- 1College of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 2Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
Objectives: This meta-analysis aims to quantify the relationship between coffee and tea consumption and the risk of osteoporosis and explore whether such consumption positively or negatively impacts this risk, thereby providing a scientific basis for understanding the effects of coffee and tea on bone health.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library, and Embase for observational studies published up to November 5, 2024, using medical subject headings (MeSH) and keywords related to “osteoporosis, tea, and coffee.” Statistical analyses were conducted using Stata software version 14.0. A fixed-effects model was used when heterogeneity was low (I2 ≤ 50% and p > 0.1). A random-effects model was used for greater heterogeneity (I2 > 50%). Publication bias was assessed using funnel plots and Egger’s regression tests.
Results: This meta-analysis included 14 observational studies comprising 562,838 participants published between 2008 and 2024. The pooled analysis showed that coffee consumption is significantly associated with a reduced risk of osteoporosis (odds ratio [OR] = 0.79, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.73–0.84, I2 = 28.9%, p < 0.05). Tea consumption also demonstrated a protective effect, with a lower risk of osteoporosis (OR = 0.75, 95% CI: 0.62–0.91, I2 = 80.4%, p < 0.05). Subgroup analysis revealed that high-frequency coffee consumption (more than one cup per day) was associated with a greater reduction in osteoporosis risk (OR = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.74–0.93, p = 0.001) compared to low-frequency consumption (less than one cup per day), which showed no statistically significant reduction (OR = 0.86, 95% CI: 0.68–1.07, p = 0.171). Similarly, high-frequency tea consumption (more than four times per week) exhibited a slightly stronger protective effect against osteoporosis compared to low-frequency consumption (OR = 0.82, 95% CI: 0.70–0.97, p = 0.02).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis suggests that long-term coffee and tea consumption is associated with a reduced risk of osteoporosis. Moreover, a higher frequency of consumption within a moderate range appeared to enhance the protective effect against osteoporosis.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42024612101, PROSPERO CRD42024612101.
Introduction
Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disorder characterized by reduced bone density and compromised bone structure, resulting in increased fragility and fracture risk (1). Osteoporosis affects approximately 18.3% of the global population and is a major health concern (2). Advances in molecular neurology, clinical pathology, and diagnostic markers have enhanced our understanding of osteoporosis (3). Environmental and lifestyle factors, including vitamin D deficiency, smoking, alcohol consumption, inadequate calcium intake, high-protein diets, and physical inactivity, contribute to its development (4). However, the role of coffee and tea in osteoporosis remains controversial.
Coffee, a major global commodity with an annual production exceeding 9.2 million tons (5), is a significant source of antioxidants and offers various health benefits such as anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects (6). However, excessive consumption has been linked to adverse health outcomes including high blood pressure, seizures, sleep disturbances, and potentially osteoporosis (7). Tea, the second most widely consumed beverage globally (8), also has antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-obesity benefits (9). However, its effect on osteoporosis risk remains unclear.
Bone mineral density (BMD) is a key diagnostic criterion for osteoporosis, defined by the World Health Organization as a BMD T-score ≤ −2.5 at the hip or lumbar spine (10). Although some studies have suggested no significant link between coffee or tea consumption and BMD (11), the relationship between these beverages and osteoporotic fractures, which are key outcomes of osteoporosis, remains inconclusive. Research has shown no clear association between tea consumption and fracture risk (12), and evidence of a causal role of tea in osteoporosis is lacking (13). Caffeine in coffee may exacerbate osteoporosis, warranting further investigation into its impact (14). Conversely, some studies have suggested potential benefits of coffee and tea. A 2017 meta-analysis found that tea may reduce the risk of osteoporosis (15), whereas a 2022 study indicated that higher coffee intake may lower the risk of hip fractures in individuals with osteoporosis (16). Most previous meta-analyses have focused on low BMD or post-fracture outcomes rather than pure osteoporosis (T-score < −2.5). Therefore, we conducted an updated systematic review and meta-analysis to further clarify the association between coffee and tea intake and the risk of osteoporosis.
Methods
This meta-analysis was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Supplementary file S1) (17). The study protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under registration number CRD42024612101.
Data sources and searches
We searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library, and Embase from their inception to November 5, 2024, without language restrictions. Our search terms included Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and free words such as tea, coffee, and osteoporosis. Detailed search strategies for each database are provided in Supplementary file S2. Additionally, reference lists of the included studies and relevant meta-analyses were reviewed for additional studies.
Eligibility criteria
Studies were considered eligible for inclusion if they (a) included individuals diagnosed with osteoporosis defined according to the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria, with a BMD T-score ≤ −2.5, (b) assessed long-term consumption of coffee or tea, (c) included individuals who had never consumed coffee or tea for comparison, (d) analyzed the risk of osteoporosis as the primary outcome with effect estimates such as odds ratios (ORs), relative risks (RRs), or hazard ratios (HRs), and (e) were observational studies. Studies were excluded if osteoporosis was not the primary outcome (e.g., those combining low bone density or osteoporotic fractures) or specific effect sizes were not reported. Reviews, conference abstracts, duplicate publications, and studies that lacked relevant results were also excluded.
Study selection
Two reviewers (WPL and YJX) independently screened the studies for eligibility, first by reviewing titles and abstracts to exclude duplicates and irrelevant studies. Full-text articles were then assessed to confirm eligibility. Disagreements were resolved through consultation with a third reviewer (LJ) to ensure impartiality.
Data extraction
Data were independently extracted by two reviewers (WPL and YJX) using predesigned forms aligned with the systematic review guidelines (18). The extracted data included the first author, publication year, study design, sample size, follow-up duration, participant age, osteoporosis diagnosis, tea or coffee consumption frequency, and adjusted confounders. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and consensus.
Risk of bias assessment
Quality assessment for cohort and case–control studies was conducted using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (19), a tool designed to measure the risk of bias in nonrandomized studies. It assigns a score ranging from 0 to 9 based on aspects such as participant selection, exposure measurement, outcome assessment, and adequacy of follow-up, with scores of 0–3, 4–6, and 7–9 indicating low, moderate, and high quality, respectively. For cross-sectional studies, we applied the AHRQ (20) quality assessment criteria consisting of 11 items, where each item is scored as “1” if the answer is “yes” and “0” if the answer is “unclear” or “no.” The total score was categorized as low (0–3 points), moderate (4–7 points), or high (8–11 points) quality (21).
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using Stata 14.0. Adjusted ORs (and their 95% CIs) were extracted to evaluate the association between tea and coffee consumption and osteoporosis risk. Heterogeneity was assessed using the χ2 test and I2 statistic. A fixed-effects model was applied for I2 ≤ 50% and p > 0.1, indicating low heterogeneity. A random-effects model was used for I2 > 50%, indicating substantial heterogeneity. Sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the robustness of the results. Publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots and Egger’s regression tests. Subgroup analyses, categorized by different study designs and varying levels of consumption, were conducted to further interpret and validate the conclusions.
