
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Oncol. , 08 November 2024
Sec. Cancer Imaging and Image-directed Interventions
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1491762
 Yan Sun1,2,3
Yan Sun1,2,3 Xinyu Ge1,2,3
Xinyu Ge1,2,3 Rong Niu1,2,3
Rong Niu1,2,3 Jianxiong Gao1,2,3
Jianxiong Gao1,2,3 Yunmei Shi1,2,3
Yunmei Shi1,2,3 Xiaoliang Shao1,2,3
Xiaoliang Shao1,2,3 Yuetao Wang1,2,3
Yuetao Wang1,2,3 Xiaonan Shao1,2,3*
Xiaonan Shao1,2,3*Lung cancer is currently the leading cause of cancer-related deaths, and early diagnosis and screening can significantly reduce its mortality rate. Since some early-stage lung cancers lack obvious clinical symptoms and only present as pulmonary nodules (PNs) in imaging examinations, accurately determining the benign or malignant nature of PNs is crucial for improving patient survival rates. 18F-FDG PET/CT is important in diagnosing PNs, but its specificity needs improvement. Radiomics can provide information beyond traditional visual assessment, overcoming its limitations by extracting high-throughput quantitative features from medical images. Radiomics features based on 18F-FDG PET/CT and deep learning methods have shown great potential in the noninvasive diagnosis of PNs. This paper reviews the latest advancements in these methods and discusses their contributions to improving diagnostic accuracy and the challenges they face.
According to the 2024 statistics from the American Cancer Society, lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths (1). About 50% of patients are already at a locally advanced or distant metastasis stage at the time of diagnosis, thus missing the optimal window for surgical treatment (2). However, early-stage lung cancer often lacks obvious clinical symptoms and typically only presents as pulmonary nodules (PNs) in imaging examinations, with approximately 35% of solitary pulmonary nodules (SPNs) being diagnosed as early-stage primary lung cancer (3). Thus, accurately diagnosing the benign or malignant nature of PNs is key to improving patient prognosis and survival rates.
Although biopsy is considered the ‘gold standard’ for confirming the benign or malignant nature of PNs, it has several limitations, such as being highly invasive, having poor repeatability, carrying a high risk of complications, and being unable to provide whole-body assessment or spatial information for non-puncture sites (4). Although traditional CT has some advantages in non-invasive screening of PNs, its diagnosis mainly depends on anatomical information. Therefore, it may show false positives in some cases, especially in overdiagnosing some benign lesions (such as granulomas and calcifications). And a report (5) shows that as many as 50% of the nodules removed during surgery are benign, indicating that it is difficult for radiologists to determine whether a pulmonary nodule is malignant based on CT and other clinical information (6). Currently, dual-modality 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging, which combines the anatomical information of CT and the metabolic information of PET, is widely used in diagnosing PNs, and its diagnostic accuracy is superior to that of PET or CT alone (7–11). However, 18F-FDG PET/CT still faces the challenge of a high false-positive rate when diagnosing the benign or malignant nature of PNs (12–15). This issue often arises because certain benign lesions (such as granulomas, organizing pneumonia, or fungal infections) are difficult to distinguish from malignant PNs based on imaging features (12, 16). Although 18F-FDG PET/CT has a high sensitivity (SEN: 0.89) in detecting malignant SPNs, its specificity is relatively low (SPE: 0.70) (17). Therefore, further research is needed to improve the accuracy of PNs diagnosis.
In recent years, radiomics has been an emerging medical image analysis technology. This concept was first put forward by the Dutch scholar Lambin (18) in 2012. Radiomics generally refers to the high-throughput extraction of many quantitative features from medical images (such as CT, MRI, PET, etc.) and converting the image data of the region of interest into mineable high-dimensional data (19). Its features include intensity, shape, volume, texture features, etc. (20), which can effectively address the limitations of traditional assessment methods and offer new perspectives for diagnosing benign and malignant PNs with 18F-FDG PET/CT (21–25). Radiomics features are divided into handcrafted features (HF) and deep features (DF) according to different extraction methods. Figure 1 illustrates the differences in procedures between extracting handcrafted features and deep features. Handcrafted features are predefined or manually extracted by image processing experts, while deep learning (DL) algorithms automatically extract deep features without human intervention (26, 27). In recent years, both HF and DF have been widely used in tasks such as image classification and regression, demonstrating great potential in improving the performance of diagnostic models. However, effectively combining these features in diagnosing PNs and addressing the challenges that arise from this combination remain key areas of current research. This paper reviews the methodological advancements of 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics and deep learning in diagnosing benign and malignant PNs, focusing on the application and challenges of HF and DF in enhancing diagnostic model performance.
