- 1Faculty of Arts and Science, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
- 2Department of Physics, Osaka Metropolitan University, Osaka, Japan
- 3Nambu Yoichiro Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (NITEP), Osaka Metropolitan University, Osaka, Japan
- 4RIKEN Nishina Center, Wako, Japan
- 5Department of Physics, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
- 6Department of Physics, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan
- 7SLiCS Center, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan
Total reaction, interaction, and charge-changing cross sections, which are kinds of cross sections standing for total nuclear collision probability in medium-to high-energy region from a few to several hundred MeV, have been extensively utilized to probe nuclear sizes especially for unstable nuclei. In this mini review, experimental techniques and recent findings from these cross sections are briefly overviewed. Additionally, two new methods to extract neutron skin thickness solely from the above cross sections are explained: One is utilizing the energy and isospin dependence of the total reaction cross sections, and the other is the combination of the total reaction and charge-changing cross section measurements.
1 Introduction
In neutron-rich nuclei, a thick neutron skin forms, reflecting both the nuclear structure and the bulk properties of nuclear matter. The neutron skin thickness
This quantity is particularly anticipated as a promising observable to determine the slope parameter,
Determining
Furthermore, recent developments using
2 Overview of experimental techniques
The
The
where
At energies above 200 MeV/nucleon,
The charge-changing cross section,
3 Glauber model
There are several approaches to theoretically describe the relationship between
where
where the subscripts “
where
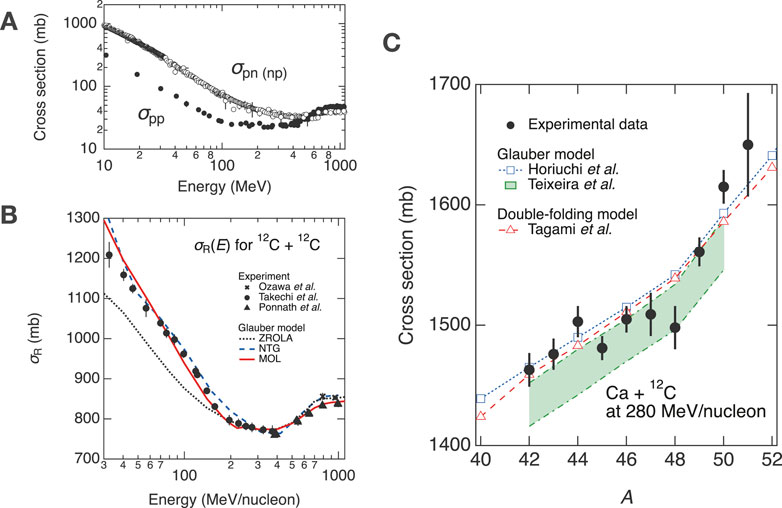
Figure 1. Properties regarding total-reaction cross sections
To calculate
Here,
Here, although Equation 7 also incorporate the isospin dependence
4 Progress of total-reaction and interaction cross section studies
4.1 Progress in recent 20 years
After the pioneering work of
Regarding nuclei near the neutron dripline, 22C [38, 79] and 29F [80] were newly identified as halo nuclei through
In the heavier region, other halo nuclei and islands of inversion have been predicted theoretically [114–116]. Regarding experimental progress in this region,
4.2 Studies on neutron skins
After revealing thick neutron skins in 6,8
Recent
The evolution of neutron skin in Ca isotopes provides new insight also into the bulk properties of nuclear matter. The Hartree–Fock calculations have pointed out that the kink structure occurs depending on the properties of the occupying valence single-neutron states to minimize the energy loss resulting from the saturation of the densities in the internal region of the nucleus [71, 116]. Evaluating the contribution of
In addition to the approach with the total collision cross sections described above and below, methods only using nucleon removal cross sections have been proposed [127].
5 Extraction of neutron skin thickness solely from collision cross sections
Recently, two novel methods have been developed to derive
5.1 Total reaction cross sections utilizing its energy and isospin dependence
This method [126, 132] utilizes the isospin and energy dependence of nucleon-nucleon total cross sections,
Horiuchi et al. analyzed the correlation between
where
The sensitivity of
5.2 Charge-changing cross sections
The
where
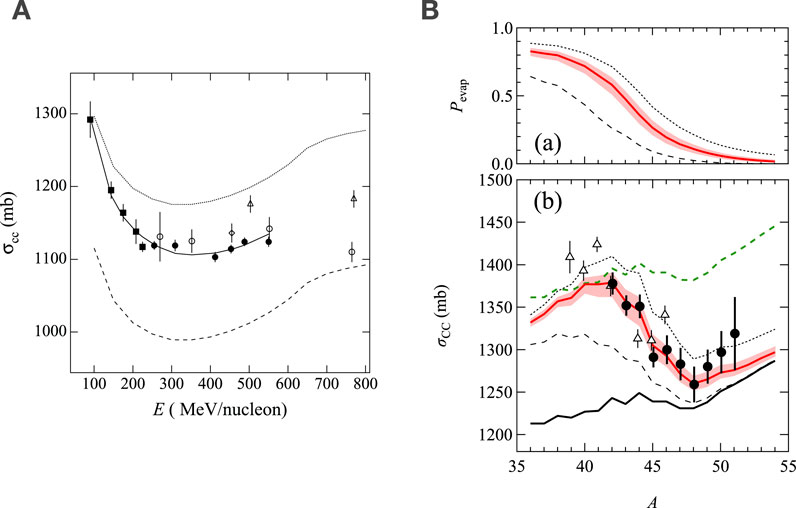
Figure 2. (A)Energy dependence of
Contrary to the description by Equation 8, it has been suggested that considering the contribution of
The
A proton target has been adopted in
To derive the EOS parameter
6 Summary
This paper has reviewed recent advancements in the total reaction
Author contributions
MT: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. WH: Writing–review and editing. MF: Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Brown BA. Neutron radii in nuclei and the neutron equation of state. Phys Rev Lett (2000) 85:5296–9. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.5296
2. Tsang MB, Stone JR, Camera F, Danielewicz P, Gandolfi S, Hebeler K, et al. Constraints on the symmetry energy and neutron skins from experiments and theory. Phys Rev C (2012) 86:015803. doi:10.1103/physrevc.86.015803
3. Trzcińska A, Jastrzȩbski J, Lubiński P, Hartmann FJ, Schmidt R, von Egidy T, et al. Neutron density distributions deduced from antiprotonic atoms. Phys Rev Lett (2001) 87:082501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.87.082501
4. Klos B, Trzcinska A, Jastrzebski J, Czosnyka T, Kisielinski M, Lubinski P, et al. Neutron density distributions from antiprotonic 208Pb and 209Bi atoms. Phys Rev C (2007) 76:014311. doi:10.1103/physrevc.76.014311
