
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 20 March 2025
Sec. Molecular and Cellular Oncology
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1557233
This article is part of the Research Topic The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Nutrition and Lifestyle in Cancer Prevention and Progression View all 4 articles
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Despite notable advancements in therapeutic strategies, HCC continues to pose significant public health challenges due to its rising incidence and high mortality rates worldwide. Selenium is an essential trace element that playing a critical role in human health. Recent studies have highlighted its potential preventive and therapeutic benefits in the context of HCC. However, some in vitro and in vivo investigations have yielded inconsistent results, and the mechanisms by which selenium influences HCC are still not completely clear. This review begins by providing an extensive evaluation of the effects and mechanisms of selenium on the primary risk factors associated with HCC, including viral infections, metabolic abnormalities, and lifestyle factors. Subsequently, we outline the roles and mechanisms by which selenium influences the proliferation, metastasis, and immune microenvironment of HCC. Finally, we emphasize the imperative for further investigation into the optimal dosage and forms of selenium, as well as its effects on the HCC microenvironment, to inform the development of effective clinical strategies. This review thus provides a foundational framework for the potential clinical application of selenium in the treatment of HCC.
Liver cancer is a major contributor to global cancer-related mortality, with projections indicating an incidence exceeding 1 million cases by 2025 (1). Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most prevalent histological subtype of liver cancer, accounting for approximately 90% of all cases (2). The primary risk factors for HCC development include viral infections, metabolic abnormalities, and lifestyle factors (3). Despite significant advancements in therapeutic strategies, HCC survival rates remain low due to late-stage diagnosis and high rates of tumor recurrence (4), highlighting the urgent need to explore strategies aimed at preventing and mitigating the progression of HCC.
Selenium (Se), an essential trace element with critical roles in human health (5), has recently gained attention for its potential in managing HCC, particularly due to its contributions to antioxidant defense, redox signaling, DNA repair, and immune function (6). Currently, 25 selenoproteins have been identified in humans, including glutathione peroxidases (GPxs), thioredoxin reductases (TrxRs), and several other selenoproteins with yet-to-be-elucidated functions. Extensive epidemiological studies have explored the link between selenium levels and HCC risk (7).
For instance, In-Wook Kim et al. reported that serum selenium levels were significantly lower in HCC patients (67.47 μg/L) compared to healthy controls (108.38 μg/L) in South Korea (8), and a study by M. Buljevac et al. observed comparable findings (9). An eight-year follow-up study in Qidong County, Jiangsu Province, demonstrated that selenium supplementation reduced HCC incidence by 35.1%, with a subsequent increase in HCC rates upon withdrawal of selenium from the treatment group. Furthermore, a meta-analysis indicated that both selenium status and selenium intake were inversely related to hepatitis, cirrhosis, and HCC (10). These results emphasize the possible benefits of selenium supplementation in managing HCC. However, some in vitro and in vivo studies have yielded conflicting results regarding selenium’s impact on HCC, and the mechanisms underlying selenium’s influence on HCC remain poorly understood.
In this review, we will offer a current overview of selenium’s roles in the prevention and treatment of HCC, as well as to discuss the potential mechanisms underlying these effects. Additionally, we will suggest prospective research directions concerning the investigation of selenium in HCC. By synthesizing existing evidence, this review seeks to establish a foundation for the clinical application of selenium in the management of HCC.
As mentioned above, viral infections, metabolic abnormalities, and lifestyle factors are the primary risk factors for HCC (Table 1). These conditions often lead to hepatitis or cirrhosis, which subsequently develop into HCC. Therefore, controlling these risk factors is crucial for reducing HCC incidence.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV) are the primary viruses related to HCC. They can persistently alter the host’s antiviral defenses and disrupt cellular pathways that regulate liver homeostasis, ultimately leading to viral hepatitis and HCC development (46). Selenium is the only nutrient directly correlated with viral infections. In the absence of selenium, viruses may become more prone to mutation, causing more severe damage to the organism (12, 13).
HBV infection is the cause of nearly 50% of HCC cases (47–50). The effects of selenium on HBV inhibition have been well documented. Studies have shown that sodium selenite (Na2SeO3) can suppress HBV protein expression, transcription, and genome replication in a dose- and time-dependent manner in human hepatoma cell lines Huh7 and HepG2.2.15 (11). Another study demonstrated that 5 μM Na2SeO3 can suppress HBV replication by ~50% in HepG2.2.15 cells by promoting apoptotic cell death and inhibiting cellular inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (cIAPs) (Figure 1). Additionally, 500 nM Na2SeO3 can reverse hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) induced hepatotoxicity by GPX4-mediated ferroptosis blockade (12). The introduction of selenoprotein P (SeP) can notably reverse HBx-induced lipid peroxidation and TNF-α upregulation in HepG2 cells (13) (Figure 1). These findings suggest that selenium can reduce the incidence of HBV-induced HCC.
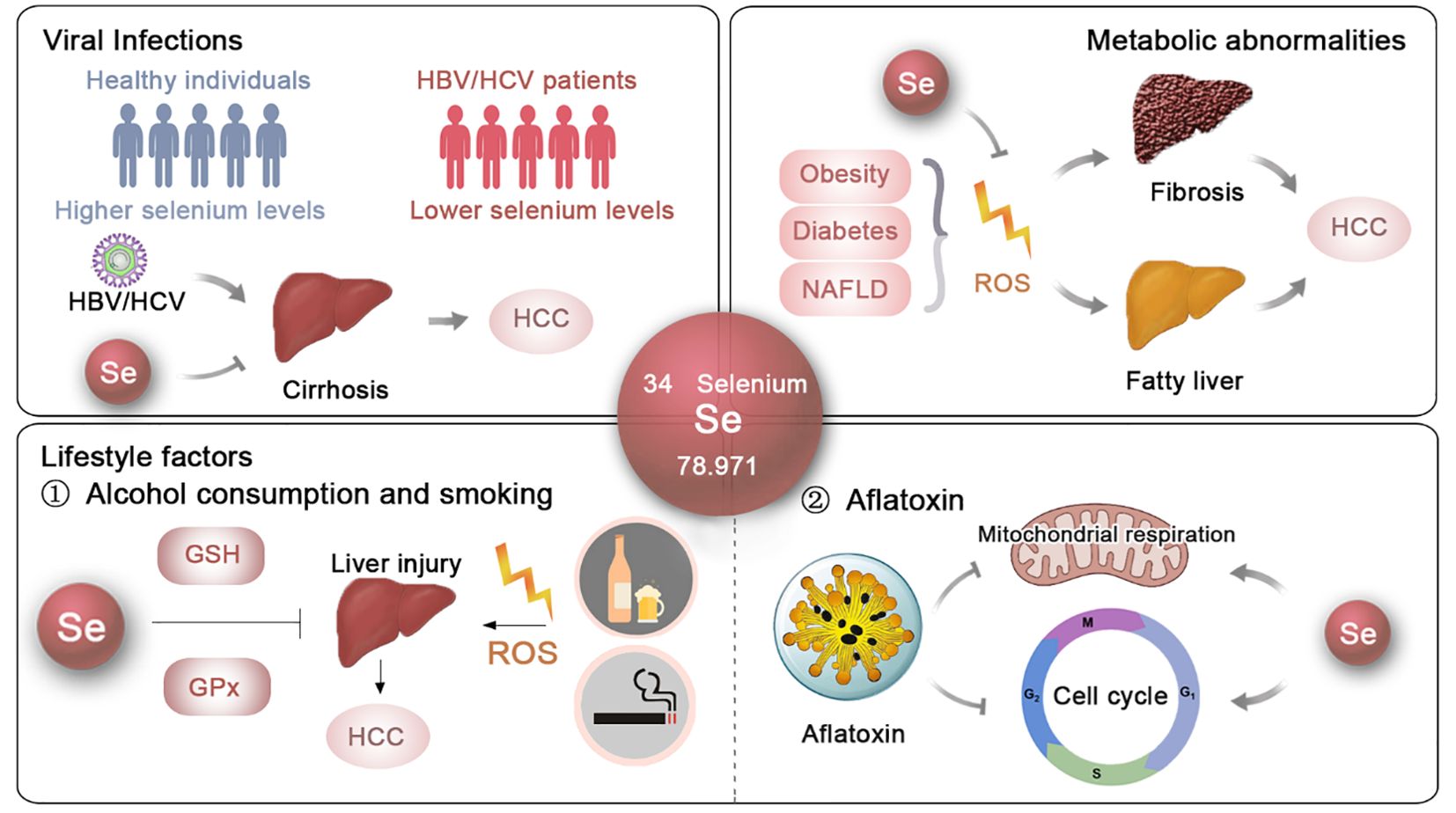
Figure 1. The potential roles and mechanisms of selenium in t he prevention of HCC. The effects and underlying mechanisms of selenium on the primary risk factors for HCC, including viral infections, metabolic abnormalities and lifestyle factors.
Actually, the NHANES 2007-2018 study data indicated that individuals testing positive for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) have reduced blood selenium concentrations (14). Shi et al. confirmed that serum selenium levels are lower in HBV-positive HCC patients, and higher selenium levels are linked to better prognosis in this group (12). Similar observations were made in Pakistan by Naseem Rauf et al., emphasizing the consistent link between selenium deficiency and HBV infection (15).
Regarding HCV, an in vitro study showed that HCV suppresses the expression of gastrointestinal glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in replicon cells, aiding viral propagation within host cells, suggesting that regulating GPx activity could provide new strategies to inhibit HCV replication (16). Clinical data also support these findings, revealing a negative correlation between HCV viral load and both selenium levels (r = -0.730) and GPx activity (r = -0.675) (17) (Figure 1). Additionally, Dominik Bettinger et al. found that HCV infection significantly lowers serum selenium levels, with an even greater decline in patients developing HCV-related cirrhosis (18) (Figure 1). In Pakistan, a significant proportion of HCV-infected patients exhibit substantially lower selenium levels compared to healthy controls (15). Overall, these findings highlight the potential effects of selenium supplementation as a therapeutic approach to reduce the risk of HBV- and HCV-induced HCC (Figure 1).
