- Department of Respiratory Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
Caveolin-1 (Cav-1), a structural and functional component in the caveolae, plays a critical role in transcytosis, endocytosis, and signal transduction. Cav-1 has been implicated in the mediation of cellular processes by interacting with a variety of signaling molecules. Cav-1 is widely expressed in the endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and fibroblasts in the various organs, including the lungs. The Cav-1-mediated internalization and regulation of signaling molecules participate in the physiological and pathological processes. Particularly, the MAPK, NF-κB, TGFβ/Smad, and eNOS/NO signaling pathways have been involved in the regulatory effects of Cav-1 in lung diseases. The important effects of Cav-1 on the lungs indicate that Cav-1 can be a potential target for the treatment of lung diseases. A Cav-1 scaffolding domain peptide CSP7 targeting Cav-1 has been developed. In this article, we mainly discuss the structure of Cav-1 and its critical roles in lung diseases, such as pneumonia, acute lung injury (ALI), asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancer.
1 Introduction
Caveolae, a subset of lipid rafts with 50–100 nm in diameter, are the flask-shaped invaginations in the cell plasma membrane. There are three caveolin proteins, including caveolin-1 (Cav-1), Cav-2, and Cav-3. The genes Cav-1 and Cav-2 are located at chromosome 7q31.1, and Cav-3 is located at 3q25. The three caveolins share significant homology. The amino acid sequence of Cav-2 has approximately 38% of identity and 58% of similarity to that of Cav-1. Cav-3 has a higher homology with approximately 65% of identity and 85% of similarity (Williams and Lisanti, 2004). Cav-1 and Cav-2 are ubiquitously co-expressed in many mammalian cells, whereas Cav-3 can be found in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. Cav-2 is generally found associated with Cav-1 and serves as an accessory protein for correct caveola formation. Caveolins are the structural and functional components in the caveolae and play an important role in physiological and pathological events. Caveolins have been associated with transcytosis, endocytosis, and signal transduction (Anderson, 1998). Cavins are caveolae-associated proteins that include cavins 1–4 (Hill et al., 2008; McMahon et al., 2009).
Caveolae formation requires caveolins, cavins, EH-domain containing protein 2 (EHD2), pacsin2 (syndapin II), and lipids (cholesterol and sphingolipids). Cavin-1 is essential for the generation of the flask-shaped structure in caveolae. Caveolae are enriched in cholesterol, which is bound by the Cav-1 scaffolding domain (Hubert et al., 2020). The specific binding of cavins to lipids may drive the membrane curvature (Lundmark et al., 2024). Cav-1 and cavin-1 are believed to form the caveolae coat machinery required to bend the membrane into the flask-shaped structure (Liu et al., 2008). Cavin-1 stabilizes Cav-1 by inhibiting its internalization and lysosomal degradation, indicating the critical role of cavin-1 in mediating Cav-1 expression and caveolae formation (Meng et al., 2015). The interaction between Cav-1 and cavin-3 is not required for caveolae biogenesis but for caveolae surface stability (Mohan et al., 2015). Caveolae emerge as the critical sensors at the plasma membrane, and the compartmentalization of certain signaling molecules within caveolae may significantly improve the efficiency of signaling transduction. The importance of caveolae has been highlighted by the association between caveolae dysfunction and human diseases (Parton and del Pozo, 2013). One study shows that Cav-1 regulates lipid transport, inflammatory responses, and has atherogenic effects, indicating the critical role of Cav-1 in atherosclerosis development (Shu and Jin, 2023). Cav-1 has been involved in the initiation and progression of cognitive decline (Tang et al., 2021). The roles of Cav-1 in the development of cancer, neurodegeneration, glaucoma, cardiovascular diseases, and infectious diseases have been discussed (Gokani and Bhatt, 2022).
The localization of Cav-1 can be caveolae-dependent and -independent (Bhowmick et al., 2023). The intracellular membranes for Cav-1 localization include the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and late endosomal/lysosomal membranes. Therefore, Cav-1 might exhibit multiple biological activities independent of caveolae (Enyong et al., 2022). Caveolae are crucial factors for sensing and transducing mechanical forces. However, it is reported that Cav-1 exhibits deformability and mechanoprotection independent of caveolae by stabilizing non-caveolar invaginations-dolines, which are capable of responding to low-medium mechanical forces and impacting downstream mechanotransduction (Lolo et al., 2023). Non-caveolar Cav-1 has been associated with increased expression of VEGFA in lymphatic endothelial cells (Nassar et al., 2015). The expression of cavin-1 is absent in PC3 and LNCaP cells but abundant in DU145 cells. Cavin-1 deficiency leads to the abundance of Cav-1 and the absence of caveolae. Non-caveolar Cav-1 can be detected on the flat plasma membrane (Nassar et al., 2015). Cav-1 has been shown to mediate cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and survival (Dalton et al., 2023). It is suggested that lipid rafts/caveolae play a role in maintaining the self-renewal of embryonic stem (ES) cells. Treatment with Cav-1 siRNA and methyl-β-cyclodextrin induces the downregulation of octamer-binding protein 4 (Oct4), SRY-box transcription factor 2 (Sox2), Forkhead box D3 (FoxD3), RNA exonuclease 1 homolog (Rex1), G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (cyclin D1), and cyclin E and the reduction of the proliferation index in ES cells (Lee et al., 2010). Dysregulation of Cav-1 may result in the occurrence of pathophysiological processes and the development of diseases. Enhanced expression of Cav-1 has been associated with high levels of glycolysis and metastasis in melanoma and breast cancer cells (Díaz-Valdivia et al., 2022). Decreased expression of Cav-1 is observed in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Irisin, a myokine, has been reported to protect against osteoporosis development by up-regulating the expression of Cav-1 (Tao et al., 2024).
The incidence of lung diseases has increased in recent years due to altered lifestyles and environmental pollution, and lung diseases have become a major cause of death and disability worldwide (GBD Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators, 2020). The most common lung diseases include pneumonia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acute lung injury (ALI), pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis (PF), and lung cancer. Notably, COPD, asthma, and lung cancer rank among the top 10 causes of death (Levine and Marciniuk, 2022). Pneumonia, due to its high incidence and susceptibility to complications, poses a significant health concern. Particularly, the global pandemic of coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) has had a profound impact on human life and health since 2019 (Ocampo et al., 2024). Accumulating evidence suggests that precise and targeted medical interventions are important, necessitating a thorough understanding of the pathogenesis of lung diseases. Caveolae and Cav-1 are widely distributed in alveolar epithelium, airway, pulmonary artery smooth muscle, and fibroblasts, indicating their potential role in the pathophysiological alterations associated with lung diseases. For instance, caveolae and Cav-1 have been involved in the mediation of agonist-induced [Ca2+]i signaling and the hyperresponsiveness of airway smooth muscle (ASM) (Sathish et al., 2011). In this article, we primarily focus on discussing the critical roles of Cav-1 in lung diseases.
2 Methods of literature research
The related articles published up to April 2024 were collected from the databases, such as Pubmed Web of Science, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, and SpringerLink. The searched keywords included caveolin-1, inflammation, pneumonia, asthma, COPD, ALI, pulmonary hypertension, PF, and lung cancer.
3 Cav-1: structure and its roles in inflammation
3.1 The structure of Cav-1
Cav-1, a 178-amino acid protein, has three distinctive regions: a hydrophilic N-terminal domain (NTD, residues 1–101), a membrane-spanning region (residues 102–134), and a hydrophilic C-terminal domain (CTD, residues 135–178) (Ohi and Kenworthy, 2022) (Figure 1). In the NTD, there is an invariant structure FEDVIAEP stretch, which has been known as the caveolin signature motif (residues 68–75) (Scherer et al., 1996). There are only three cysteine (Cys) residues (Cys133, Cys143, and Cys156) that are located at the CTD, and the three Cys residues can be palmitoylated (S-acylation) (Figure 1), indicating that the CTD is linking to the membrane (Dietzen et al., 1995). Cav-1 has a caveolin scaffolding domain (CSD, residue 82–101), which may interact with and mediate the activity of various signaling molecules. For example, Cav-1 can interact with cholesterol due to the recognition consensus VTKYWFYR (residues 94–101) and mediate the cholesterol levels in mitochondria. It is reported that Cav-1 has two isoforms: Cav-1α (24 kDa) and Cav-1β (21 kDa). Both isoforms have a complete CTD, indicating that both can be localized within the caveolae. However, Cav-1β lacks an N-terminal-specific protein sequences (residues 1–21). This might be explained by the two alternate translational start sites (Met1 and Met32) (Scherer et al., 1995).
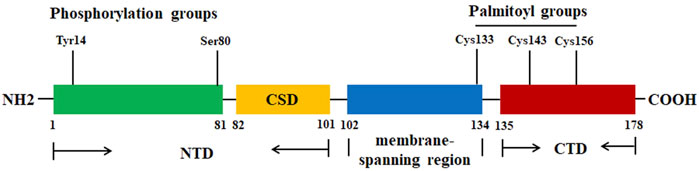
Figure 1. The protein structure of Cav-1. The Cav-1 protein has three regions: NTD (residues 1–101), membrane spanning region (residues 102–134), and CTD (residues 135–178). CSD (residue 82–101) is the region for Cav-1 to interact with various signaling molecules. The residues Tyr14 and Ser80 are the two phosphorylation sites. The residues Cys133, Cys143, and Cys156 can be palmitoylated.
Cav-1 is synthesized in the ER. Cav-1 has been reported to interact with itself to form a high-order oligomeric complex (approximately 350 kDa–400 kDa) comprised of 14–16 monomers. The presence of an ER export signal in the NTD promotes the release of Cav-1, which can be assembled into 8S complexes that accumulate in the ER exit sites. Next, Cav-1 can be further assembled into aggregates with higher molecular weight of 130–150 monomers in the Golgi (Hayer et al., 2010a). The accumulation of Cav-1 in the Golgi may lead to the loss of diffusional mobility, the occurrence of conformational changes, the association with cholesterol, and finally the assembly of 70S complexes (Hayer et al., 2010a). It is important to note that the oligomerization of caveolin might be the driving force for the assembly of caveolae (Fra et al., 1995). The NTD has been associated with the homooligomerization activity, which is independent of disulfide bond formation. Mutations in residues 1–21, 1–61, 71–101, 76–101, or 81–101 block the formation of high-order oligomers. However, it is interesting to find that GST-Cav-1α fusion and GST-Cav-1β fusion can co-migrate as high molecular mass oligomers in velocity gradients (Sargiacomo et al., 1995). Consistently, it is reported that the juxtamembrane region of Cav-1 is associated with the oligomerization activity (Couet et al., 1997a).
In addition, two phosphorylation sites Tyr14 and Ser80 (Figure 1) locate at the regulatory amino-terminal tail. Src-mediated phosphorylation of Cav-1 Tyr14 is associated with the spatial organization of Cav-1 within the oligomer, mediating the internalization (Zimnicka et al., 2016). Cav-1 Ser80 phosphorylation may affect its cellular localization within the ER, stimulate its secretory pathway, and contribute to its tumor-suppressive activity (Schlegel et al., 2001; Díaz et al., 2020). One study reports that binding of caveolin with heterotrimeric G-proteins and Src may lead to the suppression of their enzymatic activity and inhibition of signaling transduction. It has been shown that the interaction between CSD and caveolin-binding molecules (CBMs) may induce the inactivation of the signaling molecules. For example, Cav-1 may act as an inhibitor of kinases, such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and protein kinase C (PKC) (Couet et al., 1997b). However, the binding activity of Cav-1 may be independent of CSD-CBM interactions. Some molecules, such as steroid hormone receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, G-protein-couple receptors, and G-proteins, do not have the CBMs and can interact with Cav-1 (Bhowmick et al., 2023). When the levels of Cav-1 are abnormally enhanced, the accumulated Cav-1 can be ubiquitinated and subsequently degraded within endolysosomes (Hayer et al., 2010b). One study reports that LPS treatment promotes the binding of E3 ubiquitin ligase ZNRF1 to Cav-1 and induces its degradation. Interestingly, activation of the ZNRF1/Cav-1 signaling may lead to increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Lee et al., 2017).
Cav-1 can physically interact with various proteins via CSD and inhibit their activities (Van Krieken and Krepinsky, 2017). Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) catalyzes the O2-dependent degradation of heme to carbon monoxide (CO), free ferrous iron, and biliverdin IXα, playing an essential role in counteracting oxidative stress. HO-1 can bind to Cav-1, which exhibits an inhibitory activity against the enzymatic activity of HO-1. In addition, the core binding site of Cav-1 is available for HO-1 (Taira et al., 2011). One study shows that Cav-1 with deletion of the 101th residue (Δ101CSD peptide) can interact with HO-1 and disrupt the interaction between HO-1 and wild-type (WT) Cav-1. However, Δ101CSD peptide cannot enhance HO-1 activity but increase HO-1 mRNA expression. In addition, Δ101CSD peptide impairs the inhibitory activity of WT Cav-1 against the MAPK signaling and inflammatory responses (Jin et al., 2018). Structure-functional study shows that Phe92 is an essential residue for the inhibitory activity of Cav-1 against endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), and residue 90–99 in Cav-1 is the binding site for eNOS (Trane et al., 2014). It is reported that F92A-Cav-1 can abrogate the inhibitory effects of Cav-1 against eNOS and promote NO synthesis by disrupting their interaction (Bernatchez et al., 2011). Mechanically, F92A-Cav-1 increases the phosphorylation of AKT, which is one of the most prominent activators of eNOS. However, F92A-Cav-1 does not affect endogenous Cav-1 oligomerization and Cav-1 and eNOS distribution (Trane et al., 2015).
One study reports that CSD (residue 82–101) is split into three slightly overlapping shorter peptides (82–89, 88–95, and 94–101). Interestingly, all three peptides exhibit beneficial effects on bleomycin-treated mice. Both 82–89 and 88–95 peptides show inhibitory activity against fibrosis and microvascular leakage, improving ventricular functions. However, the 94–101 peptide merely decreases Collagen I expression (Reese et al., 2022). It has been reported that the GC-rich sequences (−372/−222 and −150/−91) in the mouse Cav-1 promoter are oxidative stress-responsive elements. Sp1 has been known to interact with the GC-rich boxes. Under oxidative stress, Sp1 can positively increase the promoter activity of Cav-1. Hydrogen peroxide treatment activates p38 MAPK, which upregulates Sp1-mediated Cav-1 expression in NIH 3T3 cells (Dasari et al., 2006).
3.2 The functional roles of Cav-1 in inflammation
Cav-1 has been associated with multiple cellular processes, such as immune responses, endocytosis, membrane trafficking, cellular signaling, and cancer progression (Shi et al., 2020) (Figure 2). Cholesterol is essential for forming and maintaining caveolae. Cav-1 can interact with free cholesterol and mediate cholesterol transport through a lipoprotein chaperone complex, which consists of Cav-1, cyclophilin A, cyclophilin 40, and HSP56. Cav-1 facilitates the uptake of cholesterol via this chaperone complex, and Cav-1 has been implicated in the transport of newly synthesized cholesterol from the ER to the plasma membrane (Lin et al., 2009). Caveolae present as a platforms for lipid-based signaling transduction through compartmentalizing and concentrating signaling molecules. Interestingly, Cav-1 exhibits a negative mediator of various cellular signaling pathways (Dessy et al., 2010). Cav-1 may recruit lipids and proteins to caveolae and negatively mediate the transduction of signaling pathways, which include tyrosine kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases, Gα subunits, GTPases, c-Src, H-Ras, eNOS, and components of the MAPK pathway (Feng et al., 2013). The interaction between Cav-1 and different lipid bodies (lipid rafts, lipid droplets, cholesterols, sphingolipids, and fatty acids) has been reviewed (Bhowmick et al., 2023).
