- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 2The Center for Treatment of Pre-disease, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
Background: The prevalence of obesity and its related ailments is on the rise, posing a substantial challenge to public health. Tea, widely enjoyed for its flavors, has shown notable potential in mitigating obesity. Yet, there remains a lack of exhaustive bibliometric studies in this domain.
Methods: We retrieved and analyzed multidimensional data concerning tea and obesity studies from January 2004 to June 2024, using the Web of Science Core Collection database. This bibliometric investigation utilized tools such as Bibliometrix, CiteSpace, and VOSviewer to gather and analyze data concerning geographical distribution, leading institutions, prolific authors, impactful journals, citation patterns, and prevalent keywords.
Results: There has been a significant surge in publications relevant to this field within the last two decades. Notably, China, Hunan Agricultural University, and the journal Food and Function have emerged as leading contributors in terms of country, institution, and publication medium, respectively. Zhonghua Liu of Hunan Agricultural University has the distinction of most publications, whereas Joshua D. Lambert of The State University of New Jersey is the most cited author. Analyses of co-citations and frequently used keywords have identified critical focus areas within tea anti-obesity research. Current studies are primarily aimed at understanding the roles of tea components in regulating gut microbiota, boosting fat oxidation, and increasing metabolic rate. The research trajectory has progressed from preliminary mechanism studies and clinical trials to more sophisticated investigations into the mechanisms, particularly focusing on tea’s regulatory effects on gut microbiota.
Conclusion: This study offers an intricate overview of the prevailing conditions, principal focus areas, and developmental trends in the research of tea’s role against obesity. It delivers a comprehensive summary and discourse on the recent progress in this field, emphasizing the study’s core findings and pivotal insights. Highlighting tea’s efficacy in obesity prevention and treatment, this study also points out the critical need for continued research in this area.
1 Introduction
Obesity, defined by an abnormal and excessive accumulation of fat, is witnessing a notable increase in its prevalence worldwide (1, 2). The World Health Organization (WHO) projects that by 2022, approximately 2.5 billion adults aged 18 and older will be classified as overweight globally, representing around 30% of the total population. Of these, around 890 million individuals are expected to be classified as obese (3, 4). The main objective of managing obesity is to enhance health, as achieving a sustained weight loss exceeding 10% of total body weight significantly improves various obesity-related conditions, including type 2 diabetes (T2D), hypertension, fatty liver disease, and obstructive sleep apnea, ultimately leading to a better quality of life (5).
Currently, anti-obesity medications predominantly focus on regulating food intake by acting on various neurotransmitters in the central nervous system (CNS). These medications are designed to reduce hunger, increase feelings of fullness, and diminish food reward, either individually or in combination (5). Beyond Orlistat, which inhibits gastric and pancreatic lipase activities resulting in the non-absorption of approximately 30–35% of ingested fats (6), other drugs such as Phentermine and Bupropion influence distinct neurological pathways (7, 8). The primary side effects of Orlistat are gastrointestinal, while Phentermine (with or without Topiramate) and Naltrexone-Bupropion are more prone to cause neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as agitation and insomnia (9, 10). Despite their market approval and availability, these drugs continue to pose safety concerns and are generally expensive (11–13). Additionally, while weight loss surgeries like adjustable gastric banding, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, and sleeve gastrectomy are regarded as the most effective and long-lasting methods for managing obesity (14), only 1% of eligible patients undergo these procedures. The predominant barriers to surgery are its limited accessibility, substantial cost, patient hesitance, and the risk of severe complications and mortality, although the rates of surgery-related deaths have markedly decreased, the incidence of complications persists at about 17% (14).
Lifestyle adjustments, including dietary and physical activity changes, are fundamental to obesity management. Although dependent on personal commitment, they significantly reduce the risk of diseases associated with obesity, particularly in genetically predisposed individuals (15, 16). Other therapeutic options, such as pharmacological treatments and surgical interventions, have their own limitations, including potential adverse effects, and elevated risks and expenses (17, 18). Amid these challenges, the focus on natural foods as potential alternatives has increased, with tea being a notable example.
Tea, a beverage brewed from the leaves of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis), has been used in Chinese medicine for over 3,000 years, and it is an infusion made from the leaves of the tea plant (19, 20). Over centuries, tea has spread from China to other parts of Asia, Europe, the Americas, and Africa (19). Tea is classified based on its processing techniques into six main varieties: green tea (unfermented), white tea (lightly fermented), yellow tea (mildly fermented), oolong tea (semi-fermented), black tea (fully fermented), and dark tea (post-fermented) (21–23).
Green tea, the earliest form of tea, undergoes withering, fixation, rolling, and drying processes, with fixation crucial for deactivating enzymes at high temperatures, thereby preserving high levels of catechins and eliminating moisture and grassy smells from the leaves (24). This results in its distinctive “clear soup and green leaves” appearance and a rich, astringent taste. Green tea, minimally processed, retains more natural substances and undergoes less vitamin degradation (25). Depending on the processing method, green tea is further classified into pan-fired, oven-baked, steamed, and sun-dried varieties. White tea, primarily produced in Fujian and Yunnan provinces of China, is celebrated for its unique flavor (26). Its processing involves only withering and drying, significantly reducing the moisture content of the leaves, enhancing enzyme activity, partially oxidizing polyphenols, and degrading chlorophyll, which contributes to its distinctive color, aroma, and flavor (27–29). White tea is particularly rich in catechins and their derivatives, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (30).Yellow tea, unique to China, involves fixation, rolling, “yellowing,” and drying. The “yellowing” process, conducted in a humid and warm setting, allows for the transformation of metabolites in the tea leaves through the combined action of heat and enzymes, giving it the characteristic “yellow leaves and yellow soup” appearance and a sweeter, mellower taste than green tea (31). Yellow tea is also rich in phenolic compounds, amino acids, soluble sugars, vitamins, and other nutrients (32). Oolong tea, popular in southern China and classified as semi-fermented, combines the aromas of green tea with the rich flavors of black tea (33, 34). Its production includes several steps: sun withering, oxidation, tossing, rolling, firing, final roasting, and packaging (35). The partial oxidation of catechins during the fermentation process, ranging from 10 to 70%, reduces the catechin content but increases the concentration of polymerized polyphenols (36). Black tea, the most extensively consumed globally and accounting for the majority of tea production (37), is known for its health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, antihypertensive, anticancer, and anti-obesity properties (38). Its processing involves withering, rolling, fermentation, and drying, during which tea polyphenols (TPs) undergo oxidation and polymerization to form compounds like theaflavins, thearubigins, and theabrownins, contributing to its distinctive color, flavor, and aroma (39). Pu-erh tea, originating from Yunnan province in China, is a post-fermented type noted for its unique aroma and flavor as well as various health benefits (40). Its primary processing step, “wo dui,” involves microbial fermentation through extracellular enzymes and biological heat, along with the metabolic processes of the tea leaves, leading to its distinctive flavor profile (41).
In food science and nutrition research, the health benefits of tea, particularly its potential to mitigate obesity and related diseases, have garnered increasing attention. Recent studies, including one utilizing a nonlinear dose–response assessment, have identified an inverse correlation between body weight, body mass index (BMI), and high levels of green tea consumption, specifically over 1,000 mg/day. Supplementation with green tea has been shown to reduce body weight and BMI in overweight and obese women, suggesting that healthcare professionals might recommend a daily intake of at least 1,000 mg of green tea for a minimum duration of 8 weeks (42).
Tea is abundant in active dietary compounds, and its regular consumption is associated with various health benefits, particularly in managing human metabolic diseases (43). Epidemiological studies have consistently demonstrated that regular consumption of tea and its components positively affects these diseases, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity (44, 45). Experimental research has further investigated tea’s antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, anti-obesity, cardiovascular protective, liver protective, and hypoglycemic activities and its underlying mechanisms (46). A meta-analysis has verified that supplements containing green tea catechins effectively reduce waist circumference and triglyceride levels while improving HDL-C levels (47). Additionally, black tea has been shown to alter the mRNA levels of liver lipid metabolism genes, thereby preventing excessive liver fat accumulation (48). By maintaining a balance between gut microbiota and liver lipids, supplementation with Huangshan Maofeng green tea extract (HTE) has significantly reduced fat accumulation in rats, improving conditions related to hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis (49). TPs have demonstrated significant (p < 0.01) effects in reducing the expression levels of COX-2 and iNOS, thereby decreasing liver fat content and degeneration. These findings suggest that TPs, through the involvement of TNF-α, IL-1 beta, and IL-6, could play a therapeutic role in treating obesity, liver inflammation, and fatty degeneration by inhibiting COX-2 and iNOS (50). Catechins have also been shown to prevent obesity-induced kidney damage by regulating the PPARγ/CD36 pathway and the rat intestinal-kidney axis (51).
Tea exhibits significant anti-obesity effects; however, the development of obesity is influenced by various factors, such as diet and exercise. Therefore, combining tea with other functional substances or adopting healthy lifestyles can more effectively promote weight loss and enhance weight management. Additionally, the stability of some substances is poor, and the application of nanotechnology and other methods can augment their strength and efficacy.
For instance, Winter Melon Lotus Leaf Tibetan Tea (WLTT) effectively mitigates obesity by modulating gut microbiota imbalances and stabilizing gut flora; its use is also considered safe. This blend of Tibetan tea with both medicinal and edible Chinese herbs presents a novel approach to combating obesity (52). Additionally, Compound Citrus Peel Tea (CCT), which is formulated from citrus peel, Ganoderma lucidum, and Pu-erh tea, manages gut microbiota and counters metabolic disorders related to obesity in mice (53). Research indicates that when green tea is augmented with α-glucosyl hesperidin (GT-GH), it prevents weight gain, especially in individuals younger than 50, where its anti-obesity effects are more pronounced (54). Moreover, a combination of Pu-erh tea extract and intermittent fasting (IF) addresses obesity by curbing fat accumulation and enhancing thermogenesis, which may reduce follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels and thus alleviate FSH’s suppressive impact on UCP1 (55). When used alongside physical exercise, Green Tea Extract (GTE) not only improves metrics such as weight, BMI, waist-to-hip ratio, and body fat percentage, but it also significantly enhances anti-inflammatory and metabolic responses (56). Therefore, tea, as a viable natural remedy for obesity, effectively supports a healthy lifestyle.
EGCG, a natural polyphenolic compound, exhibits multiple biological activities, including antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-obesity, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties (57). Despite these properties, its clinical utility is restricted by its low stability under neutral or alkaline conditions and poor oral bioavailability. Techniques such as esterification, the use of nanoparticle technology, silicon-based EGCG nanoparticles (EGCG-NPs), and other EGCG formulations provide optimal strategies for its modification. These adaptations result in low-toxicity, high-concentration EGCG, which facilitates effective penetration and absorption both in vitro and in vivo. Enhancements to EGCG through reduced dosages markedly increase its biological activity, efficacy, and stability, thus expanding its use across clinical settings, and the food and cosmetics sectors (58). Encapsulating EGCG with nanotechnology can improve its stability, efficacy, and pharmacokinetic characteristics (59). Additionally, researchers have developed and characterized two novel EGCG-glucose conjugates: glu-EGCG, with one glucose molecule, and 2glu-EGCG, with two glucose molecules. Experimental outcomes on animals reveal that both glu-EGCG and 2glu-EGCG exhibit substantially greater antioxidant activities than EGCG alone, effectively diminishing ischemic regions, preventing morphological alterations in brain tissue, reducing neuronal loss, and balancing oxidizing and antioxidizing agents. Notably, 2glu-EGCG displays stronger antioxidant capabilities than glu-EGCG, highlighting their substantial potential as targeted antioxidant neuroprotective agents (60). Moreover, the combination of EGCG and L-theanine in green tea not only curbs fat accumulation but also, through forming a complex with L-theanine/β-cyclodextrin, significantly boosts the bioavailability of EGCG as well as its lipid-lowering and weight reduction impacts (61). Tea mixtures treated with nanotechnology might enhance their bioavailability and efficacy, showing robust anti-obesity properties (62). Through diverse methods like esterification and nanoparticle technology, the stability and biological activity of EGCG can be significantly improved, paving the way for its broader application in functional foods and beyond (58).
Bibliometrics, the quantitative evaluation of scientific literature via mathematical and statistical techniques, can uncover developmental trends, central themes, and emergent hotspots within specific disciplines (63). In recent years, various bibliometric tools have been extensively adopted across diverse research areas. Among these, VOSviewer, developed by Van Eck and his colleagues at Leiden University, Netherlands (64); crafted by ChanSuperMax at Drexel University, USA (65); and Bibliometrix, an R-based tool from Dr. Massimo Aria at the Università degli Studi Federico II in Naples, Italy (66), stand out. Each application has unique capabilities: VOSviewer is adept at illustrating keyword relationships and their associative strengths; CiteSpace excels at detecting developmental laws, pinpointing research hotspots, and defining field boundaries; Bibliometrix offers detailed graphical representations of data from literature (64, 67, 68).
Despite increasing studies into tea’s anti-obesity effects, supported by multiple animal and human research (69, 70), there is a noticeable dearth of extensive bibliometric studies in this realm, especially concerning the prediction of research focal points. This study utilizes Bibliometrix, CiteSpace, and VOSviewer for a bibliometric review of publications related to tea and obesity spanning the last two decades. The objective is to chart the current research landscape, delineate key hotspots, and project future trends, thereby establishing a basis for further inquiry.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data sources and methods
2.1.1 Retrieval strategy
To ensure thorough and precise data collection, searches were performed within the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E) and the Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) from the Web of Science (WOS) Core Collection. The deployed search strategy was: (TS = (tea) AND TS = (obesity OR “high-fat diet” OR “overweight” OR “obes*” OR “body mass index” OR BMI OR “adiposity” OR “excess weight” OR “weight gain”)), covering the period from January 1, 2004, to June 30, 2024. This search was executed on July 1, 2024, restricting the inclusion to articles and reviews.
2.1.2 Data processing
To reduce biases from automated searches, a manual screening method was implemented, ensuring that only literature directly relevant to the anti-obesity properties of tea was analyzed for accurate and dependable assessment. Two researchers independently performed the literature search and download process. The initial search identified 3,752 potentially relevant articles, with 661 eventually selected for inclusion. Figure 1 illustrates the detailed retrieval and study selection methodology. Subsequently, after data validation and standardization, the literature was exported in both “Bibtex” and “plain text files,” which included comprehensive documents and cited references. These were analyzed further using VOSviewer (version 1.6.20), CiteSpace (version 6.2.R6), and the “bibliometrix” software package.
2.2 Bibliometric analysis
The bibliometric analysis focused on critical indicators such as titles, abstracts, keywords, authors, countries of publication, publication years, and journal details. For pivotal studies, the Web of Science (WOS) provided the most recent impact factors (IF), 5-year impact factors, journal tiers, and Hirsch index (H-index). The IF is an essential measure of a journal’s influence, determined by the citation frequency of its articles in subsequent scientific works (71). These indicators are vital for evaluating the quality of publications and serve as a core component of scholarly assessment (72). CiteSpace conducted a burst analysis of keywords and references for specific periods, aiding in the identification and clarification of emerging trends. Meanwhile, the “bibliometrix” package offered comprehensive statistics on journals, authors, countries, and institutions, while VOSviewer mapped collaborative networks among countries and institutions and conducted co-citation analyses of highly cited documents (73, 74).
