- 1Institute of Computing Science and Technology, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, China
- 2School of Computer Science and Cyber Engineering, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, China
- 3College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University, Suzhou, China
The dynamics of plant-insect interactions play a crucial role in the ecosystem, influenced by complex molecular signaling pathways. This study extends existing deterministic models of plant-insect systems by incorporating stochastic elements and molecular interactions, particularly focusing on the roles of Botrytis Induced Kinase-1 (BIK1) and Phyto Alexin Deficient-4 (PAD4) proteins. The model evaluates the effects of constant inhibition, pulsed inhibition, and adaptive feedback control on plant biomass
1 Introduction
The intricate dynamics of plant-insect interactions have long captivated ecologists and biologists due to their profound implications for ecosystem stability and agricultural productivity. A notable example of such interaction is the relationship between plants and herbivorous insects, such as aphids, which are significant contributors to crop damage and yield loss globally [1]. Plants have evolved sophisticated defense mechanisms to counteract these insect attacks, initiating a complex interplay of molecular signals and physiological responses aimed at mitigating damage and ensuring survival [2, 3]. In this context, the role of Botrytis Induced Kinase-1
The stochastic processes, particularly Lévy noise, enhances the model’s ability to capture extreme events, such as insect outbreaks, which are not well represented by Gaussian noise alone. Stochastic modeling techniques, as demonstrated by [17, 18], offer valuable insights for predicting population dynamics, evaluating control strategies, and understanding the influence of environmental variability. The use of Lévy noise in our model allows for the simulation of significant, abrupt changes in plant-insect interactions, providing a comprehensive representation of random phenomena. This approach underscores the importance of stochastic models in understanding complex biological systems and informing agricultural and environmental management practices. The characteristic function of a Lévy process is given by,
where
The plant-insect interaction system is a well-studied model in ecology, evolving from predator-prey analogies to more sophisticated mathematical models incorporating plant immunity concepts. This study extends these models by including molecular interactions in the plant defense system, inspired by [9]. The primary objective of this research is to develop a stochastic mathematical model to analyze plant-insect interaction dynamics, focusing on the molecular interplay between
2 Model equations
The system of differential equations governing the deterministic model is [9],
The stochastic differential equations is,
The choice of noise addition is grounded in both biological and mathematical reasoning. Biologically, in ecological systems like plant-insect interactions, fluctuations in population densities and molecular levels are typically influenced by current population or protein levels [19–21]. Environmental stresses, such as insect outbreaks or weather conditions, do not affect the system uniformly but have a state-dependent effect: larger populations or protein levels experience more significant impacts. As a result, multiplicative noise (state-dependent noise) is biologically appropriate because it reflects that larger variables are more susceptible to noise. Mathematically, adding noise terms directly allows for stochastic perturbation while preserving the structure of the deterministic model. This approach simplifies the analysis and is commonly used in models involving stochastic dynamics through stochastic differential equations (SDEs), providing a meaningful representation of randomness.
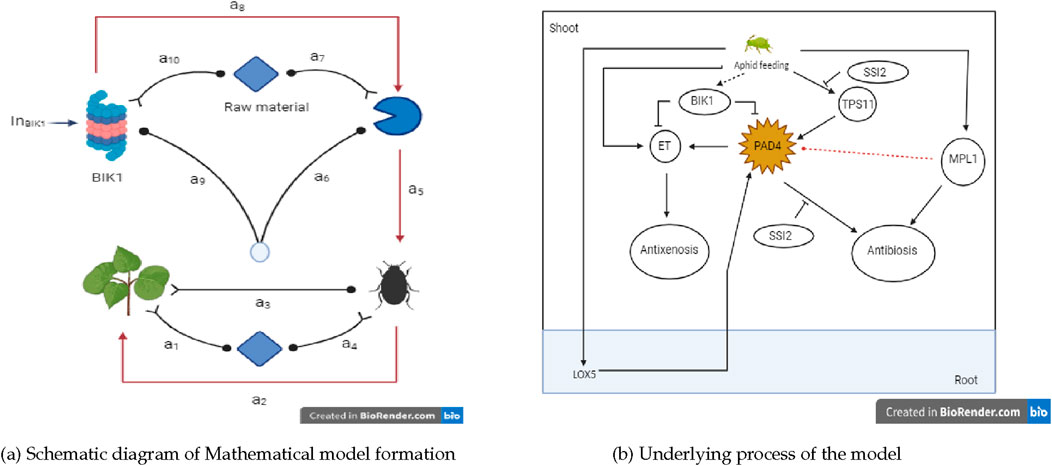
Figure 1. Insights into the plant-insects dynamical model. (A) Schematic diagram of Mathematical model formation. (B) Underlying process of the model.
