- 1The Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming Medical University, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Yunnan Tumor Hospital, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, Yunnan University, Kunming, Yunnan, China
Lung cancer is the most common malignant tumor in China. Its incidence and mortality rate increase year by year. In the synthesis treatment of lung cancer, radiotherapy (RT) plays a vital role, and radiation-induced lung injury(RILI) has become the major limiting factor in prescription dose escalation. Conventional RT is designed to minimize radiation exposure to healthy lungs without considering the inhomogeneity of lung function, which is significantly non-uniform in most patients. In accordance with the functional and structural heterogeneity of lung tissue, functional lung avoidance RT (FLART) can reduce radiation exposure to functional lung (FL), thus reducing RILI. Meanwhile, a dose-function histogram (DFH) was proposed to describe the dose parameters of the optimized image-guided RT plan. This paper reviews lung function imaging for lung cancer RT plans. It also reviews the clinical applications of function-guided RT plans and their current problems and research directions to provide better guidance for clinical selection.
1 Introduction
As the most prevalent malignancy worldwide, lung cancer is the main cause of death. Up to 77% of patients require RT during treatment (1). In some patients, RILI is significant. RILI caused by excessive radiation doses to healthy lungs is a limiting factor regarding radiation doses, treatment appropriateness, quality of life following treatment, and the appropriateness of newly introduced adjuvant immunotherapy (2). Modern advanced RT technologies, including intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) (3), volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) (4), stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) (5), and proton radiation therapy (PRT) (6), can meet conformal requirements of target volume and dose limitation requirements of normal tissues. Modern RT techniques aim to minimize the radiation dose to healthy lungs without considering the regional distribution of the lung function. Many lung cancer patients have significant regional differences in lung function due to smoking and chronic lung complications (7), and different parts and functional states respond differently to radiation; Studies have shown that the better the functional status, the more sensitive it is to radiation (8, 9). Functional images obtained with imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (10), computed tomography (CT) (11), and nuclear medicine (12), provide physiological information that can be used in RT planning. Studies have shown that the correlation between radiation pneumonitis (RP) and features calculated from functional images (13, 14) is better than that of conventional dose and volume histogram (DVH) features (15, 16). The traditional DVH algorithm regards the whole structure as a functionally uniform whole, ignoring functional and structural heterogeneity (15). DFH, as the evaluation parameter of functionally guided RT planning, groups the number of each sample point associated with the physiological or functional status. This is done using the dose and ventilation value in each pixel calculated to obtain DFH (13). It is possible to evaluate FLART plans using DFH parameters such as the mean lung function-weighted dose (f-MLD) and function-weighted Vx (fV5, fV10, and fV20) (16–19). DFH was calculated from perfusion (Q) and ventilation (V) values and the dose for each voxel (20–23), where f-MLD is obtained by weighting each dose voxel based on its V or Q value, and fV20 is defined as the percentage of total V or Q contained in the volume receiving a 20 Gy dose (24). As reported by Yamamoto et al. (25, 26), functional image-guided RT plans aim to selectively avoid irradiation of the functional regions of the lung. This reduces the probability of lung toxicity after RT while meeting standard dose limits for critical organs. This review focuses on functional imaging techniques commonly used in the literature. It also focuses on the research progress based on functional image-guided RT plans and some current problems faced. Additionally, some novel RT techniques that can be combined with adaptive radiation therapy (ART) are reviewed for FLART plans.
2 Nuclear medicine image-guided FLART
Lung functional measurements and mapping are used to evaluate lung cancer RT plans. Various lung functional imaging have been studied for lung cancer RT, such as nuclear medicine imaging, including single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) (2, 27, 28) and positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) (17, 29). SPECT and PET/CT can provide lung Q and V information and perform three-dimensional (3D) imaging. Studies recommend the use of lung functional imaging for guiding lung cancer RT (2, 17, 21, 27–29). This is aimed at minimizing the radiation dose in functionally normal lung regions while maintaining the therapeutic dose at the planning target volume (PTV).
2.1 SPECT
SPECT is a recognized functional imaging modality for diagnosing and monitoring lung diseases (30), and SPECT-based Q imaging was the earliest reported form of lung functional imaging (22). SPECT can be used for lung Q- and V-imaging. Radioactive tracers commonly used in SPECT V imaging include gas (133Xe and 81mKr), aerosol (99mTc-DTPA), and solid (99mTc-Technegas) tracers. Radioactive Q tracers commonly employ technetium-99m-labeled macroaggregated albumin (99mTc-MAA) (31– 32).
2.1.1 Lung functional imaging based on SPECT
The imaging quality of V was influenced by the size of the tracer. Patients with potential airway diseases have a higher risk of central and focal peripheral radioactive tracer deposition. As a result, SPECT-based functional imaging most commonly uses Q imaging (33). According to Hoover et al. (21), the area under the curve (AUC) values of DFH parameters weighted by Q were consistently higher than those weighted by V and their corresponding standard DVH parameters. Radioactive Q tracers enter the human body through the veins, circulate with the blood to the vascular bed tissue in the lungs through heart Q, and reflect the Q status of pulmonary blood flow. If a capillary embolism occurred in the lungs, the imaging agent was retained. Lung Q imaging can measure blood circulation in the lungs and is commonly used in clinics to display regional functional information (2). This viewpoint was also supported by previous animal experiments (34). Furthermore, several surgical studies in human patients have shown a reasonable correlation between the percentage of Q lungs resected and the percentage of lung function decline (35, 36). Patients receiving lung RT usually undergo CT and SPECT at the treatment site, and the structure to be evaluated is determined by continuously drawing contours on the CT scan images (22). The 3D images of Q were segmented based on pixel values, with higher pixel values corresponding to higher Q areas in the lungs, thus representing higher functionality (37).
2.1.2 FLART plans based on SPECT Lung functional imaging
SPECT uses radioactively labeled tracers to image lung circulation, where the Q region is equivalent to a normal functioning lung (2). In the evaluation of lung function, Q has shown predictive potential for RILI in lung cancer and other cancers involving lung RT (17, 38–40). An FL contour was created for each patient from the SPECT signal, and these contours were transferred from SPECT to the planning CT using image registration and cropped to depict the total lung volume (2). SPECT images can be integrated into numerical optimization because the count rate is linearly correlated with Q, and the regional function approximates linearly with regional Q (41). Based on published literature, the most commonly used threshold in SPECT functional zoning was 30% (42–46), followed by 50% (17, 47, 48) and 70% (17, 48, 49). Dhami et al. (50) found that 70% of the maximum Q threshold in SPECT imaging was most correlated with RP clinical endpoints. Meanwhile, Hoover et al. (21) weighted the areas exceeding 30% of the maximum Q count in SPECT with FL using dynamic blood flow images. The remaining lung tissue, which accounted for less than 30% of function, was called the non-functional lung (NFL). In the study by Shioyama et al. (47), SPECT adopts functional plans with thresholds of 50% and 90%. Compared to the anatomical plans, the median decrease in f-MLD was 2.2 Gy (17.6-14.5) and 4.2 Gy (16.0-111.8), respectively. Similar results have also been shown in other studies (43, 44, 49). It was possible to correlate pulmonary toxicity with lung function subunit quantities that exceed a certain threshold dose by scaling the volume of individual voxels according to the local SPECT intensity (21). The fusion of the Q image with the original treatment plan generated a baseline DFH, which displayed the relationship between radiation dose and functional region volume. Furthermore, treatment plan optimization could be attained by reducing the average Q-weighted lung dose derived from the histogram of the blood-flow-driven Q function (51). Additionally, Christian et al. (52) proposed minimizing the dose to the FL volume outlined on the Q-map as a planning objective.
2.1.3 Clinical benefits from FLART based on SPECT lung functional imaging
Despite these differences, all studies indicated that FLART could improve lung function protection, at least in a specific subset of patients (e.g., patients with large Q defects) (53). This improvement was usually reflected in reducing certain DVH parameters of the total lung (16, 24, 54) or certain DVH parameters of the FL (15, 16, 25). Earlier studies have shown that Q-weighted optimization-guided RT plans reduce RILI in patients with large Q defects in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (47, 51), but the reduction is less significant in patients with small Q defects. Studies by Farr et al. (55) demonstrated that f-MLD and MLD predicted the AUC of G2+RP at 0.812 and 0.716, respectively, and fV20 and V20 predicted the AUC of G2+RP at 0.792 and 0.716, respectively. Another study has yielded similar results (21).
2.2 PET/CT
With the rapid development of medical imaging technology, the application of PET/CT functional imaging in tumor RT is becoming increasingly widespread. With PET/CT, images are generated that integrate the anatomical structure and functional metabolism of patients under the same conditions, thus providing a more accurate imaging basis for treatment (56, 57). Compared to SPECT, PET has higher resolution and sensitivity, can provide more physiological and functional information, and lowers radioactive drug radiation doses (58–60). It can also be fused with imaging technologies such as CT or MRI to provide more comprehensive diagnostic information and can even be combined with four-dimensional X-ray CT (4DCT) to obtain 4D V and Q information (61–64).
2.2.1 Lung functional imaging based on PET/CT
PET imaging uses the decay mechanism of radioactive isotopes. During the decay process, radioactive isotopes release positrons that undergo annihilation when they encounter electrons, resulting in the production of two gamma rays. These rays are emitted at an 180-degree angle, and PET scanners detect the relative positions of these rays to reconstruct an image of the distribution of radioactive tracers inside the body. Previous studies have mainly used PET tracers, such as 15O, 13N, and 11C for pulmonary physiology research. However, due to their short half-lives, they are gradually being replaced by galligas and gallium-68 macroaggregated albumin (68Ga-MAA) for lung V/Q studies (64–67). PET V imaging was performed first, followed by lung Q imaging, all without moving the patient as in the SPECT V/Q program using aerosols. 68Ga was first used for PET Q imaging in 1976 by Chesler et al. (68), who injected radiolabeled albumin microspheres containing 68Ga into dogs to obtain 3D reconstructed images. In 2010, Kotzerke et al. (69) first described the use of galligas for V-PET imaging. However, owing to the influence of respiratory motion, there may be significant misalignment between PET and CT. PET/CT images can be improved by using the respiratory gate technique (4D PET/CT), which reduces artifacts caused by respiratory motion during imaging (64). In a study by Siva et al. (44), the operational procedure for performing V/Q imaging using 4D PET/CT was described. Patients first inhaled galligas and underwent V imaging with a respiratory tracking system used during the scan. Patients were instructed to breathe freely while simultaneously undergoing a low-dose 4DCT chest acquisition. The scan ranges for both 4D PET and 4DCT include the entire lung field. After the lung V-PET scan, approximately 40 MBq of 68Ga-MAA was intravenously injected, and 4D PET Q imaging was performed in the same field of view. A meta-analysis showed that Q imaging has more potential than V imaging for improving lung dose parameters in RT plans (33).
2.2.2 FLART plans based on PET/CT lung functional imaging
One of the main steps in constructing FLART plans is delineating the FL volume and integrating it into the RT plan as organs at risk (OARs). Currently, the most commonly used method of functional contouring utilizes the relative threshold method based on the maximum pixel value (pmax) and the threshold method relative to the whole lung function (WLF). Based on these two methods, current research has applied V/Q PET/CT to IMRT (17), VMAT (70), and SBRT (71) for FLART studies. Siva and Bucknell et al. (17, 70) used a visual adaptation method with a 70% SUV threshold to divide the lung into high Q lung capacity (HPLung) and high V lung capacity (HVLung). Nevertheless, Siva et al. found HVLung was much smaller than HPLung, so they derived V lung volume (VLung) as an approximation of HPLung volume, as previously reported by Munawar et al. (48). The results showed that the MLD of HPLung decreased by 13.0%, and the V5, V10, and V20 doses decreased by 13.2%, 7.3%, and 3.8%, respectively. The 50% SUV threshold, however, resulted in many small-volume regions throughout the entire lung rather than a continuous volume, limiting RT’s adaptive capabilities. Therefore, the selection of a threshold for FL definition is crucial, and there is currently no clear indicator to define an appropriate threshold. Recently, Pinot et al. (72) developed a relative whole-lung functional threshold segmentation method for PET/CT Q imaging that allowed overlapping contours and was relatively unaffected by hotspots, providing reliable and consistent functional volumes. FL volume was defined as the minimum volume within the anatomical volume that contained 50%, 70%, and 90% of total activity. By prioritizing protection of the FL region, SBRT planning significantly reduced MLD and the percentage of lung volume receiving 5-20 Gy.
2.2.3 Clinical benefits from FLART based on PET/CT lung functional imaging
The evaluation of lung Q is particularly relevant to RILI because the vascular endothelium, like lung cells, is considered to be one of the most sensitive tissues in the lung to radiation (73). Preserving intact lung parenchyma Q during RT may reduce radiation-induced vascular damage and reduce the risk of RP. Previous studies have reported a strong correlation between PET/CT lung function and pulmonary function testing (PFT) parameters (74). Furthermore, PET/CT diagnosed pulmonary embolism (PE) is more accurately than conventional lung V/Q scanning and identifies changes in lung function during RT, allowing timely adjustments to the RT plan (75, 76). A recent study validated the feasibility of using 68Ga-4D-V/Q PET/CT during RT for ART (70). According to the study, FL volume may change during the treatment process, and some patients may benefit from adjusting their RT plans in the fourth week of treatment to preserve the high-Q or high-V lung regions. This study suggests that FL volume changes during the treatment process. Further prospective research is needed to determine which patients can benefit the most from this mid-term adjustment.
2.3 Current problems and research direction of nuclear medicine image-guided FLART
Although lung function requires the Q and V of alveoli, V abnormality is more common than Q abnormality in the lungs (17). V images contained more noise than Q due to significantly reduced lung activity (70). Unless more specific indicators were available, Q imaging could reasonably be used to assess lung function. According to Forghani et al. (77), 25% of stage III lung cancer patients had low consistency on SPECT/CT V/Q. Another study found significant differences in response to V and Q doses in 20–30% of patients (78). Kimura et al. (79) found greater clinical correlation with RP using combined Q/V imaging than when using only V or Q imaging. To promote real lung function, it is necessary to maintain an appropriate ratio between V and Q. There are also potential drawbacks to V/Q SPECT technology. The most significant problem is the difficulty in image registration, especially in the lungs, where patients breathe during SPECT and CT imaging, leading to differences in the two images (22). PET/CT combined with 4DCT improves image quality and registration accuracy (61, 63, 64). In addition, a certain area of the lungs may experience reduced functionality due to proximal vascular obstruction. A lung region might regain functionality after the obstruction is removed during RT (22, 80). In this case, DFH underestimated radiation’s functional impact. Therefore, prospective clinical experiments will be needed to examine how FL changes during RT, and when RT plans need to be adjusted. Summary of the study on FLART based on nuclear medicine functional imaging is presented in Table 1.