Handcrafted features (HF) extracted by traditional radiomics can generally be divided into four categories: statistical features (such as histogram-based features and texture features), model-based features, transform-based features, and shape-based features (28).
Histogram-based features include the mean, maximum, minimum, variance, and percentiles of gray levels (28, 29). These features are typically based on single-pixel or single-voxel analysis and thus are referred to as first-order features. Texture features, also termed second-order characteristics, involve entities such as the Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) and the Neighborhood Gray-Tone Difference Matrix (NGTDM), which are employed to depict the interrelationships among voxels. Model-based features characterize the features of an object or shape by analyzing the gray-level information in space. Transform-based features are extracted through methods like Fourier transform, Gabor transform, or Haar wavelet transform and are utilized to analyze gray-level patterns in different spaces (19). Shape-based features, such as compactness and sphericity, depict the geometric attributes of the region of interest (ROI).
Multiple studies have evaluated the ability of handcrafted features (HF) from 18F-FDG PET/CT to differentiate between benign and malignant PNs (see Table 1) (22, 30–32). For example, Liu et al. (30) studied 20 CT radiomics features, including 14 gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) features, 1 intensity histogram feature, and 5 shape features, to distinguish between peripheral lung cancer and inflammatory pseudotumor. They found that GLCM features had the highest discriminative ability. Additionally, Chen et al. (22) extracted neighborhood gray-tone difference matrix (NGTDM) features from dual-time-point imaging (DTPI) 18F-FDG PET/CT images and found that these features had an AUC of 0.89 in diagnosing benign and malignant solitary pulmonary nodules (SPNs), outperforming the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax, AUC: 0.75) or visual assessment (AUC: 0.80). This finding is consistent with the results of Bomhals et al. (31). Texture features, as part of HF, capture tissue structural heterogeneity by quantifying the relationship between voxels and their surroundings, thus performing well in the diagnosis of benign and malignant PNs. However, using HF alone may be insufficient to fully describe tumor heterogeneity (32). Combining HF with other features, such as CT semantic features, PET metabolic parameters, and clinical features, can significantly improve the accuracy and reproducibility of 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics in diagnosing benign and malignant PNs (33).
Since benign lesions (such as inflammatory lesions) and malignant tumors have significant differences in biological behavior, pathological processes, and internal structures, combining the complementary nature of various features can provide a more comprehensive description of the benign and malignant differences in PNs, leading to more accurate qualitative diagnoses. Table 1 summarizes 16 studies that utilized HF for the diagnosis of benign and malignant lung nodules, of which 15 studies combined PET/CT imaging HF with other features (such as CT semantic features, PET metabolic parameters, and clinical features) for diagnosis (10, 22–25, 31, 32, 34–41). These studies reported diagnostic AUC values ranging from 0.813 to 0.980, demonstrating the great potential of combining HF with other features to improve model performance.
In clinical diagnosis, physicians typically rely on the CT semantic features of PNs (such as morphology, density, internal structure, etc.) to determine their nature. Although these features play an important role in diagnosis, their accuracy may be reduced due to the influence of subjective factors (35). In contrast, HF from PET/CT can provide objective quantitative information that is not obtainable through traditional visual assessments. Studies have shown that combining HF with CT semantic features can more effectively differentiate between benign and malignant PNs, with diagnostic AUC values ranging from 0.875 to 0.980 (22, 34, 35). For example, Kang et al. (34) extracted features from CT, thin-slice CT, PET, and PET/CT images, used the LASSO algorithm to select the most significant features and calculated a radiomics score (RS), which was then combined with manual diagnosis to construct a hybrid nomogram. The results showed that the AUC of the hybrid nomogram exceeded 0.89 and significantly reduced the false positive rate (FPR) from 30.9% in manual diagnosis to 9.1%. Additionally, studies (35) have shown that a model combining CT semantic features with radiomics features has significantly better diagnostic performance than a model using RS alone (AUC: 0.908 vs. 0.704) while substantially reducing the FPR. These findings indicate that combining radiomics with CT semantic features can significantly improve the accuracy of PNs diagnosis.
