
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Nutr. , 14 January 2025
Sec. Clinical Nutrition
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1488054
Objectives: To report the first and largest systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCT) to evaluated the efficacy and safety of post-discharge oral nutritional supplements (ONS) for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: RCT which evaluated the efficacy and/or safety of post-discharge ONS for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy.
Data sources: We conducted a systematic literature retrieval via PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane until April, 2023 for relevant RCTs.
Data analysis: Outcomes of meta-analysis included absolute change of body weight, % change of body weight, absolute change of body composition, absolute change of laboratory parameters and adverse events. All the relevant data were analyzed by Review Manager 5.4.1 and Stata 15.1.
Results: 5 RCTs including 1,586 patients (804 in ONS group versus 782 in control group) were included for meta-analysis. The two groups were comparable in age, gender (male), weight at baseline, BMI at baseline, albumin at baseline, and hemoglobin at baseline. Meta-analysis revealed a significant lower absolute body weight loss (WMD: 0.75; 95% CI: 0.11, 1.40; p = 0.02) and % body weight loss (WMD: 1.15; 95% CI: 0.20, 2.11; p = 0.02) in the ONS group compared with the control (regular diet/dietary advice) group. Moreover, this study did not observe a significant difference between the two groups for adverse events rate (RR: 1.11; 95% CI: 0.81, 1.53; p = 0.52).
Conclusion: ONS was significantly effective and safe in improving postoperative weight loss for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy.
Systematic review registration: Identifier, CRD42023414678, https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/.
Gastric cancer is a particularly common malignant tumor of digestive tract, which has become one of the main causes of cancer-related death worldwide and has caused great damage to human health (1, 2). At present, although chemotherapy, immunotherapy have made great development (3, 4), gastrectomy is still the main and most effective treatment for gastric cancer (5). However, due to various risk factors such as reduced stomach volume and food intake after gastrectomy, postoperative chemotherapy, postoperative gastrointestinal symptoms, the incidence of malnutrition in patients with gastric cancer after surgery is very high and their nutritional status would deteriorate gradually (6). A large number of studies have suggested that malnutrition is significantly associated with a variety of adverse outcomes in postoperative gastric cancer patients, including higher morbidity and mortality, lower chemotherapy tolerance and poorer survival condition (7–9). Therefore, active nutritional support is of great significance for improving the nutritional status and tumor prognosis of postoperative patients with gastric cancer (10).
Oral nutritional supplements (ONS) are currently the best way of nutritional support treatment, which can provide supplementary energy and nutrition for special groups such as gastric cancer patients after surgery (11). Despite a large number of clinical studies and systematic reviews have reported the application of ONS in patients undergoing gastrectomy, their conclusions are inconsistent (10, 12–19). One of the causes for these differences is that there is no established ONS scheme. In addition, patient compliance with ONS may be another critical factor, which is strongly influenced by nutritional consultations with surgeons, dietitians, and pharmacologists. Furthermore, although some clinical studies have observed the effectiveness of ONS on short-term nutrition-related outcomes, such as reduced postoperative infection rate and shorter hospital stay, the nutritional efficacy of ONS on medium- and long-term outcomes (such as weight loss of gastric cancer patients after gastrectomy) have not been fully demonstrated (17).
Although the meta-analysis of Chen et al. (19) and Choi et al. (20) showed that preoperative or perioperative use of ONS could significantly reduce postoperative inflammatory response and improve immune system function and nutritional status in patients with gastric cancer resection. Existing evidence-based studies have failed to clarify whether long-term regular use of ONS after surgery can improve the nutritional status and prognosis of discharged gastric cancer patients after surgery. In addition, previous meta-analyses did not discuss the impact of follow-up after the use of ONS and surgical methods for gastric cancer on the long-term efficacy of ONS, and there was a lack of standard GRADE evidence recommendation. Therefore, we report the first and largest systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of long-term regular ONS in patients undergoing gastrectomy after discharge, and to make evidence recommendations through GRADE ratings to provide evidence-based evidence for clinical use of ONS to improve long-term postoperative nutritional status in patients with gastric cancer.
No patient involved.
This meta-analysis was performed according to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis) 2020 statement (21) and has been prospectively registered in the PROSPERO (CRD42023414678).
