
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Nutr., 16 October 2024
Sec. Nutritional Immunology
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1443076
This article is part of the Research TopicMicronutrients, Immunity and InfectionView all 27 articles
Introduction: Micronutrients have significant functional implications for the human immune response, and the quality of food is a major factor affecting the severity and mortality caused by HIV in individuals undergoing antiretroviral therapy. A decrease in CD4 lymphocyte count and an increase in CD8 lymphocyte count are the hallmarks of HIV infection, which causes the CD4/CD8 ratio to invert from a normal value of >1.6 to <1.0. In this study, we tried to analyze whether the nutritional status of HIV-positive patients has an impact on the CD4/CD8 ratio inversion by utilizing a machine learning (ML) algorithm.
Methods: In this study, 55 confirmed HIV-positive patients who had not started their anti-retroviral therapy were included after obtaining their informed, written consent. Moreover, 55 age-and sex-matched relatives and caregivers of the patients who tested negative in the screening were enrolled as controls. All individual patient data points were analyzed for model development with an 80–20 train–test split. Four trace elements, zinc (Zn), phosphate (P), magnesium (Mg), and calcium (Ca), were utilized by implementing a random forest classifier. The target of the study was the inverted CD4/CD8 ratio.
Results: The data of 110 participants were included in the analysis. The algorithm thus generated had a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 83%, with a likelihood ratio (LR+) of 4.8 and LR-of 0.24. The utilization of the ML algorithm adds to the limited evidence that currently exists regarding the role of micronutrients, especially trace elements, in the causation of immune risk. Our inherent strength lies in the fact that this study is one of the first studies to utilize an ML-based decision tree algorithm to classify immune risk in HIV patients.
Conclusion: Our study uniquely corroborated the nutritional data to the immune risk in treatment-naïve HIV patients through the utilization of a decision tree ML algorithm. This could subsequently be an important classification and prognostic tool in the hands of clinicians.
HIV/AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a global pandemic. The first case of HIV infection was reported in India in 1986, and since then, the disease has spread throughout the country. The country’s estimated 2,349,000 HIV/AIDS-positive citizens had an adult prevalence of 0.22% in 2019. Moreover, 3.4% of all people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) were reported to be children. Approximately 44% of the PLWHA aged 15 years and older were reported to be female patients (1). Higher rates of HIV infection, viral load, and sexual and vertical transmission of the virus are all significantly more prevalent in developing nations, such as India, due to malnutrition and food insecurity (2). HIV is characterized by the suppression of the immune system, which increases the energy demands of the already emaciated HIV patients in the fight against the infection and triggers greater nutritional complications (3).
Micronutrients have significant functional implications for the human immune response, and the quality of food is a major factor affecting the severity and mortality caused by HIV in individuals undergoing antiretroviral therapy (4). When highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) was not available, several studies involving HIV-positive adults demonstrated that multivitamin supplementation improved overall clinical outcomes, decreased viral load, improved immunological reconstitution, and decreased mortality (5). Adequate calories from macronutrients and micronutrients constitute an acceptable diet, which is necessary to improve immunity to fight infection, sustain patients’ nutritional status, reduce the spread of HIV, and enhance quality of life (6). To improve nutrient intake and diminish viral load by boosting immunity, dietary treatments such as macronutrient and micronutrient supplements, nutrition education or counseling, and food assistance programs are crucial for HIV-positive individuals (7).
A decrease in CD4 lymphocyte count and an increase in CD8 lymphocyte count are the hallmarks of HIV infection, which causes the CD4/CD8 ratio to invert from a normal value of more than 1.6 to <1.0. It has long been known that the CD4/CD8 ratio can be used to predict the progression of HIV infection (8). Therefore, in this study, we tried to analyze whether the nutritional status of HIV-positive patients has an impact on the CD4/CD8 ratio inversion by utilizing a machine learning (ML) algorithm. This will allow us to specifically generate hierarchical rules for the early prediction of increased immune risk in treatment-naïve HIV patients based on these micronutrients.