Obesity is an independent risk factor or HCC (51, 52). A meta-analysis encompassing of 28 prospective cohort studies with 8,135,906 subjects revealed that an increase in body mass index (BMI) was associated with the occurrence of HCC (53). A prospective study involving over 900,000 American adults also corroborated that an increased BMI is significantly linked to heightened mortality rates due to cancer, including HCC (54).
In obese individuals, adipose tissue secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, which facilitate inflammation and tumorigenesis within the liver (55). Additionally, obesity is frequently associated with insulin resistance, which enhances the biological activity of IGF-1. A significant amount of evidence suggests that the IGF-1/IGF-1R pathway is crucial in the development of various cancers, including HCC (56). Moreover, obesity-induced gut microbiota alterations promote HCC development by generating harmful metabolites like deoxycholic acid (DCA), which trigger DNA damage and a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in hepatic stellate cells, fostering a pro-inflammatory, tumorigenic liver microenvironment (57).
Selenium has been extensively investigated for its anti-inflammatory effects. A study demonstrated that SeNPs could influence the expression of genes associated with adipogenesis and oxidative stress in adipose tissue, suggesting a molecular mechanism through which selenium might affect obesity (58). Also, selenium supplementation has been shown to manage hyperlipidemia, by modulating oxidative stress and improving metabolic functions (59). Additionally, selenoprotein enzyme activity is crucial for maintaining the balance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals, which are integral components of the SASP (60). These experiments indicate that selenium may play an important role in preventing obesity-induced HCC.
A research investigation explored the correlation between fingernail selenium content and the risk of obesity among Chinese children. The findings suggested an inverse relationship, where higher selenium levels were associated with a reduced risk of obesity, indicating a potential protective role of selenium against childhood obesity (61). Similar result was highlighted in women (62). Also, a study assessing the impact of L-arginine and selenium supplementation on women with central obesity revealed that selenium markedly reduced fasting insulin levels and enhanced insulin sensitivity, thereby emphasizing its potential utility in addressing obesity-related metabolic disorders (63).
Diabetes mellitus has been increasingly acknowledged as a crucial risk factor influencing the onset of HCC. Numerous meta-analyses have substantiated the association between diabetes and the incidence of HCC (20, 64). A longitudinal study conducted in Taiwan, encompassing 23,820 participants monitored over a 14-year period, demonstrated that diabetes is associated with a threefold increase in the risk of developing HCC (19).
The dysregulation of glucose metabolism in diabetic individuals can also lead to the accumulation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which contribute to cancer progression by inducing oxidative stress and inflammation (21). Insulin resistance is linked to heightened oxidative stress and persistent inflammation (65, 66). Additionally, high glucose levels can promote HCC metastasis through mechanisms involving metabolic enzymes like PKM2 (22).
Selenium plays a significant role in modulating diabetes, primarily by mitigating oxidative stress (59, 67). It also influences glucose metabolism by modulating phosphoinositide-3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling pathway, which is important for insulin action and glucose uptake. Additionally, selenium’s impact on selenoprotein P has been associated with hepatic gluconeogenesis and insulin resistance (23). Moreover, interactions between selenium levels and genetic variations in selenoprotein genes, as well as other redox-related genes, have been shown to affect diabetes risk (68). Epidemiological investigations have yielded inconsistent findings on the association between selenium levels and the likelihood of developing diabetes. Certain studies indicate that sufficient selenium intake may confer protective effects against diabetes, especially in populations with initially low selenium levels (69, 70). In contrast, other research suggests that elevated selenium exposure may be linked to an increased risk of diabetes mellitus, particularly in populations with adequate selenium status (71, 72). Thus, further research is required to determine the optimal selenium intake for diabetes prevention and management.
NAFLD is rapidly becoming the most prevalent cause of HCC (73), affecting an estimated 2 billion individuals worldwide (74). NAFLD typically starts as simple fatty liver and can progress to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and eventually HCC (24). Although the exact mechanisms underlying NAFLD remain unclear, oxidative stress is recognized as a key factor in its development (25). Hepatic iron, which facilitates electron transfer and catalyzes the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), is often elevated in NAFLD patients (26). As oxidative stress increases, lipid peroxidation occurs, leading to the formation of lipid hydroperoxides. These lipid hydroperoxides, along with elevated cytokines, contribute to the direct damage of liver cell membranes and the worsening of intrahepatic inflammation. The thiol redox systems, mainly glutathione and thioredoxin, work to counteract oxidative stress within cells by reducing H2O2 and lipid hydroperoxides (75). Consequently, therapeutic strategies focusing on modulating thiol redox systems have been proposed as potential interventions for NAFLD (76) (Figure 1).
Selenium, a key component of thiol-containing enzymes, has been extensively investigated for its role in NAFLD. Research in animal models has provided significant insights into its therapeutic potential. For instance, Ozardali et al. showed that selenium supplementation in rodents with NAFLD induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) not only restored liver enzyme activity but also reduced the number of stellate cells and alleviated fibrosis (28, 29). Similarly, Zhang et al. found that organic selenium could alleviate NAFLD in mice fed a high-fat diet and exposed to CCl4 by modulating the 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HT)/bile acid (BA) enterohepatic circulation (31). Wang et al. demonstrated that adding selenium to the diet significantly decreased liver damage and insulin resistance in the progression of NAFLD by modulating the KEAP1/Nrf2 pathway, thereby counteracting oxidative stress through increased selenoprotein P production (27). Additionally, the administration of selenium-enriched yeast and Lactobacillus was shown to decrease hepatic oxidative stress and mitigate the profibrotic response in rats with CCl4-induced liver injury (32, 33). Moreover, selenium and zinc co-supplementation was found to reverse NAFLD progression by improving serum biochemical parameters and reducing lipid droplet accumulation and size in the livers of Sprague–Dawley rats (30). Notably, Shen et al. demonstrated that selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) significantly reduced liver lipid accumulation caused by polystyrene microplastics (34), further highlighting the versatile protective effects of selenium in liver health (Figure 1).
In the field of nutritional epidemiology, previous research has highlighted a significant decrease in selenium levels among individuals with NAFLD (6). A study by the Health Management Center at Xiangya Hospital found that middle-aged and older adults with greater selenium consumption in their diet, even though it was less than the recommended dietary allowance in China, showed a higher occurrence of NAFLD in a dose-response manner (35). Furthermore, in a study conducted with 8,550 Chinese adults aged 40 and older in Shanghai, it was observed that participants with plasma selenium levels in the highest quartile (>247.4 μg/L) had a 54% greater prevalence of NAFLD than those in the lowest quartile (<181.6 μg/L), indicating a potential connection between elevated selenium levels and the prevalence of NAFLD (36). Additionally, a study on U.S. adults examined the relationships among serum selenium concentrations, serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity, and the prevalence of NAFLD. The findings indicated a positive correlation between serum selenium levels and NAFLD prevalence when selenium concentrations surpassed 130 μg/L, while no significant association was observed for levels below this threshold (77) (Figure 1).
Excessive alcohol consumption leads to alcoholic liver disease (ALD), progressing sequentially from fatty liver to alcoholic steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and ultimately HCC. Although the precise mechanisms are not fully understood, it is widely recognized that protein and lipid peroxidation, driven by free radical reactions, play a significant role in the development of ALD (78). In a cohort study of 80 male patients with alcoholic cirrhosis and 70 healthy male non-alcoholic controls, MDA levels, a known marker of lipid peroxidation, were significantly higher in those with alcoholic cirrhosis.Additionally, a negative correlation was found between MDA levels and the activities of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), GPx, and glutathione (GSH), indicating heightened oxidative stress and impaired antioxidant defense in ALD patients (79) (Figure 1). These findings strongly support the potential role of selenium in mitigating ALD (80).
In fact, a prevalence study of 99 patients with alcoholic cirrhosis and 20 healthy subjects revealed a significant depletion of serum selenium levels in ALD patients (38). Similarly, Rui M. Rua et al. reported that individuals suffering from alcohol use disorder and liver disease exhibited notably lower serum selenium concentrations, especially those diagnosed with ALD, and these levels were associated with the activity of GPx (39) (Figure 1). These observations suggest that selenium could be a potential therapeutic agent for ALD and a preventive measure against HCC (Figure 1).
Smoking is another factor leading to increased HCC risk. Numerous epidemiological studies have indicated a link between tobacco smoking and the development of HCC. For instance, the Singapore Chinese Health Study, demonstrated a dose-dependent relationship between the number of cigarettes smoked and the risk of HCC (81). Additionally, a meta-analysis highlighted the synergistic effect of smoking with HBV and HCV infections in increasing the risk of HCC, highlighting the need to tackle smoking cessation in conjunction with the prevention and treatment of viral hepatitis (82). Smoking is known to enhance the generation of reactive oxygen species, which can result in oxidative DNA damage, cytokine synthesis, and telomere dysfunction, contributing to liver carcinogenesis (83). Additionally smoking can alter the epigenetic landscape of liver cells, particularly in the context of HCV-related HCC (84).
Selenium can reduce oxidative stress by neutralizing ROS generated during smoking (42). Also, by enhancing immune function, selenium may help mitigate the immunosuppressive effects of smoking (40). Smokers have lower serum and plasma selenium levels compared to non-smokers (85, 86). Epidemiological research has looked into the connection between selenium levels and the likelihood of cancer in smokers. Some studies suggest that exposure to selenium might be connected to a decreased likelihood of lung and prostate cancer among those who have ever smoked (41, 87). Overall, selenium appears to play a multifaceted role in mitigating the adverse effects of smoking through its antioxidant and immune-modulating properties.
Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), a mycotoxin from Aspergillus species found in poorly stored food, has been extensively investigated for its contribution to the pathogenesis of HCC. The metabolic processing of AFB1 involves its conversion into a highly reactive epoxide derivative, AFB1-8,9-epoxide (AFBO). This epoxide is capable of forming covalent bonds with DNA, resulting in the formation of AFB1-DNA adducts, which are pivotal in the mutagenic process (88). Research has demonstrated that AFB1-DNA adducts are prevalent in regions with high levels of AFB1 exposure and are correlated with increased incidence of HCC (89). Furthermore, exposure to AFB1 combined with HBV infection significantly increases the likelihood of developing HCC (90). Besides its genotoxic effects, AFB1 has been shown to impair mitochondrial function and induce apoptosis through both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways, thereby causing oxidative stress and inflammation, which exacerbate liver damage and promote carcinogenesis (91, 92).
Research has shown that selenium can mitigate the toxic effects of AFB1 through several mechanisms. For one thing, selenium enhances antioxidant defense systems against AFB1 toxicity. It has been demonstrated to reduce AFB1-induced DNA damage and histological changes in the liver (43). For another thing, selenium supplementation can lessen the negative effects of AFB1 on liver mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes and improve the ratios of mitochondrial respiratory control (44). Additionally, in broilers, selenium supplementation has been observed to improve the cellular immune function impaired by AFB1, as evidenced by increased spleen weight and enhanced T cell subsets (93). Moreover, selenium’s involvement in cell cycle regulation has been underscored in studies where selenium supplementation prevented AFB1-induced G2/M phase arrest (45). Collectively, the protective effect of selenium is crucial in preventing the mutagenic and carcinogenic consequences of aflatoxin exposure.
In addition to its role in the incidence of HCC, selenium has been shown to affect various aspects of HCC progression, including tumor growth, metastasis, and the immune microenvironment.
Selenium has been shown to influence all phases of the cell cycle (94). Its anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on HCC have been extensively investigated (95) (Figure 2). Yang et al. reported that selenium sulfide (SeS2) could inhibit the C-MET/STAT3, AKT/mTOR, and MAPK signaling pathways, and trigger Bcl-2/Cyto C/Caspase-mediated intrinsic mitochondrial apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo (96) (Figure 2). Additionally, in the Hep3B cell line and its xenograft tumors, selenium promoted apoptosis by activating the GSK3β-independent AMPK/β-catenin pathway (97). Cheng Wang and colleagues demonstrated that under hyperoxic conditions, H2Se, a product of selenium compound metabolism, is oxidized into H2O2, which blocks the Nrf2 signaling pathway, activates the MAPK signaling pathway, and enhances cell apoptosis in HepG2-bearing mice (98). A selenium containing MAPK and PI3K inhibitor (Se,Se’-1,4-phenylenebis(1,2-ethanediyl) bisisoselenourea, PBISe) has also been shown to exert chemotherapeutic effects by inhibiting the PI3K, MAPK, and STAT3 signaling pathways, leading to a significant reduction in tumor sizes in a transgenic murine HCC model (99) (Figure 2). Furthermore, Tohada M Al-Noshokaty and colleagues found that selenium can overcome sorafenib resistance in thioacetamide (TAA) induced HCC in rats by modulation of mTOR, NF-κB pathways and LncRNA-AF085935/GPC3 axis (100) (Figure 2).
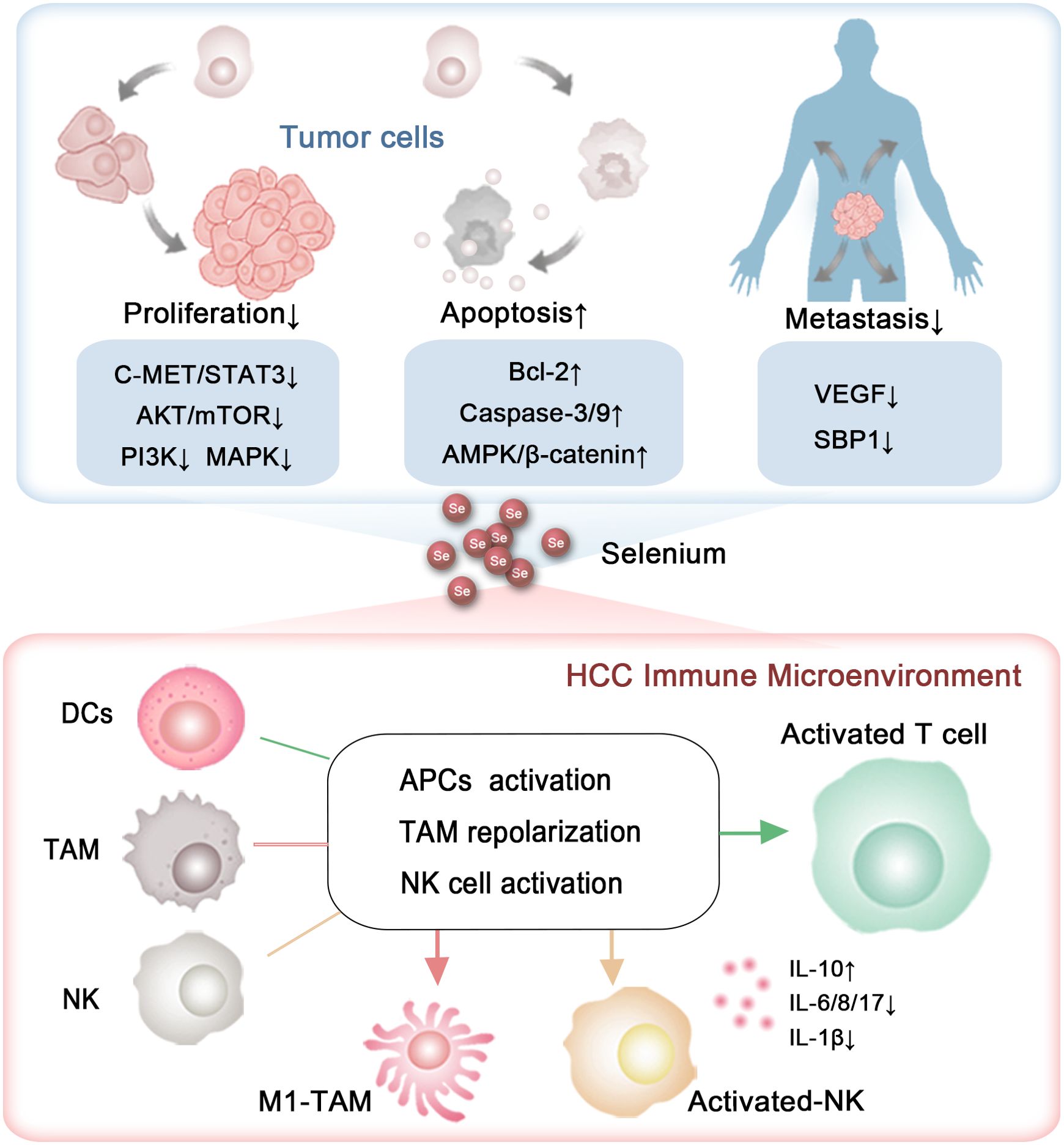
Figure 2. The capability of selenium to inhibit HCC progression. The roles and mechanisms by which selenium influences the growth, metastasis, and immune microenvironment of HCC.
In addition to selenium compounds, selenium nanocomposites, especially those incorporating additional functional components, have garnered increasing attention for their role in influencing tumor progression (101). Research by Jianshuang Jiao and colleagues revealed that selenium nanoparticles conjugated with astragalus polysaccharides induce significant morphological changes in HepG2 cells, arrest the cell cycle in the S phase and induce apoptosis through the mitochondrial route (102). Similarly, selenium nanoparticles combined with polysaccharides from Marsdenia tenacissima were shown to effectively suppress the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of HepG2 cells, a result attributed to the triggering of the Bax/Bcl-2/Caspases and p21/Akt/Cyclin A2 signaling pathways (103). Xiao Zhang et al. claimed that selenium nanoparticles conjugated with cordyceps sinensis exopolysaccharides inhibit HepG2 cell proliferation in a manner dependent on both dose and selenium content. This inhibition is linked to disruptions in cellular membrane integrity and mitochondrial function, along with elevated levels of Bax, cytochrome c, cleaved caspase-9, cleaved caspase-3, Fas, p53, and cleaved caspase-8, and reduced levels of Bcl-2 and PARP (104) (Figure 2). Additionally, selenium nanoparticles decorated with polysaccharides derived from the fermented broth of Lactarius deliciosus (FLDP) demonstrated a synergistic effect in reducing toxicity and enhancing the suppression of HepG2 cells. This was achieved by promoting early apoptosis via mitochondria-mediated cytochrome C-caspase activation and ROS-induced DNA damage pathways (105).
Khaled et al. reported that berberine-loaded selenium nanoparticles exhibited a notable antitumor impact on HepG2 cells, primarily by triggering apoptosis, which was facilitated by increased expression of p53, Bax, cytosolic cytochrome C, and caspase-3 activity, along with decreased levels of Bcl-2 (106) (Figure 2). In a similar vein, Chi et al. demonstrated that selenium-rich royal jelly induces apoptosis in H22 tumor-bearing mice through the activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 (107) (Figure 2). Moreover, selenium-enriched malt was effective in counteracting the decline in plasma glucose levels and the rise in serum calcium levels in rats with hepatoma induced by diethylnitrosamine (108). Selenium-rich amino acids were found to induce cell apoptosis in human hepatoma cells SMMC-7721 by promoting the generation of ROS (109). These studies together emphasize selenium’s potential in curbing the progression of HCC (Figure 2, Table 2).
