
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Nutr. , 12 March 2025
Sec. Nutritional Epidemiology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2025.1532080
 Yang Jiao1
Yang Jiao1 Xing Zhang1
Xing Zhang1 Lian Duan1
Lian Duan1 Ruijie Cheng1
Ruijie Cheng1 Ning Yang1
Ning Yang1 Zhao Peng2
Zhao Peng2 Ben Li2,3
Ben Li2,3 Lu Xu4
Lu Xu4 Wenwen Chen1
Wenwen Chen1 Jingrong Chen1
Jingrong Chen1 Yanchao Liu5*
Yanchao Liu5* Hong Yan1*
Hong Yan1*Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a significant risk factor for cognitive impairment. Zinc deficiency contributes to T2DM development, while copper may exacerbate diabetes through prooxidant mechanisms. Higher zinc levels may protect against copper toxicity. This study investigates the association of plasma zinc and copper levels with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in T2DM patients.
Methods: T2DM patients admitted to Tongji Hospital from 2012 to 2018 were classified into MCI (n = 136) and control (n = 136) groups, matched by age (± 3 years) and gender. Conditional logistic regression was used to assess the associations between plasma zinc, copper levels and MCI. A generalized additive model (GAM) evaluated the dose–response relationship between plasma zinc, copper levels and Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores.
Results: The median of plasma metal levels in MCI and control groups were 831.31 μg/L and 936.29 μg/L for zinc, 932.07 μg/L and 860.47 μg/L for copper, and 0.91 and 1.11 for the zinc-to-copper (Zn/Cu) ratio. Compared to participants in the lowest tertile, the multivariable-adjusted odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals (CI) for MCI in the highest tertile were 0.33 (0.13, 0.79) for zinc, 3.56 (1.42, 8.94) for copper, and 0.37 (0.15, 0.93) for the Zn/Cu ratio. Plasma Aβ40 levels were significantly lower (p = 0.009) and plasma Aβ42/40 levels were significantly higher (p = 0.008) in MCI group compared with those in control group. Zinc concentration was positively associated with Aβ42. For per SD (327.71 μg/L) increase in plasma zinc levels, the percent change (95% CI) of Aβ42 were 2.90 (0.85, 4.99).
Conclusion: Higher plasma zinc levels and higher Zn/Cu ratio were associated with lower odds of MCI in T2DM patients, while higher copper levels increased the risk of MCI. This study provides insights on plasma zinc, copper, and Zn/Cu ratio and Aβ of MCI, further studies are needed to clarify the underlying mechanisms for novel therapies that could prevent or cure multiple T2DM-related cognitive impairments.
In recent years, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been identified as a major health concern, and it has been recognized as a significant risk factor for cognitive impairment (1). Recent data show that about 116 million people in China have diabetes, the highest in the world. Epidemiological studies have shown an increased risk of dementia among patients with diabetes (2). A recent meta-analysis estimated that about 45% of patients with T2DM experience mild cognitive impairment (MCI), which is also considered a complication of T2DM (3). Over the past two decades, studies have reported that the prevalence of MCI among older adults in China has ranged from 5 to 28% (4, 5). MCI is a transitional stage of cognitive impairment that is characterized by intermediate stage between normal aging and dementia (6). It is characterized by mild memory or cognitive impairment that does not meet the dementia diagnostic criteria. MCI can further develop into Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a progressive deterioration of the central nervous system (7). Individuals with diabetes have been shown to have a 1.5–2.0 times higher risk of developing cognitive decline, cognitive impairment, or dementia compared to those without diabetes (8). The prevalence of dementia and cognitive impairment among people with diabetes has been reported to be 13.1% for those aged 65–74 years and 24.2% for those aged 75 years and over (9). However, the exact pathophysiology of MCI in patients with diabetes remains unclear. Although many studies indicate an increased risk of developing dementia in diabetic populations, the association between T2DM and MCI, and its underlying mechanisms, requires further investigation.
Zinc and copper are essential trace elements that play a critical role in inflammation, oxidative stress, energy metabolism, and insulin homeostasis and have been implicated in the pathogenesis of T2DM (10, 11). Some studies have investigated the association of plasma zinc and copper levels with T2DM patients; however, the findings remain inconclusive. A cross-sectional study reported that in comparison with controls, serum zinc levels were lower in individuals with T2DM (12). Similarly, another study also showed that serum zinc levels were significantly reduced in patients with T2DM, with levels three times less than those in the control group (13). Conversely, a study suggested a possible relationship between increasing levels of zinc and the prevalence of T2DM (14). Meanwhile, research on copper levels in patients with T2DM remains controversial. A study had found that copper levels were elevated in diabetes mellitus patients (15). In contrast, another study found that serum copper levels were significantly lower in patients with T2DM compared to controls (16). The role of zinc, copper and particularly zinc-to-copper ratio (Zn/Cu) has gained increasing attention in recent years as markers for diabetes diagnosis and management (13). Moreover, the dyshomeostasis of trace metals, such as zinc and copper, has been associated with a decline in cognitive performance (17). Zinc homeostasis imbalance leads to reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and the activation of neuronal apoptosis, contributing to cognitive decline and the formation of neurodegenerative diseases such as AD and MCI (18). It was demonstrated that copper dysregulation has been observed to affect 50–60% of patients with MCI or AD (19), while the accumulation of copper in the blood has been associated with dementia (20). Previous epidemiological studies have suggested that lower serum zinc and higher serum copper levels may be associated with impaired cognitive function (21). Nevertheless, studies investigating the association between plasma zinc and copper levels and MCI in patients with T2DM are limited.
In addition, the mechanisms underlying the progression of T2DM to MCI remain unclear. β-Amyloid polypeptide (β-Amyloid, Aβ), consisting of 36–43 amino acids, is the main component of amyloid plaques in the brain (22). Aβ can be conveyed from the brain into the bloodstream via several pathways, and about 40–60% of brain-derived Aβ is cleared in the periphery (23). T2DM patients exhibit higher plasma Aβ levels than healthy population (24). Primarily studies focused on investigating plasma Aβ as a potential biomarker for AD. The findings of these studies indicated that plasma Aβ40 and Aβ42 concentrations were higher in cognitively cases who eventually developed AD compared to the control group (25). Zinc is an essential component of several Aβ-lowering enzymes, which plays an important part in peripheral Aβ clearance and cognitive dysfunction development (10). It has been suggested that zinc deficiency in T2DM patients may impair Aβ clearance and AD development (26). Copper was shown to contribute to cognitive impairment pathogenesis through pro-oxidant properties (13), higher levels of zinc may protect against copper toxicity by competing for the same binding sites (27). However, no studies have investigated the association between plasma zinc levels, peripheral Aβ levels and cognitive function in T2DM.
Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the association between plasma zinc, copper, and Aβ levels with MCI in T2DM patients. This study aims to explore the roles of zinc and copper in T2DM-induced cognitive dysfunction and provide novel insights for the early AD prevention in T2DM patients.
Participants in this study were T2DM patients who attended Tongji Hospital of Huazhong University of Science and Technology between 2012 and 2018 with the following inclusion criteria: (1) age ≥ 50 years; (2) able to complete cognitive function tests; (3) no history of severe head trauma; (4) no history of alcohol addiction; and (5) no history of psychiatric disorders. All participants completed the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) instruction of trained professional investigators and were classified into two groups: T2DM with MCI (MCI group) and T2DM without MCI (Control group), based on MMSE scores. According to the guidelines of the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center, MCI was defined as MMSE score ≤ 26 (28, 29). Sample size estimation was performed based on the 1:1 matched case-control study equation:
The following values were used: the odds ratio (OR) was 2; power of 95% and a reference seroprevalence of 30% for controls. Thus, the minimum sample size for either cases or controls was 127. The MCI and control groups were 1:1 matched by age (± 3 years) and gender, resulting in a final sample of 136 MCI and 136 controls. The study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and all participants signed the informed consent (Clinical trials. gov; Number: NCT01830998).
After a 12-h fast, venous blood was collected in heparin tubes, centrifuged for 5 min (3,000 rpm, 4°C), and plasma, leukocytes, and red blood cells were separated, numbered, and stored at −80°C (30). The APOE genotype was detected by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a multiplex amplification-blocked mutation system. The primers were designed and synthesized for APOE with specific Cys primers (Cys112/ Cys158) and Arg primers (Arg112/ Arg158), and a common reverse primer (30–32).
Plasma metal concentrations were detected by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Plasma samples were thawed at 4°C, vortexed and mixed. Then, 2,340 μL of sample diluent was added to a 5 mL lyophilized tube, followed by 60 μL of the sample. The mixture was shaken and mixed for 1 min, then sonicated for 10 min and centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 6 min. The detection limit of zinc and copper was 0.0199 μg/L and 0.0106 μg/L, respectively. In establishing the limit of quantitation, the concentration of the lowest standard solution (0.1 μg/L) was considered as the reference point. In order to guarantee the quality of the results, the human plasma certified reference material metal controls (ClinChek No. 8885) were analyzed for every 20 samples (33). The recovery values ranged from 80 to 120%. Furthermore, the relative standard deviation of the measured triplicate samples was within 5%, thereby ensuring the accuracy and precision of the experimental methods (34).
In this study, plasma Aβ40 (EEL-H0542c 90) and Aβ42 (E-EL-H0543c) levels were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. All procedures followed the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, blank samples, the Aβ40 and Aβ42 standards, or samples of this study (100 μL each) were added to coated 96-well plates and incubated for 90 min at 37°C. Following the decanting without washing, 100 μL of the biotinylated detection antibody working solution was added, and the plate was incubated at 37°C for 1 h. Following another decant, 350 μL of washing buffer was added to each well, and the plate was washed three times. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated solution (100 μL each) was added and incubated for 30 min at 37°C. After five washes, 90 μL of substrate reagent was added, and the plate was incubated in the dark for 15 min at 37°C. Finally, 100 μL of stop solution was added, and the optical density (OD value) was recorded at 450 nm using a microplate reader (35).
Demographic data and biochemical indicators were presented by case and control. Continuous variables of baseline participant characteristics that were normally distributed were expressed as means (standard deviation). Continuous variables that were not normally distributed were expressed as medians (interquartile range). Categorical variables were expressed as frequencies (percentages). To compare the differences between the case and control groups, the Student’s t-test, Mann–Whitney U rank sum test, and chi-square test were used.
Conditional logistic regression models were used to estimate ORs and 95% CIs associated with MCI in T2DM patients. Plasma zinc, copper, and Zn/Cu levels were categorized into tertiles according to the distribution in control participants. Subsequently, several potential confounding variables were gradually adjusted in the following models. Model 1 was adjusted for sex (female or male), age (years), diabetes duration (years), and APOE ε4 carrying status (yes or no). Model 2 was additionally adjusted for BMI (<24, 24–28, or ≥ 28 kg/m2), family history of diabetes (yes or no), hypertension (yes or no), hyperlipidemia (yes or no), CHD (yes or no), current smoking status (yes or no), current drinking status (yes or no), and HbA1c level (<6.5%, or ≥ 6.5%).
To further investigate the dose–response relationship between metal exposure and the incidence of MCI in T2DM, a restricted cubic spline (RCS) regression analysis was conducted using the R package “rms.” In order to balance the optimal fitting and overfitting of the principal spline, the number of knots was set to three based on the minimum absolute value of the Akaike information criterion (36, 37). Finally, three knots corresponding to the 10th, 50th, 90th percentiles were used. The generalized additive model (GAM) was used to assess the non-linear relationship of plasma zinc and copper levels with MMSE score, as well as Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels. For the GAM analysis, Aβ40 and Aβ42 were log-transformed. In addition, β-coefficients were transformed into percent difference using the following formula: , to aid in the interpretation. Lastly, exposure-response curves were plotted based on the GAM.
All analyses in this study were performed using SPSS 26.0, R software (version 4.4.0), and SAS 9.4 software. All p-values were tested using a two-sided test, and p < 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
The demographic data and clinical and biochemical indices of 136 cases and 136 matched controls are shown in Table 1. The medians (interquartile range) of plasma metal levels in MCI and control groups were 831.31 (717.91–1043.41) μg/L and 936.29 (827.41–1205.58) μg/L for zinc, 932.07 (808.73–1032.12) μg/L and 860.47 (750.25–974.34) μg/L for copper, and 0.91 (0.75–1.17) and 1.11 (0.91–1.34) for Zn/Cu ratio. Compared with the control group, MCI patients had significantly lower levels of plasma zinc and Zn/Cu (p < 0.001), while copper levels were significantly higher (p = 0.001).
