- 1Northeast Asia Research Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
- 2Liangzhu Laboratory, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Panax ginseng (P. ginseng), a traditional and highly valued botanical drug, has been used for thousands of years and is known around the world for its uses in food, medicine, and healthcare. The comprehensive study of P. ginseng is crucial for the quality assurance of medicinal materials and optimal resource utilization. Despite being present in trace amounts, P. ginseng volatile oil has a wide range of chemical metabolites with important medicinal potential. The volatile oil has shown promise in defending the cardiovascular system, as well as in terms of its ability of antibacterial, anti-aging, anti-platelet coagulation, anti-inflammatory, support the nervous system nutritionally, and shield it from harm. Due to its low composition and lack of thorough investigation, P. ginseng volatile oil’s therapeutic applicability is still restricted although it exhibited many benefits. This review aims to provide insights into the chemical composition, extraction processes, pharmacological effects, and mechanisms of action of P. ginseng volatile oil, and to provide theoretical support and guidelines for future research and clinical application.
1 Introduction
Panax ginseng C.A.Mey. [Araliaceae, Ginseng radix et rhizoma], as a traditional botanical drug with a long history, has occupied a pivotal position in Chinese traditional medicine since ancient times. P. ginseng has a slightly bitter and warm taste, serving as a great tonic that can boost energy, restore the pulse, nourish the spleen and lungs, replenish blood, calm nerves, and improve intelligence (National Pharmacopoeia Commission, 2020). With the development of modern science and technology, more medicinal values of P. ginseng have been gradually explored by researchers around the world, and its application fields have been expanded from food and health products to the medical field (Mancuso and Santangelo, 2017). More than 300 active metabolites, including polysaccharides, ginseng peptides, ginsenosides, flavonoids (Liu et al., 2020), volatile oils, organic acids, alkaloids, trace elements, and vitamins, have been identified (Su et al., 2023). The medicinal value of P. ginseng is not only reflected in its polysaccharides, ginsenosides and other metabolites, volatile oil as one of the metabolites. Although it only accounts for about 0.02%–2.5% (Peng et al., 2017; Sun et al., 1993), its biological activity cannot be ignored. P. ginseng volatile oil (GVO) has shown significant efficacy in cardiovascular protection, antimicrobial, anti-aging, anti-platelet aggregation, anti-inflammatory, nutritional support, and neurocellular protection. The diversity of its chemical metabolites and the potential of its pharmacological activities provide a wide scope for future developmental studies.
In recent years, relatively little research has been conducted on the volatile oil of ginseng, and limited data are available for reference. This has prompted us to conduct a more comprehensive and in-depth exploration of it. In this paper, we will analyze the chemical composition of GVO, discuss the volatile oil metabolites extracted from different parts of P. ginseng and their pharmacological effects, and also investigate the effects of different regions and years of growth on the volatile oil content of P. ginseng. The summary was further refined with the help of the newidea.ai (https://www.newidea.ai/home). In terms of the extraction process, this paper will compare the advantages and disadvantages of traditional and modern methods and explore their effects on the composition and medicinal effects of volatile oils. In terms of pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action, this paper will detail the effects of GVO on the cardiovascular system, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anticancer, etc., and explore its potential molecular targets and mechanisms of action (Figure 1). In summary, this paper will provide a comprehensive theoretical basis for the research and application of GVO and point out the direction for future development and utilization. Through in-depth exploration of the chemical composition, pharmacological activity and mechanism of action of GVO, we expect to be able to provide scientific support for the in-depth development and clinical application of P. ginseng resources.
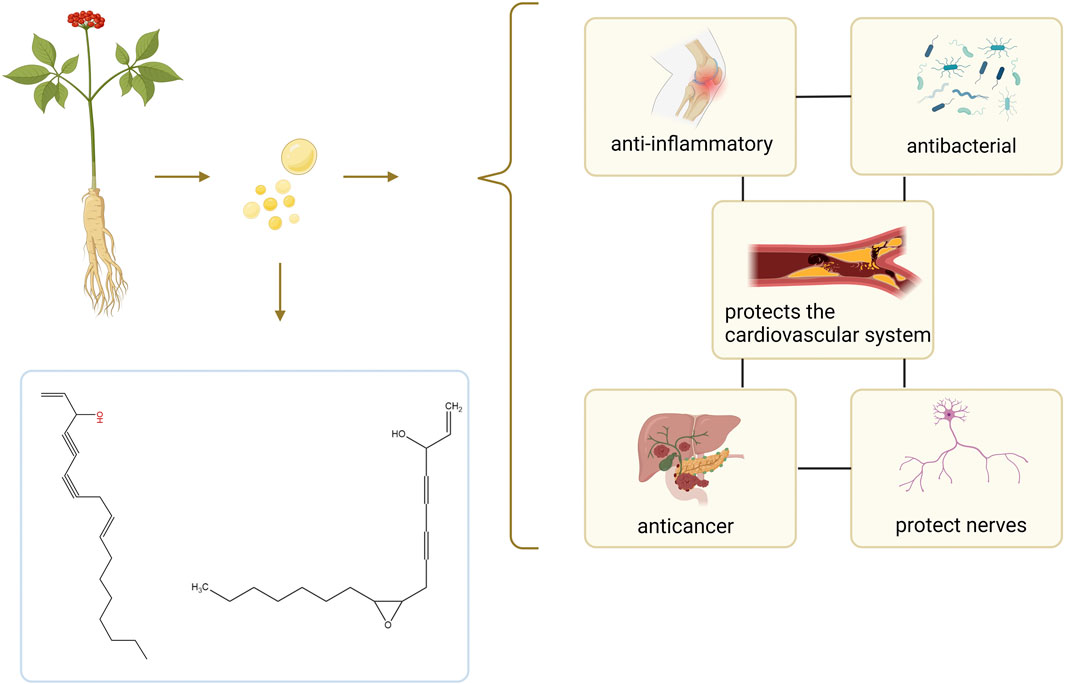
Figure 1. Summary of the composition and effect of GVO. GVO has a special aroma, and its main metabolites are Linoleic acid, panaxynol, panaxydol and so on. It has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-aging, anti-cancer, neuroprotective, and fatigue-relieving properties.
2 The phytochemical composition of GVO
GVO possesses a distinct aroma. The P. ginseng aroma developed through organic culture method (OCM) and GAP method exhibited the highest levels of beet saponin and aromatic alkene, which are recognized as key metabolites of the P. ginseng aroma (Lee et al., 2012). In research, GC-MS is commonly utilized to assess the composition and quality of volatile oils (Daferera et al., 2000). Through this method, modern scholars have identified 369 metabolites in GVO, comprising 154 hydrocarbons, 35 ketones, two aldehydes, 55 esters, 37 alcohols, 12 acids, 22 nitrogen-containing metabolites, and 52 other metabolites (Qiu et al., 2008), as shown in Figure 2; Table 1. Among the volatile metabolites of P. ginseng, closely related to the aroma properties of the plant are sesquiterpenoids, accounting for about 40% of the volatile oil, followed by panaxynol and panaxydol (Cho et al., 2012). Currently, over 20 types of polyacetylene derivatives have been isolated from P. ginseng (Yeo et al., 2017), including panaxynol, panaxydol, panaxydiol, panaxytriol, panaxacol, panaxyne epoxide, ginsenoyne A− K. Recently, new polyacetylenes metabolites with carbonyl group replacing the hydroxyl group had been isolated such as 9,10-epoxyheptadecan-4,6-diyn-3-one, one-ethoxy-9,10-epoxyheptadecan-4,6-diyn-3-one and 9,10-epoxy-16-heptadecan-4,6-diyn-3-one.
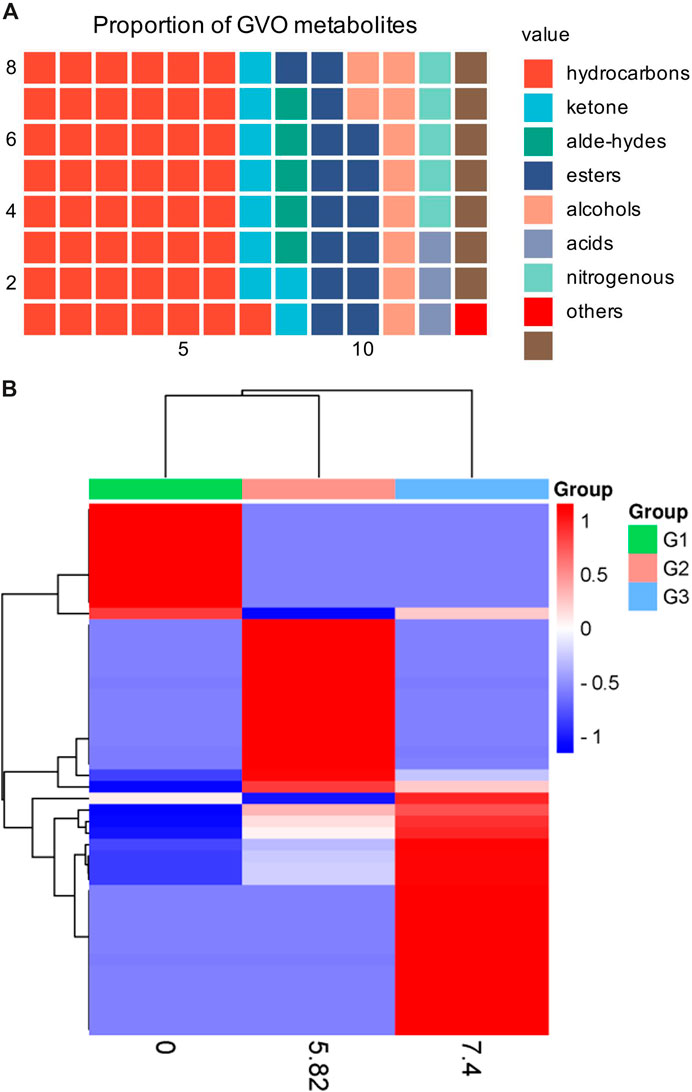
Figure 2. The main metabolites of GVO and its differences under diverse processing conditions. (A) Proportion of different types of metabolites of GVO. (B) Heat map of chemical composition differences among fresh ginseng G1, white ginseng G2, and red ginseng G3.
2.1 A chemical analysis of the volatile oils extracted from different parts of the P. ginseng plant
2.1.1 Volatile oil metabolites in flower buds
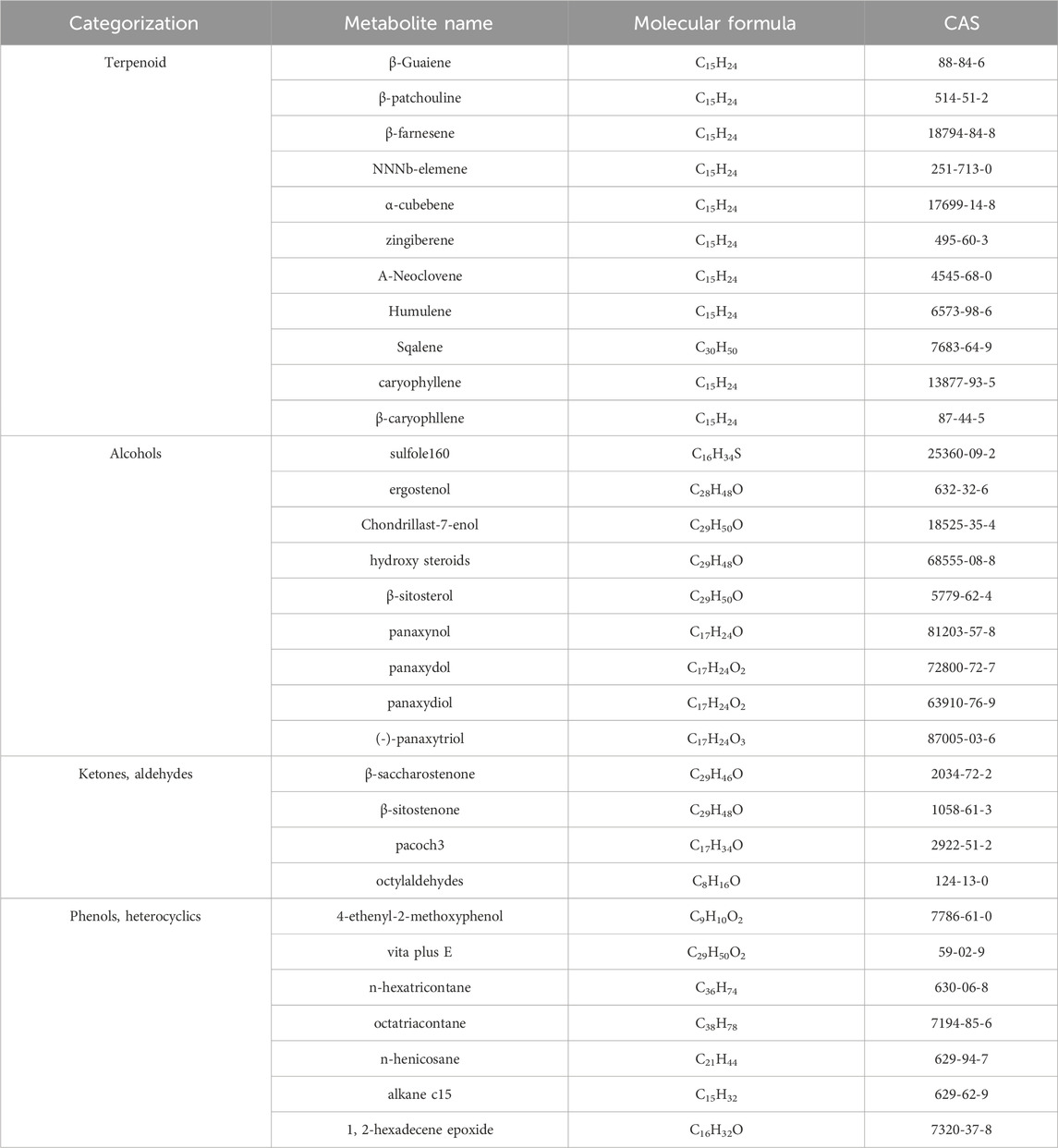
The volatile oil content of P. ginseng varies across different parts of the plant. Although P. ginseng flowers (GFs) buds are not recorded in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 edition), GFs are also non-traditional medicinal parts with anti-fatigue and immune-enhancing properties. Studies have shown that the composition of volatile oils in P. ginseng flowers generally remains consistent over time (Mao et al., 1989). The volatile oil extracted from it is a light yellow transparent oily liquid with a yield of about 0.2%. After identification, 23 chemical metabolites were identified from 51 chromatographic peaks, including 10 sesquiterpenes, eight alkanes, 2 esters, and one ketone, accounting for 43.5%, 34.8%, 8.7%, 8.796, and 4.3% of the total volatile oils, respectively (Figure 3). Among the sesquiterpenes, α-solaninene (Figure 3A), α-sandalpinene, β-sandalene and (3Z,6E)-α-farnesene were discovered for the first time.
