
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Nutr., 18 October 2024
Sec. Nutritional Epidemiology
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1469779
Background: The association between oxidative stress, as measured by the Oxidative Balance Score (OBS), and sleep quality remains unclear. The primary objective of this investigation was to clarify this relationship and to explore the potential involvement of oxidative stress and inflammation.
Methods: Data from 15,198 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2014 were analyzed. Sleep quality indicators, including sleep disorder, trouble, and duration, were assessed. The OBS, comprising information on 16 dietary nutrients and 4 lifestyle factors, was then calculated. Multivariable logistic and linear regression models were employed to investigate the correlation between OBS and sleep quality. Additionally, mediation analyses were conducted to evaluate the potential effects of oxidative stress and inflammation.
Results: We demonstrated a correlation between an elevated OBS and reduced sleep disorders (OR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.58–0.91; p = 0.0055), reduced sleep trouble (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.69–0.96; p = 0.0174), and prolonged sleep duration (β 0.009; 95% CI, 0.0002–0.0160; p = 0.015) when comparing the highest and lowest tertiles. Dietary factors exhibited autonomous correlations with sleep duration, whereas lifestyle factors displayed independent associations with sleep trouble and sleep disorders. Moreover, the relationships between OBS and both sleep disorders and trouble were influenced by albumin, γ-glutamyl transferase, total bilirubin, and white blood cells, with combined mediation effects of 34.66 and 29.54%, respectively (both p < 0.001). Sensitivity analyses revealed a significant association between OBS and sleep disorder (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: This study revealed a positive correlation between an elevated OBS and improved sleep quality, manifested by decreased sleep disorders, mitigated sleep trouble, and prolonged sleep duration. This is potentially mediated by oxidative stress and inflammation. Therefore, the study underscores the importance of adopting a diet rich in antioxidants and healthy lifestyle choices to address sleep-related concerns, providing a novel avenue for enhancing overall sleep quality.
Sleep is a crucial biological activity for maintaining physical and mental health, influencing various physiological processes, including inflammatory responses (1, 2). Deterioration in sleep quality is closely linked to a range of chronic conditions such as depression, cognitive impairment, and cardiovascular diseases (3–5). Statistical data indicate that the prevalence of sleep disorders among American adults has reached 27.1% and continues to rise (6), highlighting sleep quality issues as a significant global public health concern (7). Research has shown that insufficient sleep can elevate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6, suggesting a correlation between sleep duration and inflammation-related diseases (8–12). Sleep disorders are also recognized as known risk factors for inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus) and mental disorders (e.g., major depressive disorder) (13–15). Therefore, improving sleep quality is not only associated with the restoration of individual physiological functions but may also play a vital role in the prevention and intervention of inflammation-related diseases.
In recent years, research has revealed that oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between antioxidants and pro-oxidants, leading to cellular damage and death, may be a crucial factor in determining sleep quality (16). Previous studies have associated increased levels of oxidative stress with sleep disorders and short sleep duration (17–20). Pro-oxidants induce oxidative stress by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) or reducing the defense activity of antioxidant systems, while antioxidants may shift the balance towards a less oxidative state (21). Furthermore, supplementation of antioxidant nutrients such as vitamin C (22) and luteolin (23), and adoption of antioxidative lifestyle behaviors such as weight control (24) and physical exercise (25) have been shown to reduce oxidative stress levels and improve sleep quality.
Despite existing research exploring the relationship between oxidative stress and sleep quality, most studies have focused on isolated factors, failing to comprehensively consider the combined effects of diet and lifestyle on oxidative stress levels. To address this gap, the Oxidative Balance Score (OBS) has been proposed as a tool for a holistic assessment of individual oxidative stress, incorporating dietary and lifestyle factors. The OBS has been shown to be significantly associated with various chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and colorectal cancer. However, there remains a lack of in-depth research regarding the specific mechanisms linking OBS to sleep quality, particularly the mediating roles of oxidative stress and inflammation.
Research indicates that a decline in sleep quality is closely associated with systemic inflammation, characterized by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress biomarkers (26, 27). For instance, albumin (28) and bilirubin (29) possess strong antioxidant properties, while gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), linked to glutathione metabolism (30), serves as a key marker of oxidative stress. White blood cells (WBC) (31) act as indicators of inflammation, reflecting the body’s inflammatory status (32). High levels of OBS are negatively correlated with GGT levels and are associated with a reduction in other inflammatory markers such as WBC. These findings suggest that low OBS may adversely affect sleep quality by increasing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.
To address the knowledge gap, we analyzed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) to explore the relationship between OBS and sleep quality, focusing on the mediating roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. This is the innovation of the article and what sets it apart from previous studies (16–20). We assessed sleep quality through self-reported duration, clinically diagnosed disorders, and subjective sleep disturbances, providing a comprehensive evaluation. By integrating dietary and lifestyle factors to calculate OBS, we found a positive association between higher OBS and improved sleep parameters. Furthermore, we examined biomarkers such as albumin, GGT, bilirubin, and WBC to explore the underlying biological mechanisms, offering new insights into how oxidative stress and inflammation mediate the OBS-sleep relationship. This study provides theoretical and practical contributions, supporting targeted interventions for improving sleep quality through diet and lifestyle modifications.
This study aims to investigate the association between OBS and sleep quality using data from the NHANES, with a particular focus on the mediating roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. By analyzing multiple dimensions of sleep-including sleep duration, objective sleep disorders, and subjective sleep trouble-we explore the relationship between OBS and these sleep parameters, as well as the potential mediating effects of oxidative stress and inflammation. This research will provide a new theoretical basis for improving sleep quality and offer significant guidance for clinical practice and public health interventions.
This study used data from the NHANES, a nationally representative assessment of the health and nutritional status of the United States population, which is conducted biennially by the National Center for Health Statistics. The survey collects information through a combination of interviews, physical exams, and laboratory analyses, and the data is made publicly available (33). Our study utilized data from four consecutive NHANES survey cycles (2007–2014), as data on lifestyle factors and sleep disorder were not collected before 2007 and after 2014. Among the 40,617 participants, exclusions were made based on the following criteria: (1) age < 18 years (n = 15,885), pregnant individuals (n = 247), missing weight data (n = 5,258); (2) abnormal energy intake (men <800 or > 4,200 kcal/day, women <500 or > 3,500 kcal/day) (n = 596); (3) missing sleep (n = 11) or OBS (n = 1,087) data; and (4) missing information on biomarkers, including albumin, GGT, total bilirubin, and WBC, or covariates (n = 2,385). Ultimately, 15,198 participants were included in our analysis (Figure 1).
