
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Nutr., 16 April 2025
Sec. Clinical Nutrition
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2025.1553467
This article is part of the Research TopicThe Relationship between Nutrition and Frailty/Multimorbidity: Prevention and Clinical Nutritional ManagementView all 12 articles
Background: Frailty is a prevalent geriatric syndrome marked by diminished physiological reserves and heightened vulnerability to stressors, leading to adverse health outcomes and imposing significant economic burdens on healthcare systems.
Methods: This study investigates the relationship between the Dietary Index for Gut Microbiota (DI-GM) and the risk of frailty in middle-aged and older adults, using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) collected from 2007 to 2018. Weighted logistic regression, subgroup analysis, and restricted cubic splines (RCS) were performed to evaluate the relationship between DI-GM and frailty risk. Additionally, a mediation analysis was conducted to investigate the influence of relevant inflammatory parameters from complete blood count, including leukocyte count, neutrophil count, the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and the systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI), to elucidate how DI-GM may influence the onset and progression of frailty.
Results: In this cross-sectional analysis of 8,695 participants with a mean age of 65.56 years, 3,173 individuals were classified as frail. After adjusting for all covariates, a significant inverse relationship was observed between DI-GM and the risk of frailty. Quartile analysis revealed that participants in the highest quartile of DI-GM had significantly lower odds of frailty compared to those in the lowest quartile (OR: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.65–0.99, p = 0.04). Trend analyses across all models demonstrated a consistent inverse relationship between higher DI-GM quartiles and frailty odds (p < 0.0001 for the crude model; p = 0.001 for Model 1; p = 0.04 for Model 2). Subgroup analyses confirmed the stability of the impact of DI-GM on frailty risk across various subgroups. RCS showed that the risk of frailty decreased linearly with increasing DI-GM levels. Mediation analysis indicated significant effects for leukocyte count, neutrophil count, NLR, and SIRI, with mediation proportions of 5.7, 7.9, 4.4, and 5.5%, respectively (all p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The levels of DI-GM are inversely associated with the risk of frailty, with part of this association mediated by inflammatory parameters.
Frailty is a multifactorial clinical syndrome predominantly observed in older adults, characterized by a decline in physiological reserves and increased vulnerability to stressors. This syndrome is associated with significant morbidity, diminished quality of life, and elevated mortality rates in the elderly population (1). A growing body of literature emphasizes the importance of identifying modifiable risk factors to prevent the onset and progression of frailty. Current therapeutic modalities, including physical rehabilitation and pharmacological interventions, often exhibit limited efficacy and accessibility (2, 3), highlighting the need for novel strategies in frailty management. In this context, dietary habits emerge as a critical area of investigation, as nutrition plays a fundamental role in maintaining health and resilience in older adults (4). Consequently, there is an urgent demand for research exploring the interplay between dietary habits and frailty risk.
Recent studies have begun to investigate the complex relationship between dietary habits and frailty, particularly focusing on the role of gut microbiota in mediating health outcomes. The gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract, is significantly influenced by dietary patterns (5, 6). Emerging evidence suggests that dietary quality may correlate with the composition and diversity of gut microbiota, which, in turn, may affect various health outcomes, including frailty (7, 8). The dietary index for gut microbiota (DI-GM) has been proposed as a potential tool for assessing dietary quality in relation to gut health (9, 10). Recently, the relationship between dietary quality and human health problems has been studied using DI-GM. For example, studies have shown that DI-GM is significantly associated with biological age, with higher DI-GM scores associated with a lower risk of accelerated aging (11). DI-GM has also been used to study the relationship between diet and health outcomes such as stroke, depression, constipation, and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, further validating its potential to assess the health effects of diet (10, 12–14). While DI-GM has demonstrated significant potential in identifying the relationships between dietary quality and various health outcomes, its specific contributions to frailty remain largely underexplored. Therefore, investigating the relationship between DI-GM and frailty represents an important avenue for future research.
Despite the increasing literature linking nutrition and frailty, significant gaps persist in our understanding of how dietary interventions can effectively reduce the risk of frailty. Previous studies have predominantly focused on specific dietary components or patterns, often neglecting the broader context of gut microbiota interactions (15, 16). Furthermore, potential mediating factors, such as inflammatory responses and metabolic changes associated with dietary intake, have not been adequately addressed. This underscores the necessity for comprehensive research that integrates dietary assessment with a focus on gut microbiome dynamics and inflammatory biomarkers.
To investigate these relationships further, this study employs a cross-sectional analysis utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning from 2007 to 2018. This dataset provides a robust and nationally representative sample, facilitating a nuanced exploration of the associations between DI-GM and frailty risk in middle-aged and older adults. By employing rigorous statistical methods, this research aims to assess the relationship between dietary quality, as indicated by DI-GM, and frailty risk, while also examining potential mediating factors such as relevant inflammatory parameters from complete blood count.
The specific objectives of this research are as follows: first, to evaluate the relationship between DI-GM and frailty risk in middle-aged and older adults, and second, to investigate potential mediating factors, including inflammatory biomarkers, that may elucidate the pathways through which dietary quality impacts frailty. Previous studies have indicated that inflammation plays a critical role in the frailty phenotype, suggesting that a deeper understanding of these inflammatory pathways could enhance targeted interventions aimed at reducing frailty through dietary modifications.
In summary, this study seeks to contribute to the existing literature by elucidating the relationship between DI-GM and frailty risk among middle-aged and older adults. By integrating dietary assessment with health outcomes and inflammatory markers, we aim to provide insights that may inform future interventions and policies aimed at mitigating frailty through enhancements in dietary quality (17). The findings from this research hold the potential to improve individual health outcomes and alleviate the broader societal and economic impacts of frailty in aging populations.