Studies have also shown that combining HF from PET/CT with PET metabolic parameters can significantly enhance the diagnostic performance for differentiating between benign and malignant PNs (22–24, 35, 36, 41). For example, Palumbo et al. (24) retrospectively evaluated data from 111 patients and found that combining PET and CT shape and texture features with PET conventional metabolic parameters could improve the diagnostic accuracy of the model by 2.2% to 10.2%. Zhang et al. (23) analyzed PET/CT images from 82 patients and compared the diagnostic performance of a support vector machine (SVM) model based on SUVmax, metabolic tumor volume (MTV), and texture features, finding that the AUC of the SVM model was 0.854, which was superior to using only the SUVmax (AUC: 0.595) or MTV model (AUC: 0.616). Niu et al. (35) significantly improved the diagnostic performance by incorporating SUVmax into a CT radiomics model, with the AUC increasing from 0.704 to 0.940. These results further support the idea that combining radiomics features with PET metabolic parameters can enhance the diagnostic capability of the model.
Additionally, studies have explored strategies to improve the qualitative diagnosis of PNs by combining HF from PET/CT with clinical features (25, 40, 41). This fusion strategy is divided into pre-fusion and post-fusion (see Table 2). Pre-fusion involves merging the selected radiomics features with clinical features before model training. Wang et al. (41) studied PET/CT data from 187 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and 190 patients with benign lung nodules, incorporating clinical features such as gender, age, and smoking history. The results showed that the model’s AUC reached 0.890, significantly improving the diagnostic ability of early SPNs. Conversely, post-fusion involves independently constructing HF and clinical feature models and combining them to form a complex model. Ren et al. (40) developed clinical, radiomics, and combined models using data from 280 patients. The results showed that the combined model exhibited the best AUC (0.910 and 0.940) and the lowest false positive rate (FPR: 18.68% and 5.41%) in the classification of solid lung nodules. However, the study by Hu et al. (25) found that although the complex model combining radiomics features and clinical features had a slightly higher AUC than the radiomics model alone in distinguishing solitary pulmonary adenocarcinoma from pulmonary tuberculosis, the difference was not significant (training set AUC: 0.884 vs. 0.861; validation set AUC: 0.909 vs. 0.889). This may be related to the impact of different scanners on the accuracy of radiomics features (32). Therefore, whether combining clinical features with radiomics features can significantly improve diagnostic performance still requires further research.
Although HF is beneficial for reducing the false-positive rate of PET/CT in diagnosing pulmonary nodules, there are three major issues in extracting HF. First, image segmentation often relies on manual delineation, a process that is not only time-consuming but also prone to consistency issues between different operators and within the same operator at other times, thereby affecting the stability of the results. Second, the variability in the selection and processing of various image features can lead to inconsistencies in the analysis results, making it difficult to verify accuracy and reproducibility, increasing the likelihood of computational errors, and heightening diagnostic uncertainty. Lastly, although manual methods can extract various features, they are limited in their ability to comprehensively capture all the information within the Region of Interest (ROI), potentially missing details critical to the diagnosis (42). These limitations have driven the increasingly widespread application of DF. Deep features are automatically identified and extracted by deep learning algorithms, reducing human intervention and enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of analysis.
DF is extracted from medical images through deep neural networks, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). Compared to HF, DF can capture more complex and higher-level features (42). The extraction process of DF does not rely on manual operations, reducing human errors and significantly improving the accuracy of image data analysis. By automatically learning and identifying complex patterns within the data, DF enhances features’ representational power and substantially increases diagnoses’ accuracy and reliability. Table 3 summarizes five studies that used DF to diagnose benign and malignant pulmonary nodules (11, 43–46).
