
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Nutr., 04 March 2025
Sec. Nutrition and Metabolism
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2025.1537707
Background and objective: Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is associated with abnormal lipid metabolism and inflammation. However, a single lipid or inflammatory parameter cannot accurately predict the prognosis of DR independently, because it is prone to be affected by various confounding factors. This study aimed to explore the relationship between the inflammation-lipid indicator C-reactive protein (CRP)/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and DR occurrence in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: This hospital-based retrospective study included 784 T2DM patients. Diabetic retinopathy was diagnosed by nonmydriatic fundus photography and/or fundus examination apparatus. T2DM patients were divided into non-DR and DR groups. Demographics variables, clinical history and serum biochemical indicators of the subjects were collected. We also calculated the CRP/HDL-C ratio. The association between the CRP/HDL-C and DR was assessed using multivariate logistic regression analyses.
Results: A total of 784 participants, 612 without DR and 172 with DR, were included in the final sample analysis. Compared with non-DR participants, the DR diagnostic group had significantly higher CRP/HDL-C (4.03 ± 1.67 vs. 2.66 ± 0.97; p < 0.001). Then, the patients were grouped based on the quartiles of CRP/HDL-C, there was a gradual increase in the prevalence of DR was noted in T2DM patients along with the increased quartile of the CRP/HDL-C ratio (Q1: 7.65%; Q2: 15.31%; Q3: 19.90%; Q4: 44.90%; p = 0.028). After adjustment for the impact of various covariates, the odds ratio (OR) of the third and fourth vs. the first quartile of CRP/HDL-C were 2.905 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.372 ~ 6.152, p = 0.005) and 9.938 (95% CI: 4.987 ~ 19.804, p < 0.001), respectively. Further, multivariate logistic regression model showed that the CRP/HDL-C ratio (OR 3.176, 95% CI: 1.280 ~ 7.877, p = 0.013) was identified as risk factor for DR. Moreover, the area under the curve (AUC) to evaluate the predictive value of CRP/HDL-C for the risk of DR occurrence was 0.752 (95% CI: 0.711 ~ 0.794).
Conclusion: The ratio of C-reactive protein (CRP) to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) is associated with DR in patients with T2DM, and CRP/HDL-C may be an effective marker to help identify the risk of DR in patients with T2DM.
With demographic and lifestyle changes, the global prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) continues to increase. The global prevalence of diabetes in adults was estimated to be rising to 12.2% by 2045, of which 90% is type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (1). Diabetic retinopathy (DR), as one of the common microvascular complications of diabetes, jeopardizes the patient’s vision level and even leads to blindness, affecting patients’ survival and quality of life (2). The epidemiologic projections indicated that the prevalence of DR was 22.27% among people with DM, which increases the risk of life-threatening systemic vascular complications such as stroke, coronary heart disease and heart failure, and the global burden of DR was predicted to remain high until 2045 (3, 4). With the increase in the number of diabetic patients and the aging population, DR has become a great challenge to avoid visual impairment and blindness. However, because of the low compliance rate for DR screening, many patients with DR did not seek appropriate medical care until progressed to an irreversible stage. Thus, exploring simple and reliable biomarkers to predict the development of DR is important in comprehensive clinical management.
Previous studies have demonstrated that DR is associated with the duration of diabetes, poor glycemic control, dyslipidemia, hypertension, inflammatory response and nerve damage (5–8). In addition, several studies have reported that high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and C-reactive protein (CRP) are risk factors for diabetes and cardiovascular disease (9, 10), however, a single lipid indicator or a single inflammatory indicator is susceptible to multiple confounding factors and may not accurately predict the risk of developing DR. The CRP/HDL-C as a composite indicator, is more capable of comprehensively assessing the correlation between the inflammatory system and lipid levels and the risk of DR. As an inflammation-lipid composite marker, the ratio of CRP to HDL-C has been shown to be associated with cardiovascular and metabolism-related diseases (11–13).
Therefore, in the present study, we sought to explore the relationship between the inflammation-lipid indicator CRP/HDL-C and DR occurrence in a cross-sectional study. We aimed to corroborate whether the CRP/HDL-C ratio is an independent predictor of DR occurrence. The findings of this study are anticipated to bridge the gap between DR and markers of inflammation-lipid function and have clinical implications for the management of DR.