We conducted a systematic literature search via PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane up to April, 2023 for RCT that evaluated the efficacy and safety of post-discharge ONS for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy. We searched the literature through the following terms: “stomach neoplasms,” “gastrectomy,” “oral nutritional supplements,” and “ONS.” The detailed search strategies are as follows: (((Oral nutritional supplements) OR (ONS)) AND ((Gastrectomies) OR (“Gastrectomy”[Mesh]))) AND (((((((((((((((((((Neoplasm, Stomach[Title/Abstract]) OR (Stomach Neoplasm[Title/Abstract])) OR (Neoplasms, Stomach[Title/Abstract])) OR (Gastric Neoplasms[Title/Abstract])) OR (Gastric Neoplasm[Title/Abstract])) OR (Neoplasm, Gastric[Title/Abstract])) OR (Neoplasms, Gastric[Title/Abstract])) OR (Cancer of Stomach[Title/Abstract])) OR (Stomach Cancers[Title/Abstract])) OR (Gastric Cancer[Title/Abstract])) OR (Cancer, Gastric[Title/Abstract])) OR (Cancers, Gastric[Title/Abstract])) OR (Gastric Cancers[Title/Abstract])) OR (Stomach Cancer[Title/Abstract])) OR (Cancer, Stomach[Title/Abstract])) OR (Cancers, Stomach[Title/Abstract])) OR (Cancer of the Stomach[Title/Abstract])) OR (Gastric Cancer, Familial Diffuse[Title/Abstract])) OR (“Stomach Neoplasms”[Mesh])). Furthermore, we manually screened the bibliography lists of all included RCTs. Two authors retrieved and assessed eligible articles independently. Any differences in literature retrieval were resolved by discussion.
Articles were eligible when meeting the following PICOS standards: P: patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy; I: the long-term (continuous supplementation for ≥1 month) post-discharge supplementation of ONS; C: usual postoperative diet, or dietary advice; O: absolute change of body weight, % change of body weight (the value of weight loss as a percentage of baseline weight), change of skeletal muscle mass, change of body fat mass, change of albumin, change of total protein, change of total cholesterol, change of hemoglobin and adverse events; S: RCT. In addition, studies were eligible if there was complete data to analyze risk ratio (RR), weighted mean difference (WMD) or standard mean difference (SMD).
We excluded study protocols, unpublished studies, non-original studies (including letters, comments, abstracts, correction, and reply), non-RCT studies, studies without sufficient data, and reviews. In addition, we excluded studies in which short-term ONS administration was initiated before or perioperatively.
Data abstraction was conducted by two authors severally. Any differences were settled by another author. We abstracted following information from eligible RCTs: first author name, published year, research period, study region, study design, registration number, type of gastrectomy, intervention, control, sample size, age, gender, follow-up time, weight at baseline, body mass index (BMI) at baseline, albumin at baseline, hemoglobin at baseline, absolute change of body weight, % change of body weight, change of skeletal muscle mass, change of body fat mass, change of albumin, change of total protein, change of total cholesterol, change of hemoglobin, and adverse events. If the continuous data in the article was presented as median plus range or median plus interquartile range (IQR), we reanalyzed the mean ± standard deviation (SD) via the methods reported by Wan et al. and Luo et al. (22, 23). If the research data is insufficient, corresponding authors were contacted for full data if available.
The quality assessment of eligible RCTs was conducted using the Risk of Bias 2 (RoB 2) tool. The following items were assessed as a possible source of bias: process of randomization, deviations from intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of outcome, and reported results selection. For each item, multiple standardized questions are answered with ‘yes’, ‘probably yes’, ‘probably no’, ‘no’, and ‘no information’. Then, based on these answers, the risk of bias for each item was judged as ‘low risk’, ‘some concerns’, or ‘high risk’ (24). Two authors severally assessed the quality of all included studies, and any disagreement was settled by discussion.
Meta-analysis was conducted in Review Manager 5.4.1 edition. For continuous data, the WMD or SMD was used for data synthesis, and the RR were used for the synthesis of dichotomous data. Each metric was presented with 95% confidential intervals (CIs). The chi-squared (χ2) test (Cochran’s Q) and inconsistency index (I2) were applied for the evaluation of the heterogeneity of each outcome (25). χ2 p value less than 0.1 or I2 more than 50% were regarded as high heterogeneity. The random-effects model was applied to calculate the total WMD, SMD or RR. In addition, we performed subgroup analyses for efficacy outcomes with two or more included studies to evaluate the possible confounders, if data were sufficient. Besides, we conducted sensitivity analysis to assess the influence of every included RCT on the total WMD, SMD or RR for results with more than 2 included studies and significant heterogeneity. Moreover, we assessed the potential publication bias by producing funnel plots through Review Manager 5.4.1 edition as well as through performing Egger’s regression tests (26) through Stata 15.1 edition (Stata Corp, College Station, Texas, United States). p value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant publication bias.
