
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Nutr. , 21 October 2024
Sec. Clinical Nutrition
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1449240
 Chiung-Hsin Chang1,2
Chiung-Hsin Chang1,2 Chun-Yu Lin1,2
Chun-Yu Lin1,2 Yu-Lun Lo1,2
Yu-Lun Lo1,2 Ting-Yu Lin1,2
Ting-Yu Lin1,2 Chen-Yiu Hung1,2
Chen-Yiu Hung1,2 Meng-Heng Hsieh1,2
Meng-Heng Hsieh1,2 Yueh-Fu Fang1,2
Yueh-Fu Fang1,2 Hung-Yu Huang1,2,3
Hung-Yu Huang1,2,3 Shu-Min Lin1,2
Shu-Min Lin1,2 Horng-Chyuan Lin1,2,4*
Horng-Chyuan Lin1,2,4*Background: Patients with prolonged mechanical ventilation (PMV) is usually associated with muscle wasting and diaphragm weakness, resulting in high medical costs and mortality. Adequate energy and protein intake were beneficial in sarcopenia patients. We aimed to investigate the impact of protein intake in weaning parameters in patients with PMV.
Materials and methods: We enrolled patients with PMV (mechanical ventilation ≥6 h/day for ≥21 days) from a respiratory care center (RCC) of a tertiary medical center from December 2020 to October 2022, and classified them into weaning success and weaning failure groups. The patients’ characteristics, nutrition records, weaning parameters and outcomes were analyzed.
Results: A total of 289 patients were included (mean age 73.5 years). Of the 289 patients, 149 were weaned successfully and 140 were not. The average protein intake was higher in the weaning success group than in the weaning failure group (1.22 ± 0.320 versus 0.99 ± 0.332 g/kg/day, p < 0.001). No significant differences were noted in the average calorie intake and whey protein intake between the two groups. RSBI <90 breaths/min/L (OR = 2.38, p = 0.045), serum albumin at 4th week ≥3 g/dL (OR = 2.89, p = 0.027), daily protein intake ≥1.01 g/kg/day (OR = 8.10, p < 0.001), PaO2/FiO2 (PF) ratio ≥ 300 (OR = 2.56, p = 0.027) were independent predictors for weaning from ventilator. Weak positive correlations were found between average protein intake with PF ratio (r = 0.1576, p = 0.0227) and PaO2 (r = 0.13359, p = 0.0497).
Conclusion: Daily protein intake had positively correlated with PF ratio and had independently benefit for weaning in patients with PMV.
An estimated 50–74% of all patients in intensive care units (ICUs) receive intubation and mechanical ventilation (1, 2). Of these intubated patients, about 5–10% need prolonged mechanical ventilation (PMV) (2, 3). PMV is defined as ventilation for ≥4 days with tracheostomy placement or ≥21 days without tracheotomy (4). PMV places a heavy burden on healthcare systems and the patient’s family (5, 6), decreases the quality of life, and is associated with poor outcomes in critically ill patients. Furthermore, these patients are associated with a long hospital stay, high 6-month mortality rate, and poor long-term survival; over half of patients with PMV die within 1 year (6, 7).
In patients who survive a critical illness, protein catabolism induced by the illness can lead to decreased respiratory muscle mass, strength and endurance, which may then lead to difficulties in liberation from mechanical ventilation (8). To improve muscle mass and strength, rehabilitation, subjective muscle training and nutrition are equally important. Many studies have shown that adequate protein intake can improve the outcomes of patients with sarcopenia (9). The Liverpool Hope University Sarcopenia Aging Trial (LHU-SAT) also emphasized the importance of concurrent resistance exercise and function exercise to combat age-related muscle weakness (10). Exercise and protein intake have a synergic effect to prevent or improve sarcopenia (11, 12). However, subjective muscle training and effective rehabilitation may not be possible due to weakness or poor consciousness in patients with PMV. Adequate dietary protein intake may be a lower-cost and convenient way to improve sarcopenia in patients with PMV. Many studies have reported that sufficient protein intake can help to increase the mass and strength of muscles (13, 14). In our previous study, we found an association between higher protein intake and successful weaning in patients with PMV (15). Although the timing and amount of calorie and protein intake have been investigated in patients with critical illness (16), few studies have investigated nutritional support in patients with PMV. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate correlations of protein intake with weaning parameters, and whether protein intake can benefit in weaning outcomes in patients with PMV.
This retrospective study was a single-center analysis of patients with PMV who were admitted to the respiratory care center (RCC) of a tertiary referral teaching hospital in Taiwan between December 2020 and October 2022. The RCC is a specialized weaning unit for patients who could not have successful weaning from the ventilator in the ICU for more than 21 days under a relatively stable clinical condition. The demographic characteristics, underlying diseases, reasons for ICU admission, vital signs and hemodynamic variables, lung mechanics [i.e., tidal volume (TV) and respiratory rate (RR)], hemogram, biochemical variables, arterial blood gas analysis, fraction of inspiration O2 (FiO2), and nutritional condition (calories, amount and type of protein) were collected from the medical records of the enrolled patients. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Medical Foundation (IRB No. 202200818B0) on June 7th, 2022. All personally identifiable information was encrypted, and the need for patient consent was waived for this study.
