
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Nutr. , 17 March 2025
Sec. Clinical Nutrition
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2025.1528677
Background: Previous studies have confirmed the relationship between gut microbiota and sleep disorders, characterized by the persistent inability to achieve adequate sleep, with dietary composition playing a key role in maintaining microbiota homeostasis. Our study aims to explore the relationship between the newly proposed Dietary Index for Gut Microbiota (DI-GM) and sleep disorders, as well as whether the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) mediates this relationship.
Methods: This study is based on data from 30,406 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2005 to 2018, a cross-sectional survey that represents the U.S. adult population. We used multivariable logistic regression models to examine the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders. Subgroup interaction analyses were conducted to assess the stability of the results. Mediation analysis was employed to explore the effect of the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) on the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders.
Results: The DI-GM score was significantly negatively correlated with sleep disorders. After adjusting for covariates, each unit increase in DI-GM was associated with a 5% reduction in the prevalence of sleep disorders (p < 0.001). Additionally, there was a trend toward a decrease in the prevalence of sleep disorders with increasing DI-GM (trend p < 0.05). Dose–response curve analysis revealed a linear relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders, with higher DI-GM scores being associated with lower prevalence of sleep disorders. DII was positively correlated with sleep disorders (p < 0.001) and decreased as DI-GM increased (β = −0.37, p < 0.001). Mediation analysis showed that DII significantly mediated the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders, with a mediation proportion of 27.36% (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The results of this study indicate that the DI-GM score was significantly negatively correlated with sleep disorders. A higher DI-GM score is associated with a lower incidence of sleep disorders, while the DII significantly mediated the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders. Specifically, an increase in DII may attenuate the protective effect of DI-GM on sleep disorders.
The persistent inability to achieve adequate sleep is a hallmark of sleep disorders, often manifested by insomnia, sleep apnea syndrome, narcolepsy, and restless legs syndrome (1). According to statistics, 35% of adults in the United States are affected by varying degrees of sleep disorders, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) considers sleep disorders to be a public health epidemic (2, 3). In adults, sleep disorders can lead to daytime sleepiness, mood disturbances, and a decline in memory and motivation, which subsequently affect quality of life and work efficiency. In contrast, sleep disorders in children directly impact cognitive and behavioral development, potentially resulting in more severe consequences (4, 5). Furthermore, sleep disorders are considered risk factors for various diseases and are closely associated with increased mortality from many chronic conditions, placing a significant burden on public healthcare and the economy (6, 7).
Targeted interventions aimed at modulating the gut microbiota have been shown to have therapeutic effects on sleep disorders (8–10). Additionally, growing evidence suggests that dietary patterns are key factors influencing gut microbiota composition, with specific foods or food groups capable of inducing significant changes in the gut microbiome (11). Recently, Kase et al. developed a new dietary index (DI-GM) based on the literature (12). This index is strongly correlated biomarkers of gut microbiome diversity, enabling precise identification of dietary patterns that support microbial diversity. In contrast to HEI-2015 and modified Mediterranean Diet Score (MDS), DI-GM focuses on broader gut microbiome attributes (e.g., production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), microbial phyla changes, and specific bacterial species), providing a more comprehensive assessment of the diet-microbiome relationship. Furthermore, by emphasizing specific foods rather than food categories, DI-GM allows for more targeted dietary recommendations, while demonstrating similar effectiveness as previous indices in evaluating overall dietary health.
The Dietary Inflammation Index (DII) is designed to assess the potential inflammatory effect of dietary components (13). It has been validated in numerous studies as an effective measure of the inflammatory impact of dietary patterns (14). Sleep is strongly linked to inflammation, with diet playing a crucial role in determining systemic inflammation levels. A systematic review has shown that an anti-inflammatory diet (i.e., a lower DII score) is linked to better outcomes in at least one aspect of sleep, with sleep efficiency and wake after sleep onset being the most reported (3). Moreover, a lower DII score has been shown to benefit gut microbiome diversity, which in turn may enhance sleep quality (15).
Thus, we designed a cross-sectional study, incorporating data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) to analyze the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders. We hypothesize that a healthy diet not only promotes gut microbiota diversity but also improves sleep quality. Additionally, this study will explore whether the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) mediates this relationship.
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is based on a complex multi-stage sampling weighting design to obtain a representative sample of the non-institutionalized USA civilian population and is designed to assess the health and nutritional status of the non-institutionalized USA population. The NHANES research project has been approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), which ensures that the study adheres to ethical standards for the protection of participants’ rights and privacy (Accessed April 23, 2024).1
We extracted data from a total of 70,190 participants in the NHANES dataset spanning from 2005 to 2018. After excluding individuals under 20 years of age, pregnant women (n = 31,152), as well as those with missing DI-GM data, DII data (n = 8,559), and incomplete questionnaire data on sleep disorders (n = 33), a final cohort of 30,406 participants was included (Figure 1).

Figure 1. A flow diagram of eligible participant selection in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. DI-GM, Dietary Index for Gut Microbiota; DII, Dietary Inflammatory Index.
The DI-GM includes 14 types of foods and nutrients, with avocados, broccoli, chickpeas, coffee, cranberries, fermented dairy products, fiber, green tea, soy, and whole grains classified as beneficial components, while red meat, processed meat, refined grains, and high-fat diets (≥ 40% of energy from fat) are considered detrimental components (12). The DI-GM was calculated using dietary recall data from NHANES 2005–2018. For more detailed information regarding DI-GM, please refer to previous studies and Supplementary Table S1.
The Dietary Inflammation Index (DII) evaluates the inflammatory potential of an overall diet based on the pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory properties of individual dietary components, including vitamins and minerals (16). A higher DII score (≥ 0) indicates a pro-inflammatory diet, reflecting less healthy dietary habits, while a lower score (< 0) suggests an anti-inflammatory, healthier dietary pattern. The formula used to calculate the DII score is outlined in the Supplementary materials.
According to previous studies (17, 18), the criteria for diagnosing sleep disorders were based on the response to the question “Has a doctor ever told you that you have a sleep disorder?” in the NHANES personal interview questionnaire. Individuals who answered “Yes” were defined as having a sleep disorder (19). For further details, please refer to the NHANES website.