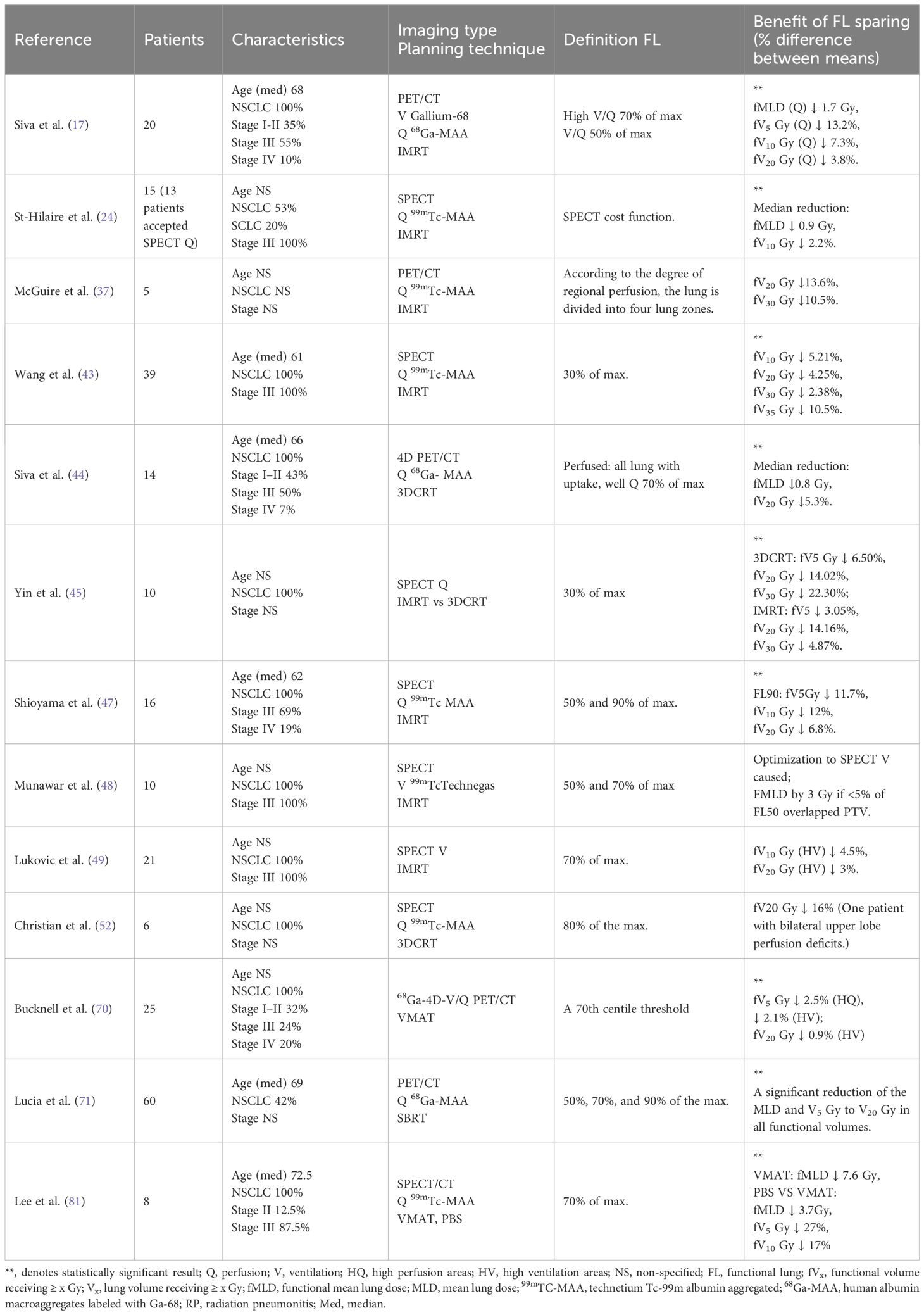
Table 1. Detailed description of nuclear medicine-guided RT research, including patient characteristics, planning techniques, and clinical benefits.
3 CT image-guided FLART
Using inhalation gas tracers or intravenous contrast agents for imaging can result in increased radiation exposure and scan times (65). While CT-based V imaging provides additional benefits by providing functional information without additional imaging tests (16, 80). The most common CT techniques used in lung functional imaging research include 4DCT (14, 16, 19, 26, 44), multi-detector CT (MDCT) (82, 83), dual-energy CT (DECT) (84, 85), and CT-enhanced imaging, which uses inert gases. In the past, CT imaging was slow and difficult to apply in clinical practice. With advances in imaging technology, MDCT, which includes multiple detector arrays, has improved imaging quality, scanning modes, and clinical applications (86, 87). However, compared to 4DCT and DECT, MDCT has certain limitations in terms of imaging quality, tissue resolution, radiation dose, respiratory motion artifacts, and tissue composition analysis (88–90). Therefore, 4DCT and DECT are gradually replacing MDCT as preferred choices in clinical practice. Use of CT lung functional imaging for the FLART project research as shown in Table 2.
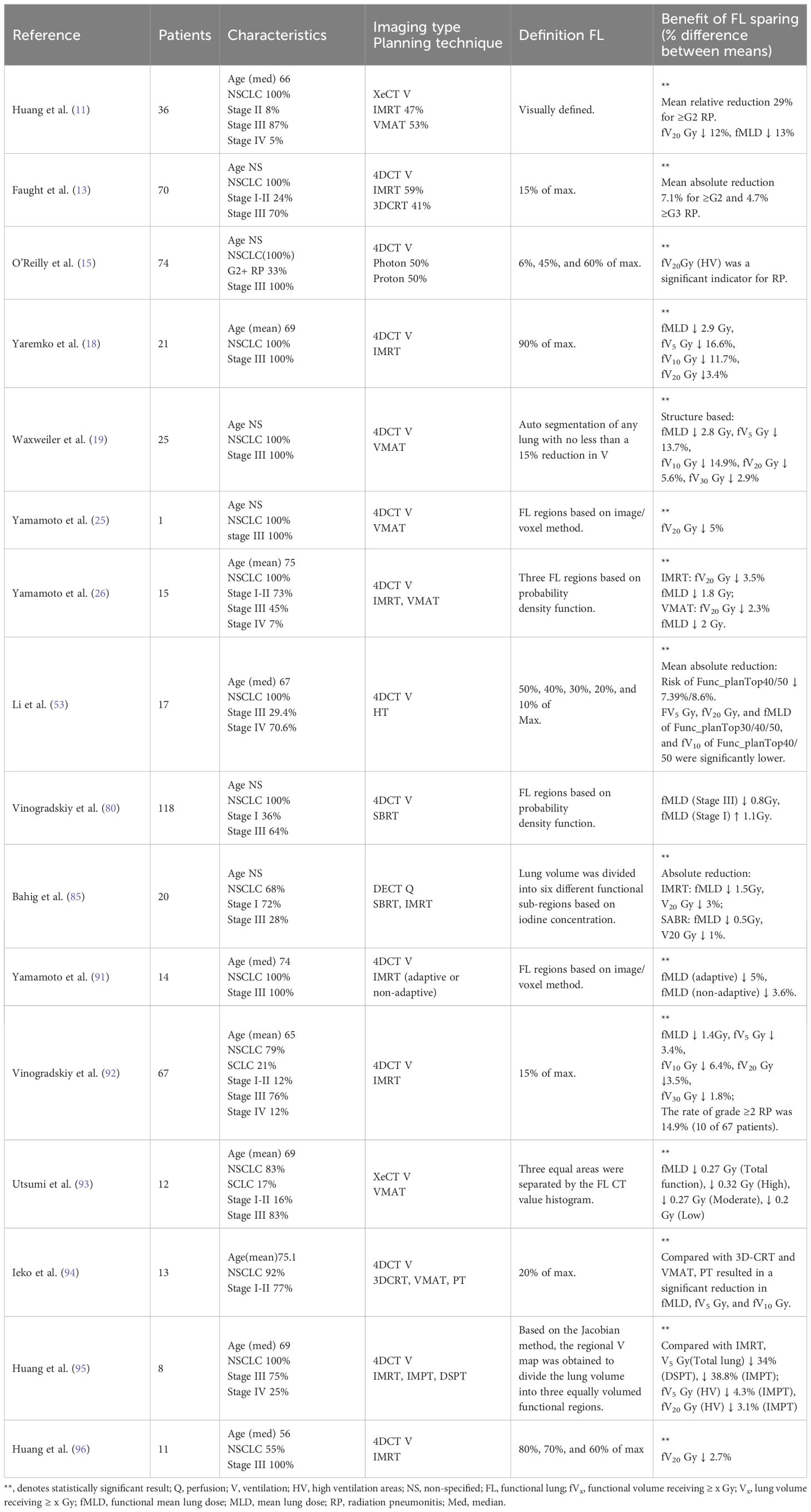
Table 2. Detailed description of CT-guided RT research, including patient characteristics, planning techniques, and clinical benefits.
3.1 4DCT
4DCT imaging was developed to provide tumor motion information and improve RT planning. Further, 4DCT images include variations in air content caused by respiration in the lung parenchyma, which can be used to produce lung V images (18). Images from SPECT V/Q (35–37, 97), PET/CT (17, 29, 44, 98), MRI (99, 100), and PFT (91, 101) confirmed the validity of 4DCT V. Numerous studies have detailed the methods (102, 103) and validation (103, 104) of 4DCT V imaging as well as its potential clinical applications as a functional imaging modality (26, 105–107). Through 4DCT scanning, maximum inhalation and exhalation images can be obtained to generate lung function maps (91) and measure breathing retention (98).
3.1.1 Lung functional imaging based on 4DCT
In the free-breathing state, 4DCT was used to collect ten-time phases of a complete breathing cycle. CT images with phase or amplitude resolution were used to calculate the V for each voxel in the lungs (102, 103, 108). By calculating the local air content change for each voxel, a 3D graph of the V function is generated (19). According to the literature, there are three main 4DCT V-imaging algorithms (VIA), which are based on density (Hounsfield units), Jacobian matrix, and region. Among them, the density VIA was described by Guerrero et al. (109), based on the physical density changes between the exhalation and inhalation peak CT images, using deformable image registration (DIR) and underlying CT density information to generate static 3D V images. Reinhardt et al. (102) introduced the Jacobian matrix VIA, which quantified regional volume changes of lung voxels by utilizing the determinant of the Jacobian matrix obtained from DIR spatial transformation. Besides, Kipritidis et al. (110) proposed a region-based VIA, estimating V situation by evaluating the 4D regional averaged time-product of air and tissue densities at each voxel without DIR. However, the correlation between the V images generated by these algorithms and clinical gold standards [including 99mTc-SPECT (111) and 68Ga-Galligas PET (112)] varies significantly (97, 113). According to studies, region-based algorithms have a higher correlation with 68Ga-Galligas PET and less variability, but they are prone to motion blur and limited in spatial resolution, possibly limited to lung voxels within HU values of (-1000, -600) (110). Further, region-based algorithms require much more computation time because they require 10 phase matrices, unlike the two other algorithms (114). Compared with the other two algorithms, the Jacobian matrix algorithm is much less accurate (91, 110). While Eslick et al. (115) demonstrated good consistency between CT density changes and PET lung V images. As 4DCT imaging becomes more common in patients with lung cancer, using 4DCT V imaging does not require additional doses or economic costs (92). To confirm its clinical applicability, these clinical trials are investigating the use of 4DCT V imaging to prioritize the protection of high-functioning lung regions (NCT02528942, NCT02773238, NCT02002052, NCT02308709, and NCT02843568).
3.1.2 FLART plans based on 4DCT Lung functional imaging
Treatment plans focused on FL commonly employ optimization techniques based on structure and images. Structure-oriented approaches optimize treatments by setting functional contours based on 4DCT images of lung volume. This methodology has been verified alongside alternative lung functional imaging methods (15–18, 25–27, 100). As functional images are transformed into binary masks, the process of generating functional contours may eliminate heterogeneous functional data (92). By contrast, image-based techniques enable the inclusion of all functional image data in optimization processes through 4DCT images of lung volumes (24, 51). Research has indicated that both structure-based and image-based optimization methods have comparable predictive impacts on RP, with superior performance over standard approaches (116). However, structure-based techniques are compatible with any modern treatment planning system (TPS), but image-based methods need a more sophisticated TPS (19).In structure-based methods, there are two main approaches: the first uses threshold-based segmentation FL. Another method divides the lung into six regions, calculates average V values, and compares them to the overall average to identify functional defect regions (116). Functional defect regions are areas where V decreases compared to a completely homogeneous lung in nuclear medicine (117). Function-based methods commonly use thresholding to partition functional regions, requiring careful consideration of thresholds. Through DIR and quantitative image analysis, V values were computed from 4DCT V images to derive DFH. A functional volume receiving dose is indicated by the vertical axis, while the “hottest” functional volume is indicated by the horizontal axis (118). V values derived from 4DCT V images were transformed into percentiles, enabling the selection of a suitable threshold for categorizing lungs into high or low functional areas (13, 15, 25, 91). Notably, the precise threshold for lung functionality in CTV images remains undefined. In a systematic review and meta-analysis of FLART (119), the range of lung function definitions varied from 20% to 90%. Among these studies, multiple definitions of lung function were used. The most commonly used maximum level lung function percentages were 70% and 30%, followed by 50% and 60%. Literature often categorizes lung tissue into high- or low-functional areas (HFA or LFA) (13, 15, 25, 92, 120). Based on two thresholds, Yamamoto et al. (26) divided the lung into three equally-sized functional areas: HFA (>66%∼100%), intermediate functional lung area (>33%∼66%), and LFA (0∼33%). Result indicated a significant reduction in HFA dosage, but no improvement in intermediate functional areas or LFA dosage, with a majority of the dosage transferred from HFA to intermediate functional areas and LFA (Figure 1). By utilizing the FLART plan to evade HFA, the treatment dose is minimized to the greatest extent possible; however, no specific strategy was employed to safeguard LFA (121). Yamamoto et al. (25) noted that the decrease in HFA parameters was not a result of an overall reduction in lung dose, but rather a deliberate avoidance of HFA. Planning strategies focused on avoiding HFA may lead to an escalation in the dose to the LFA, which still retains some level of functionality. Once the dose surpasses a certain threshold, the resulting damage becomes irreversible.
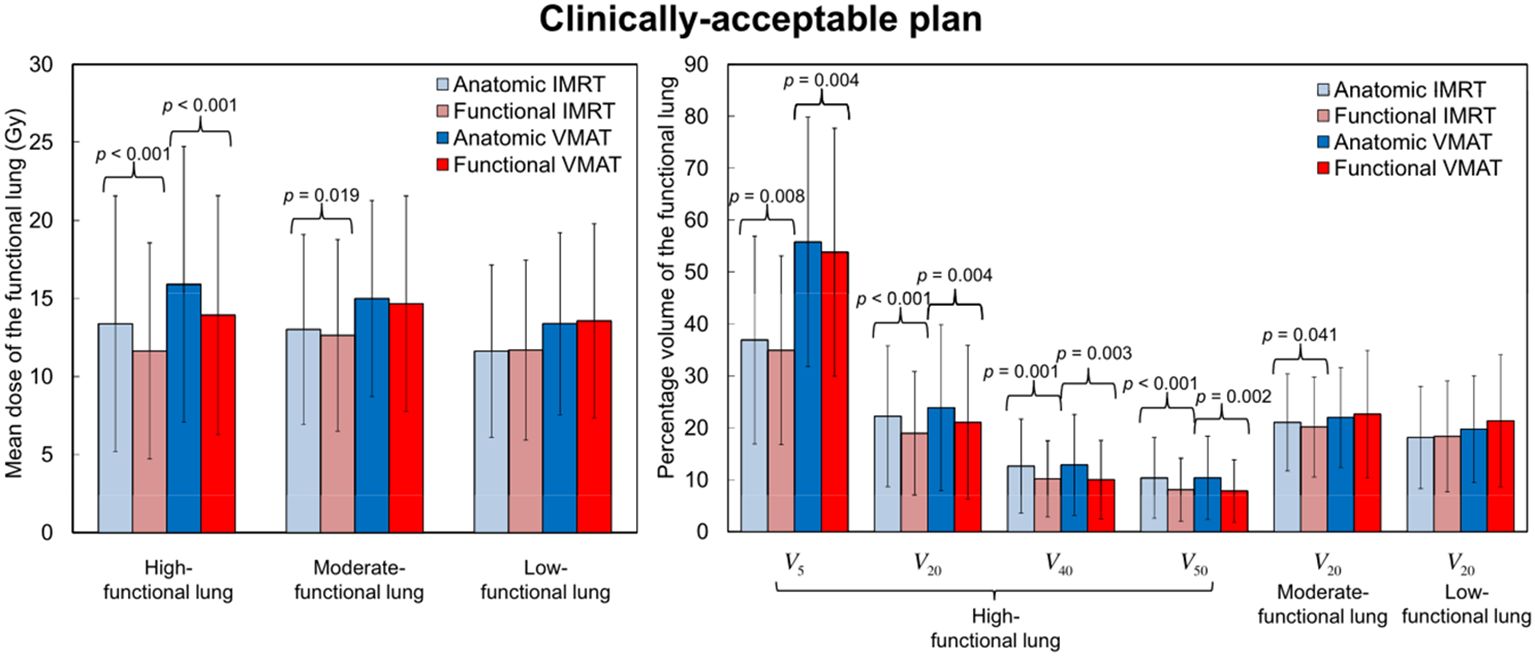
Figure 1. Comparisons between anatomical and functional treatment plans of mean dose (mean ± standard deviation) and percentage of volume receiving ≥5, ≥20, ≥40 or ≥50 Gy (Vx) for the three functional lung regions. Reproduced from reference (26) with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2011.