The data for this study were obtained from NHANES conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, aimed at assessing the health and nutritional status of non-institutionalized civilians in the United States (18). NHANES employs a complex, stratified, multi-stage probability sampling design, with data collected through in-home interviews, dietary assessments, medical examinations, and laboratory tests. All protocols were approved by the National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board, and written informed consents were obtained from participants.
This study utilized data from NHANES covering the period from 2007 to 2018 to investigate the relationship between DI-GM and the risk of frailty in middle-aged and older adults. The initial analysis included a total of 59,842 participants. The following participants were excluded: those aged less than 45 years (n = 39,540), those with missing DI-GM component data (n = 4,340), those with less than 80% of frailty index items (n = 5,013), and those with missing covariate data (n = 2,254). The final analysis included 8,695 eligible participants (Figure 1).
This study employed the scoring system developed by Kase et al. to calculate DI-GM, which is based on 14 food items or nutrients (9). Ten beneficial components included avocado, broccoli, chickpeas, coffee, cranberries, fermented dairy, fiber, green tea, soybean, and whole grains, while 4 Unfavorable components comprised red meat, processed meat, refined grains, and a high-fat diet (≥40% of energy from fat). Each component was scored according to gender-specific median intake: for beneficial components, a score of 1 was assigned if consumption met or exceeded the median, otherwise 0; for adverse components, a score of 0 was assigned if consumption met or exceeded the median or the high-fat threshold, otherwise 1. The overall DI-GM score was calculated by summing the scores of all components. In our study, DI-GM was derived by averaging the intakes reported in two 24-h dietary recall interviews. Detailed information on the components and scoring criteria of the DI-GM is provided in Supplementary Table 1.
Frailty was the outcome variable of this study. This study utilized a modified frailty index developed by Hakeem et al., which is based on 49 items (19). These items assessed deficits across multiple aspects, including cognition, dependence, depressive symptoms, comorbidities, healthcare utilization and access to care, physical performance, anthropometry, and laboratory values. The number of deficits identified for each participant was divided by the total number of considered deficits to calculate the frailty index score, which ranges from 0 to 1. In line with previous studies, we set strict inclusion criteria for frailty diagnosis, requiring participants to complete at least 80% of the index items (at least 40 out of 49) to ensure reliability (20–24). In the descriptive analysis, a cut-off point of 0.21 was used to indicate frailty (19, 25, 26). Detailed information on the variables included in the 49-item frailty index and their respective scoring criteria is provided in Supplementary Table 2.
In our study, covariates were meticulously selected based on prior research and clinical relevance. The demographic variables included age, gender, race, educational level, and the family poverty income ratio (PIR). In the logistic regression analysis, age was treated as a continuous variable. However, for the purposes of describing participant characteristics and conducting subgroup analyses, it was categorized into two groups: 45–64 years and ≥ 65 years. Race was classified into the following categories: Mexican American, non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic Asian, and other races. Educational attainment was grouped into three levels: less than high school, high school, and more than high school. The PIR served as an indicator of family income, stratified into three categories: ≤1.3, 1.3–3.5, and >3.5 (22). Lifestyle factors included smoking status, categorized as never, former, and current smokers, and drinking status, classified as never, former, mild, moderate, and heavy drinkers. Recreational activity was assessed and categorized into moderate, vigorous, and other levels of physical activity. Comorbidities were recorded as binary variables (yes/no) for conditions such as cardiovascular disease (CVD), hyperlipidemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Relevant inflammatory parameters from complete blood count included leukocyte count, neutrophil count, monocyte count, lymphocyte count, platelet count, the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte to lymphocyte ratio (MLR), platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR), systemic immune inflammation index (SII), and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI). The formula for calculating SII is platelet count × neutrophil count/lymphocyte count (27). The formula for calculating SIRI is monocyte count × neutrophil count/lymphocyte count (28).
In line with the multistage sampling framework of NHANES, our analysis incorporated sample weights and strata to account for the complexity inherent in the survey design. Continuous variables were presented as weighted means with standard errors (SE), while categorical variables were presented as weighted percentage. Comparative analyses for these variables were performed using t-tests and chi-squared tests, respectively. We used logistic regression analysis to assess the association between DI-GM and risk of frailty in three models: the crude model without adjustment, model 1 adjusted for age, gender, race, educational level and PIR, and model 2 further adjusted for smoking status, drinking status, recreational activity, CVD, hyperlipidemia, COPD and CKD. To elucidate the relationship between DI-GM and frailty, subgroup analyses were performed to stratify by key demographic and lifestyle factors and comorbidities, including age, gender, race, educational level, PIR, smoking status, drinking status, recreational activity, CVD, hyperlipidemia, COPD and CKD. We also used restricted cubic splines (RCS) to assess the potential non-linear relationship between DI-GM and risk of frailty. Mediation analysis was performed to explore the potential mediating role of relevant inflammatory parameters from complete blood count, including leukocyte, neutrophil, NLR and SIRI, in the association between DI-GM and frailty. All statistical analyses were performed in R (version 4.4.2). A 2-tailed p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Table 1 shows the characteristics of a population of 8,695 adults aged 45 years and older in the United States, with a mean age of 65.56 years (SE = 0.18). Of these, 3,173 were classified as frail. Notably, people with frailty were more likely to be older (over 65 years), female, and to have lower levels of education and income. They also had a higher prevalence of comorbid conditions, including CVD, CKD and COPD. Frail people also had elevated inflammatory markers, with significantly higher leukocyte and neutrophil counts, and their GI-DM scores were lower than those of their non-frail counterparts.
