- Department of Oncology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Objectives: Analyzing the impact of peripheral lipid levels on the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient populations and exploring whether it can serve as a biomarker for broadening precise selection of individuals benefiting from immunotherapy.
Methods: We retrospectively collected clinical data from 201 cases of NSCLC patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. The clinical information included biochemical indicators like total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). We utilized machine learning algorithms and Cox proportional hazards regression models to investigate independent predictors for both short-term and long-term efficacy of immunotherapy. Additionally, we concurrently developed a survival prediction model. Analyzing the Genes of Patients with Treatment Differences to Uncover Mechanisms
Results: Correlation analysis revealed a significant positive association between HDL and ORR, DCR, and PFS. T-test results indicated that the high-HDL group exhibited higher DCR (81.97% vs. 45.57%) and ORR (61.48% vs. 16.46%). Kruskal-Wallis test showed that the high-HDL group had a longer median PFS (11 months vs. 6 months). Utilizing six machine learning algorithms, we constructed models to predict disease relief and stability. The model built using the random forest algorithm demonstrated superior performance, with AUC values of 0.858 and 0.802. Furthermore, both univariate and multivariate Cox analyses identified HDL and LDL as independent risk factors for predicting PFS. In patients with poor immunotherapy response, there is upregulation of BCL2L11, AKT1, and LMNA expression.
Conclusion: HDL and LDL are independent factors influencing the survival prognosis of NSCLC patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. HDL is expected to become new biomarkers for predicting the immunotherapy efficacy in patients with NSCLC. In patients with poor immunotherapy response, upregulation of the LMNA gene leads to apoptosis resistance and abnormal lipid metabolism.
1 Introduction
As programmed cell-death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) targeted immunotherapy gradually becomes a predominant treatment modality, particularly for non-driver gene mutation patients, it significantly improves the survival rates of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. However, there remains a subset of individuals exhibiting poor treatment response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Currently, indicators such as Expression of PD-L1 protein (1–3), tumor mutation burden (TMB) (4) and microsatellite instability (MSI) (5) play a role in predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy. Nevertheless, these assessments have drawbacks such as high laboratory requirements and prolonged testing times, leading to limited clinical application. Peripheral blood samples, on the other hand, offer convenient sampling without invasive procedures, reflecting host immune status information, making them more accessible clinical indicators for predicting and dynamically monitoring the efficacy of immunotherapy in NSCLC.
Some studies suggest a connection between lipid metabolism alterations and the development of tumors. A cohort study indicates that NSCLC patients commonly exhibit blood lipid abnormalities, with a particularly close association between reduced levels of HDL and a higher risk of NSCLC (6). Research also indicates that compared to normal cells, tumor cells can synthesize more cholesterol not only to sustain their active proliferation but also to maintain the stability of the PD-L1 receptor expressed on tumor cells, which requires cholesterol (7, 8). Meanwhile, HDL and LDL primarily influence the occurrence and development of cancer through mechanisms such as modulating cholesterol transport and regulating inflammatory responses (9). Additionally, several clinical studies suggest the effectiveness of statin drugs in adjunct cancer treatment (10, 11). However, the value of blood lipid levels in the immune prognosis of NSCLC is not yet clear.
This study aims to explore the impact of blood lipid levels on the efficacy and prognosis of locally advanced and advanced NSCLC patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. It aims to construct a clinical prediction model to provide more refined screening indicators for the individualized treatment of NSCLC patients.
2 Material and methods
2.1 Patients
We retrospectively analyzed 201 advanced NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy at Beijing Friendship Hospital Cancer Center, Capital Medical University. All patients met the following criteria: 1. Pathologically confirmed diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer; 2. Staged as III-IV according to the 8th edition TNM staging by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, including untreated patients and those with recurrent disease after previous surgery; 3. Completed four or more cycles of monotherapy or combination therapy with anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies (mAb) and had clear efficacy assessment results; 4. Did not require additional lipid-lowering medications for diagnosed conditions during immunotherapy; 5. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) score of 0-1; 6. No EGFR mutation, ALK translocation, or ROS1 fusion; 7. No immunosuppressive drug treatment required for other diseases. The study obtained approval from the Institutional Review Board, and due to the retrospective nature of the study, the need for informed consent was waived.
Clinical characteristics of all patients were collected, including age, gender, histology, prior lines of therapy, treatment type, tumor cell proportion score (TPS), Ki-67 protein level, liver metastasis, bone metastasis, brain metastasis, smoking history, diabetes history, statin drug usage history, body mass index (BMI), as well as fasting serum total cholesterol, serum triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, and low-density lipoprotein within the first three natural days before the initial treatment. Patients were assessed for objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and progression-free survival (PFS). Tumor response was evaluated using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1. All patients underwent follow-up until death or data lock on August 1, 2023.
2.2 Statistical analysis
All data analysis and graphic plotting were conducted using R software version 4.1.2. ORR is defined as the ratio of the number of patients achieving complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) after four treatment cycles to the total number of patients. DCR is defined as the ratio of the number of patients achieving CR, PR, or stable disease (SD) after four treatment cycles to the total number of patients. PFS is defined as the time from the initiation of immune therapy to disease progression or death for any reason. Patients without events were censored at the last follow-up. Survival curves were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and comparisons were made using the log-rank test. The chi-square test was employed to analyze differences in ORR and DCR between groups. Feature selection was performed using the random forest algorithm, followed by the construction of predictive models using k-nearest neighbors (KNN), backpropagation (BP) algorithm, support vector machine (SVM) algorithm, decision tree algorithm, random forest algorithm, and Xgboosting algorithm. The Cox regression model was utilized to investigate the correlation between various variables and the survival endpoint, incorporating factors with univariate p-values < 0.05 into multivariate analysis. Statistical tests were two-sided, and p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
2.3 Gene data resource and analysis
The datasets GSE136961 were downloaded from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/. GSEA were carried out to explore the biological functions in NSCLC patients receiving immunotherapy. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) gene sets were obtained from the official GSEA website (https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/downloads.jsp).