3.1.3 Clinical benefits from FLART based on 4DCT Lung functional imaging
By acquiring functional data directly from a patient’s 4DCT simulation, 4DCT V provided a distinct advantage over SPECT imaging in treatment planning (16, 80). Moreover, the higher resolution of 4DCT V images simplifies the process of image fusion compared to SPECT (122), thus increasing its acceptance by clinicians and lung cancer patients. With the use of 4DCT-based functional planning, radiation doses are reduced in various treatment plans, such as IMRT (16, 25–27, 35, 48), VMAT (16, 26, 81, 93), and PT (94, 95). In plans using functional planning of IMRT and VMAT, fMLD was significantly reduced by 1.8 Gy and 2.0 Gy, respectively (26). Several FLART studies have shown that the mean reduction in f-MLD can be 2.5 Gy, with a maximum reduction of up to 10 Gy (17, 18, 24, 26, 48). Additionally, fV5 can be decreased by 10-16% (17, 18, 96) and fV20 by 3-9% (37, 47, 99, 123). Ieko et al. (94) conducted a study evaluating the impact of 4DCT V imaging-guided PRT on SBRT, comparing it with VMAT and 3D-CRT. PRT resulted in significant reductions in f-MLD and fV5. Clinical findings indicate that fV20 and f-MLD are the most predictive indicators of RP (Table 3) (19, 119). FLART has been shown to reduce the incidence of ≥2-grade RP from 25% to 12% compared to historical controls (92).
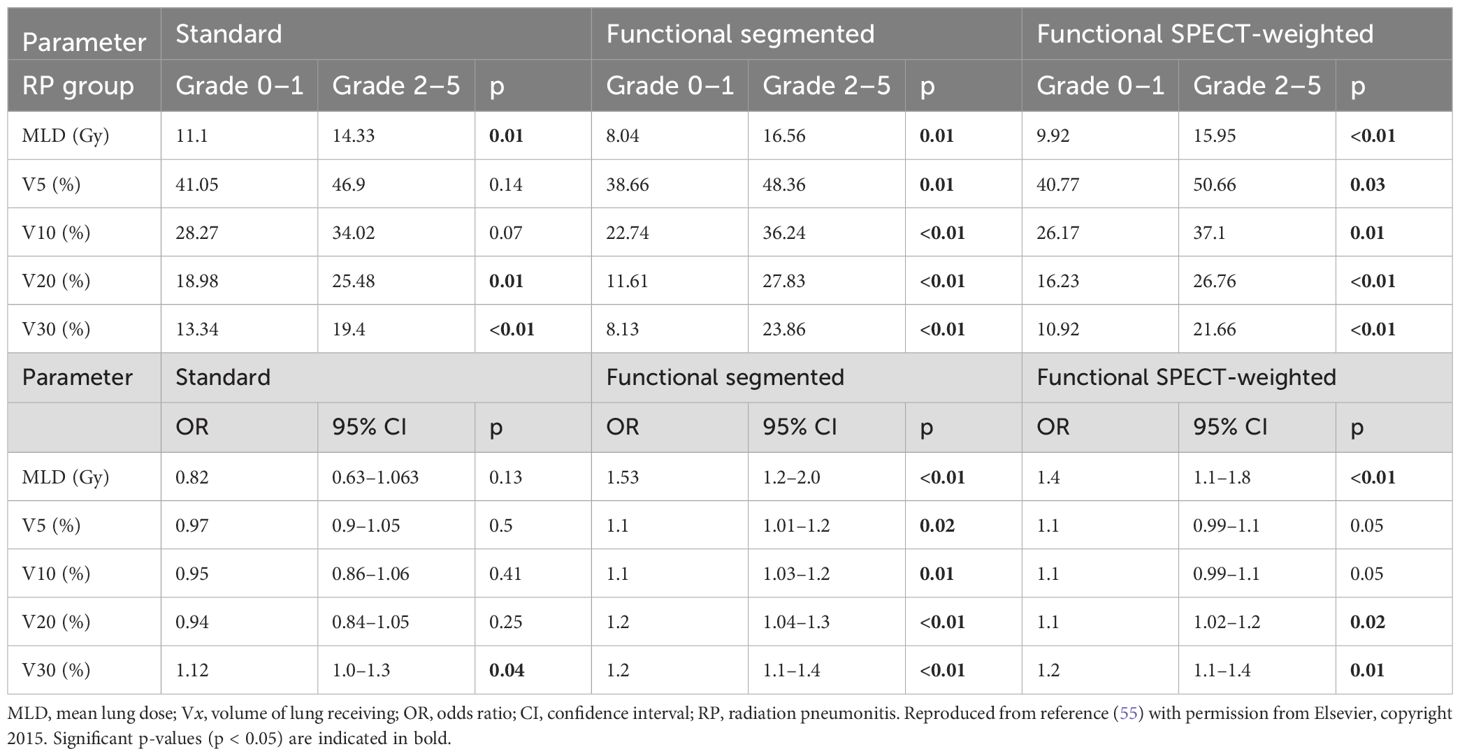
Table 3. Standard and functional measurements of individuals with RP (grade 0-1) and RP (grades 2–5).
3.2 DECT
Recent research has not only utilized 4DCT for FLART planning but also evaluated the feasibility of DECT in FLART planning (84, 85). The DECT setup comprises two X-ray tubes generating high- and low-energy X-ray beams, respectively. By employing these X-ray beams with varying energies, two sets of CT images are acquired from scanning the target. Materials with different decay coefficients can be identified and quantified by X-rays of different energies. Prior studies have primarily used DECT for diagnostic purposes, differential diagnosis, characterization of tumor differentiation and gene expression, staging, and the assessment of prognosis (124). Serving as an innovative imaging technique, DECT surmounts traditional CT constraints in tissue characterization (125, 126). Furthermore, the administration of iodine contrast agents enhances DECT imaging for lung Q assessment, while inert gases like xenon (Xe) and krypton (Kr) are utilized for lung V imaging (84, 127–129).
3.2.1 Lung functional imaging based on DECT
Quantification of lung Q involves the measurement of pulmonary blood volume (PBV), which is delineated as the proportion of capillary volume relative to lung mass (130). 68Ga-MAA PET/CT imaging accurately assesses PBV. Nonetheless, PET/CT imaging methodologies are more advanced and unavailable in many medical facilities, restricting their widespread application. Gaudreault et al. (131) demonstrated that DECT imaging enhanced by iodine contrast agents could serve as a substitute for PET/CT imaging in evaluating lung Q. In the study by Kerl et al. (132), the operation procedure for DECT Q imaging was described. During injection, a high concentration of iodine-based contrast agent is injected within a specified time by optimizing injection parameters. A mixture of contrast agent and physiological saline is injected in stages at a specific rate. Finally, DECT images are acquired during the late arterial phase. Additionally, Bahig et al. (85) generated iodine concentration maps using the double material decomposition technique. The method leverages the dual energy information from DECT images to compute iodine concentration through the establishment of a calibration curve for the production of the lung Q agent map. Research has shown that DECT is a reliable alternative to the direct measurement of local Q in lung parenchyma (133, 134). Even so, iodine contrast agents can pose challenges related to precision and consistency, such as artifacts and patient-specific injection dosages (135–137).
Apart from enabling iodine contrast-enhanced Q imaging with DECT, it can also facilitate V imaging with an enhanced Xe and Kr. Xe, a stable and radiopaque inert gas naturally found in the atmosphere. With inhaled Xe-enhanced DECT (Xe-DECT), three-material decomposition is utilized to differentiate Xe from other substances (such as air and soft tissue) and to describe and quantify V abnormalities in terms of absorption characteristics (138–140). Xe-DECT can be performed using dynamic or static scanning protocols (140). Dynamic CT scans are generated by providing high levels of oxygen (O2) followed by a mixture of 30% Xe and 70% O2 to maintain consistent coverage throughout the wash-in and wash-out phases of Xe (141–143). Conversely, the static acquisition protocol involves capturing images of the entire lung at distinct time intervals. Notably, the static DECT method is prized for its significant reduction in radiation exposure (141, 144). Nonetheless, many researchers preferred the dynamic scanning method for assessing V dynamics by tracking changes in contrast gas concentrations and distributions (138, 143). In addition to displaying normal lung V maps, Xe-DECT can evaluate regional lung V in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, bronchiolitis obliterans, bronchial atresia, and PE (138). However, Xe-DECT was limited in clinical settings by radiation exposure and adverse effects, including drowsiness, headache, and nausea (145).
Research has explored stable Kr or a combination of Xe and Kr for lung V imaging to mitigate the high costs and side effects of Xe (128, 146). Kr concentrations exceeding 70% were shown to be effective in replacing Xe in DECT lung V imaging in rabbits, although drawbacks were also noted (147). Previous studies on conventional CT and DECT have shown that Kr can serve as an inhalation contrast agent for human and animal radiographic imaging (128, 147, 148). Similar to Xe-DECT, patients inhale a mixture of Kr and O2 in a certain ratio and hold their breath during DECT scanning while taking a deep breath. By differentiating substances, Kr V images with varying degrees of enhancement can be obtained. This indicates changes in the V situation through CT density changes. Using 80% Kr and 20% O2 as a contrast agent for DECT V imaging was found to be well tolerated by patients with severe emphysema by Hachulla et al. (128). The results indicated significantly higher attenuation levels in the normal lung than in the emphysematous region, suggesting Kr is a promising contrast agent. As a contrast agent, Kr has some inherent disadvantages, such as certain radioactive properties, a relatively short half-life, and a lower atomic mass, which makes Kr less stable than Xe. Therefore, the assessment of the local V situation poses certain difficulties (149).
3.2.2 FLART plans based on DECT Lung functional imaging
The use of Xe and Kr for lung V imaging has been demonstrated in prior studies, but mostly in research settings. FLART planning with Xe and Kr for DECT V imaging has limited studies due to limitations and side effects. Studies have shown that DECT-iodine mapping can provide extensive functional data in patients undergoing lung RT, aiding FLART planning through systematic and personalized optimization (85). Studies have confirmed the association between iodine-enhanced DECT V imaging and PET (127, 131). Functional segmentation is a critical component of FLART planning. Bahig et al. (85) conducted a study in which pulmonary iodine images were obtained via DECT scanning. The lung function was divided into six equally spaced subregions according to the range of iodine concentration from minimum to maximum. Each subregion was treated as a weighted structure (OARs) influencing overall lung function via weight modifications. The results showed a strong correlation between the relative lung lobe function measured by DECT and the results obtained from SPECT/CT imaging. The average differences between V5 and MLD in anatomical and FL volumes were 16% (p = 0.03) and 15% (p = 0.047), respectively. Lapointe et al. (84) conducted a study where the lung was manually divided into five subregions comprising the upper and lower lobes of both the left and right lungs. The differential function (δF) of each subregion compared to the entire lung was determined based on iodine concentrations assigned to individual voxels within the functional area. They found strong agreement between SPECT/CT and DECT images in terms of calculated differential functions for lung subvolumes. This underscores the promising potential of employing DECT in RT to preserve FL tissue. There was currently limited research on using DECT for FLART. Future research is hoped to verify its feasibility for the FLART program and explore its potential clinical benefits.
3.2.3 Clinical benefits from FLART based on DECT Lung functional imaging
By scanning the treatment site with contrast agent, the DECT-iodine map can be obtained directly for RT plan, providing precise anatomical and functional correlation without additional radiation exams. Research demonstrated that DECT-iodine mapping effectively identified Q defects in PE (150–152) and lung parenchymal diseases (153, 154). Pansini et al. (153) examined DECT-iodine maps in 57 patients (including 37 with emphysema). They found that areas with decreased iodine distribution correlated significantly with emphysema. The severity of Q changes was related to parenchymal damage. In addition, Aoki et al. (155) established the effectiveness of DECT arterial stage iodine uptake as a predictive biomarker for lung cancer recurrence after SBRT. In the case of radiation damage changing over time, DECT Q imaging provides similar information to PET Q imaging and is an economical alternative to PET imaging (127). Despite the limited clinical validation of DECT in RT, the literature acknowledges its potential applications, including improved dose calculation accuracy (156, 157), decreased metal artifacts (158), and enhanced tumor delineation and tissue characterization (159, 160).
3.3 Current problems and research direction of CT image-guided FLART
Research indicates that about 70% of lung cancer patients exhibit regional functional variability that favors functional avoidance (35, 52). There are two important factors for FLART: functional structural heterogeneity and spatial dose distribution. When a patient’s lung function is consistent, no particular area requires prioritized protection. Functional avoidance may preferentially expose the defective area instead of the functional region, if a patient shows a heterogeneous image with significant Q and V defects (35). An assessment of functional defect size is necessary for evaluating the relevance of functional information in treatment planning, particularly when the defect exceeds approximately 25% of total lung volume. Study by Katsuta et al. (16) indicated that DFH calculation was frequently performed in advanced NSCLC, especially for patients with significant irradiation lung volumes and a greater rate of RP. And in advanced-stage NSCLC RT, patients with FL in close proximity to the tumor are particularly suitable for RP prediction using DFH characteristics (161). Yamamoto et al. (26) showed that FLART performed best in patients with substantial overlap between FL and PTV, whereas it performed poorly in patients with less overlap. However, 4DCT V imaging does have limitations, such as inaccurate registration (162) and numerical instability (163), as well as suboptimal correlation with other lung functional imaging techniques (97). 4DCT functional imaging is also limited by its focus on V volume calculation without providing Q information. However, research indicated that approximately 20% of lung cancer patients can exhibit varying V and Q distributions (77).
Currently, DECT can simultaneously acquire both lung V and Q data. Nevertheless, using Xe and iodine contrast agents to acquire V and Q DECT images simultaneously might increase radiation exposure and prolong scanning time (164, 165). Similarly, using both Xe and iodine enhancement in a single scan presents difficulties because their atomic numbers are close (iodine at 53, Xe at 54), suggesting similar DECT spectral attenuation properties (166). Moreover, research exists on Kr and iodine-enhanced DECT, since iodine exhibits significant attenuation variations with increasing contrast agent doses in CT imaging, suggesting a potentially significant impact on Kr analysis based on substance decomposition theory (129). Further research is required to determine and optimize the dose of contrast agents in mixed contrast. Iodinated contrast agents are mandatory for Q DECT implementation, which limits its applicability in patients with contraindications. Furthermore, the presence of an iodine threshold for functional zoning requires additional clinical evidence. A functional imaging approach reveals significant differences in DFH compared with traditional anatomical dosimetry, which could clarify the limitations of conventional DVH parameters. The future research aims to improve lung function preservation with weighted functional volumes.
4 MR image-guided FLART
MRI offers several benefits over CT, including detailed soft tissue images, lowering radiation exposure, and enabling multi-angle analysis of tissue (65, 120). Nevertheless, lung MRI presents many challenges due to its low proton density, rapid signal decay (caused by multiple air-soft tissue interfaces), and motion artifacts (167). The advancement of imaging technology has led to the development of new MRI techniques aimed at addressing these limitations. Several recent studies have demonstrated the feasibility of lung MRI assessment with Fourier-resolved MRI (FD-MRI) (168) (169) and MRI using hyperpolarized (HP) gases (169, 170), fluorinated gases, and oxygen (171, 172).
4.1 Lung functional imaging based on MR
FD-MRI represents a novel method for the simultaneous non-contrast-enhanced imaging of lung V and Q (169). This technique utilizes rapid 2D TrueFISP pulse sequences to efficiently capture lung images, removing the need for ECG or respiratory triggers. A non-rigid image registration algorithm is employed to address respiratory motion. Furthermore, the Fourier analysis of time variations in image intensity can distinguish between blood signals and lung parenchyma signals, enabling the computation of V and Q-weighted images. Compared to traditional methods that utilize contrast agents or radiotracers, this method provides considerable advantages. There is a significant correlation between FD-MR imaging and short-term reproducibility of PFTs (173). An animal experimental study assessing regional lung V and blood flow Q confirmed the consistency in qualitative assessment between FD-MR imaging and SPECT/CT (174). However, FD-MRI provides only indirect information about V and Q, and its sensitivity may be inferior to that of directly imaged HP gas MRI (175).
HP gas MRI accurately determines the location and severity of V deficiencies in the lungs (176). The commonly used HP gases for MRI research are 3He and 129Xe gases. These gases serve as inhalable MRI contrast agents and can provide rich supplementary information about lung function and lung microstructure (177, 178). HP 3He MRI serves as a valid alternative to SPECT for the evaluation of V (16, 27). Smith (20) and Hughes et al. (179) have provided comprehensive protocols for the acquisition of MRI data utilizing 3He. The high-pressure treatment of 3He gas using spin-exchange optical pumping technology can substantially increase the magnetization of 3He by a factor of 104 to 105. The patient was directed to inhale 1 liter of a mixture comprising 3He and medical nitrogen (N2). Static volume images of 3He were acquired using rapid gradient echo imaging over a period of 16 seconds. Matthew et al.’s study (180) provides qualitative and quantitative evidence for 3He MRI and 4DCT V maps, showing good spatial consistency. HP gas 3He MRI may not be widely used due to cost and limited global helium supplies.
