- 1Department of General Medicine, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
- 2Shenzhen University Health Science Center, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
- 3Department of Orthopedics, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
- 4Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, Guangdong, China
Background: The relationship between the Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR), a novel index integrating multiple metabolic parameters, and the risk of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) remains under explored.
Methods: Analyses were conducted on data from 2,348 participants included in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data from 2015 to 2018. Logistic regression, stratified analyses, curve-fitting analyses, and threshold effects analyses were employed to evaluate the association between METS-IR and the risk of OSA.
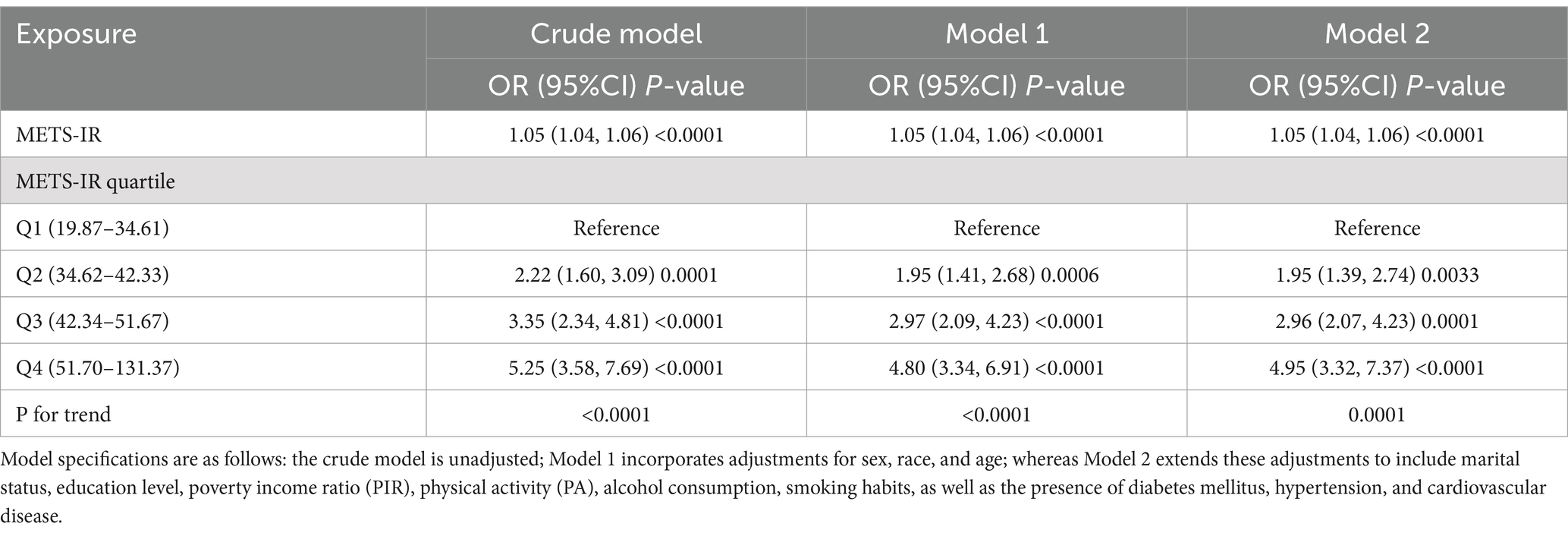
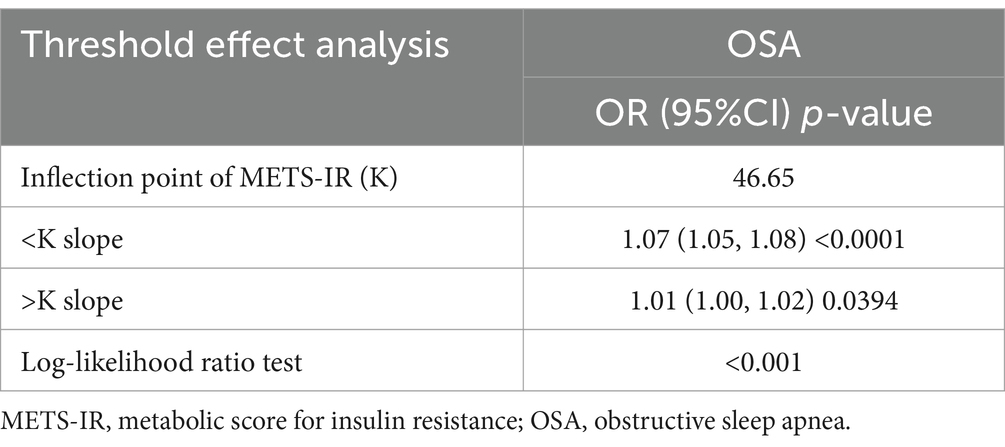
Results: Multifactorial logistic regression analyses revealed a significant positive correlation between METS-IR and the risk of OSA [OR: 1.05 (95% CI: 1.04–1.06)]. Stratified analyses showed consistent associations across various subgroups, including sex, race, age, marital status, education level, poverty income ratio, physical activity, alcohol use, smoking status, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Nonlinear analysis identified an inflection point at METS-IR 46.65. On the left of the inflection point, the risk of OSA increased significantly, with each unit increase in METS-IR associated with a 7% increase in risk [OR: 1.07 (95% CI: 1.05–1.08)]. On the right side of the inflection point, however, the rate of risk increase slowed to 1% [OR: 1.01 (95% CI: 1.00–1.02)].
