
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Nutr., 29 January 2025
Sec. Nutrition and Microbes
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2025.1519547
This article is part of the Research TopicProbiotics and Nutrient Bioavailability: Enhancing Gut Health to Combat MalnutritionView all 4 articles
Traditional fermented beverages are drinks produced locally on the basis of ethnic knowledge and consumed nearby the locality of production. Ethiopia is a country where a wide variety of traditional fermented beverages are prepared and consumed. Tella, borde, shamita, korefe, cheka, tej, booka, grawa, areki, and keribo are among the traditional fermented beverages in Ethiopia. This review paper highlights the fermentation process and nutritional value of traditional fermented beverages, microorganisms involved in the traditionally ferreted beverages, the nutritional value and shelf-life of fermented beverages, as well as the bioavailability and safety by collecting recent research articles. These traditional fermented beverages significantly enhance health due to the presence of bioactive compounds and their nutritional value relatively greater than those of nonfermented beverages. The fermentation byproducts of yeast and Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) increase the acidity of beverages and are crucial for maintaining the quality and characteristics of fermented beverages. It also helps to reduce the amount of toxins and pathogens in food. Similarly, fermented foods contain probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that help the body to digest food and absorb nutrients. The fermented foods and beverages are important in preventing non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, gastrointestinal tissues, immune disorders, and cancer. Overall, the paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge and tradition on Ethiopian fermented beverages.
Fermentation is one of the oldest methods of preservation, and fermented beverages have been known for their nutritional value since prehistoric times (1). Traditional fermented beverages are culturally and socially acknowledged products for consumption, drinking, entertainment, customary practices, and religious purposes (2). The functions of microorganisms have been linked to several health benefits; for example, fermented beverages have been shown to improve immunity and control digestive disorders, cardiovascular disease, and other health issues. Microbes such as bacteria (LAB), fungi, and molds are the main reasons for these health benefits (1).
Traditionally fermented beverages have been fermented to improve the shelf-life of the products, unlike these microorganisms, which are produced through acidification, alcoholization, proteolysis, and/or amino acid conversion, to produce products with desirable quality characteristics in terms of shelf life, texture, taste, flavor and color (3). These aspects make traditional fermented beverages not only healthy but also available on the commercial market (1). The methods for preparing these traditional beverages have passed down from generation to generation (4).
In many cases, the nutritional value and shelf life of non-fermented beverages are relatively lower than those of fermented beverages. Fermented beverages are highly important in society, with a high protein contribution, as they involve microbial processes that benefit human health (5). Fermented beverages contain bioactive substances that can help reduce or inhibit allergies and diseases. Fermentation, as a key technique for producing high-quality food products, plays a crucial role in enhancing beverages by preserving sensory and nutritional qualities such as protein and vitamins (6).
In traditional fermented beverages, the source of microorganisms involved in fermentation processes predominantly originates from the microflora naturally present in the substrates and the utensils/equipment used for fermentation. During fermentation, the microbial groups coexist to enhance fermentation processes by adapting to the changing intrinsic and extrinsic conditions caused by the physicochemical changes associated with microbial activity, duration of fermentation, temperature, and moisture content (7).
Many varieties of fermented beverages have been studied and analyzed worldwide, and new additions have been made to make them commercially viable (1). Asia is well known for its exotic, traditionally fermented food and beverage products produced from a wide range of raw materials, microorganisms, and fermentation processes (8). In several African countries, traditional fermentation processes provide a means of preserving food, improving shelf-life, and adding nutrients to food products (9). In developing countries, fermentation is a traditional food processing method for the production of relatively safe and nutritious foods (10).
Ethiopia is a country where a wide variety of traditional fermented beverages are produced and consumed for a long period of time. Traditional fermented beverages are those that are indigenous to a particular area and have been developed by people from locally available raw materials via age-old techniques (11). This study sought to review the available information on the processing techniques involved in the production of these beverages, the species of various microorganisms involved in fermentation processes and the nutritional value of these traditional fermented beverages in Ethiopia (Table 1).
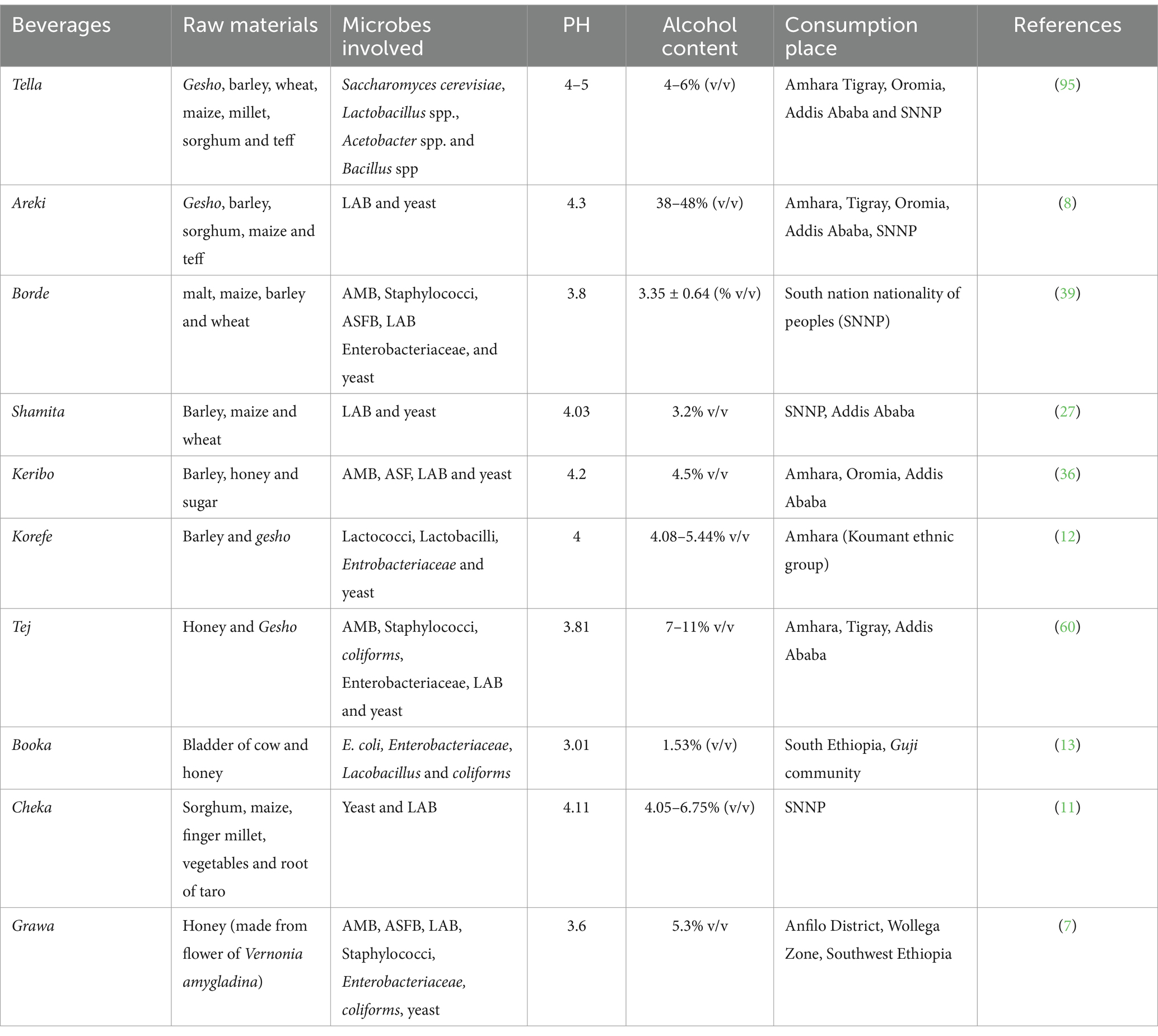
Table 1. Microbes associated with the fermentation of different Ethiopian fermented beverage product.
Traditional fermented beverages are drinks produced locally using indigenous knowledge and consumed near the vicinity of production. In Ethiopia, the preparation and consumption of cereal- and fruit-based traditional fermented beverages are very common (12). Indigenous processing methods for fermented Ethiopian beverages differ from place to place or from product to product. Among the Indigenous fermented beverages in Ethiopia, tej, tella, and areki are considered alcoholic, whereas cheka, korefe, shamita, keribo, borde, and booka are considered nonalcoholic drinks. The fermentation of traditional Ethiopian beverages is spontaneous, natural and uncontrolled (11). Low-alcoholic nutritional value Ethiopian beverages have greater nutritional value. Thus, they can be used as food replacements. These traditional alcoholic beverages also contain a significant amount of total polyphenols and antioxidants (12). The alcohol content and pH values of these beverages range from 1.53–21.7% and 2.9–4.9, respectively (13).
The source of microorganisms responsible for fermentation is mainly the ingredients and utensils. These traditional alcoholic beverages are of variable quality within and between products. This is due to the high number of live cells present in freshly produced beverages. Yeasts and lactic acid bacteria are the predominant microorganisms encountered during the fermentation of these traditional alcoholic beverages (7).
Tella is a ubiquitous and popular beverage in Ethiopia, often called traditional Ethiopian beer (14). Tella is a fermented traditional beverage with a color ranging from grayish-white to brown, depending on the degree of roasting, and it is the most widely brewed and consumed alcoholic beverage in almost every household (12, 15). The intensity of specific processing steps determines the color of a beverage during preparation. Tella is prepared in Ethiopia from cereals such as barley, wheat, maize, millet, sorghum, and teff.