Results
Literature search
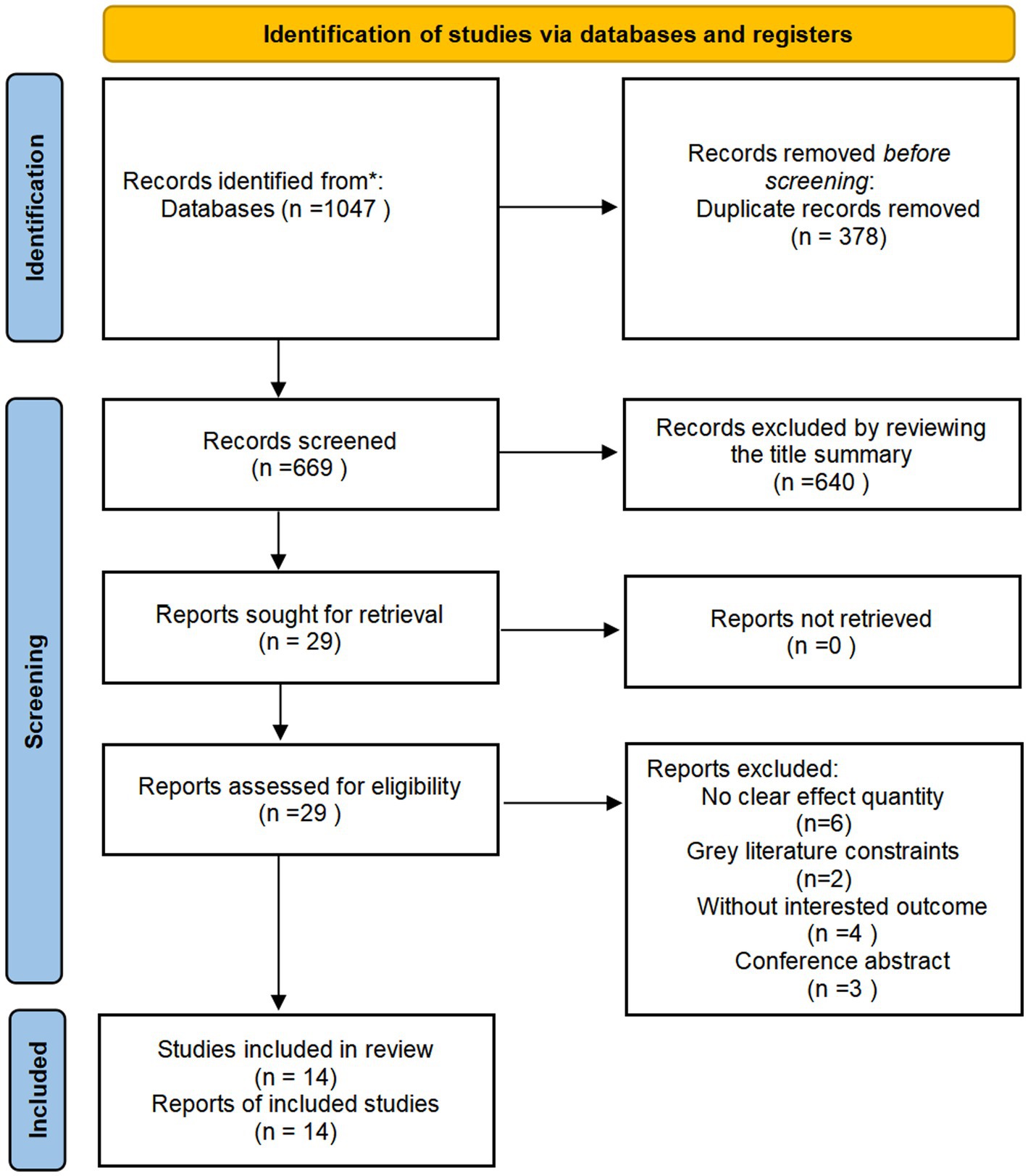
Literature screening was performed according to the PRISMA guidelines (17). A multi-database search identified 1,047 records (396 from PubMed, 607 from Embase, and 44 from the Cochrane Library). After removing 378 duplicates, the two reviewers screened the remaining 669 records using Zotero. Based on the predefined criteria, 29 records were selected for in-depth evaluation. Nine studies were excluded: six for unclear effect sizes, two for inaccessible full texts, four for lacking relevant outcomes, and three because they were conference abstracts. Ultimately, 14 studies (22–35) met all the criteria to be included in the meta-analysis (five examined the impact of both tea and coffee consumption on osteoporosis incidence, three assessed tea consumption alone, and six focused on coffee consumption). The selection process is illustrated in Figure 1.
Study characteristics
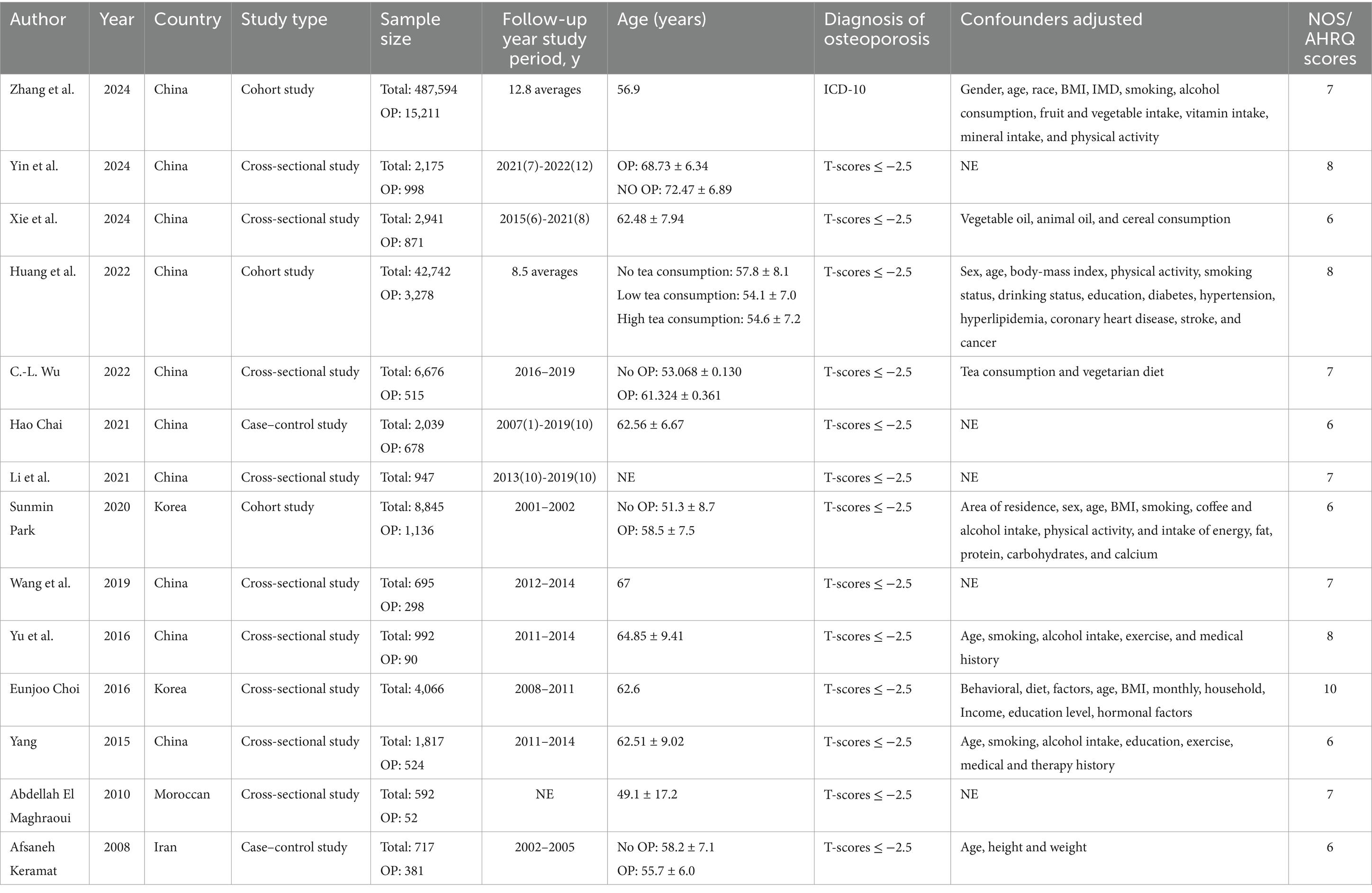
The included observational studies consisted of 14 studies, encompassing 562,838 participants aged 40 years or older. All studies used clear diagnostic criteria for osteoporosis. Adjusted estimates were available for almost all the studies, although the specific confounders varied. The key characteristics of this study are listed in Table 1.
