
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 07 February 2025
Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1534948
The 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification is a crucial epigenetic RNA modification, which is involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of genes. It plays an important role in various biological processes, including cell metabolism, growth, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. By affecting the proliferation, migration, invasion, and drug sensitivity of tumor cells, m5C methylation modification plays a vital part in the initiation and progression of tumors and is closely associated with the poor tumor prognosis. m5C-related proteins are categorized into three functional groups: m5C methyltransferases (m5C writers), m5C demethylases (m5C erasers), and m5C methyl-binding proteins (m5C readers). This paper introduces several common methodologies for detecting m5C methylation; and reviews the molecular structure and biological functions of m5C readers, including ALYREF, YBX1, YBX2, RAD52, YTHDF2, FMRP, and SRSF2. It further summarizes their roles and regulatory mechanisms in tumors, offering novel targets and insights for tumor treatment.
Research on the mechanisms of RNA regulation in tumors has increased during the last five years. Epigenetic regulation of RNAs represents an important aspect of RNA regulation, influencing the expression of mRNAs, tRNAs, rRNAs, and other non-coding RNAs at the post-transcriptional level (1, 2). The m5C methylation modification is one of the most common RNA modifications, which is associated with gene expression and stability (3). m5C modification has been found to promote tumor progression and associate with poor prognosis in several tumor types, including hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, esophageal cancer, and breast cancer (4–7).
Three functional components are necessary for m5C modification and gene regulation. Firstly, the methyltransferase transfers the methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine to the fifth carbon atom of cytosine, thereby forming the m5C modification (8) (Figure 1). Secondly, methyl-binding proteins or demethylases identify and bind methylated mRNA, which in turn affects biological behavior, realizes epigenetic regulation of genes, involves metabolism and tumorigenesis in the human body (9) (Figures 2, 3, Table 1). In addition to gene regulation, Ding et al. found a link between m5C methylation sites in hepatitis B patients and the virus’s ability to replicate and evade antiviral treatments (10). Additionally, it has been demonstrated to influence adipogenesis by regulating the cell cycle and autophagy (11). Aberrant methylation of m5C leads to malignant proliferation of gastric cancer cells and poor prognosis by promoting reprogramming of glutamine metabolism (12). It can be seen that m5C methylation modification not only leads to malignant outcomes such as tumors but also participates in some fundamental life processes of cells.
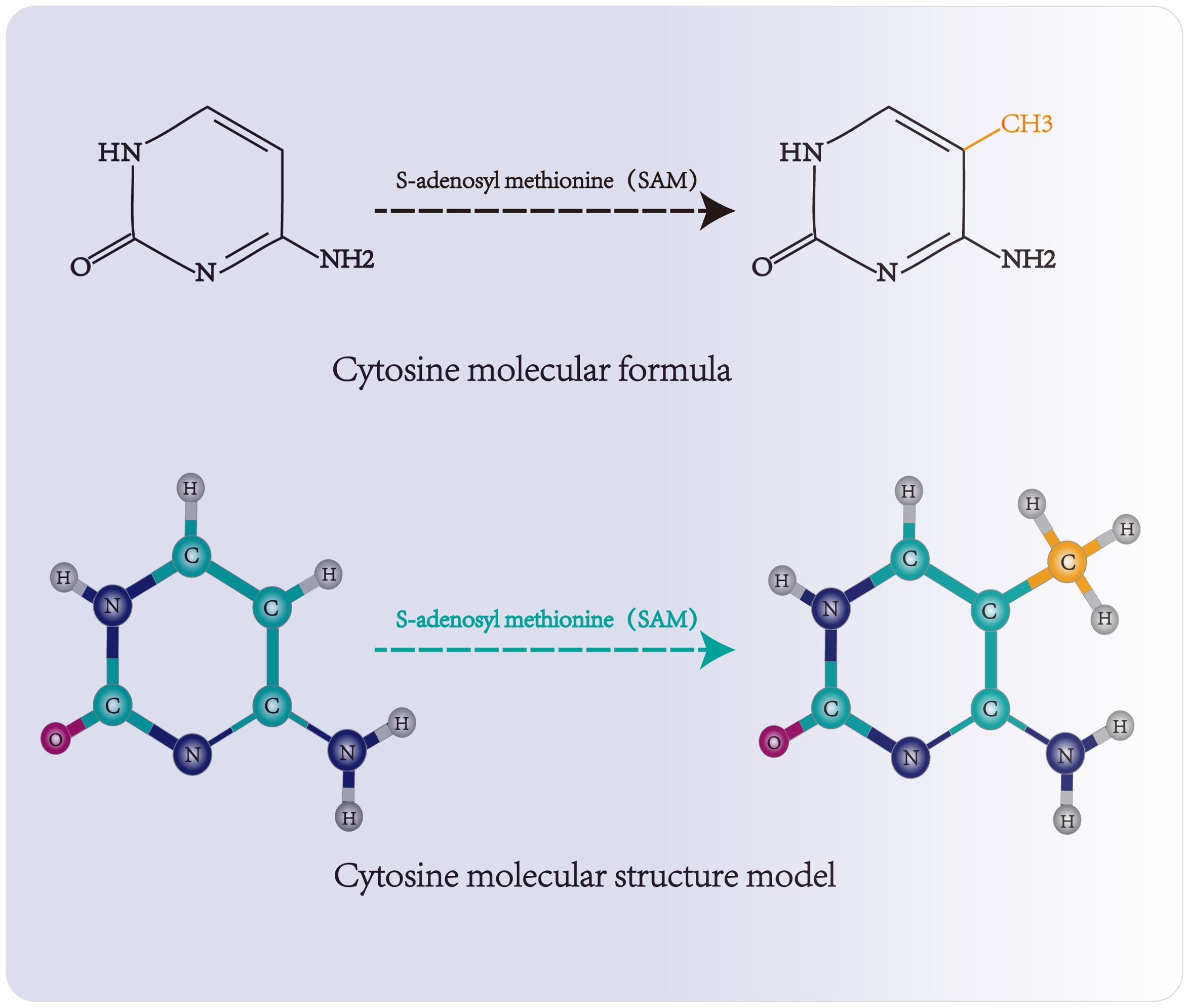
Figure 1. Molecular structure and methylation site of cytosine. Methyltransferase transfers the methyl group of S-adenosylmethionine to the fifth carbon atom of cytosine, forming 5-methylcytosine.
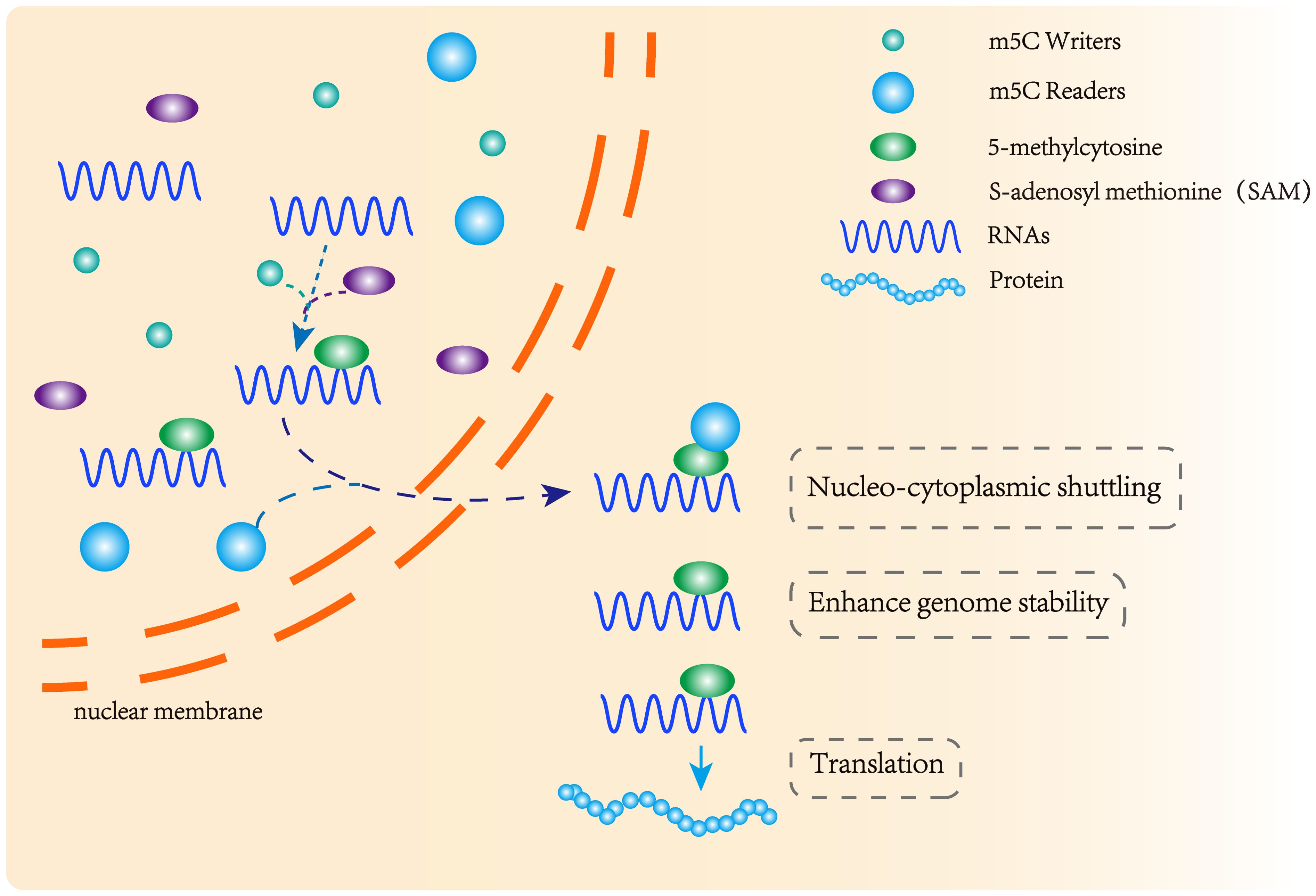
Figure 2. m5C methyltransferase and m5C binding protein participate in the formation of methylation modification. m5C methyltransferase catalyzes the formation of m5C methylation, and the methylation binding protein recognizes methylated mRNA, promoting its nuclear transport and affecting its stability and post-transcriptional translation.