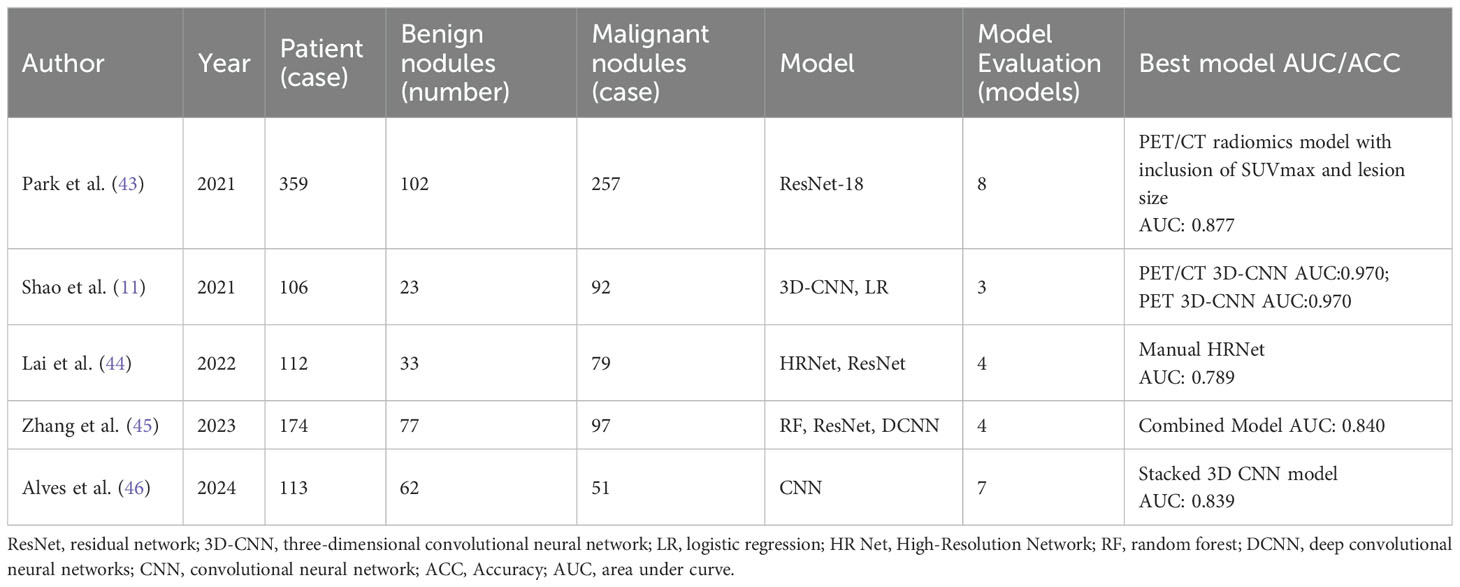
Table 3. Summary of Literature on the diagnosis of benign and malignant pulmonary nodules based on DF.
Deep Learning (DL) utilizes multi-layer feedforward neural networks to directly receive image inputs and perform end-to-end training in a supervised environment, thereby learning highly discriminative image features. The DL modeling includes image acquisition, preprocessing, model training, and analysis (47). In diagnosing benign and malignant Pulmonary Nodules (PNs), in addition to traditional 2D models, 2.5D and 3D models have also been developed. The 2.5D models input coronal, sagittal, and axial 2D images into three channels for modeling (48), while the 3D models integrate the continuous scan layers of pulmonary nodules into a three-dimensional object, further enhancing the ability to extract stereoscopic information (49). For instance, Alves et al. (46) used a 3D-CNN architecture model, and although only PET images were input, its diagnostic performance surpassed that of the 2D ResNet-50 model (AUC: 0.839 vs 0.774). Lai et al. (44) proposed a 3D High-Resolution Network (3D HRNet) architecture, which avoids stride layers and pooling layers to maintain the original dimensions of features, showing higher diagnostic accuracy than ResNet (AUC: 0.781 vs 0.650). Although 3D models generally outperform 2D models, in some cases, 2.5D models may perform more accurately (48), possibly due to overfitting issues in 3D models.
Deep learning-based radiomics (DLR) combines deep learning (DL) and traditional radiomics. While handcrafted features (HF) struggle to express tumor heterogeneity fully, limiting the performance of diagnostic models, DLR compensates for this by extracting deeper and higher-dimensional features through convolutional kernels, more comprehensively quantifying tumor heterogeneity (50). Studies show that combining HF and deep features (DF) can significantly improve model performance (45). For instance, Zhang et al. (45) extracted 100 HF and 2048 DF obtained through ResNet from PET and CT images to distinguish tuberculosis nodules from lung cancer. The results indicated that the deep convolutional neural network model with both HF and DF input (Radiomics-DCNN, AUC: 0.820) outperformed the DL model with only DF input (AUC: 0.720) and the traditional machine learning model with only HF input (AUC: 0.760). Although DLR has shown its potential, research in this field is still scarce, and further studies are needed to validate its feasibility and performance.
Although HF and DF employ different methods in radiomics, their goals and application scenarios are similar. With advancements in deep learning (DL) technology, DF typically outperforms HF in diagnostic performance, provided there is sufficient training data (see Table 4 for specific comparisons (42, 51). HF is susceptible to variations in manual segmentation and scanning parameters, whereas DL models improve robustness and generalization by organically integrating feature extraction and classification through end-to-end training (52). However, DF has weaker interpretability, requires more data, and incurs higher computational costs. Therefore, HF still holds value in situations with limited data or specific tasks.