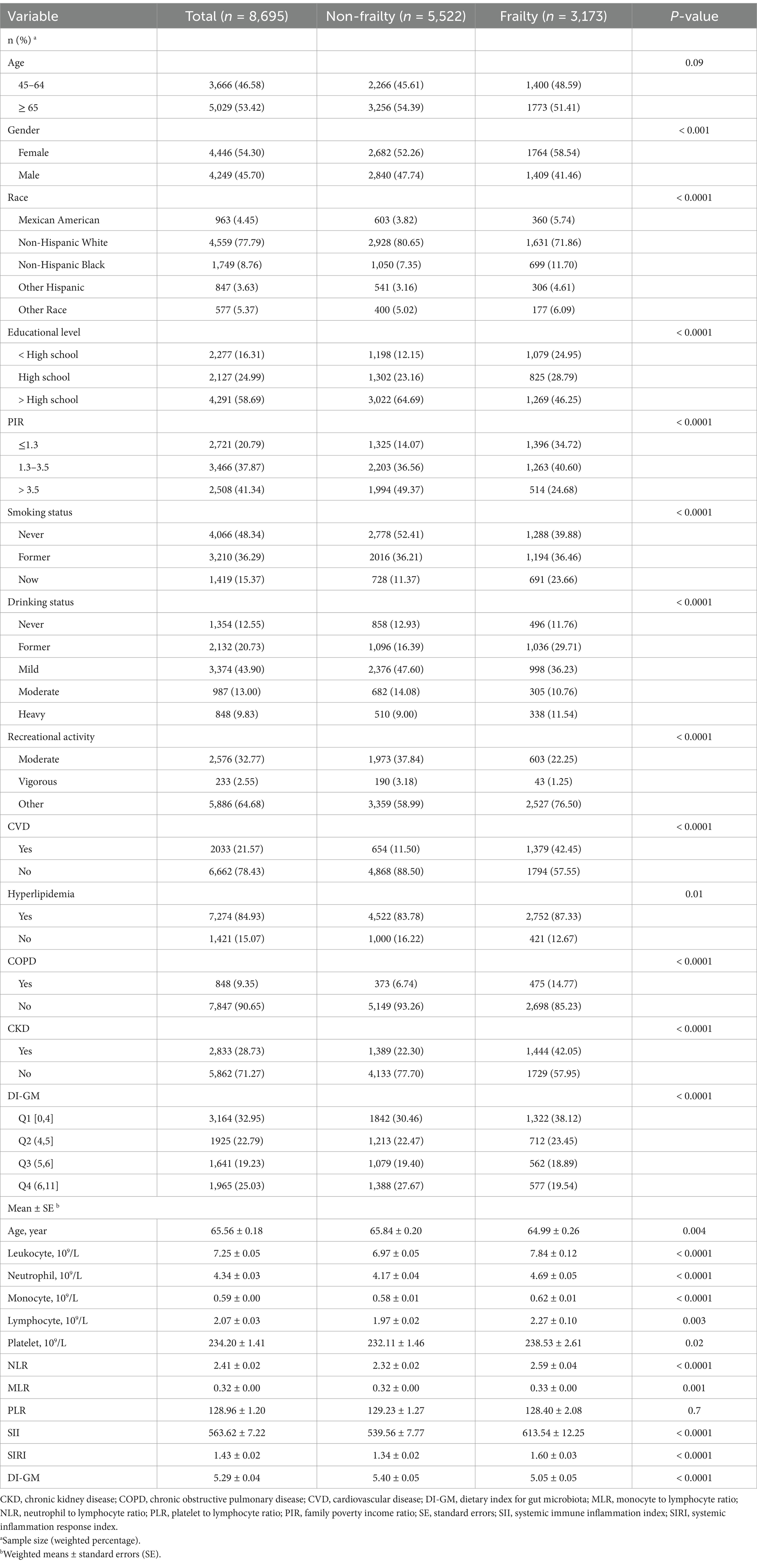
Table 1. Comparison of baseline characteristics between participants with frailty and those without frailty.
Table 2 demonstrates a significant association between DI-GM and the odds of frailty. In the crude model, each unit increase in the DI-GM was associated with a reduction in frailty odds (OR: 0.89, 95% CI: 0.86–0.94, p < 0.0001). Model 1, adjusted for demographic factors, continued to show reduced odds (OR: 0.94, 95% CI: 0.90–0.99, p = 0.01), while model 2, fully adjusted, showed a nonsignificant association (OR: 0.97, 95% CI: 0.93–1.01, p = 0.17). Although the p-value exceeds the conventional threshold of 0.05, the point estimate of 0.97 suggests a slight decrease in odds. Quartile analysis revealed that participants in the highest quartile (Q4) exhibited a significantly lower risk of frailty compared to those in the lowest quartile (Q1), (OR: 0.56, 95% CI: 0.47–0.68, p < 0.0001). Adjustments in model 1 resulted in a slight attenuation of this association for Q4 (OR: 0.72, 95% CI: 0.59–0.88, p = 0.001). Despite this attenuation, model 2 maintained a significant finding for Q4 (OR: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.65–0.99, p = 0.04). Trend analyses across all models revealed a consistent inverse relationship between higher DI-GM quartiles and frailty odds (p < 0.0001 for the crude model; p = 0.001 for model 1; p = 0.04 for model 2), supporting the hypothesis that a higher DI-GM may confer protection against frailty. The restricted cubic spline regression model was used to examine the relationship between DI-GM and frailty, revealing an inverse association: higher DI-GM scores were correlated with lower frailty. Analysis across all models indicated no significant nonlinearity, with p-values for nonlinearity of 0.077 for the Crude model, 0.173 for Model 1, and 0.473 for Model 2 (Figures 2A–C).