5. Terashima S, Sakaguchi H, Takeda H, Ishikawa T, Itoh M, Kawabata T, et al. Proton elastic scattering from tin isotopes at 295 MeV and systematic change of neutron density distributions. Phys Rev C (2008) 77:024317. doi:10.1103/physrevc.77.024317
6. Zenihiro J, Sakaguchi H, Murakami T, Yosoi M, Yasuda Y, Terashima S, et al. Neutron density distributions of 204,206,208Pb deduced via proton elastic scattering at = 295 MeV. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:044611. doi:10.1103/physrevc.82.044611
7. Zenihiro J, Uesaka T, Sagawa H, Yoshida S. Proton density polarization of the doubly magic 40Ca core in 48Ca and EoS parameters. Prog Theor Exp Phys (2021) 2021. 023D05. doi:10.1093/ptep/ptab001
8. Krasznahorkay A, Bacelar J, Bordewijk JA, Brandenburg S, Buda A, van ’t HG, et al. Excitation of the isovector giant dipole resonance by inelastic alpha scattering and the neutron skin of nuclei. Phys Rev Lett (1991) 66:1287–90. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.66.1287
9. Krasznahorkay A, Fujiwara M, van Aarle P, Akimune H, Daito I, Fujimura H, et al. Excitation of isovector spin-dipole resonances and neutron skin of nuclei. Phys Rev Lett (1999) 82:3216–9. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.82.3216
10. Tamii A, Poltoratska I, von Neumann-Cosel P, Fujita Y, Adachi T, Bertulani CA, et al. Complete electric dipole response and the neutron skin in 208Pb. Phys Rev Lett (2011) 107:062502. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.062502
11. Hashimoto T, Krumbholz AM, Reinhard PG, Tamii A, von Neumann-Cosel P, Adachi T, et al. Dipole polarizability of 120Sn and nuclear energy density functionals. Phys Rev C (2015) 92:031305. doi:10.1103/physrevc.92.031305
12. Birkhan J, Miorelli M, Bacca S, Bassauer S, Bertulani CA, Hagen G, et al. Electric dipole polarizability of 48Ca and implications for the neutron skin. Phys Rev Lett (2017) 118:252501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.118.252501
13. Fearick RW, von Neumann-Cosel P, Bacca S, Birkhan J, Bonaiti F, Brandherm I, et al. Electric dipole polarizability of 40Ca. Phys Rev Res (2023) 5:L022044. doi:10.1103/PhysRevResearch.5.L022044
14. Abrahamyan S, Ahmed Z, Albataineh H, Aniol K, Armstrong DS, Armstrong W, et al. Measurement of the neutron radius of 208Pb through parity violation in electron scattering. Phys Rev Lett (2012) 108:112502. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.112502
15. Adhikari D, Albataineh H, Androic D, Aniol K, Armstrong DS, Averett T, et al. Accurate determination of the neutron skin thickness of 208Pb through parity-violation in electron scattering. Phys Rev Lett (2021) 126:172502. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.172502
16. CREX Collaboration Adhikari D, Albataineh H, Androic D, Aniol KA, Armstrong DS, Averett T, et al. Precision determination of the neutral weak form factor of 48Ca. Phys Rev Lett (2022) 129:042501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.042501
17. Li BA, Han X. Constraining the neutron–proton effective mass splitting using empirical constraints on the density dependence of nuclear symmetry energy around normal density. Phys Lett B (2013) 727:276–81. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2013.10.006
18. Oertel M, Hempel M, Klähn T, Typel S. Equations of state for supernovae and compact stars. Rev Mod Phys (2017) 89:015007. doi:10.1103/revmodphys.89.015007
19. Tews I, Lattimer JM, Ohnishi A, Kolomeitsev EE. Symmetry parameter constraints from a lower bound on neutron-matter energy. Astrophys J (2017) 848:105. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa8db9
20. Oyamatsu K, Iida K. Saturation of nuclear matter and radii of unstable nuclei. Progr Theoret Phys (2003) 109:631–50. doi:10.1143/ptp.109.631
21. Chen LW, Ko CM, Li BA, Xu J. Density slope of the nuclear symmetry energy from the neutron skin thickness of heavy nuclei. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:024321. doi:10.1103/physrevc.82.024321
22. Iida K, Oyamatsu K. Symmetry energy, unstable nuclei and neutron star crusts. Eur Phys J (2014) 50:42. doi:10.1140/epja/i2014-14042-9
23. Horiuchi W, Ebata S, Iida K. Neutron-skin thickness determines the surface tension of a compressible nuclear droplet. Phys Rev C (2017) 96:035804. doi:10.1103/physrevc.96.035804
24. Rossi DM, Adrich P, Aksouh F, Alvarez-Pol H, Aumann T, Benlliure J, et al. Measurement of the dipole polarizability of the unstable neutron-rich nucleus 68Ni. Phys Rev Lett (2013) 111:242503. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.111.242503
25. Adrich P, Klimkiewicz A, Fallot M, Boretzky K, Aumann T, Cortina-Gil D, et al. Evidence for pygmy and giant dipole resonances in 130Sn and 132Sn. Phys Rev Lett (2005) 95:132501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.95.132501
26. Collaboration LAND, Klimkiewicz A, Paar N, Adrich P, Fallot M, Boretzky K, et al. Nuclear symmetry energy and neutron skins derived from pygmy dipole resonances. Phys Rev C (2007) 76:051603. doi:10.1103/physrevc.76.051603