In comparison to 3He, 129Xe has significant natural reserves. This guarantees stable long-term availability and strengthens its economic viability. In addition, 129Xe has a high solubility and can dissolve in lung tissue and blood, forming a “dissolved phase.” During the dissolution process, approximately 200 ppm of chemical shifts are produced, and MRI technology can separate the gaseous 129Xe from the dissolved 129Xe for imaging (181). The latest MRI technology can obtain 3D 129Xe images of lung parenchyma, blood, and alveoli in a single breath-hold scan (182). This allows for simultaneous lung V, Q, and gas exchange assessment. To perform 129Xe MRI, HP 129Xe gas needs to be prepared first. The patient needs to inhale a mixture of 129Xe and N2 gases and undergo a 3D radial pulse sequence acquisition within a breath-hold time of 15 seconds to obtain distribution images of gaseous and dissolved phase 129Xe (171). By using HP 129Xe MRI technology, non-invasive information about lung V and gas exchange can be obtained, providing a valuable physiological basis for functional planning in RT.
Recent advancements indicate that, alongside HP gas, fluorinated gas and O2 are also applicable for functional imaging in MRI. Fluorinated gas MRI (19F-MRI) generally requires patients to inhale a mixture of standard O2 with perfluoropropane (PFP) (183) or sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) (184), followed by imaging conducted during breath-holding (171). In contrast to HP 3He/129Xe gas MRI, 19F-MRI does not necessitate prior treatment of the gas with hyperpolarization and utilizes non-toxic, naturally abundant fluorinated gases as contrast agents. It is capable of conducting multiple breath imaging and analyzing the inhalation/exhalation kinetics of the gas (185–187). Currently, 19F-MRI is restricted to V imaging. Enhancements in image quality, signal-to-noise ratio, and additional repeatability and validation studies are necessary to solidify its evidence base for clinical applications. Oxygen-enhanced MRI (OE-MRI) is a technique that utilizes the influence of O2 on the T1-weighted signal intensity of the lungs to assess lung function (188, 189). T1-weighted images are acquired under standard breathing conditions with 21% O2, followed by the patient inhaling 100% pure oxygen for subsequent T1-weighted imaging. The distinction between the two indicates the conditions of lung V and oxygen supply (172, 190).
4.2 FLART plans based on MR lung functional imaging
In MRI studies of functional imaging, HP gas MRI is the sole method employed for the FLART plan. FLART uses 3He MRI scans to acquire 3He static V images, providing respiratory function information and delineating functional lung regions. Semiautomatic k-means clustering is used to identify and segment V defects, while functional region information is incorporated into the RT plan to prevent irradiation of FL as well (180, 191). Yaremko et al. (192) defined the moderately-to-highly V region as normal V lung (NVL), while V lung (VL) encompassed the entire lung. The FL volume was delineated from breath-hold CT deformation to the planning CT. The findings indicated that in FLART plans, V20 and MLD of VL and NVL were significantly decreased by 3.0 ± 0.8%, 3.5 ± 1.0%, 1.0 ± 0.5 Gy, and 1.2 ± 0.7 Gy, respectively. In the existing literature, FLART plans using 3He MRI are unproven for clinical outcomes and prognosis, necessitating further study. The aforementioned method is capable of generating both the gaseous and dissolved phases of 129Xe. According to the signal intensity of 129Xe MRI images, Ding et al. (171) classified lung volume into “V regions” and “V defect regions.” The RT plan prioritized the reduction of radiation dose to the V regions. The finding indicated that emphasizing the reduction of radiation dose in the V regions derived from 129Xe MRI gas exchange distribution maps could markedly decrease indices such as V5, V10, and V20, consequently lowering the risk of RILI. Rankine et al. (191) normalized the V and gas exchange images using linear scaling and calculated percentile values for voxels within and outside the lung. A voxel value within the lung was considered 99th percentile, while a voxel value outside of the lung, such as background, was designated as 1%. A threshold with a relative function interval of 10% was used to generate equal functional contours, which were then transferred to the planning CT via deformable registration. Compared to V-based FLART plans, gas exchange-based FLART plans decreased the dose more effectively to regions with high gas exchange and may significantly lower the incidence of RILI. Gas exchange metrics improve plan quality evaluation moderately over V-guided planning. A preliminary study revealed a moderate correlation (R = 0.53 ± 0.02) between lung 129Xe uptake in the blood prior to RT and 129Xe V in three patients with NSCLC, which diminished to R = 0.39 ± 0.07 following treatment (170). Additionally, notable differences were observed in the effective uniform dose, V20, V10, and V5, with values of 1.5 ± 1.4 Gy, 4.1 ± 3.8%, 5.0 ± 3.8%, and 5.3 ± 3.9%, respectively. Thus, V alone may not represent actual regional lung function and FLART may have limitations when using V images independently. A precise lung function assessment using 129Xe-MRI is recommended for optimizing RT.
4.3 Clinical benefits from FLART based on MR lung functional imaging
FD-MRI eliminates contrast agents and breath-holding, resulting in reduced operational costs and enhanced patient comfort. It possesses significant potential for the diagnosis and monitoring of lung diseases (193, 194). Research indicated that this method may be utilized in the diagnosis and treatment assessment of lung diseases, including lung cancer and PE, offering non-invasive lung functional data for clinical application (175). With inhaled MRI contrast agents, such as HP gases 3He and 129Xe, lung structure and function can be better understood, enabling disease classification, treatment response assessment, early diagnosis, and long-term monitoring (195, 196). Furthermore, HP gas V MRI can detect airway obstruction and show significant V changes in emphysema and more advanced COPD (197, 198). Research has demonstrated a correlation between 129Xe gas exchange function and abnormal carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (DLCO), a clinically recognized gas exchange indicator (199, 200). As a result of its low operating cost and lack of costly polarization devices, 19F-MRI is increasingly used in clinical research. 19F-MRI allows repeated imaging of breath and gas inhalation and exhalation dynamics analysis. A significant correlation has been found between 19F-MRI-measured V defects and FEV1 in COPD cohorts (201). Conversely, OE-MRI is applicable in the detection of multiple lung diseases, including asthma (202), COPD (203), and interstitial lung diseases (204), as well as in assessing the effects of bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids (205). It demonstrates comparability with quantitative CT in evaluating lung functional damage and disease severity (202–204). According to the existing literature, HP gas MRI is applicable in FLART planning and demonstrates potential for enhancing the dosage parameters of FL.
4.4 Current problems and research direction of MR image-guided FLART
The research summary on the MRI-guided FLART project is presented in Table 4. Research demonstrates a weak to moderate correlation between V and local red blood cell displacement. Defining lung function as V or red blood cell displacement reveals notable differences in dose falloff histogram and effective uniform dose (170). Gas exchange information is distinct from V information, and this significant finding will inform future research in this area. This approach will facilitate future prospective trials that directly compare these two functional planning techniques and assist in identifying which patients are most likely to benefit from gas exchange-guided FLART. Furthermore, research indicated that a reduction in red blood cell displacement, defined as the ratio of regional gas exchange to V, correlates with clinical deterioration (206). In light of the fact that Xe must reach the alveoli before interacting with red blood cells, integrating alveolar gas exchange data into functional indices would improve their predictive capability for RILI, potentially matching or surpassing V-weighted indices. In spite of this, a gas exchange-weighted index that predicts symptomatic RP better than DVH remains undeveloped, suggesting future research opportunities. There have been no studies that have directly compared multiple MRI-based lung functional imaging techniques to identify the optimal method for assessing lung V/Q or evaluating both parameters. Additionally, there should be patient population studies to help clinical practitioners make adaptive selections.
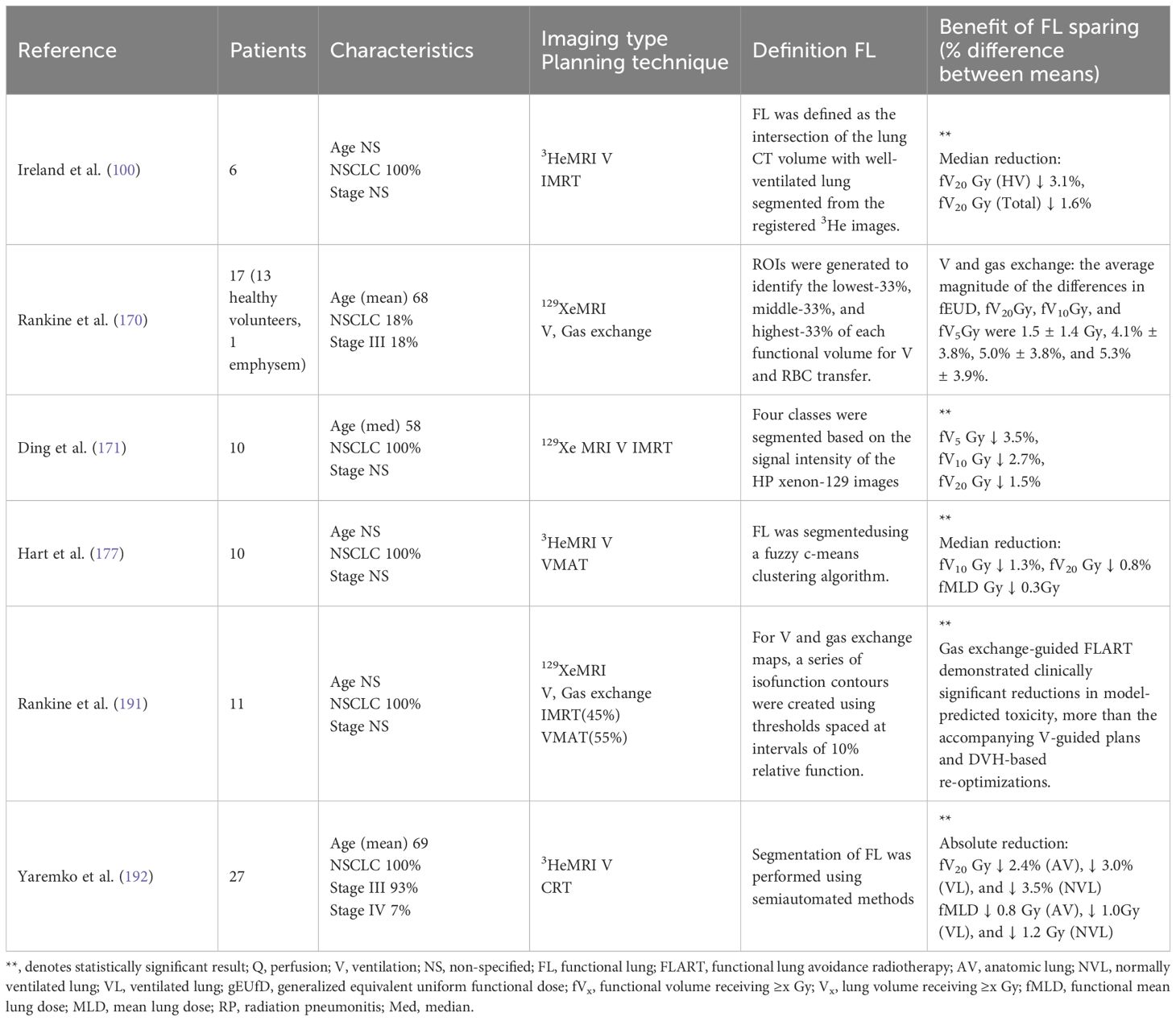
Table 4. Detailed description of MRI-guided RT studies for lung function, including patient population characteristics, planning techniques, and clinical benefits.
5 ViewRay/Unity and Reflexion: new RT technology
5.1 MRI-guided RT
RT based on functional imaging aims to preserve lung function by protecting FL regions first. During the treatment process, however, airways reopen due to shrinking of the tumor (207). As tumor anatomy or function changes, adaptive methods are required because the original treatment plan may irradiate lung tissues that were non-functional but are now functional (80). With the development of linear accelerators, MRI-guided linear accelerators (MRLs) with excellent soft tissue resolution have emerged (208–210). MRL can acquire real-time MR images during the treatment process for adjusting treatment plans to accommodate actual positional changes in tumors and normal tissues (211). This MRI-guided RT is called MR-guided RT (MRgRT) and can be used for SBRT of tumors (210). The MRL system includes two main models: ViewRay MRIdian and Elekta Unity. The MRIdian system uses a low magnetic field strength of 0.345 T, while the Unity system uses a conventional magnetic field strength of 1.5 T. Higher magnetic field strength can improve signal-to-noise ratio and imaging quality but may increase geometric distortion compared to low-field systems (210).
5.1.1 ViewRay MRIdian
MRIdian employs 60Co or 6MV linear accelerators and features a distinctive multi-leaf collimator design to improve the accuracy and adaptability of RT (212, 213). The system utilizes tracking and gating techniques to monitor tumor position in real-time, thereby ensuring treatment accuracy. It also optimizes target coverage and minimizes doses to OARs through daily online imaging and plan adjustments (210). A phase I study assessed the feasibility of MR-guided SBRT for super-central lung tumors (214). Results indicated that adaptive re-planning was required in 4 of 10 treatments to achieve target coverage and adhere to OAR dose limits. All five patients in this study attained local disease control within six months, with no occurrences of grade 3 or higher toxic reactions. In comparison to conventional linear accelerators, the MRIdian system offers enhanced visualization of the spinal cord and lumbosacral nerves, resulting in superior dose distribution quality in spinal SBRT (215). Additional studies have documented clinical experiences with MRgRT for both primary and non-primary lung tumors; however, there is a scarcity of clinical outcome reports specifically for NSCLC (216–218). Research indicated that adaptive MRgRT enhances the dose distribution to OARs and improves target coverage relative to non-adaptive methods (219, 220). Additionally, single-fraction image-guided MR-guided SBRT for lung has been documented (221). The integration of single-fraction treatment with real-time image guidance will improve the precision and effectiveness of treatment.
5.1.2 Elekta Unity
In February 2023, Unity received FDA approval for tumor tracking to facilitate ART. The Unity system employs a magnetic field strength of 1.5 T, facilitating multiparametric imaging and the application of diagnostic MRI pulse sequences at this field strength (212). The utilization of high magnetic fields enhances MR image quality, facilitating the reduction of PTV margins, promoting the sparing of OARs, and increasing equivalent toxicity doses (222). Like the MRIdian system, Unity facilitates tracking and gating techniques, enabling plan adjustments via daily online imaging (223). Besides SBRT, the system is capable of performing IMRT, thereby improving treatment accuracy and effectiveness (224). Unity received approval for tumor tracking only last year, resulting in a limited number of studies regarding its application in ART. Prior research has demonstrated the system’s feasibility in spinal SBRT (225). A prospective, multi-institutional, international cohort study registered on clinical trials (NCT04075305) is currently underway to further validate its clinical application. Additional clinical data is anticipated to validate the feasibility of its application in ART planning.
5.2 Biology-guided RT (BgRT) - Reflexion X1
Further research on ART indicates that, alongside MRgRT for ART, biology-guided RT (BgRT) is also applicable. The BgRT system utilizes the PET signal from the tumor to direct real-time radiation delivery and can enhance the RT plan according to the tumor’s biological characteristics (225–227). The BgRT mode received FDA approval for patients treatment in February 2023. The Reflexion X1 system represents the inaugural development for BgRT, with its application restricted to the head and neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvic regions (228). The system includes a 6MV linear accelerator, a 16-row kilovolt CT for anatomical positioning, and two megavolt PET detectors for the detection of patient penetrating radiation (229, 230). The X1 machine scans patients after injecting the tracer at the same dosage as the actual treatment to generate PET and CT data needed for treatment planning. PET can processes signals emitted from tumor sites in real-time, allows simultaneous RT for multiple lesions throughout the body (225). Even amid variations in contrast agent and patient movement, the X1 system delivered doses accurately and robustly under static and dynamic conditions (231). Pham et al. (232) demonstrated that the X1 system can produce clinically acceptable IMRT/SBRT plans comparable or superior to Eclipse VMAT. However, the X1 plan requires an extended irradiation duration, necessitating a trade-off between plan quality and efficiency. The standard treatment workflow for BgRT is in development, and a comprehensive process map will assist clinical professionals in the effective, safe, and high-quality implementation of this new technology (233).