This study retrospectively collected patients with T2DM who were hospitalized in the Endocrinology Department of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital between January 2015 and January 2019, aged between 18 and 80 years. T2DM was diagnosed according to the 2003 American Diabetes Association criteria (14). The International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy Scale was used to group the presence or absence of retinopathy (15). Based on the presence or absence of diabetic retinopathy, the study subjects were divided into DR group and non-DR group. Subjects with combined acute complications of diabetes mellitus, severe infections, dysfunction of vital internal organs and tissues (heart, liver, kidney, etc.), and malignant tumors were excluded. Patients with hormonal or additive medications within the last 3 months that could have an effect on endocrine metabolism were also excluded.
We reviewed the electronic medical records of all patients in order to collect demographic and biochemical variables retrospectively. Information on each participant, including their age, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), smoking, drinking, diabetes duration was collected using standard technical methods. Blood specimens of each individual were collected for laboratory analysis between 8:00 and 10:00 am after overnight fasting for at least 8 h. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) concentrations were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HLC-73G8, Tosoh, Japan), fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and 2-h postprandial blood glucose (2 h-PG) were tested using a hexokinase method (TBA-200FR, Tokyo, Japan). The automatic biochemical analyzer (Kyowa Medex Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was used to detect concentrations of triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), HDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine (Cr), uric acid (UA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. C-reactive protein was measured using the nephelometric method on the Siemens Dade Behring BN II analyzer (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Deerfield, IL). We also calculated the CRP/HDL-C ratio. Additionally, it should be noted that some of the patients included in this study were on medications for cardiovascular diseases, which has been considered in our interpretation of the results.
Continuous variables were represented as mean ± standard deviation or median (quartiles), and categorical variables were represented as frequencies or percentages. The Statistical differences in means and proportions between two independent groups were determined using independent sample t-test (normal distribution), Kruskal–Wallis test (skewed distribution), and Chi-square test (categorical variables). The binary logistic regression analysis was used to examine the overall DR risk at the CRP/HDL-C ratio quartile. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to determine the associations between the CRP/HDL-C ratio and incident DR, when the CRP/HDL-C ratio level was treated as a continuous variable. The results were evaluated within a 95% confidence interval (CI) and at a significance level of two-sided p-value less than 0.05. All data were examined by adopting the program SPSS Statistics software version 27.0 (IBM SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA). Statistics were considered significant when p < 0.05.
A total of 784 participants, 612 without DR (male, 66.34%) and 172 with DR (male, 65.70%), were included in the final sample analysis. The clinical characteristics of the two groups are presented in Table 1. Compared with non-DR participants, the DR diagnostic group tended to be older, higher SBP and a longer diabetes duration. In terms of glycemic indicators, subjects with DR had significantly higher FPG (8.62 ± 2.90 vs. 7.77 ± 2.33; p < 0.001) and 2hPG (15.19 ± 4.37 vs. 13.91 ± 4.08; p = 0.001), as well as higher HbA1c (9.21 ± 1.78 vs. 8.33 ± 2.15; p < 0.001). Additionally, participants with DR had significantly higher CRP (4.09 ± 1.47 vs. 2.96 ± 1.09; p < 0.001) and CRP/HDL-C (4.03 ± 1.67 vs. 2.66 ± 0.97; p < 0.001). Whereas, the HDL-C level and hemoglobin concentration were lower in the DR group. There was no significant difference in other indexes (p > 0.05).