According to the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE), evidence of absolute change of body weight, % change of body weight and adverse events were evaluated through the follow items: risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, publication bias, plausible confounding, magnitude of effect, and dose–response gradient. Finally, each outcome was graded as “high,” “moderate,” “low” or “very low” quality to draw conclusions (27).
Figure 1 shows the flowchart of the literature retrieval and selection process. A total of 95 related studies in PubMed (n = 28), Embase (n = 21), Web of Science (n = 35), and Cochrane (n = 11) were identified via systematically literature search. After removing duplicate studies, a total of 50 titles and abstracts were evaluated. Eventually, 5 RCTs including 1,586 patients (804 in ONS group versus 782 in control group) were included for meta-analysis (10, 15–18). Table 1 presents the characteristics of each eligible RCT. The two groups were comparable in age (WMD: 0.05; 95% CI: −1.00, 1.09; p = 0.93), gender (male; RR: 1.00; 95% CI: 0.93, 1.07; p = 1.00), weight at baseline (WMD: −0.43; 95% CI: −1.44, 0.58; p = 0.40), BMI at baseline (WMD: 0.01; 95% CI: −0.30, 0.32; p = 0.96), albumin at baseline (SMD: 0.00; 95% CI: −0.10, 0.10; p = 0.98), and hemoglobin at baseline (SMD: −0.01; 95% CI: −0.11, 0.09; p = 0.82; Table 2).
Overall, one RCTs (15) was rated as low risk and four RCTs (10, 16–18) were rated as of some concerns. Among them, all RCTs adopted the correct random allocation method. However, due to the non-blind study design, deviations from intended intervention in four RCTs (10, 16–18) were rated as of some concerns. In addition, the measurement of the outcome in three RCTs (10, 16, 17) was rated as of some concerns because the methodology of the outcome evaluation was not reported in detail. The remaining entries are all low risk. Details of the quality evaluation for all included RCTs are shown in Supplementary Figure S1.
Results of absolute change of body weight were synthesized from 4 RCTs including 1,564 patients (793 ONS versus 771 control) (10, 15–17). Meta-analysis revealed a significant lower absolute body weight loss in the ONS group (WMD: 0.75; 95% CI: 0.11, 1.40; p = 0.02) with a significant heterogeneity (I2 = 87%, p < 0.0001; Figure 2). Subgroup analysis found that there was still a significant difference in study with a follow-up time of less than 3 months (WMD: 1.18; 95% CI: 0.07, 2.29; p = 0.04) (10), while the significance disappeared in studies with a follow-up time of ≥3 months (WMD: 0.66; 95% CI: −0.06, 1.38; p = 0.07; Figure 2) (15, 16).
Data synthesis of % change of body weight was performed in 3 RCTs including 959 patients (484 ONS versus 475 control) (10, 15, 17). Meta-analysis observed a significant lower % body weight loss in the ONS group (WMD: 1.15; 95% CI: 0.20, 2.11; p = 0.02) without significant heterogeneity (I2 = 42%, p = 0.13; Figure 3). Subgroup analysis found that the significance remained in total gastrectomy group (WMD: 2.24; 95% CI: 0.13, 4.34; p = 0.04) but disappeared in distal gastrectomy group (WMD: 0.71; 95% CI: −0.40, 1.81; p = 0.21; Figure 3).
Given the absolute change of body composition between the two groups, including absolute change of skeletal muscle mass and body fat mass, was reported in only one study, we could not perform pooled analysis. Based on the findings of Hatao et al. (15), no significant difference was observed between the ONS and control group for absolute change of skeletal muscle mass and body fat mass both in distal (absolute change of skeletal muscle mass, WMD: −0.20; 95% CI: −0.73, 0.33; p = 0.47; absolute change of body fat mass, WMD: 0.10; 95% CI: −1.06, 1.26; p = 0.86) and total gastrectomy group (absolute change of skeletal muscle mass, WMD: 0.60; 95% CI: −0.49, 1.69; p = 0.29; absolute change of body fat mass, WMD: −0.30; 95% CI: −1.89, 1.29; p = 0.72).