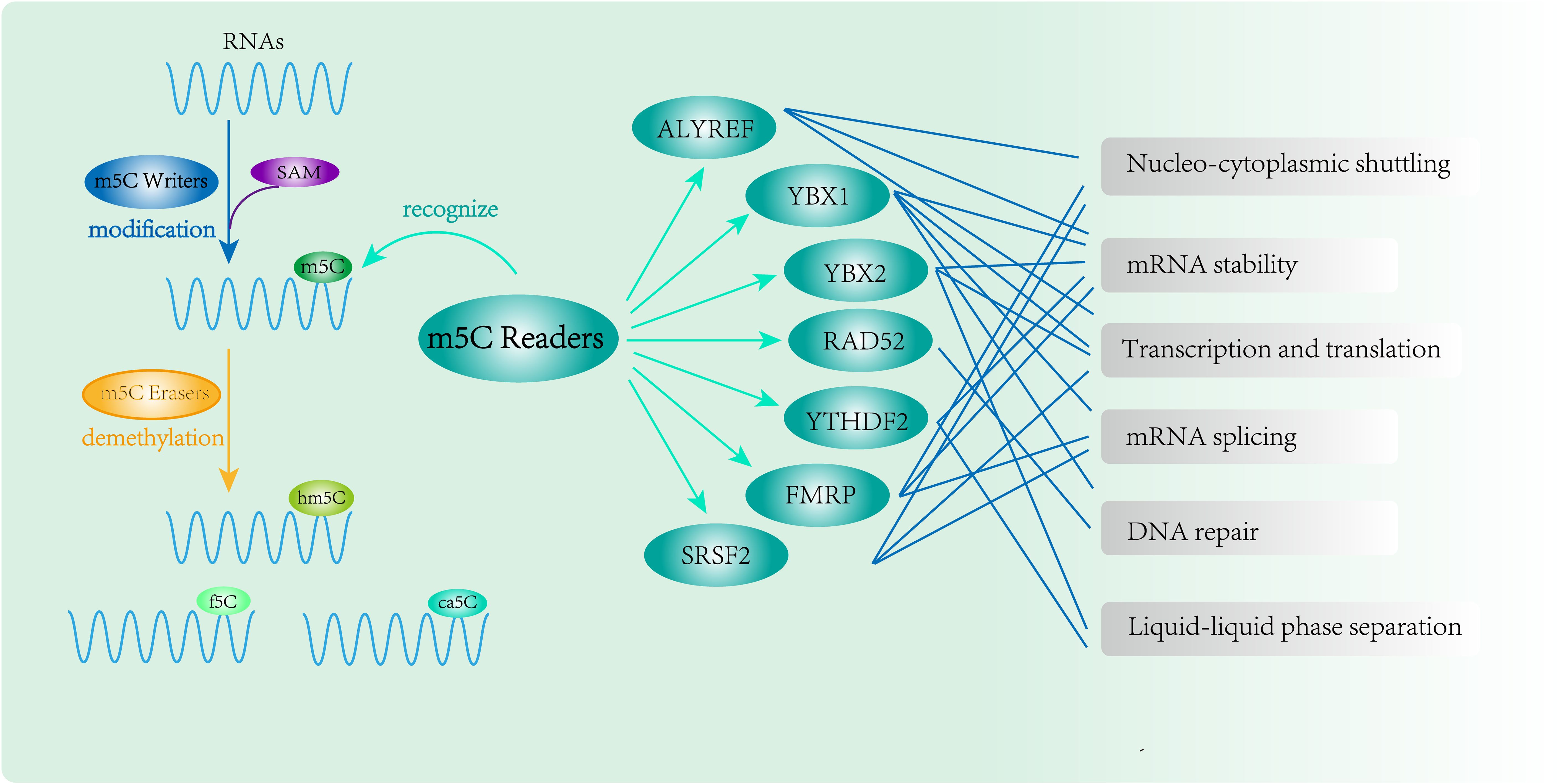
Figure 3. RNA m5C modification and function of m5C Readers. m5C binding proteins(ALYREF, YBX1, YBX2, RAD52, YTHDF2, FMRP and SRSF2) participate in methylation modification and perform complex epigenetic regulation of genes.
Although m5C methyltransferases have been thoroughly studied, the members of the m5C methyl-binding protein family have not yet been systematically elucidated. In this review, we summarize the m5C Readers identified in the literature as comprehensively as possible, refine and update the m5C methyl-binding protein members, and primarily describe the molecular structure characteristics, biological functions and mechanisms of m5C methyl-binding proteins (ALYREF, YBX1, YBX2, RAD52, YTHDF2, FMRP and SRSF2) in tumorigenesis and development.
The regulators of m5C modification can be divided into three groups according to their functional characteristics, including m5C methyltransferases (m5C writers), m5C demethylase (m5C erasers), and m5C methyl-binding proteins (m5C readers).
The m5C writers primarily consist of the NSUN family (NSUN1-NSUN7) and the methyltransferase homologue TRDMT1 (DNMT2) (8, 13, 14), which form m5C methylation by transferring the methyl group to the fifth carbon atom of cytosine. m5C methyltransferases are involved in the formation of methylation, modulate RNA function and stability, influence post-transcriptional modifications, and are involved in tumorigenesis and progression (8).
The m5C erasers including ALKBH1 and TET families (15, 16), which is capable of oxidizing m5C, thereby achieving the effect of removing methyl groups from methylated RNA, that is to say, the demethylation of the RNA. Similarly, ALKBH1 and TET play a pivotal role in tumorigenesis by influencing methylation formation and regulating the malignant phenotype of cancer cells, which is closely relevant to poor prognosis (17, 18).
The m5C readers include ALYREF, YBX1, YBX2, RAD52, YTHDF2, FMRP and SRSF2 (19–25). They can specifically recognize m5C-methylated RNAs, affect RNA stability and nucleocytoplasmic shuttling, and regulate transcription and translation. At the cellular level, they can enhance the ability of proliferation, migration, and invasion of cancer cells. They are also correlated with the immune microenvironment and drug resistance of tumors, which can further accelerate the tumor progression (26, 27).
The different acting elements of m5C work together to promote the occurrence and development of tumors. For example, the co-expression of ALYREF and NSUN2 is frequently observed in bladder cancer, and both proteins regulate RNA methylation and post-transcriptional modifications to promote bladder cancer progression (28). YBX2 and YTHDF2 interactions promote the stability of mRNA of endometrial cancer cells (29). In non-small cell lung cancer, the combined action of NSUN2 and YBX1 results in the increased expression of the target gene QSOX1, which mediates resistance to gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer (30). NSUN 2 and YBX 1 are closely related, and in addition to non-small cell lung cancer, they can also interact in pancreatic, colorectal cancer, and ovarian cancer to jointly regulate tumor progression (4, 31, 32).
Epigenetic modification of gene has increasingly become the focus of research, and the excellent performance of m5C methylation modification of RNA in the development of tumors has attracted more and more researchers. This also means that we need more convenient and efficient methods to help researchers detect the presence or extent of methylation. With the rapid development of scientific testing technology, more and more methods can be chosen to detect the existence, abundance, or type of m5C methylation, which can be selected according to the purposes of the detection, and here are some common methods.
RNA obtained by electrophoretic separation was transferred to a PVDF membrane and incubated with an antibody specific for the m5C methylation modification, followed by a chemiluminescent reaction to show the location of the bands to assess if the m5C methylation modification is present (33).
The second generation sequencing, a transcriptomic detection method, has been the preferred approach for RNA detection due to its low error and high accuracy. The examination of m6A and m5C alterations commonly uses nanopore technology, an amplification-free sequencing technique. Structural changes that occur as RNA or DNA passes through the nanopore result in differences in current blocking, which is translated into base sequences by a recurrent neural network (RNN) as a way of analyzing molecular signatures and locating regions of RNA methylation (34, 35).
In order to determine the degree of methylation in the test samples, the signal intensities of the sample RNAs are compared to standard curves obtained from known methylated and non-methylated control RNAs (34). Commercially available kits are sufficient for the assay.
RNA is broken down into nucleosides by enzymatic digestion, and these are then purified. Mass spectrometry is then used to separate the ribonucleosides and identify the methylated modified nucleosides. Individual molecules are identified and measured according to their mass-to-charge ratio (36). The method takes advantage of the fact that the modified nucleotide differs from its unmodified counterpart in terms of net charge, hydrophobicity, and polarity (34). The classical methods for the analysis of RNA methylation modification are one-dimensional (1D) or two-dimensional (2 D) thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) (36).
Spot hybridization, also known as slit hybridization, is a relatively simple method for the detection of methylation patterns in diverse RNA types. The membranes with RNA are incubated with specific antibodies or probes to determine the existence and level of methylation by the depth of the developed spots (37). This experiment should only be used to verify the presence of methylation and to compare the change in the overall abundance of methylation between different samples. However, it is equally significant to be careful to avoid contamination of the DNA, as this may affect the results.
ALYREF, also designated THOC4, is a heat-stable nuclear protein that has the unusual ability to recognize m5C sequences and act as a molecular chaperone. ALYREF is known to facilitate the dimerization of unfolded leucine zips by recognizing them, to activate transcription. It can also bind to specific molecules in the translational region of mRNAs, thereby regulating gene expression, mRNA egress from the nucleus and genome stability (38–42). In most tumors, ALYREF has a high expression level and is closely associated with tumor heterogeneity, immune infiltration, and a high mutation rate of TP53, which enhances the proliferation, migration, and invasive properties of tumor cells, as well as drug resistance, tumor progression and adverse prognosis (43–45). The activity of ALYREF is regulated by AKT-mediated phosphorylation, with reduced ALYREF phosphorylation observed to suppress cell proliferation and mRNA export (46).
YBX1 is a gene with a wide range of nucleic acid binding properties encoding a highly conserved cold-excited structural domain protein that plays a pivotal role in many basic biological functions, such as transcription, translation, DNA repair, and splicing of precursor mRNAs (47–49). YBX1 displaces translation initiation factors from messenger ribonucleic acid bodies and redistributes them to improve translation efficiency (50). However, the regulation of translation by YBX1 is not always positive. Studies have demonstrated a bell-curve relationship between the relative amount of YBX1 and the level of translation, with YBX1 acting as an inhibitor of translation when the relative amount of YBX1 is high (51–53). As a splicing regulator of messenger RNAs (mRNAs), YBX1 indirectly affects mRNA splicing and shear factors behavior by identifying particular sequences in precursor mRNAs (54). YBX1 can directly bind to m5C-methylated mRNAs and act to stabilize them (19, 20). In addition, YBX1 is essential for maintaining cardiomyocyte function. mTOR activation of YBX1 can transmit pathological signals and regulate protein synthesis in cardiomyocytes, which significantly contributes to the development of cardiac hypertrophy (55). YBX1, a known oncoprotein, shows high expression in a variety of tumors, and YBX1 can regulate tumor angiogenesis by releasing angiogenic factors into the extracellular microenvironment, playing a role as an oncogenic enhancer (56, 57).
YBX2 is a member of the Y-box protein family, and similar to YBX1, YBX2 also has an alanine/proline (A/P)-rich N-terminal domain, a variable C-terminal domain (CTD), and a highly conserved cold shock domain (CSD) (58). YBX2 is a major component of mRNP and regulates mRNA stability and translation (29, 59, 60). Because MAPK phosphorylates YBX2, ubiquitination-mediated degradation is suppressed. The accumulated YBX2 then activates brown adipose tissue, thereby promoting glucose utilization and lactic acid production in glycolysis (61). In addition, methylated YBX 2 can be recognized by ALYREF, promoting YBX 2 nucleation and increasing YBX 2 protein expression, which is an important way to regulate lipolysis (62). Moreover, YBX2 is essential for maintaining the normal function of germ cells (63). m5C methylation regulates the activity of YBX2, a novel m5C binding protein, and that can undergo liquid-liquid phase separation in vitro and in vivo (21). Pan-cancer analysis showed that YBX family genes are associated with most tumor progression and can predict tumor prognosis to a certain extent (64).
RAD52 is a multimeric cyclic DNA repair protein consisting of 418 amino acids. The human Rad52 protein, which is composed of a heptameric ring, resembles a windmill (65).In ROS-induced DNA double-strand break damage, RAD52 can preferentially bind to DNA: RNA hybrids containing m5C methylation-modified RNAs with the help of the m5C methyltransferase TRDMT1 to promote homologous recombination (23). This observation suggests that RAD52 may serve as a reader of m5C RNA in DNA: RNA hybrid at the DNA damage site and that m5C methylation modification of RNA is crucial for gene repair and maintaining genomic stability (66). Additionally, the activity, stability, and function of RAD52 are also affected by post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation and ubiquitination (67, 68). In tumors, RAD52 interacts with RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 (PAF1) to inhibit cisplatin and gemcitabine resistance (69).