3 Results
3.1 Demographic characteristics
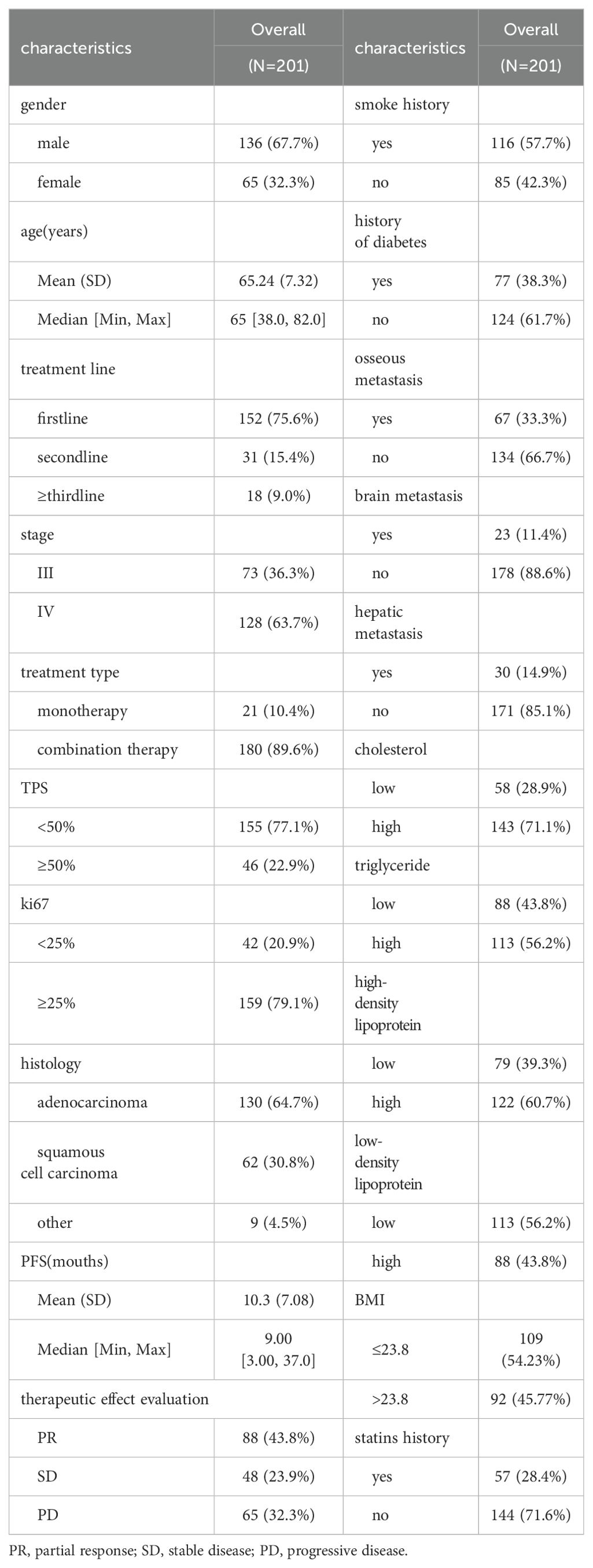
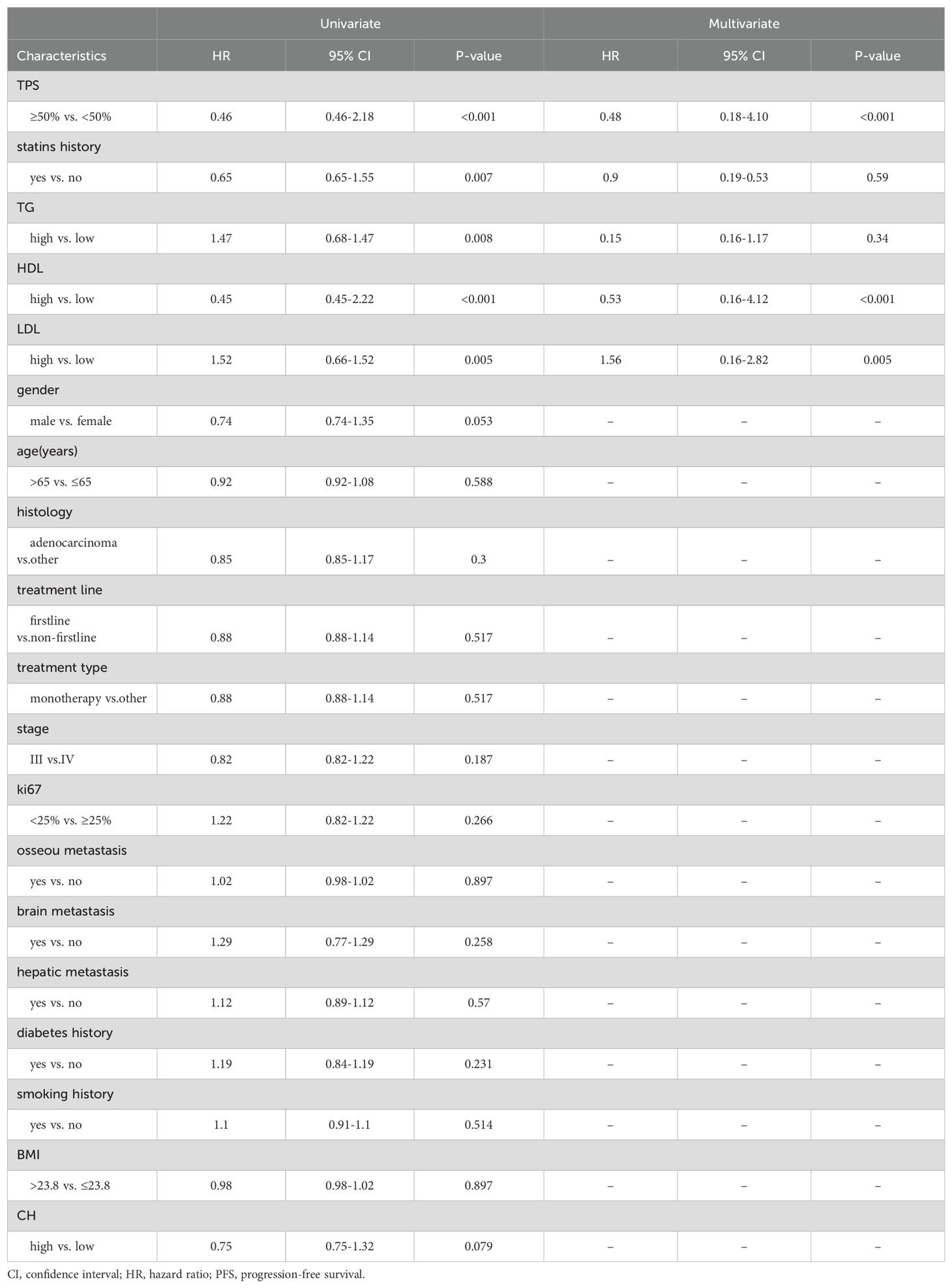
This study included a total of 201 patients (Table 1), with 136 males and 65 females. The age ranged from 38 to 82 years, with an average age of 65 years and a median age of 65 years. Among the 201 patients, adenocarcinoma accounted for the majority with 130 cases, followed by squamous cell carcinoma with 62 cases. Other histological types included 6 cases of non-small cell lung cancer with unclear histology, 2 cases of adenosquamous carcinoma, and 1 case of large cell carcinoma. Tumor PD-L1 expression was negative (TPS < 50%) in 155 patients and positive (TPS ≥ 50%) in 46 patients. Among the patients who received immune therapy, 57 had a regular history of statin drug usage before immunotherapy. Due to differences in blood lipid levels between tumor patients and the normal population, normal indicators were not selected as grouping criteria. In this study, we employed an iterative algorithm to establish a survival function related to progression-free survival (PFS). We determined the optimal cutoff points for cholesterol (CH), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) based on the maximum statistical differences (Figures 1A–D), dividing the patients into high-level and low-level groups. The optimal cutoff values were 3.43 mmol/L for CH, 1.41 mmol/L for TG, 0.94 mmol/L for HDL, and 1.04 mmol/L for LDL.
