- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine and PET Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 2Department of Radiology, Jinshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Radiology, Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 4Department of Radiology, International Peace Maternity and Child Health Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 5College of Information Engineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 6Departments of Radiology, Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Objectives: The accurate assessment of lymph node metastasis (LNM) can facilitate clinical decision-making on radiotherapy or radical hysterectomy (RH) in cervical adenocarcinoma (AC)/adenosquamous carcinoma (ASC). This study aims to develop a deep learning radiomics nomogram (DLRN) to preoperatively evaluate LNM in cervical AC/ASC.
Materials and methods: A total of 652 patients from a multicenter were enrolled and randomly allocated into primary, internal, and external validation cohorts. The radiomics features were extracted from axial T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging (CE-T1WI). The DL features from T2WI, DWI, and CE-T1WI were exported from Resnet 34, which was pretrained by 14 million natural images of the ImageNet dataset. The radscore (RS) and DL score (DLS) were independently obtained after repeatability test, Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC), minimum redundancy maximum relevance (MRMR), and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithm performed on the radiomics and DL feature sets. The DLRN was then developed by integrating the RS, DLS, and independent clinicopathological factors for evaluating the LNM in cervical AC/ASC.
Results: The nomogram of DLRN-integrated FIGO stage, menopause, RS, and DLS achieved AUCs of 0.79 (95% CI, 0.74–0.83), 0.87 (95% CI, 0.81–0.92), and 0.86 (95% CI, 0.79–0.91) in the primary, internal, and external validation cohorts. Compared with the RS, DLS, and clinical models, DLRN had a significant higher AUC for evaluating LNM (all P < 0.005).
Conclusions: The nomogram of DLRN can accurately evaluate LNM in cervical AC/ASC.
Introduction
Radical hysterectomy (RH) is widely recognized as the established standard surgical approach in early-stage cervical cancer (1). According to the 2018 version of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging system, if lymph node metastasis (LNM) is detected through preoperative imaging or pathology, the cancers will be classified as stage IIIC (2). Instead of RH, definitive radiotherapy is considered the preferred treatment approach for patients diagnosed with stage IIIC (3). On the other hand, with the routine application of RH, approximately 90% of non-metastatic lymph nodes (LN) are routinely dissected, causing various complications, such as lymphedema, neurovascular injury, and adhesion (4). Although a satisfactory 5-year survival rate is observed in early-stage cervical cancer after RH, the occurrence of LNM decreases the survival rate from 85%–90% to 50%–55% (5). Thus, the precise preoperative assessment of lymph node metastasis (LNM) holds great significance in personalized treatment plans and prognosis evaluation for patients with cervical cancer (6).
Adenocarcinoma (AC) and adenosquamous carcinoma (ASC) account for approximately 20%–25% of cervical cancers and have exhibited a rise in morbidity and mortality over the past decades, particularly in young women (6–9). Compared with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), both AC and ASC are independent risk factors for the lower overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) (7). Additionally, ASC more commonly exhibits peripheral nerve infiltration, whereas AC is linked to earlier FIGO stage, smaller tumor volume, less lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI), less deep stromal invasion (DSI), and a higher incidence of ovarian metastasis (10). The predictive factors for LNM between AC components and SCC are different (11). Therefore, it is necessary to explore reliable predictive factors and construct a powerful comprehensive model to evaluate LNM in cervical AC and ASC.
The dissected lymph nodes (LNs) can be categorized into three groups based on the size of the metastases on pathology: (1) individual tumor cells measuring less than 0.2 mm; (2) micrometastasis ranging from 0.2 mm to 2 mm; and (3) macrometastasis measuring greater than 2 mm (12). However, both the preoperative MRI and positron emission tomography (PET)-CT demonstrate a limited discriminating ability for the individual tumor cells and micrometastasis in LN with a normal size (13, 14). As parts of artificial intelligence, medical image-based radiomics and deep learning (DL) have attracted increasing attention and shown optimistic prospects in precision medicine. Radiomics is the process of the quantitative high-dimensional features extraction from medical images based on high-throughput techniques that helps to achieve precision medicine (15). Compared with radiomics, DL can achieve automatic learning and hierarchically organized task-adaptive image features and form automatic predictions for precision medicine (16).
Given the distinct biological properties and the rising morbidity and mortality of AC and ASC, the objective of this study was to construct a DL radiomics nomogram (DLRN) for the accurate evaluation of LNM in cervical AC and ASC.
Patients and methods
The approval of this retrospective study was obtained from the institutional review board, and the informed consent requirement was waived.
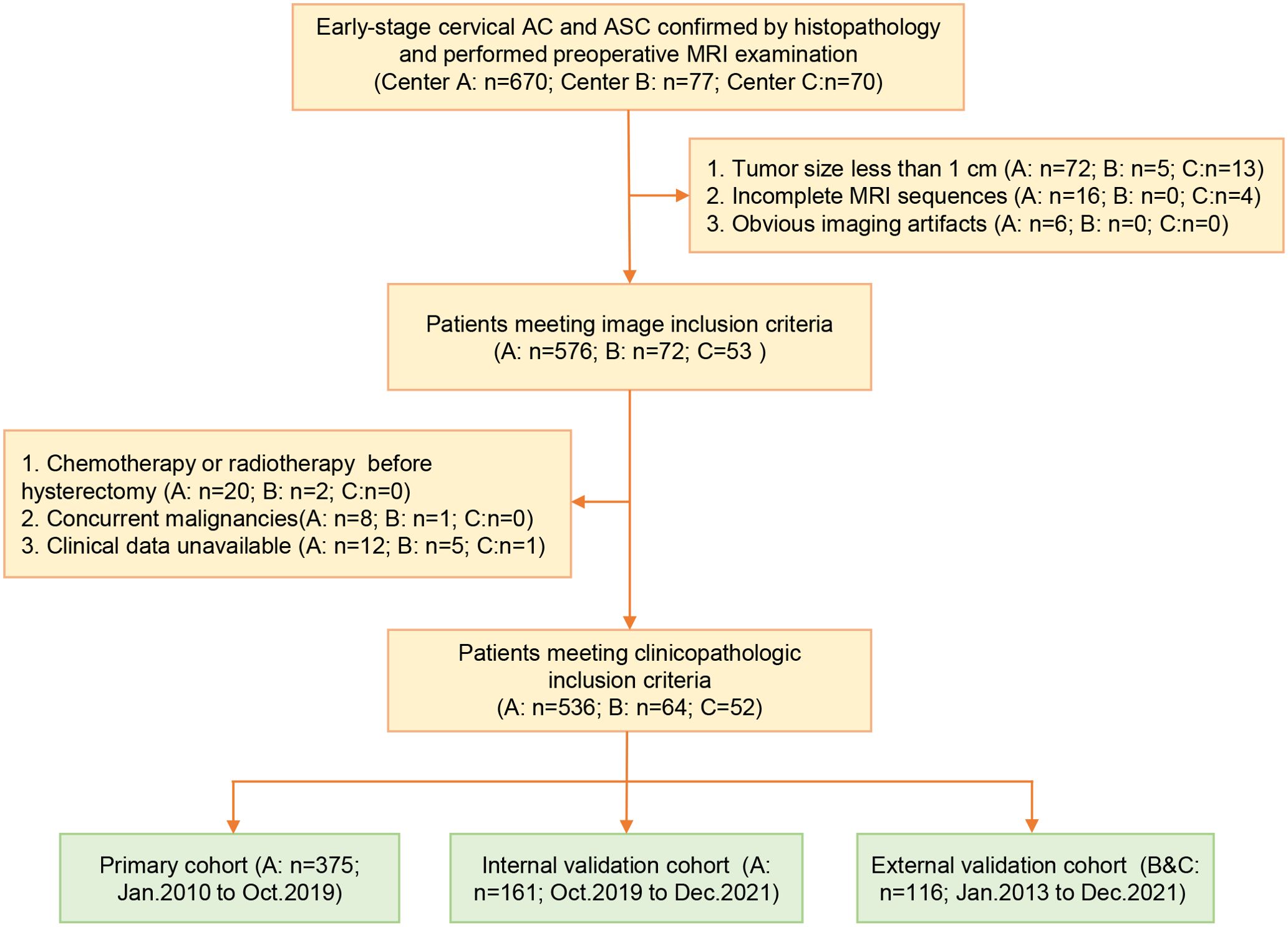
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) cervical AC or ASC confirmed by pathology; (2) pelvic MRI examination performed within 2 weeks prior to RH or trachelectomy; (3) availability of complete clinicopathological data; (4) no concurrent malignancies. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) chemoradiotherapy before surgery; (2) tumor size less than 1 cm; (3) obvious imaging artifacts; (4) incomplete MRI sequences. The lymph node status was pathologically determined based on the tissue samples from the radical trachelectomy or hysterectomy.