The key assumptions of the model 1,2 are as follow,
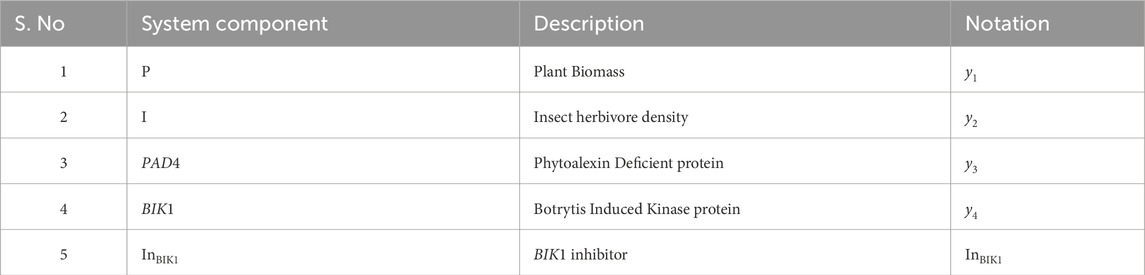
i. The model assumes that the plant biomass (P), insect herbivore density (I), PAD4 protein (PAD4), and BIK1 protein (BIK1) are homogeneously mixed within the environment. This means that these components are evenly distributed, and their interactions occur uniformly throughout the system.
ii. The environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and nutrient availability, are assumed to be constant.
iii. The model considers a closed system with no immigration or emigration of insect herbivores. The population dynamics of the insect herbivores are governed solely by the birth and death rates within the system.
iv. The concentration of the BIK1 inhibitor
v. The rate constants
vi. The model does not consider time delays in the responses of the components. All interactions and changes occur instantaneously.
vii. The model assumes that there are no external interventions, such as pesticide applications or genetic modifications.
3 Qualitative analysis of the model
3.1 Existence and uniqueness of the solution
The following section provides existence, boundedness, and equilibrium analysis for the current model. Theorem 3.1 ensures that the interactions between variables of the system are well-defined and consistent under all modeled conditions, making the system biologically predictable. While the approach used here is specific to our system, similar results in other contexts can be found in [28, 29].
Theorem 3.1. For system 1, there exists a unique solution.
Proof. The proof is given in appendix section (Theorem 3.1).
Theorem 3.2. The solutions of the system 1 are bounded for all
Proof. The proof is given in appendix section (Theorem 3.1). Theorem 3.2 reflects that the population levels of plants, insects, and proteins will not grow indefinitely or collapse to zero, showing the natural limits on growth due to environmental factors and resource constraints. The proof is given in appendix section (Theorem 3.2).
3.2 Equilibrium analysis
In this section, we analyze the equilibrium points of the system and assess their stability. The variational matrix is a matrix of first-order partial derivatives that encapsulates the local linearization of a nonlinear dynamical system around its equilibrium points. If the system is described by a set of ordinary differential equations
This matrix captures the infinitesimal behavior of the system around the equilibrium points by linearizing the system. The eigenvalue spectrum of the variational matrix governs the local stability properties of the equilibrium. If all eigenvalues have negative real parts, the system exhibits asymptotic stability at the equilibrium point. If any eigenvalue has a positive real part, the equilibrium is unstable. The variational matrix of our model is given by,
3.2.1
The variational matrix
So, the eigenvalues at the equilibrium point
Theorem 3.3. The equilibrium point
Proof. The proof is easy to follow.
3.2.2
The variational matrix
So, the eigenvalues at the equilibrium point
Theorem 3.4. The equilibrium point
Proof. The proof is easy to follow.
3.2.3
The variational matrix for
The eigenvalues are for the equilibrium point
Theorem 3.5. The equilibrium point
Proof. The proof is easy to follow.
3.2.4
The variational matrix for
The eigenvalues are for the equilibrium point
Theorem 3.6. The equilibrium point
Proof. The proof is easy to follow.
3.2.5
The variational matrix for
The eigenvalues are for the equilibrium point
Theorem 3.7. The equilibrium point
Proof. The proof is easy to follow.
3.2.6
The variational matrix for
The eigenvalues are for the equilibrium point
Theorem 3.8. The equilibrium point
Proof. The proof is easy to follow.
3.2.7
The variational matrix at
The eigenvalues are for the equilibrium point
Theorem 3.9. The equilibrium point
Proof. The proof is easy to follow.
3.2.8
The variational matrix at
The eigenvalues are for the equilibrium point
Theorem 3.10. The equilibrium point
Proof. The proof is easy to follow.
3.3 Biological significance
The equilibrium analysis emphasizes the essential dynamics between plant biomass, insect herbivores, and defense proteins, PAD4 and BIK1, in maintaining ecological stability. Theorems 3.4, 3.5 establish the foundational roles of plants and insects in the system, highlighting how their coexistence is necessary for sustaining balanced populations. The most biologically significant results are demonstrated in Theorems 3.9, 3.10, where plants maintain stable coexistence with PAD4 or both PAD4 and BIK1 proteins. These equilibria reflect the plant’s defensive mechanisms being actively regulated by these proteins, ensuring preparedness for potential herbivore attacks. Theorem 3.8 presents the ecologically balanced state, where both plants and insect herbivores coexist, with PAD4 and BIK1 proteins playing a regulatory role. This equilibrium ensures that plant defense systems, driven by these proteins, manage herbivore populations effectively, maintaining system stability. This section highlights the crucial role of plant defense proteins in regulating insect interactions, ensuring long-term ecological balance.
3.4 Basic reproduction number
The basic reproduction number
Theorem 3.11. If
Proof. The proof is given in appendix (Theorem 3.11).
3.5 Stochastic analysis
For stochastic system with
We need to show that
Theorem 3.12. The closed set
Proof. This theorem guarantees that the system remains within realistic bounds even under stochastic influences, indicating that the ecosystem is robust to fluctuations in population and protein levels. The proof is given in appendix section (Theorem 3.12).
Theorem 3.13. For
Proof. This theorem assures that despite randomness, the system’s biological variables (plants, insects, proteins) maintain positive values, ensuring the ecological system remains functional. The proof is given in appendix section (Theorem 3.13).