Based on the quartiles of the CRP/HDL-C ratio at baseline, the patients were divided into four groups. Specifically, Quartile 1 (Q1): CRP/HDL-C < 2.087, n = 196; Quartile 2 (Q2): CRP/HDL-C 2.088 ~ 2.764, n = 196; Quartile 3 (Q3): CRP/HDL-C 2.765 ~ 3.551, n = 196; Quartile 4 (Q4): CRP/HDL-C > 3.551, n = 196. The prevalence of DR across the Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 groups was7.65, 15.31, 19.90, and 44.90%, respectively, indicating a significant upward trend (P for trend<0.001). Then, taking Q1 as the reference group, Q2, Q3 and Q4 all showed a significant association with increased incidence of DR (Q2, OR 2.218, 95% CI: 1.133 ~ 4.197, p = 0.020; Q3, OR 2.997, 95% CI: 1.592 ~ 5.643, p < 0.001; Q4, OR 9.832, 95% CI: 5.412 ~ 17.864, p < 0.001) after the logistic regression analysis (Table 2). Further, after adjustment for age, SBP, diabetes duration, FPG, 2 h-PG, HbA1c, and HBG, compared to the Q1 of CRP/HDL-C, the Q3 and Q4 groups still had a markedly increased risk of DR by 190.5% (OR 2.905, 95% CI: 1.372 ~ 6.152, p = 0.005) and 893.8% (OR 9.938, 95% CI: 4.987 ~ 19.804, p < 0.001), separately, while no difference was observed in Q2 group (OR 1.803, 95% CI: 0.825 ~ 3.940, p = 0.139).
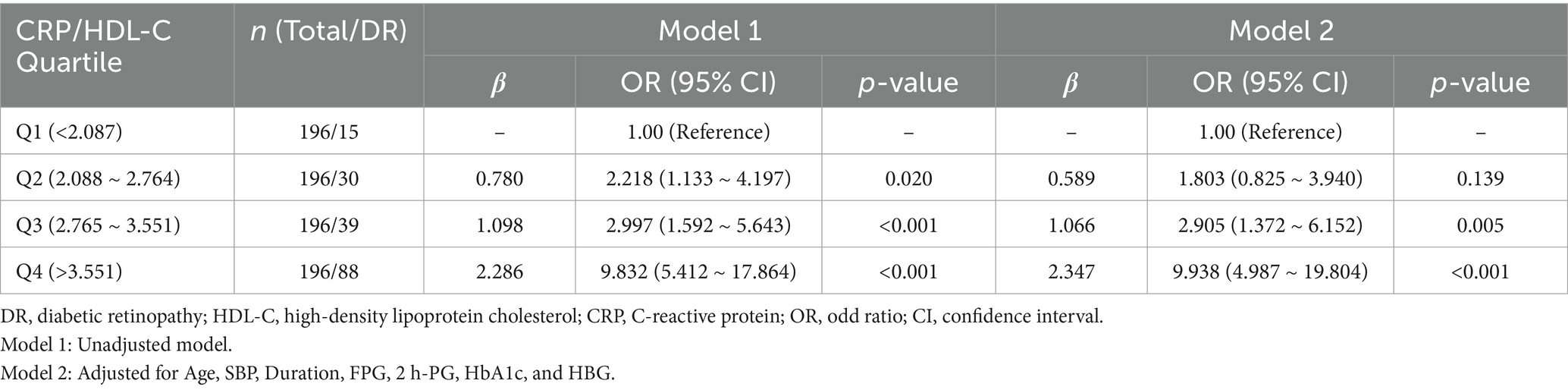
Table 2. Results of logistic regression analysis comparing the effects of different CRP/HDL-C level subgroups on DR.
Furthermore, to investigate which indexes were vulnerable to increased DR occurrence, the relationship of DR occurrence with different indexes was evaluated. Based on the findings of univariate analysis, the following parameters were entered in the multivariate logistic regression model: age, SBP, diabetes duration, FPG, 2 h-PG, HbA1c, HDL-C, CRP, HBG, CRP/HDL-C. After conducted, the odds ratios (ORs) of DR showed that age (OR 1.036, 95% CI: 1.004 ~ 1.069, p = 0.029), diabetes duration (OR 1.106, 95% CI: 1.061 ~ 1.153, p = 0.001), FPG (OR 1.126, 95% CI: 1.003 ~ 1.264, p = 0.045), HbA1c (OR 1.197, 95% CI: 1.051 ~ 1.363, p = 0.007) and the CRP/HDL-C ratio (OR 3.176, 95% CI: 1.280 ~ 7.877, p = 0.013) were identified as risk factors for DR (Table 3). Moreover, we conducted the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and area under the curve (AUC) to evaluate the predictive value of parameters for the risk of DR occurrence. The CRP/HDL-C ratio had the best diagnostic performance AUC = 0.752 (95% CI: 0.711 ~ 0.794), followed by diabetes duration AUC = 0.672(95% CI: 0.626 ~ 0.719), HbA1c AUC = 0.653 (95% CI: 0.605 ~ 0.701), FPG AUC = 0.636 (95% CI: 0.580 ~ 0.692) and age AUC = 0.557 (95% CI: 0.500 ~ 0.613). Then, we combined indicators of the five AUCs and found that the AUC of the mixture could reach 0.838 (95% CI: 0.801 ~ 0.875) (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) of DR in T2DM. (A) CRP/HDL-C; (B) CRP/HDL-C combined other 4-indicators (Age, Duration, FPG, and HbA1c).