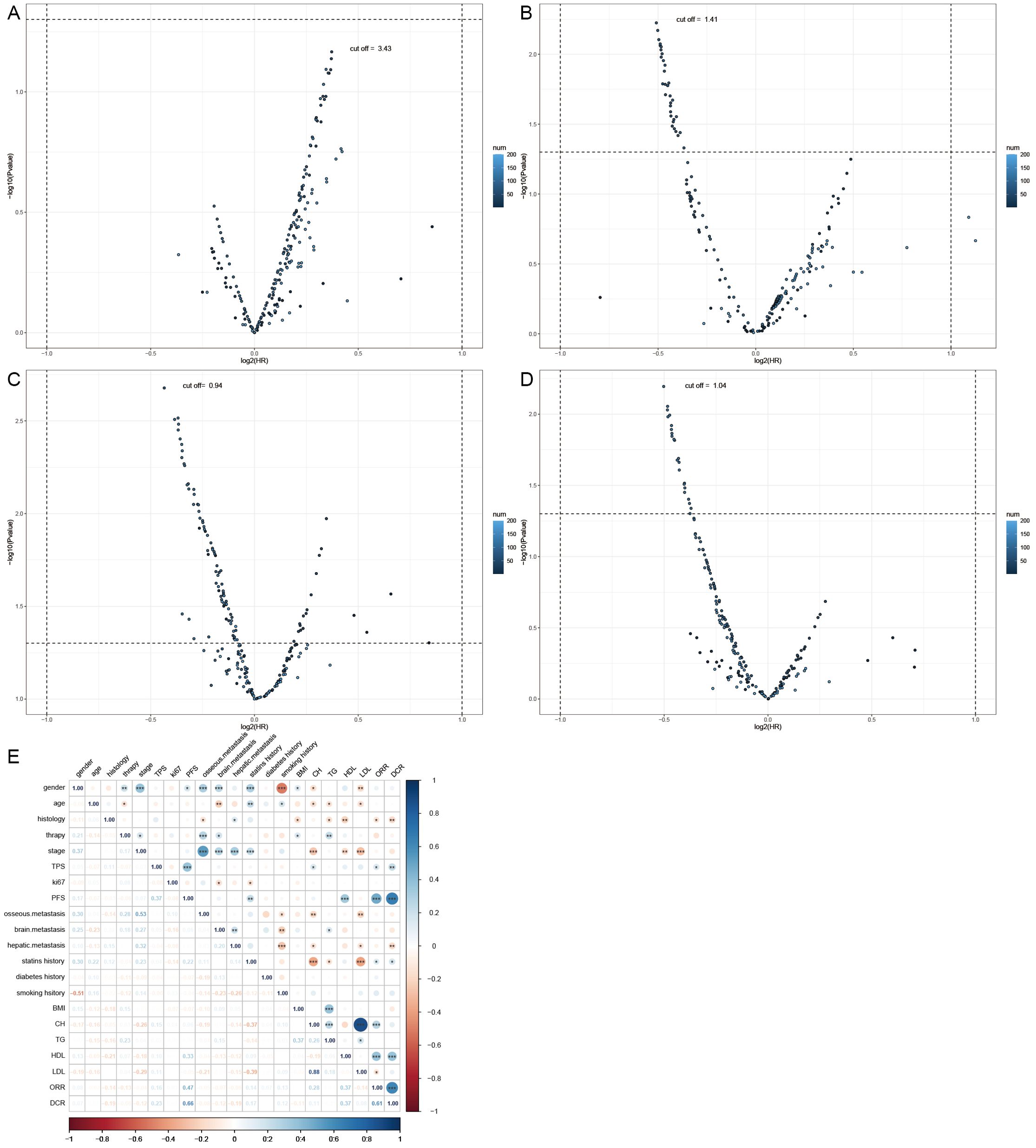
Figure 1. Demographic characteristics. (A) Calculating the optimal cutoff points using the iterative algorithm, for are 3.43 mmol/L, (B) for TG are 1.41 mmol/L, (C) for HDL are 0.94 mmol/L, (D) and for LDL are 1.04 mmol/L. (E) Calculate the correlation between demographic features and plot them as a bubble chart, bule indicates positive correlation, while red indicates negative correlation. PFS, progression-free survival; ORR, objective response rate; DCR, disease control rate *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Correlation analyses of baseline data were conducted (Figure 1E), revealing a positive correlation of HDL levels with objective response rate (ORR) (0.37), disease control rate (DCR) (0.37), and PFS (0.33). Cholesterol levels also showed a positive correlation with ORR (0.28). Similarly, the history of statin drug usage was a positive factor for ORR (0.14), DCR (0.17), and PFS (0.22). LDL levels were a negative factor for ORR (-0.14). Additionally, a strong positive correlation (0.88) was observed between CH levels and LDL levels. Smoking history showed a strong correlation with male patients (0.51), while female patients were more prone to brain (0.25) and bone metastasis (0.3), potentially associated with longer PFS (0.17).
3.2 Short-term treatment response
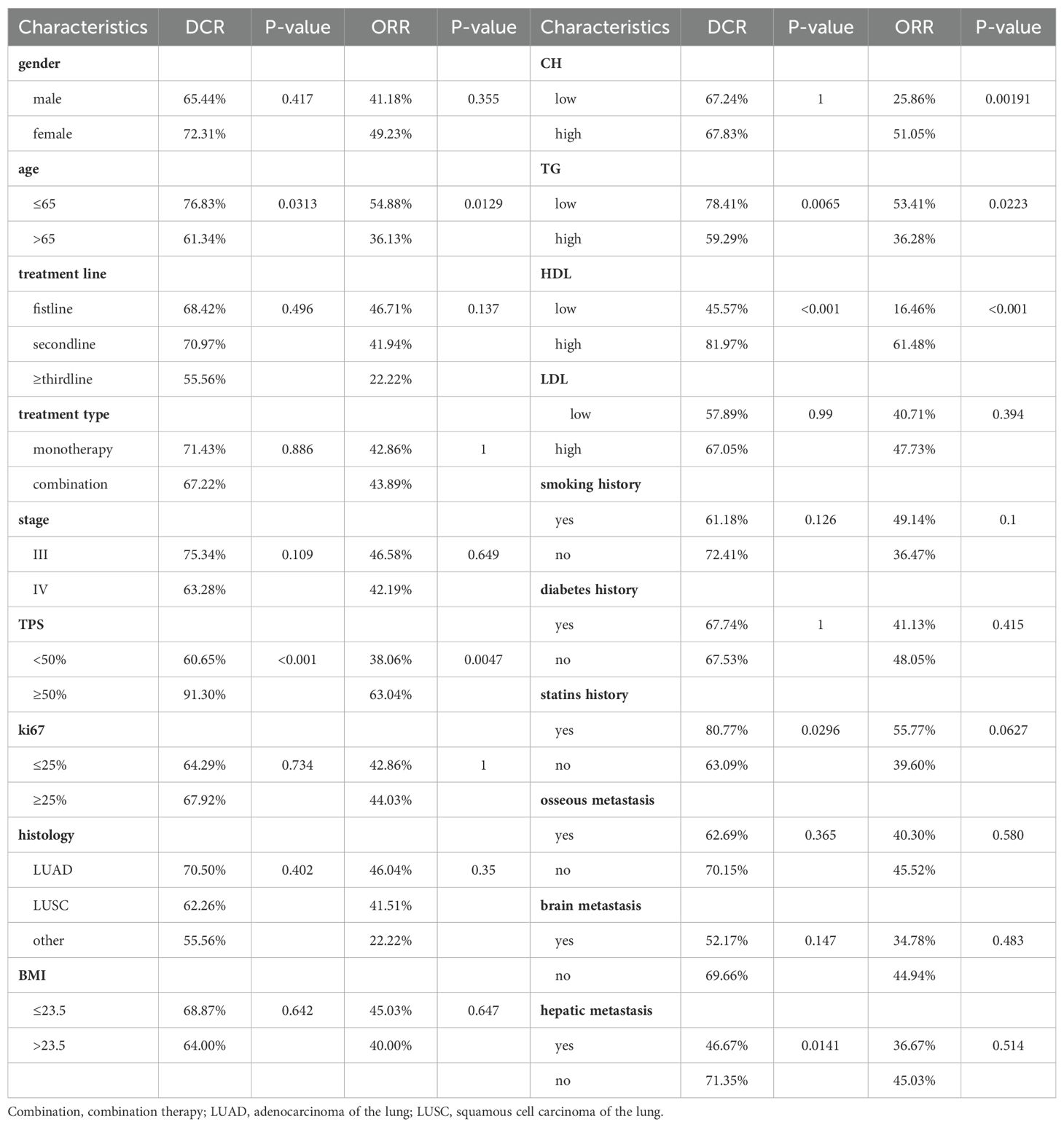
After the fourth treatment cycle, we evaluated target lesions in patients according to RECIST1.1 criteria and calculated ORR and DCR for each group separately (Table 2). We used Chi-square tests to analyze differences between groups, applying Fisher’s test when n<5. The results show that the high-cholesterol group achieved a superior ORR (51.05% vs. 25.86%). The low triglyceride group exhibited higher DCR (78.41% vs. 59.29%) and ORR (53.41% vs. 36.28%) compared to the high-level group. Similarly, the high HDL group significantly improved both DCR (81.97% vs. 45.57%) and ORR (61.48% vs. 16.46%), while LDL showed no significant impact on DCR and ORR. The group with a history of statin drug usage had a higher DCR (80.77% vs. 63.09%) compared to the group without a history, but it had no significant impact on ORR. Consistent with other studies, higher TPS indicated a higher treatment response rate, and younger individuals had better DCR and ORR. Additionally, patients without liver metastasis had a higher DCR (71.35% vs. 46.67%) than the group with liver metastasis.