The metastatic capability of liver cancer cells presents a significant challenge, greatly affecting the unfavorable prognosis of HCC. Research by Cheng Huang and colleagues has revealed a reduction in the expression of selenium-binding protein 1 (SBP1), a key protein involved in selenium metabolism, enhances the invasive characteristics of HCC. Patients with reduced SBP1 levels had shorter overall survival and increased disease recurrence rates (110, 111) (Figure 2). These results indicate that selenium supplementation could be pivotal in mitigating the metastatic progression of HCC.
To date, many studies have explored the impact of selenium on the migration and invasion of HCC. For instance, Yu Xia and colleagues discovered that selenium nanoparticles loaded with anisomycin significantly inhibit the invasive and migratory capabilities of HepG2 cells (112). Additionally, tumor metastasis relies on the development of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis, which selenium has been shown to suppress by modulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Nataliya Rohr-Udilova et al. observed that selenium treatment in a rat model of HCC enhanced hepatic GPx4 expression while decreasing VEGF (Figure 2). Further analysis confirmed that selenium levels had an inverse relationship with VEGF, IL-8, and the size of tumors in HCC patients (113) (Figure 2). Also, Fabiola Rusolo et al. reported that increasing selenite concentrations in HepG2 and Huh7 cells led to reduced levels of VEGF and three pro-inflammatory cytokines: IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17 (114) (Figure 2). Jia-Guo Liu et al. demonstrated that selenium-enriched malt inhibited HCC angiogenesis in rats, partly through the downregulation of VEGF and interactions with key factors such as insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), nitric oxide (NO), and tumor-associated nitric oxide synthase (T-NOS) (115, 116) (Figure 2). These findings were supported by a cohort of 29 HCC patients, where selenium levels had an inverse correlation with VEGF and IL-8 (113). The results emphasize selenium’s promise as a therapeutic option to prevent HCC metastasis (Table 3).
The tumor immune microenvironment (TIM) plays a crucial role in the progression of various cancers by regulating the infiltration and function of immune cells within the tumor milieu. Recently, an increasing number of studies have emphasized the effects of selenium on immune cell activity, garnering greater attention from the scientific community.
T cells are capable of directly eliminating cancer cells and are crucial in orchestrating the immune response against tumors. Selenium has been shown to enhance T cell function, including proliferation, activation, and cytotoxic activity (117, 118). A Phase I clinical trial indicated that selenite treatment effectively induced tumor shrinkage in patients with squamous cell lung carcinoma. Notably, tumor reduction was observed 4 months after the initiation of selenite therapy at a dosage of 1 mg/m². Additionally, dynamic and individual variations in sPD-L1 levels were noted, and there was considerable variability in survival rates among patients. These observations suggest that selenium may possess potential therapeutic value in cancer immunotherapy (119). In mice, selenoprotein deficiency impairs T cell maturation and their response to T cell receptor stimulation (120). Supplementation of selenium in male C57B1/6J mice increases the expression of GPx4 within T cells, thereby boosting the population of T follicular helper cells (121). Also, the nanocomplex of selenium and the polysaccharide component of Pholiota adiposa significantly elevates the levels of CD3+ CD4+ T cells and CD3+ CD8+ T cell in H22 tumor-bearing mice (122).
In human subjects, supplementing with selenium boosts GPx enzyme activity in lymphocytes, which is linked to better T cell functions, including enhanced proliferation and cytokine production (123). Yi Hu and collaborators found that γδ T cells pretreated with SeNPs showed enhanced efficacy in killing cancer cells and inhibiting tumor growth compared to untreated cells, as SeNPs significantly upregulating cytotoxicity-related molecules like NKG2D, CD16, and IFN-γ while downregulating PD-1 expression in γδ T cells (124). A study derived from generally healthy population also proposed that selenium’s immune-boosting properties in humans may, at least in part, be due to enhanced activation and proliferation of B-lymphocytes and potentially improved T-cell function (125). These findings highlight the potential of selenium to activate T cells (Figure 2).
Natural killer (NK) cells, which play a pivotal role in the innate immune system, enable the recognition and eradication of virus-infected and tumor cells through their cytotoxic functions (126). Research has shown that selenite, an inorganic form of selenium, can increase the susceptibility of tumor cells to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity by reducing the expression of HLA-E (127). In male C57B1/6J mice, selenium led to a substantial boost in the lytic activity of activated NK cells, which demonstrated a marked increase in intermediate affinity interleukin-2 receptors (128). In mice bearing H22 tumors, seleno-ovalbumin has been shown to enhance NK cell cytotoxicity (129). Selenium-containing nanoparticles have been demonstrated to enhance NK cell function, which can be synergistically combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy in tumor-bearing mice (130). Additionally, selenium-based nanocomplexes have been found to reverse NK cell exhaustion by downregulating the immune checkpoint PD-L1 (131, 132). Moreover, research found that in liver cancer patients, selenium metabolism in CD8+ T cells and NK cells within tumor tissues is abnormal, characterized by increased SEPP1 and decreased SELENBP (133, 134) (Figure 2).
Selenium has also been reported to enhance the immune response by modulating the function of DCs. It can increase the expression of co-stimulatory molecules on the surface of DCs, such as CD80 and CD86, which are essential for the activation of T cells (135, 136). In addition, selenium influences cytokine production by DCs, promoting the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-12 (IL-12), which is essential for fostering a Th1 immune response that is advantageous in combating viral infections and suppressing tumor growth (136).
Research by Zhepeng Sun and colleagues revealed that selenium deficiency significantly inhibits the differentiation and immune function of chicken DCs by decreasing the expression of CD11c, CD40, CD86 and MHCII, as well as altering the secretion of IL-10, IL-12p40, and IFN-γ (137). Similarly, Liangliang Zhang and his team found that selenium modulates the immune function of mouse DCs through the ROS- and SELENOK-mediated ERK, Akt, and RhoA/ROCK signaling pathways (138). In both mouse and swine models, selenium nanoadjuvants have been demonstrated to be more effective than commercial inactivated vaccines in activating DCs by engaging Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling and regulating selenoprotein expression (139). Mohammad Hossein Yazdi et al. also revealed that administering SeNPs to mice enables DCs to generate IL-12 after interacting with tumor antigens (140). These studies collectively highlight the vital role of selenium in the differentiation and activation of DCs (Figure 2).
Selenium has the ability to modulate macrophage polarization towards an anti-tumor phenotype, thereby enhancing the immune response against cancer cells. Research by Jie Xu and colleagues showed that SeNPs significantly activated the Tlr4/Myd88/NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to the conversion of M2 macrophages into M1 macrophages and effectively stimulating an anti-tumor immune response in mice with the H22 tumor model (122). Similarly, Shuang Li et al. found that selenium-containing membrane components can inhibit the M2-like polarization, thereby slowing the in vivo growth of transplanted H22 ascites hepatoma cells (141). Moreover, selenium-enriched lactobacilli have been demonstrated to alleviate CCl4-induced liver damage in mice by boosting macrophage functional activity (33). Moreover, inhibition of selenoprotein synthesis in myeloid cells led to reduced macrophage migration within a protein gel matrix (142). Additionally, the absence of selenoprotein K was linked to reduced receptor-mediated Ca2+ flux in macrophages (143). These findings highlight the crucial role of selenium in macrophage remodeling.
This study has reviewed the role of selenium in HCC, highlighting that selenium supplementation appears to be a promising approach for preventing and mitigating the progression of HCC, based on experimental trials and epidemiological data. Selenium shows great promise in lowering risk factors associated with HCC, such as viral infections, metabolic abnormalities, and lifestyle factors, primarily due to its potent antioxidant properties (Figure 1). Moreover, selenium has been shown to inhibit the growth of HCC cells and promote their apoptosis by enhancing its pro-antioxidant effects and modulating pathways associated with tumor development. Selenium also holds promise in controlling cancer cell migration and invasion, thereby reducing the risk of HCC recurrence and relapse. Additionally, selenium may act as an immunostimulant, activating immune cells and counteracting immune checkpoint-mediated immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment (Figure 2). Despite the encouraging findings and notable advancements, several critical issues require careful consideration, and further research is needed before selenium can be widely implemented in clinical practice.
First, the dosage is crucial (Figure 3). Selenium demonstrates a bimodal effect. At low, nutritional doses, selenium serves as an antioxidant, mitigating oxidative stress and thereby reducing the primary risk factors associated with HCC. In contrast, at supra-nutritional, pharmacological levels, selenium might act as a pro-oxidant, which could result in cell death in HCC. However, there is currently no consensus on the optimal reference intake levels of selenium, primarily due to the insufficient epidemiological data regarding the dose-response link between selenium and certain health effects. Given the narrow range between preventive and therapeutic doses of selenium, it is essential to conduct dose-specific preclinical studies and clinical trials to effectively utilize selenium in the prevention and treatment of HCC.