4 Numerical simulations
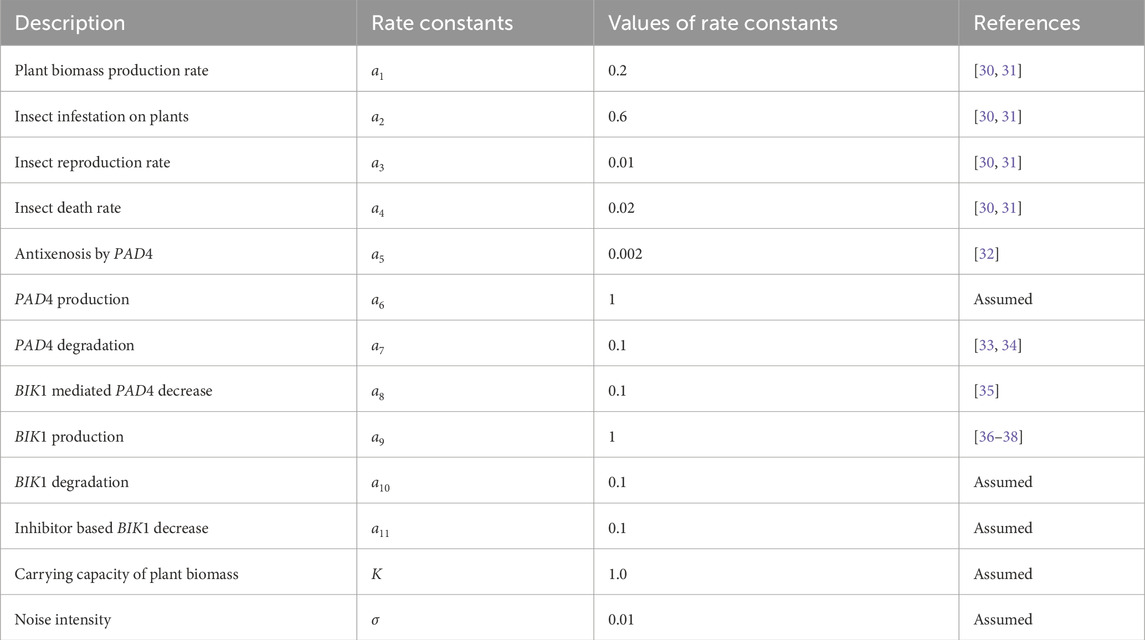
In the following subsections, various numerical results are provided. The values of the parameters used in the model are given in Table 2. The Euler-Maruyama method is used to solve the stochastic differential equations iteratively as follow,
where
For Lévy noise,
where,
And
where
4.1 Noises comparison
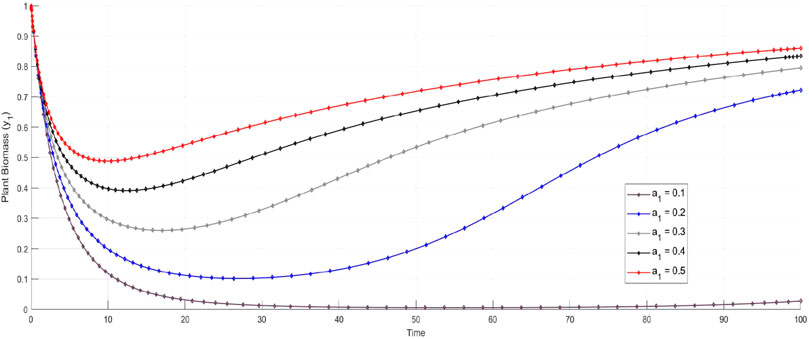
Figure 2A shows the dynamics of plant biomass
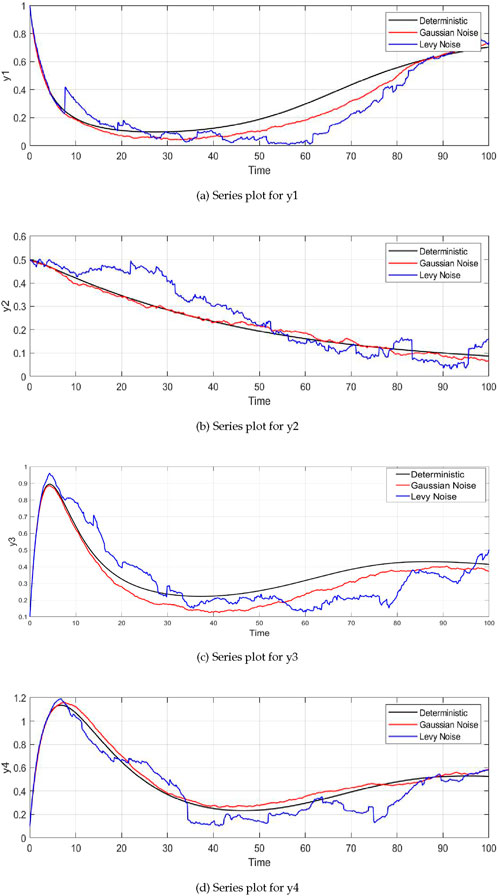
Figure 2. Time series plots of the system variables under different noise conditions (deterministic, Gaussian, and Lévy noise). For all variables—plant biomass
The dynamics of insect herbivore density
The parameter
4.2 Lévy noise
The insect herbivore density
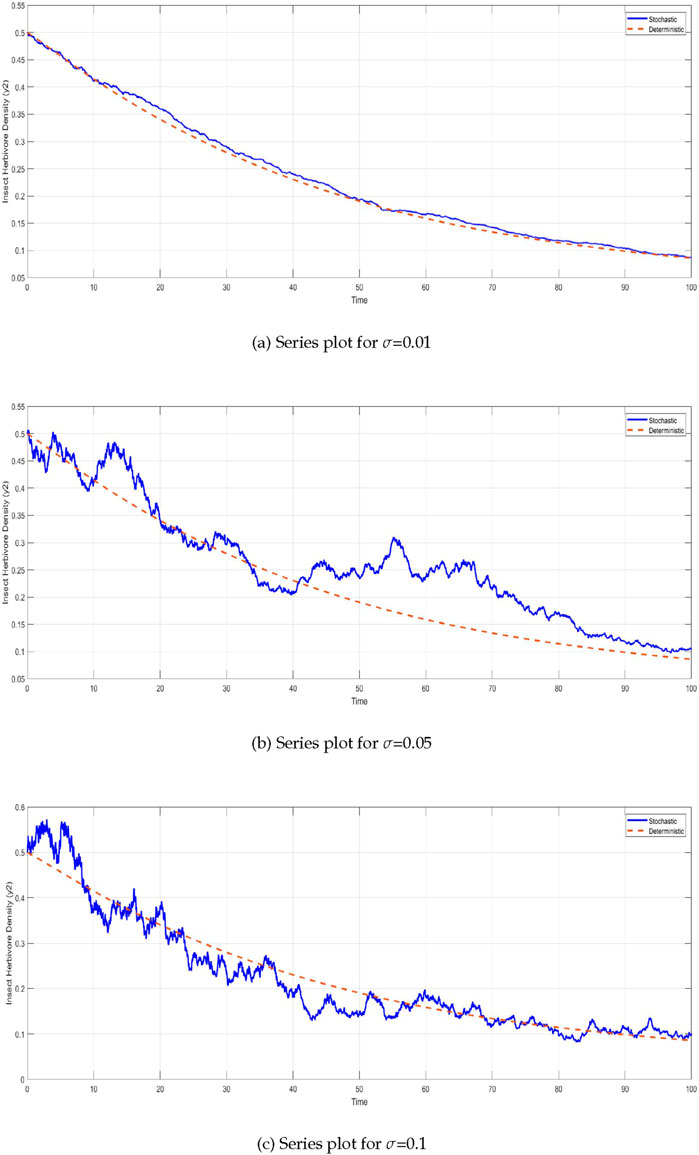
Figure 4. Time series of insect herbivore density
