
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Nutr., 21 February 2025
Sec. Nutrition and Microbes
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2025.1553674
This article is part of the Research TopicStrain-Specific Probiotics: Enhancing Children's Health Through Targeted Clinical ResearchView all 9 articles
 Yang Liu1,2,3,4*†
Yang Liu1,2,3,4*† Yan Chen2,3,5
Yan Chen2,3,5 Huijuan Liao2,3,5
Huijuan Liao2,3,5 Shijie Sun2,3,5
Shijie Sun2,3,5 Xiaohu Zhang2,3,5,6
Xiaohu Zhang2,3,5,6 Liang Xie1,2,3,4
Liang Xie1,2,3,4 Hanmin Liu1,2,3,4,6*†
Hanmin Liu1,2,3,4,6*†Respiratory diseases are a leading cause of morbidity in children globally, with significant healthcare costs. The overuse of conventional treatments like antibiotics has raised concerns about antibiotic resistance and side effects. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG), one of the most extensively studied probiotics, has gained attention as a potential adjunct therapies due to their ability to modulate the gut microbiota and immune responses. This review aims to assess the effectiveness of LGG in managing pediatric respiratory diseases, including respiratory tract infections (RTI), cystic fibrosis (CF), and asthma. Clinical trials suggest LGG can reduce the incidence and severity of RTI, improving CF symptoms, and enhancing quality of life in children. However, evidence for its benefits in asthma remains inconclusive. Its mechanisms include modulating immune responses, enhancing gut barrier function, and maintaining a microbial homeostasis via the gut-lung axis. Existing studies are often limited by small sample sizes, heterogeneity in intervention protocols, and short follow-up periods. Emerging technologies and novel formulations, hold promise for unraveling the complex interactions among LGG, the gut-lung axis, and respiratory health. These advancements could pave the way for personalized probiotic therapies, highlighting the potential of LGG as a cost-effective, adjunctive therapy for pediatric respiratory diseases. This review underscores the broader significance of integrating LGG into pediatric healthcare, while calling for future research to overcome current limitations, optimize clinical protocols, and explore innovative therapeutic strategies.
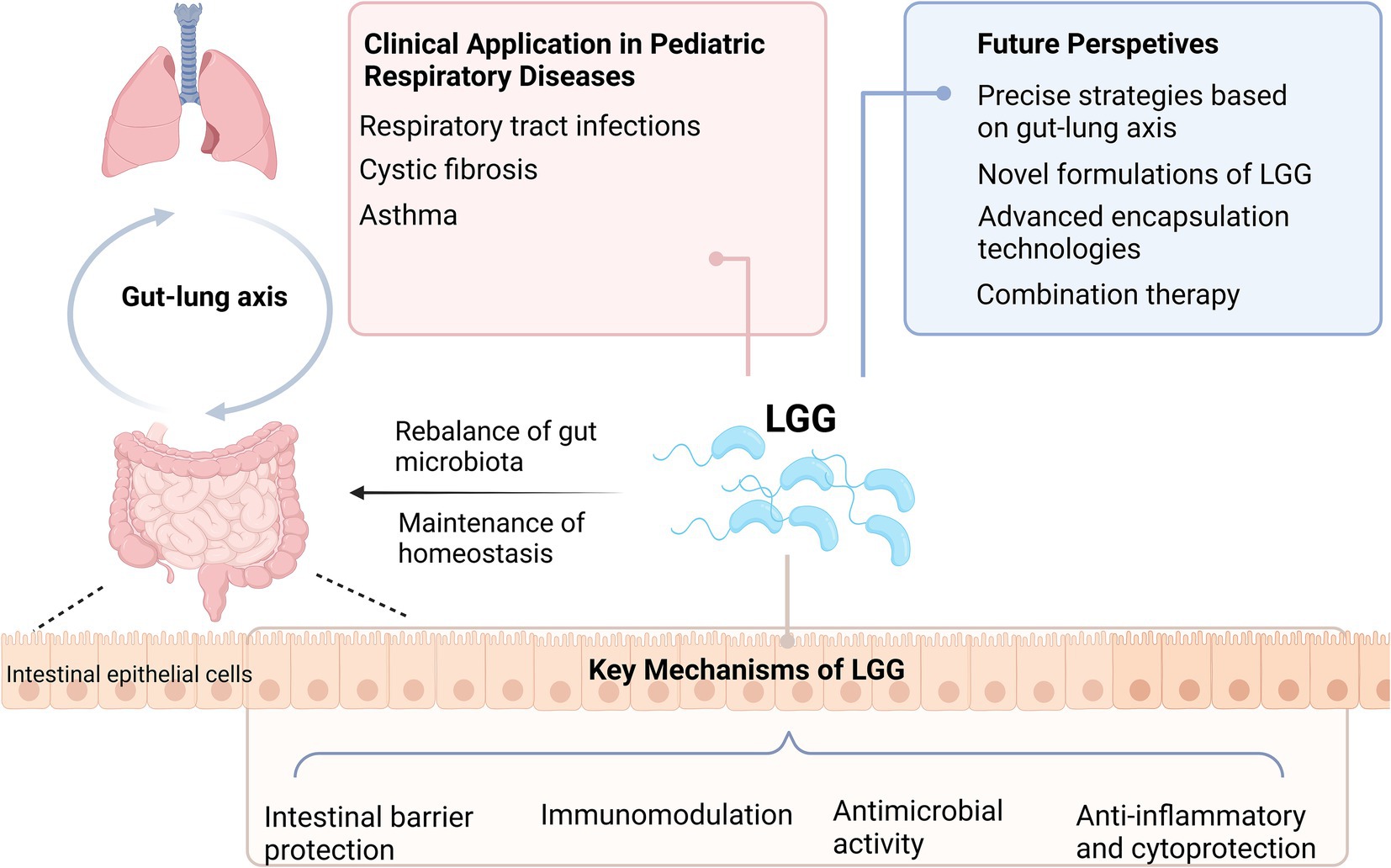
Graphical Abstract. Created in BioRender.com.