Conclusion: This investigation reveals a significant and nonlinear relationship between METS-IR and OSA. Further investigation is needed to explore their association more comprehensively and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Introduction
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a frequently encountered sleep disorder characterized by intermittent upper airway obstruction during sleep, which results in hypoxia and sleep disturbances (1). Extensive studies have confirmed a strong link between OSA and multiple chronic conditions, particularly cardiovascular, metabolic, and cerebrovascular diseases (2, 3). Evidence shows that metabolic syndrome (4), which includes obesity (5), hypertension (6), diabetes mellitus (7), and hyperlipidemia (8), markedly elevates the likelihood of developing OSA. Among these, obesity is particularly influential, as the accumulation of adipose tissue within the upper airway can precipitate airway obstruction; additionally, OSA has the potential to aggravate metabolic disorders, engendering a harmful cycle (9, 10).
Furthermore, there exists a strong association between OSA and insulin resistance (11), a critical pathological element in metabolic conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (12). Insulin resistance promotes a reciprocal interaction between OSA and metabolic disorders through mechanisms such as sympathetic nervous system activation, oxidative stress, and systemic inflammation (13, 14). Given the complex interrelations between OSA and metabolic dysfunction, it is imperative to detect and intervene in OSA risk factors early to prevent further disease progression.
The Metabolic Insulin Resistance Score (METS-IR) is a newly formulated, non-invasive index that provides a reliable estimate of insulin resistance by incorporating fasting glucose levels, triglyceride concentrations, and body mass index (BMI) (15). METS-IR has demonstrated efficacy in predicting various metabolic diseases, including hypertension, NAFLD, and cardiovascular conditions (16, 17). However, there is a scarcity of comprehensive studies exploring the link between METS-IR and OSA. Considering the shared pathophysiological mechanisms linking insulin resistance and OSA, examining the connection between METS-IR and OSA could provide critical insights for both diagnosis and therapeutic approaches.
The objective of this research was to analyze the link between METS-IR and OSA. This study sought to clarify the potential role of METS-IR as a predictive marker for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) by analyzing a nationally representative dataset, thereby providing a scientific foundation for developing targeted intervention strategies for at-risk populations.
Methods
Study design and population
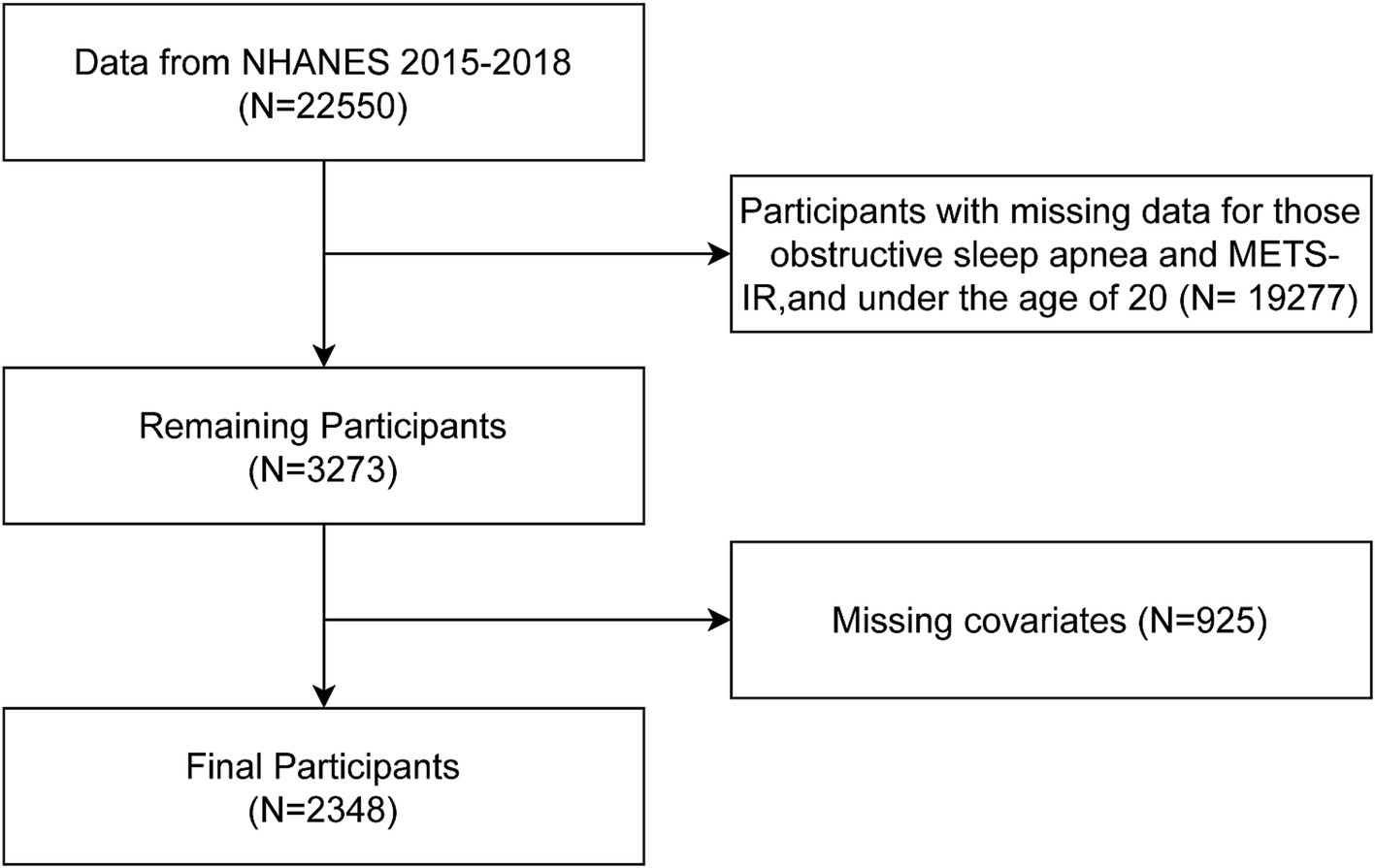
This study’s dataset was derived from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), encompassing data collected between 2015 and 2018.Established by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), which operates under the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the NHANES program is designed to assess the health and nutritional conditions of the general U.S. civilian population. Detailed information about the program, including data collection methods and available data files, can be found at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.html. This study was conducted in compliance with the ethical standards set by the NCHS Ethics Review Board, with each NHANES survey cycle obtaining the necessary clearance. Participant consent was secured at the recruitment stage, ensuring the ethical integrity of the research. In this research, we strictly followed the guidelines of the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) for the reporting of cross-sectional observational studies. The research leveraged data from NHANES 2015–2018, comprising a participant pool of 22,550 individuals. Exclusion criteria included: individuals with incomplete records regarding OSA and METS-IR, those below the age threshold of 20 years, and subjects with incomplete covariate data. After exclusions, the study encompassed a refined group of 2,348 participants for analysis, as delineated in Figure 1.
