
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 04 March 2025
Sec. Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention
Volume 15 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2025.1509457
 Yanhong Pei1
Yanhong Pei1 Haijie Liang1
Haijie Liang1 Yu Guo1
Yu Guo1 Boyang Wang1
Boyang Wang1 Han Wu1
Han Wu1 Zhijian Jin1
Zhijian Jin1 Shanyi Lin1
Shanyi Lin1 Fanwei Zeng1
Fanwei Zeng1 Yifan Wu1
Yifan Wu1 Qianyu Shi1
Qianyu Shi1 Jiuhui Xu1
Jiuhui Xu1 Yi Huang1
Yi Huang1 Tingting Ren1
Tingting Ren1 Jiarui Liu2,3
Jiarui Liu2,3 Wei Guo1*
Wei Guo1*Background: Liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) is a novel concept that could explain how living cells precisely modulate internal spatial and temporal functions. However, a comprehensive bibliometric analysis on LLPS and immune signaling processes in cancer is still scarce. This study aims to perform a bibliometric assessment of research to explore the landscape of LLPS research in immune signaling pathways for cancer.
Methods: Utilizing the Web of Science Core Collection database and multiple analysis software, we performed quantitative and qualitative analyses of the study situation between LLPS and immune signaling in cancer from 1992 to 2024.
Results: The corresponding authors were primarily from China and the USA. The most relevant references were the “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”, “Proteomics”. The annual number of publications exhibited a fast upward tendency from 2020 to 2024. The most frequent key terms included expression, separation, activation, immunotherapy, and mechanisms. Qualitative evaluation emphasized the TCR, BCR, cGAS-STING, RIG-1, NF-κB signaling pathways associated with LLPS processes.
Conclusion: This research is the first to integratively map out the knowledge structure and forward direction in the area of immune transduction linked with LLPS over the past 30 years. In summary, although this research area is still in its infancy, illustrating the coordinated structures and communications between cancer and immune signaling with LLPS within a spatial framework will offer deeper insights into the molecular mechanisms of cancer development and further enhance the effectiveness of existing immunotherapies.
Cancer is distinguished by genomic instability resulting in the accumulation of gene mutations and structural alterations throughout tumor progression (1, 2). These genomic changes may generate tumor-derived antigens, which can be identified by the immune system as foreign antigens and then trigger the cellular immune response (3, 4). The immune system exhibits a crucial role in immune surveillance (5, 6), as immune cells from both the innate and adaptive immune system infiltrate into the tumor derived microenvironment and further modulate tumor growth and progression (7, 8). In particular, innate immune cells are involved in suppressing tumors by either directly eliminating cancer cells or initiating adaptive immune responses (8–10). As for the adaptive immune system, it is functionalized with T cells and B cells (5, 11, 12). The aforementioned immune systems have developed complex signaling networks to protect against pathogens or sterile threats. Nevertheless, cancer cells have developed multiple mechanisms, including deficiencies in antigen presentation machinery, the enrollment of immunosuppressive cell populations, and the upregulation of the negative signaling pathways (13–17).
Immunotherapy, which aims to bolster the body’s natural defenses to eradicate cancerous cells, stands as a significant advancement in cancer treatment, reshaping the landscape of oncology. While, various types of cancer have shown positive responses to immunotherapy (18–23),, the rates of response remain limited, and the underlying mechanisms are still elusive (24).Therefore, it is particularly important to explore the immune mechanism of cancer progression for cancer treatments.
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) is a cellular biological process wherein macromolecules spontaneously segregate into dilute and dense phases, forming bio-molecular condensates (25, 26). These compounds create a heterogeneous cellular microenvironment, specifically enhancing nucleic acids and proteins and exhibiting special features that promote biomolecule organization and concentration (27, 28). Anomalies in the separation of phases and transitions have been verified from liquid to solid in various neurodegenerative diseases (29). For instance, in a study conducted by Meng and colleagues, they discovered that Merlin (NF2) could induce the formation of phase-separated droplets when examining tissue samples extracted from individuals with vestibular schwannoma (30). However, growing research also suggests that altered LLPS plays a vital role in the phenotypes of cancer cells. It is proposed that cancer mutations could influence the ability of macromolecules to generate bio-molecular complexes, consequently impacting functionality indirectly. Additionally, bio-molecular condensates could serve as a formidable mechanism for spatial modulation in cancer cells (31), potentially explaining tumor heterogeneity and chemotherapy drug resistance by non-genetic theories. Despite the well-documented evidence of LLPS in fields such as transcriptional regulation and stress responses, there is still a lack of research on its relevance to immune signaling pathways.
The field of bibliometric utilizes both quantitative and qualitative analysis to study journals, publications, and their citation patterns, tracking changes over time and distribution trends within specific areas of interest, disciplines, institutions, and countries (32, 33). By employing bibliometric, researchers can pinpoint emerging research topics, plan out research directions, and forecast upcoming research trends (34). Co-citation and co-linearity methods are performed in bibliometric to identify the research foundation and highlight current research hotspots.
In this article, we use bibliometric analysis to detect the worldwide research trends between LLPS and immune signaling in cancer, and foresee potential future hotspots. Furthermore, we also provide an up-to-date insight of LLPS in driving the immune signaling pathway, including those triggered by TCR, BCR, cGAS-STING, and RIG-1 in cancer. As researchers focused on bone tumor disease, we have also reviewed the literature on LLPS and immune signaling related to bone tumors. However, there is no single literature that further elucidates the pathogenesis of bone tumor disease. Meanwhile, we discuss studies that have designed immunotherapy drugs involving LLPS process, and highlight some unresolved questions in the field of immunotherapy with LLPS. Hence, we conceive of the LLPS process as a promising strategy for cancer treatments. In general, understanding the role of LLPS in immune signaling transduction could reveal novel mechanisms of cancer progression and resistance, providing new targets for immunotherapy
Recognized as a leading database platform, the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) is known for its comprehensive coverage and authority. With a vast collection of over 12,000 international academic journals (35), it serves as a valuable source of global academic structure for R package “bibliometrix” software analysis, following the approach of previous studies (36–38).
Following the outlined procedure, all of the online literatures were extracted originated from the WoS database, covering period from January 1, 1992, to January 1, 2024. The search algorithm was as follows: TS = (tumor OR tumor OR cancer OR oncology) AND TS = (immune) AND TS = (liquid-liquid phase separation OR LLPS) AND publishing year = (1992-2024). The inclusion criteria for this study are as follows: (1) Peer-reviewed publications that primarily focus on the research field of LLPS and immune responses in tumor disease; (2) The document types must be either Article or Review; (3) The publications must be written in English; (4) The publication date must fall between 1992 and 2024. The exclusion criteria are as follows: (1) Publications that do not pertain to the themes of LLPS and immune responses in tumor disease; (2) literatures that are categorized as news, meetings, abstracts, briefings, etc. Then, obtained all valid data of literatures, including literature titles, authors, countries, institutions, abstracts, keywords, journals, and publishing years were stored in download_.txt files. The titles and abstracts of retrieved publications were independently screened by two reviewers, with any discrepancies being resolved through discussion with a third reviewer. Furthermore, both reviewers conducted a full-text review of all included references independently. A second full-text review was then performed on the discrepant articles to make the final decision for inclusion/exclusion. All disagreements were addressed by consulting with experts to reach a final consensus. Finally, all data were cleaned and analyzed individually by the co-authors and then cleaned separately using an R package. In addition, as part of the qualitative assessment, we further conducted a bibliometric screening of the literatures with an average annual citation ≥ 10. Figure 1A was the scheme of this study for cancer.
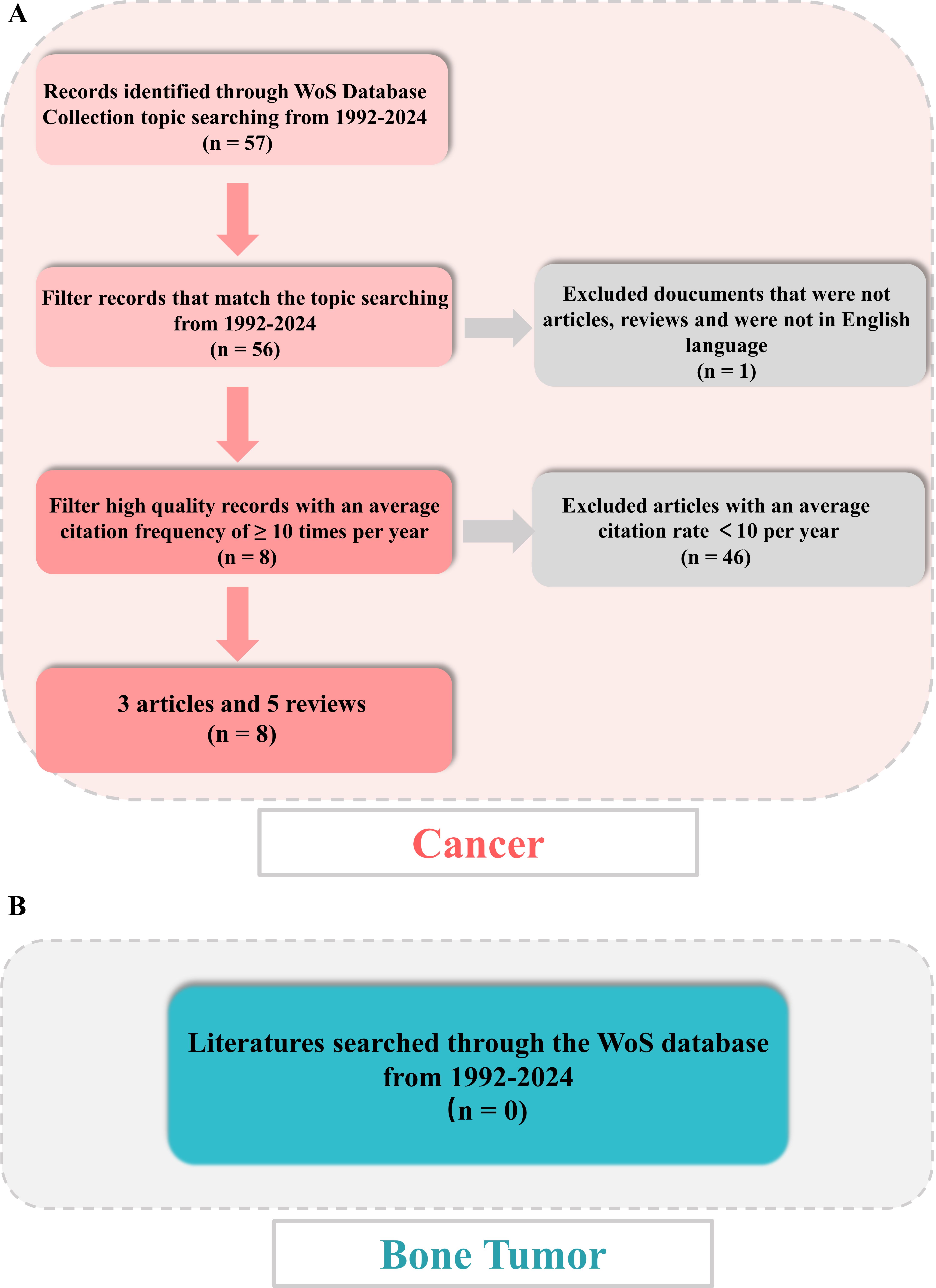
Figure 1. Flowchart of literature screening under bibliometric analysis. (A) Flow diagram in cancer. (B) Flow diagram in bone tumor.
Meanwhile, for a deeper exploration of immune and LLPS, we further searched for literatures in bone tumor disease from 1992-2024, using the TS = (bone tumor OR bone cancer OR bone tumour) AND TS = (immune) AND TS = (liquid liquid phase separation OR LLPS) algorithm. The documents were presented in plain-text form and contained comprehensive citations for references to enhance the analysis and visualization by the R package “bibliometrix” software and CiteSpace software. Figures 1B (bone tumor) provided an in-depth summary of the data selected.
This study is a bibliometric article. Bibliometric articles typically do not require ethical approval because such studies do not involve direct experiments on humans or animals, but rather analyze and quantify research that has already been published.
