- 1Department of Pharmacy, Sanya Central Hospital (The Third People's Hospital of Hainan Province), Hainan, China
- 2Scientific Research Center, Guilin Medical University, Guilin, China
Objective: The Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) has been found to have benefits for diabetes mellitus (DM), but a bibliometric analysis of its association with DM has yet to be conducted. This paper aims to explore the current status and research hotspots on the connection between the Mediterranean diet and DM from 2014 to 2024, providing a reference for future studies.
Methods: We retrieved articles published between 2014 and 2024 from the Web of Science database and analyzed them using R software, VOSviewer, and CiteSpace.
Results: A total of 2,806 articles were included in this study. Research on the relationship between the MedDiet and DM showed a steady increase in publication volume from 2014 to 2019, followed by a sharp rise from 2020 to 2023. Spain was the leading country in terms of publication volume, followed by Italy, the United States, China, and Greece. Spain also led in international collaborations, with CIBER—Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red and Harvard University being the most prominent collaboration centers. Nutrients was the most frequently published and cited journal in this field. Common keywords in this literature included components such as olive oil, legumes, and red wine. Mechanisms studied in this field primarily focused on antioxidant effects, improvements in insulin sensitivity and secretion, regulation of lipid metabolism, and modulation of gut microbiota.
Conclusion: Research on the beneficial effects of the MedDiet on DM patients has garnered significant attention from researchers worldwide, and it is expected to become a major focus for future DM prevention and treatment. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the current status and research hotspots regarding the relationship between the MedDiet and DM, offering valuable references for future research.
1 Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM), as a prevalent and serious chronic disease (1), has a profound impact on individuals and families worldwide (2). It is not only one of the leading causes of adult mortality but is also increasing at an alarming rate. As of 2019, the number of people with DM worldwide had reached 464 million, and this figure is projected to rise to 578 million by 2030. By 2045, it may increase to 700 million (3). The complications of DM can pose fatal threats to patients’ health (4), such as the risk of death from macrovascular complications (5), and the damage to renal cells and microvasculature due to hyperglycemia, which can lead to diabetic nephropathy (6). Additionally, hyperglycemia may trigger the polarization and activation of retinal microglia, potentially causing chronic neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration (7). Conditions such as gastroparesis and diabetic foot are also closely related to DM (8, 9), highlighting the severe threat DM poses to individual health.
Research indicates that lifestyle habits, dietary patterns, and regular exercise are key factors in the development of DM (10). Unhealthy dietary patterns may promote the onset of DM (11). Therefore, researching how to change unhealthy dietary behaviors and promoting healthy dietary patterns that help reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes is of critical importance (12). In recent years, numerous studies have confirmed the benefits of healthy eating in reducing the incidence of DM (12). Specifically, the Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) has gained attention for its potential benefits in DM prevention (13). The MedDiet, a concept proposed by Ancel Keys (14), is one of the most extensively researched and well-known dietary patterns globally. Originating in the Mediterranean region, this diet is closely tied to the social behaviors and lifestyles of the area. UNESCO has recognized the MedDiet as an intangible cultural heritage, reflecting its deep geographical and cultural roots (15). The MedDiet includes various foods such as extra virgin olive oil, legumes, grains, nuts, fruits, vegetables, dairy products, fish, and wine, which are rich in phytonutrients, especially polyphenols and vitamins, that play a vital role in health (16). Studies have identified key components of the MedDiet, such as olive oil and polyphenols—particularly hydroxytyrosol—as potent agents in cancer prevention through the reduction of oxidative DNA damage (17). Recent bibliometric analyses using tools like CiteSpace have provided insights into the global trends and emerging research hotspots related to the MedDiet. These studies highlight the MedDiet’ s association with the prevention of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular conditions, DM, obesity, and cancer. Additionally, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease has been identified as a growing area of interest (18). The MedDiet’s antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antimicrobial properties have also been linked to a protective effect against severe COVID-19 outcomes (19). Research on the MedDiet has evolved beyond traditional health benefits, extending into interdisciplinary fields such as neurodegenerative diseases and immunology. In this context, the Mediterranean-DASH Diet Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) diet-a fusion of the MedDiet and the Dietary Approaches to stop Hypertension (DASH) diet-emerges as a promising intervention targeting cognitive health. By prioritizing brain-friendly foods, the MIND diet aims to delay or prevent the onset of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease (20).
Parallel bibliometric studies have uncovered the multi-dimensional nature of DM research. Key areas include gestational diabetes (21), the role of exercise in DM management (22), and regional research outputs from Middle Eastern countries (23). These studies underscore the intricate relationships between DM and various factors, such as physical activity, pregnancy, and population-specific risks. Although the MedDiet has demonstrated potential in DM prevention through various mechanisms, further research is needed to fully elucidate the underlying pathways.
Although existing research confirms that the MedDiet may prevent DM through various mechanisms, the specific pathways of these mechanisms require further investigation. Therefore, there is still much to explore in the research area concerning the relationship between the MedDiet and DM. Bibliometrics, a discipline that applies mathematics, statistics, and other quantitative research methods to analyze bibliographic information (24, 25), offers advantages over conventional literature review methods. Specifically, bibliometrics can conduct targeted quantitative and qualitative analyses of publications within a specific field, which helps assess the current state, development trends, and emerging frontiers of the research area (26, 27). Additionally, this method allows for comparative analysis of the contributions of different countries/regions, research institutions, academic journals, authors, and researchers.
A significant advantage of high-quality bibliometric research is its ability to highlight the forefront of research, effectively saving time for researchers (28). However, despite the growing number of academic articles on the relationship between MedDiet and DM, there is currently a lack of comprehensive bibliometric studies in this field. As a result, it is challenging to gain a complete understanding of the overall trends, key research focuses, and knowledge evolution trajectories. This study aims to conduct an in-depth bibliometric analysis of research literature published between 2014 and 2024 on the relationship between MedDiet and DM, using analytical tools such as R software, VOSviewer, and CiteSpace. Our primary objective is to explore the evolution of research hotspots in this field over time, identify potential future research directions, and deepen the understanding of existing knowledge as well as the potential applications of the MedDiet in DM. By constructing a macro perspective of current research and identifying trends, differences, and connections in the literature, we aim to provide guidance on potential research directions and emerging areas for future studies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data collection
The data used in this study were retrieved and downloaded from WoS (Guilin Medical College Edition) on July 18, 2023. The search formula is (TS = (“Mediterranean diet” OR “Mediterranean dietary pattern”) AND TS = (diabetes OR hyperglycemia OR “insulin resistance” OR “glucose intolerance” OR “metabolic syndrome”)) AND (DT = (“Article” OR “Review”)) AND (LA = (“English”)) AND (DOP = 2014-01-01/2024-07-18). Duplicate documents were removed, and the remaining retrieved articles were saved in plain text format and their cited references were exported as complete records.
2.2 Data analysis
This study utilized Origin 2018 software to analyze annual publication trends and employed R software (version 3.6.3) with the bibliometrix package (version 4.0) (29), VOSviewer (version 1.6.17) (30), and CiteSpace (version 6.1.4) (31) for bibliometric data analysis and visualization. These tools were selected to ensure the accuracy and reliability of data extraction and analysis processes.
VOSviewer was used to create various visualizations, including co-authorship networks by country and institution, co-citation analysis, and keyword co-occurrence networks. In the co-authorship network construction, only countries with at least five publications and institutions with at least 13 publications were included in the analysis. For co-citation analysis, we focused solely on documents that were cited 110 times or more. The keyword co-occurrence analysis included keywords that appeared in at least 10 publications. Journal impact factor (IF) data were sourced from the 2023 Journal Citation Reports (JCR). The combination of these analytical methods and tools provided a comprehensive and in-depth perspective for understanding the research dynamics and trends related to the MedDiet and DM.
3 Results
3.1 General landscapes of included documents on MedDiet and DM
After conducting a search in the WoS database, we identified a total of 2,806 publications related to the MedDiet and DM. As shown in Figure 1A, the number of publications in this field has generally increased over the past decade. From 2014 to 2019, the number of articles published grew slowly, while from 2020 to 2023, there was a rapid rise in publication volume. For 2024, with data available only up to July, the publication count stands at 178. To date, a total of 2,806 articles have been published in this field.
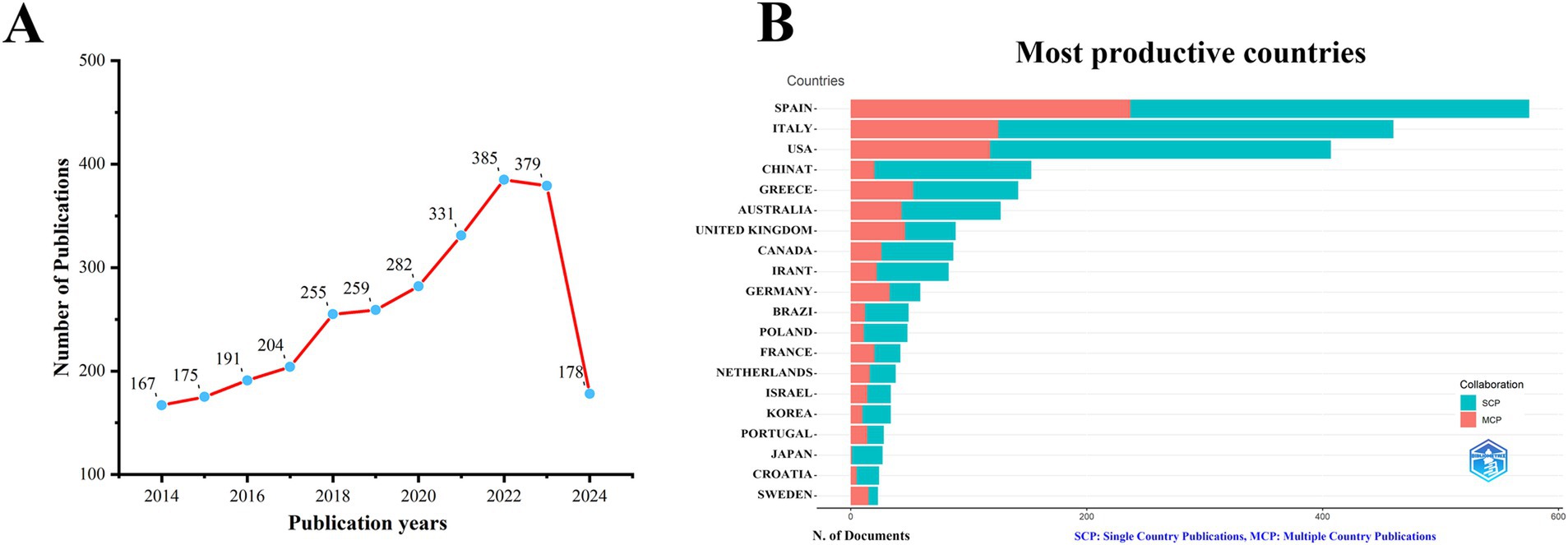
Figure 1. Trends in annual publication outputs the relationship between MedDiet and DM from 2014 to 2024. (A) Trends of annual publication outputs. (B) Distribution of corresponding authors’ countries and cooperation.