Quality assessment
Based on the NOS and AHRQ scoring systems, the average quality score of the included studies was 7.07, with all studies exceeding the threshold of 7, indicating high methodological quality (Table 1).
Coffee consumption and risk of osteoporosis
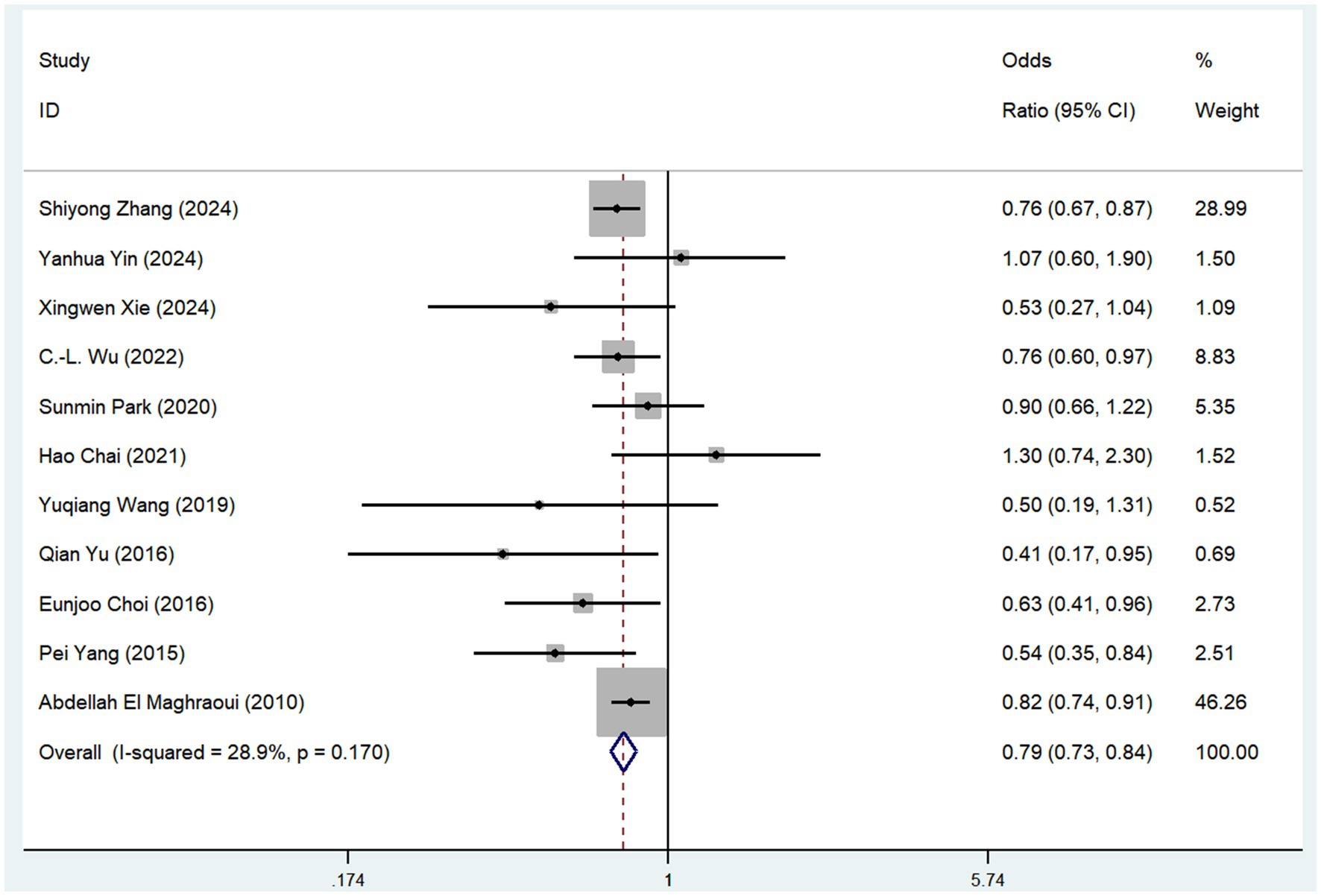
Eleven observational studies investigated the relationship between coffee consumption and risk of osteoporosis. The pooled analysis revealed that coffee consumption was associated with a reduced risk of osteoporosis (OR = 0.79, 95% CI: 0.73–0.84, I2 = 28.9%, p < 0.05; Figure 2). Sensitivity analysis revealed that no single study significantly altered the magnitude of the pooled effect, confirming the robustness of the results (Supplementary file S3).