Assessment of the OSA
Diagnoses of OSA were based on participants’ responses to a questionnaire specifically designed to evaluate sleep habits and disorders (18). Participants were classified as having OSA if they indicated “yes” to any of the following criteria: (1) experiencing snoring three or more times per week; (2) having wheezing, snoring, or episodes of breathing cessation on at least three nights per week; (3) feeling excessively sleepy during the day 16–30 times a month, even after sleeping seven or more hours each night.
Measurement of METS-IR
The METS-IR was identified as a principal variable within the context of this study. The formula employed for calculating METS-IR is defined as follows (19):
Fasting glucose and triglyceride levels were measured enzymatically using automated biochemical analyzers, namely the Roche Cobas 6000 and Roche Modular P systems. These tools guarantee accurate quantification of serum triglyceride levels. Deriving the body mass index (BMI) entails the division of an individual’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. Participant data regarding weight and height were sourced from the Examination Data within the “Body Measure” section.
Study covariates
The identification of covariates was informed by a synthesis of prior research and theoretical models. This study pinpointed various demographic and health-related elements as potential covariates. Physical activity (PA) was evaluated based on whether participants engaged in walking or cycling. Smoking status was classified according to total lifetime cigarette consumption, with individuals having smoked 100 or more cigarettes categorized as smokers. The term “alcohol consumption” was defined as the consumption of 4/5 or more drinks per day. Hypertension was recognized as a diagnosis provided by a licensed healthcare professional. The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus was based on clinical identification by a qualified healthcare provider. Cardiovascular disease was identified through diagnoses of coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, angina, or stroke, all confirmed by a qualified medical professional. Participants affirmatively reporting these health conditions were classified as having hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or cardiovascular disease. Evaluations of health status were derived from both self-reported data and assessments conducted by healthcare professionals regarding hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using EmpowerStats (version 4.2)1 and R software (version 4.3.2).2 Continuous variables were expressed as means with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) or medians with interquartile ranges, while categorical variables were represented as counts and proportions. Further evaluations utilized multivariable logistic regression and linear models to assess the influence of METS-IR on obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The analysis without adjustments was termed the “crude model,” while Model 1 incorporated adjustments for gender, race, and age. Model 2 included additional controls for factors such as marital status, education level, poverty income ratio (PIR), physical activity (PA), alcohol intake, diabetes mellitus, smoking status, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Subgroup analyses and interaction tests were also conducted to explore potential variations across different populations. Non-linear associations between OSA and METS-IR were examined using smoothing spline fitting techniques. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all outcomes assessed.