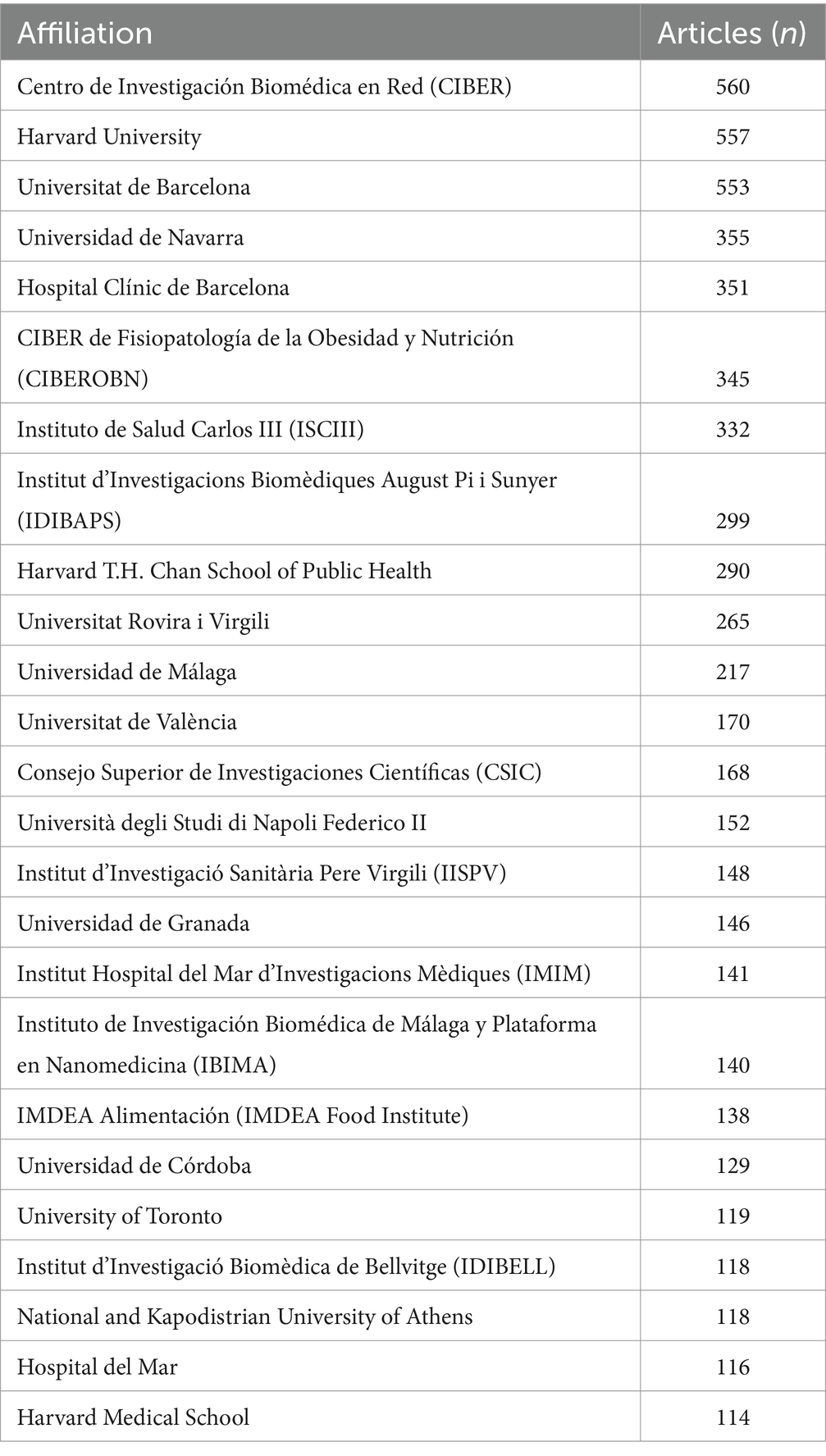
Analysis of the corresponding authors’ institutional affiliations by country reveals that Spain (237 articles) leads in research output, followed by Italy (460 articles), the USA (407 articles), China (153 articles), and Greece (142 articles). These results may be related to Spain and Italy, being Mediterranean countries, having a deeper understanding and research focus on the MedDiet. Interestingly, among the top five countries in terms of publication volume, China’s international collaboration rate (13.1%) is significantly lower than that of Spain (41.2%) and Greece (37.3%), indicating less international cooperation in this field from China, as illustrated in Figure 1B and Table 1. Additionally, Figure 2A shows that Spain has the most extensive collaboration with other countries in the field of MedDiet and DM. Furthermore, the collaboration map indicates that Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red (n = 560) and Harvard University (n = 557) are prominent centers of collaboration (Figure 2B; Table 2).
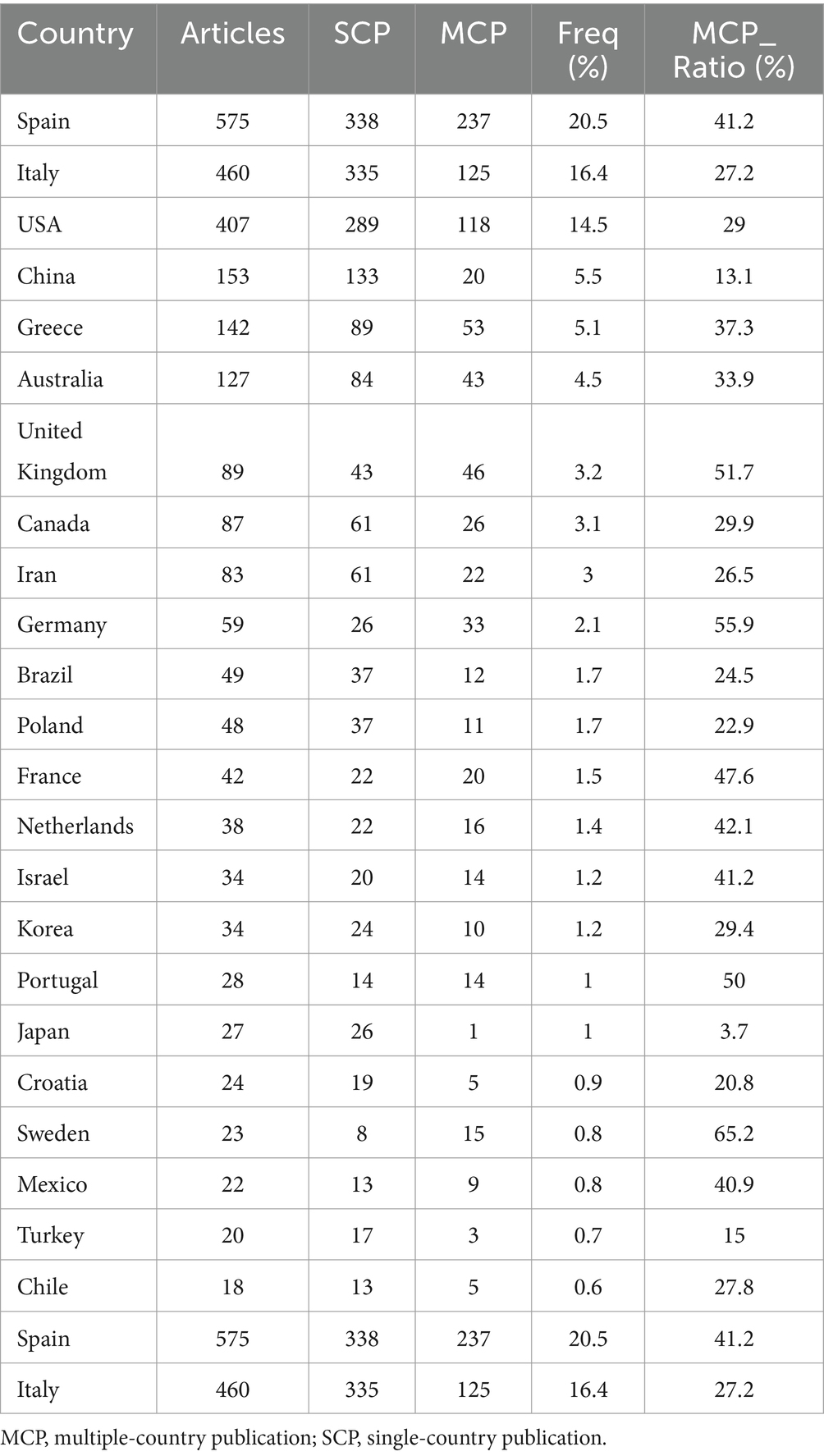
Table 1. Most relevant countries by corresponding authors of the relationship between MedDiet and DM.