With the advancement of nuclear medicine technology, many studies have shown that dual-modality PET/CT radiomics models outperform models using CT or PET alone in the qualitative diagnosis of pulmonary nodules (PNs) (10, 11). Techniques such as dual-tracer imaging (e.g., using 18F-FLT and 18F-FDG) (37) and dual-time-point imaging (DTPI) (22, 38) have also significantly improved diagnostic accuracy.
Data imbalance is a major challenge in radiomics research for diagnosing benign and malignant pulmonary nodules (PNs), leading to biased diagnostic results. Several strategies can be employed to address this issue. First, data augmentation can increase the diversity and quantity of samples. Second, resampling or oversampling at the feature level: for example, using SMOTE (Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique) (53) to generate synthetic samples can help avoid model overfitting. Lastly, semi-supervised learning methods can be used: for example, pseudo-labeling, which involves vote-based classification of unlabeled samples, can improve model robustness. Additionally, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have shown significant effectiveness in generating high-fidelity synthetic data (54). For instance, GAN-based methods have successfully synthesized high-quality PET images from diagnostic CT scans, achieving quality and tumor contrast comparable to actual PET images (55). Applying these emerging methods in medical image analysis has already seen some success (56–58).
Most radiomics studies still rely on single-center and small-scale retrospective research, lacking prospective studies and external independent validation. This limitation results in models with constrained generalization ability. To improve these models’ performance and clinical applicability, future efforts should focus on establishing large databases through multi-center collaborations and using external validation sets to evaluate the models. This approach will enhance the models’ generalization ability and reliability.
With the rapid development of radiomics and deep learning technologies, the role of PET/CT radiomics and deep learning in clinical practice is increasingly prominent. Through the in-depth mining and accurate analysis of massive imaging data, it can generate more valuable non-invasive diagnostic indicators. This not only enables patients to avoid the pain and risks brought by unnecessary biopsies but also significantly reduces the incidence of biopsy-related complications. Meanwhile, it provides a reliable basis for clinical treatment decisions, helping patients obtain accurate diagnosis and timely treatment in the early stage of the disease, thus effectively improving the cure rate. In addition, it can also reduce unnecessary repeated examinations and long-term follow-up observations. In conclusion, PET/CT radiomics and deep learning show broad clinical application prospects in pulmonary nodule diagnosis and have important value that cannot be ignored.
PET/CT radiomics has significantly improved the accuracy of diagnosing the benign or malignant nature of pulmonary nodules (PNs) by deeply exploring the vast amount of hidden information in conventional imaging. However, issues related to the availability of technology, the reproducibility of results, and the robustness and precision of features still limit its widespread clinical application. As multi-center research progresses, large-scale datasets are established, and new technologies continue to develop, radiomics is expected to play an increasingly important role in diagnosing PNs, providing strong support for clinical decision-making.
YS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. XG: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. RN: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JG: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YMS: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XLS: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XNS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Top Talent of Changzhou “The 14th Five-Year Plan” High-Level Health Talents Training Project (2022CZBJ037); Top Talent of Changzhou “The 14th Five-Year Plan” High-Level Health Talents Training Project (2024CZBJ008); Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (SJCX24_1820); Changzhou Science and Technology Program (CJ20220228); Key Laboratory of Changzhou High-tech Research Project (CM20193010); Changzhou Clinical Medical Center (Nuclear Medicine) (CZZX202204).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
ACC, Accuracy; AUC, Area under curve; CNN, Convolutional neural network; CT, Computed tomography; DCNN: Deep convolutional neural network; DF, Deep features; DL, Deep learning; DLR, Deep learning-based radiomics; FPR, False positive rate; GAN, Generative adversarial network; GLCM, Gray-level co-occurrence matrix; GLZLM, Gray-level zone length matrix; HF, Handcrafted features; HRNet, High-resolution network; J48, Decision tree; KNN, k-Nearest Neighbors; LR, Logistic regression; LASSO, Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; MTV, Metabolic tumor volume; NA, Not available; NB, Naive bayes; NGTDM, Neighborhood gray-tone difference matrix; NSCLC, Non-small cell lung cancer; OPLS-DA, Orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis; PCs, Principal components; PET, Positron emission tomography; PNs, Pulmonary nodules; RF, Random forest; RS, Radiomics score; SEN, Sensitivity; SPE, Specificity; SPNs, Solitary pulmonary nodules; SUVmax, Maximum standardized uptake value; SVM, Support vector machine.