Tea consumption and risk of osteoporosis
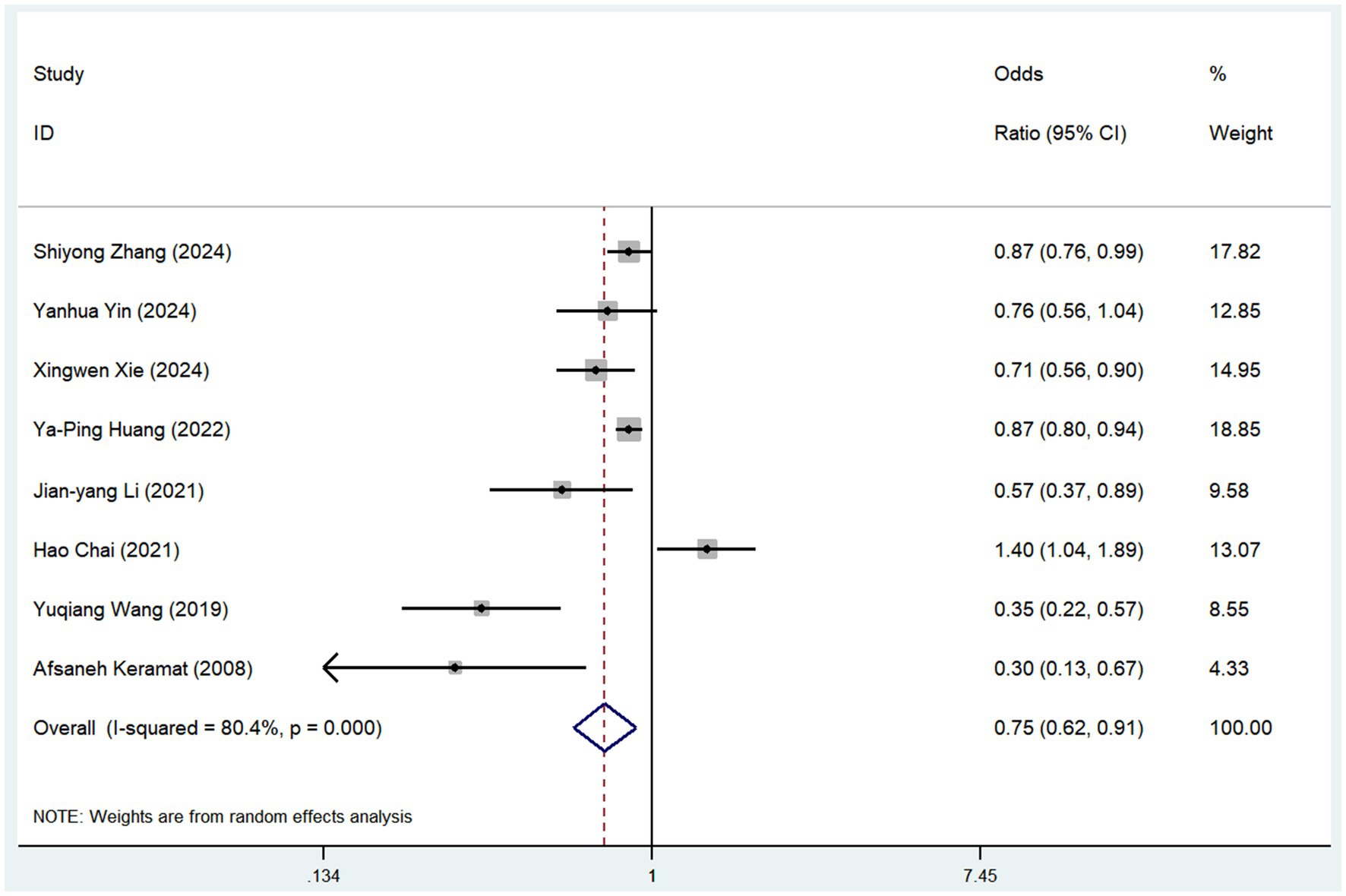
Eight studies examined the association between tea consumption and risk of osteoporosis (Figure 3). The pooled analysis showed that tea consumption was linked to a reduced risk of osteoporosis (OR = 0.75, 95% CI: 0.62–0.91, I2 = 80.4%, p < 0.05; Figure 3). The sensitivity analysis indicated that no individual study reversed the direction of the effect, supporting the robustness of these findings (Supplementary file S4).
Subgroup analysis
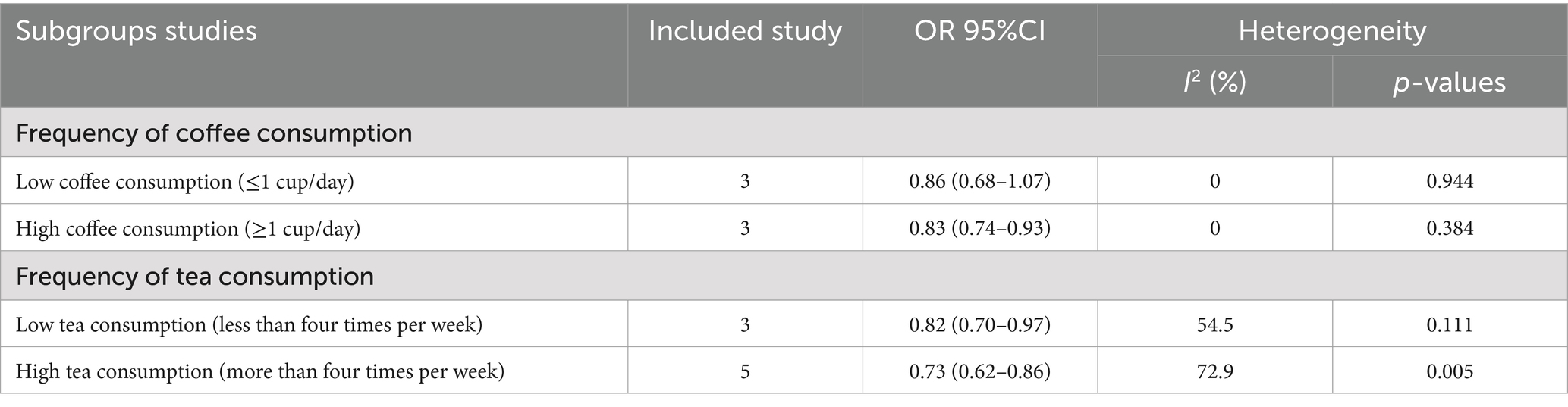
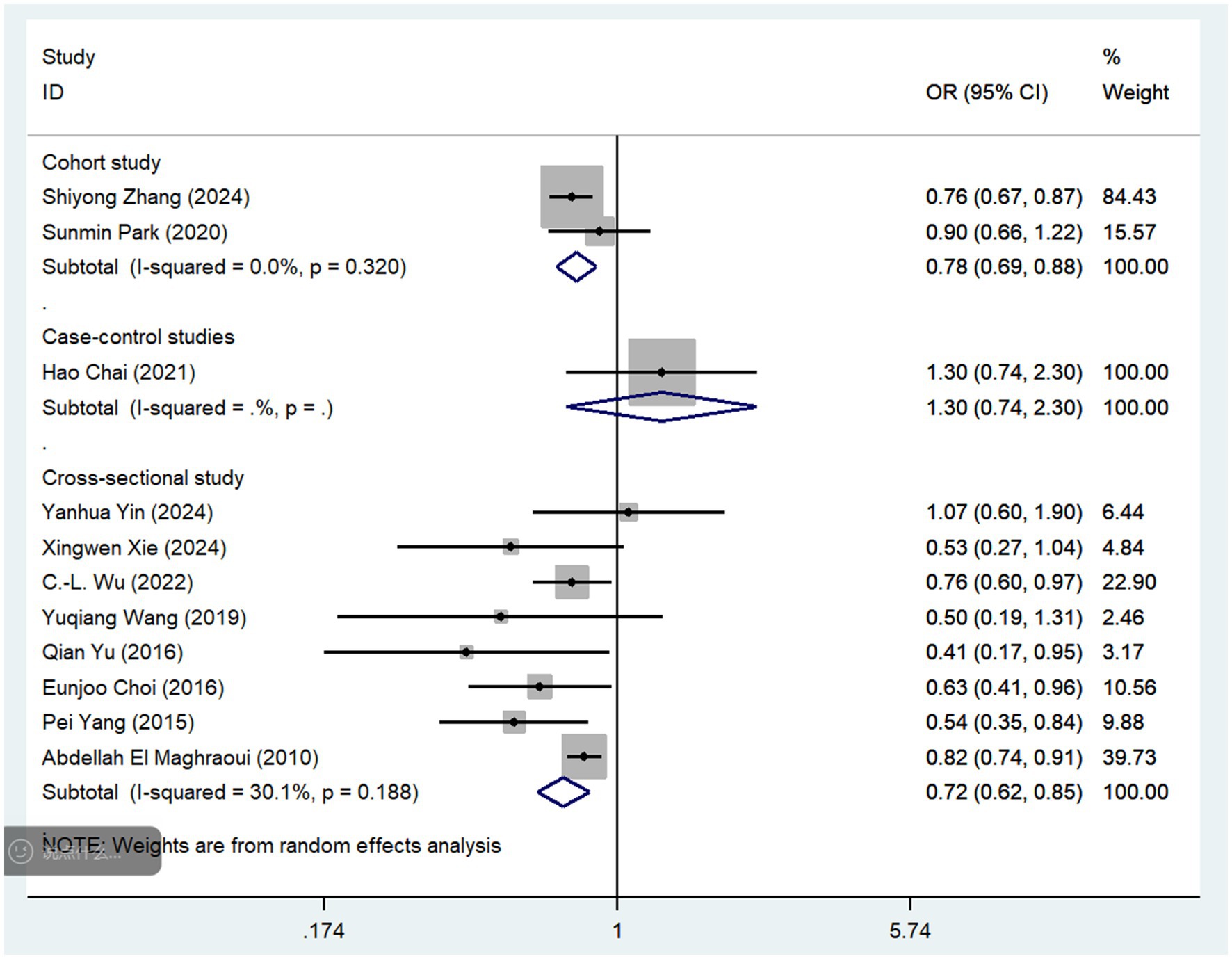
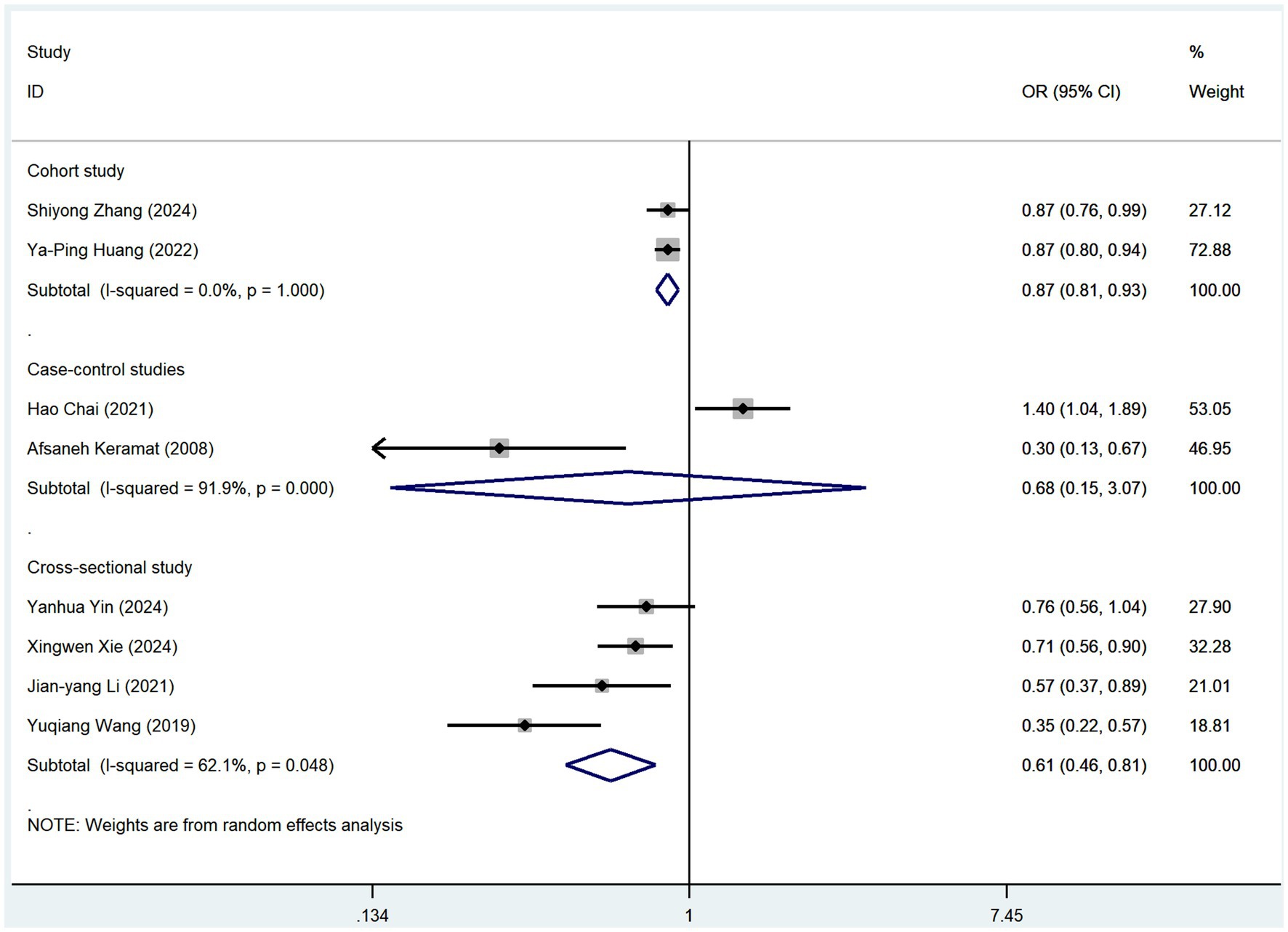
Subgroup analyses were conducted based on the frequency of coffee and tea consumption (Table 2; Supplementary file S5). For coffee, high-frequency consumption (defined as more than one cup per day) was associated with a slightly greater reduction in osteoporosis risk (OR = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.74–0.93, p = 0.001) than low-frequency consumption (defined as less than one cup per day), which showed no statistically significant reduction (OR = 0.86, 95% CI: 0.68–1.07, p = 0.171). Similarly, for tea consumption, high-frequency drinkers (defined as consuming tea more than four times per week) had a slightly stronger protective effect against osteoporosis (OR = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.62–0.86, p = 0.005) than low-frequency drinkers (OR = 0.82, 95% CI: 0.70–0.97, p = 0.111). To further mitigate potential bias risks associated with various study designs, we conducted subgroup analyses of coffee and tea consumption across three types of studies: cohort, case–control, and cross-sectional (Figures 4, 5). In cohort studies, coffee consumption exhibited low heterogeneity (OR = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.69–0.88, I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.320), and tea consumption also showed no significant heterogeneity among studies (OR = 0.87, 95% CI: 0.81–0.93, I2 = 0%, p = 1.000). In case–control studies, coffee consumption was not assessed for heterogeneity due to a single study (OR = 1.30, 95% CI: 0.74–2.30), but tea consumption had a high level of heterogeneity (OR = 0.68, 95% CI: 0.15–3.07, I2 = 91.9%, p = 0.000). Cross-sectional studies revealed low heterogeneity for coffee consumption (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.62–0.85, I2 = 30.1%, p = 0.188) and a moderate level of heterogeneity for tea consumption (OR = 0.61, 95% CI: 0.46–0.81, I2 = 62.1%, p = 0.048).
