to achieve demoiréing on high-frequency textures. Different from this hand-crafted feature-based method, [18] primarily utilized the CNN for moiré image restoration. Considering that moiré patterns widely span in different resolution scales, multiple resolutions were jointly exploited in [18]. Followed by it, [21] also presented a multi-scale feature enhancement network for moiré image restoration. In addition, a coarse-to-fine strategy was presented in [24], which introduced another fine-scale network to refine the demoiréd image obtained from the coarse-scale network. In addition, instead of relying solely on real captured images like [18], [24] modeled the formation of moiré patterns and generated a large-scale synthetic dataset. Furthermore, [20] proposed a learnable bandpass filter and a two-step tone-mapping strategy for moiré pattern removal and color restoration, respectively. [25] constructed a moiré removal and brightness improvement (MRBI) database using aligned moiré-free and moiré images and proposed a CNN with additive and multiplicative modules to transfer the low light moiré image to the bright moiré-free image. Considering that the moiré patterns mainly located on the high-frequency domain, the wavelet was embedded into the network [26], in which the features represented by the wavelet transformation were then processed. To compensate for the difference in domains between the training and the testing sets, a domain adaptation mechanism was further exploited to fine-tune the output. Similarly, [27] also introduced a wavelet-based dual-branch network to separate the frequencies of moiré patterns from the image content. By exploiting progressive feature fusion and channel-wise attention, the attentive fractal network was proposed in [28]. In addition, [29] proposed another attention network named C3Net, which focuses on channel, color, and concatenation. Different from these aforementioned methods from single-image demoiréing, the multi-frame-based image demoiréing was also studied in [19].
Despite the fact that a number of deep learning-based approaches have been proposed for moiré-free image restoration, almost all of them are designed for natural images, which are not particularly adaptive for the text images.
2.2 Text image processing
The quality of the text image has a key influence on the accuracy of ORC. According to this purpose, some works on text image processing have been studied. For instance, several artificial filters were compared on low-resolution text images [30]. Subsequently, SRCNN [31] was applied to the text image super-resolution [32]. To achieve the scene text image super-resolution, [33] designed a text-oriented network, in which the sequential information and character boundaries were enhanced. In addition, in [34], the image was decomposed into the text, foreground, and background, which were beneficial for text boundary recovery and color restoration, respectively. Considering the text-specific properties, [35] utilized the text-level layouts and character-level details for text image super-resolution. Apart from this super-resolution application, some deblurring approaches [36–42] have also been proposed for text images. Specifically,[38] introduced two-tone prior to estimate the kernel for image deblurring. The deep neural network followed by sequential highway connections was exploited to restore the blurry image to a clear image. Furthermore, by constructing a text-specific hybrid dictionary, the powerful contextual information was then extracted for blind text image deblurring [39, 43, 44]. For the text image detection and recognition, [45] proposed a mathematical model based on the Riesz fractional operator to enhance details of the edge information in license plate images, hence improving the performance. In addition, a method [46] for predicting hidden (masked) text parts was proposed to fill the gaps of non-transcribable parts in the unstructured document OCR.
Although these methods were studied for text image super-resolution or deblurring, they are not adaptive for the application of demoiréing, due to the much more complex distributions or structures of the moiré patterns. Therefore, it is quite significant to propose a specific network for text image demoiréing. A related work named MsMa-Net [47] was proposed for moiré removal in document images. However, our proposed method is quite different from that of [47]. Referring to the dataset, only 80 images were used for dataset construction, whereas 551 images were used in our dataset, resulting in 3,739 pairs. Furthermore, we further take text priors, e.g., gradient, channel, and semantic information, into account, which contribute to our performance improvement on detection and recognition. In addition, although MsMa-Net also mentioned binarization for the output, it still first enforced the output to be the same to the reference image in the color version, which was then followed by a threshold processing to achieve binarization. By contrast, our proposed dataset TIDNet directly transforms various inputs to a binary-like ground-truth without any reference estimation, making it easier to remove the influences of diverse backgrounds and contributes to image reconstruction. Thus, this work will considerably benefit future research on text image processing and OCR.
3 Dataset
In this study, for training and testing purposes, we collect 3,739 pairs of contaminated moiré images and uncontaminated reference images to serve as a text image benchmark for moiré pattern removal. Specifically, we download the reference text images in Chinese or English from the internet, which are then used for capturing contaminated images.
3.1 Image capture
Similar to [18], each reference image is surrounded by a black border for alignment, which will be analyzed in Subsection 3.2. As displayed in Figure 3, the image is first located in the center of the display screen, which is then captured using a mobile phone. Notably, the black border is always completely captured, and each photo is taken from a random distance or viewpoint, guaranteeing the diversity of the moiré patterns.
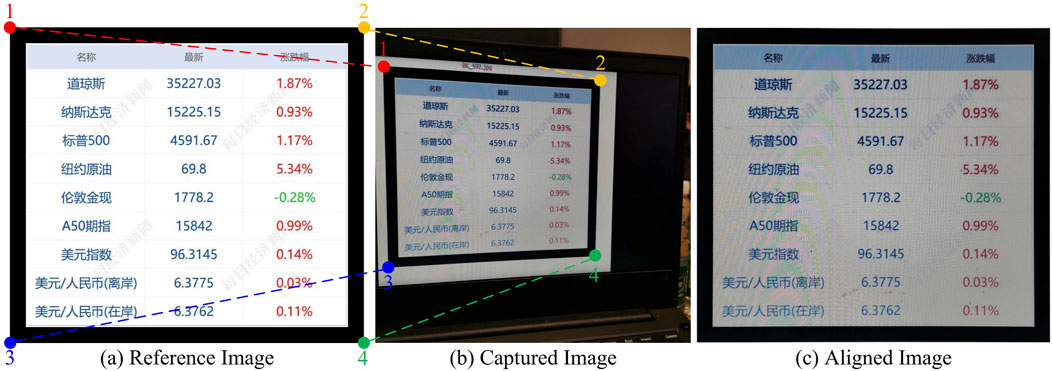
Figure 3. Image alignment. The reference image and the captured image contaminated with moiré patterns are aligned according to their corresponding corners: (A) reference image, (B) captured image, and (C) aligned image.