Plasma Aβ40 levels were significantly lower, while Aβ42/40 ratio was higher in MCI compared with controls. The median (interquartile range) plasma Aβ40 levels in MCI and control groups were 173.95 (83.82–253.67) ng/L and 207.61 (139.84–266.17) ng/L, respectively; plasma Aβ42 levels were 67.27 (54.18–88.19) ng/L and 69.15 (55.37–85.61) ng/L; and plasma Aβ42/40 ratio levels were 0.45 (0.27–0.90) and 0.36 (0.24–0.52).
The plasma zinc level was non-linearly associated with lower MCI risk in T2DM patients (Figure 1). Compared to the lowest tertile, the OR (95% CI) for MCI were 0.28 (0.12, 0.64) and 0.33 (0.13, 0.79) for participants in the middle and highest tertiles of plasma zinc level, respectively (Table 2). For copper, a linear association between plasma copper and MCI risk was observed in T2DM patients (Figure 1). Compared with those in the lowest tertile of copper levels, participants in the middle and highest tertiles had 182 and 256% higher risk of MCI (adjusted OR [95% CI]: 2.82 [1.08, 7.38], 3.56 [1.42, 8.94], p for trend = 0.022), respectively. In addition, the Zn/Cu ratio was significantly associated with lower MCI risk in T2DM patients in a non-linear manner (Figure 1). Compared with those in the lowest tertile of Zn/Cu ratio, the multivariable-adjusted OR (95% CI) for MCI in the highest tertile was 0.37 (0.15, 0.93).
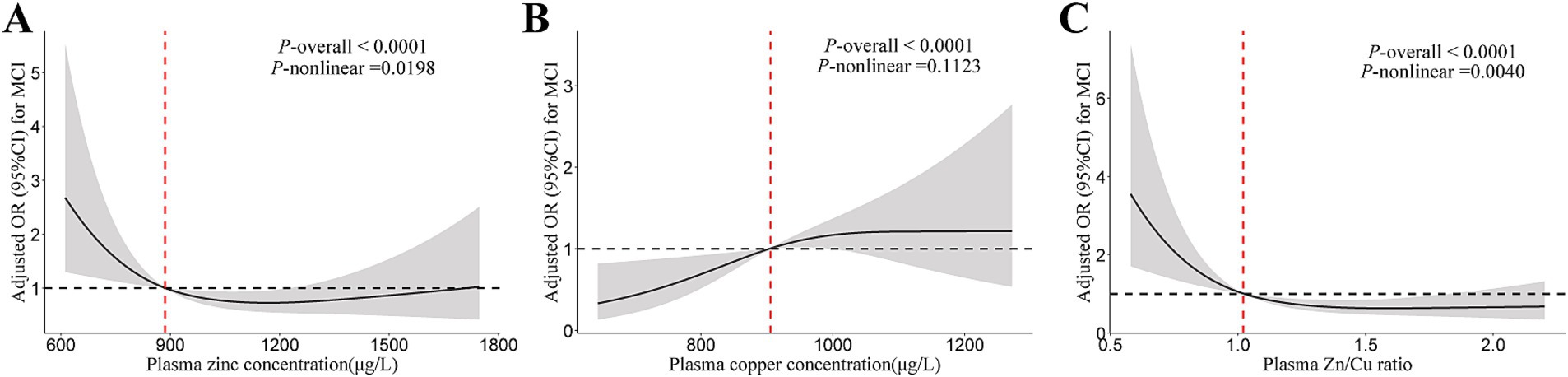
Figure 1. The restricted cubic spline for the association of plasma zinc, copper, and Cu/Zn ratio with MCI. (A) Plasma zinc; (B) Plasma copper; (C) Zn/Cu ratio. Results were adjusted for age, sex, diabetes duration, APOE ε4 carrier status, BMI, current smoking status, current drinking status, family history of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, HbA1c, and CHD. Model for plasma zinc was additionally adjusted for plasma copper. Model for plasma copper was additionally adjusted for plasma zinc. MCI, mild cognitive impairment; Zn/Cu, the ratio of zinc to copper.
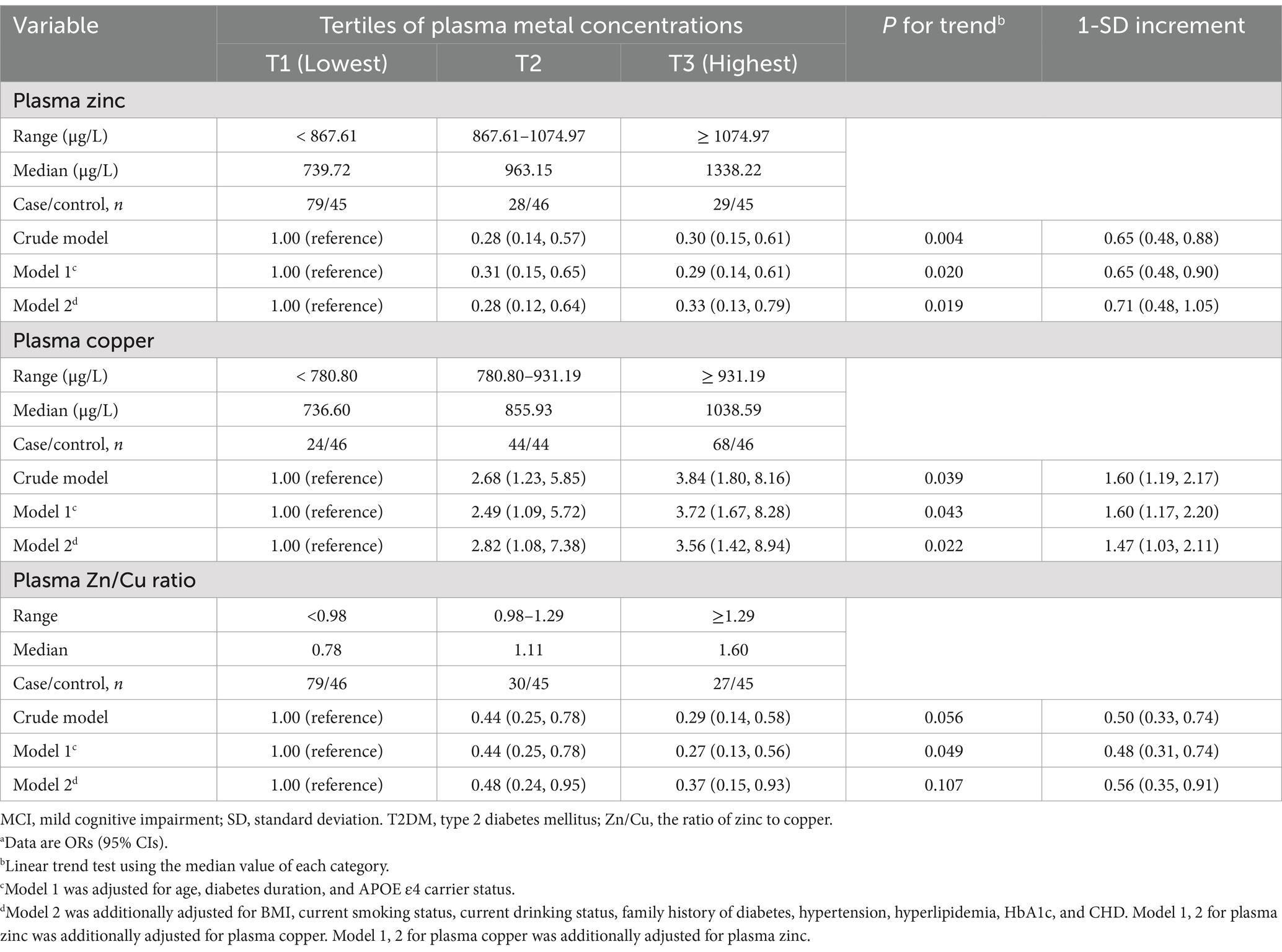
Table 2. Odds ratio of plasma zinc and copper concentrations with risk of MCI among individuals with T2DMa.