Publication bias
Visual inspection of the funnel plots and Egger’s regression tests showed no significant evidence of publication bias for either coffee (p = 0.132) or tea (p = 0.328) consumption with respect to the risk of osteoporosis (Figure 6).
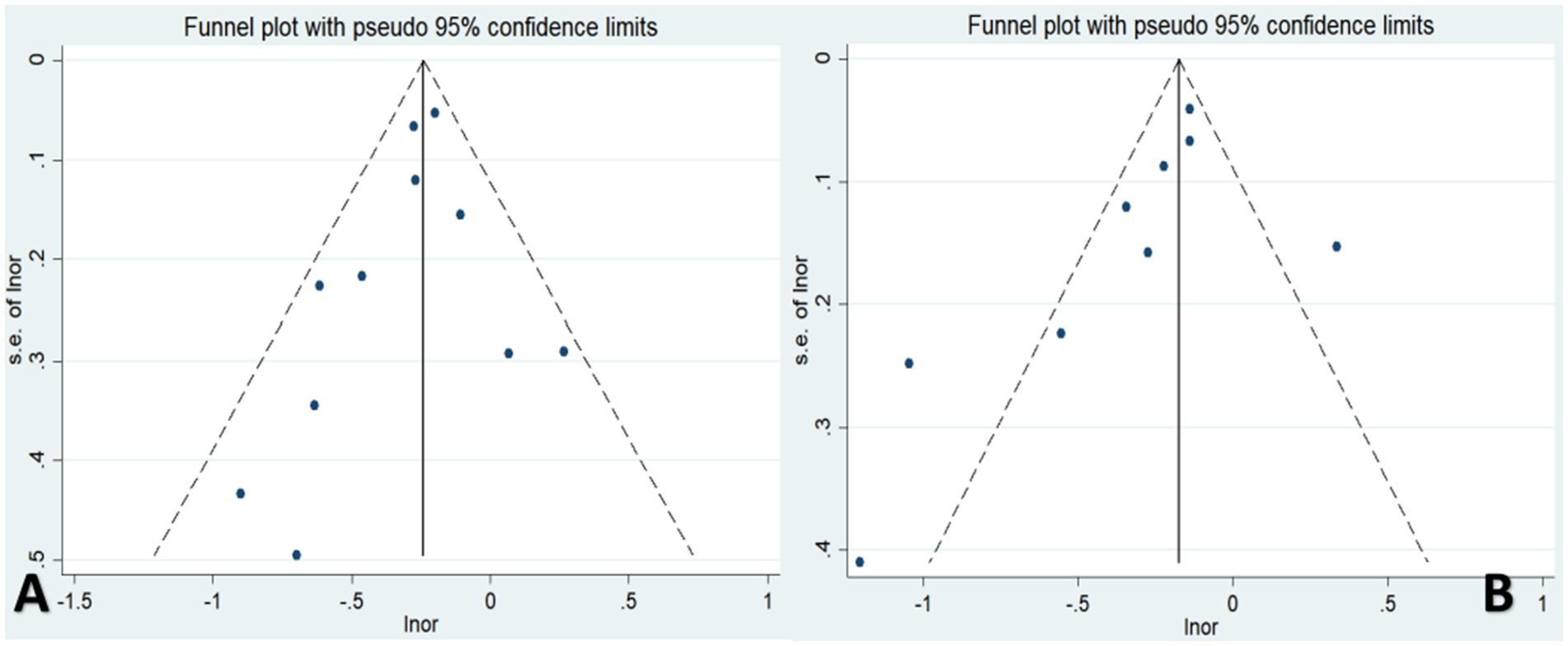
Figure 6. Publication bias of the risk of osteoporosis associated with coffee or tea consumption (A,B).
Discussion
Main findings
This meta-analysis, comprising 14 observational studies with 562,838 participants, evaluated the relationship between coffee and tea consumption and risk of osteoporosis. Our preliminary findings suggest that participants who regularly consume coffee and tea may have a lower risk of developing osteoporosis than non-consumers. Specifically, coffee drinkers showed a risk reduction of approximately 21%, and tea drinkers showed a risk reduction of approximately 25%. These findings tentatively imply that moderate daily consumption of coffee and tea can positively affect bone health and potentially reduce the risk of osteoporosis. It is noteworthy that the overall results of subgroup analyses by study design are consistent with the conclusions drawn. Although the subgroup analyses of the two case–control studies did not yield statistically significant results, this may be attributed to their small sample sizes or conflicting outcomes among individual studies. However, the impact on the overall results is minimal. However, it is important to note that this conclusion is based solely on the data available in the current study. The true relationship may be influenced by various factors such as individual genetic differences, lifestyle choices, dietary habits, and other potential confounders. Therefore, further investigation through larger-scale, multicenter, and more rigorously designed studies is necessary to confirm and validate the association between coffee and tea consumption and the reduction in osteoporosis risk.
Interpretation of findings
Previous meta-analyses have explored the link between tea consumption and osteoporosis risk (15), with most studies showing a protective effect. However, because the outcomes considered here included BMD and osteoporotic fractures, we caution that the observed associations may not directly reflect a reduction in osteoporosis risk. However, the quality and heterogeneity of the studies included in these analyses varied, limiting the strength of the conclusions. For instance, one study found a negative correlation between tea consumption and osteoporosis risk, but did not observe differences in risk based on tea consumption frequency, likely because of the small sample size (36). Regarding coffee consumption, only one previous meta-analysis investigated its association with osteoporosis risk; however, its small sample size (only four studies) limited the robustness of its findings (16). This analysis did not show significant effects related to varying frequencies of coffee consumption, possibly due to the inclusion of osteoporotic fractures as an outcome rather than a direct osteoporosis diagnosis. In contrast, our study controlled for specific outcome variables and analyzed coffee and tea consumption at different frequencies, revealing a clear benefit of long-term consumption in reducing osteoporosis risk.