The WoSCC database was utilized to analyze the fundamental characteristics of qualified literature, focusing on the number of publications and citations. The Relative Research Interest (RRI) was calculated as the ratio of publications in a specific field per year to the total literature across all fields. The world map was generated using the R software, which integrates numpy, python, matplotlib, and scipy. The publication timeline was created based on the method described in a previous article (39).
The H-index is an indicator of the impact of scientific research, reflecting a scholar’s publication of literatures that have been cited at least H times (40).
We utilized the VOSviewer (version: 1.6.20) to construct and visualize bibliometric networks. VOSviewer was used to analyze bibliometric coupling, co-occurrence, and co-citation in detail. Additionally, R package (version: 4.4.1) “bibliometrix” software was utilized to visualize publications among states, map international collaboration, and create a three-field plot analysis.
Furthermore, CiteSpace (version: 6.3.R1), developed by Professor Chen C, was utilized to construct a dual-map overlay for journals, to perform cluster-analysis of authors, institutions, nations and co-cited keywords, and to detect keywords and references with demonstrate citation bursts.
At last, we used the online website: http://www.bibliometric.com to further analysis the landscape of nations, affiliations, and authors according to the enrolled literatures.
On January 1, 2024, a scientific literature search of the WoS was done to gain all online documents related to tumor, immune and LLPS. Based on the search criteria, a total of 57 literatures were gathered from 1992 to 2024, of which 43 articles (76.79%) and 13 reviews (23.21%) (Figure 2A).
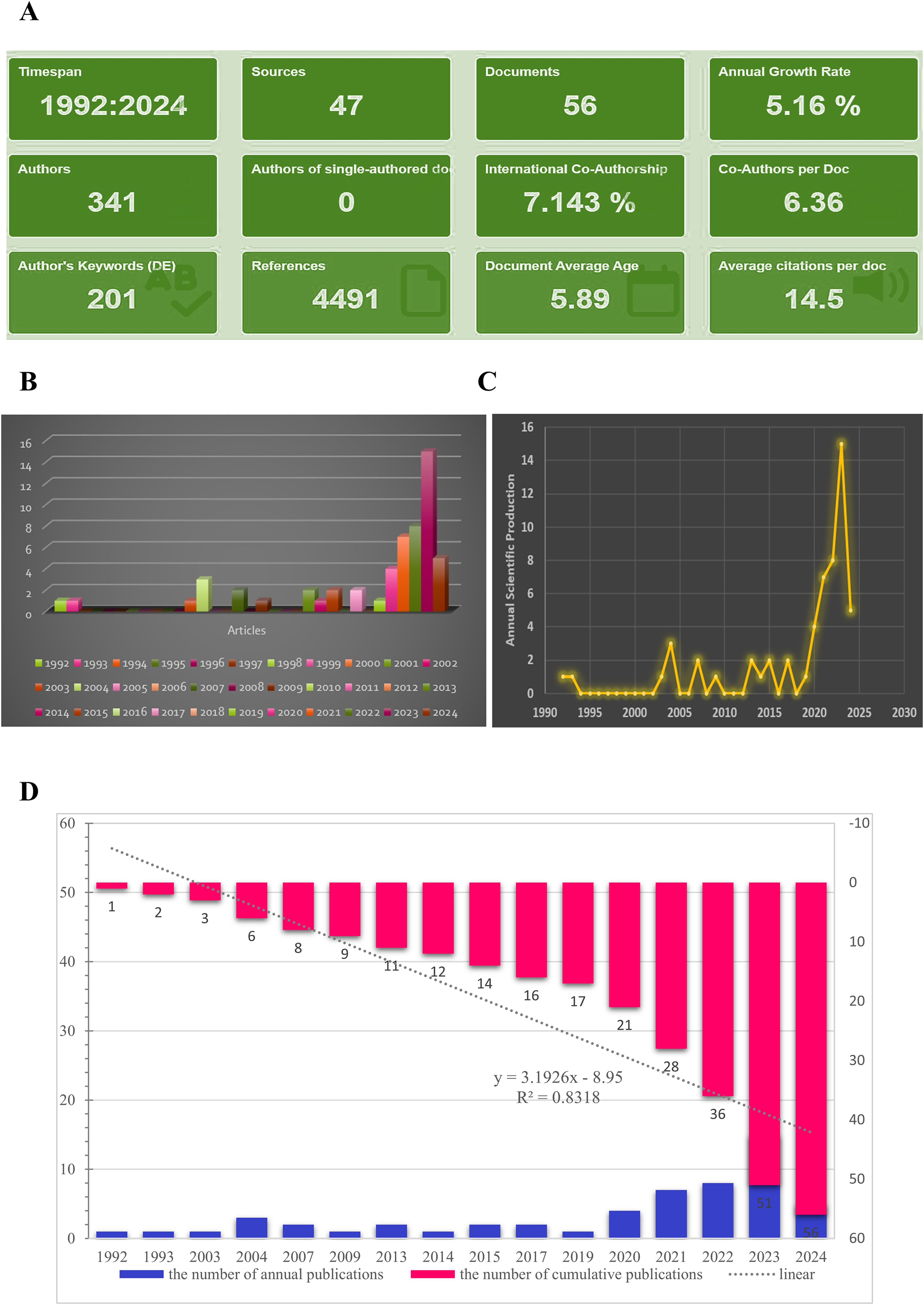
Figure 2. Main information. (A) Relevant literature from 1992-2024 under bibliometric analysis. (B, C) Graphs about the number of annual scientific production. (D) The number of cumulative publications from 1992-2024.
As shown in Figure 2A, the annual growth rate was 5.16%, and the rate of international co-authorship was 7.143%. In addition, from 1992 to 2024, although only 1-2 literatures were published in the past nearly 30 years, the annual number of publications exhibited a fast upward tendency from 2020 to 2024 (Figure 2B, and 2C). The evolution trend of the cumulative number of productions followed the fitting curve y = 3.1926x – 8.95 (R² = 0.8318) (Figure 2D), indicating that LLPS has become a progressively prominent research area for scientists and may represent an enduring and promising field of study.
The corresponding authors were primarily from China, the USA and the Czech Republic (Figure 3A). As depicted in Figure 3B, China is the nation that has published the largest number of literatures, compared to other states. The number of literatures linked to China presented a rapid and consistent increase over time, contrasting with the USA, where the increase was more moderate (Figures 3B, C).
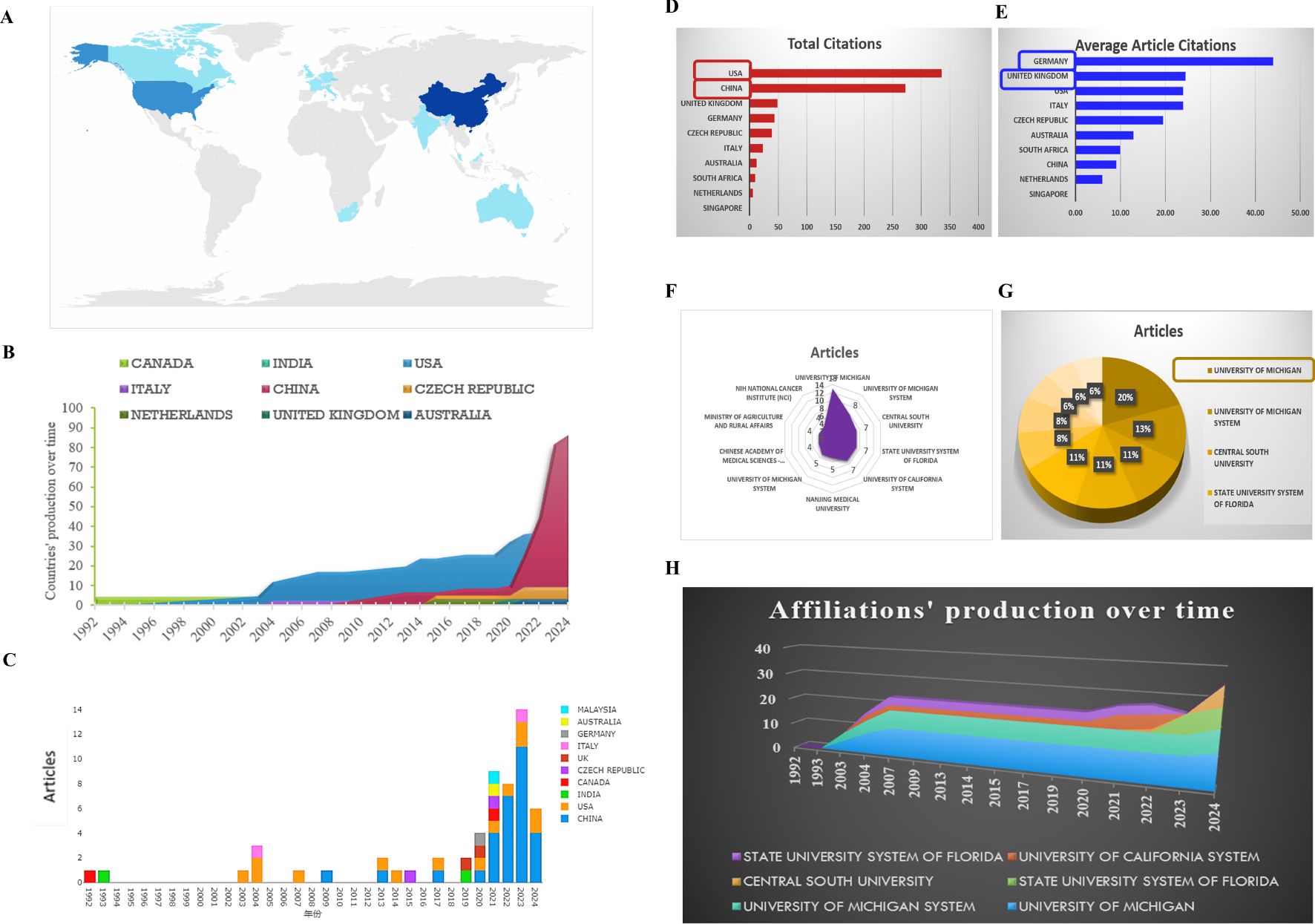
Figure 3. Analysis of the distribution over the world. (A) Country’s scientific production. (B) Country production over time. (C) Column chart exhibiting the countries production over time. (D) Most cited countries. (E) Average cited countries. (F, G) Most relevant affiliations exhibited by radar map and pie chart. (H) Affiliations’ production over time.
The USA (total citations: 336) and China (total citations:273) are the main nations with the most total citations, demonstrating the superior quality of their articles in this research field (Figure 3D). While, for the average article citations, Germany reaches the highest rank (44.00%, ranks 1), followed by the United Kingdom (24.50%, ranks 2), the USA (24.00%, ranks 3), ITALY (24.00%, ranks 3) (Figure 3E). According to the total citations and the average article citations, a deep reflection should be needed as a member of the Chinese scientific researcher.
A filled radar chart, also known as a solid radar chart, is a visual representation that uses filled areas to show data points in a multi-dimensional space. This chart includes multiple axes, each representing a different variable or category, radiating from a central point like the spokes of a wheel. Each data point is plotted on the chart using coordinates on the axes, with the distance from the center indicating the value for that category. The data points are connected to create a closed shape, which can be filled with color or shading to show the overall performance or value across all categories. Points that are further from the center represent higher values, while points closer to the center indicate lower values. As shown in Figures 3F, 3G and 3H, the University of Michigan (14, 20%), the University of Michigan system are the primary affiliation of these studies, followed by the Central South University, the state university system of Florida and University of California system. Regrettably, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences - Peking Union Medical College ranks last, not containing Peking University.
At last, by the online website (http://www.bibliometric.com), top 10 for author’s impact was exhibited in Table 1.