Based on structural and functional studies of YTHDF2, it was found to be a versatile reader that recognizes M6A, M1A and M5C (70, 71). Dai et al. demonstrated that three aromatic amino acid residues in the hydrophobic pocket of YTHDF2 that bind m6A can bind directly to m5C-methylated RNA. Considering that YTHDF2 recognizes multiple methylated forms, whether YTHDF2 acts on the m5C site can be verified by immunoprecipitation in vitro pull-down assays and LC-MS/MS, and can also be distinguished by the difference in YTHDF2 binding to the m5C and m6A docking structural domains (22). Functionally, YTHDF2 participates in the processing of precursor ribosomal RNAs (pre-rRNAs) in an m5C-dependent manner and regulates translation (22, 72). Histone lactation controls YTHDF2 expression, and tumors with high levels of YTHDF2 are associated with a poor prognosis. Additionally, YTHDF2 regulates immune processes by affecting immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment (73, 74). The deletion of YTHDF2 in the tumor microenvironment has been observed to result in increased apoptosis and impaired suppression of Treg cells (75). Additionally, it has been shown to promote reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages, enhance antigen cross-presentation, inhibit tumor growth, and enhance the efficacy of PDL-1 antibodies (76, 77). As YTHDF2 interacts with more than one type of methylation modification, the mechanism by which it acts needs to be further explored and differentiated. However, the role of YTHDF2 in tumor is still controversial, showing very different effects in different cancer types. For example, it plays a dual role in gastric cancer (78, 79). A comprehensive and detailed examination is necessary to clarify its precise mechanism of action.
FMRP is an RNA-binding protein with three structural domains: the N-terminus, the central structure, and the C-terminus, which is associated with the structure and function of synapses, is involved in the exit of mRNA from the nucleus, and also has a wide range of regulation of gene expression (80, 81). Early nervous system development requires FMRP to identify and bind mRNAs in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex, which are critical for memory and learning (82). Furthermore, FMRP plays a role in RNA methylation modification as an m5C reader, facilitates the interaction between the methyltransferase TRDMT1 and the demethylase TET1, influences transcription and translation, and contributes to DNA damage repair and cell survival (24, 83). Beyond its role in gene regulation, FMRP is also important in metabolic processes. It has been demonstrated that FMRP deficiency increases hepatic protein synthesis and affects lipid metabolism, indicating that FMRP is involved in the regulation of systemic metabolic homeostasis (84). In solid tumors, FMRP up-regulation contributes to poor prognosis, inhibits immune attack, promotes tumor growth, immune escape and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) conversion (85, 86).
SRSF2 belongs to the family of RNA-binding proteins known as serine/arginine-rich (SR) proteins, which are involved in constitutive and selective splicing of RNAs and suppress intron splicing (87–89). SRSF2 contains an RNA recognition motif (RRM) and an RS domain, the former for binding to RNA and the latter for binding to other proteins. Additionally, the interactions between different SR splicing factors are realized in the RS domain (90). It has been reported that SR proteins play a role in the process of mRNA egress and translation, in addition to RNA splicing (91). Aberrant expression of SRSF2 is closely associated with tumorigenesis (92). Recent studies find that knockdown of NSUN2 decreases RNA methylation levels, reduces SRSF2 binding, and alters RNA splicing, which evidences SRSF2 can act as an m5C reader and may be associated with the development of malignancy (25, 93). Besides, SRSF2 has been linked to immune system depletion in the tumor microenvironment. It is a potential therapeutic target for reversing immune depletion because it regulates the transcription of immune checkpoint genes by influencing signal transduction and promoter recruitment (94). SRSF2 is a key molecule for cell survival and not only has a role in tumors but also regulates myocyte proliferation and myogenesis by preventing premature aging, differentiation, and apoptosis of myocytes (95). Moreover, SRSF2 acts as a strong transcriptional activator that promotes hepatic energy homeostasis and bile acid metabolism. Mutation or deletion in the expression of SRSF2 can lead to aberrant hepatic splicing, metabolic dysfunction, bile acid accumulation, and the subsequent induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress, ultimately leading to liver failure (96).
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the material cause of morbidity and mortality among all cancers, and is a major threat to global health (97). The majority of liver cancer patients are concentrated in Asia, with China having the most liver cancer cases (98, 99). The low survival rates of liver cancer creates a significant challenge for treating this disease (100, 101). As a binding protein for m5C methylation, ALYREF can stabilize RNA and activate subsequent signaling pathways to exert a tumorigenic effect (102). Xue et al. found that ALYREF deficiency can inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cells proliferation and tumor growth, increase the rate of apoptosis, and is associated with tumor immune infiltration (103, 104). In hepatocellular carcinoma, the overexpression of YBX1 remodels the tumor microenvironment, increasing the infiltration of immune cells and the transcription of PD-L1 (105, 106). YBX1 interacts with circular RNA to promote metastasis and drug resistance of liver cancer: circASH2 influences the liquid-liquid phase separation and cytoskeletal remodeling of YBX1, thereby promoting the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (107, 108); cFAM210A binds to YBX1, which reduces YBX1 phosphorylation and inhibits the trans-activating effect on EMT. At the same time, cFAM210A is regulated by YTHDF2, which induces cFAM210A degradation and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression (109). The elevated expression of RAD52 in hepatocellular carcinoma is linked to age and gender, and it is associated with promoting proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells (110). YTHDF2 is associated with stemness and drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, improving genomic stability and promoting immune escape and angiogenesis, while also facilitating hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis in vivo (111–114). SRSF2 is frequently mutated or overexpressed in cancerous cells, and SRSF2 deletion can stimulate the regeneration of hepatic progenitor cells and the activation of oncogenes in hepatocellular carcinoma, which increases the proliferative and tumorigenic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma cells, mediates drug resistance, and promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (115, 116). FMRP is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes the translation of STAT3, and can bind to STAT3 mRNA, thereby facilitating its localization to cellular protrusions and the promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis (117).
Pancreatic cancer is globally recognized as one of the deadliest malignant tumors, and clinical treatment is facing great challenges. There is an urgent demand to explore its pathogenesis, discover therapeutic targets, and prevent its progression more effectively (118). ALYREF can affect amino acid metabolism in pancreatic cancer cells, promote immune escape, and is associated with poor prognosis (119). YBX1 directly promotes mucin expression and establishes a barrier to prevent chymotrypsin from digesting pancreatic cancer cells, a mechanism that ensures the survival of pancreatic cancer cells in the pancreatic microenvironment (120). Overexpression of YBX1 in pancreatic cancer binds to the promoter of GSK3β, resulting in upregulation of CBX3, which activates TGF-β signaling to regulate the cell cycle and promotes the growth and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells (121, 122). YBX1 also promotes IL-18 transcription, increases immune cell infiltration, and regulates the immune microenvironment in pancreatic cancer (123). YTHDF2 regulates EMT via YAP, which in turn hinders the migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells (124).
Esophageal cancer belongs to malignant tumors of the digestive system and progresses rapidly in the later stages. As the tumor grows in size, it can nearly completely obstruct the esophagus, which greatly reduces patients’ quality of life. Research shows that esophageal cancer occurs more frequently in men, with higher morbidity and mortality rates compared to women (125). m5C, one of the most common RNA modifications, plays an important role in esophageal cancer progression. YBX1 is upregulated in most cancers and esophageal cancer is no exception. Both in vivo and in vitro, YBX1 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal cancer cells (5). In esophageal carcinogenesis, long non-coding RNAs are significant (126). LINC00941 can interact with YBX1, bind to the promoter region of SOX2, upregulate SOX2 transcription, increase RNA stability, and promote the malignant phenotype of esophageal cancer (127). MiR-323a-3p inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by regulating FMR1 (128).
Breast cancer is the most prevalent malignant tumor and the second principal cause of cancer deaths in women (129, 130). ALYREF has been demonstrated to promote the development of breast cancer by affecting transcriptional regulation and mitochondrial energy metabolism, and regulate the growth, apoptosis, and migration of breast cancer cells (6). Jin et al. found that ALYREF, in addition to regulating the nuclear export of mRNA, also affects the stemness of breast cancer cells and is associated with adriamycin resistance (131). In breast cancer, YBX1 is linked to genetic stability; it can interact with m5C methyltransferase NSUN2 to influence mRNA stability, protein synthesis, and promote tumor progression (132–134). YBX1 regulates the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells by down-regulating the levels of the protein coronin-1C (135). The YBX1 protein has been demonstrated to regulate the proliferation of breast cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Furthermore, there is evidence that YBX1 is connected to the development of tamoxifen resistance (136). The interaction between DSCAM-AS1 and YBX1 in positive feedback regulates the expression of ERα and promotes the progression of breast cancer (137). Wu et al. identified a new piRNA, named piR-YBX1. This piRNA can bind directly to YBX1, resulting in a reduction in the levels of both mRNA and protein. Additionally, YBX1 has been observed to bind to RAF1, an important role in the MAPK signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in the development and progression of triple-negative breast cancer (138). RAD52 is connected to the breast cancer susceptibility genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. Research has shown that mutations in RAD52 can suppress certain BRCA2-related phenotypes in breast cancer (139, 140). In cells lacking BRCA2, overexpression of RAD52 can compensate for the loss of BRCA2-associated function. However, simultaneous deficiencies of both RAD52 and BRCA2 have been shown to be lethal to cells (141). YTHDF2 reverses RNA demethylase-induced alterations in cellular phenotype by increasing mRNA stability (72). Furthermore, it has been found to promote cell proliferation, invasion, and tumorigenic properties in vitro, as well as promoting osteolytic metastasis of breast cancer in vivo (142, 143). Triple-negative breast cancer is characterized by the absence of specific markers and therapeutic targets, which contributes to worse outcome and high recurrence and metastasis rates. The main treatment modalities for triple-negative breast cancer are chemotherapy and immunotherapy. YTHDF2 has been reported to affect the pre-tumor phenotypic polarization of macrophages and antigen-presenting signals between immune cells in triple-negative breast cancer. Furthermore, it also inhibits immune activity and associates with drug resistance (144). SRSF2, another m5C methylation binding protein, promotes angiogenesis under hypoxic conditions by selectively splicing vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer (145). Similar to other tumors, FMRP expression is elevated in breast cancer. Furthermore, there are considerable variations in FMRP expression among metastatic breast cancer lesions, with low expression in the brain and bones and high expression in the liver and lungs. Consequently, FMRP is regarded as a prognostic factor for site-specific metastasis (146).
Lung cancer has a high incidence rate in both men and women, and common types include lung adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and small cell lung cancer, of which adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are collectively known as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (97, 147). A recent study has indicated that ALYREF and YTHDF2 are correlated with mRNA stability in lung adenocarcinoma and act on the YAP signaling pathway to alter immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment (148, 149). Furthermore, they have been shown to enhance the secretion of exosomes and activate the downstream pathway in lung adenocarcinoma by regulating YAP transcription, which promotes drug resistance, tumor progression, and metastasis (150, 151). In lung adenocarcinoma, YBX1 is highly expressed and binds to the promoter region of CDC25a and HOXC8, thereby regulating cell cycle progression, cell proliferation, and apoptosis (152, 153). The Runx3-miR-148a-3p axis targets and regulates YBX1, adjusting the levels of multiple genes like Cyclin D1 and MMP2. This affects the proliferation, migration, and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer, and promotes NSCLC progression (154). `The regulation of YBX1 on the stemness of NSCLC is complex: on the one hand, it can inhibit the expression of MUC5AC and the integrin β4/pSrc/p53 signaling pathway, reducing lung cancer cell stemness and increasing the therapeutic sensitivity of erlotinib (155). On the other hand, YBX1 can promote the activation of NANOG to enhance the stemness and spheroidal ability of non-small cell lung cancer and regulates MUC1 transcription to promote cancer metastasis and stem cell properties (156, 157). The phase separation of YBX1 is identified as a key process in the development of non-small-cell lung cancer, affecting carcinogenesis and progression by regulating the biological behavior of cancer cells (158). RAD52 is expressed at high levels in non-small cell lung cancer, and regulates cell cycle and apoptosis and correlates with tumor size, degree of differentiation, lymphatic metastasis, and susceptibility (159, 160). SRSF2 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and interacts with long non-coding RNAs to up-regulate the expression of VEGFR1-i13, affecting the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells (161–163). In neuroendocrine lung tumors, SRSF2 also makes a difference. Highly expressed SRSF2 acts as a cell cycle regulatory protein that regulates the proliferation of lung cancer cells and promotes cancer progression (164).
