
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Organ. Psychol. , 07 January 2025
Sec. Performance and Development
Volume 2 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/forgp.2024.1499248
This article is part of the Research Topic Impact of Remote Work on Individual and Organizational Performance Constructs View all 4 articles
Introduction: Leadership in organizations is facing important challenges related to technological and social developments. The widespread use of teleworking and remote work requires organizations to identify and develop leadership competencies adapted to this work context. This structured literature review explores empirical evidence on theleadership competencies that facilitate telework and how they contribute to achieving high levels of performance in teleworkers.
Methods: We analyzed 22 quantitative and 15 qualitative empirical articles (2000–2024) following PRISMA guidelines. We selected only research that concentrates on specific leadership competencies.
Results: The review shows that competencies oriented to decrease operational and social distance at work are positively related to individual and team task performance in organizations. There is some evidence of the relationship of those competencies with other dimensions of performance such as innovative performance or OCB. Leaders' digital communication emerges as the foremost competency, along with goal management, support and empowerment. To some extent, mechanisms such as trust, autonomy, and media usage have been found as intervening mechanisms. Moderators such as teleworkers' self-management and geographical distance have been identified.
Discussion: Substantial gaps in the literature were identified, including the lack of longitudinal studies, limited research on contextual/adaptive performance, and lack of attention to adapting leadership competencies to digital settings. The findings provide guidelines for leadership training and development interventions tailored to telework, considering that traditional leadership competencies may need adaptation for telework and consider specific issues in this context.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42023473498, identifier: CRD42023473498.
In the current hybrid and virtual organizations, there is a growing need for training and developing leaders in competencies that are effective in telework (Arora and Suri, 2020; Gohoungodji et al., 2022). This type of work arrangement has gone from being rather exceptional to a new way of shaping labor markets worldwide (Baert et al., 2020). According to the World Economic Forum (2023), 20.5% of global companies indicated that offering more opportunities for telework is one of their short-term strategies, and remote job offers have increased compared to previous years (Aksoy et al., 2023). These changes require HR professionals to re-skill and adapt different roles to the “new” working environment, especially in leadership (Bondarouk and Brewster, 2016). In fact, successful telework implementation has been suggested to depend more on how leadership is developed than on the correct use of technology (Beauregard et al., 2019; Bondarouk and Brewster, 2016).
Telework refers to work performed regularly outside the employers' location, at least once weekly, excluding business travel, mobile work across multiple sites, or client offices (Nakrošiene et al., 2019). It includes remote and hybrid setups, where employees alternate between working from home and the organizations' headquarters in varying proportions. In fact, as Vartiainen and Vanharanta (2024) state, the concept of hybridity refers to a temporal dimension that fluctuates between telework and on-site work.
The widespread adoption of telework has introduced unique challenges that can impact worker performance. These include blurred work-life boundaries, social and professional isolation, potential loss of tacit knowledge, and ergonomic difficulties (Beauregard et al., 2019; Waight et al., 2022). Additionally, teleworkers may face technological barriers and communication constraints (Shirmohammadi et al., 2022). These factors can affect teleworkers' performance and effectiveness, particularly for those unaccustomed to remote work arrangements (Offstein et al., 2010). This could be challenging for performance indicators beyond task performance that could be especially relevant for nowadays organizations, such as innovative or contextual behaviors.
In this context, understanding and measuring performance at multiple levels becomes crucial. Following Koopmans et al. (2011, 2014), we conceptualize work performance as behaviors or actions contributing to organizational goals. At the individual level, this includes four dimensions: task performance (completing core work duties), contextual performance (behaviors supporting the organizational, social, and psychological environment), adaptive performance (adapting to changes in work roles or environment), and counterproductive work behavior (behaviors harmful to organizational wellbeing). At the team level, performance encompasses collective task accomplishment, team member behaviors that maintain the group's social context, and the team's ability to adapt to changes (Kozlowski and Ilgen, 2006).
The discussion about whether telework improves or worsens worker performance has continued for the past two decades, yielding inconsistent findings (Brown et al., 2021; Pyöriä, 2011). This may be due to the variability in the operationalization of performance measures (Brown, 2021), as well as other organizational factors that might influence those relationships, such as leadership. Thus, more research is needed to identify and design work environments that facilitate different types of performance during telework. In this context, leadership requires to be considered In fact, leaders have been pointed out to be a crucial factor for effective telework, as they can contribute to addressing telework challenges and supporting both individual and team performance (Avolio et al., 2009; Bell et al., 2023; Cortellazzo et al., 2019; Inceoglu et al., 2018; Kozlowski et al., 2021; Peiró et al., 2024; Zeike et al., 2019).
Recent research emphasizes that leadership in telework requires more than simply extending traditional leadership practices to virtual settings. Instead, it demands developing specific competencies to manage remote work effectively (Alkhayyal and Bajaba, 2023; Contreras et al., 2020; Delanoeije and Verbruggen, 2020). In this sense, Peiró and Martínez-Tur (2022) proposed that leaders must adapt their behaviors and develop new ones that respond adequately to a digitalized and geographically dispersed work environment.
There have been different attempts to establish specific leadership competencies models for the digital era (Avolio et al., 2000; Liao et al., 2024). In this context, research has defined e-leadership as “a social influence process mediated by AIT (advanced information technologies) to produce a change in attitudes, feelings, thinking, behavior, and performance with individuals, groups, and/or organizations” (Avolio et al., 2000, p. 617). When the focus is put on the spatial and temporal dimensions in which digital leadership occurs, digital leadership is considered as “social influence that occurs when leaders and followers are geographically dispersed, temporally asynchronous, and completely mediated by technology” (Banks et al., 2022, p. 2). Thus, leadership focus is set in its contribution to the reduction of virtual distance.
As a response to this challenge, the virtual distance framework (Lojeski and Reilly, 2020) suggests that leaders can improve performance in remote work or telework by implementing strategies that bring workers closer together According to Lojeski and Reilly (2020), organizations need to overcome operational and affinity distance for effective performance in telework settings. Operational distance involves challenges in technology-mediated work coordination and information sharing, while affinity distance refers to the psychological and social separation that emerges from physical dispersion. Leaders might greatly contribute to both aspects by digitalizing the social process of influence. Beyond the development of specifc leadership competency models for this context, research needs also to ascertain which is the empirical evidence about how traditional, digital or digitalized competencies facilitate performance in telework contexts (Peiró and Martínez-Tur, 2022). Lack of clarity about which specific aspects of leadership need to be trained and developed in remote and hybrid workplaces could lead organizations to implement ineffective or less efficient interventions (Arora and Suri, 2020). Despite several studies indicating that telework leadership, as in face-to-face work, is fundamental for individual and team performance (Brown, 2021), there is still no consensus about the empirical relationship between specific leadership competencies and performance in telework. Therefore, our study focuses on the need to identify and understand effective leadership competencies that are related to performance in telework. This leads to our main research question:
RQ1: What leadership competencies are most relevant for performance in telework arrangements?
Identifying the mechanisms through which leaders influence performance in telework settings is also crucial to better understand how leadership contributes to performance in these types of work arrangements. Moreover, leadership does not occur isolated. Telework characteristics, contextual factors, leader characteristics, and team member attributes can significantly affect how leadership competencies influence performance outcomes. Thus, it is important to address and understand both the mechanisms and boundary conditions enabling or hindering leaders from demonstrating effective leadership in telework. This leads to our second research question:
RQ2. What mechanisms and boundary conditions intervene in the relationship between leadership competencies and performance in telework?
In summary, this study conducts a structured literature review (SLR) of the relationships between leadership competencies and different individual and team performance indicators in telework contexts. SLR is a comprehensive method for collecting literature that meets specific criteria to discover themes, patterns, trends, or gaps, especially in human resource development (Rocco et al., 2023). Over the past two decades, several studies have examined these relationships (Bell et al., 2023; Brown et al., 2021; Cortellazzo et al., 2019; Efimov et al., 2022). However, this knowledge remains fragmented, and there is a lack of a clear framework for telework leadership at the individual and team levels (Cortellazzo et al., 2019). Therefore, this study will contribute to the field by thematically analyzing the leadership competencies and components contributing to performance in telework contexts at both levels by exploring and analyzing the competencies presented in the literature.
Finally, this analysis will provide an initial understanding of effective telework leadership competencies applicable to teams and organizations in telework arrangements. As a result, for HR managers and practitioners, it could serve as a starting point for determining implications for future telework leadership training interventions, helping to build thriving and solid businesses and organizations (Di Fabio and Peiró, 2018).
Considering the above, the three main objectives of this research are:
1. Identifying relevant leadership competencies for promoting performance in telework, considering different operationalizations of the construct (dimensions and level of analysis).
2. Analyze the mechanisms and contextual factors that might affect those relationships.
3. Propose general guidelines and recommendations for future leadership development interventions tailored to the telework context.
To answer the research questions, we analyzed empirical research from January 2000 to June 2024, following PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews (see Figure 1). We systematically reviewed empirical studies on Scopus, Psycarticles, PsycINFO, ABI/INFORM, and Web of Science databases, encompassing quantitative and qualitative methods published in English, Spanish, and Portuguese.
Search terms combined the different variables regarding the study: concepts of phenomenon (e.g., telework), population (e.g., leaders), competencies (e.g., competencies), and performance.