The inclusion criteria were: (1) age ≥ 18 years old, and (2) receiving PMV (≥6 h/day for ≥21 days) with an endotracheal tube or tracheostomy. The exclusion criteria were: (1) Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score ≤10 points, (2) patients who died within 7 days of being admitted to the RCC, (3) patients who were transferred back to the ICU within 7 days of being admitted to the RCC, and (4) total RCC stay <4 weeks for incomplete data analysis.
Nutritional data including daily protein intake, daily caloric intake, and the feeding regimen for each patient were collected during the RCC stay. All of the patients received bolus enteral feeding with commercial feed via a nasogastric tube. Nutritionist would review and modified the feeding formula at initial RCC admission. Total daily energy and protein requirements were estimated by a dietitian using weight-based formulae (25–30 kcal/kg/day and 0.6–1.5 g/kg/day of protein, respectively) according to the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) and the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN) guidelines (17–19). Estimated requirements and feeding regimens were reviewed three times per week by nutritionist according to changes in the patient’s clinical condition. We collected the actual feeding amount according to medical records weekly and analyzed the daily nutrition intake accordingly. Daily whey protein intake was calculated according to the feeding regimen. Enteral feeding was suspended if there were contraindications such as intestinal obstruction, active gastrointestinal bleeding, or severe hemodynamic instability.
The following demographic and clinical characteristics were collected: age, sex, height, weight, body mass index, APACHE II score, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score, hospital length of stay, ICU length of stay, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), the presence of tracheostomy, duration of mechanical ventilation, comorbidities, mortality, and weaning parameters. The initial variables were collected at the time of admission to the RCC, and the final variables were collected at week 4 of admission to the RCC or at the time before extubation. The weaning parameters included RR, TV, maximal inspiratory pressure (PIMax), rapid shallow breathing index (RSBI), partial pressure of oxygen in the arterial blood (PaO2), partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood (PaCO2), FiO2, PF ratio (the ratio of PaO2/FiO2) and pH. Of these, RSBI was calculated as RR (breaths/min) divided by TV (liters). RR, TV and PIMax were determined on a breath-by-breath basis and averaged for the first and last 5 min of the spontaneous breathing trial recording. Arterial blood gas and FiO2 were obtained under the pressure support mode of the mechanical ventilator in low setting (FiO2: 35%). Nutritional data were collected weekly for 4 weeks, including body weight, daily actual calorie intake, daily actual protein intake, and the type of protein in the feeding regimen (soy, casein, or whey).
The primary outcome of this study was to evaluate the implications of daily protein intake and nutritional status for weaning and their associations with weaning parameters. The secondary outcomes were in-hospital mortality and changes in serum albumin and creatinine levels. Successful weaning was defined as complete liberation from mechanical ventilation (or a requirement for only nocturnal non-invasive ventilation) for 5 consecutive days. Successful weaning and in-hospital mortality were ascertained as of December 2022.
Categorical variables were expressed as count and percentage (%) and compared using the chi-squared test or Fisher’ exact test, as appropriate. Quantitative variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and compared using the Student’s t-test or Wilcoxon test, as appropriate. The odds ratio (OR) of weaning success [plus 95% confidence interval (CI)] were estimated using logistic regression analysis adjusted for all covariates. Variables included in multivariate analysis were those that were significant at a two-sided p-value of <0.05 in univariate analysis using the stepwise method.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to identify the optimal cut-off values providing the highest sensitivity and specificity. Correlations of the significant variables were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism version 8 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, United States) and SPSS version 26 (IBM Inc., Armonk, NY, United States).
A total of 493 patients with PMV were enrolled, of whom 204 were excluded (Figure 1). Of the remaining 289 patients, 149 were successfully weaned (weaning success group) and 140 were not (weaning failure group). The characteristics of the two groups are summarized in Table 1. The mean age of the enrolled patients was 73.5 ± 12.90 years. The mean ICU length of stay before RCC admission was 30.6 ± 19.98 days, the mean hospital stay was 91.9 ± 50.00 days, and the mean duration of mechanical ventilation was 66.3 ± 37.42 days. There were no significant differences in sex, age, body mass index, ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, and SOFA score between the weaning success and weaning failure groups. However, the APACHE II score was higher in the weaning failure group than in the weaning success group (19.8 ± 5.83 vs. 18.4 ± 4.97, p = 0.024).
Among the reasons for ICU admission, more patients had pneumonia (57.1% vs. 44.3%, p = 0.029) and fewer patients had neurologic disorders (7.9% vs. 16.8%, p = 0.022) in the weaning failure group than in the weaning success group. There were no significant differences between the two groups in comorbidities except for hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, and malignancy. More patients underwent tracheostomy (70.7% vs. 40.3%, p < 0.001) and the mortality rate was higher (29.3% vs. 12.1%, p < 0.001) in the weaning failure group than in the weaning success group.