Finally, a total of 652 patients were enrolled and allocated into the primary cohort (center A, n1 = 375, from January 2010 to October 2019), internal validation cohort (center A, n1 = 161, from October 2019 to December 2021), and external validation cohort (center B and C, n1 = 116, from January 2013 to December 2021). The patient selection process and sample size consideration are independently presented in Figure 1 and Supplementary 1 in Supplementary Data Sheet 1. The baseline data were extracted from the medical records. The tumor diameter, LNM, disruption of the cervical stromal ring (DCSR), and parametrial invasion (PMI) were measured and assessed on MRI, and the MRI definition of the above features is illustrated in Supplementary 1 in Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
MRI examination
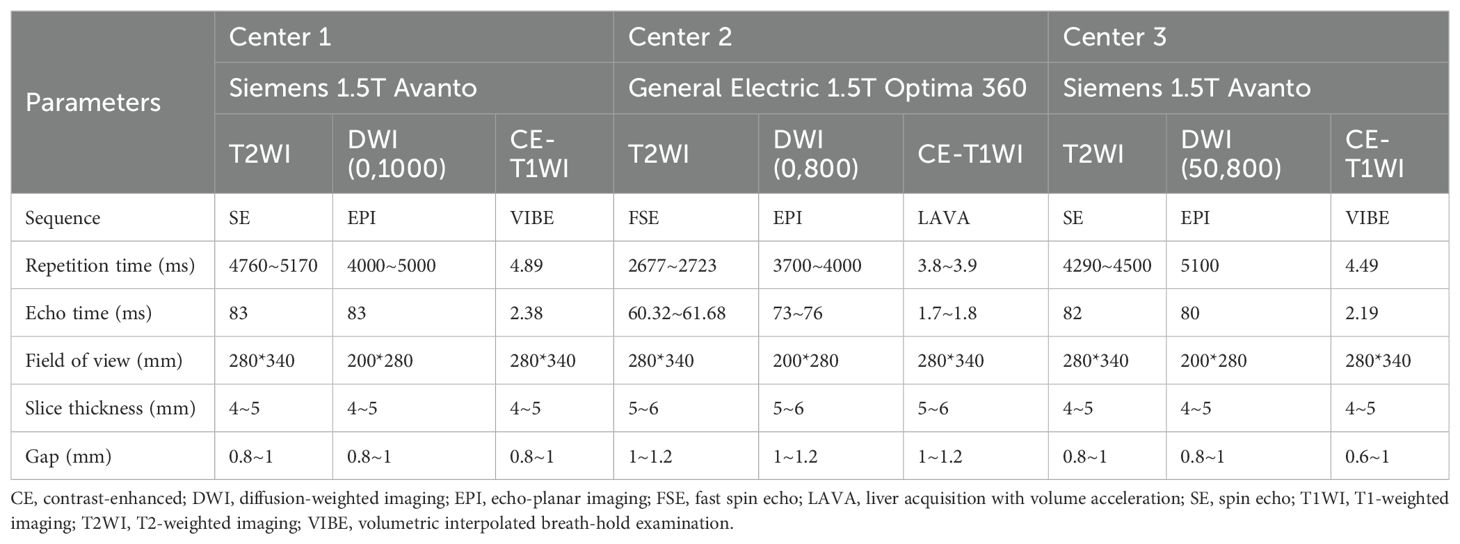
The MRI examination was performed on 1.5 T systems (MAGNETOM Avanto, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany; Optima 360, General Electric Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). The detailed MRI parameters are listed in Table 1.
Image segmentation and preprocessing
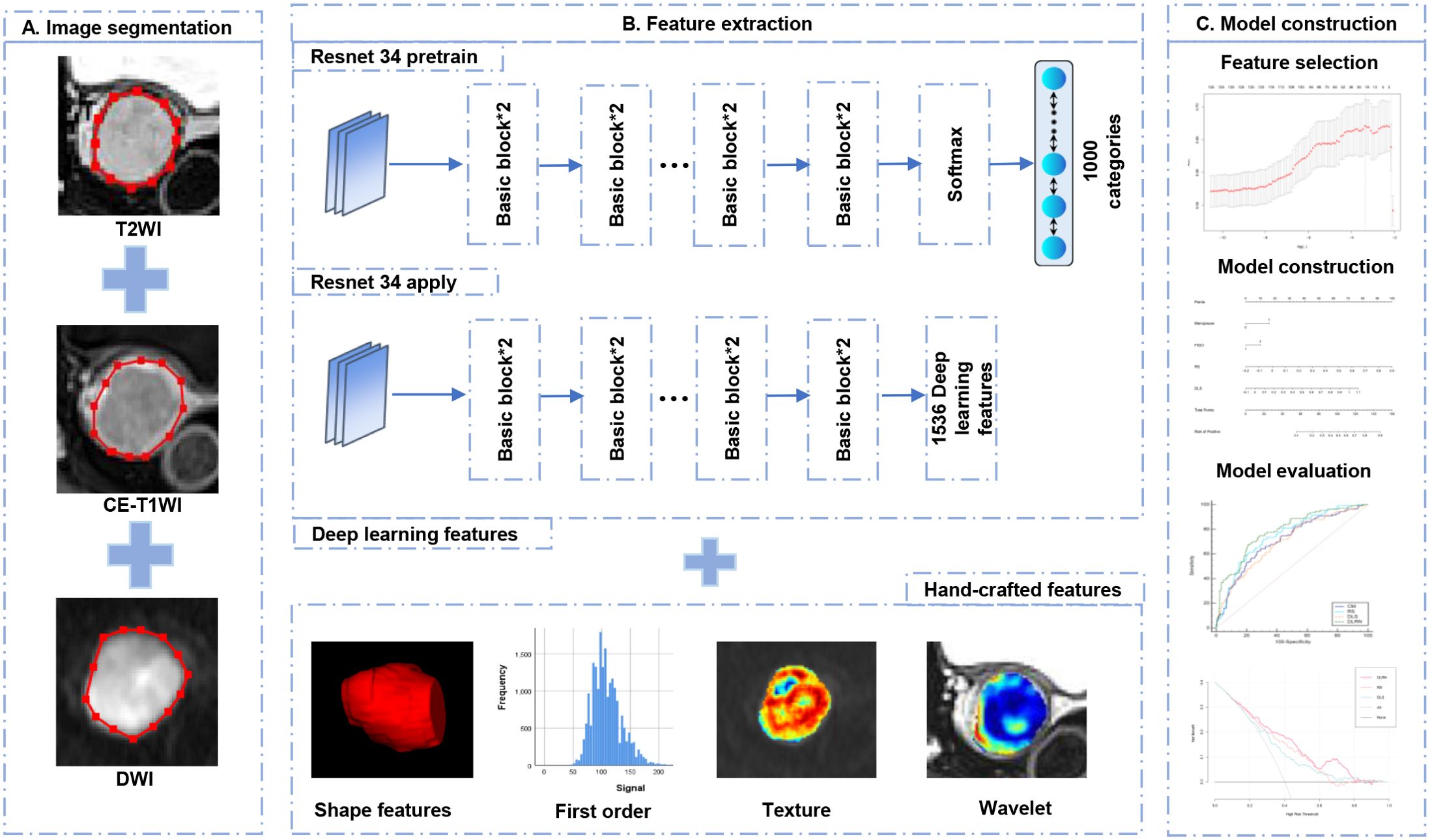
The regions of interest (ROIs) were manually delineated along the tumor margin on the slice of T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and CE-T1WI with the largest tumor based on ITK-SNAP (Version 3.8.0) by Radiologist 1 (with 7 years of experience in pelvic MR imaging). Normalization was performed on T2WI and CE-T1WI by rescaling the gray values within the range of 0–800 (17). To evaluate the features repeatability, 30 patients were randomly selected and delineated by Radiologist 2 (with 5 years of experience in pelvic MR imaging) and by Radiologist 1 repeatedly 1 month later after initial segmentation. The features with intra- and inter-class correlation coefficients (ICCs) more than 0.75 were considered the reliable features and reserved for further data analysis. The construction workflow of the DLRN can be observed in Figure 2.
Radiomics and deep learning features extraction and selection
Pyradiomics (version 3.0.1) was adopted to extract all radiomics features, including shape, first-order statistics, texture, and wavelet-transform features. The texture features consist of gray-level cooccurrence matrix (GLCM), gray-level run-length matrix (GLRLM), gray-level-size-zone matrix (GLSZM), gray-level-dependence matrix (GLDM), and neighborhood-gray-tone-difference matrix (NGTDM). The ResNet 34 architecture was adopted to extract DL features on PyTorch Lightning (Version 1.6.4). To make full use of the DL features, the full connection and softmax layers of the ResNet 34 were removed, and the output value of the last layer node was defined as the DL features. Then, the Z-score normalization was applied to each radiomics and DL feature by subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard error.