As inclusion criteria, we focused on peer-reviewed empirical research on real-world teleworking populations related to organizational psychology and HRM. As exclusion criteria, we excluded research that has not been carried out on teleworkers or teleworking contexts (students' samples were excluded) and research that does not address leadership as an independent or antecedent variable. We also excluded studies that did not directly examine specific leadership competencies (for example, studies that address leadership models such as LMX and transformational leadership).
The database search yielded 1,307 initial results. Applying exclusions criteria, we left 92 articles for full-text review by two subject matter experts. Fifty-five articles were excluded for not meeting methodological criteria or lacking dependent variables related to performance.
A total of 37 articles were reviewed in full. Studies of virtual teams were included, as these comprise teleworkers by default. Experimental studies were also reviewed. Also, as telework is considered a continuum that can include on-site working days, research on hybrid arrangements was also included. Two experts confirmed consistency in applying the selection criteria.
A systematic assessment of publication bias was undertaken using an ad-hoc scale developed for this literature review, using guidelines from Acosta et al. (2020). This scale evaluated: (1) the comprehensiveness of the literature search strategy, including sources searched and search terms used; (2) the inclusion of significant findings; (3) the adequate sample (teleworkers and leaders from real organizations); and (4) the quality of the document. This scale was created to provide an indicator of publication bias tailored to the parameters and scope of this review. This assessment provided an additional lens for readers to gauge the objectivity and perspective of the review critically.
Each article was coded according to methodology, leadership framework, analysis level, sample characteristics, sample size, leadership variables, and outcome variables. According to the SLR method (Rocco et al., 2023), similar behaviors were thematically grouped to derive a final set of leadership competencies related to individual or team performance.
The systematic review results are presented in two sections. First, we describe the reviewed literature regarding theoretical and methodological approaches. Then, we address the research questions regarding the relationships between leadership and performance in telework.
We found 22 quantitative, 15 qualitative, and one mixed-method study. Details are shown in Table 1 for quantiative studies and in Table 2 for qualitative studies.
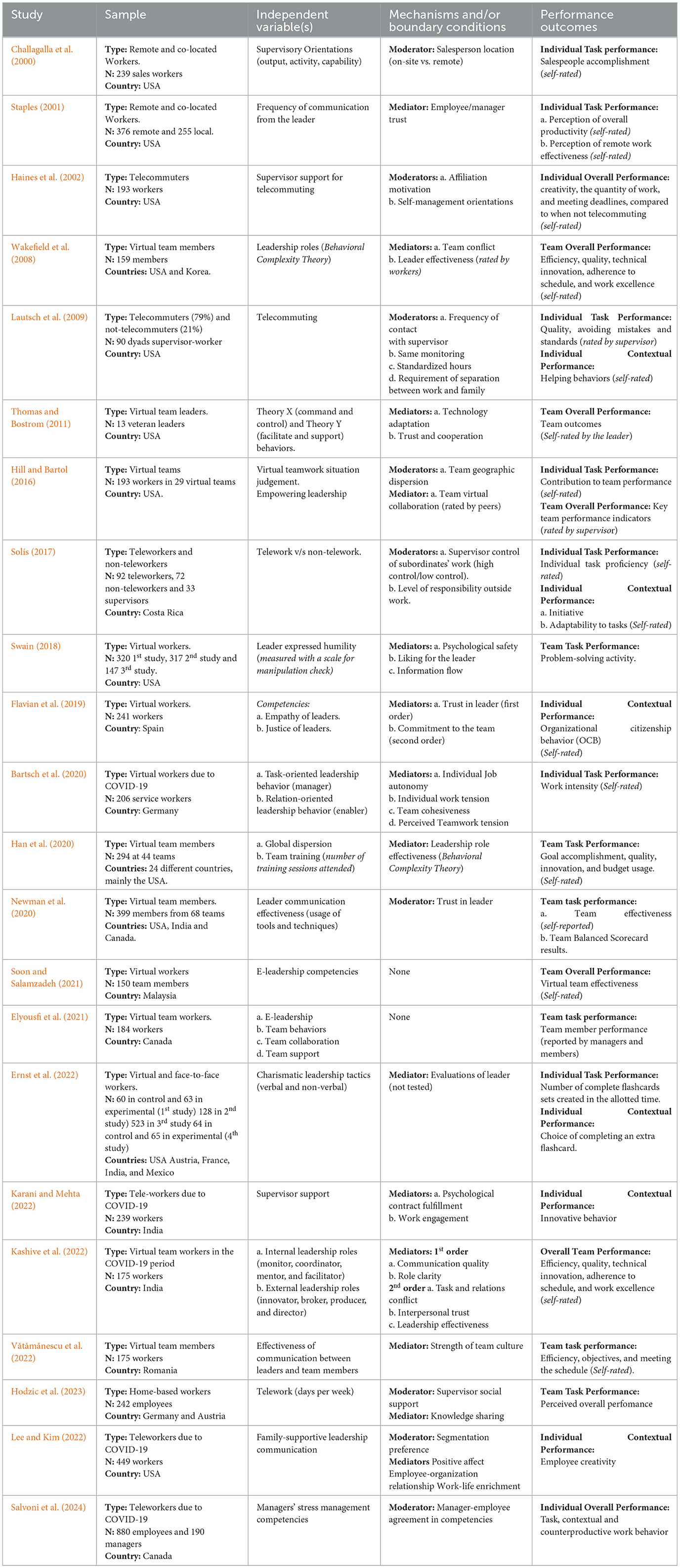
Table 1. Quantitative papers analyzing the relationship between leadership for telework and performance indicators (22).
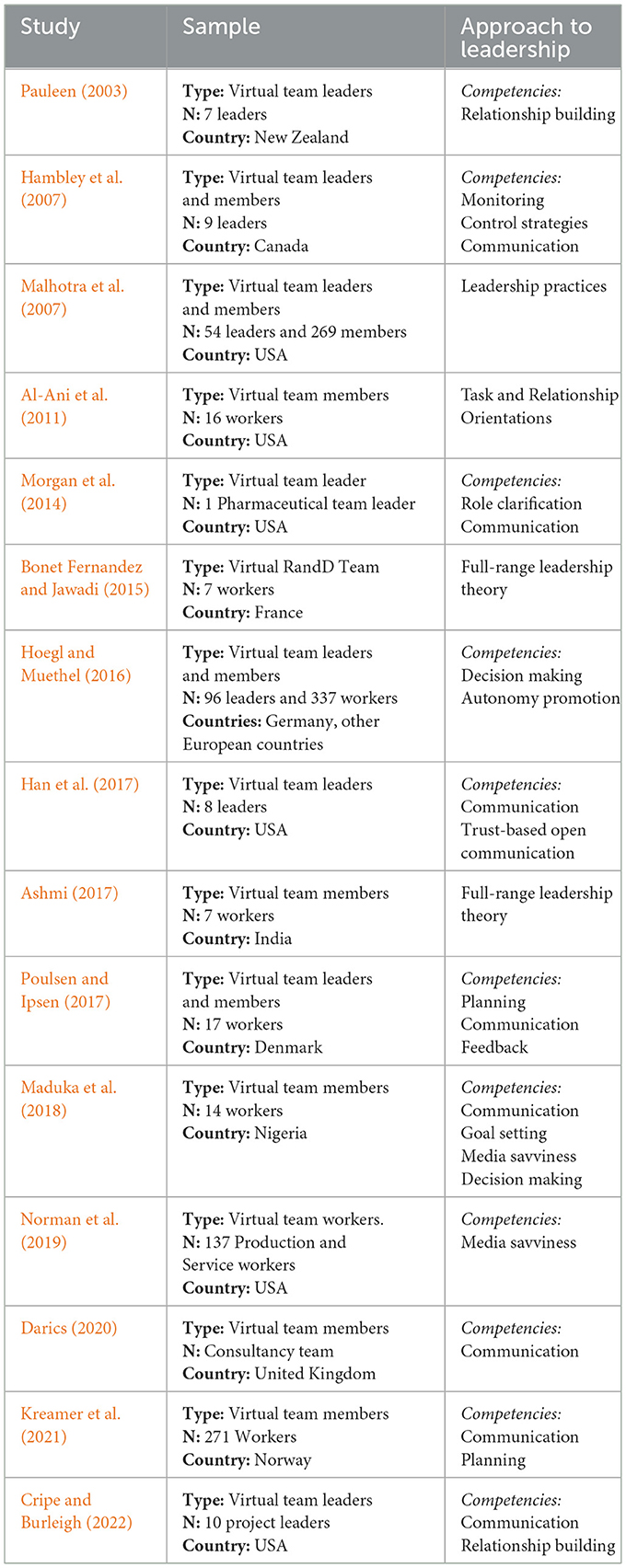
Table 2. Qualitative papers analyzing the relationship between leadership for telework and performance indicators (15).
Most reviewed articles (25) were published within the last decade, with 15 published within the past 5 years (see Figure 2). Most papers were published in 2020 and 2022, coinciding with the beginning and end of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Regarding sample populations, most studies focused on the service sector and tech/finance workers. Geographically, most studies were conducted in the United States (14), North Europe (6), Asia (4 studies, mainly India), Canada (3), and Southern Europe (2). A few studies were conducted in other regions: Costa Rica (Latin America), New Zealand (Oceania), and Nigeria (Africa). Five of them were cross-national, considering distributed teams.