There were no significant differences in creatinine level and creatinine clearance between the two groups either at admission to the RCC or at 4 weeks of admission. The mean serum albumin level at admission to the RCC (3.00 ± 0.360 vs. 2.82 ± 0.423 g/dL, p < 0.001), at week 4 (3.15 ± 0.383 vs. 2.84 ± 0.477 g/dL, p < 0.001), and the difference between the two values (0.19 ± 0.418 vs. 0.02 ± 0.477 g/dL, p = 0.004) were all higher in the weaning success group than in the weaning failure group. Although the initial GCS score was similar between the two groups, the patients in the weaning success group had a higher final GCS score than the weaning failure group (11.1 ± 2.68 vs. 8.2 ± 3.27, p < 0.001).
The weaning parameters were similar initially in the two groups. However, at week 4 of RCC admission, the RSBI was significantly lower (80.2 ± 37.62 vs. 102.4 ± 73.62 breaths/min/L, p = 0.004) and the PF ratio and PaO2 were significantly higher (337.6 ± 111.40 vs. 270.4 ± 118.63, p < 0.001; 121.5 ± 39.81 vs. 102.0 ± 34.30 mmHg, p < 0.001) in the weaning success group than in the weaning failure group. The average calorie intake (26.42 ± 6.819 vs. 22.54 ± 7.521 kcal/kg/day, p < 0.001) and average protein intake (1.22 ± 0.320 vs. 0.99 ± 0.332 g/kg/day, p < 0.001) were also significantly higher in the weaning success group than in the weaning failure group. There was no significant difference in average whey protein intake between the two groups.