Results
Baseline characteristics
In terms of baseline characteristics, the final sample for this study comprised 2,348 participants, with 50.11% identifying as male and 49.89% as female. The analysis indicated that the METS-IR was significantly elevated in the fourth quartile (Q4), suggesting a considerable prevalence of insulin resistance in this subset. A significant portion of the participants identified as Non-Hispanic White; nevertheless, notable racial disparities were observed across the quartiles (p = 0.0146). Individuals in the top quartile of METS-IR showed a higher prevalence of conditions associated with insulin resistance. Key factors contributing to this trend included older age (≥51.70 years), decreased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels, elevated triglycerides (TG), and increased fasting blood glucose (FBG) concentrations. In contrast, participants with lower METS-IR scores were generally younger, displaying higher HDL levels alongside reduced triglyceride and fasting blood glucose concentrations. The distribution of body mass index (BMI) across the quartiles exhibited significant variation (p < 0.0001), with a greater prevalence of individuals with a BMI of 30 or higher in the upper quartile. When comparing the highest quartile to the lowest, there was a markedly higher incidence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease (CVD) (p < 0.0001 for all), emphasizing a significant link between insulin resistance and these comorbidities (Table 1).
Association between METS-IR and risk for OSA
The multivariable logistic regression analysis indicated a statistically significant positive link between METS-IR and the risk of OSA, which was consistent across all analytical models (p < 0.05). Following adjustments for all covariates, each additional unit of METS-IR was linked to a 5% increase in the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) among the participants (OR = 1.05, 95% CI 1.04–1.06). This trend remained stable across the three models evaluated. Participants within the top quartile of METS-IR experienced nearly a fivefold increase in OSA prevalence relative to those in the lowest quartile (OR = 4.95, 95% CI 3.32–7.37) (Table 2).
Analysis of curve fitting and threshold effects
The analysis of threshold effects revealed a non-linear association between METS-IR and OSA risk (Figure 2). A significant increase in OSA risk was observed with METS-IR values under 46.65, with each unit increase correlating to a 7% rise in risk (OR = 1.07; 95% CI 1.05–1.08; p < 0.0001). Beyond this threshold, the rate of risk increase slowed to 1% (OR = 1.01; 95% CI 1.00–1.02; p = 0.0394). This finding was further corroborated by the likelihood ratio test (p < 0.001), suggesting a meaningful improvement in model fit (Table 3).
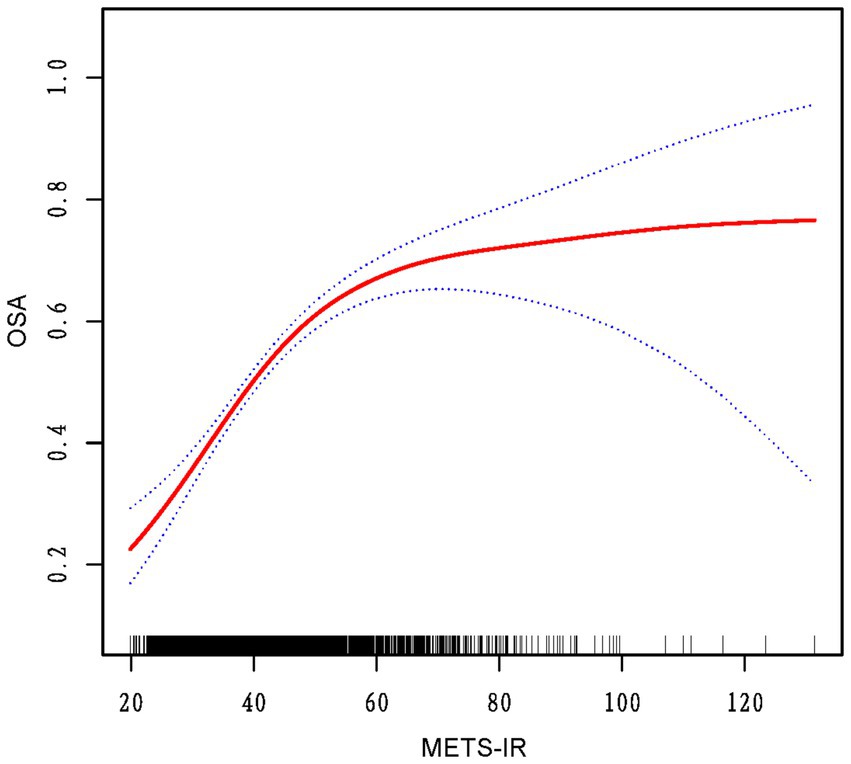
Figure 2. The red curve on the graph denotes the smoothed fit between the variables, with the blue lines outlining the 95% confidence intervals around the fit.