In quantitative studies, most of the data outcomes were gathered from the formal leaders' subordinates/followers (20 studies), except for Thomas and Bostrom (2011) who gathered data from leaders. In qualitative studies, 8 studies collected information exclusively from leaders, while 5 studies included both leaders and team members. Two studies employed case study designs.
Regarding sociodemographic characteristics of the samples, sex of respondents is reported (28) but primarily to describe the sample. However, many articles do not report it (9). Among those reporting sex, 12 studies had predominantly female samples, 8 had predominantly male samples, and 8 had relatively balanced gender distributions. Age was reported in 24 studies, typically as a mean ranging from 21 to 48 years old. Only three articles include sex and age as a control variable.
Specific patterns regarding the conceptual and operational approach to performance can be identified in quantitative research. Eight studies defined and operationalized performance as task performance, which includes indicators such as quality of work, productivity, efficiency, planning, knowledge, decision-making, and communication. Six articles analyzed the relationship between leadership and contextual performance, such as helping behaviors (Lautsch et al., 2009), innovation (Karani and Mehta, 2022), creativity (Lee and Kim, 2022), initiative and adaptability (Solís, 2017), organizational citizenship behaviors (Flavian et al., 2019), and extra task choice (Karani and Mehta, 2022). Finally, 12 articles measured overall performance. Notably, no articles were found that explicitly considered adaptive performance or counterproductive work behavior in the context of telework leadership.
In terms of the level of analysis, 12 studies focused on individual-level outcomes, examining task performance (e.g., Challagalla et al., 2000; Bartsch et al., 2020) and contextual performance indicators (e.g., Karani and Mehta, 2022). Nine studies analyzed team-level performance, investigating outcomes such as team efficiency and innovation (Wakefield et al., 2008), project success (Thomas and Bostrom, 2011), team effectiveness (Soon and Salamzadeh, 2021), and goal accomplishment (Han et al., 2020). One study conducted multilevel analyses examining individual and team-level outcomes (Hill and Bartol, 2016). No studies were found examining organizational-level performance outcomes in telework contexts.
Most of the studies using quantitative data (22) were correlational (20), except for two experimental studies (Ernst et al., 2022; Swain, 2018). Moreover, most of the correlational studies used a cross-sectional design (19), except for two studies that used a panel design (Lautsch et al., 2009; Hill and Bartol, 2016) and a diary (weekly) study (Hodzic et al., 2023).
In general terms, the samples were composed of remote workers, but five studies included both remote and non-remote workers (Challagalla et al., 2000; Ernst et al., 2022; Lautsch et al., 2009; Solís, 2017; Staples, 2001).
Regarding the referent of the performance measures, seven studies used workers' perceptions about their team performance, and 1 used subordinates' self-reported performance. Three studies included workers' individual or team performance rated by their supervisors. Also, other measures of performance were included: Thomas and Bostrom (2011) measured project success from the leaders' perspective; Hill and Bartol (2016) included key team performance indicators; Swain (2018) conducted an online problem-solving activity, and Newman et al. (2020) used workers Balanced Score Card results.
In the case of qualitative studies, most of them (11) used individual semi-structured interviews, while two employed case study methodology and two combined interviews with questionnaires.
As indicated in the descriptive part of the results, research has analyzed several performance indicators in relation to leadership competencies in telework. Following the virtual distance framework, we have grouped the results into two types: competencies aimed to reduce operational distance and competencies aimed to reduce affinity (or relationship) distance.
Considerable research addresses the relationship between competencies directed to reduce operational distance and performance in telework (12 of 22 quantitative studies and 9 of 15 qualitative studies). Most of the research considers task performance as an outcome, but some also analyzed team innovation, prosocial behavior, or creativity.
First, 5 quantitative studies and 2 qualitative studies show evidence for the importance of goal management behaviors. They have been found to be relevant, especially for team-level performance 3 studies. Concerning team task performance, Wakefield et al. (2008) found that leadership roles emphasizing direction-setting and production—characterized by behaviors such as prioritizing, planning, and initiating action—showed the strongest correlation with teleworkers' perceived team performance, outweighing other managerial roles like monitoring and coordination, which were significative but less important. On the contrary, in Kashive et al. (2022) both internal and external leadership roles positively influenced team performance; nevertheless, the association was stronger for internal roles (which include monitoring and coordinating). Thomas and Bostrom (2011) showed that forcing-oriented leadership behaviors (defined as “evidence of formal authority and control mechanisms to directly manipulate individuals' behavior.”, p. 50), particularly monitoring goal achievement, rule enforcement, and personnel reassignment, were positively related to team project outcomes in virtual settings by fostering trust and cooperation.
This is complemented by the qualitative study of Maduka et al. (2018), which interviewed members from two virtual teams. They highlighted that leadership behaviors aimed at clarifying the structure and goals, guidelines, and leader expectations to the team are conducive to better team performance in telework. They underlined that it is essential for leaders to structure work in remote arrangements, which is crucial for proper goal achievement in virtual contexts. Also, team leaders and members interviewed by Hambley et al. (2007) identified that providing clarity is the most important virtual leadership behavior to achieve team effectiveness.
Research on the relationship between individual level performance and goal management presents mixed findings (2 studies). Challagalla et al. (2000) found that leaders who excelled at task structuring and role clarification significantly enhanced individual task performance. Expressly, leaders who provided precise instructions, set specific goals, established structured work environments, helped workers understand their tasks, and reduced ambiguity were associated with higher self-reported task performance. Regarding goal monitoring and control, Solís (2017) analyzed differences between teleworkers or not-teleworkers in three indicators of individual performance (task, contextual, and adaptative performance) under different conditions of supervisory monitoring behaviors (high and low control). He found a direct negative relationship between supervisor control and two performance indicators: task performance, and adaptative performance. Interestingly, in terms of adaptative and contextual performance, teleworkers under low supervisor control showed significantly higher individual adaptative and contextual performance than non-teleworkers. No differences between both groups of teleworkers were observed for task performance. These findings suggest that leadership monitoring and control effectiveness may differ between traditional and telework contexts and for different dimensions of performance.
Seven quantiative studies explored the relationship between leaders' task-focused communication and task performance. Vǎtǎmǎnescu et al. (2022) found that leadership communication effectiveness—characterized by successful multi-channel information exchange, knowledge sharing for clarity, and empathetic relationship building—positively influenced team task performance.
Newman et al. (2020) also established that leaders who deliberately increased communication frequency and fostered information exchange among team members achieved higher team task effectiveness (as perceived by members); nevertheless, the degree to which virtual team members perceived their leader to be an effective communicator was not related to an objective measure, in this case, a balanced scorecard performance score.
Replicating this finding at the individual level, Staples (2001) also found that frequent communication from the leader is positively correlated with trust in the leader, which is also correlated positively with individual perception of overall productivity. Nevertheless, Lautsch et al. (2009) found no correlation between supervisor communication frequency and task performance rated by the supervisor itself.
Regarding communication tactics, experimental research conducted by Ernst et al. (2022) did not find support for the relationship between charismatic leadership tactics (such as telling stories/anecdotes, enlisting tasks, enhancing body gestures, facial expressions, and using an animated voice tone) and individual task performance between the control and experimental group. Despite this, they make a difference in the perceived leaders' influence ability. On the opposite, and regarding to contextual performance, in Flavian et al. (2019) study, empathic communication of leaders and perceived justice were positively correlated with trust in leaders and commitment to the team, which also were positively correlated with individual organizational citizenship behavior (OCB).
Thus, hard measures of performance and leaders' rating of individual performance were not related to task-focused communication (mainly frequency), and nor verbal and non-verbal charismatic leadership tactics. However, a richer measure of communication that considers other aspects such as multi-channel use has been shown to be positively related to perceptual measures of team performance.
Quantitative research focused on specific e-leadership competency models found also contradictory results for the role of leader communication behavior. More concretely, Soon and Salamzadeh (2021) found that E-communication, one of the competencies of the six e-leadership competencies model proposed by Roman et al. (2019) (which includes message clarity, minimizing unintended communications, and managing information flow), significantly improved team effectiveness. However, grounding on the same model, Elyousfi et al. (2021) found that none of the e-leadership competencies positively affected team member performance.
These contradictory results point out the importance of understanding which specific aspects of leaders' communication or under which circumstances those behaviors might be more relevant for performance. Qualitative research (7 studies) adds further insights on how task-oriented communication behaviors are related to performance in telework. Through interviews with virtual leaders, Pauleen (2003) and Morgan et al. (2014) identified the critical role of establishing regular communication channels and soliciting employee feedback for individual performance. These studies emphasized that effective leadership communication must be proactive, structured, and predictable to create a systematic information flow. Qualitative studies that interviewed virtual workers also highlighted the relevance of the correct usage of virtual communications and the timing of the information the leader needs to address. In Bonet Fernandez and Jawadi (2015), workers addressed the need to boost synchronous communications between the leader and collaborators instead of asynchronous communications such as emails or chats. The interviewed leaders indicated that synchronous communications are better for requesting information and favoring the flow of messages through virtual media.