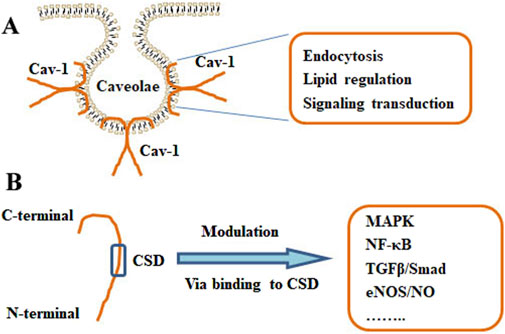
Figure 2. Structure and functions of Cav-1. (A) The localization of Cav-1 in caveolae. The primary actions of Cav-1 include endocytosis, lipid regulation, and signaling transduction. (B) The monomer of Cav-1 and the Cav-1 scaffolding domain (CSD) were shown. Cav-1 can modulate various pathways, such as MAPK, NF-κB, TGFβ/Smad, and eNOS/NO signaling, via binding to the CSD.
It has been reported that Cav-1 plays a role in inflammatory responses. Cav-1 can decrease the production and release of various inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-2, IL-4, IL-12, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted (RANTES) (Qin et al., 2016). Mechanically, caveolae provide an ideal platform for signaling transduction. It has been demonstrated that many different types of receptors or signaling molecules are associating with caveolin proteins (Pike, 2005; Chidlow and Sessa, 2010). Many receptors, such as MAPK pathway components, receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), and GTPase have been sequestered within caveolae by interacting with Cav-1 (Anderson et al., 1992; Schnitzer et al., 1996). Cav-1 can enhance the phosphorylation of p38 but suppress that of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), Akt, and ERK1/2. SB203580, an inhibitor of p38 MAPK, can abolish the effects of Cav-1 on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses (Wang et al., 2006). Cav-1 silence may block IL-1β-induced activation of p38 MPAK, reducing tube formation and migration of endothelial cells (ECs) (Jagielska et al., 2012). COX-2, a mediator of inflammation, is localized in the ER, nuclear envelope, cavelae-like structures. The interacting of COX-2 and Cav-1 in the ER may induce the degradation of COX-2. Knockdown of Cav-1 may enhance the protein levels of COX-2 (Chen S. F. et al., 2010). The eNOS/NO signaling pathway also plays a critical role in inflammatory responses. The associating of Cav-1 with eNOS can inhibit the release of eNOS and the synthesis of NO (Bucci et al., 2000).
Cav-1 can interact with toll-like receptors (TLRs) to mediate phagocytosis and cell activation (Sivanantham et al., 2023). LPS can recognize and activate TLR4, leading to the recruitment of the adaptor MyD88, IL-1R-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), IRAK4, and TRAF6 and the activation of TAK1. Consequently, TAK1 activation can induce the stimulation of NF-κB and increase the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, TNFα, and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP). It is reported that Cav-1 interacts with TLR4 and inhibits the assembly of TLR4 complex with MyD88. Interestingly, the binding motif for Cav-1 in murine TLR4 (739FIQSRWCIF747) has been identified. W744A mutation in TLR4 may abolish the interaction of Cav-1 with TLR4 (Wang et al., 2009). Another study shows that TLR4-mediated recruitment of MyD88 may induce Cav-1 Tyr14 phosphorylation, IκB degradation, and translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus (Jiao et al., 2013). Recently, it is reported that oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDLs) may disrupt the eNOS/iNOS balance by mediating the HGMB1/TLR4/Cav-1 signaling, leading to the impairment of autophagic/apoptotic responses in vascular and nonvascular cells (Gliozzi et al., 2019). The discrepancy of the regulatory effects of Cav-1 on the TLR4 signaling might be associated with many factors, such as cell lines and micro-environment. Thus, more efforts are still needed.
Caveolae and caveolins are also expressed in macrophages. In LPS-treated murine alveolar and peritoneal macrophages, Cav-1 can decrease the production of TNFα and IL-6 and increase the generation of IL-10 (Wang et al., 2006). Cav-1 deletion has been associated with enhanced inflammatory responses, decreased phagocytic activity of macrophages, and increased superoxide release (Yuan et al., 2011). Cav-1 expression and intracellular cholesterol levels are mutually mediated to maintain cholesterol homeostasis. In the pathological processes of atherosclerosis, macrophages derived from monocytes are transformed into lipid-loaded cells via uptake of lipoproteins, especially ox-LDL. It is reported that Cav-1 interacts with scavenger receptor-BI (SR-BI), which regulates the transfer of lipid from lipoproteins into cells via selective cholesterol. Co-expression of Cav-1 and SR-BI can lead to increased uptake of selective cholesterol in macrophages (Matveev et al., 1999; Puddu et al., 2023). In the Cav-1-deleted mice, the levels of free cholesterol in peritoneal macrophages are decreased and the expression of ABCA1 in macrophages is also decreased. Cav-1 deficiency decreases the synthesis of free cholesterol (Lin et al., 2007; Qin et al., 2016). In addition, macrophages derived from Cav-1-deleted mice show severe LPS-induced inflammatory responses (Medina et al., 2006). The co-localization of TLR4 with Cav-1 in caveolae of peritoneal macrophages indicates a connection between Cav-1-regulated cellular cholesterol efflux and the inflammatory responses (Wang et al., 2009). PPARγ and RXR may promote the expression of Cav-1, SR-BI, and ABCA1. Activation of PPARγ and/or RXR leads to upregulation of Cav-1 expression and downregulation of NF-κB, STAT, and AP-1 in macrophages (Luo et al., 2010).
Sterile inflammation is a process that reside cells sense pro-inflammatory signals, release extracellular mediators, and then recruit circulating immune cells that trigger and escalate the inflammatory responses. Various cell types, including mesothelial cells, endothelial cells, and immune cells (such as macrophages) may promote the initiation and progression of sterile inflammation. However, the exact mechanisms are not fully understood (Su et al., 2024). Endosomal TLRs recognize self-derived nucleic acids via damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in cases of apoptosis or cellular damage, triggering sterile inflammation. TLR-3, -7, -8, and -9 are located inside endosomes. TLR-3 recognizes double-stranded RNA, TLR-7 and TLR-8 detect single-stranded RNA, and TLR-9 identifies DNA (Zhou et al., 2020). However, LPS-induced endocytosis takes TLR4 to early endosome, where it recognizes endosomal LPS to activate MyD88-independent inflammatory responses (Kawai and Akira, 2010). Flotillin-1, a marker of membrane rafts, is essential for TLR signaling. Knockdown of flotillin-1 decreases TLR3-regulated inflammatory responses. Flotillin-1 and Cav-1 co-localize within the caveolae. The interaction between flotillin-1 and Cav-1 may facilitate the transport of TLR3-ligands to its intracellular receptor and activates inflammatory TLR3 signaling (Fork et al., 2014). Lumican is an ECM protein associated with collagens. Lumican can attach to Cav-1 and the TLR co-receptor CD14 and promote TLR4-but restrict TLR9-mediated inflammatory responses in macrophages (Maiti et al., 2021). During ischemia-reperfusion injury, endothelial DAMPs can decrease the expression of Cav-1 and eNOS and aggravate endothelial barrier disruption (Kumphune et al., 2024).
4 The roles of Cav-1 in lung diseases
4.1 Pneumonia and acute lung injury (ALI)
Pneumonia is a leading cause of global pediatric morbidity and mortality. Bacterial infections have been associated with activation of innate and adaptive immunity, regulation of antigen presentation, pathogen recognition, and phagocytosis. Cav-1 is required for pathogen invasion of host cells. However, Cav-1 negatively modulates inflammatory responses (Zaas et al., 2009). During infection, lung epithelial cells directly recognize the pathogen-associated molecular patterns via TLRs and trigger the innate immune responses for pathogen clearance (Grainge and Davies, 2013). ALI, a clinical syndrome of acute respiratory failure, is associated with acute lung inflammation, damaged alveolar-capillary barrier, airway edema, and abnormal gas exchange (Jones and Minshall, 2022). The potential mechanisms of ALI pathogenesis are still unclear. Cav-1 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of ALI. A bioinformatics study using GO, KEGG, and PPI analysis shows that the Cav-1/NF-κB signaling is one of the most effective targets for ALI prevention (Qu et al., 2022).
In Cav-1 knockout mice, increased lung inflammatory responses and higher mortality rates are related to the enhanced STAT3/NF-κB signaling (Yuan et al., 2011) (Table 1) (Figure 3). It has been reported that Cav-1 can suppress LPS-induced inflammatory responses, microvascular barrier breakdown, and edema formation by inhibiting the NF-κB and eNOS signaling pathways (Garrean et al., 2006). One study shows that plasma albumin leakage, infiltration of immune cells, and levels of IL-6/IL-6R and p-TGFβ/p-Smad2/3 in LPS-treated Cav-1 knockout mice are significantly elevated. In contrast, the expression of BMPRII and the uncoupling of eNOS are reduced in LPS-treated ECs from Cav-1 knockout mice (Oliveira et al., 2017) (Table 1). TNFα contributes to various inflammatory conditions, including acute respiratory distress syndrome and COPD. TNFα plays a critical role in the activation of the NF-κB signaling, which can be mediated by the PI3K/AKT and p44/42 MAPK signaling pathways. TNFα acts as a ligand of TNF receptor (TNFR), which includes TNFR1 and TNFR2. In TNFR knockout mice, ozone-induced formation of the TNFR adaptor complex is attenuated, and activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways is suppressed (Cho et al., 2007). Ozone inhalation significantly induces TNFα expression and increases the PI3K/AKT and p44/42 MAPK signaling pathways, which can be negatively regulated by Cav-1 in alveolar macrophages (AMs) (Fakhrzadeh et al., 2008) (Table 1).
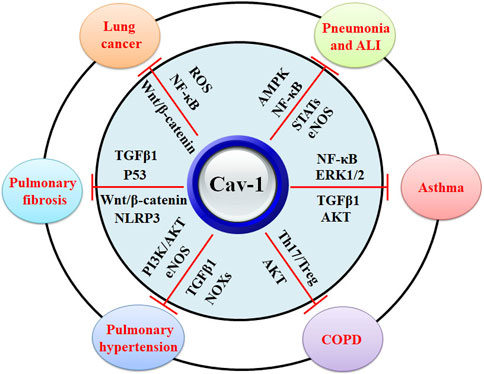
Figure 3. The biological functions of Cav-1 in protection against lung diseases. Cav-1 exhibits protective effects against pneumonia, ALI, asthma, COPD, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancers. The potential mechanisms might be associated with the inhibitory activity of Cav-1 against MAPK, NF-κB, STATs, eNOS, ERK1/2, TGFβ1, Th17/Treg disruption, NOXs, AKT, Wnt/β-catenin, and ROS.
Streptococcus pneumonia has become a major cause of community-acquired pneumonia. Although effective antibiotics have been advanced, pneumonia-associated morbidity and mortality have increased worldwide (Nishimoto et al., 2020). Pneumolysin (PLY), a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin (CDC), is a bacterial pore-forming toxin and primary virulence factor, affecting the plasma membrane homeostasis in the endothelial cells and being involved in all stages of pneumococcal diseases. It has been reported that Cav-1 and CSD peptide can protect the endothelial barrier from the disruption induced by PLY by promoting the endocytosis of damaged membrane (Batori et al., 2022). Klebsiella pneumoniae is the 3rd most commonly separated microorganism from patients with bacterial sepsis. In Cav-1 knockout mice, the infection of K. pneumoniae significantly decreases survival rate and increases pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Cav-1 exhibits protective effects against K. pneumoniae infection by mediating the signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5)/GSK-3β/β-catenin/AKT signaling pathway (Guo et al., 2012) (Table 1).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) infection increases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in alveolar macrophages. In Cav-1 knockout mice, the sensitivity to P. aeruginosa increases, the mortality rate is enhanced, and the inflammatory responses are elevated. These indicate the important contribution of Cav-1 to the innate host immunity to P. aeruginosa (Gadjeva et al., 2010). Cav-1, a common component of extracellular vesicles (EVs), is exclusively expressed in the miRNA-rich EVs, which are derived from lung epithelium. The miRNA-rich EVs have been associated with P. aeruginosa-induced inflammasome activation, neutrophil recruitment, and M1-macrophage polarization (Lee et al., 2019). Flagellar hook protein E (FlgE) in P. aeruginosa has been reported to stimulate human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs), enhance the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and promote the Th2-biased humoral responses to ovalbumin. However, the knockdown of Cav-1 abrogates FlgE-induced inflammation and extracellular regulated protein kinase1/2 (ERK1/2) activation (Shen et al., 2017) (Table 1). Alpha-toxin (Hla), a major virulence factor of staphylococcus aureus, plays a critical role in pneumonia. Hla can interact with the cell surface of eukaryotic host cells and form heptameric transmembrane pores. Cav-1 acts as a pore-stabilizing factor and facilitates the binding of Hla to its receptor α5β1 integrin. However, both Cav-1 and α5β1 integrin are not associated with toxin sensitivity (Möller et al., 2020).
Gram-positive infection-induced ALI is characterized by impaired endothelial cell (EC) barrier integrity and extensive permeability, which is associated with the excretion of cholesterol-dependent cytolysins, such as PLY and listeriolysin (LLO). It has been reported that LLO treatment can induce Ca2+-activated PKCα and stimulate the dissociation of Cav-1 and Hsp90 from eNOS, uncoupling eNOS and promoting NO synthesis. However, Cav-1 peptide may block the effects of LLO-induced eNOS signaling in human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVECs) (Chen et al., 2014b) (Table 1). However, one study reports that the upregulated expression of Cav-1 in polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) is associated with PMN activation, adhesion, and migration, stimulating lung inflammation and vascular injury (Hu et al., 2008). This discrepancy might be associated with the different cell lines and microenvironment.
Cav-1 has been associated with the internalization of some viruses, such as the BK virus (Moriyama et al., 2007) and Simian virus-40 (Pelkmans et al., 2001). It has been reported that there are several caveolin-binding sites in coronavirus (Padhan et al., 2007), supporting the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and lung injury. It has been reported that some coronavirus family members can cause acute alveolar damage by stimulating the Cav-1 signaling. However, they do not enter the lung cells in a caveolin-dependent manner (Buckley et al., 1998). During viral infection, the lung epithelial cell injury induces an accumulation of TGFβ1, which can be negatively mediated by Cav-1. In the lung samples from COVID-19-infected patients, the expression of Cav-1 is downregulated, and the transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) signaling pathway is enhanced (Vaz de Paula et al., 2021) (Table 1).
During lung injury, pulmonary surfactant protein C (SP-C) expression is decreased in type II alveolar epithelial cells (AECs). Decreased expression of SP-C contributes to cell apoptosis by enhancing the expression of p53 and activating the Src/Cav-1 signaling in AECs (Puthusseri et al., 2017). Sirt1 exhibits protective activity against LPS-induced ALI by inhibiting inflammatory responses. The Sirt1 agonist SRT1720 can upregulate Cav-1 expression and downregulate STAT3, TLR4, TNFα, and IL-6 expression in rats (Tong et al., 2023) (Table 1). Mechanical ventilation can induce ventilator-induced lung injury. Ropivacaine, an amide-linked local anesthetic, exhibits anti-inflammatory effects in ALI. It is reported that ropivacaine may decrease pulmonary edema, leukocyte infiltration, and vascular hyperpermeability by inhibiting the Src/Cav-1 signaling (Piegeler et al., 2014). The CpG motif in bacterial DNA has been associated with pathogen-induced inflammation. It is reported that the synthetic CpG oligonucleotide (ODN) can promote the secretion of CCN1, which stimulates host immune responses via mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathways in epithelial cells (Dalpke et al., 2002) (Figure 3). Mechanically, CpG ODN induces ER stress, enhances the phosphorylation of Src and Cav-1, and increases the secretion of CCN1 by modulating the interaction of p-Cav-1 and the CCN1 IGFbp domain (Moon et al., 2015) (Table 1).