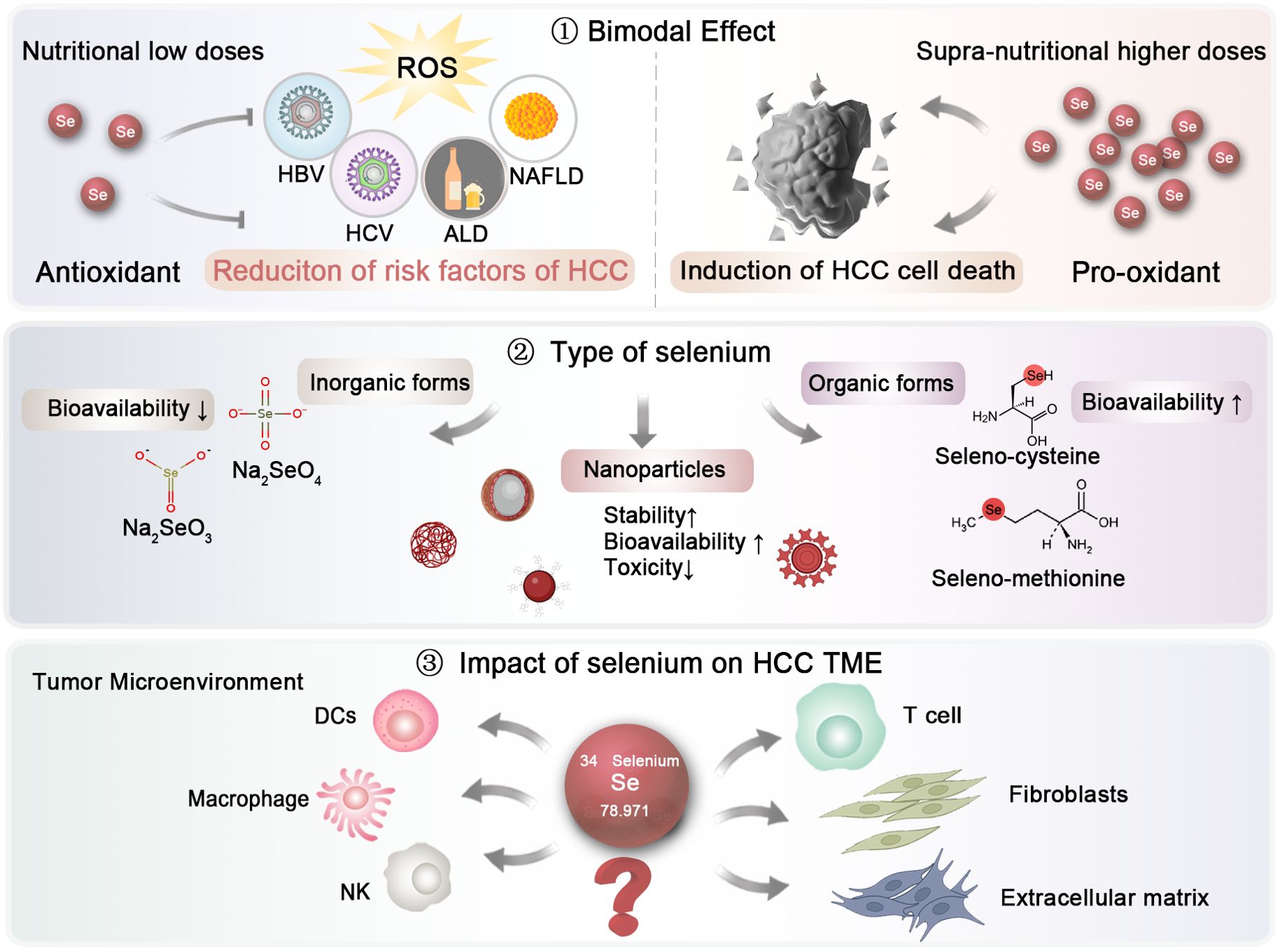
Figure 3. Future research directions regarding selenium investigation in HCC. The dosage and types of selenium, as well as their impact on the HCC microenvironment, should be further elucidated to establish optimal clinical application strategies.
Second, the form of selenium is also of paramount importance, as it significantly influences its absorption and effects (Figure 3). Generally speaking, Selenium is typically absorbed from dietary sources in both inorganic and organic forms. The inorganic forms, primarily consisting of selenate (Na₂SeO₄) and sodium selenite (Na₂SeO₃), are relatively simple to synthesize and can be produced on a large scale (144). However, their bioavailability is limited, and they may exhibit genotoxic effects in the human body. In contrast, organic forms of selenium, such as selenocysteine and selenomethionine, are more readily absorbed (145). In a study involving ten groups of selenium-deficient individuals, participants were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or daily doses of 200 or 600 μg of selenium in various supplement forms, including selenomethionine, sodium selenite, or high-selenium yeast. The differences between various selenium types in their bioavailability have not been fully elucidated. In a study, ten groups of individuals lacking selenium were randomly given either a placebo or daily doses of 200 or 600 μg of selenium in different supplement forms, such as selenomethionine, sodium selenite, or high-selenium yeast. Urinary excretion data revealed that selenomethionine had the highest bioavailability, while selenite showed the lowest (146). Recently, selenium nanoparticles have emerged as a novel supplementation approach, encapsulating zero-valent selenium within nano-carriers like proteins and polysaccharides to improve stability (147). This nanoform has attracted growing interest due to its enhanced bioavailability and reduced toxicity compared to traditional inorganic and organic forms. For example, Gao and colleagues demonstrated the antioxidant properties of hollow spherical selenium nanoparticles, suggesting their potential to mitigate systemic toxicity through targeted delivery (148). Consequently, selenium nanoparticles may represent a promising trend in future selenium supplementation.
Finally, the impact of selenium on HCC microenvironment warrants further exploration (Figure 3). While a substantial body of literature has highlighted the effects of selenium on immune cells, more in-depth investigations are essential to uncover the underlying molecular mechanisms. Comprehensive studies are also needed to evaluate the role of selenium on other elements of the tumor microenvironment (TME), including the extracellular matrix and fibroblasts, particularly at the clinical and pharmacological stages.
In summary, although selenium exhibits promise in mitigating the occurrence and progression of HCC, additional research is required to fully elucidate its effects, mechanisms, and to develop optimal strategies for its clinical implementation.
QL: Writing – review & editing. XB: Writing – original draft. XL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Institutional Foundation of The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (2024-MS-10), the Pudong New Area Science and Technology Development Fund public institution livelihood research project (PKJ2024-Y27), and the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2024JC-YBQN-0797).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. (2018) 391:1301–14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30010-2
2. Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7:6. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3
3. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
4. Liu D, Song T. Changes in and challenges regarding the surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in China. Biosci Trends. (2021) 15:142–7. doi: 10.5582/bst.2021.01083
5. He L, Zhang L, Peng Y, He Z. Selenium in cancer management: exploring the therapeutic potential. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1490740. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1490740
6. Loguercio C, De Girolamo V, Federico A, Feng SL, Cataldi V, Del Vecchio Blanco C, et al. Trace elements and chronic liver diseases. J Trace Elem Med Biol. (1997) 11:158–61. doi: 10.1016/S0946-672X(97)80045-4
7. Mueller AS, Klomann SD, Wolf NM, Schneider S, Schmidt R, Spielmann J, et al. Redox regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B by manipulation of dietary selenium affects the triglyceride concentration in rat liver. J Nutr. (2008) 138:2328–36. doi: 10.3945/jn.108.089482
8. Kim IW, Bae SM, Kim YW, Liu HB, Bae SH, Choi JY, et al. Serum selenium levels in Korean hepatoma patients. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2012) 148:25–31. doi: 10.1007/s12011-012-9344-6
9. Buljevac M, Romic Z, Vucelic B, Banic M, Krznaric Z, Plesko S. Serum selenium concentration in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Med Croatica. (1996) 50:11–4.
10. Yu SY, Zhu YJ, Li WG. Protective role of selenium against hepatitis B virus and primary liver cancer in Qidong. Biol Trace Elem Res. (1997) 56:117–24. doi: 10.1007/BF02778987
11. Cheng Z, Zhi X, Sun G, Guo W, Huang Y, Sun W, et al. Sodium selenite suppresses hepatitis B virus transcription and replication in human hepatoma cell lines. J Med Virol. (2016) 88:653–63. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24366
12. Shi J, Liu Z, Li W, Wang D. Selenium donor inhibited hepatitis B virus associated hepatotoxicity via the apoptosis and ferroptosis pathways. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). (2023) 2023:6681065. doi: 10.1155/2023/6681065
13. Yi YS, Park SG, Byeon SM, Kwon YG, Jung G. Hepatitis B virus X protein induces TNF-alpha expression via down-regulation of selenoprotein P in human hepatoma cell line, HepG2. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2003) 1638:249–56. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4439(03)00090-5
14. Li X, Bi L, Han L. Associations of five blood heavy metals with hepatitis B virus infection and immunity in adults: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:266. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17799-1
15. Rauf N, Tahir SS, Dilawar S, Ahmad I, Parvez S. Serum selenium concentration in liver cirrhotic patients suffering from hepatitis B and C in Pakistan. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2012) 145:144–50. doi: 10.1007/s12011-011-9182-y
16. Morbitzer M, Herget T. Expression of gastrointestinal glutathione peroxidase is inversely correlated to the presence of hepatitis C virus subgenomic RNA in human liver cells. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:8831–41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413730200
17. Ko WS, Guo CH, Yeh MS, Lin LY, Hsu GS, Chen PC, et al. Blood micronutrient, oxidative stress, and viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. (2005) 11:4697–702. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4697
18. Bettinger D, Schultheiss M, Hennecke N, Panther E, Knuppel E, Blum HE, et al. Selenium levels in patients with hepatitis C virus-related chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma: a pilot study. Hepatology. (2013) 57:2543–4. doi: 10.1002/hep.26142
19. Chen CL, Yang HI, Yang WS, Liu CJ, Chen PJ, You SL, et al. Metabolic factors and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma by chronic hepatitis B/C infection: a follow-up study in Taiwan. Gastroenterology. (2008) 135:111–21. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.073
20. Vancsa S, Nemeth D, Hegyi P, Szakacs Z, Farkas A, Kiss S, et al. Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after direct-acting antiviral therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:744512. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.744512
21. Menini S, Iacobini C, de Latouliere L, Manni I, Vitale M, Pilozzi E, et al. Diabetes promotes invasive pancreatic cancer by increasing systemic and tumour carbonyl stress in Kras(G12D/+) mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 39:152. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01665-0
22. Qian J, Huang C, Wang M, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Li M, et al. Nuclear translocation of metabolic enzyme PKM2 participates in high glucose-promoted HCC metastasis by strengthening immunosuppressive environment. Redox Biol. (2024) 71:103103. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103103
23. Steinbrenner H, Speckmann B, Pinto A, Sies H. High selenium intake and increased diabetes risk: experimental evidence for interplay between selenium and carbohydrate metabolism. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2011) 48:40–5. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.11-002FR
24. Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM. Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2011) 34:274–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04724.x
25. Arroyave-Ospina JC, Wu Z, Geng Y, Moshage H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: implications for prevention and therapy. Antioxidants (Basel). (2021) 10:174–98. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020174
26. Pisano G, Lombardi R, Fracanzani AL. Vascular damage in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: possible role of iron and ferritin. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17:675–87. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050675
27. Wang Y, Liu B, Wu P, Chu Y, Gui S, Zheng Y, et al. Dietary selenium alleviated mouse liver oxidative stress and NAFLD induced by obesity by regulating the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:349–65. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020349
28. Ozardali I, Bitiren M, Karakilcik AZ, Zerin M, Aksoy N, Musa D. Effects of selenium on histopathological and enzymatic changes in experimental liver injury of rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol. (2004) 56:59–64. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2004.05.001
29. Ding M, Potter JJ, Liu X, Torbenson MS, Mezey E. Selenium supplementation decreases hepatic fibrosis in mice after chronic carbon tetrachloride administration. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2010) 133:83–97. doi: 10.1007/s12011-009-8414-x
30. Shidfar F, Faghihi A, Amiri HL, Mousavi SN. Regression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with zinc and selenium co-supplementation after disease progression in rats. Iran J Med Sci. (2018) 43:26–31. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2018.40508