Similarly, the
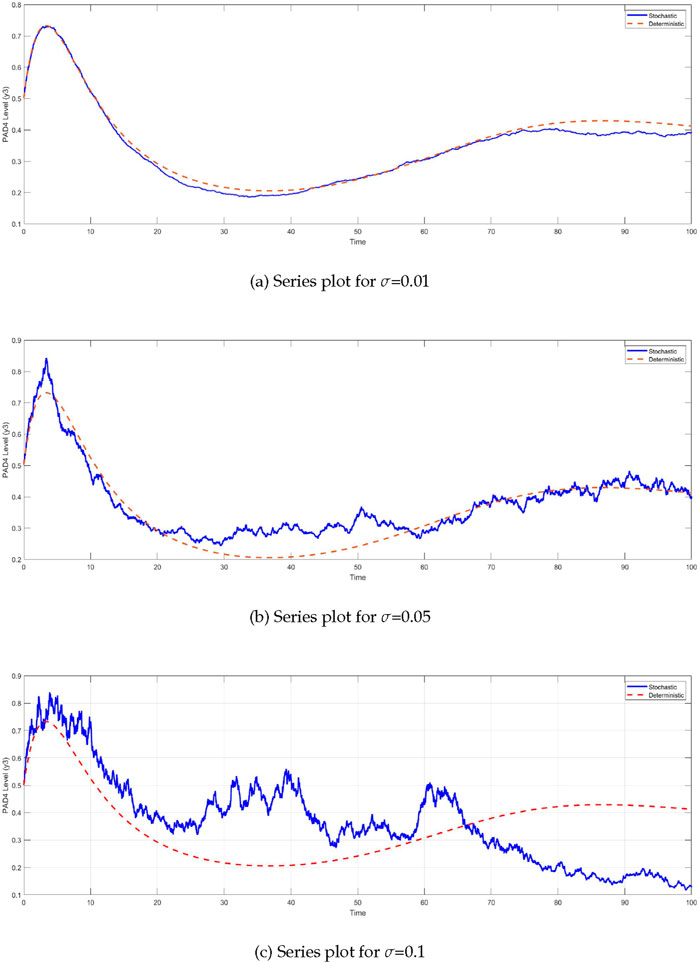
Figure 5. Time series of PAD4 protein levels
The comparison between the deterministic and stochastic models reveals critical insights into the behavior of the system under different noise intensities (Figure 6). One of the most notable observations is the impact of stochasticity on the
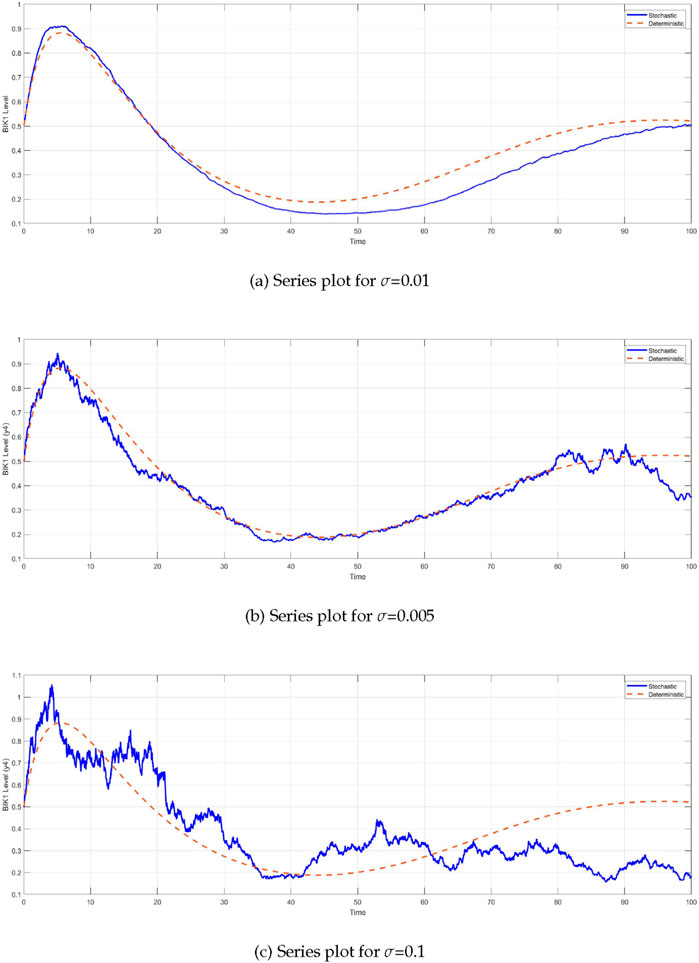
Figure 6. Time series of BIK1 protein levels
4.3 Queir plots
Queir plots visually represent how the states of a system evolve over time, especially in complex, nonlinear systems. These plots show the system’s trajectory or path in a simplified, multi-dimensional space, focusing on key variables.
Theorem 4.1. Consider the system defined by,
If
Proof. The proof is given in appendix section (Theorem 4.1).
Theorem 4.2. Consider the system defined by,