5.3 Current problems and research direction
The use of MRL in ART may be advantageous based on current research. MRL combined with the previously mentioned MR functional imaging techniques can help facilitate implementation of the FLART plan by providing lung function information. Also, combining FLART with ART plans may allow RT plans to be adjusted in real time based on functional information provided by MR images. Both MRIdian and Unity systems exhibit certain limitations in the treatment of lung cancer. Firstly, lung tissue’s low proton density, differences in magnetization among tissues, and motion-induced artifacts contribute to suboptimal MR imaging outcomes (234, 235). The hardware differences between MR-linear accelerators and conventional diagnostic MRI systems have an impact on image quality and data acquisition (222). Furthermore, MRI does not yield electron density information; therefore, synthetic CT images must be generated using techniques such as volumetric density assignment, atlas-based methods, or artificial intelligence (236–238). The reliability of this method in the chest area is inadequate (238). As compared to MRIdian, Unity’s strong magnetic field influences secondary electron propagation, resulting in a higher dose at the air-tissue interface. Therefore, adjustments to the irradiation field are necessary to mitigate this electron return effect (234, 235). Further, respiratory and cardiac motion can affect the positioning and dose accuracy of tumor targets (239). While both systems can track motion around a target area, only MRIdian can modify irradiation time based on tumor imaging in real-time (222). Moreover, neither system can perform 4D MR imaging, limiting precision in multi-target treatment.
In contrast, BgRT does not require respiratory motion management as tumor motion is relatively static in the 60-RPM (round-per-minute) ring platform (233). The uptake of the PET tracer, primarily fluorodeoxyglucose-FDG, provides functional information regarding the lungs (240). BgRT facilitates ART through real-time monitoring of the PET signal during treatment (231). Functional information derived from PET images can inform BgRT, potentially enabling adaptive FLART plans. Nonetheless, PET-based BgRT technology encounters numerous issues and challenges in clinical applications. Firstly, the spatial resolution of PET is significantly lower than that of anatomical imaging, which does not meet the accuracy requirements of contemporary RT (241). As a result, PET is ineffective at accurately delineating target areas and fails to deliver non-uniform doses to dynamic target regions. Furthermore, BgRT relies on a high tumor signal-to-background noise ratio (TBR); however, FDG uptake is also present in healthy tissues, and TBR may diminish during treatment (231). Thus, cases with inadequate FDG uptake should be treated with conventional CT imaging. Injections of PET tracer and waiting for activity distribution before each treatment extend treatment duration and decrease patient tolerance and RT center efficiency (227). Additionally, medical technicians must have advanced skills and collaborate among various departments during BgRT treatment. Finally, BgRT equipment incurs higher costs due to the inclusion of PET, while the PET tracers used during treatment increase costs further, hindering widespread application. The evaluation of BgRT’s cost-effectiveness and target population should be conducted from a health economics perspective.
6 Summary
FLART has been incorporated into clinical trials. The clinical results indicate that FLART effectively reduces HFA dosage, thereby decreasing the incidence of RILI, which supports its clinical feasibility. Nonetheless, numerous practical issues require attention for FLART. Evaluating the suitability of patients for FLART is one aspect of the process. Establishing a comprehensive set of inclusion criteria is essential, encompassing tumor grading, target area size and volume, the relationship and overlap with FL, and underlying lung conditions such as smoking and COPD. Furthermore, different clinical studies have different criteria for classifying FL, and thresholds used in RT plans depend on their own patient cohorts. To be comprehensively applied in clinical practice in the future, guidelines and standardized thresholds must be developed. Presently, the majority of FLART plans predominantly assesses a single lung function imaging modality, either Q or V. Different physiological phenomena, including airway reopening, tumor vessel obstruction, and related thoracic disorders, can result in variations in patient responses to V or Q dosage. In cases of V and Q mismatch, it is advisable to utilize a combination of imaging modalities. However, this patient population is relatively small, as the majority can be sufficiently assessed through either V or Q dosage response alone. The present emphasis of FLART research is primarily on HFA. The literature provides limited information on the assessment of dose volume and functional weight, as strategies to minimize HFA exposure inherently lead to increased LFA dosage. Nonetheless, LFA is not completely non-functional; certain regions may experience temporary loss of functionality, but they may fail to recover once the radiation dose reaches a critical threshold, resulting in irreversible lung damage. Consequently, the development of new technologies is essential for the real-time adjustment of RT planning through the continuous monitoring of OARs, tumor volume, and lung function. The image quality of cone-beam CT from conventional linear accelerators is inadequate for delivering lung function data. The integration of MRI and PET with linear accelerators has enhanced image quality, and research studies indicate the potential of combining FLART with ART. Further clinical research is required to validate its feasibility. Additionally, the DFH index employed in the study solely represents the dose parameters for FL, and reducing the DFH index impacts only the dose in FL, rather than the entire lung. Consequently, a novel functional weighting algorithm is required to enhance both HFA and LFA through the assignment of weights according to functional significance. The DFH derived from the novel weighted optimization algorithm will represent the integrated whole lung dose function, akin to the conventional DVH. The DFH index serves as an intuitive tool for assessing RT planning and forecasting the likelihood of post-radiotherapy toxicity. Further clinical evaluation of new DFH indices, guided by the weighted optimization algorithm, is necessary to establish guidelines and progressively integrate FLART as a routine option for RT.
Author contributions
JY: Writing – original draft. XT: Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – original draft. ZZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. BL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. LL: Writing – review & editing. HB: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
2. Khalil AA, Hau E, Gebski V, Grau C, Gee H, Nyeng TB, et al. Personal innovative approach in radiation therapy of lung cancer- functional lung avoidance SPECT-guided (ASPECT) radiation therapy: a study protocol for phase II randomised double-blind clinical trial. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:940. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08663-1
3. Lim HS, Yang K, Noh JM, Pyo H, Kim JM, Kwon D, et al. Reduced frequency and severity of radiation esophagitis without marginal failure risk by contralateral esophagus sparing IMRT in stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing definitive concurrent chemoradiotherapy. RADIOTHER Oncol. (2024) 199:110436. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110436
4. Ono T, Adachi T, Hirashima H, Iramina H, Kishi N, Ono T, et al. Unifying gamma passing rates in patient-specific QA for VMAT lung cancer treatment based on data assimilation. Phys Eng Sci Med. (2024). doi: 10.1007/s13246-024-01448-3
5. Ciérvide R, Hernando O, López M, Montero Á, Zucca D, Sánchez E, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for spinal metastases: 12 years of a single center experience. Clin Transl Oncol. (2023) 25:3395–404. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03188-4
6. Jin Y, Shimizu S, Li Y, Yao Y, Liu X, Si H, et al. Proton therapy (PT) combined with concurrent chemotherapy for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer with negative driver genes. Radiat Oncol. (2023) 18:189. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02372-8
7. Farr KP, Kramer S, Khalil AA, Morsing A, Grau C. Role of perfusion SPECT in prediction and measurement of pulmonary complications after radiotherapy for lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2015) 42:1315–24. doi: 10.1007/s00259-015-3052-3
8. De Ruysscher D, Niedermann G, Burnet NG, Siva S, Lee AWM, Hegi-Johnson F. Radiotherapy toxicity. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2019) 5:13. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0064-5
9. Partridge M, Yamamoto T, Grau C, Grau C, Høyer M, Muren LP. Imaging of normal lung, liver and parotid gland function for radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. (2010) 49:997–1011. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2010.504735
10. Garrison WJ, Qing K, Tafti S, Mugler JP, Shim YM, Mata JF, et al. Highly accelerated dynamic acquisition of 3D grid-tagged hyperpolarized-gas lung images using compressed sensing. MAGNET Reson Med. (2023) 89:2255–63. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29595
11. Huang YS, Chen JL, Lan HT, Tai MH, Kuo SH, Shih JY, et al. Xenon-enhanced ventilation computed tomography for functional lung avoidance radiation therapy in patients with lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2023) 115:356–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.07.034
12. Xing H, Wang T, Jin X, Tian J, Ba J, Jing H. Direct attenuation correction for 99mTc-3PRGD2 chest SPECT lung cancer images using deep learning. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1165664. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1165664
13. Faught AM, Miyasaka Y, Kadoya N, Castillo R, Castillo E, Vinogradskiy Y, et al. Evaluating the toxicity reduction with computed tomographic ventilation functional avoidance radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2017) 99:325–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.04.024
14. Zhang GG, Latifi K, Du K, Reinhardt JM, Christensen GE, Ding K, et al. Evaluation of the ΔV 4D CT ventilation calculation method using in vivo xenon CT ventilation data and comparison to other methods. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2016) 17:550–60. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i2.5985
15. O'Reilly S, Jain V, Huang Q, Cheng C, Teo BK, Yin L, et al. Dose to highly functional ventilation zones improves prediction of radiation pneumonitis for proton and photon lung cancer radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2020) 107:79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.01.014
16. Katsuta Y, Kadoya N, Mouri S, Tanaka S, Kanai T, Takeda K, et al. Prediction of radiation pneumonitis with machine learning using 4D-CT based dose-function features. J Radiat Res. (2022) 63:71–9. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrab097
17. Siva S, Thomas R, Callahan J, Hardcastle N, Pham D, Kron T, et al. High-resolution pulmonary ventilation and perfusion PET/CT allows for functionally adapted intensity modulated radiotherapy in lung cancer. RADIOTHER Oncol. (2015) 115:157–62. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.04.013
18. Yaremko BP, Guerrero TM, Noyola-Martinez J, Guerra R, Lege DG, Nguyen LT, et al. Reduction of normal lung irradiation in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients, using ventilation images for functional avoidance. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2007) 68:562–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.01.044
19. Waxweiler T, Schubert L, Diot Q, Faught A, Stuhr K, Castillo R, et al. A complete 4DCT-ventilation functional avoidance virtual trial: Developing strategies for prospective clinical trials. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2017) 18:144–52. doi: 10.1002/acm2.2017.18.issue-3
20. Smith LJ, Collier GJ, Marshall H, Hughes PJC, Biancardi AM, Wildman M, et al. Patterns of regional lung physiology in cystic fibrosis using ventilation magnetic resonance imaging and multiple-breath washout. Eur Respir J. (2018) 52(5):1800821. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00821-2018
21. Hoover DA, Reid RH, Wong E, Stitt L, Sabondjian E, Rodrigues GB, et al. SPECT-based functional lung imaging for the prediction of radiation pneumonitis: a clinical and dosimetric correlation. J Med Imag Radiat ON. (2013) 58:214–22. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12145
22. Marks LB, Sherouse GW, Munley MT, Bentel GC, Spencer DP. Incorporation of functional status into dose-volume analysis. Med Phys. (1999) 26:196–9. doi: 10.1118/1.598503
23. Palma DA, Senan S, Tsujino K, Barriger RB, Rengan R, Moreno M, et al. Predicting radiation pneumonitis after chemoradiation therapy for lung cancer: an international individual patient data meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2013) 85:444–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.04.043
24. St-Hilaire J, Lavoie C, Dagnault A, Beaulieu F, Morin F, Beaulieu L, et al. Functional avoidance of lung in plan optimization with an aperture-based inverse planning system. Radiother Oncol. (2011) 100:390–5. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2011.09.003
25. Yamamoto T, Kabus S, Bal M, Keall P, Benedict S, Daly M. The first patient treatment of computed tomography ventilation functional image-guided radiotherapy for lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. (2016) 118:227–31. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.11.006
26. Yamamoto T, Kabus S, von Berg J, Lorenz C, Keall PJ. Impact of four-dimensional computed tomography pulmonary ventilation imaging-based functional avoidance for lung cancer radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2011) 79:279–88. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.02.008
27. Bates EL, Bragg CM, Wild JM, Hatton MQ, Ireland RH. Functional image-based radiotherapy planning for non-small cell lung cancer: A simulation study. Radiother Oncol. (2009) 93:32–6. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2009.05.018
28. Owen DR, Boonstra PS, Viglianti BL, Balter JM, Schipper MJ, Jackson WC, et al. Modeling patient-specific dose-function response for enhanced characterization of personalized functional damage. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2018) 102:1265–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.05.049
29. McIntosh L, Jackson P, Hardcastle N, Bressel M, Kron T, Callahan JW, et al. Automated assessment of functional lung imaging with 68Ga-ventilation/perfusion PET/CT using iterative histogram analysis. EJNMMI Phys. (2021) 8:23. doi: 10.1186/s40658-021-00375-6
30. Mortensen J, Gutte H. SPECT/CT and pulmonary embolism. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2014) 41 Suppl 1:S81–90. doi: 10.1007/s00259-013-2614-5
31. Elojeimy S, Cruite I, Bowen S, Zeng J, Vesselle H. Overview of the novel and improved pulmonary ventilation-perfusion imaging applications in the era of SPECT/CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2016) 207:1307–15. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.15071
32. Hess S, Madsen PH. Radionuclide diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2017) 906:49–65. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_105
33. Lee SJ, Park HJ. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) or positron emission tomography (PET) imaging for radiotherapy planning in patients with lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:14864. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71445-5
34. Flakus MJ, Wuschner AE, Wallat EM, Graham M, Shao W, Shanmuganayagam D, et al. Validation of CT-based ventilation and perfusion biomarkers with histopathology confirms radiation-induced pulmonary changes in a porcine model. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:9377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36292-0
35. Mallaev M, Chirindel AF, Lardinois D, Tamm M, Vija AH, Cachovan M, et al. 3D-quantitated single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography: impact on intended management compared to lung perfusion scan in marginal candidates for pulmonary resection. Clin Lung Cancer. (2023) 24(7):621–30. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2023.07.006
36. Mallaev M, Chirindel A, Nicolas G, Tamm M, Vija AH, Cachovan M, et al. 3D-quantitated lung perfusion SPECT/CT: Impact on intended management compared to lung perfusion scan in marginal candidates for lung resection surgery. BRIT J Surg. (2022) 109. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znac185.001
37. McGuire SM, Zhou S, Marks LB, Dewhirst M, Yin FF, Das SK. A methodology for using SPECT to reduce intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) dose to functioning lung. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2006) 66:1543–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.07.1377
38. Scheenstra AEH, Rossi MMG, Belderbos JSA, Damen EMF, Lebesque JV, Sonke JJ. Local dose–effect relations for lung perfusion post stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. (2013) 107:398–402. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.04.003
39. Farr KP, Møller DS, Khalil AA, Kramer S, Morsing A, Grau C. Loss of lung function after chemo-radiotherapy for NSCLC measured by perfusion SPECT/CT: Correlation with radiation dose and clinical morbidity. Acta Oncol. (2015) 54:1350–4. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2015.1061695
40. Liss A, Marsh RB, Kapadia NS, McShan DL, Rogers VE, Balter JM, et al. Decreased lung perfusion after breast/Chest Wall irradiation: quantitative results from a prospective clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2017) 97:296–302. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.10.012
41. Miften MM, Das SK, Su M, Marks LB. Incorporation of functional imaging data in the evaluation of dose distributions using the generalized concept of equivalent uniform dose. Phys Med Biol. (2004) 49:1711–21. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/49/9/009
42. Xiao L, Yang G, Chen J, Yang Y, Meng X, Wang X, et al. Comparison of predictive powers of functional and anatomic dosimetric parameters for radiation-induced lung toxicity in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. (2018) 129(2):242–8. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.09.005
43. Wang ZT, Wei LL, Ding XP, Sun MP, Sun HF, Li BS. Spect-guidance to reduce radioactive dose to functioning lung for stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2013) 14:1061–5. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.2.1061
44. Siva S, Devereux T, Ball DL, MacManus MP, Hardcastle N, Kron T, et al. Ga-68 MAA perfusion 4D-PET/CT scanning allows for functional lung avoidance using conformal radiation therapy planning. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2016) 15:114–21. doi: 10.1177/1533034614565534
45. Yin Y, Chen JH, Li BS, Liu TH, Lu J, Bai T, et al. Protection of lung function by introducing single photon emission computed tomography lung perfusion image into radiotherapy plan of lung cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). (2009) 122:509–13.