Prostate cancer is a common malignant tumor in males, representing a substantial risk to the quality and longevity of life (165). Methylation modification of RNA has a visible impact on prostate cancer. The m5C-binding protein YBX1 inhibits ubiquitination of the androgen receptor, increasing intracellular androgen levels and stability. While AURKA phosphorylates residues of YBX1 and promotes its stabilization and nuclear translocation so that a positive feedback loop is formed and plays an important role in prostate cancer (166). YTHDF2 promotes mRNA stabilization and protein expression in androgen-negative prostate cancer, upregulates EMT-related factors, and activates the AKT pathway, which in turn promotes cell proliferation to promote metastasis (114, 167). Besides, A high level of SRSF2 expression is correlated with an adverse prognosis in prostate cancer (168).
Bladder cancer is a malignant cancers with a high recurrence and metastasis rates and has a poor prognosis (169, 170). Studies show that bladder cancer is strongly associated with genetic mutations and partly with epigenetic dysregulation (171, 172). In bladder cancer, ALYREF enhances the stability of mRNA encoding the glycolysis rate-limiting enzyme PKM2 in an m5C-dependent manner, upregulates PKM2 expression, and promotes the progression and deterioration of bladder cancer (173). ALYREF recognizes the NSUN2 locus on methylated mRNA and promotes mRNA stabilization to enhance the proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer cells in an m5C-dependent manner (28). The study revealed that YBX1 is crucial in bladder carcinogenesis and the tumorigenic effects of YBX1 were closely associated with glycolysis (19). Furthermore, the upregulation of glycolytic enzymes to facilitate glycolysis by regulating c-MYC and HIF1-α expression (56). SRSF2 interacts with miR-193a-3p, and compelling evidence suggests that this interaction is strongly associated with multidrug resistance in bladder cancer (174).
Due to the unique disease characteristics of colorectal cancer, symptoms usually appear at a late stage, resulting in most cases being diagnosed late and treatment being passive. Research find that the morbidity of colorectal cancer is generally on the rise (175). Therefore, clarifying the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer will provide more possibilities for treatment. In colorectal cancer, the function of YBX1 is regulated by non-coding RNAs, transcription factor NF-κb, etc, and is associated with the activation of various signaling pathways (176, 177). Lnc-SOX9-4 inhibits YBX1 degradation, stabilizes YBX1 protein levels, and accelerates the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells (178). YBX1 is an m5C reader and can also be modified by methylation, and the modified YBX1 shows different effects in tumors: when methylated by PRMT5, YBX1 can inhibit the growth, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer cells (176). Phosphorylated YBX1 activates the NF-κB signaling pathway and promotes colorectal cancer progression (179). The reprogramming of glucose metabolism by YBX1 and NSUN2 in an m5C-dependent manner promotes lactate production and accumulation. Furthermore, lactate accumulation positively feedback regulates the pro-cancer effects of NSUN2 by promoting NSUN2 transcription (32). YTHDF2 is widely involved in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer, recognizing methylated XIST and mediating its degradation to inhibit colorectal cancer progression (180). YTHDF2 also plays a role in aerobic glycolysis in P53 wild-type colorectal cancer and suppresses the malignant phenotype of the tumor (181). In terms of treatment, YTHDF2 increases the sensitivity of post-surgical radiotherapy in colorectal cancer patients (182). The expression of SRSF2 in colorectal cancer is apparently higher than that in normal tissues. The high expression of SRSF2 acts as a cell cycle regulator, promoting the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells both in vivo and in vitro, and contributing to the progression of colorectal cancer (92). Overexpression of FMRP and RAD52 is associated with colorectal cancer progression. FMRP regulates necrotic activation of cancer cells by controlling the expression of RIPK1 and results in poorer prognosis (66, 183).
Gastric cancer is one of the most common malignancies, with high malignancy and lethality. It is prone to metastasis, recurrence, and drug resistance, and is the second most common cause of cancer death (184). The study indicated that ALYREF has an influence on accelerating cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating the cell cycle and preventing cell apoptosis (185). Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been reported to play a multitude of roles in cancer. One example is the lncRNA PIN1P1, which has a high expression in gastric cancer and promotes cancer progression by interacting with the YBX1 (186). Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1 mediates high expression of YTHDF2, which is correlated with unfavorable prognosis of gastric cancer and increases the expression and stability of CyclinD1, promoting the proliferation of gastric cancer cells, and being associated with chemotherapy resistance (78). In contrast, the study conducted by Shen et al. reveals that YTHDF2 has the potential to impede the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by negatively modulating the FOXC2 signaling pathway (79). It can be seen that YTHDF2 exercises multiple functions in gastric cancer, acting on different molecules or pathways and producing distinct regulatory effects on tumors. Acetylated SRSF2 promotes the methylation of precursor RNA in gastric cancer cells, stimulates cell proliferation and migration, and mediates the malignant phenotype of gastric cancer cells, which correlates with poor prognosis of gastric cancer (187).
YBX1 functions as a splicing factor, upregulating pro-carcinogenic VEGF165 to promote the proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells and induce angiogenesis (188). YTHDF2 plays a role in osteosarcoma demethylation, inactivating the STAT3 pathway and inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, while simultaneously blocking the cell cycle and accelerating apoptosis (189). YBX1 is a key molecule in acute myeloid leukemia cell survival, regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, and cell signal transduction (190). In ovarian cancer, high expression of YBX1 and YTHDF2 is relevant to poor prognosis, with YBX1 up-regulating the expression of E2F1 by a phase separation manner, leading to tumor progression (31, 191). In addition, YBX1 is closely related to drug resistance in ovarian cancer, improving the ability of cell gene damage repair by increasing the stability of mRNA, thereby enhancing the resistance of tumor cells to platinum-based chemotherapy drugs (192). YBX2 promotes the properties of endometrial cancer stem cells and enhances their pellet-forming ability and chemotherapy resistance (193). YBX1 inhibits apoptosis of renal clear cell carcinoma cells, promotes migration and invasion, and is a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target for renal cell carcinoma (194). SRSF2 is not only involved in alternative splicing but also related to the expression of apoptotic genes. The expression of SRSF2 in renal clear cell carcinoma is lower, which inhibits the activity of caspase-9 and enhances the survival ability of renal cell carcinoma (195). m5C binding proteins YBX1, YBX2, and ALYREF are highly expressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, accelerating cell proliferation and tumor metastasis, and are associated with poor prognosis (196–199).
m5C methylation has been shown to contribute to the development of various diseases, and m5C methylation-binding proteins are vital elements of m5C methylation that have an indispensable impact on the function of m5C methylation. The increasing popularity of m5C methylation research will inevitably lead to a greater demand for m5C methylation detection to more intuitively identify the presence and type of methylation. This article comprehensively summarizes the structure, function, and common detection methods of m5C methyl-binding proteins that have been identified so far, and focuses on the impact these proteins have on the development and progression of various tumorigenesis, providing potential targets and new perspectives for the clinical treatment of tumors.
In addition to ALYREF and YBX1, this article complements the recently discovered m5C readers, enriching the understanding of m5C methylation. Current studies show that m5C methylation-binding proteins include ALYREF, YBX1, YBX2, RAD52, YTHDF2, FMRP, and SRSF2, which can perform functions independently or work together. m5C methylation-binding proteins can specifically recognize methylated genes, affect s, participate in RNA nucleation and other processes, and realize the regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. As important methylation forms, m6A and m5C are closely related, and some m5C methylation-binding proteins also act on m6A, such as YTHDF2, which can specifically recognize m5C and catalyze m6A. Understanding their interactions can help us to explore the synergies and networks between them, and benefit us to understand their mechanisms more comprehensively.
The m5C reader is associated with a variety of diseases, including various malignancies, and affects tumor proliferation, migration, invasion, and drug resistance by inducing cancer stem cell properties and promoting EMT transformation. In addition, methylation modification is related to tumor immunity. It regulates immune cell infiltration, changes the tumor immune microenvironment, mediates immune escape, and is closely associated with poor prognosis. Of course, there are two sides to everything, and m5C methylated binding proteins do not always contribute to promoting cancer, different binding proteins play varied roles in different tumors, and even the role of the same protein in the same cancer type is inevitably controversial. For example, high expression of YTHDF2 under hypoxic conditions promotes the proliferation and chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells (78). Similarly in gastric cancer, Shen et al. find that YTHDF2 can inhibit the growth of gastric cancer cells by negatively regulating the FOXC2 signaling pathway (79). Of course, current research on the mechanism of m5C methylation is still limited and one-sided and needs to be further explored and supplemented.
There is a rich variety of RNA modifications, and while abundant modification types have been discovered, other forms of modifications may still exist. Therefore, it is necessary to develop more precise and sensitive detection methods. For m5C methylation, in addition to the several detection methods described here, more specific strategies and innovative techniques are needed to detect RNA modification.
While it is essential to understand the molecular mechanisms of methylation, the ultimate goal of studying microstructure is to serve clinical treatment. Currently, there is still a gap in targeted drugs for m5C methylated molecules, and specific targeted inhibitors are worth further exploring. In addition, m5C methylation is associated with tumor immune invasion and can mediate drug resistance, suggesting that the use of targeted inhibitors may be expected to improve the effectiveness of immunotherapy and improve tumor prognosis. However, targeted RNA modification still faces great challenges, and it is necessary to overcome the difficulties of off-target and specificity, minimize the impact on unmethylated RNA, reduce side effects, and maximize the efficacy as much as possible. Secondly, RNA modification is a dynamic process, and achieving precise targeting of the modification site requires advanced technology. In a word, although the mechanism of action of m5C methylation-binding protein in tumors is controversial, various studies have shown that it is still a potential target for tumor treatment, providing new ideas for tumor treatment and bringing new hope to cancer patients.
TZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Resources, Software. ZZ: Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. GX: Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. FW: Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
m5C: 5-Methylcytosine
ALYREF: RNA and export factor-binding protein 2
YBX1: Y-box-binding protein 1
YBX2: Y-box-binding protein 2
RAD52: DNA repair protein
YTHDF2: YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein F2
FMRP : Fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1
SRSF2: Serine and arginine-rich splicing factor 2
NSUN: NOL1/NOP2/sun
DNMT2: DNA methyltransferase 2
ALKBH1: 1Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase ABH1
TET: Ten-eleven translator family proteins
QSOX1: Quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase 1
PVDF: Polyvinylidene fluoride
m6A: N6-methyladenosine
ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
MS: Mass Spectrometry
1D: One-dimensional
2D: Two-dimensional
TLC: Thin layer chromatography
LC-MS/MS: Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
TP53: Tumor protein p53
mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin
CTD: C-terminal domain
CSD: Cold shock domain
mRNP: Messenger ribonucleoprotein
MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase
ROS: Reactive Oxygen Species
PAF1: RNA polymerase-associated factor 1
PD-L1: Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1
EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
SR: Serine/arginine-rich
RRM: RNA recognition motif
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma
FAM210A: Family with sequence similarity 210 member A
STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta Gene
CBX3: Chromobox 3
TGF-β: Transforming Growth Factor Beta
IL-18: Interleukin 18
YAP: Yes1 Associated Transcriptional Regulator
NANOG: Nanog Homeobox
SOX2: SRY-Box Transcription Factor 2
PI3K: Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase
AKT: AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase
LINC00941: Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 941
BRCA1: BRCA1 DNA Repair Associated
BRCA2: BRCA2 DNA Repair Associated
VEGFA: Vascular endothelial growth factor A
NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer
CDC25a : Cell Division Cycle 25A
HOXC8: Homeobox C8
MMP2: Matrix Metallopeptidase 2
MUC5AC: Mucin 5AC, Oligomeric Mucus/Gel-Forming
MUC1: Mucin 1, Cell Surface Associated
AURKA: Aurora Kinase A
PKM2: Pyruvate Kinase M2
MYC : MYC Proto-Oncogene, BHLH Transcription Factor
HIF1-α: Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 Subunit Alpha
PRMT5: Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5
NF-κB: Nuclear Factor Kappa B
RIPK1: Receptor Interacting Serine/Threonine Kinase 1
FOXC2: Forkhead Box C2
VEGF165: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 165
E2F1: E2F Transcription Factor 1
SAM: S-adenosyl methionine
f5 C: 5-Formylcytosince
hm5 C: 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine
ca5C: 5-Carboxycytosine.