The dose–response relationship between plasma zinc, copper levels and MMSE scores are shown in Table 3. The higher plasma zinc was non-linearly associated with a higher MMSE score in T2DM patients (Figure 2). In contrast, the association between plasma copper levels and MMSE scores was negative. The relationship curve of Zn/Cu ratio showed an increasing trend; as the Zn/Cu ratio increases, the MMSE score also continue to increase.
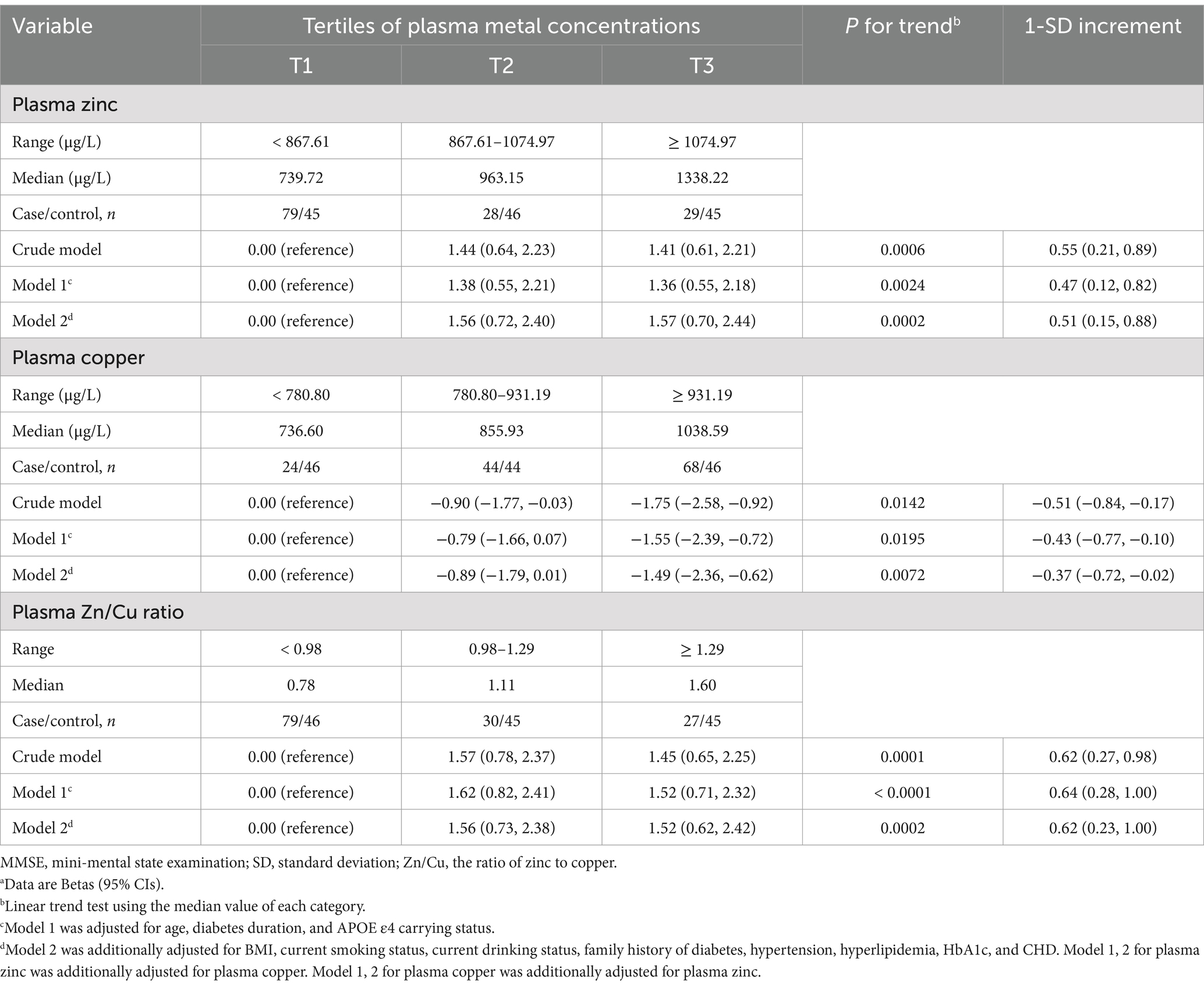
Table 3. Generalized additive models for the association of plasma zinc, copper, and the Zn/Cu ratio with MMSE scoresa.