However, the mechanisms by which coffee affects osteoporosis are not yet fully understood. Although the effects of caffeine on bone health are controversial, some studies have suggested that low caffeine concentrations inhibit osteoclastogenesis and improve osteoporosis outcomes (37). However, higher concentrations have been shown to disrupt bone formation and increase the risk (14). Coffee also contains other bioactive compounds, such as flavonoids and potassium, which have positive effects on bone health through their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (38, 39). Coffee is rich in phenolic compounds with osteoprotective potential, including chlorogenic acid (CGA). Polyphenols in CGA can stimulate osteoblast differentiation via the BMP-2/Wnt signaling pathway (40) and inhibit osteoclast genesis by regulating RANKL/OPG (41). Maillard reaction products (MRPs) formed during coffee roasting exhibit strong antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties. However, research suggests that advanced glycation end-products from the Maillard reaction may reduce bone mechanical properties and disrupt bone metabolism (42, 43), potentially affecting bone health. Further clinical studies are required to clarify the precise effects of MRPs on bone quality. Despite the potential synergistic effects of these compounds in reducing the risk of osteoporosis, their specific mechanisms require further investigation.
Tea, particularly its polyphenolic compounds, shows promise in protecting against osteoporosis. Studies have demonstrated that tea polyphenols improve bone microstructure, increase bone density, and modulate gut microbiota, thereby contributing to better bone health (44). Green tea catechins such as EGCG (Epigallocatechin gallate) have been shown to improve osteoblast and osteoclast activity, suggesting that tea consumption may prevent osteoporosis through multiple mechanisms (45). However, the potential adverse effects of tea on bone health, due to the complexity of its components, require further investigation.
Implications and limitations
Our meta-analysis highlights the protective role of both coffee and tea in reducing osteoporosis risk, emphasizing the potential of a moderate, balanced diet in preventing osteoporosis. However, this study had several limitations. While controlling for confounders, the multivariable regression analyses used in most of the included studies did not provide deeper insights into sex differences or specific dosage effects. Future research should address these aspects to better understand the influence of coffee and tea consumption on the risk of osteoporosis. Furthermore, while the results of subgroup analyses align with the overall findings, the inherent heterogeneity in studies of various types necessitates caution in interpreting the results. In addition, this study has certain limitations in exploring the impact of coffee and related beverages on osteoporosis. It focused primarily on the general effects of coffee without considering the differences in components between various coffee varieties, such as Robusta and Arabica, and their specific effects on bone health. These coffee varieties differ significantly in the content of caffeine and bioactive compounds, which may lead to different mechanisms and varying effects on osteoporosis. Furthermore, this study did not address various coffee preparation methods, such as espresso, Turkish coffee, and filter coffee, which can alter the bioactive components in coffee and consequently influence bone health outcomes. Additionally, the research did not examine various tea beverages, including green, black, and oolong tea, which are rich in beneficial compounds and may have osteoporosis-related effects, either similar to or different from those of coffee. Future research exploring the relationship among coffee varieties, preparation methods, and tea beverages could provide a clearer understanding of their impact on osteoporosis and contribute to a more robust research framework.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis demonstrated that daily coffee consumption exceeding one cup significantly reduced the risk of osteoporosis. However, no statistically significant effect was observed for low-frequency coffee consumption, suggesting that low coffee doses may not effectively prevent osteoporosis. Drinking tea more than four times a week appeared to have a stronger protective effect against osteoporosis, although the precise dosage was not clearly defined. Overall, for individuals within a moderate intake range—approximately one cup of coffee per day and tea more than four times a week—the protective effect against osteoporosis was more pronounced. These findings support the notion that moderate coffee and tea consumption as part of a balanced diet can prevent osteoporosis. Further research is required to explore the underlying mechanisms and clarify the effects of specific consumption patterns and dosages.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YX: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. LJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1559835/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Consensus development conference. Diagnosis, prophylaxis, and treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med. (1993) 94:646–50. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90218-E
2. Salari, N, Ghasemi, H, Mohammadi, L, Behzadi, MH, Rabieenia, E, Shohaimi, S, et al. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg. (2021) 16:609. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02772-0
3. Pouresmaeili, F, Kamali Dehghan, B, Kamarehei, M, and Yong, MG. A comprehensive overview on osteoporosis and its risk factors. Ther Clin Risk Manag. (2018) 14:2029–49. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S138000
4. Tański, W, Kosiorowska, J, and Szymańska-Chabowska, A. Osteoporosis - risk factors, pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical treatment. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2021) 25:3557–66. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202105_25838
5. De Melo Pereira, GV, de Carvalho Neto, DP, Magalhães Júnior, AI, Do Prado, FG, MGB, P, Karp, SG, et al. Chemical composition and health properties of coffee and coffee by-products. Adv Food Nutr Res. (2020) 91:65–96. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2019.10.002
6. Islam, MT, Tabrez, S, Jabir, NR, Ali, M, Kamal, MA, Da Silva, AL, et al. An insight into the therapeutic potential of major coffee components. Curr Drug Metab. (2018) 19:544–56. doi: 10.2174/1389200219666180302154551
7. Butt, MS, and Sultan, MT. Coffee and its consumption: benefits and risks. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2011) 51:363–73. doi: 10.1080/10408390903586412
9. Shang, A, Li, J, Zhou, DD, Gan, RY, and Li, HB. Molecular mechanisms underlying health benefits of tea compounds. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) 172:181–200. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.06.006
10. LeBoff, MS, Greenspan, SL, Insogna, KL, Lewiecki, EM, Saag, KG, Singer, AJ, et al. The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. (2022) 33:2049–102. doi: 10.1007/s00198-021-05900-y
11. Chen, CC, Shen, YM, Li, SB, Huang, SW, Kuo, YJ, and Chen, YP. Association of coffee and tea intake with bone mineral density and hip fracture: a meta-analysis. Medicina (Kaunas). (2023) 59:1177. doi: 10.3390/medicina59061177
12. Zhang, L, Chen, H, and Song, J. A meta-analysis on the association between tea consumption and the risk of osteoporotic fractures. Altern Ther Health Med. (2023) 29:290–6.