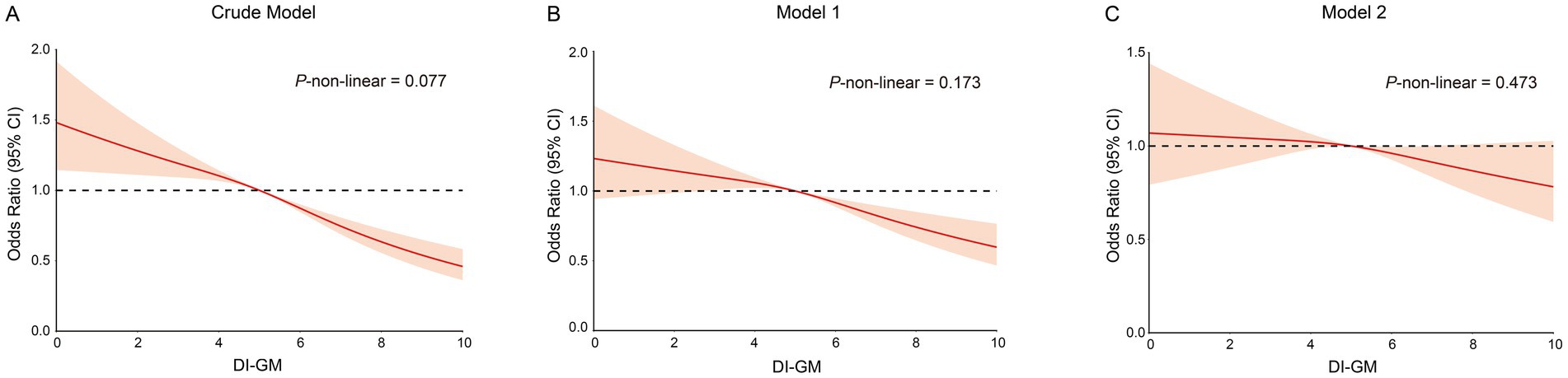
Figure 2. The restricted cubic spline curves for the association between DI-GM and frailty. (A) Restricted cubic spline for crude model. (B) Restricted cubic spline for model 1. (C) Restricted cubic spline for model 2. DI-GM, dietary index for gut microbiota. Crude model adjust for: none; Model 1 adjusted for: age, gender, race, educational level and PIR; Model 2 adjusted for: age, gender, race, educational level, PIR, smoking status, drinking status, recreational activity, CVD, Hyperlipidemia, COPD and CKD. DI-GM, Dietary index for gut microbiota.
Subgroup analyses revealed significant reductions in frailty risk associated with DI-GM across various age groups: individuals aged 45–64 years (OR: 0.879, 95% CI: 0.823–0.939, p < 0.001) and those aged 65 years and older (OR: 0.911, 95% CI: 0.864–0.961, p < 0.001). Furthermore, the results were consistent across gender groups, with females demonstrating an OR of 0.872 (95% CI: 0.821–0.925, p < 0.0001) and males an OR of 0.917 (95% CI: 0.860–0.978, p = 0.009). Consistency in the effect of DI-GM on frailty was also observed across races, PIR, smoking status, drinking status, recreational activity, and comorbidities including CVD, hyperlipidemia, COPD, and CKD (Figure 3).
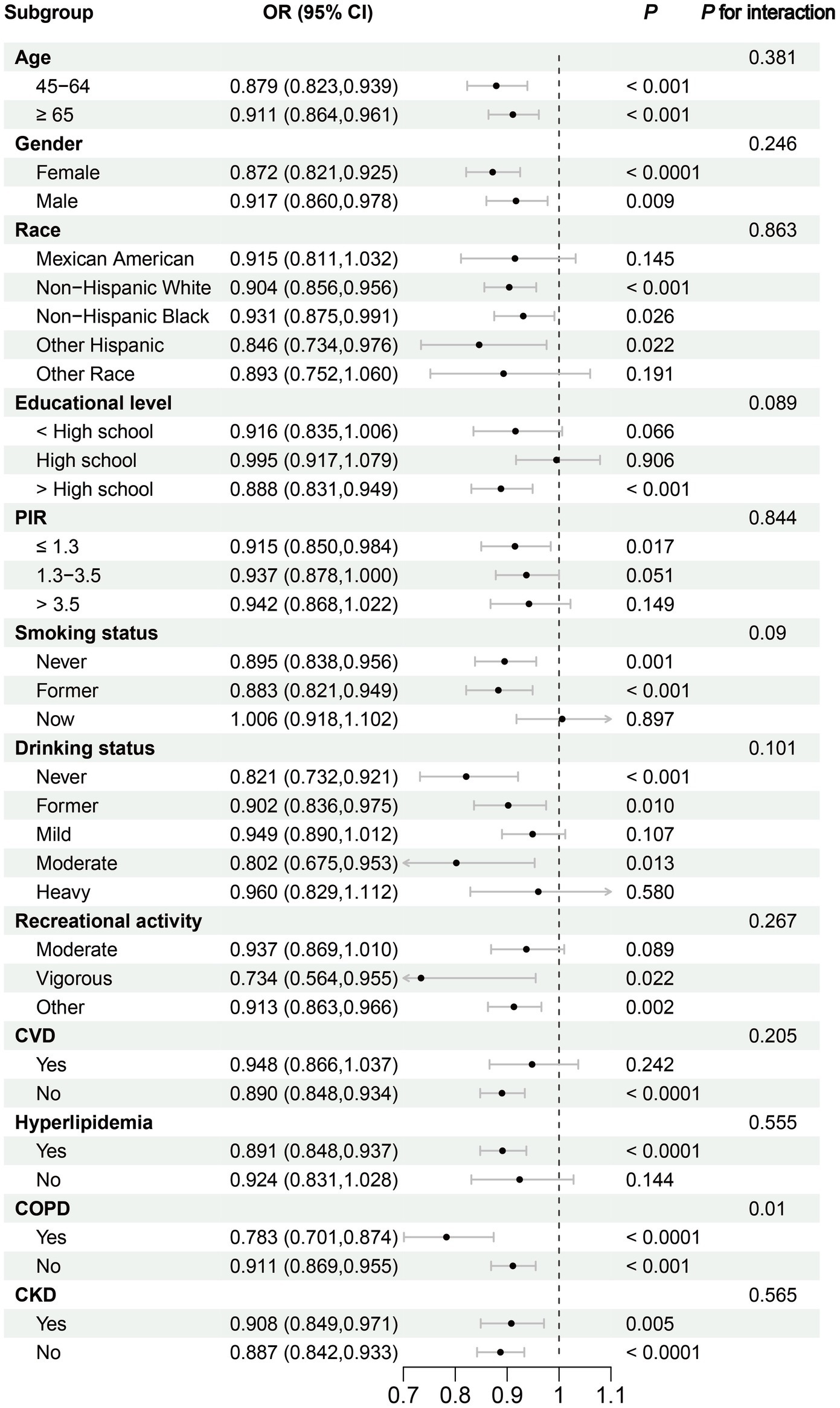
Figure 3. Subgroup analysis of the association between Dietary Index for Gut Microbiota and Frailty. CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; PIR, family poverty income ratio.
The mediation analysis assessed the roles of relevant inflammatory parameters from complete blood count, specifically leukocyte count, neutrophil count, NLR, and SIRI, in the relationship between DI-GM and frailty. The results indicated significant mediation effects for leukocyte count, neutrophil count, NLR and SIRI with mediation proportions of 5.7% (95% CI: 0.019–0.106, p < 0.001),7.9% (95% CI: 0.048–0.117, p < 0.001), 4.4% (95% CI: 0.021–0.068, p < 0.001), 5.5% (95% CI, 0.027–0.088, p < 0.001), respectively (Figure 4). These findings suggest that inflammatory markers play a vital mediating role in the association between DI-GM and frailty, highlighting the potential pathways through which dietary indices may impact frailty. Detailed information on the mediation effect of relevant inflammatory parameters from complete blood count is provided in Supplementary Table 3.
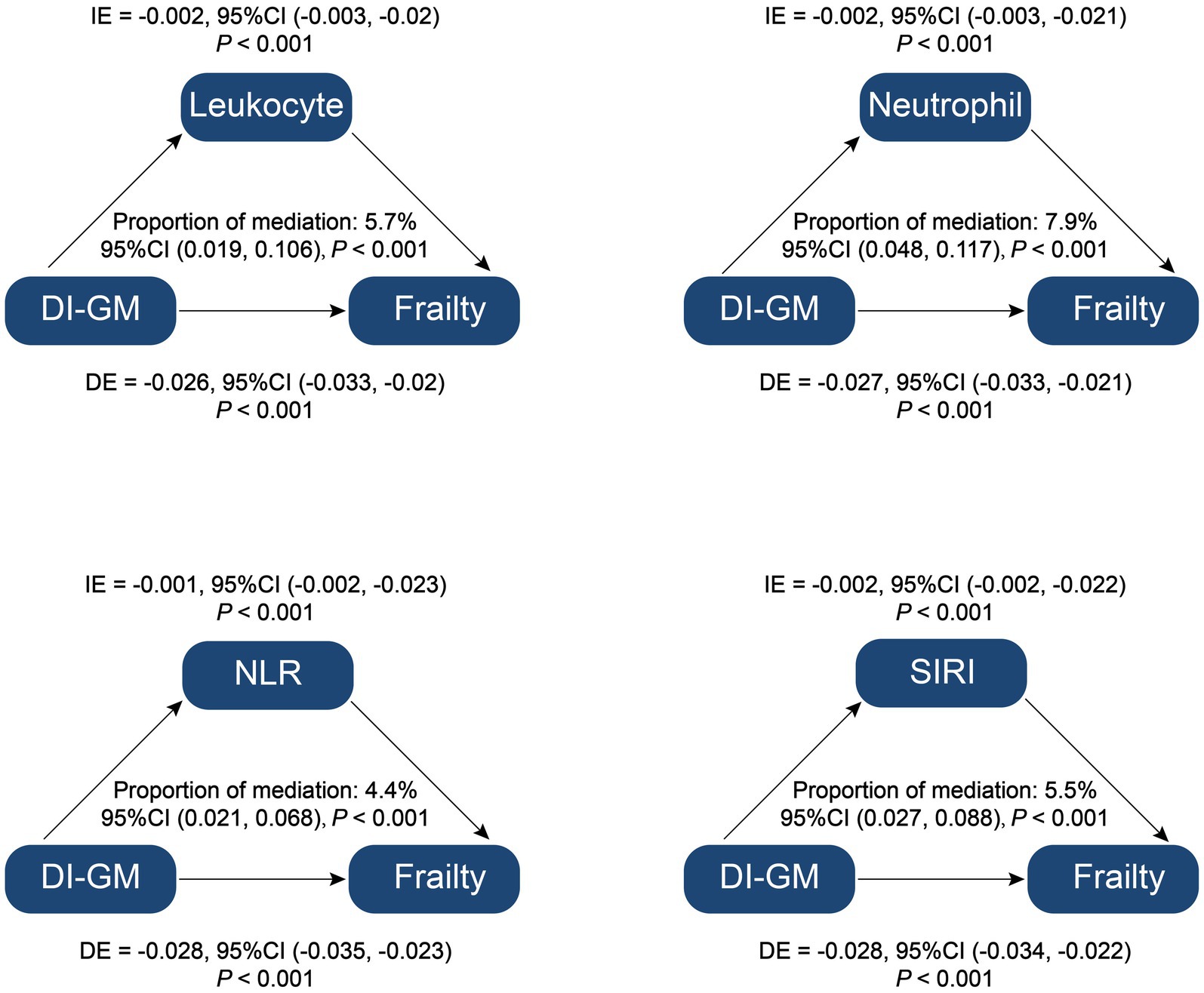
Figure 4. Mediation analysis of inflammation parameters on the association between Dietary Index for Gut Microbiota and Frailty. DI-GM, dietary index for gut microbiota; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; SIRI, systemic inflammation response index; IE, indirect effect; DE, direct effect; Proportion of mediation = IE/(DE + IE).