Oxidative stress promotes the pathogenesis of sepsis-triggered ALI. Cav-1 and adiponectin are important modulators of oxidative stress. In Cav-1 and adiponectin double knockout mice, LPS dramatically triggers oxidative stress, nitrative stress, inflammatory responses, lung vascular permeability, and mouse mortality rate. Treatment with a superoxide scavenger MnTMPyP may rescue LPS-induced ALI. This indicates the critical role of Cav-1 and adiponectin in negatively mediating oxidative/nitrative stress and inflammation (Cai et al., 2014). Intestinal ischemic reperfusion (I/R) can induce ALI. Dexmedetomidine (Dexm), a highly selective alpha2-noradrenergic receptor (α2AR) agonist, can alleviate pulmonary inflammation after intestinal I/R by up-regulating Cav-1 expression and inhibiting the p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways (Xu et al., 2021) (Table 1). Dexm also exhibits protective effects by mediating the Cav-1/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in ALI induced by LPS (Liu et al., 2019) or heatstroke (Geng et al., 2019).
4.2 Asthma
Asthma is associated with paroxysmal/persistent wheezing, dyspnea, and coughing, and these might be due to inflammation, hyperresponsiveness, and remodeling in the airway. Airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) are the main effector for airway remodeling, and the proliferation and hypertrophy of ASMCs may result in irreversible pathological alterations in the airway (Yuan et al., 2024). ASMCs contain caveolae that expression constituent protein Cav-1 and Cav-2. It has been reported that the expression of Cav-1 in endobronchial biopsies of asthmatic patients is decreased (Bains et al., 2012). Decreased Cav-1 expression has been involved in airway diseases and contributed to airway hyperresponsiveness and remodeling. In hyperoxia-exposed animals, downregulated Cav-1 expression in ASM has been found, and intraperitoneal injection of CSD peptide can ameliorate hyperoxia-induced pathophysiological alterations (Vogel et al., 2019) (Table 1). One study shows that Cav-1-knockout mice have significantly high proliferation marker expression and airway hyperresponsiveness and remodeling (Aravamudan et al., 2012).
Cav-1 acts as a negative regulator of cellular signaling, such as the ERK1/2 signaling (Mao et al., 2022). Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling mediates the secretion, proliferation, and hyperresponsiveness of ASMCs. Inhibition of the ERK1/2 signaling can be the therapeutic strategy for asthma treatment. Roxithromycin (RXM) has been reported to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced SMC proliferation by up-regulating Cav-1 expression and inhibiting the ERK1/2 signaling (Pei et al., 2016). TGFβ1 secretion is significantly enhanced in asthmatic ASMCs, and it is positively correlated with ASMC proliferation. However, RXM inhibits TGFβ1-induced ASMC proliferation by up-regulating Cav-1 expression and down-regulating p-ERK1/2 and p-AKT expression (Dai et al., 2014) (Table 1) (Figure 3).
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), a gastrointestinal hormone, participates in various biological effects, including smooth muscle relaxation, modulation of immune response, and immune homeostasis maintenance (Gonzalez-Rey and Delgado, 2007). VIP suppresses airway remodeling in vivo and inhibits IL-13-induced ASMC proliferation by up-regulating Cav-1 expression and decreasing the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (Wang et al., 2018). Sprouty2 (Spry2) is a well-known mediator of Ras/ERK signaling and a positive regulator of CD4+ T cell function and type II immunity. In Spry2-knockout mice, ERK1/2 activation, T-cell differentiation, and cytokine secretion are abrogated. Spry2 stimulates T-cell-driven asthma by increasing the levels of Th2 cytokines. Mechanically, Spry2 promotes ubiquitin proteasome-mediated degradation of Cav-1, which binds and enhances CSK activity. Spry2 deficiency increases Cav-1/CSK association, enhances CSK/LCK interaction, abrogates ERK1/2 activation, and diminishes TCR-induced responses in CD4+ T cells (Sripada et al., 2021) (Table 1).
MUC5AC, a major mucin glycoprotein, is responsible for the viscoelastic property of mucus and can be hypersecreted in asthmatic subjects. VEGF expression is correlated with inflammation and airway blood vessel remodeling in asthma. VEGF can enhance the expression of MUC5AC by stimulating VEGFR2 (Kim et al., 2020). VEGFR2 and Cav-1 are co-localized on caveolae, and Cav-1 may negatively regulate the VEGFR2 signaling (Wu et al., 2013). Glucocorticoids (GCs), such as dexamethasone (Dex), are the first-line drugs for treating airway inflammation in asthmatic patients. It has been reported that Dex decreases VEGF-induced MUC5AC expression in PBECs by up-regulating Cav-1 expression and increasing the interaction between Cav-1 and VEGFR2 (Kim S. H. et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2020). Licochalcone A, a chalcone from licorice root, has been shown to suppress ASM cell proliferation by inhibiting the activation of VEGF, VEGFR2, and ERK1/2 and blocking the downregulation of Cav-1 expression (Kim et al., 2017).
However, another study shows that MUC5AC expression is mediated by NF-κB, which can be stimulated by intracellular Ca2+ signaling. Cav-1-containing lipid raft aggregation is involved in Ca2+ influx, NF-κB activation, and MUC5AC expression in bronchial epithelial cells (Xia et al., 2017). Cav-1 is an important mediator of IgE-dependent store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) and promotes Orai1 expression. MS4A gene family is clustered around 11q12-13, a region associated with allergy and asthma susceptibility. MS4A4A has been reported to enhance PLCγ1 phosphorylation, SOCE, and degranulation by interacting with Cav-1 in human mast cells (Arthur et al., 2020). The pro-inflammatory cytokine TNFα can increase agonist-induced [Ca2+]i responses in ASM. Knockdown of Cav-1 decreases the responses of [Ca2+]i to histamine and blocks TNFα-triggered [Ca2+]i responses in ASM (Sathish et al., 2014). In addition, the knockdown of Cav-1 decreases caveolar and Orai1 expression and blunts SOCE in TNFα-treated ASM (Sathish et al., 2012). Consistently, Cav-1 siRNA transfection blocks the amplitude and frequency of arachidonic acid (AA)-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations in human ASM (Thompson et al., 2014). One study shows that the expression of Src and p-Cav-1 Tyr14 in toluene diisocyanate (TDI)-induced asthma mice is significantly increased. Inhibition of the Src/Cav-1 axis and RAGE expression can improve the redistribution of β-catenin from the membrane to cytosolic compartments, attenuating TDI-induced airway inflammation (Zhao et al., 2018). TDI exposure upregulates the expression of autotaxin (ATX) and its major product lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Interestingly, Cav-1 is essential for the induction of ATX, but not IL-1β, by TDI (Broström et al., 2018).
It has been reported that Cav-knockout mice develop increased hyperresponsiveness and thickness of the subepithelial layers (Gabehart et al., 2013). Increased extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition contributes to airway remodeling. It is reported that treatment with CSD peptide may abrogate hyperoxia-induced ECM alterations by maintaining the balance between matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (TIMPs) in human fetal ASMCs (Vogel et al., 2017). Upregulated expression of GATA-6 promotes airway inflammation and remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma. Down-regulation of GATA-6 decreases ovalbumin (OVA)-induced inflammation, infiltration, mucus production, and MMPs (MMP-2 and MMP-9) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAMTSs). However, the expression of Cav-1 is inversely related to the abundance of GATA-6 in mice with asthma (Fang et al., 2016) (Table 1). Consistently, Roxithromycin can decrease the thickness of the bronchial wall and bronchial smooth muscle cell layers and the phosphorylation of p42/p44 MAPK and increase the expression of Cav-1, suppressing airway remodeling in rats (Wu et al., 2015).
4.3 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the third leading cause of death, is characterized by airflow limitations due to chronic bronchitis and alveolar emphysema, while no effective treatments are available to reduce the mortality or inhibit the pathological progression due to a lack of full understanding the underlying mechanisms. The 3′-untranslated region single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the Cav-1 gene loci rs8713 and rs1049337 have been reported to be related to a risk of pulmonary hypertension in patients with COPD (Li et al., 2019). Consistently, the expression of Cav-1 in medial smooth muscle cells of pulmonary arteries in patients with COPD has been reported to be correlated with pulmonary hypertension (Huber et al., 2009). Multiple immune cells, such as CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, and inflammatory cytokines have been implicated in the immunopathogenesis of COPD. The roles of T helper 17 (Th17) cells and regulatory T (Treg) cells in the development of COPD have been reviewed (Ma et al., 2023). Hsp70 plays a role in inflammation and innate immunity response and contributes to the conversion of Treg cells into Th17 cells (Guo et al., 2018). In COPD patients, the expression of Cav-1 is decreased. Cav-1 disrupts the balance between Th17 and Treg cells by mediating Hsp70 expression (Figure 3). In addition, Cav-1 overexpression may lead to an increase in Hsp70 and Th17 levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (Zhang et al., 2023a) (Table 1).
Cigarette smoke (CS) exposure has become a risk factor for the pathogenesis of COPD. In CS-exposed airway epithelial cells (AECs) and type II alveolar epithelial (AT2) cells, the expression of Cav-1, p53, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is significantly upregulated. Treatment with a seven amino acid CSD peptide (CSP7) can decrease mucus hypersecretion in CS-exposed AECs (Das et al., 2023). CS extract (CSE) can enhance MUC5AC expression and increase EGFR and AKT phosphorylation levels in 16HBE cells. Cav-1 knockdown can abrogate CSE-induced up-regulation of MUC5AC, p-EGFR, and p-AKT expression (Yu et al., 2015) (Table 1). Autophagy-related factor LC3B has been associated with CS-induced lung epithelial cell death. Cav-1 deficiency can cause higher levels of autophagy and apoptosis in CS-treated mouse lungs (Chen Z. H. et al., 2010). Cav-1 deficiency in lung fibroblasts can suppress CS-induced premature senescence by inactivating the ATM/p53/PP2A-C signaling pathway (Volonte and Galbiati, 2009; Volonte et al., 2009). Treatment of bronchial chondrocytes with IL-1β can generate a stable COPD-related tracheobronchomalacia (TBM) cell model. The Tiao-bu-fei-shen (TBFS) formula, a traditional Chinese medicine, can significantly reduce inflammatory responses and cell apoptosis by down-regulating the Cav-1/p38 MAPK signaling pathway (Zhou et al., 2022) (Table 1).
4.4 Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is associated with high mean pulmonary arterial pressure (more than 25 mmHg at rest) and pulmonary vascular resistance (more than 3 Wood units). Endothelial dysfunction, pulmonary vasoconstriction, and vascular remodeling are the main characteristics, and they may lead to increased pulmonary artery pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy, right heart failure, and premature death (Zaiman et al., 2005). Many signaling molecules, such as endothelial NO synthase (eNOS), VEGF receptor, prostacyclin receptors, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), and TGFβ, have been implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension (Chettimada et al., 2015) (Figure 3). The expression of these molecules may be mediated by Cav-1. In addition, one study reports that Cav-1 deficiency is associated with an increase in collagen content and artery stiffness, promoting the development of pulmonary hypertension (Moreno et al., 2021) (Table 1). The critical roles of Cav-1 in the development of pulmonary hypertension have been comprehensively reviewed in recent years (Chettimada et al., 2015; Mathew, 2021).
Nitro oxide (NO), synthesized by eNOS, plays an important role in cardiovascular homeostasis. Genetic deletion of eNOS may lead to various cardiovascular phenotypes, such as elevated blood pressure, impaired angiogenesis, and abnormal vascular remodeling (Fernández-Hernando et al., 2006). It has been reported that the interaction between eNOS and caveolin-1 in caveolae leads to enzyme inhibition of eNOS. Upon stimulation, eNOS is translocated from the caveolae to the cytoplasm where it produces NO. Chlamydia pneumoniae, a Gram-negative bacterium, infects epithelial cells in the respiratory tract. C. pneumoniae can colocalize with eNOS, interfere with its trafficking from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane, and inhibit NO synthesis in AECs (Mueller and Wolf, 2015). ECs synthesize low levels of NO, which maintains vessel homeostasis. Inflammation contributes to the dysfunction of ECs and affects the eNOS/NO signaling. The absence of Cav-1, hyper-activation of eNOS, and impairment of PKG activity may lead to vascular damage and remodeling and the development of pulmonary hypertension (Zhao et al., 2009) (Table 1).
Inflammation can disrupt the alveolar endothelial barrier and promote pulmonary microvascular permeability, leading to the development of ALI. Pravastatin, an inhibitor of HMG CoA reductase, exhibits anti-inflammatory activity. It is reported that pravastatin suppresses sepsis-induced inflammatory responses and apoptosis in LPS-treated pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) by mediating the Cav-1/eNOS signaling pathway (Ren et al., 2021). The expression of STAT and PI3K/AKT is constitutively activated in PAECs. Cav-1 deficiency induces the JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways and activation of type I inflammatory responses. Cav-1 silence also promotes AKT-induced phosphorylation of NOS3 Ser1177. Knockdown of NOS3 can abrogate the activation of STAT and AKT in PAECs (Gairhe et al., 2021) (Table 1).
BMP2 receptor (BMPR2) interacts with Cav-1 in the caveolae, and it is commonly mutated in pulmonary hypertension. Decreased BMPR2 signaling contributes to the hyper-activation of the TGFβ pathway, switching from the protective p-Smad1/5/8 signaling to the p-Smad2/3 pathway in pulmonary vascular cells (Erewele et al., 2022). In Cav-1 knockout mice, the localization of BMPR2 at the plasma membrane is attenuated, the phosphorylation of Smad1/5/9 is decreased, and the BMP/Smad signaling is inhibited. Cavin-1 competitively attenuates the interaction of Cav-1 with BMPR2 and inhibits the BMP/Smad signaling (Tomita et al., 2024). Consistently, Cav-1 depletion in ECs is also associated with pulmonary hypertension in hypoxia-treated rats. Cav-1 depletion reduces BMPR22 expression and increases the TGFβ/Smad2/3 signaling in the lung (Oliveira et al., 2019). In BMPR2+/R899X mice, the expression of Cav-1 is decreased, and the eNOS/NO signaling is increased in the lung. In addition, the pulmonary TGFβ levels are increased (Erewele et al., 2022). Cav-1 is negatively associated with the TGFβ/Smad signaling molecules and inhibits the phosphorylation of TGFβ and Smad2/3. Abnormal expression of Cav-1 may lead to dysregulation of the TGFβ/Smad signaling and alterations of the extracellular matrix (Le Saux et al., 2008). DJ-1/park7 is a multifunctional protein implicated in several biological activities. DJ-1 has been reported to ameliorate hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in vivo and in vitro by up-regulating Cav-1 expression and inhibiting the TGFβ1/Smad2/3 signaling (Gao et al., 2017).