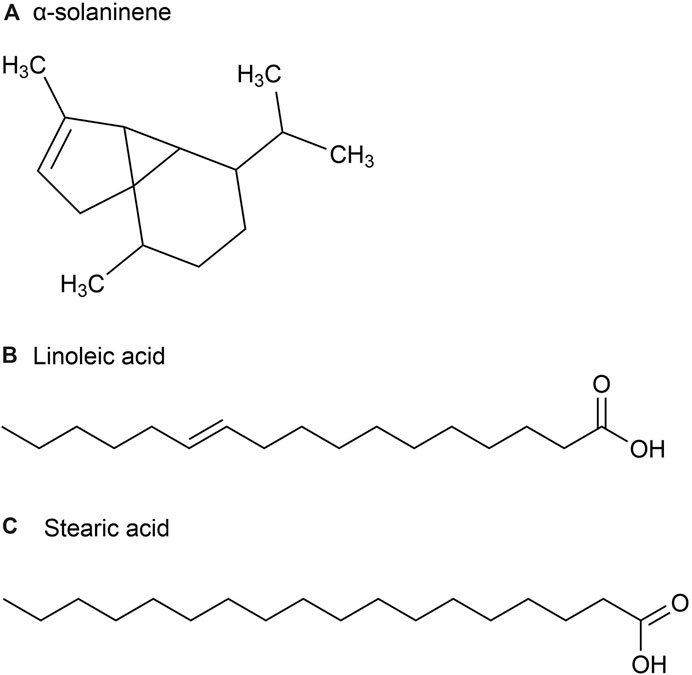
Figure 3. The main metabolites of GVO in flower buds. (A) α-solaninene. (B) Linoleic acid. (C) Stearic acid.
Furthermore, some scholars have used GC-MS analysis to identify 45 chemical metabolites in the volatile oil of P. ginseng flowers (Ma et al., 1992). Among them, the highest content is Linoleic acid (37.06%) (Figure 3B), followed by Stearic acid (17.77%) (Figure 3C). Other main metabolites include aldehydes, enals, unsaturated alcohols, higher alkanes, alkynes, etc. Distribution density and accumulation of oil cells affect volatile oil content. Therefore, P. ginseng flowers may contain volatile oils that are closely related to oil cell growth and development (McAdam et al., 2020). As P. ginseng blooms after 3 years, its early accumulation of substances is deeper, providing more energy and nutrients to oil cells. Consequently, the volatile oil content is the highest in three-year-old P. ginseng flowers (Du et al., 2023).
2.1.2 Volatile oil metabolites in stems and leaves
Traditionally, P. ginseng leaves have been utilized in China as a medicine for treating diseases. In comparison to P. ginseng roots, its leaves have a shorter growth period and lower cost, making them both economically and medicinally valuable. However, little attention has been given to the chemical composition of the volatile oil in P. ginseng leaves. In a study, P. ginseng leaves and stems were extracted, yielding a black-green crystalline volatile oil of 0.14% (Liu et al., 2002).
A total of 54 metabolites were identified, predominantly consisting of aliphatic (69.0%), terpenoids (21.5%) and aromatic (2.4%). The major metabolites identified in these parts include Palmitic acid (36.1%) (Figure 4A), followed by (E)-β-farnesene (15.4%), Linoleic acid (9.8%) (Figure 4B), phytol (5.6%) (Figure 4C) and methyl hexadecoate (2.9%) (Figure 4D). Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons accounted for 20.3%, while oxidized sesquiterpene hydrocarbons accounted for 0.6%, and monoterpene hydrocarbons accounted for 0.6% of terpenoids (Jiang et al., 2014).
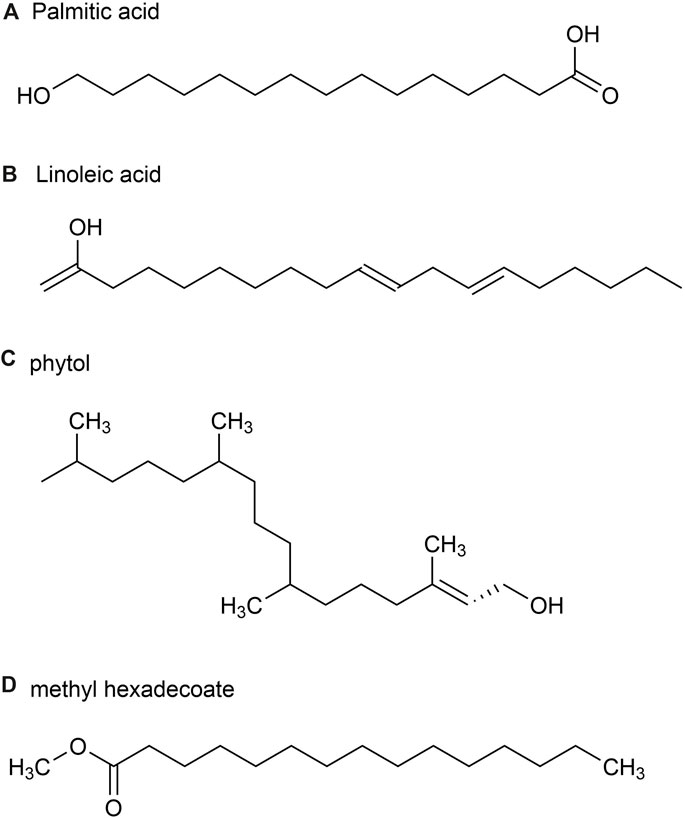
Figure 4. The main metabolites of GVO in stems and leaves. (A) palmitic acid. (B) Linoleic acid. (C) phytol. (D) methyl hexadecoate.
2.1.3 Volatile oil metabolites in fruits
P. ginseng fruit is the dried ripe fruit of P. ginseng. Its chemical metabolites include ginsenoside, volatile oil, carbohydrate and sugar, amino acid and allaloids, vitamins and minerals. A total of 23 volatile metabolites, mainly composed of sesquiterpenes, have been identified from P. ginseng fruits of three different colors, red fruit, yellow fruit, and orange fruit, such as (E)-β-farnesene (Figure 5A), β-Elemene (Figure 5B), Santene, Cedarene (Figure 5C), and α-neoclovene (Figure 5D). The total sesquiterpene content of red fruits is the highest, followed by orange and yellow fruits, with significant differences between samples. Yellow fruits contain a significant amount of δ-selinene (Figure 5E), β-caryophyllene, α-farnesene ginsenosol and cadinol (Figure 5F). As a consequence, P. ginseng fruit has different volatile (Cui et al., 2020).
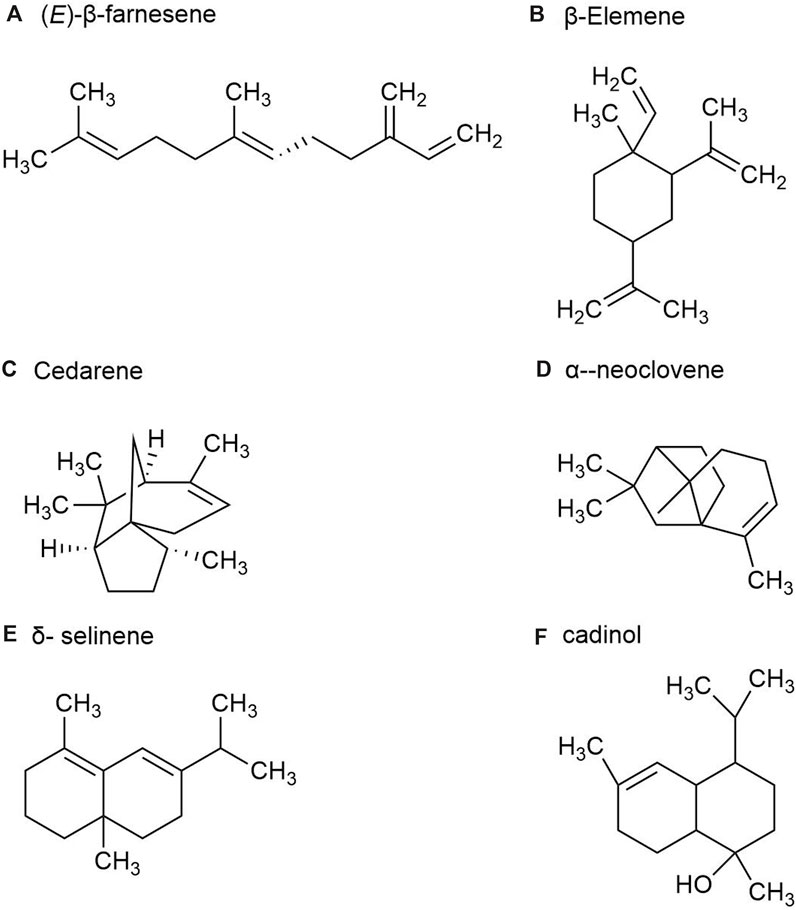
Figure 5. The main metabolites of GVO in fruits. (A) (E)-β-farnesene. (B) β-Elemene. (C) Cedarene. (D) α-neoclovene. (E) δ-selinene. (F) cadinol.
2.1.4 Volatile oil metabolites in rhizomes
There are more than 40 kinds of chemical metabolites in the volatile oil of P. ginseng root, mainly including esters, monoterpenes, alkanes, and sesquiterpenes. As part of the sesquiterpene family, sesquiterpenoids are characteristic metabolites of GVO. Such as β-Ginsenene, (−)-α- Gurjunene (Figure 6A), β-Elemene, β-Caryophyllene (Figure 6B), β-New clove tricycline (molecular formula C15H24) and sesquiterpene oxygen-containing metabolites (mainly referring to alcohols such as spartanol, ginsenosol, and -(−)globulol (Figure 6C)) α-Juniperol, etc., with a molecular formula of C15H24O) (Richter et al., 2005; Ding, 2008). It was found that the content of total volatile oil in roots increased with the growth age of P. ginseng. A study was conducted by steam distillation to extract the volatile oil content in P. ginseng reeds, and the yield was 0.35%. The main differences with P. ginseng root were palmitic acid, 2,6-ditert-butyl-4-methylphenol (Figure 6D) and methyl octadenoate, with the contents of 2.08%, 1.80% and 1.44%, respectively (Zheng et al., 1989).
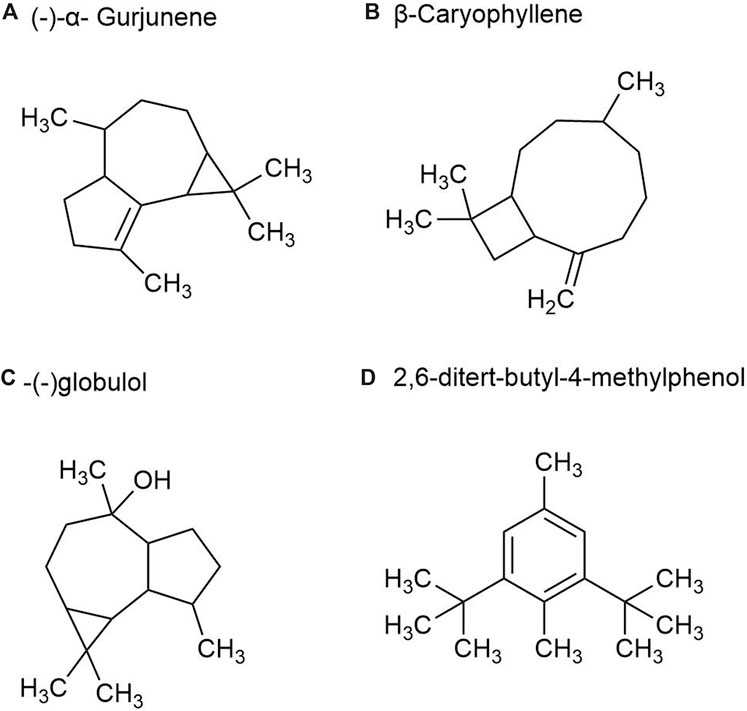
Figure 6. The main metabolites of GVO in rhizomes. (A) (-)-α- Gurjunene. (B) β-Caryophyllene. (C) -(-)globulol. (D) 2,6-ditert-butyl-4-methylphenol.
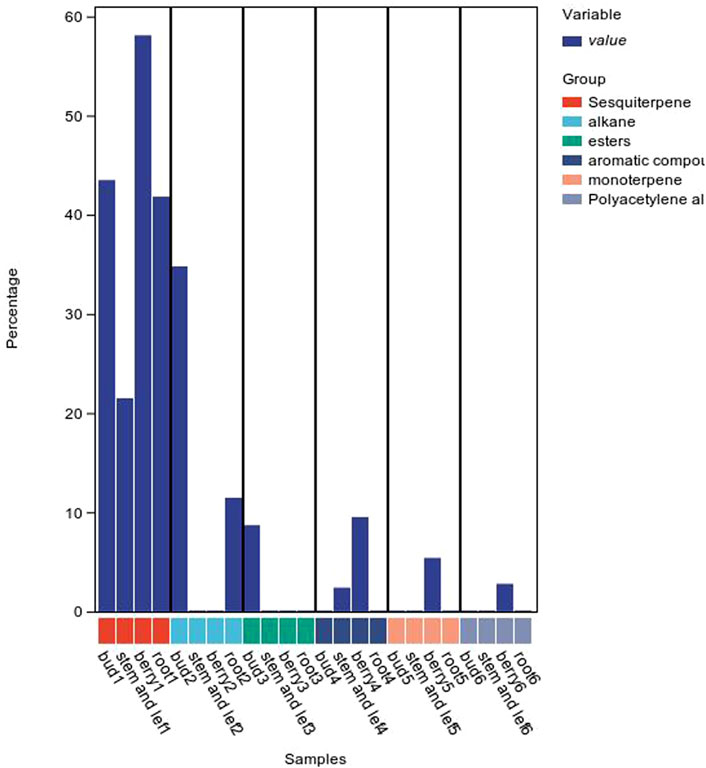
The composition of volatile oils from different parts of P. ginseng varies, as shown in Figure 7. Sesquiterpenes were the most abundant metabolites in flowers, followed by alkanes and esters. The stems and leaves contain sesquiterpenes, aromatic metabolites. The fruit of P. ginseng has the highest percentage of sesquiterpene content compared to other parts of the plant. In P. ginseng root, the main metabolites are sesquiterpenes and alkanes. In addition to this, there is also oil in P. ginseng seeds. P. ginseng seed oil is mainly composed of non-volatile fatty acids, followed by phenolic compounds (Zhu et al., 2010; Lee et al., 2013)
2.2 Effects of different regions on the volatile oil content of P. ginseng
The volatile oil composition and content of P. ginseng varied in different regions and years of growth, as shown in Figure 8. A study was conducted to compare and summarize the quality and yield of GVO from several counties under the provinces of Jilin, Liaoning, and Heilongjiang with those of Korean ginseng. Among the P. ginsengs of different ages and origins, the one with the highest volatile oil yield was the four-year-old Antu P. ginseng, and the one with the lowest yield was the six-year-old Jian P. ginseng. The mean value of the volatile oil yield of P. ginseng roots from all origins was 0.056%, with an RSD of 26%, indicating that the volatile oil content of P. ginseng differed significantly among different origins and ages (Wang, 2016).