We determined the cutoff values of the quantitative variables using ROC curve analyses, which showed a final GCS score of ≥10, final RSBI of <90 breaths/min/L, serum albumin level at week 4 of ≥3.00 g/dL, APACHE II score of ≤19, average calorie intake of ≥24.5 kcal/kg/day, average protein intake of ≥1.01 g/kg/day, and PF ratio ≥ 300 were associated with successful weaning (Table 2). Final RSBI of <90 breaths/min/L, serum albumin level at week 4 of ≥3.00 g/dL, average protein intake of ≥1.01 g/kg/day, and PF ratio ≥ 300 were independently predictors for successful weaning.
We also analyzed correlations of the nutrition parameters with the final weaning parameters (Figures 2, 3). There were no correlations of average calorie intake with the PiMax, RSBI, PaO2, PaCO2. There were positive correlations between average calorie intake with RR (r = 0.1464, p = 0.0363) and PF ratio (r = 0.1362, p = 0.0493). Negative correlation between average calorie intake with TV was shown (r = −0.17, p = 0.0103). There were no significant correlations between average protein intake and RR, TV, PiMax, RSBI, and PaCO2. There were positive correlations between average protein intake with PF ratio (r = 0.1576, p = 0.0227) and PaO2 (r = 0.13359, p = 0.0497). However, these statistically significant correlation coefficients were interpretated as being weak according to Dancey and Reidy’s definition (20).
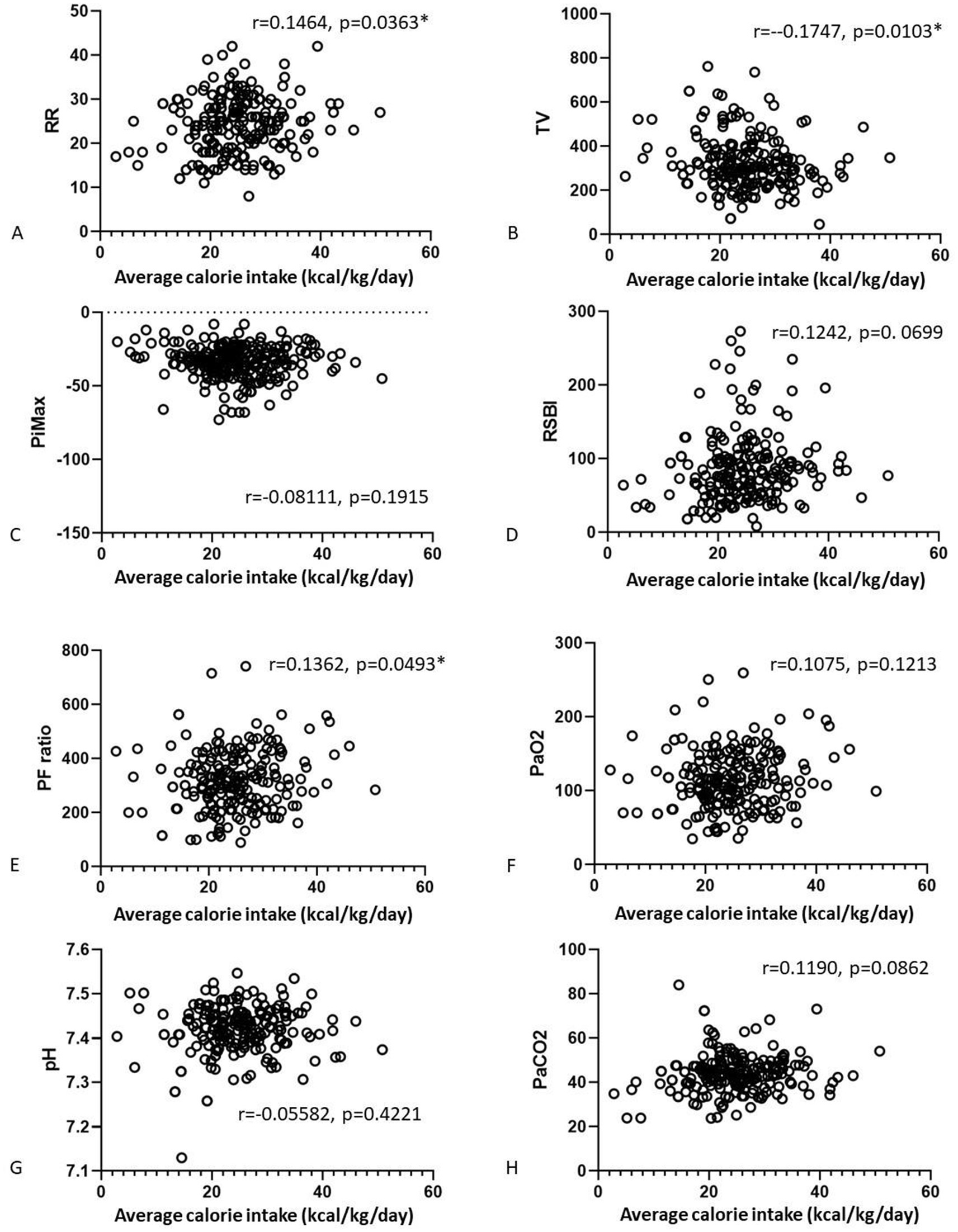
Figure 2. Correlations of the average calorie (A–D) and average protein (E–H) intake associated with the final weaning parameters.
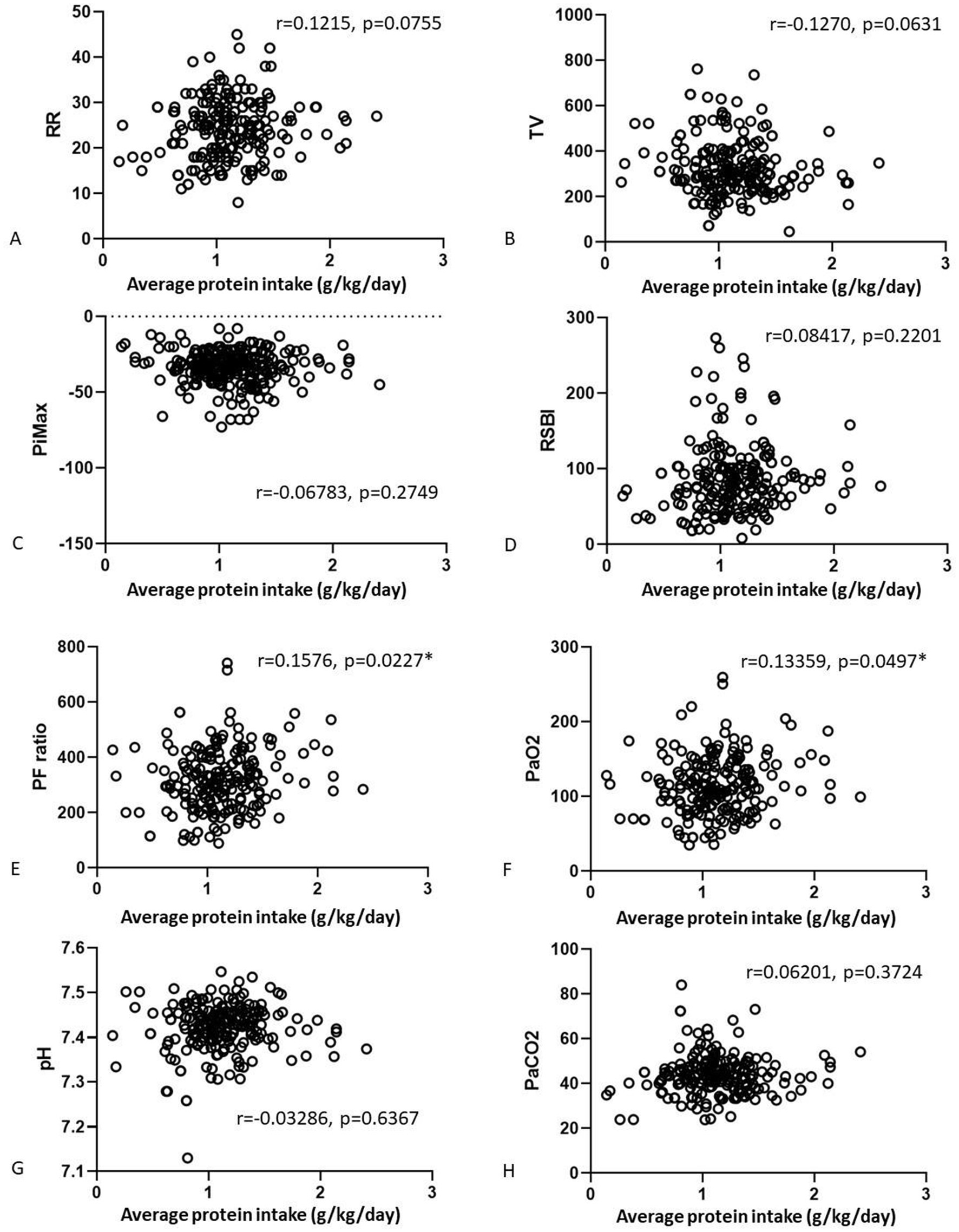
Figure 3. Correlations of the average calorie (A–D) and average protein (E–H) intake associated with final arterial blood gas parameters.