In the current study, we found that after adjustment for the impact of various covariates, the odds ratio of the third and fourth vs. the first quartile of CRP/HDL-C were 2.905 (95% CI: 1.372 ~ 6.152) and 9.938 (95% CI: 4.987 ~ 19.804), respectively, while no significant correlation was observed in the second vs. the first quartile of CRP/HDL-C. Additionally, the CRP/HDL-C ratio is independently and positively associated with the occurrence of DR in patients with T2DM (OR 3.176, 95% CI: 1.280 ~ 7.877; p = 0.013), which highlighted CRP/HDL-C level raise as a high-risk factor for higher risk of DR. It is implied that the CRP/HDL-C ratio can be applied as a risk predictor for DR in T2DM. In addition, we confirmed that age, FPG, HbA1c and diabetes duration are strongly associated with DR risk.
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) as one of the most common microvascular complications of DM (16), remains a leading cause of preventable blindness in the adult working population and the global DR burden is expected to remain high through 2045 (4). Approximately 19.5 million people have diagnosed with DR, the overall prevalence of any DR among those aged 18–74 was 16.3% in our country (17). With the increasing prevalence of diabetes globally and increasing longevity and aging of the global population, DR has consequently become a serious global health challenge. Therefore, it is very important to find more predictors for DR.
The combination of CRP level and lipid indices, CRP/HDL-C, is applied in clinical practice as a predictor of metabolic syndrome (12, 13). Compared with a single indicator, it can simultaneously consider the correlation between lipid metabolism, inflammatory metabolism and DR in T2DM patients, thereby improving the accuracy of clinical prognosis prediction. According to the present study, there is a correlation between the CRP/HDL-C ratio and the likelihood of DR risk. Lipid metabolism and inflammation have been reported to be among the most affected pathways in the proteome or metabolome of various tissues affected by diabetes (18). Dyslipidemia is a pivotal pathological mechanism in DM and its complications. Lipid levels depend on a variety of regulatory mechanisms, among which the regulation of reverse cholesterol transport and its specific receptors, has been receiving increasing attention in relation to inflammation, especially DR and diabetic nephropathy (19, 20). Moreover, previous studies have demonstrated that inflammatory processes play an essential role in the pathogenesis of DR, increasing retinal vascular permeability and neovascularization, as well as leading to retinal neurodegeneration, which in turn accelerates DR progression (21). The interplay between lipid metabolism and inflammation is of utmost importance in the development of DR. Several studies reported that plasma HDL-C elevation has been considered a therapeutic approach to reduce the risk of T2DM and the vascular complications associated with DM (22, 23). The plasma levels of CRP exhibit a positive correlation with the severity of inflammation, making it a commonly employed nonspecific biomarker in clinical practice (24). Meanwhile, CRP is the most widely studied of the inflammatory markers associated with cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), and has even been used as the “gold standard” for CVD risk assessment. A prospective cohort study found that CRP as a mediator biomarker mediated a higher risk of microvascular complications in patients with T2DM (25). Qiu et al. reported that human CRP-induced overexpression of pro-inflammatory, pro-oxidative, and pro-angiogenic factors was associated with up-regulation of CD32 and the NF-κB signaling in the retinas, suggesting that elevated CRP levels play a pathogenic role in DR (26). Therefore, the CRP/HDL-C ratio could provide a more accurate and comprehensive reflection of the severity of DR risk in patients with T2DM. Similarly, our study confirmed the CRP/HDL-C ratio good diagnostic value in assessing the risk of DR occurrence with an area under the ROC curve of 0.752, also suggested that elevated CRP/HDL-C levels are connected with a higher risk of DR, and changes of this composite indicator should be emphasized in clinical care, especially in T2DM patients with CRP/HDL-C higher than 3.734.