The tella-making process and its raw materials vary among ethnic groups and among economic and traditional situations (16). Although there are minor changes in the process in different localities, the basic steps are similar throughout the country. The making of tejets, tenses and difdifs is the fundamental step in the tella preparation process (17). The tella-making process starts by soaking the barley in water for approximately 24 h at room temperature to produce malt, which is locally called bikil. After 24 h, the moistened grain was covered with fresh banana leaves and kept in a dry place for an additional three days (18). The germinated barley grain was sun-dried and ground to produce malt flour. At the same time, gesho (Rhamnus prinoides) leaves and stems are sun-dried and ground. Then, the bikil flour and gesho powder are mixed with an adequate amount of water in a clean and smoked traditional bioreactor known as an insera.
This mixture is left to ferment for two days to form a tejet. The millet, sorghum and teff (Eragrostis tef) flours in equal proportions were subsequently mixed with water to form a dough. The dough is then baked to produce unleavened bread locally known as ye tella kita, which is sliced into pieces and added to the earlier, produced tejet. The mixture is then sealed tightly to ferment anaerobically for 5 to 7 days to turn into tenses. While the tenses ferment, the maize grain is soaked in water for approximately 3 days and then dried, roasted and ground to make dark maize flour called asharo. Asharo is the main ingredient that determines the color of the tella (19). Asharo is then added to the previously produced tenses and fermented anaerobically for a period of 10--20 days. After this period of fermentation, a thick mixture locally called difdif is formed. Water is added to difdif and left to ferment for an additional 5 to 6 h. Finally, solid residues are removed by filtration and serve to consumers as tella. To produce 25 to 28 L of pure tella, 1 kg of gesho (R. prinoides) powder, 0.5 kg of bikil, 5 kg of ye tella, 10 kg of asharo and 30 L of water are needed (20).
The grawa (Vernonia amygdalina), also known as the bitter leaf, is used as a cleaning agent for tella containers and has medicinal properties. Additionally, weira (Olea europaea), a subspecies of olive, contains various chemicals that act as a multii-chemical defense against insect and microbial attacks. In Ethiopia, weira is commonly used for smoke fermentation in traditional drink containers, including those for tella, water, milk, and milk products. After the container is cleaned and prepared, it is inverted over smoking wood fragments of weira for 10–15 min, removing microorganisms sensitive to wood smoke and adding flavor to tella (8). Weyra provides flavor for tella, can kill bacteria, and extends tella shelf life. The quality of tella depends on the quality and safety of the raw materials used and the method of preparation. Tella typically has a shelf life of 5–7 days at room temperature (17). In addition to being used in some parts of the country, the leaf of Croton macrostachyus is used for cleaning, and dry Aloe vera is used for smoking the equipment used for tella fermentation (Figure 1).
The ingredients and utensils used to prepare tella are the major sources of microorganisms for fermentation. The genera Saccharomyces, Lactobacillus and Acetobacter are the predominant fermenting microorganisms present in tella (17). The fermenting organisms were composed of Saccharomyces spp. (mostly S. cerevisiae) and Lactobacillus spp. (mostly Lactobacillus pastorianumi). The yeasts dominated the fermenting flora after the end of the first stage until the completion of fermentation (21).
The microbial population of a control tella sample on the first day after its preparation, which contained yeast and some bacterial species. The control tella on the 14th day contained even more yeast and bacteria. The number of colonies found in the pasteurized tella samples was 1 × 102 CFU/mL, and the number of colonies found in the vacuum-filtered tella samples was 3 × 103 CFU/mL on the 14th day of observation. The vacuum filtration and pasteurization processes dramatically decreased the number of bacterial colonies in the tella samples. Further investigation of the microbial profile revealed that although there was no yeast inoculation stage during tella fermentation, all the tella samples collected on the first day contained yeast, indicating the utilization of the natural yeast present on the cereals for fermentation. The control tella exhibited a very large microbial flora, which further increased to 1.05 × 109 on the 14th day from 9.86 × 105 on the 1st day after tella preparation. Furthermore, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Shigella flexneri were identified in the control tella after the 14th day of preparation (17) (Table 2).
Areki is a traditional distilled alcoholic beverage in Ethiopia (22). It is clear, colorless liquor that is more frequently brewed and consumed by farmers and individuals in semi urban and rural areas than in urban areas (23). Areki holds significant cultural importance in Ethiopia, serving as a traditional alcoholic beverage that is deeply intertwined with social rituals and community gatherings and is often consumed during celebrations, family gatherings, communal events and cultural identities. It is often consumed by individuals with alcohol dependence who cannot pay for factory-made alcohol (24).
The production process of areki closely resembles that of tella, except for a more concentrated fermentation mass and higher alcohol content. The areki fermentation product is known as Yereki-tinsis, which is prepared by mixing powdered gesho leaves and powdered malt in a 1-to-2 ratio with water to form a mixture with a free-flowing consistency that is fermented for approximately five days (11). Then, the powdered dagussa (Elusine coracann) is kneaded with water into the dough, baked into cakes, broken into small pieces, mixed well with the first mixture, and allowed to ferment for four days. Then, a part of the mixture is transferred to a traditional distillation material to produce a distilled beverage known as terra-areki, which has an alcohol content of 22–34% (v/v). Traditionally, areki is classified as terra-areki or dagim-areki. Terra in Amharic refers to ordinary, an amount of dagussa (Elusine coracann) roughly equivalent to four times that of the bikil that is powdered. However, dagim-areki is a stronger type prepared by redistilling terra-areki, resulting in an alcohol content of approximately 45% (v/v). It is prepared in the same way as terra-areki, except that the distillation process is allowed to proceed for a shorter period of time, or three volumes of terra-areki are redistributed to yield approximately one volume of dagim-areki. Finally, the mixture was left to ferment before distillation for 5–6 days. This results in a more concentrated, colorless, and clear traditional alcoholic beverage (18) (Figure 2).
Borde is a cereal-based traditional fermented beverage that is widely consumed in southern and western Ethiopia. It is an opaque, effervescent, whitish-gray to brown-colored beverage with a thick consistency and a sweet–sour taste (7). The borde is an important product because both adults and children often consume it as a low-cost meal replacement (7). It is consumed daily, especially during the dry season. An average worker consumes approximately 3 to 5 gourd bottles (1 to 2 litters) of borde per day, which would sustain her/him without additional food for most of the day. It is consumed in large quantities at cultural festivals, on market days and at collective work gatherings. The popularity of bonders among the population in the region indicates their production in very large volumes. High prices and poor availability of raw materials and cooking fuel during the food-deficient rainy season, from July to September, result in a reduction of the Main Ingredient Tella’s microflora or cessation of borde production for some vendors (25). Additionally, it is considered to have a low alcoholic libe of the Main Ingredient tella’s Microflora Ratio value of 3.35 ± 0.64 (v/v) (26). Borde holds special importance for lactating mothers, as its consumption postchildbirth is believed to increase lactation, as highlighted by Kitessa et al. (27).
Borde is produced by spontaneous fermentation via simple equipment. It is prepared from various bowls of cereal, such as maize (Zea mays), barley (Hordeum vulgare), wheat (Triticum sativum), finger millet (Eleusine coracana), sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and/or tef (Eragrostis tef) and their malt, sorghum and tef being the primary ingredients. The major equipment used for the preparation of the borde is earthenware pots and griddles, ground stones, bowls, and wonnfit (a sieve with a mesh of interwoven grass-fiber threads at the bottom) (8). The specific ingredients and methods can vary by region, reflecting local preferences and availability (11). The traditional preparation of borde involves a series of steps. The first step is soaking; cereal grains (such as maize, barley or millet) are soaked in water for approximately two days to initiate germination. After soaking, the water is drained, and the grains are spread out to germinate for 2–3 days. The germinated grains are then dried and ground into coarse flour. The flour is mixed with water and allowed to ferment for approximately 3–4 days, resulting in a sweet–sour beverage (26).
Barley is important for the preparation of malt. However, the processing steps are not markedly different. For malt preparation, barley is cleansed to remove dirt and extraneous materials and is steeped in water for approximately one day. Excess water is drained, and the soaked barley is allowed to germinate for five days, after which it is wrapped in banana leaves. Later, germinated barley can be sun-dried and ground finely (11) (Figure 3).
A previous study by Ashenaf (28) on the microbiological and nutritional properties of ready-to-consume borde in Awassa town reported that the mean pH value of the borde was reduced to 4.1 and that the counts of aerobic mesophilic bacteria and lactic acid bacteria were high (approximately 109 CFU/mL). The counts of Enterobacteriaceae were approximately 106 CFU/mL, whereas the yeast count ranged between 107 CFU/mL and 108 CFU/mL for the product. Lactic acid bacteria had initial counts of 105 CFU/mL and reached counts as high as 109 CFU/mL after 24 h. Hetero fermentative lactobacilli dominated the lactic flora throughout fermentation, and a steady increase in the yeast count was observed as fermentation proceeded (25). During fermentation, the early hours of fermentation are dominated by AMB, Staphylococci, Enterobacteriaceae, and ASFB. However, at the end of fermentation, LAB and yeast dominated the fermentation and reached maximum counts of 7.33 ± 0.07 and 6.91 ± 0.04, respectively. Microbes such as Streptococcus, Bacillus, and Corynebacterium started fermentation, which was later dominated by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and yeast. In a microbial challenge test of a borde sample, the counts of all pathogens increased significantly until the end of the challenge test. However, the rate of growth varied: the counts of E. coli (3.15 ± 0.03 to 5.82 ± 0.08 log CFU/mL) and S. aureus (3.72 ± 0.05 to 6.05 log CFU/mL) increased by more than 2.3 log CFU/mL, whereas those of S. typhimurium (3.48 ± 0.04 to 5.44 ± 0.01 log CFU/mL) and Candida albicans (3.57 ± 0.07 to 5.09 ± 0.09 log CFU/mL) increased by less than 2 log CFU/mL (7). All pathogens reach the infective dose in borde beverages. Borde supported the growth of pathogens because of its low alcoholic content, low acidity (4.22) due to the short fermentation time of the beverages (overnry fermentation), and good nutritional profile for the proliferation of microorganisms (26) (Table 3).
