- 1Laboratory Animal Center, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, China
- 2Guangdong Longseek Testing Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, the Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Foshan, China
Introduction: Hyperlipidemia is regarded as one of the crucial factors leading to atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. Gut microbiota plays an important role in regulating host lipid metabolism. Nevertheless, the exact mechanisms behind this remain unclear.
Methods: In the present study, a hyperlipidemic zebrafish model was established using a high-cholesterol diet (HCD) to evaluate the anti-hyperlipidemic effects of Lactobacillus fermentum E15 (L. fermentum E15).
Results: Results showed that L. fermentum E15 effectively reduced lipid accumulation in the blood vessels and liver of HCD-fed zebrafish larvae. Meanwhile, L. fermentum E15 improved abnormal lipid levels, and normalized liver enzyme activity. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis revealed that L. fermentum E15 downregulated the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding factor (SREBP-1), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ), and fatty acid synthase (Fasn), while upregulated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-α). Additionally, metabolomic analysis revealed that L. fermentum E15 produced a series of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), including acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and isovaleric acid. Notably, isovaleric acid contributed to the reduction of lipid droplet accumulation in the liver and blood vessels of HCD-fed zebrafish larvae. In contrast, blocking G-protein coupled receptor 43 (GPR43) with pertussis toxin (PTX) abolished the effects of L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid on reducing lipid accumulation in HCD-fed zebrafish larvae. RT-qPCR results further suggested that both L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid promoted the expression of GPR43 and leptin A, which was inhibited by PTX.
Conclusion: These findings suggested that L. fermentum E15 alleviates HCD-induced hyperlipidemia by activating GPR43 through SCFAs.
1 Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is a common lipid metabolism disorder, which is primarily characterized by elevated levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and low level of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (1). Numerous evidences have shown that hyperlipidemia can cause atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of stroke, hypertension and coronary heart disease, thereby threating human health (2, 3). The liver is a key organ in lipid metabolism involved in a series of physiological activities, including digestion, absorption, transport, degradation and synthesis of lipids (4, 5). Previous study has reported that lipid accumulation in liver can induce hepatotoxicity and inflammatory responses, thereby exacerbating lipid metabolism disorder (6). However, the etiology of hyperlipidemia is complex, and the underlying mechanisms are still required to be fully clarified. Gut microbiota has been associated with hyperlipidemia due to its regulatory role in the storage, degradation and distribution of lipids (7–10). Thus, targeting the gut microbiota is a potential effective strategy for hyperlipidemia treatment.
Probiotics have been applied to alleviate and treat metabolic diseases induced by a high-fat diet (11). Supplementation of a mix of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis LA804 and Lactobacillus gasseri LA806 has been reported to reduce body weight and fat tissue accumulation in mice, simultaneously reducing the plasma triglyceride level, hepatic lipid accumulation, and preventing inflammation (12). Besides, under the hypercholesterolemia condition, the colonization of Lactobacillus plantarum in rats has been shown to reduce TC, TG, LDL-C, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), very-low-density lipoprotein, and atherosclerotic index in the serum (13). In another study by Park et al. regarding the effects of Lactobacillus plantarum in a human clinical trial, Lactobacillus plantarum Q180 was found to decrease the maximum postprandial concentration levels of TG, LDL-C, apolipoprotein B-100, and apolipoprotein B-48 (14). Nevertheless, the mechanisms of action of probiotics require further investigation. Microbiota-driven metabolites including short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), lipopolysaccharides, and bile acids have been reported to act as key signal transduction molecules that couple gut microbiota with the host (7, 15–17). Many studies have demonstrated that microbial metabolite SCFAs can coordinate signals involved in the lipid metabolism and inflammatory physiological regulation of host through mediating G protein-coupled receptors (GPRs) in gut or liver (7, 15, 18, 19). Zebrafish are small freshwater fish which have been proposed to be an emerging and promising animal model for drug screening due to the unique advantages of small size, transparent embryos and short experimental cycles as compared to the mammalian models (20). The lipid metabolism in zebrafish is similar to that of humans, such as intestinal lipid absorption and lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol transport (21), making zebrafish an excellent model for studying lipid metabolism-related diseases (22–24).
In this study, our objective is to evaluate the potential hypolipidemic effect of L. fermentum E15 and the mechanism underlying such an effect. For this purpose, zebrafish were fed a HCD supplemented with L. fermentum E15. Zebrafish larvae were stained using Oil Red O and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) to evaluate lipid deposition after 26 days of incubation. In addition, lipid (TG, TC, LDL-C, and HDL-C) concentrations, liver enzyme (AST and ALT) activities, and the level of oxidative stress were analyzed using relevant assay kits. Furthermore, the content of SCFAs produced by L. fermentum E15 was assessed using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) technology. To verify the hypothesis that the anti-hyperlipidemic effects of L. fermentum E15 occur through SCFAs, we blocked GPR43 in zebrafish larvae by using PTX, an antagonist of GPRs, to investigate the alleviating effects of L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid on lipid metabolism disorders. In addition, the expression levels of key genes involved in lipid metabolism were evaluated using RT-qPCR. The obtained results provide theoretical evidence for the development of L. fermentum E15 dietary supplements.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and reagents
In this experiment, wild-type AB strain zebrafish were purchased from the National Zebrafish Resource Center (Wuhan, China). L. fermentum E15 was isolated from the feces of healthy infants and preserved at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the accession number 22009.
De-Man Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) medium was purchased from Qingdao Hi-Tech Industrial Park Hope Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Qingdao, China). The RNA rapid extraction kit and FastQuant RT Kit (with gDNase) were obtained from Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Sodium isovalerate was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Commercial assay kits for total protein (BCA), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China). Cholesterol, pertussis toxin (PTX), 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA), and Oil Red O were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. All reagents of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) grade and short-chain fatty acid metabolite standards were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
2.2 Morphological identification of Lactobacillus fermentum E15
To observe the macroscopic morphology of L. fermentum E15, the strain was streaked onto MRS solid medium and incubated at 37°C for 48 h in an anaerobic workstation (E500G, GeneScience, United States). The strain was then identified using Gram staining.
2.3 Cultivation and preparation of Lactobacillus fermentum E15
Lactobacillus fermentum E15 was inoculated in MRS medium (5 mL liquid medium, autoclaved at 121°C for 15 min) and cultured at 37°C with gentle shaking at 100 rpm for 24 h. Following this, the inoculum was prepared by inoculating 1 mL of the culture to a 50 mL centrifuge tube containing 40 mL of MRS broth medium. The centrifuge tube was then incubated at 37°C and 100 rpm for 24 h. After incubation, bacterial pellet was collected by centrifuging at 10000 rpm for 5 min, followed by two washes with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and resuspension in E3 water (5 mM NaCl, 0.17 mM KCl, 0.33 mM CaCl₂, and 0.33 mM MgSO₄). The bacterial pellet was adjusted to final concentrations of 1 × 104 CFU/mL, 1 × 105 CFU/mL, and 1 × 106 CFU/mL, respectively.
2.4 Preparation of high cholesterol diet
The normal diet (AP100) for zebrafish larvae supplemented with 12% crude fat and 50% crude protein was purchased from Zeigler (Pennsylvania, United States). After the mixture of cholesterol ether solution with the normal diet, the ether was evaporated to obtain the HCD diet and the final concentration of cholesterol in the HCD diet was determined to be 4% (w/w).
2.5 Maintenance and treatment of zebrafish larvae
Wild-type AB strain adult zebrafish were maintained in a zebrafish breeding system (28.5°C, pH 7.5, conductivity 500–550 μS/cm, 14:10 h light–dark cycle). Afterwards, zebrafish embryos were obtained from those adult zebrafish through natural mating, and then incubated in E3 water (5 mM NaCl, 0.17 mM KCl, 0.33 mM CaCl2, and 0.33 mM MgSO4) and cultured in an incubator at a constant temperature of 28°C. Five days post fertilization (dpf) wild-type AB strain zebrafish larvae were randomly divided into 5 groups with 100 zebrafish larvae in each group, followed by incubation in a 1 L water tank. There were 5 treatments, namely, normal diet (control), 4% HCD (HCD group), 4% HCD + 1 × 104 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 (1 × 104 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 group), 4% HCD + 1 × 105 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 (1 × 105 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 group), or 4% HCD + 1 × 106 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 (1 × 106 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 group). After 5 dpf, the control group was fed with a normal diet. The HCD group and the L. fermentum E15 group were fed with a HCD for a period of 7 days (5–12 dpf). In the following 14-day period (12–26 dpf), the control group continued to be fed with a normal diet, while the HCD group continued to be fed with a HCD. Meanwhile, the L. fermentum E15 group was fed with a HCD supplemented with L. fermentum E15 for 14 days (12–26 dpf). All the groups were fed with the same amount of feed 30 mg/d (twice a day), as described in Figure 1A, and the residual food was removed after 1 h of feeding. All the zebrafish experiments were approved by Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee of Guangdong Human Microecology Engineering Technology Research Center’s Laboratory (approval number: IACUC MC 0329-01-2024).