This study has a number of benefits. First, to our knowledge, this study is the first to report the relationship between the CRP/HDL-C ratio and the risk of diabetic retinopathy in T2DM patients, which provides a new sight for predicting the incidence of retinopathy. Second, this study had a relatively large sample size and sufficient clinical information, and the associations of the CRP/HDL-C ratio and risk of DR remained stable even after multivariable adjustments, making the produced results more compelling. Although our study provided CRP/HDL-C, as an inflammation-lipid composite marker, can predict of DR by the simple and easy calculation, some limitations should be acknowledged. First, the study was a single-center cross-sectional study, and there is a disproportion in number of cases with and without retinopathy, in addition, we did not compare the CRP/HDL-C ratio with other known biomarkers (e.g., PTX3) enables a more comprehensive assessment of its predictive value, so it is indispensable to future validate by expanding the sample size and including multicenter data to improve the generalizability and reliability of our findings. Second, our study did not demonstrate a direct causal relationship between CRP/HDL-C and DR. Third, although we conducted rigorous adjusting for potential confounders, the possibility of residual confounders cannot be ruled out, such as the treatment of cardiovascular medications.
Our study elucidated the association between the risk of diabetic retinopathy (DR) and the CRP/HDL-C ratio in patients with T2DM, the higher CRP/HDL-C levels were correlated with the higher risk of DR. The CRP/HDL-C ratio is a significant predictor of DR. A composite index based on the CRP/HDL-C ratio effectively predicts the risk of DR.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by Drum Tower Hospital, affiliated with Nanjing University Medical School. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. GC: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. WW: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant Awards (82374554) and funding for Clinical Trials from the Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University (2024-LCYJ-ZXY-02).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Sun, H, Saeedi, P, Karuranga, S, Pinkepank, M, Ogurtsova, K, Duncan, BB, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2022) 183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
2. Zayed, MG, Karsan, W, Peto, T, Saravanan, P, Virgili, G, and Preiss, D. Diabetic retinopathy and quality of life: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Ophthalmol. (2024) 142:199–207. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.6435
3. Cheung, N, Mitchell, P, and Wong, TY. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet. (2010) 376:124–36. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)62124-3
4. Teo, ZL, Tham, YC, Yu, M, Chee, ML, Rim, TH, Cheung, N, et al. Global prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and projection of burden through 2045: systematic review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. (2021) 128:1580–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2021.04.027
5. Wang, W, and Lo, ACY. Diabetic retinopathy: pathophysiology and treatments. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:1816. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061816
6. Ghamdi, AHA. Clinical predictors of diabetic retinopathy progression; a systematic review. Curr Diabetes Rev. (2020) 16:242–7. doi: 10.2174/1573399815666190215120435
7. Jenkins, AJ, Joglekar, MV, Hardikar, AA, Keech, AC, O'Neal, DN, and Januszewski, AS. Biomarkers in diabetic retinopathy. Rev Diabet Stud. (2015) 12:159–95. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2015.12.159
8. Guo, H, Han, F, Qu, JR, Pan, CQ, Sun, B, and Chen, LM. Scoring and validation of a simple model for predicting diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes based on a meta-analysis approach of 21 cohorts. Ann Med. (2024) 56:2413920. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2413920
9. Wu, D, Chen, G, Lan, Y, Chen, S, Ding, X, Wei, C, et al. Measurement of cumulative high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio in the risk prediction of type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:110. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04895-4
10. Ebtehaj, S, Gruppen, EG, Parvizi, M, Tietge, UJF, and Dullaart, RPF. The anti-inflammatory function of HDL is impaired in type 2 diabetes: role of hyperglycemia, paraoxonase-1 and low grade inflammation. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2017) 16:132. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0613-8
11. Gao, Y, Wang, M, Wang, R, Jiang, J, Hu, Y, Wang, W, et al. The predictive value of the hs-CRP/HDL-C ratio, an inflammation-lipid composite marker, for cardiovascular disease in middle-aged and elderly people: evidence from a large national cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:66. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02055-7