Subgroup analyses
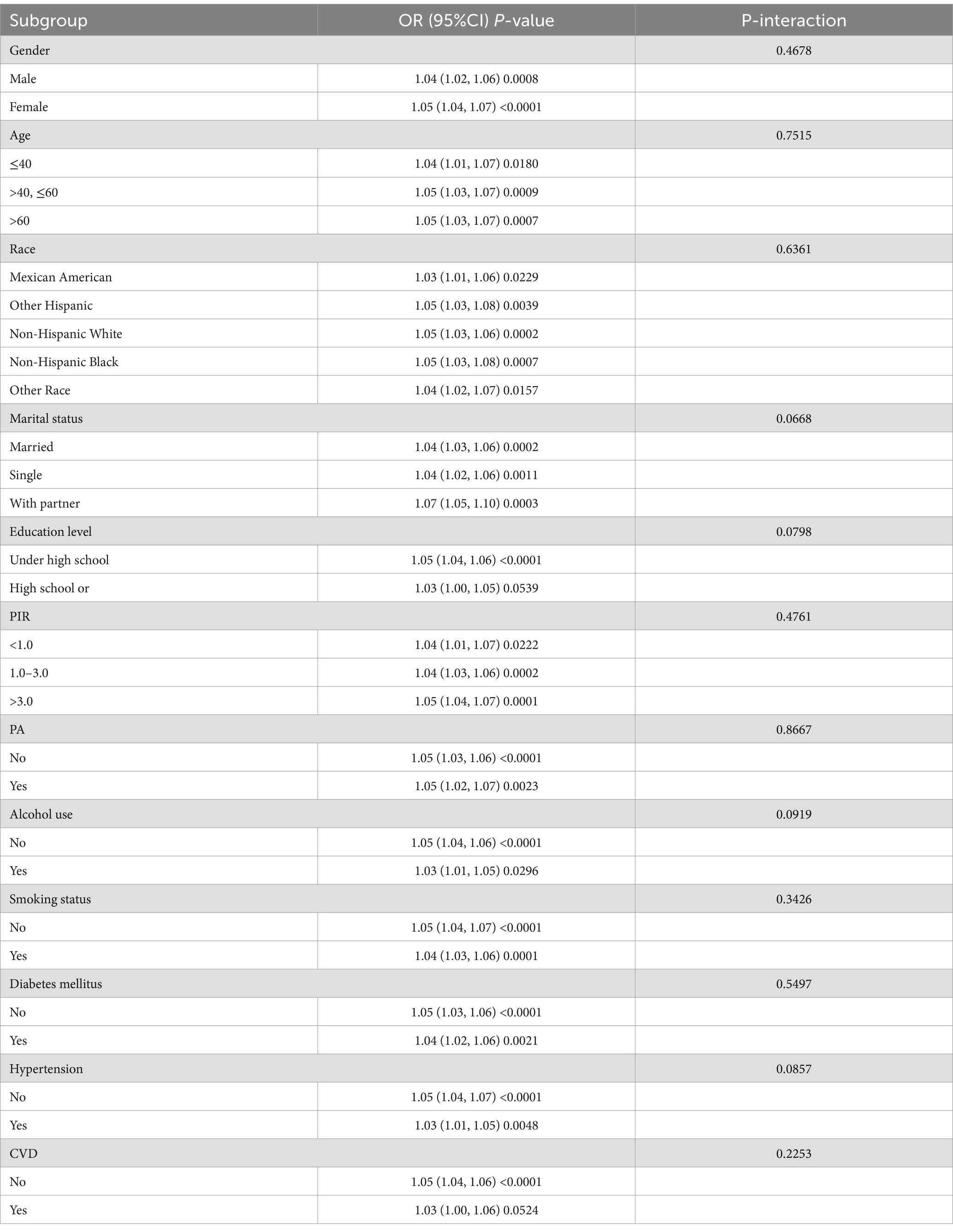
Subgroup analyses were undertaken to investigate the stability of the link between METS-IR and the risk of OSA, incorporating tests for interaction effects. In model 3, all potential confounders were included in the analysis alongside variables that defined the study subgroups. The results consistently indicated a stable relationship between METS-IR and various demographic factors, such as race, gender, age, education level, marital status, and socioeconomic status, along with physical activity, alcohol consumption, smoking habits, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions across all groups. No significant interaction effects were found since all interaction p-values exceeded 0.05 (Table 4).
Discussion
This study, leveraging data from the NHANES conducted between 2015 and 2018, seeks to elucidate the link between METS-IR and OSA. The results indicate a statistically significant positive link between METS-IR and the prevalence of OSA. Specifically, an increment of one unit in METS-IR is associated with a 5% increase in the probability of OSA (odds ratio [OR] 1.05, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.04–1.06). This association remains significant even after accounting for various confounding factors. Potential confounding variables such as ethnicity, sex, age, and health-related aspects have been evaluated in our study. Significantly, participants categorized in the uppermost quartile of METS-IR demonstrate a risk of OSA that is approximately five times greater than that observed in those within the lowest quartile (OR: 4.95, 95% CI: 3.32–7.37). Furthermore, our investigation reveals a non-linear correlation between METS-IR and the risk of OSA, identifying a pivotal threshold at a METS-IR value of 46.65.
The intricate relationship between insulin resistance and OSA has attracted considerable attention in the fields of sleep medicine and metabolic research. This study contributes to an extensive body of literature that has largely focused on individual metabolic parameters, often overlooking the complex interactions between these two conditions. For example, Soo-Young Yoon has found a correlation between fasting blood glucose levels and an elevated risk of cardiovascular events (20). Moreover, insulin sensitivity has been linked with cardiovascular risk factors treated as continuous variables, as shown in the research by Laakso (21). The relationship between triglycerides, a marker for dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance has been systematically reviewed by Bjornstad and Eckel (22). Additionally, Schmiegelow et al. provided a comprehensive review of the association involving high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, recognized for its protective role against cardiovascular diseases, and insulin resistance (23). The association between body mass index, a widely recognized obesity indicator, and insulin resistance has been thoroughly explored in a study conducted by Abdelhamed et al. (24). In contrast to these studies that concentrate on isolated metrics, our research employs METS-IR, a composite index that integrates fasting blood glucose, triglycerides, BMI, and HDL-C, thereby effectively representing the overall metabolic profile linked to insulin resistance and OSA (15). Furthermore, Januzzi has emphasized the significance of multiple biomarkers in predicting cardiovascular events (25), which aligns with our approach of utilizing the METS-IR to assess the correlation between insulin resistance and OSA.
