- 1Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Chongqing University FuLing Hospital, Chongqing, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 3Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Objective: The objectives of this study were to integrate the Prognostic Nutritional Index, Controlling Nutritional Status, and Nutritional Risk Index, into a novel Nutrition-combined Prognostic Index (NCPI), and to develop and validate a nomogram to predict overall survival (OS) in patients with gastric cancer (GC).
Materials and methods: Data from 609 patients with GC, collected between January 1, 2017, and April 30, 2023, were retrospectively analyzed. Optimal cut-off values for nutritional parameters were determined using X-Tile software, and the Kaplan–Meier method applied for survival analysis. Univariate, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, and multivariate Cox regression analyses were conducted, and a nomogram for predicting OS in patients with GC constructed and validated.
Results: Inferior nutritional status was strongly correlated with worse clinicopathologic features and prognosis of patients with GC. NCPI, body mass index, American Joint Committee on Cancer T stage, and lymph node ratio were identified as independent risk factors for OS. A nomogram including these factors predicted 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS, with training and validation set C-index values of 0.716 and 0.77, respectively. Calibration curves demonstrated that the predicted outcomes closely matched the actual results, and decision curve analysis highlighted the high practical value of the model.
Conclusion: The novel nutritional marker, NCPI, is closely associated with the clinicopathologic features and OS of patients with GC. The practical value of the NCPI-based nomogram was demonstrated and a web-based calculator developed.
1 Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is among the most prevalent malignant tumors (GLOBOCAN)1 (1), and results in high mortality, contributing significantly to the global disease burden (2). Surgery remains the primary treatment for resectable gastric tumors, and offers the sole curative option (3). Adequate surgical resection and meticulous lymph node dissection are crucial to preventing postoperative recurrence. Health status and tolerance of the side effects caused by surgery and systemic therapy significantly influence patient prognosis (4, 5). Hence, nutritional status is critical in patients with GC.
More broadly, clinicians are increasingly recognizing the significance of the nutritional status of oncology patients (6), where nutritional status serves as a potential prognostic factor that can be addressed prior to surgery (7). In cases of severe nutritional risk, the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism guidelines (8) advise that administration of preoperative nutritional support is essential, even if it requires a delay to surgery.
There are several clinical tools that can be applied to evaluate patient nutritional status, including: the Simple Nutrition Screening Tool (9), Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (10), Subjective Global Assessment (11), Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 (12), and the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (13); however, these assessment methods are cumbersome, complex, and time-consuming, making them difficult to apply in routine practice. Additionally, some of the data required to complete these scales are not readily available or are significantly flawed due to subjective processes used in their collection; for example, some patients may struggle to recall and provide accurate nutritional data (14). Hence, according to Xiao et al., clinicians face challenges in accurately assessing patient nutritional status and evaluating the efficacy of nutritional interventions using traditional assessment tools (15), underscoring the need for a simple, practical, and objective method to assess patient nutritional status.
The Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) integrates lymphocyte and serum albumin data to reflect the nutritional and immune status of patients with cancer (16), and is associated with the prognosis of patients with breast, colorectal, and non-small cell lung cancers (17, 18). The Controlled Nutritional Status (CONUT) scoring system was recently introduced to evaluate nutritional status, based on serum albumin, total cholesterol levels, and lymphocyte counts (19). Lee et al. emphasized the importance of the CONUT score in assessing the nutritional status of patients with gastrointestinal or lung tumors (20). Further, the Nutritional Risk Index (NRI), which was initially introduced by Buzby in 1988 (21), is used to evaluate nutritional status based on weight and serum albumin levels, and serves as an indicator of malnutrition in hospitalized adults (22). The French Nutrition and Health Program recommends application of the NRI to assess the nutritional status of hospitalized adults (23).