Shamita is a traditional fermented beverage widely consumed in different regions of Ethiopia, especially by the Gurage people. It is low in alcohol content and is made by overnight fermentation of mainly roasted barley flour. Because of its thick consistency and ability to be a good source of protein, shamita is known to be used as a meal replacement. However, it has poor quality and must be consumed within a few hours after being ready for consumption (8). Shamita is a locally produced and consumed porridge that is used mainly to support the strength and recovery of lactating women after birth (10). Shamita plays a significant role in Ethiopia, particularly among the Gurage people and other communities where it is traditionally consumed. This fermented beverage not only is a staple in the diet but also plays vital roles in various social and cultural contexts. In Ethiopian culture, shamita is consumed during various social gatherings and ceremonies, such as weddings, naming ceremonies, and festivals. It serves not only as a beverage but also as a medium for social interaction and bonding among community members (29).
Shamita is typically prepared from maize and wheat. The availability of soluble protein initially increases but then gradually decreases during the preparation process. Often, shamita is made by grinding roasted barley and mixing it with salt, ground linseed, and spices to enhance its flavor. Unlike other varieties, shamita is a fermented porridge with differences in fermentation time, preparation methods, utilization and ingredient composition (4). The preparation process of shamita starts by mixing 2 liters of water with little flour. Bake the dough into bread and shred the bread into smaller pieces. Then, a clean container was prepared, and the pieces of bread were mixed with minimal malt. Three more liters of water were added and mixed thoroughly. After that, the container was covered, and the mixture was allowed to sit for 3 days, after which it was fermented. On the third day, 7 more liters of water were poured. The mixture was then strained via a sieve into another clean container. The container was covered and allowed to sit for approximately 2 h. In the meantime, a large bowl was used to add the besso to the first mixture. Two liters of water were then added, and the mixture was mixed thoroughly. Next, this mixture was added to the main mixture, and 3 more liters of water were added to the spices. The samples were mixed thoroughly and covered. Finally, the mixture was filtered into a new container. You now have your shamita ready to serve and enjoy (29) (Figure 4).
Bacha et al., studied Shamita fermentation microbial dynamics and the microbial load of raw materials. Their study revealed that barley is the major source of fermentative microorganisms. The count of these fermentative microbes reached 109 CFU/mL after a 24-h fermentation period (29). Later (30), studied the antimicrobial effect of LAB isolated from shamita on pathogenic microorganisms. The isolated LAB were found to inhibit the growth of the Salmonella species S. flexneri and S. aureus (31). LAB are the predominant microorganisms during shamita fermentation, with significant contributions from both homofermentative and heterofermentative Lactobacillus species. Its count can reach 109 CFU/mL by the end of fermentation, playing a crucial role in acidifying the product and enhancing its flavor and safety by inhibiting spoilage organisms and pathogens. Various Bacillus species, including B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. megaterium, B. coagulans, and B. circulans, are also commonly associated with shamita fermentation. These aerobic mesophilic bacteria contribute to the overall microbial profile and can be found in high numbers, particularly in the initial phases of fermentation (32). In addition to LAB and Bacillus species, other aerobic mesophilic bacteria are present, contributing to fermentation dynamics. Their levels are generally lower than those of LAB but are significant in the overall microbial community. Initially, present in fermentation substrates, coliforms and other members of Enterobacteriaceae are typically eliminated during fermentation due to the competitive advantage of LAB, which produce organic acids that lower the pH and create an unfavorable environment for these bacteria (29).
Keribo is a traditional beverage in Ethiopia that is favored by those seeking low-alcohol drinks with limited financial resources (33). It is widely consumed in Ethiopia’s rural and urban areas, particularly in the southern, southwestern, and eastern regions. This beverage has a brief shelf life of 2 days when stored at room temperature (11). In Ethiopia, especially in the southwestern region, the fermentation of keribo is intertwined with sociocultural practices, mainly due to religious reasons for people who do not consume alcoholic beverages, with keribo serving as a source of energy (34). It is used for household consumption and during wedding ceremonies and holidays in various parts of Ethiopia.
Barley, honey, and sugar are primarily used to produce keribo. To make keribo, roasted barley is mixed with hot water. The barley grains are meticulously cleaned before being processed for keribo (11). The fermentation of keribo starts by preparing a clean container and adding 3 liters of water along with half of the wheat malt. Then, the pots were covered, and the plants were allowed to sit for 3 days. Simultaneously, in a different container, 2 liters of water were mixed with the teff flour. After 3 days, the bread was prepared from the teff flour mixture that was previously made, which was allowed to cool and then shred into small pieces. Then, the pieces of bread were added to the first mixture, which was made 3 days prior, along with 250 grams of wheat malt and 5 liters of water, and mixed well. Next, 5 kilograms of barley flour were prepared by roasting it in a separate pan until it changed color to dark brown while sprinkling it with water. The enkuro was allowed to cool before mixing with the remaining malt. The mixture was then added to the previous mixture along with 1 liter of water and mixed thoroughly. The mixture was covered and allowed to sit until the next day. The next day, 15 liters of water were poured into the enkuro mix, which was covered, and allowed to sit for 3 more days. After 3 days, filter your mixture, and you now have your keribo ready to serve and enjoy (35) (Figure 5).
A study by Abawari, examined samples of keribo from open markets and households in the Jimma zone. The average LAB, aerobic mesophilic bacteria (AMB), aerobic spore formers (ASFs), and yeasts had mean counts of 2.70 ± 2.07, 2.34 ± 2.37, 4.96 ± 2.80, and 4.96 ± 0.60 (log CFU/mL), respectively, after 6 h of fermentation (36). However, the microbiology of the keribo samples drawn at intervals during controlled laboratory fermentation was associated with mean counts of coliform bacteria, Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococci, and Staphylococci below the detection level. The initial high pH of 5.75 during keribo fermentation at 0 h could explain the growth of aerobic mesophilic bacteria (AMB), while the lower pH (pH = 4.47) at 6 h of fermentation inhibited their growth. The high numbers of LAB attained after 6 h of fermentation were responsible for the marked reduction in pH and increase in titrable acidity, resulting in the inhibition of most aerobic mesophilic bacteria (AMB). The mean counts of yeasts increased throughout fermentation (for 48 h) of the laboratory-prepared keribo. Similarly, there was an increase in the number of LAB and aerobic spore formers (18).
Korefe is the name offer the traditional indigenous fermented beverage made in the northern and northwestern parts of Ethiopia (8). Like other fermented Ethiopian beverages, its fermentation system is natural and spontaneous. Barley, malted barley, gesho (R. prinoides), and water are the major ingredients used to prepare this indigenous beverage (37).
The first stage in the production of korefe is combining water and gesho (Rhamnus prinoides) to produce tijit in a traditional container called Gan. This mixture is left for 72 h to extract flavor, aroma, bitterness, and fermenting microorganisms (38). The non-malted powder is then mixed with water to form dough, which is then baked into unleavened bread called kitta. Tijit, a small mixture of kitta and water is mixed and left to ferment for approximately 48 h, resulting in a semisolid mixture called tenses (18). At this stage, the non-malted roasted barley powder (derekot) is added to the tenses and allowed to ferment for an additional 72 h. Finally, water was added to the mixture at a ratio of 1:3. After 2–3 h of fermentation, the korefe is ready to drink (38) (Figure 6).
According to (38), the colony count of microorganisms during fermentation varies between 3.6 log CFU/mL and 9.7 log CFU/mL. The numbers of Lactococci and Lactobacilli increased from 4 log CFU/mL to 9.7 log CFU/mL during fermentation. Yeasts are organisms that are responsible for fermentation. The bacterial count increased from 3.6 log CFU/mL to 9.3 log CFU/mL, whereas the Enterobacteriaceae count was below the detectable limit because of the antagonistic effect of lactic acid bacteria. In addition, a study by Hirbo et al., on the effects of microbial activity on fermented korefe for 1 month revealed 0.11 ± 0.21 CFU/mL E. coli, 0.34 × 103 CFU/mL Enterobacteriaceae, 0.22 × 103 CFU/mL Lactobacillus, and 0.02 × 103 CFU/mL coliforms (39).
Tej is an Ethiopian traditional alcoholic beverage with significant social and economic importance. It is one of the most popular traditional alcoholic beverages in the country. Tej is typically household commercial products sold for consumption at the point of production (12). The traditional fermented beverage tej is yellow in color, has a sweet taste, is used to satisfy thirst, and has medicinal value similar to traditional methods (7).
Ethiopia has the potential to produce 500,000 tons of bee honey annually. However, production has not surpassed 10% of that potential (40). Approximately 80% of the total honey produced in the country serves as raw material for producing tej (41). Traditionally, crude honey rather than refined honey is preferred for the production of tej due to the distinct sensorial properties that local consumers prefer (42).