Respiratory diseases are among the most common health issues affecting children worldwide, contributing significantly to morbidity and healthcare costs (1, 2). While conventional treatments such as antibiotics and bronchodilators are widely used, their overuse has raised concerns about antibiotic resistance and adverse side effects. Consequently, there is growing interest in alternative or adjunctive therapies, such as probiotics, which have shown promise in modulating host immunity and maintaining microbial homeostasis.
Probiotics, are living microorganisms that, when provided in sufficient quantities, offer beneficial effects on the health of the host (3). They primarily achieve their benefits through interactions with the gut microbes, enhancing the gut barrier function, and modulating systemic immune responses. Among the emerging concepts in microbiome research, the gut-lung axis has gained significant attention in recent years (4–6). This bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the lungs highlights how gut-derived factors can influence pulmonary immunity and inflammation through microbial metabolites, cytokine signaling, and immune cell trafficking. An imbalance in the gut microbial communities, known as dysbiosis, has been linked to increased susceptibility to respiratory infections and chronic respiratory diseases, emphasizing the potential role of probiotics in restoring microbial equilibrium and improving respiratory health (7).
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG), previously known as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, is one of the most extensively studied probiotic strains. Reclassified in 2020 due to advancements in genomic analysis (8). LGG has demonstrated remarkable resilience in the gastrointestinal tract and the ability to adhere to intestinal epithelial cells, thereby exerting beneficial effects on the host’s immune system. Recent studies have suggested that LGG may play a role in reducing the incidence and severity of respiratory infections by enhancing mucosal immunity and mitigating inflammation. This article reviews the application of LGG in managing pediatric respiratory diseases, focusing on its mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, and potential as a preventive and therapeutic agent. By synthesizing evidence from clinical trials and recent meta-analyses, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of LGG’s role in pediatric respiratory health and identify areas for future research (see Graphical abstract).
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG was first isolated and named by American professors Sherwood Gorbach and Barry Goldin from healthy humans in 1983. It is a naturally occurring strain of Lacticaseibacillus, a beneficial bacterium commonly found in the human gut. In 2020, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) was reclassified as Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG following a comprehensive genomic analysis of the Lactobacillus genus. This reclassification highlights the genetic diversity within the genus and provides a more accurate taxonomic framework for studying probiotics. LGG is known for its ability to survive the harsh conditions of the stomach and intestines due to its high tolerance to acid and bile. This allow it to reach the intestines alive and exert its beneficial effects, unlike many other probiotics that are already killed by the effects of stomach acid and bile before entering the intestines.
Over the years, many studies have explored the mechanism of action of LGG (9), mainly including the following points:
LGG exhibits strong adhesion capabilities, which are essential for its colonization and beneficial effects in the gut. This is facilitated by specific surface proteins, such as LGG-0186 and SpaCBA pili (10–12). These proteins enable LGG to bind effectively to intestinal epithelial cells, thereby outcompeting pathogenic bacteria for attachment sites. Additionally, LGG produces exopolysaccharides (EPS) rich in galactose, which form a protective shield against complement-mediated lysis (13, 14). This EPS layer not only protects LGG cells but also contributes to the overall stability of the gut microbiota. Moreover, LGG has been shown to normalizes intestinal permeability and improves intestinal barrier function (15).
LGG exerts significant immunomodulatory effects, which are central to its health benefits. It stimulates nonspecific immune responses, including IgA, IgG, and IgM, which play crucial roles in defensing against pathogens (16, 17). LGG modulates cellular responses through its soluble factors, with effects that are cell-type and context-dependent. For instance, in dendritic cells (DCs), LGG can either enhance or suppress the expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), depending on the microenvironment and overall health status. In inflammatory settings, it may promote IL-6 production to trigger defense mechanisms. By contrast, under anti-inflammatory or homeostatic conditions, it can indirectly suppress IL-6 secretion by inducing anti-inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-10 (IL-10) and Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β). In macrophages, LGG typically reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-12 (IL-12) while boosting the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-β (18–20). This dual action helps to fine-tune the immune response, preventing excessive inflammation while ensuring effective pathogen clearance.
Furthermore, LGG influences the balance between T helper cell 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cells (Treg cell) by regulating dendritic cell function (20–22). Through these mechanisms, LGG can reduce the overreaction of CD4 + T cells, a phenomenon often associated with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases (21, 23). Additionally, LGG promotes the secretion of IL-23 by dendritic cells in certain inflammatory contexts, which further facilitates the activation of type 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) and enhance the production of IL-22. IL-22 plays a critical role in maintaining intestinal epithelial barrier integrity and promoting antimicrobial defense (24, 25).
LGG produces lactic acid and various antimicrobial peptides, which inhibit the adhesion and growth of pathogens such as Salmonella and E. coli (12, 13). These antimicrobial substances create an unfavorable environment for pathogens, reducing their ability to colonize the gut. LGG’s competitive exclusion mechanism further prevents pathogen overgrowth by outcompeting them for nutrients and attachment sites on the intestinal epithelium.