The following feature selection steps were performed respectively on radiomics and DL feature sets in the primary cohort: (1) Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) of any pair of features was calculated. If PCC was greater than 0.9, one of pair features will be randomly eliminated to reduce redundancy (18). (2) The 125 highest-ranking features strongly correlated with LNM were selected by using maximum relevance and minimum redundancy (MRMR) (19). (3) The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithm was applied with 10-fold cross-validation using the minimum criteria (1-SE criteria) to select the optimal feature set from the primary cohort. After the LASSO method, the radiomics and deep learning signature were generated, which were represented as radscore (RS) and deep learning score (DLS). The RS and DLS were independently obtained by the linear combination of selected optimal features and the corresponding weight coefficients.
Deep learning radiomics nomogram construction and evaluation
The independent risk factors for LNM in cervical AC/ASC were identified using multivariate analysis by inputting significant variables found using univariate analysis. Backward stepwise selection was applied, in which the stopping rule was the likelihood ratio test with Akaike’s information criterion. The DLRN and clinical models were then constructed by integrating their respective independent risk factors based on logistic regression analysis. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed on the RS, DLS, clinical model, and DLRN to assess their diagnostic abilities. The area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), positive/negative predictive values (PPV/NPV), and positive/negative likelihood ratios (+LR/−LR) were calculated in the primary, internal, and external validation cohorts. The calibration curves, measuring how similar the evaluation outcome was to the observed ones, were drawn based on the Hosmer–Lemeshow (H–L) test. Decision curve analysis was plotted to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of DLRN by calculating the net benefits at varied threshold probabilities (20).
Statistical analysis
R software (version 3.5.0, http://www.Rproject.org) and SPSS (version 26.0.0.0; IBM Corp., USA) were used to implement the statistical analyses. The normality was assessed based on the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Continuous variables with normal and non-normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and median with interquartile range, respectively. The differences of variables between LNM positive and negative groups were assessed based on Student’s t-test, Mann–Whitney U test, or chi-squared test. The DeLong test was employed to compare the diagnostic performances of different models. A p-value of statistical significance level was set as 0.05.
Results
Patients
The clinicopathological characteristics of the LNM-positive and -negative patients in the primary, internal, and external validation cohorts are compared in Table 2. The menopause, FIGO stage, tumor diameter, and PMIMR and were determined as clinical independent risk factors and were used to build the clinical model (Table 3). The clinical mode achieved AUCs of 0.71 (95% CI, 0.66–0.76), 0.75 (95% CI, 0.67–0.81), and 0.71 (95% CI, 0.61–0.79) in the primary, internal, and external validation cohorts.
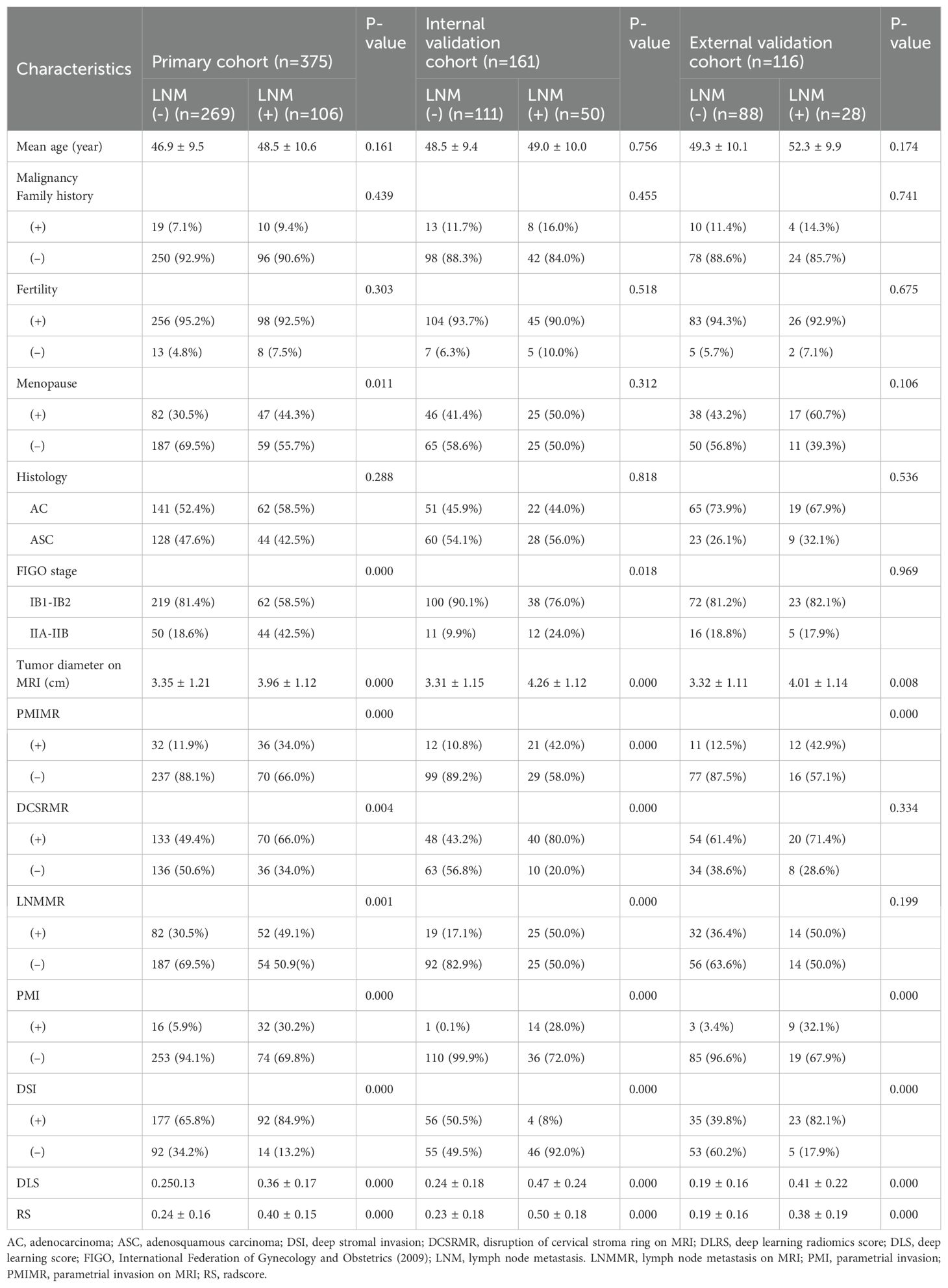
Table 2. The characteristic comparisons of LNM-positive and LNM-negative in the primary and validation cohorts.
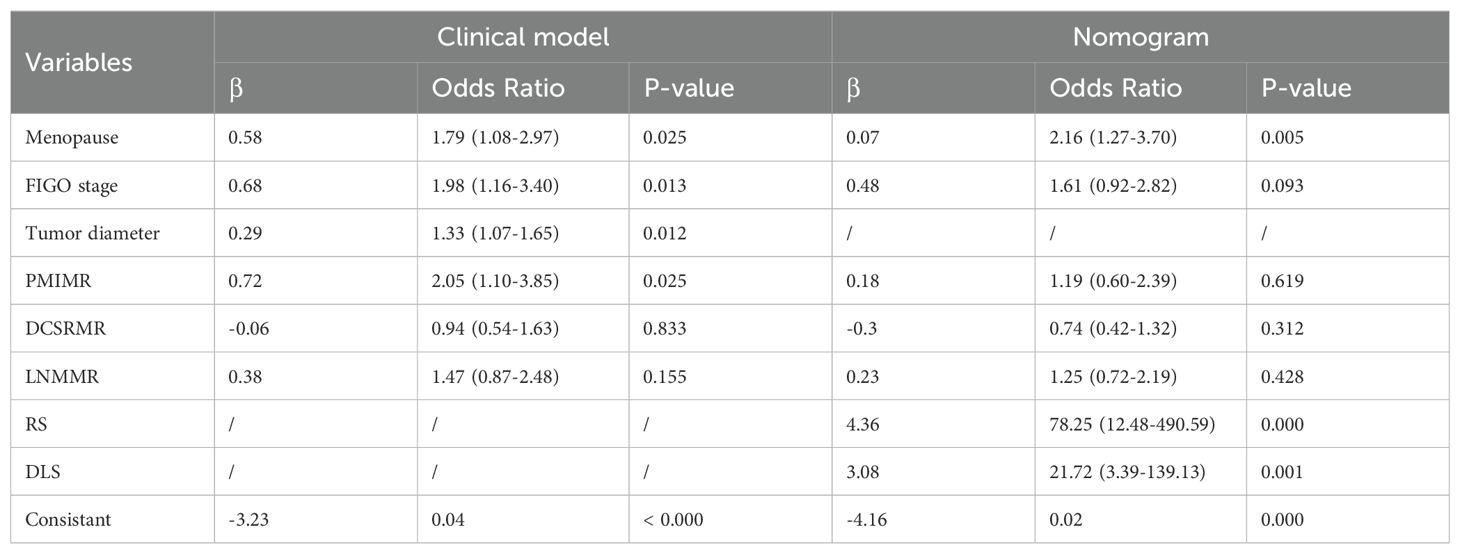
Table 3. The construction of the clinical model and nomogram using multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Feature selection
A total of 2,499 radiomics features were extracted from ROIs of T2WI, DWI, and CE-T1WI. After ICC, PCC, MRMR, and LASSO algorithm, the 22 most optimal features were reserved. A total of 1,536 DL features were extracted from ROIs of T2WI, DWI, and CE-T1WI. After ICC, PCC, MRMR, and LASSO algorithms, the 25 most optimal features were reserved. Figures 3, 4 show the feature selection process, optimal radiomics and DL feature sets and their respective weight coefficients. After linear combination with their respective weight coefficients, the RS and DLS were independently calculated. The RS and DLS differences between LNM-positive and LNM-negative groups in three cohorts are shown in Figure 5.