The influx of Ca2+ is mediated by transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) in ECs. It has been reported that the absence of both TRPV4 and Cav-1 in mice can decrease pulmonary arterial pressure. Cav-1 is colocalized with NOX1 and iNOS, which induce the generation of the oxidant molecule peroxynitrite and promote the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension (Daneva et al., 2021). The activation of PPARγ by the specific agonist GW1929 is Cav-1-dependent, and the knockdown of Cav-1 abrogates the upregulation of GW1929 on PPARγ expression. GW1929 significantly decreases the expression of the proliferative mediators and increases the apoptosis-related factors in hypoxia-treated pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) (Yang et al., 2018) (Table 1). However, one study shows that the ubiquitin-proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (BTZ) can ameliorate hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by promoting the degradation of Cav-1, which mediates the SOCE/[Ca2+]i signaling in PASMCs (Wang et al., 2021).
4.5 Pulmonary fibrosis
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), the most common interstitial lung disease, is characterized by progressive lung scarring due to loss of epithelial regeneration induced by chronic lung injury, replicative senescence, and type II alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis. Current anti-fibrotic therapies cannot cure IPF but slow down its progression. The release of pro-fibrotic mediators, the activation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, and the secretion of ECM proteins lead to the pathogenesis of IPF (Glassberg, 2019). TGFβ has been reported to be implicated in the fibrogenic process. More specifically, TGFβ stimulates the differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and mediates the remodeling of ECM (Vaz de Paula et al., 2021). The expression of Cav-1 is negatively correlated with the TGFβ signaling in pulmonary fibrosis (PF) development (Xing et al., 2017) (Table 1) (Figure 3). Cav-1 has become a therapeutic target for PF treatment, and Cav-1 scaffolding domain peptides (CSPs) have been developed. The full-length CSP (DGIWKASFTTFTVTKYWFYR) can inhibit AEC apoptosis and suppress fibrotic lung fibroblast activation, attenuating bleomycin-induced PF. CSP7 (FTTFTVT), a seven-amino acid fragment of CSP, exhibits anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting the TGFβ signaling and restoring the expression of p53 (Nagaraja et al., 2018; Marudamuthu et al., 2019). The critical roles of CSP7 in protecting against fibrotic lung diseases have been comprehensively reviewed (Shetty and Idell, 2023).
Excessive collagen content in ECM may result in fibrosis development. Chemoattractant receptor homologous molecule expressed on TH2 cells (CRTH2), a receptor for prostaglandin D2, has been transported to the ER membrane in a Cav-1-dependent manner. CRTH2 deficiency promotes collagen synthesis in fibroblasts and increases the risk of fibrosis (Zuo et al., 2021) (Table 1). Fyn kinase has been implicated in the TGFβ signaling, and Cav-1 is colocalized with Fyn in the caveolae. Dysregulation of the Fyn/TGFβ signaling is involved in the impairment of alveolar barrier function and the development of PF (Menzel et al., 2022). Loss of Cav-1 is associated with reduced alveolar barrier functions and fibrosis-like alterations of the lung parenchyma. Overexpression of Cav-1 protects against PF by suppressing the expression of inflammasome NLRP3 and IL-1β (Lin et al., 2019). The mTOR signaling plays a key role in the pathogenesis of IPF. In Sftpc-mTORSL1+IT transgenic mice, bleomycin treatment promotes severe fibrotic alterations. mTOR activation up-regulates the expression of ANGPTL4, downregulates the expression of Cav-1, and promotes tight junction vulnerability and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Saito et al., 2020). A long non-coding RNA DNM3OS has been verified as a downstream effector of the TGFβ signaling in promoting myofibroblast activation and PF development. DNM3OS can be further processed into three distinct microRNAs, namely, miR-199a-5p, miR-199a-3p, and miR-214-3p. It has been demonstrated that miR-199a-5p promotes PF in a Cav-1-dependent manner (Savary et al., 2019) (Table 1).
Air pollution has been associated with respiratory diseases. It is reported that PM2.5 exposure is correlated with the development of PF. Mechanically, PM2.5 exposure decreases Cav-1 expression and activates the TGFβ1/Smad2/3, ER stress, and autophagy signaling pathways (Liu et al., 2023). Molybdenum (Mo) and Cadmium (Cd) are harmful heavy metals in the environment. Exposure of Mo and Cd may cause significant pathological alterations, oxidative stress, and iron overload-induced ferroptosis in sheep lungs. Furthermore, Mo- and Cd-activated ferroptosis promotes the pathogenesis of PF by activating the Cav-1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (Zhang et al., 2023b). CS exposure causes ROS accumulation, interstitial inflammation, and fibroblast proliferation and fibrosis. Combined CS and bleomycin exposure is associated with differential Cav-1 expression, heterogeneous parenchymal remodeling, and an increase in fibrosis (Kulshrestha et al., 2020). In the silicosis mouse models, the expression of Cav-1 is reduced. In Cav-1 knockout mice, wider alveolar septa, increased collagen content, and more silicotic nodules are found. The protective activity of Cav-1 against silica-induced PF might be associated with the suppression of the NF-κB signaling (He et al., 2022) (Table 1). In silica-inhaled mouse models, Cav-1 can attenuate PF by decreasing the expression of YAP1 and suppressing its nuclear translocation for the transcriptional regulation of GLS1 expression (Li et al., 2022).
4.6 Lung cancers
Lung cancer is characterized by high malignancy, high morbidity, and high mortality. Early diagnosis and treatment may achieve effectiveness in minimizing the mortality rate of lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are the two forms of lung cancer. SCLC accounts for approximately 15% of lung cancer cases and is more malignant with a 5 year survival rate of 5%. NSCLC can be divided into squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), adenocarcinoma (AC), and large cell lung cancer (LCLC). It is interesting to find that lung cancer preferentially develops in the vicinity of the fibrotic area in patients with IPF (Kinoshita and Goto, 2019). In addition, the risk of malignancy in patients with IPF is higher up to approximately eightfold than that of general individuals (Jang et al., 2021). A positive correlation of IPF with lung cancer has been demonstrated (Tzouvelekis et al., 2019). However, the underlying mechanisms in mediating the initiation and progression of lung cancers are still unclear. Dysregulation of Cav-1 is associated with cancer progression, such as cell proliferation, migration, apoptosis, and drug resistance. The roles of Cav-1 in lung cancer have been comprehensively reviewed (Blandin Knight et al., 2017). The potential molecular mechanism in protecting against tumor development is related to the interaction of Cav-1 with the molecules in various signaling pathways (Leiser et al., 2021; Yin et al., 2022; Kamposioras et al., 2023).
Cav-1 is a negative mediator of ROS, which is produced by NADPH oxidases (NOX1-5). It has been reported that Cav-1 knockout mice have higher expression of hypoxia-induced NOX-2 and NOX-4 and higher production of superoxide. Treatment of NOX-expression cells with CSP can significantly reverse the effects of hypoxia on human lung microvascular endothelial cells by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2014a) (Table 1) (Figure 3). The antioxidant defense system includes superoxide dismutases (SODs), such as the copper (Cu)/Zn SOD (SOD1) in the cytoplasm, the SOD2 in the mitochondria, and SOD3 outside the cells. SOD3, a Cu-containing enzyme, is produced by vascular smooth muscle cells or fibroblasts and interacts with the endothelial cells. It is reported that Cav-1 deficiency significantly reduces the activity of SOD3, but not SOD1, by promoting the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of ATP7A, which is a Cu transporter and colocalized with Cav-1 in the caveolae (Sudhahar et al., 2020). ROS has been reported to facilitate the processes of tumorigenesis under the tumor microenvironment. ROS can disrupt the vessel structure, impair vascular perfusion, and promote the internalization of secreted acidic and cysteine-rich protein (SPARC) protein by enhancing the Tyr14 phosphorylation of Cav-1 (Zhao et al., 2023). Nitric oxide (NO) is frequently increased in tumors and promotes the stability of Oct4, which drives the stemness of lung cancer cells. Mechanically, NO enhances Akt-mediated Tyr14 phosphorylation of Cav-1 and disrupts the interaction of Cav-1 with Oct4, preventing the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Oct4 by Cav-1 in human lung cancer H460 cells (Maiuthed et al., 2018) (Table 1).
MicroRNAs in small extracellular vesicles (sEV-miRNAs) are prepared by tumor cells for communication. A loading pathway of batched tumor-promoting sEV-miRNAs in A549 cells has been designed. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNPA1) is selected as a sEV-miRNAs loading protein, and SUMOylated hnRNPA1 in sEVs is used for evaluating the efficacy of sEV-miRNA loading. It is reported that Cav-1 is essential for hnRNPA1-loaded sEV-miRNAs. However, Cav-1 deletion prevents the encapsulation of SUMOylated hnRNPA1 into sEVs and inhibits tumor cell proliferation (Li et al., 2021). LINC81507 is associated with the cell growth, proliferation, migration, and EMT of lung adenocarcinoma by up-regulating Cav-1 expression through sponging miR-199b-5p (Peng et al., 2019). Human serum albumin (HAS) has been identified as a good drug carrier. Cav-1 is reported to promote HAS uptake, developing a biomarker-directed therapy. Recently, an effective HAS-SN-38 conjugate (SSH20) has been developed. Deletion of Cav-1 significantly decreases the uptake and cytotoxicity of SSH20 (Robb et al., 2021) (Table 1).
O-glcNAcylation, a post-translational modification, is associated with metabolic dynamics, cell motility, and protein stability and functions. Cav-1 can be a target of O-glcNAcylation by TRPM7, which is aberrantly expressed in lung cancers. O-glcNAcylation prevents the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Cav-1, leading to the enhanced stability of Cav-1. Inhibition of TRPM7 suppresses cell migration and invasion by mediating the O-glcNAcylation of Cav-1 in NCI-H292 cells (Luanpitpong et al., 2020). PM2.5 exposure increases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the EMT and migration of lung cancer cells. Mechanically, PM2.5 exposure induces upregulation of PVT1 expression, which sponges miR-199a. Cav-1 is a direct target of miR-199a. Thus, the downregulation of the PVT1/miR-199a/Cav-1 contributes to the inhibition of PM2.5 exposure-induced lung cell development (Qi et al., 2021). Cav-1 can form a complex with E-cadherin, which is associated with β-catenin (Sun et al., 2012). However, one study reports that inhibition of Cav-1 enhances the migration and invasion of human lung cancer cell line NCI-H460 by decreasing E-cadherin expression and increasing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling (Song et al., 2012) (Table 1). It has been reported that approximately 40% of NSCLC patients develop brain metastasis, resulting in a dismal prognosis. Enhanced Cav-1 expression after brain metastasis in lung primary tumors has been found. Knockdown of Cav-1 suppresses the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells due to the downregulation of SNAIL expression (Kim Y. J. et al., 2019).
A bioinformatics study using GO, KEGG, and PPI analysis of lung cancer reveals that Cav-1 can be a prognostic predictor for patients with lung cancer. It has been demonstrated that Cav-1 acts as a tumor suppressor, and Cav-1 alterations have been associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Cav-1 has been involved in radio-resistance and tumor progression in lung cancer (Leiser et al., 2021). It has been demonstrated that Cav-1 is overexpressed in NSCLCs irradiation (IR)-resistant cell lines H358-IRR and A549-IRR. Cav-1 promotes autophagy and enhances IR-resistant cell survival by increasing the expression of immunity-related GTPase family M protein (IRGM) (Chen et al., 2021) (Table 1). Molecular targeted therapy has advanced the management of various diseases. EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been used to treat NSCLC. However, the acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs limits their clinical applications. It is reported that atorvastatin can effectively suppress tumor growth in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cells by inhibiting the interaction of Cav-1 with GLUT3, which mediates the uptake of glucose (Ali et al., 2019).
5 Clinical perspectives
Human adenovirus type 26 (HAdV26) has been extensively explored for vaccine development. Recently, HAdV26-based vaccines against Ebola and COVID-19 in the European Union have received marketing authorization. The αvβ3 integrin has been reported to be a receptor for HAdV26 in cell infection (Nestić et al., 2019). One study shows that αvβ3 integrin-mediated HAdV26 infection is associated with endocytosis in a Cav-1-dependent manner in A549 cells (Nestić et al., 2022). Aging may increase the susceptibility to infections and decrease vaccine efficacy. It has been reported that the expression of flagellin (FlaB)-dependent TLR5 is not significantly affected by aging in old macrophages. The expression of TLR5 is mediated by Cav-1 through their interaction, and Cav-1 is involved in FlaB-dependent TLR5 signaling. FlaB can be a mucosal adjuvant in aged mice. In Streptococcus pneumonia-infected mice, FlaB-PspA fusion exhibits a higher IgG and IgA response and TLR5 enhances the immune responsiveness (Lim et al., 2015).
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-based therapy has received increasing recognition due to the high activities in MSC proliferation and multidirectional differentiation. The Cav-1F92A-modified rat BMSCs (rBMSC/Cav-1F92A) have been prepared. Treatment with rBMSC/Cav-1F92A can significantly decrease right ventricular systolic pressure, vascular stenosis, and oxidative stress in monocrotaline (MCT)-induced rat pulmonary hypertension. Mechanically, rBMSC/Cav-1F92A suppresses oxidative stress by mediating the CA1/kininogen and SelW/14-3-3η signaling pathways via activating the eNOS/NO/cGMP pathway (Yu W. C. et al., 2019). In addition, rBMSC/Cav-1F92A decreases the expression of TNFα, TGFβ1, thrombospondin-1, and MGP and increases SM22α and H-caldesmon expression. Cav-1F92A increases the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10 and decreases IL-1α and TNFα (Yu W. et al., 2019). Consistently, intravenous delivery of rBMSC expressing eNOS/Cav-1F92A to rats with pulmonary hypertension suppresses PASMC proliferation and improves vascular remodeling by activating the KLF4/p53 signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2017). Another study shows that adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) show inhibitory effects against bleomycin-induced PF by mediating the Cav-1/NF-κB signaling pathway (Chen Z. et al., 2022).
In senescent hMSCs, the expression of Cav-1 is upregulated, and the EGF signaling is attenuated. Overexpression of Cav-1 may lead to inhibition of ERK1/2-mediated insulin signaling and PPARγ-induced adipogenic differentiation in young hMSCs (Park et al., 2005). However, one study shows that the expression of Cav-1 is downregulated in human lung adenocarcinoma. Cav-1 expression is correlated with oncogenic K-Ras-induced premature senescence. Overexpression of Cav-1 can restore cellular senescence in A549 and H460 lung cancer cells (Volonte et al., 2018). In Cav-1 knockout mice, the osteogenic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), bone formation rate, and bone mass have been significantly enhanced. SiRNA-mediated Cav-1 knockdown can enhance the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human MSCs (Baker et al., 2012). This differential effect of Cav-1 in stem cells might be associated with the different contexts and microenvironment.
Consistently, bone marrow (BM) transplantation from healthy mice to Cav-1 knockout mice exhibits preventive effects against spontaneous development of PH. However, BM transplantation does not affect pulmonary endothelial remodeling (Asosingh et al., 2017). The phase 1a clinical trial (NCT04233814) of LTI-03/CSP7 for treating IPF by dry powder inhalation has been successfully completed. It has been demonstrated that aerosolized CSP7 dry powder is well tolerated without any obvious impact on respiratory functions. A phase 1b clinical trial testing the efficacy and safety of CSP7 in patients with IPF will begin soon (Shetty and Idell, 2023). Several studies have reported that Cav-1 can be a potential biomarker for therapeutic management and prognosis prediction. However, one study shows that the monoclonal Cav-1 cannot be used to distinguish between malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) and pulmonary adenocarcinoma (PA), as shown that 32.35% of MPM and 6.5% of PA are positive for Cav-1 expression (Bozdag et al., 2020).