This study investigates DI-GM as a potential dietary exposure factor linked to frailty. Prior research has established that dietary patterns significantly influence gut microbiota composition, which is associated with various health outcomes, including frailty (8). Utilizing data from NHANES from 2007 to 2018, this cross-sectional analysis aims to elucidate the relationship between DI-GM and frailty risk, while exploring inflammatory markers as potential mediators of this association. A significant inverse relationship between DI-GM and frailty risk was shown, with part of this relationship mediated by inflammatory parameters. These results underscore the importance of dietary interventions as a promising avenue for frailty prevention strategies in this vulnerable population.
This study presents significant innovations in exploring the association between DI-GM and frailty risk among middle-aged and older adults, addressing a critical gap in the existing literature. While prior research has established the correlation between diet and gut microbiota, our robust population-based analysis utilizing NHANES data, spanning over 6 cycles, distinguishes our findings.
For the first time in a diverse human cohort, we demonstrate that higher DI-GM scores are significantly associated with reduced frailty risk, aligning with previous animal studies and human studies that indicated the potential of dietary interventions to modulate gut health and improve frailty outcomes (29, 30). Unlike earlier studies that primarily focused on individual dietary components or rehabilitation approaches, our research underscores the holistic perspective offered by dietary indices like the DI-GM (16, 31, 32). This advancement not only provides evidence of the long-term implications of dietary choices on frailty risk but also highlights the potential for targeted dietary interventions aimed at enhancing gut health as effective strategies for mitigating frailty in vulnerable populations.
In our study, mediation analysis revealed that inflammatory parameters significantly influenced the association between DI-GM and frailty, accounting for 4.4 to 7.9% of the total effect. This finding underscores the role of systemic inflammation as a mediating factor that may explain how DI-GM impacts frailty risk.
The DI-GM is a tool for assessing the impact of diet on gut microbiota, which may reflect the impact of dietary patterns on overall health (14). Studies have shown a strong association between dietary patterns and markers of inflammation. For example, diets with high inflammatory potential (such as high DII score) are often associated with higher white blood cell (WBC) count, neutrophil count and NLR (33). Elevated levels of these inflammatory markers reflect the role of diet in promoting systemic inflammation, which in turn may influence the onset and progression of frailty (34).