3 Results
Utilizing the R package Bibliometrix, we conducted an analysis of the literature on tea anti-obesity research (Supplementary Figure S1). Over the period from 2004 to 2024, the field demonstrated a positive trajectory with a total of 661 publications, including 541 research papers and 120 review articles. These publications spanned 208 different journals, demonstrating the breadth of research interest in this area. On average, each publication received 46.1 citations, emphasizing the substantial impact of these studies. The mean age of these publications was 7.24 years, indicating a mature and well-established research continuum.
3.1 Annual trends in the number of publications
Figure 2 displays both the annual and cumulative publication trends from 2004 to 2024, illustrating the dynamic evolution of research within this domain. The data show a consistent annual increase in publications, with a marked rise beginning in 2016. Despite some variability in yearly publication numbers, the overall volume has grown steadily, with an average annual growth rate of 5.86%, pointing to an increasing focus on tea anti-obesity research. We employed a polynomial model y = 1.3535x2 + 3.1687x + 23.973 to describe the growth trend of cumulative publications, achieving a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.9987. This result confirms that the polynomial model accurately represents the growth trend in the cumulative number of articles and predicts a continued increase, suggesting that tea anti-obesity research is an emerging and vibrant area of study.
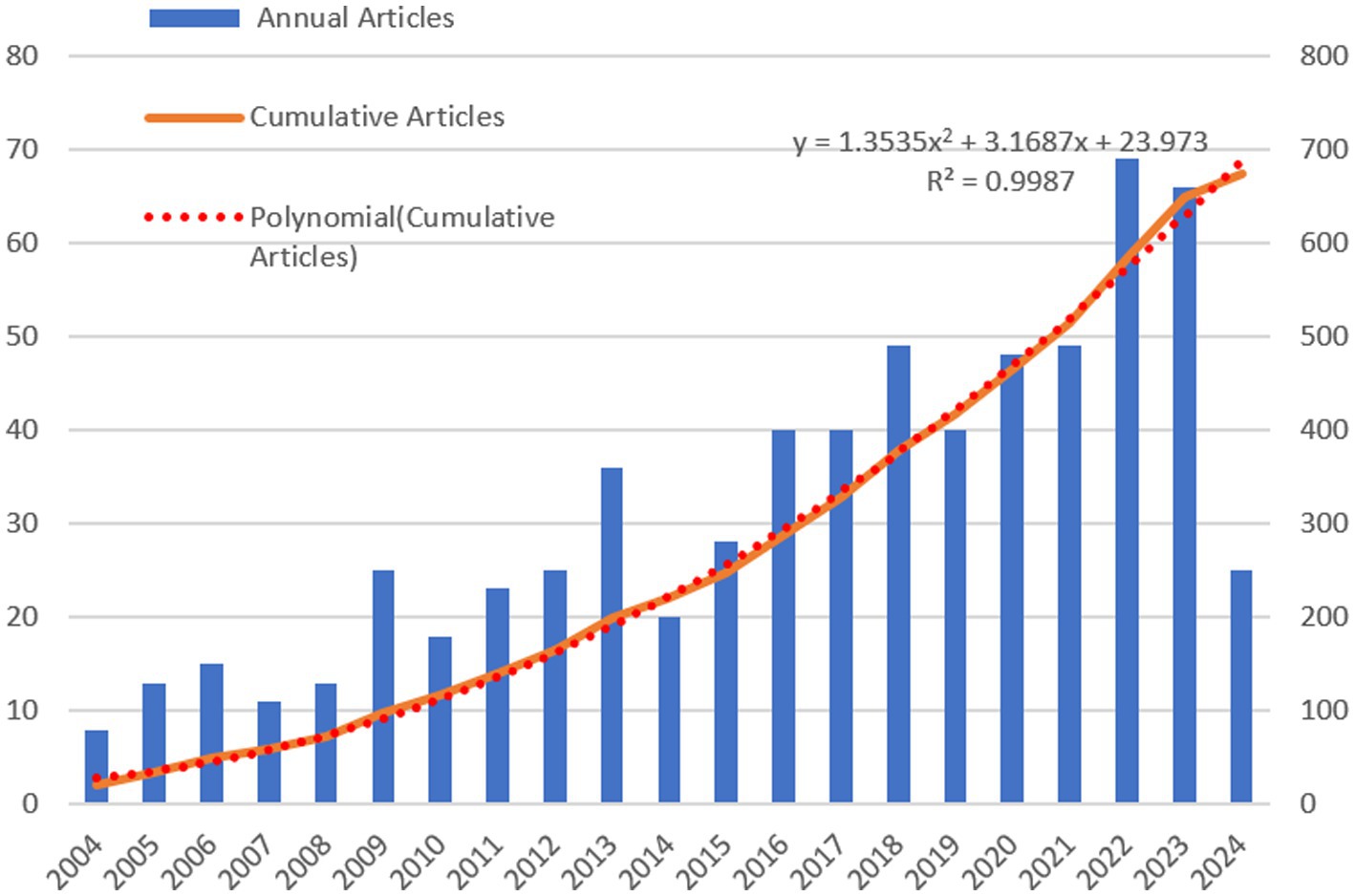
Figure 2. Publication growth trend of tea and obesity from 2004 to 2024. This graph shows annual publications in blue bars, the cumulative publications in an orange curve, and the red dashed line models the growth trend.
3.2 Countries and affiliations collaborative network
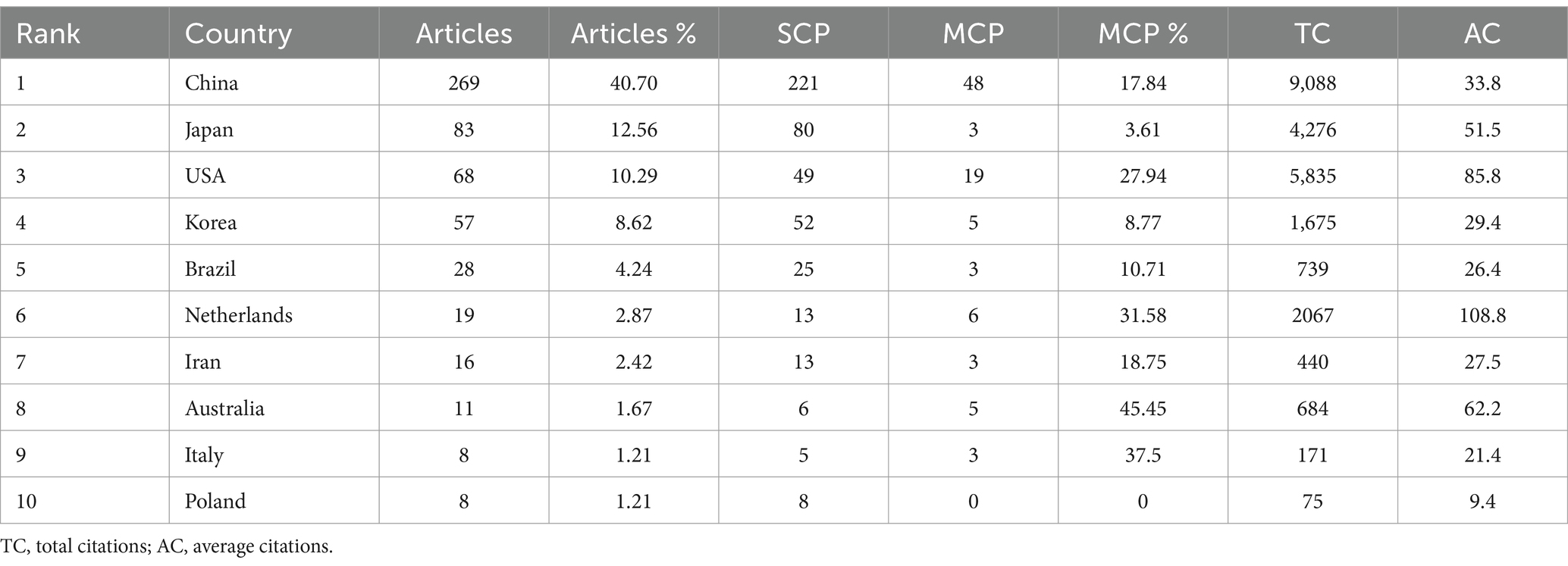
Tea anti-obesity research spans 41 countries, displaying considerable variation in scholarly output. China, with 269 publications representing 40.7% of the total, leads in this research area, likely driven by its extensive tea culture (TC) and consumption. These publications have accrued 9,088 citations, averaging 33.8 per article, reflecting significant global recognition (Table 1). Japan and the United States are next, with 83 and 68 publications respectively, accounting for 12.6 and 10.3% of the total. The citation average for Japan is 51.5, whereas it is higher in the United States at 85.8, underscoring the significant impact of American research. South Korea ranks fourth with 57 contributions. Other nations such as Brazil, the Netherlands, and Iran have made smaller contributions, with 28, 19, and 16 publications, respectively. Notably, Switzerland, despite having only eight publications, boasts an average citation count of 205.1 per article, highlighting the notable attention its research has received in the academic sphere. Figure 3a depicts the distribution of tea anti-obesity research across these countries, differentiating between single-country publications (SCP) and multi-country collaborative publications (MCP). The top five countries generally have low MCP ratios; for instance, China’s MCP ratio is 17.84%, indicating a strong domestic focus but also significant international collaboration. Japan has the lowest MCP ratio at 3.61%, suggesting a reliance on national resources with minimal international engagement. Conversely, the United States, with more SCPs, shows a higher propensity for international collaboration with an MCP ratio of 27.94%. Figure 3b highlights the most robust collaboration between China and the U.S., as indicated by the thickest connecting line. Among the top 10 countries by publication volume, Australia and Italy display the highest MCP ratios at 45.45 and 37.5%, respectively, reflecting strong international cooperation in tea anti-obesity research.
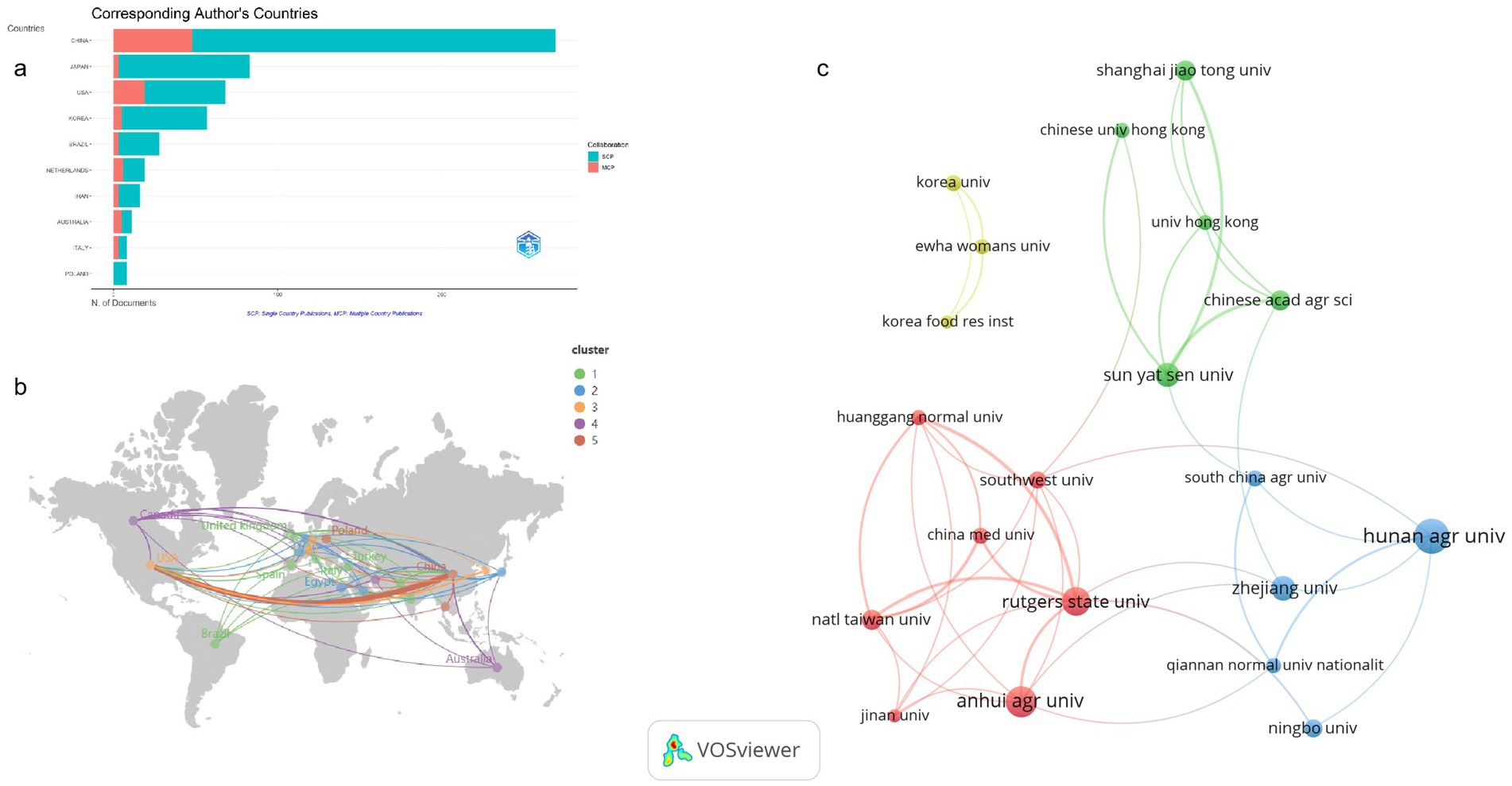
Figure 3. Analysis of countries and institutions publications. (a) Corresponding Author’s Countries. The figure’s blue segments illustrate SCPs, while the red segments represent MCPs. (b) Network diagram of collaborative relations between the top 22 most productive countries. The size of each node reflects the respective country’s publication count, with different colors distinguishing various clusters. The thickness of the lines between nodes indicates the level of collaborative intensity. (c) Collaboration of the top 20 most productive institutions.
A total of 899 institutions contributed to research in this field. Of the top 10 institutions, seven are located in China, accounting for 322 publications or 48.71% of the total (Supplementary Table S1). This underscores China’s pivotal role in tea-related anti-obesity research. Leading the count is Hunan Agricultural University with 96 publications, followed by Anhui Agricultural University with 75, and Yunnan Agricultural University with 33. The significant representation of agricultural universities highlights the importance of agrarian science in China, aligning with national priorities on agricultural science, technological innovation, and food security. Figure 3c delineates the collaborative networks of these institutions based on publication volume.