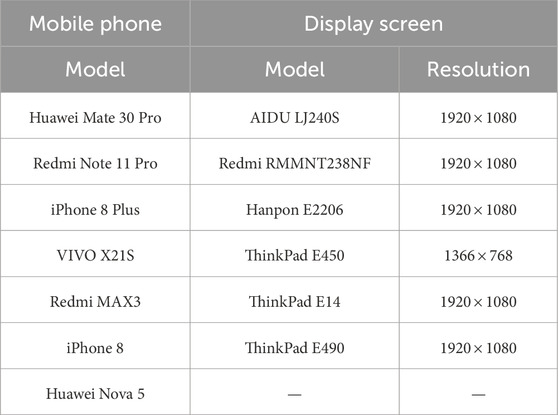
To further enhance diversity in our created dataset, we use a variety of mobile phones and monitor screens. Table 1 lists the detailed information of our used mobile phones and display screens. Specifically, eight types of mobile phones and seven types of display screens are used for capturing images. Taking other aforementioned variables into account such as distances and viewpoints, 3,739 pairs of images are totally obtained.
3.2 Image alignment
To achieve the training phase in an end-to-end way, the contaminated image should be aligned with its corresponding reference image at the pixel-to-pixel level. Although [18, 25] proposed the corner or patch matching algorithms for image alignment, these automatic strategies still encounter a slight misalignment. Different from the natural images, the misalignment under even several pixels would make a great influence on the text image restoration. Thus, we manually detect the corresponding corners for the text image alignment. As shown in Figures 3A, B, four corners in the reference image and contaminated image are detected, respectively, through which the geometric transformation between these two images is estimated. Finally, we obtained the aligned image with moiré patterns, as displayed in Figure 3C.
4 Proposed method
The pipeline in our proposed method is shown in Figure 4. It is clear that there are two branches for the moiré-free image generation. From the bottom to top, our proposed rough moiré extraction module and the three-channel network are first exploited to remove the moiré pattern in a rough way. By combining the feature maps from this branch with the backbone network and introducing the character attention module, a more accurate moiré-free image is generated. Notably, we follow [48] as the backbone, in which the original resolution subnetwork (ORS-Net), channel attention block (CAB), and supervised attention module (SAM) are utilized.
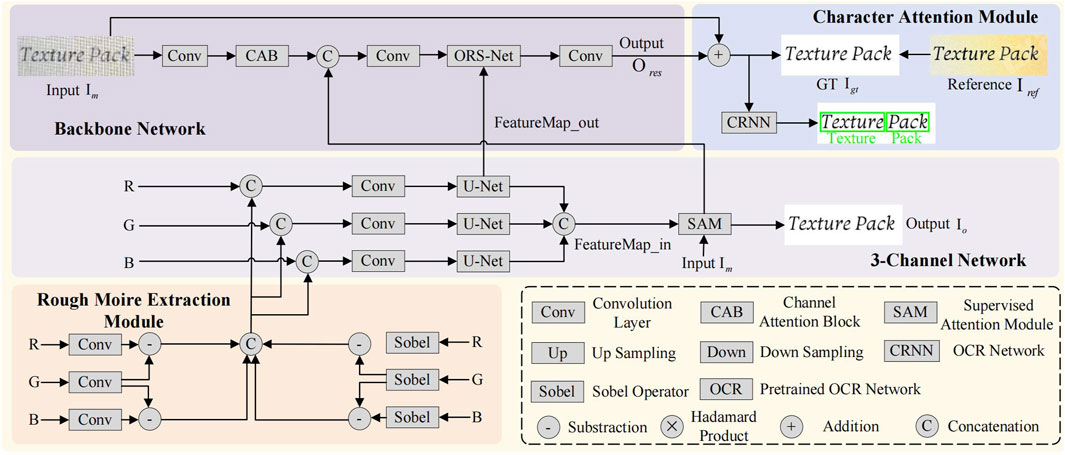
Figure 4. Pipeline of our proposed TIDNet. The rough moiré pattern extraction module in the first branch is introduced to estimate the moiré-free image in a simple but efficient way. By enforcing feature maps from this branch to the second branch and taking the character attention module into account, a more accurate image without moiré patterns is finally obtained. Notably, all blocks in our proposed method enjoy different weights.
4.1 Rough moiré pattern extraction module
According to [17], moiré patterns are mainly shaped in curves and stripes, which benefit from their specific properties. Obviously, extracting these properties that are different from those in the reference image would help to remove the moiré patterns. Fortunately, similar to [17], we statistically find that by decomposing the contaminated image into R, G, and B (red, green, and blue) channels, the G channel encounters much slighter moiré patterns than those in the R and B channels, as displayed in Figure 5. Of course, subtraction between the G channel and the R/B channel is a simple way to roughly obtain moiré-associated information for image restoration. However, despite the fact that different channels suffer from different moiré patterns, they also exhibit different scales of values. In other words, it is possible that one channel may have much larger or smaller values than that in the remaining one or two channels, subsequently making the aforementioned channel subtraction strategy useless. In order to tackle this problem, in this study, we introduce a learnable strategy through which the differences in value scales are adaptively alleviated.