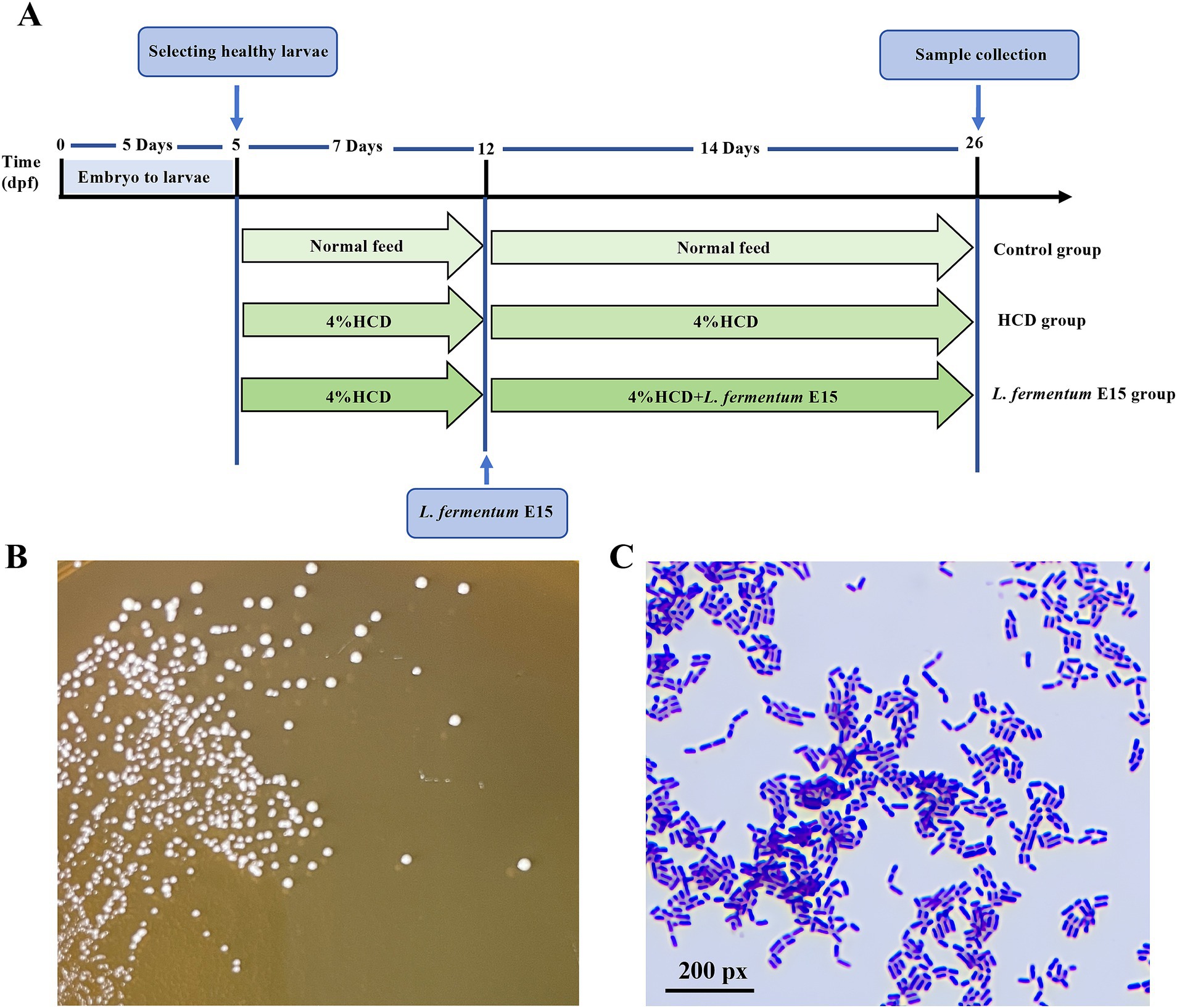
Figure 1. Experiment outline and Characterization of L. fermentum E15. (A) Experimental outline of L. fermentum E15 treated zebrafish larval fed by HCD. (B) L. fermentum E15 colonies on MRS agar cultured anaerobically after 48 h at 37°C. (C) Gram staining properties of L. fermentum E15.
2.6 Oil red O staining
After the intervention, 20 zebrafish larvae were randomly collected from each group, washed twice with E3 water, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde solution for 24 h. These zebrafish larvae were subjected to 25, 50, 75, and 100% 1,2-propanediol gradient dehydration with each gradient for 25 min. Afterwards, these zebrafish were stained with Oil Red O for 48 h and then destained with 1,2-propanediol for 30 min, followed by two washes with PBS. A stereomicroscope (SZ680) was used to capture the images and analyze the lipid accumulation in the zebrafish. The integrated optical density (IOD) values were quantified using ImageJ software to determine the relative quantitative index of lipid accumulation.
2.7 Analysis of body mass index
After 14 days of treatment with L. fermentum E15, 20 zebrafish larvae were randomly selected from each group and anesthetized using tricaine (0.1 g/L). The body length of zebrafish larvae was measured using a stereomicroscope (SZ680), while the weight of zebrafish larvae was measured using an analytical balance. Subsequently, the BMI value (mg/mm2) was calculated as the ratio of the measured weight to body length.
2.8 Biochemical analysis
For each group, 10 zebrafish larvae were randomly selected as one sample, and 3 samples were prepared for subsequent assessments. Briefly, zebrafish larvae were anesthetized in a tricaine solution (0.1 g/L) and subsequently euthanized by immersion in ice-cold E3 water bath as previously described (25). Afterwards, the larvae were washed with pre-chilled PBS and then homogenized in 500 μL of physiological saline. The supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 4°C and 13,000 rpm g for 10 min. The levels of TG, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, AST activity, ALT activity, SOD activity and MDA were measured using commercial assay kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.9 Hematoxylin and eosin staining
The zebrafish larvae were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde solution for 24 h before being processed according to standard procedures for H&E staining. Afterwards, the zebrafish larvae were embedded in paraffin then sectioned and stained with H&E. Microscopy was performed to observe the pathological changes in zebrafish liver tissue using a microscope (Nikon Eclipse E100).
2.10 Measurement of reactive oxygen species
The ROS levels in zebrafish larvae were assessed using the fluorescent probe dye DCFH-DA (Sigma-Aldrich). Fourteen days after the treatment with L. fermentum E15, 10 zebrafish larvae were randomly collected from each group and placed in a 6-well cell culture plate with 5 mL DCFH-DA (5 μM) solution into each well. All the samples were incubated in the dark at 28.5°C for 1 h followed by three washes with E3 water and observation under a fluorescence microscope (Leica DMi8). The statistical analysis of fluorescence intensity of individual zebrafish larvae was performed using the ImageJ software.
2.11 Real-time quantitative PCR analysis
After the intervention, 20 zebrafish larvae were randomly selected from each group and then subjected to euthanasia for total RNA extraction using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, United States) after the intervention. Reverse transcription was conducted using HiScript II Q RT SuperMix (Vazyme, China) to synthesize cDNA. The resultant cDNA served as a template for qPCR analysis on a StepOnePlus real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR system using ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme, China). The PCR cycling protocol consisted of pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 10 s, annealing at 60°C for 15 s, extension at 60°C for 15 s, and a final extension at 60°C for 2 min. The expression levels of target mRNAs were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method by normalizing to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and the corresponding primers are listed in Table 1.
2.12 Detection of SCFAs in the culture supernatant of Lactobacillus fermentum E15
Lactobacillus fermentum E15 was inoculated into MRS broth and cultured at 37°C for 24 h, followed by centrifugation (10,000 rpm, 5 min) to collect the supernatant. Afterwards, 10 μL of internal standard (L-2-chlorophenylalanine, 0.3 mg/mL, prepared in methanol) was added into 100 μL of fermentation supernatant and vortexed for 10 s. 300 μL of methanol-acetonitrile (2:1, v/v) was added and vortexed for 1 min. Ultrasonic extraction was performed in ice water bath for 10 min and maintained at −20°C for 30 min. The supernatant was then collected by centrifugation at 13000 rpm, 4°C for 15 min. Next, 200 μL of the supernatant was transferred to an LC–MS/MS injection vial. The concentrations of SCFAs including acetic acid, propionic acid, isobutyric acid, butyric acid, 2-methylbutyric acid, isovaleric acid, valeric acid, 2,2-dimethylbutyric acid, 2-ethylbutyric acid, 3,3-dimethylbutyric acid, 2-methylhexanoic acid, 3-methylhexanoic acid, 4-methylhexanoic acid in the culture supernatant were analyzed using LC - MS/MS.
2.13 Detection of SCFAs of Lactobacillus fermentum E15 in zebrafish
A total of 400 wild-type AB strain zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf were randomly divided into four groups (100 larvae in each group) and incubated in 1 L tanks. There are four groups in this experiment: the normal diet group, the normal diet+ L. fermentum E15 group, the HCD group, the HCD + L. fermentum E15 group. Starting from 5 dpf, the normal diet group was fed a normal diet. The normal diet+ L. fermentum E15 group was fed a normal diet together with 1 × 106 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15. The HCD group was fed a HCD. The HCD + L. fermentum E15 group was fed a HCD together with 1 × 106 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15. Each group was fed an equal amount of feed, 30 mg/day (twice daily), and residual food was removed one hour after feeding. After 10 days, 20 zebrafish larvae in each group were randomly selected as one sample, and 3 samples were prepared for assessing SCFAs. Thirty zebrafish were put into a 1.5 mL EP tube with 400 μL of extract solution (methanol-acetonitrile-water = 2:2:1, v/v/v) and forty small steel balls. The EP tube was placed in the refrigerator at −80°C for 5 min, and then the contents of the EP tube were ground in the grinder (60 Hz, 2 min). The sample was centrifuged at low temperature for 15 min (13,000 rpm, 4°C) to collect the supernatant. The acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and isovaleric acid in the supernatant were detected using LC–MS/MS.
2.14 Effects of isovaleric acid on lipid accumulation and expression of GPR43 and leptin a mRNA in zebrafish
A total of 420 wild-type AB strain zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf were randomly divided into six groups (70 zebrafish larvae in each group) then incubated in 1 L water tanks. These six groups comprised a series of treatments, including the control group (fed a normal diet), the HCD group (fed a HCD), the L. fermentum E15 group (fed a HCD and 1 × 106 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15), the L. fermentum E15+ pertussis toxin (PTX) group (fed a HCD, 1 × 106 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 and 50 ng/mL PTX), the isovaleric acid group (fed a HCD and 100 μM isovaleric acid), and the isovaleric acid + PTX group (fed a HCD, 100 μM isovaleric acid and 50 ng/mL PTX). After 5 dpf, the control group was fed a normal diet (30 mg/d, twice a day), while the other groups were fed a HCD (30 mg/d, twice a day) for 7 days (5–12 dpf). In the following 14-day period (12–26 dpf), the control group and HCD group continued to be fed as described above. Meanwhile, the L. fermentum E15 group was fed a HCD with the addition of L. fermentum E15 (30 mg/d, twice a day). The L. fermentum E15 + PTX group was fed a HCD, 1 × 106 CFU/mL of L. fermentum E15, and 50 ng/mL of PTX. The isovaleric acid group was fed a HCD and 100 μM of isovaleric acid. The isovaleric acid+PTX group was fed a HCD, 100 μM of isovaleric acid, and 50 ng/mL PTX. All the groups had residual food removed after 1 h of feeding. After the intervention, the lipid accumulation in the zebrafish body was evaluated using Oil Red O staining. Meanwhile, the RT-qPCR was employed to analyze the expression of GPR43 and leptin A mRNA.
2.15 Statistical analysis
All the data were expressed as mean values ± standard deviation (SD), and the statistical analyses were performed using SPSS (version 20.0). One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey multiple comparisons test was used for comparison between multiple groups. A p value<0.05 was considered as statistically significant. The graphs were obtained using GraphPad Prism 5 software.
3 Results
3.1 Morphological characteristics of Lactobacillus fermentum E15
Lactobacillus fermentum E15 grew well on MRS medium. After 48 h of incubation, the bacterial colonies appeared circular, with a milky, waxy, and white surface, with entire margin (Figure 1B). Gram staining confirmed that the strain is Gram-positive (Figure 1C).