Lubman DM (articles: 3, articles fractionalized: 0.62), is closely followed by Zhou L (3, 0.37), Goodison S (2, 0.45), Krcmova LK (2, 0.27), Kreumin P (2, 0.45), Li H (2, 0.15), Li Y (2, 0.27), Liu J (2, 0.17), Mechref Y (2, 0.30), and Melichar B (2, 0.27) as the most relevant authors with fractionalized articles, as shown in Figure 4A. Furthermore, all of these researchers have consistently authored highly cited studies every year
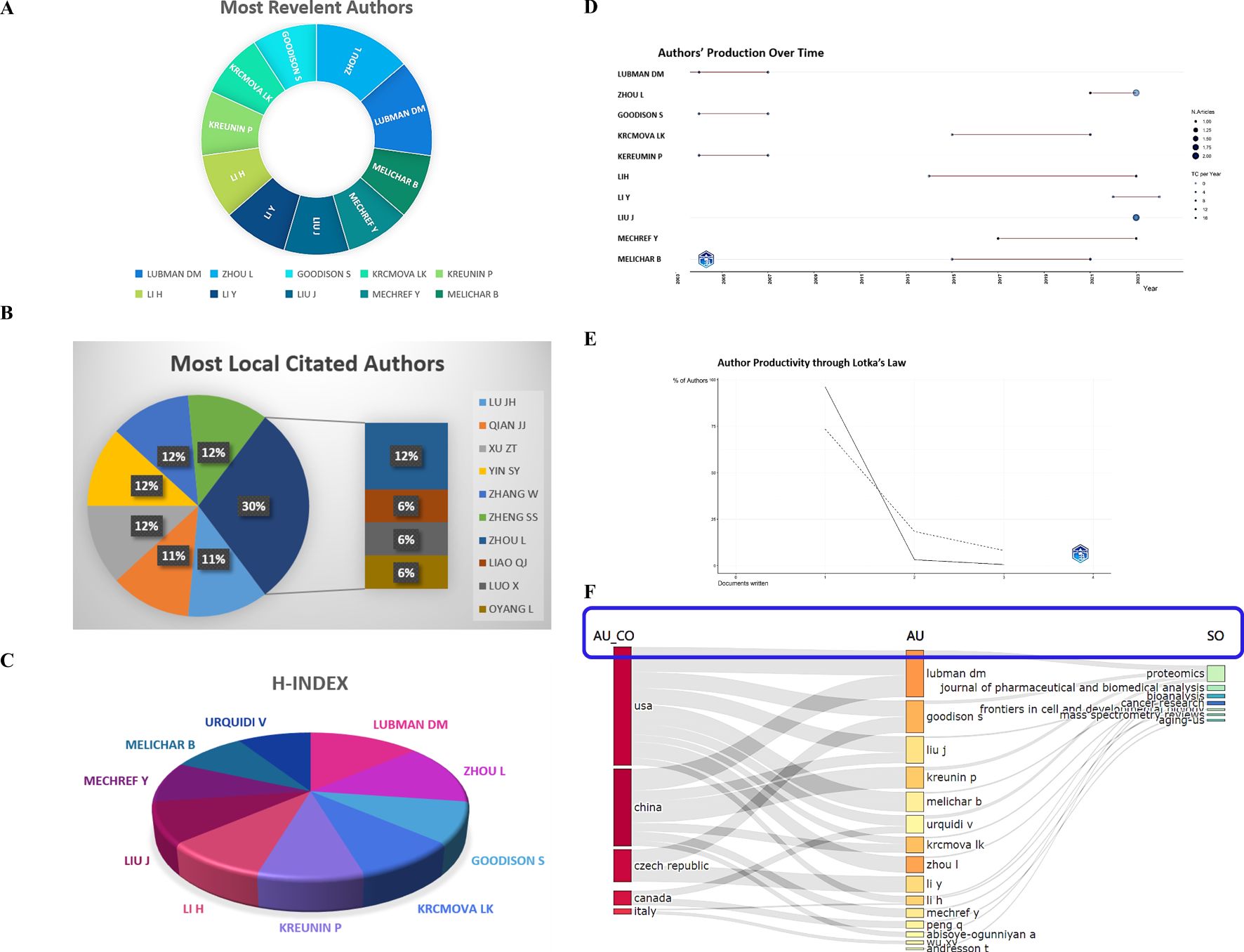
Figure 4. Authors analysis. (A) Most relevant authors. (B) Most local cited authors. (C) The H-index with authors. (D) Authors’ production over time. (E) Authors’ productivity through Lotka’s law. (F) The correlation of the states (left), authors (middle), and journals (right) based on the alluvial flow map under R package in cancer.
The local citations of the researchers were measured, with Lu JH, Qian JJ, Xu ZT, Yin SY, Zhang W, Zheng SS, and Zhou L each having 6 local citations, as exhibited in Figure 4B. Other authors had an average of 3 local citations.
The H-index and the author’s production over time were shown in Figure 4C, D, and the authors’ productivity through Lotka’s law was presented in Figure 4E. Additionally, a cluster analysis of cooperative institutes was performed, revealing that the USA researchers predominantly published in the “Proteomics”, “Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis”, “Bioanalysis”, and “Cancer Research” journals, while authors originated from China tended to publish in the “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” and “Cancer Research” journals (Figure 4F). At last, by the online website (http://www.bibliometric.com), the top 10 authors’ impact was exhibited in Table 2.
The most relevant references were obtained in the journals “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” (articles: 4), “Proteomics” (articles: 3), and “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” (articles: 2), which are leading publications in the field of immune and LLPS in cancer (Figure 5A). The most locally cited sources are mainly in the journals “Cell”, “Nature”, “Analytical Chemistry”, “Molecular Cell”, “Science” and “Nature Communications” (Figure 5B). Moreover, according to Figure 5C, the primary journals where the key sources contributing to the local impact were published include “International Journal of Molecular Sciences (H-index: 3)”, “Proteomics (H-index: 3)”, and “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology (H-index: 2)”. Furthermore, it is worth noting that, in the field of cancer, the relevant literature between immune and LLPS started to emerge in 2002, as indicated in Figure 5D. Lastly by the online website (http://www.bibliometric.com), the top 10 authors’ impact was exhibited in Table 3.
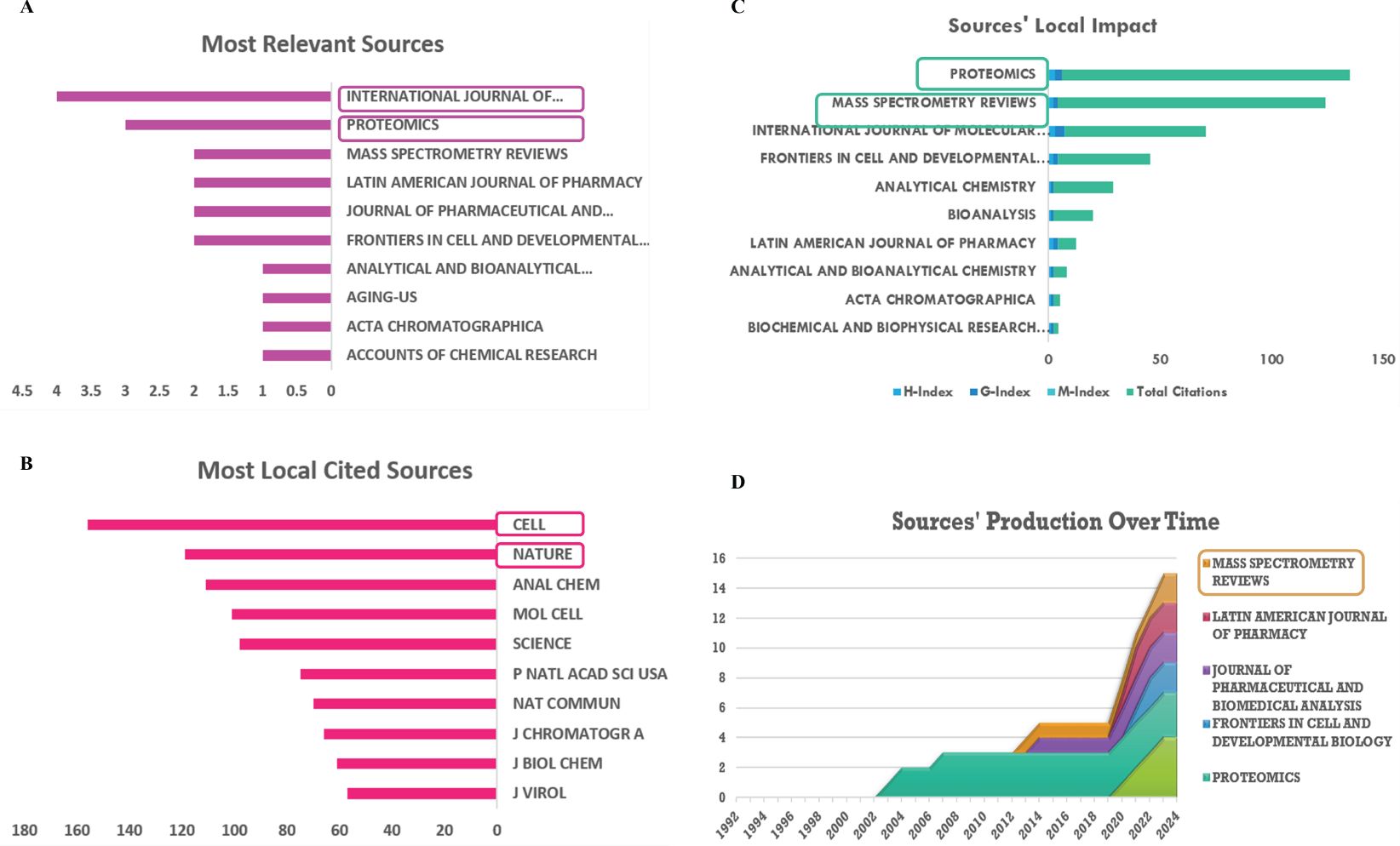
Figure 5. Analysis of sources. (A) Most relevant sources. (B) Most local cited journals. (C) Sources’ local impact. (D) Sources’ production over time.
Thus, selecting an appropriate journal is essential for scientists, as it enables them to align their research objectives with the specific aims and scope of the journal. This alignment is crucial to establish a solid and strong theoretical basis for the study of immune and LLPS, especially in the field of cancer.
The most globally cited document was “Advanced hyphenated chromatographic-mass spectrometry in mycotoxin determination: current status and prospects” (total citations: 86), which was published online in the journal “Mass Spectrom review” by Li PW, et al., in 2013. The ranked 2 (total citations: 69) was published in “Electrophoresis” with the title “Recent advances in mass spectrometric analysis of glycoproteins” by Banazadeh A., et al., in 2017. Tied for the third most globally cited were, “Respiratory Syncytial Virus Sequesters NF-κB Subunit p65 to Cytoplasmic Inclusion Bodies To Inhibit Innate Immune Signaling” (total citations: 46), published in “Journal of Virology” by Jobe F, et al., in 2020 and “Identification of metastasis-associated proteins in a human tumor metastasis model using the mass-mapping technique” (total citations: 46), published in the journal “Proteomics” by Kreunin P, et al., in 2004 (Figure 6A).