LGG secretes soluble proteins such as main secreting protein (Msp), Msp/p40 and Msp1/p75, which reduce apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells and protect the gut epithelial barrier (26, 27). These proteins help maintain the integrity of the intestinal lining, preventing the loss of barrier function that can lead to inflammation and infection. Additionally, LGG regulates the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-10, thereby modulating the inflammatory responses and promoting a more balanced immune environment (28, 29).
Given the intricate gut-lung axis, where the gut microbiota can influence respiratory health, LGG’s immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties make it a promising candidate for managing pediatric respiratory diseases. With this foundation, we now delve into the specific applications of LGG in addressing respiratory issues in children. Table 1 summarized the random clinical trials (RCT) of LGG in pediatric respiratory disease.
Increasing clinical evidence suggests that LGG have a positive effect on RTI. A Finnish RCT study (30) included 94 preterm infants administrated oral prebiotics, LGG, or placebo between 3 to 60 days after birth. The results showed that the incidence of RTI was significantly lower in infants receiving prebiotics or LGG. Additionally, the incidence of rhinovirus-induced episodes (accounting for 80% of all RTI episodes) was notably reduced in these groups. However, the study focused on preterm infants born at 32 to 36 weeks of gestation. This specific population has a different immune system and gut microbiota composition compared to full-term infants, making the findings difficult to generalize to full-term infants or other age groups.
Another Finish study included 523 children aged 2–6 years and lasted for 28 weeks. (31) LGG intake was confirmed via fecal samples. Children who provided fecal samples at both the beginning and end of the study were classified as completed cases. In the completed cases, the number of respiratory symptom days in the LGG group was significantly reduced (4.71 days vs. 5.67 days). Hatakka et al. (32) studied 571 children aged 1 to 6 years who were given milk containing LGG or placebo milk for 7 months. The LGG group had fewer sick leave days (4.9 days vs. 5.8 days), lower rate of respiratory infections, fewer complications and less antibiotic use. Hojsak et al. (33, 34) also reported similar findings. In two studies conducted on healthy children attending daycare centers and hospitalized children, respectively, they observed a significant reduction in the risk of upper respiratory tract infections in children receiving LGG.
A meta-analysis (35) included 15 RCTs involving 5,121 children (aged 3 months to 7 years) in daycare centers. Among them, a pooled analysis of the above 3 RCTs, involving a total of 1,295 participants, showed that LGG significantly shortened the duration of RTIs (95% confidence interval [CI] −1.46; −0.09). However, another analysis involving 343 participants showed that Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 had no effect on the duration of RTIs or absenteeism.
Despite the promising results, these studies have several limitations such as small sample sizes, heterogeneous interventions (e.g., LGG capsules vs. fermented dairy products), and short follow-up periods, which limit the evaluation of LGG’s long-term protective effects. Additionally, study populations often vary in living environments, infection risks, and baseline health conditions.
Research on LGG in CF began as early as 2007. An Italian randomized, placebo-controlled crossover study found that 19 patients receiving LGG treatment had significantly reduced pulmonary exacerbations and hospitalization rates compared to those treated with oral rehydration solution (36). The research team later conducted a study on 22 children with CF. They found that oral LGG treatment significantly increased the intestinal Bacteroides counts in CF children, partially restored the composition of the gut microbiota, and reduced fecal calprotectin (CLP), a marker of intestinal inflammatory status (37). Another RCT (38) in Iran recruited 37 CF children who were treated with a multi-strain probiotic capsule containing LGG for 1 month. Using the PedsQL 4.0 questionnaire, the parents of the children reported a significantly lower rate of pulmonary exacerbations within 3 months after the intervention (p < 0.01). Additionally, the average total quality-of-life score showed significant improvement at the third month (p = 0.01) but not significant at 6 month, suggesting temporary benefits. Continuous intake may result in more stable improvements in quality of life. Since it was a multi-strain probiotic, it is difficult to individually evaluate the contribution of LGG to CF patients in this study.
Coffey et al. (39) conducted a systematic review of 17 trials (12 RCTs, 464 participants) on LGG and other probiotics for CF. Among these, 8 trials included only children, while four trials included both children and adults. Four trials specifically used LGG. The analysis showed that LGG may reduce intestinal inflammation but have limited effects on pulmonary exacerbations, lung function, or growth.
While research on LGG in CF started early, but to date, studies in children remain limited, with most involving small sample sizes. For example, one study included only 19 children in LGG group, resulting in insufficient statistical power that may fail to detect small but clinically significant effects. Additionally, some studies used multi-strain probiotic formulations, making it difficult to determine the specific effects of LGG. Existing studies have also primarily focused on short-term intervention effects, lacking long-term effects of LGG on key indicators such as lung function and nutritional status.
In children with asthma, gut microbiota dysbiosis is commonly observed (40–42). Therefore, multiple studies have explored the preventive and therapeutic effects of various probiotics, including LGG, on asthma and related allergic diseases (43–47).
Prenatal and perinatal supplementation with LGG and other probiotics appears to have minimal preventive effects (48).Ou et al. included 191 pregnant women who received LGG starting from the mid-pregnancy. While LGG reduced the severity of allergic diseases in mothers, it did not lower the incidence of allergic sensitization or allergic diseases in children (49). Boyle et al. had similar findings, but they only provided LGG to pregnant women during pregnancy without postnatal supplementation (50).