46. Meng X, Frey K, Matuszak M, Paul S, Ten Haken R, Yu J, et al. Changes in functional lung regions during the course of radiation therapy and their potential impact on lung dosimetry for non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2014) 89:145–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.01.044
47. Shioyama Y, Jang SY, Liu HH, Guerrero T, Wang X, Gayed IW, et al. Preserving functional lung using perfusion imaging and intensity-modulated radiation therapy for advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2007) 68:1349–58. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.02.015
48. Munawar I, Yaremko BP, Craig J, Oliver M, Gaede S, Rodrigues G, et al. Intensity modulated radiotherapy of non-small-cell lung cancer incorporating SPECT ventilation imaging. Med Phys. (2010) 37:1863–72. doi: 10.1118/1.3358128
49. Lukovic J, Yaremko B, Reid R. Functional lung avoidance using ventilation SPECT in the treatment of advanced-stage carcinoma of the lung: A treatment planning and feasibility study. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2014) 90:S212. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.05.780
50. Dhami G, Zeng J, Vesselle HJ, et al. Framework for radiation pneumonitis risk stratification based on anatomic and perfused lung dosimetry. STRAHLENTHER ONKOL. (2017) 193:410–8. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1114-0
51. Seppenwoolde Y, Engelsman M, De Jaeger K, Muller SH, Baas P, McShan, et al. Optimizing radiation treatment plans for lung cancer using lung perfusion information. Radiother Oncol. (2002) 63:165–77. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8140(02)00075-0
52. Christian JA, Partridge M, Nioutsikou E, Cook G, McNair HA, Cronin B, et al. The incorporation of spect functional lung imaging into inverse radiotherapy planning for non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. (2005) 77:271–7. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2005.08.008
53. Li S, Liu J, Gao S, Yin Y, Zhang L, Han Y, et al. CT ventilation image-guided helical Tomotherapy at sparing functional lungs for locally advanced lung cancer: analysis of dose-function metrics and the impact on pulmonary toxicity. Radiat Oncol. (2023) 18:6. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02189-x
54. Kamer S, Yilmaz Susluer S, Balci Okcanoglu T, Kayabasi C, Ozmen Yelken B, Hoca S, et al. Evaluation of the effect of intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy (VMAT) techniques on survival response in cell lines with a new radiobiological modeling. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:19874–88. doi: 10.1002/cam4.v12.19
55. Farr KP, Kallehauge JF, Moller DS, Khalil AA, Kramer S, Bluhme H, et al. Inclusion of functional information from perfusion SPECT improves predictive value of dose-volume parameters in lung toxicity outcome after radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective study. Radiother Oncol. (2015) 117:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.08.005
56. Lammertsma AA. PET/SPECT: functional imaging beyond flow. Vision Res. (2001) 41:1277–81. doi: 10.1016/S0042-6989(00)00262-5
57. Sarinas PS, Chitkara RK. PET and SPECT in the management of lung cancer. Curr Opin Pulm Med. (2002) 8:257–64. doi: 10.1097/00063198-200207000-00003
58. Bateman TM. Advantages and disadvantages of PET and SPECT in a busy clinical practice. J Nucl Cardiol. (2012) 19 Suppl 1:S3–S11. doi: 10.1007/s12350-011-9490-9
59. Rahmim A, Zaidi H. PET versus SPECT: strengths, limitations and challenges. Nucl Med Commun. (2008) 29:193–207. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e3282f3a515
60. Slough C, Masters SC, Hurley RA, Taber KH. Clinical positron emission tomography (PET) neuroimaging: advantages and limitations as a diagnostic tool. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2016) 28:A4–71. doi: 10.1176/appi.neuropsych.16030044
61. Bailey DL, Roach PJ. A brief history of lung ventilation and perfusionimaging over the 50-year tenure of the editors of seminars in nuclear medicine. Semin Nucl Med. (2020) 50:75–86. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2019.07.004
62. Garcia EV. Physical attributes, limitations, and future potential for PET and SPECT. J Nucl Cardiol. (2012) 19 Suppl 1:S19–29. doi: 10.1007/s12350-011-9488-3
63. Ireland RH, Tahir BA, Wild JM, Lee CE, Hatton MQ. Functional image-guided radiotherapy planning for normal lung avoidance. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). (2016) 28:695–707. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2016.08.005
64. Le Roux P, Hicks RJ, Siva S, Hofman MS. PET/CT lung ventilation and perfusion scanning using galligas and gallium-68-MAA. Semin Nucl Med. (2019) 49:71–81. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2018.10.013
65. Zhang G, Dilling TJ, Stevens CW, Forster KM. Functional lung imaging in thoracic cancer radiotherapy. Cancer Control. (2008) 15:112–9. doi: 10.1177/107327480801500203
66. Bailey DL, Eslick EM, Schembri GP, Roach PJ. (68)Ga PET ventilation and perfusion lung imaging-current status and future challenges. Semin Nucl Med. (2016) 46:428–35. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2016.04.007
67. Oehme L, Zöphel K, Golgor E, Andreeff M, Wunderlich G, Brogsitter C, et al. Quantitative analysis of regional lung ventilation and perfusion PET with (68) Ga-labelled tracers. Nucl Med Commun. (2014) 35:501–10. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000084
68. Chesler DA, Hales C, Hnatowich DJ, Hoop B. Three-dimensional reconstruction of lung perfusion image with positron detection. J Nucl Med. (1975) 16:80–2.
69. Kotzerke J, Andreeff M, Wunderlich G. PET aerosol lung scintigraphy using Galligas. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2010) 37:175–7. doi: 10.1007/s00259-009-1304-9
70. Bucknell N, Hardcastle N, Gunewardena R, Nguyen L, Callahan J, Ball D, et al. Mid-treatment adaptive planning during thoracic radiation using 68 Ventilation-Perfusion Positron emission tomography. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. (2023) 40:100599. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100599
71. Lucia F, Hamya M, Pinot F, Goasduff G, Blanc-Béguin F, Bourhis D, et al. A feasibility study of functional lung volume preservation during stereotactic body radiotherapy guided by gallium-68 perfusion PET/CT. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:1726. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061726
72. Pinot F, Bourhis D, Bourbonne V, Floch R, Mauguen M, Blanc-Béguin F, et al. New automated method for lung functional volumes delineation with lung perfusion PET/CT imaging. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15(7):2166. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072166
73. Hill RP. Radiation effects on the respiratory system. Br J Radiol. (2005) 27:75–81. doi: 10.1259/bjr/34124307
74. Le Roux P, Siva S, Steinfort DP, Callahan J, Eu P, Irving LB, et al. Correlation of 68Ga ventilation-perfusion PET/CT with pulmonary function test indices for assessing lung function. J Nucl Med. (2015) 56:1718–23. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.162586
75. Hofman MS, Beauregard J-M, Barber TW, Neels OC, Eu P, Hicks RJ. 68Ga PET/CT ventilation–perfusion imaging for pulmonary embolism: A pilot study with comparison to conventional scintigraphy. J Nucl Med. (2011) 52:1513–9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.093344
76. Le Roux P-Y, Iravani A, Callahan J, Burbury K, Eu P, Steinfort DP, et al. Independent and incremental value of ventilation/perfusion PET/CT and CT pulmonary angiography for pulmonary embolism diagnosis: Results of the PECAN pilot study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2019) 46:1596–604. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04338-z
77. Forghani F, Patton T, Kwak J, Thomas D, Diot Q, Rusthoven C, et al. Characterizing spatial differences between spect-ventilation and spect-perfusion in patients with lung cancer undergoing radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. (2021) 160:120–4. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2021.04.022
78. Forghani F, Castillo R, Castillo E, PhD BJ, Rusthoven C, Kwak J, et al. Is individual perfusion dose-response different than ventilation dose-response for lung cancer patients treated with radiotherapy? BRIT J Radiol. (2023) 96(1143):20220119. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220119
79. Kimura T, Doi Y, Nakashima T, Imano N, Kawabata H, Nishibuchi I, et al. Combined ventilation and perfusion imaging correlates with the dosimetric parameters of radiation pneumonitis in radiation therapy planning for lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2015) 93:778–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.08.024
80. Vinogradskiy Y, Schubert L, Diot Q, Waxweiller T, Koo P, Castillo R, et al. Regional lung function profiles of stage I and III lung cancer patients: an evaluation for functional avoidance radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2016) 95:1273–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.02.058
81. Lee E, Zeng J, Miyaoka RS, Saini J, Kinahan PE, Sandison GA, et al. Functional lung avoidance and response-adaptive escalation (FLARE) RT: Multimodality plan dosimetry of a precision radiation oncology strategy. Med Phys. (2017) 44:3418–29. doi: 10.1002/mp.2017.44.issue-7
82. Wang J, Wu N, Cham MD, Song Y. Tumor response in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: perfusion CT evaluation of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2009) 193:1090–6. doi: 10.2214/AJR.08.1367
83. Ohno Y, Ozawa Y, Nagata H, Bando S, Cong S, Takahashi T, et al. Area-detector computed tomography for pulmonary functional imaging. Diagnostics (Basel). (2023) 13:2518. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152518
84. Lapointe A, Bahig H, Blais D, Bouchard H, Filion É, Carrier JF, et al. Assessing lung function using contrast-enhanced dual-energy computed tomography for potential applications in radiation therapy. Med Phys. (2017) 44:5260–9. doi: 10.1002/mp.2017.44.issue-10
85. Bahig H, Campeau MP, Lapointe A, Bedwani S, Roberge D, De Guise J, et al. Phase 1-2 study of dual-energy computed tomography for assessment of pulmonary function in radiation therapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2017) 99:334–43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.05.051
86. Tang X, Krupinski EA, Xie H, Stillman AE. On the data acquisition, image reconstruction, cone beam artifacts, and their suppression in axial MDCT and CBCT - A review. Med Phys. (2018). doi: 10.1002/mp.2018.45.issue-9
87. Saini S. Multi-detector row CT: principles and practice for abdominal applications. Radiology. (2004) 233:323–7. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2332030994
88. Carrino JA, Ibad H, Lin Y, Ghotbi E, Klein J, Demehri S, et al. CT in musculoskeletal imaging: still helpful and for what? Skeletal Radiol. (2024) 53:1711–25. doi: 10.1007/s00256-024-04737-w
89. Demehri S, Baffour FI, Klein JG, Ghotbi E, Ibad HA, Moradi K, et al. Musculoskeletal CT imaging: state-of-the-art advancements and future directions. RADIOLOGY. (2023) 308:e230344. doi: 10.1148/radiol.230344
90. Forghani R, De Man B, Gupta R. Dual-energy computed tomography: physical principles, approaches to scanning, usage, and implementation: part 2. NEUROIMAG Clin N Am. (2017) 27:385–400. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2017.03.003
91. Yamamoto T, Kabus S, Bal M, Bzdusek K, Keall PJ, Wright C, et al. Changes in regional ventilation during treatment and dosimetric advantages of CT ventilation image guided radiation therapy for locally advanced lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2018) 102:1366–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.04.063
92. Vinogradskiy Y, Castillo R, Castillo E, Schubert L, Jones BL, Faught A, et al. Results of a multi-institutional phase 2 clinical trial for 4DCT-ventilation functional avoidance thoracic radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2022) 112:986–95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.10.147
93. Utsumi N, Takahashi T, Hatanaka S, Hariu M, Saito M, Kondo S, et al. VMAT planning with xe-CT functional images enables radiotherapy planning with consideration of lung function. Cancer Diagn Progn. (2021) 1:193–200. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10026
94. Ieko Y, Kadoya N, Kanai T, Nakajima Y, Arai K, Kato T, et al. The impact of 4DCT-ventilation imaging-guided proton therapy on stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer. Radiol Phys Technol. (2020) 13:230–7. doi: 10.1007/s12194-020-00572-5
95. Huang Q, Jabbour SK, Xiao Z, Yue N, Wang X, Cao H, et al. Dosimetric feasibility of 4DCT-ventilation imaging guided proton therapy for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol. (2018) 13:78. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1018-x
96. Huang T-C, Hsiao C-Y, Chien C-R, Liang J-A, Shih T-C, Zhang GG. IMRT treatment plans and functional planning with functional lung imaging from 4D-CT for thoracic cancer patients. Radiat Oncol. (2013) 8:3. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-3
97. Kipritidis J, Tahir BA, Cazoulat G, et al. The vampire challenge: A multi-institutional validation study of CT ventilation imaging. Med Phys. (2019) 46:1198–217. doi: 10.1002/mp.2019.46.issue-3
98. Castillo R, Castillo E, Martinez J, Guerrero T. Ventilation from four-dimensional computed tomography: density versus Jacobian methods. Phys Med Biol. (2010) 55:4661–85. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/16/004
99. Astley JR, Biancardi AM, Marshall H, Hughes PJC, Collier GJ, Hatton MQ, et al. A hybrid model- and deep learning-based framework for functional lung image synthesis from multi-inflation CT and hyperpolarized gas MRI. Med Phys. (2023) 50:5657–70. doi: 10.1002/mp.16369
100. Ireland RH, Bragg CM, McJury M, Woodhouse N, Fichele S, van Beek EJ. Feasibility of image registration and intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning with hyperpolarized helium-3 magnetic resonance imaging for non–small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2007) 68:273–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.068
101. Brennan D, Schubert L, Diot Q, Castillo R, Castillo E, Guerrero T, et al. Clinical validation of 4-dimensional computed tomography ventilation with pulmonary function test data. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2015) 92:423–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.01.019
102. Reinhardt JM, Ding K, Cao K, Christensen GE, Hoffman EA, Bodas SV. Registration-based estimates of local lung tissue expansion compared to xenon ct measures of specific ventilation. Med Image Analysis. (2008) 12:752–763. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2008.03.007
103. Vinogradskiy Y, Koo PJ, Castillo R, Castillo E, Guerrero T, Gaspar LE, et al. Comparison of 4-dimensional computed tomography ventilation with nuclear medicine ventilation-perfusion imaging: A clinical validation study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2014) 89:199–205. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.01.009
104. Du KF, Bayouth JE, Cao KL, Christensen GE, Ding K, Reinhardt JM. Reproducibility of registration-based measures of lung tissue expansion. Med Physics. (2012) 39:1595–608. doi: 10.1118/1.3685589
105. Yamamoto T, Kabus S, Klinder T, Lorenz C, von Berg J, Blaffert T, et al. Investigation of four-dimensional computed tomography based pulmonary ventilation imaging in patients with emphysematous lung regions. Phys Med Biol. (2011) 56:2279–98. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/56/7/023
106. Bayouth J, Du K, Christensen G, Smith B, Buatti J, Reinhardt J. Establishing a relationship between radiosensitivity of lung tissue and ventilation. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2012) 84:S31–2. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.07.086
107. Ding K, Bayouth JE, Buatti JM, Christensen GE, Reinhardt JM. 4dct-based measurement of changes in pulmonary function following a course of radiation therapy. Med Physics. (2010) 37:1261–72. doi: 10.1118/1.3312210
108. Christensen GE, Song JH, Lu W, El Naqa I, Low DA. Tracking lung tissue motion and expansion/compression with inverse consistent image registration and spirometry. Med physics. (2007) 34:2155–63. doi: 10.1118/1.2731029
109. Guerrero T, Sanders K, Noyola-Martinez J, Castillo E, Zhang Y, Tapia R, et al. Quantification of regional ventilation from treatment planning CT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2005) 62:630–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.03.023
110. Kipritidis J, Hofman MS, Siva S, Callahan J, Le Roux PY, Woodruff HC, et al. Estimating lung ventilation directly from 4D CT Hounsfield unit values. Med Phys. (2016) 43:33. doi: 10.1118/1.4937599
111. Suga K. Technical and analytical advances in pulmonary ventilation SPECT with xenon-133 gas and Tc-99m-Technegas. Ann Nucl Med. (2002) 16:303–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02988614
112. Callahan J, Hofman MS, Siva S, Kron T, Schneider ME, Binns D, et al. High-resolution imaging of pulmonary ventilation and perfusion with 68Ga-VQ respiratory gated (4-D) PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2014) 41:343–9. doi: 10.1007/s00259-013-2607-4
113. Yamamoto T, Kabus S, Lorenz C, Mittra E, Hong JC, Chung M, et al. Pulmonary ventilation imaging based on 4-dimensional computed tomography: comparison with pulmonary function tests and SPECT ventilation images. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2014) 90:414–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.06.006
114. Tian Y, Miao J, Liu Z, Huang P, Wang W, Wang X, et al. Availability of a simplified lung ventilation imaging algorithm based on four-dimensional computed tomography. Phys MEDICA. (2019) 65:53–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2019.08.006
115. Eslick EM, Kipritidis J, Gradinscak D, Stevens MJ, Bailey DL, Harris B, et al. CT ventilation imaging derived from breath hold CT exhibits good regional accuracy with Galligas PET. Radiother Oncol. (2018) 127:267–73. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.12.010
116. Faught AM, Yamamoto T, Castillo R, Castillo E, Zhang J, Miften M, et al. Evaluating which dose-function metrics are most critical for functional-guided radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2017) 99:202–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.03.051