Regarding team performance, virtual team members indicated that how changes are communicated makes a difference in peoples' cohesion and, thus, in their team success (Maduka et al., 2018). Moreover, through extensive interviews with virtual team members, Kreamer et al. (2021) identified three critical elements of successful leadership facilitation: adequate meeting planning, savvy technology usage, and connecting on a personal level with teleworkers. The importance of this facilitative leadership role is further corroborated by Ashmi (2017), who interviewed team members and stated that leaders who share knowledge, information, and assistance with the team favor team performance. Also, the study of Al-Ani et al. (2011) with virtual workers found that performance depends on the leaders' usage and promotion of digital tools, where members can exchange messages and improve the flow of key information for teamwork. Finally, the qualitative study by Darics (2020) with virtual team members documented that the use of verbal and non-verbal online communication strategies (e.g., signals in writing, para verbal nuances in calls) also helps to improve the leader-team member exchange, so leaders must be aware of the corresponding communicational cues and semiotics at each moment of connection with their teleworkers.
In summary, the reviewed literature shows empirical evidence for the importance of competencies oriented to reduce operational distance, such as goal setting, monitoring, and task-focused communication, in promoting individual and team performance in telework settings. However, they also show contradictory results, and the need to better understand the specific components of those characteristics that foster performance. Moreover, the review shows that research is mostly focused on team-level task performance, impairing our knowledge about the relationship between leadership and important aspects of individual and team performance such as innovation or contextual performance.
Twenty out of the 37 studies examined the relevance of affinity or relationship-oriented leadership for performance during telework (13 quantitative, 6 qualitative, and 1 mixed).
First, 5 studies examined the relationship between leaders' trust-building competencies and performance indicators. Regarding team performance, Wakefield et al. (2008) and Kashive et al. (2022) showed that internal/flexible leadership roles—particularly the facilitator and mentor roles—were positively related to team task performance. While facilitator role is associated with fostering collective effort, building cohesion and teamwork, facilitating participation, and resolving conflict (Denison et al., 1995 in Wakefield et al., 2008), the mentor role involves “the showing of empathy and concern, and treating each team member in a sensitive and caring way” (Denison et al., 1995, in Wakefield et al., 2008, p. 440). Also, Soon and Salamzadeh (2021) found that e-trust (defined as fostering team trust, respecting work-life boundaries, and managing diversity) was positively related to virtual team effectiveness. Contrarely, as mentioned before, Elyousfi et al. (2021) found that none of the e-leadership competencies, which includes e-trust, was positively related to team member performance. In the same way, when considering behaviors that create trust in workers, the experimental research by Swain (2018) found that the expression of humility from the leader was not found to be related to team performance.
Again, the conflicting results found can be explained by the analysis offered in qualitative research. Five qualitative studies show additional evidence about the specific conditions under which trust building competencies could be especially important for telework. As indicated by the IT virtual leaders interviewed by Cripe and Burleigh (2022) at the beginning of team creation, building personal relationships with virtual workers is crucial to project goals' success. This is also highlighted by the virtual team leaders interviewed in Pauleen (2003). Relationship-building initiated before task execution was found to benefit the performance and effectiveness of teams. Qualitative research based on virtual team members' responses (Maduka et al., 2018; Norman et al., 2019) concludes that trust-building becomes critical in the initial stages of integrating workers into virtual teams and requires specific ways to develop trust that overcome the limitations and lack of bonding instances in telework. This is also pointed out in Malhotra et al. (2007). In this case, responses from both, team members and leaders, indicated the need to establish and maintain trust using communication technology, ensuring that diversity is understood and appreciated, enhancing the visibility of virtual members' contributions, and enabling individual members to benefit from the team.
Second, 5 quantitative studies examined the relationship of leadership competencies for social support with team and individual performance. In the case of teams, Thomas and Bostrom (2011) also found that leaders' facilitation and support behaviors, those that foster team openness, vulnerability, and commitment in teams were positively related to overall team performance. This is also supported by Hodzic et al. (2023) who found a positive relationship between supervisor social support, knowledge sharing and team overall performance. Moreover, Hodzic et al. (2023) found that supervisor social support moderated the relationship between amount of telework (days of telework per week) and knowledge sharing, which in turn was found to be related to team overall performance. When supervisor social support was higher the relationship between amount of telework and knowledge sharing was positive, while when supervisor social support was lower the relationship was negative.
Regarding individual performance, Haines et al. (2002) found that supervisor support for telecommuting was positively related to individual overall performance. Haines et al. (2002) highlighted the importance influence of those leadership competencies for teleworkers' performance because they provide the type of social and emotional resources employees need to adapt and perform in dynamic environments.
Three studies examined the relationship of social support, with contextual dimensions of performance related to innovation. Lee and Kim (2022) revealed that family-supportive leadership behaviors, characterized by supervisors' active support of work-family balance, indirectly enhance teleworkers' creativity through positive emotional states and related mechanisms as we will analyze in the next sections. In a similar vein, Karani and Mehta (2022) found that supervisor support was related to innovative individual behavior through work engagement. Nevertheless, Lautsch et al. (2009), in their two-wave mixed-study, found that family-supportive supervisor behaviors aimed to requirement of separation between work and family reduced individual helping behaviors in telecommuters.
Third, empowering behaviors of leaders were explored in 2 studies in relationship to team and individual performance. By means of a multilevel panel design, Hill and Bartol (2016) showed that at the team level, team level-empowering leadership (sharing power with team members and creating facilitative environments) had a significant effect on team performance rated by the supervisor. Leaders empowering behaviors also enhance individual performance, operationalized as the perceived individual contribution to team task performance. Focusing on individual performance, Bartsch et al. (2020) found that enabling leadership behaviors—characterized by promoting non-hierarchical teamwork, encouraging flexible work methods, and fostering experiment with new ideas- was positively and significantly related to individual task performance.
In line with the quantitative results, qualitative research also highlights the importance of empowering and providing autonomy in teleworking. In Hoegl and Muethel's (2016) research, managers, and workers concluded that leaders who monopolize decision-making authority and provide insufficient autonomy for team members diminish virtual team performance.
Finally, Salvoni et al. (2024) found that when employees perceived their managers as having strong stress management competencies, they reported better overall job performance. These competencies describe the following behaviors: (a) being respectful and responsible, (b) managing and communicating existing and future work (which reported the strongest relationship), (c) reasoning and managing difficult situations, and (d) managing the individual within the team.
Overall, the findings underscore the importance of relationship-oriented leadership competencies, including support, trust-building, empowerment, and stress management, for fostering performance in remote work environments. Most of empirical evidence is focused on task performance at the team and individual level.
The importance of leadership for performance in telework settings is related to the potential of leadership to influence work related factors such as collaboration, communication, autonomy, work-life balance, that might be relevant for performance. Besides their direct effect on employees through personal interaction, leaders have the capability to affect working conditions, offer or limit important resources, and favor individual or team processes (e.g., sense making). Moreover, leadership does not occur in a vacuum. Organizational, leaders and team member characteristics can have an important effect in how leader competencies for telework influence performance. Thus, in this review, we also analyze empirical evidence about the mechanisms and boundary conditions that mediate or moderate the relationship between leadership and the performance of teleworkers and teams. Sixteen of the 22 quantitative studies included mediation (12) and/or moderation (6) analyses. Fifteen of the 16 studies have a cross-sectional design, except for Hill and Bartol (2016) who conducted panel data with two measures.
Three team mechanisms were found to mediate the relationship between leadership behaviors and team performance during telework (4 studies). They all refer to team processes expected to enable or facilitate team performance.
First, 1 study found that the relationship between leadership competencies and team performance was mediated by interpersonal trust within teams. Concretely, Kashive et al. (2022) found that team members' interpersonal trust mediated the relationship between internal leadership roles (monitor, coordinator, mentor, and facilitator behaviors) and overall team performance.
Second, another team mechanism, collaboration between members, was found to be relevant for team performance in 2 quantitative studies. Thomas and Bostrom (2011) found that both task-oriented and relationship-oriented behaviors were positively related to overall team performance through the development of higher levels of cooperation between team members. Hill and Bartol (2016) also found team virtual collaboration to mediate the relationship between empowering behaviors and team task performance, through a longitudinal panel design.
Finally, 2 studies found the use of media and technologies to mediate the relationship between task and relationship-oriented leadership and team-level performance. Thomas and Bostrom (2011) showed that team technology adaptation (changes in behavior when using new technologies and usage of new tools) mediated the relationship between support behaviors and team project outcomes evaluation. Also, Kashive et al. (2022) concluded that communication quality perceived by the team members (correct usage of technology, time and space, and patterns regarding the usage of synchronous and asynchronous media) mediated the relationship between task and relationships-oriented behaviors (monitoring, coordinating, and mentoring) and overall team performance. Qualitative research also supports this finding. Han et al. (2017) showed that leadership behaviors promoting teleworkers' effective use of technologies, in turn, contributed to enhance team creativity and success.
As it is the case for team mechanisms, only a limited number of studies (5) explored and found support for 5 mechanisms mediating the relationship between leadership competencies and individual performance in remote work.
Flavian et al. (2019) found subordinates' trust in leaders to mediate the relationship between leaders' perceived empathy and justice and teleworkers' organizational citizenship behaviors. In a comparative analysis, Staples (2001) found that trust in leaders mediated the relationship between communication frequency and individual overall productivity for remote workers, but not in traditional office settings. Lee and Kim (2022) also provided support for trust as a mediating mechanism with contextual performance, strengthening leader-employee relationship quality. They also studied other two mechanisms through which family-supportive leadership communication enhances employee creativity in work-from-home contexts designed to promote work-life balance: (a) Cultivating positive emotional states among employees and (b) Facilitating work-life enrichment (WLE), where positive experiences transfer between professional and personal domains.