Systemic inflammation is an important pathophysiological mechanism of frailty. Studies have shown that inflammatory markers (such as white blood cell count, NLR and SIRI, etc.) are significantly increased in frail patients (20, 35–37). DI-GM regulates inflammation levels by influencing the composition and function of the gut microbiota. For example, a diet rich in fiber and polyphenols (with a high DI-GM score) promotes the proliferation of beneficial bacteria and inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria, thereby reducing the production of inflammatory mediators (14). This anti-inflammatory effect may reduce the risk of frailty by lowering levels of inflammatory markers (24). In addition, dysregulation of the gut microbiota, such as reduced microbiota diversity, is strongly associated with elevated inflammatory markers (35). Dietary patterns with low DI-GM scores, such as diets high in processed foods and red meat, may lead to dysregulation of the gut microbiota, which in turn promotes an inflammatory response (38). This inflammatory response not only affects gut health, but also can affect systemic health through the gut-brain axis and other pathways, accelerating the process of frailty (35).
This study has several limitations that require careful interpretation of the findings. Firstly, the reliance on cross-sectional data from NHANES constrains our ability to draw causal inferences regarding the relationship between DI-GM and frailty risk. This study was an observational design, and although we minimized the effect of confounders through multivariate adjustment and sensitivity analysis, potential reverse causation could not be completely excluded. Additionally, potential biases stemming from self-reported dietary intake may compromise the accuracy of our results, as participants may not accurately recall or report their dietary behaviors. While we attempted to control for various confounding factors, the presence of residual confounding cannot be entirely ruled out, which may influence the observed associations. Moreover, the lack of wet lab experiments limits our insights into the biological mechanisms that could explain the relationship between dietary factors and frailty. Finally, despite the substantial sample size enhancing statistical power, the generalizability of the findings may be restricted by demographic variations, underscoring the need for further validation in more diverse populations. Future research should prioritize longitudinal studies and experimental interventions to confirm these findings and investigate the causal mechanisms linking diet, gut microbiota, and frailty.