In this study, only one RCT (10) reported the absolute change of laboratory parameters between the two groups (mainly including absolute change of albumin, absolute change of total protein, absolute change of total cholesterol, and absolute change of hemoglobin). According to this RCT, no significant difference was observed between the ONS and control group for the any absolute change of laboratory parameters (absolute change of albumin, WMD: −0.03; 95% CI: −0.21, 0.15; p = 0.75; absolute change of total protein, WMD: 0.12; 95% CI: −0.18, 0.43; p = 0.45; absolute change of total cholesterol, WMD: 5.36; 95% CI: −6.50, 17.22; p = 0.37; absolute change of hemoglobin, WMD: 0.69; 95% CI: −0.10, 1.48; p = 0.10).
Data of adverse events were available in 3 RCTs with 1,136 patients (569 ONS versus 567 control) (10, 17, 18). No significant difference was found between the ONS and control group for adverse events rate (RR: 1.11; 95% CI: 0.81, 1.53; p = 0.52), and no significant heterogeneity (I2 = 29%, p = 0.24) was observed (Figure 4).
We assessed the potential publication bias through funnel plots and Egger’s regression tests for absolute change of body weight, % change of body weight, and adverse events. No statistical (Egger’s test) or visual (funnel plots) evidence of publication bias was detected for absolute change of body weight (Egger’s test p = 0.397; Figure 5A), % change of body weight (Egger’s test p = 0.874; Figure 5B), and adverse events (Egger’s test p = 0.787; Figure 5C).
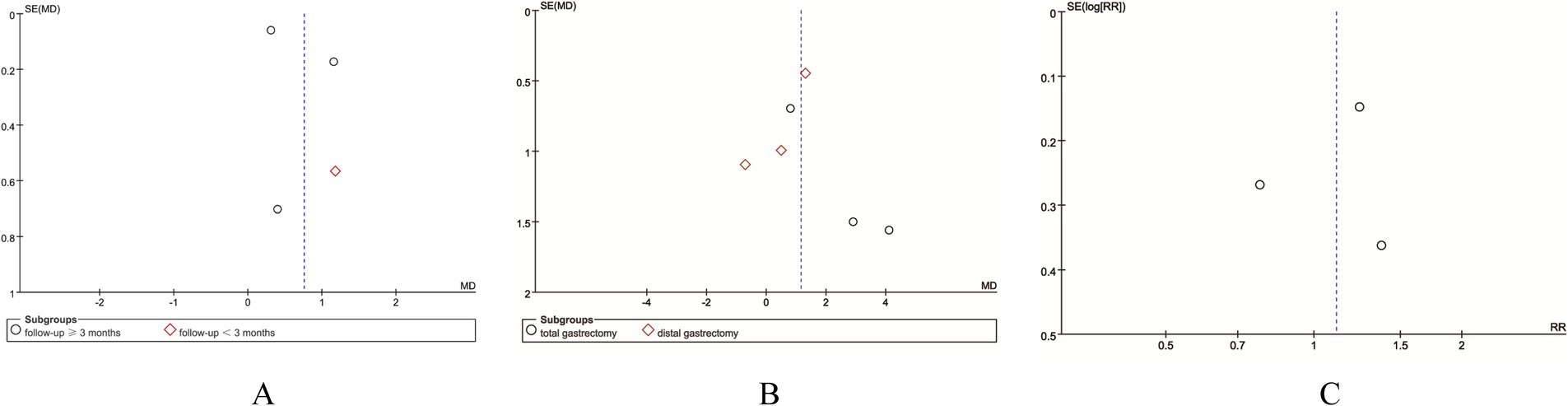
Figure 5. Funnel plots of (A) absolute change of body weight, (B) % change of body weight, and (C) adverse events.
We performed sensitivity analysis for the results of absolute change of body weight (Figure 6A) and adverse events (Figure 6B) to assess the effect of each RCT on the total WMD or RR via excluding eligible RCTs one by one. Sensitivity analysis found that the new total RR kept stable after removing of each RCT for adverse events (Figure 6B). However, when we removed the study reported by Imamura et al. in 2016 (10), the pooled analysis of absolute change of body weight changed from significant to nonsignificant (WMD: 0.66; 95% CI: −0.06, 1.38; p = 0.07; Figure 6A). In addition, after excluding the data reported by Miyazaki et al. (17), the heterogeneity of absolute change of body weight reduced from 87 to 0%, suggesting that this paper may be the main cause of the significant heterogeneity in the absolute change of body weight.