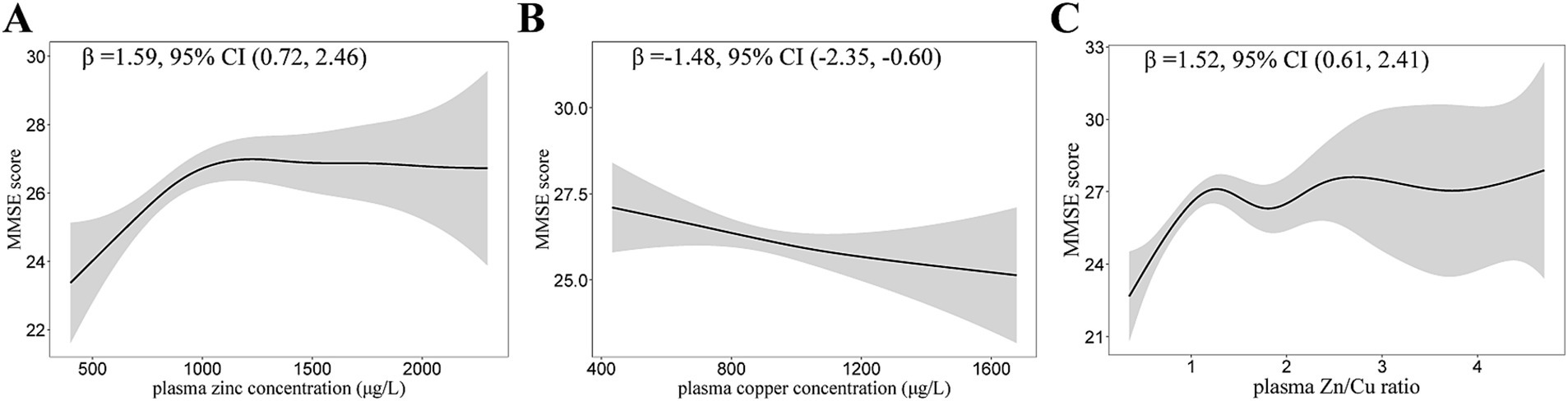
Figure 2. Generalized Additive Models (GAMs) for the association of plasma zinc, copper, and Zn/Cu ratio with MMSE scores. (A) Plasma zinc; (B) Plasma copper; (C) Zn/Cu ratio. Adjusted for age, diabetes duration, APOE ε4 carrier status, BMI, current smoking status, current drinking status, family history of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, HbA1c, and CHD. Model for plasma zinc was additionally adjusted for plasma copper. Model for plasma copper was additionally adjusted for plasma zinc. MMSE, mini-mental state examination; Zn/Cu, the ratio of zinc to copper.
The relationship of plasma zinc and copper levels with Aβ40 and Aβ42 are shown in Table 4. Plasma zinc and copper concentration were both positively associated with Aβ42 (Figure 3). For per SD (327.71 μg/L) increase in plasma zinc levels, the percent change (95% CI) of Aβ42 was 2.90 (0.85, 4.99). Plasma zinc and copper levels were not significantly associated with Aβ40 nor Aβ42/40.
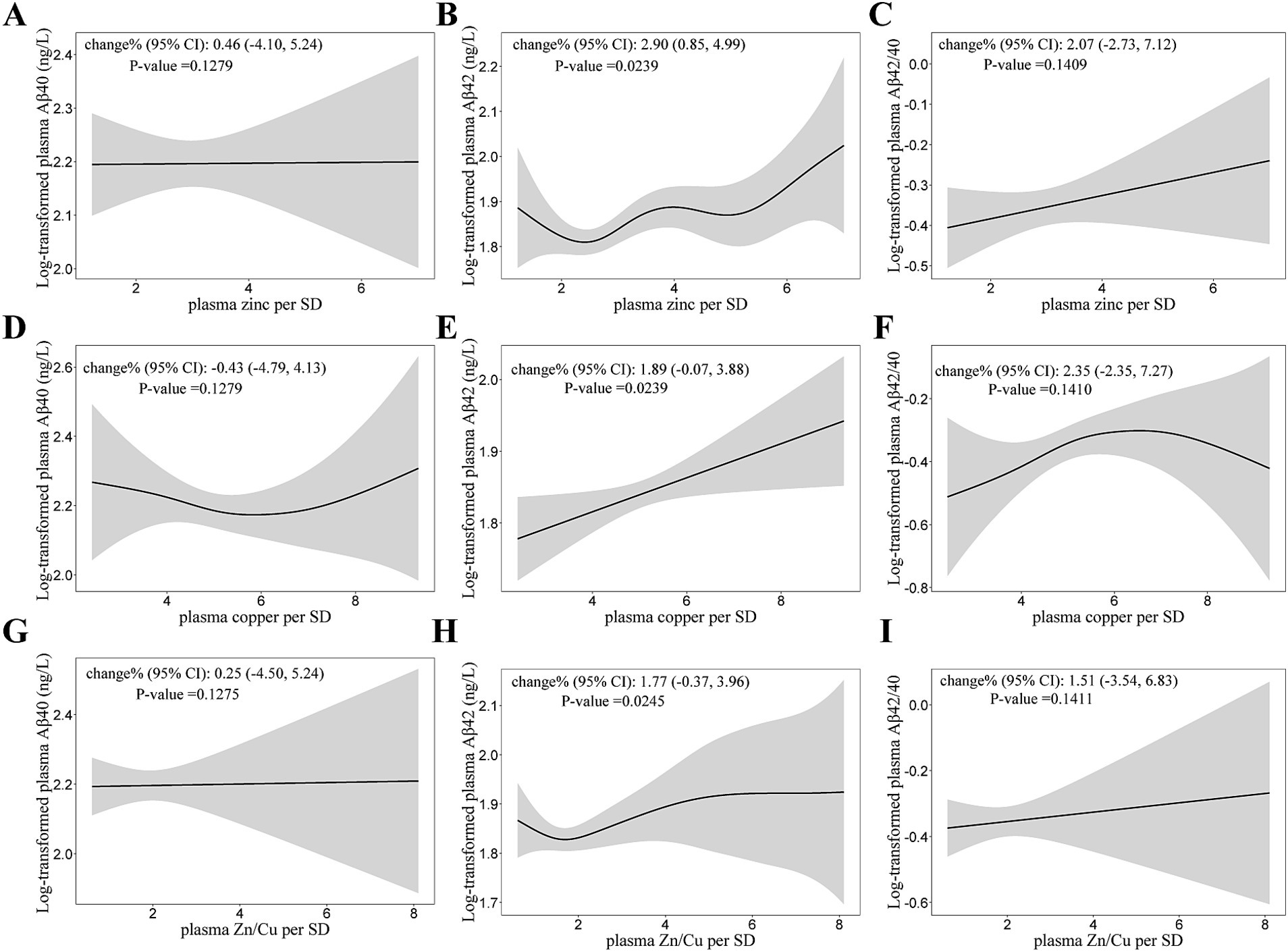
Figure 3. Generalized Additive Models (GAMs) for the association of log-transformed Aβ with plasma zinc, copper concentrations, and Zn/Cu ratio. (A,D,G) GAMs for the association of log-transformed Aβ40 with zinc, copper and Zn/Cu ratio; (B,E,H) GAMs for the association of log-transformed Aβ42 with zinc, copper and Zn/Cu ratio; (C,F,I) GAMs for the association of log-transformed Aβ42/40 with zinc, copper and Zn/Cu ratio. Adjusted for age, diabetes duration, APOE ε4 carrier status, BMI, current smoking status, current drinking status, family history of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, HbA1c, and CHD. Model for plasma zinc was additionally adjusted for plasma copper. Model for plasma copper was additionally adjusted for plasma zinc. Aβ, β-Amyloid; Aβ42/40, the ratio of Aβ42 to Aβ40; Zn/Cu, the ratio of zinc to copper.