Karani and Mehta (2022) also established that psychological contract fulfillment—defined as employees' perception that their employer will honor commitments, leading to reciprocal positive attitudes and behaviors—mediates the relationship between supervisor support and innovative behaviors in virtual work settings.
Finally, Bartsch et al. (2020) identified employee autonomy as a critical mediator between relationship-oriented leadership and perceived individual performance in remote settings.
We could not find much research investigating potential moderators of the relationship between leadership and performance during telework. Only two studies addresed moderators: First, the research developed by Haines et al. (2002) analyzed how subordinate's self-management orientations (the ability to discipline their own performance and manage time) could be moderating the relationship between supportive behaviors of leaders and telecommuters' behaviors. Concretly, they found that for telecommuters with higher self-management skills (more autonomous, with higher capability to self-organize and self-direct), supportive behaviors of leaders were more strongly associated with their individual performance.
Hill and Bartol (2016) analyzed specific features of telework and showed that team geographical dispersion (as computed index point of the geographical distance between team members) strengthened the positive relationship between empowering team leadership and team virtual collaboration, which, in turn, was related to individual task performance. Empowering leadership was more strongly related to team performance through virtual collaboration when team members were more geographically dispersed.
Regarding qualitative studies, Hoegl and Muethel (2016) noted that teleworkers with a better fit with the job (job fit) reported more benefits from leadership actions, especially when their technical, digital, and self-leadership competencies are adequate for their roles. The qualitative research by Poulsen and Ipsen (2017) also supports this idea, showing that in telework, it is important to assign the appropriate tasks to each collaborator according to the competencies they have developed the most.
Qualitative research also has suggested some possible moderators of these relationships. As indicated previously, some researchers have highlighted that the stage of development of teams could influence the importance of leadership competencies such as trust building (Cripe and Burleigh, 2022; Maduka et al., 2018; Malhotra et al., 2007; Newman et al., 2020; Pauleen, 2003). Thus, in the initial stages of development of the relationship or when team members visibility is needed this competency could have a stronger effect on results.
In summary, the reviewed literature reveals important patterns in how leadership competencies relate to performance in telework contexts. Quantitative research has identified specific leadership behaviors that enhance performance, while qualitative studies provide insights into how these behaviors are implemented effectively in practice. Research has examined to some extent potential mediators (trust, autonomy, collaboration, adequate use of technologies or WLE) and moderators (self-management and job fit) of the relationship between leadership competencies and performance in telework. However, there is still limited knowledge of how context might facilitate or impede the influence of leaders on teleworkers' performance. Moreover, more profound knowledge of the mechanisms activated by different types of leadership competencies in telework is needed. Indeed, only one study used a longitudinal design for testing mediating mechanisms (Hill and Bartol, 2016). Thus, this area of research needs to be further developed.
This systematic review aimed to (a) identify key leadership competencies fostering performance in telework, (b) identify mechanisms and moderators influencing those relationships, and (c) provide suggestions for leadership competencies that should be addressed in leadership development programs considering telework.
Our review shows empirical evidence that leadership competencies aimed at reducing operational and affinity distance (Lojeski and Reilly, 2020) are associated with higher levels of individual and team performance in telework settings, especially task performance. Therefore, based on our systematic review, we have identified five key leadership competencies crucial for fostering performance in telework contexts.
Firstly, task-focused communication emerges in multiple studies (8 quantitative and 9 qualitative) emphasizing the importance of frequent, effective, and high-quality interaction between leaders and team members. In-depth, task-oriented communication related to clarifying information, providing guidelines, and requesting feedback, has been linked mainly to team task performance (e.g., Newman et al., 2020; Vǎtǎmǎnescu et al., 2022).
Secondly, goal management appears in seven studies. Delineating objectives and expectations emerge as a key leadership competency for enabling team performance (i.e., Kashive et al., 2022). Also, behaviors aimed to provide clear goals and expectations and monitor progress (Al-Ani et al., 2011) enable teleworkers to effectively self-manage and achieve better performance.
Third, leaders' social support, the ability to provide individualized concern and assistance to teleworkers through virtual media, emerges as a fundamental competency in six studies. Quantitative evidence demonstrates its significant effect on individual task and contextual performance (Hodzic et al., 2023; Karani and Mehta, 2022; Lee and Kim, 2022).
A fourth competence is trust-building, which also appears in six studies. It was reported significant relationships between leaders' trust-building competencies and various performance indicators (Kashive et al., 2022; Thomas and Bostrom, 2011), with qualitative research emphasizing its particular importance during team formation stages (Maduka et al., 2018).
Finally, a fifth competence is empowerment, which appears in four studies, regarding leaders' capability to grant autonomy, facilitate self-management, and promote collaboration among remote team members. This favors both team and individual performance (Hill and Bartol, 2016).
As can be seen, the results of our review largely align with traditional leadership research, suggesting that many fundamental principles of effective leadership apply across both co-located and virtual contexts. Some of the competencies identified in previous research are similar to those identified as necessary for the 21st-century overall work context, i.e., communication, goal planning/organization, and trust-building (Ngayo Fotso, 2021). This is aligned with traditional models, such as Leader-Member Exchange (LMX): our findings—for example- show that competencies related to the development of high-quality exchanges between leaders and team members—characterized by trust, mutual liking, and respect and the development of autonomy—enhance employee performance in telework settings (e.g., Bauer and Erdogan, 2015; Kuruzovich et al., 2021).
However, our findings also indicate that specific leadership competencies may be critical in telework settings (i.e., Challagalla et al., 2000; Kelley and Kelloway, 2012; Staples, 2001). For instance, digital communication may have heightened relevance for remote teams, even if they still provide value in co-located ones; also, leaders' social support becomes critical for addressing the blurred boundaries of teleworkers' personal and work lives. The qualitative research considered in this review offers some insights with specific examples of how communication or goal management competencies must be adapted when working remotely; for instance, establishing regular communication channels or boosting synchronous communications at certain key moments. In brief, the principles of good leadership fundamentally apply across contexts; however, virtual settings may require greater emphasis and intention in certain areas, incorporating digitally enabled management practices (Peiró and Martínez-Tur, 2022). With awareness of the increased challenges inherent to virtual distance, successful telework leadership approaches can enrich the overall leadership theory.
Moreover, we also found some conflicting results. Some studies did not find significant relationships between the examined leadership competencies and performance. For instance, Newman et al. (2020), the only study with an objective performance indicator. found no relationship between leaders' communication and Team Balanced Scorecard. Also, Ernst et al. (2022) found no differences between leaders using charismatic or non-charismatic tactics and virtual workers' extra-role performance. Regarding the frequency of communication, while Staples (2001) found that frequent leader communication is related to perceived productivity, Lautsch et al. (2009) found no link between communication frequency and supervisor-rated task performance. Research also shows contradictory results about the role of monitoring behaviors. While some researchers showed positive results on team performance (Thomas and Bostrom, 2011; Kashive et al., 2022) others found that initiating and structuring were more important than monitoring (Wakefield et al., 2008). Moreover, some research has shown that monitoring, meaning increasing levels of supervisory control, could be detrimental to contextual and adaptation behavior of teleworkers (Solís, 2017). Research focused on specific e-leadership competencies models also found contradictory results. Soon and Salamzadeh (2021) found support for e-trust and e-comunication competencies to be associated with performance indicators, while Elyousfi et al. (2021) found that none of the six e-leadership competencies was related to team member performance.
Moving forward, we also identified several mechanisms mediating the relationship between leadership competences and performance in telework. Literature shows that leaders contribute to the achievement of team performance by through the development higher levels of trust (within the team and with the leader) (Kashive et al., 2022), team collaboration (Hill and Bartol, 2016) and adaptation to technologies (Thomas and Bostrom, 2011). The mechanisms linking affinity-oriented competencies to individual performance were autonomy (Bartsch et al., 2020), psychological contract fulfillment (Karani and Mehta, 2022) and work-life enrichment (Lee and Kim, 2022). Our review also highlighted a few studies examining potential moderators or potential boundary conditions, such as subordinates' characteristics (self-management) (Haines et al., 2002), geographical dispersion (Hill and Bartol, 2016) and individual-job adjustment (job fit) (Hoegl and Muethel, 2016).