27. Wieland O, Bracco A, Camera F, Benzoni G, Blasi N, Brambilla S, et al. Search for the pygmy dipole resonance in 68Ni at 600 MeV/nucleon. Phys Rev Lett (2009) 102:092502. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.102.092502
28. Angeli I, Marinova KP. Table of experimental nuclear ground state charge radii: an update. At. Data Nucl Data Tables (2013) 99:69–95. doi:10.1016/j.adt.2011.12.006
29. Li T, Luo Y, Wang N. Compilation of recent nuclear ground state charge radius measurements and tests for models. At. Data Nucl Data Tables (2021) 140:101440. doi:10.1016/j.adt.2021.101440
30. Nakamura T, Sakurai H, Watanabe H. Exotic nuclei explored at in-flight separators. Prog Part Nucl Phys (2017) 97:53–122. doi:10.1016/j.ppnp.2017.05.001
31. Kohama A, Iida K, Oyamatsu K. Difference between interaction cross sections and reaction cross sections. Phys Rev C (2008) 78:061601. doi:10.1103/physrevc.78.061601
32. Hatakeyama S, Horiuchi W. Complete Glauber calculations for proton–nucleus inelastic cross sections. Nucl Phys A (2019) 985:20–37. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2019.02.004
33. Takechi M, Suzuki S, Nishimura D, Fukuda M, Ohtsubo T, Nagashima M, et al. Evidence of halo structure in 37Mg observed via reaction cross sections and intruder orbitals beyond the island of inversion. Phys Rev C (2014) 90:061305. doi:10.1103/physrevc.90.061305
34. Kox S, Gamp A, Perrin C, Arvieux J, Bertholet R, Bruandet JF, et al. Trends of total reaction cross sections for heavy ion collisions in the intermediate energy range. Phys Rev C (1987) 35:1678–91. doi:10.1103/physrevc.35.1678
35. Mittig W, Chouvel JM, Long ZW, Bianchi L, Cunsolo A, Fernandez B, et al. Measurement of total reaction cross sections of exotic neutron-rich nuclei. Phys Rev Lett (1987) 59:1889–91. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.59.1889
36. Fukuda M, Mihara M, Fukao T, Fukuda S, Ishihara M, Ito S, et al. Density distribution of 8B studied via reaction cross sections. Nucl Phys A (1999) 656:209–28. doi:10.1016/s0375-9474(99)00308-5
37. Ozawa A, Baumann T, Chulkov L, Cortina D, Datta U, Fernandez J, et al. Measurements of the interaction cross sections for Ar and Cl isotopes. Nucl Phys A (2002) 709:60–72. doi:10.1016/s0375-9474(02)01071-0
38. Togano Y, Nakamura T, Kondo Y, Tostevin JA, Saito AT, Gibelin J, et al. Interaction cross section study of the two-neutron halo nucleus 22C. Phys Lett B (2016) 761:412–8. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2016.08.062
39. Kanungo R, Horiuchi W, Hagen G, Jansen GR, Navratil P, Ameil F, et al. Proton distribution radii of 12-19C illuminate features of neutron halos. Phys Rev Lett (2016) 117:102501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.117.102501
40. Bagchi S, Kanungo R, Horiuchi W, Hagen G, Morris TD, Stroberg SR, et al. Neutron skin and signature of the shell gap found from measured proton radii of 17-22N. Phys Lett B (2019) 790:251–6. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2019.01.024
41. Kaur S, Kanungo R, Horiuchi W, Hagen G, Holt JD, Hu BS, et al. Proton distribution radii of 16–24O: signatures of new shell closures and neutron skin. Phys Rev Lett (2022) 129:142502. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.129.142502
42. Tanihata I, Terashima S, Kanungo R, Ameil F, Atkinson J, Ayyad Y, et al. Observation of large enhancements of charge exchange cross sections with neutron-rich carbon isotopes. Prog Theor Exp Phys (2016) 2016:043D05. doi:10.1093/ptep/ptw034
43. Kohama A, Iida K, Oyamatsu K. Reaction cross section described by a black sphere approximation of nuclei. Phys Rev C (2005) 72:024602. doi:10.1103/physrevc.72.024602
44. Iida K, Kohama A, Oyamatsu K. Formula for proton–nucleus reaction cross section at intermediate energies and its application. J Phys Soc Jpn (2007) 76:044201. doi:10.1143/jpsj.76.044201
45. Sihver L, Kohama A, Iida K, Oyamatsu K, Hashimoto S, Iwase H, et al. Current status of the “hybrid kurotama model†for total reaction cross sections. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B (2014) 334:34–9. doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2014.04.021
46. Minomo K, Sumi T, Kimura M, Ogata K, Shimizu YR, Yahiro M. Deformation effect on total reaction cross sections for neutron-rich ne isotopes. Phys Rev C (2011) 84:034602. doi:10.1103/physrevc.84.034602
47. Minomo K, Sumi T, Kimura M, Ogata K, Shimizu YR, Yahiro M. Determination of the structure of 31Ne by a fully microscopic framework. Phys Rev Lett (2012) 108:052503. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.108.052503
48. Watanabe S, Minomo K, Shimada M, Tagami S, Kimura M, Takechi M, et al. Ground-state properties of neutron-rich Mg isotopes. Phys Rev C (2014) 89:044610. doi:10.1103/physrevc.89.044610
49. Bonaccorso A, Carstoiu F, Charity RJ. Imaginary part of the 9C–9Be single-folded optical potential. Phys Rev C (2016) 94:034604. doi:10.1103/physrevc.94.034604