To the best of our knowledge, this is probably the first study to investigate the associations between high protein intake and weaning parameters in patients with PMV. Our results showed that higher protein intake was associated with successful liberation from mechanical ventilation in the patients with PMV. Daily protein intake also had positive correlation with PF ratio and PaO2, presenting with better oxygenation.
Caloric and protein malnutrition have been associated with an increased duration of ventilator days and longer length of ICU stay in critically ill patients, as well as higher rates of morbidity and mortality (21–24). Many studies have indicated that increasing the dietary protein intake can prevent sarcopenia and improve the outcomes of patients with sarcopenia (25–28). Several studies have suggested the optimal timing and amount of calorie and protein intake for patients with acute critical illness (29, 30), however these values for the survivors of critical illness who need PMV are unclear. Because of chronic inflammation, prolonged bedridden status, use of sedatives and muscle relaxants in critically ill patients with mechanical ventilation, they are prone to develop respiratory muscle and limb muscle weakness, which can subsequently delay weaning (31–34). Moreover, prolonged controlled mechanical ventilation may lead to diaphragm disuse and subsequent oxidative stress with protein catabolism in the diaphragm, contributing to diaphragm contractility, dysfunction and atrophy, and thereby increasing the risk of weaning failure (35–38). Zhang et al. (39) reported that intensive nutritional therapy with a target protein intake of up to 2.0 g/kg/day could improve diaphragm atrophy and muscle mass in critically ill patients receiving PMV, but not respiratory mechanical indices or clinical outcomes. In our previous study of 172 patients with PMV, we found an association of high dietary calorie and protein intake with successful liberation from mechanical ventilator (15). In the present study, we extended these findings and investigated the correlations between average calorie/protein intake and weaning parameters. Daily protein intake ≥1.01 g/kg/day, and higher PF ratio were independently beneficial for weaning success. In addition, we found weak, but positive correlations between daily protein intake with PF ratio and PaO2. Askanazi et al. (40) reported that ventilatory drive could be enhanced by increasing the intake of nitrogen via continuous parenteral amino acid infusion, and that PaO2, minute ventilation and TV increased while PaCO2 and respiratory frequency decreased in the high nitrogen intake group. The authors also reported that the increased ventilatory drive observed may not be therapeutic, but depends on the clinical condition of the patients (40). However, another study showed that higher total protein intake failed to affect pulmonary gas exchange or ventilatory response to CO2 in postoperative patients (41). Few studies have investigated the effect of nutrition on pulmonary gas exchange and ventilatory drive. Our report found that daily caloric intake had negatively correlated with TV. This may attribute to higher total nutrition intake may increase the intra-abdominal pressure, subsequently decrease the tidal volume and increase the respiratory rate. The highly heterogenous characteristics of our enrolled patients from surgical and medical ICUs and differences between the operators who measured the weaning parameters may also have contributed to the weak correlations. Nevertheless, we still demonstrated that daily protein intake may have benefit in better oxygenation, presenting as positive correlation with PF ratio and PaO2.
Some studies have indicated that high-quality proteins (i.e., protein sources with a higher proportion of essential amino acids) such as milk, whey, casein and soy can support muscle protein synthesis (11). However, another study reported that leucine-enriched whey protein supplementation (3 times/day) did not yield further benefits in previously untrained older participants with resistant and functional exercise (10). In the present study, there was no significant difference in average whey protein intake between the weaning success and weaning failure groups. This may be because differences between different proteins (e.g., whey, soy, or casein) are due to postprandial protein metabolism kinetics (42).
Our findings are compatible with a previous study which reported that APACHE II score could not predict successful weaning from PMV (43). In the previous studies, albumin and prealbumin can be both important in the nutrition status survey in the hemodialysis patients (44). Although there was a higher serum albumin level in the weaning success group than in the weaning failure group in this study, many studies have implied that albumin may not be a reliable predictor of successful weaning from a ventilator. A systematic review of 10 studies found no association between outcomes and serum albumin level measured variously on day 5, 7, 10, 12, 14, 15, or 21 of ICU stay (45), while another study showed he patients with serum albumin concentration < 30 g/L have higher 180-mortality whether the nutritional risk and inflammation status are high or not (46). The metabolism of albumin is multifactorial, and the serum level may not reflect the total level in the body, especially as patients with PMV have multiple comorbidities and chronic inflammation (47–49). The amount of protein included in the daily nutritional plan should therefore differ according to the patients’ comorbidities, including those who have acute or chronic renal disease with or without hemodialysis. The impact of serum albumin level was not conclusive in the current study.