Within Cluster 1 (red), encompassing seven institutions, Rutgers State University is noted for its extensive collaborations within the cluster, as well as significant ties to Qiannan Normal University for Nationalities and Zhejiang University from other clusters, emphasizing its central role in the network. Cluster 2 (blue), consisting of five institutions, sees Qiannan Normal University for Nationalities demonstrating the closest cooperation with Hunan Agricultural University. In Cluster 3 (green), involving five institutions, Sun Yat-sen University forms key links with the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Cluster 4 (yellow), which includes three institutions, features close collaboration among Ewha Womans University, Korea Food Research Institute, and Korea University.
3.3 Author and sources analysis
The quantity of publications and citations are crucial indicators of academic impact. In this domain, 3,215 authors have contributed, with Liu Zhonghua from Hunan Agricultural University leading with 15 publications, although these have accumulated a relatively modest 288 citations (Supplementary Table S2). Qitang He from Rutgers University holds second place with 13 publications, which have garnered 683 citations. Joshua Lambert from the State University of New Jersey, ranked fifth with nine publications, has a notable citation count of 1,009, reflecting the high esteem and practical relevance of his research.
In the realm of tea anti-obesity studies, the journal Food & Function is at the forefront with 35 pertinent publications (Supplementary Table S3). A high h-index (20) and g-index (33) indicate broad citation and recognition across the academic landscape. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry and Nutrients also play significant roles, with 30 and 25 publications respectively, emphasizing their impact in nutrition and functional foods research. As shown in Figure 4a, there is a consistent year-on-year increase in publication output across these journals. Bradford’s law, which describes the distribution of articles in scientific journals (75) (Figure 4b), where the gray areas represent core journals in the field.
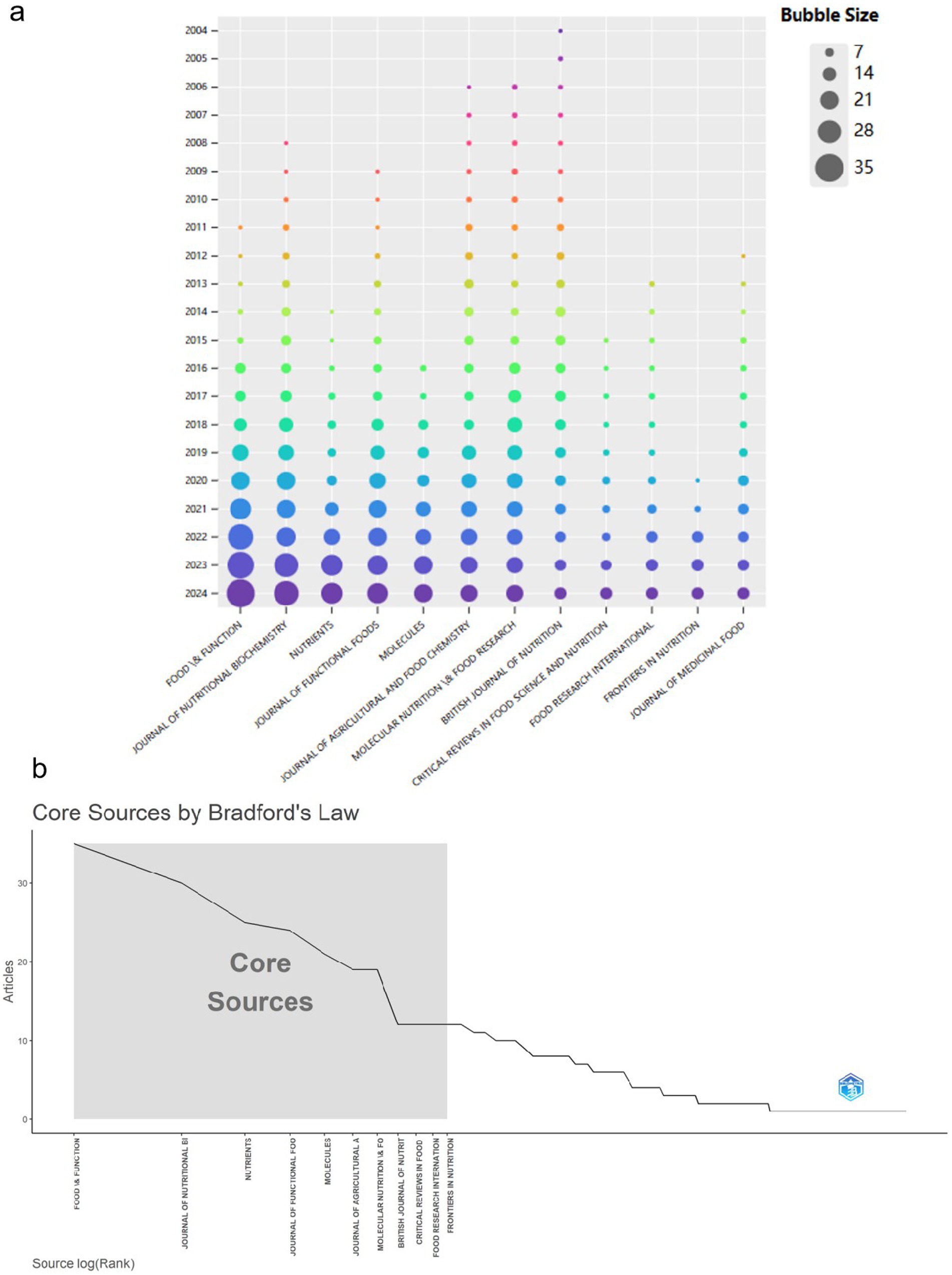
Figure 4. Analysis of sources publications. (a) Bubble plots depict the top 12 most productive sources. The legend categorizes the bubble sizes into five levels (7, 14, 21, 28, 35), with the bubble color gradually shifting from light to dark over time. (b) Core Sources according to Bradford’s Law.
3.4 Keywords analysis
Keywords facilitate the identification and extraction of core themes and directions in research. By analyzing keyword frequency and co-occurrence, researchers can pinpoint emerging hotspots and trends. Keywords Plus, derived from titles, abstracts, and references, augments author-provided keywords to expand the scope of the search (76). The keyword plus cloud (Figure 5a) prominently features “green tea,” surrounded by related terms such as “obesity,” “metabolic syndrome,” “insulin resistance,” and “weight loss,” signifying a strong focus on the potential benefits of green tea for weight management and metabolic health. Additional keywords like “catechins,” “polyphenols,” and “epigallocatechin-3-gallate” (commonly abbreviated as EGCG), along with “oxidative stress,” “inflammation,” “lipid metabolism,” and “intestinal flora,” elucidate the mechanisms through which green tea components may exert anti-obesity effects.
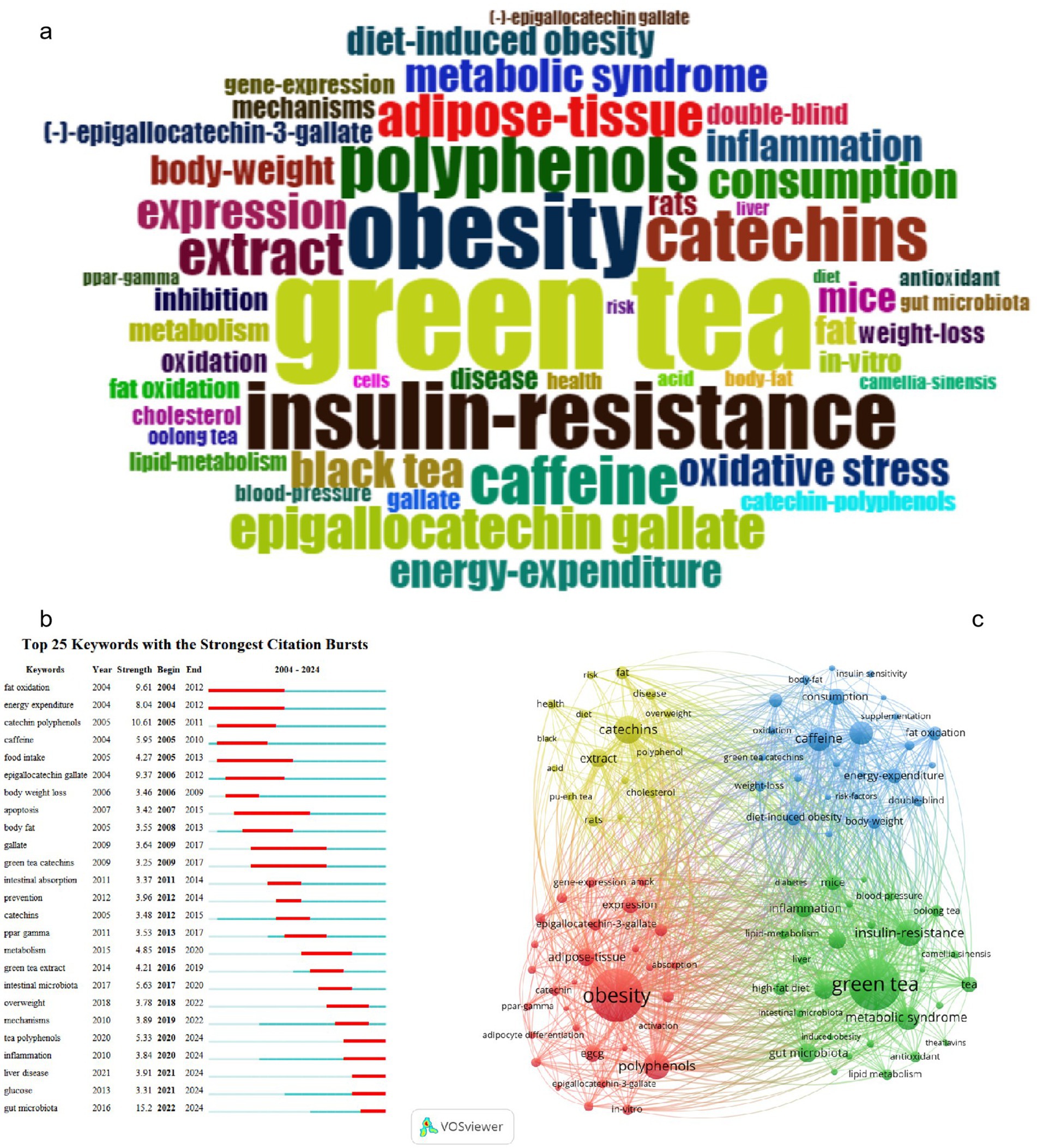
Figure 5. Keyword analysis. (a) Plus keyword cloud map. (b) Top 25 keywords with the strongest citation bursts. (c) Top 100 keyword co-occurrence map.
Using Vosviewer we analyzed the top 10 keywords by occurrence frequency (Supplementary Table S4). “Obesity” emerged as the most frequent appearing 291 times underscoring its prominence in the literature. “Green tea” was a close second with 283 occurrences highlighting its vital role in anti-obesity research. “Black tea” ranked ninth with 80 mentions. Notably “catechins” were third with 121 occurrences while “EGCG” was seventh with 96. “Polyphenols” were fourth with 113 mentions “caffeine” ninth with 97 and “gut microbiota” tenth with 71. “Insulin resistance” and “metabolic syndrome” ranked fifth and eighth with 112 and 95 occurrences, respectively, indicating their significance in obesity-related research. This data suggests that tea components might help in preventing and treating obesity by improving insulin sensitivity.
A “citation burst” indicates a sharp increase in the citation frequency of specific keywords within a particular period, often signaling trending topics or emergent trends within a discipline. As illustrated in Figure 5b,” gut microbiota” topped the list with a burst intensity of 15.2 between 2022 and 2024, underscoring its increasing importance in obesity and metabolic health research. Research has established a substantial correlation between the composition of gut microbiota and the metabolic state of the host, implying its influence on obesity and associated conditions through the modulation of energy metabolism and inflammatory responses. “Catechin polyphenols” and “EGCG” were ranked second and fourth in citation intensity, respectively, highlighting the therapeutic potential of these tea constituents, renowned for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and fat oxidation-enhancing properties. “Fat oxidation” and “energy expenditure” were ranked third and fifth, further accentuating the contribution of tea components to enhancing fat metabolism and energy expenditure.
Figure 5c presents an intricate keyword co-occurrence map of studies on tea’s anti-obesity effects, delineating four principal research areas (Supplementary Table S5). The first cluster (red, 27 clusters) is dedicated to metabolic regulation and cellular mechanisms, including keywords such as “obesity,” “epigallocatechin-3-gallate,” “adipogenesis,” “adipose tissue,” and “polyphenols.” The second cluster (blue, 25 clusters) pertains to population studies and weight management, encompassing “caffeine,” “energy expenditure,” “supplementation,” “consumption,” and “diet-induced obesity.” The third cluster (green, 24 clusters) centers on chronic diseases and metabolic health, featuring “green tea,” “metabolic syndrome,” “insulin resistance,” “inflammation,” and “gut microbiota.” The fourth cluster (yellow, 24 clusters) focuses on the antioxidant attributes of tea and its extensive impact on health, with keywords like “catechins,” “extract,” “polyphenol,” and “disease.”
3.5 Reference analysis
The literature cited in tea anti-obesity research spans several disciplines, with a primary focus on clinical and nutritional sciences, food science and molecular nutrition, and biochemistry and molecular biology. This diversity highlights the research’s application in clinical settings and dietary interventions, as well as its exploration of molecular mechanisms and biochemical underpinnings. Journals such as the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, and Nature exhibit high citation figures, reflecting the significant impact and broad academic attention garnered by this research, indicative of a trend toward multidisciplinary cross-research. The cited sources are divided into three groups (Figure 6a). The inaugural category (red, 28 entries) pertains to clinical and nutritional sciences. Esteemed publications include American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, BioScience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, British Journal of Nutrition, Clinical Nutrition, Diabetes Care, Endocrinology, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition Journal, International Journal of Obesity, Journal of the American College of Nutrition, Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, Journal of Medicinal Dietetics, Journal of Nutrition, Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, Journal of Nutritional Sciences and Vitamins, JAMA, The Lancet, Metabolism, New England Journal of Medicine, Nutrition Research, Nutrition, Obesity Research, The Obesity Reviews, Obesity, Physiology and Behavior, Phytomedicine, and Phytotherapy Research. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition and the Journal of Nutrition received 852 and 758 citations respectively, ranking them as the second and third most referenced journals (Supplementary Table S6), emphasizing the critical role of nutrition research in both clinical nutrition and public health sectors. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry stands as the fourth most-referenced journal, garnering 734 citations. The subsequent category (green, 22 references) is devoted to food science and molecular nutrition, including foremost journals such as Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, Carcinogenesis, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, European Journal of Nutrition, European Journal of Pharmacology, Food Chemistry, Food and Chemical Toxicology, Food and Function, Food Research International, Free Radicals Biology and Medicine, International Journal of Biomacromolecules, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Journal of Food Science, Journal of Functional Foods, Journal of Food and Agricultural Sciences, Life Sciences, Molecular Nutrition and Food Research, Molecules, Nutrients, Scientific Reports. The Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry is notable for the highest citation count (1,353) and total link strength (101,091), its significant influence on academic discourse. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research ranked fifth with 715 citations. The third category (blue, 18 items) delves into biochemistry and molecular biology, with prominent journals such as Biochemical and Biophysical Research Letters, Biochemical Pharmacology, Cell, Cell Metabolism, Diabetes Mellitus, The FASEB Journal, Gut, The Journal of Biological Chemistry, The Journal of Clinical Investigation, The Journal of Lipid Research, Nature Communications, Nature Medicine, The Nature Reviews Endocrinology, Nature, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Pharmacological Research, PLOS ONE, and Science.