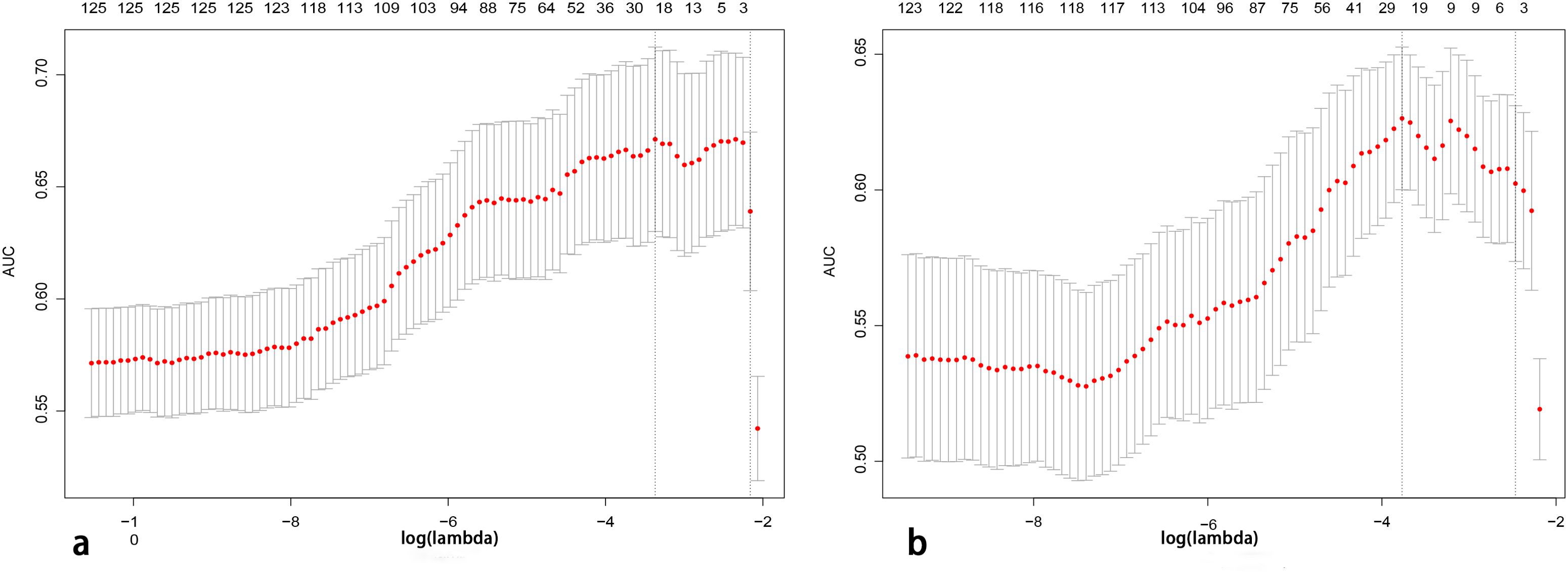
Figure 3. Features determined by the LASSO algorithm. The lambda (λ) is selected based on 10-fold cross-validation via minimum criteria (1-SE criteria). (A, B) A total of 22 and 25 features were selected from radiomics and deep learning feature sets (LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator).
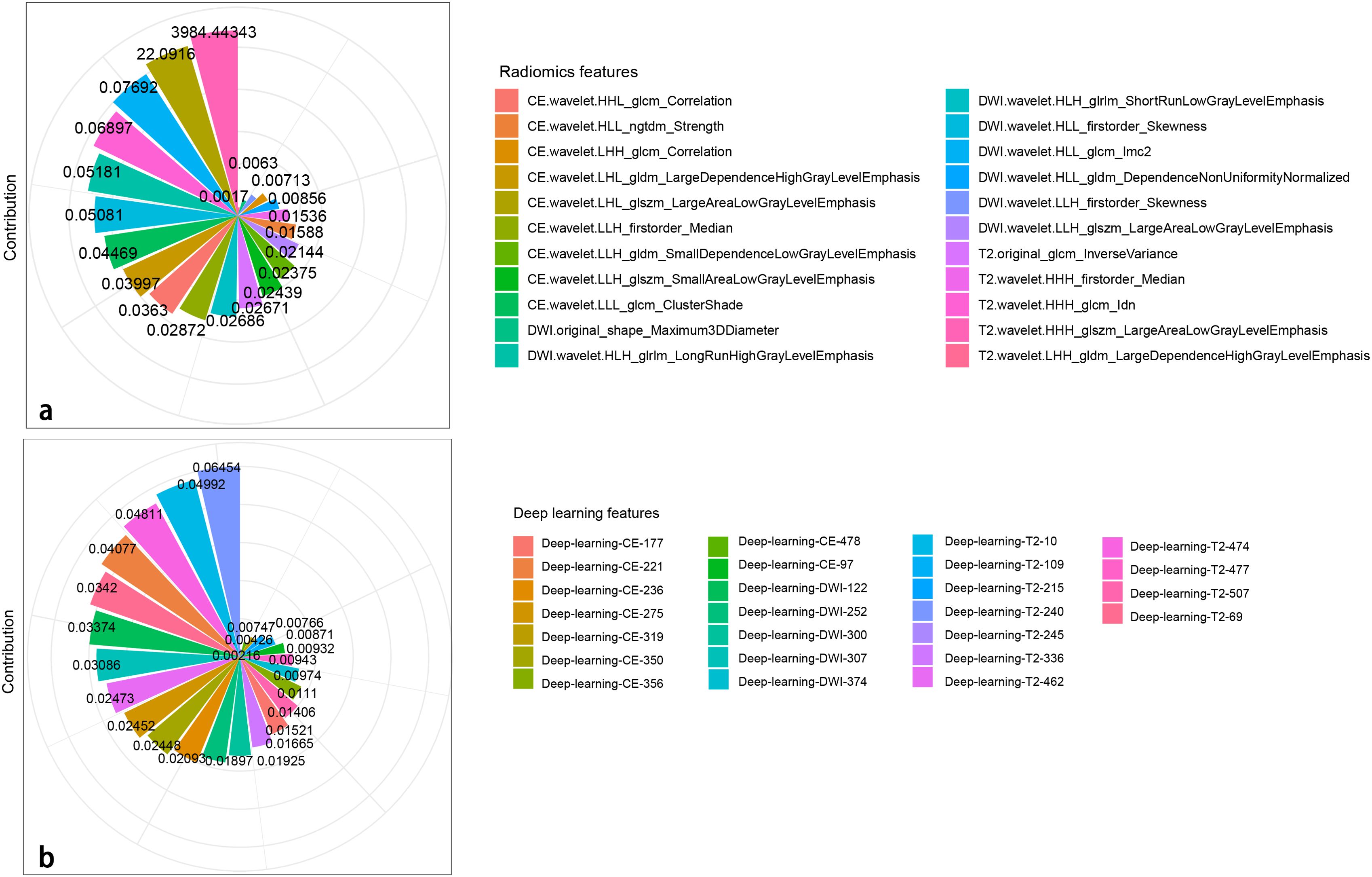
Figure 4. Radiomics (A) and DL (B) features with their respective weight coefficients after LASSO regression.