Crude honey and gesho (Rhamnus prinoides) are the basic ingredients of high-quality tej (8). The process begins by mixing honey and water in a 1:3 ratio. After 2–3 days of primary fermentation, the blend was subsequently filtered through a clean cheesecloth. Then, boiled gesho leaves and stems are added to the honey water filtrate. At this point, some communities use fresh gesho leaves instead of dried and boiled leaves and stems. Furthermore, some producers add small amounts of malt powder to boiled gesho leaves (7). Regardless of the ingredients, the blend underwent secondary fermentation for 8–21 days. Finally, the mixture was filtered and served as the final product, tej (Figure 7).
The microorganisms involved in the fermentation process originate from the raw materials, equipment and utensils. Because of this, tej fermentation is lengthy, spontaneous, and uncontrolled. Thus, the final product has inconsistent physicochemical properties, microbiological profiles, and sensory attributes (26). In tej fermentation, the counts of AMB until 36 h and staphylococci and ASFB until 24 h increased by more than 1 log CFU/mL. However, the count of yeast increased by more than 5 logs (4.16 ± 0.04 to 9.41 ± 0.06 log CFU/mL), and the count of LAB increased by nearly 5 logs (4.01 ± 0.03 to 8.88 ± 0.01 log CFU/mL), with a significant difference in counts between fermentation hours analyzed from the beginning (0 h) to the end of fermentation (144 h) (7). This value was much greater than that reported by Nemo and Bacha (26), who reported values of 6.31 ± 0.63 and 6.09 ± 0.53 log CFU/mL from Jimma town tej vendors. In tej fermentation, the highest counts of yeast and LAB coexisted, originating from the raw materials: honey, malt, and hops. A report on the growth potential of pathogens in the tej sample revealed that E. coli and S. typhimurium had greater survival abilities than did S. aureus and L. monocytogenes. Moreover, C. albicans was reduced to a lesser extent (0.88 CFU/mL) than the other pathogens were. However, L. monocytogenes was highly reduced (2.2 CFU/mL), with a significant difference among counts (7) (Table 4).
Booka is an indigenous traditional fermented beverage in South Ethiopia that is particularly consumed in Guji communities. It is the first animal-origin traditional fermented beverage in which a slightly yellowish liquid is made of booka from cow bladders, so the product is named booka. Booka is sometimes found at the bottom of buttee (a traditional instrument that is used to ferment milk). However, the beverage that is used to ferment the beverage (booka) is usually cow bladder. People of all ages, including infants, pregnant, and lactating women, drink bookas (13). It has been consumed for ceremonies such as marriage, blessing (Eebbaa), Gadaa power transition (Baallii dabarsaa), and conflict resolution (Araara) and as a source of income generation.
The indigenous production and preparation methods of bookas are very simple; they can be prepared using equipment such as a wooden bowl (Qorii), cup (Kookkii), container (gan), or filter. In contrast, ingredients such as honey, sugar (sometimes), water and booka are from certain types of cow bladders. The Guji people (mostly older people) know which cows to select for this process, but the exact cause of the existence of the booka in the bladder of a cow is unknown. The liquid from the bladder of a cow is carefully removed, cleaned, and then filled with honey and water in a container. This mixture is subsequently enhanced with pure honey and used immediately because the fertility of this booka will increase if this type of pure honey is used. However, if they need to preserve for a long period, they mix fresh booka with honey and water at an appropriate ratio and then dry, pack, and put for future usage. For immediate use, they inoculated this active booka in honey and water in a container and stored it for two to three days, during which time it underwent fermentation. After fermentation is complete, the upper layer is then ready to drink, while the bottom layer (sediment) is reused again to ferment another booka (beverage). The good-quality booka is yellowish in color, sweet in taste, and attractive in odor. The popularity of this traditional fermented beverage is greater among all age groups (13) (Figure 8).
The microbial activities of E. coli, Enterobacteriaceae, Lactobacillus and coliform bacteria in booka were 0.51, 1.67 × 101, 1.2 × 104 and 3.67 × 105, respectively. The effects of microbial activity on fermented booka during the first month of the study included E. coli 0.41 ± 0.20 (CFU/mL), Enterobacteriaceae 0.13 × 102 (CFU/mL), Lactobacillus 0.07 × 103 (CFU/mL), and coliforms 1.67 × 101 (CFU/mL) (39).
Cheka is a traditional fermented beverage primarily consumed in southwestern Ethiopia, especially in the Dirashe and Konso districts. This beverage is made from a mixture of cereals and vegetables, and it plays a significant role in local culture and diet (43). Cheka is not just a beverage but also a cultural staple consumed by people of all ages, including infants and pregnant women. It is often seen as a low-cost meal alternative, particularly for low-income individuals. The beverage is consumed throughout the day, with some adults reportedly drinking up to 8 liters daily. It is commonly served during social gatherings and special occasions, reinforcing its role in community bonding and cultural practices (44).
Cheka is mainly prepared from cereals such as sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and maize (Zea mays) and vegetables such as leaf cabbage (Brassica spp.), moringa (Moringa stenoptella), and decne (Leptadenia hastata). Additionally, the root and leaf parts of the taro were used. The processes of Cheka preparation are very complex and vary among households and localities. There are three types of Cheka produced in Konso and Dirashe: hiba, chaqa, and menna (45). The study by Worku et al. (46) reported a survey of raw materials and the production process of Cheka. According to their report, Cheka preparation starts with malting. The malt is prepared from either a single or a combination of the cereals listed above. Cabbage leaves and/or taro roots are cut into pieces and fermented anaerobically for approximately 4 to 6 d in a clean container. Then, a small amount of maize flour is added to the vegetable mixture, which is fermented for an additional 2 to 3 days. The fermented vegetable mixture was then ground, filtered, and mixed with fresh maize flour. The fermentation continues for another 12 to 24 h. Then, water was added to the mixture, and the mixture was allowed to ferment for one month. This fermented mixture is shaped into a dough ball, locally called gafuma, and cooked at a temperature of 96°C. After cooling, the cooked gafuma is mixed with an adequate amount of previously prepared malt. The mixture was then allowed to ferment for an extra 12 h. This fermented mixture is locally called sokatet. At this stage of the process, a very thick porridge, locally called koldhumat, is prepared from maize flour. The prepared porridge was added to a vessel containing a sokatet with a sufficient amount of water. Finally, the mixture is left to ferment for other 4 to 12 h and serves consumers as Cheka. It has a shelf-life of 2–4 days. However, it is usually produced on a small-scale basis to avoid loss. Cheka is ready for consumption after 4–12 h of fermentation. As the duration of fermentation in the preparation of hiba (Dirashe Cheka) is too long, the sokatet becomes much bitter, and as a result, the amount of malt added into hanshalt in the preparation of fasha (Konso Cheka) is slightly greater than that added to hiba, and the proportion of sokatet in the final product is much greater than that of hanshalt in fasha (Figure 9).
Cheka, a traditional fermented beverage from Ethiopia, is produced through the action of various microorganisms during fermentation. The main types of microorganisms involved in the fermentation of Cheka include Lactobacillus spp., which are crucial for fermentation, contributing to sour flavor, preserving, lowering pH, and enhancing beverage safety and stability. Additionally, Saccharomyces cerevisiae is involved in converting sugar present in cereal ingredients into ethanol and carbon dioxide, which contribute to the alcohol content of beverages. The fermentation process is typically spontaneous and can involve a mixed culture of various other bacteria and yeast, which may vary depending on local practices and environmental conditions (44). The presence of these microorganisms not only contributes to the organoleptic properties (taste, aroma, etc.) of Cheka but also affects its nutritional value and safety. The fermentation process can increase the bioavailability of nutrients and may also introduce probiotic properties that are beneficial for gut health (11). However, the uncontrolled nature of traditional fermentation can also lead to contamination, including the presence of harmful substances such as aflatoxins, which are produced by certain molds that can grow on the cereal ingredients used in Cheka (47).
The grawa is a traditional Ethiopian beverage particularly popular in the Qellem Wollega Zone, Anfilo district. This beverage has not been extensively documented in the literature, making it a lesser-known aspect of Ethiopian culinary traditions than other drinks, such as tella or tej. Grawas are consumed during social gatherings or special occasions, reflecting their cultural significance (26). Its production is often a household practice, reflecting the traditional methods of beverage-making in Ethiopian culture. It is yellow, has a sweet taste, is used to quench thirst and has medicinal value similar to that of tej. It is a fermented beverage prepared from specific honey made from flowers of Vernonia amygdalina and water from Anfilo District. Grawa from previous fermentation methods (back slope) has been used as a starter culture, and the whole fermentation process takes approximately 72 h (7).
Smoking the clay container used for preparing grawa, a traditional Ethiopian honey-based beverage, contributes to the flavor profile. The first step in the preparation of grawa is mixing honey with water in appropriate proportions. The exact ratio can vary on the basis of local preferences and desired sweetness. The mixture was then allowed to ferment naturally. This process typically relies on wild yeasts and bacteria present in the environment, which can vary by location. Traditionally, fermentation containers may be washed with fresh leaves of grawa (vernonia amygdalina) to impart flavor and potentially introduce beneficial microorganisms. The fermentation process was monitored over several days. The duration can vary, but it usually lasts until the desired level of fermentation is achieved, which is indicated by the development of carbonation and a slight alcoholic content. Once fermentation is complete, grawa is ready to be consumed (26) (Figure 10).