This study was a case–control study conducted in the Department of Biochemistry at a tertiary care institute in eastern India. Ethical clearance was obtained from the Institutional Ethics Committee with reference no. T/IM-F/18–19/07 dated 15 May 2023.
A total of 55 patients over 18 years of age attending the Integrated Counselling and Testing Centre (ICTC) clinic, were included. Pre-operative patients, clinically symptomatic patients referred by the clinician, and normal or high-risk patients who directly walked into the clinic for HIV testing with a positive screening test (MeriScreen) and a confirmatory test for HIV (HIV TRI-DOT test) and who had not started anti-retroviral therapy were included in this study, after obtaining written, informed consent from them. Patients who were seriously ill, pregnant women, those taking vitamin supplements, and those unable to answer the questions were excluded from the study. Furthermore, 55 age- and sex-matched relatives and caregivers of the patients, who were matched by age and sex and tested negative on screening, were enrolled as controls after obtaining written informed consent from them.
A detailed dietary history of the patients, with the frequency of non-vegetarian foods and drug intake, was recorded on their datasheets. Anthropometric measurements, such as height, weight, and body mass index (BMI), were recorded for both the patients and controls. A clinical examination of the patients was also performed before blood collection. A total of 5 mL of blood—2 mL in an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) vial and 3 mL in a plain vial—was collected from both patients and controls at the ICTC clinic itself. The CD4+ and CD8+ cell counts were analyzed using a Beckman Coulter Navios Flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter Ireland, Inc., Lismeehan). The total concentration of calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), phosphate (P), and zinc (Zn) in the serum was estimated using a Beckman Coulter AU480 Autoanalyzer. For zinc concentration, Randox quality control material was used and for the rest of the biochemical parameters, Bio-Rad internal quality control samples were used daily.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v26. The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Independent samples t-test was performed to compare groups, and correlation was performed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The data were entered into MS Excel for modeling. All machine learning-related analyses were performed using Python 3.6 in a Jupyter Notebook. All individual patient data points were analyzed for model development with an 80–20 train–test split. In the training dataset, the four micronutrients, i.e., Zn, P, Ca, and Mg, were processed using a custom sequential permutation model based on a random forest classifier model (minimum split = 100, criterion = Gini, and max. Depth = none), with the inverted CD4/CD8 ratio as the target. Each of the iterative classifiers was evaluated for accuracy, recall, precision, F1 value, Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC), and area under the curve (AUC) for the test parameters. Using the means of these matrices, the overall optimized score (OOS) was calculated. The parameter or combination of the parameters with the highest OOS value was selected as the most optimal combination. To generate a clinical decision algorithm, this selected combination was applied to a decision tree model (based on classification and regression tree (CART) with criterion = Gini, splitter = best, max. Depth = 5, and min. Sample splits = 2). This model was validated by a 10-fold cross-validation (scoring = F1 score). The model predictions were evaluated by area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and likelihood ratio (LR).
The data from 110 participants in total were included in the analysis. The demographic and biochemical data of the population are tabulated in Table 1.
The correlation analysis showed a significant positive correlation of calcium, magnesium, and zinc with the CD4 count and CD4/CD8 ratio. The Pearson’s correlation coefficients and p-value are tabulated in Table 2. The correlation heatmap is shown in Figure 1.