The relationships of PNI, CONUT, and NRI scores with GC prognosis remain contentious, and no study has combined the PNI, COUNT, and NRI systems to predict overall survival (OS) in patients with GC. In this study, we separately assessed the correlations of these indices with OS in patients with GC. Additionally, we introduce a novel nutritional parameter, the Nutrition-Combined Prognostic Index (NCPI), that integrates the PNI, CONUT, and NRI. Finally, we developed and validated a nomogram based on the NCPI for predicting OS in patients with GC.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study subjects, inclusion criteria, and exclusion criteria
Clinicopathological data of patients diagnosed with GC who underwent radical surgical operation between January 1, 2017, and April 30, 2023, at the Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, the First Hospital Affiliated of Chongqing Medical University, and the Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Chongqing University FuLing Hospital, were retrospectively analyzed. The inclusion criteria were: a. postoperative histological validation of gastric carcinoma, b. patients who had received curative operation for gastric carcinoma, and c. age ≥ 18 years. The exclusion criteria were: a. patients with concurrent multi-site in situ tumors; b. history of other malignant tumors; c. neoadjuvant therapy prior to surgery; d. systemic immune diseases or other significant comorbidities; e. recent use of hormones, immunosuppressants, or similar medications; and f. incomplete clinicopathological data.
2.2 Clinicopathological data
Data on the following variables were collected: age, sex, body mass index (BMI), underlying diseases, tumor size, primary site, American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM stage, histological differentiation, pathological classification, positive lymph nodes, total lymph nodes, lymph node ratio (LNR), chemotherapy, postoperative complications, and OS. BMI was defined as weight (kg)/height(m) (2). Underlying diseases considered were hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (stable phase), and cerebral infarction. Disease count was determined as follows: patients were scored 0 if none of the specified diseases were present, 1 for one disease, and 2 for two diseases, etc. AJCC TNM stage was as defined by the AJCC and the Union for International Cancer Control (24). LNR was the number of positive lymph nodes divided by the total number of lymph nodes. Postoperative adjuvant therapy was conducted according to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines (25). Postoperative complications included fistulas, infections (lung, incision, abdominal, etc.), and other issues (bleeding, bowel obstruction, etc.). OS was measured from the date of surgery to last follow-up, patient loss, death from any cause, or follow-up cutoff.
2.3 Nutritional biomarkers
Blood sampling and collection of relevant nutritional markers were completed within 24 h of admission for patients diagnosed with GC and intended for surgery (26). PNI (16) was calculated as follows:
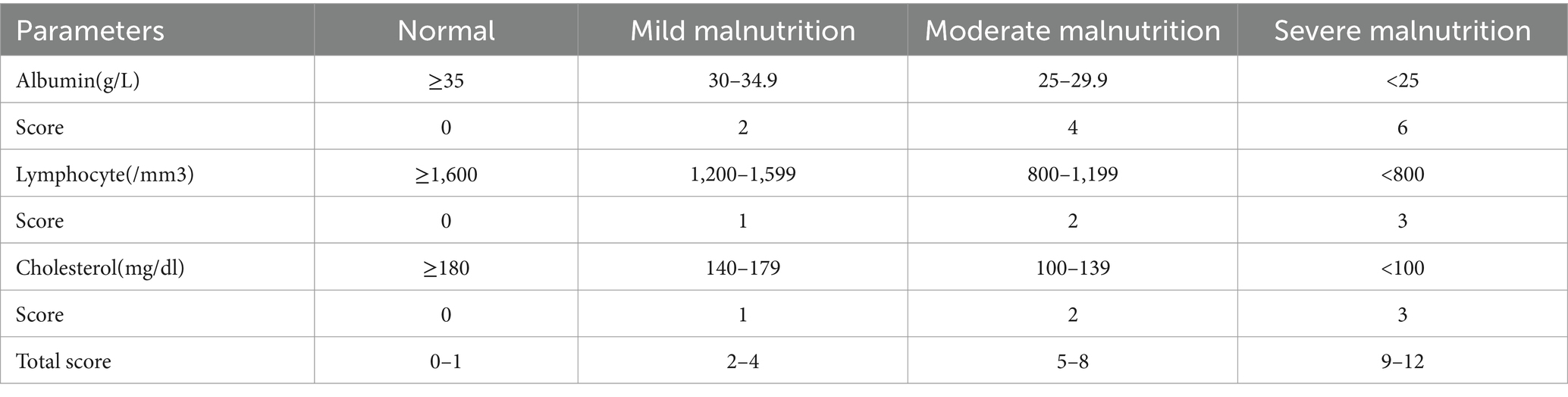
CONUT is a newly proposed scoring system that calculates a nutritional assessment score, based on serum albumin, total cholesterol, and lymphocyte counts, and is mainly used to assess the nutritional status of patients (19) (Table 1). NRI (21) was calculated as:
where ideal body weight formulae (27) were:
Patients were stratified according to the risk of malnutrition as follows: NRI = 100, no risk; NRI = 97.5–100, mild risk; NRI = 83.5–97.5, moderate risk; NRI ≤ 83.5, significant risk.