3.2 Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can reduce lipid accumulation in the HCD-fed zebrafish larvae
No obvious lipid accumulation can be observed in the liver and blood vessels of the control group, whereas a substantial accumulation of lipid droplets can be detected in those of the HCD group (Figure 2A). Notably, the accumulation of red lipid droplets in the liver and blood vessels of zebrafish larvae treated with L. fermentum E15 was significantly reduced compared with the HCD group. Meanwhile, the DOI values in the L. fermentum E15 group (1 × 104 CFU/mL group: 2955.18 ± 418.74; 1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 1984.73 ± 344.58; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 1536.17 ± 354.87) were significantly lower than those in the HCD group (3881.41 ± 397.32) (p < 0.001; Figure 2B). Additionally, the BMI was increased by HCD diet (0.029 ± 0.002 mg/mm2) as compared with the control group (0.023 ± 0.004 mg/mm2) (p < 0.001), suggesting that obesity was induced (Figure 2C, Table S1). The L. fermentum E15 treatment (1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 0.027 ± 0.002 mg/mm2; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 0.027 ± 0.001 mg/mm2) significantly inhibited the increase of BMI as compared to the HCD group (p < 0.05). The liver histopathological observations showed that the liver tissue of the control group was intact with dense arrangement of liver cells (Figure 2D). Meanwhile, many lipid vacuoles, deformed hepatocytes, and irregular arrangements in the liver tissue were observed in the HCD group, and the liver cells lost normal features with irregular arrangement. In contrast, there was a significant amelioration in the L. fermentum E15 (1 × 106 CFU/mL) group, which showed a significant reduction of lipid vacuoles in the liver issue with normal morphology and arrangement of liver cells. These results suggested that L. fermentum E15 can remarkably improve the HCD diet-induced lipid accumulation in the liver and blood vessels.
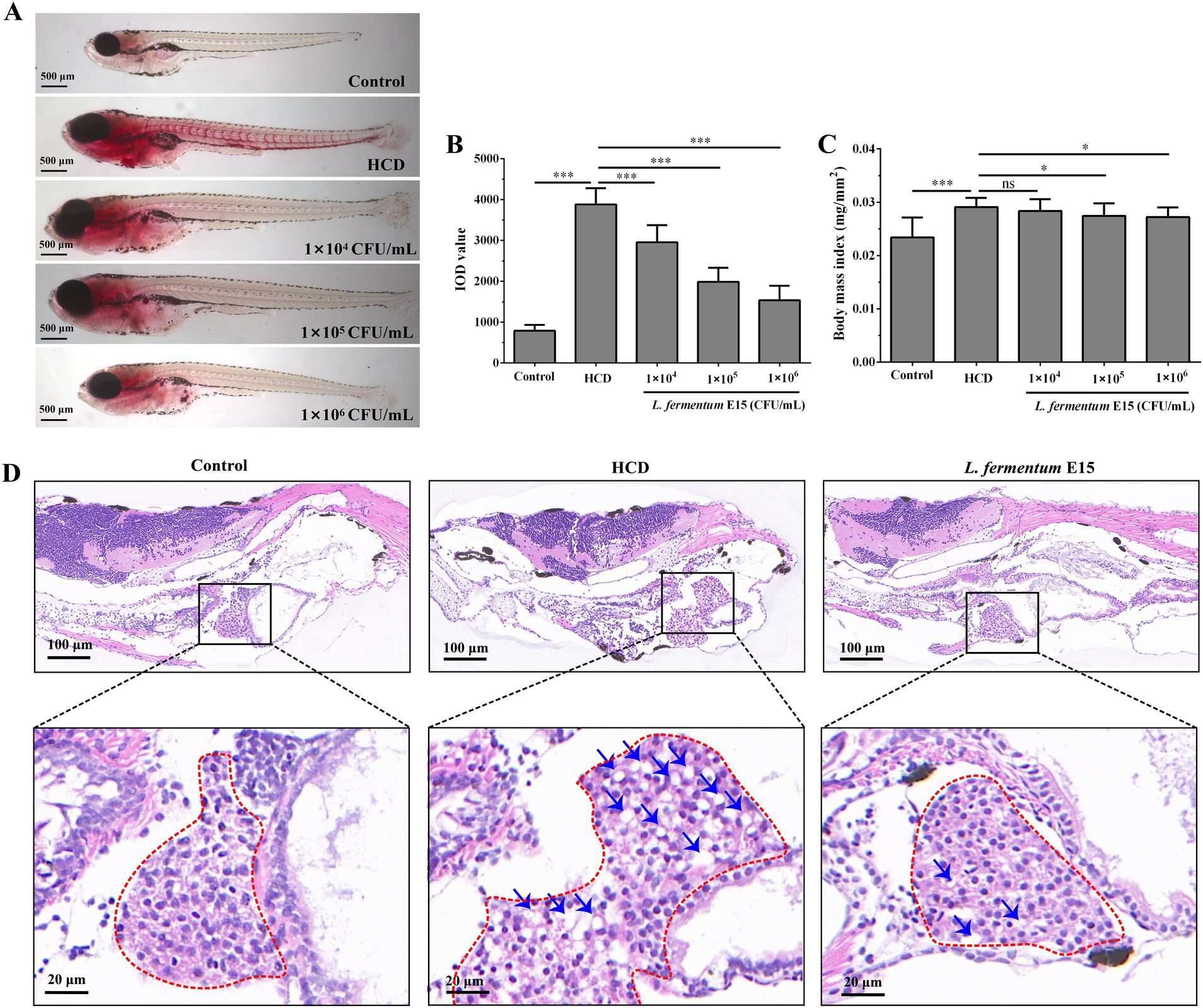
Figure 2. Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can improve lipid accumulation induced by a HCD in the liver and blood vessels of zebrafish. (A) Representative images of lipid accumulation in zebrafish using Oil Red O staining. (B) Zebrafish IOD values. The data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 20). (C) Zebrafish BMI index. The data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 20). (D) H&E staining of zebrafish liver paraffin sections (lipid droplets indicated by blue arrows). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, and ns indicates that it is not statistically significant. p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant calculated by One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
3.3 Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can improve lipid metabolic disorder and liver function abnormalities in the HCD-fed zebrafish larvae
The lipid-lowering effect of L. fermentum E15 was further evaluated by assessing the levels of TG, TC, LDL-C and HDL-C. As compared with the control group (TG: 1.910 ± 0.113 mmol/g prot; TC: 0.594 ± 0.100 mmol/g prot; LDL-C: 0.095 ± 0.016 mmol/g prot), higher levels of TG (4.916 ± 0.427 mmol/g prot), TC (1.260 ± 0.042 mmol/g prot) and LDL-C (0.186 ± 0.005 mmol/g prot) were detected in the HCD group (p < 0.001), while the level of HDL-C (0.009 ± 0.002 mmol/g prot) was significantly lower than in the control group (0.023 ± 0.004 mmol/g prot) (p < 0.01) (Figures 3A–D). After the intervention of L. fermentum E15, compared with the HCD group, the levels of TG (1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 3.182 ± 0.446 mmol/g prot; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 2.753 ± 0.186 mmol/g prot), TC (1 × 104 CFU/mL group: 1.008 ± 0.041 mmol/g prot; 1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 0.941 ± 0.076 mmol/g prot; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 0.682 ± 0.083 mmol/g prot), and LDL-C (1 × 104 CFU/mL group: 0.155 ± 0.011 mmol/g prot; 1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 0.143 ± 0.014 mmol/g prot; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 0.116 ± 0.013 mmol/g prot) were significantly reduced (p < 0.05), and the level of HDL-C (1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 0.017 ± 0.002 mmol/g prot; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 0.019 ± 0.003 mmol/g prot) was increased significantly (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, the biochemical indicators ALT and AST were also assessed to reflect liver function. The activity of ALT (31.972 ± 2.379 U/g prot) and AST (57.963 ± 4.214 U/g prot) in zebrafish larvae was significantly increased by feeding HCD as compared to the control group (ALT: 11.522 ± 0.737 U/g prot; AST: 37.432 ± 3.618 U/g prot) (p < 0.05). As compared to the HCD group, the ALT (1 × 104 CFU/mL group: 27.405 ± 1.340 U/g prot; 1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 19.764 ± 0.889 U/g prot; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 16.508 ± 1.289 U/g prot) and AST (1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 45.659 ± 2.560 U/g prot; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 43.881 ± 2.971 U/g prot) activities of zebrafish larvae in L. fermentum E15 group were significantly decreased (p < 0.05), suggesting that L. fermentum E15 can ameliorate lipid metabolic disorder and liver function abnormalities (Figures 3E,F).