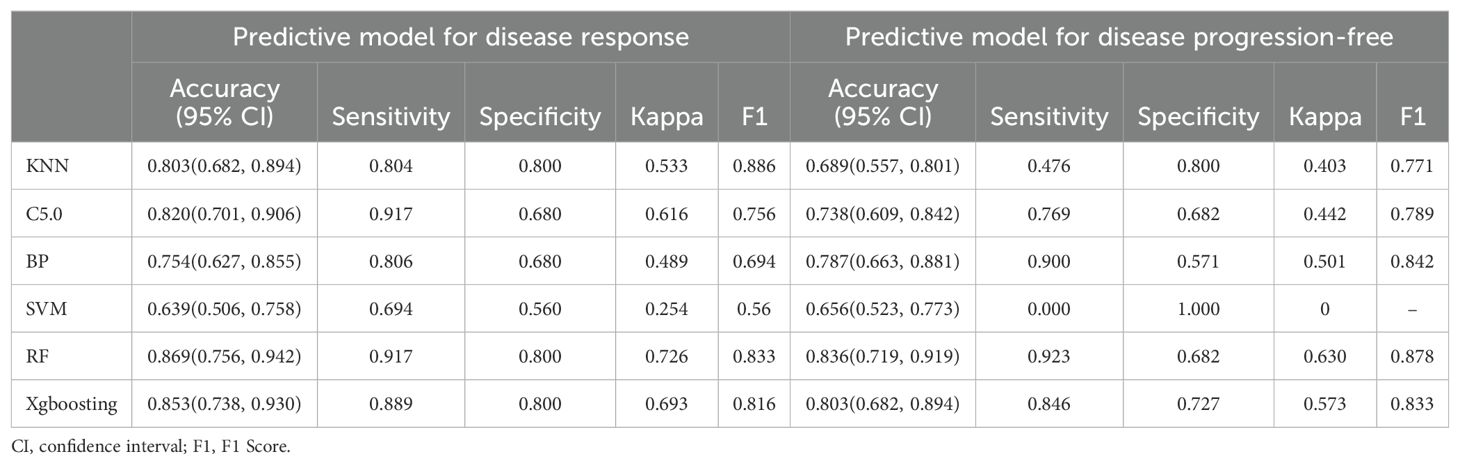
DCR and ORR, as short-term indicators for immune therapy assessment, demonstrated correlation with blood lipid levels. Therefore, we constructed corresponding predictive models using machine learning algorithms. Initially, the Boruta algorithm was employed for feature selection, identifying significant factors for ORR (Figure 2A): HDL, CH, LDL, age, TG, Ki-67, statins history, BMI, TPS, smoking history, gender, stage, osseous metastasis, histology. Similarly, significant factors for DCR (Figure 2B) included HDL, CH, TPS, LDL, TG, BMI, age, Ki-67, stage, hepatic metastasis, brain metastasis. After feature selection, patients were divided into training and validation sets in a 7:3 ratio, and predictive models were constructed using random forest, BP algorithm, SVM algorithm, decision tree algorithm, Xgboosting algorithm, and KNN algorithm, and the performance of each model was evaluated (Figures 2C, D). The random forest model demonstrated the best performance in predicting ORR (Figure 2E), with an AUC of 0.858, Kappa of 0.726, and F1 of 0.833 (Table 3). In the prediction model for DCR, the random forest model also performed optimally (Figure 2F), achieving an AUC of 0.802, Kappa of 0.630, and F1 of 0.878 (Table 3).
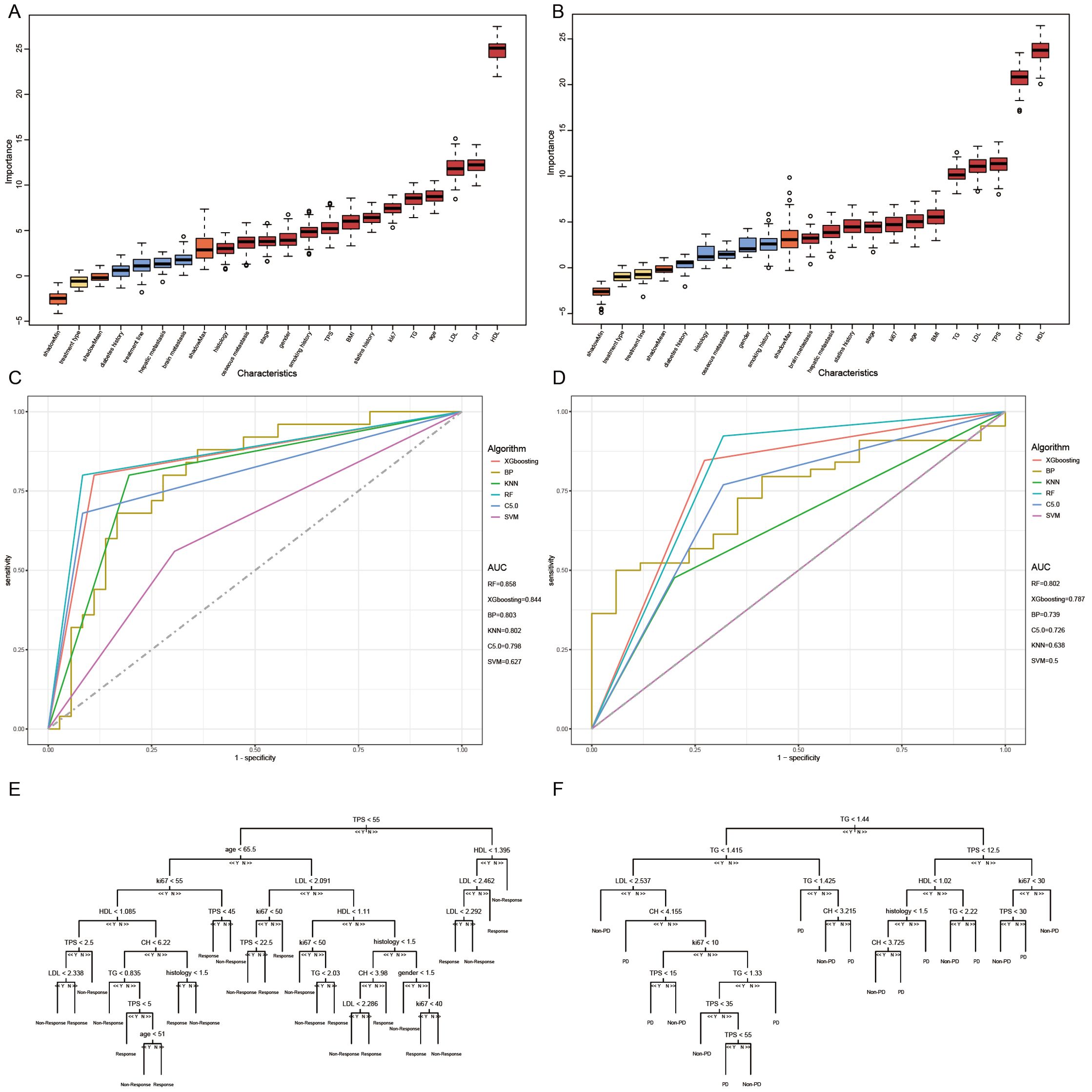
Figure 2. Short-term efficacy prediction model. (A) We employed the Boruta algorithm to calculate the importance of each feature in influencing disease remission, ranking them from low to high. Red indicates that the feature significantly affects remission, blue suggests some impact but lacks statistical significance, and yellow denotes no influence. HDL was identified as the most influential factor on disease response, (B) while both HDL and CH had the greatest impact on preventing disease progression. (C) We plotted ROC curves for six machine learning models, and the random forest algorithm exhibited the best performance in predicting disease response, with an AUC of 0.858. (D) In the model predicting disease progression, the random forest algorithm demonstrated the best performance, achieving an AUC of 0.802. (E) Flowchart for predicting whether patients can achieve disease response after four cycles of treatment. (F) Flowchart for predicting whether patients can prevent disease progression after four cycles of treatment.