2.4 Follow-up
Follow-up visits were conducted every 3 months during the initial 2 years post-surgery, followed by visits every 6 months thereafter (25). Data were collected from hospital records and patient or family telephone calls, and encompassed details including missed appointments, last known survival dates, or dates of demise. Overall mortality status encompassed all causes of death post-surgery, ensuring comprehensive tracking of patient outcomes over time.
2.5 Survival analysis and establishment of independent risk factors for OS
X-Tile software2 was used to determine optimal threshold values for nutritional markers, including PNI, CONUT, and NRI. Data were then stratified into high and low nutritional groups, based on parameter cut-off values. Subsequently, differences in clinicopathological characteristics and OS were compared between two groups. Univariate Cox, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO), and multivariate Cox regression analyses were employed to identify independent prognostic factors influencing the prognosis (OS) of patients with GC, using the aforementioned nutritional parameters. Hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) values were calculated accordingly.
2.6 Establishment and validation of prognostic model for GC
Initially, patient data were randomly divided into training and validation sets (ratio, 7:3). Subsequently, independent prognostic factors identified in the previous step were utilized to construct a nomogram prediction model for OS at 1, 3, and 5 years. C-index values were calculated to compare the model performance with that of traditional TNM staging. Time-area under the curve (AUC) values for 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS were used to evaluate the predictive ability of the model in the training and validation datasets. Calibration curves were used to assess the agreement between predicted and actual OS. Decision curve analysis was applied to compare the model performance in predicting patient OS at 1, 3, and 5 years with that of traditional TNM stage. Patient scores were calculated and categorized into high, medium, and low-risk groups using X-Tile software, to evaluate survival differences. Finally, a dynamic web calculator was developed, based on the prediction model.
2.7 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using R software (version 4.3.1).3 Categorical variables are expressed as frequencies and percentages and were compared using either the chi-square (χ2) or Fisher’s exact probability tests. Continuous variables are described using median and interquartile range. Between-group comparisons of normally distributed continuous variables were made using the independent samples t-test (Student’s test), while the Mann–Whitney rank sum test (Mann–Whitney U test) was applied to compare non-normally distributed continuous variables. Significance was determined at p < 0.05 (two-tailed).