The fermentation of grawa typically involves a mix of microorganisms, primarily yeasts and lactic acid bacteria, which contribute to the flavor, aroma, and alcoholic content of the beverage. The spontaneous fermentation process allows for a diverse microbial community, which can influence the final characteristics of grawa (26). The microbial dynamics in grawa beverages at 0 h were greater (5.06 ± 0.02 log CFU/mL) than those of other microorganisms. The dominance of AMB continued until 24 h, and after 24 h, yeast and LAB dominated the fermentation process until the end of fermentation (72 h) and reached maximum counts of 7.88 ± 0.02 and 7.64 ± 0.04 log CFU/mL, respectively (7). A previous study by Nemo and Bacha (26) reported 8.43 ± 0.72 log CFU/mL of yeast and 8.13 ± 0.67 log CFU/mL of LAB from the grawa beverage collected from Anfilo District of the Qellem Wollega Zone, Southwest Ethiopia. The lower count of yeast and LAB in the present study could be due to environmental factors. In the study by Nemo and Bacha (7) in the grawa sample, a fast reduction (0.52 log) in L. monocytogenes was observed from the initial 0 h (3.90 ± 0.02 CFU/mL) to 6 h (3.38 ± 0.03 log CFU/mL), with a significant difference (p < 0.05) between counts, whereas S. typhimurium and E. coli were reduced by 0.1 log, with no significant difference (p > 0.05) between counts of different sampling hours. At the end of microbial challenge testing, E. coli, S. typhimurium, S. aureus, and L. monocytogenes were reduced by >1 log unit. However, C. albicans was reduced by 0.7 logs (Table 5).
Ethiopia has a rich tradition of producing and consuming a variety of traditional fermented beverages, which are integral to local food culture and nutrition. These beverages, including Korefe, Booka, Tella, Shamita, Borde, Keribo, and Areki, are typically made from locally sourced raw materials and reflect regional cultural practices. Apart from their cultural significance, these drinks are also valued for their nutritional benefits, such as providing essential nutrients and improving food security in rural areas. The fermentation process itself may contribute to the development of beneficial microorganisms, enhancing the nutritional value and digestibility of the drinks (4). Although the traditional fermented beverages produced in uncontrolled way of microbiota, they are sources of amino acids, antioxidant compounds, bioactive beeps, short chain fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals (48). Furthermore, a beverage made from oat blend increases the content of fat, carbohydrate, gross energy, and mineral contents (Fe, Zn) (49). It also increases the digestibility and bioavailability of different nutrients (50). The nature of beverage preparation in Ethiopia, traditional household processing, associated microorganisms with a fermented beverage, and their contribution toward improving the nutritional value and safety, the extent, and its prospect in supporting the livelihood of people in Ethiopia need concern (11). The diverse microbial species involved in beverage products result in distinct aromatic and flavor profiles (51) and extend the shelf life of the food (52). In some of the traditionally fermented beverages, Ethiopians use “gesho” (Rhamnus prinoides) providing unique characteristics of flavor (16). Moreover, traditionally fermented beverages and condiments are rich in different essential vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and antioxidants, which are enhanced through the process of traditional fermentation (8).
Fermentation is a traditional food processing method that produces safe and nutritious foods, although the nutritional composition and health benefits of many such foods have not been extensively studied. One example is “Tella,” a locally prepared beer made using ingredients like “gesho” (Rhamnus prinoides) and malt. The antioxidants in “gesho” have been shown to have potential health benefits, including improving bioavailability, preventing metabolic syndrome-related diseases, and offering anti-cancer effects (53). On the other hand, beverages are not usually consumed for their food value, particularly the fruit drinks, contain quite a high percentage of sugar, vitamins and minerals, and, therefore, add to the energy content of the diet (54). Study conducted in Jimma, Ethiopia confirmed that Tella contains crude protein content (16.47–18.72%), crude fat content (3.73–5.43%), crude fiber content (15.52–19.73%), total ash content (3.58–4.47%), and carbohydrate content (35.02–40.50%) (55). Checka, a traditional beverage from cereals and vegetables in Southwestern Ethiopia, provides essential nutrients such as crude protein (3.12–4.44 g/100 g), crude fat (1.17–1.81 g/100 g), crude fiber (0.65–0.93 g/100 g) and carbohydrates (82.04–107.17Kcal) (44) and it is the source of probiotics like Weissella paramesenteroides and Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides isolates, which showed promising probiotic properties (56). On the other hand, there are various locally prepared beverages such as Keribo, Borde, Areki, Tella, Shamita, Booka, Korefe, and Cheka, which are naturally fermented. These beverages rely on lactic acid bacteria and yeast as the dominant microbes. These microbes serve as probiotics, enhancing the organoleptic properties, nutritional quality, and providing biopreservative benefits (11). While beverages are not intended to replace foods, they play an important role in providing nutrients and phytonutrients, especially phenolic acids and flavonoids. However, they are not sufficient on their own to meet requirements for vitamin E, dietary fiber, or essential fatty acids (57). The “Grawa” is a traditional Ethiopian beverage particularly popular in the Qellem Wollega Zone. The leaf of the plant is used to clean “Tella” containers, enhancing its flavor, and serves as an antimicrobial agent. It contains compounds such as flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, tannins, triterpenoids, sesquiterpene lactones, steroids, cardiac glycosides, oxalates, phytates, cyanogenic glycosides, and phenols, which contributes to its anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties (58). Cheka is also an indigenous alcoholic beverages commonly consumed in Konso, Southwestern, Ethiopia contains protein (5.97–4.95) %, carbohydrate (59.08–64.41) %, and fibre (1.2 to 1.9) %. It also contains magnesium, calcium, iron, and zinc ranging from (10.65–11.82) mg/l, (11.05–7.79) mg/l, (7.64–10.73) mg/l and (2.57–5.33) mg/l, respectively (59). Tej (Ethiopian honey wine) is a home-made and traditionally fermented product. The nutritional composition of Tej varies across regions. It contains protein (1.38) %, fat (0.47) %, and carbohydrates (3.91) % (60). In contrast, others reported Tej as having lipids (0.13) %, protein (0.10) %, and carbohydrates (3.02) % (61).
The organoleptic properties, texture, aroma, and flavor improve through microorganisms, which makes fermented beverages tasty (62). Fermentation of tej depends on microorganisms (LAB and yeast), and their metabolic products contribute to acidity and enhance the distinctive flavor and aroma of the fermentation material (31). LAB isolated from various fermented foods produces organic acids and diverse antimicrobial agents, which are responsible for maintaining the quality and sweetness of fermented foods. Yeasts of the genus Saccharomyces were reported to be responsible for the conversion of sugars to ethanol in tej.
A previous study by Debela et al. (63) revealed that after 10 days of fermentation, tella becomes more acidic because of the growth of Acetobacter spp., which converts ethanol to acetic acid under anaerobic conditions. The organoleptic properties of fermented beverages make them more important since they have broader acceptance (64).
Microorganisms contribute to bio preservation by producing natural antimicrobials to extend the shelf-life of food products. Many bacteria involved in the fermentation of foods produce bioactive molecules such as hydrogen peroxide, organic acids, and bacteriocins, which act as effective bio preservatives (65). The acid content of alcoholic beverages plays a crucial role in maintaining freshness and extending shelf-life by inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microbes. LAB for example, displays antifungal properties, contributing to the prolonged shelf-life of fermented foods by preventing spoilage. This bio preservation helps ensure that fermented foods maintain quality over time.
As fermentation continues, from a fermentation dynamics point of view, only a limited number of microorganisms resist the adverse environmental effects of the growth medium. Thus, the microorganisms that do not survive in the new environment will be lysed and become a source of protein for cell maintenance for the surviving species. This analysis works even better in natural, spontaneous and uncontrolled fermentation systems. Hence, this competition in turn decreases the nutritional value of beverages while increasing secondary metabolites such as ethanol (66).
Fermentation processes increase the digestibility and availability of nutrients (11). Enzymes such as amylases, proteases, lipases, and phytates modify primary food products through the hydrolysis of polysaccharides, phytates, proteins, and lipids (64). For example, those beverages that use malt are known to contain much more free amino nitrogen than the original grain, i.e., the partial degradation of reserve proteins in cereals makes free amino nitrogen available (67). The number of proteins and the content of water-soluble vitamins increase, whereas antinutrient factors (ANFs) in foods decrease during fermentation (62).
Lactic acid fermentation of cereals has been used as a strategy to decrease the content of anti-nutrients, such as phytate and tannins (68). This leads to increased bioavailability of micronutrients such as zinc, calcium, phosphorous, iron, and amino acids. The high microbial loads of yeast and lactic acid bacteria qualify as good sources of microbial protein (69). The mean crude protein content of fermented food increased from 0.74 to 4.58% (3-fold increase) after 48 h of fermentation (18). The highest levels of crude protein were also observed in fermentation samples enriched with 1.5 mL of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for 48 h (70).