We can conclude that the blood lipid levels of patients have a certain impact on the efficacy of immune therapy, especially HDL, which provides indications for short-term disease relief and stability. Using blood lipid level data can also construct excellent efficacy prediction models.
3.3 Long-term treatment response
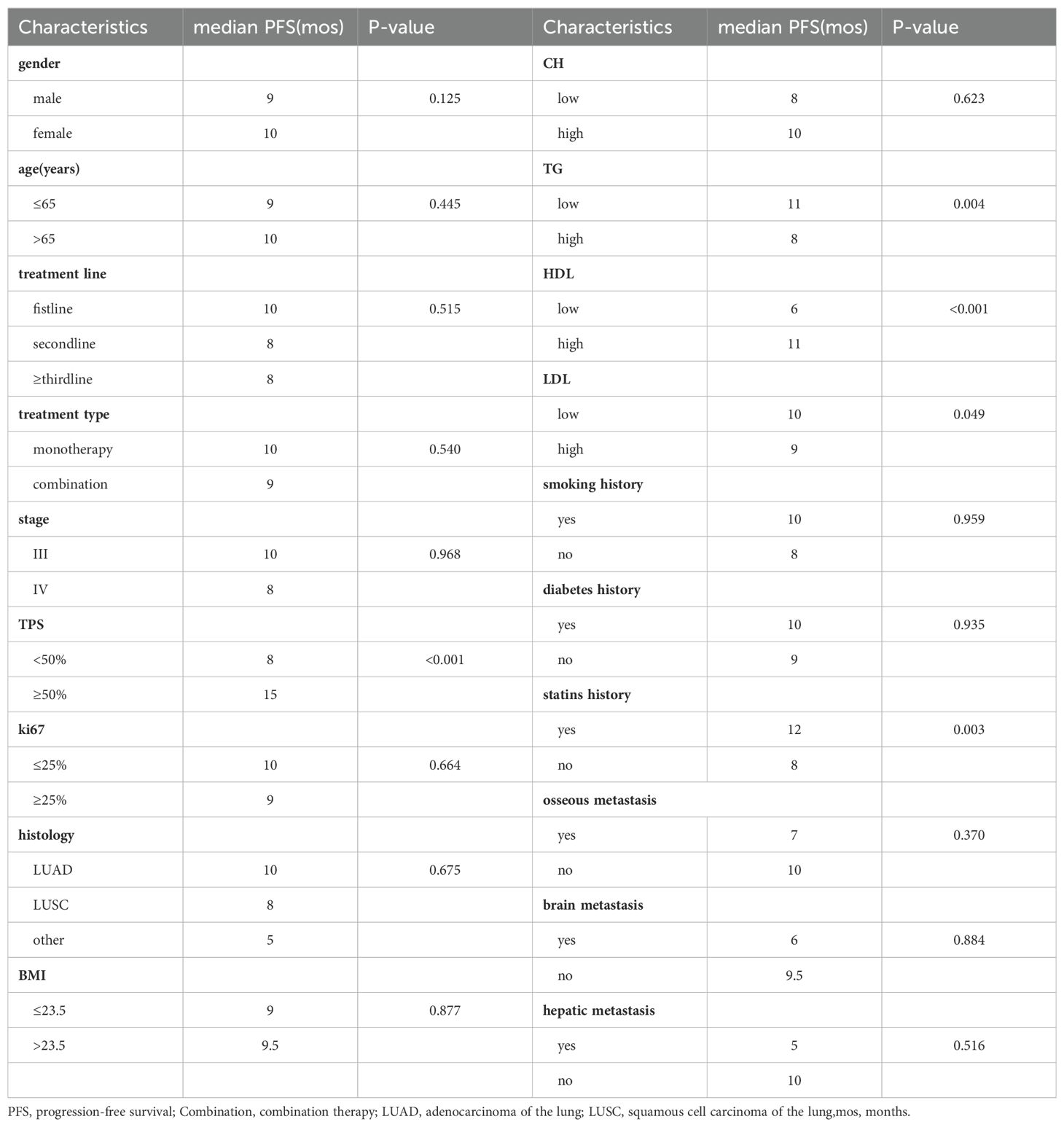
To elucidate the long-term impact of blood lipid levels on the efficacy of immune therapy, we first analyzed the differences in median PFS under clinical feature grouping using Kruskal-Wallis test. The results showed (Table 4) that the high-HDL group (11 months vs. 6 months), high-TPS group (15 months vs. 8 months), low-TG group (11 months vs. 8 months), low-LDL group (10 months vs. 9 months), and statin drug usage history group (12 months vs. 8 months) had longer PFS.
Subsequently, we conducted univariate COX analysis based on PFS for clinical features (Table 5). Factors with statistically significant (P<0.05) and clinically meaningful results, such as HDL, LDL, TG, TPS, and statin drug usage history, were included in the multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model analysis (Table 5). The results indicated that TPS, HDL levels, and LDL levels were independent prognostic factors for PFS in patients with locally advanced and advanced NSCLC undergoing immune therapy (Figures 3A, B).