The effects of ONS on the % change of body weight and adverse events were graded as “moderate” quality evidence due to the serious imprecision. However, the effect of ONS on the absolute change of body weight was graded as “low” quality evidence because of the serious inconsistency and serious imprecision observed in this outcome (Table 3).
The continuous loss of body weight after gastrectomy is a symptom correlated to malnutrition, a non-avoidable and fatal problem which related with a damage in postoperative quality of life, decreased function of immune system, and a poor gastric cancer prognosis (28–31). Although several strategies against harmful impact on weight loss caused by gastrectomy have been proposed, significant weight loss associated with a severe malnutrition is still an unsolved problem, notably for patients with gastric cancer after total gastrectomy (17). In a meta-analysis including 13 articles, ONS was observed to significantly improve nutritional intake and some fields of quality of life in malnourished patients suffer from cancer (32). The efficacy of nutritional support through ONS for gastrointestinal diseases in the early period after surgery has also been observed (33). Depending on the degree of preoperative malnutrition, perioperative and postoperative nutritional support could be provided by the simplest means of ONS (34).
In this meta-analysis, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of post-discharge ONS for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy. Our results demonstrated that the patients in ONS group had significantly less absolute and % reduction of body weight than those in control (regular diet/dietary advice) group. In addition, compared with the control (regular diet/dietary advice) group, there was no significant increase in the risk of adverse events in the ONS group, suggesting that long-term regular use of ONS after gastrectomy is effective and safe. Results of this meta-analysis are similar to those of previous studies (10, 15–18), which found that post-discharge ONS is an effective and safe nutritional support therapy strategy to improve nutritional parameters after gastrectomy.
Moreover, our subgroup analysis found that the efficacy of ONS remains significant in study with a follow-up time of less than 3 months, while the significance disappeared in studies with a follow-up time of ≥3 months. The time trend of weight loss after gastrectomy may be one of the main reasons for this outcome. It is reported that weigh loss after gastrectomy is time dependent (17). Weight loss that arose after total gastrectomy has been observed to be 15 ~ 20%, of which more than 80% of weight loss occurred during the first 3 months and the remaining 20% of weight loss developed slowly over time (35). This condition may be attributed to the gradually increment of food intake in the early period after gastrectomy and the stabilization of food intake 6 months after gastrectomy (17). Furthermore, subgroup analysis found that the significant efficacy of ONS on the % change of body weight remained in total gastrectomy group but disappeared in distal gastrectomy group. Interestingly, postoperative weight loss was observed to be more serious in total gastrectomy than in distal gastrectomy patients, suggesting that these patients may benefit more from the nutritional improvements provided by ONS (15, 36). On the other hand, the subgroup analysis of total gastrectomy had a significant heterogeneity, which could affect the reliability of the results. In addition, tumor stage and pathological type may also affect the efficacy of ONS. Although the vast majority of gastric cancer patients who undergo gastrectomy are early- to middle-stage patients (I-III), the stages of patients included in different studies are not completely consistent. At the same time, due to insufficient data, we were unable to perform subgroup analysis by tumor stage and pathological type, and it is not yet certain whether the conclusions of this study will be affected by tumor stage and pathological type. Future studies comparing the differences in the absorption and metabolism of ONS between distal and total gastrectomy patients may explain these findings.
The findings in this paper are consistent with the conclusions of the meta-analysis by Choi et al. (20). However, Choi et al.’s meta-analysis focused on the efficacy of perioperative ONS (including short-term application of ONS before and after surgery), but this paper mainly focused on the efficacy of long-term ONS supplementation after surgery for gastric cancer. In addition, due to differences in inclusion criteria, the RCTs published by Toyomasu et al. (18) were included in this study, making the safety assessment of ONS realized in this paper. Furthermore, Choi et al.’s meta-analysis conducted subgroup analysis on energy intake, while this paper conducted subgroup analysis on primary outcomes through follow-up time (≥3 months and < 3 months) and surgical method (distal gastrectomy and total gastrectomy), revealing the potential impact of follow-up time and surgical method on the efficacy of ONS. It provides theoretical support for exploring the optimal suitable population and applicable conditions of ONS. In addition, this study explored the stability of results and potential sources of heterogeneity through sensitivity analysis, and made evidence recommendations for all outcomes through GRADE rating, which is crucial for guideline recommendation of ONS. Therefore, to sum up, the findings of this study mainly confirmed the efficacy and safety of long-term postoperative use of ONS for patients with gastric cancer, and provided the most comprehensive and latest evidence for clinical application of ONS to improve the long-term postoperative nutritional status of patients with gastric cancer.