Penehyclidine hydrochloride (PHC) is a novel anticholinergic drug that exhibits protective activity against LPS-induced ALI by suppressing the p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways (Shen et al., 2009). The protective effects of PHC against LPS-induced ALI might be associated with the upregulation of Cav-1 expression in J774A.1 cells (Wu et al., 2019). SZ168 (Podoplanin (PDPN) monoclonal antibody) (Heng et al., 2023) and Salidroside (Jingyan et al., 2017) show similar protection against LPS-induced ALI. Glycyrrhizic acid (GA), a bioactive compound from licorice, has been reported to protect against LPS-induced ALI by regulating the expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the Cav-1/NF-κB signaling pathway. However, an ACE2 inhibitor MLN-4760 can abrogate the protective effects of GA (Chen Y. et al., 2022). The traditional Chinese medicine Qi-Dong-Huo-Xue-Yin (QDHXY) has been reported to treat ALI by mediating the expression of Cav-1 and protecting against inflammatory responses in LPS-treated mice (Xu et al., 2018). Andrographolide pills (AP) is a labdane diterpene lactone isolated from Andrographis, which is a traditional Chinese medicine. AP consistently protects against LPS-induced pulmonary injury and dysfunction by up-regulating the expression of Cav-1, Src, p47phox, and p67phox (Yang et al., 2014). YiPingFeng, a traditional Chinese medicine, has been reported to treat PF by up-regulating Cav-1 expression and inhibiting the TGFβ1/Smad2 signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2024). Quercetin, a natural flavonoid distributed widely in plants, exhibits protective effects against PF by restoring the susceptibility of senescent IPF fibroblasts to apoptosis via up-regulating Cav-1 and FasL expression and inhibiting AKT activation (Hohmann et al., 2019). Chrysotobibenzyl, extracted from Dendrobium pulchellum, has been reported to inhibit cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT in H460 and H292 cells by suppressing the expression of Cav-1 (Petpiroon et al., 2019).
6 Conclusion
Cav-1, a vital protein for transcytosis, endocytosis, and signal transduction, has been involved in regulating the physiological and pathological processes. The critical roles of Cav-1 in lung diseases, such as pneumonia, asthma, COPD, ALI, pulmonary hypertension, PF, and lung cancer, have been demonstrated. Mechanically, Cav-1 interacts with various pathways, such as MAPK, NF-κB, PI3K/AKT, TGFβ, BMP/Smad, and eNOS/NO signaling, which are associated with the pathogenesis of lung diseases. Targeting caveolae and Cav-1 can be a therapeutic strategy in the mediation of cell signaling pathways and the treatment of lung disease. Owing to the versatile effects of Cav-1 in mediating the signaling pathways, strategies relating to the functional regulation of Cav-1 might be a more effective way to treat lung diseases. It is important to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of Cav-1 in the pathogenesis of lung diseases. Although a Cav-1 scaffolding domain peptide CSP7 has been developed, the structural analysis of Cav-1 should be further deepened. More agents like CSP7 should be developed. Till now, no small molecules as the ligands targeting Cav-1 have been reported.
However, Cav-1 is a challenging protein due to its ubiquitous expression in many organ systems, tissue types, and pathological processes. The interaction of Cav-1 with a variety of signaling molecules is complex, and the biological effects of Cav-1 can be positive or negative. The applications of transgenic or gene-knockout models have been explored for determining the effects of Cav-1. Understanding how one set of gene-profile mediation is controlled over the other remains to be elucidated. The systematic effects of Cav-1 on the physiological and pathological events in vivo and in vitro need further investigation.
Author contributions
JF: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing–original draft. SZ: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing–original draft. MW: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing–original draft. XY: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Ganzhou Science and Technology Plan Project (2023LN37008).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ali, A., Levantini, E., Fhu, C. W., Teo, J. T., Clohessy, J. G., Goggi, J. L., et al. (2019). CAV1 - GLUT3 signaling is important for cellular energy and can be targeted by Atorvastatin in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Theranostics 9 (21), 6157–6174. doi:10.7150/thno.35805
Anderson, R. G. (1998). The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 199–225. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.199
Anderson, R. G., Kamen, B. A., Rothberg, K. G., and Lacey, S. W. (1992). Potocytosis: sequestration and transport of small molecules by caveolae. Science 255 (5043), 410–411. doi:10.1126/science.1310359
Aravamudan, B., VanOosten, S. K., Meuchel, L. W., Vohra, P., Thompson, M., Sieck, G. C., et al. (2012). Caveolin-1 knockout mice exhibit airway hyperreactivity. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 303 (8), L669–L681. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00018.2012
Arthur, G. K., Ehrhardt-Humbert, L. C., Snider, D. B., Jania, C., Tilley, S. L., Metcalfe, D. D., et al. (2020). The FcεRIβ homologue, MS4A4A, promotes FcεRI signal transduction and store-operated Ca2+ entry in human mast cells. Cell Signal 71, 109617. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109617
Asosingh, K., Wanner, N., Weiss, K., Queisser, K., Gebreab, L., Kassa, B., et al. (2017). Bone marrow transplantation prevents right ventricle disease in the caveolin-1-deficient mouse model of pulmonary hypertension. Blood Adv. 1 (9), 526–534. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2016002691
Bains, S. N., Tourkina, E., Atkinson, C., Joseph, K., Tholanikunnel, B., Chu, H. W., et al. (2012). Loss of caveolin-1 from bronchial epithelial cells and monocytes in human subjects with asthma. Allergy 67 (12), 1601–1604. doi:10.1111/all.12021
Baker, N., Zhang, G., You, Y., and Tuan, R. S. (2012). Caveolin-1 regulates proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell Biochem. 113 (12), 3773–3787. doi:10.1002/jcb.24252
Batori, R. K., Chen, F., Bordan, Z., Haigh, S., Su, Y., Verin, A. D., et al. (2022). Protective role of Cav-1 in pneumolysin-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction. Front. Immunol. 13, 945656. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.945656
Bernatchez, P., Sharma, A., Bauer, P. M., Marin, E., and Sessa, W. C. (2011). A noninhibitory mutant of the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain enhances eNOS-derived NO synthesis and vasodilation in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 121 (9), 3747–3755. doi:10.1172/jci44778
Bhowmick, S., Biswas, T., Ahmed, M., Roy, D., and Mondal, S. (2023). Caveolin-1 and lipids: association and their dualism in oncogenic regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1878 (6), 189002. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189002
Blandin Knight, S., Crosbie, P. A., Balata, H., Chudziak, J., Hussell, T., and Dive, C. (2017). Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 7 (9), 170070. doi:10.1098/rsob.170070
Bozdag, Z., Tutar, E., Dizibuyuk, O. F., and Bakir, K. (2020). Monoclonal caveolin 1 expression in the differential diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma and pulmonary adenocarcinoma: is it useful? Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26 (3), 1651–1656. doi:10.1007/s12253-019-00751-9
Broström, J. M., Ghalali, A., Zheng, H., Högberg, J., Stenius, U., Littorin, M., et al. (2018). Toluene diisocyanate exposure and autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid signalling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 355, 43–51. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2018.06.019
Bucci, M., Gratton, J. P., Rudic, R. D., Acevedo, L., Roviezzo, F., Cirino, G., et al. (2000). In vivo delivery of the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain inhibits nitric oxide synthesis and reduces inflammation. Nat. Med. 6 (12), 1362–1367. doi:10.1038/82176
Buckley, S., Barsky, L., Driscoll, B., Weinberg, K., Anderson, K. D., and Warburton, D. (1998). Apoptosis and DNA damage in type 2 alveolar epithelial cells cultured from hyperoxic rats. Am. J. Physiol. 274 (5), L714–L720. doi:10.1152/ajplung.1998.274.5.L714
Cai, L., Yi, F., Dai, Z., Huang, X., Zhao, Y. D., Mirza, M. K., et al. (2014). Loss of caveolin-1 and adiponectin induces severe inflammatory lung injury following LPS challenge through excessive oxidative/nitrative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 306 (6), L566–L573. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00182.2013
Chen, F., Barman, S., Yu, Y., Haigh, S., Wang, Y., Black, S. M., et al. (2014a). Caveolin-1 is a negative regulator of NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 73, 201–213. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.04.029
Chen, F., Kumar, S., Yu, Y., Aggarwal, S., Gross, C., Wang, Y., et al. (2014b). PKC-dependent phosphorylation of eNOS at T495 regulates eNOS coupling and endothelial barrier function in response to G+ -toxins. PLoS One 9 (7), e99823. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099823
Chen, H., Yang, H., Yue, H., Strappe, P. M., Xia, P., Pan, L., et al. (2017). Mesenchymal stem cells expressing eNOS and a Cav1 mutant inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in a rat model of pulmonary hypertension. Heart Lung Circ. 26 (5), 509–518. doi:10.1016/j.hlc.2016.08.002
Chen, S. F., Liou, J. Y., Huang, T. Y., Lin, Y. S., Yeh, A. L., Tam, K., et al. (2010). Caveolin-1 facilitates cyclooxygenase-2 protein degradation. J. Cell Biochem. 109 (2), 356–362. doi:10.1002/jcb.22407
Chen, X., Wei, M., Li, G. D., Sun, Q. L., Fan, J. Q., Li, J. Y., et al. (2024). YuPingFeng (YPF) upregulates caveolin-1 (CAV1) to alleviate pulmonary fibrosis through the TGF-β1/Smad2 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 3), 117357. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117357
Chen, X., Yan, Y. L., Zeng, S. S., Gong, Z. C., and Xu, Z. J. (2021). Caveolin-1 promotes radioresistance via IRGM-regulated autophagy in lung cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 9 (1), 47. doi:10.21037/atm-20-3293
Chen, Y., Qu, L., Li, Y., Chen, C., He, W., Shen, L., et al. (2022). Glycyrrhizic acid alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced acute lung injury by regulating angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and caveolin-1 signaling pathway. Inflammation 45 (1), 253–266. doi:10.1007/s10753-021-01542-8
Chen, Z., Ruan, B., Long, G., and Lin, W. (2022). Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate lung inflammation and fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis rat model via caveolin-1/NF-kB signaling axis. Physiol. Res. 71 (5), 657–666. doi:10.33549/physiolres.934892
Chen, Z. H., Lam, H. C., Jin, Y., Kim, H. P., Cao, J., Lee, S. J., et al. (2010). Autophagy protein microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain-3B (LC3B) activates extrinsic apoptosis during cigarette smoke-induced emphysema. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107 (44), 18880–18885. doi:10.1073/pnas.1005574107
Chettimada, S., Yang, J., Moon, H. G., and Jin, Y. (2015). Caveolae, caveolin-1 and cavin-1: emerging roles in pulmonary hypertension. World J. Respirol. 5 (2), 126–134. doi:10.5320/wjr.v5.i2.126
Chidlow, J. H., and Sessa, W. C. (2010). Caveolae, caveolins, and cavins: complex control of cellular signalling and inflammation. Cardiovasc Res. 86 (2), 219–225. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq075
Cho, H. Y., Morgan, D. L., Bauer, A. K., and Kleeberger, S. R. (2007). Signal transduction pathways of tumor necrosis factor--mediated lung injury induced by ozone in mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 175 (8), 829–839. doi:10.1164/rccm.200509-1527OC
GBD Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators (2020). Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Respir. Med. 8 (6), 585–596. doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30105-3
Couet, J., Li, S., Okamoto, T., Ikezu, T., and Lisanti, M. P. (1997a). Identification of peptide and protein ligands for the caveolin-scaffolding domain. Implications for the interaction of caveolin with caveolae-associated proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 272 (10), 6525–6533. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.10.6525
Couet, J., Sargiacomo, M., and Lisanti, M. P. (1997b). Interaction of a receptor tyrosine kinase, EGF-R, with caveolins. Caveolin binding negatively regulates tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 272 (48), 30429–30438. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.48.30429
Dai, Y., Li, F., Wu, L., Wang, R., Li, P., Yan, S., et al. (2014). Roxithromycin treatment inhibits TGF-β1-induced activation of ERK and AKT and down-regulation of caveolin-1 in rat airway smooth muscle cells. Respir. Res. 15 (1), 96. doi:10.1186/s12931-014-0096-z
Dalpke, A., Zimmermann, S., and Heeg, K. (2002). CpG DNA in the prevention and treatment of infections. BioDrugs 16 (6), 419–431. doi:10.2165/00063030-200216060-00003
Dalton, C. M., Schlegel, C., and Hunter, C. J. (2023). Caveolin-1: a review of intracellular functions, tissue-specific roles, and epithelial tight junction regulation. Biol. (Basel) 12 (11), 1402. doi:10.3390/biology12111402
Daneva, Z., Marziano, C., Ottolini, M., Chen, Y. L., Baker, T. M., Kuppusamy, M., et al. (2021). Caveolar peroxynitrite formation impairs endothelial TRPV4 channels and elevates pulmonary arterial pressure in pulmonary hypertension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118 (17), e2023130118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2023130118
Das, D. N., Puthusseri, B., Gopu, V., Krishnan, V., Bhagavath, A. K., Bolla, S., et al. (2023). Caveolin-1-derived peptide attenuates cigarette smoke-induced airway and alveolar epithelial injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 325 (5), L689–l708. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00178.2022
Dasari, A., Bartholomew, J. N., Volonte, D., and Galbiati, F. (2006). Oxidative stress induces premature senescence by stimulating caveolin-1 gene transcription through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/Sp1-mediated activation of two GC-rich promoter elements. Cancer Res. 66 (22), 10805–10814. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-1236
Dessy, C., Feron, O., and Balligand, J. L. (2010). The regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by caveolin: a paradigm validated in vivo and shared by the 'endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor. Pflugers Arch. 459 (6), 817–827. doi:10.1007/s00424-010-0815-3
Díaz, M. I., Díaz, P., Bennett, J. C., Urra, H., Ortiz, R., Orellana, P. C., et al. (2020). Caveolin-1 suppresses tumor formation through the inhibition of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death Dis. 11 (8), 648. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-02792-4
Díaz-Valdivia, N., Simón, L., Díaz, J., Martinez-Meza, S., Contreras, P., Burgos-Ravanal, R., et al. (2022). Mitochondrial dysfunction and the glycolytic switch induced by caveolin-1 phosphorylation promote cancer cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cancers (Basel) 14 (12), 2862. doi:10.3390/cancers14122862
Dietzen, D. J., Hastings, W. R., and Lublin, D. M. (1995). Caveolin is palmitoylated on multiple cysteine residues. Palmitoylation is not necessary for localization of caveolin to caveolae. J. Biol. Chem. 270 (12), 6838–6842. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.12.6838
Enyong, E. N., Gurley, J. M., De Ieso, M. L., Stamer, W. D., and Elliott, M. H. (2022). Caveolar and non-Caveolar Caveolin-1 in ocular homeostasis and disease. Prog. Retin Eye Res. 91, 101094. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2022.101094
Erewele, E. O., Castellon, M., Loya, O., Marshboom, G., Schwartz, A., Yerlioglu, K., et al. (2022). Hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension upregulates eNOS and TGF-β contributing to sex-linked differences in BMPR2+/R899X mutant mice. Pulm. Circ. 12 (4), e12163. doi:10.1002/pul2.12163
Fakhrzadeh, L., Laskin, J. D., and Laskin, D. L. (2008). Regulation of caveolin-1 expression, nitric oxide production and tissue injury by tumor necrosis factor-alpha following ozone inhalation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 227 (3), 380–389. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2007.11.012
Fang, P., Shi, H. Y., Wu, X. M., Zhang, Y. H., Zhong, Y. J., Deng, W. J., et al. (2016). Targeted inhibition of GATA-6 attenuates airway inflammation and remodeling by regulating caveolin-1 through TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB in murine model of asthma. Mol. Immunol. 75, 144–150. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2016.05.017
Feng, H., Guo, W., Han, J., and Li, X. A. (2013). Role of caveolin-1 and caveolae signaling in endotoxemia and sepsis. Life Sci. 93 (1), 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2013.05.016
Fernández-Hernando, C., Fukata, M., Bernatchez, P. N., Fukata, Y., Lin, M. I., Bredt, D. S., et al. (2006). Identification of Golgi-localized acyl transferases that palmitoylate and regulate endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J. Cell Biol. 174 (3), 369–377. doi:10.1083/jcb.200601051
Fork, C., Hitzel, J., Nichols, B. J., Tikkanen, R., and Brandes, R. P. (2014). Flotillin-1 facilitates toll-like receptor 3 signaling in human endothelial cells. Basic Res. Cardiol. 109 (6), 439. doi:10.1007/s00395-014-0439-4
Fra, A. M., Williamson, E., Simons, K., and Parton, R. G. (1995). De novo formation of caveolae in lymphocytes by expression of VIP21-caveolin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92 (19), 8655–8659. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.19.8655
Gabehart, K. E., Royce, S. G., Maselli, D. J., Miyasato, S. K., Davis, E. C., Tang, M. L., et al. (2013). Airway hyperresponsiveness is associated with airway remodeling but not inflammation in aging Cav1-/- mice. Respir. Res. 14 (1), 110. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-14-110
Gadjeva, M., Paradis-Bleau, C., Priebe, G. P., Fichorova, R., and Pier, G. B. (2010). Caveolin-1 modifies the immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Immunol. 184 (1), 296–302. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900604
Gairhe, S., Awad, K. S., Dougherty, E. J., Ferreyra, G. A., Wang, S., Yu, Z. X., et al. (2021). Type I interferon activation and endothelial dysfunction in caveolin-1 insufficiency-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118 (11), e2010206118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2010206118
Gao, W., Shao, R., Zhang, X., Liu, D., Liu, Y., and Fa, X. (2017). Up-regulation of caveolin-1 by DJ-1 attenuates rat pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting TGFβ/Smad signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 361 (1), 192–198. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.10.019
Garrean, S., Gao, X. P., Brovkovych, V., Shimizu, J., Zhao, Y. Y., Vogel, S. M., et al. (2006). Caveolin-1 regulates NF-kappaB activation and lung inflammatory response to sepsis induced by lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 177 (7), 4853–4860. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4853
Geng, Y., Li, R., He, S. X., Yang, H. H., Deng, Q. T., Shao, X. Y., et al. (2019). Dexmedetomidine attenuates acute lung injury induced by heatstroke and improve outcome. Shock 52 (5), 532–539. doi:10.1097/shk.0000000000001289
Glassberg, M. K. (2019). Overview of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, evidence-based guidelines, and recent developments in the treatment landscape. Am. J. Manag. Care 25 (Suppl. l), S195–S203.