50. Tagami S, Tanaka M, Takechi M, Fukuda M, Yahiro M. Chiral matrix folding-model approach to reaction cross sections for scattering of Ca isotopes on a C target. Phys Rev C (2020) 101:014620. doi:10.1103/physrevc.101.014620
51. Moumene I, Bonaccorso A. Localization of peripheral reactions and sensitivity to the imaginary potential. Nucl Phys (2021) 1006:122109. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2020.122109
52. Tagami S, Wakasa T, Matsui J, Yahiro M, Takechi M. Neutron skin thickness of 208Pb determined from the reaction cross section for proton scattering. Phys Rev C (2021) 104:024606. doi:10.1103/physrevc.104.024606
53. Matsuzaki M, Tagami S, Yahiro M. Neutron skin thickness of 208Pb, 116,120,124Sn, and 40Ca determined from reaction cross sections of 4He scattering. Phys Rev C (2021) 104:054613. doi:10.1103/physrevc.104.054613
54. Moumene I, Bonaccorso A. Optical potentials and nuclear reaction cross sections for n C and N C scattering. Phys Rev C (2023) 108:044609. doi:10.1103/physrevc.108.044609
55. Wakasa T, Tagami S, Matsui J, Takechi M, Yahiro M. Neutron-skin values and matter and neutron radii determined from reaction cross sections of proton scattering on 12C, 40,48Ca, 58Ni, and 208Pb. Phys Rev C (2023) 107:024608. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.107.024608
57. Ray L. Proton-nucleus total cross sections in the intermediate energy range. Phys Rev C (1979) 20:1857–72. doi:10.1103/physrevc.20.1857
58. Particle Data Group Tanabashi M, Hagiwara K, Hikasa K, Nakamura K, Sumino Y, Takahashi F, et al. Review of particle physics. Phys Rev D (2018) 98:030001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.98.030001
59. Varga K, Pieper SC, Suzuki Y, Wiringa RB. Monte Carlo integration in Glauber model analysis of reactions of halo nuclei. Phys Rev C (2002) 66:034611. doi:10.1103/physrevc.66.034611
60. Nagahisa T, Horiuchi W. Examination of the 22C radius determination with interaction cross sections. Phys Rev C (2018) 97:054614. doi:10.1103/physrevc.97.054614
61. Abu-Ibrahim B, Suzuki Y. Utility of nucleon-target profile function in cross section calculations. Phys Rev C (2000) 61:051601. doi:10.1103/physrevc.61.051601
62. Abu-Ibrahim B, Suzuki Y. Scatterings of complex nuclei in the Glauber model. Phys Rev C (2000) 62:034608. doi:10.1103/physrevc.62.034608
63. Horiuchi W, Suzuki Y, Abu-Ibrahim B, Kohama A. Systematic analysis of reaction cross sections of carbon isotopes. Phys Rev C (2007) 75:044607. doi:10.1103/physrevc.75.044607
64. Takechi M, Fukuda M, Mihara M, Tanaka K, Chinda T, Matsumasa T, et al. Reaction cross sections at intermediate energies and fermi-motion effect. Phys Rev C (2009) 79:061601. doi:10.1103/physrevc.79.061601
65. Tran DT, Ong HJ, Nguyen TT, Tanihata I, Aoi N, Ayyad Y, et al. Charge-changing cross-section measurements of 12-16C at around MeV and development of a Glauber model for incident energies MeV. Phys Rev C (2016) 94:064604. doi:10.1103/physrevc.94.064604
66. Abu-Ibrahim B, Horiuchi W, Kohama A, Suzuki Y. Reaction cross sections of carbon isotopes incident on a proton. Phys Rev C (2008) 77:034607. doi:10.1103/physrevc.77.034607
67. Abu-Ibrahim B, Horiuchi W, Kohama A, Suzuki Y. Erratum: reaction cross sections of carbon isotopes incident on a proton [Phys. Rev. C 77, 034607 (2008)]. Phys Rev C (2009) 80:029903. doi:10.1103/physrevc.80.029903
68. Abu-Ibrahim B, Horiuchi W, Kohama A, Suzuki Y. Publisher’s Note: reaction cross sections of carbon isotopes incident on a proton [Phys. Rev. C77, 034607 (2008)]. Phys Rev C (2010) 81:019901. doi:10.1103/physrevc.81.019901
69. Teixeira EA, Aumann T, Bertulani CA, Carlson BV. Nuclear fragmentation reactions as a probe of neutron skins in nuclei. The Eur Phys J A (2022) 58:205. doi:10.1140/epja/s10050-022-00849-w
70. Tanaka M, Takechi M, Homma A, Fukuda M, Nishimura D, Suzuki T, et al. Swelling of doubly magic 48Ca core in Ca isotopes beyond. Phys Rev Lett (2020) 124:102501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.124.102501
71. Horiuchi W, Inakura T. Core swelling in spherical nuclei: an indication of the saturation of nuclear density. Phys Rev C (2020) 101:061301. doi:10.1103/physrevc.101.061301
72. Ponnath L, Aumann T, Bertulani CA, Gernhäuser R, Heil M, Almusidi T, et al. Measurement of nuclear interaction cross sections towards neutron-skin thickness determination. Phys Lett B (2024) 855:138780. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2024.138780
73. Moriguchi T, Ishimoto S, Igarashi S, Ozawa A, Abe Y, Ishibashi Y, et al. Developments of a thick and large solid hydrogen target for radioisotope beams. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A (2010) 624:27–32. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.09.005
74. Moriguchi T, Amano M, Ozawa A, Horiuchi W, Abe Y, Fujii T, et al. Energy dependence of total reaction cross sections for 17Ne on a proton target. Nucl Phys A (2020) 994:121663. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2019.121663