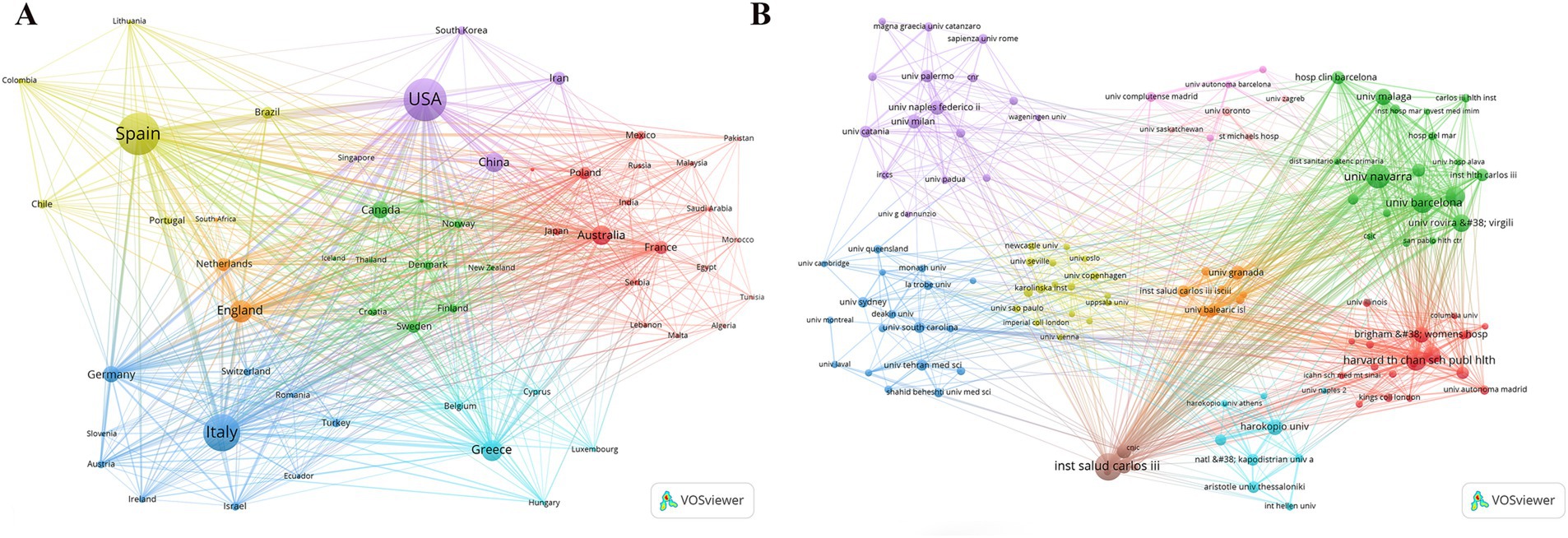
Figure 2. Map of countries/regions and institutions the relationship between MedDiet and DM from 2014 to 2024. (A) Map of cooperation between different countries. (B) Map of cooperation between different institutions.
3.2 Journals and co-cited journals
Using R software (version 3.6.3) with the Bibliometrix and ggplot2 packages, we analyzed the journals with the highest number of publications and the most frequently cited journals in the field of the MedDiet and DM. Additionally, VOSviewer (version 1.6.17) was used for co-citation journal analysis. The analysis revealed that a total of 2,806 articles were published across 668 different academic journals (Annex 1).
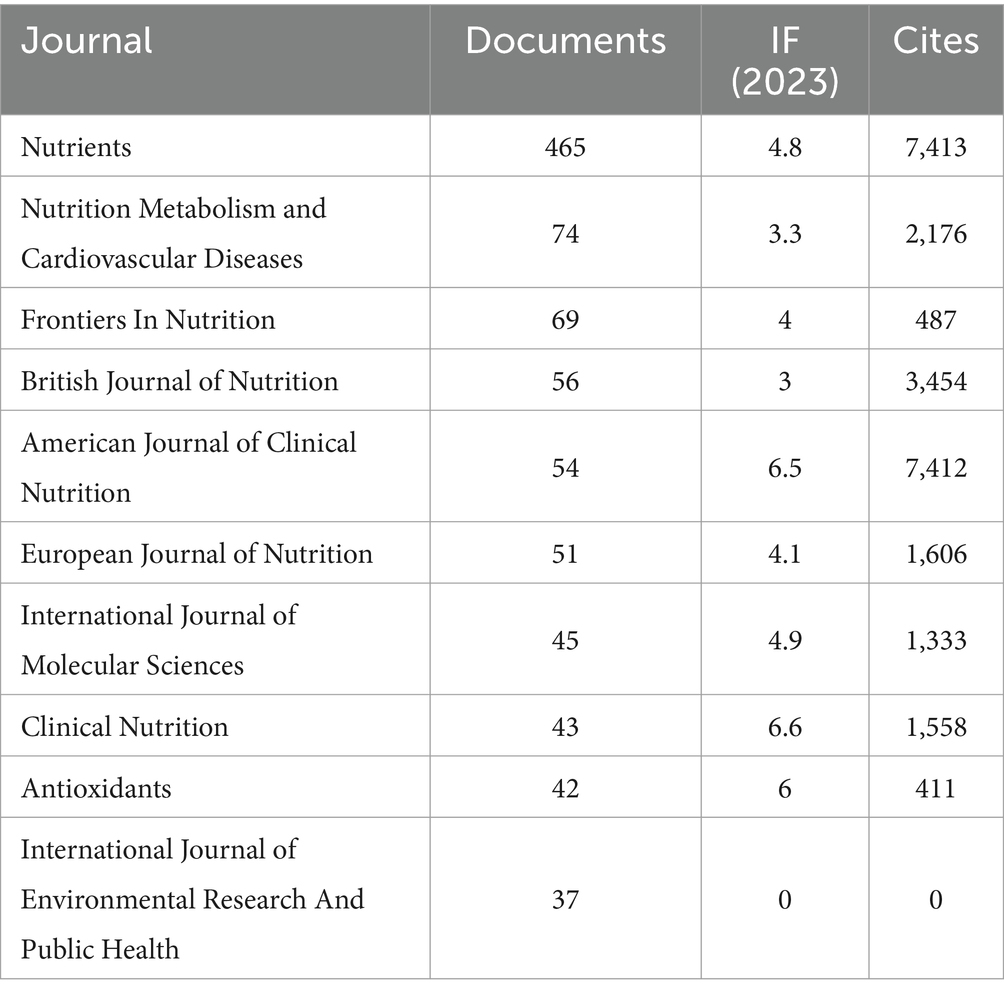
Table 3 show that Nutrients (n = 465, IF = 4.8) is the journal with the highest number of publications, followed by Nutrition Metabolism And Cardiovascular Diseases (n = 74, IF = 3.3), Frontiers In Nutrition (n = 69, IF = 4), British Journal of Nutrition (n = 56, IF = 3), and American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (n = 54, IF = 6.5).
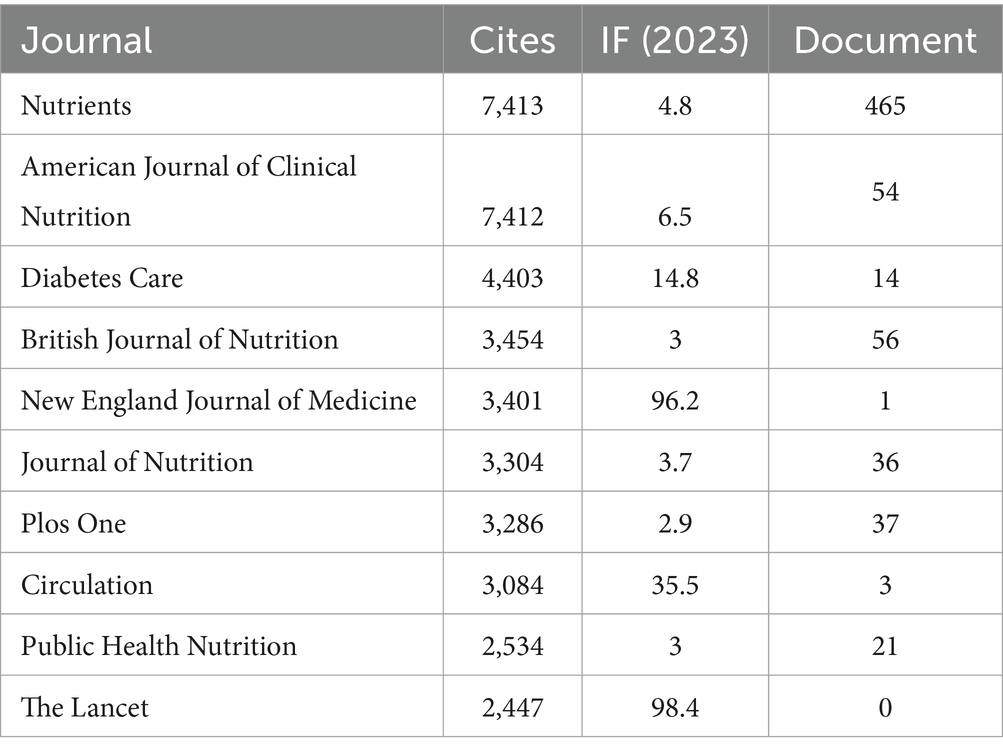
Further, Table 4 display the most frequently cited journals, with Nutrients (n = 7,413, IF = 4.8) leading, followed by American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (n = 7,412, IF = 6.5), Diabetes Care (n = 4,403, IF = 6.5), British Journal of Nutrition (n = 3,454, IF = 3.0), and New England Journal of Medicine (n = 3,401, IF = 96.2).