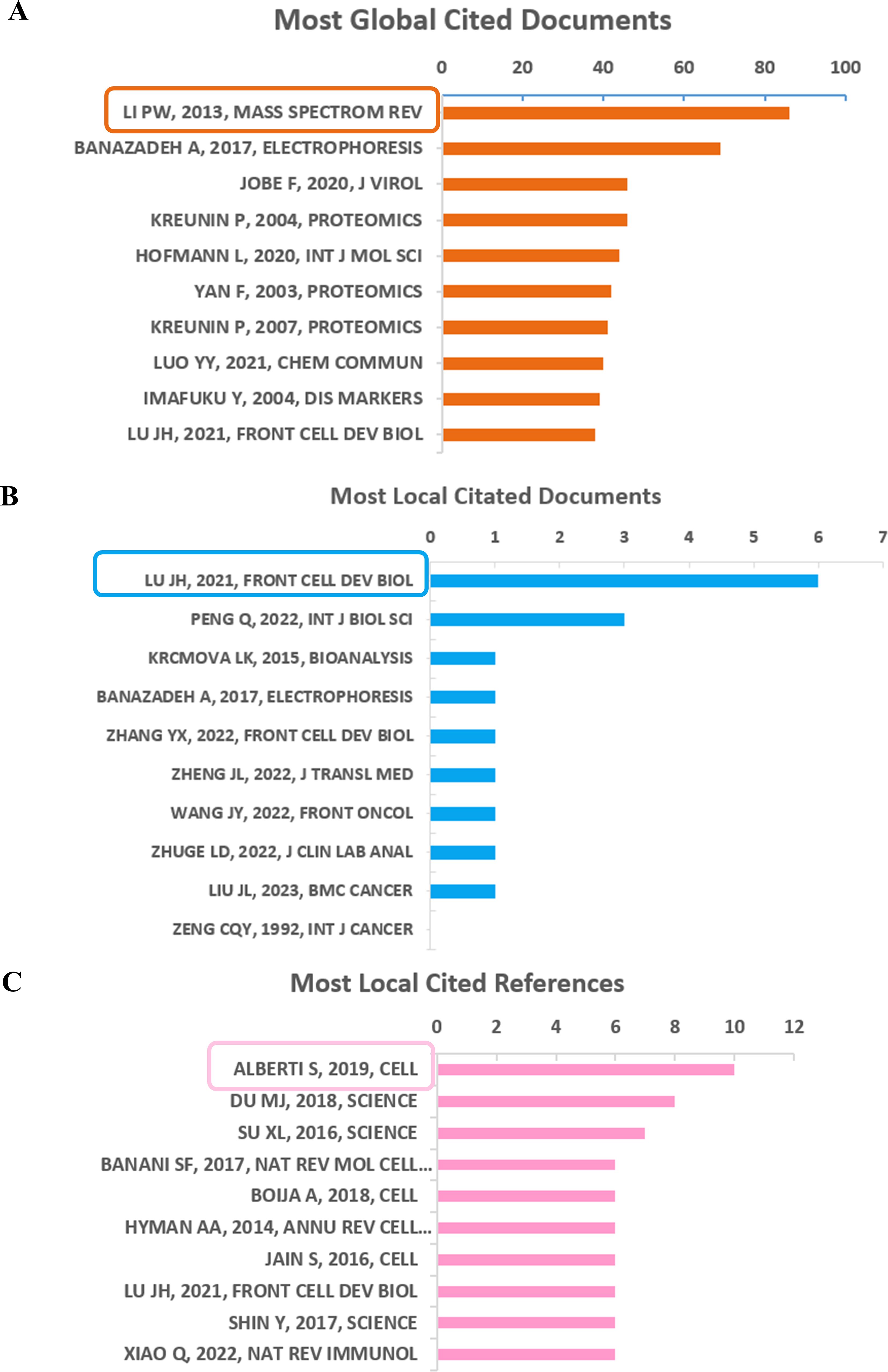
Figure 6. Analysis of documents based on R package. (A) Most global cited documents. (B) Most local cited documents. (C) Most local cited references.
Furthermore, the most frequently referenced documents within the local community were “Emerging Roles of Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Cancer: From Protein Aggregation to Immune-Associated Signaling” (local citation = 6), which was authored by Lu JH, et al., and published in “Frontier in cell and developmental biology” in 2021. Following closely behind (local citation = 3) was “Phase Separation in Cancer: From the Impacts and Mechanisms to Treatment Potentials” in the journal “International Journal of Biological Sciences” by Peng Q, et al., in 2022 (Figure 6B).
However, the most locally cited references were Alberti S, 2019, Cell; Du MJ, 2018, Science; Su XL, 2016, Science; Banani SF, 2017, Nat Rev Mol Cell, as shown in Figure 6C.
The most frequent key terms included expression, separation, activation, immunotherapy, carcinoma, delivery, mechanisms, proteins, resistance, and cells. These mentioned key words are also displayed in a plot chart, a word cloud, and a tree map, with their size reflecting the significance and frequency (Figure 7A–C).
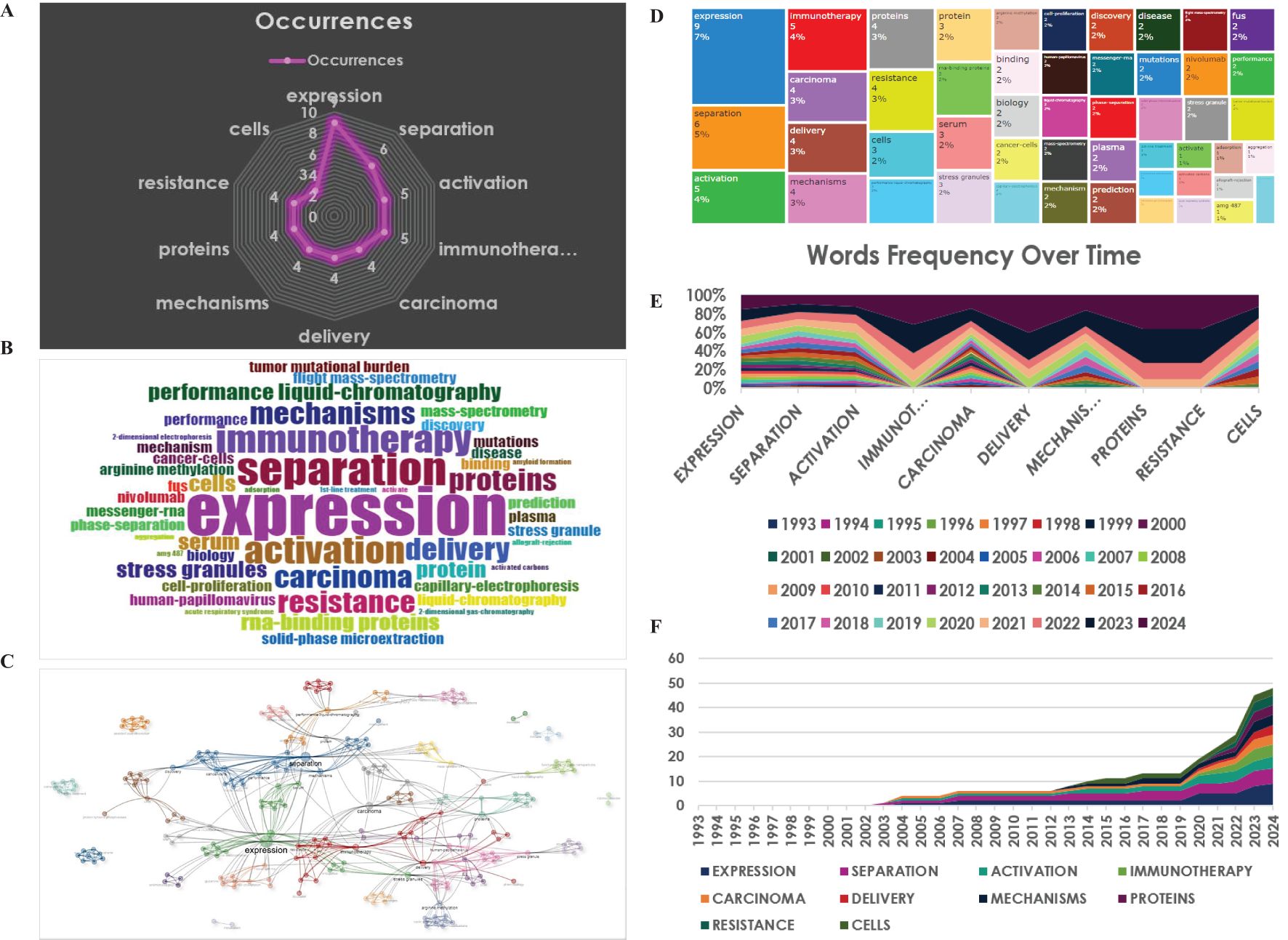
Figure 7. Analysis of key words. (A) Radar map for the most frequent words. (B) World-Cloud for the relevant words (C) Thematic map under the clustered analysis. (D) Tree-Map for the relevant words. (E, F) Words frequency over time.
Moreover, trend topics were depicted in Figure 7D, E, exhibiting that separation was the most researched topic in the nearly past 10 years, while immunotherapy has been the hotspot and the primary area of study in the recent 10 years (Figure 7D, E). This subtle shift indicated a growing interest in exploring the potential links between immunity and LLPS in cancer therapy (Figure 7F).
Then, a total of 57 documents were analyzed for collaborations between authors, institutions, and countries using the CiteSpace visualization. As shown in Figure 8A, Jaynes, Jesse M, Abisoye-ogunniyan, Abisola, Cray, Jeffrey W, Chan King, Knotts, Zachary, Kozlov, Serguel, O’neill Martinic, and Andresson, Thorkell worked closely with one another. Furthermore, by the bibliometric analysis, the collaboration network for the authors: Lubman DM, Goodison S, Barder TJ; Zhou I, Liu J, Cang S, Li H, Chen CS, Byrd JC, as exhibited by the Figure 8B. Additionally, we also conducted the cluster analysis of authors using the online website at http://www.bibliometric.com. As shown in Figure 8C, there were numerous co-authors, which indicated that the online analysis bibliometric website is greater than the other software.
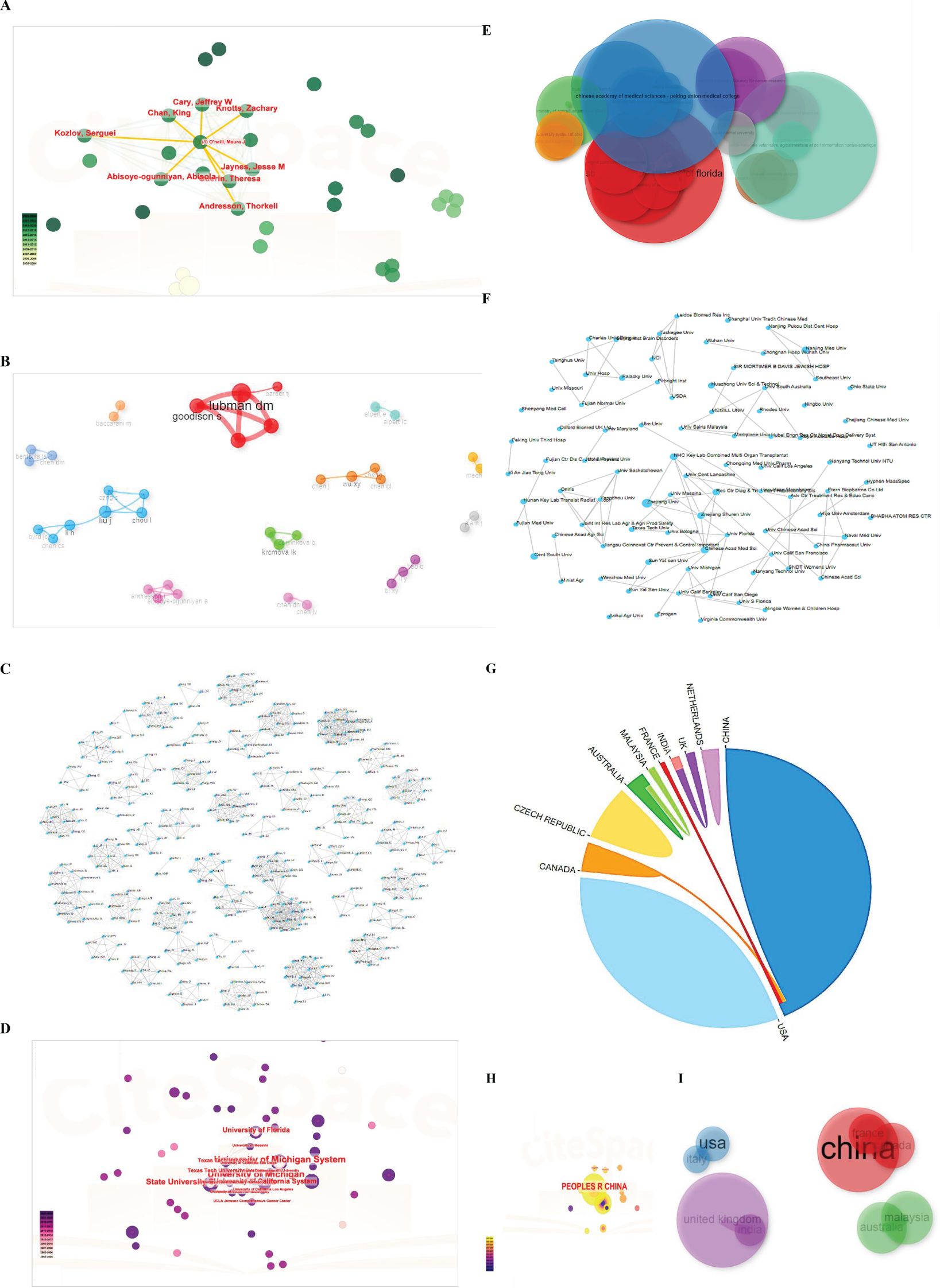
Figure 8. Cluster analysis of authors, affiliations, collaborated nations. (A) Cluster analysis of authors by CiteSpace software. (B) Cluster analysis of authors by Bibliometric software. (C) Cluster analysis of authors under http://www.bibliometric.com. (D) Cluster analysis of affiliations by CiteSpace software. (E) Cluster evaluation under bibliometric software based on R package. (F) Cluster analysis of collaborated institutions by http://www.bibliometric.com. (G) Cluster analysis of collaborated nations by http://www.bibliometric.com. (H, I) Cluster analysis of states under CiteSpace software and bibliometric software.