75. Moriguchi T, Kagesawa R, Ozawa A, Horiuchi W, Abe Y, Amano M, et al. Investigation of total reaction cross sections for proton-dripline nuclei 17F and 17Ne on a proton target. Phys Rev C (2024) 110:014607. doi:10.1103/physrevc.110.014607
76. Tanihata I, Hamagaki H, Hashimoto O, Nagamiya S, Shida Y, Yoshikawa N, et al. Measurements of interaction cross sections and radii of He isotopes. Phys Lett B (1985) 160:380–4. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(85)90005-x
77. Tanihata I, Hamagaki H, Hashimoto O, Shida Y, Yoshikawa N, Sugimoto K, et al. Measurements of interaction cross sections and nuclear radii in the light p-shell region. Phys Rev Lett (1985) 55:2676–9. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.55.2676
78. Ozawa A, Suzuki T, Tanihata I. Nuclear size and related topics. Nucl Phys A (2001) 693:32–62. doi:10.1016/s0375-9474(01)01152-6
79. Tanaka K, Yamaguchi T, Suzuki T, Ohtsubo T, Fukuda M, Nishimura D, et al. Observation of a large reaction cross section in the drip-line nucleus 22C. Phys Rev Lett (2010) 104:062701. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.104.062701
80. Bagchi S, Kanungo R, Tanaka YK, Geissel H, Doornenbal P, Horiuchi W, et al. Two-neutron halo is unveiled in 29F. Phys Rev Lett (2020) 124:222504. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.124.222504
81. Horiuchi W, Suzuki Y. 22C: an s-wave two-neutron halo nucleus. Phys Rev C (2006) 74:034311. doi:10.1103/physrevc.74.034311
82. Singh J, Casal J, Horiuchi W, Fortunato L, Vitturi A. Exploring two-neutron halo formation in the ground state of 29F within a three-body model. Phys Rev C (2020) 101:024310. doi:10.1103/physrevc.101.024310
83. Fortunato L, Casal J, Horiuchi W, Singh J, Vitturi A. The 29F nucleus as a lighthouse on the coast of the island of inversion. Commun Phys (2020) 3:132–5. doi:10.1038/s42005-020-00402-5
84. Masui H, Horiuchi W, Kimura M. Two-neutron halo structure of 31F and a novel pairing antihalo effect. Phys Rev C (2020) 101:041303. doi:10.1103/physrevc.101.041303
85. Kanungo R, Prochazka A, Uchida M, Horiuchi W, Hagen G, Papenbrock T, et al. Exploring the anomaly in the interaction cross section and matter radius of 23O. Phys Rev C (2011) 84:061304. doi:10.1103/physrevc.84.061304
86. Homma A, Takechi M, Ohtsubo T, Nishimura D, Fukuda M, Suzuki T, et al. Measurements of interaction cross sections for 19-27F isotopes. JPS Conf Proc (2017) 14:021010. doi:10.7566/jpscp.14.021010
87. Takechi M, Ohtsubo T, Fukuda M, Nishimura D, Kuboki T, Suzuki T, et al. Interaction cross sections for Ne isotopes towards the island of inversion and halo structures of 29Ne and 31Ne. Phys Lett B (2012) 707:357–61. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2011.12.028
88. Suzuki S, Takechi M, Ohtsubo T, Nishimura D, Fukuda M, Kuboki T, et al. Measurements of interaction cross sections for 22-35Na isotopes. EPJ Web of Conferences (2014) 66:03084. doi:10.1051/epjconf/20146603084
89. Suzuki T, Geissel H, Bochkarev O, Chulkov L, Golovkov M, Fukunishi N, et al. Nuclear radii of Na and Mg isotopes. Nucl Phys A (1998) 630:661–77. doi:10.1016/s0375-9474(98)00799-4
90. Kanungo R, Prochazka A, Horiuchi W, Nociforo C, Aumann T, Boutin D, et al. Matter radii of 32-35Mg. Phys Rev C (2011) 83:021302. doi:10.1103/physrevc.83.021302
91. Nakamura T, Kobayashi N, Kondo Y, Satou Y, Aoi N, Baba H, et al. Halo structure of the island of inversion nucleus 31Ne. Phys Rev Lett (2009) 103:262501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.103.262501
92. Kobayashi N, Nakamura T, Kondo Y, Tostevin JA, Utsuno Y, Aoi N, et al. Observation of a p-wave one-neutron halo configuration in 37Mg. Phys Rev Lett (2014) 112:242501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.112.242501
93. Horiuchi W, Suzuki Y, Capel P, Baye D. Probing the weakly-bound neutron orbit of 31Ne with total reaction and one-neutron removal cross sections. Phys Rev C (2010) 81:024606. doi:10.1103/physrevc.81.024606
94. Horiuchi W, Inakura T, Nakatsukasa T, Suzuki Y. Glauber-model analysis of total reaction cross sections for Ne, Mg, Si, and S isotopes with Skyrme-Hartree-Fock densities. Phys Rev C (2012) 86:024614. doi:10.1103/physrevc.86.024614
95. Takatsu R, Suzuki Y, Horiuchi W, Kimura M. Microscopic study of the deformed neutron halo of 31Ne. Phys Rev C (2023) 107:024314. doi:10.1103/physrevc.107.024314
96. Zhang HY, Shen WQ, Ren ZZ, Ma YG, Jiang WZ, Zhu ZY, et al. Measurement of reaction cross section for proton-rich nuclei at intermediate energies. Nucl Phys A (2002) 707:303–24. doi:10.1016/S0375-9474(02)01007-2
97. Zheng T, Yamaguchi T, Ozawa A, Chiba M, Kanungo R, Kato T, et al. Study of halo structure of 16C from reaction cross section measurement. Nucl Phys A (2002) 709:103–18. doi:10.1016/S0375-9474(02)01043-6
98. Fang DQ, Yamaguchi T, Zheng T, Ozawa A, Chiba M, Kanungo R, et al. One-neutron halo structure in 15C. Phys Rev C (2004) 69:034613. doi:10.1103/physrevc.69.034613