The effects of direct administration of LGG to children with asthma are also inconsistent. Jerzynska et al. reported significant improvements in lung function, regulatory T cells induction, and fractional exhaled nitric oxide concentration (FeNO) in children with allergic rhinitis sensitive to grass pollen who received LGG supplementation (51). However, Cabana et al. found different results. In high-risk infants with at least one parent with asthma and eczema, LGG supplementation within the first 6 months after birth did not prevent eczema or asthma by age 2. By age 5, the cumulative incidence of asthma in the LGG group showed a decreasing trend compared to the control group (9.7% vs. 17.4%), but the difference was not statistically significant (52). Similarly, Rose et al. found no significant differences in atopic dermatitis or asthma-related events. The study focused on children with at least two wheezing episodes and a family history of first-degree atopic disease who received LGG (53). Furthermore, in a subgroup of children previously sensitized to allergens, asthma symptoms showed a slight worsening.
The inconsistent results of LGG may partly stem from the multifaced nature of asthma pathogenesis, involving intricate interactions among genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Variability in study design may also contribute to these discrepancies.
It is worth noting that in the treatment of asthma, researchers tend to favor the use of multi-strain probiotics in recent years. These combinations may also enhance gut microbial diversity and stability, which are critical for immune homeostasis. Stronger evidence supports the therapeutic effects of multi-strain probiotics, including combinations of Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria, on asthma (44, 45, 54). As asthma involves complex interactions between the immune system and the gut-lung axis, it is necessary to further explore not only how different probiotic strains exert their specific mechanisms through this pathway but also how these strains interact synergistically to enhance and amplify their collective effects, particularly in the context of advancing microbiome research.
The dosage of LGG is one of the key factors influencing their clinical effects, yet significant gaps remain on its use in pediatric respiratory diseases. Current studies report a wide range of dosage, typically between 108–1010 colony-forming units (CFU) /day, reflecting the lack of consensus on optimal amounts. For example, LGG was generally administered at 108–109 CFU/day for RTI, 2 × 109–6 × 109 CFU/day for CF, and 3 × 109–1010 CFU/day for asthma prevention or treatment.
However, there is no clear dose–response relationship established, making it difficult to determine the optimal dosage for different populations. Several gaps remain in understanding the optimal dosages of LGG. Firstly, the majority of studies have focused on specific age groups or health conditions, such as preterm infants or children in day care centers. This limits the generalizability of findings to other pediatric populations like adolescents or those with chronic respiratory conditions. Secondly, the duration of LGG intervention has varied across studies, from weeks to months. This variation makes it difficult to determine the long-term effects of LGG. Thirdly, the form of LGG administration (e.g., in milk, fermented products, or capsules) may influence its bioavailability and efficacy.
Future research should prioritize multicenter, large-scale, and long-term RCTs, explore LGG’s synergy with other probiotics, and develop personalized dosage recommendations based on microbiome profiles. Addressing these gaps will help optimize LGG’s use in managing RTI, CF, asthma, and other pediatric conditions.
Although research on LGG’s effects in respiratory diseases is still limited, recent studies have begun to shed light on its potential mechanisms, primarily mediated via the gut-lung axis (4–6).
Through its well-documented immunomodulatory properties, as described earlier, LGG exerts systemic effects that extend to the respiratory system. For example, studies have shown that Th17 cells in the gut can migrate to the lungs through the lymphatic system and bloodstream, where they contribute to immune regulation and pathogen defense (6). By promoting the balance of Th17 and regulatory T cells (Treg), LGG may indirectly influence pulmonary immune responses and reduce excessive inflammation.
LGG has also been shown to modulate the gut microbiota by increasing the abundance of beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli while reducing dysbiosis (10, 55). This rebalancing enhances the production of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs). SCFAs have been shown to reduce airway inflammation and improve lung function by modulating the activity of immune cells, including macrophages and dendritic cells (56–60).