As an auxiliary means of nutritional supplementation, ONS is mainly used to supplement the various nutrients needed by the human body (37). Its main ingredients include: protein (including whey protein powder, soy protein, etc.), vitamins and minerals (including vitamin C, vitamin B complex, vitamin D, iron, magnesium, calcium, zinc, etc.) and special adult supplements such as fish oil, flaxseed oil, plant extracts, barley grass, spirulina, etc. (38, 39). ONS increases the stimulation of food on mucosal cells while ensuring nutritional balance, which is beneficial to the proliferation of mucosal cells, repairing the mucosal tissue that has atrophied or damaged during the perioperative period as soon as possible, and maintaining the barrier function of the mucosa (40). During ONS, patients have good self-control over the temperature and intake rate of the nutrient solution, so the incidence of adverse reactions such as abdominal distension and diarrhea is low (37). When gastric cancer patients use chemotherapy drugs, normal cells are also damaged to a certain extent, which stimulates the digestive tract to produce a large amount of serotonin, activates the vagus nerve, and is prone to adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, and anorexia (38). ONS contain effective active ingredients such as gingerol, which can reduce patients’ gastrointestinal reactions.
We must acknowledge several limitations of this meta-analysis. Firstly, only 2 of 5 included RCTs had low risk in the allocation concealment and only 1 RCT had low risk in the blinding of participants, personnel, and outcome assessment. Secondly, the RCTs included in our study had different intervention (different type of ONS), which may be one of the sources of heterogeneity. Thirdly, most of included studies did not report the specific caloric consumption of the regular diet, and the quantity of ONS consumption was self-recorded by the patients using a custom dietary notebook. In this case, the effects of ONS consumption on the patient’s daily diet and the discrepancy in total dietary energy intake between the two groups remain unclear, which could lead to bias to some extent. Fourthly, all of the included studies were from Asian countries (including Japan and China) and the data of other populations were still deficient. Despite several limitations of this meta-analysis, we conducted the first and largest meta-analysis of RCTs to evaluate the efficacy and safety of post-discharge ONS for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy. Results of this meta-analysis validated the superiority of the ONS for the nutritional support of postoperative gastric cancer reported by previous studies. More large-scale, multi-center RCTs are needed to further confirm our findings.
Pooled analyses revealed that ONS was significantly effective and safe in improving postoperative weight loss for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy. Subgroup analysis found that the efficacy of ONS remained significant in total gastrectomy group and study with a follow-up time of less than 3 months, while it seemed to be noneffective in distal gastrectomy group and studies with a follow-up time of ≥3 months. More large-scale, multi-center RCTs are needed to further evaluated the efficacy and safety of post-discharge ONS for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
QL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Investigation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. BW: Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2024.1488054/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1 | Details of the quality evaluation for included RCTs.