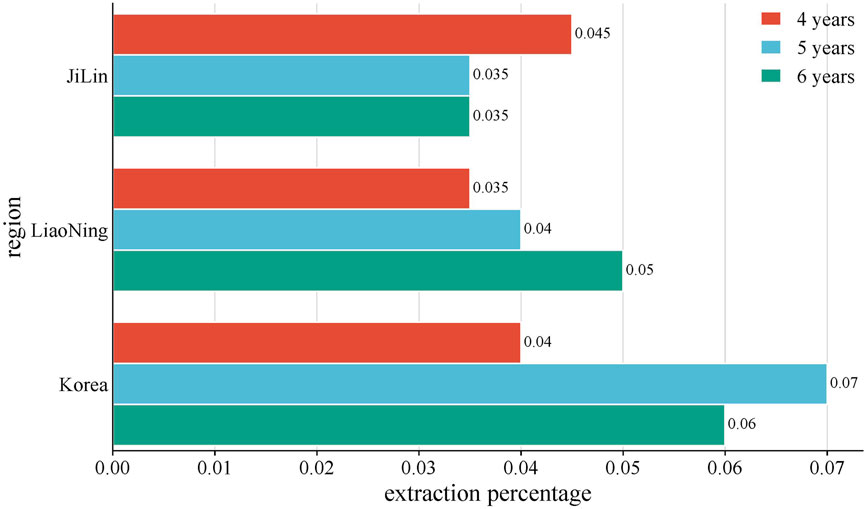
Figure 8. Average yield of GVO by region. The average volatile oil yield of P. ginseng from Jilin, Liaoning, and South Korea in China was compared with. It was found that the volatile oil content of four-year-old P. ginseng: Jilin Province > Liaoning Province > Korea. Five-year-old P. ginseng: Korea > Liaoning Province > Jilin Province. Six-year-old P. ginseng: Liaoning Province > Korea > Jilin Province.
Different growth forms of P. ginseng have varying levels of volatile oil content. The volatile oils of cultivated P. ginseng (CG), transplanted P. ginseng (TG) and mountain cultivated P. ginseng (MCG) were extracted by headspace solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, followed by chromatographic identification using n-alkane standard (C7-C30). Calculating and comparing the aldehydes, terpenes, alcohols, alkynes, esters, and other metabolites of three types of P. ginseng, it was found that the content of terpenoids was the highest, with CG (85.91%), MCG (90.27%), and TG (76.89%), respectively. However, a difference in alkyl alcohol content between P. ginseng samples of different origins was not statistically significant (Gu et al., 2022).
2.3 Effect of concoction on the volatile oil composition of P. ginseng
When P. ginseng is steamed and dried, it is produced as red ginseng. Research has indicated that the conversion of P. ginseng into red ginseng leads to a loss in total volatile oil content ranging from 63.89% to 74.54%, averaging 69.50% (Wu et al., 1992). In addition, the composition of volatile oil is altered during this process, as depicted in Figure 2B. The transformation of P. ginseng into red ginseng results in a change in the composition of GVO. The main metabolites of red ginseng oil (RGO) include linoleic acid, palmitic acid, β-sitosterol, γ-sitosterol, and stigmasterol, which are also present in GVO. The relative content of C4-C6 metabolites in red ginseng and fresh ginseng differs significantly, with fresh ginseng containing 1.04% of C4-C6 metabolites compared to red ginseng. Fresh ginseng contains three C10 monoterpenes, while red ginseng contains only one. The content of soy sterols and β-sitosterol also differed in red ginseng and P. ginseng. Notably, the content of stigmasterol in five-year-old and six-year-old red ginseng was reported to be 23.84 mg/g and 27.46 mg/g, respectively. The content of beta-sitosterol in five and six-year-old P. ginseng was 72.58 mg/g and 82.14 mg/g (Lee et al., 2018) respectively. In addition, a study comparing the volatile characteristics of fresh, white and red ginseng, found that fresh P. ginseng had a stronger odor than red ginseng (Abd El-Aty et al., 2008). The main functional groups identified in white and red ginseng were alcohols, ketones, esters, and phenols, with acids being found only in fresh P. ginseng. Therefore, it can be hypothesized that during the processing of fresh ginseng, many volatile metabolites may disappear or increase (Cho, 2015).
For different concoctions, the content of stigmasterol (metabolite 1) and beta-sitosterol (metabolite 2) in P. ginseng varied greatly from year to year. Of the three concocted forms, the total metabolite content of red ginseng was least affected by year. White P. ginseng showed the greatest variation in content and had the highest levels of metabolites in the six-year-old. So when it comes to experiments related to P. ginseng phytosterols, researchers need to choose according to their own experimental requirements (Lee et al., 2018).
Although there are differences in the composition of volatile oils derived from red ginseng and P. ginseng, their pharmacological effects, mechanism of action, targets and pathways are comparable. RGO has been found to possess antitumor activity (Lee et al., 2010). It inhibits tumor transformation and blocks the activation of NF-kB, AP-1, and MAPK, as well as the expression of COX-2 (Truong et al., 2018). This anticancer pathway is similar to that of GVO. β-sitosterol and linoleic acid (Yasuda et al., 2009) present in RGO have been identified as effective substances with anti-tumor and neuroprotective properties (Lee et al., 2017). β-Sitosterol promotes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in breast cancer cells (Vundru et al., 2013), prostate cancer cells (von Holtz et al., 1998), and inhibits proliferation of human gastric adenocarcinoma cells and xenograft tumors. Furthermore, RGO also has anti-inflammatory effects (Bak et al., 2012a), which can significantly reduce the serum levels of NO, IL-6 and TNF-a in mice, as well as the expression of colon inflammation markers iNOS, COX-2, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α (Truong et al., 2019). Similarly, GVO can also reduce the aforementioned inflammatory factors in the serum to achieve anti-inflammatory effects.
Red ginseng, exhibits higher antioxidant activity due to the increase in phenolic metabolites induced by steam during the preparation process (Kang et al., 2006). RGO can effectively inhibit DPPH and ABTS free radicals. It may also significantly reduce the levels of liver enzymes (ALT and AST) in the serum of mice, increase the levels of antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT), reduce the content of DNA oxidation products (8-OHdG) (Ullah et al., 2021), and protect the liver from oxidative stress. Moreover, red ginseng oil also directly scavenges ROS (Meerson et al., 1982), inhibits lipid peroxidation, and protects cells from oxidative damage by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway to induce the expression of cellular antioxidant enzyme activity (Abe and Berk, 1998). In addition, RGO also has antibacterial effects (Reyes et al., 2017) and has the ability to control acne. It promotes anti-melanin production (Saba et al., 2020), hair growth, and protects the skin from UVC radiation (Truong et al., 2021). GVO is similar to red GVO chemical composition. However, during the processing of red ginseng, some metabolites are lost while new substances are produced. Both types of volatile oil exhibit similar pharmacological effects, but further comparative studies are necessary to determine which one yields superior results.
2.4 Effects of different growth years on the volatile oil content of P. ginseng
The volatile oil content of P. ginseng varies with the plant’s age, generally showing an increasing trend as the ages. The older the P. ginseng, the better its quality, mainly due to the accumulation of active metabolites with age. Research has found that the relative abundance of a-cadinol, a-bisabolol, thujob-sene, and n-hexadecanoic acids in volatile oils increases most significantly. By comparing the relative amounts of these metabolites, the quality of GVO can be evaluated (Qiu et al., 2008).
Principal metabolite analysis (PCA) was performed on the volatile oil of P. ginseng during the third, fifth and eighth year growth periods, and it was found that there were significant differences in the volatile oil of different years. In particular, the samples of groups 7, 8 and 9 had obvious dispersion compared with other groups, which proved that there was a significant difference in the composition of eight-year-old P. ginseng compared to samples of other ages. The spots on samples 1, 2, and three are located in smaller areas, indicating that the chemical composition differences of the samples over the past 3 years are relatively small.
Samples 1, 2, and three all have spots located in smaller areas, indicating that there is very little difference in chemical composition between the samples over the course of the past 3 years.
3 Extraction process of GVO
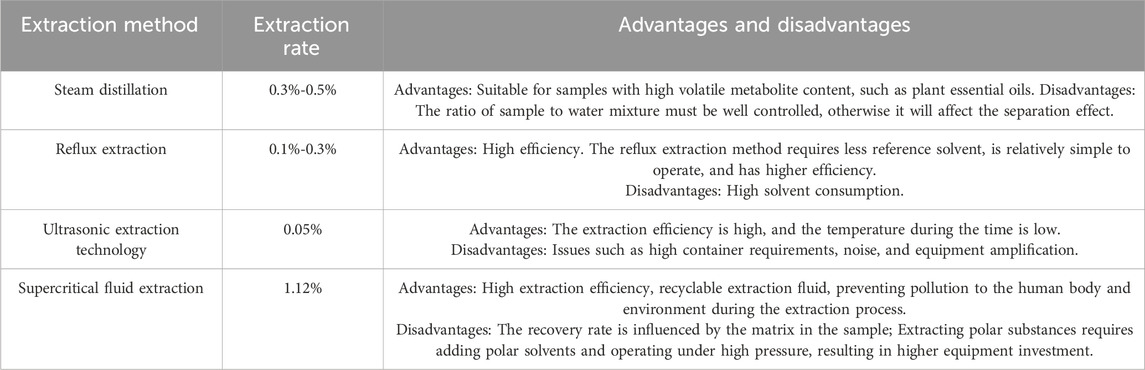
The volatile oil of P. ginseng is composed of various metabolites with low content, solubility, and boiling points, as well as highly unstable properties. Therefore, the efficiency and rationality of the extraction method are crucial. Volatile oil extraction methods can be classified into traditional and innovative methods. Traditional methods include steam distillation, impregnation, infiltration, and reflux extraction. With technological advancements, new methods such as ultrasonic extraction, microwave extraction, semi-biomimetic extraction, and solid phase microextraction have been developed (Table 2). Among the available techniques, supercritical fluid extraction technology offers a higher extraction rate and less pollution, although it is not suitable for large-scale production. The composition of volatile oils from traditional Chinese medicine can vary based on the extraction method. The most appropriate extraction method should be chosen based on the specific circumstances.
3.1 Traditional extraction methods
3.1.1 solvent extraction (SO)
Solvent extraction is a common method used in practice. Based on the solubility properties of GVO, it can be extracted using the soxhlet extraction method or cold immersion method with organic solvents like petroleum ether (30–60°C), ether, or carbon tetrachloride. The working principle involves the solvent penetrating the cell membrane of botanical drugs, dissolving soluble substances, creating a concentration difference between the inside and outside of the cells, and allowing the solute to permeate out of the cell membrane (Kuang, 2011). After vacuum distillation to eliminate organic solvents, the extract is obtained. Subsequently, hot ethanol is employed to dissolve the extract, which is then cooled, filtered to remove impurities, and the ethanol is reclaimed to obtain clean oil.
The extract can also be re-distilled to acquire a purer essential oil. Studies have explored the extraction of volatile oil using various solvents. Research indicates that the extraction process utilizing water as the solvent can yield the highest levels of phenolic substances and flavonoids (El et al., 2011). This extraction method is straightforward, practical, and enables the extraction of the natural metabolites of plant volatile oil. However, extracting essential oils through leaching with organic solvents is more intricate and often leads to significant solvent residue problems.
3.1.2 Steam distillation method
Research has shown that steam distillation is the most efficient method for obtaining volatile oils, with an extraction efficiency of 93% according to studies (Aziz et al., 2018). The volatile oil is not mixed with water. When the combined vapor pressures of the volatile oil and water equal the atmospheric pressure, the solution boils. If further heated, the volatile oil can be distilled out with water vapor.
During extraction, the crude powder of the raw material can be soaked in water in a still and then directly heated and distilled, or the raw material can be placed on a perforated partition plate net. As the steam generated by heating the water passes through the raw material, the volatile oil is heated and distilled out simultaneously with the water vapor. Collect distillate, cool it and separate the oil layer (Pei, 2016). This method for extracting GVO offers advantages such as simple equipment, easy operation, low cost, large yield, and high recovery rate of volatile oil, However, it should be noted that the raw materials are prone to coking due to the intense heat. Additionally, the heating of volatile oil during the extraction process can lead to chemical reactions such as molecular isomerization, which can affect the composition and reduce the value of the volatile oil (Ma et al., 1985).
Although traditional extraction methods are commonly used in production, they come with some inherent drawbacks. Apart from long extraction times, they necessitate a large amount of solvent and energy. Prolonged contact with hot water or steam can degrade certain metabolites and hydrolyze them. Furthermore, the lack of adjustable parameters in these methods makes it challenging to control the process selectivity and essential oil concentration (Yang et al., 2014).
3.2 Modern extraction methods
3.2.1 Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE)
For the extraction of plant volatile oils, supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) is a relatively new and efficient method. SFE is faster, more convenient, and more selective than traditional extraction methods, with higher extraction rates and lower temperatures. In a study, the process of extracting volatile oil from supercritical CO2 was optimized by using raw sun-dried P. ginseng as raw material. Response surface analysis was employed to determine the optimal extraction conditions (Cui et al., 2016). The results indicated that an extraction pressure of 38 MPa, an extraction temperature of 55°C, a static extraction time of 2 h, and a dynamic extraction time of 1 h resulted in an extraction rate of 1.12%. This method allows for the simultaneous separation of high and low boiling point substances, resulting in a product that is richer in oil metabolites. In addition, it enables the extraction of both volatile and non-volatile GVO, significantly improving the overall yield (Pourmortazavi and Hajimirsadeghi et al., 2007). In the study of P. ginseng seed oil extraction, it was found that supercritical fluid extraction yielded higher oil content compared to compression or solvent extraction. The highest yield of P. ginseng seed oil extracted by supercritical fluid extraction was 17.48% at 500 bar and 65°C (Lee et al., 2013). This technology utilizes CO2 as a supercritical fluid, which prevents the destruction of active metabolites and facilitates the development of new drugs. Furthermore, it reduces labor requirements and the use of organic solvents, thereby reducing pollution from the three wastes, making it a modern technology for the extraction of natural essential oils that is vigorously promoted and widely used.
3.2.2 Microwave-assisted extraction method
Microwave-assisted water distillation (MAHD), which employs water as a solvent, is a sustainable and eco-friendly approach for extracting volatile oils from plants (Golmakani and Rezaei, 2008). During the extraction process, microwave power, liquid-material ratio, extraction time and other parameters have a significant impact on the extraction efficiency. Compared with traditional extraction methods, MAHD significantly shortens extraction time and improves extraction efficiency of essential oils (Shang et al., 2020). There are studies using this method to extract essential oil and polyphenols from camphor leaves, and the yield of essential oil under optimal conditions is 3.26% ± 0.05%. Microwave radiation has the potential to harm cell membranes through cell expansion, modification of intracellular structures, impairment of oil-rich glands and cells, acceleration of the movement of aqueous solutions, and dispersion of internal metabolites (Chen et al., 2016).
3.2.3 Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE)
The ultrasonic extraction method is the use of ultrasound cavitation, mechanical effects, and thermal effects to increase the frequency and speed of the molecular movement of substances, to promote contact between the solution and the material, from the target to obtain more metabolites (Raj and Dash, 2020; Yang et al., 2021). It has the advantages of time-saving, energy-saving, and low-temperature extraction is conducive to the protection of active metabolites, it is a rapid and efficient new extraction method.
In one study, raw natural-dried P. ginseng powder was used as raw material and ether as solvent in a soxhlet extractor with ultrasonic cleaner at reflux for 90 min in this method. The ether was recovered to obtain the ether leachate, which was subjected to hydrodistillation to collect the distillate. Extracted with ether 5 times, followed by dehydration with anhydrous sodium sulfate and drying to a constant weight. The content determination results revealed that the volatile oil content obtained from the 90-min extraction using the ultrasonic extraction method was in line with the findings reported in the literature (Song, 1991). In another study, ultrasound-assisted pretreatment extraction (UAPE) was employed to extract essential oils from the peels of Tribute citrus (TC) peels, resulting in significantly higher yields compared to traditional hydrodistillation (HD). It has been demonstrated that ultrasonic extraction has a higher extraction rate compared to the conventional method. However, this technique is not suitable for large-scale production (Li et al., 2022).