31. Zhang L, Fan J-B, Zhang X-W, Liu Y, Shi W-Y, Hidayat K, et al. Organic selenium ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through 5-hydroxytryptamine/bile acid enterohepatic circulation in mice. J Funct Foods. (2023) 106:105596. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2023.105596
32. Hamid M, Abdulrahim Y, Liu D, Qian G, Khan A, Huang K. The hepatoprotective effect of selenium-enriched yeast and gum arabic combination on carbon tetrachloride-induced chronic liver injury in rats. J Food Sci. (2018) 83:525–34. doi: 10.1111/jfds.2018.83.issue-2
33. Chen L, Pan DD, Zhou J, Jiang YZ. Protective effect of selenium-enriched Lactobacillus on CCl4-induced liver injury in mice and its possible mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol. (2005) 11:5795–800. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5795
34. Shen Q, Liu YJ, Qiu TT, Loon KS, Zhou D, Microplastic-induced NAFLD. Hepatoprotective effects of nanosized selenium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2024) 272:115850. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115850
35. Wu J, Zeng C, Yang Z, Li X, Lei G, Xie D, et al. Association between dietary selenium intake and the prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study. J Am Coll Nutr. (2020) 39:103–11. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2019.1613271
36. Yang Z, Yan C, Liu G, Niu Y, Zhang W, Lu S, et al. Plasma selenium levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese adults: a cross-sectional analysis. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:37288. doi: 10.1038/srep37288
37. Wang X, Seo YA, Park SK. Serum selenium and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in U.S. adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2011-2016. Environ Res. (2021) 197:111190. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111190
38. Prystupa A, Kicinski P, Luchowska-Kocot D, Blazewicz A, Kurys-Denis E, Niedzialek J, et al. Relationships between serum selenium and zinc concentrations versus profibrotic and proangiogenic cytokines (FGF-19 and endoglin) in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Ann Agric Environ Med. (2017) 24:544–8. doi: 10.26444/aaem/76937
39. Rua RM, Ojeda ML, Nogales F, Rubio JM, Romero-Gomez M, Funuyet J, et al. Serum selenium levels and oxidative balance as differential markers in hepatic damage caused by alcohol. Life Sci. (2014) 94:158–63. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.10.008
40. Xia X, Zhang X, Liu M, Duan M, Zhang S, Wei X, et al. Toward improved human health: efficacy of dietary selenium on immunity at the cellular level. Food Funct. (2021) 12:976–89. doi: 10.1039/D0FO03067H
41. Kim Y, Wei J, Citronberg J, Hartman T, Fedirko V, Goodman M. Relation of vitamin E and selenium exposure to prostate cancer risk by smoking status: A review and meta-analysis. Anticancer Res. (2015) 35:4983–96.
42. Charab MA, Abouzeinab NS, Moustafa ME. The protective effect of selenium on oxidative stress induced by waterpipe (Narghile) smoke in lungs and liver of mice. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2016) 174:392–401. doi: 10.1007/s12011-016-0737-9
43. Shi D, Liao S, Guo S, Li H, Yang M, Tang Z. Protective effects of selenium on aflatoxin B1-induced mitochondrial permeability transition, DNA damage, and histological alterations in duckling liver. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2015) 163:162–8. doi: 10.1007/s12011-014-0189-z
44. Shi D, Guo S, Liao S, Su R, Guo M, Liu N, et al. Protection of selenium on hepatic mitochondrial respiratory control ratio and respiratory chain complex activities in ducklings intoxicated with aflatoxin B(1). Biol Trace Elem Res. (2012) 145:312–7. doi: 10.1007/s12011-011-9195-6
45. Fang J, Yin H, Zheng Z, Zhu P, Peng X, Zuo Z, et al. The molecular mechanisms of protective role of se on the G(2)/M phase arrest of jejunum caused by AFB(1). Biol Trace Elem Res. (2018) 181:142–53. doi: 10.1007/s12011-017-1030-2
46. Boulahtouf Z, Virzi A, Baumert TF, Verrier ER, Lupberger J. Signaling induced by chronic viral hepatitis: dependence and consequences. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:2787–804. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052787
47. Levrero M, Zucman-Rossi J. Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2016) 64:S84–S101. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.02.021
48. Gao Q, Zhu H, Dong L, Shi W, Chen R, Song Z, et al. Integrated proteogenomic characterization of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. (2019) 179:1240. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.038
49. Wild CP, Montesano R. A model of interaction: aflatoxins and hepatitis viruses in liver cancer aetiology and prevention. Cancer Lett. (2009) 286:22–8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.053
50. Papatheodoridi M, Tampaki M, Lok AS, Papatheodoridis GV. Risk of HBV reactivation during therapies for HCC: A systematic review. Hepatology. (2022) 75:1257–74. doi: 10.1002/hep.32241
51. Calle EE, Kaaks R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. (2004) 4:579–91. doi: 10.1038/nrc1408
52. Sun B, Karin M. Obesity, inflammation, and liver cancer. J Hepatol. (2012) 56:704–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.09.020
53. Sohn W, Lee HW, Lee S, Lim JH, Lee MW, Park CH, et al. Obesity and the risk of primary liver cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2021) 27:157–74. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0176
54. Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U. S. adults. N Engl J Med. (2003) 348:1625–38. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021423
55. Shimizu M, Tanaka T, Moriwaki H. Obesity and hepatocellular carcinoma: targeting obesity-related inflammation for chemoprevention of liver carcinogenesis. Semin Immunopathol. (2013) 35:191–202. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0336-6
56. Pollak M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. (2008) 8:915–28. doi: 10.1038/nrc2536
57. Yoshimoto S, Loo TM, Atarashi K, Kanda H, Sato S, Oyadomari S, et al. Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer through senescence secretome. Nature. (2013) 499:97–101. doi: 10.1038/nature12347
58. Nogales F, Pajuelo E, Romero-Herrera I, Carreras O, Merchan F, Carrasco Lopez JA, et al. Uncovering the role of selenite and selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) in adolescent rat adipose tissue beyond oxidative balance: transcriptomic analysis. Antioxidants (Basel). (2024) 13:750–69. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060750
59. Wang N, Tan HY, Li S, Xu Y, Guo W, Feng Y. Supplementation of micronutrient selenium in metabolic diseases: its role as an antioxidant. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:7478523. doi: 10.1155/2017/7478523
60. Akahoshi N, Anan Y, Hashimoto Y, Tokoro N, Mizuno R, Hayashi S, et al. Dietary selenium deficiency or selenomethionine excess drastically alters organ selenium contents without altering the expression of most selenoproteins in mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2019) 69:120–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.03.020
61. Xu R, Chen C, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Wan Y. Fingernail selenium levels in relation to the risk of obesity in Chinese children: A cross-sectional study. Med (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e0027. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010027
62. Morais JBS, Cruz KJC, de Oliveira ARS, Cardoso BEP, da Silva Dias TM, de Sousa Melo SR, et al. Association between parameters of cortisol metabolism, biomarkers of minerals (Zinc, selenium, and magnesium), and insulin resistance and oxidative stress in women with obesity. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2023) 201:5677–91. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03639-7
63. Neeland IJ, Marso SP, Ayers CR, Lewis B, Oslica R, Francis W, et al. Effects of liraglutide on visceral and ectopic fat in adults with overweight and obesity at high cardiovascular risk: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2021) 9:595–605. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00179-0
64. El-Serag HB, Hampel H, Javadi F. The association between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of epidemiologic evidence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2006) 4:369–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2005.12.007
65. Singh MK, Das BK, Choudhary S, Gupta D, Patil UK. Diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: A pathophysiological link and pharmacological management. BioMed Pharmacother. (2018) 106:991–1002. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.095
66. Agosti P, Sabba C, Mazzocca A. Emerging metabolic risk factors in hepatocellular carcinoma and their influence on the liver microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2018) 1864:607–17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.11.026
67. Lee KH, Jeong D. Bimodal actions of selenium essential for antioxidant and toxic pro-oxidant activities: the selenium paradox (Review). Mol Med Rep. (2012) 5:299–304. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2011.651
68. Galan-Chilet I, Grau-Perez M, De Marco G, Guallar E, Martin-Escudero JC, Dominguez-Lucas A, et al. A gene-environment interaction analysis of plasma selenium with prevalent and incident diabetes: The Hortega study. Redox Biol. (2017) 12:798–805. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.04.022
69. Febiyanto N, Yamazaki C, Kameo S, Sari DK, Puspitasari IM, Sunjaya DK, et al. Effects of selenium supplementation on the diabetic condition depend on the baseline selenium status in KKAy mice. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2018) 181:71–81. doi: 10.1007/s12011-017-1013-3
70. Park K, Rimm EB, Siscovick DS, Spiegelman D, Manson JE, Morris JS, et al. Toenail selenium and incidence of type 2 diabetes in U.S. men and women. Diabetes Care. (2012) 35:1544–51. doi: 10.2337/dc11-2136
71. Vinceti M, Filippini T, Wise LA, Rothman KJ. A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of exposure to environmental selenium and the risk of type 2 diabetes in nonexperimental studies. Environ Res. (2021) 197:111210. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111210