1. Bray, F, Ferlay, J, Soerjomataram, I, Siegel, RL, Torre, LA, and Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2018) 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
2. Thrift, AP, and El-Serag, HB. Burden of gastric Cancer. Clinical Gastroenterol Hepatol: Official Clin Prac J American Gastroenterolog Assoc. (2020) 18:534–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.045
3. Coutzac, C, Pernot, S, Chaput, N, and Zaanan, A. Immunotherapy in advanced gastric cancer, is it the future? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2019) 133:25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.10.007
4. Das, M. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy: survival benefit in gastric cancer. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:e307. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30321-2
5. Yu, J, Huang, C, Sun, Y, Su, X, Cao, H, Hu, J, et al. Effect of laparoscopic vs open distal gastrectomy on 3-year disease-free survival in patients with locally advanced gastric Cancer: the CLASS-01 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2019) 321:1983–92. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.5359
6. Oh, SE, Choi, MG, Seo, JM, An, JY, Lee, JH, Sohn, TS, et al. Prognostic significance of perioperative nutritional parameters in patients with gastric cancer. Clin Nutrit (Edinburgh, Scotland). (2019) 38:870–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.02.015
7. Fujiya, K, Kawamura, T, Omae, K, Makuuchi, R, Irino, T, Tokunaga, M, et al. Impact of malnutrition after gastrectomy for gastric Cancer on long-term survival. Ann Surg Oncol. (2018) 25:974–83. doi: 10.1245/s10434-018-6342-8
8. Li, YF, Nie, RC, Wu, T, Li, SM, Chen, S, Wang, W, et al. Prognostic value of the nutritional risk screening 2002 scale in metastatic gastric Cancer: a large-scale cohort study. J Cancer. (2019) 10:112–9. doi: 10.7150/jca.27729
9. Yang, Y, Gao, P, Song, Y, Sun, J, Chen, X, Zhao, J, et al. The prognostic nutritional index is a predictive indicator of prognosis and postoperative complications in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. European J Surgical Oncol: J European Society Surg Oncol British Assoc Surg Oncol. (2016) 42:1176–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.05.029
10. Imamura, H, Nishikawa, K, Kishi, K, Inoue, K, Matsuyama, J, Akamaru, Y, et al. Effects of an Oral elemental nutritional supplement on post-gastrectomy body weight loss in gastric Cancer patients: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. (2016) 23:2928–35. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5221-4
11. Cederholm, T, Barazzoni, R, Austin, P, Ballmer, P, Biolo, G, Bischoff, SC, et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Clin Nutrit (Edinburgh, Scotland). (2017) 36:49–64. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.09.004
12. Aoyama, T, Yoshikawa, T, Ida, S, Cho, H, Sakamaki, K, Ito, Y, et al. Effects of perioperative Eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched oral nutritional supplement on lean body mass after total gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J Cancer. (2019) 10:1070–6. doi: 10.7150/jca.29632
13. Ida, S, Hiki, N, Cho, H, Sakamaki, K, Ito, S, Fujitani, K, et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing standard diet with perioperative oral immunonutrition in total gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Br J Surg. (2017) 104:377–83. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10417
14. Kong, SH, Lee, HJ, Na, JR, Kim, WG, Han, DS, Park, SH, et al. Effect of perioperative oral nutritional supplementation in malnourished patients who undergo gastrectomy: a prospective randomized trial. Surgery. (2018) 164:1263–70. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2018.05.017
15. Hatao, F, Chen, KY, Wu, JM, Wang, MY, Aikou, S, Onoyama, H, et al. Randomized controlled clinical trial assessing the effects of oral nutritional supplements in postoperative gastric cancer patients. Langenbeck's Arch Surg. (2017) 402:203–11. doi: 10.1007/s00423-016-1527-8
16. Meng, Q, Tan, S, Jiang, Y, Han, J, Xi, Q, Zhuang, Q, et al. Post-discharge oral nutritional supplements with dietary advice in patients at nutritional risk after surgery for gastric cancer: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutrit (Edinburgh, Scotland). (2021) 40:40–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.04.043
17. Miyazaki, Y, Omori, T, Fujitani, K, Fujita, J, Kawabata, R, Imamura, H, et al. Oral nutritional supplements versus a regular diet alone for body weight loss after gastrectomy: a phase 3, multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial. Gastric Cancer: Official J Int Gastric Cancer Assoc Japanese Gastric Cancer Assoc. (2021) 24:1150–9. doi: 10.1007/s10120-021-01188-3
18. Toyomasu, Y, Mochiki, E, Yanai, M, Suzuki, M, Yanoma, T, Kimura, A, et al. A prospective pilot study of an elemental nutritional supplement for prevention of oral mucositis during S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Surgical Oncol-Oxford. (2019) 29:97–101. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2019.04.003
19. Chen, X, Yang, K, Zhang, X, and Li, K. Meta-analysis of preoperative oral nutritional supplements for patients with gastric cancer: East Asian experience. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2020) 74:991–1000. doi: 10.1038/s41430-019-0483-0
20. Choi, M, Kim, JY, Kang, HH, Park, E, and Shim, SR. Oral nutritional supplements reduce body weight loss after gastrectomy in patients with gastric Cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients. (2023) 15:3924. doi: 10.3390/nu15183924
21. Page, MJ, McKenzie, JE, Bossuyt, PM, Boutron, I, Hoffmann, TC, Mulrow, CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical Res). (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
22. Wan, X, Wang, W, Liu, J, and Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
23. Luo, D, Wan, X, Liu, J, and Tong, T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat Methods Med Res. (2018) 27:1785–805. doi: 10.1177/0962280216669183
24. Cumpston, M, Li, T, Page, MJ, Chandler, J, Welch, VA, Higgins, JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10:Ed000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
25. Higgins, JP, and Thompson, SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
26. Egger, M, Davey Smith, G, Schneider, M, and Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ (Clinical Res). (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
27. Guyatt, G, Oxman, AD, Akl, EA, Kunz, R, Vist, G, Brozek, J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol. (2011) 64:383–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026
28. Andreyev, HJ, Norman, AR, Oates, J, and Cunningham, D. Why do patients with weight loss have a worse outcome when undergoing chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies? Eur J Cancer. (1998) 34:503–9.