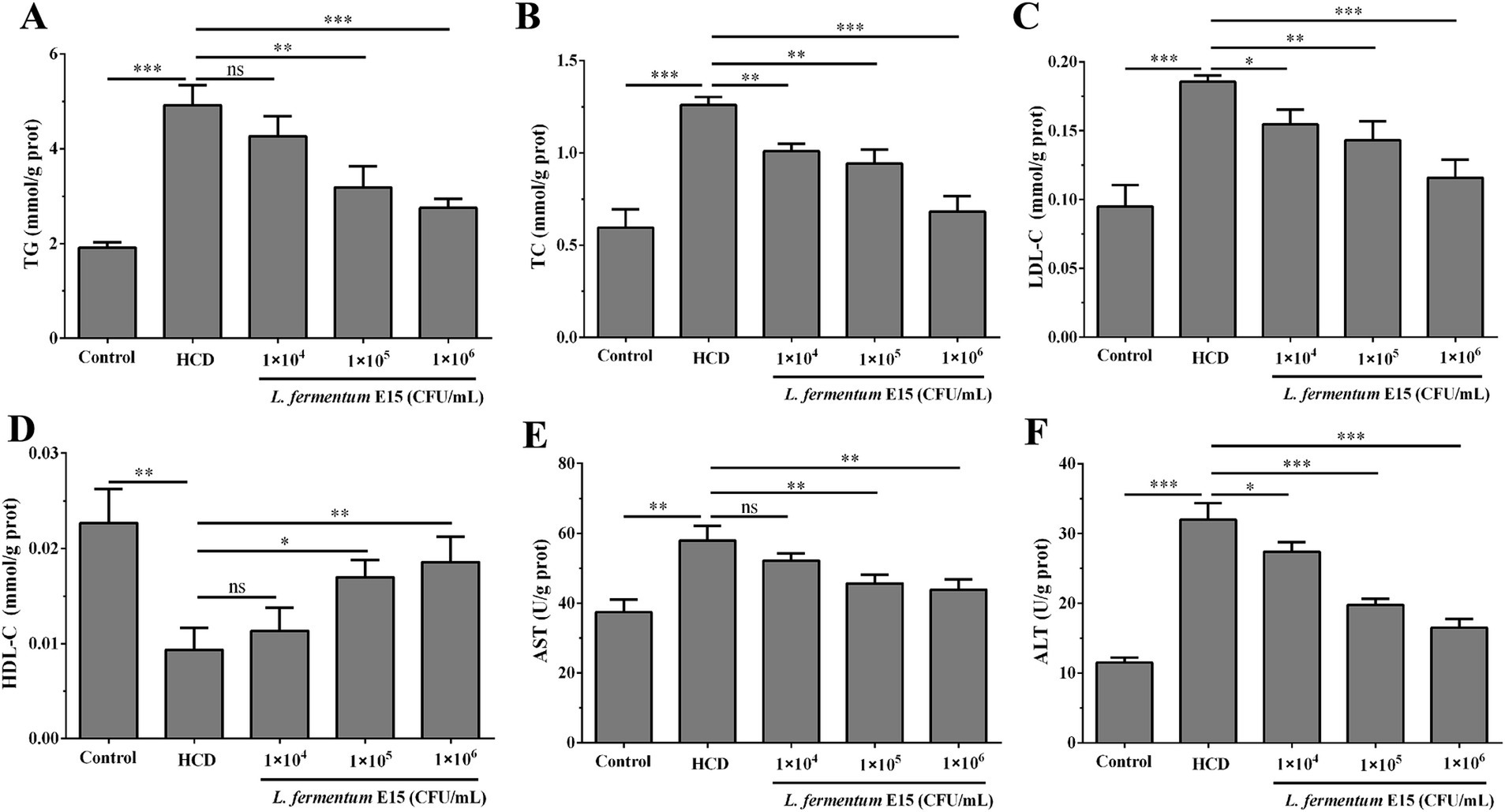
Figure 3. Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can improve lipid metabolic disorder and liver function abnormalities. The levels of (A) TC, (B) TG, (C) LDL-C, and (D) HDL-C in zebrafish larvae. Activities of (E) ALT and (F) AST in zebrafish larvae. The data are presented as mean values ± SD of three samples (n = 10 zebrfish for each sample). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ns indicates that it is not statistically significant. p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant calculated by One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
3.4 Effects of Lactobacillus fermentum E15 on genes related to lipid metabolism
To determine the association between the alterations in the aforementioned biochemical parameters and the alterations in gene expression, the mRNA expression levels of SREBP-1, PPAR-γ, Fasn, and PPAR-α lipid metabolism-related molecules were detected. The RT-qPCR analysis showed that compared with the control group, mRNA expression levels of SREBP-1 (2.81 fold), PPAR-γ (3.16 fold) and Fasn (3.07 fold) in HCD-induced zebrafish larvae were significantly increased (p < 0.001) (Figures 4A–C), while those of PPAR-α (0.52 fold) were significantly decreased (p < 0.001) (Figure 4D). In addition, the zebrafish in 1 × 104 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 group (SREBP-1: 2.24 fold; PPAR-γ: 2.66 fold), 1 × 105 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 group (SREBP-1: 2.04 fold; PPAR-γ: 1.89 fold), and 1 × 106 CFU/mL L. fermentum E15 group (SREBP-1: 1.36 fold; PPAR-γ: 1.48 fold) showed a significant reduction in mRNA expression levels of SREBP-1 and PPAR-γ as compared to the HCD group (p < 0.01; Figures 4A,B). The mRNA expression levels of Fasn showed a significant reduction in the L. fermentum E15 group (1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 2.41 fold; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 1.78 fold) compared with the HCD group (p < 0.01) (Figure 4C). Moreover, the L. fermentum E15 groups had a significantly higher mRNA expression level of PPAR-α (1 × 104 CFU/mL group: 0.67 fold; 1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 0.83 fold; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 0.90 fold) compared with the HCD group (p < 0.05; Figure 4D). These results showed that L. fermentum E15 probably alleviated HCD-induced hyperlipidemia by regulating lipid metabolism disorder.
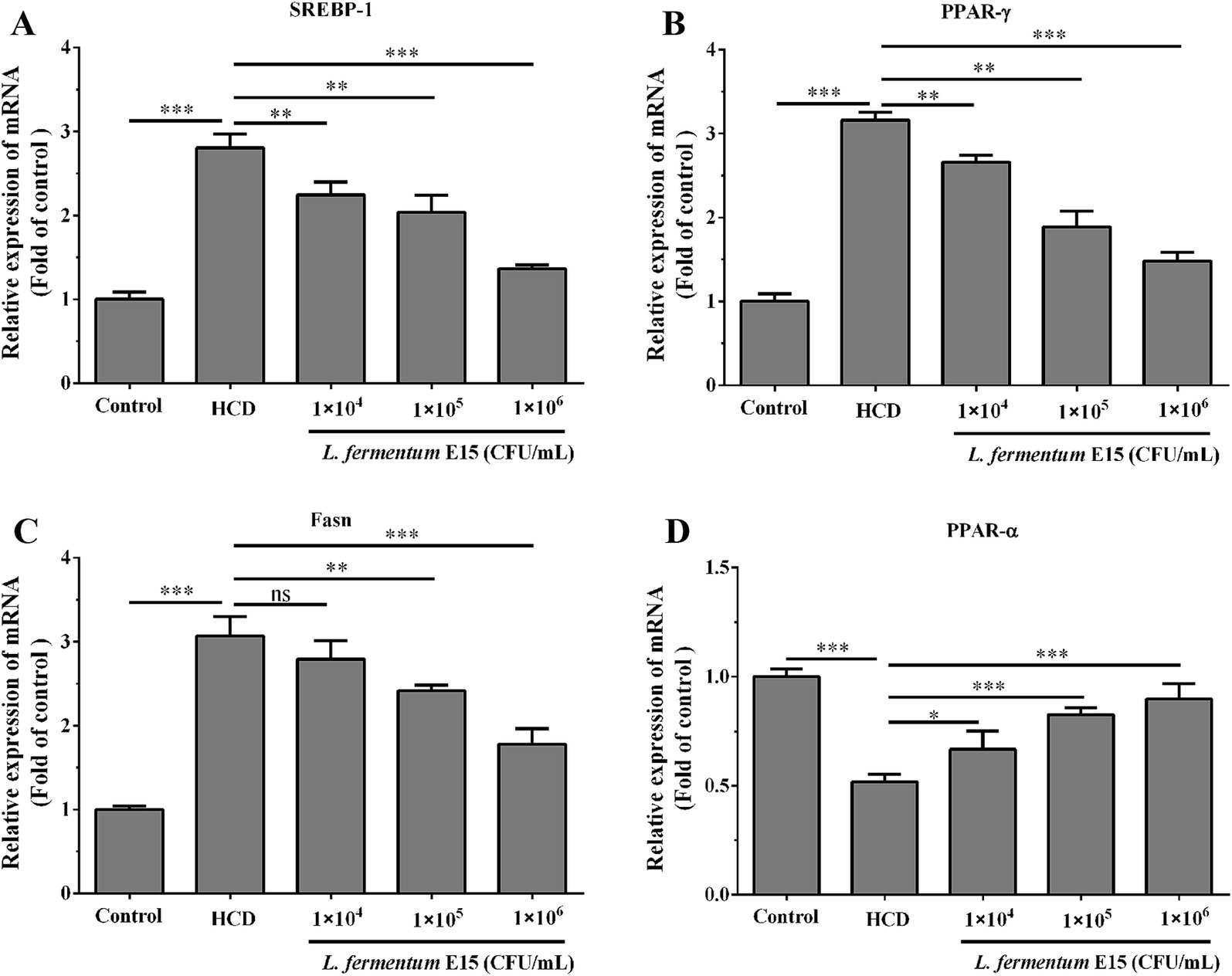
Figure 4. Expression levels of mRNA associated with lipid metabolism in zebrafish larvae regulated by L. fermentum E15. (A) mRNA expression level of SREBP-1. (B) mRNA expression level of PPAR-γ. (C) mRNA expression level of Fasn. (D) mRNA expression level of PPAR-α. The data are presented as mean values ± SD of three samples (n = 20 zebrfish for each sample). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ns indicates that it is not statistically significant. p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant calculated by One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
3.5 Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can reduce oxidative damage in the HCD-fed zebrafish larvae
High-fat dietary intake is highly associated with oxidative stress, including increased ROS production and severe oxidative damage to liver tissue (26). The fluorescence intensity of DCFH-DA staining showed that the ROS levels in zebrafish larvae in the HCD group (470.30 ± 49.57%) were significantly increased as compared to the control group (100.00 ± 23.98%) (p < 0.001; Figures 5A,B). The abdominal and liver tissues of zebrafish larvae in the HCD group showed an high ROS level, which was possibly attributed to the lipid accumulation in these regions. However, L. fermentum E15 significantly reduced the ROS level (1 × 104 CFU/mL group: 169.10 ± 10.66%; 1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 155.66 ± 26.03%; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 114.14 ± 24.78%) in the HCD-fed zebrafish larvae as compared to the HCD group (p < 0.001; Figures 5A,B). Previous study showed that SOD belongs to an essential antioxidant enzyme that plays a critical role in mitigating the negative effects of free radicals in the body. Conversely, MDA is a cytotoxic molecule that induces cross-linking and polymerization of macromolecules including proteins (24). The effects of L. fermentum E15 on SOD activity and MDA levels in the HCD-fed zebrafish larvae were further investigated. As compared to the control group (SOD: 45.42 ± 1.31 U/mg prot; MDA: 6.69 ± 1.38 nmol/mg prot), a dramatic reduction of SOD activity (14.89 ± 2.09 U/mg prot) was detected in the HCD group (p < 0.001), while the MDA level (27.21 ± 2.65 nmol/mg prot) was significantly higher (p < 0.001; Figures 5C,D). The L. fermentum E15 group showed a significantly higher SOD activity (1 × 104 CFU/mL group: 21.48 ± 3.54 U/mg prot; 1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 32.54 ± 1.63 U/mg prot; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 36.17 ± 3.06 U/mg prot) and a lower MDA level (1 × 104 CFU/mL group: 118.34 ± 2.86 nmol/mg prot; 1 × 105 CFU/mL group: 12.98 ± 2.04 nmol/mg prot; 1 × 106 CFU/mL group: 10.54 ± 0.93 nmol/mg prot) as compared to the HCD group (p < 0.05). These results suggested that L. fermentum E15 can mitigate the oxidative damage in the HCD-fed zebrafish larvae.