72. Stranges S, Sieri S, Vinceti M, Grioni S, Guallar E, Laclaustra M, et al. A prospective study of dietary selenium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes. BMC Public Health. (2010) 10:564. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-564
73. Estes C, Razavi H, Loomba R, Younossi Z, Sanyal AJ. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology. (2018) 67:123–33. doi: 10.1002/hep.29466
74. Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 15:11–20. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109
75. Averill-Bates D. Reactive oxygen species and cell signaling. Review. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2024) 1871:119573. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2023.119573
76. Harrison SA, Torgerson S, Hayashi P, Ward J, Schenker S, Vitamin E. and vitamin C treatment improves fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. (2003) 98:2485–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.08699.x
77. Song Z, Luo W, Zheng H, Zeng Y, Wang J, Chen T. Translational nanotherapeutics reprograms immune microenvironment in Malignant pleural effusion of lung adenocarcinoma. Adv Healthc Mater. (2021) 10:e2100149. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202100149
78. Namachivayam A, Valsala Gopalakrishnan A. A review on molecular mechanism of alcoholic liver disease. Life Sci. (2021) 274:119328. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119328
79. Nickovic VP, Miric D, Kisic B, Kocic H, Stojanovic M, Buttice S, et al. Oxidative stress, NOx/l-arginine ratio and glutathione/glutathione S-transferase ratio as predictors of ‘sterile inflammation’ in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis and hepatorenal syndrome type II. Ren Fail. (2018) 40:340–9. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2018.1459699
80. Yang T, Lee SY, Park KC, Park SH, Chung J, Lee S. The effects of selenium on bone health: from element to therapeutics. Molecules. (2022) 27:392–424. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020392
81. Koh WP, Robien K, Wang R, Govindarajan S, Yuan JM, Yu MC. Smoking as an independent risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma: the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Br J Cancer. (2011) 105:1430–5. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.360
82. Shadi Y, Heshmati B, Poorolajal J. Interaction between hepatitis B, hepatitis C and smoking in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Public Health (Oxf). (2024) 46:51–60. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdad214
83. Cardin R, Piciocchi M, Bortolami M, Kotsafti A, Barzon L, Lavezzo E, et al. Oxidative damage in the progression of chronic liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma: an intricate pathway. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:3078–86. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3078
84. Pan Z, Seto WK, Liu CJ, Mao Y, Alqahtani SA, Eslam M. A literature review of genetics and epigenetics of HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: translational impact. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. (2024) 13:650–61. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-562
85. Ellingsen DG, Thomassen Y, Rustad P, Molander P, Aaseth J. The time-trend and the relation between smoking and circulating selenium concentrations in Norway. J Trace Elem Med Biol. (2009) 23:107–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2009.01.004
86. Schopfer J, Drasch G, Schrauzer GN. Selenium and cadmium levels and ratios in prostates, livers, and kidneys of nonsmokers and smokers. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2010) 134:180–7. doi: 10.1007/s12011-010-8636-y
87. Goodman GE, Schaffer S, Bankson DD, Hughes MP, Omenn GS. Carotene and C.-I. Retinol Efficacy Trial, Predictors of serum selenium in cigarette smokers and the lack of association with lung and prostate cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2001) 10:1069–76.
88. Lin YC, Li L, Makarova AV, Burgers PM, Stone MP, Lloyd RS. Molecular basis of aflatoxin-induced mutagenesis-role of the aflatoxin B1-formamidopyrimidine adduct. Carcinogenesis. (2014) 35:1461–8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu003
89. Rushing BR, Selim MI. Aflatoxin B1: A review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food, occupational exposure, and detoxification methods. Food Chem Toxicol. (2019) 124:81–100. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.11.047
90. Ye D, Hao Z, Tang S, Velkov T, Dai C. Aflatoxin exposure-caused male reproductive toxicity: molecular mechanisms, detoxification, and future directions. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:1460–81. doi: 10.3390/biom14111460
91. Hua Z, Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, et al. Contamination of aflatoxins induces severe hepatotoxicity through multiple mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:605823. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.605823
92. Karamkhani M, Asilian-Mahabadi H, Daraei B, Seidkhani-Nahal A, Noori-Zadeh A. Route exposure and adverse effects monitoring of Aflatoxin B1 in the workers of wet waste management, the role of body redox system modulation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2022) 248:114305. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114305
93. Chen K, Peng X, Fang J, Cui H, Zuo Z, Deng J, et al. Effects of dietary selenium on histopathological changes and T cells of spleen in broilers exposed to aflatoxin B1. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2014) 11:1904–13. doi: 10.3390/ijerph110201904
94. LeBoeuf RA, Laishes BA, Hoekstra WG. Effects of selenium on cell proliferation in rat liver and mammalian cells as indicated by cytokinetic and biochemical analysis. Cancer Res. (1985) 45:5496–504.
95. Varlamova EG. Molecular mechanisms of the therapeutic effect of selenium nanoparticles in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells. (2024) 13:1102–17. doi: 10.3390/cells13131102
96. Yang T, Huo J, Xu R, Su Q, Tang W, Zhang D, et al. Selenium sulfide disrupts the PLAGL2/C-MET/STAT3-induced resistance against mitochondrial apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Med. (2021) 11:e536. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.v11.9
97. Park SY, Lee YK, Kim HJ, Park OJ, Kim YM. AMPK interacts with beta-catenin in the regulation of hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and survival with selenium treatment. Oncol Rep. (2016) 35:1566–72. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4519
98. Wang C, Cheng T, Lu Q, Li W, Liu B, Yue L, et al. Oxygen therapy accelerates apoptosis induced by selenium compounds via regulating Nrf2/MAPK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol Res. (2023) 187:106624. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106624
99. Tagaram HR, Desai D, Li G, Liu D, Rountree CB, Gowda K, et al. A selenium containing inhibitor for the treatment of hepatocellular cancer. Pharm (Basel). (2016) 9:18–32. doi: 10.3390/ph9020018
100. Al-Noshokaty TM, Mesbah NM, Abo-Elmatty DM, Abulsoud AI, Abdel-Hamed AR. Selenium nanoparticles overcomes sorafenib resistance in thioacetamide induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats by modulation of mTOR, NF-kappaB pathways and LncRNA-AF085935/GPC3 axis. Life Sci. (2022) 303:120675. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120675
101. An Y, Zhao J. Functionalized selenium nanotherapeutics synergizes with zoledronic acid to suppress prostate cancer cell growth through induction of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle S phase arrest. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:685784. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.685784
102. Jiao J, Yu J, Ji H, Liu A. Synthesis of macromolecular Astragalus polysaccharide-nano selenium complex and the inhibitory effects on HepG2 cells. Int J Biol Macromol. (2022) 211:481–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.05.095
103. Zhang S, Gao R, Ding B, Li J, Wang T, Chen J, et al. Antihepatoma activity of Marsdenia tenacissima polysaccharide-decorated selenium nanoparticles by regulating the Bax/Bcl-2/caspases and p21/Akt/cyclin A2 signaling pathways. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 279:134981. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134981
104. Zhang X, Xiao Y, Huang Q. The cellular uptake of Cordyceps sinensis exopolysaccharide−selenium nanoparticles and their induced apoptosis of HepG2 cells via mitochondria- and death receptor-mediated pathways. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 247:125747. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125747
105. Wu Q, Wang X, Hao S, Wu Y, Zhang W, Chen L, et al. Synergetic effects and inhibition mechanisms of the polysaccharide-selenium nanoparticle complex in human hepatocarcinoma cell proliferation. J Sci Food Agric. (2024) 104:5124–38. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.v104.9
106. Khaled AM, Othman MS, Obeidat ST, Aleid GM, Aboelnaga SM, Fehaid A, et al. Green-synthesized silver and selenium nanoparticles using berberine: A comparative assessment of in vitro anticancer potential on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HepG2). Cells. (2024) 13:287–302. doi: 10.3390/cells13030287
107. Chi X, Liu Z, Wei W, Hu X, Wang Y, Wang H, et al. Selenium-rich royal jelly inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma through PI3K/AKT and VEGF pathways in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Food Funct. (2021) 12:9111–27. doi: 10.1039/D1FO01070K
108. Liu JG, Zhao HJ, Liu YJ, Wang XL. Effect of selenium-enriched malt on hepatocarcinogenesis, paraneoplastic syndrome and the hormones regulating blood glucose in rats treated by diethylnitrosamine. Life Sci. (2006) 78:2315–21. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.09.033
109. Hu D, Liu Q, Cui H, Wang H, Han D, Xu H. Effects of amino acids from selenium-rich silkworm pupas on human hepatoma cells. Life Sci. (2005) 77:2098–110. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.02.017
110. Huang C, Ding G, Gu C, Zhou J, Kuang M, Ji Y, et al. Decreased selenium-binding protein 1 enhances glutathione peroxidase 1 activity and downregulates HIF-1alpha to promote hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness. Clin Cancer Res. (2012) 18:3042–53. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0183
111. Gao PT, Ding GY, Yang X, Dong RZ, Hu B, Zhu XD, et al. Invasive potential of hepatocellular carcinoma is enhanced by loss of selenium-binding protein 1 and subsequent upregulation of CXCR4. Am J Cancer Res. (2018) 8:1040–9.