Despite these findings, we encountered important gaps in the literature exploring the relationship between leadership competencies and telework. First, while task performance has been extensively studied, there is limited research examining other dimensions of performance such as organizational citizenship behaviors, creativity, and innovative performance (Koopmans et al., 2011, 2014). Counterproductive work behaviors in telework contexts are neglected. Second, research relies mainly on subjective data for measuring performance (mostly self-reported), almost no research was found using hard data. Third, literature has not sufficiently addressed how leaders should handle work-life interference challenges that teleworkers face, including supporting employees' right to disconnect and helping them maintain focus in home environments. Thus, leadership competencies related to work-life balance promotion and fostering healthy disconnection practices have received limited attention, despite their growing importance in remote work settings (Bhumika, 2020; Wang et al., 2023). Furthermore, the unique demands of hybrid work environments, where leaders must manage the interplay between physical and virtual spaces while maintaining social cohesion across both contexts, remain largely unexplored (Bell et al., 2023; Vartiainen and Vanharanta, 2024). Fourth, most of the studies use cross-sectional designs which prevents the possibility to extract sound conclusions about causality and possible mechanisms influencing the studied relationships. Moreover, the mediating mechanisms explored do not consider some of the most prevalent challenges that have been pointed out about telework and that good leadership might contribute to face adequately (Beauregard et al., 2019; Shirmohammadi et al., 2022; Waight et al., 2022). Fifth, we found literature that has developed leadership models more suited to digital and telework challenges, such as e-leadership. However, the initial empirical investigations using these models have yielded mixed results, showing significant findings for only some competencies (Soon and Salamzadeh, 2021) or none of the new leadership competencies at all (Elyousfi et al., 2021). Moreover, these models primarily address digital leadership, which focuses on how leaders utilize digital media, rather than focusing on remote work. Consequently, further research on new leadership frameworks specific to telework is still needed. is still needed. Finally, contextual organizational factors must be considered. Leadership occurs in the context of organizations (Kozlowski et al., 2021). Thus, research should expand its focus to examine organizational mechanisms and explore additional moderating factors related to telework arrangements. For instance, the degree or intensity of telework, team size or interdependence between tasks may significantly influence leadership effectiveness (Bell et al., 2023), yet this relationship remains understudied. Organizational factors such as telework policies (e.g., flexibility or work-family balance practices), technological infrastructure, and organizational culture (e.g., regarding digitalization) could also shape how leadership competencies translate into employee outcomes (Gohoungodji et al., 2022) and, furthermore, how social influences could be managed in the digital workspace (Banks et al., 2022). Moreover, the interaction between these contextual elements and specific telework components—such as work scheduling flexibility, communication patterns, and virtual collaboration tools—requires further investigation to understand their combined effects on leadership effectiveness (Brown et al., 2021; Kozlowski et al., 2021; Martinolli et al., 2023). Understanding these conditions is essential to determine when, where, and for whom certain leadership styles are most effective, as highlighted by Nielsen and Taris (2019).
As organizations continue embracing hybrid and fully remote arrangements, there is a growing need to implement interventions tailored to the needs of these work designs, including developing and training digitalized leadership competencies (Peiró and Martínez-Tur, 2022). Our review highlighted key leadership competencies that drive better performance in telework settings. Based on these findings, we propose that leadership development programs should structure these competencies in the following way:
a) Competencies for reducing operational distance in telework:
• Digital task-focused communication: Facilitating remote coordination and interactions by improving asynchronous and synchronous communication abilities through digital media (in the usage of collaborative tools, cloud computing, and email) so workers can self-direct with greater clarity and feel equally supported by leaders (Maduka et al., 2018; Vǎtǎmǎnescu et al., 2022). Also, leaders should provide guidelines for establishing communication rhythms, norms, and expectations around technology-enabled interactions (Maduka et al., 2018; Soon and Salamzadeh, 2021).
• Remote goal management: Promoting leaders' frequent task delegation and goal setting using digital tools, favoring teleworkers' self-organization and non-invasive monitoring. This also involves training behaviors and media usage to convey objectives and expected results to workers quickly and assertively, as Challagalla et al. (2000) and Wakefield et al. (2008) stated.
• Teleworkers' empowerment: This involves allowing workers to manage their agenda, be autonomous, arrange their tasks when working remotely, and collaborate freely with other members through virtual media by conveying autonomy and flexibility in how and when they complete tasks. As research has pointed out, this can improve both self-confidence and work-life balance (Hoegl and Muethel, 2016).
b) Competencies for reducing relational distance in telework:
• Support through digital media: Providing emotional support and facilitating the integration of teleworkers into remote teams is essential. This can be achieved through proactive check-ins on their physical and mental wellbeing, offering emotional assistance, and addressing feelings of isolation and disconnection in virtual settings (Haines et al., 2002). Additionally, leaders should address work-family conflicts both individually and as a team. Establishing psychological contracts can help delineate boundaries and address issues that arise from remote work and personal life, such as disconnection times and responsibilities related to childcare or eldercare (Lee and Kim, 2022; Poulsen and Ipsen, 2017; Wang et al., 2023).
• Digital trust-building as a base condition: promoting virtual environments where workers can trust their leaders and team members (Malhotra et al., 2007), focusing on highlighting reliability on compromise achievement, openness, and psychological safety when interacting with digital tools, addressing disagreements or critical issues. This can enable the positive effects of leadership on performance (Kashive et al., 2022).
Fostering these competencies represents an initial step toward a telework leadership development model for teams and organizations in today's rapidly evolving people management context (Arora and Suri, 2020; Bondarouk and Brewster, 2016; Gohoungodji et al., 2022). These interventions should aim to increase leaders' awareness of the new challenges of teleworking and the display of effective behaviors to face this digitalized workplace.
In addition, we must pay attention to possible intervening mechanisms and boundary conditions that may be key to developing leadership for telework contexts and the technological savviness of leaders (Maduka et al., 2018; Norman et al., 2019; Thomas and Bostrom, 2011). Leadership interventions must consider that under a higher degree of virtuality in the work arrangements, those programs should reinforce leaders' proactive behaviors to contact their teams and focus on the proficient usage of digital tools to manage goals and share leadership (Han and Hazard, 2022). Moreover, training should consider conditions that allow more contextualized telework leadership (i.e., job fit and worker autonomy). Furthermore, as McDonald et al. (2022) emphasize, in telework arrangements, it is crucial to integrate leadership into a broader organizational support system that favors sustainable careers for teleworkers. For example, the proposed interventions can be supplemented with additional programs focused on teams and collaborators (Han and Hazard, 2022) to establish work agreements and foster an environment that facilitates virtual interaction and participation.
Finally, leadership development for telework should comprehensively cover utilizing technology to enable teamwork, productivity, security, work-life balance, and an overall positive employee experience. Further research should examine the effectiveness of leadership development programs focused on these target areas.
While the research on leadership in telework contexts has grown considerably in recent years, our systematic review reveals that this area of research requires further scholarly attention.
First, as said before, research needs to address effective telework leadership competencies through a temporal lens. The field would benefit from longitudinal or multi-wave studies to understand how leadership dynamics evolve and adapt over-time in remote work settings.
Second, new investigation lines should expand to analyze the effect of organizational contexts and policies, with particular attention to regulations such as the right to disconnect, as well as cultural factors, task characteristics, and leader attributes that shape collective dynamics in dispersed contexts. This understanding would help explain varying research results and enable more targeted interventions, moving beyond one-size-fits-all approaches to telework leadership. Furthermore, traditional leadership concepts such as meaningful work, self-efficacy, justice perceptions, and psychological empowerment should be reexamined in remote settings to understand how their operation might differ in virtual environments.
Third, the relationship between leadership and non-task-performance measures in telework contexts requires deeper investigation. This includes examining contextual and adaptive performance dimensions, as well as understanding how leadership can foster prosocial and creative behaviors in remote work environments. Additionally, research should consider the potential trade-offs between different types of performance and incorporate more objective outcome measures. The field would also benefit from experimental or quasi-experimental studies that manipulate leadership competencies in real telework scenarios to determine causal impacts on performance outcomes.
Finally, intervention studies are needed to verify whether developing specific leadership competencies actually improves performance in telework settings. Such research would establish causal relationships between specific leadership behaviors and outcomes, providing practical guidance for leadership development programs. These studies should also address how to manage key challenges inherent to remote work arrangements, including work-life boundary blurring, social and professional isolation, loss of tacit knowledge, and ergonomic difficulties (Beauregard et al., 2019; Shirmohammadi et al., 2022; Waight et al., 2022).
Through addressing these research lines, scholars can develop a more comprehensive understanding of effective leadership in telework contexts, ultimately contributing to both theoretical advancement and practical applications in the evolving landscape of remote work.
Regarding limitations of this review, first, given the high presence of qualitative studies and several variables operationalized differently in the research, it was not possible to calculate the size of the effect of each of the leadership skills or competencies on wellbeing and/or performance, which is an important metric to prioritize which have the most impact on these phenomena. Therefore, a future study could be in the framework of a meta-analysis, which will provide further insights.
Another limitation is that many systematic reviews strive to stay current by focusing on only the last 10 years of research in a field. However, our review considers the previous two decades. This decision was made due to telework research experiencing slower growth before the 2010s; consequently, covering the last 24 years allowed the inclusion of some seminal studies on virtual teams and leadership from the early 2000s that still feel relevant. Therefore, the 24-year period provided a rich foundation of relevant insights compared to a strict 10-year scope.
In sum, this literature review has identified relevant leadership competencies for promoting performance in the new era of remote and hybrid work. It provides a foundation for advancing leadership theory for virtual contexts and guiding the development of telework-specific leadership training. Moreover, it provides guidelines for organizations that aim to foster good leadership in those settings. By outlining research-based leadership competencies, this review could bridge theory with practice and enhance leadership effectiveness in telework, considering the performance of teams and their leaders.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
FB-D: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. NT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. IR: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación of Spain, project “Development of leadership competencies to improve wellbeing and performance of teleworkers: evaluation of a web and app-based training (DIGYLID)” (PID2020-116742RB-100).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acosta, S., Garza, T., Hsu, H. Y., and Goodson, P. (2020). Assessing quality in systematic literature reviews: a study of novice rater training. Sage Open 10:2158244020939530. doi: 10.1177/2158244020939530
Aksoy, C. G., Barrero, J. M., Bloom, N., Davis, S. J., Dolls, M., and Zarate, P. (2023). Working from home around the globe: 2023 report. EconPol Policy Brief. Available at: https://www.econpol.eu/publications/policy_brief_53 (accessed December 10, 2024).