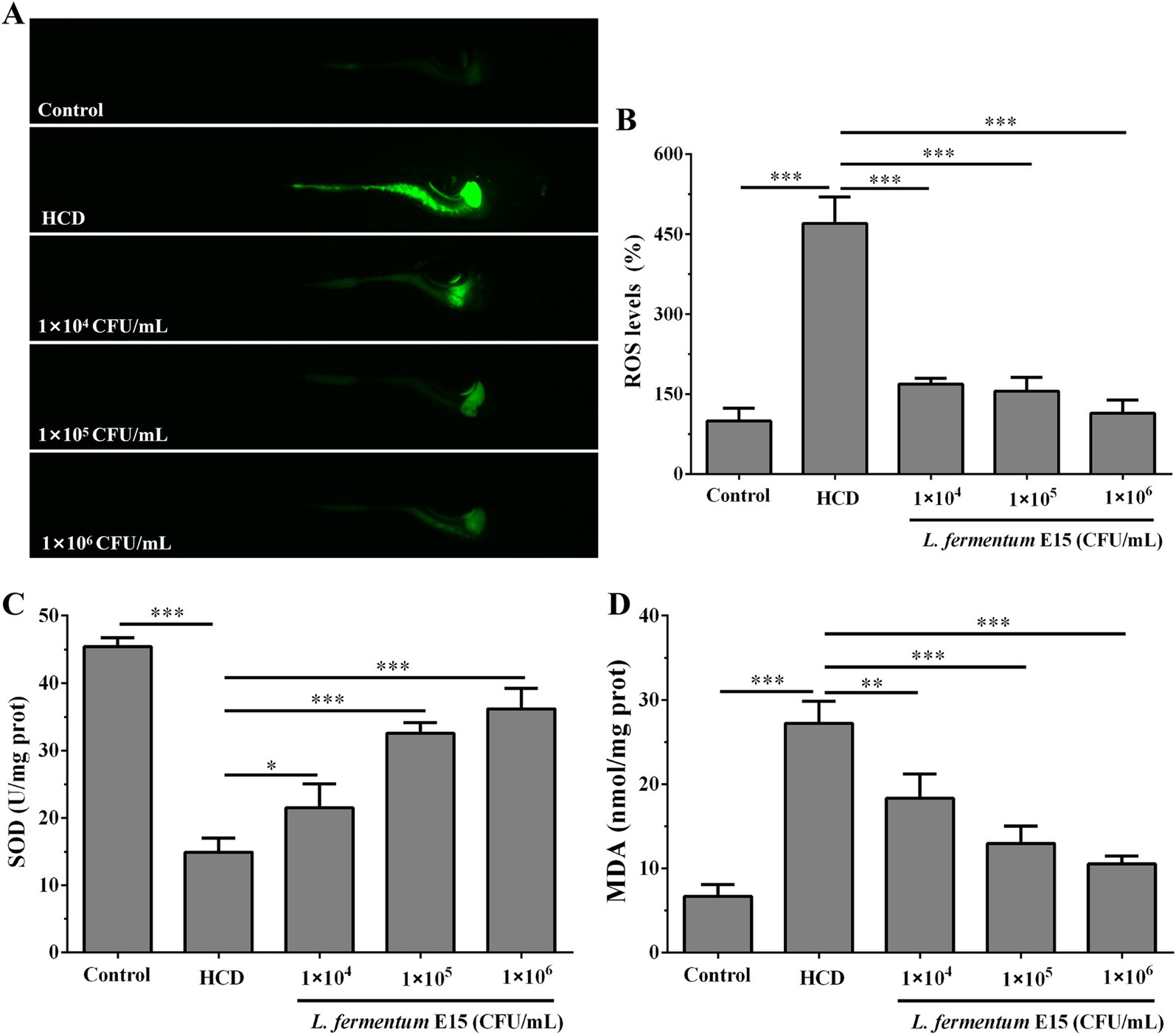
Figure 5. Effect of L. fermentum E15 on metabolic oxidative stress in HCD-fed zebrafish larvae. (A) Detection of ROS production in zebrafish larvae using DCFH-DA staining. (B) Quantification of ROS levels. The data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 10). (C) SOD activity in zebrafish larvae. The data are presented as mean values ± SD of three samples (n = 10 zebrfish for each sample). (D) MDA levels in zebrafish larvae. The data are presented as mean values ± SD of three samples (n = 10 zebrfish for each sample). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant calculated by One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
3.6 Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can produce SCFAs
SCFAs are the main metabolic products of gut microbiota that serve as an important energy source for colonic epithelial cells (27) and play a critical role in inhibiting the occurrence of obesity by regulating host energy metabolism and gut homeostasis (27, 28). Thus, the content of SCFAs in the culture supernatant of L. fermentum E15 was assessed using LC–MS/MS targeted metabolomics technology. The levels of acetic acid (1711.97 ± 72.02 ng/mL), propionic acid (79.68 ± 4.83 ng/mL), butyric acid (26.00 ± 0.80 ng/mL) and isovaleric acid (31.92 ± 1.57 ng/mL) in the culture supernatant of L. fermentum E15 were significantly increased as compared to the MRS medium group (acetic acid: 865.35 ± 7.09 ng/mL; propionic acid: 29.86 ± 0.83 ng/mL; butyric acid: 0 ng/mL; isovaleric acid: 0 ng/mL) (Figures 6A–D; p < 0.001). Additionally, we assessed the levels of acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and isovaleric acid in zebrafish larvae fed either a normal diet or a HCD. Our results showed that supplementation with L. fermentum E15 significantly increased the levels of acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and isovaleric acid both in zebrafish larvae fed either a normal diet or a HCD (Figures 6E–H) (p < 0.05).
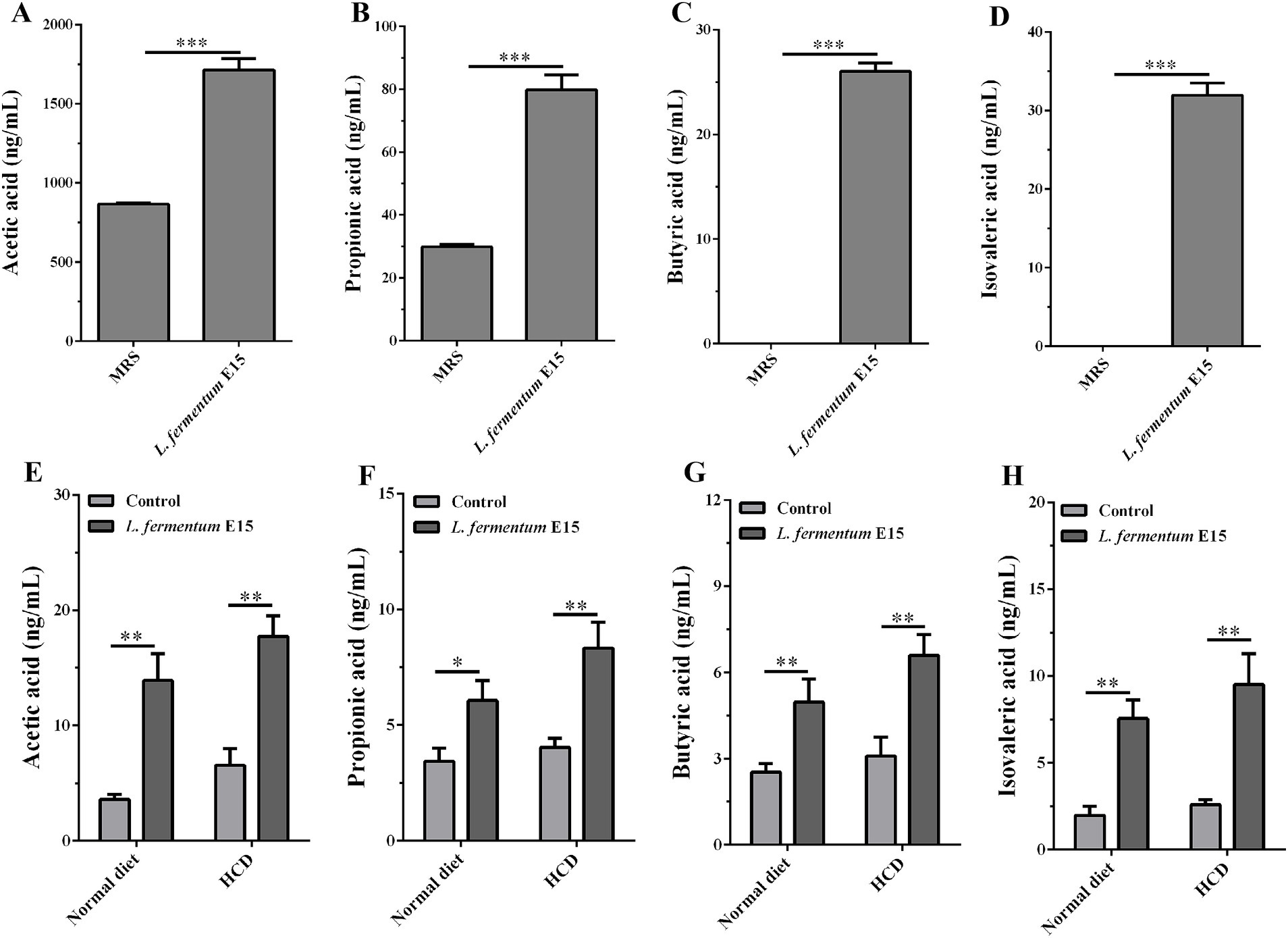
Figure 6. Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can produce SCFAs. The levels of (A) acetic acid, (B) propionic acid, (C) butyric acid, and (D) isovaleric acid in the culture supernatant of L. fermentum E15. The data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3). The levels of (E) acetic acid, (F) propionic acid, (G) butyric acid, and (H) isovaleric acid in zebrafish after supplementing with L. fermentum E15. The data are presented as mean values ± SD of three samples (n = 20 zebrfish for each sample). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant calculated by One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
3.7 Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can alleviate HCD-induced lipid accumulation via SCFAs-mediated activation of GPR43 receptor
A recent study has reported that Lactobacillus acidophilus inhibits non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through producing valeric acid (29). To shed light on the mechanisms by which L. fermentum E15 improves hyperlipidemia, the effects of isovaleric acid on lipid accumulation in HCD-fed zebrafish larvae were further investigated. The GPR43 receptor has been reported to be the primary receptor for SCFAs in intestine and liver (7, 29). To investigate whether the anti-hyperlipidemic effects of L. fermentum E15 are mediated by SCFAs, PTX was used to block the GPR43 receptor (29). A significantly lower accumulation of red lipid droplets was detected in the liver and blood vessels of zebrafish larvae from both the L. fermentum E15 group and the isovaleric acid group as compared to the HCD group (Figure 7A). In contrast, the effects of L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid on reducing lipid accumulation in HCD-fed zebrafish larvae were eliminated when the GPRs inhibitor (PTX) was used (Figures 7A,B). These findings suggested that isovaleric acid metabolized by L. fermentum E15 can reduce lipid accumulation in HCD-fed zebrafish larvae.