Additionally, LGG enhances the integrity of the intestinal barrier by upregulating tight junction proteins such as occludin and claudin (15, 29). This prevents the translocation of endotoxins and pro-inflammatory molecules into the bloodstream, thereby reducing systemic inflammation that could exacerbate respiratory conditions.
Figure 1 illustrates the key mechanisms of LGG in gut-lung axis and respiratory health.
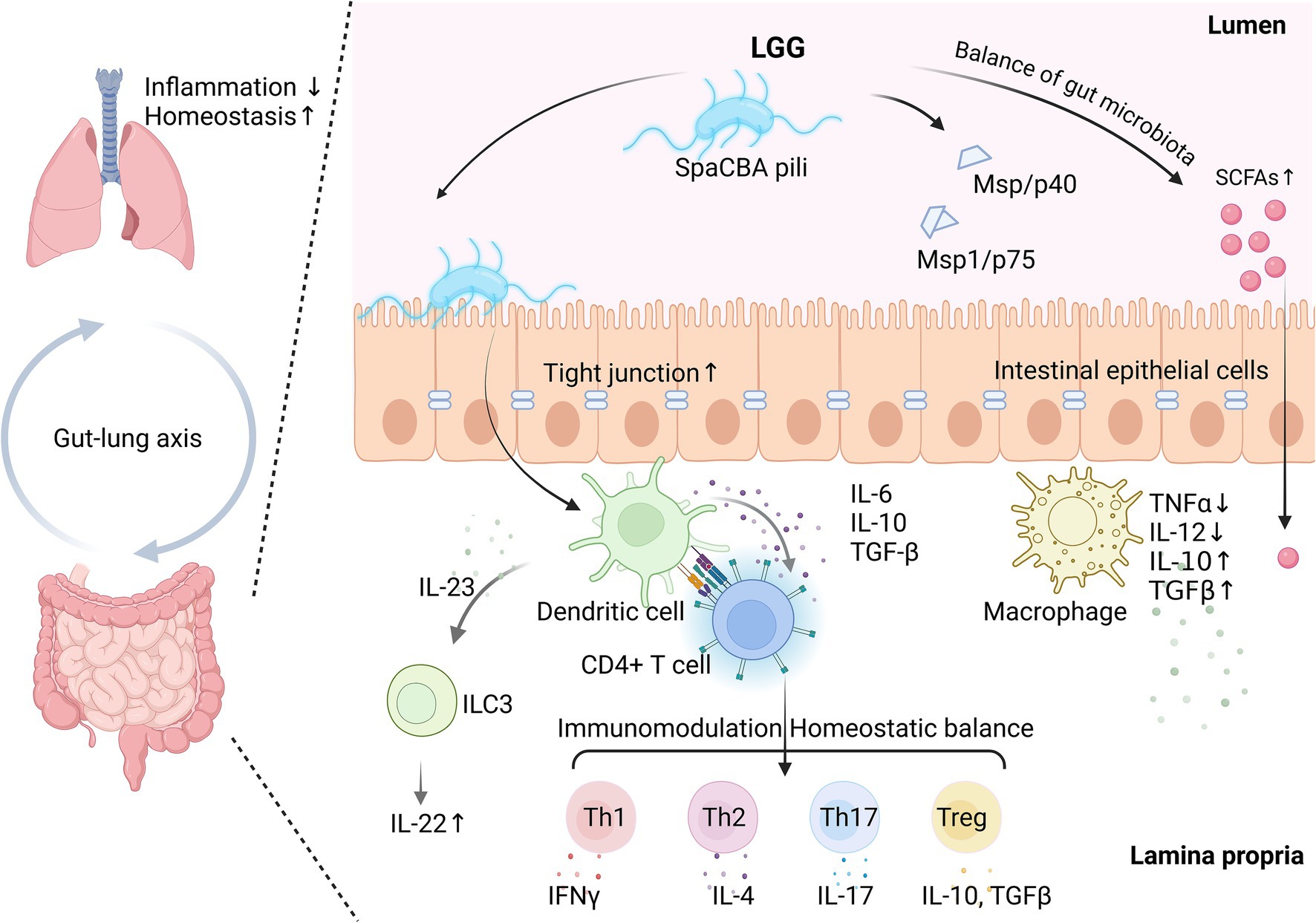
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of key mechanisms of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) in gut-gung axis and respiratory health. LGG can interacts with intestinal epithelial cells via SpaCBA pili. It can also enhance tight junction integrity and promote gut barrier function. Additionally, LGG helps balance gut microbiota and indirectly supports short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) production by improving the gut environment and promoting the growth of SCFA-producing bacteria. Its metabolites, such as main secreting protein (Msp), Msp/p40 and Msp1/p75, play a role in maintaining epithelial health and modulating immune responses. These interactions in turn influence immune responses in the lamina propria. Macrophages are activated to secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β) and reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-12). Dendritic cells further stimulate CD4+ T cells and innate lymphoid cells (ILC3), promoting IL-22 production and maintaining homeostatic balance among Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg cells. This balance supports systemic immune modulation and highlights the gut-lung axis as a key pathway through which LGG promotes broader respiratory health benefits. Created in BioRender.com.
Since 1990, the LGG has been used worldwide as an ingredient in food and dietary supplements, with no adverse events reported to date. LGG is generally considered safe for most populations, including infants, children, and adults. It is well-tolerated and has a low risk of side effects, although some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating or gas.
LGG is one of the well-studied probiotics with significant potential as a safe and effective adjunct therapy for pediatric respiratory diseases. Clinical evidence suggests that LGG reduces the incidence and severity of RTI, shortens symptom duration, and lowers antibiotic use in children. It may also alleviate certain symptoms associated with CF and asthma, though evidence remains limited and varies by population. These benefits are attributed to its ability to modulate immune responses, enhance gut barrier function, and maintain a healthy microbiota balance, likely mediated through the gut-lung axis.
However, there have been relatively few groundbreaking findings regarding LGG in the field of pediatric respiratory diseases over the past 5 years. This trend may be attributed to several factors. Firstly, research in pediatric populations faces unique challenges, including ethical considerations, variability in immune development, and difficulties in long-term follow-up. Secondly, the research focus in probiotics field has shifted toward exploring multi-strain formulations and personalized microbiome interventions, which may have diverted attention from single-strain studies like those on LGG.
As understanding of the gut-lung axis deepens, the role and mechanisms of LGG in improving pediatric respiratory health are expected to become clearer. Future research directions for LGG are promising and multifaceted. First, precise studies integrating microbiome analysis, metabolomics, and immunology are needed to elucidate how LGG modulates respiratory health through gut microbial regulation. Second, novel formulations, such as engineered nasal sprays, inhalable probiotics (61), or advanced encapsulation technologies (62, 63), could further enhance LGG’s stability, targeted delivery, and maximal efficacy. These innovations would enable LGG to better adapt to diverse clinical application scenarios. Third, combining LGG with antiviral drugs, vaccines, or immunomodulators presents opportunities for synergistic therapeutic effects.
In conclusion, while LGG has demonstrated clear benefits, further research is essential to align its application with modern clinical and technological advancements. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies, addressing pediatric research challenges, and expanding knowledge of the gut-lung axis, LGG could continue to play a valuable role in improving respiratory health in children.