3 Results
3.1 Patient clinicopathologic characteristics
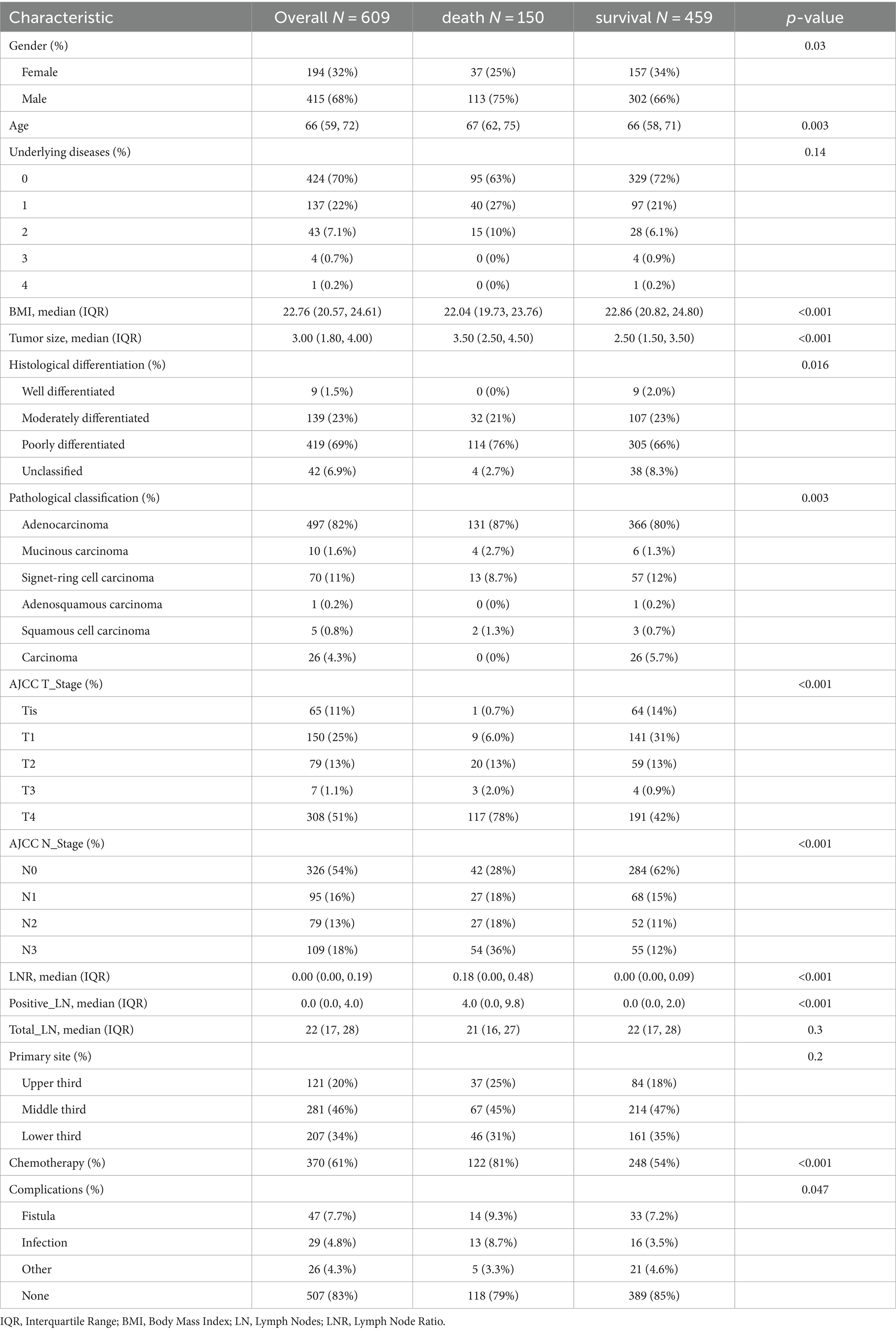
We conducted a retrospective analysis of medical records from patients diagnosed with GC and admitted for surgical treatment at two affiliated hospitals between January 1, 2017, and April 30, 2023. Initially, 1,391 patients from one hospital and 63 from the other were reviewed, yielding a final dataset of 609 patients after applying our inclusion and exclusion criteria (Figure 1A). Among these, 150 patients had deceased, while 459 were living at the time of analysis. Significant disparities in sex distribution, age, BMI, tumor characteristics, AJCC staging, lymph node involvement, chemotherapy, and postoperative complications were observed between the two groups; patients who had died were of higher median age, with larger tumor size, advanced stage tumors, more positive lymph nodes, and a higher incidence of postoperative complications than survivors (Table 2). Differences in PNI, CONUT, and NRI were also detected between patients who survived and those who died (Figures 1B–D).