Moreover, as depicted in Figures 8D-F, the University of Michigan, the State University System of Florida, the University of California System, the Texas Tech University System and the Texas Tech University had a strong collaboration with each other. However, interestingly, other institutions did not have collaborations on account of just a few researches about the immune and LLPS. The cooperation among nations predominantly occurred from China, Canada, and France, not containing the USA, demonstrating the necessity and the importance of enhancing global teamwork (Figures 8G-I).
The above analysis results suggested that potential collaborations or funding opportunities that could help bridge this gap.
The quantity and frequency of keywords appearing during a specific timeframe are essential for evaluating the current and future advancements in a specific field of research. Following that, we utilized CiteSpace software and VOSviewer software to perform a co-occurrence network analysis of the key words, and the outcomes were depicted through a visualization graph, cluster photo, and timeline chart.
Figure 9A displays the most frequently appearing keywords, which align with the presented in Figure7B. Figure 9B is the cluster photo and timeline chart, respectively, indicating immunotherapy, solid phase microextraction, antitumor activity, protein, tumor-associated, liquid chromatography, disease, enrichment, autophagy, nuclear import, and stress gauge. The focus of research constantly altered towards immunotherapy from separation, as depicted in Figure 9C. As depicted in Figure 9C, the trend topics diagram under the R package was so little because of the searched literature was scarce. The timeline of keywords presented that the focus of research gradually shifted towards immunotherapy and LLPS based on CiteSpace software and VOSviewer (Figure 9D), which indicated that this shift may be related to the fact that the prospects for cancer treatment have turned towards tumor immunotherapy as a fourth-line treatment.
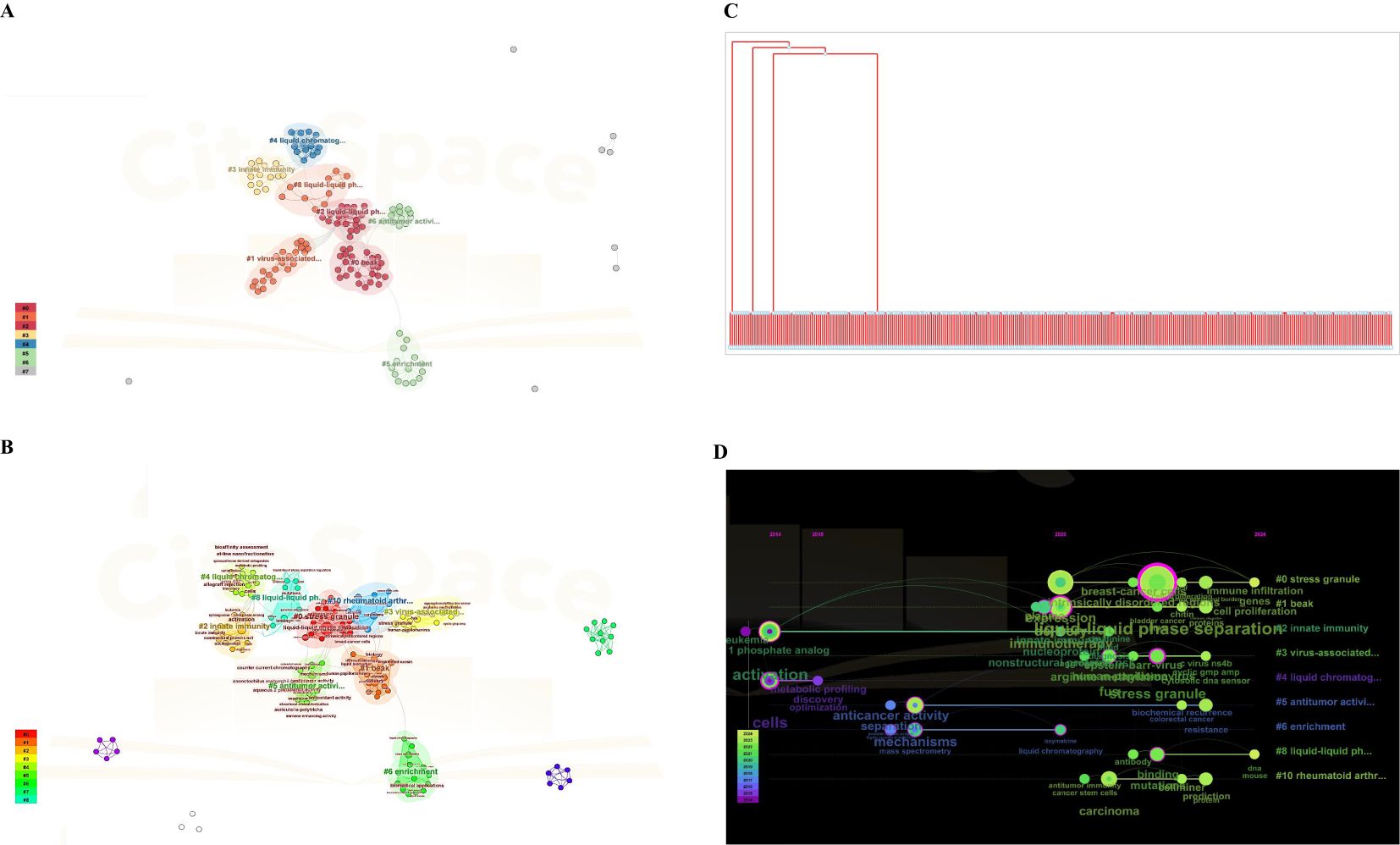
Figure 9. Cluster analysis of key words using CiteSpace software and VOS viewer. (A) Analysis of VOSviewer. (B) Co-occurrence network analysis of keywords based on VOSviewer and CiteSpace software. In the visualized graph, keywords are divided into 8 clusters with different colors. (C) Trend topics diagram under R package. (D) The timeline of keywords based on CiteSpace software and VOS viewer.
After implementing the Bibliomtrix filter with an average citation of ≥ 10 per year, 8 documents were identified. Subsequently, a qualitative assessment was performed. This evaluation aimed to not only elucidate the current research progress but also to gain a deeper level of comprehension for the intricate relationship between immune and LLPS in cancer. Multiple receptors from the surface of immune cells, in conjunction with ligands or/and downstream binding partners, can cluster ranging from nanometers to micrometers on the plasma membrane (41–43).
How do LLPS condensates affect cell functions in the physiological and pathological environment? Speculatively speaking, as liquid-like condensates progress into gel-like structures, they may potentially transmit force much more effectively. Numerous immune receptors (just like BCR, low-affinity IgG receptor FcγRIIA, and TCR), are known to be sensitive to force (44–46). This demonstrates that the shift in the properties of condensates might modulate the activation of receptors.
Here, we would elaborate on how LLPS influences the immune signaling cascades by regulating these membrane clusters but many fields still require investigation.
A predominant characteristic of the TCR signaling pathway is the formation of distinct clusters (nearly discontinuous micrometer- or submicrometer sized) on the plasma membrane. Since the 1990s, scientific researchers have constructed a variety of groups that form microclusters, including TCR, CD28, and PD1; kinases such as ZAP70 and LCK; the enzymes like PLCγ1, CBL, and SOS1; the adaptor proteins like SLP76, GADS, LAT, and GRB2 (47–49). Microcluster formation of T cell is highly dependent on the ligand binding and phosphorylation. Previous studies have indicated that SOS1, GRB2, and LAT are are pivotal oligomeric components in the generation of T cell microclusters (50).
LAT microclusters exhibit properties similar to liquids and are created through LLPS of LAT and its binding partners (51). Notably, SOS1 and PLCγ1,the two enzymes, also play a scaffolding role in enhancing LAT cluster formation in an enzyme-independent manner (52, 53). LAT condensates could facilitate tyrosine phosphorylation, a crucial marker for the activation of the TCR signaling pathway, by concentrating kinases, not excluding phosphatases in the clusters.
Despite the relatively well understood LAT microclusters, the potential mechanism of transmembrane receptor clusters (like TCR, CD28, and PD1) remains unclear. Additionally, the properties of these receptor clusters and the extent of LLPS in driving these TCR cluster formations is still uncertain and need to be further investigated. Besides, another intriguing physiological phenomenon also could be interpreted by the LLPS biophysical process in the TCR signaling pathway. As we know, a notable aspect of the TCR signaling pathway is its capability to distinguish between self and non-self antigens, although the mechanisms of which are not yet comprehended (54, 55). Despite only a slightly fold difference for antigens, the signaling response is binary. LLPS may offer a compelling rationale for this phenomenon as it is a well-coordinated and collective process that leads to a binary result. Even a minor alteration in input, like a slight enhancement in the antigen-TCR interaction affinity, could induce phase separation and initiate the subsequent signaling pathway (56). Longhui Zeng, et al. unveiled a crucial function of PLCγ1(phospholipase Cγ1, PLCγ1) in facilitating the LAT LLPS and the activation of TCR signaling transduction (53).
Protein SLP5 (called BLNK) triggers LLPS in the BCR signaling pathway. Some researchers have suggested that SLP65 could form a liquid-like complex by interacting with CIN85 (called SH3KBP1) via a traditional multivalent interaction involving the proline-rich motifs of SLP65 and the SH3 domains of trimeric CIN85 (57, 58).
It has been reported that SLP65 compounds are pre-existing in the cytoplasm of resting B cells, which is different from the time that LAT condensates formed (59). Meanwhile, in the process of condensates formed, the liposomes also are essential in facilitating condensates at physiological cellular concentrations of CIN85 and SLP65. Barbara L. Kee revealed groundbreaking activity of EBF1 as a pioneering transcription factor in B lymphocyte specification by recruiting the nucleosome remodeler Brg1 and driving the occurrence of FUS LLPS (60).
After binging with ligand, a multitude of innate immune receptors would cluster at the cell surface such as the mast cell receptorFcϵRI80-82 and phagocytic receptors-Drosophila melanogaster Draper and dectin 1 (61, 62), which are similar to the above mentioned BCR and TCR signaling clusters on accounting of the existence of immune receptor tyrosine-derived activation motifs (ITAMs) or ITAM-related sequences, micrometer/nanometer in size, and multivalent proteins that amplify signaling pathway transduction.
LLPS not only associates with signaling transduction of the plasma membrane but is also involved in the regulation of intracellular immune signaling pathways. This includes the retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) pathway, the cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS)–stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway, and the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway (56).
cGAS could detect abnormal cytosolic dsDNA originating from nuclear or mitochondrial injuries or pathogens (63). Then, dsDNA binds cGAS and activates it, synthesizes the compound of 2′3′-cyclic GMP–AMP (cGAMP), and then triggers the STING signaling pathway, resulting in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and type I interferons (63, 64). Recent research has revealed that dsDNA binding to the cGAS could induce the production of liquid-like condensates related to LLPS (65).
K432T and G303E, the two tumor-related mutations, located at DNA-binding sites of cGAS, lead to a diminished capability to form cGAS condensates and a decrease in cGAMP (30).
Furthermore, investigations are necessary to be acquired to comprehend how these cGAS mutants shape immune responses as tumor progression. Additionally, manipulating cGAS condensate could offer a novel insight into regulating immune response against tumor. Wuchang Zhang et al. reported that the inhibition of KDM4A mechanistically promoted the formation of liquid-like HP1γ puncta on heterochromatin, halted DNA replication, and subsequently triggered the activation of cancer cell-intrinsic cGAS-STING signaling transduction (66). Fansen Meng et al. demonstrated that inducing the LLPS of mutant NF2 (Neurofibromin 2, NF2) could result in quiescence of cGAS-STING signaling in antitumor immunity (30).