If
Proof. The proof is given in appendix section (Theorem 4.2).
4.3.1 Relationship between
As shown in Figure 7A, the relationship between
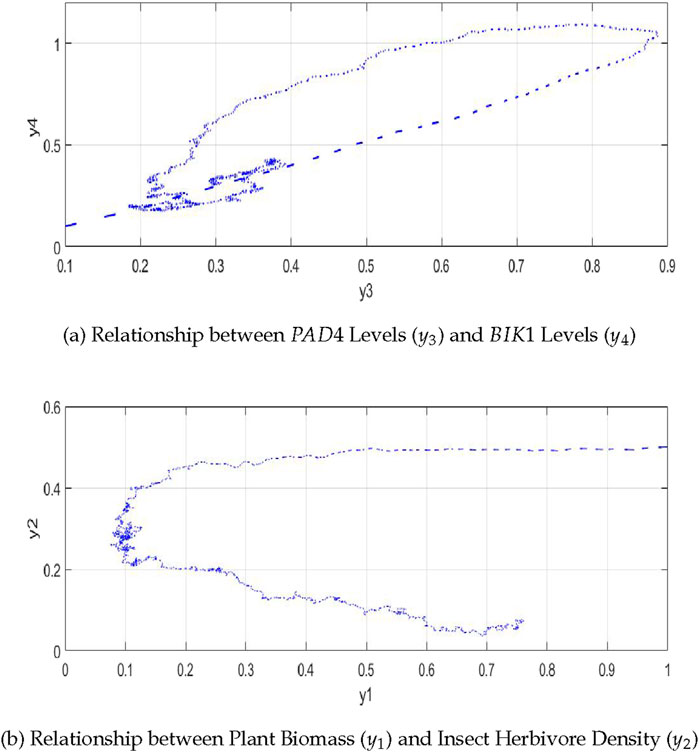
Figure 7. The plot shows the relationships in the plant-insect interaction model: (A) between
4.3.2 Relationship between plant biomass
Figure 7B shows that the relationship between plant biomass
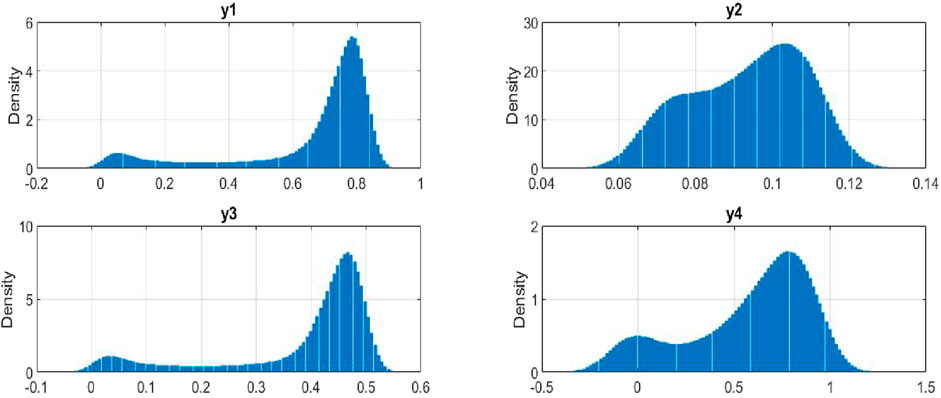
4.4 Probability density distributions
The stationary distribution describes the long-term behavior of a stochastic process, offering insights into the stability of system. A Markov process, which models a sequence of potential events, is primarily influenced by the state attained in the previous event. In simpler terms, it can be thought of as “what happens in the future depends only on the current situation.”