The diverse functional microorganisms in fermented foods and beverages include bacteria, yeasts, and fungi. The most remarkable aspects are their biological functions and enhanced health benefits due to the functional microorganisms associated with them. The possible health benefits of fermented beverages include the prevention of cardiovascular disease, cancer, hepatic disease, gastrointestinal disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, hypertension, thrombosis, osteoporosis, allergic reactions, and diabetes (71). The consumption of these traditional fermented beverages with meals supports digestion and promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria. Different microorganisms (bacteria, yeast, and molds) are involved in alcoholic beverage fermentation, and these microorganisms are naturally probiotic and important for human health (72). The traditional fermented foods and beverages play an important role in their potential positive effects on human health (73). Recent research indicates that the consumption of traditional foods and beverages has positive effects on human health. These foods are particularly beneficial in addressing non-communicable diseases (NCDs), gastrointestinal issues, and immune disorders. Different findings suggest that incorporating traditional foods and beverages in to diets could help improve overall human health. They play a significant role in preventing chronic diseases, highlighting their importance in maintaining long-term health (73). Besides, the fermented foods are very important in preventing chronic disease (74). Besides, Lactic Acid Bacteria isolated from “Borde” showed strong potential to lower cholesterol (85–90%) (75).
Probiotics have great potential for improving nutrition, soothing intestinal disorders, improving the immune system, optimizing gut ecology, and promoting overall health because of their ability to compete with pathogens for adhesion sites, antagonize pathogens, or modulate the host’s immune response, pharmaceutical preparations, and functional foods to improve public health (76). Most probiotic products contain LAB and molds that have been found to produce antibiotics and bacteriocins. LAB belong to the genera Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Enterococcus, Lactococcus, Streptococcus, and Leuconostoc; Lactobacillus plantarum strain; Lactobacillus paracasei strain; and Lactobacillus plantarum strain (77), which is inherently present in fermented Borde and Shamita and has antimicrobial properties against various foodborne pathogens invading the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, a better understanding of the intestinal microbial populations will contribute to the development of new strategies for the prevention and/or treatment of several diseases. However, some fermenting microorganisms isolated from “Checka” like, lactic acid bacteria and yeast, are used as probiotics, for improvement of organoleptic properties, for provision of nutritional quality and biopreservative methods (11).
Ethiopian locally fermented beverages result from acid–alcohol fermentation and are typically made from cereals such as barley, maize, and wheat (11). Barley, in particular, is gaining renewed interest because of its nutraceutical benefits. Its properties are known to offer protection against degenerative diseases, including diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and colon inflammation, which are often associated with unhealthy diets and lifestyles (78).
Traditional alcoholic beverages such as tej can be vital sources of calories as well as a source of vitamin B. The presence of vitamin B in tej is a result of fermenting yeasts, substrate residues and other microorganisms (79). Two ingredients in tej production honey and R. prinoides have medicinal properties. Additionally, Rhamnus staddo, which is sometimes used in tej, is being researched for its potential as an antimalarial (80) and gesho extract during tella brewing can inhibit bacteria growth and thereby help to extend the self-life of the product (81). The traditional beverage made from “grawa” (Vernonia amygdalina) helps reduce harmful microorganisms while promoting beneficial microbes, such as yeasts and lactic acid bacteria (LAB), which can contribute to human health by producing secondary metabolites (26). Various plant parts are used in traditional medicine to treat numerous health issues, such as diabetes, diarrhea, headache, malaria, gastritis, and snake bites, among others (58). These plants are known to deliver a range of bioactive compounds, acting as natural antioxidants that may support human health (82). Besides, it was reported that worldwide fermented foods are recognized as healthy and safe (83).
The fermentation process breaks down compounds in food into more easily digestible forms, making it easier for the body to process nutrients. It also helps to reduce harmful toxins and pathogens present in food, improving food safety. Fermented foods contain probiotics which are beneficial bacteria that support digestion and help the body absorb nutrients more effectively (84). The fermentation process helps to break down compounds into forms that are easier to digest. It also helps to reduce toxins and pathogens in food. Additionally, fermented foods contain probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that help the body to digest food and absorb nutrients (84). On the other hand, traditionally fermented beverages prepared from “Grawa” (Vernonia amygdalina Del) treats different types of diseases like diarrhea, diabetes, wound healing, tonsillitis, evil eye, retained placenta, headache, eye disease, intestinal parasite, bloating, hepatitis, toothache, anthrax, malaria, urine retention, gastritis, stomach disorders, and snake bites (58, 85, 86) and has antimicrobial activity (87).
Although there aren’t many reports of foodborne illnesses caused by eating traditional fermented foods, fermentation is an ancient technique that can enhance nutrient contents and sensory qualities while also possibly lowering or getting rid of harmful bacteria and natural toxins (88, 89). Though Salmonella sp., Campylobacter sp., and Shigella sp. are frequently found in beverages, the most frequently isolated harmful bacterial species were not only Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus (90). Additionally, mycotoxins have been found in traditional brewed “Cheka” and beverages made from fermented tropical crops (91, 92). Furthermore, certain beverages are susceptible to methanol contamination (93). Others contain, toxic compounds such as biogenic amines and phenols that affect the quality of the product and human health has been detected (94).
The most widely produced and consumed traditional alcoholic beverages in Ethiopia are tella, borde, shamita, korefe, cheka, keribo, tej, and booka. These drinks vary from location to location in terms of ingredients and preparation technique. These drinks also differ from one another in terms of alcohol content. Traditional low-alcoholic beverages have higher nutritional value than high-alcoholic beverages do. As fermentation progresses, mesophilic aerobic bacteria and coliform bacteria dramatically decrease, whereas lactic acid bacteria and yeast species increase. These factors help to maintain the shelf life and quality of fermented beverages. The ingredients and preparation techniques for traditional fermented beverages have been thoroughly researched. To increase the quality and safety of these traditional beverages, more research is necessary to standardize the fermentation process and identify important microbial species.
GM: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. TG: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TT: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Murali, RD, Vishnu Priya, S, Swetha,, and Antony, U. Traditionally fermented foods and beverages for nutritional security and global acceptance In: Food production, diversity, and safety under climate change. Berlin: Springer (2024). 77–87.
2. Madilo, FK, Parry-Hanson Kunadu, A, Tano-Debrah, K, Saalia, FK, and Kolanisi, U. Diversity of production techniques and microbiology of African cereal-based traditional fermented beverages. J Food Qual. (2024) 2024:1–32. doi: 10.1155/2024/1241614
3. Ashaolu, TJ. A review on selection of fermentative microorganisms for functional foods and beverages: the production and future perspectives. Int J Food Sci Technol. (2019) 54:2511–9. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.14181
4. Alemu, TT, and Kuyu, CG. A review of the production, quality, and safety of traditionally fermented cereal-based alcoholic beverages in Ethiopia. Food Sci Nutr. (2024) 12:3125–36. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4012
5. de la Bastida, AR, Langa, S, Peirotén, Á, Fernández-Gonzalez, R, Sánchez-Jiménez, A, Maroto, M, et al. Effect of fermented soy beverage in aged female mice model. Food Res Int. (2023) 169:112745. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112745
6. Kuyu, CG, and Bereka, TY. Review on contribution of indigenous food preparation and preservation techniques to attainment of food security in Ethiopian. Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 8:3–15. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1274
7. Nemo, R, and Bacha, K. Microbial dynamic and growth potential of selected pathogens in Ethiopian traditional fermented beverages. Ann Microbiol. (2021) 71:22. doi: 10.1186/s13213-021-01635-7
8. Wedajo Lemi, B. Microbiology of Ethiopian traditionally fermented beverages and condiments. Int J Microbiol. (2020) 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2020/1478536
9. Obafemi, YD, Oranusi, SU, Ajanaku, KO, Akinduti, PA, Leech, J, and Cotter, PD. African fermented foods: overview, emerging benefits, and novel approaches to microbiome profiling. npj Sci Food. (2022) 6:15. doi: 10.1038/s41538-022-00130-w
10. Kitessa, DA, Bacha, K, Tola, YB, Murimi, M, Smith, E, and Gershe, S. Nutritional compositions and bioactive compounds of “Shameta”, a traditional home made fermented porridge provided exclusively to lactating mothers in the western part of Ethiopia. Heliyon. (2022) 8:e08990. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08990
11. Hotessa, N, and Robe, J. Ethiopian indigenous traditional fermented beverage: the role of the microorganisms toward nutritional and safety value of fermented beverage. Int J Microbiol. (2020) 2020:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2020/8891259
12. Fentie, EG, Emire, SA, Demsash, HD, Dadi, DW, and Shin, JH. Cereal-and fruit-based Ethiopian traditional fermented alcoholic beverages. Food Secur. (2020) 9:1781. doi: 10.3390/foods9121781
13. Elema, T, Olana, BN, Elema, AB, and Gemeda, HF. Indigenous processing methods, physical properties and proximate analysis of fermented beverage of honey wine booka in Gujii, Ethiopia. J Nutr Food Sci. (2018) 8:2. doi: 10.4172/2155-9600.1000669
14. Tesfaye, M, and Tizazu, BZ. Characterization of physicochemical and rheological properties on qualities of “Tinsis” culture and “Tella”: Research square Ethiopian traditional fermented beer. (2022).