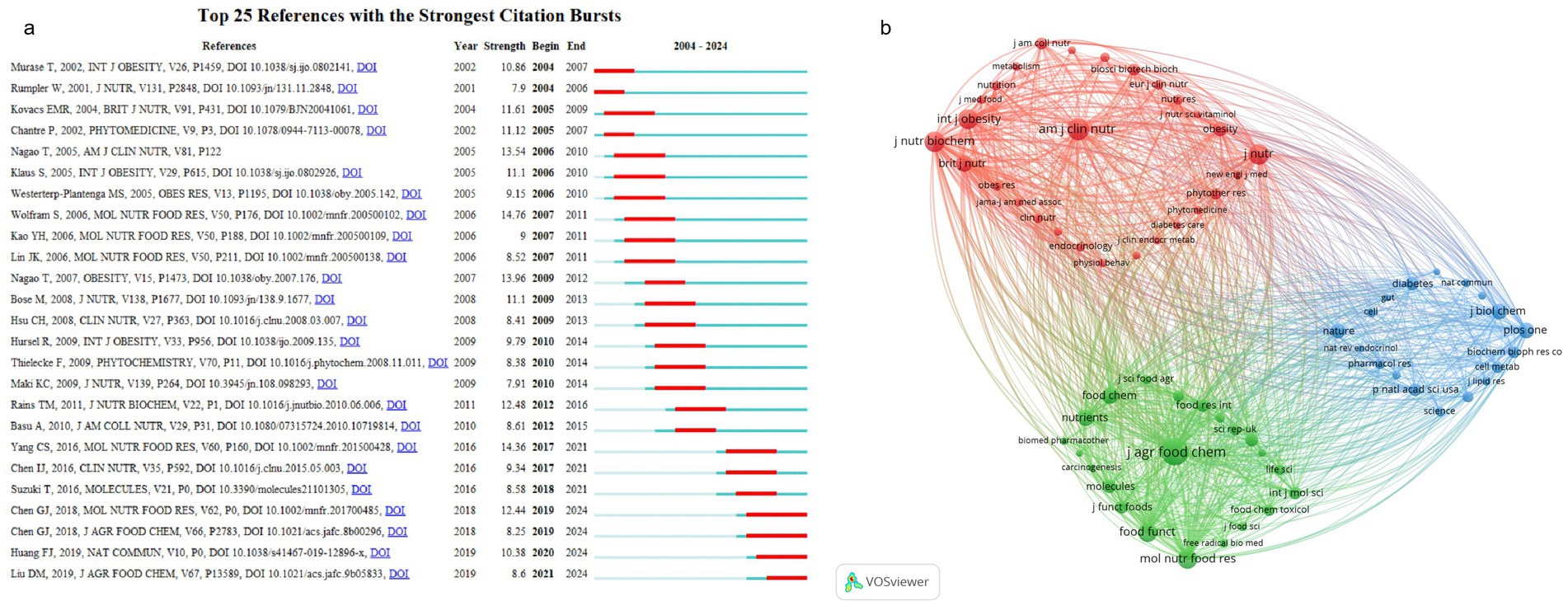
Figure 6. Reference analysis. (a) Co-occurrence of sources among the first 68 references. (b) Top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts.
The term “References with the Strongest Citation Bursts” denotes those publications experiencing a significant, sudden increase in citations within a specified timeframe, highlighting their pivotal role in sparking extensive interest and discussions across the academic landscape (77). The foremost citation burst (Figure 6b) transpired in the 2006 study by Wolfram et al. entitled “Anti-obesity effects of green tea: From bedside to bench” (78), reaching its peak between 2007 and 2011 with a burst score of 14.76. This review investigated how active tea compounds modulate fat metabolism, laying foundational insights for future inquiries.
Subsequently, Yang et al. analysis “Mechanisms of body weight reduction and metabolic syndrome alleviation by tea” (79) had a citation burst of 14.76 between 2017 and 2021. This article enhances our understanding of tea’s anti-obesity effects by delineating two main mechanisms: (i) tea components curtail the gut absorption of lipids and proteins, thus lowering calorie intake; (ii) TPs inhibit gluconeogenesis and fatty acid synthesis, boosting catabolism which ultimately aids in weight loss and remission of metabolic syndrome. The impact of these mechanisms may vary based on the type of tea ingested and individual dietary practices. Notably, Nagao’s 2007 and 2005 investigations, titled “A Green Tea Extract High in Catechins Reduces Body Fat and Cardiovascular Risks in Humans” (80) and “Ingestion of a Tea Rich in catechins leads to a reduction in body fat and malondialdehyde-modified LDL in men” (81), respectively, with citation bursts of 13.96 (2009–2012) and 13.54 (2006–2010), are significant. These clinical studies have shown that consistent consumption of catechin-rich green tea diminishes body fat, systolic blood pressure (SBP), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), underscoring its potential to mitigate obesity as well as cardiovascular disease risks.
The 2018 study by Chen et al., “Kudingcha and Fuzhuan Brick Tea Prevent Obesity and Modulate Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice” (82), ranked seventh in citation yet remains topical from 2019 to 2024, highlighting its continued relevance. This research investigates the effects of Kudingcha (KDC) and Fuzhuan Brick Tea (FBT) on the regulation of gut microbiota and obesity management. Results indicate that KDC decreases the relative abundance of the Danitaceae family, while FBT reduces the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio and enhances the relative abundance of Bifidobacterium, suggesting their role in mitigating metabolic syndrome features in mice on a HFD-fat diet by modulating the gut microbiota.
4 Discussion
4.1 Research overview and characteristics of publications
This study utilizes visualization and bibliometric analysis to outline the current research landscape concerning tea’s role in combating obesity. We document the yearly count of publications, along with data on contributing countries, institutions, journals, authors, references, and keywords, which elucidates the system, identifies research hotspots, and tracks the developmental trajectory of tea’s function against obesity, thus emphasizing the focal areas of this field. Drawing from the SCI-E and SSCI databases of WoSCC, we have compiled 661 papers and reviews from January 1, 2004, to June 30, 2024 (Figure 1). The persistent emphasis in this area is evidenced by a fluctuating yet growing trend in annual publications, with notable acceleration post-2016, marking the field’s ascension as a research hotspot.
A polynomial equation was employed to model the growth trajectory of the accumulated article count, achieving a high coefficient of determination (R2 = 0.9987) (Figure 2), which indicates robust predictive accuracy for future trends. This trend is propelled by: (1) the evolving recognition of TPs potential effects on obesity; (2) the intensifying global obesity crisis spurring the search for efficacious anti-obesity solutions; and (3) the inclination toward tea as a natural, side-effect-minimal option in line with current health trends. Although the annual growth rate of 5.86% signals active research, the steady development rate suggests the field remains exploratory, awaiting breakthroughs for accelerated progress.
The analysis (Figure 3) shows that China leads in tea and obesity research, followed by Japan, the USA, and South Korea, with Switzerland recording the highest average citation count per country, highlighting the high esteem and referential value of its research outputs. The national collaboration network indicates robust cooperation between China and the USA, with seven of the top 10 most prolific institutions based in China, where agricultural universities and research institutes play pivotal roles. This reflects China’s strong commitment to agricultural science and food research, especially concerning public health and nutrition. The institutional collaboration networks underscore the crucial role of international cooperation in driving this research area forward. Rutgers State University in the USA is particularly instrumental in fostering transnational research collaborations, facilitating knowledge exchange and advancing research.
Moreover, various Chinese institutions actively collaborate with global research entities, further bolstering China’s influence in the international tea anti-obesity research arena. Overall, the increasing globalization of the research network, with China at the helm, significantly contributes to the field’s rapid development. This global cooperation trend is poised to strengthen, underpinning more potential health applications of tea.
A total of 3,215 authors have engaged with the field of tea in combating obesity, with their influence measured by publication and citation counts. While Zhong Hualiu leads in publications, his relatively modest citation tally suggests limited research impact; conversely, Joshua Lambert’s substantial citations, despite fewer publications, denote his research’s high recognition and practical value.
An analysis of the distributed publications reveals 661 articles across 208 journals. Food and Function [IF(2023): 5.1, JCR: Q1] tops the list of journals in this research domain. Four of the top 10 journals boast impact factors above 5, with two exceeding 7 (Supplementary Table S3), indicative of the area’s propensity for more profound or innovative research. Predominantly, journals within the Q1 quartile host these high-impact studies, reflecting their broad acknowledgment and citation within the research community.
4.2 Research current status and trends
Reference co-citation and high-frequency keyword analyses have been utilized to delineate the principal areas of research within the domain of tea and obesity. Over the last two decades, “gut microbiota” has emerged as the keyword with the most significant intensity, peaking at 15.2 between 2022 and 2024; “catechin polyphenols” and “EGCG” ranked second and fourth, respectively, while “fat oxidation” and “energy expenditure” ranked third and fifth (Figure 5b). The research primarily focuses on the mechanisms through which tea constituents modulate intestinal microbiota, promote fat oxidation, and enhance energy expenditure to exert anti-obesity effects.
The timeline of Strongest Citation Bursts reveals evolving trends within the field. An initial review by Wolfram et al. (Figure 6b) in 2006 explored the impact of active green tea components, especially catechins, on fat metabolism, laying the groundwork for future studies on green tea’s anti-obesity properties. Subsequent clinical research by Nagao et al. from 2005 to 2007 substantiated the efficacy of green tea in reducing body fat and cardiovascular risks. Yang et al.’s study in 2016 further elucidated tea’s mechanisms, particularly its role in decreasing lipid absorption and activating AMPK. More recently, a 2018 study by Chen et al. has been instrumental in assessing tea’s capacity to counter obesity by influencing gut microbiota, with Citation Bursts spanning from 2019 to 2024, underscoring the persistent focus on gut microbiota in tea anti-obesity research.
The trajectory of tea anti-obesity research has progressively evolved from initial basic mechanism exploration and clinical studies to more in-depth mechanistic investigations in recent years. The modulation of gut microbiota has emerged as a focal point of research, with upcoming investigations expected to explore the interactions between tea constituents and gut microbiota in order to develop innovative anti-obesity approaches or functional food products.
4.2.1 Main anti-obesity components in tea
Tea, recognized as a natural and beneficial beverage, primarily attributes its anti-obesity effects to key components such as TPs, caffeine, amino acids (like L-theanine), thearubigins, and tea polysaccharides. These constituents collaboratively function through diverse mechanisms to regulate body weight and ameliorate health issues linked to obesity, with TPs and caffeine identified as the most potent agents for weight reduction (83). TPs, one of the main anti-obesity agents, benefit bone, liver, kidney, cardiovascular health, gut microbiota, and sleep quality (84). These include catechins, theaflavins, tannins, and flavonoids (85, 86), originate from various phenolics in tea and are present in multiple forms in both green and black teas. For instance, green tea comprises approximately 30–40% of its dry weight as catechins, which can convert into theaflavins during the fermentation process, predominantly found in black tea (87). Catechins’ anti-obesity properties are partly attributed to their beneficial effects on the gut microbiome, reduction in hepatic steatosis, and anti-inflammatory actions (88). EGCG is particularly noted for its significant role in the prevention and treatment of obesity (54). Theaflavins contribute to weight management by reducing food intake, inhibiting pancreatic lipase activity, activating AMPK proteins, and regulating gut microbiota (89). Research indicates that theaflavins TF1, TF2a, and TF3 enhance glucose and lipid metabolism in mice on a HFD by activating the SIRT6/AMPK/SREBP-1/FASN pathway, thus effectively mitigating obesity symptoms (90).
Caffeine, a natural plant-derived active compound known chemically as 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine, addresses obesity by affecting fat cell differentiation, boosting thermogenesis and fat breakdown, suppressing appetite, and reducing inflammation (91). Wu et al. (92) reported that caffeine diminishes appetite; Liu et al. (93) observed that it may decrease inflammation levels and suppress the expression of genes associated with fat production (such as SREBP1c, FAS, and ACC) and inflammatory markers (TNFα, MCP-1, and IL-6). L-theanine, an amino acid found naturally in tea leaves (94), has demonstrated substantial potential in regulating lipid metabolism. It influences gut microbiota and bile acid (BA) metabolism through the FXR-FGF15-CYP7A1 pathway (95). Tea pigments, which impart specific hues to tea, offer health benefits including anti-obesity, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties. Research has shown that raw Pu-erh tea brown pigment (R-TB) more effectively regulates blood sugar, reduces inflammation, and inhibits genes and proteins associated with fat production, whereas fermented Pu-erh tea brown pigment (F-TB) more effectively curtails genes and proteins linked to fat breakdown (96).
Tea polysaccharides (TPSs), significant bioactive components in tea, have been extensively researched for their antioxidant, anticancer, blood sugar-lowering, anti-fatigue, anticoagulant, anti-obesity, and immunomodulatory properties (97). Research demonstrated that a novel set of Fu brick tea polysaccharides (FTPS) extracted from Fuquan brick tea markedly reduced lipid levels in HepG2 cells treated with oleic acid compared to those treated with FTP3 (98). Hence, TPs, caffeine, L-theanine, and tea polysaccharides are the primary contributors to tea’s anti-obesity effects. Researchers also associate the anti-obesity properties of black tea with its alkaloid content (99). Indigestible substances in tea, such as cellulose, serve as prebiotics, further enhancing health by modulating gut microbiota and other mechanisms. These components display considerable potential and broad prospects for application in obesity research.
4.2.2 Regulation of gut microbiota
The human gut harbors a vast ecosystem, comprising billions of microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, collectively known as gut microbiota (100). These microorganisms are crucial for digesting nutrients, metabolizing energy, glucose, and cholesterol, and modulating chronic inflammation, significantly affecting the interplay between diet, obesity, and related diseases (101, 102). Research indicates that obese individuals typically have higher levels of bacteria like Lactobacillus, Escherichia coli, and Bacteroides, which are more efficient at energy harvesting, whereas levels of Bifidobacterium, which enhances gut function, are lower (103). Studies involving mice on HFDs have shown marked gut microbiota dysbiosis, notably an increase in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio (F/B ratio) (104). Reducing this ratio may aid obesity treatment, as supported by various studies (105). Clinical trials by Ley et al. (106) observed higher proportions of Firmicutes in obese subjects, which decreased following weight loss, thereby increasing Bacteroidetes levels. However, further research and meta-analyses have yet to confirm a definitive link between the F/B ratio and obesity (107), indicating that the relationship remains debatable and necessitates further exploration (108).