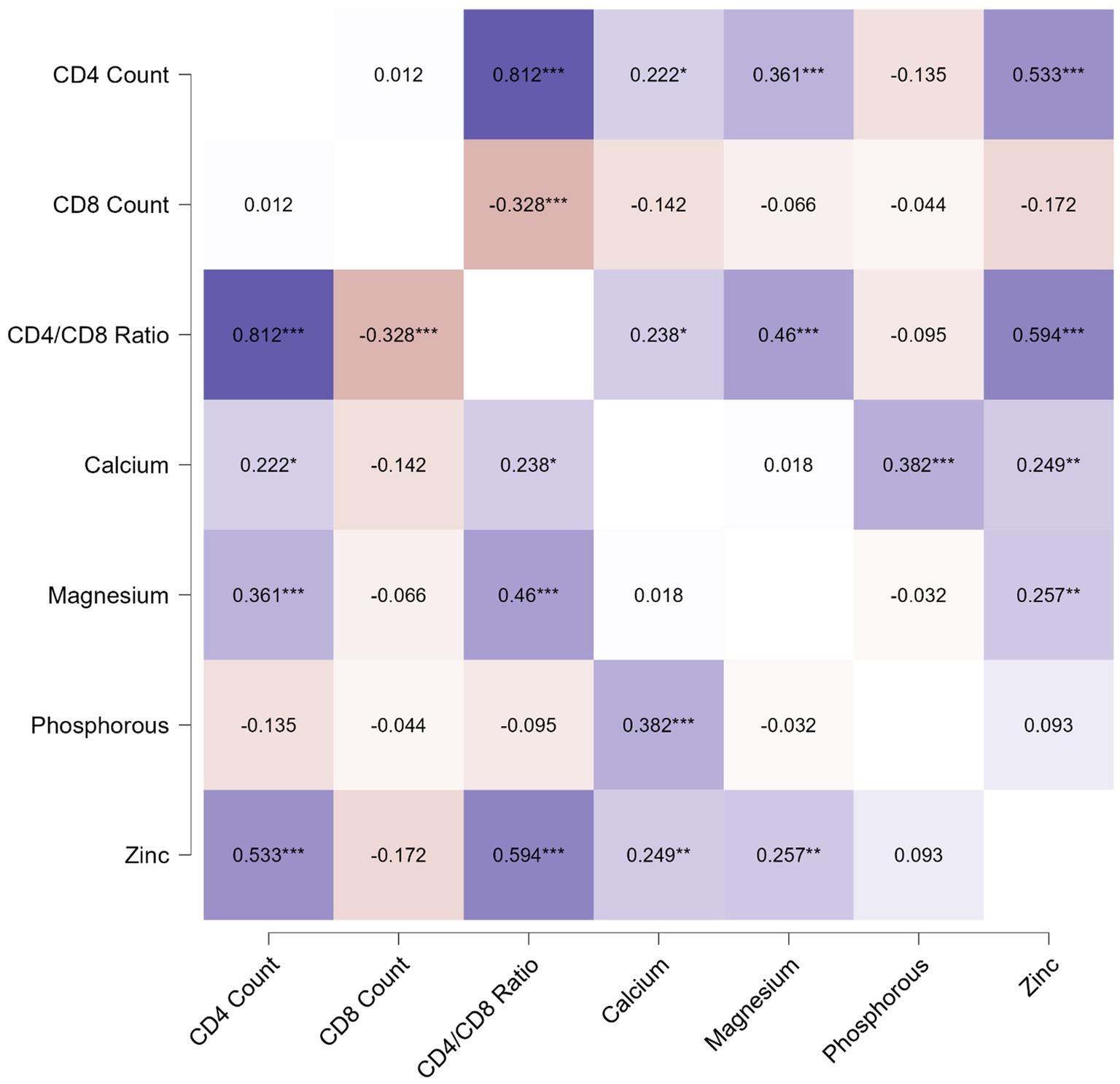
Figure 1. Pearson correlation heatmap for analysis between immunological parameters and micronutrients.
The evaluation metrics of the test data are tabulated in Table 3.