A recent preprint demonstrated that RNA binding induces LLPS of TRIM25, recruits RIG-1 to condensates, boosts the ubiquitylation of TRIM25 (67). Conversely, RNF125 has been reported to inhibit the RIG-1 signaling pathway by enhancing the K48-linked ubiquitylation and degradation of RIG-1 (67–69).
Fatoumatta Jobe has verified that viruses can prevent innate immune response by trapping the NF-κB subunit p65 in bio-molecular condensate (70). Ziran Qin has reported that in innate antiviral immunity, the LLPS of IRF3 and IRF7 were enabled by deacetylation with SIRT1 (71). In this section, our emphasis was on the activation of signaling cascades. However, there is also evidence demonstrating that PD1 could form microclusters upon engagement with PD-L1 (48). Nevertheless, it also remains unclear whether PD1 microclusters originated from LLPS. So, we would not discuss this situation here. Additionally, in the area of tumor immune infiltration, Yanling Li, et al. have found that EphA2 (Erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular A2, EphA2) could be involved in the advancement of colorectal cancer by forming LLPS condensates and further affecting the immune cell infiltration (72).
To summarize, the research on how LLPS relates to the immune signaling pathway remains still limited. While LLPS, as the biophysical process, has been verified to regulate the immune signaling pathways, just like TCR, BCR, cGAS, RIG-1, and NF-κB. Undeniably, this field is still emerging and needs to be further investigated for the functions of manipulating the immune system, including the aspects of detecting techniques and physiological studies.
As researchers devoted to elucidating the mechanisms of bone tumor disease, we also searched relative literatures on the topics: LLPS, immune, and bone tumor. Surprisingly, there is no literatures, which indicated that research in the field of immunity related to LLPS is quite rare in orthopedic research.
We know that OS is an extremely rare malignant bone cancer, which commonly occurs in children and adolescents. The diagnosis and treatment of rare diseases is a long process, requiring a professional medical team and a lot of clinical experience. In addition, the treatment of children and adolescents is very different from that of adults, because children have a long way to go in the future, and doctors need to consider the long-term effects of medication, dosage, and treatment, including future rehabilitation planning, and even life planning.
In general, based on the above research background, we think that modulating the LLPS process could be a promising approach for OS disease, especially in the biological process of the immune system. One powerful strategy to develop chemotherapy drugs tailored towards LLPS condensates by targeting specific proteins has already been verified (73–75), which could allow for the selective targeting of abnormal LLPS without the harmful effects of broader chemotherapy treatments.
In the landscape of physical chemistry, phase separation is a familiar phenomenon. However, for many biological scientists and immunologists, this concept is not entirely understood yet. It refers that the biomolecules shift from a uniform microenvironment into two separate phases (the dilute phase and the condensed phase), where the movement and concentration of solutes vary dramatically (56). LLPS is commonly observed in cells due to the properties of the fluidic and aqueous environment of the intracellular space. The condensed phase often exchanges materials with the dilute phase while in a liquid-like state, and this characteristic is significant in shaping the composition and activity of molecules in the condensed phase (56). Due to the cellular condensates are often formed by various interactions, it is possible to observe a spectrum of intermediate states between liquid and solid forms. LLPS condensates are involved in various of biological functions, including organizing higher-order chromatin, sorting misfolded proteins, modulating gene expression, setting signaling clusters, and building cytoskeletal networks utilizing actin and microtubules (76). Of course, they also help in segregating cell fate determinants symmetrically and creating signaling assemblies in pre- and postsynaptic densities.
The condensates produce a heterogeneous cellular environment, which specifically enriches nucleic acids and proteins, and then further facilitate the concentration of biomolecules and organization (27, 28). The formation of interaction networks that involve multivalent proteins or nucleic acids plays a crucial role in LLPS and is primarily boosted by peptides with intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs), folded modular domains, or polymerizing domains (77).
Moreover, it has been indicated that a majority of cell signaling proteins, as well as a significant number of cancer-derived proteins, contain extensive intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs), that are essential for driving LLPS process (78). Proteins associated with cancer and cancer-related mutations could regulate the quantity and assembly of condensates by affecting LLPS, which in turn ultimately drives the abnormal cellular activities and boosts the progression of tumorigenesis (Table 4) (79–82). Notably, irregular or abnormal transitions of condensates to a solid state are linked to some specific neurodegenerative diseases (including FUS (83, 84), TDP-43 (85, 86), HNRNPA1 (87), and DDX (88), as well as Tau (89, 90),) and cancers (such as transcriptional condensates, PRC1 condensates, super enhancers, DNA repair condensates, stress granules, Paraspeckles, SPOP/DAXX bodies and PML foci (91–96).
However, the literatures associated with LLPS and immune signaling progress was scarce in cancer, and there is a paucity of bibliometric research on these topics. Therefore, based on the relevant research background, VOSviewer software, and CiteSpace software visualization, we found the number of enrolled literatures on this topic remains low, with nearly 57 documents published from 1992-2024. Furthermore, with an average citation rate of ≥ 10 per year, only 8 high-quality studies were identified, indicating the correlated research between LLPS and immune signaling response is still in the infant stage. Meanwhile, we also searched relevant literatures in the field of bone tumor, according to the above mentioned method. The outcome was none.
On 15 February, 2024, the journal Lancet Child & Adolescent Health onlined “Holistic support for children with rare disease”. The author, Siyuan Li, a Ph.D. student engaged in the regenerative medicine of biomedical engineering, was also a patient with OS disease in childhood (97). “The former patient has become a doctoral student in biomedical engineering, and her crutches have not only seen her on the road to recovery but also given her a guiding light to a new field,” as reviewed by the Lancet Child & Adolescent Health journal. It is very lucky for children with OS to be like Siyuan Li. Therefore, increased efforts are necessary to explore the pathogenesis that could be utilized in preclinical research and clinical trials, especially the immunotherapy with LLPS in OS.
LLPS could potentially aid in immune evasion by promoting the creation of biomolecular condensates that trap immune signaling proteins or regulate the production of immune checkpoint molecules. This means that cancer cells could exploit LLPS to gather proteins that hinder the stimulation of immune cells, ultimately establishing a microenvironment that is less detectable by the immune system (98). The spatial arrangement of signaling molecules mediated by LLPS can also influence the recruitment and activation of immune cells, shaping immune cell communication. This organization may facilitate the formation of signaling complexes at the immune synapse, critical for immune cell activation. Conversely, it could also cause the segregation of signaling molecules away from the synapse, potentially dampening the immune response (99).
Additionally, LLPS could potentially contribute to the development of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) by influencing the positioning and behavior of immune cells in the tumor. This process could result in the creation of condensates that draw in immunosuppressive cells such as Tregs or MDSCs, which have the ability to dampen the function of cytotoxic T cells. Moreover, LLPS might impact the release of immunosuppressive cytokines, leading to a TME that is not conducive to successful immune attacks on cancer cells (100). Overall, the emerging role of LLPS in the tumor microenvironment highlights its critical influence on cancer progression, immune evasion, and therapeutic resistance. Understanding the mechanisms by which LLPS modulates oncogenic signaling and immune responses not only provides new insights into cancer biology but also offers promising avenues for developing novel therapeutic strategies targeting LLPS-related pathways.
Meanwhile, the study of LLPS in the field of tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) is an emerging area of research that has shown promising implications in both tumor progression and immune responses. In TAMs, LLPS might regulate signal transduction processes, ultimately leading to an upregulation of immune-suppressive molecules, such as PD-L1. It might also be involved in controlling the secretion of cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-β, and in regulating the metabolism of TAMs. Furthermore, LLPS could potentially influence the phagocytic function of TAMs by modifying the aggregation state of proteins associated with intracellular endocytosis, which in turn affects TAMs’ ability to engulf tumor cells (101, 102).
At last, chronic inflammation is also greatly influenced by LLPS, which affects intracellular signaling pathways, modulates molecular dynamics during inflammatory responses, and determines the polarization state of immune cells (103). LLPS can also affect the functionality of macrophages and potentially play a role in the formation of inflammasomes (104, 105).
Recently, the landscape of tumor treatment has shifted toward tumor immunotherapy, which stands as a beacon in research and therapy, and is now widely recognized as the fourth line of treatment (106). Tumor immunotherapy encompasses immune checkpoint blockades (ICBs) and chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) immunotherapy. Broadly speaking, LLPS could impact tumorigenesis through various signaling pathways, it is essential to devise practical strategies for treating these cancer-associated proteins. For instance, we can disrupt the LLPS process, target cancer drugs within bio-molecular condensates, and modify LLPS by interfering with PTMs (posttranslational modifications, RTMs).
For example, a study conducted in 2024 showed that Svg3, a nature-inspired oligonucleotide, is a potent cGAS agonist that activates cGAS-STING in tumor immunotherapy. The hairpin-shaped Svg3 exhibited strong binding to cGAS and facilitated LLPS to generate Svg3-cGAS liquid-like condensates, which led to specific activation of cGAS and robust IFN-1 responses. Thrillingly, Svg3 surpasses several cutting-edge STING agonists in human and murine cells/tissues (107). Si Sun, et al. (108) have found that high levels of CAL protein-coding gene transcription were significantly associated with poor prognosis in KIRP and were also linked to specific targeted therapies. The inhibitor of LLPS could also increase the effectiveness of paclitaxel and cisplatin in killing cancer cells. Targeting CAL signatures might be a promising therapeutic approach with LLPS modulating synergy. Merlin (NF2/schwannoma), is a tumor suppressor protein and boots innate immunity against cancer (30, 109). While, Merlin can also be found in various malignancies with genetic inactivation and mutations, such as skin cancer, type 2 neurofibromatosis, schwannomas, and colorectal cancer (110). A recent study by Meng et al. revealed that by forming LLPS condensates with IRF3, the mutant FERM domain of Merlin further obstructed the anticancer immunity signaling pathway. Based on the above studies, in NF2-related cancer, trying to prevent the formation of intracellular membranes structures of NF2 could restore the antitumor immune responses mediated by the cGAS-STING pathway (30).
Even though all of these initiatives are still in their early stages, we anticipate that delving into the study of LLPS will lead to a more profound comprehension of pathological processes in cancer and reveal fresh possibilities for treatment.
While the field is still in its infancy, further investigations are needed to thoroughly examine the functions of phase separation in immunity, including advancements in technology and physiological research. Looking ahead, we predict that the following areas will present exciting avenues for exploration.
Apprehending the LLPS condensates organization internally will greatly benefit the design of antagonists and agonists by disrupting liquid-like condensates and the involved immune signaling responses. While crystallography and electron microscopy have been employed to ascertain the internal structure and arrangement of the condensates, the application for liquid-like objects remains restricted. Since LLPS occurs widely in a 4D environment, Breakthroughs in nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, computational simulations, spatial omics technology, and the invention of new fluorescent probes might open up new possibilities for approaching this issue, which could be pivotal for immunotherapy with LLPS, and even for implementing personalized therapy in clinical settings (111).
Up to now, the majority of LLPS research has mainly focused on a single situation, just like the plasma membrane (TCR, BCR) or the cytoplasm (cGAS, RIG-1). Nonetheless, studies between LLPS and immunological synapse are still limited, which consist of five environments: the immune cell’s cytosol and plasma membrane, along with the intermembrane space, and the antigen-presenting cell’s plasma membrane and cytosol. The interaction between these diverse environments is facilitated by numerous ligand-receptor pairs, which can affect their assembly structures and facilitate two-way signaling. By utilizing a multiple-membrane reconstitution system alongside light-sheet microscopy on live-cell conjugates, a comprehensive understanding of the phase separation behavior at immunological synapses can be achieved.
In this research, we performed an integrated analysis of the relationship between immune and LLPS biological processes in cancer for the first time, using bibliometric estimation to present the research status, key areas of focus, and potential future research trends in this area. Moreover, by utilizing R package “bibliometrix” software, CiteSpace, and VOSviewer analyses, we have ensured the accuracy and reliability of the data, allowing us to deeply and thoroughly elucidate the evolving trends in the pathogenic mechanisms and immunotherapy associated with LLPS. We also further assessed the state of the research at the intersection of LLPS, immune signaling responses, and bone tumor disease. More surprisingly, no literature was found. Nevertheless, we cannot deny the significant importance of LLPS in immunity, especially in tumor disease. In the subcellular section, scientific research on LLPS has uncovered intracellular compartments or new membrane-less organelles involved in signaling transduction. In the molecular section, LLPS highlights the significance of unstructured protein domains and weak interactions. These components, often overlooked in previous studies on protein-protein interactions, play a crucial role in driving LLPS. In the physiological section, LLPS provides pioneering insights into the mechanisms of cellular decision-making processes in immune signaling responses.