15. Talema, A, and Nega, A. Preparations and types of local traditional alcoholic beverage (Tella) in Amhara region, Amhara, Ethiopia. J Drug Alcohol Res. (2022) 11:1–8. doi: 10.4303/jdar/236173
16. Lee, M, Regu, M, and Seleshe, S. Uniqueness of Ethiopian traditional alcoholic beverage of plant origin, tella. J Ethnic Foods. (2015) 2:110–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jef.2015.08.002
17. Tekle, B, Anuradha Jabasingh, S, Fantaw, D, Gebreslassie, T, Ram Mohan Rao, S, Baraki, H, et al. An insight into the Ethiopian traditional alcoholic beverage: Tella processing, fermentation kinetics, microbial profiling and nutrient analysis. Lwt. (2019) 107:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.02.080
18. Tafere, G. A review on traditional fermented beverages of Ethiopian. J Nat Sci Res. (2015) 5:94–102.
19. Andualem, B, Shiferaw, M, and Berhane, N. Isolation and characterization of Saccaromyces cervisiae yeasts isolates from “tella” for beer production. Ann Res Rev Biol. (2017) 15:1–12. doi: 10.9734/ARRB/2017/34129
20. Berza, B, and Wolde, A. Fermenter technology modification changes microbiological and Physico-chemical parameters, improves sensory characteristics in the fermentation of Tella: an Ethiopian traditional fermented alcoholic beverage. J Food Process Technol. (2014) 5:316. doi: 10.4172/2157-7110.1000316
21. Mogessie Ashenafi, MA A review on the microbiology of indigenous fermented foods and beverages of Ethiopia. The Biological Society of Ethiopia. (2006).
22. Alemu, F, Amhaselassie, T, Kelbessa, U, and Elias, S. Methanol, fusel oil, and ethanol contents of some Ethiopian traditional alcoholic beverages. Semantic Scholar. (1991).
23. Belete, Y, Chandravanshi, BS, and Zewge, F. Levels of the fluoride ion in six traditional alcoholic fermented beverages commonly consumed in Ethiopia. Fluoride. (2017) 50:79.
24. Assaye, M, Tamirat, B, and Fekadu, B. Ethanol concentration and calorific value of some local distilled Ethiopian alcohol (Areki): an energy potential assessment. Cogent Eng. (2021) 8:1979444. doi: 10.1080/23311916.2021.1979444
25. Abegaz, K, Beyene, F, Langsrud, T, and Narvhus, JA. Indigenous processing methods and raw materials of borde, an Ethiopian traditional fermented beverage. J Food Technol Africa. (2002) 7:59–64. doi: 10.4314/jfta.v7i2.19246
26. Nemo, R, and Bacha, K. Microbial, physicochemical and proximate analysis of selected Ethiopian traditional fermented beverages. Lwt. (2020) 131:109713. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109713
27. Kitessa, DA, Bacha, K, Tola, YB, Murimi, M, Gershe, S, and Guta, M. Microbial quality and growth dynamics in shameta: a traditional Ethiopian cereal-based fermented porridge. Fermentation. (2022) 8:124. doi: 10.3390/fermentation8030124
29. Bacha, K, Mchari, T, and Ashenafi, M. Microbiology of the fermentation of shamita, a traditional Ethiopian fermented beverage. SINET. (1999) 22:113–26.
30. Tadesse, G, Ephraim, E, and Ashenafi, M. Assessment of the antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Borde and Shamita, traditional Ethiopian fermented beverages, on some foodborne pathogens and effect of growth medium on the inhibitory activity. Internet J Food Safety. (2005) 5:13–20.
31. Tadesse, S, Chandravanshi, BS, Ele, E, and Zewge, F. Ethanol, methanol, acid content and other quality parameters of Ethiopian traditional fermented, distilled and factory-produced alcoholic beverages. SINET. (2017) 40:16–35.
32. Mulaw, G, and Tesfaye, A. Technology and microbiology of traditionally fermented food and beverage products of Ethiopia: a review. Afr J Microbiol Res. (2017) 11:825–44. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2017.8524
33. Redeat, B Nutrient intake inadequacy and its associated factors among 6–23 months aged children in Bahirdar, 2021 GC North West Ethiopia : Bahir Dar University Institutional Repository System. (2022).
34. Dibaba, K, Tilahun, L, Satheesh, N, and Geremu, M. Acrylamide occurrence in Keribo: Ethiopian traditional fermented beverage. Food Control. (2018) 86:77–82. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.11.016
35. Abawari, RA. Indigenous processing methods and raw materials of Keribo: an Ethiopian traditional fermented beverage. J Food Resource Sci. (2013) 2:13–20. doi: 10.3923/jfrs.2013.13.20
36. Abawari, RA. Microbiology of keribo fermentation: an Ethiopian traditional fermented beverage. Pakistan J Biol Sci. (2013) 16:1113–21. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2013.1113.1121
37. Gebreyohannes, BT, and Welegergs, GG. Determination of alcoholic content and other parameters of locally prepared alcoholic beverages (Korefe and Tej) at different stages in Gondar town. Semantic Scholar (2015).
38. Getnet, B, and Berhanu, A. Microbial dynamics, roles and physico-chemical properties of ‘Korefe’, a traditional fermented Ethiopian beverage. Biotechnol Int. (2016) 9:56–175.
39. Hirbo, HG, and Hola, RN. Traditional fermented drinks: Korefe, Borde, and Booka and their safety, Nutritiousness, and usefulness in southern Ethiopia. Research Square. (2023).
40. Gebretsadik, T, and Negash, D. Honeybee production system, challenges and opportunities in selected districts of Gedeo zone, southern nation, nationalities and peoples regional state, Ethiopia. Int J Res Granthaalayah. (2016) 4:49–63. doi: 10.29121/granthaalayah.v4.i4.2016.2754
41. Gebremedhin, G, Tadesse, G, and Kebede, E. Physiochemical characteristics of honey obtained from traditional and modern hive production systems in Tigray region, northern Ethiopia. Momona Ethiopian J Sci. (2013) 5:115–28. doi: 10.4314/mejs.v5i1.85335
42. Bahiru, B, Mehari, T, and Ashenafi, M. Chemical and nutritional properties of ‘tej’, an indigenous Ethiopian honey wine: variations within and between production units. J Food Technol Africa. (2001) 6:104–8. doi: 10.4314/jfta.v6i3.19299
43. Tsegaye, B, Girma, E, Agedew, E, Zerihun, E, Hailu, T, and Shibru, T. Proximal composition of indigenous alcoholic beverage cheka in Konso, southwestern, Ethiopia. J Food Process Technol. (2020) 11:840.
44. Binitu Worku, B, Gemede, HF, and Woldegiorgis, AZ. Nutritional and alcoholic contents of cheka: a traditional fermented beverage in southwestern Ethiopia. Food Sci Nutr. (2018) 6:2466–72. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.854
45. Awulachew, MT. Common Ethiopian fermented products: beverages-alcoholic/semi-alkali, dairy products. Glob Acad J Med Sci. (2021) 3:1–13. doi: 10.36348/gajms.2021.v03i01.001
46. Worku, BB, Woldegiorgis, AZ, and Gemeda, HF. Indigenous processing methods of Cheka: a traditional fermented beverage in southwestern Ethiopia. J Food Process Technol. (2015) 7:1–7. doi: 10.4172/2157-7110.1000540
47. Kayola, KK, Gebre, SG, Addisu, S, and Kussia, AD. Evaluation of aflatoxin content in Cheka (traditional beverage in South-Western Ethiopia) and its major ingredient (maize). Springer Nature. (2022).
48. Cuvas-Limon, RB, Nobre, C, Cruz, M, Rodriguez-Jasso, RM, Ruíz, HA, Loredo-Treviño, A, et al. Spontaneously fermented traditional beverages as a source of bioactive compounds: an overview. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 61:2984–3006. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1791050
49. Alemayehu, GF, Forsido, SF, Tola, YB, and Amare, E. Optimization of nutritional and sensory properties of fermented oat-based composite beverage. Heliyon. (2022) 8:e10771. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10771
50. Hidalgo-Fuentes, B, de, E, Cabrera-Hidalgo, AJ, Sandoval-Castilla, O, Espinosa-Solares, T, González-Reza, RM, et al. Plant-based fermented beverages: nutritional composition, sensory properties, and health benefits. Food Secur. (2024) 13:844. doi: 10.3390/foods13060844
51. Motlhanka, K, Zhou, N, and Lebani, K. Microbial and chemical diversity of traditional non-cereal based alcoholic beverages of sub-Saharan Africa. Beverages. (2018) 4:36. doi: 10.3390/beverages4020036
52. Srusti Udayakumar, DMDR, Priyashantha, H, Vidanarachchi, JK, and Ranadheera, CS. Probiotics and beneficial microorganisms in biopreservation of plant-based foods and beverages. Appl Sci. (2022) 12:12. doi: 10.3390/app122211737
53. Zugravu, CA, Bohiltea, RE, Salmen, T, Pogurschi, E, and Otelea, MR. Antioxidants in hops: bioavailability, health effects and perspectives for new products. Antioxidants. (2022) 11:241. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020241
54. Arora, P, Ansari, SH, and Arora, S. Nutritional beverages. American J PharmTech Res. (2020) 10:164–83. doi: 10.46624/ajptr.2020.v10.i3.015
55. Shifarew, T, Girma Asere, T, Yitibarek, M, and Diro, A. Proximate analysis and mineral contents of atella from traditional tella brewers in Jimma City, Ethiopia. Bull Chem Soc Ethiop. (2024) 38:825–37. doi: 10.4314/bcse.v38i4.1
56. Albene, D, Lema, NK, Tesfaye, G, Andeta, AF, Ali, K, and Guadie, A. Probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Ethiopian traditional fermented Cheka beverage. Ann Microbiol. (2024) 74:1–15. doi: 10.1186/s13213-024-01771-w
57. Mario, G, Ferruzzi, JT, Kris-Etherton, P, Weaver, CM, and Elizabeth, J. Johnson, perspective: the role of beverages as a source of nutrients and phytonutrients. Adv Nutr. (2019). doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz115
58. Degu, S, Meresa, A, Animaw, Z, Jegnie, M, Asfaw, A, and Tegegn, G. Vernonia amygdalina: a comprehensive review of the nutritional makeup, traditional medicinal use, and pharmacology of isolated phytochemicals and compounds. Front Natural Products. (2024) 3:1347855. doi: 10.3389/fntpr.2024.1347855
59. Reis-Dennis, S. Review of rethinking health care ethics by Stephen Scher and Kasia Kozlowska: Palgrave Macmillan, available open access. Monash Bioeth Rev. (2020) 38:83. doi: 10.1007/s40592-020-00107-z
60. Berhanu, M, Desalegn, A, Birri, DJ, Ashenafi, M, and Tigu, F. Microbial, physicochemical and proximate analysis of Tej collected from Amhara regional state of Ethiopia. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e16911. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16911
61. Gebremichael, WM, Abay, KH, Sbhatu, DB, Berhe, GG, and Gebreyohannes, G. Process standardization and characterization of Mies: Ethiopian honey wine. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e39272. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39272
62. Braide, W, Azuwike, C, and Adeleye, S. The role of microorganisms in the production of some indigenous fermented foods in Nigeria. Int J Adv Res Biol Sci. (2018) 5:86–94. doi: 10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.05.011
63. Getaye, A, Tesfaye, D, Zerihun, A, and Melese, F. Production, optimization, and characterization of Ethiopian traditional fermented beverage “Tella” from barley. J Emerg Technol Innov Res. (2018) 5:797–9.