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
2. Fletcher JW, Kymes SM, Gould M, Alazraki N, Coleman RE, Lowe VJ, et al. A comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of 18f-fdg pet and ct in the characterization of solitary pulmonary nodules. J Nucl Med. (2008) 49:179–85. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.044990
3. Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T, Thun M. Cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. (2002) 52:23–47. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.52.1.23
4. Lopes R, Betrouni N. Fractal and multifractal analysis: A review. Med Image Anal. (2009) 13:634–49. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2009.05.003
5. Swensen SJ, Jett JR, Hartman TE, Midthun DE, Sloan JA, Sykes AM, et al. Lung cancer screening with ct: mayo clinic experience. Radiology. (2003) 226:756–61. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2263020036
6. Way T, Chan HP, Hadjiiski L, Sahiner B, Chughtai A, Song TK, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodules on ct scans: roc study of its effect on radiologists’ Performance. Acad Radiol. (2010) 17:323–32. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2009.10.016
7. Kim SK, Allen-Auerbach M, Goldin J, Fueger BJ, Dahlbom M, Brown M, et al. Accuracy of pet/ct in characterization of solitary pulmonary lesions. J Nucl Med. (2007) 48:214–20.
8. Kagna O, Solomonov A, Keidar Z, Bar-Shalom R, Fruchter O, Yigla M, et al. The value of fdg-pet/ct in assessing single pulmonary nodules in patients at high risk of lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2009) 36:997–1004. doi: 10.1007/s00259-009-1061-9
9. Jeong SY, Lee KS, Shin KM, Bae YA, Kim BT, Choe BK, et al. Efficacy of pet/ct in the characterization of solid or partly solid solitary pulmonary nodules. Lung Cancer. (2008) 61:186–94. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.12.021
10. Zheng J, Hao Y, Guo Y, Du M, Wang P, Xin J. An 18f-fdg-pet/ct-based radiomics signature for estimating Malignance probability of solitary pulmonary nodule. Clin Respir J. (2024) 18:e13751. doi: 10.1111/crj.13751
11. Shao X, Niu R, Shao X, Gao J, Shi Y, Jiang Z, et al. Application of dual-stream 3d convolutional neural network based on (18)F-fdg pet/ct in distinguishing benign and invasive adenocarcinoma in ground-glass lung nodules. EJNMMI Phys. (2021) 8:74. doi: 10.1186/s40658-021-00423-1
12. Li ZZ, Huang YL, Song HJ, Wang YJ, Huang Y. The value of 18f-fdg-pet/ct in the diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules: A meta-analysis. Med (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e0130. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000010130
13. Ost D, Fein AM, Feinsilver SH. Clinical practice. The solitary pulmonary nodule. N Engl J Med. (2003) 348:2535–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp012290
14. Chen CJ, Lee BF, Yao WJ, Cheng L, Wu PS, Chu CL, et al. Dual-phase 18f-fdg pet in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules with an initial standard uptake value less than 2.5. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2008) 191:475–9. doi: 10.2214/ajr.07.3457
15. Huang YE, Lu HI, Liu FY, Huang YJ, Lin MC, Chen CF, et al. Solitary pulmonary nodules differentiated by dynamic F-18 fdg pet in a region with high prevalence of granulomatous disease. J Radiat Res. (2012) 53:306–12. doi: 10.1269/jrr.11089
16. Ruilong Z, Daohai X, Li G, Xiaohong W, Chunjie W, Lei T. Diagnostic value of 18f-fdg-pet/ct for the evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nucl Med Commun. (2017) 38:67–75. doi: 10.1097/mnm.0000000000000605
17. Deppen SA, Blume JD, Kensinger CD, Morgan AM, Aldrich MC, Massion PP, et al. Accuracy of fdg-pet to diagnose lung cancer in areas with infectious lung disease: A meta-analysis. Jama. (2014) 312:1227–36. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.11488
18. Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout RG, Granton P, et al. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer. (2012) 48:441–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036
19. Mayerhoefer ME, Materka A, Langs G, Häggström I, Szczypiński P, Gibbs P, et al. Introduction to radiomics. J Nucl Med. (2020) 61:488–95. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.222893
20. Tomaszewski MR, Gillies RJ. The biological meaning of radiomic features. Radiology. (2021) 299:E256. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021219005
21. Chen S, Harmon S, Perk T, Li X, Chen M, Li Y, et al. Diagnostic classification of solitary pulmonary nodules using dual time (18)F-fdg pet/ct image texture features in granuloma-endemic regions. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:9370. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08764-7
22. Chen S, Harmon S, Perk T, Li X, Chen M, Li Y, et al. Using neighborhood gray tone difference matrix texture features on dual time point pet/ct images to differentiate Malignant from benign fdg-avid solitary pulmonary nodules. Cancer Imaging. (2019) 19:56. doi: 10.1186/s40644-019-0243-3
23. Zhang J, Ma G, Cheng J, Song S, Zhang Y, Shi LQ. Diagnostic classification of solitary pulmonary nodules using support vector machine model based on 2-[18f]Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose pet/computed tomography texture features. Nucl Med Commun. (2020) 41:560–6. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000001193
24. Palumbo B, Bianconi F, Palumbo I, Fravolini ML, Minestrini M, Nuvoli S, et al. Value of shape and texture features from (18)F-fdg pet/ct to discriminate between benign and Malignant solitary pulmonary nodules: an experimental evaluation. Diagnostics (Basel). (2020) 10. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10090696
25. Hu Y, Zhao X, Zhang J, Han J, Dai M. Value of (18)F-fdg pet/ct radiomic features to distinguish solitary lung adenocarcinoma from tuberculosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2021) 48:231–40. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04924-6
27. Papadimitroulas P, Brocki L, Christopher Chung N, MarChadour W, Vermet F, Gaubert L, et al. Artificial intelligence: deep learning in oncological radiomics and challenges of interpretability and data harmonization. Phys Med. (2021) 83:108–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.03.009
28. Benoit-Cattin H. Texture analysis for magnetic resonance imaging. Prague, Czechoslovakia: Texture Analysis Magn Resona (2006).