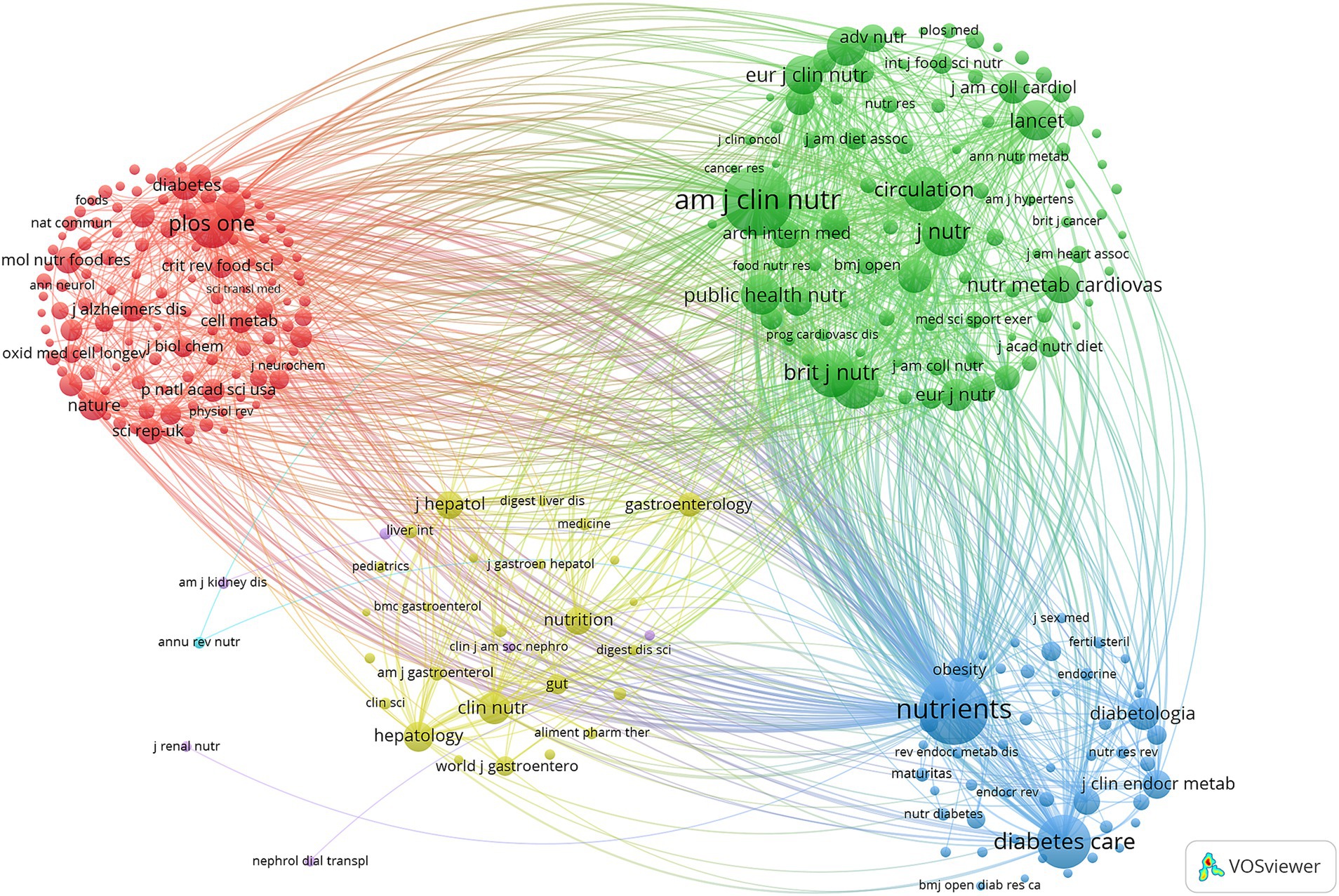
The co-citation journal visualization analysis (Figure 3) indicates that Nutrients, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, and British Journal of Nutrition are highly influential journals in this field. These findings highlight the significant roles of Nutrients and American Journal of Clinical Nutrition in MedDiet and DM research. They also suggest a lack of publications in top-tier journals, which may indicate a need for further improvement in the depth and quality of research.
3.3 Most cited references and reference burst
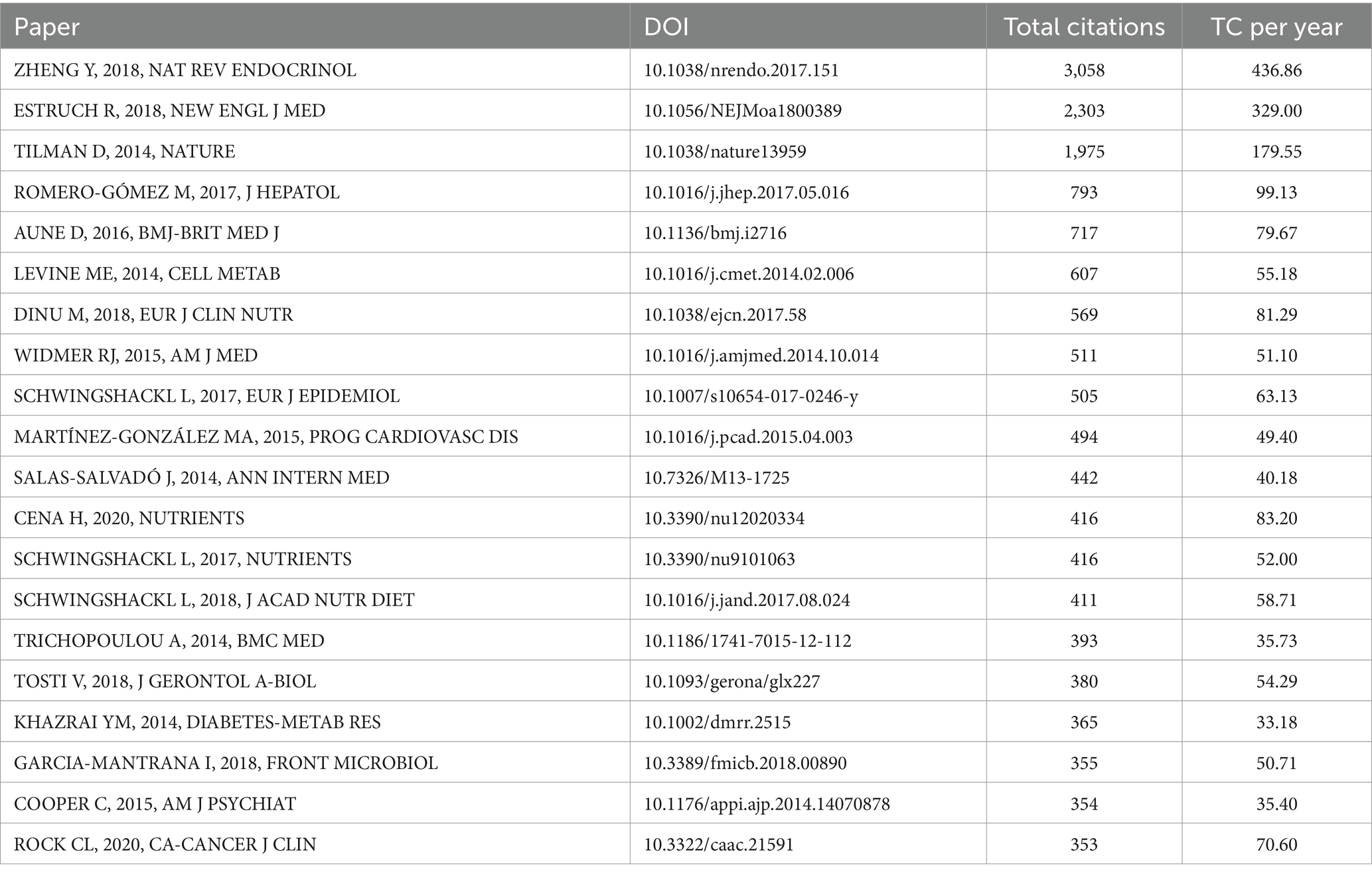
Using the bibliometrix package in R software, we carefully selected the top 20 most-cited articles in the field of MedDiet and DM, all of which have been cited more than 350 times and are scattered across 19 different academic journals (Table 5). This observation suggests that the field has not yet achieved significant theoretical breakthroughs. Notably, none of the journals among these highly cited articles shows a dominant position. The most-cited articles include “Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications,” “Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts” and “Global diets link environmental sustainability and human health” which primarily provide comprehensive descriptions of DM and its relationship with dietary habits.
Furthermore, to identify significant citation bursts in the connection between the MedDiet and DM, we used CiteSpace to detect 113 references with notable citation bursts based on specific criteria (top 25; status count: 2; minimum duration: 2), of which 25 are displayed in Figure 4. “Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet” leads with an intensity of 77.13, followed by “Meta-Analysis of 50 Studies and 534,906 Individuals” and “Accruing Evidence on Benefits of Adherence to the Mediterranean on Health,” with intensities of 37.56 and 28.68, respectively. It is noteworthy that the three leading citation bursts are “Health Effects of Dietary Risks in 195 Countries, 1990–2017” “Mediterranean Diet Effects on Type 2 DM Prevention” and “Health: A Comprehensive Overview” which provide a broad perspective on the field.