We constructed a directed acyclic graph (DAG) (20) to visualize the hypothesized associations of the primary exposure (Dietary Index for Gut Microbiota) with the outcomes of interest (the prevalence of sleep disorder), and potential covariates. Age, sex, race, marital status, education level, poverty-to-income ratio (PIR), hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia-were included in the multivariable-adjusted models based on previous relevant research (21–23). Detailed information regarding these covariates can be found in Supplementary Table S2. The resulting DAG is presented in Supplementary Figure S1.
Data were analyzed statistically using R (version 4.3.1). During the analysis, we applied the weights recommended by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) to ensure that the data from our survey were nationally representative. Both types of data in this study were analyzed using a weighted calculation method. The weighting variable was the two-day dietary sample weight (WTDR 2D), and the weight calculation formula for 2005–2018 was 1/7 × WTDR 2D. Continuous variables are presented as means ± standard deviations, with p-values determined by the weighted Student’s t-test. For categorical variables (weighted N, %), p-values were computed using the weighted chi-square test (24). The relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders was assessed using multiple multivariable logistic regression models. Additionally, DI-GM was divided into three categories. To ensure the consistency of the relationship, a trend test was performed, and p-values were calculated.
During the analysis, we constructed three multivariable logistic regression models, ranging from an unadjusted model to progressively adjusted models that accounted for confounding factors, including demographic variables and chronic diseases, to comprehensively evaluate the association between DI-GM and sleep disorders. Model 1 was the unadjusted model, Model 2 further adjusted for age, gender, race, education level, and the poverty-to-income ratio (PIR), and Model 3 was the fully adjusted model, which additionally controlled for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. We further explored potential nonlinear relationships through smooth curve fitting and conducted mediation analysis using bootstrap resampling to quantify the mediating effect of DII on the association.
Additionally, the odds ratios (ORs) corresponding to each standard deviation increase in DI-GM were calculated. In the subgroup analyses, we also adjusted for age, sex, race, marital status, education level, PIR, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia to further validate the robustness of our findings.
Finally, the ‘mediation’ package in R software was used to calculate the indirect, direct, and total effects of DI-GM, DII, and sleep disorders. Mediation analysis was conducted using 1,000 bootstrap resamples and variable adjustments to determine whether DII mediates the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders. The formula for calculating the mediation effect is: Indirect effect/ (Indirect effect + Direct effect) × 100% (25). The total effect of DI-GM on sleep disorders (path C), the direct effect of DI-GM on sleep disorders including DII as a mediator (path C′), the effect of DI-GM on DII (path A), the effect of DII on sleep disorders (path B), and the indirect effect of DII on the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders (path A*B) are all represented by regression coefficients (Figure 2).
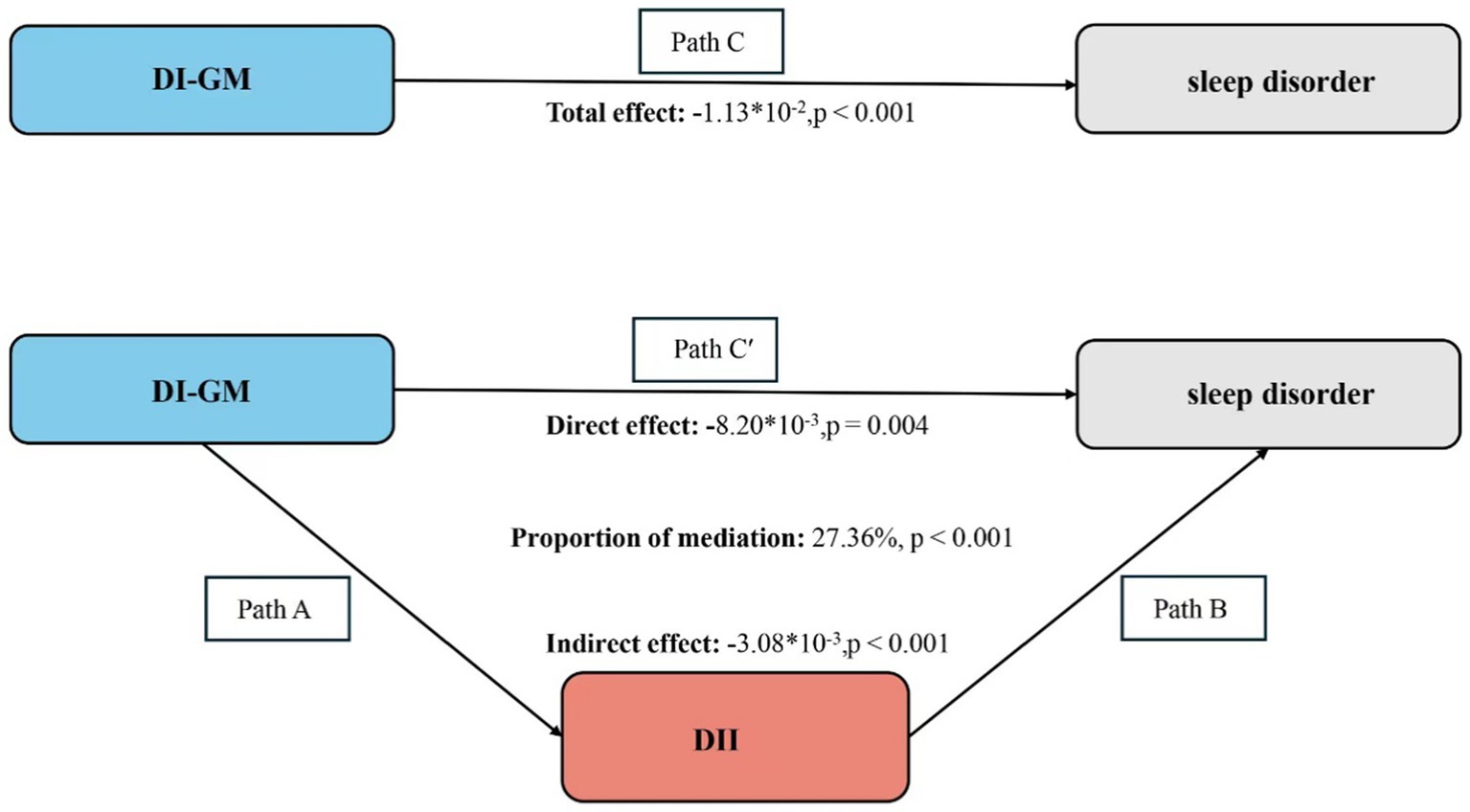
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the mediation effect analysis. Path C indicates the total effect; path C′ indicates the direct effect. The indirect effect is estimated as the multiplication of paths A and B (path A*B). The mediated proportion is calculated as indirect effect/ (indirect effect + direct effect) × 100%. DI-GM, Dietary Index for Gut Microbiota; DII, Dietary Inflammatory Index. Analyses were adjusted for age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
This study included 30,406 participants, representing 135,090,633 US residents. The prevalence of sleep disorders was 17% (equivalent to 22,322,314 individuals). Compared to other racial groups, the prevalence of sleep disorders was higher among “Non-Hispanic White people (67%). Participants with a high school education or higher had a higher prevalence of sleep disorders (84%). The prevalence of sleep disorders was higher among individuals with hypertension, diabetes, or hyperlipidemia (p < 0.05). Additionally, compared to the non-sleep disorder group, participants in the sleep disorder group had lower DI-GM and higher DII scores (p < 0.05). Baseline characteristics are detailed in Table 1.