4 The pharmacological effects of GVO and its mechanism of action
Recently, the pharmacological properties of P. ginseng have been discovered, revealing its potential in areas such as anti-aging, anti-diabetes, anti-cancer, analgesia, antipyretic, anti-stress, anti-fatigue, sedation, and protein-promoting activities (Zhou et al., 2023). The study mainly focuses on the elaboration of ginsenosides, P. ginseng polysaccharides. At present, it has been discovered that the fat-soluble metabolites of P. ginseng possess anti-inflammatory, antitussive, antihypertensive, anti-fatigue, anti-tumor, cholesterol-lowering, and central-nervous-exciting effects. In addition, it is worth mentioning that the pharmacological effects and chemical composition of P. ginseng can be influenced by various factors, including species, geographic location, cultivation, environment, harvesting, storage, and post-harvest processing.
4.1 Cardiovascular effects
GVO has a beneficial therapeutic effect on cardiovascular diseases. The petroleum ether extract of P. ginseng has been shown to significantly inhibit diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) (Lee et al., 2004) and acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) (Rho et al., 2005) in rat liver microsomes. ACAT has been explored as a potential target for drug intervention in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis (Chhabria and Mahajan, 2009). The preventive mechanism involves inhibiting ACAT in the intestines, liver, and arteries, thereby reducing plasma total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, preventing cholesterol esterification, and reducing cholesterol deposition in arterial walls (Kwon et al., 1997). Spectral analysis identified the chemical structures of metabolites in the petroleum ether extract as (9R,10S)-epoxy-16-heptadecene-4, 6-diyne-3-one, (9R,10S)-epoxyheptadecan-4,6-diyne-3-one and 1-methoxy-(9R,10S)-epoxyheptadecan-4,6-diyne-3-one, which inhibit ACAT activity in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 values of 35 µM, 47 µM, and 21 µM, respectively. Additionally, ACAT inhibitors isolated from the hairy roots of P. ginseng, identified as panaxynol, panaxydol, panaxydiol, and panaxytriol, inhibit rat liver ACAT with IC50 values of 94, 80, 45, and 79μM, respectively.
In myocardial ischemia, panaxynol reduces ST-segment elevation by decreasing serum MDA and CTn-I levels, increasing SOD, GSH, and GSH-Px enzyme activities, and enhancing NO concentration and NOS activity, thereby mitigating oxidative damage and myocardial injury (Alanko et al., 1994). GVO has been less well studied in cardiovascular disease, and limited data are available for reference. However, the pharmacological effects of panaxynol in ameliorating myocardial injury have also been demonstrated in studies in other plants. Inflammatory vesicle protein complex (NLRP3) is involved in innate immunity in ischemic heart disease (Wang et al., 2020). Panaxynol also inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome via the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB axis, significantly reducing myocardial infarction area and apoptosis, and alleviating myocardial damage and neutrophil infiltration (Ding et al., 2023).
4.2 Anti-inflammatory effect
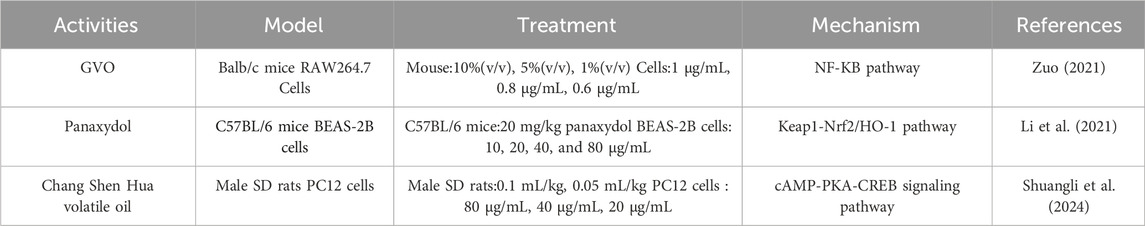
Relevant pharmacological studies have proved that GVO has anti-inflammatory effects, as shown in Table 3. The main anti-inflammatory metabolite, panaxynol, can non-competitively inhibit 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in the cytoplasm (Fujimoto et al., 1998). Zuo Xu conducted a study using xylene to induce mouse ear swelling. After treatment with GVO, the earpieces of different experimental groups of mice were weighed and their swelling and inhibition rates were calculated. The results indicated a significant inhibitory effect of GVO on ear swelling in mice. In vitro inflammatory cell experiments showed that GVO possesses the ability to suppress the expression of MyD88 and TLR4 proteins, decrease the phosphorylation level of P65 in RAW264.7 cells, and inhibit the NF-kB signaling pathway, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory effects (Zuo, 2021). Acute lung injury, an acute inflammatory disease, can also be ameliorated by panaxydol (PX), a metabolite of GVO. PX has been shown to significantly improve pathological changes in the lungs of mice, reduce pulmonary edema, inflammation, and ferroptosis (Li et al., 2021). The mechanism involves the selective inhibition and upregulation of the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which markedly attenuates LPS-induced inflammation and ferroptosis.
Depression, often linked to inflammatory factors, is another condition where GVO shows promise. Depressed patients typically exhibit elevated levels of cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α (Rethorst et al., 2013). A novel herbal inhalation preparation combining GVO with other essential oils, known as CSHVO, has been developed. CSHVO has been shown to enhance the proliferation and viability of PC12 cells by inhibiting cort-induced apoptosis. Additionally, CSHVO intervention significantly reduced the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ, while increasing the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10. This suggests that the anti-depressive activity of CSHVO may be related to the inhibition of inflammatory cytokine release and the alleviation of neuroinflammation (Shuangli et al., 2024). Moreover, panaxynol from other plants has been shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the secretion of inflammatory cytokines TNF and IL-6 in BV-2 microglial cells, preventing their overactivation. This is achieved through the suppression of the NF-κB/i-κB-α inflammatory signaling pathway, which increases the secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tyrosine kinase receptor B (TrkB) proteins in the hippocampus of mice, thereby achieving anti-depressive effects (Zhao et al., 2021).
In summary, the anti-inflammatory effects of GVO are mediated through multiple mechanisms, including the inhibition of key inflammatory pathways and cytokines, as well as the modulation of neuroinflammatory responses. These findings highlight the potential of GVO as a therapeutic agent for inflammatory diseases and related conditions. Panaxydol in P. ginseng volatile oil has anti-inflammatory effects. Panaxynol from other plants has shown anti-inflammatory effects, and it remains to be investigated whether it has the same effect in GVO.
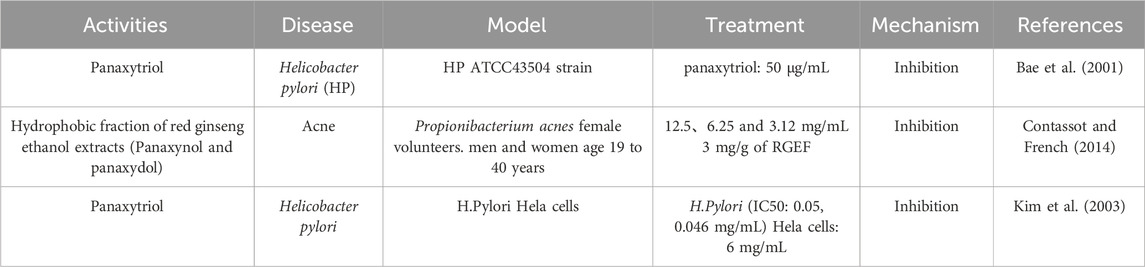
4.3 Antibacterial effects
Pharmacological studies have shown that the antibacterial mechanism of GVO may involve the synergistic action of multiple metabolites, such as disrupting bacterial cell wall and membrane permeability, affecting bacterial energy metabolism, and inhibiting protein and nucleic acid synthesis (Chen and Fan, 2016). The volatile oil present in the outer cork layer and phloem of P. ginseng roots has inhibitory effects on the growth of various Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Diphtheria, Listeria, and Streptococcus.
Panaxynol exhibits good antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Bacillus subtilis, Gram-negative bacteria, and Escherichia coli (Bae et al., 2001). Gram-negative bacteria are known to cause inflammation in the lungs, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the principal metabolite of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, is considered one of the major causes of lung diseases (Kolomaznik et al., 2017). Panaxydol can inhibit the activity of LPS, thereby effectively inhibiting gram-negative bacteria. Helicobacter pylori (HP) is recognized a risk factor for gastric cancer and plays a crucial part in the development of gastritis and peptic ulcers (Warren and Marshall, 1983). Pathogenic HP produces urease, an enzyme that breaks down urea into ammonia and carbamate. Research has confirmed that panaxytriol can achieve anti-Helicobacter pylori effects by inhibiting gastric urease and gastric H+/K + ATPase (Bae et al., 2001) (Table 4).
Moreover, polyacetylene also has good antifungal (Xie et al., 2022) and antibacterial effects (Kim et al., 2003). Acne is a chronic inflammatory skin disease caused by excessive sebum secretion, proliferation of Propionibacterium acnes, and inflammatory response (Contassot and French, 2014). Panaxynol and panaxydol have shown selective inhibitory effects on P. acnes, making them effective in treating acne (Hou et al., 2019).
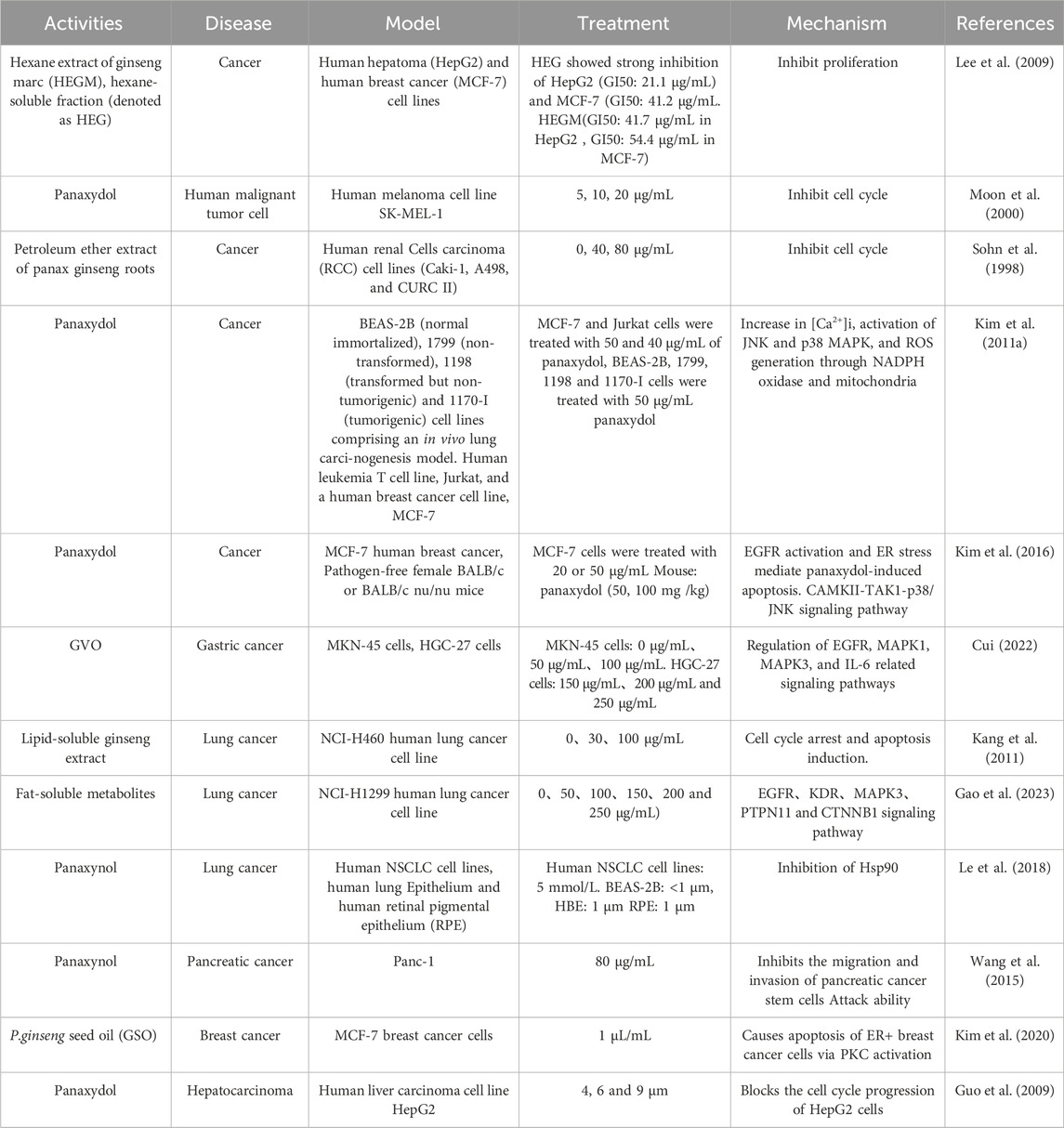
4.4 Anticancer effects
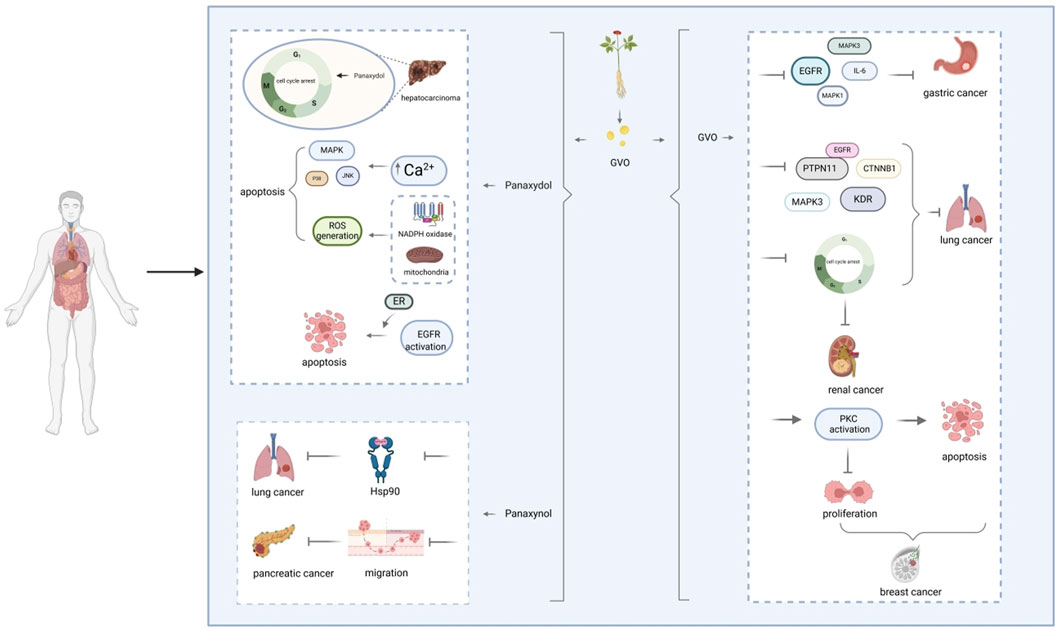
Among the pharmacological effects of GVO, its anticancer activity has been extensively studied. The anticancer activity of P. ginseng is primarily attributed to its lipophilic metabolites. Hexane extraction maximizes the recovery of anticancer active metabolites, demonstrating strong in vitro inhibitory effects on the proliferation of human liver and breast cancer cells in a concentration-dependent manner (Lee et al., 2009). Polyacetylenes such as panaxynol, panaxydol, and panaxytriol are considered the main anticancer metabolites, exhibiting antiproliferative effects on mouse sarcoma, leukemia, human colon cancer, and human ileocecal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Panaxydol accelerates cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase by reducing Cdk1 activity and upregulating p27KIP1 protein expression, inhibiting human renal cell carcinoma proliferation (Sohn et al., 1998; Moon et al., 2000). Panaxydol induces cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting EGFR activation and endoplasmic reticulum stress, suppressing tumor growth in mice (Figure 9) (Kim et al., 2011; Kim et al., 2016). Panaxynol significantly reduces MMP-2 mRNA and protein levels in melanoma cells (B16F10) at a concentration of 3 μg/mL, inhibiting cancer cell invasion and migration (Yun et al., 2015) (Table 5).