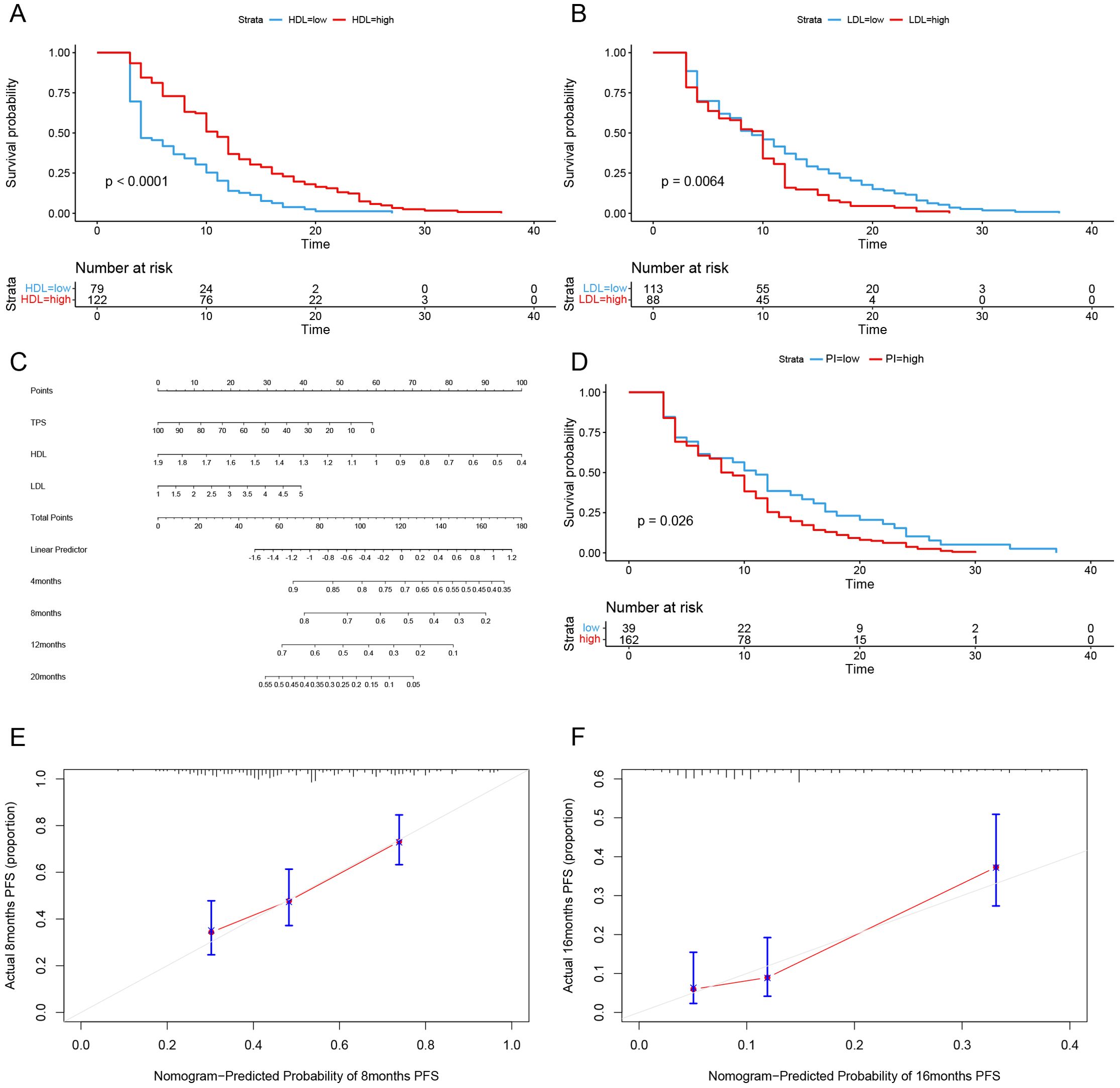
Figure 3. Long-term efficacy prediction model. (A) After Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis, HDL was identified as an independent risk factor for predicting progression-free survival (PFS). Grouped by cutoff points (0.94 mmol/L), Kaplan-Meier curves were plotted, revealing a longer survival period in the high-level group compared to the low-level group (p < 0.0001). (B) After Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis, LDL was identified as an independent risk factor for predicting progression-free survival (PFS). Grouped by cutoff points(1.04 mmol/L), Kaplan-Meier curves were plotted, revealing a longer survival period in the high-level group compared to the low-level group (p < 0.0064). (C) Based on the multivariate Cox regression analysis, a Nomogram plot was generated. (D) Grouped by cutoff points (0.2004558) of PI, Kaplan-Meier curves were plotted, revealing a longer survival period in the low PI compared to the high PI group (p=0.026). (E) The calibration curve of the model predicting at the 8th month. (F) The calibration curve of the model predicting at the 16th month.
Based on the multivariate Cox regression model, probability prediction line charts for PFS at 4 months, 12 months, and 20 months were plotted (Figure 3C). The total score was obtained by adding the scores corresponding to each influencing factor, allowing estimation of PFS probabilities for patients at 4, 8, 12, and 20 months. The C-index of model is 0.71, and calibration curves for PFS probability prediction models at 8 months and 16 months were plotted (Figures 3E, F). According to the model formula, patients’ prognostic index (PI) was calculated, and the population was divided into high-risk and low-risk groups based on the optimal cutoff value (0.2004558) for PI for survival analysis (Figure 3D). The results showed a statistically significant difference (P=0.026), confirming that this model can significantly differentiate the survival benefits of NSCLC patients clinically receiving immune therapy.
3.4 Exploration of gene mechanisms
We observed that reduced HDL levels in NSCLC patients might be associated with poor response to immunotherapy. To elucidate the mechanisms underlying this clinical phenomenon, we conducted further research. Initially, we obtained data from the GSE136961 dataset in the GEO database, which includes data from 10 patients regularly undergoing immunotherapy. Based on their response to immunotherapy, patients were divided into the Durable Clinical Benefit (DCB) group and the Non-Durable Benefit (NDB) group. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) comparing gene functions between these two groups (Figure 4A) revealed that genes in the NDB group were significantly enriched in the LIPASE INHIBITOR ACTIVITY and TRIGLYCERIDE RICH PLASMA LIPOPROTEIN PARTICLE, whereas genes in the DCB group were enriched in the NEGATIVE REGULATION OF LIPID CATABOLIC PROCESS. This suggests that the poor response to immunotherapy in NSCLC patients may be associated with upregulation of genes such as LPL and the ANX family, leading to dysregulation of lipid metabolism and consequently reduced HDL levels.