Table 2 presents the results of a multivariable logistic regression analysis, which showed a significant association between DI-GM, DII, and sleep disorders (p < 0.001). In the fully adjusted model, we found a negative association between DI-GM and the prevalence of sleep disorders (OR 0.95, 95% CI 0.92–0.98). This suggests that for each unit increase in DI-GM, there is a 5% reduction in the prevalence of sleep disorders. The authors further transformed DI-GM from a continuous variable into a categorical variable, dividing it into three tertiles. The average prevalence of sleep disorders in the highest tertile group of DI-GM was 0.18 units lower than in the lowest tertile group (OR 0.82, 95% CI 0.71–0.93), and the trend test within the model confirmed this finding (p < 0.05). Additionally, Model 3 revealed a positive association between DII and sleep disorders, with the most pronounced difference in the highest tertile group: T3 (OR 1.25, 95% CI 1.10–1.42). Finally, the smoothing curve fitting results demonstrated a nonlinear association between DI-GM, DII, and sleep disorders, suggesting a negative nonlinear correlation between DI-GM and sleep disorders (nonlinearity = 0.002) and a positive nonlinear correlation between DII and sleep disorders (nonlinearity = 0.098), as shown in Figure 3.
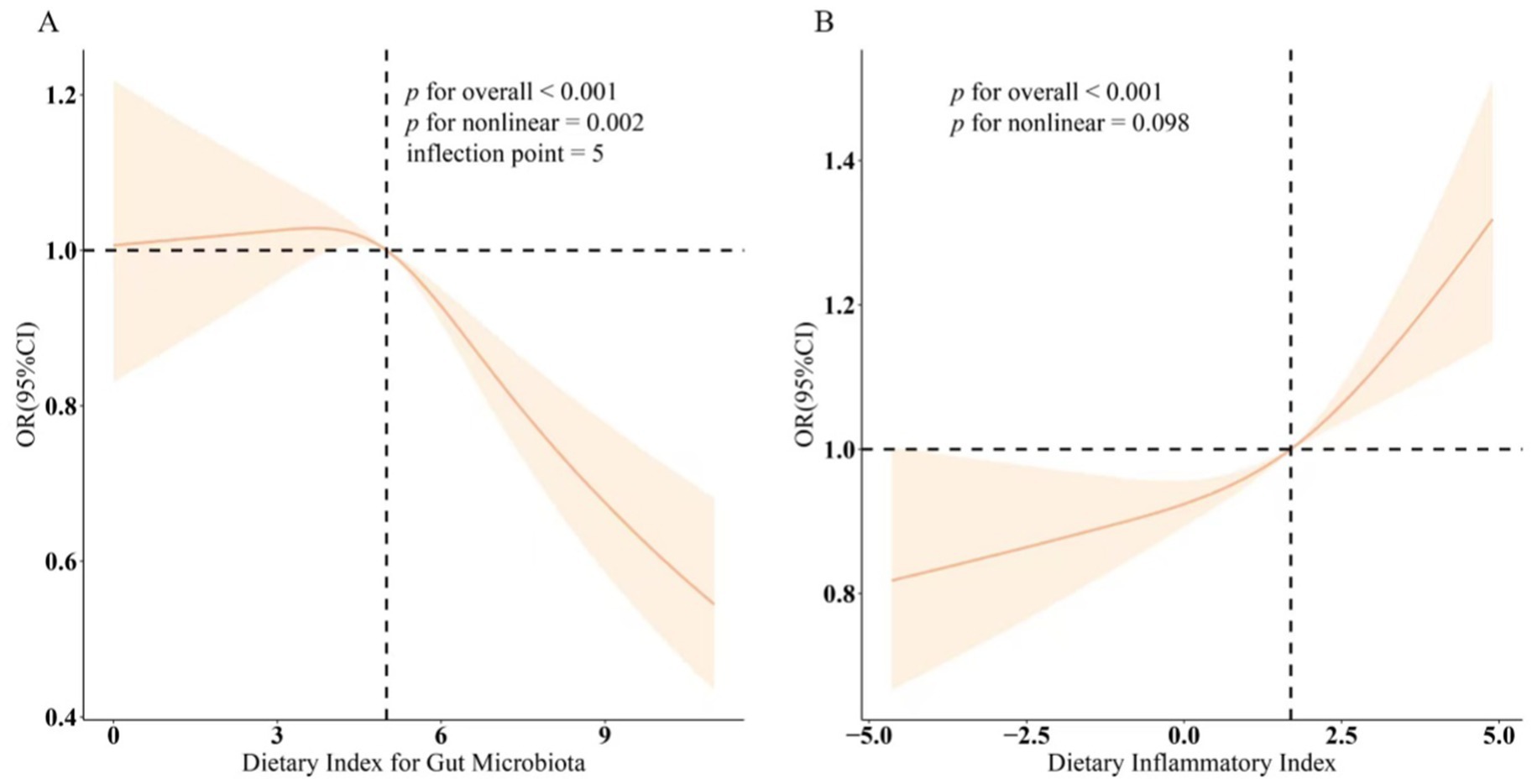
Figure 3. Dose–response relationships between DI-GM, DII, and sleep disorder. (A) DI-GM – sleep disorder. (B) DII – sleep disorder. OR (solid lines) and 95% confidence levels (shaded areas) were adjusted for age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
Figure 4 illustrates the subgroup analysis of how DI-GM is associated with sleep disorders, adjusting for and stratifying by age, gender, education level, marital status, income, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. This analysis further explores the stability of the association between DI-GM, DII, and sleep disorders, as well as potential interactions. In the subgroup analysis, no significant interactions were found between DI-GM and these stratifying variables (p > 0.05), and the negative association remained stable. However, in the analysis of the association between DII and sleep disorders, significant interactions were observed with PIR and hyperlipidemia.