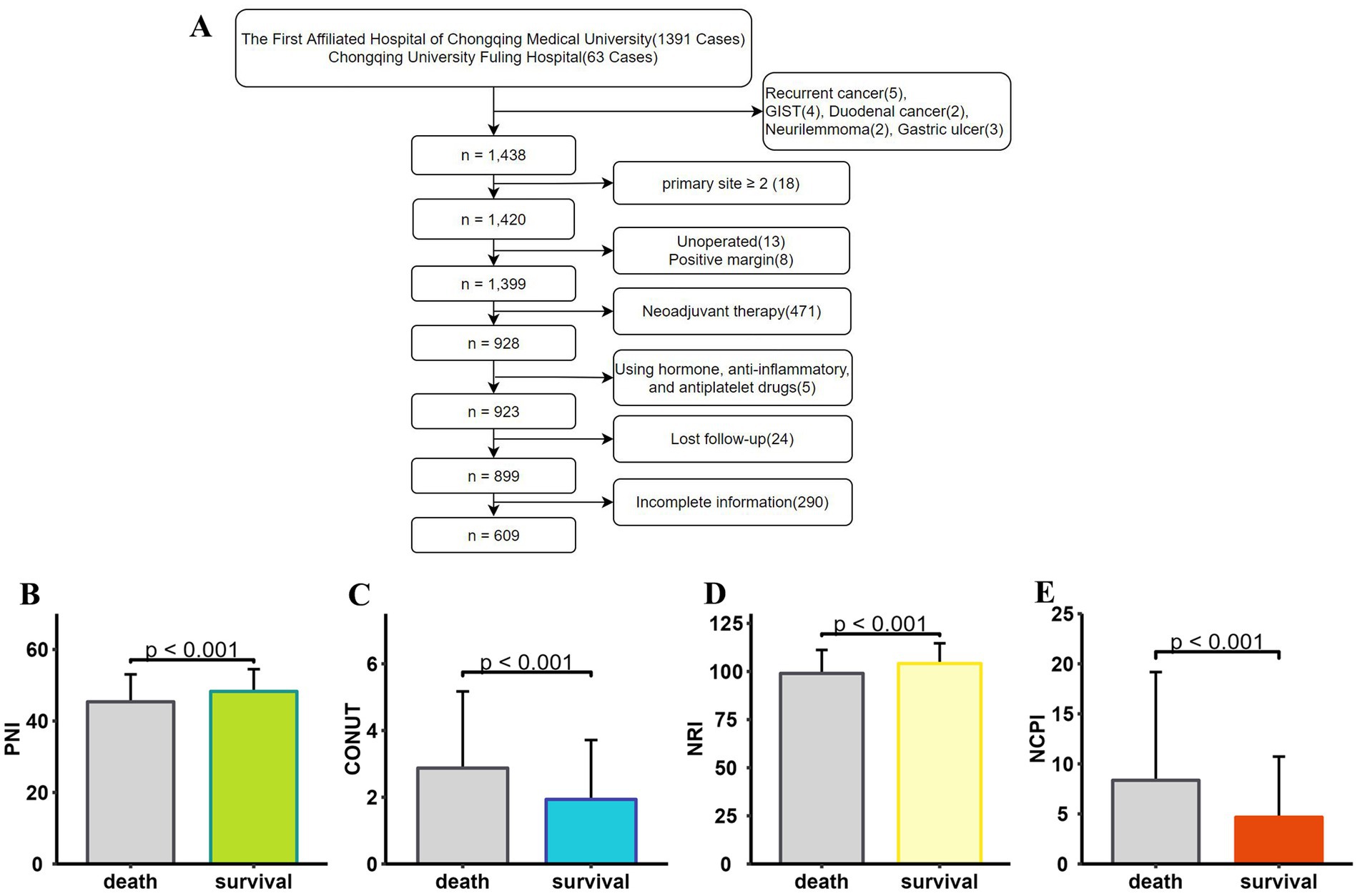
Figure 1. Data screening and histogram demonstrating that patients who died (N = 150) and those who survived (N = 459) had significantly different nutritional status (p < 0.001). (A) Flowchart showing the patient screening process. PNI values were significantly lower (B), CONUT scores were significantly higher (C), NRI values were significantly lower (D), and NCPI values were significantly higher (E) in deceased patients than those in surviving patients. PNI, Prognostic Nutritional Index; CONUT, Controlling Nutritional Status; NRI, Nutritional Risk Index; NCPI, Nutrition-Combined Prognostic Index.