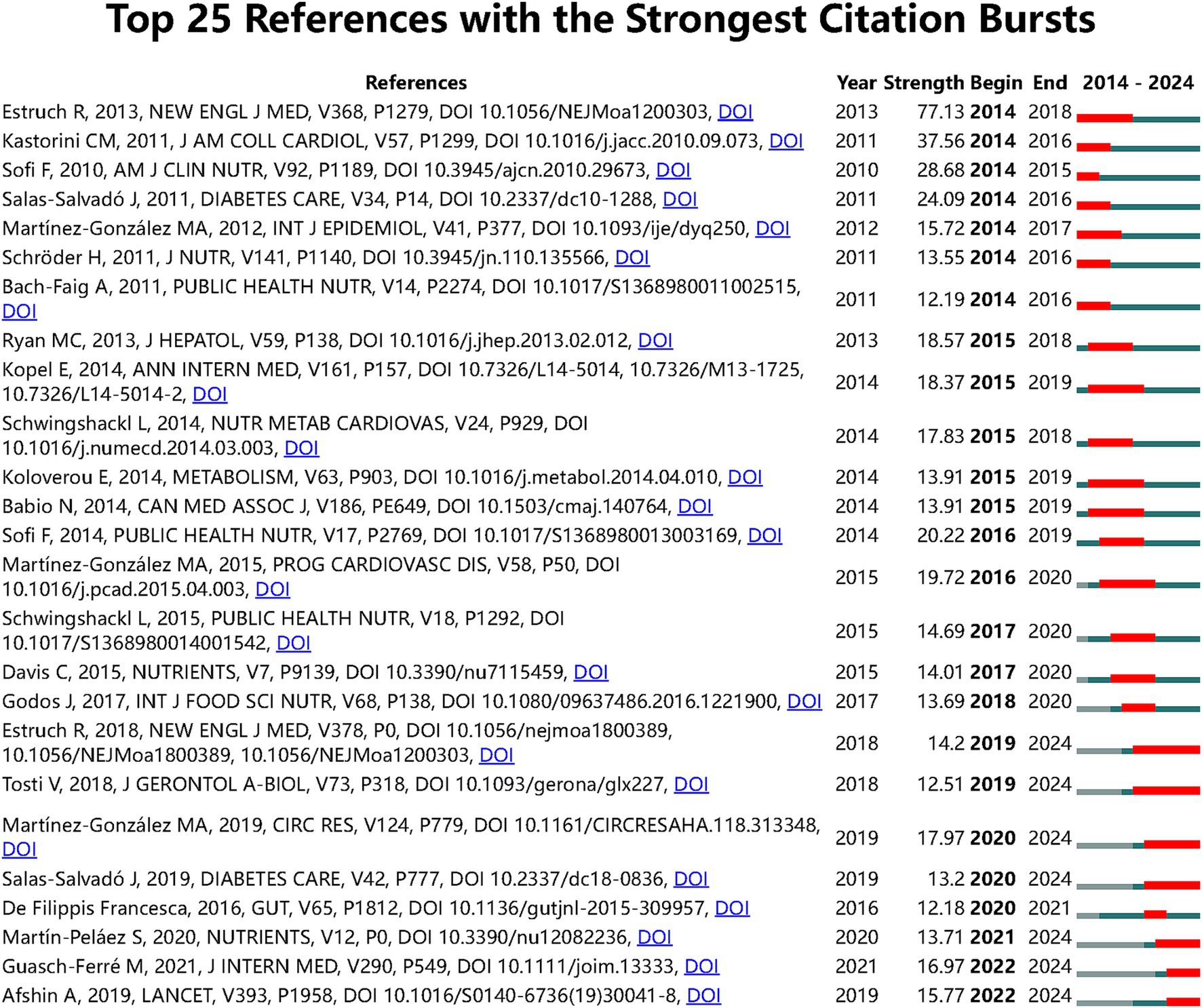
Figure 4. Top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts on the relationship between MedDiet and DM research.
To further understand the research frontiers and hotspots, we matched the DOIs of the 25 citations in Figure 4 with the titles in Annex 2. The results show that 81% of the citations focus on “The Comprehensive Impact of the MedDiet on Chronic Diseases such as Cardiovascular Diseases” 10% are related to the PREDIMED study, and the remaining 10% focus on the measurement and definition of the MedDiet. These data emphasize the importance of the MedDiet in chronic disease prevention, particularly cardiovascular diseases, and highlight the widespread application of the PREDIMED study in this field. However, we also noted that the PREDIMED study may be limited by the dietary habits of volunteers, which could affect their ability to change dietary habits and subsequently impact the accuracy of research results.
3.4 Keyword clusters and evolution
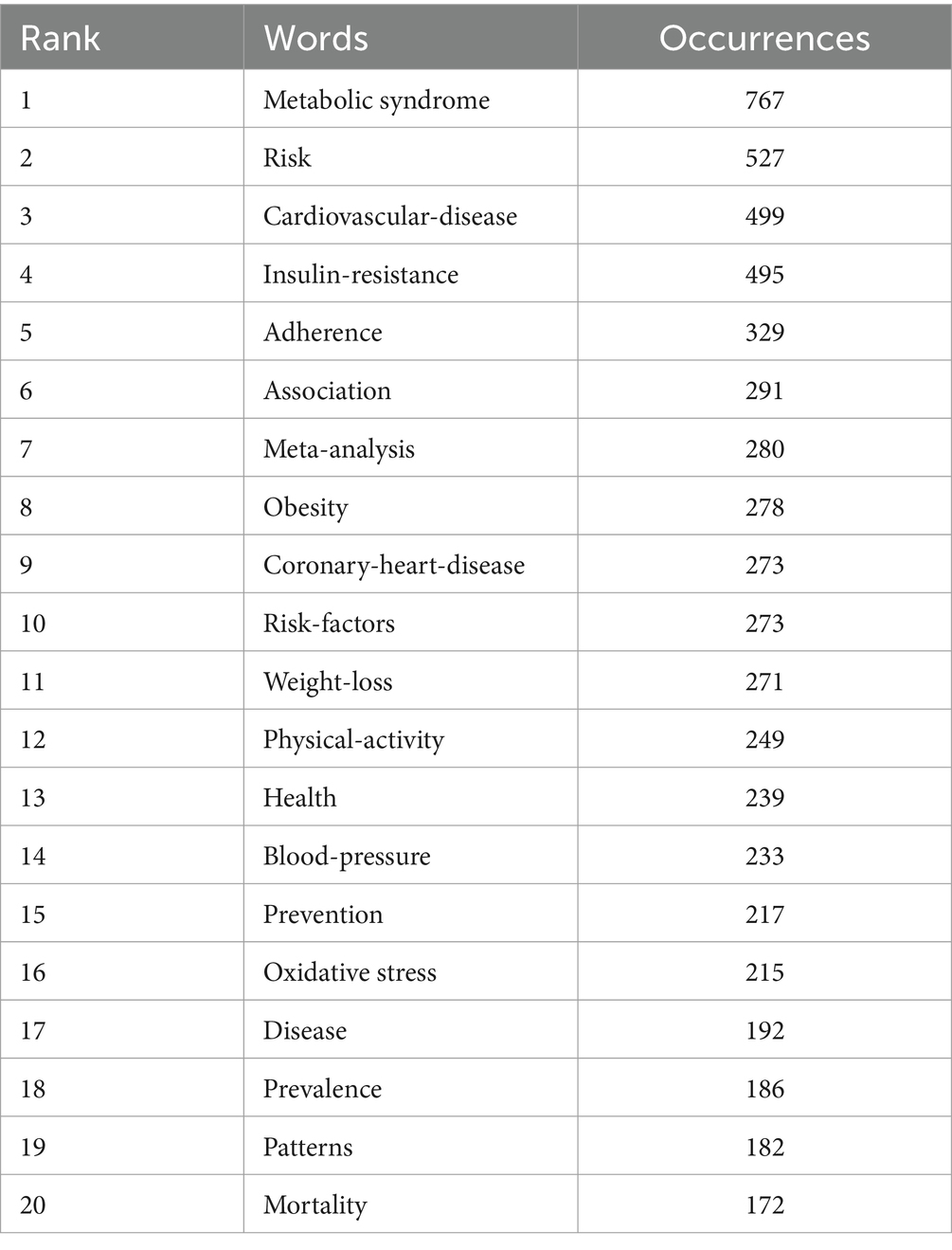
Keyword cluster analysis is an effective method for revealing research hotspots and development trends in academic fields, In this study, we used VOSviewer software to extract 4,667 keywords from the literature, According to Table 6, there are 20 keywords that appeared more than 200 times, with “metabolic syndrome” leading with 767 occurrences, followed by “risk” (527), “cardiovascular-disease” (499), “insulin-resistance” (495), “adherence” (329), “association” (291), “meta-analysis” (280), and “obesity” (278).
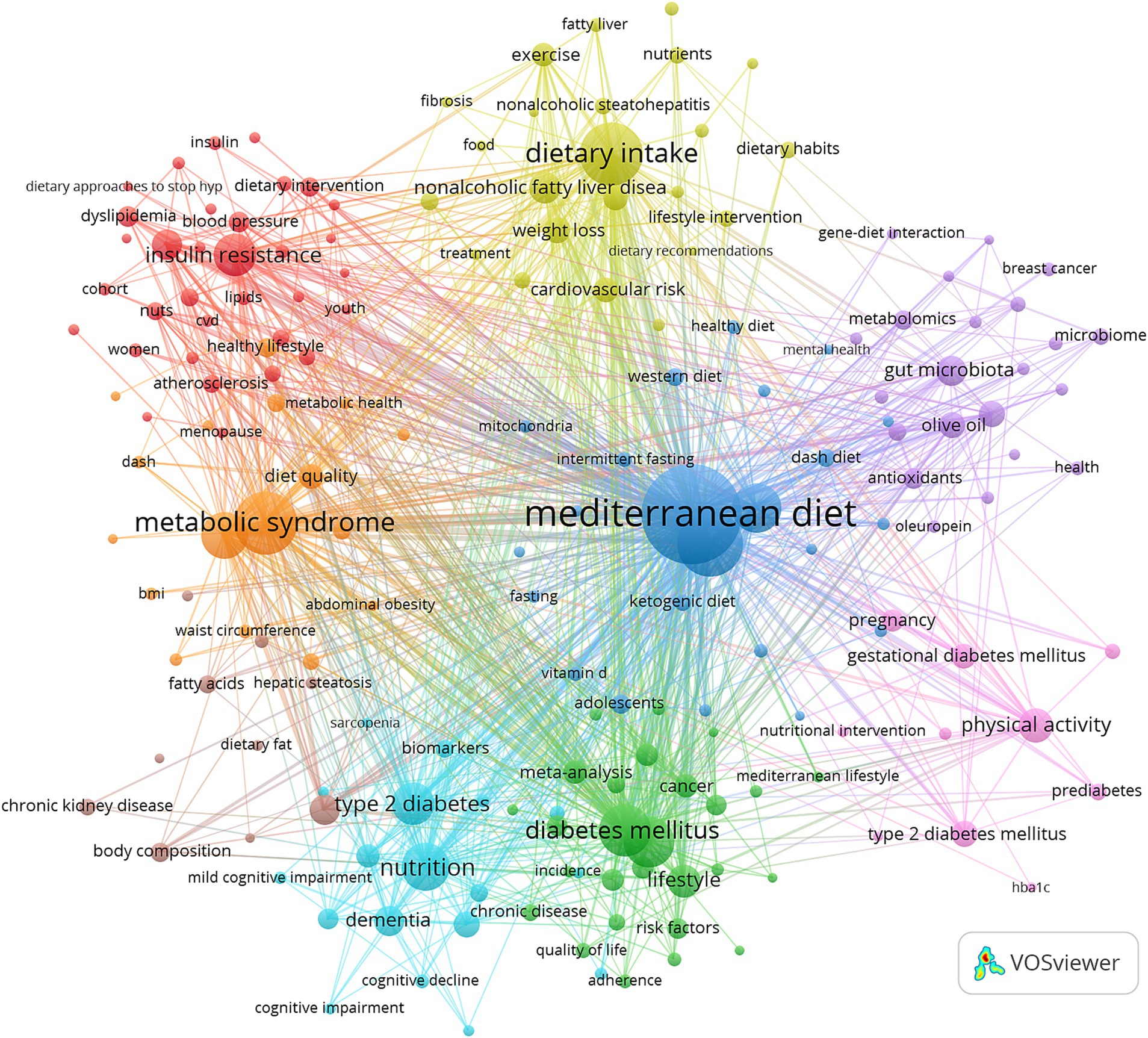
Further, we selected 183 keywords based on the criterion of a minimum occurrence of 10 times and used these to create a keyword cluster map (Figure 5). The map displays nine clusters in different colors as follows.