In accordance with methodologies outlined in the pertinent literature (34), we computed the individual OBS of each participant. The evaluation of OBS encompassed 16 dietary nutrients (carotenoids, dietary fiber, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, total folate, vitamin B12, vitamin C, vitamin E, calcium, magnesium, zinc, copper, selenium, total fat, and iron) and 4 lifestyle factors (physical activity, alcohol intake, smoking status, and Body Mass Index [BMI]). Based on prior knowledge and findings from preliminary studies, total fat, iron, alcohol, smoking, and BMI were considered pro-oxidants, whereas the remaining factors were deemed antioxidants.
Dietary nutrient intake data were derived from interviews conducted as part of NHANES. Alcohol consumption was determined by calculating the average daily intake of alcoholic beverages over the previous 12 months. Smoking was quantitatively assessed by measuring cotinine, the primary metabolite of nicotine, in the urine. BMI was calculated by dividing the individual’s weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. Information on physical activity levels was collected using a standardized physical activity questionnaire, and computed with reference to the relevant literature (35).
We divided all elements into three levels based on a weighted distribution. Antioxidant scores ranged from 0 to 2 and pro-oxidants were assigned inverse scores. Subsequently, we separately computed nutrient OBS and lifestyle OBS. Higher nutrient OBS and lifestyle OBS indicated greater exposure to antioxidants, whereas lower scores indicated greater exposure to pro-oxidants. Detailed information regarding the scoring system is provided in Supplementary Table S1.
Sleep quality is a multidimensional concept encompassing both subjective and objective measures of sleep. It integrates various aspects such as sleep initiation, maintenance, duration, and overall satisfaction with the sleep experience, including feelings of refreshment upon awakening. The term also covers a range of sleep disturbances, including insomnia, hypersomnia, parasomnia, and circadian rhythm disorders, as well as conditions like restless leg syndrome and narcolepsy (36). Similar to previous studies, this research assessed sleep quality using three dimensions, based on data from the NHANES questionnaire (37). These dimensions include: (1) Sleep duration, defined as the total number of hours slept per day; (2) Sleep trouble, defined by self-reported difficulty falling or staying asleep; (3) Sleep disorders, including insomnia and restless leg syndrome, as diagnosed by healthcare professionals. Participants were queried about whether they had reported sleep issues to healthcare professionals, with “yes” responses indicating the presence of sleep trouble. Additionally, participants were asked if they had been informed of the existence of sleep disorders by healthcare professionals, with “yes” responses indicating the presence of sleep disorders. Sleep duration was measured based on participants’ responses to the question: “How much sleep do you get (hours)?” The use of sleep medications was measured based on participants’ responses to the question: “How often take pills to help you sleep?” The frequency of sleep trouble in the depression (abbreviated as “Depression” in the table) over 2 weeks was measured based on participants’ responses to the question: “How often have you been bothered over the last 2 weeks, by the following problems: trouble falling or staying asleep, or sleeping too much?”
This study utilized biomarkers including GGT, albumin, total bilirubin, and WBC. Biomarker data were obtained through the analysis of peripheral blood samples. Detailed descriptions of the laboratory testing methods used for these biomarkers are available on the NHANES online platform (33).
In our study, variables such as sex, age, race/ethnicity, educational level, household income, marital status, depression, the use of sleep medications, and comorbidities were investigated as covariates. Additionally, factors such as caffeine intake and energy intake were considered. Household income was categorized based on the family poverty income ratio (PIR). Comorbidities included diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular diseases.
All analyses took into account the sample weights derived from the intricate sampling framework of NHANES. The baseline characteristics of the participants are expressed as mean values and standard deviations (SD) for continuous data, while categorical data are presented as counts(n) and proportions(%). The OBS was modeled in tertiles, with the first tertile serving as the reference group. Multivariable logistic regression models were utilized to compute odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals(CIs) to evaluate the association between OBS and sleep problems, in addition to sleep disorders. Trends were assessed by treating the median value of the respective intake category as a continuous variable. Weighted linear regression analysis was utilized to compute β values along with their respective 95% CIs, delineating the association between OBS and sleep duration. We established three distinct models: Model 1, which underwent adjustments for age and sex; Model 2, which underwent further adjustments for race/ethnicity, marital status, and educational level; Model 3, which underwent additional adjustments for caffeine intake (included because of the antioxidant properties of caffeine), energy intake, and comorbidities; and Model 4 was adjusted by adding variables for depression and the use of sleep medications to Model 3. Furthermore, analyses were stratified by age (<50 years or ≥ 50 years) and sex. Associations linking dietary OBS and lifestyle OBS with sleep quality were separately examined. Additionally, multiple linear regression analyses were performed to assess the relationships between OBS and sleep quality, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Two mediation pathways were constructed to explore the possible mediation mechanisms of oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in linking OBS and sleep quality. The mediation effects of biomarkers were assessed using R software version 4.1.3 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria), adjusting for the covariates used in Model 3. Our results provided the magnitude of indirect effects (βindirect), direct effects (βdirect), total effects (βtotal), proportion mediated (PM), and p-values.
Sensitivity analyses were conducted to adjust for the potential impact of depression and sleep medication on the results.
All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, United States) and R 4.1.3 (R Foundation, Vienna, Austria), with differences considered statistically significant at a two-sided p-value <0.05.
Among the 15,198 NHANES participants analyzed, the average age was 47.3 years; 7,241 (47.53%) were male and 7,957 (52.47%) were female. Those in the highest OBS tertile were more likely to be Non-Hispanic White, married, and have comorbidities than those in the lowest tertile. Moreover, individuals occupying the highest OBS tertile exhibited lower levels of educational attainment, but higher levels of PIR, total energy intake, and caffeine consumption. Notably, participants in the top OBS tertile displayed elevated levels of albumin and total bilirubin, and decreased levels of GGT and WBC compared with their counterparts in the lowest tertile. Importantly, individuals with a higher OBS were less likely to experience sleep issues than those with a lower OBS. Among participants with depression, higher OBS was associated with fewer sleep trouble in 2 weeks. Baseline participant characteristic, categorized into tertiles based on OBS, are presented in Table 1. Additionally, we have provided a breakdown of baseline characteristics by sex in Supplementary Tables S2, S3. In general, the results were consistent between the sexes.