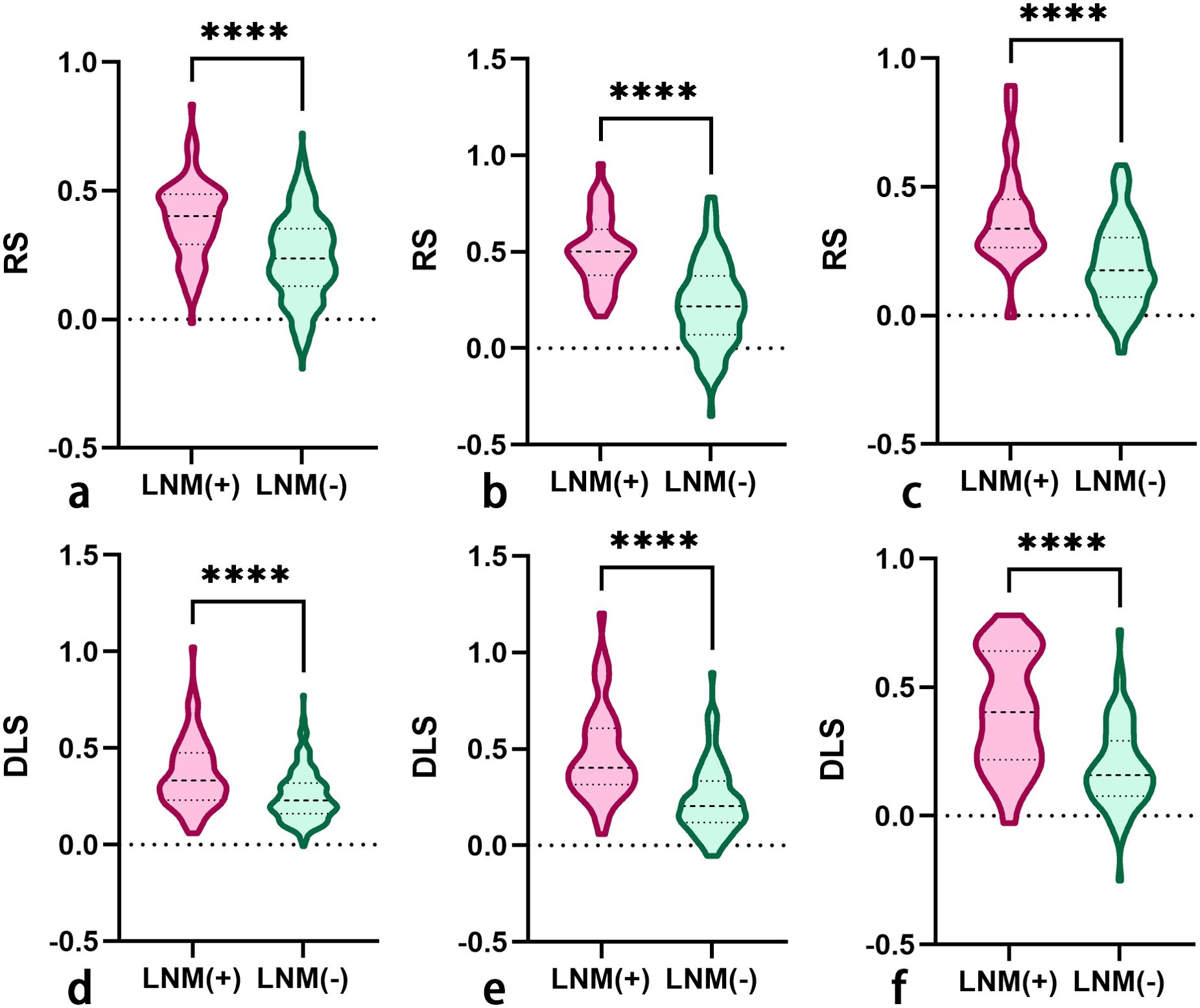
Figure 5. The RS (A–C) and DLS (D–F) differences between LNM-positive and LNM-negative groups in the primary, internal validation, and external validation cohorts (RS, radscore; DLS, deep learning score; LNM, lymph node metastasis). The symbol **** means P-value less than 0.0001.
The evaluation performance and comparison of RS and DLS
For evaluating LNM, the AUCs of RS and DLS were 0.75 (95% CI, 0.70–0.79) and 0.70 (95% CI, 0.65–0.75) in the primary cohort, were 0.84 (95% CI, 0.77–0.89) and 0.81 (95% CI, 0.74-0.96) in the internal validation cohort, and were 0.79 (95% CI, 0.70–0.86) and 0.78 (95% CI, 0.69–0.85) in the external validation cohort, respectively. The DeLong test showed that there was a comparable performance for evaluating LNM between RS and DLS in the primary (P = 0.096), internal validation (P = 0.452), and external validation cohorts (P = 0.936). Therefore, both the RS and DLS were selected to construct the DLRN.
The construction and evaluation of DLRN
In the process of constructing the nomogram, the RS, DLS, menopause, and FIGO stage were determined as the independent risk factors. The DLRN was constructed by integrating RS, DLS, menopause, and FIGO stage (Figure 6). The AUC, SEN, and SPE of DLRN were 0.79% (95% CI, 0.74–0.83), 67.9%, and 78.4% in the primary cohort; 0.87% (95% CI, 0.81–0.92), 92.0%, and 71.2% in the internal validation cohort; 0.86% (95% CI, 0.78–0.91), 89.3%, and 71.6% in the external validation cohort, respectively. The AUC of DLRN was significantly higher than those of RS, DLS, and clinical model in the primary and internal validation cohorts (all P < 0.05) than that of the clinical model in the external validation cohort (P = 0.011). The comparison details are presented in Figures 7A–C and Table 4. The H-L tests demonstrated that evaluation outcomes of the DLRN had an ideal agreement with actual observation ones in the primary (P=0.913), internal validation (P=0.958), and external validation cohorts (P = 0.803). The calibration curves of DLRN are shown in Figures 7D–F.
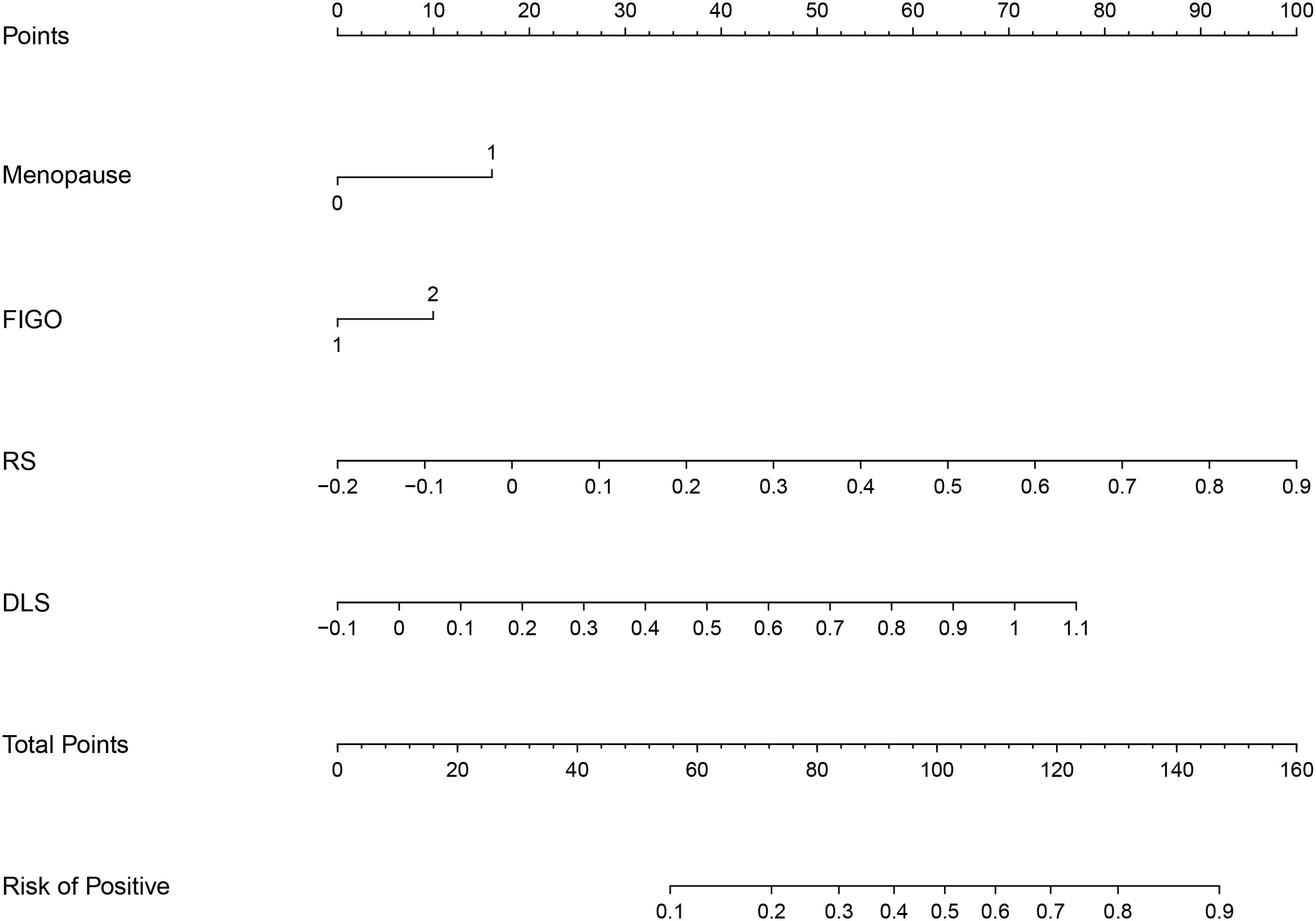
Figure 6. The DLRN based on RS, DLS, and independent risk factors of menopause and FIGO stage (FIGO, International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics).