Following the ESPEN guidelines (17) to determine the protein requirements of our patients with PMV (about 1.2 g/kg/day), no significant differences in serum creatinine level and creatinine clearance were found between the weaning success and weaning failure groups. A previous study did not find a significant link between high protein intake and the initiation or progression of renal disease in healthy individuals (50), however another study reported that daily protein intake ≥1.4 g/kg/day was associated with higher mortality in patients with impaired kidney function (estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min/1.72 m2) (51). Few studies have investigated the association between high protein intake and a decline in renal function in patients with PMV. Our results suggest that it is safe to administer a high protein diet according to the ESPEN guidelines in patients with PMV within 4 weeks of admission to an RCC.
There are several limitations to this study. First, this is a retrospective study. The actual intake may have some bias according to the daily nutritional record. Moreover, the urine urea nitrogen was not calculated routinely in our study, thus we could not evaluate the nitrogen balance in our patients. The results in our study only showed associations but not strong correlation between higher dietary protein intake and successful liberation from mechanical ventilation Second, the patients enrolled in this study were from surgical and medical ICUs, which contributed to the high variability of the patients’ characteristics and the weaning outcomes. This may have resulted in selection biases and diminished generalizability. Finally, the short follow-up period may not reflect the long-term outcomes of patients with PMV. Further prospective case–control studies are warranted to confirm our findings.
Daily protein intake was independently associated with successful liberation from mechanical ventilation in the patients with PMV, and presenting positive correlation with better oxygenation.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (IRB No. 202200818B0). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because all personally identifiable information was encrypted, and the need for patient consent was waived for this study.
C-HC: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation. C-YL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Conceptualization. Y-LL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation. T-YL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Project administration, Methodology, Conceptualization. C-YH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Software, Investigation, Conceptualization. M-HH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Resources, Project administration, Data curation. Y-FF: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization. H-YH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Software, Investigation, Data curation. S-ML: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Validation, Supervision, Project administration. H-CL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Resources.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
We thank the investigators and members of the Department of Thoracic Medicine.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
PMV, prolonged mechanical ventilator; ICU, intensive care unit; APACHE II score, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score; SOFA score, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score; GCS, Glasgow coma scale; SD, standard deviation; RSBI, rapid shallow breathing index; PIMax, maximal inspiratory pressure; PF ratio, PaO2/FiO2 ratio; PaCO2, partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood; PaO2, partial pressure of oxygen in the arterial blood; pH, potential of hydrogen.
1. Kübler, A, Maciejewski, D, Adamik, B, and Kaczorowska, M. Mechanical ventilation in ICUs in Poland: a multi-center point-prevalence study. Med Sci Monit. (2013) 19:424–9. doi: 10.12659/MSM.883930
2. Wagner, DP . Economics of prolonged mechanical ventilation. Am Rev Respir Dis. (1989) 140:S14–8. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2_Pt_2.S14
3. Peñuelas, O, Frutos-Vivar, F, Fernández, C, Anzueto, A, Epstein, SK, Apezteguía, C, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of ventilated patients according to time to liberation from mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2011) 184:430–7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201011-1887OC
4. MacIntyre, NR, Epstein, SK, Carson, S, Scheinhorn, D, Christopher, K, and Muldoon, S. Management of patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation: report of a NAMDRC consensus conference. Chest. (2005) 128:3937–54. doi: 10.1378/chest.128.6.3937
5. Lone, NI, and Walsh, TS. Prolonged mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients: epidemiology, outcomes and modelling the potential cost consequences of establishing a regional weaning unit. Crit Care. (2011) 15:1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33159-2
6. Seneff, MG, Wagner, D, Thompson, D, Honeycutt, C, and Silver, MR. The impact of long-term acute-care facilities on the outcome and cost of care for patients undergoing prolonged mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. (2000) 28:342–50. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200002000-00009
7. Damuth, E, Mitchell, JA, Bartock, JL, Roberts, BW, and Trzeciak, S. Long-term survival of critically ill patients treated with prolonged mechanical ventilation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir Med. (2015) 3:544–53. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00150-2