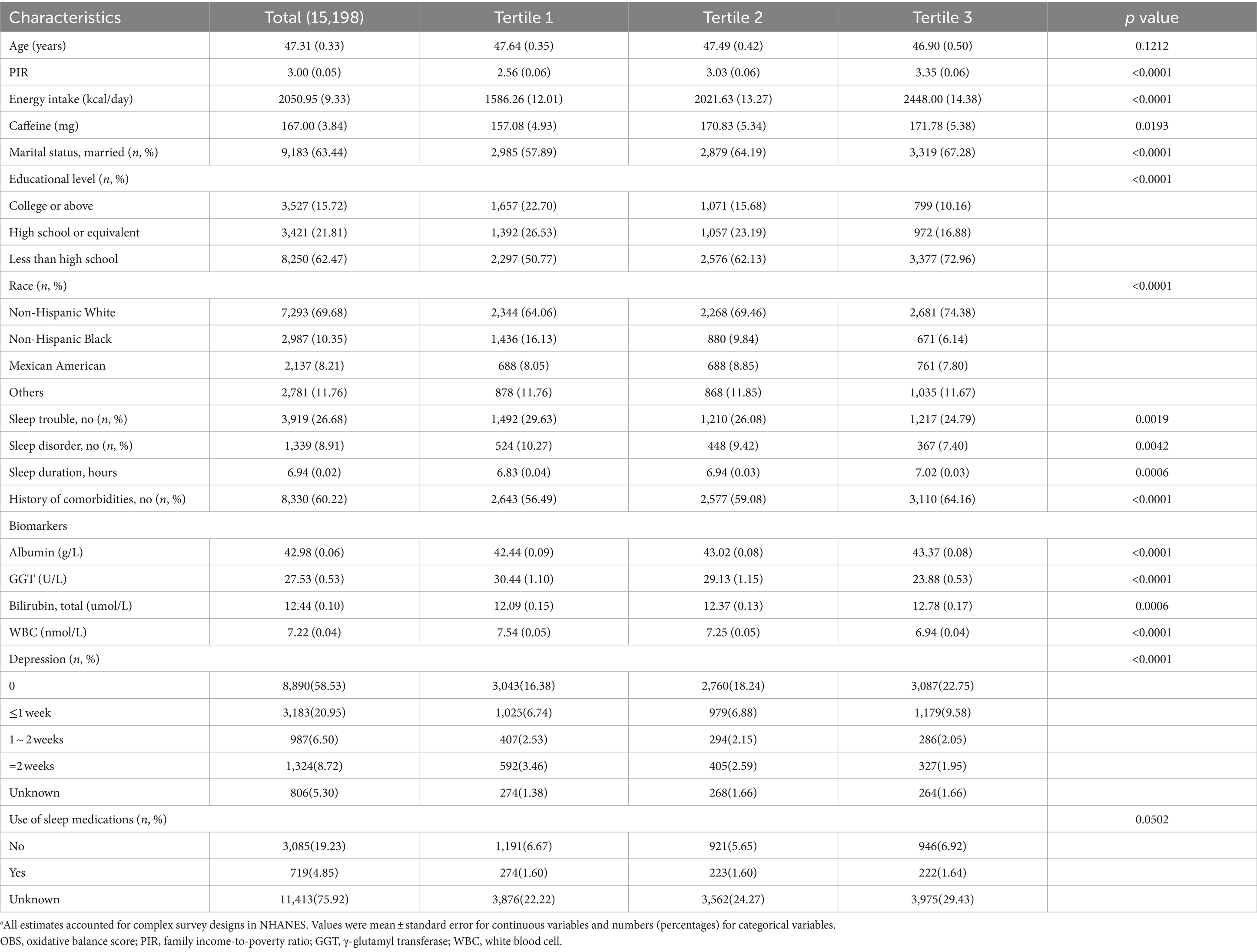
Table 1. The baseline characteristics by tertiles of the OBS: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2014 (NHANES 2007–2014).a
Table 2 displays the outcomes derived from weighted logistic regression and linear models (Models 1, 2, and 3). In Model 3, the most extensively adjusted model, an inverse correlation emerged between OBS and both sleep disorders and sleep trouble, with ORs of 0.72 (95% CI, 0.58–0.91; Ptrend = 0.0055) and 0.81 (95% CI, 0.69–0.96; Ptrend = 0.0174), for the highest versus the lowest tertile, respectively. Moreover, a higher OBS correlated with extended sleep duration (β, 0.009; 95% CI, 0.002–0.016). We further subdivided the OBS into dietary and lifestyle components. Our findings indicated that sleep disorders and sleep trouble were solely influenced by lifestyle OBS in all three models, with ORs of 0.47 (0.38–0.59; Ptrend < 0.0001) and 0.71 (0.63–0.81; Ptrend < 0.0001) in Model 3, for the highest vs. lowest tertile, respectively (Table 3). Dietary OBS was significantly associated with sleep duration only (Model 3: β, 0.009; 95% CI, 0.002–0.017). The results of the stratified analyses revealed no statistically significant interaction between the OBS and sleep when stratified by sex (p > 0.05). When stratified by age (<50 or ≥ 50 years), a statistically significant interaction was found between OBS and sleep trouble (p = 0.0118) (Supplementary Table S4). The association was only present in the younger age group (OR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.59–0.92, for the highest vs. lowest tertile) in Model 3.