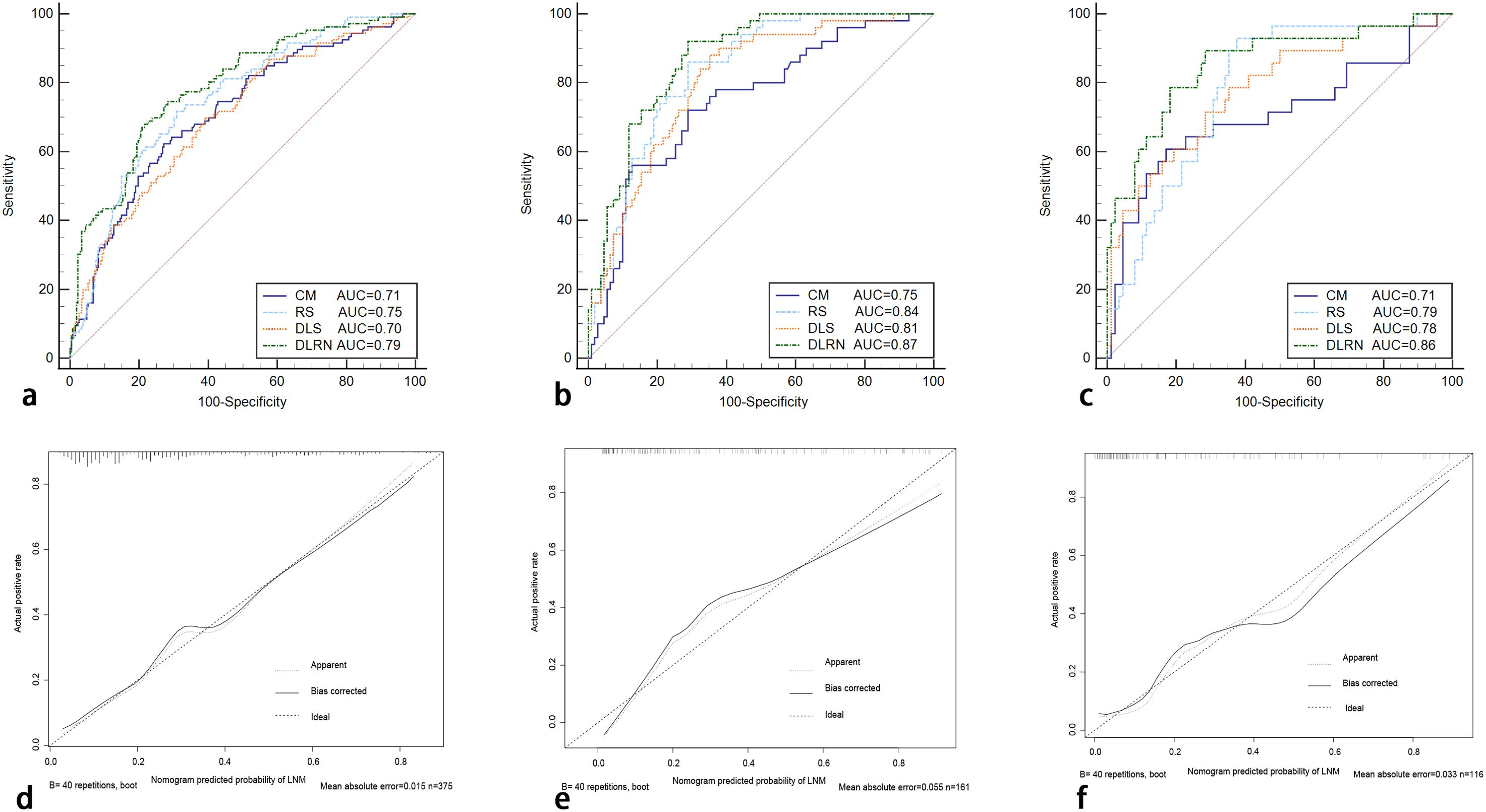
Figure 7. The ROC curves of RS, DLS, clinical model, and DLRN for predicting LNM in the primary (A), internal (B), external validation (C) cohorts. The calibration curves of the DLRN in the primary cohort [(D), P = 0.913], internal validation [(E), P = 0.958], and external validation cohorts [(F), P = 0.803] ROC, receiver operator characteristic; CM, clinical model.
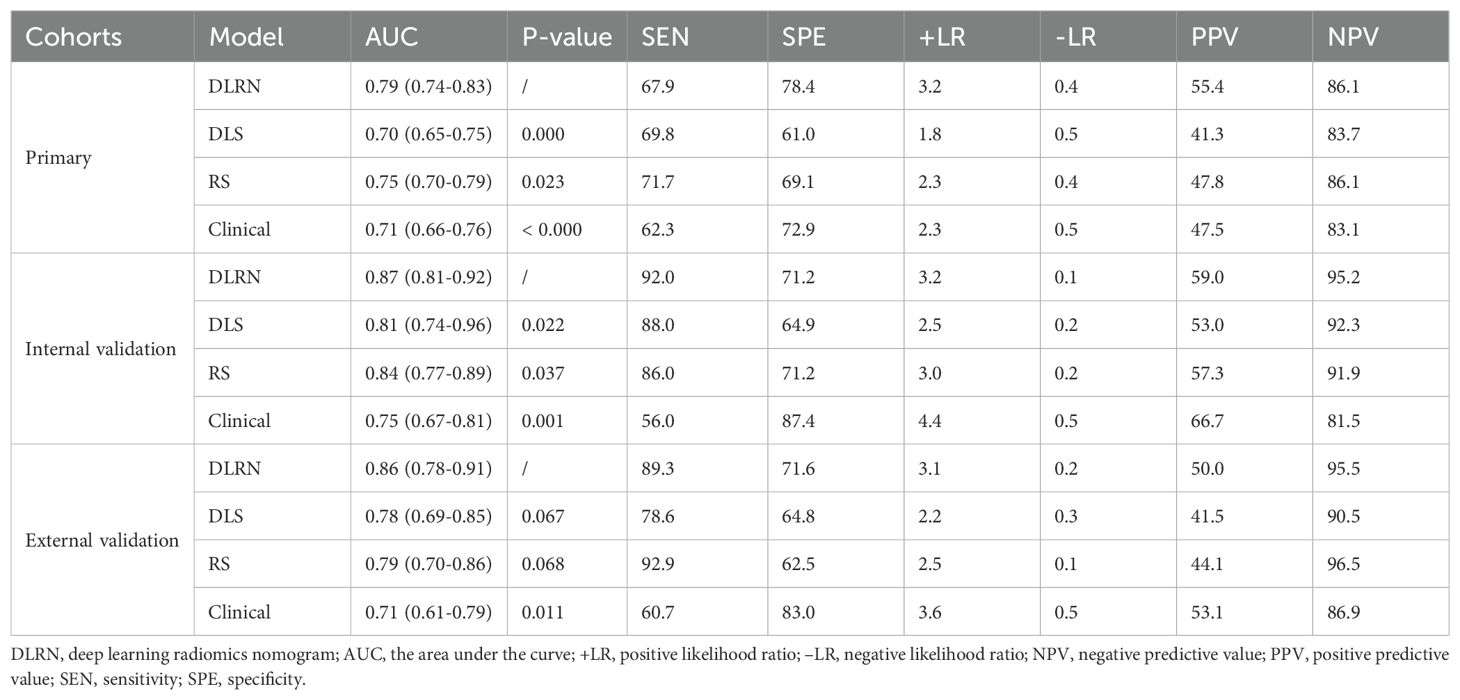
Table 4. The diagnostic performance of DLRN, DLS, RS, and clinical models for predicting the LNM in patients with cervical AC and ASC.
Clinical application of nomogram
The clinical decision curve along with clinical impact curve of DLRN in the primary internal validation and external validation cohorts are shown in Figure 8. In the external validation cohort, when the threshold probability was within the range of 0.12–0.98, the use of DLRN added more net benefits than the scheme of “treatment-all” or “treatment-none”. In the most range of the threshold probability, the net benefit of DLRN was more than those of DLS, RS, and clinical model.