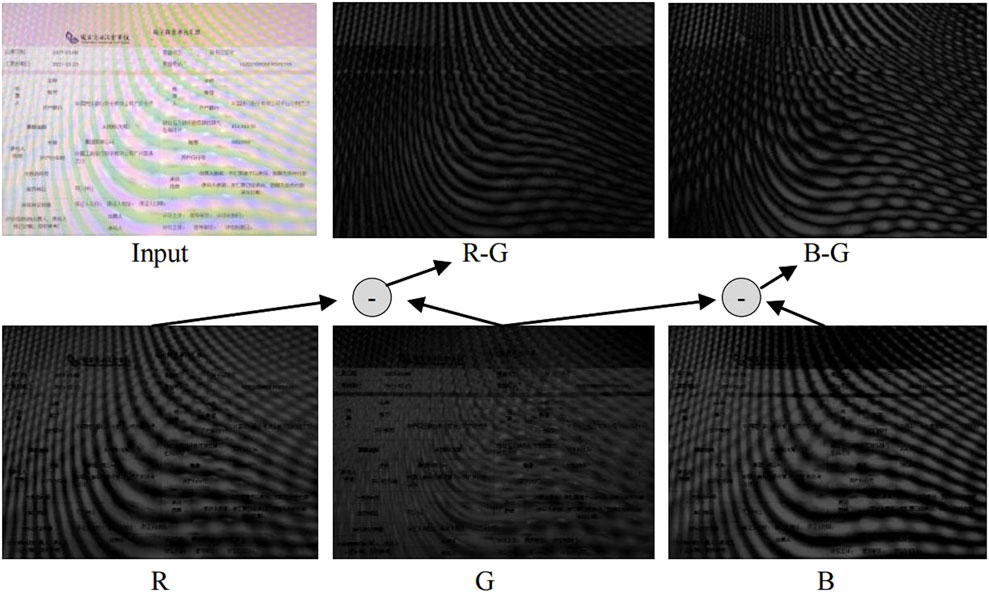
Figure 5. Display of the transformed channels and their subtraction. Images at the second row denote transformed R
Mathematically, let the contaminated image be
where
where
In addition, since the edges are also an additional prior for moiré-contaminated images, we further apply the Sobel operator [49] to enhance the edge information of three channels, as shown in the second row of Figure 6. Similar to Equation 2, these edge maps associated with the “G” channel are subtracted from the other two maps via Equation 3.
where
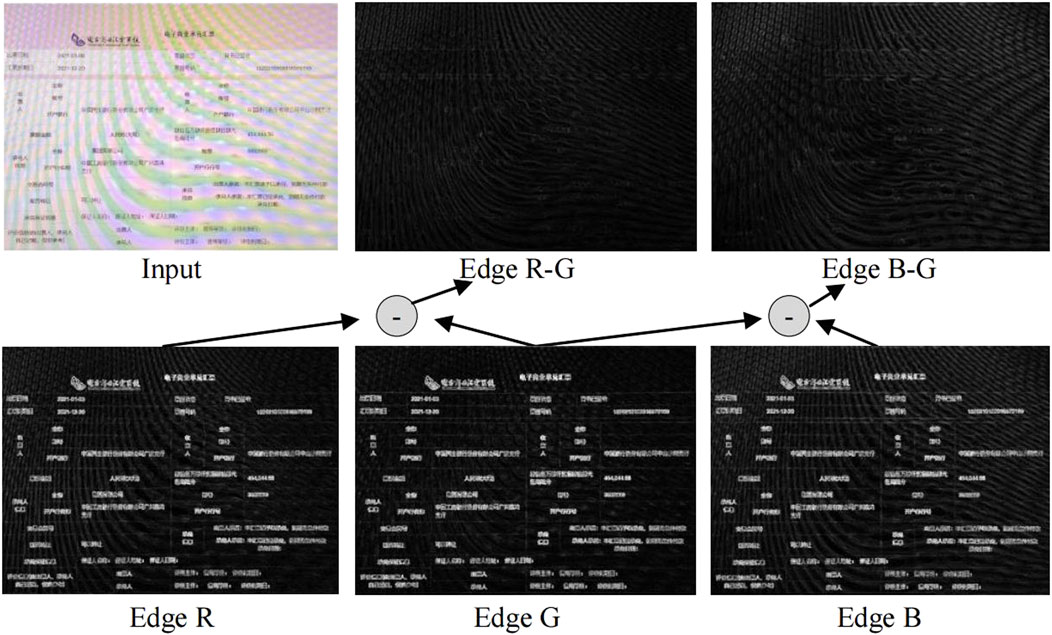
Figure 6. Display of the edge maps of the three channels and their subtraction. Images at the second row denote edge maps of R, G, and B channels, respectively. At the first row, “Edge R-G” denotes the subtraction between Edge R and Edge G. So does “Edge B-G”.
After obtaining
where the constant
4.2 Character attention module
Different from the natural image-based restoration which focuses on all pixels equally, the purpose of our task is to increase the recognition accuracy after demoiréing. In other words, we focus on the characters rather than the surrounding background pixels. In fact, as shown in Figure 2, some images indeed include quite complex backgrounds, such as watermarking and diverse colors. Strongly enforcing the inputs to be the same to these reference images with complex backgrounds are impossible. Therefore, in this paper, we first transform the reference image

Figure 7. Display of the reference image with the complex background and the ground-truth image with the binary-like background.