29. Zwanenburg A, Leger S, Vallières M, Löck S. Image biomarker standardisation initiative. (2016). arXiv preprint arXiv:161207003.
30. Liu C, Ma C, Duan J, Qiu Q, Guo Y, Zhang Z, et al. Using ct texture analysis to differentiate between peripheral lung cancer and pulmonary inflammatory pseudotumor. BMC Med Imaging. (2020) 20:75. doi: 10.1186/s12880-020-00475-2
31. Bomhals B, Cossement L, Maes A, Sathekge M, Mokoala KMG, Sathekge C, et al. Principal component analysis applied to radiomics data: added value for separating benign from Malignant solitary pulmonary nodules. J Clin Med. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247731
32. Albano D, Gatta R, Marini M, Rodella C, Camoni L, Dondi F, et al. Role of (18)F-fdg pet/ct radiomics features in the differential diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules: diagnostic accuracy and comparison between two different pet/ct scanners. J Clin Med. (2021) 10. doi: 10.3390/jcm10215064
33. Reifenberger G, Wirsching H-G, Knobbe-Thomsen CB, Weller M. Advances in the molecular genetics of gliomas—Implications for classification and therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2017) 14:434–52. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.204
34. Kang F, Mu W, Gong J, Wang S, Li G, Li G, et al. Integrating manual diagnosis into radiomics for reducing the false positive rate of (18)F-fdg pet/ct diagnosis in patients with suspected lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2019) 46:2770–9. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04418-0
35. Niu R, Gao J, Shao X, Wang J, Jiang Z, Shi Y, et al. Maximum standardized uptake value of (18)F-deoxyglucose pet imaging increases the effectiveness of ct radiomics in differentiating benign and Malignant pulmonary ground-glass nodules. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:727094. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.727094
36. Aguloglu N, Aksu A, Unat DS. Machine learning approach using 18 F-fdg pet-based radiomics in differentiation of lung adenocarcinoma with bronchoalveolar distribution and infection. Nucl Med Commun. (2023) 44:302–8. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000001667
37. Ning J, Li C, Yu P, Cui J, Xu X, Jia Y, et al. Radiomic analysis will add differential diagnostic value of benign and Malignant pulmonary nodules: A hybrid imaging study based on [(18)F]Fdg and [(18)F]Flt pet/ct. Insights Imaging. (2023) 14:197. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01530-6
38. Teramoto A, Tsujimoto M, Inoue T, Tsukamoto T, Imaizumi K, Toyama H, et al. Automated classification of pulmonary nodules through a retrospective analysis of conventional ct and two-phase pet images in patients undergoing biopsy. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol. (2019) 7:29–37. doi: 10.22038/AOJNMB.2018.12014
39. Elia S, Pompeo E, Santone A, Rigoli R, Chiocchi M, Patirelis A, et al. Radiomics and artificial intelligence can predict Malignancy of solitary pulmonary nodules in the elderly. Diagnostics. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030384
40. Ren C, Xu M, Zhang J, Zhang F, Song S, Sun Y, et al. Classification of solid pulmonary nodules using a machine-learning nomogram based on (18)F-fdg pet/ct radiomics integrated clinicobiological features. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:1265. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2647
41. Wang H, Li Y, Han J, Lin Q, Zhao L, Li Q, et al. A machine learning-based pet/ct model for automatic diagnosis of early-stage lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1192908. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1192908
42. Li Z, Wang Y, Yu J, Guo Y, Cao W. Deep learning based radiomics (Dlr) and its usage in noninvasive idh1 prediction for low grade glioma. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:5467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05848-2
43. Park YJ, Choi D, Choi JY, Hyun SH. Performance evaluation of a deep learning system for differential diagnosis of lung cancer with conventional ct and fdg pet/ct using transfer learning and metadata. Clin Nucl Med. (2021) 46:635–40. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003661