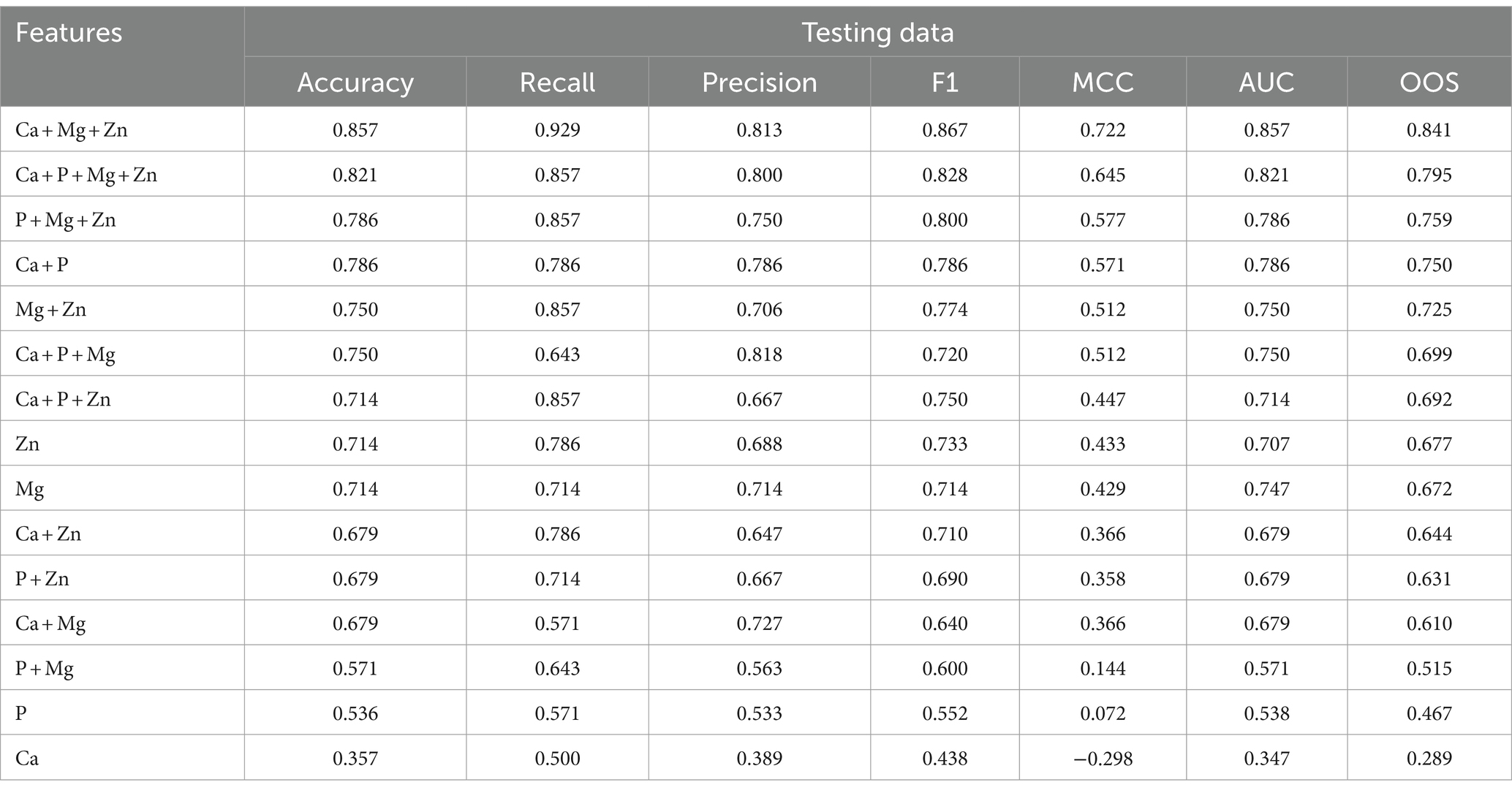
Table 3. Feature evaluation metrics for testing the dataset of various feature combinations along with the overall optimized score (OOS) in descending order.
The best model that included calcium, magnesium, and zinc was implemented to generate a decision algorithm. The algorithm thus generated had an AUC of 0.880, sensitivity of 80%, and specificity of 83%, with LR+ of 4.8 and LR-of 0.24. The diagnostic odds ratio was 20. The mean 10-fold cross-validation was 0.753. The algorithm tree and the confusion matrix are shown in Figures 2, 3, respectively.