It is important to note that, as far as we are aware, this study is one of the first to explore the nonlinear link between METS-IR and OSA. It reveals a potential threshold effect, which offers new insights that could enhance clinical decision-making and risk assessment for OSA. The identified inflection point of METS-IR at 46.65 corresponds to approximately 60% of the total OSA risk, with the rate of risk increase slowing after this threshold, reaching an estimated 75% of OSA risk. This highlights the significant role of metabolic fitness in OSA risk, while also emphasizing the importance of other factors, such as obesity, age, and comorbidities like hypertension, which become more influential at higher risk levels (26–28).While METS-IR is an important factor, these findings suggest that OSA risk is shaped by a complex interplay of metabolic, lifestyle, and traditional risk factors. Future research should explore how these factors interact to refine our understanding of OSA risk. Besides, above the inflection point, adaptability mechanisms, such as increased physical activity, play a role in reducing OSA risk (29). Physical activity improves metabolic syndrome and reduces OSA risk, while low vitamin D levels (30), linked to both OSA and metabolic dysfunction, may further influence risk. Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels could mitigate OSA risk, especially in individuals with high METS-IR scores. However, further research is required to elucidate the precise role of these adaptations in modulating OSA risk at elevated METS-IR levels.
Regarding the mechanisms that may elucidate the link between METS-IR and OSA, it is feasible that various physiological and metabolic pathways are implicated. As a comprehensive measure of insulin resistance, METS-IR effectively reflects an individual’s metabolic health status. Specifically, insulin resistance is commonly associated with an abnormal accumulation of adipose tissue, particularly in the cervical and abdominal areas, which heightens the risk of OSA. The anatomical resistance of the airway is a significant factor contributing to the worsening of OSA (31, 32). Evidence indicates that an elevated METS-IR is closely associated with alterations in body fat distribution, potentially leading to mechanical obstruction in the airway (15, 33). Additionally, elevated METS-IR is often associated with the onset of chronic low-grade inflammation. Insulin resistance may trigger the release of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6, potentially compromising airway structural integrity and disrupting central nervous system functions. The association of respiration with OSA exacerbates the severity of the condition (34–36). Additionally, persistent inflammation can elevate oxidative stress levels, a factor that has been widely studied in relation to OSA, underscoring its critical importance in the pathophysiology of the disorder (37). The influence of OSA on sleep quality may perpetuate a negative cycle, as insufficient sleep and diminished sleep quality can lead to decreased insulin sensitivity, further intensifying metabolic dysregulation (38, 39). The rise in METS-IR not only signifies an increased level of insulin resistance but may also engage in a synergistic relationship with the worsening of sleep disturbances, resulting in a complex pathological mechanism. Furthermore, both genetic susceptibility and environmental factors, such as lifestyle habits and dietary choices, could significantly impact the relationship between METS-IR and OSA (39, 40). This finding underscores the necessity for subsequent research to explore the complex interactions between these elements. Ultimately, our study underscores the pivotal role of METS-IR as an indicator of insulin resistance in the development of OSA, stressing the imperative to improve metabolic health in the context of OSA management. The findings facilitate the development of early detection and intervention strategies for OSA. This study enhances our comprehension of the pathophysiological mechanisms associated with OSA and proposes potential intervention strategies for future clinical practice.
This research represents a significant advancement in the field by performing a systematic examination of the relationship between METS-IR—a composite measure encompassing various metabolic indicators—and OSA. It offers a fresh perspective on how metabolic health correlates with the risk of developing OSA. The nonlinear analysis identified a noteworthy nonlinear link between METS-IR and the risk of OSA, pinpointing a critical threshold at 46.65. This discovery lays a scientific groundwork for early detection and targeted interventions for OSA. Furthermore, the use of the NHANES database ensures a diverse and representative sample while complying with the established guidelines of the database.
However, this research has inherent limitations. Firstly, the cross-sectional design of this investigation could restrict the robustness of conclusions drawn about causality between exposure and outcome, highlighting the necessity for future longitudinal research to validate our findings Secondly, the diagnosis of OSA relies on self-reporting rather than objective methods like polysomnography, which may introduce biases, affecting the accuracy of results. Additionally, although we controlled for various covariates, the exclusion criteria did not encompass all potential sleep disorders that could cause excessive sleepiness, which may influence the interpretation of the results. Finally, the applicability of these findings to other populations is still unclear, indicating a need for further investigation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this investigation reveals a significant and nonlinear relationship between METS-IR and OSA. Future research should include prospective and randomized controlled studies to validate these findings. Additionally, further exploration of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying these associations is essential.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found at: this data can be found at: NHANES (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/default.aspx).