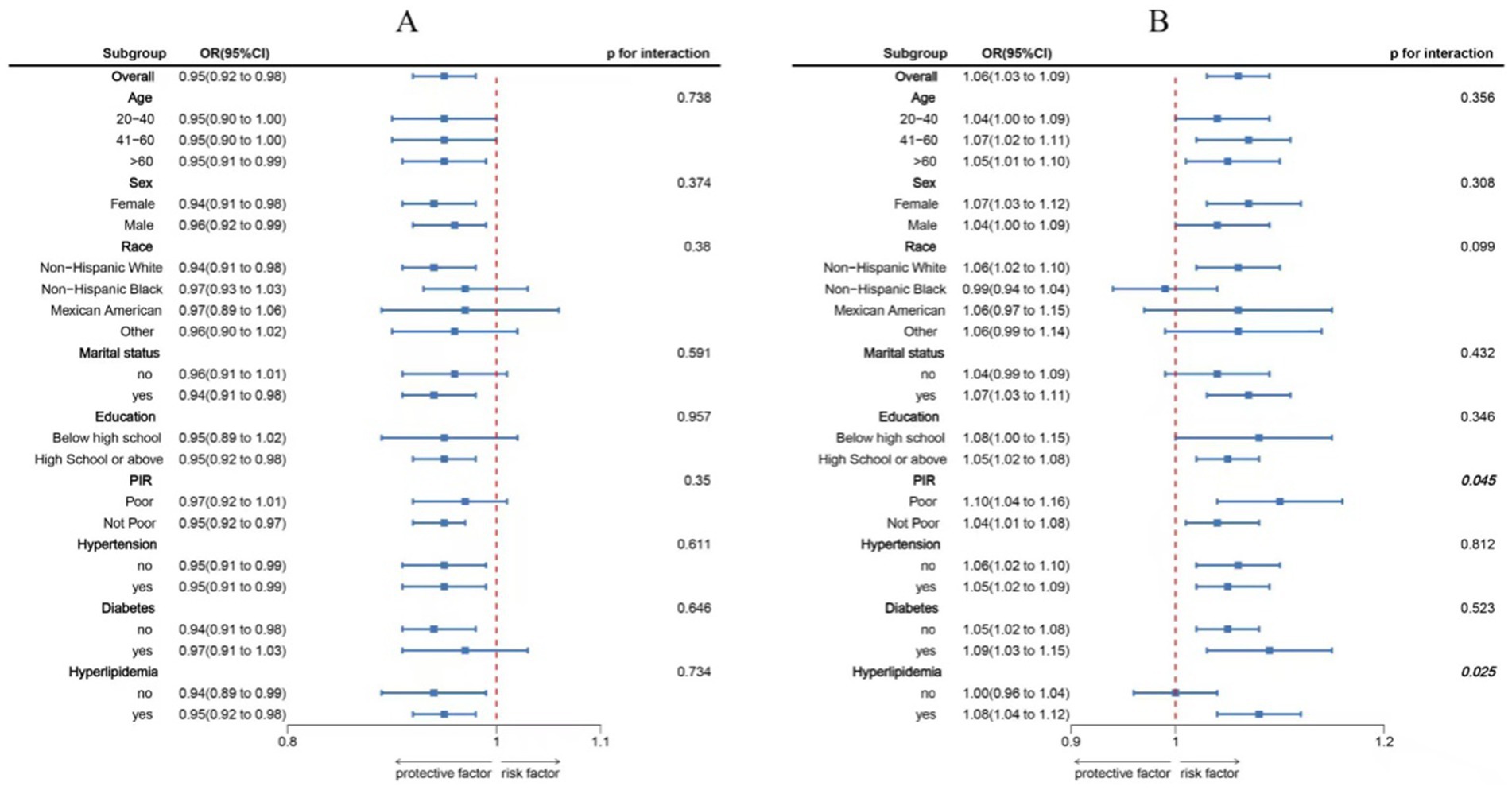
Figure 4. Subgroup analysis between DI-GM, DII, and sleep disorder. (A) DI-GM-sleep disorder. (B) DII-sleep disorder. ORs were calculated as each standard deviation increased in DI-GM/DII. Analyses were adjusted for age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
In Model 3, after adjusting for all covariates, the prevalence of sleep disorders in the highest tertile (T3) of DII was 25% higher compared to the first tertile (T1) (OR 1.25, 95% CI 1.10–1.42). Furthermore, when DII was treated as a continuous variable, its positive association with sleep disorders remained statistically significant (OR 1.06, 95% CI 1.03–1.09), as shown in Table 1. After adjusting for all covariates, there was a significant statistical correlation between DI-GM and DII (β = −0.37, 95% CI: −0.38 to −0.35, p < 0.001) (Table 3). Based on the assumptions of the mediation analysis; after adjusting for all covariates, we observed a mediating effect of DII (Figure 2). The indirect effect of DII (indirect effect = −3.08 × 10−3, p < 0.001; direct effect = −8.2 × 10−3, p = 0.004) mediated 27.36% of the association between DI-GM and sleep disorders (mediating proportion = indirect effect/ (indirect effect + direct effect) × 100%, p < 0.001).