99. Yamaguchi Y, Wu C, Suzuki T, Ozawa A, Fang DQ, Fukuda M, et al. Density distribution of 17B from a reaction cross-section measurement. Phys Rev C (2004) 70:054320. doi:10.1103/physrevc.70.054320
100. Ozawa A, Cai YZ, Chen ZQ, Chiba M, Fang DQ, Guo ZG, et al. Measurements of the interaction cross-sections for 14Be and 14,15B as projectiles with a new scheme at RIBLL. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B (2006) 247:155–60. doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2006.01.054
101. Tanaka K, Fukuda M, Mihara M, Takechi M, Nishimura D, Chinda T, et al. Density distribution of 17Ne and possible shell-structure change in the proton-rich sd-shell nuclei. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:044309. doi:10.1103/physrevc.82.044309
102. Yamaguchi T, Tanaka K, Suzuki T, Ozawa A, Ohtsubo T, Aiba T, et al. Nuclear reactions of 19,20C on a liquid hydrogen target measured with the superconducting TOF spectrometer. Nucl Phys A (2011) 864:1–37. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2011.05.095
103. Moriguchi T, Ozawa A, Ishimoto S, Abe Y, Fukuda M, Hachiuma I, et al. Density distributions of 11Li deduced from reaction cross-section measurements. Phys Rev C (2013) 88:024610. doi:10.1103/physrevc.88.024610
104. Moriguchi T, Ozawa A, Ishimoto S, Abe Y, Fukuda M, Hachiuma I, et al. Density distribution of 14Be from reaction cross-section measurements. Nucl Phys A (2014) 929:83–93. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2014.06.003
105. Fan GW, Fukuda M, Nishimura D, Cai XL, Fukuda S, Hachiuma I, et al. Structure of 8Li from a reaction cross-section measurement. Phys Rev C (2014) 90:044321. doi:10.1103/physrevc.90.044321
106. Fukuda M, Morita Y, Nishimura D, Takechi M, Iwamoto K, Wakabayashi M, et al. Nucleon density distribution of the proton drip-line nucleus 12N studied via reaction cross sections. JPS Conf Proc (2015) 6:030103. doi:10.7566/jpscp.6.030103
107. Tanaka M, Fukuda M, Nishimura D, Suzuki S, Takechi M, Mihara M, et al. Reaction cross sections for 8He and 14B on proton target for the separation of proton and neutron density distributions. JPS Conf Proc (2015) 6:020026. doi:10.7566/JPSCP.6.020026
108. Nishizuka K, Takechi M, Ohtsubo T, Nishimura D, Fukuda M, Aoki K, et al. Measurements of reaction cross sections for 9-11C. JPS Conf Proc (2017) 14:021015. doi:10.7566/JPSCP.14.021015
109. Tanaka M, Fukuda M, Nishimura D, Takechi M, Suzuki S, Du H, et al. Reaction cross sections for 13-15B and one-neutron halo in 14B. Acta Phys Pol B (2017) 48:461. doi:10.5506/aphyspolb.48.461
110. Fukuda M, Ichihara T, Inabe N, Kubo T, Kumagai H, Nakagawa T, et al. Neutron halo in 11Be studied via reaction cross sections. Phys Lett B (1991) 268:339–44. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(91)91587-l
111. Tanihata I, Kobayashi T, Suzuki T, Yoshida K, Shimoura S, Sugimoto K, et al. Determination of the density distribution and the correlation of halo neutrons in 11Li. Phys Lett B (1992) 287:307–11. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(92)90988-g
112. Negoita F, Borcea C, Carstoiu F, Lewitowicz M, Saint-Laurent MG, Anne R, et al. 8B proton halo via reaction and breakup cross section measurements. Phys Rev C (1996) 54:1787–97. doi:10.1103/physrevc.54.1787
113. Takechi M, Fukuda M, Mihara M, Chinda T, Matsumasa T, Matsubara H, et al. Reaction cross-sections for stable nuclei and nucleon density distribution of proton drip-line nucleus 8B. Eur Phys J (2005) 25:217–9. doi:10.1140/epjad/i2005-06-078-0
114. Horiuchi W, Inakura T, Michimasa S. Large enhancement of total reaction cross sections at the edge of the island of inversion in ti, cr, and fe isotopes. Phys Rev C (2022) 105:014316. doi:10.1103/physrevc.105.014316
115. Horiuchi W, Suzuki Y, Shalchi MA, Tomio L. Possible halo structure of 62,72Ca by forbidden-state-free locally peaked Gaussians. Phys Rev C (2022) 105:024310. doi:10.1103/physrevc.105.024310
116. Horiuchi W, Inakura T. Pairing core swelling effect in Pb isotopes at. Phys Rev C (2022) 105:044303. doi:10.1103/physrevc.105.044303
117. Yamaguchi T, Suzuki T, Ohnishi T, Becker F, Fukuda M, Geissel H, et al. Nuclear matter radii of neutron-deficient Kr isotopes. Phys Rev C (2008) 77:034315. doi:10.1103/physrevc.77.034315
118. Tanihata I, Hirata D, Kobayashi T, Shimoura S, Sugimoto K, Toki H. Revelation of thick neutron skins in nuclei. Phys Lett B (1992) 289:261–6. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(92)91216-v
119. Suzuki T, Geissel H, Bochkarev O, Chulkov L, Golovkov M, Hirata D, et al. Neutron skin of Na isotopes studied via their interaction cross sections. Phys Rev Lett (1995) 75:3241–4. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.75.3241
120. Huber G, Touchard F, Büttgenbach S, Thibault C, Klapisch R, Duong HT, et al. Spins, magnetic moments, and isotope shifts of 21-31Na by high resolution laser spectroscopy of the atomic line. Phys Rev C (1978) 18:2342–54. doi:10.1103/physrevc.18.2342