Based on the decision tree algorithm, a simplified textual classification was also generated.
ALGORITHM: Our inherent strength lies in the fact that this study is one of the first studies to utilize CART based decision tree for classification of inverted ratio of immune risk in HIV patients.
• If Zn is ≤51.20:
o If Zn is ≤24.45, classify as Inverted (class 1).
o If Zn is >24.45:
▪ If Mg is ≤1.65, classify as Not Inverted (class 0).
▪ If Mg is >1.65, classify as Inverted (class 1).
• If Zn is >51.20:
o If Mg is ≤2.74:
▪ If Ca is ≤7.78, classify as Not Inverted (class 0).
▪ If Ca is >7.78, classify as Not Inverted (class 0).
o If Mg is >2.74, classify as Inverted (class 1).
Our study is one of the pioneering studies in which it was attempted to achieve predictive classification potential regarding the risk of immunocompromised status in treatment-naïve HIV patients. The utilization of an ML algorithm adds to the limited evidence that currently exists regarding the role of micronutrients, especially trace elements, in the causation of immune risk.
CD8 cell proliferation in the general population indicates increased immunosenescence and independently predicts mortality, particularly in older individuals. Individuals with a CD4/CD8 ratio inversion (<1) have CD8 cells with a shorter telomere length, exhibit expression of senescence markers such as CD28-, experience oligoclonal expansion of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific CD8+ T cells, and present with impaired thymic function (9, 10). Later investigations on antiretroviral therapy (ART) have revealed that low CD4/CD8 ratios are also associated with underlying inflammation, oxidative stress, decreased thymic production, and poor control of latent viruses such as CMV, Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), or active coinfections such as hepatitis C (9). Importantly, patients with HIV with low CD4/CD8 ratios have higher levels of inflammation and immunosenescence despite receiving otherwise effective treatment (11).
In previous studies, a decrease in serum zinc levels has been implicated in the micronutrient panel of HIV patients. These studies implied that reduced zinc status is generally found in HIV patients with a higher risk of immune-risk linked to the CD+ cell count (5, 12, 13). Zinc has been primarily linked with antiviral immune responses through the mechanisms of antiviral immune signaling pathways (14). Ionic zinc possesses unique and distinct antiviral properties via an immune response led by interferons (IFNs) and is invariably required to clear infections. Vatsalya et al. (15) reported the involvement of decreased zinc levels in T cell apoptosis in an HIV-infected human T cell line, which may contribute to the depletion of CD4+ T cells. In addition, zinc has been shown to contribute to a number of innate and adaptive immune signaling pathways (16). Zinc supplementation has been linked with an increase in cell-mediated markers of immunocompetence, including the number of circulating T lymphocytes, particularly the percentage of CD4+ cells and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (17). In our study, the algorithm also correlated the propensity of lower zinc levels with a higher probability of predicting increased immune risk in the patients.
As a second intracellular messenger, calcium participates in an array of physiological and biochemical processes, including immune response, utilization of energy, cell division and proliferation, information transfer, and cell development. Furthermore, its signaling offers a target for the invasion, replication, spread, and release of viruses (18, 19). Once the host cell is taken over, viruses use calcium signaling to control apoptosis and hinder host defenses to create a persistent infection (20, 21).
It has been shown that magnesium has potent anti-inflammatory effects as low magnesium levels are linked to increased inflammation and higher magnesium levels have been linked to a decrease in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (22). The capability of magnesium to activate vitamin D is one of its additional critical roles in the body. Magnesium functions as a cofactor in the enzymes that convert vitamin D from its inactive state to an active state, thereby indirectly correlating with the ability of vitamin D to enhance immune function (23). This was demonstrated in our algorithm, which showed that a lower calcium and magnesium status was associated with an increased likelihood of an inverted CD4/CD8 ratio, consequently indicating immune risk in the patients.