13. Chen, S, Chen, T, Chen, Y, Huang, D, Pan, Y, and Chen, S. Causal association between tea consumption and bone health: a mendelian randomization study. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:872451. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.872451
14. Berman, NK, Honig, S, Cronstein, BN, and Pillinger, MH. The effects of caffeine on bone mineral density and fracture risk. Osteoporos Int J. (2022) 33:1235–41. doi: 10.1007/s00198-021-05972-w
15. Sun, K, Wang, L, Ma, Q, Cui, Q, Lv, Q, Zhang, W, et al. Association between tea consumption and osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). (2017) 96:e9034. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009034
16. Zeng, X, Su, Y, Tan, A, Zou, L, Zha, W, Yi, S, et al. The association of coffee consumption with the risk of osteoporosis and fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. (2022) 33:1871–93. doi: 10.1007/s00198-022-06399-7
17. Page, MJ, McKenzie, JE, Bossuyt, PM, Boutron, I, Hoffmann, TC, Mulrow, CD, et al. Statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2020) 2021:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
18. Taylor, KS, Mahtani, KR, and Aronson, JK. Summarising good practice guidelines for data extraction for systematic reviews and meta-analysis. BMJ Evid-Based Med. (2021) 26:88–90. doi: 10.1136/bmjebm-2020-111651
19. Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
20. Zeng, X, Zhang, Y, Kwong, JSW, Zhang, C, Li, S, Sun, F, et al. The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: a systematic review. J Evid-Based Med. (2015) 8:2–10. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12141
21. Viswanathan, M, Ansari, MT, Berkman, ND, Chang, S, Hartling, L, McPheeters, M, et al. Assessing the risk of bias of individual studies in systematic reviews of health care interventions In: Methods guide for effectiveness and comparative effectiveness reviews. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US) (2012)
22. Zhang, S, Wu, S, Xia, B, He, Q, Mi, N, Zhao, J, et al. Association of coffee and tea consumption with osteoporosis risk: a prospective study from the UK biobank. Bone. (2024) 186:117135. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2024.117135
23. Yin, YH, Lin, YQ, Wu, J, Zhao, WY, Yang, MX, Qiu, L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of osteoporosis among elderly people in Jiuting area, Songjiang District, Shanghai. Chin J Prev Med. (2024) 58:1048–54. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20231210-00423
24. Xie, X, Lin, D, Li, D, and Huang, R. Impact of beef, mutton, fruits, and green tea consumption on osteoporosis risk: a cross-sectional study in Northwest China. Asian J Surg. (2024) 47:4530–2. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2024.07.238
25. Huang, YP, Chen, LS, Feng, SH, Liang, YS, and Pan, SL. Tea consumption and the risks of osteoporosis and hip fracture: a population-based longitudinal follow-up study. Osteoporos Int. (2023) 34:101–9. doi: 10.1007/s00198-022-06569-7
26. Wu, CL, Nfor, ON, Lu, WY, Tantoh, DM, and Liaw, YP. Relationship between coffee consumption and osteoporosis risk determined by the ESR1 polymorphism rs2982573. J Nutr Health Aging. (2022) 26:558–63. doi: 10.1007/s12603-022-1796-6
27. Chai, H, Ge, J, Li, L, Li, J, and Ye, Y. Hypertension is associated with osteoporosis: a case-control study in Chinese postmenopausal women. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2021) 22:253. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04124-9
28. Li, J-y, Ge, J-r, Chen, J, Ye, Y-j, Xie, L-h, Li, L, et al. Clinical study on the influence of tea drinking habits on bone mineral density and osteoporosis in postmenopausal women in Fuzhou city, China. Prog Nutr. (2021) 23:e2021033. doi: 10.23751/pn.v23i1.9409
29. Park, S, Daily, JW, Song, MY, and Kwon, HK. Gene-gene and gene-lifestyle interactions of AKAP11, KCNMA1, PUM1, SPTBN1, and EPDR1 on osteoporosis risk in middle-aged adults. Nutrition. (2020) 79-80:110859. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110859
30. Wang, Y, Ding, H, Wang, X, Wei, Z, and Feng, S. Associated factors for osteoporosis and fracture in Chinese elderly. Med Sci Monit. (2019) 25:5580–8. doi: 10.12659/MSM.914182
31. Yu, Q, Liu, ZH, Lei, T, and Tang, Z. Subjective evaluation of the frequency of coffee intake and relationship to osteoporosis in Chinese men. J Health Popul Nutr. (2016) 35:24. doi: 10.1186/s41043-016-0060-2
32. Choi, E, Choi, KH, Park, SM, Shin, D, Joh, HK, and Cho, E. The benefit of bone health by drinking coffee among korean postmenopausal women: a cross-sectional analysis of the fourth & fifth Korea national health and nutrition examination surveys. JR Chen, editor. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0147762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147762
33. Yang, P, Zhang, XZ, Zhang, K, and Tang, Z. Associations between frequency of coffee consumption and osteoporosis in Chinese postmenopausal women. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:15958–66.
34. El Maghraoui, A, Ghazi, M, Gassim, S, Ghozlani, I, Mounach, A, Rezqi, A, et al. Risk factors of osteoporosis in healthy moroccan men. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2010) 11:148. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-11-148
35. Keramat, A, Patwardhan, B, Larijani, B, Chopra, A, Mithal, A, Chakravarty, D, et al. The assessment of osteoporosis risk factors in iranian women compared with Indian women. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2008) 9:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-9-28
36. Zhou, F, Wang, T, Li, L, Yu, J, Liu, Z, Zhang, J, et al. Tea consumption and risk of bone health: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Miner Metab. (2024) 42:99–114. doi: 10.1007/s00774-023-01479-y
37. Miao, Y, Zhao, L, Lei, S, Zhao, C, Wang, Q, Tan, C, et al. Caffeine regulates both osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation via the AKT, NF-κB, and MAPK pathways. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1405173. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1405173
38. Ortiz, A, De, C, SOM, F, CHB, R, Bellini, MZ, De SBM, PE, et al. Therapeutic effects of citrus flavonoids neohesperidin, hesperidin and its aglycone, hesperetin on bone health. Biomol Ther. (2022) 12:626. doi: 10.3390/biom12050626
39. Abate, V, Vergatti, A, Altavilla, N, Garofano, F, Salcuni, AS, Rendina, D, et al. Potassium intake and bone health: a narrative review. Nutrients. (2024) 16:3016. doi: 10.3390/nu16173016
40. Ciupei, D, Colişar, A, Leopold, L, Stănilă, A, and Diaconeasa, ZM. Polyphenols: from classification to therapeutic potential and bioavailability. Foods. (2024) 13:4131. doi: 10.3390/foods13244131
41. Shen, J, Zhang, S, Zhang, J, Wei, X, Wang, Z, and Han, B. Osteogenic mechanism of chlorogenic acid and its application in clinical practice. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1396354. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1396354
42. Delgado-Andrade, C, Roncero-Ramos, I, Carballo, J, Rufián-Henares, J, Seiquer, I, and Navarro, MP. Composition and functionality of bone affected by dietary glycated compounds. Food Funct. (2013) 4:549–56. doi: 10.1039/c2fo30187c
43. Carnovali, M, Luzi, L, Terruzzi, I, Banfi, G, and Mariotti, M. Metabolic and bone effects of high-fat diet in adult zebrafish. Endocrine. (2018) 61:317–26. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1494-z
44. Wen, X, Wu, P, Li, F, and Pi, G. Study on the relationship between tea polyphenols alleviating osteoporosis and the changes of microorganism-metabolite-intestinal barrier. Microb Pathog. (2024) 188:106564. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106564
Keywords: coffee consumption, tea consumption, osteoporosis, meta-analysis, risk
Citation: Li W, Xie Y and Jiang L (2025) Coffee and tea consumption on the risk of osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 12:1559835. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1559835
Edited by:
Fei Xu, Nanjing Municipal Center for Disease Control and Prevention, ChinaReviewed by:
Rajko Vidrih, University of Ljubljana, SloveniaShihua Shi, Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research (FMI), Switzerland
Copyright © 2025 Li, Xie and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Jiang, d3NoamxfMTk4NkAxNjMuY29t
 Wopei Li
Wopei Li Yujiao Xie
Yujiao Xie Lei Jiang
Lei Jiang