121. Garcia Ruiz RF, Bissell ML, Blaum K, Ekström A, Frömmgen N, Hagen G, et al. Unexpectedly large charge radii of neutron-rich calcium isotopes. Nat Phys (2016) 12:594–8. doi:10.1038/nphys3645
122. Minamisono K, Rossi DM, Beerwerth R, Fritzsche S, Garand D, Klose A, et al. Charge radii of neutron deficient 52,53Fe produced by projectile fragmentation. Phys Rev Lett (2016) 117:252501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.117.252501
123. Iida K, Oyamatsu K. Surface tension in a compressible liquid-drop model: effects on nuclear density and neutron skin thickness. Phys Rev C (2004) 69:037301. doi:10.1103/physrevc.69.037301
124. Warda M, Vinas X, Roca-Maza X, Centelles M. Neutron skin thickness in the droplet model with surface width dependence: indications of softness of the nuclear symmetry energy. Phys Rev C (2009) 80:024316. doi:10.1103/physrevc.80.024316
125. Warda M, Centelles M, Vinas X, Roca-Maza X. Influence of the single-particle structure on the nuclear surface and the neutron skin. Phys Rev C (2014) 89:064302. doi:10.1103/physrevc.89.064302
126. Horiuchi W, Suzuki Y, Inakura T. Probing neutron-skin thickness with total reaction cross sections. Phys Rev C (2014) 89:011601. doi:10.1103/physrevc.89.011601
127. Fang DQ, Ma YG, Cai XZ, Tian WD, Wang HW. Effects of neutron skin thickness in peripheral nuclear reactions. Chin Phys. Lett. (2011) 28:102102. doi:10.1088/0256-307x/28/10/102102
128. Fang DQ, Ma YG, Cai XZ, Tian WD, Wang HW. Neutron removal cross section as a measure of neutron skin. Phys Rev C (2010) 81:047603. doi:10.1103/physrevc.81.047603
129. Ma CW, Wei HL, Yu M. Reexamination of the neutron skin thickness using neutron removal cross sections. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:057602. doi:10.1103/physrevc.82.057602
130. Aumann T, Bertulani CA, Schindler F, Typel S. Peeling off neutron skins from neutron-rich nuclei: constraints on the symmetry energy from neutron-removal cross sections. Phys Rev Lett (2017) 119:262501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.119.262501
131. Bertulani CA, Valencia J. Neutron skins as laboratory constraints on properties of neutron stars and on what we can learn from heavy ion fragmentation reactions. Phys Rev C (2019) 100:015802. doi:10.1103/physrevc.100.015802
132. Horiuchi W, Hatakeyama S, Ebata S, Suzuki Y. Extracting nuclear sizes of medium to heavy nuclei from total reaction cross sections. Phys Rev C (2016) 93:044611. doi:10.1103/physrevc.93.044611
133. Horiuchi W, Suzuki Y, Uesaka T, Miwa M. Total reaction cross section on a deuteron target and the eclipse effect of the constituent neutron and proton. Phys Rev C (2020) 102:054601. doi:10.1103/physrevc.102.054601
134. Nishimura D, Fukuda M, Takechi M, Mihara M, Ishikawa D, Komurasaki J, et al. Distinction between proton-neutron density distribution of halo nuclei at the nuclear surface via reaction cross sections. Nucl Phys A (2010) 834:470c–2c. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2010.01.067
135. Yamaguchi T, Fukuda M, Fukuda S, Fan GW, Hachiuma I, Kanazawa M, et al. Energy-dependent charge-changing cross sections and proton distribution of si 28. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:014609. doi:10.1103/physrevc.82.014609
136. Yamaguchi T, Hachiuma I, Kitagawa A, Namihira K, Sato S, Suzuki T, et al. Scaling of charge-changing interaction cross sections and point-proton radii of neutron-rich carbon isotopes. Phys Rev Lett (2011) 107:032502. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.107.032502
137. Yamaki S, Yamaguchi T, Kouno J, Sato K, Ichihashi N, Suzuki T, et al. Systematic study of individual charge-changing cross sections of intermediate-energy secondary beams. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B (2013) 317:774–8. doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2013.05.057
138. Yamaki S, Kouno J, Nishimura D, Nagashima M, Takechi M, Sato K, et al. Charge-changing interactions probing point-proton radii of nuclei. EPJ Web of Conferences (2014) 66:03099. doi:10.1051/epjconf/20146603099
139. Ozawa A, Moriguchi T, Ohtsubo T, Aoi N, Fang DQ, Fukuda N, et al. Charge-changing cross sections of 30Ne, 32,33Na with a proton target. Phys Rev C (2014) 89:044602. doi:10.1103/physrevc.89.044602
140. Terashima S, Tanihata I, Kanungo R, Estrade A, Horiuchi W, Ameil F, et al. Proton radius of 14Be from measurement of charge-changing cross sections. Prog Theor Exp Phys (2014) 2014:101D02. doi:10.1093/ptep/ptu134
141. Estradé A, Kanungo R, Horiuchi W, Ameil F, Atkinson J, Ayyad Y, et al. Proton radii of 12–17B define a thick neutron surface in 17B. Phys Rev Lett (2014) 113:132501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.113.132501