In the space
Here,
Lemma 4.1. [42, 43] The process
1. The smallest eigenvalue of
Additionally, if
we define,
Theorem 4.3. For
Proof. The proof is given in appendix section (Theorem 4.3).
Figure 8 presents the probability density distributions for the key variables in our stochastic model of plant-insect interactions. The density of
5 MEMs in control
The integration of Micro-Electromechanical Systems (MEMS) in plant systems has revolutionized the field of precision agriculture by providing real-time monitoring and adaptive control capabilities. MEMS sensors are widely used for tracking environmental parameters such as soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels, enabling more efficient and precise irrigation and fertilization strategies. For example, The increasing demand for the miniaturization of biosensors has driven growing interest in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) [44, 45], along with nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) and microfluidic or lab-on-a-chip based biosensors [35, 46]. These compact systems provide enhanced accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and cost-efficiency, while also offering high-performance biosensing capabilities. MEMS-based biosensors leverage a range of detection methods, including optical, mechanical, magnetic, and electrochemical approaches. For optical detection, probes like organic dyes, semiconductor quantum dots, and other fluorescence markers are commonly employed. In magnetic MEMS biosensors, nanoparticles such as magnetic, paramagnetic, or ferromagnetic particles are utilized. Mechanical MEMS biosensors operate based on changes in surface stress or mass [47], where biochemical reactions or analyte adsorption on the cantilever induce surface stress changes. Electrochemical MEMS biosensors, on the other hand, rely on amperometric, potentiometric, or conductometric detection methods [48–51]. For each variable, sensor-based feedback terms can be introduced to adjust the differential equations based on real-time data gathered by MEMS. This can include intervention strategies or feedback loops that modify plant biomass growth, herbivore density, and molecular signals. We extend the stochastic Equation 2 to include MEMS input, denoted by a new variable
For each variable
The parameters
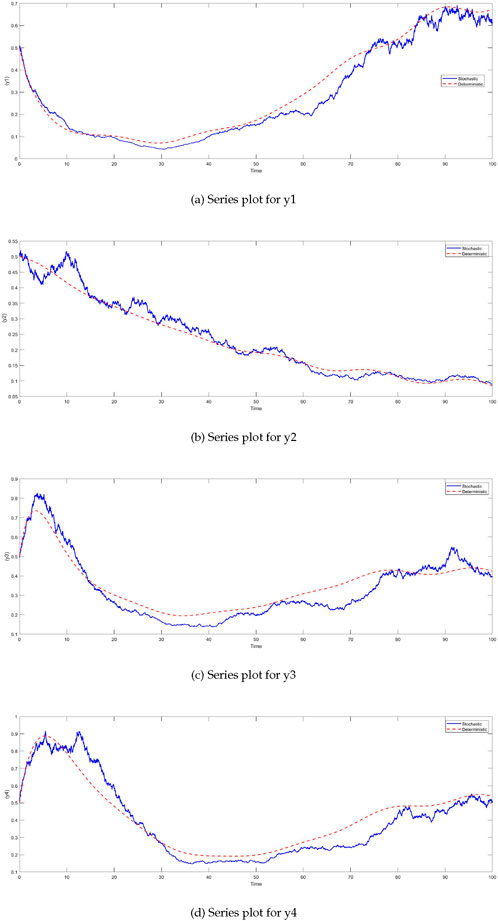
Figure 9. Time series plots of system variables with MEMS feedback under stochastic conditions. For all variables—plant biomass
6 Discussion
Our comparison of noise conditions revealed distinct behaviors in plant biomass and insect herbivore density. Deterministic conditions produced smooth trajectories, while Gaussian noise caused moderate fluctuations, and Lévy noise led to extreme variations, effectively capturing sudden changes in biological systems. High
Lévy noise had a significant impact on
7 Conclusion
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the dynamic interactions between plants and insect herbivores, focusing on the molecular interplay between
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
QA: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XQ: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. NA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. ZK: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62172114), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (2022A1515011468) and the Fundings by Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou (2023A03J0113).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the use of ChatGPT (https://chat.openai.com/) to improve the language.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphy.2024.1500423/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Girousse C, Moulia B, Silk W, Bonnemain JL. Aphid infestation causes different changes in carbon and nitrogen allocation in alfalfa stems as well as different inhibitions of longitudinal and radial expansion. Plant Physiol (2005) 137(4):1474–84. doi:10.1104/pp.104.057430
2. Bos JI, Armstrong MR, Gilroy EM, Boevink PC, Hein I, Taylor RM, et al. Phytophthora infestans effector AVR3a is essential for virulence and manipulates plant immunity by stabilizing host E3 ligase CMPG1. Proc Natl Acad Sci (2010) 107(21):9909–14. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914408107
3. De Vos M, Jander G. Myzus persicae (green peach aphid) salivary components induce defence responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell and Environ (2009) 32(11):1548–60. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02019.x
4. Lu D, Wu S, Gao X, Zhang Y, Shan L, He P. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, BIK1, associates with a flagellin receptor complex to initiate plant innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci (2010) 107(1):496–501. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909705107