Our inherent strength lies in the fact that this study is one of the first studies in India, and worldwide, to utilize an ML-based decision tree algorithm to classify immune risk in HIV patients. In addition, the innate importance of trace elements, which is frequently overlooked in clinical practice, has been quite evidently demonstrated.
However, this study has a few limitations, primarily the small sample size. Furthermore, there is a need to delve deeper into the nutritional, anthropometric, and biochemical aspects of HIV+ patients.
Our study uniquely corroborated nutritional data to immune risk in treatment-naïve HIV patients through the utilization of a decision tree ML algorithm. The findings of this study suggest that this algorithm will subsequently be an important classification and prognostic tool for clinicians while treating people with HIV. Similar studies in a multicenter setting with a larger set of data points and more comprehensive markers of an individual’s nutritional status will further validate the results of this study and increase their robustness.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Ethics Committee, AIIMS Bhubaneswar. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
SN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Software, Visualization. AS: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. MM: Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. GS: Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study received funding in the form of intramural grant from the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Bhubaneswar with Project code no. IMF/02/2018.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Shri, N, Bhattacharyya, K, Dhamnetiya, D, Singh, M, Jha, RP, and Patel, P. Long-term trends of HIV/AIDS incidence in India: an application of join point and age–period–cohort analyses: a gendered perspective. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1093310. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1093310
2. Kaye, HL, and Moreno-Leguizamon, CJ. Nutrition education and counselling as strategic interventions to improve health outcomes in adult outpatients with HIV: a literature review. Afr J AIDS Res. (2010) 9:271–83. doi: 10.2989/16085906.2010.530183
3. Obi, SN, Ifebunandu, NA, and Onyebuchi, AK. Nutritional status of HIV-positive individuals on free HAART treatment in a developing nation. J Infect Dev Ctries. (2010) 4:745–9. doi: 10.3855/jidc.863
4. Rawat, R, McCoy, SI, and Kadiyala, S. Poor diet quality is associated with low CD4 count and Anemia and predicts mortality among antiretroviral therapy–naive HIV-positive adults in Uganda. JAIDS. (2013) 62:246–53. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182797363
5. Isabirye, N, Ezeamama, AE, Kyeyune-Bakyayita, R, Bagenda, D, Fawzi, WW, and Guwatudde, D. Dietary micronutrients and gender, body mass index and viral suppression among HIV-infected patients in Kampala, Uganda. IJMA. (2020) 9:337–49. doi: 10.21106/ijma.362
6. Musoke, PM, and Fergusson, P. Severe malnutrition and metabolic complications of HIV-infected children in the antiretroviral era: clinical care and management in resource-limited settings. Am J Clin Nutr. (2011) 94:1716S–20S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.111.018374
7. Tesfay, FH, Javanparast, S, Gesesew, H, Mwanri, L, and Ziersch, A. Characteristics and impacts of nutritional programmes to address undernutrition of adults living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review of evidence. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e047205. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047205
8. Margolick, JB, Gange, SJ, Detels, R, O’Gorman, MRG, Rinaldo, CR, and Lai, S. Impact of inversion of the CD4/CD8 ratio on the natural history of HIV-1 infection. JAIDS. (2006) 42:620–6. doi: 10.1097/01.qai.0000223028.55080.9d
9. Ron, R, Moreno, E, Martínez-Sanz, J, Brañas, F, Sainz, T, Moreno, S, et al. CD4/CD8 ratio during human immunodeficiency virus treatment: time for routine monitoring? Clin Infect Dis. (2023) 76:1688–96. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad136