Gliozzi, M., Scicchitano, M., Bosco, F., Musolino, V., Carresi, C., Scarano, F., et al. (2019). Modulation of nitric oxide synthases by oxidized LDLs: role in vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (13), 3294. doi:10.3390/ijms20133294
Gokani, S., and Bhatt, L. K. (2022). Caveolin-1: a promising therapeutic target for diverse diseases. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 15 (5), 701–715. doi:10.2174/1874467214666211130155902
Gonzalez-Rey, E., and Delgado, M. (2007). Vasoactive intestinal peptide and regulatory T-cell induction: a new mechanism and therapeutic potential for immune homeostasis. Trends Mol. Med. 13 (6), 241–251. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2007.04.003
Grainge, C. L., and Davies, D. E. (2013). Epithelial injury and repair in airways diseases. Chest 144 (6), 1906–1912. doi:10.1378/chest.12-1944
Guo, D., Chen, Y., Wang, S., Yu, L., Shen, Y., Zhong, H., et al. (2018). Exosomes from heat-stressed tumour cells inhibit tumour growth by converting regulatory T cells to Th17 cells via IL-6. Immunology 154 (1), 132–143. doi:10.1111/imm.12874
Guo, Q., Shen, N., Yuan, K., Li, J., Wu, H., Zeng, Y., et al. (2012). Caveolin-1 plays a critical role in host immunity against Klebsiella pneumoniae by regulating STAT5 and Akt activity. Eur. J. Immunol. 42 (6), 1500–1511. doi:10.1002/eji.201142051
Hayer, A., Stoeber, M., Bissig, C., and Helenius, A. (2010a). Biogenesis of caveolae: stepwise assembly of large caveolin and cavin complexes. Traffic 11 (3), 361–382. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.01023.x
Hayer, A., Stoeber, M., Ritz, D., Engel, S., Meyer, H. H., and Helenius, A. (2010b). Caveolin-1 is ubiquitinated and targeted to intralumenal vesicles in endolysosomes for degradation. J. Cell Biol. 191 (3), 615–629. doi:10.1083/jcb.201003086
He, R., Yuan, X., Lv, X., Liu, Q., Tao, L., and Meng, J. (2022). Caveolin-1 negatively regulates inflammation and fibrosis in silicosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 26 (1), 99–107. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17045
Heng, J., Wu, D., Zhao, Y., and Lu, S. (2023). SZ168 treats LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and MAPKs pathways. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 307, 103965. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2022.103965
Hill, M. M., Bastiani, M., Luetterforst, R., Kirkham, M., Kirkham, A., Nixon, S. J., et al. (2008). PTRF-Cavin, a conserved cytoplasmic protein required for caveola formation and function. Cell 132 (1), 113–124. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.042
Hohmann, M. S., Habiel, D. M., Coelho, A. L., Verri, W. A., and Hogaboam, C. M. (2019). Quercetin enhances ligand-induced apoptosis in senescent idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts and reduces lung fibrosis in vivo. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 60 (1), 28–40. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2017-0289OC
Hu, G., Ye, R. D., Dinauer, M. C., Malik, A. B., and Minshall, R. D. (2008). Neutrophil caveolin-1 expression contributes to mechanism of lung inflammation and injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 294 (2), L178–L186. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00263.2007
Huber, L. C., Soltermann, A., Fischler, M., Gay, S., Weder, W., Russi, E. W., et al. (2009). Caveolin-1 expression and hemodynamics in COPD patients. Open Respir. Med. J. 3, 73–78. doi:10.2174/1874306400903010073
Hubert, M., Larsson, E., and Lundmark, R. (2020). Keeping in touch with the membrane; protein- and lipid-mediated confinement of caveolae to the cell surface. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 48 (1), 155–163. doi:10.1042/bst20190386
Jagielska, J., Kapopara, P. R., Salguero, G., Scherr, M., Schütt, H., Grote, K., et al. (2012). Interleukin-1 assembles a proangiogenic signaling module consisting of caveolin-1, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6, p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 32 (5), 1280–1288. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.111.243477
Jang, H. J., Park, M. S., Kim, Y. S., Chang, J., Lee, J. H., Lee, C. T., et al. (2021). The relationship between the severity of pulmonary fibrosis and the lung cancer stage. J. Cancer 12 (10), 2807–2814. doi:10.7150/jca.51445
Jiao, H., Zhang, Y., Yan, Z., Wang, Z. G., Liu, G., Minshall, R. D., et al. (2013). Caveolin-1 Tyr14 phosphorylation induces interaction with TLR4 in endothelial cells and mediates MyD88-dependent signaling and sepsis-induced lung inflammation. J. Immunol. 191 (12), 6191–6199. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1300873
Jin, L. G., Zeng, S., Sun, X. Q., Wu, C., Chen, J. L., Cui, M., et al. (2018). Deletion 101 residue at caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptides impairs the ability of increasing heme oxygenase-1 activity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 63, 137–144. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2018.07.025
Jingyan, L., Yujuan, G., Yiming, Y., Lingpeng, Z., Tianhua, Y., and Mingxing, M. (2017). Salidroside attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. Inflammation 40 (5), 1520–1531. doi:10.1007/s10753-017-0593-6
Jones, J. H., and Minshall, R. D. (2022). Endothelial transcytosis in acute lung injury: emerging mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front. Physiol. 13, 828093. doi:10.3389/fphys.2022.828093
Kamposioras, K., Dinas, P. C., Barriuoso, J., Trachana, V., and Dimas, K. (2023). Caveolin-1 protein expression as a prognostic biomarker of gastrointestinal tumours: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 53 (12), e14065. doi:10.1111/eci.14065
Kawai, T., and Akira, S. (2010). The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11 (5), 373–384. doi:10.1038/ni.1863
Kim, S. H., Pei, Q. M., Jiang, P., Liu, J., Sun, R. F., Qian, X. J., et al. (2019). Upregulation of MUC5AC by VEGF in human primary bronchial epithelial cells: implications for asthma. Respir. Res. 20 (1), 282. doi:10.1186/s12931-019-1245-1
Kim, S. H., Pei, Q. M., Jiang, P., Liu, J., Sun, R. F., Qian, X. J., et al. (2020). Effects of dexamethasone on VEGF-induced MUC5AC expression in human primary bronchial epithelial cells: implications for asthma. Exp. Cell Res. 389 (2), 111897. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111897
Kim, S. H., Pei, Q. M., Jiang, P., Yang, M., Qian, X. J., and Liu, J. B. (2017). Role of licochalcone A in VEGF-induced proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells: implications for asthma. Growth Factors. 35 (1), 39–47. doi:10.1080/08977194.2017.1338694
Kim, Y. J., Kim, J. H., Kim, O., Ahn, E. J., Oh, S. J., Akanda, M. R., et al. (2019). Caveolin-1 enhances brain metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer, potentially in association with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition marker SNAIL. Cancer Cell Int. 19, 171. doi:10.1186/s12935-019-0892-0
Kinoshita, T., and Goto, T. (2019). Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrogenesis and its progression to lung cancer: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (6), 1461. doi:10.3390/ijms20061461
Kulshrestha, R., Singh, H., Pandey, A., Soundarya, D., Jaggi, A. S., and Ravi, K. (2020). Differential expression of caveolin-1 during pathogenesis of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: effect of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1866 (8), 165802. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165802
Kumphune, S., Seenak, P., Paiyabhrom, N., Songjang, W., Pankhong, P., Jumroon, N., et al. (2024). Cardiac endothelial ischemia/reperfusion injury-derived protein damage-associated molecular patterns disrupt the integrity of the endothelial barrier. Heliyon 10 (2), e24600. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24600
Lee, C. Y., Lai, T. Y., Tsai, M. K., Chang, Y. C., Ho, Y. H., Yu, I. S., et al. (2017). The ubiquitin ligase ZNRF1 promotes caveolin-1 ubiquitination and degradation to modulate inflammation. Nat. Commun. 8, 15502. doi:10.1038/ncomms15502
Lee, H., Groot, M., Pinilla-Vera, M., Fredenburgh, L. E., and Jin, Y. (2019). Identification of miRNA-rich vesicles in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: insights into the function and heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Control Release 294, 43–52. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.12.008
Lee, M. Y., Ryu, J. M., Lee, S. H., Park, J. H., and Han, H. J. (2010). Lipid rafts play an important role for maintenance of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. J. Lipid Res. 51 (8), 2082–2089. doi:10.1194/jlr.M001545
Leiser, D., Samanta, S., Eley, J., Strauss, J., Creed, M., Kingsbury, T., et al. (2021). Role of caveolin-1 as a biomarker for radiation resistance and tumor aggression in lung cancer. PLoS One 16 (11), e0258951. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258951
Le Saux, O., Teeters, K., Miyasato, S., Choi, J., Nakamatsu, G., Richardson, J. A., et al. (2008). The role of caveolin-1 in pulmonary matrix remodeling and mechanical properties. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 295 (6), L1007–L1017. doi:10.1152/ajplung.90207.2008
Levine, S. M., and Marciniuk, D. D. (2022). Global impact of respiratory disease: what can we do, together, to make a difference? Chest 161 (5), 1153–1154. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.01.014
Li, G., Xu, Q., Cheng, D., Sun, W., Liu, Y., Ma, D., et al. (2022). Caveolin-1 and its functional peptide CSP7 affect silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating fibroblast glutaminolysis. Toxicol. Sci. 190 (1), 41–53. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfac089
Li, M., Cai, W., Chen, Y., and Dong, L. (2019). The CAV1 gene 3' untranslated region single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with the risk of pulmonary hypertension in Chinese han chronic obstructive pulmonary patients. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers 23 (9), 634–643. doi:10.1089/gtmb.2019.0053
Li, Y., Zhang, J., Li, S., Guo, C., Li, Q., Zhang, X., et al. (2021). Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 loads batched tumor-promoting MicroRNAs into small extracellular vesicles with the assist of caveolin-1 in A549 cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 687912. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.687912
Lim, J. S., Nguyen, K. C., Nguyen, C. T., Jang, I. S., Han, J. M., Fabian, C., et al. (2015). Flagellin-dependent TLR5/caveolin-1 as a promising immune activator in immunosenescence. Aging Cell 14 (5), 907–915. doi:10.1111/acel.12383
Lin, X., Barravecchia, M., Matthew Kottmann, R., Sime, P., and Dean, D. A. (2019). Caveolin-1 gene therapy inhibits inflammasome activation to protect from bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 19643. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-55819-y
Lin, Y. C., Lin, C. H., Kuo, C. Y., and Yang, V. C. (2009). ABCA1 modulates the oligomerization and Golgi exit of caveolin-1 during HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux in aortic endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 382 (1), 189–195. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.03.005
Lin, Y. C., Ma, C., Hsu, W. C., Lo, H. F., and Yang, V. C. (2007). Molecular interaction between caveolin-1 and ABCA1 on high-density lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol efflux in aortic endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res. 75 (3), 575–583. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.04.012
Liu, H., Lai, W., Nie, H., Shi, Y., Zhu, L., Yang, L., et al. (2023). PM(2.5) triggers autophagic degradation of Caveolin-1 via endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) to enhance the TGF-β1/Smad3 axis promoting pulmonary fibrosis. Environ. Int. 181, 108290. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2023.108290
Liu, J., Huang, X., Hu, S., He, H., and Meng, Z. (2019). Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in rats by inhibition of caveolin-1 downstream signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 109314. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109314
Liu, L., Brown, D., McKee, M., Lebrasseur, N. K., Yang, D., Albrecht, K. H., et al. (2008). Deletion of Cavin/PTRF causes global loss of caveolae, dyslipidemia, and glucose intolerance. Cell Metab. 8 (4), 310–317. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2008.07.008
Lolo, F. N., Walani, N., Seemann, E., Zalvidea, D., Pavón, D. M., Cojoc, G., et al. (2023). Caveolin-1 dolines form a distinct and rapid caveolae-independent mechanoadaptation system. Nat. Cell Biol. 25 (1), 120–133. doi:10.1038/s41556-022-01034-3
Luanpitpong, S., Rodboon, N., Samart, P., Vinayanuwattikun, C., Klamkhlai, S., Chanvorachote, P., et al. (2020). A novel TRPM7/O-GlcNAc axis mediates tumour cell motility and metastasis by stabilising c-Myc and caveolin-1 in lung carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 123 (8), 1289–1301. doi:10.1038/s41416-020-0991-7
Lundmark, R., Larsson, E., and Pulkkinen, L. I. A. (2024). The adaptable caveola coat generates a plasma membrane sensory system. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 88, 102371. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2024.102371
Luo, D. X., Cao, D. L., Xiong, Y., Peng, X. H., and Liao, D. F. (2010). A novel model of cholesterol efflux from lipid-loaded cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 31 (10), 1243–1257. doi:10.1038/aps.2010.93
Ma, R., Su, H., Jiao, K., and Liu, J. (2023). Role of Th17 cells, Treg cells, and Th17/Treg imbalance in immune homeostasis disorders in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 11 (2), e784. doi:10.1002/iid3.784
Maiti, G., Frikeche, J., Lam, C. Y., Biswas, A., Shinde, V., Samanovic, M., et al. (2021). Matrix lumican endocytosed by immune cells controls receptor ligand trafficking to promote TLR4 and restrict TLR9 in sepsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118 (27), e2100999118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2100999118
Maiuthed, A., Bhummaphan, N., Luanpitpong, S., Mutirangura, A., Aporntewan, C., Meeprasert, A., et al. (2018). Nitric oxide promotes cancer cell dedifferentiation by disrupting an Oct4:caveolin-1 complex: a new regulatory mechanism for cancer stem cell formation. J. Biol. Chem. 293 (35), 13534–13552. doi:10.1074/jbc.RA117.000287
Mao, F., Huang, F., Nong, W., Lao, D., Gong, Z., and Huang, W. (2022). N-methyl-D-aspartic acid increases tight junction protein destruction in brain endothelial cell via caveolin-1-associated ERK1/2 signaling. Toxicology 470, 153139. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2022.153139
Marudamuthu, A. S., Bhandary, Y. P., Fan, L., Radhakrishnan, V., MacKenzie, B., Maier, E., et al. (2019). Caveolin-1-derived peptide limits development of pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 11 (522), eaat2848. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aat2848