29. Aoyama, T, Sato, T, Maezawa, Y, Kano, K, Hayashi, T, Yamada, T, et al. Postoperative weight loss leads to poor survival through poor S-1 efficacy in patients with stage II/III gastric cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. (2017) 22:476–83. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1089-y
30. Daly, LE, Ní Bhuachalla, ÉB, Power, DG, Cushen, SJ, James, K, and Ryan, AM. Loss of skeletal muscle during systemic chemotherapy is prognostic of poor survival in patients with foregut cancer. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2018) 9:315–25. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12267
31. Ohkura, Y, Haruta, S, Tanaka, T, Ueno, M, and Udagawa, H. Effectiveness of postoperative elemental diet (Elental®) in elderly patients after gastrectomy. World J Surg Oncol. (2016) 14:268. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-1013-3
32. Baldwin, C, Spiro, A, Ahern, R, and Emery, PW. Oral nutritional interventions in malnourished patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2012) 104:371–85. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr556
33. Lidder, PG, Lewis, S, Duxbury, M, and Thomas, S. Systematic review of postdischarge oral nutritional supplementation in patients undergoing GI surgery. Nutrit Clin Prac: Official Pub American Society Parenteral Enteral Nutrit. (2009) 24:388–94. doi: 10.1177/0884533609332175
34. Kang, MK, and Lee, HJ. Impact of malnutrition and nutritional support after gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. (2024) 8:534–52. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12788
35. Davis, JL, Selby, LV, Chou, JF, Schattner, M, Ilson, DH, Capanu, M, et al. Patterns and predictors of weight loss after gastrectomy for Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. (2016) 23:1639–45. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-5065-3
36. Takachi, K, Doki, Y, Ishikawa, O, Miyashiro, I, Sasaki, Y, Ohigashi, H, et al. Postoperative ghrelin levels and delayed recovery from body weight loss after distal or total gastrectomy. J Surg Res. (2006) 130:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2005.08.003
37. Cawood, AL, Burden, ST, Smith, T, and Stratton, RJ. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of community use of oral nutritional supplements on clinical outcomes. Ageing Res Rev. (2023) 88:101953. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.101953
38. Lidoriki, I, Frountzas, M, Karanikki, E, Katsarlinou, E, Tsikrikou, I, Toutouzas, KG, et al. Adherence to Oral nutrition supplementation in gastrointestinal Cancer patients: a systematic review of the literature. Nutr Cancer. (2024) 76:31–41. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2023.2277519
39. Liljeberg, E, Payne, L, Skinnars Josefsson, M, Söderström, L, and Einarsson, S. Understanding the complexity of barriers and facilitators to adherence to oral nutritional supplements among patients with malnutrition: a systematic mixed-studies review. Nutr Res Rev. (2024):1–21. doi: 10.1017/S0954422424000192
Keywords: gastric cancer, gastrectomy, meta-analysis, ONS, systematic review
Citation: Liang Q, Wang S, Wang B and Hong Y (2024) Efficacy and safety of post-discharge oral nutritional supplements for patients with gastric cancer undergoing gastrectomy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Nutr. 11:1488054. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1488054
Received: 29 August 2024; Accepted: 26 November 2024;
Published: 14 January 2025.
Edited by:
Wenjun Meng, Sichuan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Dina Keumala Sari, Universitas Sumatera Utara, IndonesiaCopyright © 2025 Liang, Wang, Wang and Hong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanyan Hong, aG9uZ3l5MDMwMUAxMjYuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.