This large population-based study found a significant negative association between DI-GM and the prevalence of sleep disorders, independent of a range of confounding factors such as gender, age and ethnicity. Furthermore, the DII seems to serve as an intermediary factor in the association between DI-GM and sleep disorders. These findings suggest that a higher DI-GM is associated with a lower prevalence of sleep disorders, with DII mediating this relationship, supporting our hypothesis. Results from smooth curve fitting and subgroup analyses further confirmed the stability of these findings.
Sleep is an essential and complex physiological process that plays a critical role in maintaining both our physical and mental health (26). However, sleep disorders affect nearly 20% of adults worldwide, contributing to various chronic cardiovascular and endocrine diseases (27, 28), and are now recognized as a global public health issue (29). Research suggests that the microbiota-gut-brain (MGB) axis can directly or indirectly modulate sleep behavior. For instance, one study found that depletion of the gut microbiota in mice led to disruption of their sleep architecture, as changes in the gut microbiota affected intestinal neurotransmitters, thereby influencing the sleep/wake rhythm of the mice (30). Other studies have also confirmed that metabolites produced by the gut microbiota, such as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), dopamine, and serotonin (5-HT), can directly influence sleep rhythms (31, 32). A randomized controlled trial (RCT) demonstrated that supplementation with probiotics significantly improved sleep quality (33).
Furthermore, a recent study published in Cell Press confirmed that the gut microbiota can also regulate sleep through another pathway: the endocrine route, specifically the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis. Impairment of gut microbiota stability interferes with stress response pathways in the hippocampus and amygdala, leading to dysregulation of the circadian pacemaker in the brain, disturbances in glucocorticoid rhythms, and excessive activation of the HPA axis during sleep/wake transitions, which ultimately results in arousal and insomnia, which is the most common manifestation of sleep disorders (34, 35). The influence of the gut microbiota on the HPA axis can persist throughout the human lifespan, while the HPA axis, in turn, can regulate the MGB axis through cortisol secretion (36). Therefore, the homeostasis of the gut microbiota exerts a profound impact on sleep. Some of our research findings support the above conclusions from a population-based perspective, demonstrating that foods beneficial to gut microbiota diversity such as avocados, broccoli, chickpeas, coffee, cranberries, fermented dairy, fiber, green tea, soybeans, and whole grains, are associated with fewer sleep problems. Additionally, we focused on specific foods rather than broad food categories, which makes the research findings more easily translatable to clinical and public health decision-making.
Dietary modifications and probiotic supplementation are two major interventions for regulating the gut microbiota, with dietary adjustments being the core component. Gut microbiota utilizes dietary fiber as a fermentation substrate to produce beneficial short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), thereby exerting their effects (37). A reduction in dietary fiber intake has been shown to decrease the richness and diversity of the gut microbiota (38, 39). Animal experiments by H. Shi et al. revealed that mice deprived of dietary fiber for 15 weeks exhibited significant gut dysbiosis (reduced Bacteroidetes and increased Firmicutes), along with impaired neurocognitive function (40). In contrast, consuming more fiber boosts the population of beneficial bacteria such as Prevotella and Bifidobacterium, thereby promoting brain health (41, 42). Additionally, a healthy dietary structure is also beneficial for maintaining gut microbiota balance. The Mediterranean diet (MD), defined by a high consumption of fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, has been extensively studied and shown to improve metabolic function and reduce chronic inflammation through its favorable effects on the gut microbiota (43, 44). Studies have confirmed that MD increases the abundance of Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, and Prevotella (45, 46). Conversely, high intake of calories, fats, and processed proteins reduces beneficial Bifidobacterium and increases the abundance of Firmicutes, which are pro-inflammatory (47). A randomized controlled trial by S. Hoscheidt et al. demonstrated that after 4 weeks of adherence to MD, cognitively normal individuals showed improvements in brain perfusion and neurocognitive function (48). Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis confirmed that higher adherence to MD is associated with better sleep features (49). This aligns with our study’s findings, where we observed a lower prevalence of sleep disorders in individuals who preferred whole grains, legumes, fiber, and fresh vegetables, while consuming fewer processed meats and refined grains. This is likely attributable to DI-GM including fiber, whole grains, legumes, and fresh vegetables, all of which are food categories advocated by traditional MD.
The DI-GM framework used in this study also includes probiotic supplementation (fermented dairy products) as part of the scoring criteria. Probiotic supplementation consists of live microorganisms that confer health benefits to the host upon adequate consumption, with their origin typically traced to food production or storage methods (50). Clinical studies have confirmed the positive outcomes of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus on neural function (51). Research has shown that daily supplementation with Lactobacillus acidophilus for 5 weeks can improve sleep quality (52). Animal experiments by Y. Wang et al. also demonstrated that Lactobacillus plantarum MA2 could modulate the TLR4/MYD88/NLRP3 signaling pathway to prevent neuroinflammation (53). Another study found that oral supplementation with Lactobacillus reuteri for 9 weeks effectively increased vitamin D levels in circulation, thereby improving sleep (54). A recent meta-analysis further confirmed previous findings, showing that probiotics have a positive effect on individuals with sleep disorders or poor sleep quality (55). This study, by employing the latest DI-GM tool, explores the combined effects of diet and microbiota on sleep disorders, providing a more comprehensive understanding of how dietary patterns and gut microbiota balance influence neurological functions, including sleep and cognition.