5. Mantelin S, Bhattarai KK, Kaloshian I. Ethylene contributes to potato aphid susceptibility in a compatible tomato host. New Phytol (2009) 183(2):444–56. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02870.x
6. Thompson GA, Goggin FL. Transcriptomics and functional genomics of plant defence induction by phloem-feeding insects. J Exp Bot (2006) 57(4):755–66. doi:10.1093/jxb/erj135
7. Louis J, Singh V, Shah J (2012). Arabidopsis thaliana-aphid interaction, The Arabidopsis book/American Society of Plant Biologists, 10, e0159, doi:10.1199/tab.0159
8. Louis J, Shah J. Arabidopsis thalianaMyzus persicae interaction: shaping the understanding of plant defense against phloem-feeding aphids. Front Plant Sci (2013) 4:213. doi:10.3389/fpls.2013.00213
9. Kumar S, Ahmad S, Siddiqi MI, Raza K. Mathematical model for Plant-Insect interaction with dynamic response to PAD4-BIK1 interaction and effect of BIK1 inhibition. Biosystems (2019) 175:11–23. doi:10.1016/j.biosystems.2018.11.005
10. Predescu M, Sirbu G, Levins R, Awerbuch-Friedlander T. On the dynamics of a deterministic and stochastic model for mosquito control. Appl Mathematics Lett (2007) 20(9):919–25. doi:10.1016/j.aml.2006.12.001
11. Sgrillo RB, Moura J, Sgrillo KR. Simulation model for phytomona epidemics in coconut trees. Neotropical Entomol (2005) 34(4):527–38. doi:10.1590/s1519-566x2005000400001
12. Stella I, Ghosh M. Modeling plant disease with biological control of insect pests. Stochastic Anal Appl (2019) 37(6):1133–54. doi:10.1080/07362994.2019.1646139
13. Akman O, Comar TD, Hrozencik D. Model selection for integrated pest management with stochasticity. J Theor Biol (2017) 442:110–22. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.12.005
14. Lv Q, Schneider M, Pitchford J. Individualism in plant populations: using stochastic differential equations to model individual neighbourhood-dependent plant growth. Theor Popul Biol (2008) 74(1):74–83. doi:10.1016/j.tpb.2008.05.003
15. Zeng J, Zeng C, Xie Q, Guan L, Dong X, Yang F. Different delays-induced regime shifts in a stochastic insect outbreak dynamics. Physica A: Stat Mech its Appl (2016) 462:1273–85. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2016.06.115
16. Guerriero ML, Pokhilko A, Fernndez A, Halliday K, Millar A, Hillston J. Stochastic properties of the plant circadian clock. J R Soc Interf (2012) 9(67):744–56. doi:10.1098/rsif.2011.0378
17. Lessio F, Alma A. Models applied to grapevine pests: a review. Insects (2021) 12(2):169. doi:10.3390/insects12020169
18. Tilahun G, Woldegerima WA, Wondifraw A. Stochastic and deterministic mathematical model of cholera disease dynamics with direct transmission. Adv Difference Equations (2020) 2020(1):670–23. doi:10.1186/s13662-020-03130-w
19. Wilkinson DJ. Stochastic modelling for quantitative description of heterogeneous biological systems. Nat Rev Genet (2009) 10(2):122–33. doi:10.1038/nrg2509
20. Zhang J, Li W, Xiang T, Liu Z, Laluk K, Ding X, et al. Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases integrate signaling from multiple plant immune receptors and are targeted by a Pseudomonas syringae effector. Cell host and microbe (2010) 7(4):290–301. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2010.03.007
21. Thattai M, Van Oudenaarden A. Stochastic gene expression in fluctuating environments. Genetics (2004) 167(1):523–30. doi:10.1534/genetics.167.1.523
22. Fina J, Casadevall R, AbdElgawad H, Prinsen E, Markakis MN, Beemster GT, et al. UV-B inhibits leaf growth through changes in growth regulating factors and gibberellin levels. Plant Physiol (2017) 174(2):1110–26. doi:10.1104/pp.17.00365
23. Hll J, Lindner S, Walter H, Joshi D, Poschet G, Pfleger S, et al. Impact of pulsed UVB stress exposure on plant performance: how recovery periods stimulate secondary metabolism while reducing adaptive growth attenuation. Plant Cell and Environ (2019) 42(3):801–14. doi:10.1111/pce.13409
24. Campos ML, Yoshida Y, Major IT, de Oliveira Ferreira D, Weraduwage SM, Froehlich JE, et al. Rewiring of jasmonate and phytochrome B signalling uncouples plant growth-defense tradeoffs. Nat Commun (2016) 7(1):12570. doi:10.1038/ncomms12570
25. Wang P, Zhao Y, Li Z, Hsu CC, Liu X, Fu L, et al. Reciprocal regulation of the TOR kinase and ABA receptor balances plant growth and stress response. Mol Cel (2018) 69(1):100–12.e6. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2017.12.002
26. Mazzoleni S, Carten F, Bonanomi G, Senatore M, Termolino P, Giannino F, et al. Inhibitory effects of extracellular selfDNA: a general biological process? New Phytol (2015) 206(1):127–32. doi:10.1111/nph.13306
27. Chen Z, Zheng Z, Huang J, Lai Z, Fan B. Biosynthesis of salicylic acid in plants. Plant signaling and Behav (2009) 4(6):493–6. doi:10.4161/psb.4.6.8392
28. Sastry S Nonlinear systems: analysis, stability, and control, 10. Springer Science and Business Media (2013).
29. Lakshmikantham V, Leela S, Martynyuk AA. Stability analysis of nonlinear systems. New York: M. Dekker (1989). p. 249–75.