However, the present study also has some inherent limitations. First, the documents were only obtained from the WoS database, not from Scopus or Embase, which may potentially lead to biased results. Future research may need to search additional databases or other bibliometric tools to verify these findings. Meanwhile, as the field of LLPS in immune signaling response is still an emerging research area, related literatures, especially those focusing on cancer, are scarce. Additionally, new online publications in reputable journals may have been overlooked due to their lower citation counts. The lack of relevant keywords with strong citation bursts in the CiteSpace software indicates a scarcity of literature on this topic. Furhtermore, the use of different parameters in the CiteSpace software may have impacted the output data, leading to slight variations in the results.
In conclusion, this study is the first to conduct a bibliometric analysis that scientifically and comprehensively examines the correlation between liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) and the immune signaling system in cancer research trends over the past 30 years. It has systematically summarized global publication trends and helped researchers identify key authors, institutions, and journals in this field. Additionally, a qualitative analysis has also been conducted. Despite this research area being in its early stages, illustrating the interconnected structures and communications between cancer and immune signaling with LLPS within a spatial framework will provide deeper insights into the molecular mechanisms of cancer development and enhance the effectiveness of current immunotherapies. At the same time, the development of compounds that target LLPS and the utilization of LLPS as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis are also key points that scientists need to focus on. Nevertheless, the intricate nature of LLPS, the constantly changing condensates, and the requirement for specificity present challenges that need to be addressed thoughtfully.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
YP: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HL: Investigation, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YG: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – review & editing. BW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. HW: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SL: Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. FZ: Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. QS: Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JX: Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YH: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. TR: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WG: Funding acquisition, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers: 2101000565) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant number: 2127000364).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1509457/full#supplementary-material
1. Stratton MR, Campbell PJ, Futreal PA. The cancer genome. Nature. (2009) 458:719–24. doi: 10.1038/nature07943
2. Podlaha O, Riester M, De S, Michor F. Evolution of the cancer genome. Trends Genet. (2012) 28:155–63. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2012.01.003
3. Matsushita H, Vesely MD, Koboldt DC, Rickert CG, Uppaluri R, Magrini VJ, et al. Cancer exome analysis reveals a T-cell-dependent mechanism of cancer immunoediting. Nature. (2012) 482:400–4. doi: 10.1038/nature10755
4. Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. (2011) 331:1565–70. doi: 10.1126/science.1203486
5. Vesely MD, Kershaw MH, Schreiber RD, Smyth MJ. Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu Rev Immunol. (2011) 29:235–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101324
6. Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity. Inflammation Cancer Cell. (2010) 140(6):883–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025
7. Seager RJ, Hajal C, Spill F, Kamm RD, Zaman MH. Dynamic interplay between tumour, stroma and immune system can drive or prevent tumour progression. Converg Sci Phys Oncol (2017) 3:034002. doi: 10.1088/2057-1739/aa7e86
8. Demaria O, Cornen S, Daeron M, Morel Y, Medzhitov R, Vivier E. Harnessing innate immunity in cancer therapy. Nature. (2019) 574:45–56. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1593-5
9. Woo SR, Corrales L, Gajewski TF. Innate immune recognition of cancer. Annu Rev Immunol. (2015) 33:445–74. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112043
10. Corrales L, Matson V, Flood B, Spranger S, Gajewski TF. Innate immune signaling and regulation in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. (2017) 27:96–108. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.149
11. Alderton GK, Bordon Y. Tumour immunotherapy–leukocytes take up the fight. Nat Rev Immunol. (2012) 12:237. doi: 10.1038/nri3197
12. Yuen GJ, Demissie E, Pillai S. B lymphocytes and cancer: a love-hate relationship. Trends Cancer. (2016) 2:747–57. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.10.010
13. Khong HT, Restifo NP. Natural selection of tumor variants in the generation of "tumor escape" phenotypes. Nat Immunol. (2002) 3:999–1005. doi: 10.1038/ni1102-999
14. Thomas DA, Massague J. TGF-beta directly targets cytotoxic T cell functions during tumor evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Cell. (2005) 8:369–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.10.012
15. Blank C, Gajewski TF, Mackensen A. Interaction of PD-L1 on tumor cells with PD-1 on tumor-specific T cells as a mechanism of immune evasion: implications for tumor immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2005) 54:307–14. doi: 10.1007/s00262-004-0593-x
16. Drake CG, Jaffee E, Pardoll DM. Mechanisms of immune evasion by tumors. Adv Immunol. (2006) 90:51–81. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(06)90002-9
17. Rabinovich GA, Gabrilovich D, Sotomayor EM. Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells. Annu Rev Immunol. (2007) 25:267–96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141609
18. Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. (2010) 363:711–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1003466
19. Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, et al. Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:1803–13. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1510665
20. Ribas A. Releasing the brakes on cancer immunotherapy. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:1490–2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1510079
21. Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, Schneeweiss A, Barrios CH, Iwata H, et al. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:2108–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809615
22. Gandhi L, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:2078–92. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1801005
23. Forde PM, Chaft JE, Pardoll DM. Neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:e14. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1716078
24. Wei SC, Duffy CR, Allison JP. Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Discovery. (2018) 8:1069–86. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0367
25. Alberti S, Gladfelter A, Mittag T. Considerations and challenges in studying liquid-liquid phase separation and biomolecular condensates. Cell. (2019) 176:419–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.035
26. Che X, Wu J, Liu H, Su J, Chen X. Cellular liquid-liquid phase separation: Concept. functions regulations detections J Cell Physiol. (2023) 238:847–65. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30980
27. Zhang JZ, Mehta S, Zhang J. Liquid-liquid phase separation: a principal organizer of the cell's biochemical activity architecture. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2021) 42:845–56. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.07.003
28. Peng Q, Tan S, Xia L, Wu N, Oyang L, Tang Y, et al. Phase separation in Cancer: From the Impacts and Mechanisms to Treatment potentials. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:5103–22. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.75410
29. Alberti S, Dormann D. Liquid-liquid phase separation in disease. Annu Rev Genet. (2019) 53:171–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-112618-043527
30. Meng F, Yu Z, Zhang D, Chen S, Guan H, Zhou R, et al. Induced phase separation of mutant NF2 imprisons the cGAS-STING machinery to abrogate antitumor immunity. Mol Cell. (2021) 81:4147–4164 e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.040
31. Dine E, Gil AA, Uribe G, Brangwynne CP, Toettcher JE. Protein phase separation provides long-term memory of transient spatial stimuli. Cell Syst. (2018) 6:655–663 e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.002
32. Nielsen MW, Andersen JP, Schiebinger L, Schneider JW. One and a half million medical literatures reveal a link between author gender and attention to gender and sex analysis. Nat Hum Behav. (2017) 1:791–6. doi: 10.1038/s41562-017-0235-x
33. Boudry C, Baudouin C, Mouriaux F. International publication trends in dry eye disease research: A bibliometric analysis. Ocul Surf. (2018) 16:173–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2017.10.002
34. Fu HZ, Wang MH, Ho YS. Mapping of drinking water research: a bibliometric analysis of research output during 1992-2011. Sci Total Environ. (2013) 443:757–65. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.061
35. Wu H, Li Y, Tong L, Wang Y, Sun Z. Worldwide research tendency and hotspots on hip fracture: a 20-year bibliometric analysis. Arch Osteoporos. (2021) 16:73. doi: 10.1007/s11657-021-00929-2
36. Liao Z, Wei W, Yang M, Kuang X, Shi J. Academic publication of neurodegenerative diseases from a bibliographic perspective: A comparative scientometric analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. (2021) 13:722944. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.722944
37. Yan P, Li M, Li J, Lu Z, Hui X, Bai Y, et al. Bibliometric analysis and systematic review of global coronavirus research trends before COVID-19: prospects and implications for COVID-19 research. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:729138. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.729138
38. Liu T, Yang L, Mao H, Ma F, Wang Y, Zhan Y. Knowledge domain and emerging trends in podocyte injury research from 1994 to 2021: A bibliometric and visualized analysis. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:772386. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.772386
39. Xing D, Zhao Y, Dong S, Lin J. Global research trends in stem cells for osteoarthritis: a bibliometric and visualized study. Int J Rheum Dis. (2018) 21:1372–84. doi: 10.1111/apl.2018.21.issue-7
40. Xiong W, Wang S, Wei Z, Cai Y, Li B, Lin F, et al. Knowledge domain and hotspots predict concerning electroactive biomaterials applied in tissue engineering: A bibliometric and visualized analysis from 2011 to 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2022) 10:904629. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.904629
41. Case LB, Ditlev JA, Rosen MK. Regulation of transmembrane signaling by phase separation. Annu Rev Biophys. (2019) 48:465–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-052118-115534
42. Dustin ML, Groves JT. Receptor signaling clusters in the immune synapse. Annu Rev Biophys. (2012) 41:543–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-042910-155238
43. Jaqaman K, Ditlev JA. Biomolecular condensates in membrane receptor signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2021) 69:48–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.12.006
44. Liu B, Chen W, Evavold BD, Zhu C. Accumulation of dynamic catch bonds between TCR and agonist peptide-MHC triggers T cell signaling. Cell. (2014) 157:357–68. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.053
45. Nishi H, Furuhashi K, Cullere X, Saggu G, Miller MJ, Chen Y, et al. Neutrophil FcgammaRIIA promotes IgG-mediated glomerular neutrophil capture via Abl/Src kinases. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127:3810–26. doi: 10.1172/JCI94039
46. Wan Z, Chen X, Chen H, Ji Q, Chen Y, Wang J, et al. The activation of IgM- or isotype-switched IgG- and IgE-BCR exhibits distinct mechanical force sensitivity and threshold. Elife. (2015) 4:e06925. doi: 10.7554/eLife.06925
47. Bunnell SC, Hong DI, Kardon JR, Yamazaki T, McGlade CJ, Barr VA, et al. T cell receptor ligation induces the formation of dynamically regulated signaling assemblies. J Cell Biol. (2002) 158:1263–75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200203043
48. Hui E, Cheung J, Zhu J, Su X, Taylor MJ, Wallweber HA, et al. T cell costimulatory receptor CD28 is a primary target for PD-1-mediated inhibition. Science. (2017) 355:1428–33. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1292
49. Barda-Saad M, Braiman A, Titerence R, Bunnell SC, Barr VA, Samelson LE. Dynamic molecular interactions linking the T cell antigen receptor to the actin cytoskeleton. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:80–9. doi: 10.1038/ni1143
50. Houtman JC, Yamaguchi H, Barda-Saad M, Braiman A, Bowden B, Appella E, et al. Oligomerization of signaling complexes by the multipoint binding of GRB2 to both LAT and SOS1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2006) 13:798–805. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1133
51. Su X, Ditlev JA, Hui E, Xing W, Banjade S, Okrut J, et al. Phase separation of signaling molecules promotes T cell receptor signal transduction. Science. (2016) 352:595–9. doi: 10.1126/science.aad9964
52. Kortum RL, Balagopalan L, Alexander CP, Garcia J, Pinski JM, Merrill RK, et al. The ability of Sos1 to oligomerize the adaptor protein LAT is separable from its guanine nucleotide exchange activity in vivo. Sci Signal. (2013) 6:ra99. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004494