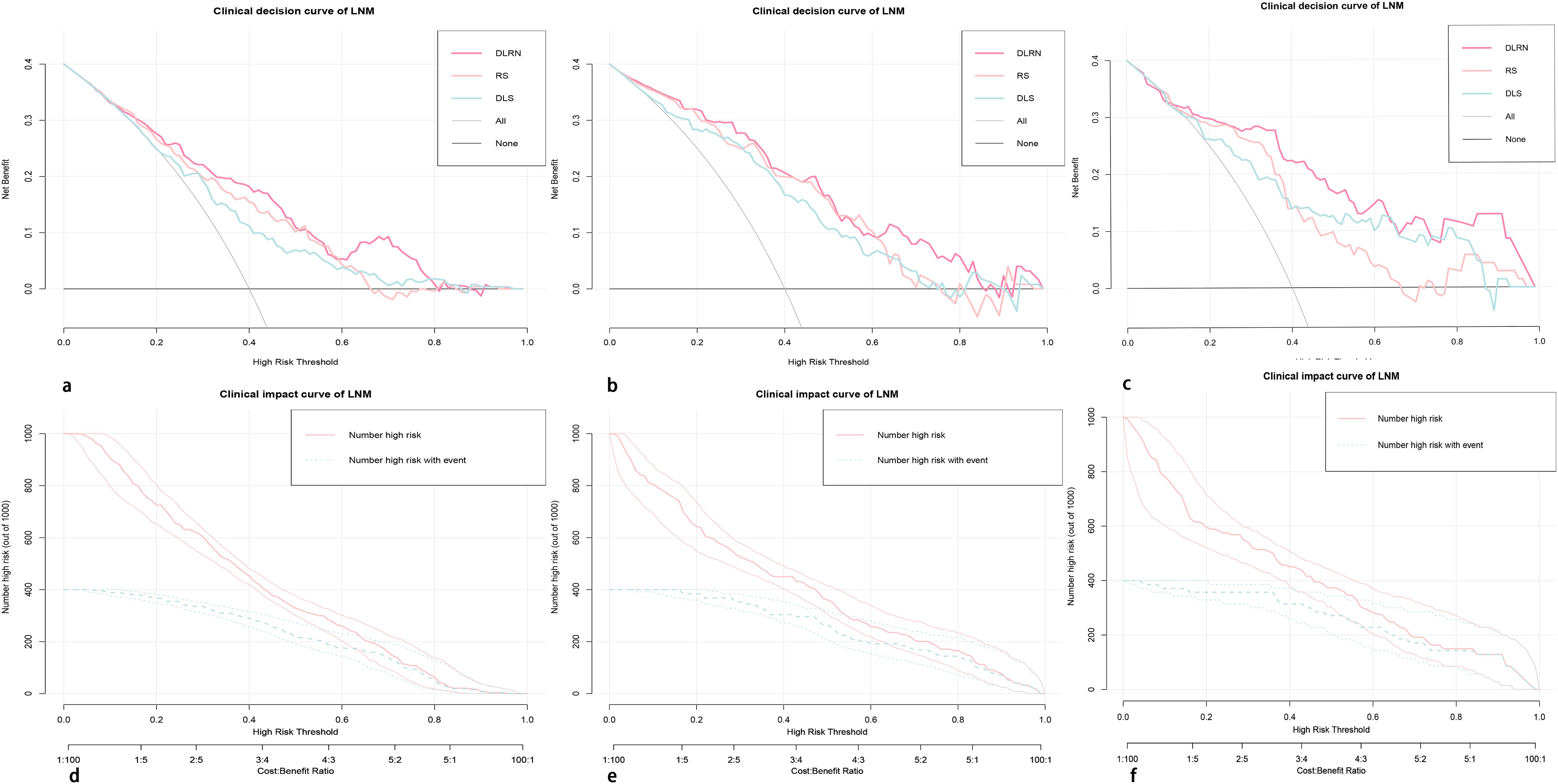
Figure 8. The clinical decision curves (A–C) and clinical impact curves (D–F) of the DLRN in the primary, internal, and external validation cohorts. In the external validation cohort, when the threshold probability is within the range of 0.12–0.98, the use of DLRN can obtain more net benefits for patients than the “all” or “none” treatment scheme.
Discussion
In this study, the DLRN, by integrating the DLS, RS, and clinical independent risk factors, could be helpful for assessing the LNM in patients with AC/ASC. The AUCs of DLRN were 0.79 (95% CI, 0.74–0.83), 0.87 (95% CI, 0.81–0.92) and 0.86 (95% CI, 0.78–0.91) in the primary, internal and external validation cohorts, respectively.
The conventional MRI morphological criteria for the diagnosis of LNM are as follows: short axis diameter > 8 mm, round shape, irregular contour, lack of fat hilus on T2WI, hyperintensity on DWI and heterogeneous enhancement on CE-T1WI (18). The conventional MRI morphological criteria had a combined SEN of 51% and SPE of 90% for evaluating the LNM in cervical cancer (13). The radiomics nomogram could accurately diagnose the LNM in cervical SCC, with the C index ranging from 0.856 to 0.909 (3, 21). A previous cervical AC/ASC study showed that the AUC of the support vector machine model for evaluating LNM was 0.79 and 0.82 in the primary and validation cohorts, respectively (19). This study had the following differences compared with aforementioned studies: (1) the sufficient multicenter samples; (2) focusing on cervical AC/ASC; (3) the established DLRN containing multiscale information (radiomics features, DL features, and clinical characteristics).
The radiomics features highly depend on the accurate tumor segmentation. The features extracted from different manual segmentations of the same lesion may vary widely (22). Compared with radiomics, DL can achieve automatic learning and hierarchically organized task-adaptive image features. To select reliable features with good reproducibility, both the radiomics and DL features with ICCs less than 0.75 were eliminated. Meanwhile, considering the possibility of redundancy between radiomics and DL features, the PCC test was performed to remove redundant features.
In the diagnostic performance comparison of radiomics features and DL features, consistent conclusion has not been reached yet. Some studies concluded that the diagnostic performance of DL features was inferior to that of the radiomics features (23, 24), whereas another study achieved a different conclusion (25). In this study, the DLS yielded a comparable diagnostic performance to the RS with no significant difference between two signatures. Therefore, both RS and DLS were adopted to construct the comprehensive nomogram.
Previous studies demonstrated that the FIGO stage and tumor size were clinical independent risk factors and were integrated into the model to evaluate LNM in cervical SCC (3, 21, 26). In this study, the factors of menopause, FIGO stage, tumor diameter, and PMIMR were determined as clinical independent risk factors and were used to build the clinical model. In the process of constructing a comprehensive nomogram, tumor diameter was excluded because of the same information that had been contained in the optimal radiomics signature. Finally, menopause, FIGO stage, RS, and DLS were determined as independent risk factors and were used to build the DLRN.
The overfitting issue needed to be carefully dealt with in the process of model building. In this study, the risk of overfitting of DLRN was low. The reasons were as follows: (1) the AUCs of DLRN were greater in the validation cohorts than in the primary cohort, which was a reliable evidence for eliminating overfitting bias. (2) To reduce the risk of overfitting, we had adopted the following guidelines in our logistic regression model: the predictor number should generally be within 1/20 to 1/8 of sample sizes of the training cohort, and the event-per-predictor ratio should remain within the range of 5 to 9 (27, 28).
The potential reasons that the accuracy of primary cohort was lower than validation cohorts are as follows: (1) To avoid the influence of random effects on model construction, the non-random method based on time grouping was adopted to construct the DLRN, which was widely used in authoritative research articles (29–31). However, this time grouping-based non-random approach led to an imbalanced distribution of features across the cohorts. (2) The morbidity of the AC/ASC was significantly lower than that of SCC. The large number of AC/ASC cases needs to collect from multiple centers over an extended period. In this study, a total of 536 patients from center A were enrolled and allocated into the primary cohort (from January 2010 to October 2019) and internal validation cohort (from October 2019 to December 2021). The data selection bias among primary and validation cohorts that from different time were inevitable due to its retrospective nature. Therefore, the imbalanced distribution of optimal clinical, radiomic, and deep learning features selected among the primary and validation cohorts was the primary factor contributing to the lower accuracy in the training data.
The nomogram is a visual tool used to generate personalized probability predictions. Gynecologists and radiologists can make preoperative individualized predictions of the risk of LNM using this user-friendly scoring system, aligning with the current trend toward personalized precision medicine. In this study, the RS, DLS, FIGO stage, and menopause were identified as independent risk factors and were utilized to develop the DLRN. When using the nomogram, the specific points of individual patients are plotted on each risk factor axis. A vertical line is drawn upward to determine the points assigned to each risk factor. Then, the total of these points is marked on the total points axis to indicate the probability of LNM in each patient.
This study had the following limitations. First, the data selection bias and data sampling bias were inevitable to some extent due to its retrospective nature. Furthermore, the DLRN should be validated in a prospective research with larger external sample size. Second, the serum tumor biomarkers were not used to develop a model due to incomplete data. Third, the DLRN built could not accurately evaluate the specific location of metastatic lymph nodes. Finally, instead of specific features of LN, such as edge, length, and diameter, the MRI morphological criteria for the diagnosis of LNM (LNMMR) were adopted to explore its potential value (28).