Tea has been found to enhance beneficial bacteria associated with favorable obesity outcomes, such as Alistipes and Lachnospiraceae, and suppress those positively correlated with obesity, thereby improving the gut microbial community structure (105). Additionally, metabolic byproducts of the gut microbiota, namely Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) including acetates, propionates, and butyrates, not only stimulate thermogenesis and fatty acid oxidation to reduce fat formation but also promote leptin secretion via G-protein coupled receptor 43 (GPR43), enhancing satiety and reducing food intake (109). SCFAs also elevate glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY) levels in the blood through G-protein coupled receptor 41 (GPR41), which enhances gut motility and appetite control via the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (110). Research by Liao et al. (111) confirmed that green tea increases Bifidobacteria levels in the gut microbiota of mice, which produce SCFAs. Additional studies have shown that combining brick tea with gut microbiota reconstruction encourages fat browning and thermogenesis, offering potential strategies for addressing obesity and its associated metabolic diseases (112).
The principal agents in tea promoting weight loss through gut microbiota regulation are TPs and tea polysaccharides. Other ingredients, such as tea pigments, caffeine, and theanine, also positively influence gut health, although research on these components is still relatively limited.
4.2.2.1 TPs regulate gut microbiota
Extensive studies have shown that TPs can modulate obesity by promoting or inhibiting the growth of specific gut bacteria (113). TPs directly influence the gut redox state and microbial community abundance (114), and are also transformed by the gut microbiota, affecting lipid metabolism processes. Research comparing the effects of TPs on conventional mice (CVZ) and pseudo-germ-free mice (PGF, treated with antibiotics) in terms of weight loss and lipid metabolism showed that TPs had a less pronounced anti-obesity effect on PGF-obese mice compared to obese CVZ mice, underscoring the significant role of gut microbiota in the impact of TPs on obesity, and suggesting that their anti-obesity effects might be diminished without a typical microbial community (115). It is believed that most TPs, possibly over 80%, remain in the gut where they are metabolized into short-chain fatty acids and phenolic acids by esterases and glucosidases produced by the gut microbiota (116), thereby enhancing the body’s capacity to break down and utilize these polyphenols, increasing the proportion of active substances involved in metabolic regulation (116). Many experiments have proven the regulatory effects of TPs on gut microbiota.
Research by Liu et al. (117) on the in vitro interactions between EGCG and human gut microbiota demonstrated that EGCG treatment stimulates beneficial bacteria such as Christensenellaceae, Bifidobacterium, and Bacteroides, and inhibit pathogens like Bilophila, Enterobacteriaceae, and Fusobacterium varium. Bacteroides and Bifidobacterium increase the production of secondary bile acids in the gut, impacting host metabolism in several crucial ways and playing an essential role in regulating lipid and glucose metabolism and energy balance.
Experiments by Li et al. (118) showed that TPs significantly mitigate the reduction in gut microbiota abundance and diversity caused by antibiotics, and increase the relative abundance of probiotics such as Eubacterium, Roseburia, and Lactobacillus. Gut microbiota, including Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria, are primary sources of short-chain fatty acids (119). Studies have proven that TP significantly boost the number of beneficial gut bacteria Akkermansia, which regulates host lipid balance through interactions with lipid metabolites, reducing endotoxin levels, increasing short-chain fatty acid production, and promoting fatty acid oxidation (120, 121). Additionally, Hussain et al. (115) found that compared with germ-free mice, the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes in conventional mice significantly decreased after catechin intake, and there was a significant reduction in epididymal fat, liver weight, glucose levels, total cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Thus, beyond directly regulating gut microbiota structure, TPs influence obesity-related diseases by affecting the production of gut microbial metabolites, including SCFAs and secondary bile acids. Furthermore, TPs can reduce weight by enhancing gut permeability, lowering endotoxin circulation levels, and alleviating inflammatory responses (122). Noel et al. (123) discovered that TPs alter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and urea cycle of gut microbiota in rats, thereby enhancing the energy conversion efficiency of rats, which aids in reducing blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
4.2.2.2 Tea polysaccharides regulate gut microbiota
As tea polysaccharides pass through the gastrointestinal tract, they undergo microbial breakdown into smaller sugar units. These microbes then utilize these sugars and produce beneficial short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (37, 124). Consequently, tea polysaccharides primarily influence gut microbiota by serving as prebiotics, which facilitates the production of bacterial metabolic products such as SCFAs—acetate, propionate, and butyrate. These changes in microbial activity subsequently alter the composition of the gut microbiota (125), leading to improvements in obesity management (126). Furthermore, studies have shown that the in vitro fermentation products of tea polysaccharides exhibit anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages, likely due to the SCFAs present in these products (127). In models of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis (128), tea polysaccharides have also been found to promote the growth of Bacteroides genus, which reduces levels of LPS in feces and plasma, thereby enhancing the intestinal epithelial barrier function and reducing both intestinal and systemic inflammation.
Taiping Houkui tea polysaccharides have shown potential in influencing lipid metabolism by reshaping the gut microbiota and its metabolic byproducts (129). In animal models, tea polysaccharides have effectively counteracted disruptions in gut microbiota in hyperlipidemic rats, reduced the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio, and increased the relative abundance of efficient SCFA producers such as Lachnospira sp., Victivallis, and Rossella spp. These microbiota alterations contribute to reducing cholesterol accumulation and fat synthesis in rats, thus aiding in the regulation of blood lipid levels (130). Research indicates that Ziyang selenium-rich green tea polysaccharides (Se-GTP) significantly raise the levels of succinate—a microbial metabolite linked to the thermogenesis of fat cells—in the colon of obese mice (131). Fu brick tea polysaccharides have been noted to promote adipocyte browning and thermogenesis by modulating gut microbiota, thereby offering a preventative measure against obesity (132). The anti-obesity impact of polysaccharides in dark tea (hmtp) correlates strongly with shifts in the relative abundance of gut microbiota, particularly with marked increases in Dubosiella and Romboutsia, which inversely correlate with body weight and positively with the IBAT index. Such microbial changes may trigger browning of inguinal white adipose tissue (iwat) and boost the thermogenic activity of brown adipose tissue (ibat) by upregulating thermogenic genes like UCP1, PRDM16, and PGC1 alpha (133). Additionally, TPs may decrease body weight by improving gut permeability, reducing endotoxin circulation levels, and alleviating inflammatory responses (122).
4.2.2.3 Other active ingredients regulate gut microbiota
Tea pigments, such as theaflavins, thearubigins, and theabrownins, regulate the abundance, diversity, and structure of gut microbiota, thereby aiding in weight loss (134). Theabrownin extract enhances the presence of beneficial gut bacteria like Prevotella and Bacteroides in individuals with metabolic diseases, boosts the production of SCFAs, aids in the breakdown of proteins and carbohydrates, improves insulin resistance, and significantly lowers blood sugar and lipid levels (135). In addition, theabrownins influence obesity and related diseases by modulating bile acid metabolism mediated by gut microbiota. The transformation of cholesterol into bile acids in the liver, via the classical pathway that produces 12α-hydroxy bile acids (cholic acid) catalyzed by CYP8B1 and the alternative pathway that yields non-12α-hydroxy bile acids (chenodeoxycholic acid) catalyzed by CYP7B1, constitutes the primary cholesterol metabolism route (136). Research has also shown that theabrownins elevate the abundance of Desulfovibrio and Clostridium, which are involved in the synthesis of secondary bile acids that activate the intestinal FXR signaling pathway by enhancing 7α-dehydroxylation, thus ameliorating lipid metabolic disorders (137, 138).
Further study reveal that a Fubrick tea supplement mitigated obesity induced by a HFD by altering gut microbiota and increased serum levels of caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine, correlating positively with the abundance of the Lachnospiraceae bacterial group (139). Post-intervention with high-caffeine tea, mice on a HFD exhibited a significant rise in Prevotella, a butyrate-producing bacterium known for its anti-inflammatory effects and enhanced energy metabolism (140). L-theanine has demonstrated efficacy in boosting the relative abundance of obesity-related probiotics such as Oscillibacter and Lactobacillus, while suppressing pathogens, thus mitigating obesity-induced gut microbiota dysbiosis (94).
4.2.3 Anti-obesity mechanisms
Tea and its components play a multifaceted role in obesity management through mechanisms such as modulating lipid metabolism, controlling dietary intake, adjusting energy metabolism, and managing oxidative stress and inflammation (89, 141).
4.2.3.1 Limiting dietary intake
Increasing food intake significantly contributes to obesity (142). Conversely, managing food intake is vital for preventing weight gain and involves regulating food consumption, selection, and absorption. Food intake correlates strongly with insulin sensitivity, leptin activity, and hypothalamic regulation (143, 144). Insulin regulates glucose homeostasis and fat metabolism through the hypothalamus, also influencing food intake. Leptin boosts lipid metabolism, inhibits fat formation, and supports related hypothalamic functions (145).
Studies demonstrate that tea and its components impact neuroendocrine metabolic regulators of appetite, reducing food consumption and limiting the gastrointestinal absorption of nutrients (146, 147). Theaflavins enhance insulin sensitivity by promoting protein kinase B signaling, reducing glucose toxicity, and suppressing inflammation (89). Matcha green tea is crucial in preventing obesity-induced hypothalamic inflammation by blocking the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby aiding in the management of obesity-related metabolic syndrome. This inhibition of inflammation-related pathways can restore normal hypothalamic functions, enhancing overall metabolic health (148). Feeding mice a 4% green tea diet for 16 weeks significantly reduced both food intake and serum leptin levels, leading to lower serum lipid levels (149). Additionally, intraperitoneal injection of green tea catechins reduced food intake by 50 to 60% in both lean and obese rats (150). Caffeine may suppress appetite by impacting hormones such as ghrelin and leptin. Combined administration of EGCG and caffeine not only prevents fat accumulation but also promotes anorexic effects in mice, elevating GLP-1 and POMC levels in the hypothalamus (151). However, the influence of green tea on reducing fat is noted to be independent of energy intake, suggesting a minimal impact on food consumption (152, 153). The effect of green tea on satiety is ambiguous and may vary based on dosage and method of administration (149, 150). Therefore, further investigations are necessary to understand the influence of factors such as gender, age, and dosage on green tea’s properties.
4.2.3.2 Inhibition of lipid absorption and synthesis
Lipid accumulation, a marker of overweight and obesity, results from increased fat synthesis, fatty acid intake, or diminished fatty acid oxidation (154). Inhibiting fat absorption and synthesis directly reduces body fat accumulation. Numerous studies confirm the efficacy of tea and its components in decreasing human fat storage and body weight (21, 79, 155). Tea components reduce the emulsification and absorption of lipids and proteins within the gastrointestinal tract, thereby lowering caloric intake (146, 156). They inhibit the differentiation and proliferation of preadipocytes (156), reducing lipid production (79, 147). Drinking Citrus Pu-erh Tea (CPT) before or after meals effectively lessens fat digestion in the small intestine, alleviating obesity due to excessive fat absorption (157). Consuming a blend of catechin-rich green tea extract and by-products like flavonols and polysaccharides blocks lipid absorption in the intestines, preventing accumulation in fat cells (158).
Another pathway to reduce lipid synthesis involves downregulating fatty acids. Research has demonstrated that tea brownie leads to a downregulation of proteins and mRNA expressions involved in fatty acid synthesis and lipid production (159). Both native and thermally modified catechins (TMC) are capable of downregulating endogenous fatty acid synthesis (160). Ganpu tea (Mandarin Pu-erh Tea) significantly reduces inflammatory cytokine levels induced by a HFD, diminishing lipid droplets and curtailing the expansion of white adipose tissue (161). Furthermore, tea affects the differentiation, growth, and deposition of fat cells. It has been shown that EGCG inhibits the differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into fat cells (162). Additionally, it restricts the growth of 3 T3-L1 cells through the miR-143/MAPK7 pathway (163). A combination of tea leaves and citrus (grapefruit) reduces lipid deposition in HepG2 cells via the AMPK/ACC pathway (164). Research also indicates that Liu Bao tea water extract (LTWE) prevents the proliferation and differentiation of preadipocytes by regulating the gene expression of transcription factors involved in fat generation and pro-inflammatory factors (165).
4.2.3.3 Promote the metabolism of energy substances
Boosting fat consumption is essential for weight loss as it helps reduce body fat and body weight, improves metabolic health, and lowers disease risk. Additionally, increasing fat consumption can enhance basal metabolic rate, improve exercise performance, and refine body composition. Research shows that tea and its components stimulate fat breakdown, lipid metabolism (79, 156), and fecal lipid excretion (146). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), extracted from oolong tea, promotes thermogenic proteins like uncoupling protein-1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator (PGC-1α), enhancing lipid metabolism and fatty acid oxidation (166).
Enhancing the number and function of mitochondria is closely linked to fat breakdown. Mitochondria promote fat oxidation, improve fat-burning efficiency, reduce body fat storage, and support energy production and metabolic health, maintaining the normal function of fat cells and overall metabolic balance. Treatment with heat-treated green tea extract (HTGT) and enzymatically modified isoquercitrin (EMIQ) is more effective than orlistat in combating obesity. In treated groups, genes related to mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and PKA signaling, associated with fat breakdown, showed dose-dependent upregulation, suggesting that this treatment enhances energy metabolism and glucose tolerance by boosting mitochondrial function and fat breakdown (167). Additional research indicates that HTGT and EMIQ have in vivo anti-obesity effects, partly by increasing mitochondrial metabolism in fat cells (168). Furthermore, studies have shown that EGCG mitigates palmitate-induced muscle atrophy by regulating mitochondrial function in C2C12 cells, increasing energy expenditure and mitochondrial content in mice to prevent obesity (169).
Brown fat cells generate heat by metabolizing fat, thereby increasing energy expenditure and reducing fat accumulation (170). Consequently, increasing the activity and number of brown fat cells is a key focus in contemporary obesity management research. Studies have shown that tea and its components facilitate the transformation of white adipose tissue to brown, enhancing its oxidation, combustion, and energy consumption through heat generation (146, 171). EGCG plays a role in anti-obesity by modulating the activity of both white and brown adipose tissues (172). Evidence suggests that EGCG significantly promotes anti-obesity effects by upregulating Beclin1-dependent autophagy and lipid breakdown in white adipose tissue (173). Additionally, studies have found that selenium-enriched green tea polysaccharides (SE-GTP) stimulate thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue (BAT) and the browning of inguinal white adipose tissue (IWAT) in obese mice by boosting the expression of thermogenesis-related marker proteins UCP1, PGC-1α, and Cidea in BAT and IWAT (131). Fu brick tea extract also increases energy expenditure and promotes the browning of subcutaneous adipose tissue by upregulating the expression of specific genes, such as uncoupling protein 1, effectively preventing weight gain (174).
4.2.3.4 Regulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory Levels
Obesity is recognized as a state of chronic low-grade inflammation where adipocytes secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 (175). Modulating oxidative stress and inflammation is critical for potential anti-obesity agents (79). Tea extracts exhibit strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, aiding in weight management and alleviating various chronic diseases (26). Matcha green tea inhibits the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, preventing hypothalamic inflammation induced by obesity (148). Aged green tea activates the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway, reducing fat accumulation and inflammatory responses prompted by a HFD (176). L-theanine effectively decreases inflammation and enhances metabolism by blocking the phosphorylation of key proteins in the NF-kappa B/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, thus preventing obesity in rats on a HFD (94). TP lower systemic LPS levels and curb the LPS-activated TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway, reducing inflammation linked to obesity (177). Tea components such as theanine and caffeine bolster antioxidant capabilities, amplify free radical scavenging activity, and lessen oxidative stress (178, 179).