By forwarding
Equation 5 is used to encourage the reconstructed image to be similar to the ground-truth at the pixel level. Notably, feature maps obtained from SAM are also introduced into this
In addition, to further allow our model to pay much more attention on the character-associated pixels, we regard
Of course, images restored from the contaminated image should be easily recognized by an OCR model. Therefore, to enforce the recovered text images to exhibit their corresponding semantic priors, a text semantic loss is further introduced. Particularly, CRNN [51] followed by its pre-trained model is exploited. In this study, we use
where
Taking the aforementioned analysis into account, the objective function of our proposed method is formulated as Equation 8:
where
4.3 Implementation details
We implement our TIDNet using PyTorch [52]. The model runs on two GPUs of NVIDIA RTX 3090 with CUDA version 11.2. Except the OCR-related network CRNN, we optimize our network through the Adam optimizer with the learning rate of
5 Experiments
To demonstrate the significance of text image demoiréing and effectiveness of our proposed TIDNet, experiments are conducted on our collected dataset. In this section, the experimental settings and evaluation metrics are first described. We then conducted ablation studies to substantiate the importance of our introduced strategies. Finally, our proposed method is compared with state of the arts to further show its superiority.
5.1 Experimental settings and evaluation metrics
In this study, we divide the dataset into two subsets: one for training and another for testing. Specifically, 3,627 pairs are regarded as the training set and 112 contaminated images are used as the testing set. Notably, in testing images, there are totally 43,152 characters.
Since the final purpose of our TIDNet is to improve the OCR performance, we introduce recall, precision, and F1-measure (F1-m) scores as the quantitative evaluations for both text detection and recognition. Recall is the ratio between the number of correctly predicted characters and the number of labeled characters. It indicates how many items are correctly identified. Correspondingly, precision is the ratio between the number of correctly predicted characters and the number of all predicted characters. F1-m is a metric define by the recall score and the precision score:
Notably, most existing methods such as natural image demoiréing and image denoising adopted the widely used quantitative evaluations: peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity (SSIM). However, they are not suitable for our task. In our text image demoiréing, the contaminated images are enforced to be close to the binary-like ground-truths, while these guided references usually encounter imbalanced numbers of foreground and background pixels. Generally, the background pixels cover much more areas than foreground pixels. Due to this constraint, PSNR or SSIM values would be inaccurate if some character-related pixels are erased but the background is clear. In other words, the erased pixels do not make an obvious influence on PSNR or SSIM. By contrast, the detection and recognition performances of images suffered from erased characters would be remarkably influenced. Thus, in this paper, recall, precision, and F1-m are more reasonable for our task.
5.2 Ablation study
5.2.1 Is text image demoiréing necessary?
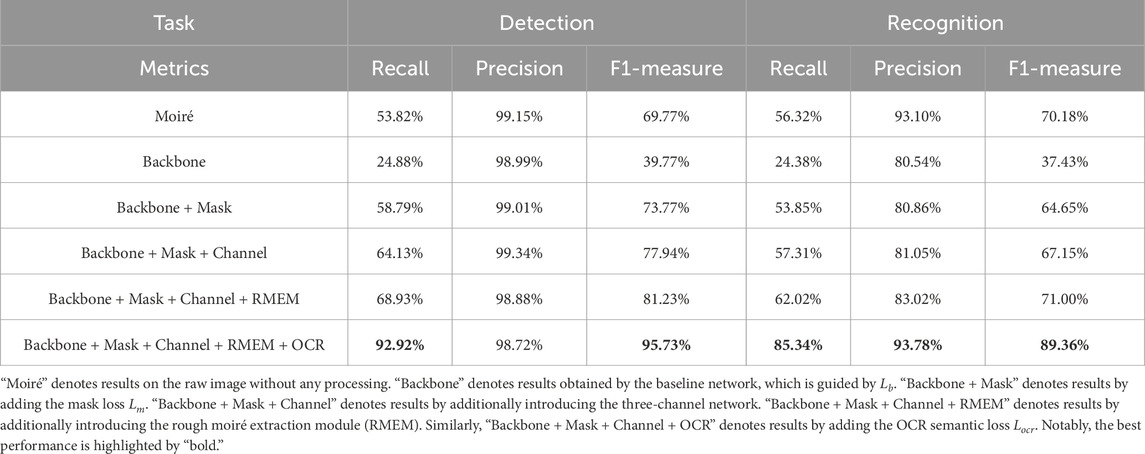
Due to the contamination of moiré patterns, it would be difficult to detect and recognize characters from the text image. As tabulated in Table 2, metrics of recall and F1-m on the contaminated images are only (53.82% and 69.77%) and (56.32% and 70.18%) for detection and recognition, respectively. However, thanks to our proposed TIDNet, these two metrics exhibit dramatic enhancement, which are (92.92% and 95.73%) and (85.34% and 89.36%). Obviously, it is quite significant for text image demoiréing.
5.2.2 Do the rough moiré extraction module and three-channel network work?
Inspired by the specific property of moiré patterns, the rough moiré extraction module is first introduced to extract the edge information related to the moiré patterns, which is then followed by our three-channel network. In detail, Table 2 shows that the 3-channel network leads to significant improvements in recall and F1-measure. By further taking the rough moiré extraction module into account, performance continues to increase.