Mathew, R. (2021). Critical role of caveolin-1 loss/dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. Med. Sci. (Basel) 9 (4), 58. doi:10.3390/medsci9040058
Matveev, S., van der Westhuyzen, D. R., and Smart, E. J. (1999). Co-expression of scavenger receptor-BI and caveolin-1 is associated with enhanced selective cholesteryl ester uptake in THP-1 macrophages. J. Lipid Res. 40 (9), 1647–1654. doi:10.1016/s0022-2275(20)33410-6
McMahon, K. A., Zajicek, H., Li, W. P., Peyton, M. J., Minna, J. D., Hernandez, V. J., et al. (2009). SRBC/cavin-3 is a caveolin adapter protein that regulates caveolae function. Embo J. 28 (8), 1001–1015. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.46
Medina, F. A., de Almeida, C. J., Dew, E., Li, J., Bonuccelli, G., Williams, T. M., et al. (2006). Caveolin-1-deficient mice show defects in innate immunity and inflammatory immune response during Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection. Infect. Immun. 74 (12), 6665–6674. doi:10.1128/iai.00949-06
Meng, F., Joshi, B., and Nabi, I. R. (2015). Galectin-3 overrides PTRF/Cavin-1 reduction of PC3 prostate cancer cell migration. PLoS One 10 (5), e0126056. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0126056
Menzel, V., Ziegler, M., Hante, N., Sake, J. A., Santos-Martinez, M. J., Ehrhardt, C., et al. (2022). Fyn-kinase and caveolin-1 in the alveolar epithelial junctional adherence complex contribute to the early stages of pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 175, 106236. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106236
Mohan, J., Morén, B., Larsson, E., Holst, M. R., and Lundmark, R. (2015). Cavin3 interacts with cavin1 and caveolin1 to increase surface dynamics of caveolae. J. Cell Sci. 128 (5), 979–991. doi:10.1242/jcs.161463
Möller, N., Ziesemer, S., Hildebrandt, P., Assenheimer, N., Völker, U., and Hildebrandt, J. P. (2020). S. aureus alpha-toxin monomer binding and heptamer formation in host cell membranes - do they determine sensitivity of airway epithelial cells toward the toxin? PLoS One 15 (5), e0233854. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0233854
Moon, H. G., Qin, Z., Quan, T., Xie, L., Dela Cruz, C. S., and Jin, Y. (2015). Matrix protein CCN1 induced by bacterial DNA and CpG ODN limits lung inflammation and contributes to innate immune homeostasis. Mucosal Immunol. 8 (2), 243–253. doi:10.1038/mi.2014.62
Moreno, J., Escobedo, D., Calhoun, C., Le Saux, C. J., and Han, H. C. (2021). Arterial wall stiffening in caveolin-1 deficiency-induced pulmonary artery hypertension in mice. Exp. Mech. 6 (1), 217–228. doi:10.1007/s11340-020-00666-6
Moriyama, T., Marquez, J. P., Wakatsuki, T., and Sorokin, A. (2007). Caveolar endocytosis is critical for BK virus infection of human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. J. Virol. 81 (16), 8552–8562. doi:10.1128/jvi.00924-07
Mueller, K. E., and Wolf, K. (2015). C. pneumoniae disrupts eNOS trafficking and impairs NO production in human aortic endothelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 17 (1), 119–130. doi:10.1111/cmi.12341
Nagaraja, M. R., Tiwari, N., Shetty, S. K., Marudamuthu, A. S., Fan, L., Ostrom, R. S., et al. (2018). p53 expression in lung fibroblasts is linked to mitigation of fibrotic lung remodeling. Am. J. Pathol. 188 (10), 2207–2222. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.07.005
Nassar, Z. D., Hill, M. M., Parton, R. G., Francois, M., and Parat, M. O. (2015). Non-caveolar caveolin-1 expression in prostate cancer cells promotes lymphangiogenesis. Oncoscience 2 (7), 635–645. doi:10.18632/oncoscience.180
Nestić, D., Custers, J., Švec, D., and Majhen, D. (2022). Human adenovirus type 26 infection mediated by αvβ3 integrin is caveolin-1-dependent. Microbiol. Spectr. 10 (4), e0109722. doi:10.1128/spectrum.01097-22
Nestić, D., Uil, T. G., Ma, J., Roy, S., Vellinga, J., Baker, A. H., et al. (2019). αvβ3 integrin is required for efficient infection of epithelial cells with human adenovirus type 26. J. Virol. 93 (1), e01474-18. doi:10.1128/jvi.01474-18
Nishimoto, A. T., Rosch, J. W., and Tuomanen, E. I. (2020). Pneumolysin: pathogenesis and therapeutic target. Front. Microbiol. 11, 1543. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01543
Ocampo, J. M. F., Santos, R. A. N., Sevilleja, J., and Gloria, C. T. (2024). The COVID-19 pandemic's effects on mental and psychosocial health in the Philippines: a scoping review. Glob. Ment. Health (Camb) 11, e27. doi:10.1017/gmh.2024.14
Ohi, M. D., and Kenworthy, A. K. (2022). Emerging insights into the molecular architecture of caveolin-1. J. Membr. Biol. 255 (4-5), 375–383. doi:10.1007/s00232-022-00259-5
Oliveira, S. D. S., Castellon, M., Chen, J., Bonini, M. G., Gu, X., Elliott, M. H., et al. (2017). Inflammation-induced caveolin-1 and BMPRII depletion promotes endothelial dysfunction and TGF-β-driven pulmonary vascular remodeling. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 312 (5), L760–L771. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00484.2016
Oliveira, S. D. S., Chen, J., Castellon, M., Mao, M., Raj, J. U., Comhair, S., et al. (2019). Injury-induced shedding of extracellular vesicles depletes endothelial cells of Cav-1 (Caveolin-1) and enables TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β)-dependent pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 39 (6), 1191–1202. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.118.312038
Padhan, K., Tanwar, C., Hussain, A., Hui, P. Y., Lee, M. Y., Cheung, C. Y., et al. (2007). Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus Orf3a protein interacts with caveolin. J. Gen. Virol. 88 (Pt 11), 3067–3077. doi:10.1099/vir.0.82856-0
Park, J. S., Kim, H. Y., Kim, H. W., Chae, G. N., Oh, H. T., Park, J. Y., et al. (2005). Increased caveolin-1, a cause for the declined adipogenic potential of senescent human mesenchymal stem cells. Mech. Ageing Dev. 126 (5), 551–559. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2004.11.014
Parton, R. G., and del Pozo, M. A. (2013). Caveolae as plasma membrane sensors, protectors and organizers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14 (2), 98–112. doi:10.1038/nrm3512
Pei, Q. M., Jiang, P., Yang, M., Qian, X. J., Liu, J. B., and Kim, S. H. (2016). Roxithromycin inhibits VEGF-induced human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation: opportunities for the treatment of asthma. Exp. Cell Res. 347 (2), 378–384. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.08.024
Pelkmans, L., Kartenbeck, J., and Helenius, A. (2001). Caveolar endocytosis of simian virus 40 reveals a new two-step vesicular-transport pathway to the ER. Nat. Cell Biol. 3 (5), 473–483. doi:10.1038/35074539
Peng, W., He, D., Shan, B., Wang, J., Shi, W., Zhao, W., et al. (2019). LINC81507 act as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-199b-5p to facilitate NSCLC proliferation and metastasis via regulating the CAV1/STAT3 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 10 (7), 533. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1740-9
Petpiroon, N., Bhummaphan, N., Tungsukruthai, S., Pinkhien, T., Maiuthed, A., Sritularak, B., et al. (2019). Chrysotobibenzyl inhibition of lung cancer cell migration through Caveolin-1-dependent mediation of the integrin switch and the sensitization of lung cancer cells to cisplatin-mediated apoptosis. Phytomedicine 58, 152888. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152888
Piegeler, T., Dull, R. O., Hu, G., Castellon, M., Chignalia, A. Z., Koshy, R. G., et al. (2014). Ropivacaine attenuates endotoxin plus hyperinflation-mediated acute lung injury via inhibition of early-onset Src-dependent signaling. BMC Anesthesiol. 14, 57. doi:10.1186/1471-2253-14-57
Pike, L. J. (2005). Growth factor receptors, lipid rafts and caveolae: an evolving story. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1746 (3), 260–273. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.05.005
Puddu, A., Montecucco, F., and Maggi, D. (2023). Caveolin-1 and atherosclerosis: regulation of LDLs fate in endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (10), 8869. doi:10.3390/ijms24108869
Puthusseri, B., Marudamuthu, A., Tiwari, N., Fu, J., Idell, S., and Shetty, S. (2017). Regulation of p53-mediated changes in the uPA-fibrinolytic system and in lung injury by loss of surfactant protein C expression in alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 312 (6), L783–L796. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00291.2016
Qi, H., Liu, Y., Wang, N., and Xiao, C. (2021). Lentinan attenuated the PM2.5 exposure-induced inflammatory response, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration by inhibiting the PVT1/miR-199a-5p/caveolin1 pathway in lung cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 40 (5), 683–693. doi:10.1089/dna.2020.6338
Qin, L., Zhu, N., Ao, B. X., Liu, C., Shi, Y. N., Du, K., et al. (2016). Caveolae and caveolin-1 integrate reverse cholesterol transport and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17 (3), 429. doi:10.3390/ijms17030429
Qu, L., Li, Y., Chen, C., Yin, T., Fang, Q., Zhao, Y., et al. (2022). Caveolin-1 identified as a key mediator of acute lung injury using bioinformatics and functional research. Cell Death Dis. 13 (8), 686. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05134-8
Reese, C. F., Chinnakkannu, P., Tourkina, E., Hoffman, S., and Kuppuswamy, D. (2022). Multiple subregions within the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain inhibit fibrosis, microvascular leakage, and monocyte migration. PLoS One 17 (2), e0264413. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0264413
Ren, Y., Li, L., Wang, M. M., Cao, L. P., Sun, Z. R., Yang, Z. Z., et al. (2021). Pravastatin attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury through decreasing pulmonary microvascular permeability via inhibition of Cav-1/eNOS pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 100, 108077. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108077
Robb, R., Kuo, J. C., Liu, Y., Corrales-Guerrero, S., Cui, T., Hegazi, A., et al. (2021). A novel protein-drug conjugate, SSH20, demonstrates significant efficacy in caveolin-1-expressing tumors. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 22, 555–564. doi:10.1016/j.omto.2021.07.013
Saito, M., Mitani, A., Ishimori, T., Miyashita, N., Isago, H., Mikami, Y., et al. (2020). Active mTOR in lung epithelium promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances lung fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 62 (6), 699–708. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2019-0255OC
Sargiacomo, M., Scherer, P. E., Tang, Z., Kübler, E., Song, K. S., Sanders, M. C., et al. (1995). Oligomeric structure of caveolin: implications for caveolae membrane organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92 (20), 9407–9411. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.20.9407
Sathish, V., Abcejo, A. J., Thompson, M. A., Sieck, G. C., Prakash, Y. S., and Pabelick, C. M. (2012). Caveolin-1 regulation of store-operated Ca(2+) influx in human airway smooth muscle. Eur. Respir. J. 40 (2), 470–478. doi:10.1183/09031936.00090511
Sathish, V., Abcejo, A. J., VanOosten, S. K., Thompson, M. A., Prakash, Y. S., and Pabelick, C. M. (2011). Caveolin-1 in cytokine-induced enhancement of intracellular Ca(2+) in human airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 301 (4), L607–L614. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00019.2011
Sathish, V., Thompson, M. A., Sinha, S., Sieck, G. C., Prakash, Y. S., and Pabelick, C. M. (2014). Inflammation, caveolae and CD38-mediated calcium regulation in human airway smooth muscle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1843 (2), 346–351. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.11.011
Savary, G., Dewaeles, E., Diazzi, S., Buscot, M., Nottet, N., Fassy, J., et al. (2019). The long noncoding RNA DNM3OS is a reservoir of FibromiRs with major functions in lung fibroblast response to TGF-β and pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 200 (2), 184–198. doi:10.1164/rccm.201807-1237OC
Scherer, P. E., Okamoto, T., Chun, M., Nishimoto, I., Lodish, H. F., and Lisanti, M. P. (1996). Identification, sequence, and expression of caveolin-2 defines a caveolin gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93 (1), 131–135. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.1.131
Scherer, P. E., Tang, Z., Chun, M., Sargiacomo, M., Lodish, H. F., and Lisanti, M. P. (1995). Caveolin isoforms differ in their N-terminal protein sequence and subcellular distribution. Identification and epitope mapping of an isoform-specific monoclonal antibody probe. J. Biol. Chem. 270 (27), 16395–16401. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.27.16395
Schlegel, A., Arvan, P., and Lisanti, M. P. (2001). Caveolin-1 binding to endoplasmic reticulum membranes and entry into the regulated secretory pathway are regulated by serine phosphorylation. Protein sorting at the level of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (6), 4398–4408. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005448200
Schnitzer, J. E., Oh, P., and McIntosh, D. P. (1996). Role of GTP hydrolysis in fission of caveolae directly from plasma membranes. Science 274 (5285), 239–242. doi:10.1126/science.274.5285.239
Shen, W., Gan, J., Xu, S., Jiang, G., and Wu, H. (2009). Penehyclidine hydrochloride attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 60 (4), 296–302. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2009.04.007
Shen, Y., Chen, L., Wang, M., Lin, D., Liang, Z., Song, P., et al. (2017). Flagellar hooks and hook protein FlgE participate in host microbe interactions at immunological level. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 1433. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-01619-1
Shetty, S., and Idell, S. (2023). Caveolin-1-Related intervention for fibrotic lung diseases. Cells 12 (4), 554. doi:10.3390/cells12040554
Shi, Y. B., Li, J., Lai, X. N., Jiang, R., Zhao, R. C., and Xiong, L. X. (2020). Multifaceted roles of caveolin-1 in lung cancer: a new investigation focused on tumor occurrence, development and therapy. Cancers (Basel) 12 (2), 291. doi:10.3390/cancers12020291
Shu, Y., and Jin, S. (2023). Caveolin-1 in endothelial cells: a potential therapeutic target for atherosclerosis. Heliyon 9 (8), e18653. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18653
Sivanantham, A., Alktaish, W., Murugeasan, S., Gong, B., Lee, H., and Jin, Y. (2023). Caveolin-1 regulates OMV-induced macrophage pro-inflammatory activation and multiple Toll-like receptors. Front. Immunol. 14, 1044834. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1044834
Song, Y., Xue, L., Du, S., Sun, M., Hu, J., Hao, L., et al. (2012). Caveolin-1 knockdown is associated with the metastasis and proliferation of human lung cancer cell line NCI-H460. Biomed. Pharmacother. 66 (6), 439–447. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2012.03.001
Sripada, A., Sirohi, K., Michalec, L., Guo, L., McKay, J. T., Yadav, S., et al. (2021). Sprouty2 positively regulates T cell function and airway inflammation through regulation of CSK and LCK kinases. PLoS Biol. 19 (3), e3001063. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3001063