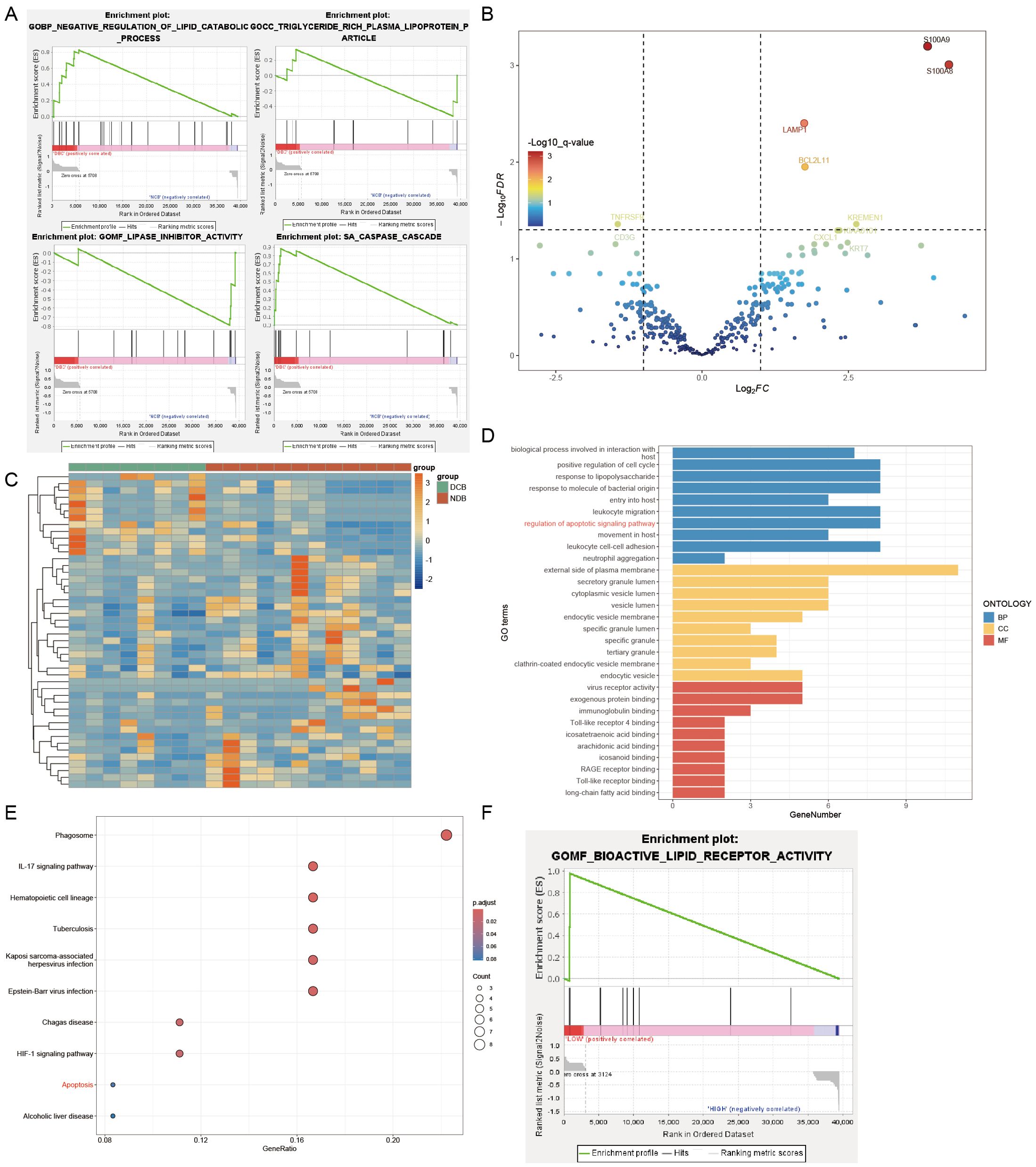
Figure 4. Genesets analysis. (A) DCB group enriched in the NEGATIVE REGULATION OF LIPID CATABOLIC PROCESS and CASPASE CASCADE. NDB group enriched in the LIPASE INHIBITOR ACTIVITY and TRIGLYCERIDE RICH PLASMA LIPOPROTEIN PARTICLE. (B) Part of the differentially expressed genes were visualized in a volcano plot. (C) Differentially expressed genes were visualized in a heatmap. (D) GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes. (E) Kegg enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes. (F) GSEA analysis: the high LMNA expression group enriched in the BIOACTIVE LIPID RECEPTOR ACTIVITY.
Furthermore, we observed silencing of the CASPASE CASCADE in the NDB group (Figure 4A), indicating potential resistance to apoptosis in these tumor cells, which may contribute to impaired immunotherapy efficacy. To investigate further, we analyzed the GSE136961 dataset, which includes expression information of 395 immune-related genes from 20 patients, obtained through the Oncomine Immune Response Research Assay. Using the R package DESeq2, we assessed gene expression differences between the two groups (Figures 4B, C) and identified 46 differentially expressed genes (Table 6), with 12 genes downregulated and 34 genes upregulated.
Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (Kegg) enrichment analyses of these 46 genes (Figures 4D, E) showed that S100A9, S100A8, BCL2L11, BRCA1, PTGS2, RB1, AKT1, and LMNA were enriched in the regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway function, while BCL2L11, AKT1, and LMNA were significantly enriched in the Apoptosis pathway. These results indicate that upregulation of BCL2L11, AKT1, and LMNA in the NDB group may collectively point to a function of inhibiting apoptosis, which could be a key factor in the poor response of these patients to immunotherapy.
To further investigate the relationship between tumor cell apoptosis resistance and HDL levels, we divided the patients in the GSE136961 dataset into high-expression and low-expression groups based on LMNA expression levels. GSEA analysis revealed that the high LMNA expression group showed significant resistance to the BIOACTIVE LIPID RECEPTOR ACTIVITY (Figure 4F).
Therefore, when tumor cells resist apoptosis signals by upregulating BCL2L11, AKT1, and LMNA genes, they simultaneously exhibit reduced responsiveness to lipid receptor activity. This change subsequently affects the concentration of HDL in the plasma. We believe that this mechanism may explain the observed reduction in HDL levels in patients with high LMNA expression, or in other words, NSCLC patients with poor immune therapy outcomes.
4 Discussion
In this study, we collected blood lipid data from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) before undergoing immunotherapy and analyzed its relationship with treatment efficacy. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) stood out, demonstrating remarkable effectiveness in promoting disease remission and long-term stability. We constructed predictive models for short-term disease relief and disease stability, with blood lipid data playing a crucial role. This confirms the potential of HDL as a novel biomarker for predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC. Additionally, we explored the potential mechanisms behind these two phenomena. The LMNA gene appears to link the two, assisting tumor cells in resisting apoptosis while simultaneously impeding the process of lipid transfer from the tumor cells to the outside.
After four cycles of treatment, patients with low HDL levels lacked responsiveness to immunotherapy, with lower DCR, ORR, and PFS compared to patients with normal HDL levels. Although HDL may not directly participate in the tumor cells’ response to the immune system, our study suggests that it can act as an indicator, with the LMNA gene being the culprit behind this phenomenon. Our research found that patients with poor immunotherapy outcomes generally exhibited upregulation of the BCL2L11, AKT1, and LMNA genes. BCL2L11 and AKT1 have been confirmed in multiple studies to resist apoptotic signals, serving as key players in tumor cells’ defense against the immune system (12, 13). The role of the lamin A/C protein encoded by the LMNA gene in the apoptosis process remains under investigation. Previous research suggests that as a major component of the nuclear lamina, lamin A/C is targeted during apoptosis. However, some studies propose that tumor cells may resist the transmission and activation of apoptotic signals within the nucleus by increasing the content of nuclear lamina proteins (14).
Although previous studies have indicated a significant role of cholesterol (CH) in the development of lung cancer, our research found its correlation with the efficacy of immunotherapy to be less significant. This may be attributed to its dual role. For instance, increasing intracellular free cholesterol can enhance the effector functions and proliferation of CD8+ T cells (15), but, conversely, the elevated cholesterol concentration in the tumor microenvironment can lead to the exhaustion of CD8+ T cells (16). Accumulation of cholesterol in macrophages can halt the apoptosis of tumor-infiltrating macrophages, preventing the transformation from M2 to M1 macrophages. Knocking out the ABCG1 gene responsible for this transport pathway in mice resulted in excellent anti-tumor characteristics (17). Moreover, lipid rafts primarily composed of cholesterol are obligatory for multiple signaling pathways involved in cancer occurrence and development (18). The contradictory nature of these effects hinders serum cholesterol from becoming a robust predictive indicator for immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer.
Although low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and triglycerides (TG) did not exhibit as pronounced predictive capabilities as HDL, they still held certain value. LDL has been found to regulate tumor growth and migration through signaling pathways in various cancers, and LDL receptor (LDLR) expression is upregulated in many cancers, primarily directing toward the significant increase in cholesterol demand due to metabolic reprogramming in tumor cells (19–21). Some studies have indicated that TG can lead to the dysfunction of the immune surveillance system composed of natural killer (NK) cells (22). Additionally, in lung cancer patients, a significant decrease in peripheral blood dendritic cell (DC) count and intracellular lipid accumulation, mainly TG, leads to reduced DC antigen presentation function (23). However, it is essential to note that LDL and TG may not be as prominent in prediction because LDL levels are often influenced by fluctuations in other lipid levels, compromising their independence. Moreover, the role of TG may be more accentuated in cardiovascular diseases, interfering with the prediction of tumor treatment efficacy.