5.2.3 Does the character attention module work?
To enforce the network to highly focus on our interested characters, the mask loss
Figure 8 displays visualizations corresponding to Table 2. It is clear that when the backbone is applied, it removes the moiré patterns. However, it also regards optical characters as the moiré, which only makes the recovered image smooth and erases many character-related pixels. By contrast, thanks to our mask loss, the model highly focuses on characters, enhancing their associated pixels, as shown in the first image in the second row. Nevertheless, as character-related pixels are quite similar to some edge information, which also exists in the moiré patterns, the reconstructed image is also contaminated by moiré patterns. Thus, we further introduce the three-channel-based strategy followed our rough moiré extraction module (RMEM). Obviously, not just the moiré patterns are alleviated, but the backgrounds are also much closer to the ground-truth compared with those obtained by “B” and “B + M.” Despite the fact that “B + M + C + RMEM” jointly enhances characters and removes moiré patterns, some recovered characters, as displayed in the enlarged details, encounter inaccurate semantic information. Fortunately, thanks to our introduced OCR loss, characters are further restored according to their semantics.
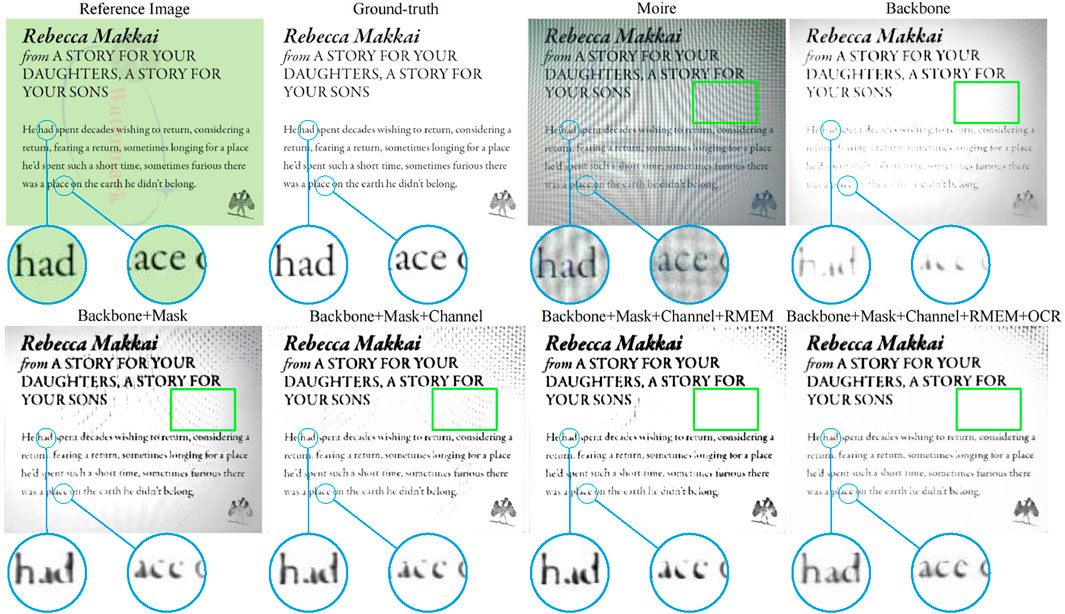
Figure 8. Visualizations of ablation studies corresponding to Table 2.
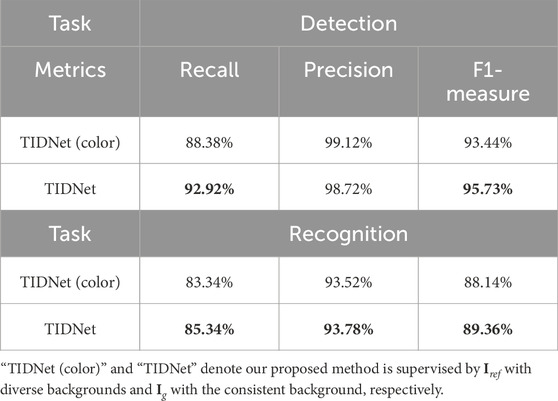
5.2.4 Does the binary-like ground-truth work?
In our proposed method, the reference image
In addition, Figure 9 further proves the significance of using the binary-like ground-truth image

Figure 9. Displays of demoiréd images obtained by our TIDNet when the reference image and ground-truth image are, respectively, used as the supervised guidance.
5.3 Comparison with state of the arts
To further demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method on the moiré pattern removal, we conducted experiments compared with state of the arts, including AFN [28], WDNet [27], C3Net [29], DnCNN [11], and FFDNet [53]. Specifically, the first three methods are designed for image demoiréing, and the last two are designed for image restoration. To make a fair comparison, we retrain them on our collected dataset according to their released source codes.
The quantitative results on detection and recognition are tabulated in Table 4. Obviously, our presented method TIDNet dramatically outperforms these state of the arts. Compared with AFN, C3Net, and DnCNN, our achieved results are much superior to those computed by them. Specifically, they are all less than 30% and 45%, respectively, on the recall and F1-measure in text detection, whereas TIDNet achieves more than 50% improvement. Referring to FFDNet, although it is slightly better than the aforementioned method, it is still much inferior to TIDNet. In comparison to WDNet, our proposed method also achieves noticeable performance enhancement.