3.2 Nutrition-combined prognostic index
Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were conducted, with univariate analysis revealing associations of OS with PNI, CONUT score, and NRI (Supplementary Table 1); however, multivariate analysis indicated that these factors were not independent risk factors for OS (Supplementary Table 1). Consequently, guided by our univariate findings, we devised a novel parameter, the NCPI, calculated as:
The deceased patient group exhibited significantly higher NCPI values than those in the surviving group (Figure 1E).
Associations of nutritional indicators and clinicopathologic features with OS.
Next, X-Tile software was employed to determine optimal cutoff values for PNI, CONUT, NRI, and NCPI (Supplementary Figure 1), which were determined to be 44.9, 1, 91.3, and 3.7, respectively. Patients were then stratified into High and Low groups based on the cutoff values for each parameter, and clinicopathological characteristics and long-term prognosis (OS) compared between the two groups.
Comparisons of the High PNI and High NRI groups with the Low PNI and Low NRI groups, respectively, revealed significant differences: patients in the former groups achieved longer survival times; included higher proportions of survivors and patients with early T and N stage tumors; and more patients with higher BMI, younger age, smaller tumor size, and lower LNR. Conversely, patients in the High PNI and High NRI groups had fewer positive lymph nodes than those in the Low PNI and Low NRI groups, respectively. All differences were significant (Supplementary Table 2). A restricted cubic spline (RCS) diagram indicated a sharp increase in the risk of death from GC as PNI and NRI decreased below their respective cutoff values (Figures 2A,C). Survival analysis further confirmed the superior prognosis of patients in the High PNI and High NRI groups relative to those in the Low PNI (HR = 2.24, p < 0.001) and Low NRI (HR = 2.56, p < 0.001) groups, respectively (Figures 2E,G).
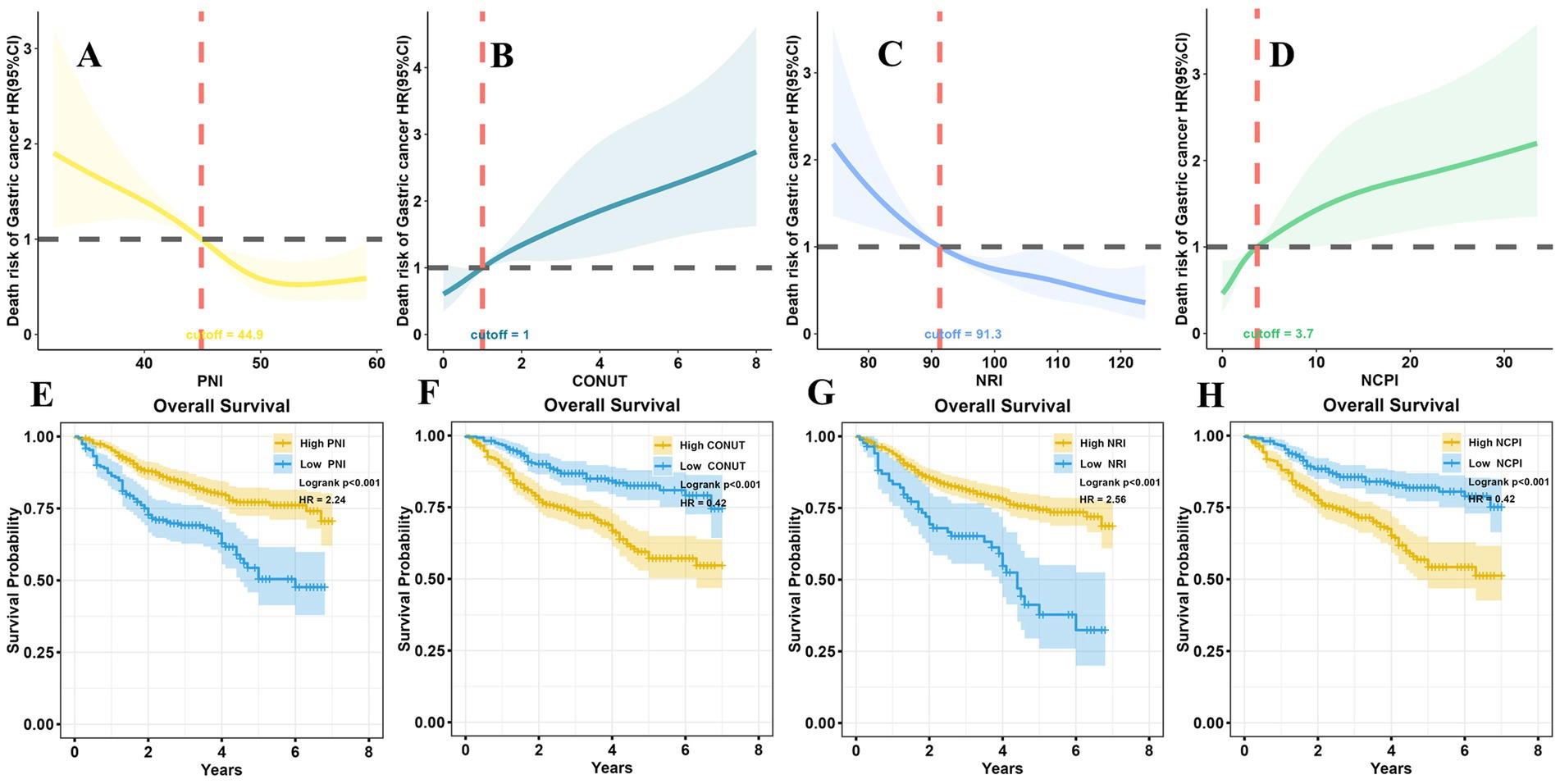