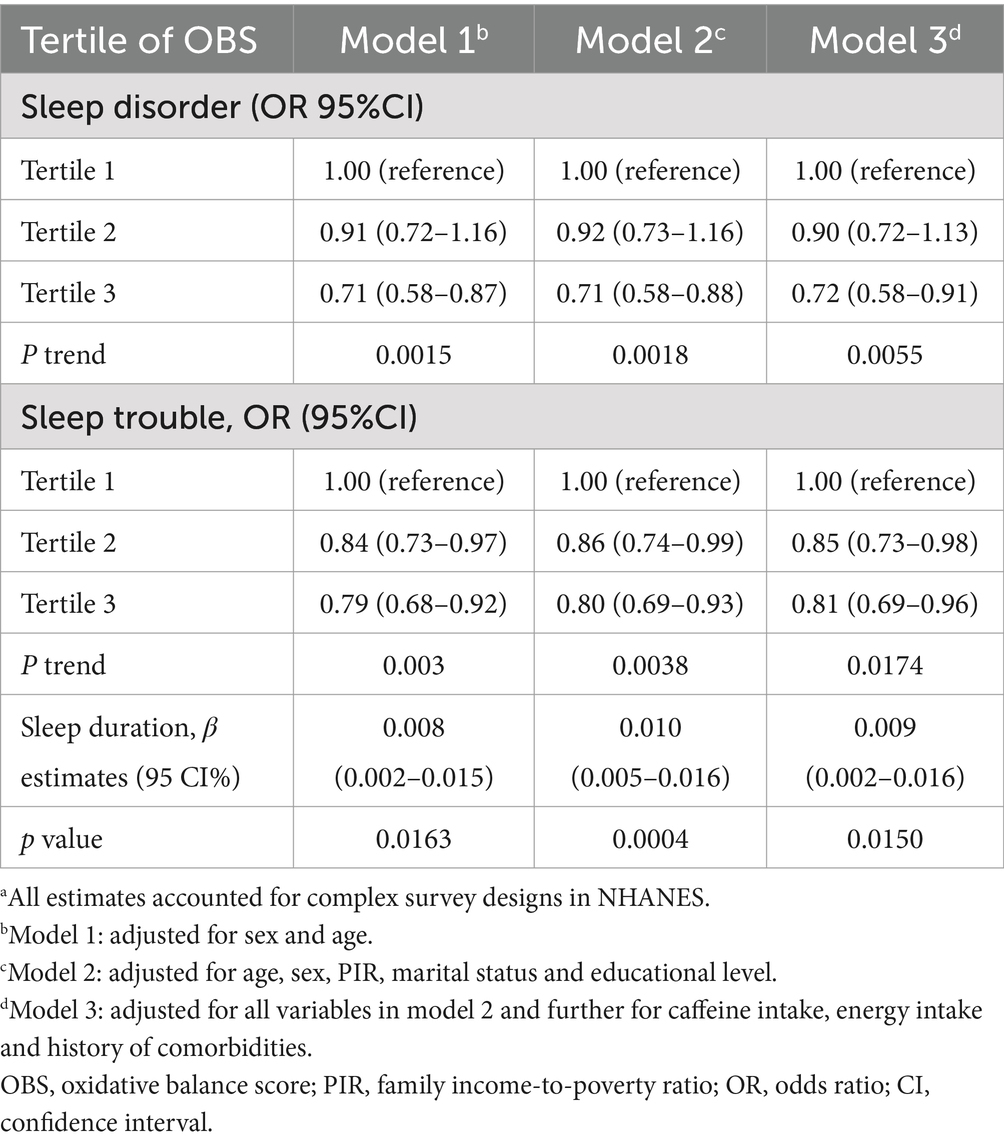
Table 2. The relationship between OBS and sleep quality in National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2014 (NHANES 2007–2014).a
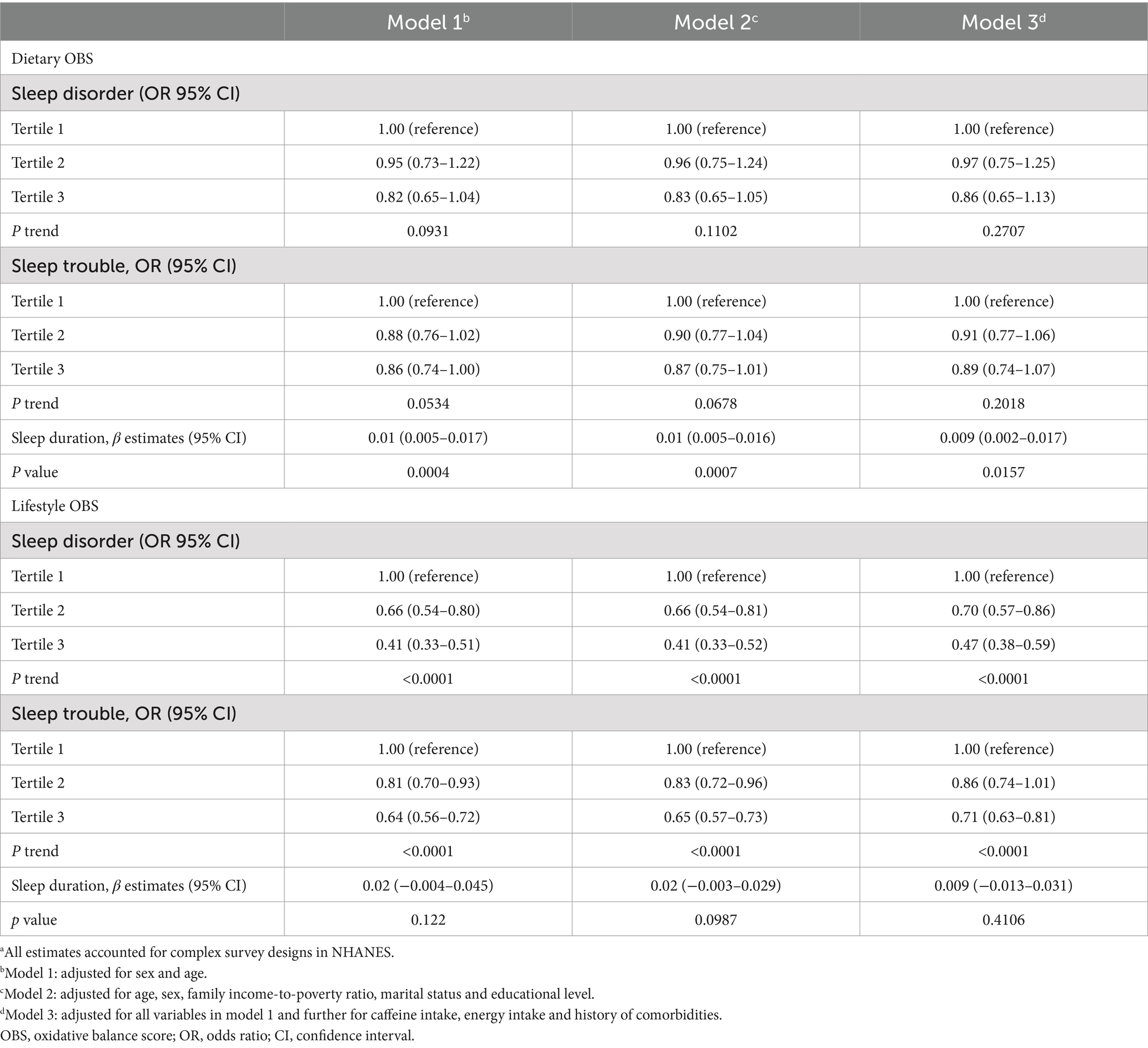
Table 3. Association between dietary/lifestyle OBS with sleep factors in US adult population, NHANES 2007–2014.a
Compared with participants with a higher OBS, those with a lower OBS had higher levels of GGT and WBC counts, but lower albumin and total bilirubin levels (Supplementary Table S5). The observed association of the OBS with sleep disorders and sleep trouble was mediated by albumin, GGT, total bilirubin, and WBC. Specifically, separate mediation analyses revealed that albumin mediated 24.55 and 12.97% of the total relationship between the OBS and sleep disorders and sleep trouble, respectively. GGT accounted for 3.68 and 7.44%, respectively; total bilirubin mediated 8.06 and 7.27%, respectively; and WBC mediated 6.59 and 6.63%, respectively (Table 4; Figure 2). Multiple mediation analysis showed that all the potential biomarkers (albumin, GGT, bilirubin, and WBC) combined mediated 34.66 and 29.54% of the total relationship for sleep disorders and sleep trouble, respectively (Table 4; Figure 2). No significant results were found in the mediation analysis of OBS and sleep duration (Table 4; Figure 2).