Cardiometabolic Health Cluster (Red Dot) contains 33 keywords, including adiponectin, adiposity, atherosclerosis, blood pressure and body weight; Chronic Diseases and Prevention Cluster (Green Dot) includes 27 keywords, such as adherence, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, chronic disease and cohort study; Dietary Patterns and Metabolic Health Cluster (Blue Dot) comprises 23 keywords, including adolescents, caloric restriction, cardiovascular risk factors, DASH diet; Nutrition and Lifestyle Interventions Cluster (Yellow Dot) has 23 keywords, such as carbohydrates, cardiovascular risk, dietary habits, exercise and fibrosis; Bioactive Compounds and Personalized Nutrition Cluster (Purple Dot) consists of 22 keywords, including bioactive compounds, epigenetics, lipid metabolism, metabolomics and oleuropein; Aging and Cognitive Health Cluster (Cyan Dot) includes 18 keywords, such as aging, biomarkers, cognition, cognitive function and elderly; Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Cluster (Orange Dot) contains keywords like abdominal obesity, body mass index, cross-sectional study, MedDiet score, nhanes; Diet and Disease Risk Cluster (Brown Dot) has 10 keywords, including advanced glycation end products, dietary fat, hepatic steatosis, cardiovascular disease risk and predimed; Diabetes and Nutritional Interventions Cluster (Red Dot) includes keywords such as coronavirus disease 2019, SARS-CoV-2 infection, cytokines, gestational diabetes mellitus, nutritional intervention and pregnancy (Annex 3).
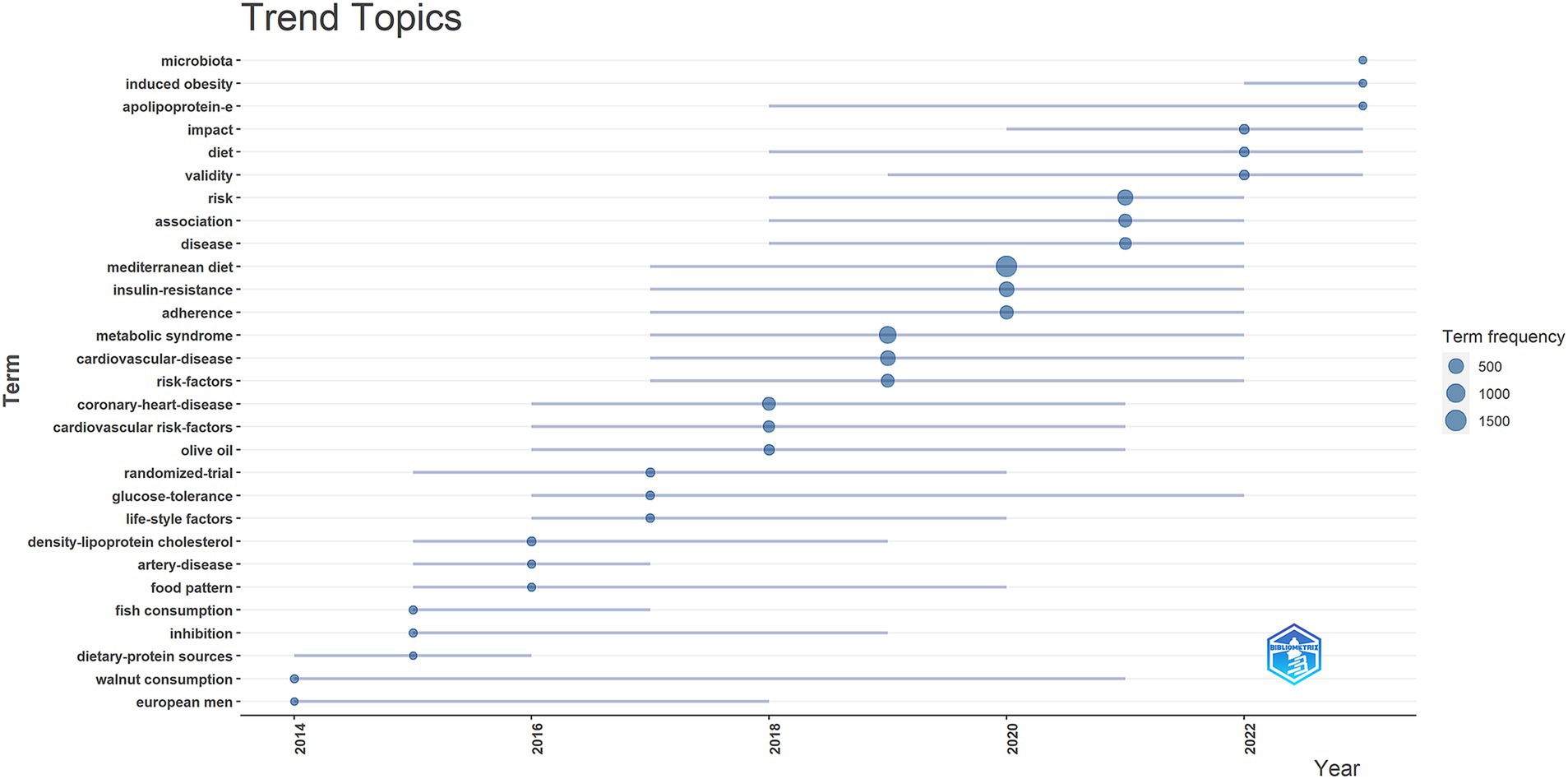
In addition, we utilized the bibliometrix package in R to generate a trend topic map. The trend topic map is a valuable tool for identifying the chronological progression of specific research topics within a given field, allowing us to examine the evolution of research over time. By analyzing the trend topic map shown in Figure 6, we were able to identify the research foci and evolutionary trajectory at different stages within the field. Our findings indicate that the current research in this area is predominantly focused on microbiota and induced obesity.
4 Discussion
4.1 General information
In this study, we compiled a comprehensive corpus of 2,806 articles covering the period from 2014 to 2024. By identifying trends and patterns within this corpus, we observed a steady increase in research publications on the interaction between the MedDiet and DM from 2014 to 2023, reflecting a growing interest in this field. In the realm of MedDiet and DM research, Spain has emerged as a leading country, with a significantly higher number of publications. This trend reflects Spain’s historical and cultural connections to the MedDiet, providing a natural advantage and keen interest in related research. Among the 668 journals where 2,806 articles were published, journals such as Nutrients, Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, and Frontiers in Nutrition have played crucial roles. Notably, Nutrients has published a substantial number of relevant articles and received extensive citations, establishing itself as a core journal and a key platform for disseminating research findings on the MedDiet and DM.
4.2 Hotspots and development trends
Through various analytical methods, including literature clustering, keyword frequency analysis, keyword clustering, and topic evolution, we have identified potential research hotspots related to the use of the MedDiet and DM link. The findings indicate that the forefront and hotspots of research in this field primarily focus on two key aspects. First, the benefits of components in the MedDiet, such as olive oil, legumes, and red wine, for DM. Second, the mechanisms by which the MedDiet prevents DM, including improvements in insulin sensitivity, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant effects, regulation of gut microbiota and fat metabolism.
