
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol., 16 June 2022
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.952598
This article is a correction to:
Ginsenoside Compound K Enhances Fracture Healing via Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis
 Lingli Ding1
Lingli Ding1 Song Gu2
Song Gu2 Bingyu Zhou1
Bingyu Zhou1 Min Wang1
Min Wang1 Yage Zhang1
Yage Zhang1 Siluo Wu1
Siluo Wu1 Hong Zou3
Hong Zou3 Guoping Zhao4,5,6,7,8,9*
Guoping Zhao4,5,6,7,8,9* Zhao Gao10*
Zhao Gao10* Liangliang Xu1*
Liangliang Xu1*A Corrigendum on
Ginsenoside Compound K Enhances Fracture Healing via Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis
by Ding L, Gu S, Zhou B, Wang M, Zhang Y, Wu S, Zou H, Zhao G, Gao Z and Xu L (2022). Front. Pharmacol. 13:855393. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.855393
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 3A as published. Figure 3A is a schematic diagram of the time points of animal modeling and samples, in which the model and time points were incorrectly marked. The corrected Figure 3 appears below.
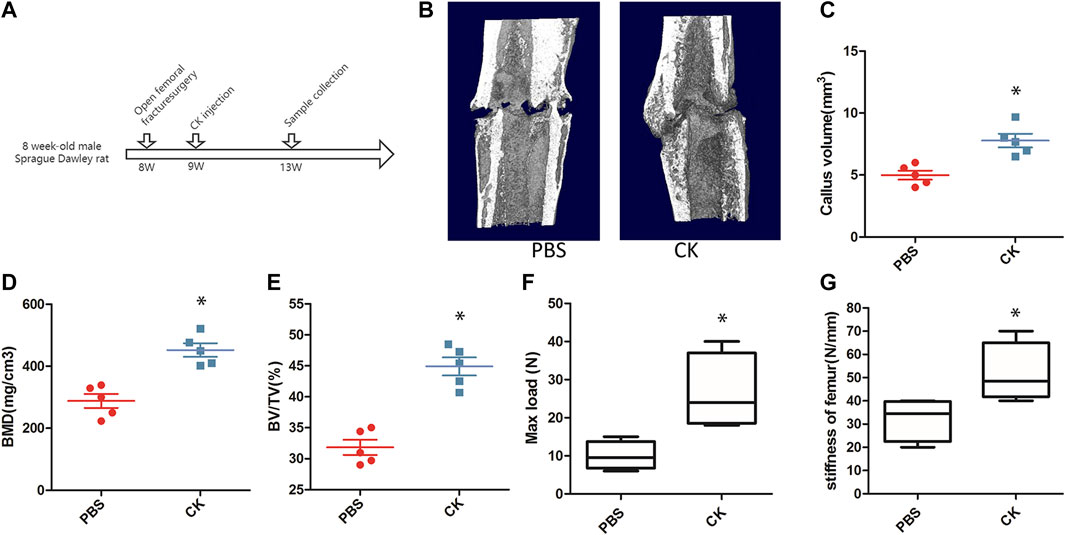
FIGURE 3. CK accelerated the progression of fracture healing. (A) Schematic illustration of time points of animal modeling and sample collection. (B) Representative 3-dimensional micro-CT images of femurs in each group. (C–E) Quantitative analysis of parameters, including CV, BMD, and BV/TV, *p < 0.05, compared with the PBS group, n = 3 (F–G) Biomechanical properties of the fractured bones by 3-point bending test, *p < 0.05, compared with the PBS group, n = 6.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: CK, fracture healing, Wnt/β-catenin, osteogenesis, angiogenesis
Citation: Ding L, Gu S, Zhou B, Wang M, Zhang Y, Wu S, Zou H, Zhao G, Gao Z and Xu L (2022) Corrigendum: Ginsenoside Compound K Enhances Fracture Healing via Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. :952598. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.952598
Received: 25 May 2022; Accepted: 30 May 2022;
Published: 16 June 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Longhuo Wu, Gannan Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2022 Ding, Gu, Zhou, Wang, Zhang, Wu, Zou, Zhao, Gao and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guoping Zhao, Z3B6aGFvQHNpYnMuYWMuY24=; Zhao Gao, cWlxaW4xOTkwQDE2My5jb20=; Liangliang Xu, eHVsbC0yMDE2QGd6dWNtLmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.