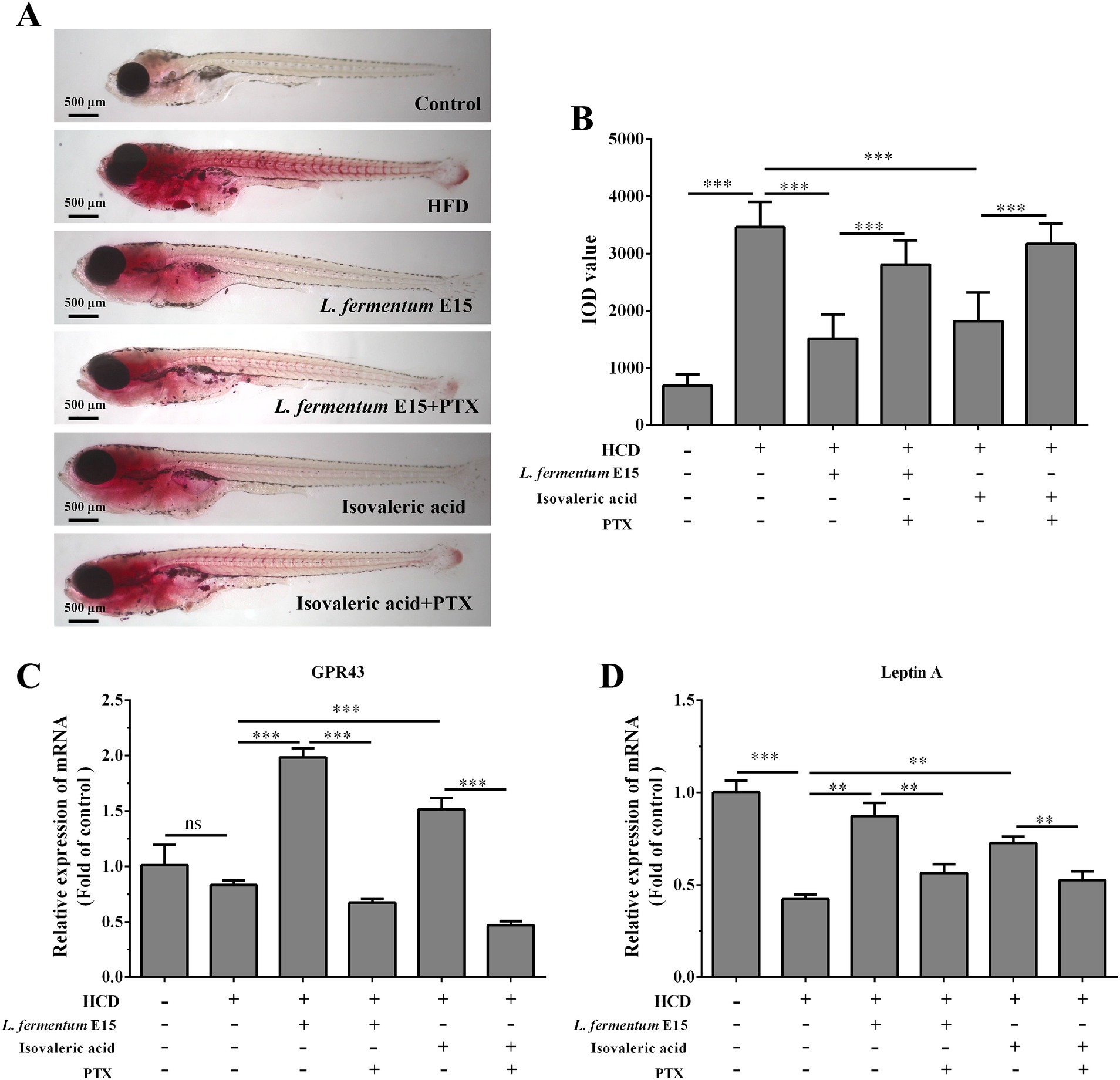
Figure 7. Lactobacillus fermentum E15 can alleviate HCD-induced lipid accumulation by activating the GPR43 receptor through the metabolism of SCFAs. (A) Representative images of lipid accumulation in zebrafish detected by Oil Red O staining. (B) IOD values in zebrafish. The data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 20). The mRNA expression levels of GPR43 (C) and leptin A (D) detected by RT-qPCR. The data are presented as mean values ± SD of three samples (n = 20 zebrfish for each sample). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ns indicates that it is not statistically significant. p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant calculated by One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
In order to investigate the mechanism behind the effects of L. fermentum E15 on HCD-induced hyperlipidemia in zebrafish larvae, the mRNA expression levels of GPR43 and leptin A were detected. Significantly increased mRNA expression levels of GPR43 and leptin A were observed in the L. fermentum E15 group (GPR43: 1.98 fold; leptin A: 0.87 fold) and isovaleric acid group (GPR43: 1.51 fold; leptin A: 0.73 fold) as compared to the HCD group (GPR43: 0.83 fold; leptin A: 0.42 fold) (p < 0.01; Figures 7C,D). In addition, the GPRs inhibitor PTX effectively inhibited the promoting effects of L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid on mRNA expression levels of GPR43 and leptin A (p < 0.01). These results suggested that L. fermentum E15 can alleviate HCD-induced lipid accumulation by activating the GPR43 receptor through the metabolism of SCFAs.
4 Discussion
Hyperlipidemia is mainly characterized by abnormal blood lipid metabolism, which can lead to various metabolism-related diseases such as atherosclerosis, diabetes and obesity (1, 2). Many studies have demonstrated a strong interaction between gut microbiota and hyperlipidemia along with its metabolic comorbidities (7, 9, 10). Nevertheless, the specific mechanism behind lipid-lowering effects of microorganisms remains unclear. In the present study, our objective was to investigate the potential hypolipidemic effect of L. fermentum E15 and the mechanisms underlying this effect. To achieve this, the anti-hyperlipidemic effects of L. fermentum E15 were assessed through Oil Red O staining, H&E staining, lipid concentrations (TG, TC, LDL-C, and HDL-C), and liver enzyme activities (AST and ALT). Additionally, the levels of SCFAs produced by L. fermentum E15 were measured using LC–MS/MS. To verify the hypothesis that the anti-hyperlipidemic effect of L. fermentum E15 occurs through SCFAs, we blocked GPR43 in zebrafish larvae using PTX to evaluate the alleviating effects of L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid on lipid metabolism disorders.
The main pathological change in hyperlipidemia is manifested as an abnormal serum lipid level. It should be noted that there is a significant positive correlation between the serum TC level and the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases (30). The increased TG, LDL-C, and reduced HDL-C are highly associated with metabolic diseases (31). Moreover, the liver is a key organ that regulates lipid metabolism including the metabolism of TG and TC (32, 33). In the case of hypercholesterolemia, excess lipids can accumulate in the form of lipid droplets in liver cells, leading to NAFLD and liver damage (34). Typically, ALT and AST are important indicators for evaluating liver damage (35). In the present study, it was found that L. fermentum E15 could effectively reduce lipid accumulation in blood vessels and liver of HCD-fed zebrafish larvae, decreasing BMI and hepatic lipid vacuoles (Figures 2A–D). Additionally, L. fermentum E15 treatment can prevent the HCD-induced abnormal levels of TC, TG, LDL-C and HDL-C (Figures 3A–D) and the increased activities of ALT and AST (Figures 3E,F). These results suggested that L. fermentum E15 can alleviate lipid accumulation in the liver and blood vessels of HCD-fed zebrafish larvae, and improve liver function. Mounting evidence indicates significant gender disparities in the incidence of hyperlipidemia, with women being more susceptible to dyslipidemia than men (36, 37). A previous study has suggested that 1-deoxynojirimycin exerts a remarkable female-preferential antihyperlipidemic effect through specifically enriching Akkermansia and Clostridium XIVa and elevating an active microbial metabolite in female mice (38). This finding suggests that gender disparities in regulating the gut microbiota could offer a novel strategy for developing next-generation antihyperlipidemic drugs (38). Therefore, further research is needed to explore gender differences in the hypolipidemic effect of L. fermentum E15 on adult zebrafish, which will provide an in-depth theoretical basis for therapeutic exploitation of L. fermentum E15 as a female-specific intervention against hyperlipidemia and provide a methodological reference for evaluating antihyperlipidemic drugs with gender differences. Previous study has confirmed that Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG can reduce hepatic lipid accumulation and suppress the progression of diet-induced liver steatosis (39). Besides, Lactobacillus fermentum HNU312 can ameliorate lipid accumulation in liver and adipose tissue of HCD-fed mice, thereby decreasing body weight and BMI. Moreover, Lactobacillus fermentum HNU312 can significantly reduce the levels of TG, TC, and LDL-C (40). These findings are consistent with our current results. However, further work is required to understand the action pathways and mechanisms of Lactobacillus fermentum HNU312.
PPAR-γ and SREBP-1 are transcription factors that promote lipid synthesis and storage in adipose tissue by positively regulating the expression of key lipogenic genes, such as Fasn (41, 42). In this work, HCD feeding caused hyperlipidemia, resulting in increased gene expression of SREBP-1, PPAR-γ and Fasn (Figures 4A–C). The reduced gene expressions of SREBP-1 and PPAR-γ might decrease lipid accumulation in the liver of hyperlipidemic zebrafish treated with L. fermentum E15. Previous studies have suggested that PPAR-α plays a role in fatty acid oxidation (35, 43). Therefore, a decrease in the expression of PPAR-α leads to dyslipidemia and lipid accumulation in the liver. The gene expression of PPAR-α was increased by L. fermentum E15 (Figure 4D), indicating that the fatty acid oxidation was enhanced. These results suggested that L. fermentum E15 might alleviate HCD-induced hyperlipidemia by regulating lipid metabolic disorders. Additionally, probiotics have the potential to exert persistent benefits after the cessation of treatment (44). Therefore, further study is needed to investigate the sustained anti-hyperlipidemia effects of L. fermentum E15 following treatment cessation.
Oxidative stress plays a critical role in the development of NAFLD (26, 45). HCD-induced cellular ROS overload can impair the antioxidant system of the liver, resulting to hepatocyte damage (46, 47). This imbalance in oxidative status can trigger lipid peroxidation, resulting in the production of MDA and excessive ROS, which further promotes the progression of hepatic steatosis (23). In this study, HCD feeding of zebrafish larvae resulted in the persistently high level of ROS, particularly observed around the abdomen and liver (Figure 5A), which correlated with lipid accumulation. It is widely believed that the accumulation of lipid droplets in the abdomen and liver is strongly associated with the increased production of ROS, which potentially leads to lipid peroxidation of liver tissue. The reduced SOD activity can disrupt cellular redox homeostasis to produce oxidative stress and damage. In the present case, L. fermentum E15 reduced the levels of ROS and MDA in HCD-fed zebrafish larvae, while enhancing SOD activity (Figures 5A–D). These results demonstrated that the antioxidant effect of L. fermentum E15 is favorable for protecting HCD-fed zebrafish larvae from the detrimental effects of NAFLD. Additionally, Chaetoceros globosum CGMCC 6882 decreased both H₂O₂-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress in RAW 264.7 cells (48, 49). Therefore, further research is needed to explore the inhibitory effect of L. fermentum E15 on LPS- or H2O2-induced oxidative stress.