8. Laghi, F, and Tobin, MJ. Disorders of the respiratory muscles. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2003) 168:10–48. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2206020
9. Paddon-Jones, D, Short, KR, Campbell, WW, Volpi, E, and Wolfe, RR. Role of dietary protein in the sarcopenia of aging. Am J Clin Nutr. (2008) 87:1562S–6S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.5.1562S
10. Kirk, B, Mooney, K, Amirabdollahian, F, and Khaiyat, O. Exercise and dietary-protein as a countermeasure to skeletal muscle weakness: Liverpool Hope University – sarcopenia aging trial (LHU-SAT). Front Physiol. (2019) 10:445. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00445
11. Martone, AM, Marzetti, E, Calvani, R, Picca, A, Tosato, M, Santoro, L, et al. Exercise and protein intake: a synergistic approach against sarcopenia. Bio Med Res Int. (2017) 2017:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2017/2672435
12. Biolo, G, Tipton, KD, Klein, S, and Wolfe, RR. An abundant supply of amino acids enhances the metabolic effect of exercise on muscle protein. Am J Physiol. (1997) 273:E122–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1997.273.1.E122
13. Koopman, R, and van Loon, LJ. Aging, exercise, and muscle protein metabolism. J Appl Physiol. (2009) 106:2040–8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.91551.2008
14. Tipton, K, and Wolfe, RR. Exercise, protein metabolism, and muscle growth. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. (2001) 11:109–32. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.11.1.109
15. Huang, SW, Lin, HC, Chou, YF, Lin, TY, Lo, CY, Huang, HY, et al. The impact of higher protein intake in patients with prolonged mechanical ventilation. Nutrients. (2022) 14:4395. doi: 10.3390/nu14204395
16. de Koning, MSLY, Koekkoek, WAC, Kars, JCN, and van Zanten, ARH. Association of protein and caloric intake and clinical outcomes in adult septic and non-septic ICU patients on prolonged mechanical ventilation: the PROCASEPT retrospective study. J Parenter Enter Nutr. (2020) 44:434–43. doi: 10.1002/jpen.1663
17. Singer, P, Blaser, AR, Berger, MM, Alhazzani, W, Calder, PC, Casaer, MP, et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit. Clin Nutr. (2019) 38:48–79. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.037
18. Thibault, R, Abbasoglu, O, Ioannou, E, Meija, L, Ottens-Oussoren, K, Pichard, C, et al. ESPEN guideline on hospital nutrition. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:5684–709. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.09.039
19. Compher, C, Bingham, AL, McCall, M, Patel, J, Rice, TW, Braunschweig, C, et al. Guidelines for the provision of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient: the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. J Parenter Enter Nutr. (2022) 46:12–41. doi: 10.1002/jpen.2267
21. Mault, J . Energy balance and outcome in critically ill patients: results of a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial by the ICU nutrition study group. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2000) 24:S4.
22. Acchiardo, SR, Moore, LW, and Latour, PA. Malnutrition as the main factor in morbidity and mortality of hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int Suppl. (1983) 16:S199–203.
23. Lowrie, EG, and Lew, NL. Death risk in hemodialysis patients: the predictive value of commonly measured variables and an evaluation of death rate differences between facilities. Am J Kidney Dis. (1990) 15:458–82. doi: 10.1016/S0272-6386(12)70364-5
24. Leavey, SF, Strawderman, RL, Jones, CA, Port, FK, and Held, PJ. Simple nutritional indicators as independent predictors of mortality in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. (1998) 31:997–1006. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.1998.v31.pm9631845
25. Beasley, JM, Shikany, JM, and Thomson, CA. The role of dietary protein intake in the prevention of sarcopenia of aging. Nutr Clin Pract. (2013) 28:684–90. doi: 10.1177/0884533613507607
26. Kim, J-S, Wilson, JM, and Lee, S-R. Dietary implications on mechanisms of sarcopenia: roles of protein, amino acids and antioxidants. J Nutr Biochem. (2010) 21:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.06.014
27. Paddon-Jones, D, and Rasmussen, BB. Dietary protein recommendations and the prevention of sarcopenia: protein, amino acid metabolism and therapy. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2009) 12:86–90. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32831cef8b
28. Yoo, JI, Lee, KH, Choi, Y, Lee, J, and Park, YG. Poor dietary protein intake in elderly population with sarcopenia and osteosarcopenia: a nationwide population-based study. J Bone Metabol. (2020) 27:301–10. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2020.27.4.301
29. Weijs, PJ, Looijaard, WG, Beishuizen, A, Girbes, AR, and Oudemans-van Straaten, HM. Early high protein intake is associated with low mortality and energy overfeeding with high mortality in non-septic mechanically ventilated critically ill patients. Crit Care. (2014) 18:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0701-z
30. Song, JH, Lee, HS, Kim, SY, Kim, EY, Jung, JY, Kang, YA, et al. The influence of protein provision in the early phase of intensive care on clinical outcomes for critically ill patients on mechanical ventilation. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2017) 26:234–40. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.032016.01
31. Latronico, N, and Bolton, CF. Critical illness polyneuropathy and myopathy: a major cause of muscle weakness and paralysis. Lancet Neurol. (2011) 10:931–41. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70178-8