Al-Ani, B., Horspool, A., and Bligh, M. C. (2011). Collaborating with “virtual strangers”: Towards developing a framework for leadership in distributed teams. Leadership 7, 219–249. doi: 10.1177/1742715011407382
Alkhayyal, S., and Bajaba, S. (2023). The impact of e-leadership competencies on workplace well-being and job performance: the mediating role of e-work self-efficacy. Sustainability 15:4724. doi: 10.3390/su15064724
Arora, P., and Suri, D. (2020). Redefining, relooking, redesigning, and reincorporating HRD in the post covid 19 context and thereafter. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 23, 438–451. doi: 10.1080/13678868.2020.1780077
Ashmi, J. (2017). Getting things done, virtually! - The role of virtual team leadership in virtual team Effectiveness. Ushus J. Bus. Manag. 16, 13–20. doi: 10.12725/ujbm.39.2
Avolio, B. J., Kahai, S., and Dodge, G. E. (2000). E-leadership: implications for theory, research, and practice. Leadersh. Q. 11, 615–668. doi: 10.1016/S1048-9843(00)00062-X
Avolio, B. J., Walumbwa, F. O., and Weber, T. J. (2009). Leadership: Current theories, research, and future directions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 60, 421–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.60.110707.163621
Baert, S., Lippens, L., Moens, E., Weytjens, J., and Sterkens, P. (2020). The COVID-19 crisis and telework: A research survey on experiences, expectations and hopes. IZA Discussion Paper No. 13229. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3596696
Banks, G. C., Dionne, S. D., Mast, M. S., and Sayama, H. (2022). Leadership in the digital era: a review of who, what, when, where, and why. Leadersh. Q. 33:101634. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2022.101634
Bartsch, S., Weber, E., Büttgen, M., and Huber, A. (2020). Leadership matters in crisis-induced digital transformation: how to lead service employees effectively during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Serv. Manag. 32, 71–85. doi: 10.1108/JOSM-05-2020-0160
Bauer, T. N., and Erdogan, B. (2015). “Leader-member exchange (LMX) theory: an introduction and overview,” in Oxford Handbook of Leader-Member Exchange, 3–9. doi: 10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199326174.013.2
Beauregard, T., Basile, K. A., and Canónico, E. (2019). “Telework: outcomes and facilitators for employees,” in The Cambridge Handbook of Technology and Employee Behavior, ed. R. N. Landers (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press), 511–543. doi: 10.1017/9781108649636.020
Bell, B. S., McAlpine, K. L., and Hill, N. S. (2023). Leading virtually. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 10, 339–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-120920-050115
Bhumika (2020). Challenges for work–life balance during COVID-19 induced nationwide lockdown: exploring gender difference in emotional exhaustion in the Indian setting. Gender Manag. 35, 705–718. doi: 10.1108/GM-06-2020-0163
Bondarouk, T., and Brewster, C. (2016). Conceptualising the future of HRM and technology research. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 27, 2652–2671. doi: 10.1080/09585192.2016.1232296
Bonet Fernandez, D., and Jawadi, N. (2015). Virtual RandD project teams: From e-leadership to performance. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 31, 1693–1708. doi: 10.19030/jabr.v31i5.9384
Brown, M. A. (2021). Analyzing Telework, Trustworthiness, and Performance Using Leader-Member Exchange: COVID-19 Perspective. New York: IGI Global. doi: 10.4018/978-1-7998-8950-2
Brown, S. G., Hill, N. S., and Lorinkova, N. N. M. (2021). Leadership and virtual team performance: a meta-analytic investigation. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 30, 672–685. doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2021.1914719
Challagalla, G., Shervani, T., and Huber, G. (2000). Supervisory orientations and salesperson work outcomes: the moderating effect of salesperson location. J. Personal Sell. Sales Manag. 20, 161–171. Available at: http://www.jstor.org/stable/40471797
Contreras, F., Baykal, E., and Abid, G. (2020). E-leadership and teleworking in times of covid-19 and beyond: what we know and where do we go. Front. Psychol. 11:590271. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.590271
Cortellazzo, L., Bruni, E., and Zampieri, R. (2019). The role of leadership in a digitalized world: a review. Front. Psychol. 10:1938. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01938
Cripe, K. M., and Burleigh, C. (2022). Examining leadership skills, behaviors, and effective communication for virtual IT project managers. Team Perfor. Manag. 28, 223–237. doi: 10.1108/TPM-11-2021-0085
Darics, E. (2020). E-Leadership or “how to be boss in instant messaging?” The role of nonverbal communication. Int. J. Bus. Commun. 57, 3–29. doi: 10.1177/2329488416685068
Delanoeije, J., and Verbruggen, M. (2020). Between-person and within-person effects of telework: a quasi-field experiment. Eur. J. Work Organiz. Psychol. 29, 795–808. doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2020.1774557
Di Fabio, A., and Peiró, J. M. (2018). Human capital sustainability leadership to promote sustainable development and healthy organizations: a new scale. Sustainability 10:2413. doi: 10.3390/su10072413
Efimov, I., Rohwer, E., Harth, V., and Mache, S. (2022). Virtual leadership in relation to employees' mental health, job satisfaction and perceptions of isolation: a scoping review. Front. Psychol. 13:960955. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.960955
Elyousfi, F., Anand, A., and Dalmasso, A. (2021). Impact of e-leadership and team dynamics on virtual team performance in a public organization. Int. J. Public Sector Manag. 34, 508–528. doi: 10.1108/IJPSM-08-2020-0218
Ernst, B. A., Banks, G. C., Loignon, A. C., Frear, K. A., Williams, C. E., Arciniega, L. M., et al. (2022). Virtual charismatic leadership and signaling theory: a prospective meta-analysis in five countries. Leaders. Quart. 33:101541. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2021.101541
Flavian, C., Guinalíu, M., and Jordan, P. (2019). Antecedents and consequences of trust on a virtual team leader. Eur. J. Manag. Bus. Econ. 28, 2–24. doi: 10.1108/EJMBE-11-2017-0043
Gohoungodji, P., N'Dri, A. B., and Matos, A. L. B. (2022). What makes telework work? Evidence of success factors across two decades of empirical research: a systematic and critical review. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 34, 605–649. doi: 10.1080/09585192.2022.2112259
Haines, V. Y., St-Onge, S., and Archambault, M. (2002). Environmental and person antecedents of telecommuting outcomes. J. End User Comput. 14, 32–50. doi: 10.4018/joeuc.2002070103
Hambley, L. A., O'Neill, T. A., and Kline, T. J. B. (2007). Virtual team leadership: Perspectives from the field. Int. J. E-Collabor. 3, 40–64. doi: 10.4018/jec.2007010103
Han, S. J., Chae, C., Macko, P., Park, W., and Beyerlein, M. (2017). How virtual team leaders cope with creativity challenges. Eur. J. Train. Dev. 41, 261–276. doi: 10.1108/EJTD-10-2016-0073
Han, S. J., and Hazard, N. (2022). Shared leadership in virtual teams at work: practical strategies and research suggestions for human resource development. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 21, 300–323. doi: 10.1177/15344843221093376
Han, S. J., Kim, M., Beyerlein, M., and DeRosa, D. (2020). Leadership role effectiveness as a mediator of team performance in new product development virtual teams. J. Leader. Stud. 13, 20–36. doi: 10.1002/jls.21677
Hill, N. S., and Bartol, K. M. (2016). Empowering leadership and effective collaboration in geographically dispersed teams. Pers. Psychol. 69, 159–198. doi: 10.1111/peps.12108
Hodzic, S., Prem, R., Nielson, C., and Kubicek, B. (2023). When telework is a burden rather than a perk: The roles of knowledge sharing and supervisor social support in mitigating adverse effects of telework during the COVID-19 pandemic. Appl. Psychol. 73, 599–621. doi: 10.1111/apps.12491
Hoegl, M., and Muethel, M. (2016). Enabling shared leadership in virtual project teams: a practitioners' guide. Project Manag. J. 47, 7–12. doi: 10.1002/pmj.21564
Inceoglu, I., Thomas, G., Chu, C., Plans, D., and Gerbasi, A. (2018). Leadership behavior and employee well-being: an integrated review and a future research agenda. Leadersh. Q. 29, 179–202. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2017.12.006
Karani, A., and Mehta, S. A. (2022). “I am OK when you are with me”–Understanding the well-being and innovative behavior in the digitized workspace. Int. J. Sociol. Soc. Policy 42, 583–602. doi: 10.1108/IJSSP-05-2021-0127
Kashive, N., Khanna, V. T., and Powale, L. (2022). Virtual team performance: E-leadership roles in the era of COVID-19. J. Manag. Dev. 41, 277–300. doi: 10.1108/JMD-05-2021-0151
Kelley, E., and Kelloway, E. K. (2012). Context matters: testing a model of remote leadership. J. Lead. Organ. Stud. 19, 437–449. doi: 10.1177/1548051812454173
Koopmans, L., Bernaards, C. M., Hildebrandt, V. H., Schaufeli, W. B., De Vet, H. C., and Van Der Beek, A. J. (2011). Conceptual frameworks of individual work performance: A systematic review. J. Occupat. Environ. Med. 53, 856–866. doi: 10.1097/JOM.0b013e318226a763