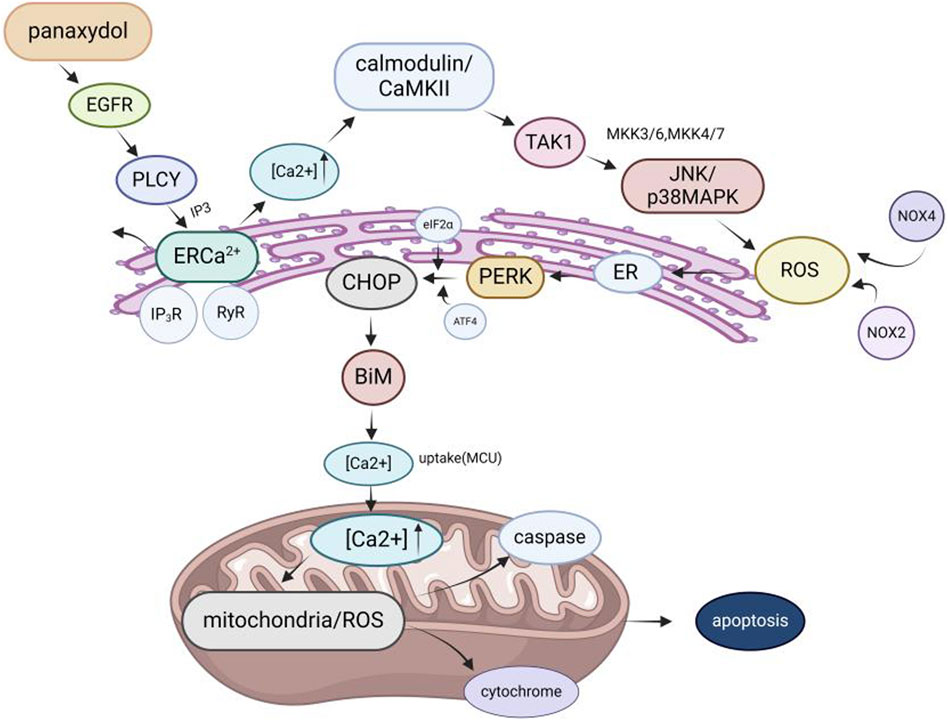
Figure 9. Molecular mechanism of GVO for anti-cancer. The mechanism of panaxydol induced cell apoptosis involves a rapid increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+concentration, with excess Ca2+ transferring from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to mitochondria. The release of E [Ca2+] and the resulting increase in Ca2+ activate p38 and JNK, while p38/JNK further activates NADPH oxidase. NADPH oxidase activates and induces oxidative stress, triggering mitochondria-dependent apoptosis.
In addition, some rare metabolites in the volatile oil of P. ginseng also have anticancer activity, such as β-elemene, (Peng et al., 2006), d-limonene (Anandakumar et al., 2021), and α-humulene (Chen et al., 2019). Among these metabolites, β-elemene, a sesquiterpene effective active monomer found in P. ginseng essential oil, demonstrates significant anticancer activity and is classified as a class II non-cytotoxic antitumor drug in China. It is clinically for the treatment of rectal cancer (Wang et al., 2022), breast cancer (Xie and Wang, 2022). Its anticancer mechanism may induce apoptosis in cancer cells through a variety of pathways, such as the ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway, cellular oxidative dysfunction, the caspase-dependent mitochondrial death pathway, and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway (Qureshi et al., 2019). Inducing autophagy in cancer cells by targeting multiple molecular targets such as kinases, transcription factors, growth factors, their receptors, and proteins (Zhai et al., 2019).
4.4.1 Anti-gastric cancer
GVO has shown promising anti-cancer properties, particularly against gastric cancer. Key metabolites such as linoleic acid, panaxynol, methyl linoleate, palmitoleic acid, and oleic acid have been identified to interact with critical targets in gastric cancer, including EGFR, MAPK1, MAPK3, and IL-6, significantly inhibiting the proliferation of gastric cancer cells (Cui, 2022). This inhibition is dose- and time-dependent, as demonstrated in vitro experiments with SGC-823 gastric cancer cells, where GVO treatment resulted in a marked reduction in glycogen and succinate dehydrogenase content, and a significant decrease in DNA content after 72 h of administration (Wang et al., 1992). This suggests that the mechanism by which GVO inhibits gastric cancer cell growth may involve disruptions in DNA, carbohydrate, and energy metabolism. Additionally, panaxytriol has been shown to exhibit cytotoxicity against human gastric cancer cell line MK-1, enhancing the cytotoxic effects of MMC by decreasing membrane fluidity and promoting MMC accumulation in MK-1 cells (Matsunaga et al., 1994).
4.4.2 Anti-lung cancer
GVO, particularly its polyacetylenes, has demonstrated significant anti-tumor activity against lung cancer and has a strong inhibitory effect on lung cancer cell lines at high concentrations (100 μg/mL). This anticancer mechanism initiates the activation of caspase-8 and caspase-9, which in turn activates caspase-3 to induce cleavage of PARPs. This process results in cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase, thereby inhibiting lung cancer cell proliferation (Kang et al., 2011). Furthermore, GVO metabolites downregulate the levels of EGFR, KDR, MAPK3, PTPN11, and CTNNB1 proteins in lung cancer cells, affecting the PI3K/Akt and RAS/ERK pathways, which are crucial for cell proliferation and survival proteins regulated by Hsp90 (Gao et al., 2023). Panaxynol treatment also significantly inhibits the interaction between HIF-1α and Hsp90, reducing HIF-1α protein levels and VEGF mRNA levels in a dose-dependent manner, further supporting its anti-lung cancer effects (Lee et al., 2018; Le et al., 2018).
Furthermore, panaxynol has been found to decreases proliferation and self-renewal of pancreatic cancer PANC-1 stem cells. Its principle may inhibit the migratory ability of SW1990 cells by down-regulating the expression of Ki67, PCNA, Vimentin, and MMP-9 as well as up-regulating the expression of E-cadherin, thus exerting its anti-tumor effect (Wang et al., 2015). In addition, some studies also illustrated the phenomenon of panaxynol inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal cell transformation at the molecular level. It exerts its anti-tumor effects by down-regulating the expression of Vimentin and MMP-9 and up-regulating the expression of E-cadherin. P. ginseng seed oil (GSO) in combination with tamoxifen inhibits the growth of ER + breast cancer cells. It induces apoptosis in ER + breast cancer cells by activating PKC (Li et al., 2012), which leads to the breakdown of caspase-9, caspase-3, and PARP (Kim et al., 2020). α-Humulene (Legault et al., 2003), β-sitosterol (Shin et al., 2016) and (Z)-β-farnesene (Afoulous et al., 2013) have been shown to be associated with the anticancer activity of several plant essential oils. The fat-soluble metabolites panaxydol and panaxynol can inhibit liver cancer and block the cell cycle progression from G1 phase to S phase at high concentrations, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of human kidney cancer cells (Guo et al., 2009).
In conclusion, the anti-cancer effects of GVO are primarily attributed to its ability to interfere with key signaling pathways and cellular processes involved in cancer cell proliferation and survival (Figure 10). The active metabolites of GVO, such as linoleic acid, panaxynol, and panaxytriol, exhibit potent inhibitory effects on gastric and lung cancer cells through mechanisms involving apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest, and disruption of critical protein interactions. These findings highlight the potential of GVO as a valuable therapeutic agent in the treatment of gastric and lung cancers.
4.5 Anti-aging, anti-oxidation
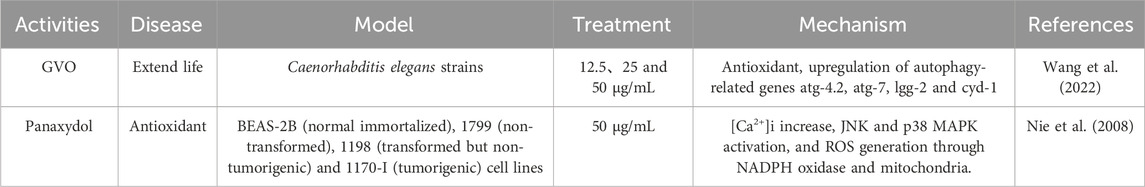
GVO has demonstrated significant anti-aging and antioxidant properties, which are crucial for mitigating the effects of oxidative stress and cellular aging (Alanko et al., 1994). Studies have shown that panaxynol and panaxydol in GVO can prolong the lifespan and health span of model organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans. The underlying mechanisms involve the upregulation of autophagy-related genes such as atg-4.2, atg-7, lgg-2, and cyd-1, as well as the increased expression of superoxide dismutase 1 (sod-1). These genetic modifications enhance the organism’s ability to manage oxidative stress, thereby promoting longevity and health without compromising reproductive capacity. Additionally, GVO has been found to activate SOD activity and autophagy, which are indicative of hormesis—a process where low doses of a stressor can stimulate beneficial effects on the organism (Table 6).
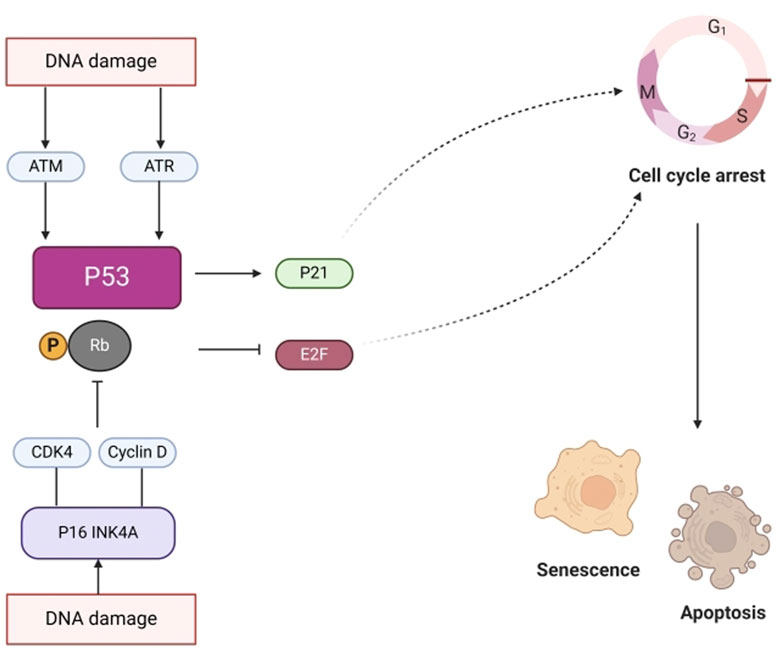
Senescence is a state in which cell division permanently ceases and cells die. Aging is closely associated with major factors such as DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction. Figure 11 illustrates that DNA damage triggers the activation of the ataxia telangiectasia mutated gene (ATM), Rad3 related gene (ATR), p53 pathways (Thompson, 2012), and cell cycle dependent protein kinase inhibitor p21, thereby promoting cell cycle arrest and inducing aging. Moreover, DNA damage activates P16INK4a and inhibits the binding of CDK4 to cyclin D. This prevents phosphorylation of retinoblastoma (RB), leading to inhibition of E2F dependent gene expression and inhibition of G1/S cell cycle progression. GVO can repair damaged pathways by increasing the expression of autophagy substrate p62 protein to delay aging (Su et al., 2023).
During oxidative stress, the increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the decrease in antioxidant defense mechanisms have a broad impact on apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death (Aruoma et al., 2006; Bak et al., 2012b). The main sources of intracellular ROS include NADPH oxidase and the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC.) (Ryter et al., 2007). Oxidative stress occurs when there is an excess production of ROS by mitochondria or NADPH oxidase. Cancer cells are more sensitive to oxidative stress, and scertain anticancer drugs work by inducing ROS production (Pelicano et al., 2003; Valko et al., 2006). Panaxydol induces apoptosis by increasing intracellular calcium level, activation of JNK and p38 MAPK and generating ROS dependent on NADPH oxidase (Kim et al., 2011). In addition, panaxydol (PX), panaxynol from other plants also showed good antioxidant activity by inhibiting oxidative stress through activation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway, reduction of LPO and its related markers, and activation of NO1 and HO - one genes, which resulted in protection of kidneys from damage (Aruoma et al., 2006; Nie et al., 2008). However, whether the antioxidant capacity of panaxydol in P. ginseng is related to the Keap1-Nrf2 system has not yet been confirmed, and it is expected that scholars will further study this.
In summary, the anti-aging and antioxidant effects of GVO are mediated through a combination of genetic regulation, enhancement of autophagy, and activation of key antioxidant pathways. These mechanisms collectively contribute to the mitigation of oxidative stress and the promotion of cellular longevity, making GVO a promising candidate for further research and potential therapeutic applications in age-related diseases.
4.6 Antiplatelet clotting
Research on the anti-platelet aggregation effects of GVO is limited, but it has shown better anti-platelet activity than ginsenosides (Kuo et al., 1990). Panaxynol, a metabolite of GVO, exhibits good anti-platelet aggregation effects by inhibiting ATP release and platelet aggregation (Teng et al., 1989). At a concentration of 0.41 μmol/mL, panaxynol inhibits platelet aggregation induced by arachidonic acid, collagen, ADP, and ionophore A23187 in rabbits, significantly inhibiting thromboxane B2 formation. Ginsenoside prevents secondary aggregation of ATP induced by adrenaline and ADP, completely blocking ATP release. It also inhibits platelet aggregation induced by collagen, ADP, and thrombin, as well as ATP release and thromboxane formation in platelets (Kwon et al., 1997). The addition of 25 mg (0.0025% of the total diet) of P. ginseng lipophilic fraction to the diet can be antithrombotic (Park et al., 1996). After feeding them to rats stimulated by thrombus and collagen, cGMP levels were significantly higher than those of rats given only 15% corn oil. In addition, by adding LF to thrombin- and collagen-stimulated platelets, cGMP and CAMP levels are elevated. This indicates that LF has a direct promoting effect on cGMP. It can be seen that the addition of LF to the diet regulates cGMP and CAMP levels, resulting in the inhibition of thrombin- or collagen-induced platelet aggregation in rats.
4.7 Nutrition and protection of nerve cells
Panaxydol (PND) and panaxynol (PNN) protect cortical neurons from toxicity-induced damage by reducing the upregulation of pro-apoptotic gene Bax and the downregulation of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 at a concentration of 5 µM, suggesting potential benefits in reducing neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease (Nie et al., 2006). In a mouse maze experiment, panaxynol and acetylenic triol at a dose of 20 mg/kg/day for three consecutive days improved scopolamine-induced memory deficits. At concentrations greater than 2mM, they significantly affect the neurodevelopment of secondary neurons such as PC12 h and Neuro2a (Yamazaki et al., 2001) (Table 7).