30. Kartal S. Dynamics of a plantherbivore model with differentialdifference equations. Cogent Mathematics (2016) 3(1):1136198. doi:10.1080/23311835.2015.1136198
31. Chattopadhayay J, Sarkar R, Fritzsche-Hoballah ME, Turlings TC, Bersier LF. Parasitoids may determine plant fitnessa mathematical model based on experimental data. J Theor Biol (2001) 212(3):295–302. doi:10.1006/jtbi.2001.2374
32. Louis J, Gobbato E, Mondal HA, Feys BJ, Parker JE, Shah J. Discrimination of Arabidopsis PAD4 activities in defense against green peach aphid and pathogens. Plant Physiol (2012) 158(4):1860–72. doi:10.1104/pp.112.193417
33. Pegadaraju V, Knepper C, Reese J, Shah J. Premature leaf senescence modulated by the Arabidopsis Phytoalexin deficient 4 gene is associated with defense against the phloem-feeding green peach aphid. Plant Physiol (2005) 139(4):1927–34. doi:10.1104/pp.105.070433
34. Pegadaraju V, Louis J, Singh V, Reese JC, Bautor J, Feys BJ, et al. Phloem-based resistance to green peach aphid is controlled by Arabidopsis phytoalexin deficient4 without its signaling partner enhanced disease susceptibility1. Plant J (2007) 52(3):332–41. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313x.2007.03241.x
35. Lei J, Finlayson A, Salzman RA, Shan L, Zhu-Salzman K. Botrytis-induced kinase 1 modulates Arabidopsis resistance to green peach aphids via Phytoalexin deficient 4. Plant Physiol (2014) 165(4):1657–70. doi:10.1104/pp.114.242206
36. Bent AF, Mackey D. Elicitors, effectors, and R genes: the new paradigm and a lifetime supply of questions. Annu Rev Phytopathol (2007) 45:399–436. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.45.062806.094427
37. Boller T, Felix G. A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol (2009) 60:379–406. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105346
38. Prince DC, Drurey C, Zipfel C, Hogenhout SA. The leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase brassinosteroid insensitive1-associated kinase 1 and the cytochrome P450 Phytoalexin deficient 3 contribute to innate immunity to aphids in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol (2014) 164(4):2207–19. doi:10.1104/pp.114.235598
39. Wu F, Chen X, Zheng Y, Duan J, Kurths J, Li X. Lévy noise induced transition and enhanced stability in a gene regulatory network. Chaos: Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci (2018) 28(7):075510. doi:10.1063/1.5025235
40. Song Y, Liu P, Din A. A novel stochastic model for human norovirus dynamics: vaccination impact with Lévy noise. Fractal and Fractional (2024) 8(6):349. doi:10.3390/fractalfract8060349
41. Ain QT, Din A, Qiang X, Kou Z. Dynamics for a nonlinear stochastic cholera epidemic model under Lévy noise. Fractal and Fractional (2024) 8(5):293. doi:10.3390/fractalfract8050293
42. Li D, Song G. Permanence and extinction for a single-species system with jump di?usion. J Math Anal Appl (2015) 430(1):438–64. doi:10.1016/j.jmaa.2015.04.050
43. Le TMT, Madec S, Gjini E. Disentangling how multiple traits drive 2 strain frequencies in SIS dynamics with coinfection. J Theor Biol (2022) 538:111041. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2022.111041
44. Kim K, Cheng J, Liu Q, Wu XY, Sun Y. Investigation of mechanical properties of soft hydrogel microcapsules in relation to protein delivery using a MEMS force sensor. J Biomed Mater Res A (2010) 92(1):103–13. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32338
45. Kim K, Cheng J, Liu Q, Wu XY, Sun Y. MEMS capacitive force sensors for micro-scale compression testing of biomaterials. In: Proceedings of the 21st IEEE international conference on Micro electro mechanical systems (MEMS’08). Tucson, Ariz, USA (2008). p. 888–91.
46. Mao S, Yu K, Chang J, Steeber DA, Ocola LE, Chen J. Direct growth of vertically-oriented graphene for field-effect transistor biosensor. Scientific Rep (2013) 3:1696. doi:10.1038/srep01696
47. Timurdogan E, Alaca BE, Kavakli IH, Urey H. MEMS biosensor for detection of Hepatitis A and C viruses in serum. Biosens Bioelectron (2011) 28(1):189–94. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2011.07.014
48. Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science (1998) 281(5385):2013–6. doi:10.1126/science.281.5385.2013
49. Ceylan Koydemir H, Alp A, Hascelik G, Hasçelik G. MEMS biosensors for detection of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron (2011) 29(1):1–12. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2011.07.071
50. He JH. Periodic solution of a micro-electromechanical system, Facta Universitatis. Ser Mech Eng (2024) 22(2):187–98. doi:10.22190/fume240603034h
Keywords: mathematical analysis, feedback mechanism, immunity dynamics, Lévy noise, MEMS
Citation: Ain QT, Qiang X, Ain NU and Kou Z (2024) Stochastic modeling of plant-insect interaction dynamics with MEMS-based monitoring and noise effects. Front. Phys. 12:1500423. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1500423
Received: 23 September 2024; Accepted: 29 October 2024;
Published: 26 November 2024.
Edited by:
Chun-Hui He, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Pei Wang, Henan University, ChinaZahra Vahdat, Baylor College of Medicine, United States
Copyright © 2024 Ain, Qiang, Ain and Kou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoli Qiang, cWlhbmd4bEBnemh1LmVkdS5jbg==; Zheng Kou, a291emhlbmdAZ3podS5lZHUuY24=
 Qura Tul Ain
Qura Tul Ain Xiaoli Qiang
Xiaoli Qiang Noor Ul Ain
Noor Ul Ain Zheng Kou1*
Zheng Kou1*