In this age- and sex-matched case–control study, plasma zinc concentration was significantly associated with lower MCI risk in T2DM patients after adjusting for multivariable confounders. In addition, higher plasma copper concentration was associated with higher MCI risk, while higher zinc-to-copper ratio was significantly associated with lower MCI risk in T2DM patients.
In this study, the median plasma zinc concentrations in the MCI group and control group were 831.31 (717.91–1043.41) μg/L and 936.29 (827.41–1205.58) μg/L, respectively. These findings are consistent with previous reports (27, 38–39). Our findings confirm previous studies linking low plasma zinc levels with a heightened risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. Specifically, the lower zinc levels in MCI patients compared to controls may indicate a diminished neuroprotective effect, potentially exacerbating cognitive dysfunction in T2DM patients. Conversely, plasma copper levels were found to be significantly higher in MCI patients. This finding is consistent with prior research suggesting that elevated copper concentrations can contribute to the formation of reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress, both of which have been implicated in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases, including AD (40). Elevated copper levels may also interfere with the balance of metal ions in the brain, exacerbating neuronal damage and accelerating cognitive decline. Furthermore, our findings indicate that the risk of MCI increases with higher copper levels corroborates the hypothesis that dysregulated metal homeostasis could be a key factor in the development of cognitive dysfunction in T2DM patients (19). Another key variable Zn/Cu ratio examined in this study was found to be inversely associated with MCI risk. This finding supports the notion that maintaining an optimal balance between zinc and copper is crucial for cognitive health (17). A dysregulated Zn/Cu ratio could impair cellular antioxidant defense, further increasing the risk of neurodegeneration. Previous studies have shown that the Zn/Cu ratio serves as an indicator of systemic metal balance, which is critical for maintaining brain health and preventing cognitive decline (41). The risk of MCI in T2DM patients significantly decreased with increasing zinc concentration and Zn/Cu ratio, and decreasing copper concentration could decrease the risk.
Additionally, we also examined the relationship between plasma zinc and copper levels and plasma Aβ peptides. In our study, plasma Aβ40 levels were lower in MCI compared with controls, while the plasma Aβ42/40 ratio was higher in MCI cases. These findings parallel with previous study, which identified an increased plasma Aβ42- to- Aβ40 ratio as an independent risk factor for cognitive decline in T2DM patients (8). The disruption of Aβ metabolism in both the brain and the periphery has been identified as the underlying mechanism linking the development of diabetes with AD patients (23). A study estimated that in the human central nerve system, the fractional production rate of Aβ is 7.6% per hour, while the clearance rate is 8.3% per hour, respectively (42). The preclinical stage of AD has been identified by the abnormal levels of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), abnormal blood biomarkers including Aβ, tau, and neurofilament light chain, and the presence of normal cognitive function (43). However, changes of CSF or plasma Aβ levels observed were contradictory in AD and control individuals. Some studies reported that the increase of plasma Aβ42 or the Aβ42/40 ratio may be risk factors for AD, while others reported a negative association (35). The differences in these findings may due to most studies being cross-sectional and regarding biomarkers in sporadic AD, failing to capture biomarkers changes during the progression from normal cognitive to AD (43).
To further investigate the potential role of plasma zinc deficiency as a critical factor and intervention target in impaired peripheral Aβ clearance and cognitive dysfunction in individuals with T2DM, this study also examined the association between plasma metals and Aβ40, Aβ42 in T2DM patients. Our findings revealed that the plasma zinc and copper levels were positively associated with Aβ42 but showed no significant association with Aβ40 or Aβ42/40. This lack of association may due to the Aβ deposition in the brain, which subsequently reduces plasma amyloid beta levels (44). On the contrary, a previous study about blood biomarker and cognitive impairment showed plasma zinc levels were negatively correlated with plasma Aβ42 levels (45). These results suggest that while zinc and copper may influence amyloid metabolism, their effects may be more pronounced in specific forms of amyloid beta, such as Aβ42, which is more closely linked to neurodegenerative processes in AD.
There are several strengths in our study. Firstly, we conducted a case-control study in T2DM patients, matching cases and controls by age and sex to minimize the potential confounding effects. Secondly, we explore the association of plasma zinc and copper levels with MCI in T2DM patients to identify potential risk factors. Moreover, the sensitive and reliable ICP-MS method was used to objectively measure plasma zinc and copper levels.
This study had several limitations. First, the retrospective and observational design prevented the evaluation of a causal relationship between plasma zinc, copper, the Zn/Cu ratio and MCI in T2DM patients. Second, the maintenance of zinc homeostasis is dependent on the dynamic equilibrium, and the factors unrelated to zinc status or dietary zinc intake, including tissue catabolism, infection, inflammation, or medications can change the zinc concentration. Third, the limitation of this study was the inability to evaluate the utility of other biomarkers, such as urinary and other tissue zinc and copper levels, in assessing zinc and copper status. Zinc and copper concentrations are known to be affected by other factors, such as inflammation, and fasting or postprandial states. Nevertheless, blood zinc and copper concentrations are currently regarded as valuable and reliable biomarkers.