Clinical and animal studies indicate that depression, a common central nervous system disorder, is associated with reduced or deficient serotonin (5-HT) (Yatham et al., 2000; Ferrari and Villa, 2017) and dopamine (DA) (Sykora et al., 2013). The combination of P. ginseng essential oil, Acorus tatarinowii essential oil, and Albizia julibrissin flower essential oil (CSHVO) from the classic Chinese herbal prescription Kai Xin San (KXS) has shown efficacy in improving depression (Cao et al., 2023). CSHVO significantly increases monoamine neurotransmitter levels in the brain tissue of depressed rats and improves hippocampal pathology. By regulating the cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling pathway, CSHVO promotes neuronal development, repairs nerves, and exerts antidepressant effects (Zhang et al., 2024). Panaxynol from other plant species also exhibits neuroprotective effects by inhibiting calcium influx and promoting free radical production, counteracting amyloid-beta 25–35 fragment-induced early neuronal degeneration (Sun et al., 2020). Panaxydol promotes neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells, protecting neurons from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (Li et al., 2018). Panaxydol enhances the expression and secretion of nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in Schwann cells (SCs), improving SC viability and biological characteristics, effectively protecting neurons from degenerative disease damage (He et al., 2009). While panaxydol and panaxynol in GVO also exhibit neuroprotective effects, further research is needed to explore the underlying mechanisms and potential clinical applications as early treatment candidates for Alzheimer’s disease (Zhu et al., 2008).
4.8 Other pharmacological effects
In addition to the main pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer, GVO also has the functions of weight loss (Kim et al., 2011), hair growth, protection against ultraviolet radiation, and reproductive system protection (Mhaibes et al., 2023). Linoleic acid (LA) or beta-sitosterol (SITOS) in volatile oils can stimulate the transition of hair follicles from the resting phase to the early/mid-growth phase. This leads to an increase in follicle density and diameter, as well as the emergence of the hair shaft from the epidermis. These metabolites synergistically induce the expression of β-catenin, phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase 3β, cyclin D1, cyclin E, and Bcl-2, all of which are associated with hair growth. Furthermore, they activate the Wnt/β-catenin and Shh/Gli pathways, promoting hair follicle development and regeneration.
GVO contains various metabolites with unsaturated double bonds, among which n-hexadecanoic acid is particularly effective as an “anti-mosquito agent” (Jiang et al., 2014). In addition, the volatile oil derived from P. ginseng root possesses pharmacological properties that benefit the skin. Through skin friction, it enhances blood circulation and the development of skin cells, while providing protection against cold and ultraviolet radiation.
Cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) plays a crucial role in cholesterol uptake, storage, and production and has been explored as a potential target for pharmacological intervention in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerotic diseases (Giovannoni et al., 2003). Polyacetylene metabolites derived from P. ginseng root exhibit modest inhibition of ACAT enzymes in rat liver microsomes (Rho et al., 2005). In the MAPK signaling pathway, JNK and p38 are the main mediators of apoptosis in proximal tubule cells (Guo et al., 2021). Panaxynol can inhibit PGDH activity in gastric mucosa, inhibit apoptosis by down-regulating cisplatin and promote the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 in cells and the expression of cleaved caspase-3, thereby improving kidney injury (Fujimoto et al., 1998; Lee et al., 2019). In addition, panaxydol exhibits anti-fatigue properties, which can significantly reduce the levels of oxidative stress markers such as serum LDH, superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde in forced swimming rats, and inhibit oxidative stress (Shin et al., 2019).
5 Discussion
P. ginseng is a widely recognized medicinal plant that has a positive effect on immune regulation and the circulatory system (Shergis et al., 2013). It has been extensively utilized in medicine, food and other fields, and has shown promising application prospects (Qin et al., 2018). Ginsenosides are known to have favorable therapeutic effects in cardiovascular diseases (Fan et al., 2020), neurodegenerative diseases (Zarneshan et al., 2022), cancer (Shah et al., 2023), and diabetes (Zhou et al., 2019). P. ginseng polysaccharides exhibit anti-inflammatory (Qi et al., 2023), anti-tumor (Li et al., 2014), antioxidant (Xiong et al., 2019), anti-asthmatic, hepatoprotective, anti-depressant, anti-radiation and blood lipid regulating properties (Zhao et al., 2019). Although P. ginseng is widely consumed and utilized, there still exists potential investment opportunities in the field of GVO. The current research mainly focuses on the main metabolites of P. ginseng, ginsenosides and P. ginseng polysaccharides, but there are fewer studies on P. ginseng volatile oils. Therefore, this paper summarizes the research results of GVO in recent years and finds that the current research has limitations. For example, in terms of pharmacological effects, in-depth research has been conducted mainly in the direction of anti-cancer. Therefore, this paper summarizes the results of the current study and serves as a starting point for future in-depth studies on GVO.
The volatile oil of P. ginseng is a complex mixture composed of hundreds of metabolites, mainly terpenes, including monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, as well as small aliphatic metabolites and small aromatic metabolites. P. ginseng contains two highly abundant polyacetylenes, namely, panaxynol and panaxydol, which are the main metabolites of P. ginseng essential oils. Polyacetylene extracted from P. ginseng exhibits significant biological effects, including induction of cytotoxicity (Yeo et al., 2017), inhibition of tumor cell proliferation (Kim et al., 2002), inhibition of platelet coagulation function (Teng et al., 1989) and inhibition of diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) enzyme activity (Lee et al., 2004). The presence of a triple bond in polyacetylene increases its reactivity towards biomolecules (He et al., 2014). In addition, polyacetylene has also been shown to be cytotoxic to many solid and leukemic cell lines (Kim et al., 2002), as well as the ability to enhance the cytotoxicity of other anticancer drugs (Matsunaga et al., 1990; Matsunaga et al., 1994). Moreover, analogs and derivatives of polyacetylene have shown promising anti-inflammatory activity, nutritive neurological effects (Wang et al., 2006), immune enhancement (Chou et al., 2011), anticancer properties (Cheung et al., 2019) and the ability to attenuate the toxicity of a range of anticancer drugs. Thus GVO might be developed as an immune-boosting product or an adjuvant anti-cancer drug.
6 Conclusion and future perspectives
As a traditional Chinese medicine, P. ginseng has been highly regarded for its therapeutic efficacy. This paper expands our understanding of P. ginseng and reveals the complex and diverse chemical compositions and pharmacological activities of GVO. The compositions of the volatile oils from different parts of the P. ginseng plant, their contents, extraction methods and pharmacological activities, as well as the mechanisms of action of their major molecules, were systematically summarized. Several factors affect the composition of volatile oils: growth year, collection season, geographical region, extraction method, extraction site, etc. The composition of the volatile oil in turn affects its biological activity. Modern techniques such as supercritical fluid extraction, microwave-assisted extraction and ultrasound-assisted extraction offer promising ways to improve the yield and bioavailability of GVO. Therefore, standardization of these extraction parameters is essential to ensure the consistency of volatile oil quality and efficacy.
From an expert’s point of view, the development and utilization of GVO is promising but faces significant challenges. For example, there are many metabolites of P. ginseng volatile oil that are not widely recognized, so there is no international standardized nomenclature. As a result, the metabolite names do not correspond to each other when the data are summarized, so the composition summary of GVO is not complete. The pharmacological activities of GVO, including cardiovascular, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, anti-aging, and neuroprotective effects, highlight its potential as a multifaceted therapeutic agent. However, the low content of volatile oil in P. ginseng, coupled with its lipophilicity, degradability and volatility, poses a significant barrier to its clinical application and efficacy. Although, the pharmacological mechanisms of P. ginseng volatile oil metabolites (especially panaxynol) highlight the potential for new drug development, little is known about their pharmacokinetic profile. Therefore, in-depth pharmacokinetic studies of GVO should be performed to check for the presence of active metabolites. The identification of these metabolites may provide key information on the bioactive forms of GVO and its pharmacological mechanisms. Therefore, this area may become a new focus for future research. The current literature on GVO remains limited and quality assessment studies are incomplete. This gap highlights the need for more comprehensive and rigorous studies to fully elucidate the therapeutic potential and safety of GVO.
In conclusion, although GVO has a wide range of pharmacological activities, it has been less studied in the areas of immunization, antimicrobial and antiplatelet coagulation. This necessitates further research to address the existing challenges and optimize its clinical applications. Future studies should focus on improving extraction techniques, standardizing quality assessment, and exploring synergistic or antagonistic effects of volatile oil metabolites. Only in this way can we fully utilize the potential of GVO as a valuable resource in the fields of medicine and healthcare.
Author contributions
XY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. SB: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. LS: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. XW: Investigation, Writing–original draft. XB: Funding acquisition, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. WZ: Investigation, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Jilin Province, China (YDZJ202301ZYTS183), Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Jilin Province, China (JJKH20220878KJ). The fund is used to cover the cost of publishing articles.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the newidea. aI website (https://www.newidea.ai/home) for proofreading the text.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1436624/full#supplementary-material
References
Abd El-Aty, A. M., Kim, I. K., Kim, M. R., Lee, C., and Shim, J. H. (2008). Determination of volatile organic compounds generated from fresh, white and red Panax ginseng (C. A. Meyer) using a direct sample injection technique. Biomed. Chromatogr. 22, 556–562. doi:10.1002/bmc.969
Abe, J. B., and Berk, C. (1998). Reactive oxygen species as mediators of signal transduction in cardiovascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 8, 59–64. doi:10.1016/S1050-1738(97)00133-3
Afoulous, S., Ferhout, H., Raoelison, E. G., Valentin, A., Moukarzel, B., Bouajila, F. C. J., et al. (2013). Chemical composition and anticancer, antiinflammatory, antioxidant and antimalarial activities of leaves essential oil of Cedrelopsis grevei. Food Chem. Toxicol. 56, 352–362. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.008
Alanko, J., Kurahashi, Y., Yoshimoto, T., and Baba, S. Y. K. (1994). Panaxynol, a polyacetylene compound isolated from oriental medicines, inhibits mammalian lipoxygenases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 48, 1979–1981. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(94)90598-3
Anandakumar, P., Kamaraj, S., and Vanitha, M. K. (2021). D-limonene: a multifunctional compound with potent therapeutic effects. J. Food Biochem. 45, e13566. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13566
Aruoma, O. I., Grootveld, M., and Bahorun, T. (2006). Free radicals in biology and medicine: from inflammation to biotechnology. Biofactors 27, 1–3. doi:10.1002/biof.5520270101
Aziz, Z. A. A., Ahmad, A., Setapar, S. H. M., Karakucuk, A., Azim, M. M., Lokhat, D., et al. (2018). Essential oils: extraction techniques, pharmaceutical and therapeutic potential - a review. Curr. Drug Metab. 19, 1100–1110. doi:10.2174/1389200219666180723144850
Bae, E. A., Han, M. J., Baek, N. I., and Kim, D. H. (2001). In vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of panaxytriol isolated from ginseng. Arch. Pharm. Res. 24, 297–299. doi:10.1007/BF02975095
Bak, M. J., Hong, S. G., Lee, J. W., and Jeong, W. S. (2012a). Red ginseng marc oil inhibits iNOS and COX-2 via NFκB and p38 pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Molecules 17, 13769–13786. doi:10.3390/molecules171213769
Bak, M. J., Jun, M., and Jeong, W. S. (2012b). Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of the red ginseng essential oil in H(2)O(2)-treated hepG2 cells and CCl(4)-treated mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13, 2314–2330. doi:10.3390/ijms13022314
Cao, Y., Li, M., Gu, L., Zhao, X., Zhou, A., Miao, Y., et al. (2023). Chinese traditional formula Kaixin San suppressed ferroptosis of hippocampal neurons and cardiomyocytes in mice with paradoxical sleep deprivation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 304, 116034. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.116034
Chen, F., Du, X., Zu, Y., Yang, L., and Technology, F. J. S. W. P. (2016). Microwave-assisted method for distillation and dual extraction in obtaining essential oil, proanthocyanidins and polysaccharides by one-pot process from Cinnamomi Cortex. Cortex 164, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2016.03.018
Chen, H., Yuan, J., Hao, J., Wen, Y., Lv, Y., Yang, L. C. X., et al. (2019). α-Humulene inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and induces apoptosis through the inhibition of Akt signaling. Food Chem. Toxicol. 134, 110830. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2019.110830
Chen, H. Y., and Fan, Z. D. (2016). Research progress on the antibacterial activity of volatile oils in traditional Chinese medicine. J. China Pharm. 27, 2011–2013.
Cheung, S. S. C., Hasman, D., Khelifi, D., Tai, J., and Warnock, R. W. S. G. L. (2019). Devil's club falcarinol-type polyacetylenes inhibit pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Nutr. Cancer 71, 301–311. doi:10.1080/01635581.2018.1559931
Chhabria, M. T. B. M. M., and Mahajan, B. M. (2009). Update on patented cholesterol absorption inhibitors. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 19, 1083–1107. doi:10.1517/13543770903036826
Cho, I. (2015). Volatile compounds of ginseng (Panax sp.): a review. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 58, 67–75. doi:10.1007/s13765-015-0007-0
Cho, I. H., Lee, H. J., and Kim, Y. S. (2012). Differences in the volatile compositions of ginseng species (Panax sp.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 7616–7622. doi:10.1021/jf301835v
Chou, T. C., Dong, H., Zhang, X., Lei, X., Hartung, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2011). Multifaceted cytoprotection by synthetic polyacetylenes inspired by the ginseng-derived natural product, panaxytriol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108, 14336–14341. doi:10.1073/pnas.1111332108
Contassot, E. L. E. F., and French, L. E. (2014). New insights into acne pathogenesis: propionibacterium acnes activates the inflammasome. J. Invest. Dermatol 134, 310–313. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.505
Cui, L., Pang, S., Li, Y., Zheng, P., Zhao, H., and Wang, Y. (2016). Optimization of supercritical-CO2 fluid extraction of essential oil from panax ginseng roots by response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. 37, 58–61.
Cui, L., Xu, J., Feng, Z., Yan, M., Piao, X., Yu, Y., et al. (2020). Simultaneous determination and difference evaluation of volatile components generated from ginseng fruit by HS-SPME Coupled with GC-MS according to fruit color. Food Sci. Technol. 40, 532–536. doi:10.1590/fst.26718
Cui, Q. (2022). Study on the mechanism of action of volatile components of ginseng in the treatment of gastric cancer based on network pharmacology Abstract. Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. [dissertation/master's thesis]. [Nan Jing].
Daferera, D. J., Ziogas, B. N., and Polissiou, M. G. (2000). GC-MS analysis of essential oils from some Greek aromatic plants and their fungitoxicity on Penicillium digitatum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 2576–2581. doi:10.1021/jf990835x
Ding, H. S., Huang, Y., Qu, J. F., Wang, Y. J., Huang, Z. Y., Wang, F. Y., et al. (2023). Panaxynol ameliorates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing NLRP3-induced pyroptosis and apoptosis via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 121, 110222. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110222
Ding, Z. (2008). Change in ginseng root volatile oil content of research. Jilin Agricultural University. [dissertation/master's thesis]. [JiLin].