117. Parker JA, Coleman RE, Grady E, Royal HD, Siegel BA, Stabin MG, et al. Snm practice guideline for lung scintigraphy 4.0. J Nucl Med technology. (2012) 40:57–65. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.111.101386
118. Nioutsikou E, Partridge M, Bedford JL, Webb S. Prediction of radiation-induced normal tissue complications in radiotherapy using functional image data. Phys Med Biol. (2005) 50:1035–46. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/50/6/001
119. Bucknell NW, Hardcastle N, Bressel M, Hofman MS, Kron T, Ball D, et al. Functional lung imaging in radiation therapy for lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. RADIOTHER Oncol. (2018) 129:196–208. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.07.014
120. van Beek EJ, Hoffman EA. Functional imaging: CT and MRI. Clin Chest Med. (2008) 29:195–vii. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2007.12.003
121. Bai H, Li W, Xia Y, Li L, Gao J, Liu X. Preliminary study on the effect of 4DCT-ventilation-weighted dose on the radiation induced pneumonia probability (RIPP). Dose Response. (2021) 19:15593258211017753. doi: 10.1177/15593258211017753
122. Petersson J, Sánchez-Crespo A, Larsson SA, Mure M. Physiological imaging of the lung: single-photon-emission computed tomography (SPECT). J Appl Physiol (1985). (2007) 102:468–76. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00732.2006
123. Kipritidis J, Siva S, Callahan J, Hofman M, Keall P. TU-A-WAB-08:Strong evidence for physiologic correlation of 4D-CT ventilation imaging with respiratory-correlated gallium 68 PET/CT in humans. Med Phys. (2013) 40:424. doi: 10.1118/1.4815342
124. Odisio EG, Truong MT, Duran C, de Groot PM, Godoy MC. Role of dual-energy computed tomography in thoracic oncology. Radiol Clin N Am. (2018) 56:535–48. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2018.03.011
125. Yanagita H, Honda N, Nakayama M, Watanabe W, Shimizu Y, Osada H, et al. Prediction of postoperative pulmonary function: preliminary comparison of single-breath dual-energy xenon CT with three conventional methods. Jpn J Radiol. (2013) 31:377–85. doi: 10.1007/s11604-013-0202-z
126. Zhang LJ, Zhou CS, Schoepf UJ, Sheng HX, Wu SY, Krazinski AW, et al. Dual-energy CT lung ventilation/perfusion imaging for diagnosing pulmonary embolism. Eur Radiol. (2013) 23:2666–75. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2907-x
127. Gaudreault M, Bucknell N, Woon B, Kron T, Hofman MS, Siva S, et al. Dose-response relationship between radiation therapy and loss of lung perfusion comparing positron emission tomography and dual-energy computed tomography in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2024) 118:1135–43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.10.038
128. Hachulla AL, Pontana F, Wemeau-Stervinou L, Khung S, Faivre JB, Wallaert B, et al. Krypton ventilation imaging using dual-energy CT in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: initial experience. Radiology. (2012) 263:253–9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12111211
129. Hong SR, Chang S, Im DJ, Suh YJ, Hong YJ, Hur J, et al. Feasibility of single scan for simultaneous evaluation of regional krypton and iodine concentrations with dual-energy CT: an experimental study. Radiology. (2016) 281:597–605. doi: 10.1148/radiol.16152429
130. Li K, Li Y, Qi Z, Garrett JW, Grist TM, Chen G. Quantitative lung perfusion blood volume using dual energy CT–based effective atomic number (Zeff) imaging Med. Phys. (2021) 48:6658–72. doi: 10.1002/mp.15227
131. Gaudreault M, Korte J, Bucknell N, Jackson P, Sakyanun P, McIntosh L, et al. Comparison of dual-energy CT with positron emission tomography for lung perfusion imaging in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Phys Med Biol. (2023) 68(3):10.1088/1361-6560/acb198. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/acb198
132. Kerl JM, Lehnert T, Schell B, Bodelle B, Beeres M, Jacobi V, et al. Intravenous contrast material administration at high-pitch dual-source CT pulmonary angiography: test bolus versus bolus-tracking technique. Eur J radiology. (2012) 81:2887–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.09.018
133. Fuld MK, Halaweish AF, Haynes SE, Divekar AA, Guo J, Hoffman EA. Pulmonary perfused blood volume with dual-energy CT as surrogate for pulmonary perfusion assessed with dynamic multidetector CT. Radiology. (2013) 267:747–56. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12112789
134. Thieme SF, Becker CR, Hacker M, Nikolaou K, Reiser MF, Johnson TR. Dual energy CT for the assessment of lung perfusion–correlation to scintigraphy. Eur J Radiol. (2008) 68:369–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.07.031
135. Wortman JR, Sodickson AD. Pearls, pitfalls, and problems in dual-energy computed tomography imaging of the body. Radiol Clin North Am. (2018) 56:625–40. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2018.03.007
136. Dinkel J, Khalilzadeh O, Phan CM, Goenka AH, Yoo AJ, Hirsch JA, et al. Technical limitations of dual-energy CT in neuroradiology: 30-month institutional experience and review of literature. J neurointerv Surg. (2015) 7:596–602. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011241
137. Yeh BM, FitzGerald PF, Edic PM, Lambert JW, Colborn RE, Marino ME, et al. Opportunities for new CT contrast agents to maximize the diagnostic potential of emerging spectral CT technologies. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2017) 113:201–22. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.09.001
138. Chae EJ, Seo JB, Goo HW, Kim N, Song KS, Lee SD, et al. Xenon ventilation CT with a dual-energy technique of dual-source CT: initial experience. Radiology. (2008) 248:615–24. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2482071482
139. Remy-Jardin M, Faivre JB, Pontana F, Hachulla AL, Tacelli N, Santangelo T, et al. Thoracic applications of dual energy. Radiol Clin North Am. (2010) 48:193–205. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2009.08.013
140. Kong X, Sheng HX, Lu GM, Meinel FG, Dyer KT, Schoepf UJ, et al. Xenon-enhanced dual-energy CT lung ventilation imaging: techniques and clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2014) 202:309–17. doi: 10.2214/AJR.13.11191
141. Park EA, Goo JM, Park SJ, Lee HJ, Lee CH, Park CM, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: quantitative and visual ventilation pattern analysis at xenon ventilation CT performed by using a dual-energy technique. Radiology. (2010) 256:985–97. doi: 10.1148/radiol.10091502
142. Goo HW, Chae EJ, Seo JB, Hong SJ. Xenon ventilation CT using a dual-source dual-energy technique: dynamic ventilation abnormality in a child with bronchial atresia. Pediatr Radiol. (2008) 38:1113–6. doi: 10.1007/s00247-008-0914-x
143. Goo HW, Yang DH, Kim N, Park SI, Kim DK, Kim EA. Collateral ventilation to congenital hyperlucent lung lesions assessed on xenon-enhanced dynamic dual-energy CT: an initial experience. Korean J Radiol. (2011) 12:25–33. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.1.25
144. Honda N, Osada H, Watanabe W, Nakayama M, Nishimura K, Krauss B, et al. Imaging of ventilation with dual-energy CT during breath hold after single vital-capacity inspiration of stable xenon. Radiology. (2012) 262:262–8. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11110569
145. Latchaw RE, Y onas H, Pentheny SL, Gur D. Adverse reactions to xenon-enhanced CT cerebral blood flow determination. Radiology. (1987) 163:251–4. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.1.3823444
146. Chon D, Beck KC, Simon BA, Shikata H, Saba OI, Hoffman EA. Effect of low-xenon and krypton supplementation on signal/noise of regional CT-based ventilation measurements. J Appl Physiol. (2007) 102:1535–44. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01235.2005
147. Chung YE, Hong SR, Lee MJ, Lee M, Lee HJ. Krypton-enhanced ventilation CT with dual energy technique: experimental study for optimal krypton concentration. Exp Lung Res. (2014) 40:439–46. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2014.946630
148. Mahnken AH, Jost G, Pietsch H. Krypton for computed tomography lung ventilation imaging: preliminary animal data. Invest Radiol. (2015) 50:305–8. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000130
149. Krypton 85. Department of human health protection and dosimetry. Paris, France: Institut de Protection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (2001).
150. Bauer RW, Frellesen C, Renker M, Schell B, Lehnert T, Ackermann H, et al. Dual energy CT pulmonary blood volume assessment in acute pulmonary embolism - correlation with D-dimer level, right heart strain and clinical outcome. Eur radiology. (2011) 21:1914–21. doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2135-1
151. Chae EJ, Seo JB, Jang YM, Krauss B, Lee CW, Lee HJ, et al. Dual-energy CT for assessment of the severity of acute pulmonary embolism: pulmonary perfusion defect score compared with CT angiographic obstruction score and right ventricular/left ventricular diameter ratio. AJR Am J roentgenology. (2010) 194:604–10. doi: 10.2214/AJR.09.2681
152. Meysman M, Everaert H, Buls N, Nieboer K, de Mey J. Comparison of ventilation-perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography (V/Q SPECT) versus dual-energy CT perfusion and angiography (DECT) after 6 months of pulmonary embolism (PE) treatment. Eur J radiology. (2015) 84:1816–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.05.023
153. Pansini V, Remy-Jardin M, Faivre JB, Schmidt B, Dejardin-Bothelo A, Perez T, et al. Assessment of lobar perfusion in smokers according to the presence and severity of emphysema: preliminary experience with dual-energy CT angiography. Eur radiology. (2009) 19:2834–43. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1475-6
154. Moon JW, Bae JP, Lee HY, Kim N, Chung MP, Park HY, et al. Perfusion- and pattern-based quantitative CT indexes using contrast-enhanced dual-energy computed tomography in diffuse interstitial lung disease: relationships with physiologic impairment and prediction of prognosis. Eur radiology. (2016) 26:1368–77. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3946-2
155. Aoki M, Hirose K, Sato M, Akimoto H, Kawaguchi H, Hatayama Y, et al. Prognostic impact of average iodine density assessed by dual-energy spectral imaging for predicting lung tumor recurrence after stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Radiat Res. (2016) 57:381–6. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrv100
156. Landry G, Gaudreault M, van Elmpt W, Wildberger JE, Verhaegen F. Improved dose calculation accuracy for low energy brachytherapy by optimizing dual energy CT imaging protocols for noise reduction using sinogram affirmed iterative reconstruction. Z fur medizinische Physik. (2016) 26:75–87. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2015.09.001
157. Hunemohr N, Paganetti H, Greilich S, Jakel O, Seco J. Tissue decomposition from dual energy CT data for MC based dose calculation in particle therapy. Med physics. (2014) 41:061714. doi: 10.1118/1.4875976
158. Mangold S, Gatidis S, Luz O, Konig B, Schabel C, Bongers MN, et al. Single-source dual-energy computed tomography: use of monoenergetic extrapolation for a reduction of metal artifacts. Invest radiology. (2014) 49:788–93. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000083
159. Ferda J, Ferdova E, Mirka H, Baxa J, Bednarova A, Flohr T, et al. Pulmonary imaging using dual-energy CT, a role of the assessment of iodine and air distribution. Eur J radiology. (2011) 77:287–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.08.005
160. Toepker M, Czerny C, Ringl H, Fruehwald-Pallamar J, Wolf F, Weber M, et al. Can dual-energy CT improve the assessment of tumor margins in oral cancer? Oral Oncol. (2014) 50:221–7. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.12.001
161. Zhang M, Li H, Li H, Zhao X, Liu X, Han Y, et al. Dynamic evaluation of acute lung injury using hyperpolarized 129 Xe magnetic resonance. NMR Biomed. (2023) 37(4):e5078. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5078
162. Yamamoto T, Kabus S, von Berg J, Lorenz C, Loo B, Keall P. 4D-CT pulmonary ventilation image-guided radiotherapy planning is significantly influenced by deformable image registration algorithms and metrics. Int J Radiat Oncol. (2010) 78:S185. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.07.450
163. Castillo E, Castillo R, Vinogradskiy Y, Guerrero T. The numerical stability of transformation-based ct ventilation. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. (2017) 12:569–80. doi: 10.1007/s11548-016-1509-x
164. Kang MJ, Park CM, Lee CH, Goo JM, Lee HJ. Dual-energy CT: clinical applications in various pulmonary diseases. Radio Graphics. (2010) 30:685–98. doi: 10.1148/rg.303095101
165. Johnson T, Fink C, Schönberg SO, Reiser MF eds. Dual energy CT in clinical practice. Berlin, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media (2011).
166. Goo HW. Dual-energy lung perfusion and ventilation CT in children. Pediatr Radiol. (2013) 43:298–307. doi: 10.1007/s00247-012-2465-4
167. Wielputz M, Kauczor HU. MRI of the lung: state of the art. Diagn Interv Radiol. (2012) 18:344–53. doi: 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.5365-11.0
168. Bauman G, Puderbach M, Deimling M, Jellus V, Chefd'hotel C, Dinkel J, et al. Non-contrast-enhanced perfusion and ventilation assessment of the human lung by means of fourier decomposition in proton MRI. Magn Reson Med. (2009) 62:656–64. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22031
169. Kjørstad Å, Corteville DM, Fischer A, Henzler T, Schmid-Bindert G, Zöllner FG, et al. Quantitative lung perfusion evaluation using Fourier decomposition perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. (2014) 72:558–62. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24930
170. Rankine LJ, Wang Z, Driehuys B, Marks LB, Kelsey CR, Das SK. Correlation of regional lung ventilation and gas transfer to red blood cells: implications for functional-avoidance radiation therapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2018) 101:1113–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.04.017
171. Ding Y, Yang L, Zhou Q, Bi J, Li Y, Pi G, et al. A pilot study of function-based radiation therapy planning for lung cancer using hyperpolarized xenon-129 ventilation MRI. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2022) 23:e13502. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13502
172. Ohno Y, Hatabu H, Takenaka D, Van Cauteren M, Fujii M, Sugimura K. Dynamic oxygen-enhanced MRI reflects diffusing capacity of the lung. Magn Reson Med. (2002) 47:1139–44. doi: 10.1002/mrm.10168
173. Kaireit TF, Gutberlet M, Voskrebenzev A, Freise J, Welte T, Hohlfeld JM, et al. Comparison of quantitative regional ventilation-weighted fourier decomposition MRI with dynamic fluorinated gas washout MRI and lung function testing in COPD patients. J Magn Reson Imaging. (2018) 47:1534–41. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25902
174. Bauman G, Lützen U, Ullrich M, Gaass T, Dinkel J, Elke G, et al. Pulmonary functional imaging: Qualitative comparison of fourier decomposition MR imaging with SPECT/CT in porcine lung. Radiology. (2011) 260:551–9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11102313
175. Foo CT, Langton D, Thompson BR, Thien F. Functional lung imaging using novel and emerging MRI techniques. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1060940. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1060940
176. Kauczor HU, Hofmann D, Kreitner KF, Nilgens H, Surkau R, Heil W, et al. Normal and abnormal pulmonary ventilation: visualization at hyperpolarized He-3 MR imaging. Radiology. (1996) 201:564–8. doi: 10.1148/radiology.201.2.8888259
177. Hart K, Marshall H, Swinscoe J, Robinson S, Matthew T, Tozer-Loft S, et al. OC-0523 3He MRI for functional lung avoidance VMAT treatment planning in lung cancer. RADIOTHER Oncol. (2019) 133:S274–5. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8140(19)30943-0
178. Marshall H, Horsley A, Taylor CJ, Smith L, Hughes D, Horn FC, et al. Detection of early subclinical lung disease in children with cystic fibrosis by lung ventilation imaging with hyperpolarised gas MRI. THORAX. (2017) 72:760–2. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208948
179. Hughes PJC, Horn FC, Collier GJ, Biancardi A, Marshall H, Wild JM, et al. Spatial fuzzy c-means thresholding for semiautomated calculation of percentage lung ventilated volume from hyperpolarized gas and 1 H MRI. J Magn Reson IMAGING. (2017) 47:640–6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25804
180. Mathew L, Wheatley A, Castillo R, Castillo E, Rodrigues G, Guerrero T, et al. Hyperpolarized (3)He magnetic resonance imaging: comparison with four-dimensional x-ray computed tomography imaging in lung cancer. Acad Radiol. (2012) 19:1546–53. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2012.08.007
181. Mugler JP, Altes TA. Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI of the human lung. J Magn Reson Imaging. (2013) 37:313–31. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23844
182. Qing K, Ruppert K, Jiang Y, Mata JF, Miller GW, Shim YM, et al. Regional mapping of gas uptake by blood and tissue in the human lung using hyperpolarized xenon-129 MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. (2014) 39:346–59. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24181
183. Halaweish AF, Moon RE, Foster WM, Soher BJ, McAdams HP, MacFall JR, et al. Perfluoropropane gas as a magnetic resonance lung imaging contrast agent in humans. Chest. (2013) 144:1300–10. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2597
184. Schreiber WG, Eberle B, Laukemper-Ostendorf S, Markstaller K, Weiler N, Scholz A, et al. Dynamic (19)F-MRI of pulmonary ventilation using sulfur hexafluoride (SF(6)) gas. Magn Reson Med. (2001) 45:605–13. doi: 10.1002/mrm.v45:4
185. Mammarappallil J, MacIntyre N, Mahmood K, Womack S, Cecil CH. Imaging ventilation using 19F perfluorinated gas magnetic resonance imaging: strategies for imaging collateral ventilation. J Lung Pulm Respir Res. (2021) 8:41–5. doi: 10.15406/jlprr.2021.08.00249
186. Goralski JL, Chung SH, Glass TM, Ceppe AS, Akinnagbe-Zusterzeel EO, Trimble AT, et al. Dynamic perfluorinated gas MRI reveals abnormal ventilation despite normal FEV1 in cystic fibrosis. JCI Insight. (2020) 5:e133400. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.133400
187. Halaweish AF, Foster WM, Moon RE, MacIntyre NR, MacFall JR, Charles HC, et al. Dynamics of pulmonary ventilation distribution at steady state via 19fluorine-enhanced MRI: initial experiences and future developments. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. (2013) 21:4111.