10. Wikby, A, Maxson, P, Olsson, J, Johansson, B, and Ferguson, FG. Changes in CD8 and CD4 lymphocyte subsets, T cell proliferation responses and non-survival in the very old: the Swedish longitudinal OCTO-immune study. Mech Ageing Dev. (1998) 102:187–98. doi: 10.1016/S0047-6374(97)00151-6
11. Serrano-Villar, S, Sainz, T, Lee, SA, Hunt, PW, Sinclair, E, Shacklett, BL, et al. HIV-infected individuals with low CD4/CD8 ratio despite effective antiretroviral therapy exhibit altered T cell subsets, heightened CD8+ T cell activation, and increased risk of non-AIDS morbidity and mortality. PLoS Pathog. (2014) 10:e1004078. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004078
12. Onyango, AC, Walingo, MK, Mbagaya, G, and Kakai, R. Assessing nutrient intake and nutrient status of HIV seropositive patients attending Clinic at Chulaimbo sub-District Hospital, Kenya. J Nutr Metab. (2012) 2012:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2012/306530
13. Vatsalya, V, Cave, MC, Kumar, R, Srivastava, S, Khanal, S, Jenson, AB, et al. Alterations in serum zinc and polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrations in treatment-naive HIV-diagnosed alcohol-dependent subjects with liver injury. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. (2019) 35:92–9. doi: 10.1089/aid.2018.0124
14. Read, SA, Obeid, S, Ahlenstiel, C, and Ahlenstiel, G. The role of zinc in antiviral immunity. Adv Nutr. (2019) 10:696–710. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz013
15. Sandstrom, PA, Tebbey, PW, Van Cleave, S, and Buttke, TM. Lipid hydroperoxides induce apoptosis in T cells displaying a HIV-associated glutathione peroxidase deficiency. J Biol Chem. (1994) 269:798–801. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)42178-8
16. Maywald, M, Wessels, I, and Rink, L. Zinc signals and immunity. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:2222. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102222
17. Jiang, Y, Mandal, K, and Lu, H. Serum zinc levels and immune status of children with persistent diarrhea following oral zinc supplementation. Yangtze Med. (2021) 5:33–42. doi: 10.4236/ym.2021.51004
18. Prentice, A, Prentice, AM, and Lamb, WH. Mastitis in rural Gambian mothers and the protection of the breast by milk antimicrobial factors. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. (1985) 79:90–5. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(85)90245-7
19. Bech, A, Van Bentum, P, Telting, D, Gisolf, J, Richter, C, and De Boer, H. Treatment of calcium and vitamin D deficiency in HIV-positive men on Tenofovir-containing antiretroviral therapy. HIV Clin Trials. (2012) 13:350–6. doi: 10.1310/hct1306-350
20. Nabwire, F, Hamill, MM, Fowler, MG, Kekitiinwa, A, and Prentice, A. Milk calcium and phosphorus in Ugandan women with HIV on Tenofovir-based antiretroviral therapy. J Hum Lact. (2023) 39:288–99. doi: 10.1177/08903344221146472
21. Qu, Y, Sun, Y, Yang, Z, and Ding, C. Calcium ions signaling: targets for attack and utilization by viruses. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:889374. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.889374
22. Eskander, M, and Razzaque, MS. Can maintaining optimal magnesium balance reduce the disease severity of COVID-19 patients? Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:843152. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.843152
Keywords: HIV, micronutrients, machine learning and AI, CD4/CD8 lymphocytes + +, treatment naive patients, zinc, calcium, magnesium
Citation: Nayak S, Singh A, Mangaraj M and Saharia GK (2024) Predicting immune risk in treatment-naïve HIV patients using a machine learning algorithm: a decision tree algorithm based on micronutrients and inversion of the CD4/CD8 ratio. Front. Nutr. 11:1443076. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1443076
Received: 03 June 2024; Accepted: 11 September 2024;
Published: 16 October 2024.
Edited by:
Philip Calder, University of Southampton, United KingdomReviewed by:
Nian Ma, University of Pennsylvania, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Nayak, Singh, Mangaraj and Saharia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gautom Kumar Saharia, YmlvY2hlbV9nYXV0b21AYWlpbXNiaHViYW5lc3dhci5lZHUuaW4=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.