1. Song P, Tayier S, Cai Z, Jia G. RNA methylation in mammalian development and cancer. Cell Biol Toxicology. (2021) 37:811–31. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09627-8
2. Boccaletto P, Machnicka MA, Purta E, Piątkowski P, Bagiński B, Wirecki TK, et al. MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways. 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. (2018) 46:D303–D7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1030
3. Nombela P, Miguel-López B, Blanco S. The role of m6A, m5C and Ψ RNA modifications in cancer: Novel therapeutic opportunities. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:18. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01263-w
4. Zhang G, Liu L, Li J, Chen Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al. NSUN2 stimulates tumor progression via enhancing TIAM2 mRNA stability in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Discovery. (2023) 9:219. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01521-y
5. Liu L, Chen Y, Zhang T, Cui G, Wang W, Zhang G, et al. YBX1 Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via m5C-Dependent SMOX mRNA Stabilization. Advanced Science. (2024) 11:e2302379. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302379
6. Klec C, Knutsen E, Schwarzenbacher D, Jonas K, Pasculli B, Heitzer E, et al. ALYREF, a novel factor involved in breast carcinogenesis, acts through transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms selectively regulating the short NEAT1 isoform. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2022) 79:391. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04402-2
7. Meng S, Jiangtao B, Haisong W, Mei L, Long Z, Shanfeng L. RNA m5C methylation: a potential modulator of innate immune pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1362159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362159
8. Li M, Tao Z, Zhao Y, Li L, Zheng J, Li Z, et al. 5-methylcytosine RNA methyltransferases and their potential roles in cancer. J Trans Med. (2022) 20:214. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03427-2
9. Xu R, Wang Y, Kuang Y. Multi-omic analyses of m5C readers reveal their characteristics and immunotherapeutic proficiency. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:1651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52110-7
10. Ding S, Liu H, Liu L, Ma L, Chen Z, Zhu M, et al. Epigenetic addition of m5C to HBV transcripts promotes viral replication and evasion of innate antiviral responses. Cell Death Disease. (2024) 15:39. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06412-9
11. Liu Y, Zhao Y, Wu R, Chen Y, Chen W, Liu Y, et al. mRNA m5C controls adipogenesis by promoting CDKN1A mRNA export and translation. RNA Biol. (2021) 18:711–21. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1980694
12. Fang L, Huang H, Lv J, Chen Z, Lu C, Jiang T, et al. m5C-methylated lncRNA NR_033928 promotes gastric cancer proliferation by stabilizing GLS mRNA to promote glutamine metabolism reprogramming. Cell Death Disease. (2023) 14:520. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06049-8
13. Chellamuthu A, Gray SG. The RNA methyltransferase NSUN2 and its potential roles in cancer. Cells. (2020) 9:1758. doi: 10.3390/cells9081758
14. Xue S, Xu H, Sun Z, Shen H, Chen S, Ouyang J, et al. Depletion of TRDMT1 affects 5-methylcytosine modification of mRNA and inhibits HEK293 cell proliferation and migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 520:60–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.098
15. Kawarada L, Suzuki T, Ohira T, Hirata S, Miyauchi K, Suzuki T. ALKBH1 is an RNA dioxygenase responsible for cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNA modifications. Nucleic Acids Res. (2017) 45:7401–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx354
16. Fu L, Guerrero CR, Zhong N, Amato NJ, Liu Y, Liu S, et al. Tet-mediated formation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in RNA. J Am Chem Society. (2014) 136:11582–5. doi: 10.1021/ja505305z
17. Chang R, Tsui K-H, Pan L-F, Li C-J. Spatial and single-cell analyses uncover links between ALKBH1 and tumor-associated macrophages in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell Int. (2024) 24(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03232-5
18. Zou Z, Dou X, Li Y, Zhang Z, Wang J, Gao B, et al. RNA m5C oxidation by TET2 regulates chromatin state and leukaemogenesis. Nature. (2024) 634:986–94. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07969-x
19. Chen X, Li A, Sun B-F, Yang Y, Han Y-N, Yuan X, et al. 5-methylcytosine promotes pathogenesis of bladder cancer through stabilizing mRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. (2019) 21:978–90. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0361-y
20. Yang X, Yang Y, Sun B-F, Chen Y-S, Xu J-W, Lai W-Y, et al. 5-methylcytosine promotes mRNA export — NSUN2 as the methyltransferase and ALYREF as an m5C reader. Cell Res. (2017) 27:606–25. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.55
21. Wang X, Wang M, Dai X, Han X, Zhou Y, Lai W, et al. RNA 5-methylcytosine regulates YBX2-dependent liquid-liquid phase separation. Fundam Res. (2022) 2:48–55. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2021.10.008
22. Dai X, Gonzalez G, Li L, Li J, You C, Miao W, et al. YTHDF2 binds to 5-methylcytosine in RNA and modulates the maturation of ribosomal RNA. Analytical Chem. (2019) 92:1346–54. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04505
23. Chen H, Yang H, Zhu X, Yadav T, Ouyang J, Truesdell SS, et al. m5C modification of mRNA serves a DNA damage code to promote homologous recombination. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:2834. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16722-7
24. Yang H WY, Xiang Y, Yadav T, Ouyang J, Phoon L, Zhu X, et al. FMRP promotes transcription-coupled homologous recombination via facilitating TET1-mediated m5C RNA modification demethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2022) 119:e2116251119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2116251119
25. Ma H-L, Bizet M, Soares Da Costa C, Murisier F, de Bony EJ, Wang M-K, et al. SRSF2 plays an unexpected role as reader of m5C on mRNA, linking epitranscriptomics to cancer. Mol Cell. (2023) 83:4239–54.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.11.003
26. Xue M SQ, Zheng L, Li Q, Yang L, Zhang Y. Gene signatures of m5C regulators may predict prognoses of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. (2020) 12:6841–52.
27. Tian Y, Li J, Cheung TC, Tam V, Lau CG, Wang X, et al. Akt3 promotes cancer stemness in triple-negative breast cancer through YB1-Snail/Slug signaling axis. Genes Diseases. (2023) 10:301–6. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.08.006
28. Wang N, Chen R-X, Deng M-H, Wei W-S, Zhou Z-H, Ning K, et al. m5C-dependent cross-regulation between nuclear reader ALYREF and writer NSUN2 promotes urothelial bladder cancer Malignancy through facilitating RABL6/TK1 mRNAs splicing and stabilization. Cell Death Disease. (2023) 14:139. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05661-y
29. Cai Y, Li N, Li H. YBX2 modulates mRNA stability via interaction with YTHDF2 in endometrial cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. (2023) 427(1):113586. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113586
30. Wang Y, Wei J, Feng L, Li O, Huang L, Zhou S, et al. Aberrant m5C hypermethylation mediates intrinsic resistance to gefitinib through NSUN2/YBX1/QSOX1 axis in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:81. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01780-4
31. Liu X, Wei Q, Yang C, Zhao H, Xu J, Mobet Y, et al. RNA m5C modification upregulates E2F1 expression in a manner dependent on YBX1 phase separation and promotes tumor progression in ovarian cancer. Exp Mol Med. (2024) 56:600–15. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01184-4
32. Chen B, Deng Y, Hong Y, Fan L, Zhai X, Hu H, et al. Metabolic Recoding of NSUN2-Mediated m5C Modification Promotes the Progression of Colorectal Cancer via the NSUN2/YBX1/m5C-ENO1 Positive Feedback Loop. Advanced Science. (2024) 11:e2309840. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309840
33. Preiss T, Mishima E, Jinno D, Akiyama Y, Itoh K, Nankumo S, et al. Immuno-northern blotting: detection of RNA modifications by using antibodies against modified nucleosides. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0143756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143756
34. Sağlam B, Akgül B. An overview of current detection methods for RNA methylation. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:3098. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063098
35. Garalde DR, Snell EA, Jachimowicz D, Sipos B, Lloyd JH, Bruce M, et al. Highly parallel direct RNA sequencing on an array of nanopores. Nat Methods. (2018) 15:201–6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4577
36. Thüring K SK, Keller P, Helm M. LC-MS analysis of methylated RNA. Methods Mol Biol. (2017) 1562:3–18. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6807-7_1
37. Miao Z, Xin N, Wei B, Hua X, Zhang G, Leng C, et al. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is detected in RNA from mouse brain tissues. Brain Res. (2016) 1642:546–52. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.055
38. Fan J, Wang K, Du X, Wang J, Chen S, Wang Y, et al. ALYREF links 3′-end processing to nuclear export of non-polyadenylated mRNAs. EMBO J. (2019) 38:e99910. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899910
39. Munschauer M, Nguyen CT, Sirokman K, Hartigan CR, Hogstrom L, Engreitz JM, et al. The NORAD lncRNA assembles a topoisomerase complex critical for genome stability. Nature. (2018) 561:132–6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0453-z
40. Virbasius Cm WS, Green MR. A human nuclear-localized chaperone that regulates dimerization, DNA binding, and transcriptional activity of bZIP proteins. Mol Cell. (1999) 4:219–28. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80369-x
41. Shi M, Zhang H, Wu X, He Z, Wang L, Yin S, et al. ALYREF mainly binds to the 5′ and the 3′ regions of the mRNA in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. (2017) 45:9640–53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx597
42. Pacheco-Fiallos B, Vorländer MK, Riabov-Bassat D, Fin L, O’Reilly FJ, Ayala FI, et al. mRNA recognition and packaging by the human transcription–export complex. Nature. (2023) 616:828–35. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05904-0
43. Wang J, Li Y, Xu B, Dong J, Zhao H, Zhao D, et al. ALYREF drives cancer cell proliferation through an ALYREF-MYC positive feedback loop in glioblastoma. OncoTargets Ther. (2021) 14:145–55. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S286408
44. Fan J, Kuai B, Wu G, Wu X, Chi B, Wang L, et al. Exosome cofactor hMTR4 competes with export adaptor ALYREF to ensure balanced nuclear RNA pools for degradation and export. EMBO J. (2017) 36:2870–86. doi: 10.15252/embj.201696139
45. Ye X, Tuo Z, Chen KAI, Wu R, Wang JIE, Yu Q, et al. Pan-cancer analysis of RNA 5-methylcytosine reader (ALYREF). Oncol Res. (2024) 32:503–15. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.045050
46. Okada M JS, Ye K. Akt phosphorylation and nuclear phosphoinositide association mediate mRNA export and cell proliferation activities by ALY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2008) 105:8649–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802533105