Du, L. Y., Zhang, H. E., Zhang, Y., Han, Y. Y., Ye, P., Meng, X. R., et al. (2023). Comparative study on chemical constituents of ginseng flowers with four consecutive cultivation age. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 1771563. doi:10.1155/2023/1771563
El, O. E. M., Tomi, P., Bouyanzer, A., Hammouti, B., Desjobert, J. M., Costa, J., et al. (2011). Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of essential oils and solvent extracts of Ptychotis verticillata from Morocco. Food Chem. Toxicol. 49, 533–536. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.11.019
Fan, W., Huang, Y., Zheng, H., Li, S., Li, Z., Yuan, L., et al. (2020). Ginsenosides for the treatment of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: pharmacology and mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 132, 110915. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110915
Ferrari, F. R., and Villa, F. (2017). The neurobiology of depression: an integrated overview from biological theories to clinical evidence. Mol. Neurobiol. 54, 4847–4865. doi:10.1007/s12035-016-0032-y
Fujimoto, Y., Sakuma, S., Komatsu, S., Sato, D., Nishida, H., Xiao, Y. Q., et al. (1998). Inhibition of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase activity in rabbit gastric antral mucosa by panaxynol isolated from oriental medicines. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 50, 1075–1078. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1998.tb06925.x
Gao, D., Li, Y., Xiang, S., and Zhang, J. (2023). Key targets and molecular mechanisms of the fat-soluble components of ginseng for lung cancer treatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 195, 6495–6515. doi:10.1007/s12010-023-04409-w
Giovannoni, M. P., Piaz, V. D., and Barlocco, C. V. D. (2003). Selective ACAT inhibitors as promising antihyperlipidemic, antiathero-sclerotic and anti-Alzheimer drugs. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 3, 576–584. doi:10.2174/1389557033487890
Golmakani, M. T., and Rezaei, K. (2008). Comparison of microwave-assisted hydrodistillation withthe traditional hydrodistillation method in the extractionof essential oils from Thymus vulgaris L. Food Chem. 109, 925–930. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.084
Gu, W. T., Li, L. Y., Rui, W. J., Diao, Z. W., Zhuang, G. D., Chen, X. M., et al. (2022). Non-targeted metabolomic analysis of variation of volatile fractions of ginseng from different habitats by HS-SPME-GC-MS coupled with chemometrics. Anal. Methods 14, 3583–3597. doi:10.1039/d2ay01060g
Guo, L., Song, L., Wang, Z., Zhao, W., and Yin, W. M. M. (2009). Panaxydol inhibits the proliferation and induces the differentiation of human hepatocarcinoma cell line HepG2. Chem. Biol. Interact. 181, 138–143. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2009.04.015
Guo, Y., Hu, M., Ma, J., Chinnathambi, A., Alharbi, S. A., Ge, O. H. M. S. P., et al. (2021). Protective effect of panaxydol against repeated administration of aristolochic acid on renal function and lipid peroxidation products via activating Keap1-Nrf2/ARE pathway in rat kidney. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 35, e22619. doi:10.1002/jbt.22619
He, J., Ding, W. L., Li, F., Xia, R., and Zhu, W. J. W. H. (2009). Panaxydol treatment enhances the biological properties of Schwann cells in vitro. Chem. Biol. Interact. 177, 34–39. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.08.012
He, J. Y., Zhu, S., and Komatsu, K. (2014). HPLC/UV analysis of polyacetylenes, phenylpropanoid and pyrrolidine alkaloids in medicinally used Codonopsis species. Phytochem. Anal. 25, 213–219. doi:10.1002/pca.2494
Hou, J. H., Shin, H., Jang, K. H., Park, C. K., Koo, B., Shin, H., et al. (2019). Anti-acne properties of hydrophobic fraction of red ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) and its active components. Phytother. Res. 33, 584–590. doi:10.1002/ptr.6243
Jiang, R., Sun, L., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Liu, X., Zhao, H. F. D., et al. (2014). Chemical composition, and cytotoxic, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of the essential oil from ginseng leaves. Nat. Prod. Commun. 9, 1934578X1400900–8. doi:10.1177/1934578x1400900637
Kang, K. S., Kim, H. Y., and Yokozawa, J. S. P. T. (2006). Increase in the free radical scavenging activity of ginseng by heat-processing. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29, 750–754. doi:10.1248/bpb.29.750
Kang, M. R., Kim, H. M., Kang, J. S., Lee, K., Lee, S. D., Hyun, D. H., et al. (2011). Lipid-soluble ginseng extract induces apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in NCI-H460 human lung cancer cells. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 66, 101–106. doi:10.1007/s11130-011-0232-6
Kim, H. J., Kang, H. J., Seo, J. Y., Lee, C. H., Kim, Y. S., and Kim, J. S. (2011a). Antiobesity effect of oil extract of ginseng. J. Med. Food 14, 573–583. doi:10.1089/jmf.2010.1313
Kim, H. S., Lim, J. M., Kim, J. Y., Kim, Y., and Sohn, S. P. J. (2016). Panaxydol, a component of Panax ginseng, induces apoptosis in cancer cells through EGFR activation and ER stress and inhibits tumor growth in mouse models. Int. J. Cancer 138, 1432–1441. doi:10.1002/ijc.29879
Kim, J. M., Shin, J. E., Han, M., Baek, N.-I., and Kim, D.-H. (2003). Inhibitory effect of ginseng polyacetylenes on infection and vacuolation of Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Product. Sci. 9, 158–160.
Kim, J. Y., Lee, K. W., Kim, S. H., Wee, J. J., and Lee, H. J. (2002). Inhibitory effect of tumor cell proliferation and induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest by panaxytriol. Planta Med. 68, 119–122. doi:10.1055/s-2002-20240
Kim, J. Y., Yu, S. J., Oh, H. J., Lee, J. Y., and Sohn, J. (2011b). Panaxydol induces apoptosis through an increased intracellular calcium level, activation of JNK and p38 MAPK and NADPH oxidase-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. Apoptosis 16, 347–358. doi:10.1007/s10495-010-0567-8
Kim, T. H., Kwon, S. C., Kim, J. N., Yoon, J. H., and Cho, S. G. (2020). Ginseng seed oil inhibits the growth of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 40, 4529–4535. doi:10.21873/anticanres.14458
Kolomaznik, M., Nova, Z., and Calkovska, A. (2017). Pulmonary surfactant and bacterial lipopolysaccharide: the interaction and its functional consequences. Physiol. Res. 66, S147–S157. doi:10.33549/physiolres.933672
Kuo, S. C., Teng, C. M., Lee, J. C., Ko, F. N., and Wu, S. C. C. T. S. (1990). Antiplatelet components in Panax ginseng. Planta Med. 56, 164–167. doi:10.1055/s-2006-960916
Kwon, B. M., Ro, S. H., Kim, M. K., Nam, J. Y., Jung, H. J., Lee, I. R., et al. (1997). Polyacetylene analogs, isolated from hairy roots of Panax ginseng, inhibit Acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase. Planta Med. 63, 552–553. doi:10.1055/s-2006-957763
Le, H. T., Nguyen, H. T., Min, H. Y., Hyun, S. Y., Kwon, S., Lee, Y., et al. (2018). Panaxynol, a natural Hsp90 inhibitor, effectively targets both lung cancer stem and non-stem cells. Cancer Lett. 412, 297–307. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.013
Lee, D., Lee, J., Vu-Huynh, K. L., Van Le, T. H., Tuoi Do, T. H., Hwang, G. S., et al. (2019). Protective effect of panaxynol isolated from panax vietnamensis against cisplatin-induced renal damage: in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomolecules 9, 890. doi:10.3390/biom9120890
Lee, D. G., Lee, J., Kim, K. T., Lee, S. W., Kim, Y. O., Cho, I. H., et al. (2018a). High-performance liquid chromatography analysis of phytosterols in Panax ginseng root grown under different conditions. J. Ginseng Res. 42, 16–20. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2016.10.004
Lee, J. H., Leem, D. G., Chung, K. S., Kim, K. T., Choi, S. Y., and Lee, K. T. (2018b). Panaxydol derived from panax ginseng inhibits G(1) cell cycle progression in non-small cell lung cancer via upregulation of intracellular Ca(2+) levels. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 41, 1701–1707. doi:10.1248/bpb.b18-00447
Lee, K. S., Kim, G. H., Kim, H. H., Chang, Y. I., and Lee, G. H. (2012). Volatile compounds of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer cultured with different cultivation methods. J. Food Sci. 77, C805–C810. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2012.02765.x
Lee, M. H., Kim, S. S., Cho, C. W., Choi, S. Y., and Kim, K. T. (2013). Quality and characteristics of ginseng seed oil treated using different extraction methods. J. Ginseng Res. 37, 468–474. doi:10.5142/jgr.2013.37.468
Lee, S., Youn, K., Jeong, W. S., and Jun, C. T.Ho M. (2017). Protective effects of red ginseng oil against aβ25-35-induced neuronal apoptosis and inflammation in PC12 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 2218. doi:10.3390/ijms18102218
Lee, S. D., Park, S. K., Lee, E. S., Kim, H. M., Lee, C. W., Lee, K., et al. (2010). A lipid-soluble red ginseng extract inhibits the growth of human lung tumor xenografts in nude mice. J. Med. Food 13, 1–5. doi:10.1089/jmf.2009.1142
Lee, S. D., Yoo, G., Chae, H. J., In, M.-J., Oh, N.-S., Hwang, Y. K., et al. (2009). Lipid-soluble extracts as the main source of anticancer activity in ginseng and ginseng marc. J. Am. Oil Chemists' Soc. 86, 1065–1071. doi:10.1007/s11746-009-1460-x
Lee, S. W., Kim, K., Rho, M. C., Chung, M. Y., Kim, Y. H., Lee, S., et al. (2004). New Polyacetylenes, DGAT inhibitors from the roots of Panax ginseng. Planta Med. 70, 197–200. doi:10.1055/s-2004-815534
Legault, J., Dahl, W., Debiton, E., and Madelmont, A. P. J. C. (2003). Antitumor activity of balsam fir oil: production of reactive oxygen species induced by alpha-humulene as possible mechanism of action. Planta Med. 69, 402–407. doi:10.1055/s-2003-39695
Li, C., Tian, Z. N., Cai, J. P., Chen, K. X., Zhang, B., Feng, M. Y., et al. (2014). Panax ginseng polysaccharide induces apoptosis by targeting Twist/AKR1C2/NF-1 pathway in human gastric cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 102, 103–109. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.11.016
Li, G., Liu, S., Zhou, Q., Han, J., Qian, C., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Effect of response surface methodology-optimized ultrasound-assisted pretreatment extraction on the composition of essential oil released from Tribute citrus peels. Front. Nutr. 9, 840780. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.840780
Li, J., Lu, K., Sun, F., Tan, S., Zhang, X., Sheng, W., et al. (2021). Panaxydol attenuates ferroptosis against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J. Transl. Med. 19, 96. doi:10.1186/s12967-021-02745-1
Li, W. P., Ma, K., Jiang, X. Y., Yang, R., Lu, P. H., Lu, B. M. N. Y., et al. (2018). Molecular mechanism of panaxydol on promoting axonal growth in PC12 cells. Neural Regen. Res. 13, 1927–1936. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.239439
Li, Z., Wang, N., Fang, J., Huang, J., Tian, F., Xie, C.Li F., et al. (2012). Role of PKC-ERK signaling in tamoxifen-induced apoptosis and tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 27, 1879–1886. doi:10.3892/or.2012.1728
Liu, L., Xu, F. R., and Wang, Y. Z. (2020). Traditional uses, chemical diversity and biological activities of Panax L. (Araliaceae): a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 263, 112792. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.112792
Ma, J., Wang, J., Ding, S., and Li, Y. (1992). Study on the chemical composition of volatile oils from ginseng flowers and leaves. J.Chinese Tradit. Pat. Med., 35–36+53.
Ma, X., Song, C., Xu, J., Cao, S., and Li, N. (1985). Studies on the chemical constituents of volatile oils of Panax Ginseng. Journal of Jilin UniversityMedicine Edition, 377–380.