4.2.1 The benefits of components in the MedDiet, such as olive oil, legumes, and red wine, for DM
Analyzing the articles published in this field, we find that identifying which key components of the MedDiet are beneficial for DM is a current research hotspot and cutting-edge area. The MedDiet is characterized by its high olive oil content, which is the primary source of fat in this diet (32). Moreover, consuming this specific type of olive oil helps reduce the risk of DM (33). Common nuts in the MedDiet, such as almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, and pistachios, as well as legumes like lentils and chickpeas, are rich in fiber, vitamin B6, magnesium, potassium, and copper (34). These nutrients significantly lower the risk of developing DM (35). The monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) found in nuts have been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of DM and its associated cardiovascular diseases (34, 36, 37). Additionally, moderate consumption of red wine, an important component of the MedDiet, has been found to effectively lower the incidence of DM in women (38, 39). Additionally, obesity is a major exacerbating factor for DM, and the MedDiet is superior to low-fat diets in controlling weight and preventing overweight (40–42). These findings provide new perspectives and methods for the prevention and treatment of DM. But it is worth noting that there are still some shortcomings in this kind of research field. (1) Complexity of Components: The analysis in the passage focuses on individual components of the Mediterranean diet, such as olive oil, nuts, and red wine, without considering the potential synergistic or antagonistic effects of these components. The Mediterranean diet is a complex dietary pattern, and interactions between different food components may influence its overall health benefits. Existing research often overlooks these complex interactions, which may lead to an incomplete understanding of the overall benefits of the Mediterranean diet. (2) Generalizability of Findings: The findings mentioned in the passage may be primarily based on specific populations, such as residents of the Mediterranean region or particular gender groups, which could limit their generalizability to different populations globally. For example, the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet may vary among people from different geographical areas, cultural backgrounds, or genetic profiles. Therefore, extrapolating these research findings to all populations may have certain limitations. (3) Consideration of Comorbidities: The research referred to in the passage primarily addresses individual diabetes patients and seldom considers populations with diabetes combined with other conditions. For instance, while the Mediterranean diet recommends moderate red wine consumption, for some patients, consuming red wine may lead to other health issues.
4.2.2 Research on the mechanisms by which the MedDiet prevents DM
In research on the mechanisms by which the MedDiet influences DM, analysis of keywords and citation literature reveals that common research mechanisms in this field include anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, regulation of gut microbiota, improvement of insulin sensitivity and secretion, and enhancement of fat metabolism. Oxidative stress is a pathological state caused by an imbalance between the excessive generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s antioxidant defenses (43). ROS, including free radicals and other highly reactive molecules, are byproducts of normal cellular metabolism; however, excessive levels can impair β-cell function, lead to insulin resistance, and disrupt glucose regulation (44). Moreover, oxidative stress is closely related to DM-associated retinopathy and cardiovascular diseases (45, 46). Research indicates that inflammation is also a significant factor in inducing insulin resistance, which contributes to the development of DM (47).
Analysis of published literature in this field shows that the Mediterranean diet is rich in antioxidants, such as polyphenols, plant sterols, and carotenoids, which inhibit oxidative stress and inflammatory responses through various molecular mechanisms. For example, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) in green tea reduces inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the NF-kB pathway (48). Lycopene improves type 2 diabetes by activating antioxidant systems like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (49). In the same vein, leafy greens and nuts rich in vitamin E protect cell membranes by activating NRF2 and heat shock proteins, reducing ROS damage to cells, and inhibiting NF-kB activity, thereby alleviating oxidative stress in DM patients (50).
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in human health, with its dysregulation closely linked to various diseases, including DM (51, 52). Recent studies suggest that the MedDiet increases the abundance of Roseburia in the gut, a microbiota negatively associated with DM (53, 54). The MedDiet provides abundant fermentable substrates, promoting the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (55). SCFAs help improve insulin secretion, reduce insulin resistance, suppress glucose production, and decrease food intake by regulating the secretion of hormones like GLP-1, leptin, and ghrelin, thereby playing a positive role in DM prevention and management (56).
The MedDiet emphasizes extra-virgin olive oil as its primary fat source and promotes moderate consumption of animal proteins and fats, favoring fish, eggs, and low-fat dairy products. Recent studies suggest that strong adherence to the MedDiet is significantly linked to reductions in both fasting and postprandial insulin resistance in individuals with overweight or obesity, with fish consumption being a key contributor to this effect (57). Fish is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which offer various metabolic benefits that enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Moreover, a recent meta-analysis of 46 randomized clinical trials involving omega-3 fatty acids (n = 4,991 patients with type 2 diabetes) demonstrated improvements in HbA1c levels (58). The beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acids can be attributed to multiple mechanisms. Notably, these fatty acids inhibit lipolysis, thereby limiting the release of free fatty acids into the bloodstream and alleviating their interference with insulin signaling pathways (59). Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis, enhance the expression of genes involved in fatty acid oxidation, and suppress lipid synthesis, which collectively decrease fat accumulation in adipose tissue (60). In addition, their anti-inflammatory properties boost the production of adiponectin, an adipokine that plays a crucial role in improving insulin sensitivity (61). In summary, the diverse actions of omega-3 fatty acids significantly contribute to metabolic health and help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
In fact, our analysis of the literature reveals that many mechanisms underlying the MedDiet benefits for DM patients remain inadequately understood. While there are indications of beneficial effects, the specific molecular mechanisms are not fully clear. The interplay between oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, as well as the mechanisms by which the MedDiet influences DM through gut microbiota and regulation of fat metabolism, have only been superficially explored. Therefore, future research should focus on analyzing the interactions between these mechanisms, with particular emphasis on gut microbiota, to enhance our understanding of the molecular pathways involved.
4.3 Limitations
This study utilized the WoSCC database as a data source, providing a comprehensive overview of the field, including its overall scope, hotspots, and research trends. This approach aids in a deeper understanding of the field and helps explore future research direction. However, there are several notable limitations to this study.
First, reliance solely on the WoSCC database may result in the omission of some relevant publications, despite the database’s high quality and widespread recognition as an ideal tool for bibliometric analysis (62–64). Second, the study only includes English-language publications, which may introduce language bias and limit the generalizability of the findings. Third, due to the presence of many authors with the same name in China, the study did not conduct an in-depth analysis of authors to avoid potential misleading results. Despite these limitations, the conclusions of this study remain highly reliable and provide valuable insights and references for academic research in the field.
5 Conclusion
This study systematically reveals the major research hotspots and frontiers in the relationship between the MedDiet and DM, summarized as follows:
a. Research on the association between the MedDiet and DM has garnered widespread attention from scholars globally. Spain, Italy, the United States, China, and Greece are the most active countries in this field, with close and extensive international research collaborations.
b. Nutrients and Nutrition, Metabolism & Cardiovascular Diseases are the most prolific journals in this area. Notably, Nutrients stands out as a representative journal due to its high citation rate.
c. Components such as olive oil, legumes, and red wine are key research hotspots and trends in the prevention and management of DM within the MedDiet.
d. Core mechanisms of interest in the relationship between the MedDiet and DM include anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, improvement of insulin sensitivity and secretion, and regulation of fat metabolism. Additionally, the “gut microbiota” is an emerging area of research that is receiving increasing attention.
In summary, this study provides in-depth and valuable insights into the research trends and hotspots concerning the MedDiet and DM. These findings not only offer researchers essential background knowledge for a comprehensive understanding of the field but also lay the foundation for exploring new research directions. By identifying current research frontiers and potential key areas, our study provides strong support and guidance for future innovative research.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: Web of Science database (https://www.webofscience.com/).
Author contributions
YY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Methodology, Writing – original draft. YL: Software, Writing – original draft. PL: Visualization, Writing – original draft. BZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2024.1480856/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Wu, Y, Ding, Y, Tanaka, Y, and Zhang, W. Risk factors contributing to type 2 diabetes and recent advances in the treatment and prevention. Int J Med Sci. (2014) 11:1185–200. doi: 10.7150/ijms.10001
2. Bommer, C, Heesemann, E, Sagalova, V, Manne-Goehler, J, Atun, R, Bärnighausen, T, et al. The global economic burden of diabetes in adults aged 20-79 years: a cost-of-illness study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2017) 5:423–30. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30097-9
3. Saeedi, P, Petersohn, I, Salpea, P, Malanda, B, Karuranga, S, Unwin, N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2019) 157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
4. Harding, JL, Pavkov, ME, Magliano, DJ, Shaw, JE, and Gregg, EW. Global trends in diabetes complications: a review of current evidence. Diabetologia. (2019) 62:3–16. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4711-2
5. Ritchie, RH, and Abel, ED. Basic mechanisms of diabetic heart disease. Circ Res. (2020) 126:1501–25. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315913
6. Sagoo, MK, and Gnudi, L. Diabetic nephropathy: an overview. Methods Mol Biol. (2020) 2067:3–7. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9841-8_1
7. Li, X, Yu, ZW, Li, HY, Yuan, Y, Gao, XY, and Kuang, HY. Retinal microglia polarization in diabetic retinopathy. Vis Neurosci. (2021) 38:E006. doi: 10.1017/S0952523821000031
8. Ramos, GP, and Camilleri, M. Ten controversies in gastroparesis and a look to the future. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2023) 35:e14494. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14494
9. Armstrong, DG, Tan, TW, Boulton, AJM, and Bus, SA. Diabetic foot ulcers: a review. JAMA. (2023) 330:62–75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.10578