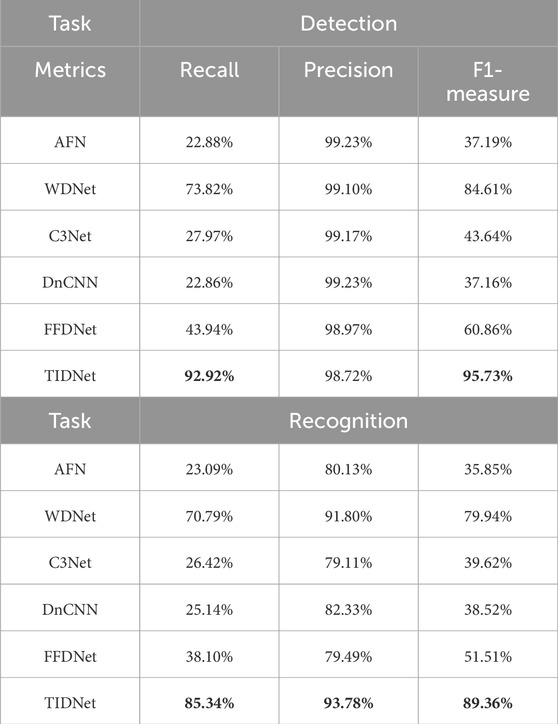
Table 4. Quantitative results on our collected dataset obtained by different comparison methods and TIDNet.
The comparison visualizations in Chinese and English are, respectively, shown in Figures 10, 11. It is easy to observe that no matter whether the text images are in Chinese or English, our presented method exhibits much better visualizations compared with existing image demoiréing and image restoration methods. Referring to AFN and C3Net, although moiré patterns are removed from the contaminated images, many character-related pixels are also erased, significantly making an inferior influence on text detection and recognition. The main reason is that these two methods regard the characters as moiré patterns since they have similar attributes. By contrast, WDNet overcomes this problem, however its recovered images are still corrupted by more or less moiré patterns. For DnCNN, it also suffers from the similar problem compared with AFN and C3Net. Although a better visualization is obtained by FFDNet in comparison to DnCNN, its reconstructed characters are blurred. Different from these comparison approaches, our proposed method not only efficiently erases moiré patterns but also restores the characters which are quite similar to the ground-truth.
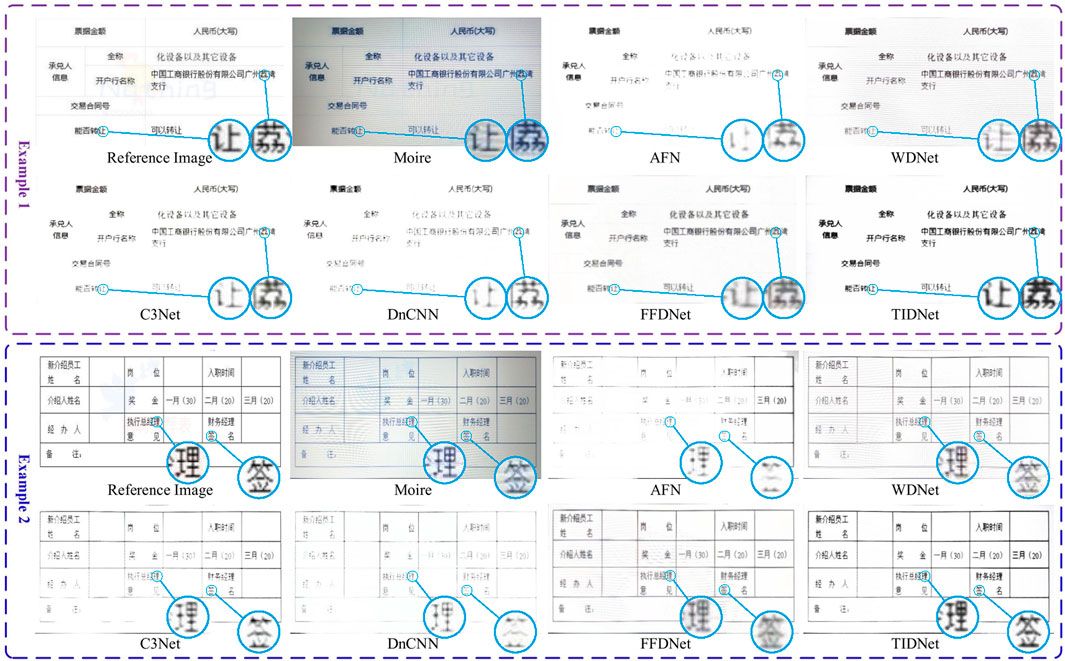
Figure 10. Displays of demoiréd images (in Chinese) obtained by different comparison methods and TIDNet.

Figure 11. Displays of demoiréd images (in English) obtained by different comparison methods and TIDNet.
6 Conclusion
To fill the gap between the OCR and image demoiréing, in this paper, a text image-based dataset is primarily collected for text image demoiréing, allowing for supervised study. Furthermore, we propose a novel network named TIDNet, which is particularly adaptive for text image demoiréing. Inspired by the specific priors of moiré patterns, a rough moiré extraction module followed by a three-channel network is introduced so that the moiré pattern-associated information is easily extracted. Since our purpose is to improve the detection and recognition performance, a character attention module is also proposed in our TIDNet, through which the network highly pays attention on character-associated pixels and their semantic information. As a result of the aforementioned strategies, our proposed method enjoys a dramatic performance improvement on the OCR application.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
ZZ: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, writing–original draft, writing–review and editing, and visualization. BL: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, and writing–original draft. TR: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing–original draft. CF: data curation, investigation, software, and writing–original draft. RL: data curation, software, and writing–original draft. ML: funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This project was supported in part by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China 62472124, Shenzhen Colleges and Universities Stable Support Program GXWD20220811170130002.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
2. Kim MD, Ueda J. Dynamics-based motion deblurring improves the performance of optical character recognition during fast scanning of a robotic eye. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatronics (2018) 23:491–5. doi:10.1109/tmech.2018.2791473
3. Shi X, Shen X. Oracle recognition of oracle network based on ant colony algorithm. Front Phys (2021) 9:768336. doi:10.3389/fphy.2021.768336
4. Guo X, Li J, Chen B, Lu G. Mask-most net: mask approximation based multi-oriented scene text detection network. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME); 08-12 July 2019; Shanghai, China. IEEE (2019) p. 206–11.