YL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Visualization. YC: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software. HuL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Software. SS: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology. XZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation. LX: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. HaL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of the China Joint Fund for Regional Innovation and Development (No. U21A20333), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Nos. 2023NSFSC0530 and 2023ZYD0118), and Research Grant of Chengdu Science and Technology Bureau (Nos. 2022-GH03-00013-HZ and 2023-YF06-00024-HZ).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Sirota, SB, Doxey, MC, Dominguez, R-MV, Bender, RG, Vongpradith, A, Albertson, SB, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of upper respiratory infections and otitis media, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet Infect Dis. (2025) 25:36–51. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00430-4
2. Kyu, HH, Vongpradith, A, Sirota, SB, Novotney, A, Troeger, CE, Doxey, MC, et al. Age-sex differences in the global burden of lower respiratory infections and risk factors, 1990-2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Infect Dis. (2022) 22:1626–47. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00510-2
3. Latif, A, Shehzad, A, Niazi, S, Zahid, A, Ashraf, W, Iqbal, MW, et al. Probiotics: mechanism of action, health benefits and their application in food industries. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1–15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1216674
4. Budden, KF, Gellatly, SL, Wood, DL, Cooper, MA, Morrison, M, Hugenholtz, P, et al. Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2017) 15:55–63. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.142
5. Mjösberg, J, and Rao, A. Lung inflammation originating in the gut. Science (New York, NY). (2018) 359:36–7. doi: 10.1126/science.aar4301
6. Wypych, TP, Wickramasinghe, LC, and Marsland, BJ. The influence of the microbiome on respiratory health. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:1279–90. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0451-9
7. Wang, Y, He, F, Liu, B, Wu, X, Han, Z, Wang, X, et al. Interaction between intestinal mycobiota and microbiota shapes lung inflammation. iMeta. (2024) 3:e241. doi: 10.1002/imt2.241
8. Zheng, J, Wittouck, S, Salvetti, E, Franz, CMAP, Harris, HMB, Mattarelli, P, et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. (2020) 70:2782–858. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.004107
9. Capurso, L. Thirty years of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: A review. J Clin Gastroenterol. (2019) 53:S1–S41. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001170
10. Segers, ME, and Lebeer, S. Towards a better understanding of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG - host interactions. Microb Cell Factories. (2014) 13:S7. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-S1-S7
11. Vélez, MP, Petrova, MI, Lebeer, S, Verhoeven, TL, Claes, I, Lambrichts, I, et al. Characterization of MabA, a modulator of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG adhesion and biofilm formation. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. (2010) 59:386–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2010.00680.x
12. Nataraj, BH, Ramesh, C, and Mallappa, RH. Probiotic and postbiotic interference exhibit anti-adhesion effects against clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and impede MRSA-induced intestinal epithelial hyper-permeability in HT-29 cell line. Microb Pathog. (2025) 199:107215. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.107215
13. Li, J, Li, Q, Wu, Q, Gao, N, Wang, Z, Yang, Y, et al. Exopolysaccharides of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorate Salmonella typhimurium-induced intestinal inflammation via the TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK pathway. J Animal Sci Biotechnol. (2023) 14:23. doi: 10.1186/s40104-023-00830-7
14. Zhang, L, Chichlowski, M, Gross, G, Holle, MJ, Lbarra-Sánchez, LA, Wang, S, et al. Milk fat globule membrane protects Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG from bile stress by regulating exopolysaccharide production and biofilm formation. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:6646–55. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02267
15. Wang, X, Hu, R, Lin, F, Yang, T, Lu, Y, Sun, Z, et al. Lactobacillus reuteri or Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG intervention facilitates gut barrier function, decreases corticosterone and ameliorates social behavior in LPS-exposed offspring. Food Res Int (Ottawa, Ont). (2024) 197:115212. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.115212
16. Wang, Y, Liu, L, Moore, DJ, Shen, X, Peek, RM, Acra, SA, et al. An LGG-derived protein promotes IgA production through upregulation of APRIL expression in intestinal epithelial cells. Mucosal Immunol. (2017) 10:373–84. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.57
17. Yan, F, Liu, L, Cao, H, Moore, DJ, Washington, MK, Wang, B, et al. Neonatal colonization of mice with LGG promotes intestinal development and decreases susceptibility to colitis in adulthood. Mucosal Immunol. (2017) 10:117–27. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.43
18. Fong, FLY, Kirjavainen, PV, and El-Nezami, H. Immunomodulation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG)-derived soluble factors on antigen-presenting cells of healthy blood donors. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:1–8. doi: 10.1038/srep22845
19. Si, W, Zhao, X, Li, R, Li, Y, Ma, C, Zhao, X, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG induces STING-dependent IL-10 in intestinal monocytes and alleviates inflammatory colitis in mice. J Clin Invest. (2025) 135:1–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI174910
20. Guo, M, Liu, H, Yu, Y, Zhu, X, Xie, H, Wei, C, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2190304. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2190304
21. Chen, X, Zhao, X, Hu, Y, Zhang, B, Zhang, Y, and Wang, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG alleviates β-conglycinin-induced allergy by regulating the T cell receptor signaling pathway. Food Funct. (2020) 11:10554–67. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02124E
22. Shi, CW, Cheng, MY, Yang, X, Lu, YY, Yin, HD, Zeng, Y, et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG promotes mouse gut microbiota diversity and T cell differentiation. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:1–16. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.607735