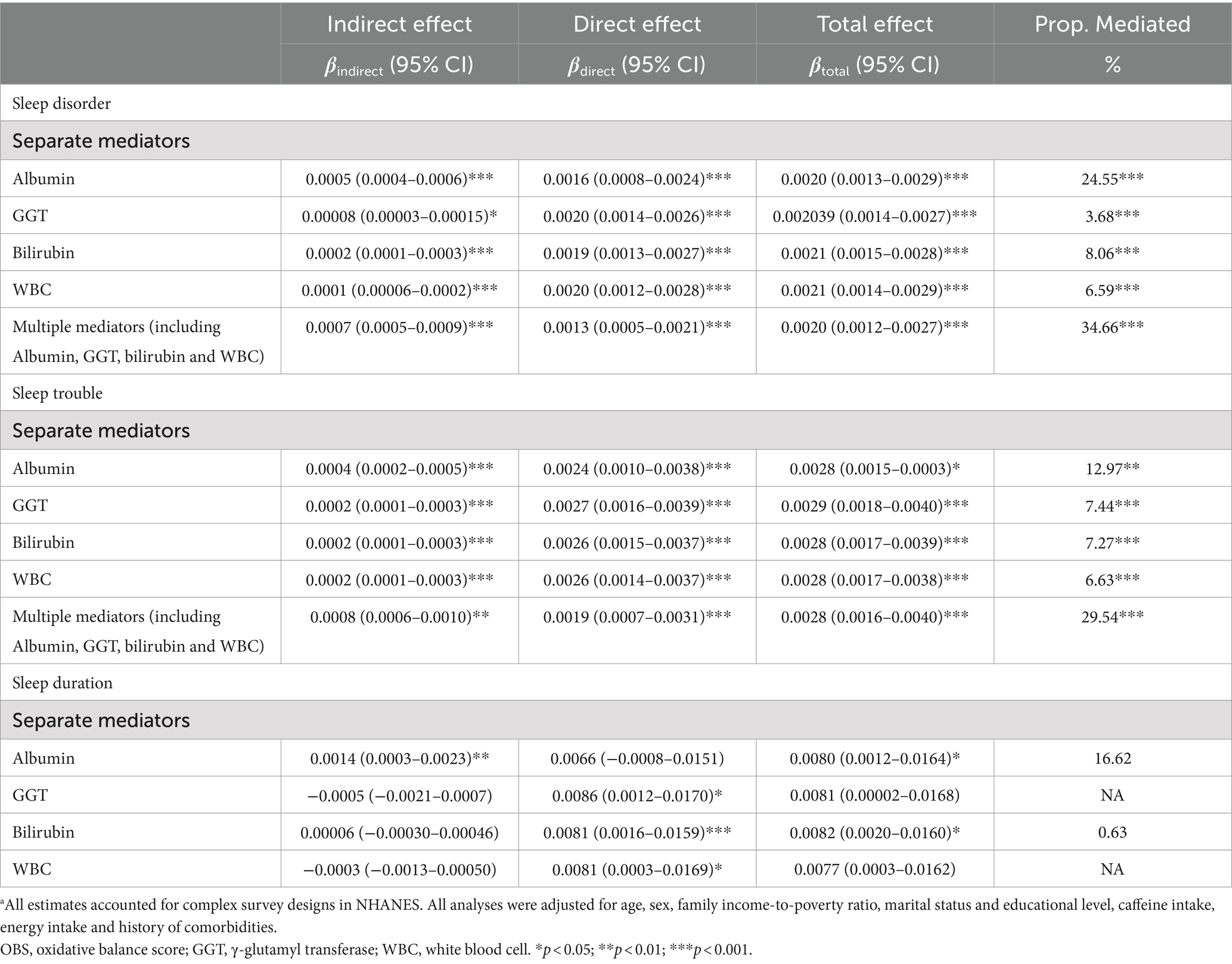
Table 4. Mediation analyses with separate and multiple mediators between OBS and sleep factors (n = 15,198) in National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2014 (NHANES 2007–2014).a
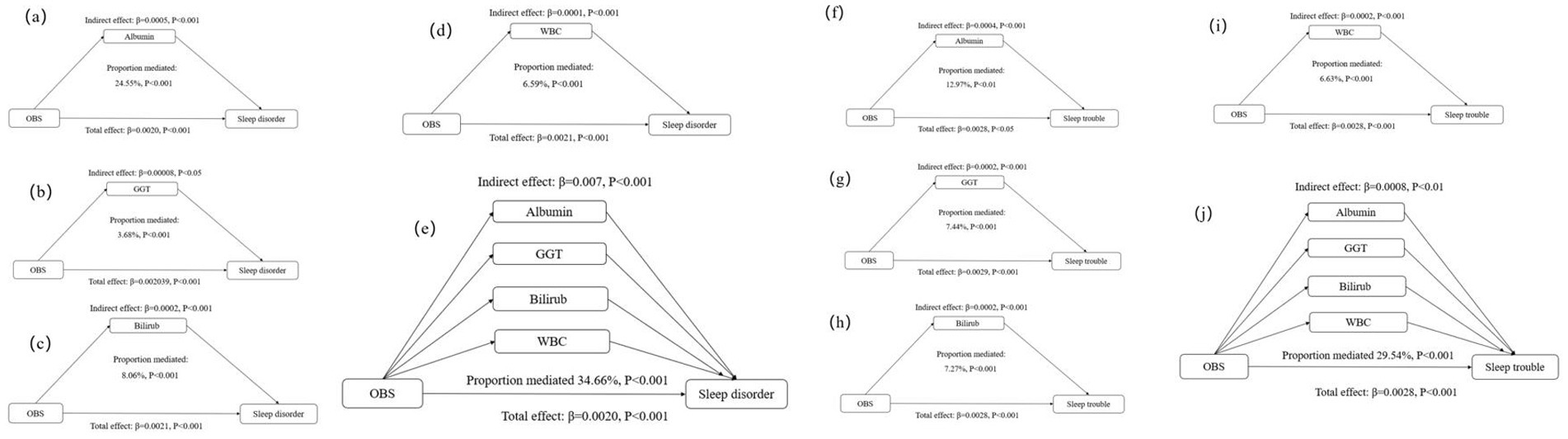
Figure 2. Estimated proportion of the association between OBS and sleep disorder mediated by oxidative stress and inflammatory markers: (a) Albumin; (b) GGT; (c) Bilirubin; (d) WBC; (e) Albumin, GGT, Bilirubin, and WBC. Estimated proportion of the association between OBS and sleep trouble mediated by oxidative stress and inflammatory markers: (f) Albumin; (g) GGT; (h) Bilirubin; (i) WBC; (j) Albumin, GGT, Bilirubin, and WBC. All analyses were adjusted for age, sex, family income-to-poverty ratio, marital status and educational level, caffeine intake, energy intake and history of comorbidities. OBS, oxidative balance score; GGT, y-glutamyl transferase; WBC, white blood cell.