64. Chelule, PK, Mbongwa, HP, Carries, S, and Gqaleni, N. Lactic acid fermentation improves the quality of amahewu, a traditional south African maize-based porridge. Food Chem. (2010) 122:656–61. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.026
65. Amiri, S, Motalebi Moghanjougi, Z, Rezazadeh Bari, M, and Mousavi Khaneghah, A. Natural protective agents and their applications as bio-preservatives in the food industry: an overview of current and future applications. Italian J Food Sci. (2021) 33:55–68. doi: 10.15586/ijfs.v33iSP1.2045
66. Cason, ED, Mahlomaholo, BJ, Taole, MM, Abong, GO, Vermeulen, JG, de Smidt, O, et al. Bacterial and fungal dynamics during the fermentation process of sesotho, a traditional beer of southern Africa. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:1451. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01451
67. Wassie, M, and Wassie, T. Isolation, characterization and identification of lactic acid bacteria from ready to consume Shamita: Ethiopian traditional fermented beverage. Int J Life Sci Technol. (2016) 9:51.
68. Mokoena, MP, Mutanda, T, and Olaniran, AO. Perspectives on the probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria from African traditional fermented foods and beverages. Food Nutr Res. (2016) 60:29630. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v60.29630
69. Tefera, T, Ameha, K, and Biruhtesfa, A. Cassava based foods: microbial fermentation by single starter culture towards cyanide reduction, protein enhancement and palatability. Int Food Res J. (2014) 21:1751.
70. Halake, NH, Chinthapalli, B, and Chitra, DV. Role of selected fermentative microorganisms on cyanide reduction, protein enhancement and palatability of cassava based food. Int J Res Agric Forestry. (2019) 6:1–12.
72. Sharma, R, Garg, P, Kumar, P, Bhatia, SK, and Kulshrestha, S. Microbial fermentation and its role in quality improvement of fermented foods. Fermentation. (2020) 6:106. doi: 10.3390/fermentation6040106
73. Cuamatzin-García, L, Rodríguez-Rugarcía, P, el-Kassis, E, Galicia, G, Meza-Jiménez, M, Baños-Lara, M, et al. Traditional fermented foods and beverages from around the world and their health benefits. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:1151. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061151
74. Saeed, F, Afzaal, M, Shah, YA, Khan, MH, Hussain, M, Ikram, A, et al. Miso: a traditional nutritious & health-endorsing fermented product. Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 10:4103–11. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3029
75. Gebre, TS, Emire, SA, Chelliah, R, Aloo, SO, and Oh, DH. Isolation, functional activity, and safety of probiotics from Ethiopian traditional cereal-based fermented beverage, “Borde”. Lwt. (2023) 184:115076. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.115076
76. Mulaw, G, Muleta, D, Tesfaye, A, and Sisay, T. Protective effect of potential probiotic strains from fermented ethiopian food against Salmonella Typhimurium DT104 in mice. Int J Microbiol. (2020) 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2020/7523629
77. Mulaw, G, Sisay Tessema, T, Muleta, D, and Tesfaye, A. In vitro evaluation of probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from some traditionally fermented Ethiopian food products. Int J Microbiol. (2019) 2019:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2019/7179514
78. Farag, MA, Xiao, J, and Abdallah, HM. Nutritional value of barley cereal and better opportunities for its processing as a value-added food: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 62:1092–104. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1835817
79. Steinkraus, K. Handbook of indigenous fermented foods, revised and expanded. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press (2018).
80. Dhyani, A, Semwal, KC, Semwal, KC, Yonas, M, Yadav, VK, and Chaturvedi, P Ethnobotanical knowledge and socioeconomic potential of honey wine in the horn of Africa. National Institute of Science Communication and Information Resources (NISCAIR) (2019).
81. Eyasu, M, Benedí, J, Romero, JA, and Martín-Aragón, S. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of selected medicinal plants from Addis Ababa against MDR-Uropathogenic Bacteria. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:10281. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910281
82. Hussen, EM, and Endalew, SA. In vitro antioxidant and free-radical scavenging activities of polar leaf extracts of Vernonia amygdalina. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2023) 23:146. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03923-y
83. Todorovic, S, Akpinar, A, Assunção, R, Bär, C, Bavaro, SL, Berkel Kasikci, M, et al. Health benefits and risks of fermented foods-the PIMENTO initiative. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1458536. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1458536
84. Siddiqui, SA, Erol, Z, Rugji, J, Taşçı, F, Kahraman, HA, Toppi, V, et al. An overview of fermentation in the food industry - looking back from a new perspective. Bioresour Bioprocess. (2023) 10:85. doi: 10.1186/s40643-023-00702-y
85. Asante, D-B, Wiafe, GA, Tsegah, KM, and Domey, NK. Therapeutic benefits of Vernonia amygdalina in the treatment of inflammation and its associated diseases. Clin Complement Med Pharmacol. (2024) 4:100122. doi: 10.1016/j.ccmp.2023.100122
86. Ugbogu, EA, Emmanuel, O, Dike, ED, Agi, GO, Ugbogu, OC, Ibe, C, et al. The Phytochemistry, ethnobotanical, and pharmacological potentials of the medicinal plant-Vernonia amygdalina L. (bitter Leaf). Clin Complement Med Pharmacol. (2021) 1:100006. doi: 10.1016/j.ccmp.2021.100006
87. Tura, AM, Anbessa, M, Tulu, ED, and Tilinti, B. Exploring Vernonia amygdalina’s leaf extracts for phytochemical screening and its anti-bacterial activities. Int J Food Prop. (2024) 27:960–74. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2024.2377242
88. Kitessa, DA. Review on effect of fermentation on physicochemical properties, anti-nutritional factors and sensory properties of cereal-based fermented foods and beverages. Ann Microbiol. (2024) 74. doi: 10.1186/s13213-024-01763-w
89. Skowron, K, Budzyńska, A, Grudlewska-Buda, K, Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N, Andrzejewska, M, Wałecka-Zacharska, E, et al. Two faces of fermented foods-the benefits and threats of its consumption. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:845166. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.845166
90. Nesterova, E, Morozova, P, Gladkikh, M, Kazemzadeh, S, and Syromyatnikov, M. Molecular methods for detecting microorganisms in beverages. Beverages. (2024) 10:46. :1–15. doi: 10.3390/beverages10020046
91. Granados-Chinchilla, F, Redondo-Solano, M, and Jaikel-Víquez, D. Mycotoxin contamination of beverages obtained from tropical crops. Beverages. (2018) 4:83. doi: 10.3390/beverages4040083
92. Kayola, KK, Gebre, SG, Addisu, S, and Kussia, AD. Evaluation of aflatoxin content in “Cheka” (traditional beverage in South-Western Ethiopia) and its major ingredient (maize). Discov Food. (2024) 4:1–15. doi: 10.1007/s44187-024-00079-7
93. Ohimain, EI. Methanol contamination in traditionally fermented alcoholic beverages: the microbial dimension. Springerplus. (2016) 5:1607. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-3303-1
94. Lasso García, C, German Bermúdez, FA, vanden Berghe, W, Gabriela Zurita-Benavides, M, and Orellana-Manzano, A. Fermented beverages among indigenous Latin American societies. Front Sustain Food Syst. (2024) 8:8. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1390162
Keywords: bioavailability, fermentation, nutritional value, traditional beverage, Ethiopia
Citation: Mulaw G, Gebregziabher T and Tesfay T (2025) A review on the microbiology of Ethiopian traditional fermented beverage products. Front. Nutr. 12:1519547. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1519547
Received: 30 October 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 29 January 2025.
Edited by:
Ravinder Nagpal, Florida State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Yiannis Kourkoutas, Democritus University of Thrace, GreeceCopyright © 2025 Mulaw, Gebregziabher and Tesfay. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guesh Mulaw, Z2h1ZXMyMDAxQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; Teklemichael Tesfay, dGVrbGVtaWNoYWVsMjAxMEBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†ORCID: Guesh Mulaw, orcid.org/0000-0001-9596-7895
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.