53. Zeng L, Palaia I, Saric A, Su X. PLCgamma1 promotes phase separation of T cell signaling components.
54. Pielak RM, O'Donoghue GP, Lin JJ, Alfieri KN, Fay NC, Low-Nam ST, et al. Early T cell receptor signals globally modulate ligand:receptor affinities during antigen discrimination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2017) 114:12190–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613140114
55. Lin JJY, Low-Nam ST, Alfieri KN, McAffee DB, Fay NC, Groves JT. Mapping the stochastic sequence of individual ligand-receptor binding events to cellular activation: T cells act on the rare events. Sci Signal. (2019) 12. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aat8715
56. Xiao Q, McAtee CK, Su X. Phase separation in immune signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. (2022) 22:188–99. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00572-5
57. Wong LE, Bhatt A, Erdmann PS, Hou Z, Maier J, Pirkuliyeva S, et al. Tripartite phase separation of two signal effectors with vesicles priming B cell responsiveness. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:848. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14544-1
58. Engelke M, Pirkuliyeva S, Kuhn J, Wong L, Boyken J, Herrmann N, et al. Macromolecular assembly of the adaptor SLP-65 at intracellular vesicles in resting B cells. Sci Signal. (2014) 7:ra79. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.2005104
59. Oellerich T, Bremes V, Neumann K, Bohnenberger H, Dittmann K, Hsiao HH, et al. The B-cell antigen receptor signals through a preformed transducer module of SLP65 and CIN85. EMBO J. (2011) 30:3620–34. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.251
60. Kee BL. It's a phase that EBF1 is going through. Immunity. (2020) 53:1123–5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.11.013
61. Williamson AP, Vale RD. Spatial control of Draper receptor signaling initiates apoptotic cell engulfment. J Cell Biol. (2018) 217:3977–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201711175
62. Goodridge HS, Reyes CN, Becker CA, Katsumoto TR, Ma J, Wolf AJ, et al. Activation of the innate immune receptor Dectin-1 upon formation of a 'phagocytic synapse'. Nature. (2011) 472:471–5. doi: 10.1038/nature10071
63. Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science. (2013) 339:786–91. doi: 10.1126/science.1232458
64. Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, et al. Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science. (2013) 339:826–30. doi: 10.1126/science.1229963
65. Du M, Chen ZJ. DNA-induced liquid phase condensation of cGAS activates innate immune signaling. Science. (2018) 361:704–9. doi: 10.1126/science.aat1022
66. Zhang W, Liu W, Jia L, Chen D, Chang I, Lake M, et al. Targeting KDM4A epigenetically activates tumor-cell-intrinsic immunity by inducing DNA replication stress. Mol Cell. (2021) 81:2148–2165 e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.02.038
67. Lin H, Jiang M, Liu L, Yang Z, Ma Z, Liu S, et al. The long noncoding RNA Lnczc3h7a promotes a TRIM25-mediated RIG-I antiviral innate immune response. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:812–23. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0379-0
68. Gack MU, Shin YC, Joo CH, Urano T, Liang C, Sun L, et al. TRIM25 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for RIG-I-mediated antiviral activity. Nature. (2007) 446:916–20. doi: 10.1038/nature05732
69. Arimoto K, Takahashi H, Hishiki T, Konishi H, Fujita T, Shimotohno K. Negative regulation of the RIG-I signaling by the ubiquitin ligase RNF125. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2007) 104:7500–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611551104
70. Jobe F, Simpson J, Hawes P, Guzman E, Bailey D. Respiratory syncytial virus sequesters NF-kappaB subunit p65 to cytoplasmic inclusion bodies to inhibit innate immune signaling. J Virol. (2020) 94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01380-20
71. Qin Z, Fang X, Sun W, Ma Z, Dai T, Wang S, et al. Deactylation by SIRT1 enables liquid-liquid phase separation of IRF3/IRF7 in innate antiviral immunity. Nat Immunol. (2022) 23:1193–207. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01269-0
72. Li Y, Peng Q, Wang L. EphA2 as a phase separation protein associated with ferroptosis and immune cell infiltration in colorectal cancer. Aging (Albany NY). (2023) 15:12952–65. doi: 10.18632/aging.205212
73. Zhang Z, Boskovic Z, Hussain MM, Hu W, Inouye C, Kim HJ, et al. Chemical perturbation of an intrinsically disordered region of TFIID distinguishes two modes of transcription initiation. Elife. (2015) 4. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07777
74. Ban D, Iconaru LI, Ramanathan A, Zuo J, Kriwacki RW. A small molecule causes a population shift in the conformational landscape of an intrinsically disordered protein. J Am Chem Soc. (2017) 139:13692–700. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01380
75. Iconaru LI, Ban D, Bharatham K, Ramanathan A, Zhang W, Shelat AA, et al. Discovery of small molecules that inhibit the disordered protein, p27(Kip1). Sci Rep. (2015) 5:15686. doi: 10.1038/srep15686
76. Zhang H, Ji X, Li P, Liu C, Lou J, Wang Z, et al. Liquid-liquid phase separation in biology: mechanisms, physiological functions and human diseases. Sci China Life Sci. (2020) 63:953–85. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1702-x
77. Li P, Banjade S, Cheng HC, Kim S, Chen B, Guo L, et al. Phase transitions in the assembly of multivalent signalling proteins. Nature. (2012) 483:336–40. doi: 10.1038/nature10879
78. Iakoucheva LM, Radivojac P, Brown CJ, O'Connor TR, Sikes JG, Obradovic Z, et al. The importance of intrinsic disorder for protein phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. (2004) 32:1037–49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh253
79. Peng PH, Hsu KW, Wu KJ. Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) in cellular physiology and tumor biology. Am J Cancer Res. (2021) 11:3766–76.
80. Spegg V, Altmeyer M. Biomolecular condensates at sites of DNA damage: More than just a phase. DNA Repair (Amst). (2021) 106:103179. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103179
81. Dao TP, Castaneda CA. Ubiquitin-modulated phase separation of shuttle proteins: does condensate formation promote protein degradation? Bioessays. (2020) 42:e2000036. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000036
82. Hnisz D, Shrinivas K, Young RA, Chakraborty AK, Sharp PA. A phase separation model for transcriptional control. Cell. (2017) 169(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.007
83. Patel A, Lee HO, Jawerth L, Maharana S, Jahnel M, Hein MY, et al. A liquid-to-solid phase transition of the ALS protein FUS accelerated by disease mutation. Cell. (2015) 162:1066–77. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.047
84. Maharana S, Wang J, Papadopoulos DK, Richter D, Pozniakovsky A, Poser I, et al. RNA buffers the phase separation behavior of prion-like RNA binding proteins. Science. (2018) 360:918–21. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7366
85. Mann JR, Gleixner AM, Mauna JC, Gomes E, DeChellis-Marks MR, Needham PG, et al. RNA binding antagonizes neurotoxic phase transitions of TDP-43. Neuron. (2019) 102:321–338 e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.01.048
86. Gasset-Rosa F, Lu S, Yu H, Chen C, Melamed Z, Guo L, et al. Cytoplasmic TDP-43 de-mixing independent of stress granules drives inhibition of nuclear import, loss of nuclear TDP-43, and cell death. Neuron. (2019) 102:339–357 e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.02.038
87. Lin Y, Protter DS, Rosen MK, Parker R. Formation and maturation of phase-separated liquid droplets by RNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell. (2015) 60:208–19. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.08.018
88. Nott TJ, Petsalaki E, Farber P, Jervis D, Fussner E, Plochowietz A, et al. Phase transition of a disordered nuage protein generates environmentally responsive membraneless organelles. Mol Cell. (2015) 57:936–47. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.013
89. Zhang X, Vigers M, McCarty J, Rauch JN, Fredrickson GH, Wilson MZ, et al. The proline-rich domain promotes Tau liquid-liquid phase separation in cells. J Cell Biol. (2020) 219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202006054
90. Zhang X, Lin Y, Eschmann NA, Zhou H, Rauch JN, Hernandez I, et al. RNA stores tau reversibly in complex coacervates. PloS Biol. (2017) 15:e2002183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2002183
91. Yamazaki T, Souquere S, Chujo T, Kobelke S, Chong YS, Fox AH, et al. Functional Domains of NEAT1 Architectural lncRNA Induce Paraspeckle Assembly through Phase Separation. Mol Cell. (2018) 70:1038–1053 e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.019
92. Plys AJ, Davis CP, Kim J, Rizki G, Keenen MM, Marr SK, et al. Phase separation of Polycomb-repressive complex 1 is governed by a charged disordered region of CBX2. Genes Dev. (2019) 33:799–813. doi: 10.1101/gad.326488.119
93. Kilic S, Lezaja A, Gatti M, Bianco E, Michelena J, Imhof R, et al. Phase separation of 53BP1 determines liquid-like behavior of DNA repair compartments. EMBO J. (2019) 38:e101379. doi: 10.15252/embj.2018101379
94. de The H, Pandolfi PP, Chen Z. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: A paradigm for oncoprotein-targeted cure. Cancer Cell. (2017) 32:552–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.10.002
95. Cai D, Feliciano D, Dong P, Flores E, Gruebele M, Porat-Shliom N, et al. Phase separation of YAP reorganizes genome topology for long-term YAP target gene expression. Nat Cell Biol. (2019) 21:1578–89. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0433-z
96. Bouchard JJ, Otero JH, Scott DC, Szulc E, Martin EW, Sabri N, et al. Cancer mutations of the tumor suppressor SPOP disrupt the formation of active. Phase-Separated Compartments Mol Cell. (2018) 72:19–36 e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.027
97. Li S, Hua Y. Holistic support for children with rare disease. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. (2024) 8(6):397. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(24)00045-2
98. Ahn JH, Davis ES, Daugird TA, Zhao S, Quiroga IY, Uryu H, et al. Phase separation drives aberrant chromatin looping and cancer development. Nature. (2021) 595:591–5. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03662-5
99. TaNiue K, Akimitsu N. Aberrant phase separation and cancer. FEBS J. (2022) 289:17–39. doi: 10.1111/febs.v289.1
100. Li X, Song J, Yi C. Genome-wide mapping of cellular protein-RNA interactions enabled by chemical crosslinking. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. (2014) 12:72–8. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2014.03.001
101. Haynes NM, Chadwick TB, Parker BS. The complexity of immune evasion mechanisms throughout the metastatic cascade. Nat Immunol. (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01960-4
102. Pan Y, Yu Y, Wang X, Zhang T. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immunity. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:583084. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.583084
103. Wang W, Chen J, Yu X, Lan HY. Signaling mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein in viral infection, cell death and inflammation. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:4704–13. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.72663
104. Jia P, Li X, Wang X, Yao L, Xu Y, Hu Y, et al. ZMYND8 mediated liquid condensates spatiotemporally decommission the latent super-enhancers during macrophage polarization. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:6535. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26864-x
105. Sanders DW, Kedersha N, Lee DSW, Strom AR, Drake V, Riback JA, et al. Competing protein-RNA interaction networks control multiphase intracellular oganization. Cell. (2020) 181:306–324 e28. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.050
106. Li H, Ding JY, Zhang MJ, Yu HJ, Sun ZJ. Tertiary lymphoid structures and cytokines interconnections: The implication in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. (2023) 568:216293. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216293
107. Zhou S, Su T, Cheng F, Cole J, Liu X, Zhang B, et al. Engineering cGAS-agonistic oligonucleotides as therapeutics for cancer immunotherapy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2024) 35:102126. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102126
108. Sun S, Wang W, Li G, Xiao M, Peng M, Cai J, et al. Rational therapeutic targets with biomolecular liquid-liquid phase separation regulating synergy: A pan-cancer analysis. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0287574. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287574
109. Stamenkovic I, Yu Q. Merlin, a "magic" linker between extracellular cues and intracellular signaling pathways that regulate cell motility, proliferation, and survival. Curr Protein Pept Sci. (2010) 11:471–84. doi: 10.2174/138920310791824011
110. Asthagiri AR, Parry DM, Butman JA, Kim HJ, Tsilou ET, Zhuang Z, et al. Neurofibromatosis type 2. Lancet. (2009) 373:1974–86. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60259-2
Keywords: liquid liquid phase separation (LLPS), immune transduction, bibliometric, CiteSpace, cancer
Citation: Pei Y, Liang H, Guo Y, Wang B, Wu H, Jin Z, Lin S, Zeng F, Wu Y, Shi Q, Xu J, Huang Y, Ren T, Liu J and Guo W (2025) Liquid-liquid phase separation drives immune signaling transduction in cancer: a bibliometric and visualized study from 1992 to 2024. Front. Oncol. 15:1509457. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1509457
Received: 11 October 2024; Accepted: 28 January 2025;
Published: 04 March 2025.
Edited by:
Tamer Saad Kaoud, The University of Texas at Austin, United StatesReviewed by:
Om Prakash Narayan, The University of Texas at Austin, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Pei, Liang, Guo, Wang, Wu, Jin, Lin, Zeng, Wu, Shi, Xu, Huang, Ren, Liu and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Guo, Ym9uZXR1bW91cl9ndW9AYmptdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.