In conclusion, the DLRN, by integrating menopause, FIGO stage, RS, and DLS, achieved a significantly better performance than DLS, RS, and clinical model in evaluating LNM in patients with cervical AC and ASC. The prediction outcome derived from DLRN may facilitate clinical decision-making of radiotherapy or RH.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Jinshan Hospital of Fudan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The written informed consent was waived due to its retrospective nature.
Author contributions
MX: Methodology, Validation, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Resources. TQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Investigation. YW: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Supervision, Validation. FM: Formal analysis, Resources, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization. YL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Project administration. JC: Resources, Supervision, Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZQ: Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. GZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. JQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study has received funding from China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No.2023M743024), Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. GZC20232302), and Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (No.2020YJZK0209).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1414609/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Huang H, Feng YL, Wan T, Zhang YN, Cao XP, Huang YW, et al. Effectiveness of sequential chemoradiation vs. concurrent chemoradiation or radiation alone in adjuvant treatment after hysterectomy for cervical cancer: The STARS phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2021) 7:361–9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.7168
2. Lee SI, Atri M. 2018 FIGO staging system for uterine cervical cancer: enter cross-sectional imaging. Radiology. (2019) 292:15–24. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019190088
3. Cibula D, Pötter R, Planchamp F, Avall-Lundqvist E, Fischerova D, Haie Meder C, et al. The European Society of Gynaecological Oncology/European Society for radiotherapy and Oncology/European Society of Pathology guidelines for the management of patients with cervical cancer. Radiother Oncol. (2018) 127:404–16. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.03.003
4. Xiao M, Ma F, Li Y, Li Y, Li M, Zhang G, et al. Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics nomogram for predicting lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. (2020) 52:885–96. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27101
5. Gien LT, Covens A. Lymph node assessment in cervical cancer: prognostic and therapeutic implications. J Surg Oncol. (2009) 99:242–7. doi: 10.1002/jso.21199
6. Mereu L, Pecorino B, Ferrara M, Tomaselli V, Scibilia G, Scollo P. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus radical surgery in locally advanced cervical cancer: retrospective single-center study. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:5207. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215207
7. Baek MH, Park JY, Kim D, Suh DS, Kim JH, Kim YM, et al. Comparison of adenocarcinoma and adenosquamous carcinoma in patients with early-stage cervical cancer after radical surgery. Gynecol Oncol. (2014) 135:462–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.10.004
8. Yokoi E, Mabuchi S, Takahashi R, Matsumoto Y, Kuroda H, Kozasa K, et al. Impact of histological subtype on survival in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer that were treated with definitive radiotherapy: adenocarcinoma/adenosquamous carcinoma versus squamous cell carcinoma. J Gynecol Oncol. (2017) 28:e19. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2017.28.e19
9. Mabuchi S, Okazawa M, Matsuo K, Kawano M, Suzuki O, Miyatake T, et al. Impact of histological subtype on survival of patients with surgically-treated stage IA2-IIB cervical cancer: adenocarcinoma versus squamous cell carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. (2012) 127:114–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.06.021
10. Cao L, Wen H, Feng Z, Han X, Wu X. Distinctive clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis for different histologic subtypes of early cervical cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. (2019) 29:1244–51. doi: 10.1136/ijgc-2019-000556
11. Roma AA, Mistretta TA, Diaz De Vivar A, Park KJ, Alvarado-Cabrero I, Rasty G, et al. New pattern-based personalized risk stratification system for endocervical adenocarcinoma with important clinical implications and surgical outcome. Gynecol Oncol. (2016) 141:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.02.028
12. Olawaiye AB, Baker TP, Washington MK, Mutch DG. The new (Version 9) American Joint Committee on Cancer tumor, node, metastasis staging for cervical cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:287–98. doi: 10.3322/caac.21663
13. Xiao M, Yan B, Li Y, Lu J, Qiang J. Diagnostic performance of MR imaging in evaluating prognostic factors in patients with cervical cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. (2020) 30:1405–18. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06461-9
14. Sironi S, Buda A, Picchio M, Perego P, Moreni R, Pellegrino A, et al. Lymph node metastasis in patients with clinical early-stage cervical cancer: detection with integrated FDG PET/CT. Radiology. (2006) 238:272–9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2381041799
15. Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology. (2016) 278:563–77. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151169
16. Wu Q, Wang S, Zhang S, Wang M, Ding Y, Fang J, et al. Development of a deep learning model to identify lymph node metastasis on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cervical cancer. JAMA Netw Open. (2020) 3:e2011625. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.11625
17. Yan BC, Li Y, Ma FH, Zhang GF, Feng F, Sun MH, et al. Radiologists with MRI-based radiomics aids to predict the pelvic lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer: a multicenter study. Eur Radiol. (2021) 31:411–22. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07099-8
18. Xiao ML, Wei Y, Zhang J, Jian JM, Song Y, Lin ZJ, et al. MRI texture analysis for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in patients with nonsquamous cell cervical carcinoma. Acad Radiol. (2022) 29(11):1661–71. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2022.01.005
19. Dong D, Fang MJ, Tang L, Shan XH, Gao JB, Giganti F, et al. Deep learning radiomic nomogram can predict the number of lymph node metastasis in locally advanced gastric cancer: an international multicenter study. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:912–20. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.003
20. Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Elkin EB, Gonen M. Extensions to decision curve analysis, a novel method for evaluating diagnostic tests, prediction models and molecular markers. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. (2008) 8:53. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-8-53
21. Wang T, Gao T, Yang J, Yan X, Wang Y, Zhou X, et al. Preoperative prediction of pelvic lymph nodes metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer using radiomics nomogram developed based on T2-weighted MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. (2019) 114:128–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.01.003
22. Zwanenburg A, Leger S, Agolli L, Pilz K, Troost EGC, Richter C, et al. Assessing robustness of radiomic features by image perturbation. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:614. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36938-4
23. Wang S, Shi J, Ye Z, Dong D, Yu D, Zhou M, et al. Predicting EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma on computed tomography image using deep learning. Eur Respir J. (2019) 53:1800986. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00986-2018
24. Ardila D, Kiraly AP, Bharadwaj S, Choi B, Reicher JJ, Peng L, et al. Author correction: End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat Med. (2019) 25:1319. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0536-x
25. Nijiati M, Guo L, Abulizi A, Fan S, Wubuli A, Tuersun A, et al. Deep learning and radiomics of longitudinal CT scans for early prediction of tuberculosis treatment outcomes. Eur J Radiol. (2023) 169:111180. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.111180
26. Deng X, Liu M, Sun J, Li M, Liu D, Li L, et al. Feasibility of MRI-based radiomics features for predicting lymph node metastases and VEGF expression in cervical cancer. Eur J Radiol. (2021) 134:109429. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109429
27. Shur JD, Doran SJ, Kumar S, Ap Dafydd D, Downey K, O'Connor JPB, et al. Radiomics in oncology: A practical guide. Radiographics. (2021) 41:1717–32. doi: 10.1148/rg.2021210037
28. Song J, Hu Q, Ma Z, Zhao M, Chen T, Shi H. Feasibility of T2WI-MRI-based radiomics nomogram for predicting normal-sized pelvic lymph node metastasis in cervical cancer patients. Eur Radiol. (2021) 31:6938. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07735-x
29. Cui Y, Zhang J, Li Z, Wei K, Lei Y, Ren J, et al. A CT-based deep learning radiomics nomogram for predicting the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer: A multicenter cohort study. EClinicalMedicine. (2022) 46:101348. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101348
30. Choi YS, Bae S, Chang JH, Kang SG, Kim SH, Kim J, et al. Fully automated hybrid approach to predict the IDH mutation status of gliomas via deep learning and radiomics. Neuro Oncol. (2021) 23:304–13. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa177
Keywords: magnetic resonance imaging, cervical adenosquamous carcinoma, cervical adenocarcinoma, radiomics, deep learning, lymph node metastasis
Citation: Xiao ML, Fu L, Qian T, Wei Y, Ma FH, Li YA, Cheng JJ, Qian ZX, Zhang GF and Qiang JW (2024) The deep learning radiomics nomogram helps to evaluate the lymph node status in cervical adenocarcinoma/adenosquamous carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 14:1414609. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1414609
Received: 15 April 2024; Accepted: 20 November 2024;
Published: 13 December 2024.
Edited by:
Sharon R. Pine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesReviewed by:
Harshan Ravi, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, United StatesBasilio Pecorino, Kore University of Enna, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Xiao, Fu, Qian, Wei, Ma, Li, Cheng, Qian, Zhang and Qiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jin Wei Qiang, ZHIuamlud2VpcWlhbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Mei Ling Xiao
Mei Ling Xiao Le Fu
Le Fu Ting Qian4
Ting Qian4 Yong Ai Li
Yong Ai Li Guo Fu Zhang
Guo Fu Zhang Jin Wei Qiang
Jin Wei Qiang