10. Kolb, H, and Martin, S. Environmental/lifestyle factors in the pathogenesis and prevention of type 2 diabetes. BMC Med. (2017) 15:131. doi: 10.1186/s12916-017-0901-x
11. Martín-Peláez, S, Fito, M, and Castaner, O. Mediterranean diet effects on type 2 diabetes prevention, disease progression, and related mechanisms. A review. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2236. doi: 10.3390/nu12082236
12. Jannasch, F, Kröger, J, and Schulze, MB. Dietary patterns and type 2 diabetes: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Nutr. (2017) 147:1174–82. doi: 10.3945/jn.116.242552
13. Schwingshackl, L, Missbach, B, König, J, and Hoffmann, G. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. (2015) 18:1292–9. doi: 10.1017/S1368980014001542
14. Keys, A, Menotti, A, Karvonen, MJ, Aravanis, C, Blackburn, H, Buzina, R, et al. The diet and 15-year death rate in the seven countries study. Am J Epidemiol. (1986) 124:903–15. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114480
15. Barros, VC, and Delgado, AM. Mediterranean diet, a sustainable cultural asset. Encyclopedia. (2022) 2:761–77. doi: 10.3390/encyclopedia2020053
16. Tosti, V, Bertozzi, B, and Fontana, L. Health benefits of the Mediterranean diet: metabolic and molecular mechanisms. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2018) 73:318–26. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glx227
17. Liu, Y, and Lu, J. A bibliometric analysis of Mediterranean diet on cancer from 2012 to 2021. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1128432. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1128432
18. Pan, C, Jiang, N, Cao, B, and Dong, C. Global trends and performances of Mediterranean diet: a bibliometric analysis in CiteSpace. Medicine. (2021) 100:e27175. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027175
19. Li, C, Baek, JH, Huang, J, and Jia, B. Bibliometric analysis reveals the Mediterranean diet can benefit against coronavirus disease 2019. New Microbes New Infect. (2023) 52:101105. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101105
20. Dai, L, Lin, X, Wang, S, Gao, Y, and He, F. The Mediterranean-dietary approaches to stop hypertension diet intervention for neurodegenerative delay (MIND) diet: a bibliometric analysis. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1348808. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1348808
21. Iftikhar, PM, Ali, F, Faisaluddin, M, Khayyat, A, De Sa, MDG, and Rao, T. A bibliometric analysis of the top 30 most-cited articles in gestational diabetes mellitus literature (1946-2019). Cureus. (2019) 11:e4131. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4131
22. Zhang, Z, Zhu, Y, Wang, Q, Chang, T, Liu, C, Zhu, Y, et al. Global trends and research hotspots of exercise for intervening diabetes: a bibliometric analysis. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:902825. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.902825
23. Sweileh, WM, SeH, Z, Al-Jabi, SW, and Sawalha, AF. Bibliometric analysis of diabetes mellitus research output from middle eastern Arab countries during the period (1996–2012). Scientometrics. (2014) 101:819–32. doi: 10.1007/s11192-014-1361-0
24. Smith, DR . Bibliometrics, dermatology and contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. (2008) 59:133–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.2008.01405.x
25. Li, Z, Liao, X, Qin, Y, Jiang, C, Lian, Y, Lin, X, et al. Exploring the impact of coffee consumption on liver health: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e31132. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31132
26. Shan, M, Dong, Y, Chen, J, Su, Q, and Wan, Y. Global tendency and frontiers of research on myopia from 1900 to 2020: a bibliometrics analysis. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:846601. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.846601
27. Chen, C, Liu, Y, Yang, S, Chen, M, and Liao, J. A bibliometric and visual analysis of research trends and hotspots of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a review. Medicine. (2024) 103:e37969. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037969
28. Nie, K, Deng, T, Wang, J, Qi, L, Liu, N, Chen, Z, et al. Bibliometric and visual analysis of intestinal flora and immunity. Medicine. (2024) 103:e36575. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036575
29. Van Eck, N, and Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. (2010) 84:523–38. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
30. Yeung, AWK, Tzvetkov, NT, Balacheva, AA, Georgieva, MG, Gan, RY, Jozwik, A, et al. Lignans: quantitative analysis of the research literature. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:37. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00037
31. Chen, C . CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology. (2006) 57:359–377. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317
32. Finicelli, M, Squillaro, T, Galderisi, U, and Peluso, G. Polyphenols, the healthy brand of olive oil: insights and perspectives. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3831. doi: 10.3390/nu13113831
33. Schwingshackl, L, Schwedhelm, C, Galbete, C, and Hoffmann, G. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and risk of cancer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2017) 9:1063. doi: 10.3390/nu9101063
34. Finicelli, M, Squillaro, T, Di Cristo, F, Di Salle, A, Melone, MAB, Galderisi, U, et al. Metabolic syndrome, Mediterranean diet, and polyphenols: evidence and perspectives. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:5807–26. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27506
35. Lisciani, S, Marconi, S, Le Donne, C, Camilli, E, Aguzzi, A, Gabrielli, P, et al. Legumes and common beans in sustainable diets: nutritional quality, environmental benefits, spread and use in food preparations. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1385232. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1385232
36. Kelly, JHJr, and Sabaté, J. Nuts and coronary heart disease: an epidemiological perspective. Br J Nutr. (2006) 96:S61–7. doi: 10.1017/BJN20061865
37. Nishi, SK, Viguiliouk, E, Kendall, CWC, Jenkins, DJA, Hu, FB, Sievenpiper, JL, et al. Nuts in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. (2023) 15:878. doi: 10.3390/nu15040878
38. Trichopoulou, A, Costacou, T, Bamia, C, and Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N Engl J Med. (2003) 348:2599–608. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa025039
39. Hu, FB, Manson, JE, Stampfer, MJ, Colditz, G, Liu, S, Solomon, CG, et al. Diet, lifestyle, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. N Engl J Med. (2001) 345:790–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa010492
40. Ruze, R, Liu, T, Zou, X, Song, J, Chen, Y, Xu, R, et al. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Front Nutr. (2023) 14:1161521. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1161521
41. Bendall, CL, Mayr, HL, Opie, RS, Bes-Rastrollo, M, Itsiopoulos, C, and Thomas, CJ. Central obesity and the Mediterranean diet: a systematic review of intervention trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2018) 58:3070–84. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1351917
42. Mancini, JG, Filion, KB, Atallah, R, and Eisenberg, MJ. Systematic review of the Mediterranean diet for long-term weight loss. Am J Med. (2016) 129:407–15.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.11.028
43. Forman, HJ, and Zhang, H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2021) 20:689–709. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1
44. Darenskaya, MA, Kolesnikova, LI, and Kolesnikov, SI. Oxidative stress: pathogenetic role in diabetes mellitus and its complications and therapeutic approaches to correction. Bull Exp Biol Med. (2021) 171:179–89. doi: 10.1007/s10517-021-05191-7
45. Luc, K, Schramm-Luc, A, Guzik, T, and Mikolajczyk, T. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2019) 70:809–24. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2019.6.01
46. Sasso, FC, Salvatore, T, Tranchino, G, Cozzolino, D, Caruso, AA, Persico, M, et al. Cochlear dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: a complication independent of neuropathy and acute hyperglycemia. Metabolism. (1999) 48:1346–50. doi: 10.1016/S0026-0495(99)90141-5
47. Rehman, K, and Akash, MSH. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: how are they interlinked? J Biomed Sci. (2016) 23:87. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0303-y
48. Nani, A, Murtaza, B, Sayed Khan, A, Khan, NA, and Hichami, A. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of polyphenols contained in Mediterranean diet in obesity: molecular mechanisms. Molecules. (2021) 26:985. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040985
49. Leh, HE, and Lee, LK. Lycopene: a potent antioxidant for the amelioration of type II diabetes mellitus. Molecules. (2022) 27:2335. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072335
50. Martucci, M, Ostan, R, Biondi, F, Bellavista, E, Fabbri, C, Bertarelli, C, et al. Mediterranean diet and inflammaging within the hormesis paradigm. Nutr Rev. (2017) 75:442–55. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nux013
51. Thursby, E, and Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J. (2017) 474:1823–36. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160510
52. Fan, Y, and Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2021) 19:55–71. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0433-9
53. Zhu, C, Sawrey-Kubicek, L, Beals, E, Rhodes, CH, Houts, HE, Sacchi, R, et al. Human gut microbiome composition and tryptophan metabolites were changed differently by fast food and Mediterranean diet in 4 days: a pilot study. Nutr Res. (2020) 77:62–72. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2020.03.005
54. Gurung, M, Li, Z, You, H, Rodrigues, R, Jump, DB, Morgun, A, et al. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine. (2020) 51:102590. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.051
55. Pagliai, G, Russo, E, Niccolai, E, Dinu, M, Di Pilato, V, Magrini, A, et al. Influence of a 3-month low-calorie Mediterranean diet compared to the vegetarian diet on human gut microbiota and SCFA: the CARDIVEG study. Eur J Nutr. (2020) 59:2011–24. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-02050-0
56. Glass, GV . Primary, secondary, and Meta-analysis of research. Educ Res. (1976) 5:3–8. doi: 10.3102/0013189X005010003
57. Vetrani, C, Verde, L, Colao, A, Barrea, L, and Muscogiuri, G. The Mediterranean diet: effects on insulin resistance and secretion in individuals with overweight or obesity. Nutrients. (2023) 15:4524. doi: 10.3390/nu15214524
58. Xiao, Y, Zhang, Q, Liao, X, Elbelt, U, and Weylandt, KH. The effects of omega-3 fatty acids in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids. (2022) 182:102456. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2022.102456
59. Puglisi, MJ, Hasty, AH, and Saraswathi, V. The role of adipose tissue in mediating the beneficial effects of dietary fish oil. J Nutr Biochem. (2011) 22:101–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.07.003
60. Sinha, S, Haque, M, Lugova, H, and Kumar, S. The effect of omega-3 fatty acids on insulin resistance. Life. (2023) 13:1322. doi: 10.3390/life13061322
61. Bayram, SŞ, and Kızıltan, G. The role of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in diabetes mellitus management: a narrative review. Curr Nutr Rep. (2024) 13:527–51. doi: 10.1007/s13668-024-00561-9
62. Thelwall, M . Bibliometrics to webometrics. J Inf Sci. (2008) 34:605–21. doi: 10.1177/0165551507087238
63. Cheng, P, Tang, H, Dong, Y, Liu, K, Liu, Y, and Liu, Y. Knowledge mapping of research on land use change and food security: a visual analysis using CiteSpace and VOSviewer. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:13065. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182413065
Keywords: bibliometric analysis, insulin sensitivity, antioxidant, gut microbiota, chronic disease prevention
Citation: Yan Y, Li Z, Lian Y, Liu P, Zhang B and Chen J (2024) Global research dynamics in the Mediterranean diet and diabetes mellitus: a bibliometric study from 2014 to 2024. Front. Nutr. 11:1480856. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1480856
Edited by:
Jose Paulo Andrade, University of Porto, PortugalReviewed by:
Andy Wai Kan Yeung, University of Hong Kong, ChinaJoao Rocha-Neves, University of Porto, Portugal
Copyright © 2024 Yan, Li, Lian, Liu, Zhang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juan Chen, Y2hlbmp1YW4xMjI3QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yuanyuan Yan
Yuanyuan Yan Zonghuai Li
Zonghuai Li Yuanchu Lian2
Yuanchu Lian2 Bo Zhang
Bo Zhang