142. Sawahata K, Ozawa A, Saito Y, Abe Y, Ichikawa Y, Inaba N, et al. Investigations of charge-changing processes for light proton-rich nuclei on carbon and solid-hydrogen targets. Nucl Phys A (2017) 961:142–53. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2017.02.012
143. Tran DT, Ong HJ, Hagen G, Morris TD, Aoi N, Suzuki T, et al. Evidence for prevalent Z = 6 magic number in neutron-rich carbon isotopes. Nat Commun (2018) 9:1594. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04024-y
144. Tanaka M, Takechi M, Homma A, Prochazka A, Fukuda M, Nishimura D, et al. Charge-changing cross sections for 42–51Ca and effect of charged-particle evaporation induced by neutron-removal reactions. Phys Rev C (2022) 106:014617. doi:10.1103/physrevc.106.014617
145. Wang CJ, Guo G, Ong HJ, Song YN, Sun BH, Tanihata I, et al. Charge-changing cross section measurements of 300 MeV/nucleon 28Si on carbon and data analysis. Chin Phys C (2023) 47:084001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/acd366
146. Zhao JW, Sun BH, Tanihata I, Terashima S, Prochazka A, Xu JY, et al. Isospin-dependence of the charge-changing cross-section shaped by the charged-particle evaporation process. Phys Lett B (2023) 847:138269. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2023.138269
147. Zhao JW, Sun BH, Tanihata I, Xu JY, Zhang KY, Prochazka A, et al. Charge radii of 11–16C, 13–17N and 15–18O determined from their charge-changing cross-sections and the mirror-difference charge radii. Phys Lett B (2024) 858:139082. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2024.139082
148. Bhagwat A, Gambhir YK. Microscopic investigations of mass and charge changing cross sections. Phys Rev C (2004) 69:014315. doi:10.1103/physrevc.69.014315
149. Akaishi T, Hagino K. Analysis of charge changing cross sections with the Glauber-Abrasion-Ablation model. JPS Conf Proc (2015) 6:030097. doi:10.7566/JPSCP.6.030097
150. Fan GW, Zhan X. Influence of neutrons on charge-changing cross-sections. Int J Mod Phys E (2019) 28:1950070. doi:10.1142/s0218301319500708
151. Abdul-Magead IAM, Abu-Ibrahim B. Contribution of the projectile neutrons to the total charge-changing cross sections. Nucl Phys (2020) 1000:121804. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2020.121804
152. Gaimard JJ, Schmidt KH. A reexamination of the abrasion-ablation model for the description of the nuclear fragmentation reaction. Nucl Phys A (1991) 531:709–45. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(91)90748-u
153. Scheidenberger C, Pshenichnov IA, Sümmere K, Ventura A, Bondorf JP, Botvina AS, et al. Charge-changing interactions of ultrarelativistic Pb nuclei. Phys Rev C (2004) 70:014902. doi:10.1103/physrevc.70.014902
154. Suzuki Y, Horiuchi W, Terashima S, Kanungo R, Ameil F, Atkinson J, et al. Parameter-free calculation of charge-changing cross sections at high energy. Phys Rev C (2016) 94:011602. doi:10.1103/physrevc.94.011602
155. Wang N, Li T. Shell and isospin effects in nuclear charge radii. Phys Rev C (2013) 88:011301. doi:10.1103/physrevc.88.011301
156. Brown BA. Mirror charge radii and the neutron equation of state. Phys Rev Lett (2017) 119:122502. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.119.122502
157. Yang J, Piekarewicz J. Difference in proton radii of mirror nuclei as a possible surrogate for the neutron skin. Phys Rev C (2018) 97:014314. doi:10.1103/physrevc.97.014314
158. Gaidarov MK, Moumene I, Antonov AN, Kadrev DN, Sarriguren P, Moya de Guerra E. Proton and neutron skins and symmetry energy of mirror nuclei. Nucl Phys A (2020) 1004:122061. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2020.122061
159. Brown BA, Minamisono K, Piekarewicz J, Hergert H, Garand D, Klose A, et al. Implications of the 36Ca–36S and 38Ca–38Ar difference in mirror charge radii on the neutron matter equation of state. Phys Rev Res (2020) 2:022035. doi:10.1103/physrevresearch.2.022035
160. Pineda SV, König K, Rossi DM, Brown BA, Incorvati A, Lantis J, et al. Charge radius of neutron-deficient 54Ni and symmetry energy constraints using the difference in mirror pair charge radii. Phys Rev Lett (2021) 127:182503. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.182503
Keywords: total reaction cross sections, interaction cross sections, charge-changing cross sections, root-mean-square radii, neutron skin thickness, unstable nuclei
Citation: Tanaka M, Horiuchi W and Fukuda M (2024) Unveiling radii and neutron skins of unstable atomic nuclei via nuclear collisions. Front. Phys. 12:1488428. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1488428
Received: 30 August 2024; Accepted: 13 November 2024;
Published: 10 December 2024.
Edited by:
Masayuki Matsuzaki, Fukuoka University of Education, JapanReviewed by:
Nobuo Hinohara, University of Tsukuba, JapanCopyright © 2024 Tanaka, Horiuchi and Fukuda. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Masaomi Tanaka, bXRhbmFrYUBhcnRzY2kua3l1c2h1LXUuYWMuanA=
 Masaomi Tanaka
Masaomi Tanaka Wataru Horiuchi
Wataru Horiuchi Mitsunori Fukuda
Mitsunori Fukuda