47. Chen J, Liu Z, Zhang H, Yang Y, Zeng H, Zhong R, et al. YBX1 promotes MSC osteogenic differentiation by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. (2023) 18:513–21. doi: 10.2174/1574888X17666220805143833
48. Suresh PS, Tsutsumi R, Venkatesh T. YBX1 at the crossroads of non-coding transcriptome, exosomal, and cytoplasmic granular signaling. Eur J Cell Biol. (2018) 97:163–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2018.02.003
49. Lyabin DN, Eliseeva IA, Ovchinnikov LP. YB-1 protein: functions and regulation. WIREs RNA. (2013) 5:95–110. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1200
50. Svitkin Yv OL, Dreyfuss G, Sonenberg N. General RNA binding proteins render translation cap dependent. EMBO J. (1996) 15:7147–55. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb01106.x
51. Evdokimova Eak VM, Nashchekin DV, Davydova EK, Hershey JW, Ovchinnikov LP. The major core protein of messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (p50) promotes initiation of protein biosynthesis in vitro. J Biol Chem. (1998) 273:3574–81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.6.3574
52. Evdokimova Pr V, Imataka H, Raught B, Svitkin Y, Ovchinnikov LP. N Sonenberg: The major mRNA-associated protein YB-1 is a potent 5' cap-dependent mRNA stabilizer. EMBO J. (2001) 20:5491–502. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.19.5491
53. Nekrasov MP, Ivshina MP, Chernov KG, Kovrigina EA, Evdokimova VM, Thomas AAM, et al. The mRNA-binding Protein YB-1 (p50) Prevents Association of the Eukaryotic Initiation Factor eIF4G with mRNA and Inhibits Protein Synthesis at the Initiation Stage. J Biol Chem. (2003) 278:13936–43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209145200
54. Watermann DO, Tang Y, Zur Hausen A, JäGer M, Stamm S, Stickeler E. Splicing factor tra2-β1 is specifically induced in breast cancer and regulates alternative splicing of theCD44Gene. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:4774–80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3294
55. Varma E, Burghaus J, Schwarzl T, Sekaran T, Gupta P, Górska AA, et al. Translational control of Ybx1 expression regulates cardiac function in response to pressure overload in vivo. Basic Res Cardiol. (2023) 118:25. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-00996-1
56. Xu L LH, Wu L, Huang S. YBX1 promotes tumor growth by elevating glycolysis in human bladder cancer. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:65946–56. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19583
57. Gopal Sk GD, Mathias RA, Ji H, Rai A, Chen M, Zhu HJ, et al. YBX1/YB-1 induces partial EMT and tumorigenicity through secretion of angiogenic factors into the extracellular microenvironment. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:13718–30. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3764
58. Prabhu L, Hartley A-V, Martin M, Warsame F, Sun E, Lu T. Role of post-translational modification of the Y box binding protein 1 in human cancers. Genes Diseases. (2015) 2:240–6. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2015.05.001
59. Cullinane DL, Chowdhury TA, Kleene KC. Mechanisms of translational repression of the Smcp mRNA in round spermatids. Reproduction. (2015) 149:43–54. doi: 10.1530/REP-14-0394
60. He Y LY, Zhu Y, Ping P, Wang G, Sun F. Murine PAIP1 stimulates translation of spermiogenic mRNAs stored by YBX2 via its interaction with YBX2. Biol Reprod. (2019) 100:561–72. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy213
61. Zhao Q, Yu C, Xu X, Jin W, Zhang Z, Huang H, et al. Phosphorylated YBX2 is stabilized to promote glycolysis in brown adipocytes. iScience. (2023) 26:108091. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108091
62. Liu Y, Yang Y, Wu R, Gao C-C, Liao X, Han X, et al. mRNA m5C inhibits adipogenesis and promotes myogenesis by respectively facilitating YBX2 and SMO mRNA export in ALYREF-m5C manner. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2022) 79:481. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04474-0
63. Hammoud S EB, Dunn D, Weiss RB, Carrell DT. Sequence alterations in the YBX2 gene are associated with male factor infertility. Fertil Steril. (2009) 91:1090–5. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.01.009
64. Yuan Z, Li B, Liao W, Kang D, Deng X, Tang H, et al. Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis of YBX family reveals YBX2 as a potential biomarker in liver cancer. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1382520. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1382520
65. Stasiak el AZ, Stasiak A, Müller S, Engel A, Dyck EV, West SC, et al. The human Rad52 protein exists as a heptameric ring. Curr Biol. (2000) 10:337–40. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00385-7
66. Ho V CL, Singh A, Lea V, Abubakar A, Lim SH, Chua W, et al. Aberrant expression of RAD52, its prognostic impact in rectal cancer and association with poor survival of patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:1768. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051768
67. Ohuchi T, Seki M, Branzei D, Maeda D, Ui A, Ogiwara H, et al. Rad52 sumoylation and its involvement in the efficient induction of homologous recombination. DNA Repair. (2008) 7:879–89. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.02.005
68. Honda M, Okuno Y, Yoo J, Ha T, Spies M. Tyrosine phosphorylation enhances RAD52-mediated annealing by modulating its DNA binding. EMBO J. (2011) 30:3368–82. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.238
69. Rauth S, Ganguly K, Atri P, Parte S, Nimmakayala RK, Varadharaj V, et al. Elevated PAF1-RAD52 axis confers chemoresistance to human cancers. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:112043. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112043
70. Dai X, Wang T, Gonzalez G, Wang Y. Identification of YTH domain-containing proteins as the readers for N1-methyladenosine in RNA. Analytical Chem. (2018) 90:6380–4. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01703
71. Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. (2012) 485:201–6. doi: 10.1038/nature11112
72. Li X, Zhang K, Hu Y, Luo N. YTHDF2 regulates cell growth and cycle by facilitating KDM1A mRNA stability. Am J Pathology. (2023) 193:442–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2022.12.010
73. Liu W, Liu C, You J, Chen Z, Qian C, Lin W, et al. Pan-cancer analysis identifies YTHDF2 as an immunotherapeutic and prognostic biomarker. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:954214. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.954214
74. Yu J, Chai P, Xie M, Ge S, Ruan J, Fan X, et al. Histone lactylation drives oncogenesis by facilitating m6A reader protein YTHDF2 expression in ocular melanoma. Genome Biol. (2021) 22:85. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02308-z
75. Zhang L, Dou X, Zheng Z, Ye C, Lu TX, Liang HL, et al. YTHDF2/m6A/NF-κB axis controls anti-tumor immunity by regulating intratumoral Tregs. EMBO J. (2023) 42:e113126. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022113126
76. Ma S, Sun B, Duan S, Han J, Barr T, Zhang J, et al. YTHDF2 orchestrates tumor-associated macrophage reprogramming and controls antitumor immunity through CD8+ T cells. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24:255–66. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01398-6
77. Wang L, Hui H, Agrawal K, Kang Y, Li N, Tang R, et al. m6A RNA methyltransferases METTL3/14 regulate immune responses to anti-PD-1 therapy. EMBO J. (2020) 39:e104514. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104514
78. Yang J, Chen Y, He Y, Da M. YTHDF2 promotes gastric cancer progression and enhances chemoradiotherapy resistance. Drug Dev Res. (2024) 85:e22179. doi: 10.1002/ddr.22179
79. Shen X, Zhao K, Xu L, Cheng G, Zhu J, Gan L, et al. YTHDF2 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth by regulating FOXC2 signaling pathway. Front Genet. (2021) 11:592042. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.592042
80. Richter JD, Zhao X. The molecular biology of FMRP: new insights into fragile X syndrome. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2021) 22:209–22. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00432-0
81. Hsu PJ, Shi H, Zhu AC, Lu Z, Miller N, Edens BM, et al. The RNA-binding protein FMRP facilitates the nuclear export of N6-methyladenosine–containing mRNAs. J Biol Chem. (2019) 294:19889–95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC119.010078
82. D'Annessa I, Cicconardi F, Di Marino D. Handling FMRP and its molecular partners: Structural insights into Fragile X Syndrome. Prog Biophysics Mol Biol. (2019) 141:3–14. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2018.07.001
83. Zou Z, Wei J, Chen Y, Kang Y, Shi H, Yang F, et al. FMRP phosphorylation modulates neuronal translation through YTHDF1. Mol Cell. (2023) 83:4304–17. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.10.028
84. Leboucher A, Pisani DF, Martinez-Gili L, Chilloux J, Bermudez-Martin P, Van Dijck A, et al. The translational regulator FMRP controls lipid and glucose metabolism in mice and humans. Mol Metab. (2019) 21:22–35. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.01.002
85. Zeng Q, Saghafinia S, Chryplewicz A, Fournier N, Christe L, Xie Y-Q, et al. Aberrant hyperexpression of the RNA binding protein FMRP in tumors mediates immune evasion. Science. (2022) 378:eabl7207. doi: 10.1126/science.abl7207
86. Lucá R, Averna M, Zalfa F, Vecchi M, Bianchi F, Fata GL, et al. The Fragile X Protein binds mRNAs involved in cancer progression and modulates metastasis formation. EMBO Mol Med. (2013) 5:1523–36. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201302847
87. Jeong S. SR proteins: binders, regulators, and connectors of RNA. Molecules Cells. (2017) 40:1–9. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2017.2319
88. Moon H, Cho S, Loh TJ, Jang HN, Liu Y, Choi N, et al. SRSF2 directly inhibits intron splicing to suppresses cassette exon inclusion. BMB Rep. (2017) 50:423–8. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2017.50.8.103
89. Li K, Wang Z. Splicing factor SRSF2-centric gene regulation. Int J Biol Sci. (2021) 17:1708–15. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.58888
90. Phelan MM, Goult BT, Clayton JC, Hautbergue GM, Wilson SA, Lian L-Y. The structure and selectivity of the SR protein SRSF2 RRM domain with RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. (2012) 40:3232–44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1164
91. Garza E, Fabiani E, Noguera N, Panetta P, Piredda ML, Borgia L, et al. Development of a high-resolution melting curve analysis screening test for SRSF2 splicing factor gene mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Mol Diagnostics. (2015) 17:85–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2014.08.002
92. Liu W, Li D, Lu T, Zhang H, Chen Z, Ruan Q, et al. Comprehensive analysis of RNA-binding protein SRSF2-dependent alternative splicing signature in Malignant proliferation of colorectal carcinoma. J Biol Chem. (2023) 299(2):102876. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.102876
93. Kim E, Ilagan Janine O, Liang Y, Daubner Gerrit M, Lee Stanley CW, Ramakrishnan A, et al. SRSF2 mutations contribute to myelodysplasia by mutant-specific effects on exon recognition. Cancer Cell. (2015) 27:617–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.04.006
94. Wang Z, Li K, Chen W, Wang X, Huang Y, Wang W, et al. Modulation of SRSF2 expression reverses the exhaustion of TILs via the epigenetic regulation of immune checkpoint molecules. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2019) 77:3441–52. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03362-4