Sensitivity analyses revealed a significant association between OBS and sleep disorder. The OR for OBS was 0.78 (95% CI: 0.61–0.99, p = 0.0421) (Supplementary Table S6).
Our findings suggest that an elevated OBS correlates with enhanced sleep quality, marked by decreased sleep disorders, mitigated sleep trouble, and prolonged sleep duration. Notably, oxidative stress and inflammatory factors partially mediate the relationship between OBS and sleep disorders.
This study utilized demographic data from the NHANES database, a cross-sectional survey representing the entire population of the United States, to explore the correlation between OBS and sleep quality, as well as the potential mechanisms underlying this association. The central focus of our analysis was the OBS. Our results robustly affirm the notion that an elevated OBS is closely linked to improved sleep quality among American adults. These findings are consistent with prior research suggesting that modifications in dietary elements, such as increasing dietary fiber intake (38), optimizing serum zinc levels and zinc/copper and zinc/selenium ratios (39), and augmenting vitamin C intake (40), significantly enhance sleep quality by elevating the OBS. Likewise, embracing healthier lifestyle habits, such as refraining from smoking (41) and participating in moderate to vigorous physical activity (42), has been demonstrated to increase OBS levels, thereby enhancing sleep quality. Moreover, individuals with an elevated BMI and those classified as overweight or obese are more susceptible to suboptimal sleep quality than individuals with a lower BMI (24). A previous cross-sectional study involving American adults revealed the potential influence of diet and lifestyle factors on sleep quality, through their effects on oxidative stress (43). However, this specific investigation did not investigate the mechanisms underlying this association.
Our study demonstrated an association between the OBS and sleep disorders, sleep trouble, and sleep duration. Specifically, dietary OBS was correlated with sleep duration, whereas lifestyle OBS was associated with sleep disorders and sleep trouble. This suggests that distinct aspects of sleep are influenced by different OBS components. Enhancing sleep quality and quantity therefore requires the consideration of both dietary and lifestyle factors. However, after adjusting for variables such as depression and the use of sleep medications, the association was limited to a reduction in sleep disorders, which is inconsistent with the main results. This discrepancy may be attributed to incomplete data or insufficient expression of certain data aspects.
Although the mechanism by which the OBS affects sleep remains unclear, studies have shown that OBS regulates oxidative stress (44), levels of albumin (45), levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (43), and WBC counts. Sleep and inflammation are closely related, and previous studies have demonstrated a positive association between CRP concentrations and both subjectively and objectively assessed poor sleep quality, as well as insufficient sleep duration (46, 47). Chronic sleep deprivation has been associated with low-grade inflammation (48). Experimental sleep deprivation leads to elevated levels of circulating inflammatory markers (49, 50). Additionally, in vitro studies have provided evidence that quetiapine significantly diminishes the release of proinflammatory cytokines from microglial cells, into the cerebrospinal fluid, leading to improved sleep quality (51).
The multiple mediation analysis conducted in our study demonstrated that oxidative stress factors, including albumin, total bilirubin, and GGT, along with WBC, a marker of inflammation, mediated the association between OBS and sleep quality. These results support the involvement of oxidative stress and inflammation in the relationship between OBS and sleep quality.
Modulating the OBS can impact sleep quality through oxidative stress and inflammatory factors. Previous studies and our own findings suggest various potential mechanisms: (1) Antioxidant effects. Increased antioxidant capacity leads to the scavenging of free radicals and therefore, enhanced sleep quality (52). Previous studies have suggested that antioxidant administration may ameliorate sleep disorders and regulate sleep cycles (53). (2) Anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammatory mediators can traverse the blood–brain barrier, thereby affecting neurons and neurotransmitters in the brain, and disturbing sleep patterns (54, 55). (3) Neurotransmitter balance. Oxidative stress can decrease the levels of neurotransmitters including dopamine and serotonin (56). Interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α, among other inflammatory factors, have the potential to hinder neurotransmitter synthesis and release, resulting in an imbalance that could subsequently impact sleep patterns (57). (4) Maintenance of vascular homeostasis. Oxidative stress may impair the functionality of endothelial cells that line blood vessels, reducing vasodilation and potentially leading to hypertension and other vascular conditions (58). Inflammation can also cause endothelial dysfunction and disrupt vascular performance (59), culminating in inadequate blood flow, thus affecting cerebral perfusion and disturbing sleep (60). (5) Hormonal regulation. Oxidative stress and inflammation can modulate the secretion of hormones, including those pertinent to sleep regulation (61).
This study has several strengths. Firstly, the OBS, a detailed composite score integrating dietary and lifestyle factors, was used to evaluate antioxidant status. Secondly, a large, nationally representative sample was employed to explore the link between OBS and sleep patterns. Thirdly, mediation analyses were conducted to investigate the mechanisms underlying the OBS–sleep relationship. However, this study also has certain limitations. Firstly, the reliance on self-reported sleep data may have introduced a degree of imprecision into the results. Secondly, the estimation of dietary components was contingent upon the averaging of two 24-h recalls, potentially introducing bias. Thirdly, the presence of unaccounted for and unmeasured confounding variables may have influenced the results. Lastly, due to the cross-sectional design of the study, causal relationships could not be established. Cautious interpretation of our research findings is therefore recommended.