The immune environment is crucial in obesity and metabolic syndrome, and modulating immune cells within adipose tissue can ameliorate metabolic issues. M2 macrophages foster anti-inflammatory responses and fat metabolism, enhancing insulin sensitivity. Polysaccharides from Da-Huang tea may aid in weight loss and improve metabolic syndrome by promoting the polarization of macrophages toward the M2 type (180). Further research shows that selenium-enriched green tea polysaccharides (SE-GTP) significantly increase the number of M2 macrophages in IWAT, which possess anti-inflammatory properties, promote metabolism, and enhance the thermogenic capacity of fatty tissue (131). Tibetan tea reduces chronic inflammation by suppressing inflammatory responses in white adipose tissue, decreasing adipocyte proliferation and immune cell infiltration. It also induces metabolic remodeling, promotes glutamine synthesis, and inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory chemokines, effectively aiding in weight loss (181).
5 Conclusion
This study utilized CiteSpace, VOSviewer, and bibliometrics online analysis platforms to thoroughly assess the current status, hotspots, and trends in tea anti-obesity research. Although China is leading in this domain, collaboration and communication among countries, institutions, and authors are still inadequate. While there has been progress in the research on preventing and treating obesity and its associated metabolic diseases, significant breakthroughs have yet to be achieved, indicating that the research remains largely exploratory. Further advancements in key areas are essential to hasten research progress, especially in deeper mechanistic studies and interdisciplinary collaboration. In conclusion, this bibliometric study offers a comprehensive overview of the field and provides valuable insights for future research.
Author contributions
SL: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BF: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. XL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. GS: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Project funded by the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (2024JJ5309) and the First National Young Qihuang Scholars Training Program (1022/000103101201).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the staff who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2024.1496582/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | Main information for details.
Supplementary Table S1 | Affiliations.
Supplementary Table S2 | Top 10 most productive authors.
Supplementary Table S3 | Top 12 most productive sources.
Supplementary Table S4 | Top 10 most productive keywords.
Supplementary Table S5 | The top 100 keyword clusters.
Supplementary Table S6 | Co-occurring sources of top 68 references.
References
1. Ng, M, Fleming, T, Robinson, M, Thomson, B, Graetz, N, Margono, C, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet. (2014) 384:766–81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8
2. Seravalle, G, and Grassi, G. Obesity and hypertension. Pharmacol Res. (2017) 122:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.05.013
3. Caballero, B . Humans against obesity: who will win? Adv Nutr. (2019) 10:S4–9. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy055
4. World Health Organization . Available at: https://www.who.int/ (Accessed September 15, 2024)
5. Perdomo, CM, Cohen, RV, Sumithran, P, Clément, K, and Frühbeck, G. Contemporary medical, device, and surgical therapies for obesity in adults. Lancet. (2023) 401:1116–30. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02403-5
6. Zhi, J, Melia, AT, Guerciolini, R, Chung, J, Kinberg, J, Hauptman, JB, et al. Retrospective population-based analysis of the dose-response (fecal fat excretion) relationship of orlistat in normal and obese volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. (1994) 56:82–5. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.104
7. Müller, TD, Blüher, M, Tschöp, MH, and DiMarchi, RD. Anti-obesity drug discovery: advances and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2022) 21:201–23. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00337-8
8. Billes, SK, Sinnayah, P, and Cowley, MA. Naltrexone/bupropion for obesity: an investigational combination pharmacotherapy for weight loss. Pharmacol Res. (2014) 84:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.04.004
9. Choi, YJ, Chung, EK, and Shin, S. A 10-year Nationwide pharmacovigilance assessment on anti-obesity medications and factors associated with serious adverse events. FASEB J. (2022) 36. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2022.36.S1.R3296
10. Pi-Sunyer, X, Apovian, CM, McElroy, SL, Dunayevich, E, Acevedo, LM, and Greenway, FL. Psychiatric adverse events and effects on mood with prolonged-release naltrexone/bupropion combination therapy: a pooled analysis. Int J Obes. (2019) 43:2085–94. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0302-z
11. Patel, D . Pharmacotherapy for the management of obesity. Metabolism. (2015) 64:1376–85. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.08.001
12. Rankin, W, and Wittert, G. Anti-obesity drugs. Curr Opin Lipidol. (2015) 26:536–43. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000232
13. Fujioka, K . Current and emerging medications for overweight or obesity in people with comorbidities. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2015) 17:1021–32. doi: 10.1111/dom.12502
14. Chang, S-H, Stoll, CRT, Song, J, Varela, JE, Eagon, CJ, and Colditz, GA. The effectiveness and risks of bariatric surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis, 2003-2012. JAMA Surg. (2014) 149:275–87. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2013.3654
15. Kim, MS, Shim, I, Fahed, AC, Do, R, Park, W-Y, Natarajan, P, et al. Association of genetic risk, lifestyle, and their interaction with obesity and obesity-related morbidities. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:1494–1503.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.06.004
16. Bray, GA, and Ryan, DH. Evidence-based weight loss interventions: individualized treatment options to maximize patient outcomes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2021) 23:50–62. doi: 10.1111/dom.14200
17. Kakkar, AK, and Dahiya, N. Drug treatment of obesity: current status and future prospects. Eur J Intern Med. (2015) 26:89–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2015.01.005
18. Kim, SH, Chun, HJ, Choi, HS, Kim, ES, Keum, B, and Jeen, YT. Current status of intragastric balloon for obesity treatment. World J Gastroenterol. (2016) 22:5495–504. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i24.5495
19. Hinojosa-Nogueira, D, Pérez-Burillo, S, Pastoriza de la Cueva, S, and Rufián-Henares, JÁ. Green and white teas as health-promoting foods. Food Funct. (2021) 12:3799–819. doi: 10.1039/D1FO00261A
20. Xing, L, Zhang, H, Qi, R, Tsao, R, and Mine, Y. Recent advances in the understanding of the health benefits and molecular mechanisms associated with Green tea polyphenols. J Agric Food Chem. (2019) 67:1029–43. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06146
21. Rothenberg, DO, Zhou, C, and Zhang, L. A review on the weight-loss effects of oxidized tea polyphenols. Molecules. (2018) 23:1176. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051176
22. Tang, G-Y, Meng, X, Gan, R-Y, Zhao, C-N, Liu, Q, Feng, Y-B, et al. Health functions and related molecular mechanisms of tea components: An update review. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:6196. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246196
23. Gao, Y, Xu, Y, Ruan, J, and Yin, J. Selenium affects the activity of black tea in preventing metabolic syndrome in high-fat diet-fed Sprague-Dawley rats. J Sci Food Agric. (2020) 100:225–34. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10027
24. Chen, M, Zhu, Y, Zhang, H, Wang, J, Liu, X, Chen, Z, et al. Phenolic compounds and the biological effects of Pu-erh teas with long-term storag. Int J Food Prop. (2017) 20:1715–28. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2016.1217877
25. Green tea (Camellia sinensis): a review of its Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology - PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35745040/ [Accessed October 15, 2024]
26. Abiri, B, Amini, S, Hejazi, M, Hosseinpanah, F, Zarghi, A, Abbaspour, F, et al. Tea’s anti-obesity properties, cardiometabolic health-promoting potentials, bioactive compounds, and adverse effects: a review focusing on white and green teas. Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 11:5818–36. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3595
27. Li, X, Smid, SD, Lin, J, Gong, Z, Chen, S, You, F, et al. Neuroprotective and anti-amyloid β effect and Main chemical profiles of White tea: comparison against green, oolong and black tea. Molecules. (2019) 24:1926. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101926
28. Wang, Y, Zheng, P-C, Liu, P-P, Song, X-W, Guo, F, Li, Y-Y, et al. Novel insight into the role of withering process in characteristic flavor formation of teas using transcriptome analysis and metabolite profiling. Food Chem. (2019) 272:313–22. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.013
29. Yue, W, Sun, W, Rao, RSP, Ye, N, Yang, Z, and Chen, M. Non-targeted metabolomics reveals distinct chemical compositions among different grades of Bai Mudan white tea. Food Chem. (2019) 277:289–97. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.113
30. Sanlier, N, Atik, I, and Atik, A. A minireview of effects of white tea consumption on diseases. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2018) 82:82–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.10.004
31. Xu, J, Wang, M, Zhao, J, Wang, Y-H, Tang, Q, and Khan, IA. Yellow tea (Camellia sinensis L.), a promising Chinese tea: processing, chemical constituents and health benefits. Food Res Int. (2018) 107:567–77. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.01.063
32. Wei, Y, Li, T, Xu, S, Ni, T, Deng, W-W, and Ning, J. The profile of dynamic changes in yellow tea quality and chemical composition during yellowing process. LWT. (2021) 139:110792. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110792
33. Ng, K-W, Cao, Z-J, Chen, H-B, Zhao, Z-Z, Zhu, L, and Yi, T. Oolong tea: a critical review of processing methods, chemical composition, health effects, and risk. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2018) 58:2957–80. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1347556
34. Salman, S, Öz, G, Felek, R, Haznedar, A, Turna, T, and Özdemir, F. Effects of fermentation time on phenolic composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of green, oolong, and black teas. Food Biosci. (2022) 49:101884. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101884
35. Wang, S, Zeng, T, Zhao, S, Zhu, Y, Feng, C, Zhan, J, et al. Multifunctional health-promoting effects of oolong tea and its products. Food Sci Human Wellness. (2022) 11:512–23. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2021.12.009
36. Chen, P-Y, Li, S, Koh, Y-C, Wu, J-C, Yang, M-J, Ho, C-T, et al. Oolong tea extract and Citrus Peel Polymethoxyflavones reduce transformation of l-carnitine to trimethylamine-N-oxide and decrease vascular inflammation in l-carnitine feeding mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2019) 67:7869–79. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03092
37. Zhao, Z, Chen, R, and Ng, K. Effects of differently processed tea on the gut microbiota. Molecules. (2024) 29:4020. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174020
38. Nasir, NF, Mohamad, NE, and Alitheen, NB. Fermented black tea and its relationship with gut microbiota and obesity: a Mini review. Fermentation. (2022) 8:603. doi: 10.3390/fermentation8110603
39. Xie, G, Ye, M, Wang, Y, Ni, Y, Su, M, Huang, H, et al. Characterization of pu-erh tea using chemical and metabolic profiling approaches. J Agric Food Chem. (2009) 57:3046–54. doi: 10.1021/jf804000y
40. Wang, S, Qiu, Y, Gan, R-Y, and Zhu, F. Chemical constituents and biological properties of Pu-erh tea. Food Res Int. (2022) 154:110899. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110899
41. Wong, M, Sirisena, S, and Ng, K. Phytochemical profile of differently processed tea: a review. J Food Sci. (2022) 87:1925–42. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16137
42. Zhang, Y, Tang, N, Xia, W, Sanjid Seraj, S, Pereira, M, Velu, P, et al. The effect of green tea supplementation on the anthropometric outcomes in overweight and obese women: a time and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2024) 64:10138–47. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2220796
43. Zhang, Z, Liu, C, Fang, W, Tang, Q, Zhan, L, Shi, Y, et al. Research progress on the lipid-lowering and weight loss effects of tea and the mechanism of its functional components. J Nutr Biochem. (2023) 112:109210. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109210
44. Al-Zalabani, AH, Wesselius, A, Yu, EY-W, van den Brandt, P, Grant, EJ, White, E, et al. Tea consumption and risk of bladder cancer in the bladder Cancer epidemiology and nutritional determinants (BLEND) study: pooled analysis of 12 international cohort studies. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:1122–30. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.03.020
45. James, A, Wang, K, and Wang, Y. Therapeutic activity of Green tea Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on metabolic diseases and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases: the current updates. Nutrients. (2023) 15:3022. doi: 10.3390/nu15133022
46. Shang, A, Li, J, Zhou, D-D, Gan, R-Y, and Li, H-B. Molecular mechanisms underlying health benefits of tea compounds. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) 172:181–200. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.06.006
47. Wang, Y, Xia, H, Yu, J, Sui, J, Pan, D, Wang, S, et al. Effects of green tea catechin on the blood pressure and lipids in overweight and obese population-a meta-analysis. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e21228. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21228
48. Liao, W, Liu, S, Chen, Y, Kong, Y, Wang, D, Wang, Y, et al. Effects of Keemun and Dianhong black tea in alleviating excess lipid accumulation in the liver of obese mice: a comparative study. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:849582. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.849582
49. Wu, G, Gu, W, Cheng, H, Guo, H, Li, D, and Xie, Z. Huangshan Maofeng Green tea extracts prevent obesity-associated metabolic disorders by maintaining homeostasis of gut microbiota and hepatic lipid classes in leptin receptor knockout rats. Food Secur. (2022) 11:2939. doi: 10.3390/foods11192939
50. Rahman, SU, Huang, Y, Zhu, L, Chu, X, Junejo, SA, Zhang, Y, et al. Tea polyphenols attenuate liver inflammation by modulating obesity-related genes and down-regulating COX-2 and iNOS expression in high fat-fed dogs. BMC Vet Res. (2020) 16:234. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02448-7
51. Patial, V, Katoch, S, Chhimwal, J, Dadhich, G, Sharma, V, Rana, A, et al. Catechins prevent obesity-induced kidney damage by modulating PPARγ/CD36 pathway and gut-kidney axis in rats. Life Sci. (2023) 316:121437. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121437
52. Yuan, Y, Zhang, B, He, J, Wei, T, Liu, D, Yang, W, et al. Combinations of Tibetan tea and medicine food homology herbs: a new strategy for obesity prevention. Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 11:504–15. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3081
53. Wang, J, Hao, J, Miao, D, Xiao, P, Jiang, X, and E-Hu, L. Compound chenpi tea consumption reduces obesity-related metabolic disorders by modulating gut microbiota and serum metabolites in mice. J Sci Food Agric. (2024) 104:431–42. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12940
54. Yoshitomi, R, Yamamoto, M, Kumazoe, M, Fujimura, Y, Yonekura, M, Shimamoto, Y, et al. The combined effect of green tea and α-glucosyl hesperidin in preventing obesity: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:19067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98612-6
55. Zhao, S, Hu, S, Sun, K, Luo, L, and Zeng, L. Pu-erh tea intake enhances the anti-obesity effect of intermittent fasting via modulating follicle-stimulating hormone and gut dysbacteriosis in female high-fat-diet mice. J Funct Food. (2023) 104:105495. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2023.105495
56. Bagheri, R, Rashidlamir, A, Ashtary-Larky, D, Wong, A, Alipour, M, Motevalli, MS, et al. Does green tea extract enhance the anti-inflammatory effects of exercise on fat loss? Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2020) 86:753–62. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14176
57. Luo, Z, Mao, D, Guo, J, Jia, X, Zhu, Y, Ke, J, et al. Experimental study of EGCG on endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced renal apoptosis in T2DM rats. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. (2024) 38:3909–18. doi: 10.23812/j.biol.regul.homeost.agents.20243805.309
58. Mehmood, S, Maqsood, M, Mahtab, N, Khan, MI, Sahar, A, Zaib, S, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate: Phytochemistry, bioavailability, utilization challenges, and strategies. J Food Biochem. (2022) 46:e14189. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14189
59. Peng, X, Mcclements, DJ, Liu, X, and Liu, F. EGCG-based nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, and applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2024) 22:1–22. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2328184
60. Lu, J, Chen, J, Yang, C, Xia, C, Deng, J, Xiang, Z, et al. Synthesis of novel EGCG-glucose conjugates and studies of their antioxidative properties for neuroprotections. Food Biosci. (2022) 49:101973. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101973
61. Liu, B, Chen, Z, Zhang, Y, Liu, E, Han, S, Gong, Z, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate + L-theanine/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes enhance epigallocatechin-3-gallate bioavailability and its lipid-lowering and weight loss effects. J Funct Food. (2022) 90:104998. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.104998
62. Salem, MA, Aborehab, NM, Abdelhafez, MM, Ismail, SH, Maurice, NW, Azzam, MA, et al. Anti-obesity effect of a tea mixture Nano-formulation on rats occurs via the upregulation of AMP-activated protein kinase/Sirtuin-1/glucose transporter type 4 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma pathways. Meta. (2023) 13:871. doi: 10.3390/metabo13070871
63. Li, D, Yu, D, Li, Y, and Yang, R. A bibliometric analysis of PROTAC from 2001 to 2021. Eur J Med Chem. (2022) 244:114838. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114838
64. van Eck, NJ, and Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. (2010) 84:523–38. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
65. Chen, C . Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2004) 101:5303–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307513100
66. Aria, M, and Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informet. (2017) 11:959–75. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
67. Zhao, J, and Li, M. Worldwide trends in prediabetes from 1985 to 2022: a bibliometric analysis using bibliometrix R-tool. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1072521. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1072521
68. Mao, J, Li, C, Wu, F, Wang, Y, Zhu, J, and Wen, C. The relationship between kidney disease and mitochondria: a bibliometric study. Ren Fail. (2024) 46:2302963. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2302963
69. Li, M, Duan, Y, Wang, Y, Chen, L, Abdelrahim, MEA, and Yan, J. The effect of Green green tea consumption on body mass index, lipoprotein, liver enzymes, and liver cancer: An updated systemic review incorporating a meta-analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2024) 64:1043–51. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2113360
70. Yang, CS, Wang, H, and Sheridan, ZP. Studies on prevention of obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and cancer by tea. J Food Drug Anal. (2018) 26:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.10.010
72. Everard, A, Belzer, C, Geurts, L, Ouwerkerk, JP, Druart, C, Bindels, LB, et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2013) 110:9066–71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219451110
73. van Eck, NJ, and Waltman, L. VOS: a new method for visualizing similarities between objects In: R Decker and H-J Lenz, editors. Advances in data analysis. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer (2007). 299–306.