The investigation confirms a significant association between plasma zinc and copper concentrations and the prevalence of MCI in patients with T2DM.Furthermore, our study provides insights into the relationships between plasma zinc, copper, the Zn/Cu ratio, and Aβ levels in MCI, highlighting their potential role as biomarkers for T2DM-related cognitive impairments. These findings underscore the importance of trace element homeostasis in cognitive function and may inform the development of novel therapeutic strategies aimed at preventing or mitigating cognitive decline in T2DM patients.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from gifted from another research group. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
YJ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LD: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. RC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. NY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ZP: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. BL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LX: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. WC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. HY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81973092) and the Angel Nutrition Research Fund (grant number AF2019003). Both funding bodies funded the study design, and the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data, as well as the writing of the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
AD, Alzheimer’s disease; APOE, Apolipoprotein E; Aβ, β-Amyloid; Aβ42/40, the ratio of Aβ42 to Aβ40; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary atherosclerotic heart disease; CI, confidence interval; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1C; ICP-MS, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; MMSE, mini-mental state examination; SD, standard deviation; RCS, restricted cubic spline; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; Zn/Cu, the ratio of zinc to copper; GAM, generalized additive model.
1. Srikanth, V, Sinclair, AJ, Hill-Briggs, F, Moran, C, and Biessels, GJ. Type 2 diabetes and cognitive dysfunction-towards effective Management of both Comorbidities. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2020) 8:535–45. doi: 10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30118-2
2. Biessels, GJ, and Despa, F. Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes mellitus: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2018) 14:591–604. doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0048-7
3. You, Y, Liu, Z, Chen, Y, Xu, Y, Qin, J, Guo, S, et al. The prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol. (2021) 58:671–85. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01648-9
4. Jia, L, Du, Y, Chu, L, Zhang, Z, Li, F, Lyu, D, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and Management of Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health. (2020) 5:e661–71. doi: 10.1016/s2468-2667(20)30185-7
5. Cong, L, Ren, Y, Wang, Y, Hou, T, Dong, Y, Han, X, et al. Mild cognitive impairment among rural-dwelling older adults in China: a community-based study. Alzheimers Dement. (2023) 19:56–66. doi: 10.1002/alz.12629
6. Petersen, RC, Lopez, O, Armstrong, MJ, Getchius, TSD, Ganguli, M, Gloss, D, et al. Practice guideline update summary: mild cognitive impairment: report of the guideline development, dissemination, and implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of neurology. Neurology. (2018) 90:126–35. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000004826
7. Alzheimer's Association. 2024 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. (2024) 20:3708–821. doi: 10.1002/alz.13809
8. Luo, A, Xie, Z, Wang, Y, Wang, X, Li, S, Yan, J, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated cognitive dysfunction: advances in potential mechanisms and therapies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2022) 137:104642. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104642
9. Pu, S, Xu, Y, Tong, X, Zhang, Y, Sun, X, and Gao, X. Correlation of dietary inflammation index and dietary pattern with mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición English ed. (2024) 71:152–62. doi: 10.1016/j.endien.2024.01.008
10. Ventriglia, M, Brewer, GJ, Simonelli, I, Mariani, S, Siotto, M, Bucossi, S, et al. Zinc in Alzheimer's disease: a Meta-analysis of serum, plasma, and cerebrospinal fluid studies. J Alzheimers Dis. (2015) 46:75–87. doi: 10.3233/jad-141296
11. Galvez-Fernandez, M, Powers, M, Grau-Perez, M, Domingo-Relloso, A, Lolacono, N, Goessler, W, et al. Urinary zinc and incident type 2 diabetes: prospective evidence from the strong heart study. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:2561–9. doi: 10.2337/dc22-1152
12. Singh, H, Jain, DJ, Jain, DA, and Devendra, DC. Evaluate and analyze of trace elements in type 2 diabetes mellitus journal of Population Therapeutics & Clinical. Pharmacology. (2024) 31:151–7. doi: 10.53555/jptcp.v31i7.6907
13. Samadi, A, Isikhan, SY, Tinkov, AA, Lay, I, Doşa, MD, Skalny, AV, et al. Zinc, copper, and oxysterol levels in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Nutr. (2020) 39:1849–56. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.07.026
14. Hansen, AF, Simić, A, Åsvold, BO, Romundstad, PR, Midthjell, K, Syversen, T, et al. Trace elements in early phase type 2 diabetes mellitus-a population-based study. The Hunt study in Norway. J Trace Elem Med Biol. (2017) 40:46–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.12.008
15. Zargar, AH, Shah, NA, Masoodi, SR, Laway, BA, Dar, FA, Khan, AR, et al. Copper, Zinc, and Magnesium Levels in Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Postgrad Med J. (1998) 74:665–8. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.74.877.665
16. Gembillo, G, Labbozzetta, V, Giuffrida, AE, Peritore, L, Calabrese, V, Spinella, C, et al. Potential role of copper in diabetes and diabetic kidney disease. Meta. (2022) 13:17. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010017
17. Gong, Z, Song, W, and Gu, M. Serum copper and zinc concentrations and cognitive impairment in older adults aged 60 years and older. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2022) 200:1495–501. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02765-4
18. Yu, J, He, Y, Yu, X, Gu, L, Wang, Q, Wang, S, et al. Associations between mild cognitive impairment and whole blood zinc and selenium in the elderly cohort. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2023) 201:51–64. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03136-3
19. Sensi, SL, Granzotto, A, Siotto, M, and Squitti, R. Copper and zinc dysregulation in Alzheimer's disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2018) 39:1049–63. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.10.001
20. Mravunac, M, Szymlek-Gay, EA, Daly, RM, Roberts, BR, Formica, M, Gianoudis, J, et al. Greater circulating copper concentrations and copper/zinc ratios are associated with lower psychological distress, but not cognitive performance, in a sample of Australian older adults. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2503. doi: 10.3390/nu11102503