DII is widely used to assess the inflammatory effects of dietary patterns (56). A recent cohort study involving 17,637 European adults confirmed that an increase in the DII is associated with elevated expression of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukins (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (57). Similarly, a cross-sectional study conducted on European adolescents revealed a strong relationship between the DII score and the expression of inflammatory markers such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-2 (58). Sleep is regulated by various inflammatory factors (59), and studies have found that the expression of IL-1β is positively correlated with the duration of non-REM (NREM) sleep (60). Elevated levels of TNF-α are known to enhance the depth of physiological sleep. The NF-κB signaling pathway plays a key role in mediating this effect, which in turn increases the expression of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and adenosine A1 receptors. These molecules play key roles in regulating sleep by influencing neuronal activity and promoting sleep induction and maintenance. Specifically, nitric oxide and COX-2 are involved in sleep regulation by affecting the central nervous system, while adenosine A1 receptors contribute to sleep promotion, particularly during the NREM sleep phase (61). In addition, a higher Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) can lead to an increase in pro-inflammatory microbes in the gut, which subsequently promotes the release of inflammatory factors. This cascade of inflammation can disrupt sleep architecture (15, 62). Our findings are consistent with previous studies.
Our subgroup analysis revealed an interaction between PIR and hyperlipidemia in the relationship between DII and sleep disorders, while no such interaction was found between covariates and the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders. These results highlight the potential benefits of increasing the dietary intake of foods that nourish the gut microbiota in improving sleep in the general population, with a particular focus on health education for low-income groups and individuals with hyperlipidemia. Additionally, our study demonstrated that the DII mediated the inverse relationship between DI-GM and the incidence of sleep disorders, suggesting that a diet with reduced inflammation may contribute to improved sleep (63).
This study provides the first evidence of a link between the DI-GM and sleep disorders. The findings highlight the importance of a health-promoting dietary pattern—such as increasing the intake of broccoli, coffee, fermented dairy, fiber, green tea, and whole grains—that benefits gut microbiota. These results offer a theoretical foundation for incorporating gut microbiota factors into dietary guidelines. Based on this, we propose dietary interventions as a potential strategy to alleviate sleep disorders. The study is based on the NHANES dataset, which provides nationally representative data and accounts for sample weights, making the conclusions reliable and highly generalizable. We also adjusted for confounding factors and covariates, conducting subgroup analyses to examine the stability of the connection between DI-GM and sleep disorders across diverse population groups. Finally, we also identified the mediating role of the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) in the relationship between DI-GM and sleep disorders for the first time (64). However, our study has certain limitations. Initially, the cross-sectional design of this study limits our ability to draw causal conclusions between DI-GM and sleep disorders. To confirm our results, future longitudinal research is necessary. Second, despite adjusting for multiple confounders, it is not possible to eliminate the influence of all potential confounding factors. Moreover, DI-GM may not encompass all beneficial foods related to gut microbiota, and the NHANES dietary and sleep questionnaire data are self-reported, which may introduce recall bias. Lastly, our findings are based on the US population, and further studies in diverse populations are needed to validate and expand our results.
This study identified a significant negative correlation between the DI-GM, a novel index that effectively characterizes dietary patterns favorable to gut microbiota diversity, and sleep disorders. Furthermore, mediation analysis revealed the mediating role of the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) in this relationship. The findings further underscore the role of maintaining a healthy diet and gut microbiota homeostasis in improving sleep quality, highlighting the importance of a balanced dietary structure for gut microbiota diversity and sleep health. However, these conclusions require validation through large-scale prospective studies. In summary, studying dietary health, gut microbiota homeostasis, and sleep quality as an integrated whole could benefit a broader population and reduce the global disease burden.
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found at: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/.
YL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FP: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. XS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1528677/full#supplementary-material
1. Karna, B, Sankari, A, and Tatikonda, G. Sleep disorder In: Stat pearls. Treasure Island, FL: Stat Pearls Publishing LLC (2024)
2. Watson, NF, Badr, MS, Belenky, G, Bliwise, DL, Buxton, OM, Buysse, D, et al. Joint consensus statement of the American Academy of sleep medicine and Sleep Research Society on the recommended amount of sleep for a healthy adult: methodology and discussion. Sleep. (2015) 38:1161–83. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4886
3. Farrell, ET, Hébert, JR, Heflin, K, Davis, JE, Turner-McGrievy, GM, and Wirth, MD. Dietary inflammatory index (DII) and sleep quality, duration, and timing: a systematic review. Sleep Med Rev. (2024) 77:101964. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2024.101964
4. Kansagra, S. Sleep Disorders in Adolescents. Pediatrics. (2020) 145:S204–s209. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2056I
5. Thabet, F, and Tabarki, B. Common sleep disorders in children: assessment and treatment. Neurosciences (Riyadh). (2023) 28:85–90. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2023.2.20220111
6. Robbins, R, and Quan, SF. Sleep Disorders. NEJM Evid. (2024) 3:p. EVIDra2400096. doi: 10.1056/EVIDra2400096
7. Mogavero, MP, DelRosso, LM, Fanfulla, F, Bruni, O, and Ferri, R. Sleep disorders and cancer: state of the art and future perspectives. Sleep Med Rev. (2021) 56:101409. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2020.101409
8. Santi, D, Debbi, V, Costantino, F, Spaggiari, G, Simoni, M, Greco, C, et al. Microbiota composition and probiotics supplementations on sleep quality-a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Clocks Sleep. (2023) 5:770–92. doi: 10.3390/clockssleep5040050
9. Li, L, Liang, T, Jiang, T, Li, Y, Yang, L, Wu, L, et al. Gut microbiota: candidates for a novel strategy for ameliorating sleep disorders. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2024) 64:10772–88. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2228409