74. Hamidah, I, Pawinanto, RE, Mulyanti, B, and Yunas, J. A bibliometric analysis of micro electro mechanical system energy harvester research. Heliyon. (2021) 7:e06406. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06406
75. Brookes, BC . Bradford’s law and the bibliography of science. Nature. (1969) 224:953–6. doi: 10.1038/224953a0
76. Ninkov, A, Frank, JR, and Maggio, LA. Bibliometrics: methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect Med Educ. (2022) 11:173–6. doi: 10.1007/S40037-021-00695-4
77. Amjad, T, Shahid, N, Daud, A, and Khatoon, A. Citation burst prediction in a bibliometric network. Scientometrics. (2022) 127:2773–90. doi: 10.1007/s11192-022-04344-3
78. Wolfram, S, Wang, Y, and Thielecke, F. Anti-obesity effects of green tea: from bedside to bench. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2006) 50:176–87. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200500102
79. Yang, CS, Zhang, J, Zhang, L, Huang, J, and Wang, Y. Mechanisms of body weight reduction and metabolic syndrome alleviation by tea. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2016) 60:160–74. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500428
80. Nagao, T, Hase, T, and Tokimitsu, I. A green tea extract high in catechins reduces body fat and cardiovascular risks in humans. Obesity. (2007) 15:1473–83. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.176
81. Nagao, T, Komine, Y, Soga, S, Meguro, S, Hase, T, Tanaka, Y, et al. Ingestion of a tea rich in catechins leads to a reduction in body fat and malondialdehyde-modified LDL in men. Am J Clin Nutr. (2005) 81:122–9. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/81.1.122
82. Chen, G, Xie, M, Dai, Z, Wan, P, Ye, H, Zeng, X, et al. Kudingcha and Fuzhuan brick tea prevent obesity and modulate gut microbiota in high-fat diet fed mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2018) 62:e1700485. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700485
83. Zhu, M, Zhou, F, Ouyang, J, Wang, Q, Li, Y, Wu, J, et al. Combined use of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and caffeine in low doses exhibits marked anti-obesity synergy through regulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Food Funct. (2021) 12:4105–16. doi: 10.1039/D0FO01768J
84. Zhao, X, Yan, F, Li, X-S, Qu, D, and Xu, Y-L. A systematic review of tea pigments: prevention of major diseases, protection of organs, and potential mechanisms and applications. Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 11:6830–44. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3666
85. Mangels, DR, and Mohler, ER. Catechins as potential mediators of cardiovascular health. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2017) 37:757–63. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309048
86. Babu, PVA, and Liu, D. Green tea catechins and cardiovascular health: an update. Curr Med Chem. (2008) 15:1840–50. doi: 10.2174/092986708785132979
87. Chen, H, and Sang, S. Biotransformation of tea polyphenols by gut microbiota. J Funct Foods. (2014) 7:26–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2014.01.013
88. Liu, J, Ding, H, Yan, C, He, Z, Zhu, H, and Ma, KY. Effect of tea catechins on gut microbiota in high fat diet-induced obese mice. J Sci Food Agric. (2023) 103:2436–45. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12476
89. Fang, Y, Wang, J, Cao, Y, Liu, W, Duan, L, Hu, J, et al. The Antiobesity effects and potential mechanisms of Theaflavins. J Med Food. (2024) 27:1–11. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2023.K.0180
90. Cai, X, Liu, Z, Dong, X, Wang, Y, Zhu, L, Li, M, et al. Hypoglycemic and lipid lowering effects of theaflavins in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. (2021) 12:9922–31. doi: 10.1039/D1FO01966J
91. dePaula, J, and Farah, A. Caffeine consumption through coffee: content in the beverage, metabolism, health benefits and risks. Beverages. (2019) 5:37. doi: 10.3390/beverages5020037
92. Wu, L, Meng, J, Shen, Q, Zhang, Y, Pan, S, Chen, Z, et al. Caffeine inhibits hypothalamic A1R to excite oxytocin neuron and ameliorate dietary obesity in mice. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:15904. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15904
93. Liu, C-W, Tsai, H-C, Huang, C-C, Tsai, C-Y, Su, Y-B, Lin, M-W, et al. Effects and mechanisms of caffeine to improve immunological and metabolic abnormalities in diet-induced obese rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 314:E433–47. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00094.2017
94. Fang, C, Shen, Y, Ma, Z, Li, Y, Zhang, J, Liu, C, et al. L-Theanine prevents colonic damage via NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathways induced by a high-fat diet in rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2024) 68:e2300797. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202300797
95. Xu, W, Kong, Y, Zhang, T, Gong, Z, and Xiao, W. L-Theanine regulates lipid metabolism by modulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. J Sci Food Agric. (2023) 103:1283–93. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12222
96. Deng, X, Zhang, N, Wang, Q, Huang, Y, Huang, Y, Lin, Y, et al. Theabrownin of raw and ripened pu-erh tea varies in the alleviation of HFD-induced obesity via the regulation of gut microbiota. Eur J Nutr. (2023) 62:2177–94. doi: 10.1007/s00394-023-03089-w
97. Hu, T, Wu, P, Zhan, J, Wang, W, Shen, J, Wang, M, et al. Structure variety and its effects on biological activity of tea polysaccharides. Food Sci Human Wellness. (2022) 11:587–97. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2021.12.015
98. Yang, W, Cheng, S, Liu, M, Li, N, Wang, J, Yao, W, et al. Lipid-lowering effects of a novel polysaccharide obtained from Fuzhuan brick tea in vitro. Food Secur. (2023) 12:3428. doi: 10.3390/foods12183428
99. Liu, X, Hu, G, Wang, A, Long, G, Yang, Y, Wang, D, et al. Black tea reduces diet-induced obesity in mice via modulation of gut microbiota and gene expression in host tissues. Nutrients. (2022) 14:1635. doi: 10.3390/nu14081635
100. Chen, W, Liu, D, Ren, C, Su, X, Wong, C-K, and Yang, R. A special network comprised of macrophages, epithelial cells, and gut microbiota for gut homeostasis. Cells. (2022) 11:307. doi: 10.3390/cells11020307
101. Tremaroli, V, and Bäckhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature. (2012) 489:242–9. doi: 10.1038/nature11552
102. Li, X, Wang, H, Wang, T, Zheng, F, Wang, H, and Wang, C. Dietary wood pulp-derived sterols modulation of cholesterol metabolism and gut microbiota in high-fat-diet-fed hamsters. Food Funct. (2019) 10:775–85. doi: 10.1039/C8FO02271B
103. de Groot, P, Scheithauer, T, Bakker, GJ, Prodan, A, Levin, E, Khan, MT, et al. Donor metabolic characteristics drive effects of faecal microbiota transplantation on recipient insulin sensitivity, energy expenditure and intestinal transit time. Gut. (2020) 69:502–12. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318320
104. Wang, L, Zeng, B, Liu, Z, Liao, Z, Zhong, Q, Gu, L, et al. Green tea polyphenols modulate colonic microbiota diversity and lipid metabolism in high-fat diet treated HFA mice. J Food Sci. (2018) 83:864–73. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14058
105. Liu, Z, Chen, Z, Guo, H, He, D, Zhao, H, Wang, Z, et al. The modulatory effect of infusions of green tea, oolong tea, and black tea on gut microbiota in high-fat-induced obese mice. Food Funct. (2016) 7:4869–79. doi: 10.1039/C6FO01439A
106. Ley, RE, Turnbaugh, PJ, Klein, S, and Gordon, JI. Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. (2006) 444:1022–3. doi: 10.1038/4441022a
107. Tseng, C-H, and Wu, C-Y. The gut microbiome in obesity. J Formos Med Assoc. (2019) 118:S3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2018.07.009
108. Zsálig, D, Berta, A, Tóth, V, Szabó, Z, Simon, K, Figler, M, et al. A review of the relationship between gut microbiome and obesity. Appl Sci. (2023) 13:610. doi: 10.3390/app13010610
109. Cornejo-Pareja, I, Muñoz-Garach, A, Clemente-Postigo, M, and Tinahones, FJ. Importance of gut microbiota in obesity. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2019) 72:26–37. doi: 10.1038/s41430-018-0306-8
110. Liu, X, Li, X, Xia, B, Jin, X, Zou, Q, Zeng, Z, et al. High-fiber diet mitigates maternal obesity-induced cognitive and social dysfunction in the offspring via gut-brain axis. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:923–938.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.02.002
111. Liao, Z-L, Zeng, B-H, Wang, W, Li, G-H, Wu, F, Wang, L, et al. Impact of the consumption of tea polyphenols on early atherosclerotic lesion formation and intestinal Bifidobacteria in high-fat-fed ApoE−/− mice. Front Nutr. (2016) 3:42. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2016.00042
112. Du, H, Shi, L, Yan, T, Wang, Q, Wang, Y, Zhao, Y, et al. Fu brick tea protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity phenotypes via promoting adipose browning and thermogenesis in association with gut microbiota. Food Funct. (2022) 13:11111–24. doi: 10.1039/D2FO02063G
113. Pérez-Burillo, S, Navajas-Porras, B, López-Maldonado, A, Hinojosa-Nogueira, D, Pastoriza, S, and Rufián-Henares, JÁ. Green tea and its relation to human gut microbiome. Molecules. (2021) 26:3907. doi: 10.3390/molecules26133907
114. Wu, Z, Huang, S, Li, T, Li, N, Han, D, Zhang, B, et al. Gut microbiota from green tea polyphenol-dosed mice improves intestinal epithelial homeostasis and ameliorates experimental colitis. Microbiome. (2021) 9:184. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01115-9
115. Hussain, K, Yang, Y, Wang, J, Bian, H, Lei, X, Chen, J, et al. Comparative study on the weight loss and lipid metabolism by tea polyphenols in diet induced obese C57BL/6J pseudo germ free and conventionalized mice. Food Sci Human Wellness. (2022) 11:697–710. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2021.12.027
116. Zhao, Y, and Zhang, X. Interactions of tea polyphenols with intestinal microbiota and their implication for anti-obesity. J Sci Food Agric. (2020) 100:897–903. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10049
117. Liu, Z, de Bruijn, WJC, Bruins, ME, and Vincken, J-P. Reciprocal interactions between Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and human gut microbiota in vitro. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:9804–15. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03587
118. Li, J, Chen, C, Yang, H, and Yang, X. Tea polyphenols regulate gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by antibiotic in mice. Food Res Int. (2021) 141:110153. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110153
119. Ikeda, T, Nishida, A, Yamano, M, and Kimura, I. Short-chain fatty acid receptors and gut microbiota as therapeutic targets in metabolic, immune, and neurological diseases. Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 239:108273. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108273
120. Mei, H, Li, J, Liu, S, Jeyaraj, A, Zhuang, J, Wang, Y, et al. The role of Green tea on the regulation of gut microbes and prevention of high-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome in mice. Food Secur. (2023) 12:2953. doi: 10.3390/foods12152953
121. Hasani, A, Ebrahimzadeh, S, Hemmati, F, Khabbaz, A, Hasani, A, and Gholizadeh, P. The role of Akkermansia muciniphila in obesity, diabetes and atherosclerosis. J Med Microbiol. (2021) 70:001435. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001435
122. Liu, J-Y, He, D, Xing, Y-F, Zeng, W, Ren, K, Zhang, C, et al. Effects of bioactive components of Pu-erh tea on gut microbiomes and health: a review. Food Chem. (2021) 353:129439. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129439
123. Noel, G, Baetz, NW, Staab, JF, Donowitz, M, Kovbasnjuk, O, Pasetti, MF, et al. A primary human macrophage-enteroid co-culture model to investigate mucosal gut physiology and host-pathogen interactions. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:45270. doi: 10.1038/srep46790
124. Song, Q, Wang, Y, Huang, L, Shen, M, Yu, Y, Yu, Q, et al. Review of the relationships among polysaccharides, gut microbiota, and human health. Food Res Int. (2021) 140:109858. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109858
125. Xu, X, Xu, P, Ma, C, Tang, J, and Zhang, X. Gut microbiota, host health, and polysaccharides. Biotechnol Adv. (2013) 31:318–37. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.12.009
126. Zhu, M, Ouyang, J, Zhou, F, Zhao, C, Zhu, W, Liu, C, et al. Polysaccharides from Fu brick tea ameliorate obesity by modulating gut microbiota and gut microbiota-related short chain fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. J Nutr Biochem. (2023) 118:109356. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109356
127. Chen, G, Wang, M, Zeng, Z, Xie, M, Xu, W, Peng, Y, et al. Fuzhuan brick tea polysaccharides serve as a promising candidate for remodeling the gut microbiota from colitis subjects in vitro: fermentation characteristic and anti-inflammatory activity. Food Chem. (2022) 391:133203. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133203
128. Zeng, Z, Xie, Z, Chen, G, Sun, Y, Zeng, X, and Liu, Z. Anti-inflammatory and gut microbiota modulatory effects of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick tea on colitis in mice induced by dextran sulfate sodium. Food Funct. (2022) 13:649–63. doi: 10.1039/D1FO02702F
129. Liu, Y, Lei, S, Hou, R, Li, D, Wan, X, Cai, H, et al. Tea polysaccharides from Taiping Houkui may serve as a potential candidate for regulation of lipid metabolism: roles of gut microbiota and metabolite in vitro. J Funct Foods. (2023) 102:105469. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2023.105469