23. Braat, H, van den Brande, J, van Tol, E, Hommes, D, Peppelenbosch, M, and van Deventer, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus induces peripheral hyporesponsiveness in stimulated CD4+ T cells via modulation of dendritic cell function. Am J Clin Nutr. (2004) 80:1618–25. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/80.6.1618
24. Wang, J, Gao, M, Wang, J, Zeng, Y, Wang, C, and Cao, X. LGG promotes activation of intestinal ILC3 through TLR2 receptor and inhibits salmonella typhimurium infection in mice. Virulence. (2024) 15:2384553. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2384553
25. Ge, Y, Sun, H, Xu, L, Zhang, W, Lv, J, and Chen, Y. The amelioration of alcohol-induced liver and intestinal barrier injury by Lactobacillus rhamnosus Gorbach-Goldin (LGG) is dependent on interleukin 22 (IL-22) expression. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:12650–60. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2070998
26. Chen, D, Tang, H, Li, Y, Yang, H, Wang, H, Tan, B, et al. Vitamin D3 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG/p40 synergize to protect mice from colitis by promoting vitamin D receptor expression and epithelial proliferation. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2023) 29:620–32. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izac238
27. Kang, SJ, Kim, MJ, Son, DY, Kang, SS, and Hong, KW. Effects of spore-displayed p75 protein from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG on the transcriptional response of HT-29 cells. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:1–17. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071276
28. Long, H, He, G, He, J, Du, TF, Feng, P, and Zhu, C. The protective effect and immunomodulatory ability of orally administrated Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG against Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in BALB/c mice. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0312318. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312318
29. Mao, J, Qi, S, Cui, Y, Dou, X, Luo, XM, Liu, J, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and barrier dysfunction by regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling and modulating metabolome in the piglet intestine. J Nutr. (2020) 150:1313–23. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxaa009
30. Luoto, R, Ruuskanen, O, Waris, M, Kalliomäki, M, Salminen, S, and Isolauri, E. Prebiotic and probiotic supplementation prevents rhinovirus infections in preterm infants: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2014) 133:405–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.08.020
31. Kumpu, M, Kekkonen, RA, Kautiainen, H, Järvenpää, S, Kristo, A, Huovinen, P, et al. Milk containing probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and respiratory illness in children: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2012) 66:1020–3. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2012.62
32. Hatakka, K, Savilahti, E, Pönkä, A, Meurman, JH, Poussa, T, Näse, L, et al. Effect of long term consumption of probiotic milk on infections in children attending day care centres: double blind, randomised trial. BMJ (Clinical Res). (2001) 322:1327. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7298.1327
33. Hojsak, I, Snovak, N, Abdović, S, Szajewska, H, Misak, Z, and Kolacek, S. Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections in children who attend day care centers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Nutrit (Edinburgh, Scotland). (2010) 29:312–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2009.09.008
34. Hojsak, I, Abdović, S, Szajewska, H, Milosević, M, Krznarić, Z, and Kolacek, S. Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of nosocomial gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections. Pediatrics. (2010) 125:e1171–7. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-2568
35. Laursen, RP, and Hojsak, I. Probiotics for respiratory tract infections in children attending day care centers-a systematic review. Eur J Pediatr. (2018) 177:979–94. doi: 10.1007/s00431-018-3167-1
36. Bruzzese, E, Raia, V, Spagnuolo, MI, Volpicelli, M, De Marco, G, Maiuri, L, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus GG supplementation on pulmonary exacerbations in patients with cystic fibrosis: a pilot study. Clin Nutrit (Edinburgh, Scotland). (2007) 26:322–8. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2007.01.004
37. Bruzzese, E, Callegari, ML, Raia, V, Viscovo, S, Scotto, R, Ferrari, S, et al. Disrupted intestinal microbiota and intestinal inflammation in children with cystic fibrosis and its restoration with Lactobacillus GG: a randomised clinical trial. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e87796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087796
38. Jafari, SA, Mehdizadeh-Hakkak, A, Kianifar, HR, Hebrani, P, Ahanchian, H, and Abbasnejad, E. Effects of probiotics on quality of life in children with cystic fibrosis; a randomized controlled trial. Iran J Pediatr. (2013) 23:669–74.
39. Coffey, MJ, Garg, M, Homaira, N, Jaffe, A, and Ooi, CY. Probiotics for people with cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2020) 1:Cd012949. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012949.pub2
40. Aslam, R, Herrles, L, Aoun, R, Pioskowik, A, and Pietrzyk, A. Link between gut microbiota dysbiosis and childhood asthma: insights from a systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Global. (2024) 3:100289. doi: 10.1016/j.jacig.2024.100289
41. Liu, C, Makrinioti, H, Saglani, S, Bowman, M, Lin, LL, Camargo, CA Jr, et al. Microbial dysbiosis and childhood asthma development: integrated role of the airway and gut microbiome, environmental exposures, and host metabolic and immune response. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1028209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1028209
42. Patrick, DM, Sbihi, H, Dai, DLY, Al Mamun, A, Rasali, D, Rose, C, et al. Decreasing antibiotic use, the gut microbiota, and asthma incidence in children: evidence from population-based and prospective cohort studies. Lancet Respir Med. (2020) 8:1094–105. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30052-7
43. Ciprandi, G, and Tosca, MA. Probiotics in children with asthma. Children (Basel, Switzerland) (2022)9:1–13. doi: 10.3390/children9070978