10. Huang, S, Hu, H, and Gong, H. Association between the planetary health diet index and biological aging among the U.S. population. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1482959. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1482959
11. Tang, M, Song, X, Zhong, W, Xie, Y, Liu, Y, and Zhang, X. Dietary fiber ameliorates sleep disturbance connected to the gut-brain axis. Food Funct. (2022) 13:12011–20. doi: 10.1039/D2FO01178F
12. Kase, BE, Liese, AD, Zhang, J, Murphy, EA, Zhao, L, and Steck, SE. The development and evaluation of a literature-based dietary index for gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1045. doi: 10.3390/nu16071045
13. Tang, M, Chang, X, Zheng, H, Zeng, F, Zhang, G, He, M, et al. Association of dietary inflammatory index and systemic inflammatory markers with mortality risk in depressed adults: a mediation analysis of NHANES data. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1472616. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1472616
14. Zhao, M, Tuo, H, Wang, S, and Zhao, L. The effects of dietary nutrition on sleep and sleep disorders. Mediat Inflamm. (2020) 2020:3142874. doi: 10.1155/2020/3142874
15. Mirhosseini, SM, Mahdavi, A, Yarmohammadi, H, Razavi, A, Rezaei, M, Soltanipur, M, et al. What is the link between the dietary inflammatory index and the gut microbiome? A systematic review. Eur J Nutr. (2024) 63:2407–19. doi: 10.1007/s00394-024-03470-3
16. Marx, W, Veronese, N, Kelly, JT, Smith, L, Hockey, M, Collins, S, et al. The dietary inflammatory index and human health: an umbrella review of Meta-analyses of observational studies. Adv Nutr. (2021) 12:1681–90. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab037
17. Chen, Y, Zhao, Z, Ding, W, Zhou, Z, and Xiao, M. Association between dietary Fiber intake and sleep disorders: based on the NHANES database. Brain Behav. (2024) 14:e70123. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70123
18. Jiang, J, Li, D, Huang, T, Huang, S, Tan, H, and Xia, Z. Antioxidants and the risk of sleep disorders: results from NHANES and two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1453064. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1453064
19. Watson, NF, Badr, MS, Belenky, G, Bliwise, DL, Buxton, OM, Buysse, D, et al. Recommended amount of sleep for a healthy adult: a joint consensus statement of the American Academy of sleep medicine and Sleep Research Society. Sleep. (2015) 38:843–4. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4716
20. Li, Y, Liu, X, Lv, W, Wang, X, du, Z, Liu, X, et al. Metformin use correlated with lower risk of cardiometabolic diseases and related mortality among US cancer survivors: evidence from a nationally representative cohort study. BMC Med. (2024) 22:269. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03484-y
21. Zhong, M, and Wang, Z. The association between sleep disorder, sleep duration and chronic back pain: results from National Health and nutrition examination surveys, 2009-2010. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:2809. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20263-9
22. Pan, H, and Lin, S. Association between dietary total antioxidant capacity and sleep problems and depressive symptoms among U.S. adults. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1450815. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1450815
23. Wen, Q, Li, J, Li, S, Wang, X, Zhu, H, and Zhang, F. Association between sleep disorder and depression in stroke in the National Health and nutrition examination surveys (NHANES) 2005 to 2014. Sleep Med. (2024) 124:201–8. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2024.09.021
24. Feng, G, Huang, S, Zhao, W, and Gong, H. Association between life's essential 8 and overactive bladder. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:11842. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62842-1
25. Zhang, Q, Yi, J, and Wu, Y. Oxidative stress and inflammation mediate the association between elevated oxidative balance scores and improved sleep quality: evidence from NHANES. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1469779. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1469779
26. Irwin, MR. Why sleep is important for health: a psychoneuroimmunology perspective. Annu Rev Psychol. (2015) 66:143–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010213-115205
27. Huang, T, Mariani, S, and Redline, S. Sleep irregularity and risk of cardiovascular events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 75:991–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.12.054
28. Pugliese, G, Barrea, L, Laudisio, D, Salzano, C, Aprano, S, Colao, A, et al. Sleep apnea, obesity, and disturbed glucose homeostasis: epidemiologic evidence, biologic insights, and therapeutic strategies. Curr Obes Rep. (2020) 9:30–8. doi: 10.1007/s13679-020-00369-y
29. Morin, CM, and Jarrin, DC. Epidemiology of insomnia: prevalence, course, risk factors, and public health burden. Sleep Med Clin. (2022) 17:173–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2022.03.003
30. Ogawa, Y, Miyoshi, C, Obana, N, Yajima, K, Hotta-Hirashima, N, Ikkyu, A, et al. Gut microbiota depletion by chronic antibiotic treatment alters the sleep/wake architecture and sleep EEG power spectra in mice. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:19554. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76562-9
31. Gao, K, Mu, CL, Farzi, A, and Zhu, WY. Tryptophan metabolism: a link between the gut microbiota and brain. Adv Nutr. (2020) 11:709–23. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz127
32. You, M, Chen, N, Yang, Y, Cheng, L, He, H, Cai, Y, et al. The gut microbiota-brain axis in neurological disorders. MedComm. (2020) 5:e656. doi: 10.1002/mco2.656
33. Çİn, NNA, Açik, M, Tertemİz, OF, Aktan, Ç, Akçali, DT, Çakiroğlu, FP, et al. Effect of prebiotic and probiotic supplementation on reduced pain in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Psychol Health Med. (2024) 29:528–41. doi: 10.1080/13548506.2023.2216464
34. Tofani, GSS, Leigh, S-J, Gheorghe, CE, Bastiaanssen, TFS, Wilmes, L, Sen, P, et al. Gut microbiota regulates stress responsivity via the circadian system. Cell Metab. (2024) 37:138–153.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.10.003
35. Nicolaides, NC, Vgontzas, AN, Kritikou, I, and Chrousos, G. HPA Axis and sleep In: KR Feingold, editor. Endotext. South Dartmouth, MA: MDText.Com, Inc (2000)
36. Rusch, JA, Layden, BT, and Dugas, LR. Signalling cognition: the gut microbiota and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1130689. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1130689
37. Wastyk, HC, Fragiadakis, GK, Perelman, D, Dahan, D, Merrill, BD, Yu, FB, et al. Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell. (2021) 184:4137–4153.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.019
38. Sonnenburg, ED, and Sonnenburg, JL. Starving our microbial self: the deleterious consequences of a diet deficient in microbiota-accessible carbohydrates. Cell Metab. (2014) 20:779–86. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.07.003