In recent years, statin drugs have gained recognition for their ability to combat tumors, showing excellent anti-cancer performance in both in vitro and clinical trials (24, 25). Statins not only inhibit abnormal cholesterol uptake and synthesis by tumor cells but also promote tumor cell apoptosis through the mechanism mediated by geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) (26). Furthermore, statins can inhibit tumor metastasis by disrupting the geranylgeranylation and farnesylation of small GTPases (27). However, in this study, we only observed a clear positive impact of statin drugs on short-term efficacy, and their status as independent prognostic factors for long-term survival was not confirmed. This could be attributed to the limitations of our study, including a retrospective nature and a relatively small sample size. Some patients had follow-up periods exceeding one year, during which detailed collection of drug dosage adjustments or discontinuations was not conducted.
Therefore, our findings align with the perspective that blood lipid levels can serve as valuable indicators for predicting the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. HDL levels reflect the expression of the LMNA gene in tumor tissues, which in turn indicates the extent of apoptosis resistance in tumor cells. Additionally, we developed predictive models using machine learning algorithms, demonstrating the feasibility of incorporating blood lipid levels into clinical prediction models. We explored the impact of blood lipid levels on long-term treatment response, revealing that groups with high HDL, low LDL, and a history of statin use have a longer progression-free survival (PFS). Multivariate Cox regression analysis identified tumor proportion score (TPS), HDL levels, and LDL levels as independent prognostic factors for PFS. The constructed predictive model showed significant discriminative power in categorizing patients into high-risk and low-risk groups.
However, due to the retrospective nature of this study and the relatively small sample size, these conclusions lack generalizability. Additionally, the absence of a validation cohort necessitates external validation in larger cohorts to confirm the robustness of the predictive models. The underlying mechanisms of the observed correlations between blood lipid levels and treatment response require further in vivo and in vitro investigation.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Bioethics Committee, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from a by- product of routine care or industry. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. BC: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation Program (grant no.7222032) and the National Natural Science Foundation of Chain (grant no.82173056).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR, Steins M, Ready NE, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:1627–39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1507643
2. Horn L, Spigel DR, Vokes EE, Holgado E, Ready N, Steins M, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: two-year outcomes from two randomized, open-label, phase III trials (CheckMate 017 and checkMate 057). J Clin Oncol. (2017) 35:3924–33. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.3062
3. Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2017) 389:255–65. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X
4. Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, Kvistborg P, Makarov V, Havel JJ, et al. Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science. (2015) 348:124–8. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa1348
5. Hause RJ, Pritchard CC, Shendure J, Salipante SJ. Classification and characterization of microsatellite instability across 18 cancer types. Nat Med. (2016) 22:1342–50. doi: 10.1038/nm.4191
6. Hao B, Yu M, Sang C, Bi B, Chen J. Dyslipidemia and non-small cell lung cancer risk in Chinese population: a case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. (2018) 17:278. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0925-z
7. Bian X, Liu R, Meng Y, Xing D, Xu D, Lu Z. Lipid metabolism and cancer. J Exp Med. (2021) 218:e20201606. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201606
8. Wang Q, Cao Y, Shen L, Xiao T, Cao R, Wei S, et al. Regulation of PD-L1 through direct binding of cholesterol to CRAC motifs. Sci Adv. (2022) 8(34):eabq4722. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq4722
9. Revilla G, Cedó L, Tondo M, Moral A, Pérez JI, Corcoy R, et al. HDL and endocrine-related cancer: From pathogenic mechanisms to therapies. Semin Cancer Biol. (2021) 73:134–57. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.11.012
10. Lin JJ, Ezer N, Sigel K, Mhango G, Wisnivesky JP. The effect of statins on survival in patients with stage IV lung cancer. Lung Cancer. (2016) 99:137–42. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.07.006
11. Huang WY, Li CH, Lin CL, Liang JA. Long-term statin use in patients with lung cancer and dyslipidemia reduces the risk of death. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:42208–15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i27
12. Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, González-Barón M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. (2004) 30:193–204. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2003.07.007
13. Kashiwagi H, McDunn JE, Goedegebuure PS, Gaffney MC, Chang K, Trinkaus K, et al. TAT-Bim induces extensive apoptosis in cancer cells. Ann Surg Oncol. (2007) 14:1763–71. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9298-z
14. Lindenboim L, Zohar H, Worman HJ, Stein R. The nuclear envelope: target and mediator of the apoptotic process. Cell Death Discovery. (2020) 6:29. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-0256-5
15. Yang W, Bai Y, Xiong Y, et al. Potentiating the antitumour response of CD8+ T cells by modulating cholesterol metabolism. Nature. (2016) 531:651–5. doi: 10.1038/nature17412
16. Ma X, Bi E, Lu Y, Su P, Huang C, Liu L, et al. Cholesterol induces CD8+ T cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. (2019) 30:143–156.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.04.002
17. Sag D, Cekic C, Wu R, Linden J, Hedrick CC. The cholesterol transporter ABCG1 links cholesterol homeostasis and tumour immunity. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:6354. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7354
18. Mollinedo F, Gajate C. Lipid rafts as major platforms for signaling regulation in cancer. Adv Biol Regul. (2015) 57:130–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.10.003
19. dos Santos CR, Domingues G, Matias I, Matos J, Fonseca I, de Almeida JM, et al. LDL-cholesterol signaling induces breast cancer proliferation and invasion. Lipids Health Dis. (2014) 13:16. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-13-16
20. Naito S, Makhov P, Astsaturov I, Golovine K, Tulin A, Kutikov A, et al. LDL cholesterol counteracts the antitumour effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors against renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. (2017) 116:1203–7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.77
21. Jung YY, Ko JH, Um JY, Chinnathambi A, Alharbi SA, Sethi G, et al. LDL cholesterol promotes the proliferation of prostate and pancreatic cancer cells by activating the STAT3 pathway. J Cell Physiol. (2021) 236:5253–64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v236.7
22. Sun JC, Beilke JN, Lanier LL. Adaptive immune features of natural killer cells. Nature. (2009) 457:557–61. doi: 10.1038/nature07665
23. Arai R, Soda S, Okutomi T, Morita H, Ohmi F, Funakoshi T, et al. Lipid accumulation in peripheral blood dendritic cells and anticancer immunity in patients with lung cancer. J Immunol Res. (2018) 2018:5708239. doi: 10.1155/2018/5708239
24. Cantini L, Pecci F, Hurkmans DP, Belderbos RA, Lanese A, Copparoni C, et al. High-intensity statins are associated with improved clinical activity of PD-1 inhibitors in Malignant pleural mesothelioma and advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. (2021) 144:41–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.10.031
25. Jiang W, Hu JW, He XR, Jin WL, He XY. Statins: a repurposed drug to fight cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 40:241. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02041-2
26. Göbel A, Zinna VM, Dell'Endice S, Jaschke N, Kuhlmann JD, Wimberger P, et al. Anti-tumor effects of mevalonate pathway inhibition in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:703. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07164-x
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, high-density lipoprotein, enrich analysis, machine learning, LMNA
Citation: Li J, Wang J and Cao B (2024) Exploring the impact of HDL and LMNA gene expression on immunotherapy outcomes in NSCLC: a comprehensive analysis using clinical & gene data. Front. Oncol. 14:1448966. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1448966
Received: 14 June 2024; Accepted: 02 September 2024;
Published: 24 September 2024.
Edited by:
Daniel Heudobler, University Hospital Regensburg, GermanyReviewed by:
Artuo Simoni-Nieves, Foundation for Liver Research, United KingdomChan-Juan Zhang, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2024 Li, Wang and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bangwei Cao, b25jb2xvZ3lAY2NtdS5lZHUuY24=
 Jingru Li
Jingru Li Jingting Wang
Jingting Wang Bangwei Cao
Bangwei Cao