95. Guo R, You X, Meng K, Sha R, Wang Z, Yuan N, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals heterogeneity of myf5-derived cells and altered myogenic fate in the absence of SRSF2. Advanced Science. (2022) 9:e2105775. doi: 10.1002/advs.202105775
96. Cheng Y, Luo C, Wu W, Xie Z, Fu X, Feng Y. Liver-specific deletion of SRSF2 caused acute liver failure and early death in mice. Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 36:1628–38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01071-15
97. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
98. McGlynn KA, Petrick JL, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. (2020) 73:4–13. doi: 10.1002/hep.31288
99. Singal AG, Lampertico P, Nahon P. Epidemiology and surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: New trends. J Hepatology. (2020) 72:250–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.08.025
100. Wang Y, Deng B. Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2023) 42:629–52. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10084-4
101. Delire B, Stärkel P. The Ras/MAPK pathway and hepatocarcinoma: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Eur J Clin Invest. (2015) 45:609–23. doi: 10.1111/eci.2015.45.issue-6
102. Nulali J ZK, Long M, Wan Y, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Yang L, et al. ALYREF-mediated RNA 5-Methylcytosine modification Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Via Stabilizing EGFR mRNA and pSTAT3 activation. Int J Biol Sci. (2024) 20:331–46. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.82316
103. Xue C, Gu X, Zheng Q, Shi Q, Yuan X, Su Y, et al. ALYREF mediates RNA m5C modification to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2023) 8:130. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01395-7
104. Wang Z-Z, Meng T, Yang M-Y, Wang W, Zhang Y, Liu Y, et al. ALYREF associated with immune infiltration is a prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Trans Oncol. (2022) 21:101441. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101441
105. Li Z, Lu W, Yin F, Huang A. YBX1 as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive investigation through bioinformatics analysis and in vitro study. Trans Oncol. (2024) 45:101965. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.101965
106. Ru J, Lu J, Ge J, Ding B, Su R, Jiang Y, et al. IRGM is a novel regulator of PD-L1 via promoting S6K1-mediated phosphorylation of YBX1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Letters. (2024) 581:216495. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216495
107. Xu J, Ji L, Liang Y, Wan Z, Zheng W, Song X, et al. Cai X: CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2020) 5:298. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00375-5
108. Liu B, Shen H, He J, Jin B, Tian Y, Li W, et al. Cytoskeleton remodeling mediated by circRNA-YBX1 phase separation suppresses the metastasis of liver cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2023) 120:e2220296120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2220296120
109. Yu J, Li W, Hou G-J, Sun D-P, Yang Y, Yuan S-X, et al. Circular RNA cFAM210A, degradable by HBx, inhibits HCC tumorigenesis by suppressing YBX1 transactivation. Exp Mol Med. (2023) 55:2390–401. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01108-8
110. Li P, Xu Y, Zhang Q, Li Y, Jia W, Wang X, et al. Evaluating the role of RAD52 and its interactors as novel potential molecular targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. (2019) 19:279. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0996-6
111. Zhang C, Huang S, Zhuang H, Ruan S, Zhou Z, Huang K, et al. YTHDF2 promotes the liver cancer stem cell phenotype and cancer metastasis by regulating OCT4 expression via m6A RNA methylation. Oncogene. (2020) 39:4507–18. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1303-7
112. Yang Y, Yan Y, Yin J, Tang N, Wang K, Huang L, et al. O-GlcNAcylation of YTHDF2 promotes HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma progression in an N6-methyladenosine-dependent manner. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2023) 8:63. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01316-8
113. Liao Y, Liu Y, Yu C, Lei Q, Cheng J, Kong W, et al. HSP90β Impedes STUB1-induced ubiquitination of YTHDF2 to drive sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Advanced Science. (2023) 10:e2302025. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302025
114. Wen J, Xue L, Wei Y, Liang J, Jia W, Yong T, et al. Zhang B: YTHDF2 is a therapeutic target for HCC by suppressing immune evasion and angiogenesis through ETV5/PD-L1/VEGFA axis. Advanced Science. (2024) 11:e2307242. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307242
115. Zhang C, Shen L, Yuan W, Liu Y, Guo R, Luo Y, et al. Loss of SRSF2 triggers hepatic progenitor cell activation and tumor development in mice. Commun Biol. (2020) 3:210. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0893-5
116. Luo C CY, Liu Y, Chen L, Liu L, Wei N, Xie Z, et al. SRSF2 regulates alternative splicing to drive hepatocellular carcinoma development. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:1168–78. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1919
117. Shen Z, Liu B, Wu B, Zhou H, Wang X, Cao J, et al. FMRP regulates STAT3 mRNA localization to cellular protrusions and local translation to promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Commun Biol. (2021) 4:540. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02071-8
118. Hu ZI, O’Reilly EM. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatology. (2023) 21:7–24. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00840-w
119. Meng Q, Xie Y, Sun K, He L, Wu H, Zhang Q, et al. ALYREF-JunD-SLC7A5 axis promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through epitranscriptome-metabolism reprogramming and immune evasion. Cell Death Discovery. (2024) 10:97. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01862-2
120. Lv J, Liu Y, Mo S, Zhou Y, Chen F, Cheng F, et al. Gasdermin E mediates resistance of pancreatic adenocarcinoma to enzymatic digestion through a YBX1–mucin pathway. Nat Cell Biol. (2022) 24:364–72. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00857-4
121. Zhang H, Yu H, Ren D, Sun Y, Guo F, Cai H, et al. CBX3 regulated by YBX1 promotes smoking-induced pancreatic cancer progression via inhibiting SMURF2 expression. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:3484–97. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.68995
122. Liu Z, Li Y, Li X, Zhao J, Wu S, Wu H, et al. Overexpression of YBX1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth via the GSK3B/cyclin D1/cyclin E1 pathway. Mol Ther - Oncolytics. (2020) 17:21–30. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.03.006
123. Zhang H-R, Li T-J, Yu X-J, Liu C, Wu W-D, Ye L-Y, et al. The GFPT2-O-GlcNAcylation-YBX1 axis promotes IL-18 secretion to regulate the tumor immune microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Disease. (2024) 15:244. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06589-7
124. Chen J, Sun Y, Xu X, Wang D, He J, Zhou H, et al. YTH domain family 2 orchestrates epithelial-mesenchymal transition/proliferation dichotomy in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Cycle. (2017) 16:2259–71. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1380125
125. Morgan E, Soerjomataram I, Rumgay H, Coleman HG, Thrift AP, Vignat J, et al. The global landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in 2020 and projections to 2040: new estimates from GLOBOCAN 2020. Gastroenterology. (2022) 163:649–58. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.05.054
126. Liu J SX, Zhu H, Qin Q, Yang X, Sun X. Long noncoding RNA POU6F2-AS2 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Biochem. (2016) 160:195–204. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvw025
127. Lu J-T, Yan Z-Y, Xu T-X, Zhao F, Liu L, Li F, et al. Reciprocal regulation of LINC00941 and SOX2 promotes progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Disease. (2023) 14:72. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05605-6
128. Men Y, Zhai Y, Wu L, Liu L, Zhang W, Jiang W, et al. MiR-323a-3p acts as a tumor suppressor by suppressing FMR1 and predicts better esophageal squamous cell carcinoma outcome. Cancer Cell Int. (2022) 22:140. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02541-x
129. Qureshi R, Picon-Ruiz M, Sho M, Van Booven D, Nunes de Paiva V, Diaz-Ruano AB, et al. Estrone, the major postmenopausal estrogen, binds ERa to induce SNAI2, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and ER+ breast cancer metastasis. Cell Rep. (2022) 41:111672. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111672
130. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA: A Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
131. Jin T, Yang L, Chang C, Luo H, Wang R, Gan Y, et al. HnRNPA2B1 ISGylation Regulates m6A-Tagged mRNA Selective Export via ALYREF/NXF1 Complex to Foster Breast Cancer Development. Advanced Science. (2024) 11:e2307639. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307639
132. Goodarzi H, Liu X, Nguyen Hoang CB, Zhang S, Fish L, Tavazoie Sohail F. Endogenous tRNA-Derived Fragments Suppress Breast Cancer Progression via YBX1 Displacement. Cell. (2015) 161:790–802. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.053
133. Lin Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Guo W, Chen L, Chen M, et al. CTPS1 promotes Malignant progression of triple-negative breast cancer with transcriptional activation by YBX1. J Trans Med. (2022) 20:17. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03206-5
134. Zhang X, An K, Ge X, Sun Y, Wei J, Ren W, et al. Tian X: NSUN2/YBX1 promotes the progression of breast cancer by enhancing HGH1 mRNA stability through m5C methylation. Breast Cancer Res. (2024) 26:94. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01847-0
135. Lim JP, Shyamasundar S, Gunaratne J, Scully OJ, Matsumoto K, Bay BH. YBX1 gene silencing inhibits migratory and invasive potential via CORO1C in breast cancer in vitro. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:201. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3187-7
136. Hussain SA, Venkatesh T. YBX1/lncRNA SBF2-AS1 interaction regulates proliferation and tamoxifen sensitivity via PI3K/AKT/MTOR signaling in breast cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. (2023) 50:3413–28. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08308-5
137. Zhang Y, Huang Y-X, Wang D-L, Yang B, Yan H-Y, Lin L-H, et al. LncRNA DSCAM-AS1 interacts with YBX1 to promote cancer progression by forming a positive feedback loop that activates FOXA1 transcription network. Theranostics. (2020) 10:10823–37. doi: 10.7150/thno.47830
138. Wu L, Huang S, Tian W, Liu P, Xie Y, Qiu Y, et al. PIWI-interacting RNA-YBX1 inhibits proliferation and metastasis by the MAPK signaling pathway via YBX1 in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Discovery. (2024) 10:7. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01771-w
139. Lustig AJ, Hamid AB, Frank LE, Bouley RA, Petreaca RC. Pan-cancer analysis of co-occurring mutations in RAD52 and the BRCA1-BRCA2-PALB2 axis in human cancers. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0273736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273736
140. Tong D VT, Eberhardt E, Krainer M, Leodolter S, Kreienberg R, Zeillinger R. Rad52 gene mutations in breast/ovarian cancer families and sporadic ovarian carcinoma patients. Oncol Rep. (2003) 10(5):1551–3.