39. Cronin, P, Joyce, SA, O’Toole, PW, and O’Connor, EM. Dietary fibre modulates the gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1655. doi: 10.3390/nu13051655
40. Shi, H, Ge, X, Ma, X, Zheng, M, Cui, X, Pan, W, et al. A fiber-deprived diet causes cognitive impairment and hippocampal microglia-mediated synaptic loss through the gut microbiota and metabolites. Microbiome. (2021) 9:223. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01172-0
41. Trefflich, I, Jabakhanji, A, Menzel, J, Blaut, M, Michalsen, A, Lampen, A, et al. Is a vegan or a vegetarian diet associated with the microbiota composition in the gut? Results of a new cross-sectional study and systematic review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 60:2990–3004. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1676697
42. Losno, EA, Sieferle, K, Perez-Cueto, FJA, and Ritz, C. Vegan diet and the gut microbiota composition in healthy adults. Nutrients. (2021) 13:2402. doi: 10.3390/nu13072402
43. Zhao, L, Zhang, F, Ding, X, Wu, G, Lam, YY, Wang, X, et al. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science. (2018) 359:1151–6. doi: 10.1126/science.aao5774
44. Ghosh, TS, Rampelli, S, Jeffery, IB, Santoro, A, Neto, M, Capri, M, et al. Mediterranean diet intervention alters the gut microbiome in older people reducing frailty and improving health status: the NU-AGE 1-year dietary intervention across five European countries. Gut. (2020) 69:1218–28. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319654
45. Gutiérrez-Díaz, I, Fernández-Navarro, T, Sánchez, B, Margolles, A, and González, S. Mediterranean diet and faecal microbiota: a transversal study. Food Funct. (2016) 7:2347–56. doi: 10.1039/C6FO00105J
46. Merra, G, Noce, A, Marrone, G, Cintoni, M, Tarsitano, MG, Capacci, A, et al. Influence of Mediterranean diet on human gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2020) 13:7. doi: 10.3390/nu13010007
47. Malesza, IJ, Malesza, M, Walkowiak, J, Mussin, N, Walkowiak, D, Aringazina, R, et al. High-fat, Western-style diet, systemic inflammation, and gut microbiota: a narrative review. Cells. (2021) 10:3164. doi: 10.3390/cells10113164
48. Hoscheidt, S, Sanderlin, AH, Baker, LD, Jung, Y, Lockhart, S, Kellar, D, et al. Mediterranean and Western diet effects on Alzheimer's disease biomarkers, cerebral perfusion, and cognition in mid-life: a randomized trial. Alzheimers Dement. (2022) 18:457–68. doi: 10.1002/alz.12421
49. Godos, J, Ferri, R, Lanza, G, Caraci, F, Vistorte, AOR, Yelamos Torres, V, et al. Mediterranean diet and sleep features: a systematic review of current evidence. Nutrients. (2024) 16:282. doi: 10.3390/nu16020282
50. Salminen, S, Collado, MC, Endo, A, Hill, C, Lebeer, S, Quigley, EMM, et al. The international scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:649–67. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
51. Wang, LJ, Yang, CY, Kuo, HC, Chou, WJ, Tsai, CS, and Lee, SY. Effect of Bifidobacterium bifidum on clinical characteristics and gut microbiota in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Pers Med. (2022) 12:227. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020227
52. Nishida, K, Sawada, D, Kawai, T, Kuwano, Y, Fujiwara, S, and Rokutan, K. Para-psychobiotic Lactobacillus gasseri CP2305 ameliorates stress-related symptoms and sleep quality. J Appl Microbiol. (2017) 123:1561–70. doi: 10.1111/jam.13594
53. Wang, Y, Wang, D, Lv, H, Dong, Q, Li, J, Geng, W, et al. Modulation of the gut microbiota and Glycometabolism by a probiotic to alleviate amyloid accumulation and cognitive impairments in AD rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2022) 66:e2200265. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202200265
54. Jones, ML, Martoni, CJ, and Prakash, S. Oral supplementation with probiotic L. reuteri NCIMB 30242 increases mean circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D: a post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 98:2944–51. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-4262
55. Yu, B, Wang, KY, Wang, NR, Zhang, L, and Zhang, JP. Effect of probiotics and paraprobiotics on patients with sleep disorders and sub-healthy sleep conditions: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1477533. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1477533
56. Hébert, JR, Shivappa, N, Wirth, MD, Hussey, JR, and Hurley, TG. Perspective: the dietary inflammatory index (DII)-lessons learned, improvements made, and future directions. Adv Nutr. (2019) 10:185–95. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy071
57. Lécuyer, L, Laouali, N, Viallon, V, Artaud, F, Hébert, JR, Shivappa, N, et al. Associations between dietary inflammatory scores and biomarkers of inflammation in the European prospective investigation into Cancer and nutrition (EPIC) cohort. Clin Nutr. (2023) 42:1115–25. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.05.012
58. Shivappa, N, Hebert, JR, Marcos, A, Diaz, LE, Gomez, S, Nova, E, et al. Association between dietary inflammatory index and inflammatory markers in the HELENA study. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2017) 61:707. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600707
59. Huang, S, Zhao, W, Choi, S, and Gong, H. Associations of composite dietary antioxidant index with suicidal ideation incidence and mortality among the U.S. population. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1457244. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1457244
60. Veler, H. Sleep and inflammation: bidirectional relationship. Sleep Med Clin. (2023) 18:213–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2023.02.003
61. Kheirandish-Gozal, L, and Gozal, D. Obstructive sleep apnea and inflammation: proof of concept based on two illustrative cytokines. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:459. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030459
62. Zheng, J, Hoffman, KL, Chen, JS, Shivappa, N, Sood, A, Browman, GJ, et al. Dietary inflammatory potential in relation to the gut microbiome: results from a cross-sectional study. Br J Nutr. (2020) 124:931–42. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520001853
63. Wu, R, and Gong, H. The association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the mediating role of dietary inflammatory index. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1427586. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1427586
Keywords: DI-GM, sleep disorder, DII, NHANES, cross-sectional study
Citation: Li Y, Pan F and Shen X (2025) Association of the dietary index for gut microbiota with sleep disorder among US adults: the mediation effect of dietary inflammation index. Front. Nutr. 12:1528677. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1528677
Received: 15 November 2024; Accepted: 28 February 2025;
Published: 17 March 2025.
Edited by:
Gang Ye, Sichuan Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Leila Sadeghi-Reeves, Independent Reviewer, Sion, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2025 Li, Pan and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaofei Shen, Zmx5Zmx5MTIwNUAxMjYuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.