One of the primary mechanisms by which the gut microbiota can influence host physiological functions is related to its metabolic activity (50, 51). Numerous studies have demonstrated that SCFAs produced by the gut microbiota act as an energy source for epithelial cells, signaling molecules and gene expression regulators, exerting significant impacts on host physiology (50–53). Gut microbiota has been reported to influence energy supply, blood glucose and lipid homeostasis through SCFAs like butyrate and propionate, thereby regulating the obesity-related physiological and pathological processes (54). A recent study has reported that Lactiplantibacillus plantarum A5 alleviates HCD-induced hyperlipidemia in hamsters by modulating the gut microbiota to enhance the production of SCFAs (55). Additionally, the correlation analysis has indicated that Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y44 complex fermented milk influences hepatic lipid metabolism in HCD-fed C57BL/6 mice by regulating the intestinal flora and promoting SCFA production, ultimately contributing to weight reduction (56). Furthermore, Lactobacillus acidophilus has been reported to inhibit NAFLD-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through the production of valeric acid (29). Taken together, these findings suggest that Lactobacillus spp. may play a role in mitigating HCD-induced hyperlipidemia by promoting the production of SCFAs. In this study, targeted metabolomics analysis was employed to identify the SCFAs metabolized by L. fermentum E15 in vitro, which were identified as acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid and isovaleric acid (Figures 6A–D). Furthermore, in the presence of L. fermentum E15, the levels of acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and isovaleric acid increased in both zebrafish larvae fed a normal diet and those fed an HCD (Figures 6E–H). SCFAs can induce the release of hormones by binding to GPRs, thereby increasing satiety and reducing the food intake (7). Additionally, the increased leptin level can modulate lipid metabolism through signaling regulation (57, 58). The combination of SCFAs, such as butyrate and propionate, with GPR43 suppresses fatty acid breakdown, promotes the secretion of the well-known adipokine leptin, increases energy expenditure and inhibits adipocyte synthesis, thereby reducing lipid metabolism in mice (59). Notably, these effects are absent in GPR43 knockout mice (59). To explore the mechanisms by which L. fermentum E15 influences HCD-induced hyperlipidemia in zebrafish larvae, GPRs antagonist PTX was used to block GPR43 to verify the anti-hyperlipidemic effects of L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid. These findings suggested that L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid can reduce the accumulation of red lipid droplets in the liver and blood vessels of HCD-fed zebrafish larvae (Figures 7A,B). However, PTX could eliminate the effects of L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid on reducing lipid accumulation in HCD-fed zebrafish larvae. Additionally, both L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid enhanced the mRNA expression levels of GPR43 and leptin A (Figures 7C,D). However, PTX significantly inhibited the ability of L. fermentum E15 and isovaleric acid to enhance mRNA expression of GPR43 and leptin A. SCFA acts on GPR43 to mediate leptin response to control the cholesterol levels (58). Leptin has been proposed as a signaling molecule that reduces hepatic lipogenesis and cholesterol synthesis by inhibiting the expression of SREBP-1 and cholesterol-related genes, thereby reducing cholesterol levels and alleviating hepatic steatosis (60, 61). These findings indicated that L. fermentum E15 alleviates HCD-induced hyperlipidemia in zebrafish larvae by activating GPR43 through SCFAs. However, Lactobacillus rhamnosus TR08 has been shown to improve the intestinal microbiota of mice to increase the production of SCFAs, and then improve dyslipidemia (62). Lactiplantibacillus plantarum A5 alleviated HCD-induced hyperlipidemia via regulating gut microbiota to promote SCFAs production (55). Therefore, we will explore the potential of L. fermentum E15 to mediate changes in microbiome composition to promote the production of SCFAs in future work. In addition, previous studies have demonstrated that Lactobacillus plantarum can induce changes in food components, and then the active components in foods are absorbed by the body and exert bioactivity (63–65). Therefore, we will explore the potential of L. fermentum E15 to mediate changes in food components and evaluate whether the resulting active components can exert biological activity in future work.
In summary, the present study reveals that L. fermentum E15 can activate the GPR43 receptors through the metabolism of SCFAs to regulate the gene expression of lipid metabolism-related factors. As a result, L. fermentum E15 ameliorates obesity in HCD-fed zebrafish larvae, reduces the lipid accumulation, and consequently decreases oxidative stress and liver damage.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee of Guangdong Human Microecology Engineering Technology Research Center’s Laboratory (approval no. IACUC MC 0329-01-2024; date of approval: 29 March 2024). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YC: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. KZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YL: Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. XlingL: Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. XyanL: Investigation, Writing – original draft. HO: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. MW: Data curation, Writing – original draft. FQ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. HY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant no. 2023A1515011439), Research Fund of Guangdong Medical University (Grant no. GDMUM2020031), Zhanjiang Non-Funded Science and Technology Tackling Plan Projects (Grant no. 2021B01211), Zhanjiang Science and Technology Tackling Projects (Grant no. 2019A01021).
Conflict of interest
KZ and ZZ were employed by Guangdong Longseek Testing Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1522982/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sun, J, Du, B, Chen, M, Jia, J, Wang, X, and Hong, J. FBXO28 reduces high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in mice by alleviating abnormal lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses. J Endocrinol Investig. (2024) 47:2757–74. doi: 10.1007/s40618-024-02376-5
2. Li, N. Platelets as an inter-player between hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis. J Intern Med. (2024) 296:39–52. doi: 10.1111/joim.13794
3. Siddiqui, R, Ahamed, HN, and Yusuff, I. Bisflavonoids fraction from Araucaria bidwilli hook., reverses hyperlipidemia induced atherosclerosis in high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia, future. J Pharm Sci. (2020) 6:89. doi: 10.1186/s43094-020-00109-y
4. Hodson, L. Hepatic fatty acid synthesis and partitioning: the effect of metabolic and nutritional state. Proc Nutr Soc. (2019) 78:126–34. doi: 10.1017/S0029665118002653
5. ten Hove, M, Pater, L, Storm, G, Weiskirchen, S, Weiskirchen, R, Lammers, T, et al. The hepatic lipidome: from basic science to clinical translation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. (2020) 159:180–97. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.027
6. Gong, X, Li, T, Wan, R, and Sha, L. Cordycepin attenuates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via down-regulation of lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 91:107173:107173. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107173
7. Jia, X, Xu, W, Zhang, L, Li, X, Wang, R, and Wu, S. Impact of gut microbiota and microbiota-related metabolites on hyperlipidemia. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2021) 11:634780. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.634780
8. Nuankham, K, Sitdhipol, J, Chonpathompikunlert, P, Khongrum, J, Kittichaiworakul, R, Noisagul, P, et al. Impact of Lactocaseibacillus (Lactobacillus) paracasei sup. paracasei TISTR 2593 probiotic supplementation on the gut microbiome of hypercholesterolemia patients: a randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. (2024) 16:916. doi: 10.3390/nu16172916
9. Wang, C, Zhao, J, Zhang, H, Lee, YK, Zhai, Q, and Chen, W. Roles of intestinal bacteroides in human health and diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 61:3518–36. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1802695
10. Xu, W, Yu, J, Yang, Y, Li, Z, Zhang, Y, Zhang, F, et al. Strain-level screening of human gut microbes identifies Blautia producta as a new anti-hyperlipidemic probiotic. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2228045. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2228045
11. Le Barz, M, Anhe, FF, Varin, TV, Desjardins, Y, Levy, E, Roy, D, et al. Probiotics as complementary treatment for metabolic disorders. Diabetes Metab J. (2015) 39:291–303. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.291
12. Beau, A, Benoit, B, Le Barz, M, Meugnier, E, Penhoat, A, Calzada, C, et al. Inhibition of intestinal FXR activity as a possible mechanism for the beneficial effects of a probiotic mix supplementation on lipid metabolism alterations and weight gain in mice fed a high fat diet. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2281015. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2281015
13. Aminlari, L, Shekarforoush, SS, Hosseinzadeh, S, Nazifi, S, Sajedianfard, J, and Eskandari, MH. Effect of probiotics Bacillus coagulans and Lactobacillus plantarum on lipid profile and feces Bacteria of rats fed cholesterol-enriched diet, probiotics. Antimicrob Proteins. (2019) 11:1163–71. doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9480-1
14. Park, YE, Kim, MS, Shim, KW, Kim, YI, Chu, J, Kim, BK, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Q180 on postprandial lipid levels and intestinal environment: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel trial. Nutrients. (2020) 12:255. doi: 10.3390/nu12010255
15. Kim, S, Seo, SU, and Kweon, MN. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites tune host homeostasis fate. Semin Immunopathol. (2024) 46:2. doi: 10.1007/s00281-024-01012-x
16. Pathak, P, Helsley, RN, Brown, AL, Buffa, JA, Choucair, I, Nemet, I, et al. Small molecule inhibition of gut microbial choline trimethylamine lyase activity alters host cholesterol and bile acid metabolism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2020) 318:H1474–86. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00584.2019
17. Yang, L, Wu, Y, Yang, J, Li, Y, Zhao, X, Liang, T, et al. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum P470 isolated from fermented Chinese chives has the potential to improve in vitro the intestinal microbiota and biological activity in feces of coronary heart disease (CHD) patients. Nutrients. (2024) 16:945. doi: 10.3390/nu16172945
18. Pi, Y, Fang, M, Li, Y, Cai, L, Han, R, Sun, W, et al. Interactions between gut microbiota and natural bioactive polysaccharides in metabolic diseases: review. Nutrients. (2024) 16:838. doi: 10.3390/nu16172838
19. Secor, JD, Fligor, SC, Tsikis, ST, Yu, LJ, and Puder, M. Free fatty acid receptors as mediators and therapeutic targets in liver disease. Front Physiol. (2021) 12:656441. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.656441
20. Vedder, VL, Aherrahrou, Z, and Erdmann, J. Dare to compare. Development of atherosclerotic lesions in human, mouse, and zebrafish. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2020) 7:109. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00109
21. He, LF, Wang, C, Zhang, YF, Guo, CC, Wan, Y, and Li, YX. Effect of Emodin on hyperlipidemia and hepatic lipid metabolism in zebrafish larvae fed a high-cholesterol diet. Chem Biodivers. (2022) 19:e202100675. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202100675
22. Deng, X, Cheng, L, Qiao, Y, Liu, X, Zhou, Y, Liu, H, et al. Rutin ameliorates HCD-induced cholesterol metabolism disorder in zebrafish larvae revealed by transcriptome and metabolome analysis. Phytomedicine. (2024) 135:156058:156058. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156058
23. Ma, J, Yin, H, Li, M, Deng, Y, Ahmad, O, Qin, G, et al. A comprehensive study of high cholesterol diet-induced larval zebrafish model: a short-time in vivo screening method for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease drugs. Int J Biol Sci. (2019) 15:973–83. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.30013