21. Zhao, D, Huang, Y, Wang, B, Chen, H, Pan, W, Yang, M, et al. Dietary intake levels of Iron, copper, zinc, and manganese in relation to cognitive function: a cross-sectional study. Nutrients. (2023) 15:704. doi: 10.3390/nu15030704
22. Hunt, KW, Cook, AW, Watts, RJ, Clark, CT, Vigers, G, Smith, D, et al. Spirocyclic Β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (Bace1) inhibitors: from hit to lowering of cerebrospinal fluid (Csf) amyloid Β in a higher species. J Med Chem. (2013) 56:3379–403. doi: 10.1021/jm4002154
23. Cheng, Y, Tian, DY, and Wang, YJ. Peripheral clearance of brain-derived Aβ in Alzheimer's disease: pathophysiology and therapeutic perspectives. Transl Neurodegener. (2020) 9:16. doi: 10.1186/s40035-020-00195-1
24. Peng, X, Xu, Z, Mo, X, Guo, Q, Yin, J, Xu, M, et al. Association of Plasma Β-amyloid 40 and 42 concentration with type 2 diabetes among Chinese adults. Diabetologia. (2020) 63:954–63. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05102-x
25. Sun, M, Yan, G, Sun, S, Li, X, Sun, W, and Wang, Y. Malondialdehyde and zinc may relate to severity of microvascular complications in diabetes: a preliminary study on older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Northeast China. Clin Interv Aging. (2024) 19:1141–51. doi: 10.2147/cia.S464615
26. Song, MK, Bischoff, DS, Song, AM, Uyemura, K, and Yamaguchi, DT. Metabolic relationship between diabetes and Alzheimer's disease affected by Cyclo(his-pro) plus zinc treatment. BBA Clin. (2017) 7:41–54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.09.003
27. Hamasaki, H, Kawashima, Y, and Yanai, H. Serum Zn/cu ratio is associated with renal function, glycemic control, and metabolic parameters in Japanese patients with and without type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol. (2016) 7:7. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00147
28. Chun, CT, Seward, K, Patterson, A, Melton, A, and MacDonald-Wicks, L. Evaluation of available cognitive tools used to measure mild cognitive decline: a scoping review. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3974. doi: 10.3390/nu13113974
29. Petersen, RC, Smith, GE, Waring, SC, Ivnik, RJ, Tangalos, EG, and Kokmen, E. Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol. (1999) 56:303–8. doi: 10.1001/archneur.56.3.303
30. Xu, ZP, Yang, SL, Zhao, S, Zheng, CH, Li, HH, Zhang, Y, et al. Biomarkers for early diagnostic of mild cognitive impairment in Type-2 diabetes patients: a multicentre, retrospective, Nested Case-Control Study. EBioMedicine. (2016) 5:105–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.02.014
31. Donohoe, GG, Salomäki, A, Lehtimäki, T, Pulkki, K, and Kairisto, V. Rapid identification of Apolipoprotein E genotypes by multiplex amplification refractory mutation system Pcr and capillary gel electrophoresis. Clin Chem. (1999) 45:143–6. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/45.1.143
32. Zivelin, A, Rosenberg, N, Peretz, H, Amit, Y, Kornbrot, N, and Seligsohn, U. Improved method for genotyping Apolipoprotein E polymorphisms by a Pcr-based assay simultaneously utilizing two distinct restriction enzymes. Clin Chem. (1997) 43:1657–9. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/43.9.1657
33. Li, P, Yin, J, Zhu, Y, Li, S, Chen, S, Sun, T, et al. Association between plasma concentration of copper and gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin Nutr. (2019) 38:2922–7. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.12.032
34. Li, B, Huang, Y, Luo, C, Peng, X, Jiao, Y, Zhou, L, et al. Inverse Association of Plasma Molybdenum with metabolic syndrome in a Chinese adult population: a case-control study. Nutrients. (2021) 13:4544. doi: 10.3390/nu13124544
35. Liu, Y, Zhang, S, He, B, Chen, L, Ke, D, Zhao, S, et al. Periphery biomarkers for objective diagnosis of cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes patients. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:752753. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.752753
36. Chen, Y, Pan, Z, Shen, J, Wu, Y, Fang, L, Xu, S, et al. Associations of exposure to blood and urinary heavy metal mixtures with psoriasis risk among U.S. adults: a cross-sectional study. Sci Total Environ. (2023) 887:164133. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164133
37. Johannesen, CDL, Langsted, A, Mortensen, MB, and Nordestgaard, BG. Association between low density lipoprotein and all cause and cause specific mortality in Denmark: prospective cohort study. BMJ. (2020) 371:m4266. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m4266
38. Shan, Z, Bao, W, Zhang, Y, Rong, Y, Wang, X, Jin, Y, et al. Interactions between zinc Transporter-8 gene (Slc30a8) and plasma zinc concentrations for impaired glucose regulation and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. (2014) 63:1796–803. doi: 10.2337/db13-0606
39. Król, E, Bogdański, P, Suliburska, J, and Krejpcio, Z. The relationship between dietary, serum and hair levels of minerals (Fe, Zn, cu) and glucose metabolism indices in obese type 2 diabetic patients. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2019) 189:34–44. doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1470-3
40. Davies, KM, Mercer, JF, Chen, N, and Double, KL. Copper Dyshomoeostasis in Parkinson's disease: implications for pathogenesis and indications for novel therapeutics. Clin Sci (Lond). (2016) 130:565–74. doi: 10.1042/cs20150153
41. Socha, K, Klimiuk, K, Naliwajko, SK, Soroczyńska, J, Puścion-Jakubik, A, Markiewicz-Żukowska, R, et al. Dietary habits, selenium, copper, zinc and Total antioxidant status in serum in relation to cognitive functions of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Nutrients. (2021) 13:287. doi: 10.3390/nu13020287
42. Bateman, RJ, Munsell, LY, Morris, JC, Swarm, R, Yarasheski, KE, and Holtzman, DM. Human amyloid-Β synthesis and clearance rates as measured in cerebrospinal fluid in vivo. Nat Med. (2006) 12:856–61. doi: 10.1038/nm1438
43. Jia, J, Ning, Y, Chen, M, Wang, S, Yang, H, Li, F, et al. Biomarker changes during 20 years preceding Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390:712–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2310168
44. Iadecola, C. Cerebrovascular effects of amyloid-Beta peptides: mechanisms and implications for Alzheimer's dementia. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2003) 23:681–9. doi: 10.1023/a:1025092617651
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus, zinc, copper, mild cognitive impairment, case-control study
Citation: Jiao Y, Zhang X, Duan L, Cheng R, Yang N, Peng Z, Li B, Xu L, Chen W, Chen J, Liu Y and Yan H (2025) Association of plasma zinc and copper levels with mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front. Nutr. 12:1532080. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1532080
Received: 21 November 2024; Accepted: 27 February 2025;
Published: 12 March 2025.
Edited by:
Amanda N. Carey, Simmons University, United StatesReviewed by:
Yin Li, Tianjin University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Jiao, Zhang, Duan, Cheng, Yang, Peng, Li, Xu, Chen, Chen, Liu and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanchao Liu, bHljQHRqaC50am11LmVkdS5jbg==; Hong Yan, eWFuaG9uZ0BtYWlscy50am11LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.