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the NHANES project was established by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), which is affiliated with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
ZC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. JCL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. HP: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YY: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. SC: Visualization, Writing – original draft. LZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JSL: Writing – review & editing. WC: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Shenzhen science and technology research and development fund (No. JCYJ20230807115302006).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge NHANES databases for their generous provision of platforms and researchers who contributed their datasets.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
METS-IR, metabolic score for insulin resistance; OSA, obstructive sleep apnea; NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; PIR, poverty income ratio; PA, physical activity; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; BMI, body mass index; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; TG, triglycerides; FBG, fasting blood glucose.
Footnotes
References
1. Lv, R, Liu, X, Zhang, Y, Dong, N, Wang, X, He, Y, et al. Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:218. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01496-3
2. Schahab, N, Sudan, S, Schaefer, C, Tiyerili, V, Steinmetz, M, Nickenig, G, et al. Sleep apnoea is common in severe peripheral arterial disease. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0181733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181733
3. Sorajja, D, Gami, AS, Somers, VK, Behrenbeck, TR, Garcia-Touchard, A, and Lopez-Jimenez, F. Independent association between obstructive sleep apnea and subclinical coronary artery disease. Chest. (2008) 133:927–33. doi: 10.1378/chest.07-2544
4. Castaneda, A, Jauregui-Maldonado, E, Ratnani, I, Varon, J, and Surani, S. Correlation between metabolic syndrome and sleep apnea. World J Diabetes. (2018) 9:66–71. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v9.i4.66
5. Punjabi, NM. The epidemiology of adult obstructive sleep apnea. Proc Am Thorac Soc. (2008) 5:136–43. doi: 10.1513/pats.200709-155MG
6. Torres, G, Sánchez-de-la-Torre, M, and Barbé, F. Relationship between OSA and hypertension. Chest. (2015) 148:824–32. doi: 10.1378/chest.15-0136
7. Aurora, RN, and Punjabi, NM. Obstructive sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a bidirectional association. Lancet Respir Med. (2013) 1:329–38. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70039-0
8. Barros, D, and García-Río, F. Obstructive sleep apnea and dyslipidemia: from animal models to clinical evidence. Sleep. (2019) 42:zsy236. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsy236
9. Theorell-Haglöw, J, Zhou, X, Wittert, G, Adams, R, Appleton, S, Reynolds, A, et al. Does obstructive sleep apnea increase the risk of cancer and cancer mortality in combined community-based cohorts? J Sleep Res. (2024) 33:e14089. doi: 10.1111/jsr.14089
10. Lin, H, Xiong, H, Ji, C, Wang, C, Li, Y, An, Y, et al. Upper airway lengthening caused by weight increase in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Respir Res. (2020) 21:272. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01532-8
11. Ip, MSM, Lam, B, Ng, MMT, Lam, WK, Tsang, KWT, and Lam, KSL. Obstructive sleep apnea is independently associated with insulin resistance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2002) 165:670–6. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.5.2103001
12. Strachan, MWJ, Reynolds, RM, Frier, BM, Mitchell, RJ, and Price, JF. The relationship between type 2 diabetes and dementia. Br Med Bull. (2008) 88:131–46. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldn042
13. Framnes, SN, and Arble, DM. The bidirectional relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic disease. Front Endocrinol. (2018) 9:440. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00440
14. Jean-Louis, G, Zizi, F, Clark, LT, Brown, CD, and McFarlane, SI. Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease: role of the metabolic syndrome and its components. J Clin Sleep Med. (2008) 4:261–72. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.27191
15. Bello-Chavolla, OY, Almeda-Valdes, P, Gomez-Velasco, D, Viveros-Ruiz, T, Cruz-Bautista, I, Romo-Romo, A, et al. METS-IR, a novel score to evaluate insulin sensitivity, is predictive of visceral adiposity and incident type 2 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol. (2018) 178:533–44. doi: 10.1530/EJE-17-0883
16. Kim, SS, and Cheong, JY. Screening and prediction of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease using a peripheral insulin resistance index: potential benefits and limitations. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2022) 28:802–5. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0249
17. Wang, Z, Xie, J, Wang, J, Feng, W, Liu, N, and Liu, Y. Association between a novel metabolic score for insulin resistance and mortality in people with diabetes. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:895609. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.895609
18. Gu, X, Tang, D, Xuan, Y, Shen, Y, and Lu, LQ. Association between obstructive sleep apnea symptoms and gout in US population, a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:10192. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36755-4
19. Tsai, K-Z, Chu, C-C, Huang, W-C, Sui, X, Lavie, CJ, and Lin, G-M. Prediction of various insulin resistance indices for the risk of hypertension among military young adults: the CHIEF cohort study, 2014-2020. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:141. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02229-8