24. Wang, Y, Pan, Y, Hou, M, Luo, R, He, J, Lin, F, et al. Danggui Shaoyao san ameliorates the lipid metabolism via the PPAR signaling pathway in a Danio rerio (zebrafish) model of hyperlipidemia. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115736. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115736
25. Liu, D, Yu, H, Pang, Q, and Zhang, X. Investigation of the lipid-lowering effect of vitamin C through GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling in zebrafish. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:1023. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01023
26. Haridevamuthu, B, Seenivasan, B, Priya, PS, Muthuraman, S, Kumar, RS, Manikandan, K, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of dihydroxy piperlongumine in high cholesterol-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease zebrafish via antioxidant activity. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 945:175605. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175605
27. May, KS, and den Hartigh, LJ. Modulation of adipocyte metabolism by microbial short-chain fatty acids. Nutrients. (2021) 13:666. doi: 10.3390/nu13103666
28. Granado-Serrano, AB, Martin-Gari, M, Sanchez, V, Riart, SM, Berdun, R, Ludwig, IA, et al. Faecal bacterial and short-chain fatty acids signature in hypercholesterolemia. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:1772. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38874-3
29. Lau, HC, Zhang, X, Ji, F, Lin, Y, Liang, W, Li, Q, et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus suppresses non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through producing valeric acid. EBioMedicine. (2024) 100:104952. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104952
30. Liu, Y, Zhang, Y, Zhang, X, Xu, Q, Yang, X, and Xue, C. Medium-chain fatty acids reduce serum cholesterol by regulating the metabolism of bile acid in C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. (2017) 8:291–8. doi: 10.1039/c6fo01207h
31. Alwardat, N, Di Renzo, L, de Miranda, RC, Alwardat, S, Sinibaldi, SP, and De Lorenzo, A. Association between hypertension and metabolic disorders among elderly patients in North Jordan. Diabetes Metab Syndr. (2018) 12:661–6. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.04.011
32. Wan, XZ, Ai, C, Chen, YH, Gao, XX, Zhong, RT, Liu, B, et al. Physicochemical characterization of a polysaccharide from green microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa and its Hypolipidemic activity via gut microbiota regulation in rats. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:1186–97. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06282
33. Zeng, BB, Zhang, LY, Chen, C, Zhang, TT, Xue, CH, Yanagita, T, et al. Sea cucumber sterol alleviates the lipid accumulation in high-fat-fructose diet fed mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:9707–17. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03794
34. Lee, KS, Chun, SY, Kwon, YS, Kim, S, and Nam, KS. Deep sea water improves hypercholesterolemia and hepatic lipid accumulation through the regulation of hepatic lipid metabolic gene expression. Mol Med Rep. (2017) 15:2814–22. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6317
35. Pai, SA, Munshi, RP, Panchal, FH, Gaur, IS, Mestry, SN, Gursahani, MS, et al. Plumbagin reduces obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by fructose in rats through regulation of lipid metabolism, inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 111:686–94. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.139
36. Vimalananda, VG, Miller, DR, Hofer, TP, Holleman, RG, Klamerus, ML, and Kerr, EA. Accounting for clinical action reduces estimates of gender disparities in lipid management for diabetic veterans. J Gen Intern Med. (2013) 28:S529–35. doi: 10.1007/s11606-013-2340-5
37. Vimalananda, VG, Miller, DR, Palnati, M, Christiansen, CL, and Fincke, BG. Gender disparities in lipid-lowering therapy among veterans with diabetes. Womens Health Issues. (2011) 21:S176–81. doi: 10.1016/j.whi.2011.04.009
38. Li, Y, Xu, W, Zhang, F, Zhong, S, Sun, Y, Huo, J, et al. The gut microbiota-produced Indole-3-propionic acid confers the Antihyperlipidemic effect of mulberry-derived 1-Deoxynojirimycin. mSystems. (2020) 5:e00313. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00313-20
39. Jang, HR, Park, HJ, Kang, D, Chung, H, Nam, MH, Lee, Y, et al. A protective mechanism of probiotic Lactobacillus against hepatic steatosis via reducing host intestinal fatty acid absorption. Exp Mol Med. (2019) 51:1–14. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0293-4
40. Li, J, Zhang, Z, Xu, Y, Li, W, Jiang, S, Zhang, J, et al. Limosilactobacillus fermentum HNU312 alleviates lipid accumulation and inflammation induced by a high-fat diet: improves lipid metabolism pathways and increases short-chain fatty acids in the gut microbiome. Food Funct. (2024) 15:8878–92. doi: 10.1039/d4fo02390k
41. Evans, RM, Barish, GD, and Wang, YX. PPARs and the complex journey to obesity. Nat Med. (2004) 10:355–61. doi: 10.1038/nm1025
42. Li, H, Fang, Q, Nie, Q, Hu, J, Yang, C, Huang, T, et al. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic mechanism of tea polysaccharides on type 2 diabetic rats via gut microbiota and metabolism alteration. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:10015–28. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01968
43. Silva, AKS, and Peixoto, CA. Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2018) 75:2951–61. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2838-4
44. Hsiao, KC, Ponsonby, AL, Axelrad, C, Pitkin, S, Tang, MLK, and Team, PS. Long-term clinical and immunological effects of probiotic and peanut oral immunotherapy after treatment cessation: 4-year follow-up of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. (2017) 1:107173, 107173–05. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30041-X
45. Sumida, Y, Niki, E, Naito, Y, and Yoshikawa, T. Involvement of free radicals and oxidative stress in NAFLD/NASH. Free Radic Res. (2013) 47:869–80. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2013.837577
46. Koek, GH, Liedorp, PR, and Bast, A. The role of oxidative stress in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Chim Acta. (2011) 412:1297–305. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2011.04.013
47. Rolo, AP, Teodoro, JS, and Palmeira, CM. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2012) 52:59–69. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.10.003
48. Wang, Z, Liu, X, Bao, Y, Wang, X, Zhai, J, Zhan, X, et al. Characterization and anti-inflammation of a polysaccharide produced by Chaetomium globosum CGMCC 6882 on LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Carbohydr Polym. (2021) 251:117129. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117129
49. Wang, Z, Zheng, Y, Dai, Y, Yang, R, Zhao, R, Sun, G, et al. Effect of probiotic fermentation on the extraction rate and bioactivity of plant-based polysaccharides: a review. Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol. (2024) 98:103863:103863. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2024.103863
50. Morrison, DJ, and Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes. (2016) 7:189–200. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2015.1134082
51. Rios-Covian, D, Ruas-Madiedo, P, Margolles, A, Gueimonde, M, de Los Reyes-Gavilan, CG, and Salazar, N. Intestinal short chain fatty acids and their link with diet and human health. Front Microbiol. (2016) 7:185. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00185
52. Koh, A, De Vadder, F, Kovatcheva-Datchary, P, and Backhed, F. From dietary Fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell. (2016) 165:1332–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041
53. Schoeler, M, Ellero-Simatos, S, Birkner, T, Mayneris-Perxachs, J, Olsson, L, Brolin, H, et al. The interplay between dietary fatty acids and gut microbiota influences host metabolism and hepatic steatosis. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:5329. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41074-3
54. Liang, Z, He, Y, Wei, D, Fu, P, Li, Y, Wang, H, et al. Tree peony seed oil alleviates hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites in high-fat diet mice. Food Sci Nutr. (2024) 12:4421–34. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4108
55. Lu, Y, Sun, W, Zhang, Z, Yu, J, Zhang, J, and Guo, Q. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum A5 alleviates high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia via regulating gut microbiota to promote short-chain fatty acids production. Food Biosci. (2025) 64:105848. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2025.105848
56. Gao, F, Mu, G, and Tuo, Y. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y44 complex fermented Milk regulates lipid metabolism in mice fed with high-fat diet by modulating gut microbiota. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:25767–81. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c08671
57. He, J, Ding, Y, Nowik, N, Jager, C, Eeza, MNH, Alia, A, et al. Leptin deficiency affects glucose homeostasis and results in adiposity in zebrafish. J Endocrinol. (2021) 249:125–34. doi: 10.1530/JOE-20-0437
58. Li, X, He, M, Yi, X, Lu, X, Zhu, M, Xue, M, et al. Short-chain fatty acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: new prospects for short-chain fatty acids as therapeutic targets. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e26991. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26991
59. Ge, H, Li, X, Weiszmann, J, Wang, P, Baribault, H, Chen, JL, et al. Activation of G protein-coupled receptor 43 in adipocytes leads to inhibition of lipolysis and suppression of plasma free fatty acids. Endocrinology. (2008) 149:4519–26. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0059
60. Stern, JH, Rutkowski, JM, and Scherer, PE. Adiponectin, leptin, and fatty acids in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis through adipose tissue crosstalk. Cell Metab. (2016) 23:770–84. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.011
61. Zaibi, MS, Stocker, CJ, O'Dowd, J, Davies, A, Bellahcene, M, Cawthorne, MA, et al. Roles of GPR41 and GPR43 in leptin secretory responses of murine adipocytes to short chain fatty acids. FEBS Lett. (2010) 584:2381–6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.04.027
62. Feng, X, Ding, L, Ma, G, Zhang, Y, Sun, Y, Li, Z, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus TR08 improves dyslipidemia in mice fed with a high fat diet by regulating the intestinal microbiota, reducing systemic inflammatory response, and promoting sphingomholipid metabolism. Molecules. (2022) 27:7357. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217357
63. Wang, Z, Zheng, Y, Lu, W, Yang, J, Feng, Y, Li, Z, et al. Antioxidant protection of a polysaccharide produced by Chaetomium globosum CGMCC 6882 on H2O2-challenged HepG2 cells. Carbohydr Polym Technol Appl. (2024) 8:100530. doi: 10.1016/j.carpta.2024.100530
64. Wang, Z, Zheng, Y, Zhou, X, Wang, X, Liu, X, Wang, Q, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus fermentation on the structural feature, physicochemical property, and bioactivity of plant and fungal polysaccharides: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2024) 148:104492:104492. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2024.104492
Keywords: Lactobacillus fermentum E15, short-chain fatty acids, hyperlipidemia, high-cholesterol diet, zebrafish
Citation: Chen Y, Zheng K, Leng Y, Zhang Z, Li X, Li X, Ou H, Wen M, Qiu F and Yu H (2025) Alleviating effect of Lactobacillus fermentum E15 on hyperlipidemia and hepatic lipid metabolism in zebrafish fed by a high-fat diet through the production of short-chain fatty acids. Front. Nutr. 12:1522982. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1522982
Edited by:
Shafiya Imtiaz Rafiqi, University of Toledo, United StatesReviewed by:
Ramcharan Singh Angom, Mayo Clinic Florida, United StatesZichao Wang, Henan University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Zheng, Leng, Zhang, Li, Li, Ou, Wen, Qiu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Qiu, cWl1ZmVuZzMwNzlAc211LmVkdS5jbg==; Huajun Yu, aGp5dUBnZG11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yishu Chen1†
Yishu Chen1† Kangdi Zheng
Kangdi Zheng Zhao Zhang
Zhao Zhang Feng Qiu
Feng Qiu