12. Djesevic, M, Hasic, S, Lepara, O, Jahic, R, Kurtovic, A, and Fajkic, A. CRP/HDL-C and monocyte/HDL-C ratios as predictors of metabolic syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Inform Med. (2023) 31:254–9. doi: 10.5455/aim.2023.31.254-259
13. Jialal, I, Adams-Huet, B, and Remaley, AT. A comparison of the ratios of C-reactive protein and triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol as biomarkers of metabolic syndrome in African Americans and non-Hispanic whites. J Diabetes Complicat. (2022) 36:108231. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108231
14. Genuth, S, Alberti, KG, Bennett, P, Buse, J, Defronzo, R, Kahn, R, et al. Expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus: follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. (2003) 26:3160–7. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.11.3160
15. Wilkinson, CP, Ferris, FL 3rd, Klein, RE, Lee, PP, Agardh, CD, Davis, M, et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology. (2003) 110:1677–82. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00475-5
16. Faselis, C, Katsimardou, A, Imprialos, K, Deligkaris, P, Kallistratos, M, and Dimitriadis, K. Microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. (2020) 18:117–24. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190502103733
17. Hou, X, Wang, L, Zhu, D, Guo, L, Weng, J, Zhang, M, et al. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy in adults with diabetes in China. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:4296. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39864-w
18. Eid, S, Sas, KM, Abcouwer, SF, Feldman, EL, Gardner, TW, Pennathur, S, et al. New insights into the mechanisms of diabetic complications: role of lipids and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia. (2019) 62:1539–49. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4959-1
19. Hammer, SS, Beli, E, Kady, N, Wang, Q, Wood, K, Lydic, TA, et al. The mechanism of diabetic retinopathy pathogenesis unifying key lipid regulators, Sirtuin 1 and liver X receptor. EBioMedicine. (2017) 22:181–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.07.008
20. Wang, XX, Wang, D, Luo, Y, Myakala, K, Dobrinskikh, E, Rosenberg, AZ, et al. FXR/TGR5 dual agonist prevents progression of nephropathy in diabetes and obesity. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2018) 29:118–37. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017020222
21. Semeraro, F, Morescalchi, F, Cancarini, A, Russo, A, Rezzola, S, and Costagliola, C. Diabetic retinopathy, a vascular and inflammatory disease: therapeutic implications. Diabetes Metab. (2019) 45:517–27. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2019.04.002
22. Drew, BG, Rye, KA, Duffy, SJ, Barter, P, and Kingwell, BA. The emerging role of HDL in glucose metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2012) 8:237–45. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.235
23. von Eckardstein, A, Nordestgaard, BG, Remaley, AT, and Catapano, AL. High-density lipoprotein revisited: biological functions and clinical relevance. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:1394–407. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac605
24. Zhou, HH, Tang, YL, Xu, TH, and Cheng, B. C-reactive protein: structure, function, regulation, and role in clinical diseases. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1425168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425168
25. Li, Y, Lai, Y, Geng, T, Zhang, YB, Xia, PF, Chen, JX, et al. Association of ultraprocessed food consumption with risk of microvascular complications among individuals with type 2 diabetes in the UK biobank: a prospective cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. (2024) 120:674–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.07.022
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy (DR), the CRP to HDL-C ratio, biomarker, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), dyslipidemia, inflammation
Citation: Zhang Y, Chen G, Wang W and Jing Y (2025) C-reactive protein to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio: an independent risk factor for diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes patients. Front. Nutr. 12:1537707. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1537707
Received: 01 December 2024; Accepted: 19 February 2025;
Published: 04 March 2025.
Edited by:
Jasmina D. Debeljak Martacic, University of Belgrade, SerbiaReviewed by:
Nevena Vidovic, University of Belgrade, SerbiaCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Chen, Wang and Jing. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yali Jing, amluZ3lhbGlkckAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.