20. Yoon, S-Y, Kim, JS, Ko, GJ, Choi, YJ, Moon, JY, Jeong, K, et al. Fasting blood glucose and the risk of all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis. Kidney Res Clin Pract. (2024) 43:680–9. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.23.098
21. Laakso, M. Is insulin resistance a feature of or a primary risk factor for cardiovascular disease? Curr Diab Rep. (2015) 15:105. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0684-4
22. Bjornstad, P, and Eckel, RH. Pathogenesis of lipid disorders in insulin resistance: a brief review. Curr Diab Rep. (2018) 18:127. doi: 10.1007/s11892-018-1101-6
23. Schmiegelow, MD, Hedlin, H, Stefanick, ML, Mackey, RH, Allison, M, Martin, LW, et al. Insulin resistance and risk of cardiovascular disease in postmenopausal women: a cohort study from the Women’s health initiative. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. (2015) 8:309–16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.114.001563
24. Abdelhamed, MH, Salah, S, Lqudsi, AKK, Jan, MM, Alahdal, DK, Alfaifi, SA, et al. Indices of insulin resistance and adiposity can detect obesity-related morbidity in pediatrics. Saudi Med J. (2022) 43:161–8. doi: 10.15537/smj.2022.43.2.20210720
25. Januzzi, JL. Biomarkers to predict risk in apparently well populations. JAMA Cardiol. (2016) 1:528–9. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2016.1019
26. Young, T, Peppard, PE, and Gottlieb, DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2002) 165:1217–39. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2109080
27. Srivali, N, Thongprayoon, C, Cheungpasitporn, W, Zinchuk, A, and Koo, BB. Impact of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on restless legs syndrome in patients with coexistent obstructive sleep apnea: a qualitative systematic review. J Clin Neurosci. (2025) 133:111075. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2025.111075
28. Joskin, A, and Bruyneel, M. Challenges in obstructive sleep apnea management in elderly patients. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:7718. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247718
29. Kariuki, JK, Yang, K, Scott, PW, Chasens, ER, Godzik, C, Luyster, FS, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea risk is associated with severity of metabolic syndrome: a secondary analysis of the 2015-2018 National Health and nutrition examination survey. J Cardiovasc Nurs. (2022) 37:482–9. doi: 10.1097/JCN.0000000000000868
30. Georgoulis, M, Kontogianni, MD, Kechribari, I, Tenta, R, Fragopoulou, E, Lamprou, K, et al. Associations between serum vitamin D status and the cardiometabolic profile of patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Horm Athens Greece. (2023) 22:477–90. doi: 10.1007/s42000-023-00456-4
31. Llanos, OL, Galiatsatos, P, Guzmán-Vélez, E, Patil, SP, Smith, PL, Magnuson, T, et al. Pharyngeal collapsibility during sleep is elevated in insulin-resistant females with morbid obesity. Eur Respir J. (2016) 47:1718–26. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00918-2015
32. Eckert, DJ, and Oliven, A. When insulin has to work hard to keep the sugar at bay the upper airway collapses away. Eur Respir J. (2016) 47:1611–4. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00590-2016
33. Kim, CY, Park, Y, Leem, AY, Chung, KS, Jung, JY, Park, MS, et al. Relationship between airway obstruction and incidence of metabolic syndrome in Korea: a community-based cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2018) 13:2057–63. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S157453
34. Kheirandish-Gozal, L, and Gozal, D. Obstructive sleep apnea and inflammation: proof of concept based on two illustrative cytokines. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:459. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030459
35. Park, YH, Oh, EY, Han, H, Yang, M, Park, HJ, Park, KH, et al. Insulin resistance mediates high-fat diet-induced pulmonary fibrosis and airway hyperresponsiveness through the TGF-β1 pathway. Exp Mol Med. (2019) 51:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0258-7
36. McNicholas, WT, and Bonsigore, MR. Management committee of EU COST ACTION B26. Sleep apnoea as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: current evidence, basic mechanisms and research priorities. Eur Respir J. (2007) 29:156–78. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00027406
37. Zeng, S, Wang, Y, Ai, L, Huang, L, Liu, Z, He, C, et al. Chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced oxidative stress activates TRB3 and phosphorylated JNK to mediate insulin resistance and cell apoptosis in the pancreas. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2024) 51:e13843. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13843
38. Stamatakis, KA, and Punjabi, NM. Effects of sleep fragmentation on glucose metabolism in normal subjects. Chest. (2010) 137:95–101. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-0791
39. Greenlund, IM, and Carter, JR. Sympathetic neural responses to sleep disorders and insufficiencies. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2022) 322:H337–49. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00590.2021
Keywords: obstructive sleep apnea, metabolic score for insulin resistance, insulin resistance, NHANES, cross-sectional study
Citation: Cai Z, Li J, Peng H, Ye Y, Chen S, Zeng L, Lin J and Chen W (2025) Non-linear association of the metabolic score for insulin resistance with obstructive sleep apnea: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2015–2018. Front. Nutr. 12:1545140. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1545140
Edited by:
Jasmina D. Debeljak Martacic, University of Belgrade, SerbiaReviewed by:
Tijana Bojić, University of Belgrade, SerbiaMartin Popević, Military Medical Academy, Serbia
Copyright © 2025 Cai, Li, Peng, Ye, Chen, Zeng, Lin and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weifeng Chen, d2VpZmVuZ0BsZHkuZWR1LnJz
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Zhimao Cai
Zhimao Cai Jiachen Li3,4†
Jiachen Li3,4† Hui Peng
Hui Peng Weifeng Chen
Weifeng Chen