This study shows a significant inverse association between DI-GM and frailty risk in middle-aged and older adults, with inflammatory parameters mediating part of this association. Our findings suggest that dietary interventions that increase DI-GM may reduce frailty risk by modulating inflammatory pathways. This suggests that public health strategies should promote high-fiber, fermented foods that support gut health, especially in middle-aged and older adults. In addition, these findings may guide future research on specific dietary patterns and their impact on inflammation to help health professionals develop effective frailty prevention strategies.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available in the NHANES repository, https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm.
The study involving human participants was reviewed and approved by the NCHS Research Ethics Review Board (ERB). The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
QY: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. JD: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. YC: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. TY: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Zhang Cuntai Expert Workstation of Yunnan Province (grant no. 202405AF140057), the Jointed Project of Scientific and Technological Commission of Yunnan Province and Kunming Medical University (grant no. 202201AY070001-260), and the Project of the Clinical Medical Research Center for Geriatric Diseases in Yunnan (grant nos. 2023YJZX-LN05, 2023YJZX-LN24, and 2023YJZX-LN27).
We want to express our gratitude to all of the NHANES participants.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1553467/full#supplementary-material
CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; CI, confidence interval; DE, direct effect; DI-GM, dietary index for gut microbiota; IE, indirect effect; MLR, monocyte to lymphocyte ratio; NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; OR, odds ratio; PIR, family poverty income ratio; PLR, platelet to lymphocyte ratio; RCS, restricted cubic splines; SE, standard errors; SII, systemic immune inflammation index; SIRI, systemic inflammation response index; WBC, white blood cell.
1. Vejux, J, le Bruchec, S, Bernat, V, Beauvais, C, Beauvais, N, and Berrut, G. Fragility and quality of life, the benefits of physical activity for the elderly. Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil. (2021) 19:127–36. doi: 10.1684/pnv.2021.0924
2. Shimizu, A, Maeda, K, Inoue, T, Mori, N, and Momosaki, R. Early physical rehabilitation effectiveness in frail older patients hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia: analysis of a nationwide database in Japan. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2023) 35:341–8. doi: 10.1007/s40520-022-02302-w
3. Espinoza, SE, Jiwani, R, Wang, J, and Wang, CP. Review of interventions for the frailty syndrome and the role of metformin as a potential pharmacologic agent for frailty prevention. Clin Ther. (2019) 41:376–86. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.01.006
4. Sotos-Prieto, M, Ortolá, R, López-García, E, Rodríguez-Artalejo, F, and García-Esquinas, E. Adherence to the mediterranean diet and physical resilience in older adults: the seniors-enrica cohort. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2021) 76:505–12. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glaa277
5. Videhult, FK, and West, CE. Nutrition, gut microbiota and child health outcomes. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2016) 19:1–13. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000266
6. Voreades, N, Kozil, A, and Weir, TL. Diet and the development of the human intestinal microbiome. Front Microbiol. (2014) 5:494. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00494
7. De Haas, S, De Jonge, E, Voortman, T, Graaff, JS, Franco, OH, Ikram, MA, et al. Dietary patterns and changes in frailty status: the Rotterdam study. Eur J Nutr. (2018) 57:2365–75. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1509-9
8. Tamayo, M, Olivares, M, Ruas-Madiedo, P, Margolles, A, Espín, JC, Medina, I, et al. How diet and lifestyle can fine-tune gut microbiomes for healthy aging. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. (2024) 15:283–305. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-072023-034458
9. Kase, BE, Liese, AD, Zhang, J, Murphy, EA, Zhao, L, and Steck, SE. The development and evaluation of a literature-based dietary index for gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1045. doi: 10.3390/nu16071045
10. Zhang, X, Yang, Q, Huang, J, Lin, H, Luo, N, and Tang, H. Association of the newly proposed dietary index for gut microbiota and depression: the mediation effect of phenotypic age and body mass index. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2024). doi: 10.1007/s00406-024-01912-x
11. An, S, Qin, J, Gong, X, Li, S, Ding, H, Zhao, X, et al. The mediating role of body mass index in the association between dietary index for gut microbiota and biological age: a study based on nhanes 2007-2018. Nutrients. (2024) 16:16. doi: 10.3390/nu16234164
12. Liu, J, and Huang, S. Dietary index for gut microbiota is associated with stroke among us adults. Food Funct. (2025) 16:1458–68. doi: 10.1039/d4fo04649h
13. Zhang, Z, Bi, C, Wu, R, and Qu, M. Association of the newly proposed dietary index for gut microbiota and constipation: a cross-sectional study from nhanes. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1529373. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1529373
14. Zheng, Y, Hou, J, Guo, S, and Song, J. The association between the dietary index for gut microbiota and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2025) 17:17. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01589-9
15. Wang, Y, Hao, Q, Su, L, Liu, Y, Liu, S, and Dong, B. Adherence to the mediterranean diet and the risk of frailty in old people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr Health Aging. (2018) 22:613–8. doi: 10.1007/s12603-018-1020-x
16. Cheng, X, Hu, Y, Ruan, Z, Zang, G, Chen, X, and Qiu, Z. Association between b-vitamins intake and frailty among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2023) 35:793–801. doi: 10.1007/s40520-023-02353-7