5. Ding H, Du Z, Wang Z, Xue J, Wei Z, Yang K, et al. Intervoxnet: a novel dual-modal audio-text fusion network for automatic and efficient depression detection from interviews. Front Phys (2024) 12:1430035. doi:10.3389/fphy.2024.1430035
6. Zhan F, Lu S. Esir: end-to-end scene text recognition via iterative image rectification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 16-20 June 2019; Long Beach, CA, United States: IEEE (2019) p. 2059–68.
7. Satyawan W, Pratama MO, Jannati R, Muhammad G, Fajar B, Hamzah H, et al. Citizen id card detection using image processing and optical character recognition. In: Journal of physics: Conference series, 1235. Bristol, United Kingdom: IOP Publishing (2019), 012049.
8. Schreiber S, Agne S, Wolf I, Dengel A, Ahmed S. Deepdesrt: deep learning for detection and structure recognition of tables in document images. In: 2017 14th IAPR international conference on document analysis and recognition (ICDAR); 09-15 November 2017; Kyoto, Japan, 1. IEEE (2017) p. 1162–7. doi:10.1109/icdar.2017.192
9. Zhuang J, Hou S, Wang Z, Zha ZJ. Towards human-level license plate recognition. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on computer vision. 8-14 September 2018. Munich, Germany: ECCV (2018) p. 306–21.
10. Zhu Z, Wang Z, Qi G, Mazur N, Yang P, Liu Y. Brain tumor segmentation in mri with multi-modality spatial information enhancement and boundary shape correction. Pattern Recognition (2024) 153:110553. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2024.110553
11. Zhang K, Zuo W, Chen Y, Meng D, Zhang L. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans image Process (2017) 26:3142–55. doi:10.1109/tip.2017.2662206
12. Jiang B, Lu Y, Wang J, Lu G, Zhang D. Deep image denoising with adaptive priors. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Tech (2022) 32:5124–36. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3149518
13. Ren D, Zuo W, Hu Q, Zhu P, Meng D. Progressive image deraining networks: a better and simpler baseline. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 15-20 June 2019; Long Beach, CA, USA (2019) p. 3937–46.
14. Zhang H, Sindagi V, Patel VM. Image de-raining using a conditional generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Tech (2020) 30:3943–56. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2920407
15. Qu Y, Chen Y, Huang J, Xie Y. Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2019) p. 8160–8.
16. Wang P, Zhu H, Huang H, Zhang H, Wang N. Tms-gan: a twofold multi-scale generative adversarial network for single image dehazing. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Tech (2022) 32:2760–72. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3097713
17. He B, Wang C, Shi B, Duan LY. Mop moire patterns using mopnet. Proc IEEE/CVF Int Conf Comput Vis (2019) 2424–32.
18. Sun Y, Yu Y, Wang W. Moiré photo restoration using multiresolution convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Image Process (2018) 27:4160–72. doi:10.1109/tip.2018.2834737
19. Liu S, Li C, Nan N, Zong Z, Song R. Mmdm: multi-frame and multi-scale for image demoiréing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops; 14-19 June 2020; Seattle, WA (2020) p. 434–5.
20. Zheng B, Yuan S, Slabaugh G, Leonardis A. Image demoireing with learnable bandpass filters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 13-19 June 2020; Seattle, WA (2020) p. 3636–45.
21. Gao T, Guo Y, Zheng X, Wang Q, Luo X. Moiré pattern removal with multi-scale feature enhancing network. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops (ICMEW); 08-12 July 2019; Shanghai, China. IEEE (2019) p. 240–5.
22. Qi W, Yu X, Li X, Kang S. A moiré removal method based on peak filtering and image enhancement. Mathematics (2024) 12:846. doi:10.3390/math12060846
23. Liu F, Yang J, Yue H. Moiré pattern removal from texture images via low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition. In: 2015 Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP); 13-16 December 2015; Singapore: IEEE (2015) p. 1–4.
24. Liu B, Shu X, Wu X. Demoiréing of camera-captured screen images using deep convolutional neural network (2018) arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03809.
25. Yue H, Mao Y, Liang L, Xu H, Hou C, Yang J. Recaptured screen image demoiréing. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Tech (2020) 31:49–60. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2020.2969984
26. Luo X, Zhang J, Hong M, Qu Y, Xie Y, Li C. Deep wavelet network with domain adaptation for single image demoireing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops; 14-19 June 2020; Seattle, WA, USA (2020) p. 420–1.
27. Liu L, Liu J, Yuan S, Slabaugh G, Leonardis A, Zhou W, et al. Wavelet-based dual-branch network for image demoiréing. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XIII 16. Springer (2020) p. 86–102.
28. Xu D, Chu Y, Sun Q. Moiré pattern removal via attentive fractal network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops; 14-19 June 2020; Seattle, WA (2020) p. 472–3.
29. Kim S, Nam H, Kim J, Jeong J. C3net: demoiréing network attentive in channel, color and concatenation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops; 14-19 June 2020; Seattle, WA (2020) p. 426–7.
30. Mancas-Thillou C, Mirmehdi M. An introduction to super-resolution text. In: Digital document processing. Springer (2007) p. 305–27.