Su, H., Zou, R., Su, J., Chen, X., Yang, H., An, N., et al. (2024). Sterile inflammation of peritoneal membrane caused by peritoneal dialysis: focus on the communication between immune cells and peritoneal stroma. Front. Immunol. 15, 1387292. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1387292
Sudhahar, V., Okur, M. N., O'Bryan, J. P., Minshall, R. D., Fulton, D., Ushio-Fukai, M., et al. (2020). Caveolin-1 stabilizes ATP7A, a copper transporter for extracellular SOD, in vascular tissue to maintain endothelial function. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 319 (5), C933–c944. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00151.2020
Sun, G. Y., Wu, J. X., Wu, J. S., Pan, Y. T., and Jin, R. (2012). Caveolin-1, E-cadherin and β-catenin in gastric carcinoma, precancerous tissues and chronic non-atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 24 (1), 23–28. doi:10.1007/s11670-012-0023-0
Taira, J., Sugishima, M., Kida, Y., Oda, E., Noguchi, M., and Higashimoto, Y. (2011). Caveolin-1 is a competitive inhibitor of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) with heme: identification of a minimum sequence in caveolin-1 for binding to HO-1. Biochemistry 50 (32), 6824–6831. doi:10.1021/bi200601t
Tang, W., Li, Y., Li, Y., and Wang, Q. (2021). Caveolin-1, a novel player in cognitive decline. Neurosci. Biobehav Rev. 129, 95–106. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.06.044
Tao, L., Wang, J., Wang, K., Liu, Q., Li, H., Xu, S., et al. (2024). Exerkine FNDC5/irisin-enriched exosomes promote proliferation and inhibit ferroptosis of osteoblasts through interaction with Caveolin-1. Aging Cell 23 (8), e14181. doi:10.1111/acel.14181
Thompson, M. A., Prakash, Y. S., and Pabelick, C. M. (2014). Arachidonate-regulated Ca(2+) influx in human airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 51 (1), 68–76. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2013-0144OC
Tomita, S., Nakanishi, N., Ogata, T., Higuchi, Y., Sakamoto, A., Tsuji, Y., et al. (2024). The Cavin-1/Caveolin-1 interaction attenuates BMP/Smad signaling in pulmonary hypertension by interfering with BMPR2/Caveolin-1 binding. Commun. Biol. 7 (1), 40. doi:10.1038/s42003-023-05693-2
Tong, F., Shen, W., Zhao, J., Hu, Y., Zhao, Q., Lv, H., et al. (2023). Silencing information regulator 1 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats via the upregulation of caveolin-1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165, 115018. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115018
Trane, A. E., Hiob, M. A., Uy, T., Pavlov, D., and Bernatchez, P. (2015). Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain residue phenylalanine 92 modulates Akt signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 766, 46–55. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.09.033
Trane, A. E., Pavlov, D., Sharma, A., Saqib, U., Lau, K., van Petegem, F., et al. (2014). Deciphering the binding of caveolin-1 to client protein endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS): scaffolding subdomain identification, interaction modeling, and biological significance. J. Biol. Chem. 289 (19), 13273–13283. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.528695
Tzouvelekis, A., Gomatou, G., Bouros, E., Trigidou, R., Tzilas, V., and Bouros, D. (2019). Common pathogenic mechanisms between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. Chest 156 (2), 383–391. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2019.04.114
Van Krieken, R., and Krepinsky, J. C. (2017). Caveolin-1 in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: potential therapeutic target? Curr. Diab Rep. 17 (3), 19. doi:10.1007/s11892-017-0844-9
Vaz de Paula, C. B., Nagashima, S., Liberalesso, V., Collete, M., da Silva, F. P. G., Oricil, A. G. G., et al. (2021). COVID-19: immunohistochemical analysis of TGF-β signaling pathways in pulmonary fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (1), 168. doi:10.3390/ijms23010168
Vogel, E. R., Britt, R. D., Faksh, A., Kuipers, I., Pandya, H., Prakash, Y. S., et al. (2017). Moderate hyperoxia induces extracellular matrix remodeling by human fetal airway smooth muscle cells. Pediatr. Res. 81 (2), 376–383. doi:10.1038/pr.2016.218
Vogel, E. R., Manlove, L. J., Kuipers, I., Thompson, M. A., Fang, Y. H., Freeman, M. R., et al. (2019). Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide prevents hyperoxia-induced airway remodeling in a neonatal mouse model. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 317 (1), L99–L108. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00111.2018
Volonte, D., and Galbiati, F. (2009). Caveolin-1, cellular senescence and pulmonary emphysema. Aging (Albany NY) 1 (9), 831–835. doi:10.18632/aging.100079
Volonte, D., Kahkonen, B., Shapiro, S., Di, Y., and Galbiati, F. (2009). Caveolin-1 expression is required for the development of pulmonary emphysema through activation of the ATM-p53-p21 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 284 (9), 5462–5466. doi:10.1074/jbc.C800225200
Volonte, D., Vyas, A. R., Chen, C., Dacic, S., Stabile, L. P., Kurland, B. F., et al. (2018). Caveolin-1 promotes the tumor suppressor properties of oncogene-induced cellular senescence. J. Biol. Chem. 293 (5), 1794–1809. doi:10.1074/jbc.M117.815902
Wang, C., Li, Y., Xu, L., Zhang, Q., Gegentuya, , and Tian, G. (2021). Bortezomib inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation by suppressing caveolin-1/SOCE/[Ca(2+)](i) signaling Axis in human PASMCs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 5551504. doi:10.1155/2021/5551504
Wang, J., Shang, Y. X., Cai, X. X., and Liu, L. Y. (2018). Vasoactive intestinal peptide inhibits airway smooth muscle cell proliferation in a mouse model of asthma via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 364 (2), 168–174. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.01.042
Wang, X. M., Kim, H. P., Nakahira, K., Ryter, S. W., and Choi, A. M. (2009). The heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide pathway suppresses TLR4 signaling by regulating the interaction of TLR4 with caveolin-1. J. Immunol. 182 (6), 3809–3818. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0712437
Wang, X. M., Kim, H. P., Song, R., and Choi, A. M. (2006). Caveolin-1 confers antiinflammatory effects in murine macrophages via the MKK3/p38 MAPK pathway. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 34 (4), 434–442. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2005-0376OC
Williams, T. M., and Lisanti, M. P. (2004). The Caveolin genes: from cell biology to medicine. Ann. Med. 36 (8), 584–595. doi:10.1080/07853890410018899
Wu, L. Q., Wang, R. L., Dai, Y. R., Li, F. Q., Wu, H. Y., Yan, S. S., et al. (2015). Roxithromycin suppresses airway remodeling and modulates the expression of caveolin-1 and phospho-p42/p44MAPK in asthmatic rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 24 (2), 247–255. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2014.11.015
Wu, T., Zhang, B., Ye, F., and Xiao, Z. (2013). A potential role for caveolin-1 in VEGF-induced fibronectin upregulation in mesangial cells: involvement of VEGFR2 and Src. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 304 (6), F820–F830. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00294.2012
Wu, X., Kong, Q., Xia, Z., Zhan, L., Duan, W., and Song, X. (2019). Penehyclidine hydrochloride alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats: potential role of caveolin-1 expression upregulation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 43 (5), 2064–2074. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4117
Xia, Y., Cai, P. C., Yu, F., Xiong, L., He, X. L., Rao, S. S., et al. (2017). IL-4-induced caveolin-1-containing lipid rafts aggregation contributes to MUC5AC synthesis in bronchial epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 18 (1), 174. doi:10.1186/s12931-017-0657-z
Xing, Y., Wang, L., Wang, H., Kong, X., and Zhan, L. (2017). Dynamic expression of transformating growth factor-β1 and caveolin-1 in the lung of Bleomycin-induced interstitial lung disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 9 (8), 2360–2368. doi:10.21037/jtd.2017.07.01
Xu, L., Li, T., Chen, Q., Liu, Z., Chen, Y., Hu, K., et al. (2021). The α2AR/Caveolin-1/p38MAPK/NF-κB axis explains dexmedetomidine protection against lung injury following intestinal ischaemia-reperfusion. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25 (13), 6361–6372. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16614
Xu, L. Y., Cai, W. R., Ma, C. F., Shou, Q. Y., Qian, J. L., and Huseyin, T. S. (2018). Qi-dong-huo-xue-yin inhibits inflammation in acute lung injury in mice via toll-like receptor 4/caveolin-1 signaling. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2373609. doi:10.1155/2018/2373609
Yang, K., Zhao, M., Huang, J., Zhang, C., Zheng, Q., Chen, Y., et al. (2018). Pharmacological activation of PPARγ inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation through a caveolin-1-targeted and -dependent mechanism in PASMCs. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 314 (4), C428–C438. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00143.2017
Yang, N., Liu, Y. Y., Pan, C. S., Sun, K., Wei, X. H., Mao, X. W., et al. (2014). Pretreatment with andrographolide pills(®) attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary microcirculatory disturbance and acute lung injury in rats. Microcirculation 21 (8), 703–716. doi:10.1111/micc.12152
Yin, D., Qiu, J., Hu, S., Cheng, L., Li, H., Cheng, X., et al. (2022). CAV1 is a prognostic predictor for patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer. J. Biosci. 47, 13. doi:10.1007/s12038-021-00245-4
Yu, Q., Chen, X., Fang, X., Chen, Q., and Hu, C. (2015). Caveolin-1 aggravates cigarette smoke extract-induced MUC5AC secretion in human airway epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 35 (5), 1435–1442. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2015.2133
Yu, W., Chen, H., Yang, H., Ding, J., Xia, P., Mei, X., et al. (2019). Dissecting molecular mechanisms underlying pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation in pulmonary hypertension: role of mutated caveolin-1 (Cav1(F92A))-bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Heart Lung Circ. 28 (10), 1587–1597. doi:10.1016/j.hlc.2018.08.002
Yu, W. C., Chen, H. Y., Yang, H. L., Xia, P., Zou, C. W., Sun, T. W., et al. (2019). rBMSC/Cav-1(F92A) mediates oxidative stress in PAH rat by regulating SelW/14-3-3η and CA1/kininogen signal transduction. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 6768571. doi:10.1155/2019/6768571
Yuan, K., Huang, C., Fox, J., Gaid, M., Weaver, A., Li, G., et al. (2011). Elevated inflammatory response in caveolin-1-deficient mice with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection is mediated by STAT3 protein and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB). J. Biol. Chem. 286 (24), 21814–21825. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.237628
Yuan, Y., Zhu, H., Huang, S., Zhang, Y., and Shen, Y. (2024). SFRP5 partially inhibits the proliferation and migration of airway smooth muscle cells in children with asthma by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Discov. Med. 36 (181), 323–331. doi:10.24976/Discov.Med.202436181.30
Zaas, D. W., Swan, Z., Brown, B. J., Wright, J. R., and Abraham, S. N. (2009). The expanding roles of caveolin proteins in microbial pathogenesis. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2 (6), 535–537. doi:10.4161/cib.2.6.9259
Zaiman, A., Fijalkowska, I., Hassoun, P. M., and Tuder, R. M. (2005). One hundred years of research in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 33 (5), 425–431. doi:10.1165/rcmb.F307
Zhang, T., Shang, F., Ma, Y., Xu, Y., Sun, W., and Song, H. (2023a). Caveolin-1 promotes the imbalance of Th17/Treg in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by regulating Hsp70 expression. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 18, 565–574. doi:10.2147/copd.S398780
Zhang, T., Yang, F., Dai, X., Liao, H., Wang, H., Peng, C., et al. (2023b). Role of Caveolin-1 on the molybdenum and cadmium exposure induces pulmonary ferroptosis and fibrosis in the sheep. Environ. Pollut. 334, 122207. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122207
Zhao, W., Lin, Y., Xiong, J., Wang, Y., Huang, G., Deng, Q., et al. (2018). RAGE mediates β-catenin stabilization via activation of the Src/p-Cav-1 axis in a chemical-induced asthma model. Toxicol. Lett. 299, 149–158. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.09.010
Zhao, Y., Yu, J., Huang, A., Yang, Q., Li, G., Yang, Y., et al. (2023). ROS impairs tumor vasculature normalization through an endocytosis effect of caveolae on extracellular SPARC. Cancer Cell Int. 23 (1), 152. doi:10.1186/s12935-023-03003-8
Zhao, Y. Y., Zhao, Y. D., Mirza, M. K., Huang, J. H., Potula, H. H., Vogel, S. M., et al. (2009). Persistent eNOS activation secondary to caveolin-1 deficiency induces pulmonary hypertension in mice and humans through PKG nitration. J. Clin. Invest. 119 (7), 2009–2018. doi:10.1172/jci33338
Zhou, P., Yu, W., Zhang, C., Chen, K., Tang, W., Li, X., et al. (2022). Tiao-bu-fei-shen formula promotes downregulation of the caveolin 1-p38 mapk signaling pathway in COPD - associated tracheobronchomalacia cell model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 293, 115256. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115256
Zhou, Y., Little, P. J., Downey, L., Afroz, R., Wu, Y., Ta, H. T., et al. (2020). The role of toll-like receptors in atherothrombotic cardiovascular disease. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 3 (3), 457–471. doi:10.1021/acsptsci.9b00100
Zimnicka, A. M., Husain, Y. S., Shajahan, A. N., Sverdlov, M., Chaga, O., Chen, Z., et al. (2016). Src-dependent phosphorylation of caveolin-1 Tyr-14 promotes swelling and release of caveolae. Mol. Biol. Cell 27 (13), 2090–2106. doi:10.1091/mbc.E15-11-0756
Zuo, S., Wang, B., Liu, J., Kong, D., Cui, H., Jia, Y., et al. (2021). ER-anchored CRTH2 antagonizes collagen biosynthesis and organ fibrosis via binding LARP6. Embo J. 40 (16), e107403. doi:10.15252/embj.2020107403
Glossary
Keywords: caveolin-1, pneumonia, asthma, COPD, ali, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis
Citation: Fan J, Zheng S, Wang M and Yuan X (2024) The critical roles of caveolin-1 in lung diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1417834. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1417834
Received: 17 April 2024; Accepted: 09 September 2024;
Published: 24 September 2024.
Edited by:
Jadranka Milosevic, Captis Diagnostics Inc., United StatesReviewed by:
Ayyanar Sivanantham, Versiti Blood Research Institute, United StatesSuellen Darc Oliveira, University of Illinois Chicago, United States
Ygor Marinho, University of Illinois, Chicago, United States, in collaboration with reviewer SDO
Copyright © 2024 Fan, Zheng, Wang and Yuan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoliang Yuan, eXhseXl4c0AxMjYuY29t
 Jiarun Fan
Jiarun Fan Xiaoliang Yuan
Xiaoliang Yuan