32. Saccheri, C, Morawiec, E, Delemazure, J, Mayaux, J, Dubé, BP, Similowski, T, et al. ICU-acquired weakness, diaphragm dysfunction and long-term outcomes of critically ill patients. Ann Intensive Care. (2020) 10:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s13613-019-0618-4
33. De Jonghe, B, Bastuji-Garin, S, Durand, MC, Malissin, I, Rodrigues, P, Cerf, C, et al. Respiratory weakness is associated with limb weakness and delayed weaning in critical illness. Crit Care Med. (2007) 35:2007–15. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000281450.01881.d8
34. Shi, ZH, Jonkman, A, de Vries, H, Jansen, D, Ottenheijm, C, Girbes, A, et al. Expiratory muscle dysfunction in critically ill patients: towards improved understanding. Intensive Care Med. (2019) 45:1061–71. doi: 10.1007/s00134-019-05664-4
35. Hussain, SN, Mofarrahi, M, Sigala, I, Kim, HC, Vassilakopoulos, T, Maltais, F, et al. Mechanical ventilation–induced diaphragm disuse in humans triggers autophagy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2010) 182:1377–86. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201002-0234OC
36. Powers, SK, Wiggs, MP, Sollanek, KJ, and Smuder, AJ. Ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction: cause and effect. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys. (2013) 305:R464–77. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00231.2013
37. Zergeroglu, MA, McKenzie, MJ, Shanely, RA, Van Gammeren, D, DeRuisseau, KC, and Powers, SK. Mechanical ventilation-induced oxidative stress in the diaphragm. J Appl Physiol. (2003) 95:1116–24. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00824.2002
38. Shanely, RA, Zergeroglu, MA, Lennon, SL, Sugiura, T, Yimlamai, T, Enns, D, et al. Mechanical ventilation–induced diaphragmatic atrophy is associated with oxidative injury and increased proteolytic activity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2002) 166:1369–74. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200202-088OC
39. Zhang, Q, Zhou, J, Zhu, D, and Zhou, S. Evaluation of the effect of high protein supply on diaphragm atrophy in critically ill patients receiving prolonged mechanical ventilation. Nutr Clin Pract. (2022) 37:402–12. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10672
40. Askanazi, J, Weissman, C, LaSala, PA, Milic-Emili, J, and Kinney, JM. Effect of protein intake on ventilatory drive. Anesthesiology. (1984) 60:106–10. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198402000-00005
41. Delafosse, B, Bouffard, Y, Bertrand, O, Viale, JP, Annat, G, and Motin, J. Effects of protein intake on pulmonary gas exchange and ventilatory drive in postoperative patients. Anesthesiology. (1989) 70:404–7. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198903000-00006
42. Tang, JE, and Phillips, SM. Maximizing muscle protein anabolism: the role of protein quality. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2009) 12:66–71. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32831cef75
43. Rojek-Jarmuła, A, Hombach, R, and Krzych, ŁJ. APACHE II score cannot predict successful weaning from prolonged mechanical ventilation. Chron Respir Dis. (2017) 14:270–5. doi: 10.1177/1479972316687100
44. Chertow, GM, Ackert, K, Lew, NL, Lazarus, JM, and Lowrie, EG. Prealbumin is as important as albumin in the nutritional assessment of hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. (2000) 58:2512–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00435.x
45. Ferrie, S, and Allman-Farinelli, M. Commonly used “nutrition” indicators do not predict outcome in the critically ill: a systematic review. Nutr Clin Pract. (2013) 28:463–84. doi: 10.1177/0884533613486297
46. Bretscher, C, Boesiger, F, Kaegi-Braun, N, Hersberger, L, Lobo, DN, Evans, DC, et al. Admission serum albumin concentrations and response to nutritional therapy in hospitalised patients at malnutrition risk: secondary analysis of a randomised clinical trial. EClinicalMedicine. (2022) 45:101301. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101301
47. Throop, JL, Kerl, ME, and Cohn, LA. Albumin in health and disease: protein metabolism and function. Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet. (2004) 26:932–9.
48. Moshage, HJ, Janssen, JA, Franssen, JH, Hafkenscheid, JC, and Yap, SH. Study of the molecular mechanism of decreased liver synthesis of albumin in inflammation. J Clin Invest. (1987) 79:1635–41. doi: 10.1172/JCI113000
49. Chojkier, M . Inhibition of albumin synthesis in chronic diseases: molecular mechanisms. J Clin Gastroenterol. (2005) 39:S143–6. doi: 10.1097/01.mcg.0000155514.17715.39
50. Martin, WF, Armstrong, LE, Rodriguez, NR, Hafkenscheid, JC, and Yap, SH. Dietary protein intake and renal function. Nutr Metabol. (2005) 2:1–9. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-2-25
Keywords: protein intake, weaning parameter, prolonged mechanical ventilation (PMV), nutrition, PF ratio
Citation: Chang C-H, Lin C-Y, Lo Y-L, Lin T-Y, Hung C-Y, Hsieh M-H, Fang Y-F, Huang H-Y, Lin S-M and Lin H-C (2024) Higher protein intake may benefit in patients with prolonged mechanical ventilation. Front. Nutr. 11:1449240. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1449240
Received: 14 June 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 21 October 2024.
Edited by:
Cristian Deana, Azienda Sanitaria Universitaria Integrata di Udine, ItalyReviewed by:
Marialaura Scarcella, Azienda Ospedaliera Santa Maria di Terni, ItalyCopyright © 2024 Chang, Lin, Lo, Lin, Hung, Hsieh, Fang, Huang, Lin and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Horng-Chyuan Lin, TGluNTM0MjRAZ21haWwuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.