The present study observed a positive correlation between OBS and sleep quality. Moreover, our data indicate that albumin levels, total bilirubin levels, GGT levels, and WBC counts may modulate the connection between OBS and sleep. To substantiate this relationship and clarify its underlying mechanisms, further prospective and experimental investigations are essential.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by the National Center for Health Statistics of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
QZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JY: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. YW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2024.1469779/full#supplementary-material
1. Medic, G, Wille, M, and Hemels, M. Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption. Nat Sci Sleep. (2017) 9:151–61. doi: 10.2147/nss.s134864
2. Ma, Q-Q, Yao, Q, Lin, L, Chen, G-C, and Yu, J-B. Sleep duration and total cancer mortality: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sleep Med. (2016) 27-28:39–44. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2016.06.036
3. Scott, AJ, Webb, TL, Martyn-St James, M, Rowse, G, and Weich, S. Improving sleep quality leads to better mental health: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev. (2021) 60:101556. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101556
4. Behrens, A, Anderberg, P, and Berglund, JS. Sleep disturbance predicts worse cognitive performance in subsequent years: a longitudinal population-based cohort study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2023) 106:104899. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2022.104899
5. Huyett, P, Siegel, N, and Bhattacharyya, N. Prevalence of sleep disorders and association with mortality: results from the NHANES 2009–2010. Laryngoscope. (2021) 131:686–9. doi: 10.1002/lary.28900
6. Kase, BE, Liu, J, Wirth, MD, Shivappa, N, and Hebert, JR. Associations between dietary inflammatory index and sleep problems among adults in the United States, NHANES 2005-2016. Sleep Health. (2021) 7:273–80. doi: 10.1016/j.sleh.2020.09.002
7. Watson, NF, Badr, MS, Belenky, G, Bliwise, DL, Buxton, OM, Buysse, D, et al. Recommended amount of sleep for a healthy adult: a joint consensus statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society. Sleep. (2015) 38:843–4. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4716
8. Simpson, N, and Dinges, DF. Sleep and inflammation. Nutr Rev. (2007) 65:244–52. doi: 10.1301/nr.2007.dec.S244-S252
9. Shearer, WT, Reuben, JM, Mullington, JM, Price, NJ, Lee, BN, Smith, EO’B, et al. Soluble TNF-α receptor 1 and IL-6 plasma levels in humans subjected to the sleep deprivation model of spaceflight. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2001) 107:165–70. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.112270
11. Krueger, JM . The role of cytokines in sleep regulation. CPD. (2008) 14:3408–16. doi: 10.2174/138161208786549281
12. Qazi, T, and Farraye, FA. Sleep and inflammatory bowel disease: an important bi-directional relationship. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2019) 25:843–52. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy334
13. Westhovens, R, Van der Elst, K, Matthys, A, Tran, M, and Gilloteau, I. Sleep problems in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. (2014) 41:31–40. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.130430
14. Palagini, L, Tani, C, Mauri, M, Carli, L, Vagnani, S, Bombardieri, S, et al. Sleep disorders and systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2014) 23:115–23. doi: 10.1177/0961203313518623
15. Baglioni, C, Nanovska, S, Regen, W, Spiegelhalder, K, Feige, B, Nissen, C, et al. Sleep and mental disorders: a meta-analysis of polysomnographic research. Psychol Bull. (2016) 142:969–90. doi: 10.1037/bul0000053
16. Bin Heyat, MB, Akhtar, F, Sultana, A, Tumrani, S, Teelhawod, BN, Abbasi, R, et al. Role of oxidative stress and inflammation in insomnia sleep disorder and cardiovascular diseases: herbal antioxidants and anti-inflammatory coupled with insomnia detection using machine learning. Curr Pharm Des. (2022) 28:3618–36. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221201161636
17. Kanagasabai, T, and Ardern, CI. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and antioxidants contribute to selected sleep quality and Cardiometabolic health relationships: a cross-sectional study. Mediat Inflamm. (2015) 2015:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2015/824589
18. Nagata, C, Tamura, T, Wada, K, Konishi, K, Goto, Y, Nagao, Y, et al. Sleep duration, nightshift work, and the timing of meals and urinary levels of 8-isoprostane and 6-sulfatoxymelatonin in Japanese women. Chronobiol Int. (2017) 34:1187–96. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2017.1355313
19. Villafuerte, G, Miguel-Puga, A, Murillo Rodríguez, E, Machado, S, Manjarrez, E, and Arias-Carrión, O. Sleep deprivation and oxidative stress in animal models: a systematic review. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2015) 2015:1–15. doi: 10.1155/2015/234952
20. Shelton, RC, Falola, M, Li, L, Zajecka, J, Fava, M, and Papakostas, GI. The pro-inflammatory profile of depressed patients is (partly) related to obesity. J Psychiatr Res. (2015) 70:91–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.09.001
21. Hernández-Ruiz, Á, García-Villanova, B, Guerra-Hernández, EJ, Carrión-García, CJ, Amiano, P, Sánchez, MJ, et al. Oxidative balance scores (OBSs) integrating nutrient, food and lifestyle dimensions: development of the nutrientL-OBS and foodL-OBS. Antioxidants. (2022) 11. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020300
22. Hahad, O, Herzog, J, Röösli, M, Schmidt, FP, Daiber, A, and Münzel, T. Acute exposure to simulated nocturnal train noise leads to impaired sleep quality and endothelial dysfunction in young healthy men and women: a sex-specific analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192113844
23. Rahimpour, P, Nasehi, M, Zarrindast, MR, and Khalifeh, S. Dose-dependent manner of luteolin in the modulation of spatial memory with respect to the hippocampal level of HSP70 and HSP90 in sleep-deprived rats. Gene. (2023) 852:147046. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.147046
24. Aronsen, S, Conway, R, Lally, P, Roberts, A, Croker, H, Beeken, RJ, et al. Determinants of sleep quality in 5835 individuals living with and beyond breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer: a cross-sectional survey. J Cancer Surviv. (2022) 16:1489–501. doi: 10.1007/s11764-021-01127-2
25. Kredlow, MA, Capozzoli, MC, Hearon, BA, Calkins, AW, and Otto, MW. The effects of physical activity on sleep: a meta-analytic review. J Behav Med. (2015) 38:427–49. doi: 10.1007/s10865-015-9617-6
26. Howren, MB, Lamkin, DM, and Suls, J. Associations of depression with C-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: a meta-analysis. Psychosom Med. (2009) 71:171–86. doi: 10.1097/psy.0b013e3181907c1b
27. Rigobon, AV, Kanagasabai, T, and Taylor, VH. Obesity moderates the complex relationships between inflammation, oxidative stress, sleep quality and depressive symptoms. Obesity. (2018) 5:32–10. doi: 10.1186/s40608-018-0208-2
28. Deng, S, Liu, S, Jin, P, Feng, S, Tian, M, Wei, P, et al. Albumin reduces oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via the ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:1–14. doi: 10.1155/2021/8891373
29. Shen, B, Zhao, C, Wang, Y, Peng, Y, Cheng, J, Li, Z, et al. Aucubin inhibited lipid accumulation and oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 and AMPK signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:4063–75. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14293
30. Cho, A-R, Kwon, Y-J, Lim, H-J, Lee, HS, Kim, S, Shim, J-Y, et al. Oxidative balance score and serum γ-glutamyltransferase level among Korean adults: a nationwide population-based study. Eur J Nutr. (2018) 57:1237–44. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1407-1
31. Lee, H-S, and Park, T. Pathway-driven approaches of interaction between oxidative balance and genetic polymorphism on metabolic syndrome. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2017/6873197
32. Shin, G, Jang, K, Kim, M, Lee, JH, and Yoo, HJ. Inflammatory markers and plasma fatty acids in predicting WBC level alterations in association with glucose-related markers: a cross-sectional study. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:629. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00629
33. National Center for Health Statistics . National health and nutrition examination survey. Available at: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/Default.aspx (Accessed October 21, 2023).