Mancuso, C., and Santangelo, R. (2017). Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius: from pharmacology to toxicology. Food Chem. Toxicol. 107, 362–372. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.07.019
Matsunaga, H., Katano, M., Saita, T., and Mori, H. Y. M. (1994). Potentiation of cytotoxicity of mitomycin C by a polyacetylenic alcohol, panaxytriol. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 33, 291–297. doi:10.1007/BF00685902
Matsunaga, H., Katano, M., Yamamoto, H., Fujito, H., and Takata, M. M. K. (1990). Cytotoxic activity of polyacetylene compounds in Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 38, 3480–3482. doi:10.1248/cpb.38.3480
McAdam, K. G., Tetteh, J., Bishop, L., Digard, H., Cote, J., Liu, S. L. C., et al. (2020). A combined study of headspace volatiles using human sensory, mass spectrometry and chemometrics. Sci. Rep. 10, 7773. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-64491-6
Meerson, F. Z., Kagan, V. E., Kozlov, Y., Arkhipenko, L. M. B. Y., and Arkhipenko YuV, (1982). The role of lipid peroxidation in pathogenesis of ischemic damage and the antioxidant protection of the heart. Basic Res. Cardiol. 77, 465–485. doi:10.1007/BF01907940
Mhaibes, A. A., Madhi, A. S., and Hasan, B. F. (2023). Physiological and histological effects of ginseng oil on reproductive efficiency in adult male rats. Arch. Razi Inst. 78, 145–150. doi:10.22092/ARI.2022.358488.2229
Moon, J., Yu, S. J., Kim, H. S., and Sohn, J. (2000). Induction of G(1) cell cycle arrest and p27(KIP1) increase by panaxydol isolated from Panax ginseng. Biochem. Pharmacol. 59, 1109–1116. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00235-5
Nie, B. M., Jiang, X. Y., Cai, J. X., Fu, S. L., Yang, L. M., Lin, L., et al. (2008). Panaxydol and panaxynol protect cultured cortical neurons against Abeta25-35-induced toxicity. Neuropharmacology 54, 845–853. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.01.003
Nie, B. M., Yang, L. M., Fu, S. L., Jiang, X. Y., and Lu, P. H.Lu Y. (2006). Protective effect of panaxydol and panaxynol on sodium nitroprusside-induced apoptosis in cortical neurons. Chem. Biol. Interact. 160, 225–231. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2006.02.001
Park, H. J., Lee, J. H., Song, Y. B., and Park, K. H. (1996). Effects of dietary supplementation of lipophilic fraction from Panax ginseng on cGMP and cAMP in rat platelets and on blood coagulation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 19, 1434–1439. doi:10.1248/bpb.19.1434
Pelicano, H., Feng, L., Zhou, Y., Carew, J. S., Hileman, E. O., Plunkett, W., et al. (2003). Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration: a novel strategy to enhance drug-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells by a reactive oxygen species-mediated mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 37832–37839. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301546200
Peng, X., Zhao, Y., Liang, X., Wu, L., Cui, S., Wang, A. G. W., et al. (2006). Assessing the quality of RCTs on the effect of beta-elemene, one ingredient of a Chinese herb, against malignant tumors. Contemp. Clin. Trials 27, 70–82. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2005.07.002
Pourmortazavi, S. M. S., and Hajimirsadeghi, S. (2007). Supercritical fluid extraction in plant essential and volatile oil analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 1163, 2–24. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.06.021
Qi, X., Lu, X., Han, Y., Xing, Y., Zheng, Y., and Cui, C. (2023). Ginseng polysaccharide reduces autoimmune hepatitis inflammatory response by inhibiting PI3K/AKT and TLRs/NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 116, 154859. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154859
Qin, Z., Jia, C., Liao, D., Chen, X., and Li, X. (2018). Comparison of serum metabolite changes of radiated mice administered with panax quinquefolium from different cultivation regions using UPLC-Q/TOF-MS based metabolomic approach. Molecules 23, 1014. doi:10.3390/molecules23051014
Qiu, Y., Lu, X., Pang, T., Ma, C., and Xu, X.Li G. (2008). Determination of radix ginseng volatile oils at different ages by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 31, 3451–3457. doi:10.1002/jssc.200800253
Qureshi, M. Z., Attar, R., Romero, M. A., Sabitaliyevich, U. Y., Nurmurzayevich, S. B., Ozturk, O., et al. (2019). Regulation of signaling pathways by β-elemene in cancer progression and metastasis. J. Cell Biochem. 120, 12091–12100. doi:10.1002/jcb.28624
Raj, B., and Dash, G. V. S. K. K. (2020). Ultrasound-assisted extraction of phytocompounds from dragon fruit peel: optimization, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Ultrason. Sonochem 68, 105180. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105180
Rethorst, C. D., Toups, M. S., Greer, T. L., Nakonezny, P. A., Carmody, T. J., Grannemann, B. D., et al. (2013). Pro-inflammatory cytokines as predictors of antidepressant effects of exercise in major depressive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 18, 1119–1124. doi:10.1038/mp.2012.125
Reyes, A. W. B., Hop, H. T., Arayan, L. T., Huy, T. X. N., Park, S. J., Kim, K. D., et al. (2017). The host immune enhancing agent Korean red ginseng oil successfully attenuates Brucella abortus infection in a murine model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 198, 5–14. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.026
Rho, M. C., Lee, H. S., Lee, S. W., Chang, J. S., Kwon, O. E., Kim, M. Y. C. Y. K., et al. (2005). Polyacetylenic compounds, ACAT inhibitors from the roots of Panax ginseng. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 919–922. doi:10.1021/jf040370x
Richter, R., Basar, S., Koch, A., and Konig, W. A. (2005). Three sesquiterpene hydrocarbons from the roots of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer (Araliaceae). Phytochemistry 66, 2708–2713. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.09.012
Ryter, S. W., Kim, H. P., Hoetzel, A., Park, J. W., Nakahira, K., Choi, X. W. A. M., et al. (2007). Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal 9, 49–89. doi:10.1089/ars.2007.9.49
Saba, E., Kim, S. H., Lee, Y. Y., Kim, H. K., Roh, S. S., Kwak, Y. S., et al. (2020). Anti-melanogenic effects of Korean red ginseng oil in an ultraviolet B-induced hairless mouse model. Molecules 25, 4755. doi:10.3390/molecules25204755
Shah, M. A., Abuzar, S. M., Ilyas, K., Qadees, I., Bilal, M., Yousaf, R., et al. (2023). Ginsenosides in cancer: targeting cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 382, 110634. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110634
Shang, A., Gan, R. Y., Zhang, J. R., Xu, X. Y., Luo, M., Liu, H. Y., et al. (2020). Optimization and characterization of microwave-assisted hydro-distillation extraction of essential oils from cinnamomum camphora leaf and recovery of polyphenols from extract fluid. Molecules 25, 3213. doi:10.3390/molecules25143213
Shergis, J. L., Zhang, A. L., Zhou, W., and Xue, C. C. (2013). Panax ginseng in randomised controlled trials: a systematic review. Phytother. Res. 27, 949–965. doi:10.1002/ptr.4832
Shin, E., Kim, S. H., and Hwang, J. T. (2016). Anti-tumor properties of beta-sitosterol in AGS human gastric adenocarcinoma cells and tumor xenograft mice. FASEB J. 30. doi:10.1096/fasebj.30.1_supplement.688.11
Shin, I. S., Kim, D. H., Jang, E. Y., Kim, H. Y., and Yoo, H. S. (2019). Anti-fatigue properties of cultivated wild ginseng distilled extract and its active component panaxydol in rats. J. Pharmacopuncture 22, 68–74. doi:10.3831/KPI.2019.22.008
Shuangli, Z., Yilong, H., Yinan, Z., Yifan, F., Xiaoxue, W., Mingsan, M., et al. (2024). Molecular mechanism of Chang Shen Hua volatile oil modulating brain cAMP-PKA-CREB pathway to improve depression-like behavior in rats. Phytomedicine 130, 155729. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155729
Sohn, J., Lee, C. H., Chung, D. J., Park, S. H., Kim, I., and Hwang, W. I. (1998). Effect of petroleum ether extract of Panax ginseng roots on proliferation and cell cycle progression of human renal cell carcinoma cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 30, 47–51. doi:10.1038/emm.1998.7
Song, X. K. (1991). Discussion on the extraction method of ginseng volatile oil. J. J. Jilin For. Univ. 78+43.
Su, J., Su, Q., Hu, S., Ruan, X., and Ouyang, S. (2023). Research progress on the anti-aging potential of the active components of ginseng. Nutrients 15, 3286. doi:10.3390/nu15153286
Sun, X., Zhang, T., Zhao, Y., Cai, E., Zhu, H., and Liu, S. (2020). Panaxynol attenuates CUMS-induced anxiety and depressive-like behaviors via regulating neurotransmitters, synapses and the HPA axis in mice. Food Funct. 11, 1235–1244. doi:10.1039/c9fo03104a
Sun, Y., Jiang, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., and Mao, K. (1993). Studies on chemical constituents of volatile oil obtained from fresh ginseng, red ginseng and natural active ginseng and their by-products. J. Jilin Univ. Sci. Ed., 86–88.
Sykora, C., Amor, M., and Schlenker, E. (2013). Age and hypothyroidism affect dopamine modulation of breathing and D2 receptor levels. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 185, 257–264. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2012.10.004
Teng, C. M., Kuo, S. C., Ko, F. N., Lee, J. C., Lee, L. G., Chen, S. C., et al. (1989). Antiplatelet actions of panaxynol and ginsenosides isolated from ginseng. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 990, 315–320. doi:10.1016/s0304-4165(89)80051-0
Thompson, L. H. (2012). Recognition, signaling, and repair of DNA double-strand breaks produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: the molecular choreography. Mutat. Res. 751, 158–246. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2012.06.002
Truong, V. L., Bak, M. J., and Jeong, W. S. (2019). Chemopreventive activity of red ginseng oil in a mouse model of azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammation-associated colon carcinogenesis. J. Med. Food 22, 578–586. doi:10.1089/jmf.2018.4328
Truong, V. L., Keum, Y. S., and Jeong, W. S. (2021). Red ginseng oil promotes hair growth and protects skin against UVC radiation. J. Ginseng Res. 45, 498–509. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2020.12.008
Truong, V. L., Kong, A. N., and Jeong, W. S. (2018). Red ginseng oil inhibits TPA-induced transformation of skin epidermal JB6 cells. J. Med. Food 21, 380–389. doi:10.1089/jmf.2017.4082
Ullah, H. M. A., Lee, Y. Y., Kim, M., Kim, T. W., Saba, E., Kwak, Y. S., et al. (2021). Red ginseng oil attenuates oxidative stress and offers protection against ultraviolet-induced photo toxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 5538470. doi:10.1155/2021/5538470
Valko, M., Rhodes, C. J., Moncol, J., Izakovic, M., and Mazur, M. (2006). Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 160, 1–40. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009
von Holtz, R. L., Fink, C. S., and Awad, A. B. (1998). beta-Sitosterol activates the sphingomyelin cycle and induces apoptosis in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 32, 8–12. doi:10.1080/01635589809514709
Vundru, S. S., Kale, R. K., and Singh, R. P. (2013). β-Sitosterol induces G1 arrest and causes depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential in breast carcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 13, 280. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-13-280
Wang, G. Y., Zhang, L., Geng, Y. D., Wang, B., Feng, X. J., Chen, Z. L., et al. (2022). β-Elemene induces apoptosis and autophagy in colorectal cancer cells through regulating the ROS/AMPK/mTOR pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 20, 9–21. doi:10.1016/S1875-5364(21)60118-8
Wang, M., Li, F., Li, X., and Zhang Z. E, L. (1992). Effects of ginseng volatile oil on cytochemical components of SGC-823 gastric carcinoma in cell culture. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 17, 110–112.
Wang, Q. (2016). Study on bioactive ingredients of saccharides, volatile oils and inorganic elements from Panax ginseng C. A. Mayer. Jilin University. [dissertation/master's thesis]. [JiLin].
Wang, Y., Zhu, H., Huang, W., Wu, Y., Zhu, L., Song, l., et al. (2015). Role of Panaxynol on inhibiting metastasis of human pancreatic carcinoma cell line SW1990 in vitro. J. Chin. J. Cancer Prev. Treat. 22, 1662–1666.
Wang, Z., Zhang, S., Xiao, Y., Zhang, W., Wu, S., Qin, T., et al. (2020). NLRP3 inflammasome and inflammatory diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 4063562. doi:10.1155/2020/4063562
Wang, Z. J., Nie, B. M., and Lu, H. Z. C. Y. (2006). Panaxynol induces neurite outgrowth in PC12D cells via cAMP- and MAP kinase-dependent mechanisms. Chem. Biol. Interact. 159, 58–64. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2005.09.003
Warren, J. R., and Marshall, B. (1983). Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1, 1273–1275. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92719-8
Wu, J. Z., Yi, J., Lin, R. H., and Ye, G. W. (1992). Comparative study on total volatile oil content and sugar content of fresh ginseng and red ginseng. J. J. Guiyang Med. Coll., 58–59.
Xie, L., Zhang, J., Yan, H., Cai, Y., and Xu, L. (2022). β-elemene induced apoptosis and senescence of triple-negative breast cancer cells through IGF1/IGF1R pathway. Tissue Cell 79, 101914. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2022.101914
Xie, Q., and Wang, C. (2022). Polyacetylenes in herbal medicine: a comprehensive review of its occurrence, pharmacology, toxicology, and pharmacokinetics (2014-2021). Phytochemistry 201, 113288. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113288
Xiong, X., Huang, G., and Huang, H. (2019). The antioxidant activities of phosphorylated polysaccharide from native ginseng. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 126, 842–845. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.266
Yamazaki, M., Hirakura, K., Miyaichi, Y., Imakura, K., Kita, M., Chiba, K., et al. (2001). Effect of polyacetylenes on the neurite outgrowth of neuronal culture cells and scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 24, 1434–1436. doi:10.1248/bpb.24.1434
Yang, J., Li, N., Wang, C., Chang, T., and Jiang, H. (2021). Ultrasound-homogenization-assisted extraction of polyphenols from coconut mesocarp: optimization study. Ultrason. Sonochem 78, 105739. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105739
Yang, Y. C., Wei, M. C., and Hong, S. J. (2014). Ultrasound-assisted extraction and quantitation of oils from Syzygium aromaticum flower bud (clove) with supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Chromatogr. A 1323, 18–27. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2013.10.098
Yasuda, M., Nishizawa, T., Ohigashi, H., Tanaka, T., Hou, D. X., Murakami, A., et al. (2009). Linoleic acid metabolite suppresses skin inflammation and tumor promotion in mice: possible roles of programmed cell death 4 induction. Carcinogenesis 30, 1209–1216. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp106
Yatham, L. N., Liddle, P. F., Shiah, I. S., Scarrow, G., Lam, R. W., Adam, M. J., et al. (2000). Brain serotonin2 receptors in major depression: a positron emission tomography study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 57, 850–858. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.57.9.850
Yeo, C. R., Yong, J. J., and Popovich, D. G. (2017). Isolation and characterization of bioactive polyacetylenes Panax ginseng Meyer roots. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 139, 148–155. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2017.02.054
Yun, J., Kim, B. G., Kang, J. S., Park, S. K., Lee, K., Hyun, D. H., et al. (2015). Lipid-soluble ginseng extract inhibits invasion and metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells. J. Med. Food 18, 102–108. doi:10.1089/jmf.2013.3138
Zarneshan, S. N., Fakhri, S., and Khan, H. (2022). Targeting Akt/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway by ginsenosides in neurodegenerative diseases: a mechanistic approach. Pharmacol. Res. 177, 106099. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106099
Zhai, B., Zhang, N., Han, X., Li, Q., Zhang, M., Chen, X., et al. (2019). Molecular targets of β-elemene, a herbal extract used in traditional Chinese medicine, and its potential role in cancer therapy: a review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 114, 108812. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108812
Zhang, S., Hu, Y., Zhao, Y., Feng, Y., Wang, X., Miao, M., et al. (2024). Molecular mechanism of Chang Shen Hua volatile oil modulating brain cAMP-PKA-CREB pathway to improve depression-like behavior in rats. Phytomedicine 130, 155729. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155729
Zhao, B., Lv, C., and Lu, J. (2019). Natural occurring polysaccharides from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer: a review of isolation, structures, and bioactivities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 133, 324–336. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.229
Zhao, Y., Sun, X., Zhang, T., Liu, S., Cai, E., and Zhu, H. (2021). Study on the antidepressant effect of panaxynol through the IκB-α/NF-κB signaling pathway to inhibit the excessive activation of BV-2 microglia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 138, 111387. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111387
Zheng, Y., Zhang, C., and Li, X. (1989). Separation and identification of volatile oil components of ginseng reed. J.Chinese Pharm. J., 5305.
Zhou, G., Wang, C. Z., Mohammadi, S., Sawadogo, W. R., and Yuan, C. S. (2023). Pharmacological effects of ginseng: multiple constituents and multiple actions on humans. Am. J. Chin. Med. 51, 1085–1104. doi:10.1142/S0192415X23500507
Zhou, P., Xie, W., He, S., Sun, Y., Meng, X., Sun, X., et al. (2019). Ginsenoside Rb1 as an anti-diabetic agent and its underlying mechanism analysis. Cells 8, 204. doi:10.3390/cells8030204
Zhu, H., Wang, W. J., Ding, W. L., and He, F.Li J. (2008). Effect of panaxydol on hypoxia-induced cell death and expression and secretion of neurotrophic factors (NTFs) in hypoxic primary cultured Schwann cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 174, 44–50. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.04.041
Zhu, X.-M., Hu, J.-N., Shin, J.-A., Lee, J.-H., and Lee, K.-T. (2010). Comparison of seed oil characteristics from Korean ginseng, Chinese ginseng (panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) and American ginseng (panax quinquefolium L.). J. Food Sci. Nutr. 15, 275–281. doi:10.3746/jfn.2010.15.4.275
Keywords: P. ginseng volatile oil, Phytochemistry, pharmacological effect, polyacetylenol, mechanism of action
Citation: Xu Y, Bian S, Shang L, Wang X, Bai X and Zhang W (2024) Phytochemistry, pharmacological effects and mechanism of action of volatile oil from Panax ginseng C.A.Mey: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1436624. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1436624
Received: 22 May 2024; Accepted: 25 July 2024;
Published: 13 August 2024.
Edited by:
Alessandro Venditti, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyReviewed by:
Neelam S. Sangwan, Central University of Haryana, IndiaLi-Wei Sun, The Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Bian, Shang, Wang, Bai and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xueyuan Bai, YmFpeHkxMjEyQDE2My5jb20=; Wei Zhang, d2VpemNhYXNAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yanan Xu
Yanan Xu Shuai Bian1,2†
Shuai Bian1,2† Xin Wang
Xin Wang Xueyuan Bai
Xueyuan Bai Wei Zhang
Wei Zhang