130. Wu, Z, Lei, Z, Zeng, W, and Yang, J. Effect of tea polysaccharides on faecal microbiota and their short-chain fatty acid metabolic products. Int Food Res J. (2023) 30:151–62. doi: 10.47836/ifrj.30.1.12
131. Li, D, Cheng, Y, Zeng, X, Li, Y, Xia, Z, Yang, X, et al. Polysaccharide from Ziyang selenium-enriched Green tea prevents obesity and promotes adipose thermogenesis via modulating the gut microbiota. J Agric Food Chem. 71:3363–13375. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c04193
132. Du, H, Shi, L, Wang, Q, Yan, T, Wang, Y, Zhang, X, et al. Fu brick tea polysaccharides prevent obesity via gut microbiota- controlled promotion of adipocyte Browning and Thermogenesis. J Agric Food Chem. (2022) 70:13893–903. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c04888
133. Wang, Y, Li, T, Liu, Y, Yang, C, Liu, L, Zhang, X, et al. Heimao tea polysaccharides ameliorate obesity by enhancing gut microbiota-dependent adipocytes thermogenesis in mice fed with high fat diet. Food Funct. (2022) 13:13014–27. doi: 10.1039/D2FO02415B
134. Li, H-Y, Huang, S-Y, Xiong, R-G, Wu, S-X, Zhou, D-D, Saimaiti, A, et al. Anti-obesity effect of Theabrownin from dark tea in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet by metabolic profiles through gut microbiota using untargeted metabolomics. Food Secur. (2022) 11:3000. doi: 10.3390/foods11193000
135. Yue, S, Shan, B, Peng, C, Tan, C, Wang, Q, and Gong, J. Theabrownin-targeted regulation of intestinal microorganisms to improve glucose and lipid metabolism in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Food Funct. (2022) 13:1921–40. doi: 10.1039/d1fo03374c
136. Jia, W, Wei, M, Rajani, C, and Zheng, X. Targeting the alternative bile acid synthetic pathway for metabolic diseases. Protein Cell. (2021) 12:411–25. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00804-9
137. Kuang, J, Zheng, X, Huang, F, Wang, S, Li, M, Zhao, M, et al. Anti-Adipogenic effect of Theabrownin is mediated by bile acid alternative synthesis via gut microbiota remodeling. Meta. (2020) 10:475. doi: 10.3390/metabo10110475
138. Li, M, Wang, S, Li, Y, Zhao, M, Kuang, J, Liang, D, et al. Gut microbiota-bile acid crosstalk contributes to the rebound weight gain after calorie restriction in mice. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:2060. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29589-7
139. Jing, N, Liu, X, Jin, M, Yang, X, Hu, X, Li, C, et al. Fubrick tea attenuates high-fat diet induced fat deposition and metabolic disorder by regulating gut microbiota and caffeine metabolism. Food Funct. (2020) 11:6971–86. doi: 10.1039/D0FO01282C
140. Dai, A, Hoffman, K, Xu, AA, Gurwara, S, White, DL, Kanwal, F, et al. The association between caffeine intake and the colonic mucosa-associated gut microbiota in humans-a preliminary investigation. Nutrients. (2023) 15:1747. doi: 10.3390/nu15071747
141. Xu, X-Y, Zhao, C-N, Li, B-Y, Tang, G-Y, Shang, A, Gan, R-Y, et al. Effects and mechanisms of tea on obesity. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 63:3716–33. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1992748
142. Blundell, JE, and Gillett, A. Control of food intake in the obese. Obes Res. (2001) 9:263S–70S. doi: 10.1038/oby.2001.129
143. Ahima, RS, Qi, Y, Singhal, NS, Jackson, MB, and Scherer, PE. Brain adipocytokine action and metabolic regulation. Diabetes. (2006) 55:S145–54. doi: 10.2337/db06-S018
144. Schwartz, MW, Woods, SC, Porte, D, Seeley, RJ, and Baskin, DG. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature. (2000) 404:661–71. doi: 10.1038/35007534
145. Unger, RH . Minireview: weapons of lean body mass destruction: the role of ectopic lipids in the metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology. (2003) 144:5159–65. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0870
146. Huang, J, Wang, Y, Xie, Z, Zhou, Y, Zhang, Y, and Wan, X. The anti-obesity effects of green tea in human intervention and basic molecular studies. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2014) 68:1075–87. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2014.143
147. Sirotkin, AV, and Kolesárová, A. The anti-obesity and health-promoting effects of tea and coffee. Physiol Res. (2021) 70:161–8. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934674
148. Zhou, J, Lin, H, Xu, P, Yao, L, Xie, Q, Mao, L, et al. Matcha green tea prevents obesity-induced hypothalamic inflammationviasuppressing the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Food Funct. (2020) 11:8987–95. doi: 10.1039/d0fo01500h
149. Sayama, K, Lin, S, Zheng, G, and Oguni, I. Effects of green tea on growth, food utilization and lipid metabolism in mice. In Vivo. (2000) 14:481–4.
150. Kao, YH, Hiipakka, RA, and Liao, S. Modulation of endocrine systems and food intake by green tea epigallocatechin gallate. Endocrinology. (2000) 141:980–7. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.3.7368
151. Liu, L, and Sayama, K. The combined administration of EGCG and caffeine induces not only suppression of fat accumulation but also anorexigenic action in mice. J Funct Foods. (2018) 47:156–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.05.030
152. Auvichayapat, P, Prapochanung, M, Tunkamnerdthai, O, Sripanidkulchai, B, Auvichayapat, N, Thinkhamrop, B, et al. Effectiveness of green tea on weight reduction in obese Thais: a randomized, controlled trial. Physiol Behav. (2008) 93:486–91. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.10.009
153. Hasegawa, N, Yamda, N, and Mori, M. Powdered green tea has antilipogenic effect on Zucker rats fed a high-fat diet. Phytother Res. (2003) 17:477–80. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1177
154. Ipsen, DH, Lykkesfeldt, J, and Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2018) 75:3313–27. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2860-6
155. Vázquez Cisneros, LC, López-Uriarte, P, López-Espinoza, A, Navarro Meza, M, Espinoza-Gallardo, AC, and Guzmán Aburto, MB. Effects of green tea and its epigallocatechin (EGCG) content on body weight and fat mass in humans: a systematic review. Nutr Hosp. (2017) 34:731–7. doi: 10.20960/nh.753
156. Pan, H, Gao, Y, and Tu, Y. Mechanisms of body weight reduction by black tea polyphenols. Molecules. (2016) 21:1659. doi: 10.3390/molecules21121659
157. Kou, X, Li, W, Meng, Q, Zhang, Y, Huang, X, and Ke, Q. Citrus Pu-erh tea extract intake before or after lipolysis in simulated digestion reduces the release of free fatty acids. J Food Meas Charact. (2024) 18:3042–53. doi: 10.1007/s11694-024-02385-1
158. Yoo, S-H, Lee, Y-E, Chung, J-O, Rha, C-S, Hong, Y-D, Park, M-Y, et al. Enhancing the effect of catechins with green tea flavonol and polysaccharides on preventing lipid absorption and accumulation. LWT Food Sci Technol. (2020) 134:110032. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110032
159. Xu, Q, Ye, J, Gong, M, Zhang, Y, Yuan, Y, and Zhao, J. Theabrownin from Wuniuzao dark tea regulates hepatic lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice fed high-fat diet. Nutrients. (2023) 15:4912. doi: 10.3390/nu15234912
160. Mika, M, Wikiera, A, Antonczyk, A, and Grabacka, M. The impact of catechins included in high fat diet on AMP-dependent protein kinase in apoE knock-out mice. Int J Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 72:348–56. doi: 10.1080/09637486.2020.1817345
161. Liao, Y, Wang, C, Gao, Z, Pan, Z, Peng, M, Ma, J, et al. Anti-obesity mechanism of Ganpu tea revealed by microbiome, metabolome and transcriptome analyses. Food Chem. (2023) 412:135048. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135048
162. Suarez, NG, Torres, SR, Ouanouki, A, El Cheikh-Hussein, L, and Annabi, B. EGCG inhibits adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into adipocytes and prevents a STAT3-mediated paracrine oncogenic control of triple-negative breast Cancer cell invasive phenotype. Molecules. (2021) 26:1506. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061506
163. Chen, C-P, Su, T-C, Yang, M-J, Chen, W-T, Siao, A-C, Huang, L-R, et al. Green tea epigallocatechin gallate suppresses 3T3-L1 cell growth via microRNA-143/MAPK7 pathways. Exp Biol Med. (2022) 247:1670–9. doi: 10.1177/15353702221108925
164. An, R, Wen, S, Li, D-L, Li, Q-H, Lai, X-F, Zhang, W-J, et al. Mixtures of tea andCitrus maxima(pomelo) alleviate lipid deposition in HepG2 cells through the AMPK/ACC signaling pathway. J Med Food. (2020) 23:943–51. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2020.4706
165. Wu, Z, Yu, W, Ni, W, Teng, C, Ye, W, Yu, C, et al. Improvement of obesity by Liupao tea is through the IRS-1/PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 signaling pathway according to network pharmacology and experimental verification. Phytomedicine. (2023) 110:154633. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154633
166. Weerawatanakorn, M, He, S, Chang, C-H, Koh, Y-C, Yang, M-J, and Pan, M-H. High gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) oolong tea alleviates high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. ACS Omega. (2023) 8:33997–4007. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04874
167. Moon, Y, Kim, H, Kim, M, Im, H, and Lee, Y. Synergistic effects of heat-treated Green tea extract and enzymatically-modified Isoquercitrin in preventing obesity. Nutrients. (2023) 15:2931. doi: 10.3390/nu15132931
168. Im, H, Lee, J, Kim, K, Son, Y, and Lee, Y-H. Anti-obesity effects of heat-transformed green tea extract through the activation of adipose tissue thermogenesis. Nutr Metab. (2022) 19:14. doi: 10.1186/s12986-022-00648-6
169. Yoo, A, Ahn, J, Seo, HD, Hahm, J-H, Jung, CH, Ly, SY, et al. Fuzhuan brick tea extract ameliorates obesity-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2024) 125:109532. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109532
170. Li, J, Chen, Q, Zhai, X, Wang, D, Hou, Y, and Tang, M. Green tea aqueous extract (GTAE) prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity by activating fat browning. Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 9:6548–58. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2580
171. Willems, MET, Şahin, MA, and Cook, MD. Matcha Green tea drinks enhance fat oxidation during brisk walking in females. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. (2018) 28:536–41. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2017-0237
172. Zhang, P, Wu, W, Du, C, Ji, X, Wang, Y, Han, Q, et al. RNA-seq profiling of white and brown adipocyte differentiation treated with epigallocatechin gallate. Sci Data. (2022) 9:41. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01149-0
173. Choi, C, Song, H-D, Son, Y, Cho, YK, Ahn, S-Y, Jung, Y-S, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate reduces visceral adiposity partly through the regulation of Beclin1-dependent autophagy in White adipose tissues. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3072. doi: 10.3390/nu12103072
174. Yoo, A, Kim, MJ, Ahn, J, Jung, CH, Seo, HD, Ly, SY, et al. Fuzhuan brick tea extract prevents diet-induced obesity via stimulation of fat browning in mice. Food Chem. (2022) 377:132006. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.132006
175. Taylor, EB . The complex role of adipokines in obesity, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Clin Sci. (2021) 135:731–52. doi: 10.1042/CS20200895
176. Chen, R, Lai, X, Xiang, L, Li, Q, Sun, L, Lai, Z, et al. Aged green tea reduces high-fat diet-induced fat accumulation and inflammation via activating the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Food Nutr Res. (2022) 66:7923. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v66.7923
177. Ye, Y, Warusawitharana, H, Zhao, H, Liu, Z, Li, B, Wu, Y, et al. Tea polyphenols attenuates inflammation via reducing lipopolysaccharides level and inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway in obese mice. Plant Food Hum Nutr. (2022) 77:105–11. doi: 10.1007/s11130-021-00937-0
178. Lee, S-J, Cho, KH, Kim, JC, Choo, HJ, Hwang, J-Y, Cho, HC, et al. Comparative analysis of anti-obesity effects of green, fermented, and γ-aminobutyric acid teas in a high-fat diet-induced mouse model. Appl Biol Chem. (2024) 67:36. doi: 10.1186/s13765-024-00888-5
179. Asbaghi, O, Rezaei Kelishadi, M, Larky, DA, Bagheri, R, Amirani, N, Goudarzi, K, et al. The effects of green tea extract supplementation on body composition, obesity-related hormones and oxidative stress markers: a grade-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. (2024) 131:1125–57. doi: 10.1017/S000711452300260X
180. Wang, H, Wang, L, Cheng, H, Ge, H, Xie, Z, and Li, D. Large yellow tea polysaccharides ameliorate obesity-associated metabolic syndrome by promoting M2 polarization of adipose tissue macrophages. Food Funct. (2023) 14:9337–49. doi: 10.1039/D3FO01691A
Keywords: obesity, bibliometric analysis, tea, epigallocatechin gallate, tea polyphenols, tea polysaccharides, gut microbiota, lipid metabolism
Citation: Liu S, Fan B, Li X and Sun G (2024) Global hotspots and trends in tea anti-obesity research: a bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2024. Front. Nutr. 11:1496582. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1496582
Edited by:
Ana Sanches Silva, National Institute for Agricultural and Veterinary Research (INIAV), PortugalReviewed by:
Qi Wang, Yibin Vocational and Technical College, ChinaKunyi Liu, Yibin Vocational and Technical College, China
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Fan, Li and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoping Li, MTA3NDc3MjAzN0BxcS5jb20=; Guixiang Sun, ODQ2NjM0MjNAcXEuY29t
 Shan Liu
Shan Liu Boyan Fan1
Boyan Fan1