44. Chen, X, Yong, S-B, Yii, C-Y, Feng, B, Hsieh, K-S, and Li, Q. Intestinal microbiota and probiotic intervention in children with bronchial asthma. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e34916. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34916
45. Drago, L, Cioffi, L, Giuliano, M, Pane, M, Amoruso, A, Schiavetti, I, et al. The probiotics in pediatric asthma management (PROPAM) study in the primary care setting: A randomized, controlled, double-blind trial with Ligilactobacillus salivarius LS01 (DSM 22775) and Bifidobacterium breve B632 (DSM 24706). J Immunol Res. (2022) 2022:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2022/3837418
46. Zuccotti, G, Meneghin, F, Aceti, A, Barone, G, Callegari, ML, di, A, et al. Probiotics for prevention of atopic diseases in infants: systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy. (2015) 70:1356–71. doi: 10.1111/all.12700
47. Kuitunen, M, Kukkonen, K, Juntunen-Backman, K, Korpela, R, Poussa, T, Tuure, T, et al. Probiotics prevent IgE-associated allergy until age 5 years in cesarean-delivered children but not in the total cohort. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2009) 123:335–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.11.019
48. Colquitt, AS, Miles, EA, and Calder, PC. Do probiotics in pregnancy reduce allergies and asthma in infancy and childhood? A systematic review. Nutrients. (2022) 14:1–12. doi: 10.3390/nu14091852
49. Ou, CY, Kuo, HC, Wang, L, Hsu, TY, Chuang, H, Liu, CA, et al. Prenatal and postnatal probiotics reduces maternal but not childhood allergic diseases: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Experimental Allergy: J British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunol. (2012) 42:1386–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2012.04037.x
50. Boyle, RJ, Ismail, IH, Kivivuori, S, Licciardi, PV, Robins-Browne, RM, Mah, LJ, et al. Lactobacillus GG treatment during pregnancy for the prevention of eczema: a randomized controlled trial. Allergy. (2011) 66:509–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02507.x
51. Jerzynska, J, Stelmach, W, Balcerak, J, Woicka-Kolejwa, K, Rychlik, B, Blauz, A, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and vitamin D supplementation on the immunologic effectiveness of grass-specific sublingual immunotherapy in children with allergy. Allergy Asthma Proc. (2016) 37:324–34. doi: 10.2500/aap.2016.37.3958
52. Cabana, MD, McKean, M, Caughey, AB, Fong, L, Lynch, S, Wong, A, et al. Early probiotic supplementation for eczema and asthma prevention: A randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics. (2017) 140:1–9. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-3000
53. Rose, MA, Stieglitz, F, Köksal, A, Schubert, R, Schulze, J, and Zielen, S. Efficacy of probiotic Lactobacillus GG on allergic sensitization and asthma in infants at risk. Clin Experimental Allergy: J British Society for Allergy Clin Immunol. (2010) 40:1398–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03560.x
54. Miraglia Del Giudice, M, Indolfi, C, Capasso, M, Maiello, N, Decimo, F, and Ciprandi, G. Bifidobacterium mixture (B longum BB536, B infantis M-63, B breve M-16V) treatment in children with seasonal allergic rhinitis and intermittent asthma. Ital J Pediatr. (2017) 43:25. doi: 10.1186/s13052-017-0340-5
55. Kristensen, NB, Bryrup, T, Allin, KH, Nielsen, T, Hansen, TH, and Pedersen, O. Alterations in fecal microbiota composition by probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Genome Med. (2016) 8:52. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0300-5
56. Hu, L, Sun, L, Yang, C, Zhang, DW, Wei, YY, Yang, MM, et al. Gut microbiota-derived acetate attenuates lung injury induced by influenza infection via protecting airway tight junctions. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:570. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05376-4
57. Saint-Martin, V, Guillory, V, Chollot, M, Fleurot, I, Kut, E, Roesch, F, et al. The gut microbiota and its metabolite butyrate shape metabolism and antiviral immunity along the gut-lung axis in the chicken. Communications Biol. (2024) 7:1185. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06815-0
58. Richards, LB, Li, M, Folkerts, G, Henricks, PAJ, Garssen, J, and van Esch, B. Butyrate and propionate restore the cytokine and house dust mite compromised barrier function of human bronchial airway epithelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 22:1–16. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010065
59. Liang, M, Dong, Q, Wu, W, and Fan, J. Short-chain fatty acids: promising therapeutic targets for respiratory syncytial virus infection. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2025) 68:8. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-09018-x
60. Li, X, Zheng, P, Cao, W, Cao, Y, She, X, Yang, H, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates noise-induced cognitive deficits and systemic inflammation in rats by modulating the gut-brain axis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1–13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1067367
61. Tran, TT, Phung, TTB, Tran, DM, Bui, HT, Nguyen, PTT, Vu, TT, et al. Efficient symptomatic treatment and viral load reduction for children with influenza virus infection by nasal-spraying Bacillus spore probiotics. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:14789. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41763-5
62. Njoku, EN, Mottawea, W, Hassan, H, Gomaa, A, Bordenave, N, and Hammami, R. Bioengineered wheat Arabinoxylan - fostering next-generation prebiotics targeting health-related gut microbes. Plant foods for human Nutrit (Dordrecht, Netherlands). (2023) 78:698–703. doi: 10.1007/s11130-023-01120-3
Keywords: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG, pediatrics, respiratory diseases, gut-lung axis, probiotics, immunomodulation, microbiota
Citation: Liu Y, Chen Y, Liao H, Sun S, Zhang X, Xie L and Liu H (2025) Research progress on the application of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG in pediatric respiratory diseases. Front. Nutr. 12:1553674. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1553674
Received: 09 January 2025; Accepted: 11 February 2025;
Published: 21 February 2025.
Edited by:
Ke Chen, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, ChinaReviewed by:
Semih Esin, University of Pisa, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Liu, Chen, Liao, Sun, Zhang, Xie and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Liu, bGl1eWFuZ2x5QHNjdS5lZHUuY24= Hanmin Liu, bGl1aG1Ac2N1LmVkdS5jbg==
†ORCID: Yang Liu, orcid.org/0000-0003-4626-3618
Hanmin Liu, orcid.org/0000-0002-4633-911X
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.