188. Ohno Y, Hatabu H. Basics concepts and clinical applications of oxygen-enhanced MR imaging. Eur J Radiol. (2007) 64:320–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.08.006
189. Renne J, Lauermann P, Hinrichs J, Schonfeld C, Sorrentino S, Gutberlet M, et al. Clinical use of oxygen-enhanced T1 mapping MRI of the lung: reproducibility and impact of closed versus loose fit oxygen delivery system. J Magn Reson Imaging. (2015) 41:60–6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24535
190. Hatabu H, Tadamura E, Chen Q, Stock KW, Li W, Prasad PV, et al. Pulmonary ventilation: dynamic MRI with inhalation of molecular oxygen. Eur J Radiol. (2001) 37:172–8. doi: 10.1016/S0720-048X(00)00298-9
191. Rankine LJ, Wang Z, Kelsey CR, Bier E, Driehuys B, Marks LB, et al. Hyperpolarized 129Xe magnetic resonance imaging for functional avoidance treatment planning in thoracic radiation therapy: A comparison of ventilation- and gas exchange-guided treatment plans. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2021) 111:1044–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.07.002
192. Yaremko BP, Capaldi DPI, Sheikh K, Palma DA, Warner A, Dar AR, et al. Functional lung avoidance for individualized radiation therapy: results of a double-masked, randomized controlled trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2022) 113:1072–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.04.047
193. Glandorf J, Klimes F, Voskrebenzev A, Gutberlet M, Behrendt L, Crisosto C, et al. Comparison of phase-resolved functional lung (PREFUL) MRI derived perfusion and ventilation parameters at 1.5T and 3T in healthy volunteers. PloS One. (2020) 15:e0244638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244638
194. Hirsch FW, Sorge I, Vogel-Claussen J, Roth C, Gräfe D, Päts A, et al. The current status and further prospects for lung magnetic resonance imaging in pediatric radiology. Pediatr Radiol. (2020) 50:734–49. doi: 10.1007/s00247-019-04594-z
195. Saam BT, Y ablonskiy DA, Kodibagkar VD, Leawoods JC, Gierada DS, Cooper JD, et al. MR imaging of diffusion of (3)He gas in healthy and diseased lungs. Magn Reson Med. (2000) 44:174–9. doi: 10.1002/1522-2594(200008)44:2<174::AID-MRM2>3.0.CO;2-4
196. Stewart NJ, Smith LJ, Chan HF, Eaden JA, Rajaram S, Swift AJ, et al. Lung MRI with hyperpolarised gases: current & future clinical perspectives. Br J Radiol. (2022) 95:20210207. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20210207
197. Driehuys B, Martinez- Jimenez S, Cleveland ZI, Metz GM, Beaver DM, Nouls JC, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: safety and tolerability of hyperpolarized 129Xe MR imaging in healthy volunteers and patients. Radiology. (2012) 262:279–89. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11102172
198. Lutey BA, Lefrak SS, Woods JC, Tanoli T, Quirk JD, Bashir A, et al. Hyperpolarized 3He MR imaging: physiologic monitoring observations and safety considerations in 100 consecutive subjects. Radiology. (2008) 248:655–61. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2482071838
199. Wang JM, Robertson SH, Wang Z, He M, Virgincar RS, Schrank GM, et al. Using hyperpolarized 129 Xe MRI to quantify regional gas transfer in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. (2017) 73(1):21–8. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2017-210070
200. Kaushik SS, Freeman MS, Yoon SW, Liljeroth MG, Stiles JV, Roos JE, et al. Measuring diffusion limitation with a perfusion-limited gas-Hyperpolarized 129Xe gas-transfer spectroscopy in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Appl Physiol. (2014) 117:577–85. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00326.2014
201. Gutberlet M, Kaireit TF, Voskrebenzev A, Lasch F, Freise J, Welte T, et al. Free-breathing dynamic (19)F gas MR imaging for mapping of regional lung ventilation in patients with COPD. Radiology. (2018) 286:1040–51. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017170591
202. Ohno Y, Koyama H, Matsumoto K, Onishi Y, Nogami M, Takenaka D, et al. Oxygen-enhanced MRI vs. quantitatively assessed thin-section CT: pulmonary functional loss assessment and clinical stage classification of asthmatics. Eur J Radiol. (2011) 77:85–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.06.027
203. Ohno Y, Iwasawa T, Seo JB, Koyama H, Takahashi H, Oh YM, et al. Oxygen-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography: multicenter study for clinical stage classification of smoking-related chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2008) 177:1095–102. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200709-1322OC
204. Ohno Y, Nishio M, Koyama H, Y oshikawa T, Matsumoto S, Seki S, et al. Oxygen-enhanced MRI for patients with connective tissue diseases: comparison with thin section CT of capability for pulmonary functional and disease severity assessment. Eur Radiol. (2014) 83:391–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.11.001
205. Morgan AR, Parker GJ, Roberts C, Buonaccorsi GA, Maguire NC, Hubbard Cristinacce PL, et al. Feasibility assessment of using oxygen-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for evaluating the effect of pharmacological treatment in COPD. Eur J Radiol. (2014) 83:2093–101. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.08.004
206. Rankine LJ, Wang Z, Wang JM, He M, McAdams HP, Mammarappallil J, et al. 129 xenon gas exchange magnetic resonance imaging as a potential prognostic marker for progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. (2020) 17:121–5. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201905-413RL
207. Vinogradskiy YY, Castillo R, Castillo E, Chandler A, Martel MK, Guerrero T. Use of weekly 4DCT-based ventilation maps to quantify changes in lung function for patients undergoing radiation therapy. Med Phys. (2012) 39:289–98. doi: 10.1118/1.3668056
208. Guerini AE, Nici S, Magrini SM, Riga S, Toraci C, Pegurri L, et al. Adoption of hybrid MRI-linac systems for the treatment of brain tumors: A systematic review of the current literature regarding clinical and technical features. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2023) 22:15330338231199286. doi: 10.1177/15330338231199286
209. Datta A, Aznar MC, Dubec M, Parker GJM, O'Connor JPB. Delivering functional imaging on the MRI-linac: current challenges and potential solutions. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). (2018) 30:702–10. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2018.08.005
210. Bryant JM, Weygand J, Keit E, Cruz-Chamorro R, Sandoval ML, Oraiqat IM, et al. Stereotactic magnetic resonance-guided adaptive and non-adaptive radiotherapy on combination MR-linear accelerators: current practice and future directions. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:2081. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072081
211. Carr HY. Steady-state free precession in nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys Rev. (1958) 112:1693–701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.112.1693
212. Liney GP, Whelan B, Oborn B, Barton M, Keall P. MRI-linear accelerator radiotherapy systems. Clin Oncol. (2018) 30:686–91. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2018.08.003
213. Cai B, Li H, Yang D, Rodriguez V, Curcuru A, Wang Y, et al. Performance of a multi leaf collimator system for MR-guided radiation therapy. Med Phys. (2017) 44:6504–14. doi: 10.1002/mp.2017.44.issue-12
214. Henke LE, Olsen JR, Contreras JA, Curcuru A, DeWees TA, Green OL, et al. Stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) forUltracentral thorax Malignancies: results of a phase 1 trial. Adv Radiat Oncol. (2018) 4:201–9. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2018.10.003
215. Redler G, Stevens T, Cammin J, Malin M, Green O, Mutic S, et al. Dosimetric feasibility of utilizing the viewRay magnetic resonance guided linac system for image-guided spine stereotactic body radiation therapy. Cureus. (2019) 11:e6364. doi: 10.7759/cureus.6364
216. Tetar S, Lagerwaard F, Palacios M, Haasbeek N, Bohoudi O, Slotman B, et al. MA13.10 magnetic resonance imaging-guided delivery of lung stereotactic radiotherapy using patient-controlled visual guidance. J Thorac Oncol. (2017) 12:S420–1. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.485
217. Thomas DH, Santhanam A, Kishan AU, Cao M, Lamb J, Min Y, et al. Initial clinical observations of intra- and interfractional motion variation in MR-guided lung SBRT. Br J Radiol. (2018) 91:20170522. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20170522
218. Van Sörnsen de Koste JR, Palacios MA, Bruynzeel AME, Slotman BJ, Senan S, Lagerwaard FJ. MR-guided gated stereotactic radiation therapy delivery for lung, adrenal, and pancreatic tumors: A geometric analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2018) 102:858–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.05.048
219. Finazzi T, Palacios MA, Spoelstra FOB, Haasbeek CJA, Bruynzeel AME, Slotman BJ, et al. Role of on-table plan adaptation in MR-guided ablative radiation therapy for central lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2019) 104:933–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.035
220. Padgett KR, Simpson GN, Llorente R, Samuels MA, Dogan N. Feasibility of adaptive MR-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) of lung tumors. Cureus. (2018) 10:e2423. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2423
221. Finazzi T, van Sörnsen de Koste JR, Palacios MA, Spoelstra FOB, Slotman BJ, Haasbeek CJA, et al. Delivery of magnetic resonance-guided single-fraction stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. (2020) 14:17–23. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2020.05.002
222. Crockett CB, Samson P, Chuter R, Dubec M, Faivre-Finn C, Green OL, et al. Initial clinical experience of MR-guided radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:617681. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.617681
223. Benitez CM, Steinberg ML, Cao M, Qi XS, Lamb JM, Kishan AU, et al. MRI-guided radiation therapy for prostate cancer: the next frontier in ultrahypofractionation. Cancers. (2023) 15:4657. doi: 10.3390/cancers15184657
224. Kontaxis C, Woodhead PL, Bol GH, Lagendijk JJW, Raaymakers BW. Proof-of-concept delivery of intensity modulated arc therapy on the Elekta Unity 1.5 T MR-linac. Phys Med Biol. (2021) 66:04LT01. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/abd66d
225. Han EY, Aima M, Hughes N, Briere TM, Yeboa DN, Castillo P, et al. Feasibility of spinal stereotactic body radiotherapy in Elekta Unity® MR-Linac. J Radiosurg SBRT. (2020) 7:127–34.
226. Han C, Da Silva A, Liang J, Wohlers C, Huntzinger C, Neylon J, et al. Comparative evaluation of treatment plan quality for a prototype biology-guided radiotherapy system in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med Dosim. (2021) 46:171–8. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2020.11.002
227. Yang X, Zhao W, Tian X, Cai J, Xie S, Liu Q, et al. Application of PET-LINAC in biology-guided radiotherapy. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. (2023) 47:237–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7104.2023.03.001
228. Shi M, Simiele E, Han B, Pham D, Palomares P, Aguirre M, et al. First-year experience of stereotactic body radiation therapy/intensity modulated radiation therapy treatment using a novel biology-guided radiation therapy machine. Adv Radiat Oncol. (2023) 9:101300. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2023.101300
229. Shirvani SM, Huntzinger CJ, Melcher T, Olcott PD, Voronenko Y, Bartlett-Roberto J, et al. Biology-guided radiotherapy: Redefining the role of radiotherapy in metastatic cancer. Br J Radiol. (2021) 94:20200873. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200873
230. Oderinde OM, Shirvani SM, Olcott PD, Kuduvalli G, Mazin S, Larkin D. The technical design and concept of a PET/CT linac for biology-guided radiotherapy. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. (2021) 29:106–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2021.04.003
231. Surucu M, Ashraf MR, Romero IO, Zalavari LT, Pham D, Vitzthum LK, et al. Commissioning of a novel PET-Linac for biology-guided radiotherapy (BgRT). Med Phys. (2024) 51:4389–401. doi: 10.1002/mp.17114
232. Pham D, Simiele E, Breitkreutz D, Capaldi D, Han B, Surucu M, et al. IMRT and SBRT treatment planning study for the first clinical biology-guided radiotherapy system. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2022) 21:15330338221100231. doi: 10.1177/15330338221100231
233. Hwang MS, Lalonde R, Huq MS. A detailed process map for clinical workflow of a new biology-guided radiotherapy (BgRT) machine. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2022) 23:e13606. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13606
234. Chin S, Eccles CL, McWilliam A, Chuter R, Walker E, Whitehurst P, et al. Magnetic resonance-guided radiation therapy: A review. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. (2020) 64:163–77. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.12968
235. van Herk M, McWilliam A, Dubec M, Faivre-Finn C, Choudhury A. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided radiation therapy: A short strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2018) 101:1057–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.11.009
236. Edmund JM, Nyholm T. A review of substitute CT generation for MRI-only radiation therapy. Radiat Oncol. (2017) 12:28. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0747-y
237. Han X. MR-based synthetic CT generation using a deep convolutional neural network method. Med Phys. (2017) 44:1408–19. doi: 10.1002/mp.12155
238. Menten MJ, Wetscherek A, Fast MF. MRI-guided lung SBRT: Present and future developments. Phys Med Eur J Med Phys. (2017) 44:139–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.02.003
239. Sim AJ, Kaza E, Singer L, Rosenberg SA. A review of the role of MRI in diagnosis and treatment of early stage lung cancer. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. (2020) 24:16–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2020.06.002
240. Da Silva A, Olcott P, Tian S, Yang X, Sethi I, Shirvani S, et al. Feasibility of using FDG in the stereotactic ablative setting for tracked dose delivery with BgRT: results from a prospective study of serial inter-fraction PET/CTs. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2021) 111:S97. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.07.226
Keywords: radiotherapy, lung function imaging, lung functional image-based radiotherapy, radiation-induced lung injury, clinical benefit
Citation: Yu J, Tang X, Lei Y, Zhang Z, Li B, Bai H and Li L (2024) A review on functional lung avoidance radiotherapy plan for lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 14:1429837. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1429837
Received: 08 May 2024; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 05 December 2024.
Edited by:
Srinivas Raman, University Health Network (UHN), CanadaReviewed by:
Corrado Spatola, University of Catania, ItalyChunhui Han, City of Hope National Medical Center, United States
Copyright © 2024 Yu, Tang, Lei, Zhang, Li, Bai and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Han Bai, Y2VsbGJhaWhhbkAxNjMuY29t; Lan Li, a21sYW5tbUBzaW5hLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jinhui Yu
Jinhui Yu Xiaofeng Tang2
Xiaofeng Tang2 Han Bai
Han Bai Lan Li
Lan Li