141. Mahajan S, Raina K, Verma S, Rao BJ. Human RAD52 protein regulates homologous recombination and checkpoint function in BRCA2 deficient cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2019) 107:128–39. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.12.013
142. Zhang M, Wang J, Jin Y, Zheng Q, Xing M, Tang Y, et al. YTHDF2-mediated FGF14-AS2 decay promotes osteolytic metastasis of breast cancer by enhancing RUNX2 mRNA translation. Br J Cancer. (2022) 127:2141–53. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-02006-y
143. Sui L, Sanders A, Jiang WG, Ye L. Deregulated molecules and pathways in the predisposition and dissemination of breast cancer cells to bone. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2022) 20:2745–58. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.05.051
144. Jin H, Chen Y, Zhang D, Lin J, Huang S, Wu X, et al. YTHDF2 favors protumoral macrophage polarization and implies poor survival outcomes in triple negative breast cancer. iScience. (2024) 27:109902. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109902
145. Yadav P, Pandey A, Kakani P, Mutnuru SA, Samaiya A, Mishra J, et al. Hypoxia-induced loss of SRSF2-dependent DNA methylation promotes CTCF-mediated alternative splicing of VEGFA in breast cancer. iScience. (2023) 26:106804. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106804
146. Brown JAL, Caredda E, Pedini G, D’Amico F, Scioli MG, Pacini L, et al. FMRP expression in primary breast tumor cells correlates with recurrence and specific site of metastasis. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0287062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287062
147. Canale M, Andrikou K, Priano I, Cravero P, Pasini L, Urbini M, et al. The role of TP53 mutations in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: clinical significance and implications for therapy. Cancers. (2022) 14:1143. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051143
148. Liu T, Hu X, Lin C, Shi X, He Y, Zhang J, et al. 5-methylcytosine RNA methylation regulators affect prognosis and tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Trans Med. (2022) 10:259–. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-500
149. Chen G, Ren D, Wang Y, Wang H, Zhang J, Yang S. YTHDF2 negatively correlates with tumor immune infiltration in small cell lung cancer. J Mol Histology. (2023) 54:365–77. doi: 10.1007/s10735-023-10129-6
150. Yu W, Zhang C, Wang Y, Tian X, Miao Y, Meng F, et al. YAP 5-methylcytosine modification increases its mRNA stability and promotes the transcription of exosome secretion-related genes in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. (2022) 30:149–62. doi: 10.1038/s41417-022-00533-7
151. Yang Q, Wang M, Xu J, Yu D, Li Y, Chen Y, et al. LINC02159 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via ALYREF/YAP1 signaling. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:122. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01814-x
152. Su H, Fan G, Huang J, Qiu X. LncRNA HOXC-AS3 promotes non-small-cell lung cancer growth and metastasis through upregulation of YBX1. Cell Death Disease. (2022) 13:307. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04723-x
153. Zhao S WY, Guo T, Yu W, Li J, Tang Z, Yu Z, et al. YBX1 regulates tumor growth via CDC25a pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. (2016) 7:82139–57. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10080
154. Su H, Fan G, Huang J, Qiu X. YBX1 regulated by Runx3-miR-148a-3p axis facilitates non-small-cell lung cancer progression. Cell Signaling. (2021) 85:110049. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110049
155. Lu L, Zeng Y, Yu Z, Chen S, Xie J, Rao B, et al. EIF4a3-regulated circRABL2B regulates cell stemness and drug sensitivity of lung cancer via YBX1-dependent downregulation of MUC5AC expression. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:2725–39. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.78588
156. Guo T, Kong J, Liu Y, Li Z, Xia J, Zhang Y, et al. Transcriptional activation of NANOG by YBX1 promotes lung cancer stem-like properties and metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 487:153–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.033
157. Xie Q, Zhao S, Liu W, Cui Y, Li F, Li Z, et al. YBX1 enhances metastasis and stemness by transcriptionally regulating MUC1 in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:702491. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.702491
158. Lu X, Wang J, Wang W, Lu C, Qu T, He X, et al. Copy number amplification and SP1-activated lncRNA MELTF-AS1 regulates tumorigenesis by driving phase separation of YBX1 to activate ANXA8 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. (2022) 41:3222–38. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02292-z
159. Xu G, Du J, Wang F, Zhang F, Hu R, Sun D, et al. RAD52 motif−containing protein1 promotes non−small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and survival via cell cycle regulation. Oncol Rep. (2018) 40:833–40. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6459
160. Toland AE, Delahaye-Sourdeix M, Oliver J, Timofeeva MN, Gaborieau V, Johansson M, et al. The 12p13.33/RAD52 locus and genetic susceptibility to squamous cell cancers of upper aerodigestive tract. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0117639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117639
161. International BR. Retracted: lncRNA MRUL Suppressed Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting miR-17-5p/SRSF2 Axis. BioMed Res Int. (2024) 2024:1–. doi: 10.1155/2024/9857357
162. Medeiros R, Gout S, Brambilla E, Boudria A, Drissi R, Lantuejoul S, et al. Abnormal expression of the pre-mRNA splicing regulators SRSF1, SRSF2, SRPK1 and SRPK2 in non-small cell lung carcinoma. PloS One. (2012) 7:e46539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046539
163. Abou Faycal C, Gazzeri S, Eymin B. A VEGF-A/SOX2/SRSF2 network controls VEGFR1 pre-mRNA alternative splicing in lung carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:336. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36728-y
164. Edmond V, Merdzhanova G, Gout S, Brambilla E, Gazzeri S, Eymin B. A new function of the splicing factor SRSF2 in the control of E2F1-mediated cell cycle progression in neuroendocrine lung tumors. Cell Cycle. (2014) 12:1267–78. doi: 10.4161/cc.24363
165. Sekhoacha M, Riet K, Motloung P, Gumenku L, Adegoke A, Mashele S. Prostate cancer review: genetics, diagnosis, treatment options, and alternative approaches. Molecules. (2022) 27:5730. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175730
166. Nikhil K, Raza A, Haymour HS, Flueckiger BV, Chu J, Shah K. Aurora kinase A-YBX1 synergy fuels aggressive oncogenic phenotypes and chemoresistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancers. (2020) 12:660. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030660
167. Li J, Xie H, Ying Y, Chen H, Yan H, He L, et al. YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors to induce AKT phosphorylation in N6-methyladenosine-dependent way in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:152. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01267-6
168. Chen Z, Hu H. Identification of prognosis biomarkers of prostatic cancer in a cohort of 498 patients from TCGA. Curr Problems Cancer. (2019) 43:100503. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2019.100503
169. Lobo N, Mount C, Omar K, Nair R, Thurairaja R, Khan MS. Landmarks in the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urology. (2017) 14:565–74. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2017.82
170. Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, Mariotto AB, Yabroff KR, Jemal A, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA: A Cancer J Clin. (2022) 72:409–36. doi: 10.3322/caac.21731
171. Leão R, Lee D, Figueiredo A, Hermanns T, Wild P, Komosa M, et al. Combined genetic and epigenetic alterations of the TERT promoter affect clinical and biological behavior of bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. (2018) 144:1676–84. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31935
172. Tran L, Xiao J-F, Agarwal N, Duex JE, Theodorescu D. Advances in bladder cancer biology and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2020) 21:104–21. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-00313-1
173. Wang JZ, Zhu W, Han J, Yang X, Zhou R, Lu HC, et al. The role of the HIF-1α/ALYREF/PKM2 axis in glycolysis and tumorigenesis of bladder cancer. Cancer Commun. (2021) 41:560–75. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12158
174. Lv L, Deng H, Li Y, Zhang C, Liu X, Liu Q, et al. The DNA methylation-regulated miR-193a-3p dictates the multi-chemoresistance of bladder cancer via repression of SRSF2/PLAU/HIC2 expression. Cell Death Disease. (2014) 5:e1402–e. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.367
175. Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM, Wallace MB. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. (2019) 394:1467–80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32319-0
176. Hartley A-V, Wang B, Mundade R, Jiang G, Sun M, Wei H, et al. PRMT5-mediated methylation of YBX1 regulates NF-κB activity in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:15934. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72942-3
177. Shi Q, He Y, He S, Li J, Xia J, Chen T, et al. RP11-296E3.2 acts as an important molecular chaperone for YBX1 and promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by activating STAT3. J Trans Med. (2023) 21:418. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04267-4
178. Zhao Y, Yang S, Nie H, Zhang D, Wang T, Sun Q, et al. Promotion of colorectal cancer progression by immune-related lnc-SOX9–4 via suppression of YBX1 poly-ubiquitination and degradation. Cell Signaling. (2023) 111:110854. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110854
179. Martin M, Hua L, Wang B, Wei H, Prabhu L, Hartley A-V, et al. Novel serine 176 phosphorylation of YBX1 activates NF-κB in colon cancer. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292:3433–44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.740258
180. Yang X, Zhang S, He C, Xue P, Zhang L, He Z, et al. METTL14 suppresses proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by down-regulating oncogenic long non-coding RNA XIST. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:46. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1146-4
181. Hou Y, Zhang X, Yao H, Hou L, Zhang Q, Tao E, et al. METTL14 modulates glycolysis to inhibit colorectal tumorigenesis in p53-wild-type cells. EMBO Rep. (2023) 24:e56325. doi: 10.15252/embr.202256325
182. Shao Y, Liu Z, Song X, Sun R, Zhou Y, Zhang D, et al. ALKBH5/YTHDF2-mediated m6A modification of circAFF2 enhances radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by inhibiting Cullin neddylation. Clin Trans Med. (2023) 13:e1318. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.v13.7
183. Di Grazia A, Marafini I, Pedini G, Di Fusco D, Laudisi F, Dinallo V, et al. The fragile X mental retardation protein regulates RIPK1 and colorectal cancer resistance to necroptosis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatology. (2021) 11:639–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2020.10.009
184. Rao X, Zhang C, Luo H, Zhang J, Zhuang Z, Liang Z, et al. Targeting gastric cancer stem cells to enhance treatment response. Cells. (2022) 11:2828. doi: 10.3390/cells11182828
185. Yuan Y, Fan Y, Tang W, Sun H, Sun J, Su H, et al. Identification of ALYREF in pan cancer as a novel cancer prognostic biomarker and potential regulatory mechanism in gastric cancer. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:6270. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56895-5
186. Wang YW, Zhu WJ, Ma RR, Tian YR, Chen X, Gao P. PIN1P1 is activated by CREB1 and promotes gastric cancer progression via interacting with YBX1 and upregulating PIN1. J Cell Mol Med. (2023) 28:e18022. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18022
187. Liu S LC, Lin X, Lin P, He R, Pan X, Lin Y, et al. NAT10 phase separation regulates YTHDF1 splicing to promote gastric cancer progression. Cancer Res. (2024) 84(19):3207–222. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-4062
188. Quan B, Li Z, Yang H, Li S, Yan X, Wang Y. The splicing factor YBX1 promotes the progression of osteosarcoma by upregulating VEGF165 and downregulating VEGF165b. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e18706. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18706
189. Yang Z, Cai Z, Yang C, Luo Z, Bao X. ALKBH5 regulates STAT3 activity to affect the proliferation and tumorigenicity of osteosarcoma via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. eBioMedicine. (2022) 80:104019. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104019
190. Huan Li DZ, Fu Q, Wang S, Wang Z, Zhang X, Chen X, et al. YBX1 as an oncogenic factor in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Adv. (2023) 7:4874–85. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009648
191. Li J, Wu L, Pei M, Zhang Y. YTHDF2, a protein repressed by miR-145, regulates proliferation, apoptosis, and migration in ovarian cancer cells. J Ovarian Res. (2020) 13:111. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-00717-5
192. Meng H, Miao H, Zhang Y, Chen T, Yuan L, Wan Y, et al. YBX1 promotes homologous recombination and resistance to platinum-induced stress in ovarian cancer by recognizing m5C modification. Cancer Letters. (2024) 597:217064. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217064
193. Suzuki I, Yoshida S, Tabu K, Kusunoki S, Matsumura Y, Izumi H, et al. YBX2 and cancer testis antigen 45 contribute to stemness, chemoresistance and a high degree of Malignancy in human endometrial cancer. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:4220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83200-5
194. Wang Y, Su J, Wang Y, Fu D, Ideozu JE, Geng H, et al. The interaction of YBX1 with G3BP1 promotes renal cell carcinoma cell metastasis via YBX1/G3BP1-SPP1- NF-κB signaling axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:386. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1347-0
195. Kędzierska H, Popławski P, Hoser G, Rybicka B, Rodzik K, Sokół E, et al. Decreased expression of SRSF2 splicing factor inhibits apoptotic pathways in renal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17:1598. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101598
196. Che X, Liu M, Li D, Li Z, Guo J, Jia R. RAN and YBX1 are required for cell proliferation and IL-4 expression and linked to poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. (2021) 406:112767. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112767
197. Du M, Hu X, Jiang X, Yin L, Chen J, Wen J, et al. LncRNA EPB41L4A-AS2 represses Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Metastasis by binding to YBX1 in the Nucleus and Sponging MiR-107 in the Cytoplasm. Int J Biol Sci. (2021) 17:1963–78. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.55557
198. Jin Y, Yao J, Fu J, Huang Q, Luo Y, You Y, et al. ALYREF promotes the metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by increasing the stability of NOTCH1 mRNA. Cell Death Disease. (2024) 15:578. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06959-1
Keywords: 5-methylcytosine, m5C-binding proteins, detection techniques, biological functions, tumor regulation
Citation: Zhao T, Zhang Z, Chen Z, Xu G, Wang Y and Wang F (2025) Biological functions of 5-methylcytosine RNA-binding proteins and their potential mechanisms in human cancers. Front. Oncol. 15:1534948. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1534948
Received: 26 November 2024; Accepted: 21 January 2025;
Published: 07 February 2025.
Edited by:
Hengbin Wang, Virginia Commonwealth University, United StatesReviewed by:
Guoqiang Chang, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Zhao, Zhang, Chen, Xu, Wang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fang Wang, MzI0NDM0OTQ0M0BxcS5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.