44. Lai YC, Wu KC, Tseng NC, Chen YJ, Chang CJ, Yen KY, et al. Differentiation between Malignant and benign pulmonary nodules by using automated three-dimensional high-resolution representation learning with fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:773041. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.773041
45. Zhang X, Dong X, Saripan MIB, Du D, Wu Y, Wang Z, et al. Deep learning pet/ct-based radiomics integrates clinical data: A feasibility study to distinguish between tuberculosis nodules and lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. (2023) 14:1802–11. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14924
46. Alves VM, Dos Santos Cardoso J, Gama J. Classification of pulmonary nodules in 2-[(18)F]Fdg pet/ct images with a 3d convolutional neural network. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2024) 58:9–24. doi: 10.1007/s13139-023-00821-6
47. Yamashita R, Nishio M, Do RKG, Togashi K. Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging. (2018) 9:611–29. doi: 10.1007/s13244-018-0639-9
48. Kim H, Lee D, Cho WS, Lee JC, Goo JM, Kim HC, et al. Ct-based deep learning model to differentiate invasive pulmonary adenocarcinomas appearing as subsolid nodules among surgical candidates: comparison of the diagnostic performance with a size-based logistic model and radiologists. Eur Radiol. (2020) 30:3295–305. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06628-4
49. Zhao W, Yang J, Sun Y, Li C, Wu W, Jin L, et al. 3d deep learning from ct scans predicts tumor invasiveness of subcentimeter pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. (2018) 78:6881–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-0696
50. Zhang J, Zhao Y, Lu Y, Li P, Dang S, Li X, et al. Meningioma consistency assessment based on the fusion of deep learning features and radiomics features. Eur J Radiol. (2024) 170:111250. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.111250
51. Ypsilantis PP, Siddique M, Sohn HM, Davies A, Cook G, Goh V, et al. Predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with pet imaging using convolutional neural networks. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0137036. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137036
52. Zhao W, Yang J, Ni B, Bi D, Sun Y, Xu M, et al. Toward automatic prediction of egfr mutation status in pulmonary adenocarcinoma with 3d deep learning. Cancer Med. (2019) 8:3532–43. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2233
53. Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP. Smote: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res. (2002) 16:321–57. doi: 10.1613/jair.953
54. Buczak AL, Babin S, Moniz L. Data-driven approach for creating synthetic electronic medical records. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. (2010) 10:59. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-59
55. Salehjahromi M, Karpinets TV, Sujit SJ, Qayati M, Chen P, Aminu M, et al. Synthetic pet from ct improves diagnosis and prognosis for lung cancer: proof of concept. Cell Rep Med. (2024) 5:101463. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101463
56. Xia Y, Yang D, Yu Z, Liu F, Cai J, Yu L, et al. Uncertainty-aware multi-view co-training for semi-supervised medical image segmentation and domain adaptation. Med image Anal. (2020) 65:101766. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101766
57. He Y, Yang G, Yang J, Chen Y, Kong Y, Wu J, et al. Dense biased networks with deep priori anatomy and hard region adaptation: semi-supervised learning for fine renal artery segmentation. Med image Anal. (2020) 63:101722. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101722
Keywords: pulmonary nodules, lung neoplasms, PET/CT, radiomics, deep learning
Citation: Sun Y, Ge X, Niu R, Gao J, Shi Y, Shao X, Wang Y and Shao X (2024) PET/CT radiomics and deep learning in the diagnosis of benign and malignant pulmonary nodules: progress and challenges. Front. Oncol. 14:1491762. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1491762
Received: 06 September 2024; Accepted: 25 October 2024;
Published: 08 November 2024.
Edited by:
Santosh Kumar Yadav, Johns Hopkins Medicine, United StatesReviewed by:
Yashika Kamte, University of California, Los Angeles, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Sun, Ge, Niu, Gao, Shi, Shao, Wang and Shao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaonan Shao, c2NvcmV5QHNpbmEuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.