Figure 2. RCS analysis and survival analysis according to nutritional parameters. (A) At PNI > 44.9, the risk of death in patients with GC remained relatively stable; however, it significantly increased as PNI decreased to <44.9. (B) The risk of death in patients with GC was not significantly changed with CONUT <1; however, it notably increased with CONUT ≥1. (C) When NRI > 91.3, the risk of death in GC patients did not vary significantly; conversely, it increased markedly as NRI decreased <91.3. (D) The risk of death in patients with GC remained relatively stable with NCPI <3.7; however, it exponentially increased as NCPI rose >3.7. Long-term survival outcomes were notably better in the high PNI group than those in the low PNI group (E), in the low CONUT group than those in the high CONUT group (F), in the high NRI group than those in the low NRI group (G), and in the low NCPI group than those in the high NCPI group (H). RCS, restricted cubic spline; PNI, Prognostic Nutritional Index; CONUT, Controlling Nutritional Status; NRI, Nutritional Risk Index; NCPI, Nutrition-combined Prognostic Index.
Further, notable differences were detected in patients in the High CONUT and High NCPI groups compared with those in the Low CONUT and Low NCPI groups, respectively. Those in the former groups had shorter survival times and included higher proportions of patients who died of the disease. Additionally, they included higher percentages of male patients, and of those with advanced age, greater presence of underlying diseases, and higher proportions of advanced T and N stage tumors, as well as higher LNR. Furthermore, individuals in these groups tended to have lower BMI, larger tumor size, and more positive lymph nodes (Supplementary Table 2). RCS illustrated a significant elevation in the risk of death from GC with increasing CONUT and NCPI when they surpassed their respective cutoff values (Figures 2B,D). Survival analysis corroborated these findings, indicating that the prognosis of patients in the High CONUT and High NCPI groups was notably poorer than that of patients in the Low CONUT and Low NCPI groups, respectively (HR = 0.42, p < 0.001 for both comparisons; Figures 2F,H).
3.3 Regression analysis of nutritional markers
To ascertain whether NCPI represents an independent risk factor for OS in patients with GC, we conducted both univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. Our findings revealed that NCPI indeed emerged as an independent risk factor for OS in patients with GC (Supplementary Table 3).