34. Zhang, W, Peng, SF, Chen, L, Chen, HM, Cheng, XE, and Tang, YH. Association between the oxidative balance score and telomere length from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2022/1345071
35. Tian, X, Xue, B, Wang, B, Lei, R, Shan, X, Niu, J, et al. Physical activity reduces the role of blood cadmium on depression: a cross-sectional analysis with NHANES data. Environ Pollut. (2022) 304:119211. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119211
36. Kline, C . Sleep quality In: MD Gellman and JR Turner, editors. Encyclopedia of behavioral medicine. New York, NY: Springer (2013)
37. Zhang, J, Yu, S, Zhao, G, Jiang, X, Zhu, Y, and Liu, Z. Associations of chronic diarrheal symptoms and inflammatory bowel disease with sleep quality: a secondary analysis of NHANES 2005–2010. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:858439. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.858439
38. Tang, M, Song, X, Zhong, W, Xie, Y, Liu, Y, and Zhang, X. Dietary fiber ameliorates sleep disturbance connected to the gut-brain axis. Food Funct. (2022) 13:12011–20. doi: 10.1039/d2fo01178f
39. Deng, M-G, Liu, F, Liang, Y, Chen, Y, Nie, J-Q, Chai, C, et al. Associations of serum zinc, copper, and selenium with sleep disorders in the American adults: data from NHANES 2011–2016. J Affect Disord. (2023) 323:378–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.11.088
40. Otocka-Kmiecik, A, and Król, A. The role of vitamin C in two distinct physiological states: physical activity and sleep. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3908. doi: 10.3390/nu12123908
41. Amiri, S, and Behnezhad, S. Smoking and risk of sleep-related issues: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Can J Public Health. (2020) 111:775–86. doi: 10.17269/s41997-020-00308-3
42. Memon, AR, Gupta, CC, Crowther, ME, Ferguson, SA, Tuckwell, GA, and Vincent, GE. Sleep and physical activity in university students: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. (2021) 58:101482. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101482
43. Lei, X, Xu, Z, and Chen, W. Association of oxidative balance score with sleep quality: NHANES 2007-2014. J Affect Disord. (2023) 339:435–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.07.040
44. Li, H, Song, L, Cen, M, Fu, X, Gao, X, Zuo, Q, et al. Oxidative balance scores and depressive symptoms: mediating effects of oxidative stress and inflammatory factors. J Affect Disord. (2023) 334:205–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.04.134
45. Song, L, Li, H, Fu, X, Cen, M, and Wu, J. Association of the oxidative balance score and cognitive function and the mediating role of oxidative stress: evidence from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) 2011–2014. J Nutr. (2023) 153:1974–83. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2023.05.014
46. Irwin, MR, Olmstead, R, and Carroll, JE. Sleep disturbance, sleep duration, and inflammation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies and experimental sleep deprivation. Biol Psychiatry. (2016) 80:40–52. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.05.014
47. Smagula, SF, Stone, KL, Redline, S, Ancoli-Israel, S, Barrett-Connor, E, Lane, NE, et al. Actigraphy- and polysomnography-measured sleep disturbances, inflammation, and mortality among older men. Psychosom Med. (2016) 78:686–96. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000312
48. Besedovsky, L, Lange, T, and Haack, M. The sleep-immune crosstalk in health and disease. Physiol Rev. (2019) 99:1325–80. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00010.2018
49. Irwin, M, Rinetti, G, Redwine, L, Motivala, S, Dang, J, and Ehlers, C. Nocturnal proinflammatory cytokine-associated sleep disturbances in abstinent African American alcoholics. Brain Behav Immun. (2004) 18:349–60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2004.02.001
50. Meier-Ewert, HK, Ridker, PM, Rifai, N, Regan, MM, Price, NJ, Dinges, DF, et al. Effect of sleep loss on C-reactive protein, an inflammatory marker of cardiovascular risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2004) 43:678–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.07.050
51. Gao, H, Zhang, Y, Luo, D, Xu, J, Tan, S, Li, Y, et al. Activation of the hippocampal DRD2 alleviates neuroinflammation, synaptic plasticity damage and cognitive impairment after sleep deprivation. Mol Neurobiol. (2023) 60:7208–21. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03514-5
52. Khalyfa, A, and Sanz-Rubio, D. The mystery of red blood cells extracellular vesicles in sleep apnea with metabolic dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:4301. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094301
53. Hasebe, K, Gray, L, Bortolasci, C, Panizzutti, B, Mohebbi, M, Kidnapillai, S, et al. Adjunctive N-acetylcysteine in depression: exploration of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Acta Neuropsychiatr. (2017) 29:337–46. doi: 10.1017/neu.2017.2
54. Irwin, MR . Sleep and inflammation: partners in sickness and in health. Nat Rev Immunol. (2019) 19:702–15. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0190-z
55. Gamaldo, CE, Shaikh, AK, and McArthur, JC. The sleep-immunity relationship. Neurol Clin. (2012) 30:1313–43. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2012.08.007
56. Pizzino, G, Irrera, N, Cucinotta, M, Pallio, G, Mannino, F, Arcoraci, V, et al. Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2017/8416763
57. Dantzer, R, O'Connor, JC, Freund, GG, Johnson, RW, and Kelley, KW. From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2008) 9:46–56. doi: 10.1038/nrn2297
58. Harrison, DG . Endothelial function and oxidant stress. Clin Cardiol. (1997) 20. doi: 10.1002/j.1932-8737.1997.tb00007.x
59. Prather, AA, Janicki-Deverts, D, Hall, MH, and Cohen, S. Behaviorally assessed sleep and susceptibility to the common cold. Sleep. (2015) 38:1353–9. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4968
60. Rubina, SS, Makarova, II, and Yusufov, AA. The relationship of vascular complications with cerebrovascular reactivity and endothelial dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Zh Nevropatol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. (2023) 123:82. doi: 10.17116/jnevro202312305282
Keywords: oxidative balance score, sleep quality, inflammation, mediation analysis, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Citation: Zhang Q, Yi J and Wu Y (2024) Oxidative stress and inflammation mediate the association between elevated oxidative balance scores and improved sleep quality: evidence from NHANES. Front. Nutr. 11:1469779. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1469779
Received: 24 July 2024; Accepted: 04 October 2024;
Published: 18 October 2024.
Edited by:
Mauro Serafini, University of Teramo, ItalyReviewed by:
Jia Luo, Qingdao University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Zhang, Yi and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yemei Wu, d3V5ZW1laTIwMTBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.