31. Dong C, Loy CC, He K, Tang X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans pattern Anal machine intelligence (2015) 38:295–307. doi:10.1109/tpami.2015.2439281
32. Dong C, Zhu X, Deng Y, Loy CC, Qiao Y. Boosting optical character recognition: a super-resolution approach (2015) arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.02211.
33. Wang W, Xie E, Liu X, Wang W, Liang D, Shen C, et al. Scene text image super-resolution in the wild. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. 2020: 16th European Conference. August 23–28. Glasgow, United Kingdom: Springer (2020) p. 650–66.
34. Lin K, Liu Y, Li TH, Liu S, Li G. Text image super-resolution by image matting and text label supervision. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW); 16-17 June 2019; Long Beach, CA, USA. IEEE (2019) p. 1722–7.
35. Chen J, Li B, Xue X. Scene text telescope: text-focused scene image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 20-25 June 2021; Nashville, TN, USA (2021) p. 12026–35.
36. Mei J, Wu Z, Chen X, Qiao Y, Ding H, Jiang X. Deepdeblur: text image recovery from blur to sharp. Multimedia tools Appl (2019) 78:18869–85. doi:10.1007/s11042-019-7251-y
37. Cho H, Wang J, Lee S. Text image deblurring using text-specific properties. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. October 7-13. Florence, Italy: Springer (2012) p. 524–37.
38. Jiang X, Yao H, Zhao S. Text image deblurring via two-tone prior. Neurocomputing (2017) 242:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.080
39. Lee H, Jung C, Kim C. Blind deblurring of text images using a text-specific hybrid dictionary. IEEE Trans Image Process (2019) 29:710–23. doi:10.1109/tip.2019.2933739
40. Li J, Guo X, Lu G, Zhang B, Xu Y, Wu F, et al. Drpl: deep regression pair learning for multi-focus image fusion. IEEE Trans Image Process (2020) 29:4816–31. doi:10.1109/tip.2020.2976190
41. Li J, Liang B, Lu X, Li M, Lu G, Xu Y. From global to local: multi-patch and multi-scale contrastive similarity learning for unsupervised defocus blur detection. IEEE Trans Image Process (2023) 32:1158–69. doi:10.1109/tip.2023.3240856
42. Li J, Fan D, Yang L, Gu S, Lu G, Xu Y, et al. Layer-output guided complementary attention learning for image defocus blur detection. IEEE Trans Image Process (2021) 30:3748–63. doi:10.1109/tip.2021.3065171
43. Liu Y, Qi Z, Cheng J, Chen X. Rethinking the effectiveness of objective evaluation metrics in multi-focus image fusion: a statistic-based approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intelligence (2024) 46:5806–19. doi:10.1109/tpami.2024.3367905
44. Li H, Liu J, Zhang Y, Liu Y. A deep learning framework for infrared and visible image fusion without strict registration. Int J Comput Vis (2024) 132:1625–44. doi:10.1007/s11263-023-01948-x
45. Raghunandan KS, Shivakumara P, Jalab HA, Ibrahim RW, Kumar GH, Pal U, et al. Riesz fractional based model for enhancing license plate detection and recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Tech (2018) 28:2276–88. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2713806
46. Karthikeyan S, de Herrera AGS, Doctor F, Mirza A. An ocr post-correction approach using deep learning for processing medical reports. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Tech (2022) 32:2574–81. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3087641
47. Guo Y, Ji C, Zheng X, Wang Q, Luo X. Multi-scale multi-attention network for moiré document image binarization. Signal Processing: Image Commun (2021) 90:116046. doi:10.1016/j.image.2020.116046
48. Zamir SW, Arora A, Khan S, Hayat M, Khan FS, Yang MH, et al. Multi-stage progressive image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 20-25 June 2021; Nashville, TN, USA (2021) p. 14821–31.
49. Kanopoulos N, Vasanthavada N, Baker RL. Design of an image edge detection filter using the sobel operator. IEEE J solid-state circuits (1988) 23:358–67. doi:10.1109/4.996
50. Charbonnier P, Blanc-Feraud L, Aubert G, Barlaud M. Two deterministic half-quadratic regularization algorithms for computed imaging. In: Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Image Processing; 13-16 November 1994; Austin, TX, USA, 2. IEEE (1994) p. 168–72.
51. Shi B, Bai X, Yao C. An end-to-end trainable neural network for image-based sequence recognition and its application to scene text recognition. IEEE Trans pattern Anal machine intelligence (2016) 39:2298–304. doi:10.1109/tpami.2016.2646371
52. Paszke A, Gross S, Chintala S, Chanan G, Yang E, DeVito Z, et al. Automatic differentiation in pytorch (2017).
Keywords: multi-sensor imaging, deep learning, text image, demoiréing, multi-channel, moiré pattern, optical character recognition
Citation: Zhang Z, Liang B, Ren T, Fan C, Li R and Li M (2024) Character-interested binary-like image learning for text image demoiréing. Front. Phys. 12:1526412. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1526412
Received: 11 November 2024; Accepted: 19 November 2024;
Published: 13 December 2024.
Edited by:
Zhiqin Zhu, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, ChinaReviewed by:
Lingxiao Yang, Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaDuo Chen, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, China
Xixi Jia, Xidian University, China
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Liang, Ren, Fan, Li and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mu Li, bGltdTIwMjJAaGl0LmVkdS5jbg==
 Zhanpei Zhang
Zhanpei Zhang Beicheng Liang
Beicheng Liang Mu Li
Mu Li