17. Hubbard, RE, O'Mahony, MS, Savva, GM, Calver, BL, and Woodhouse, KW. Inflammation and frailty measures in older people. J Cell Mol Med. (2009) 13:3103–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00733.x
18. Ahluwalia, N, Dwyer, J, Terry, A, Moshfegh, A, and Johnson, C. Update on nhanes dietary data: focus on collection, release, analytical considerations, and uses to inform public policy. Adv Nutr. (2016) 7:121–34. doi: 10.3945/an.115.009258
19. Hakeem, FF, Bernabé, E, and Sabbah, W. Association between oral health and frailty among american older adults. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2021) 22:559–563.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2020.07.023
20. Zhang, H, Liu, X, Wang, X, and Jiang, Y. Association of two novel systemic inflammatory biomarkers and frailty based on NHANES 2007-2018. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1377408. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1377408
21. Liu, X, Wang, Y, Shen, L, Sun, Y, Zeng, B, Zhu, B, et al. Association between frailty and chronic constipation and chronic diarrhea among american older adults: national health and nutrition examination survey. BMC Geriatr. (2023) 23:745. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04438-4
22. Jia, S, Huo, X, Sun, L, Yao, Y, and Chen, X. The association between the weight-adjusted-waist index and frailty in us older adults: a cross-sectional study of nhanes 2007-2018. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1362194. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1362194
23. Sun, L, Huo, X, Jia, S, and Chen, X. The association between circadian syndrome and frailty in us adults: a cross-sectional study of nhanes data from 2007 to 2018. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2024) 36:105. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02745-3
24. Huo, X, Jia, S, Sun, L, Yao, Y, Liao, H, and Chen, X. Association of dietary live microbe intake with frailty in us adults: evidence from nhanes. J Nutr Health Aging. (2024) 28:100171. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2024.100171
25. Hakeem, FF, Bernabé, E, and Sabbah, W. Self-rated oral health and frailty index among older Americans. Gerodontology. (2021) 38:185–90. doi: 10.1111/ger.12513
26. Chen, C, Winterstein, AG, Fillingim, RB, and Wei, YJ. Body weight, frailty, and chronic pain in older adults: a cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. (2019) 19:143. doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1149-4
27. Ma, R, Cui, L, Cai, J, Yang, N, Wang, Y, Chen, Q, et al. Association between systemic immune inflammation index, systemic inflammation response index and adult psoriasis: evidence from NHANES. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1323174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1323174
28. Gu, L, Xia, Z, Qing, B, Wang, W, Chen, H, Wang, J, et al. Systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI) is associated with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in population with chronic kidney disease: evidence from NHANES (2001-2018). Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1338025. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1338025
29. Guan, L, Eisenmenger, A, Crasta, KC, Sandalova, E, and Maier, AB. Therapeutic effect of dietary ingredients on cellular senescence in animals and humans: a systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. (2024) 95:102238. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102238
30. Magzal, F, Turroni, S, Fabbrini, M, Barone, M, Vitman, SA, Ofran, A, et al. A personalized diet intervention improves depression symptoms and changes microbiota and metabolite profiles among community-dwelling older adults. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1234549. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1234549
31. Pan, Y, Tang, XY, Yang, J, Feng, ZQ, Yuan, Y, Jiang, Y, et al. Cognitive frailty in relation to vitamin b12 and 25-hydroxyvitamin d in an elderly population: a cross-sectional study from nhanes. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1430722. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1430722
32. Sheshadri, A, and Johansen, KL. Prehabilitation for the frail patient approaching ESRD. Semin Nephrol. (2017) 37:159–72. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2016.12.006
33. Xu, J, Xie, L, Fan, R, Shi, X, Xu, W, Dong, K, et al. The role of dietary inflammatory index in metabolic diseases: the associations, mechanisms, and treatments. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41430-024-01525-6
34. Li, W, Sheng, RW, Cao, MM, and Rui, YF. Exploring the relationship between gut microbiota and sarcopenia based on gut-muscle axis. Food Sci Nutr. (2024) 12:8779–92. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4550
35. Pu, Y, Sun, Z, Zhang, H, Huang, Q, Wang, Z, Mei, Z, et al. Gut microbial features and circulating metabolomic signatures of frailty in older adults. Nat Aging. (2024) 4:1249–62. doi: 10.1038/s43587-024-00678-0
36. Guan, L, Liu, Q, Yao, Y, Wang, L, Peng, Y, Chen, S, et al. Do neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio associate with frailty in elderly inpatient with comorbidity? Exp Gerontol. (2022) 169:111955. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2022.111955
37. Asik, Z, and Özen, M. Evaluation of frailty and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios relationship in elderly people. Nagoya J Med Sci. (2022) 84:101–10. doi: 10.18999/nagjms.84.1.101
Keywords: dietary index for gut microbiota, DI-GM, frailty, inflammation, NHANES
Citation: Yang Q, Wu X, Duan J, Chen Y and Yang T (2025) Inflammatory parameters mediates the relationship between dietary index for gut microbiota and frailty in middle-aged and older adults in the United States: findings from a large-scale population-based study. Front. Nutr. 12:1553467. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1553467
Received: 30 December 2024; Accepted: 31 March 2025;
Published: 16 April 2025.
Edited by:
Akio Shimizu, Mie University, JapanReviewed by:
Lixing Zhou, Sichuan University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Yang, Wu, Duan, Chen and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tianrui Yang, eXRyNDI0QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.