Koopmans, L., Coffeng, J., Bernaards, C., Boot, C. R. L., Hildebrandt, V., Vet, H. C., et al. (2014). Responsiveness of the individual work performance questionnaire. BMC Public Health 14, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-513
Kozlowski, S. W., Chao, G. T., and Van Fossen, J. (2021). Leading virtual teams. Organ. Dyn. 50:100842. doi: 10.1016/j.orgdyn.2021.100842
Kozlowski, S. W. J., and Ilgen, D. R. (2006). Enhancing the effectiveness of work groups and teams. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 7, 77–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-1006.2006.00030.x
Kreamer, L., Stock, G., and Rogelberg, S. (2021). Optimizing virtual team meetings: attendee and leader perspectives. Am. J. Health Promot. 35, 744–747. doi: 10.1177/08901171211007955e
Kuruzovich, J., Paczkowski, W., Golden, T. D., Goodarzi, S., and Venkatesh, V. (2021). Telecommuting and job outcomes: a moderated mediation model of system use, software quality, and social exchange. Inf. Manag. 58:103431. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2021.103431
Lautsch, B. A., Kossek, E. E., and Eaton, S. C. (2009). Supervisory approaches and paradoxes in managing telecommuting implementation. Hum. Relat. 62, 795–827. doi: 10.1177/0018726709104543
Lee, Y., and Kim, J. (2022). How family-supportive leadership communication enhances the creativity of work-from-home employees during the covid-19 pandemic. Manag. Commun. Quart. 37, 599–628. doi: 10.1177/08933189221144997
Liao, M., Li, S., and Liu, H. (2024). The impact mechanism of telework on job performance: a cross-level moderation model of digital leadership. Sci. Rep. 14:12520. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63518-6
Lojeski, K. S., and Reilly, R. R. (2020). The Power of Virtual Distance: A Guide to Productivity and Happiness in the Age of Remote Work. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Maduka, N. S., Edwards, H., Greenwood, D., Osborne, A., and Babatunde, S. O. (2018). Analysis of competencies for effective virtual team leadership in building successful organisations. Benchmarking 25, 696–712. doi: 10.1108/BIJ-08-2016-0124
Malhotra, A., Majchrzak, A., and Rosen, B. (2007). Leading virtual teams. Acad. Manag. Persp. 21, 60–70. doi: 10.5465/amp.2007.24286164
Martinolli, G., Posada, A. S., Belli, S., Tomas, I., and Tordera, N. (2023). Teleworking components and scientific productivity in Spanish ERC-granted teams: the mediating role of climate and well-being. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 39, 131–143. doi: 10.5093/jwop2023a14
McDonald, K. S., Hite, L. M., and O'Connor, K. W. (2022). Developing sustainable careers for remote workers. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 25, 182–198. doi: 10.1080/13678868.2022.2047148
Morgan, L., Paucar-Caceres, A., and Wright, G. (2014). Leading effective global virtual teams: the consequences of methods of communication. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 27, 607–624. doi: 10.1007/s11213-014-9315-2
Nakrošiene, A., Bučiuniene, I., and Goštautaite, B. (2019). Working from home: characteristics and outcomes of telework. Int. J. Manpow. 40, 87–101. doi: 10.1108/IJM-07-2017-0172
Newman, S. A., Ford, R. C., and Marshall, G. W. (2020). Virtual team leader communication: employee perception and organizational reality. Int. J. Bus. Commun. 57, 452–473. doi: 10.1177/2329488419829895
Ngayo Fotso, G. M. (2021). Leadership competencies for the 21st century: a review from the Western world literature. Eur. J. Train. Dev. 45, 566–587. doi: 10.1108/EJTD-04-2020-0078
Nielsen, K., and Taris, T. W. (2019). Leading well: Challenges to researching leadership in occupational health psychology – and some ways forward. Work Stress 33, 107–118. doi: 10.1080/02678373.2019.1592263
Norman, S. M., Avey, J., Larson, M., and Hughes, L. (2019). The development of trust in virtual leader–follower relationships. Qualit. Res. Organiz. Manag. 15, 279–295. doi: 10.1108/QROM-12-2018-1701
Offstein E. H. Morwick J. M. and Koskinen L. (2010). Making telework work: leading people and leveraging technology for competitive advantage. Strat. HR Rev. 9, 32–37. doi: 10.1108/14754391011022244
Pauleen, D. J. (2003). An inductively derived model of leader-initiated relationship building with virtual team members. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 20, 227–256. doi: 10.1080/07421222.2003.11045771
Peiró, J. M., Bravo-Duarte, F., González-Anta, B., and Todolí-Signes, A. (2024). Supervisory performance in telework: the role of job demands, resources, and satisfaction with telework. Front. Organiz. Psychol. 2:1430812. doi: 10.3389/forgp.2024.1430812
Peiró, J. M., and Martínez-Tur, V. (2022). ‘Digitalized' competences. A crucial challenge beyond digital competences. Rev. Psicol. Trabajo Organ. 38, 189–199. doi: 10.5093/jwop2022a22
Poulsen, S., and Ipsen, C. (2017). In times of change: how distance managers can ensure employees' wellbeing and organizational performance. Saf. Sci. 100, 37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2017.05.002
Pyöriä, P. (2011). Managing telework: risks, fears and rules. Manag. Res. Rev. 34, 386–399. doi: 10.1108/01409171111117843
Rocco, T. S., Plakhotnik, M. S., McGill, C. M., Huyler, D., and Collins, J. C. (2023). Conducting and writing a structured literature review in human resource development. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 22, 104–125. doi: 10.1177/15344843221141515
Roman, A. V., Van Wart, M., Wang, X. H., Liu, C., Kim, S., and McCarthy, A. (2019). Defining e-leadership as competence in ict-mediated communications: an exploratory assessment. Public Adm. Rev. 79, 853–866. doi: 10.1111/puar.12980
Salvoni, S., Biron, C., Gilbert, M., Dextras-Gauthier, J., and Ivers, H. (2024). Managing virtual presenteeism during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multilevel study on managers' stress management competencies to foster functional presenteeism. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 21:1115. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21091115
Shirmohammadi, M., Chan Au, W., and Beigi, M. (2022). Antecedents and outcomes of work-life balance while working from home: a review of the research conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 21, 473–516. doi: 10.1177/15344843221125834
Solís, M. (2017). Moderators of telework effects on the work-family conflict and on worker performance. Eur. J. Manag. Bus. Econ. 26, 21–34. doi: 10.1108/EJMBE-07-2017-002
Soon, C. C., and Salamzadeh, Y. (2021). The impact of digital leadership competencies on virtual team effectiveness in mnc companies in Penang, Malaysia. J. Entrepr. Bus. Econ. 8, 219–253. Available at: https://scientificia.com/index.php/JEBE/article/view/147
Staples, D. S. (2001). A study of remote workers and their differences from non-remote workers. J. End User Comput. 13, 3–14. doi: 10.4018/joeuc.2001040101
Swain, J. E. (2018). Effects of leader humility on the performance of virtual groups. J. Leader. Stud. 12, 21–37. doi: 10.1002/jls.21552
Thomas, D., and Bostrom, R. (2011). Building trust and cooperation through technology adaptation in virtual teams: empirical field evidence. Inf. Syst. Manag. 25, 45–56. doi: 10.1080/10580530701777149
Vartiainen, M., and Vanharanta, O. (2024). True nature of hybrid work. Front. Organ. Psychol. 2:1448894. doi: 10.3389/forgp.2024.1448894
Vǎtǎmǎnescu, E. M., Dinu, E., Stratone, M. E., Stǎneiu, R. M., and Vintilǎ, F. (2022). Adding knowledge to virtual teams in the new normal: from leader-team communication to the satisfaction with teamwork. Sustainability 14:6424. doi: 10.3390/su14116424
Waight, C. L., Nery-Kjerfve, T., Kite, A., and Smith, B. C. (2022). Connecting and relating in Brazil: implications of remote work. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 25, 231–253. doi: 10.1080/13678868.2022.2048435
Wakefield, R. L., Leidner, D. E., and Garrison, G. (2008). A model of conflict, leadership, and performance in virtual teams. Inf. Syst. Res. 19, 434–455. doi: 10.1287/isre.1070.0149
Wang, H., Xiao, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, H., and Chen, X. (2023). “Who knows me understands my needs”: the effect of home-based telework on work engagement. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 16, 619–635. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S402159
World Economic Forum (2023). The Future of Jobs Report 2023. Geneva, Switzerland: World Economic Forum.
Keywords: telework, remote work, virtual work, leadership, competencies, performance, systematic review
Citation: Bravo-Duarte F, Tordera N and Rodríguez I (2025) Overcoming virtual distance: a systematic review of leadership competencies for managing performance in telework. Front. Organ. Psychol. 2:1499248. doi: 10.3389/forgp.2024.1499248
Received: 20 September 2024; Accepted: 11 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Ron Landis, Clemson University, United StatesReviewed by:
Waheeda Lillevik, The College of New Jersey, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Bravo-Duarte, Tordera and Rodríguez. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Núria Tordera, TnVyaWEudG9yZGVyYUB1di5lcw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.