112. Xia Y, You P, Xu F, Liu J, Xing F. Novel functionalized selenium nanoparticles for enhanced anti-hepatocarcinoma activity in vitro. Nanoscale Res Lett. (2015) 10:1051. doi: 10.1186/s11671-015-1051-8
113. Rohr-Udilova N, Sieghart W, Eferl R, Stoiber D, Bjorkhem-Bergman L, Eriksson LC, et al. Antagonistic effects of selenium and lipid peroxides on growth control in early hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. (2012) 55:1112–21. doi: 10.1002/hep.24808
114. Rusolo F, Pucci B, Colonna G, Capone F, Guerriero E, Milone MR, et al. Evaluation of selenite effects on selenoproteins and cytokinome in human hepatoma cell lines. Molecules. (2013) 18:2549–62. doi: 10.3390/molecules18032549
115. Liu JG, Zhao HJ, Liu YJ, Wang XL. Effect of selenium-enriched malt on VEGF and several relevant angiogenic cytokines in diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinoma rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol. (2010) 24:52–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2009.10.001
116. Liu JG, Zhao HJ, Liu YJ, Liu YW, Wang XL. Effect of two selenium sources on hepatocarcinogenesis and several angiogenic cytokines in diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinoma rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol. (2012) 26:255–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2012.02.001
117. Huang LJ, Mao XT, Li YY, Liu DD, Fan KQ, Liu RB, et al. Multiomics analyses reveal a critical role of selenium in controlling T cell differentiation in Crohn’s disease. Immunity. (2021) 54:1728–1744.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.07.004
118. Steinbrenner H, Al-Quraishy S, Dkhil MA, Wunderlich F, Sies H. Dietary selenium in adjuvant therapy of viral and bacterial infections. Adv Nutr. (2015) 6:73–82. doi: 10.3945/an.114.007575
119. Razaghi A, Mansouri L, Brodin O, Bjornstedt M, Lundahl J. Soluble PD-L1 expression after intravenous treatment of cancer patients with selenite in phase I clinical trial. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:906134. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.906134
120. Carlson BA, Yoo MH, Shrimali RK, Irons R, Gladyshev VN, Hatfield DL, et al. Role of selenium-containing proteins in T-cell and macrophage function. Proc Nutr Soc. (2010) 69:300–10. doi: 10.1017/S002966511000176X
121. Yao Y, Chen Z, Zhang H, Chen C, Zeng M, Yunis J, et al. Selenium-GPX4 axis protects follicular helper T cells from ferroptosis. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22:1127–39. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00996-0
122. Xu J, Liu Z, Zhang S, Xiang J, Lan H, Bao Y. Anti-hepatoma immunotherapy of Pholiota adiposa polysaccharide-coated selenium nanoparticles by reversing M2-like tumor-associated macrophage polarization. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 277:133667. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133667
123. Broome CS, McArdle F, Kyle JA, Andrews F, Lowe NM, Hart CA, et al. An increase in selenium intake improves immune function and poliovirus handling in adults with marginal selenium status. Am J Clin Nutr. (2004) 80:154–62. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/80.1.154
124. Hu Y, Liu T, Li J, Mai F, Li J, Chen Y, et al. Selenium nanoparticles as new strategy to potentiate gammadelta T cell anti-tumor cytotoxicity through upregulation of tubulin-alpha acetylation. Biomaterials. (2019) 222:119397. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119397
125. Hawkes WC, Kelley DS, Taylor PC. The effects of dietary selenium on the immune system in healthy men. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2001) 81:189–213. doi: 10.1385/BTER:81:3:189
126. Liu C, Lai H, Chen T. Boosting natural killer cell-based cancer immunotherapy with selenocystine/transforming growth factor-beta inhibitor-encapsulated nanoemulsion. ACS Nano. (2020) 14:11067–82. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b10103
127. Enqvist M, Nilsonne G, Hammarfjord O, Wallin RP, Bjorkstrom NK, Bjornstedt M, et al. Selenite induces posttranscriptional blockade of HLA-E expression and sensitizes tumor cells to CD94/NKG2A-positive NK cells. J Immunol. (2011) 187:3546–54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100610
128. Kiremidjian-Schumacher L, Roy M, Wishe HI, Cohen MW, Stotzky G. Supplementation with selenium augments the functions of natural killer and lymphokine-activated killer cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. (1996) 52:227–39. doi: 10.1007/BF02789164
129. Sun N, Teng A, Zhao Y, Liu H, Tu J, Jia Q, et al. Immunological and anticancer activities of seleno-ovalbumin (Se-OVA) on H22-bearing mice. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 163:657–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.006
130. Gao S, Li T, Guo Y, Sun C, Xianyu B, Xu H. Selenium-containing nanoparticles combine the NK cells mediated immunotherapy with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Adv Mater. (2020) 32:e1907568. doi: 10.1002/adma.201907568
131. Xianyu B, Pan S, Gao S, Xu H, Li T. Selenium-containing nanocomplexes achieve dual immune checkpoint blockade for NK cell reinvigoration. Small. (2024) 20:e2306225. doi: 10.1002/smll.202306225
132. Pan S, Guan J, Xianyu B, Tan Y, Li T, Xu H. A nanotherapeutic strategy to reverse NK cell exhaustion. Adv Mater. (2023) 35:e2211370. doi: 10.1002/adma.202211370
133. Zhou C, Lu Z, Sun B, Yi Y, Zhang B, Wang Z, et al. Peripheral lymphocytes in primary liver cancers: elevated NK and CD8+ T cells and dysregulated selenium metabolism. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:222–36. doi: 10.3390/biom14020222
134. Lai H, Zeng D, Liu C, Zhang Q, Wang X, Chen T. Selenium-containing ruthenium complex synergizes with natural killer cells to enhance immunotherapy against prostate cancer via activating TRAIL/FasL signaling. Biomaterials. (2019) 219:119377. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119377
135. Jia Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Zhang S, Dai J, Huang J, et al. Selenium can regulate the differentiation and immune function of human dendritic cells. Biometals. (2021) 34:1365–79. doi: 10.1007/s10534-021-00347-4
136. Qin T, Ren Z, Huang Y, Song Y, Lin D, Li J, et al. Selenizing Hericium erinaceus polysaccharides induces dendritic cells maturation through MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Int J Biol Macromol. (2017) 97:287–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.039
137. Sun Z, Xu Z, Wang D, Yao H, Li S. Selenium deficiency inhibits differentiation and immune function and imbalances the Th1/Th2 of dendritic cells. Metallomics. (2018) 10:759–67. doi: 10.1039/C8MT00039E
138. Zhang L, Xia H, Xia K, Liu X, Zhang X, Dai J, et al. Selenium regulation of the immune function of dendritic cells in mice through the ERK, akt and rhoA/ROCK pathways. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2021) 199:3360–70. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02449-5
139. Deng B, He X, Wang D, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Chen T, et al. Designing selenium nanoadjuvant as universal agent for live-killed virus-based vaccine. Small Methods. (2023) 7:e2300293. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202300293
140. Yazdi MH, Mahdavi M, Faghfuri E, Faramarzi MA, Sepehrizadeh Z, Hassan ZM, et al. Th1 immune response induction by biogenic selenium nanoparticles in mice with breast cancer: preliminary vaccine model. Iran J Biotechnol. (2015) 13:1–9. doi: 10.15171/ijb.1056
141. Li S, Bian F, Yue L, Jin H, Hong Z, Shu G. Selenium-dependent antitumor immunomodulating activity of polysaccharides from roots of A. membranaceus. Int J Biol Macromol. (2014) 69:64–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.05.020
142. Carlson BA, Yoo MH, Sano Y, Sengupta A, Kim JY, Irons R, et al. Selenoproteins regulate macrophage invasiveness and extracellular matrix-related gene expression. BMC Immunol. (2009) 10:57. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-10-57
143. Verma S, Hoffmann FW, Kumar M, Huang Z, Roe K, Nguyen-Wu E, et al. Selenoprotein K knockout mice exhibit deficient calcium flux in immune cells and impaired immune responses. J Immunol. (2011) 186:2127–37. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002878
144. Kieliszek M, Blazejak S. Selenium: Significance, and outlook for supplementation. Nutrition. (2013) 29:713–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.11.012
145. Mahan DC, Cline TR, Richert B. Effects of dietary levels of selenium-enriched yeast and sodium selenite as selenium sources fed to growing-finishing pigs on performance, tissue selenium, serum glutathione peroxidase activity, carcass characteristics, and loin quality. J Anim Sci. (1999) 77:2172–9. doi: 10.2527/1999.7782172x
146. Burk RF, Norsworthy BK, Hill KE, Motley AK, Byrne DW. Effects of chemical form of selenium on plasma biomarkers in a high-dose human supplementation trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2006) 15:804–10. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0950
147. Hosnedlova B, Kepinska M, Skalickova S, Fernandez C, Ruttkay-Nedecky B, Peng Q, et al. Nano-selenium and its nanomedicine applications: a critical review. Int J Nanomedicine. (2018) 13:2107–28. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S157541
148. Mahmoodi NM, Karimi B, Mazarji M, Moghtaderi H. Cadmium selenide quantum dot-zinc oxide composite: Synthesis, characterization, dye removal ability with UV irradiation, and antibacterial activity as a safe and high-performance photocatalyst. J Photochem Photobiol B. (2018) 188:19–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.08.023
Keywords: selenium, preventive effects, therapeutic effects, mechanism, hepatocellular carcinoma
Citation: Luo Q, Bai X, Li X and Liu C (2025) The role and mechanism of selenium in the prevention and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 15:1557233. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1557233
Received: 08 January 2025; Accepted: 05 March 2025;
Published: 20 March 2025.
Edited by:
Fabiana Ourique, Universidade Federal de Juiz de Fora, BrazilReviewed by:
Sivapar V. Mathan, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Luo, Bai, Li and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaojiao Li, bGl4aWFvamlhb0B4anR1LmVkdS5jbg==; Chang Liu, Y2xpdTk0QHNpYnMuYWMuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.