To establish a prediction model for OS, we initially divided the data into training and validation sets (ratio, 7:3), with no statistically significant variance between them (Supplementary Table 4). Following univariate Cox regression analysis of the training set, we identified patient age, BMI, tumor size, AJCC T-stage, AJCC N-stage, LNR, positive lymph nodes, chemotherapy, and NCPI as factors associated with OS in patients with GC. Prior to conducting multivariate Cox analysis, these parameters were analyzed by LASSO regression, to mitigate overfitting. Subsequently, based on minimum λ (Figure 3), we selected five parameters (age, BMI, AJCC T-stage, LNR, and NCPI) for further multivariate Cox regression analysis. Our results demonstrated that patient BMI (HR: 0.92, 95% CI: 0.86–0.98), AJCC T-stage (HR: 1.42, 95% CI: 1.17–1.72), LNR (HR: 7.57, 95% CI: 3.57–16.08), and NCPI (HR: 1.03, 95% CI: 1.01–1.05) were independent risk factors for OS in patients with GC (Table 3).
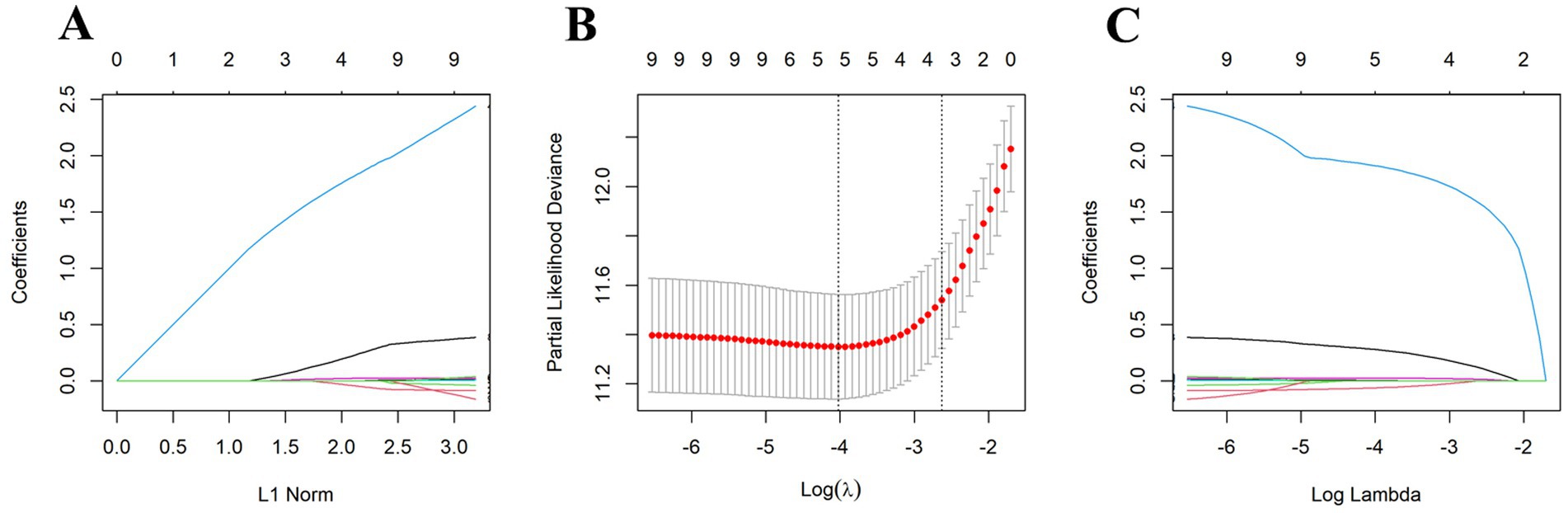
Figure 3. Five clinical and pathological features were selected by LASSO regression analysis at the minimum λ value. (A) LASSO coefficient path plot, (B) LASSO cross-validation curve, (C) LASSO feature selection path plot.
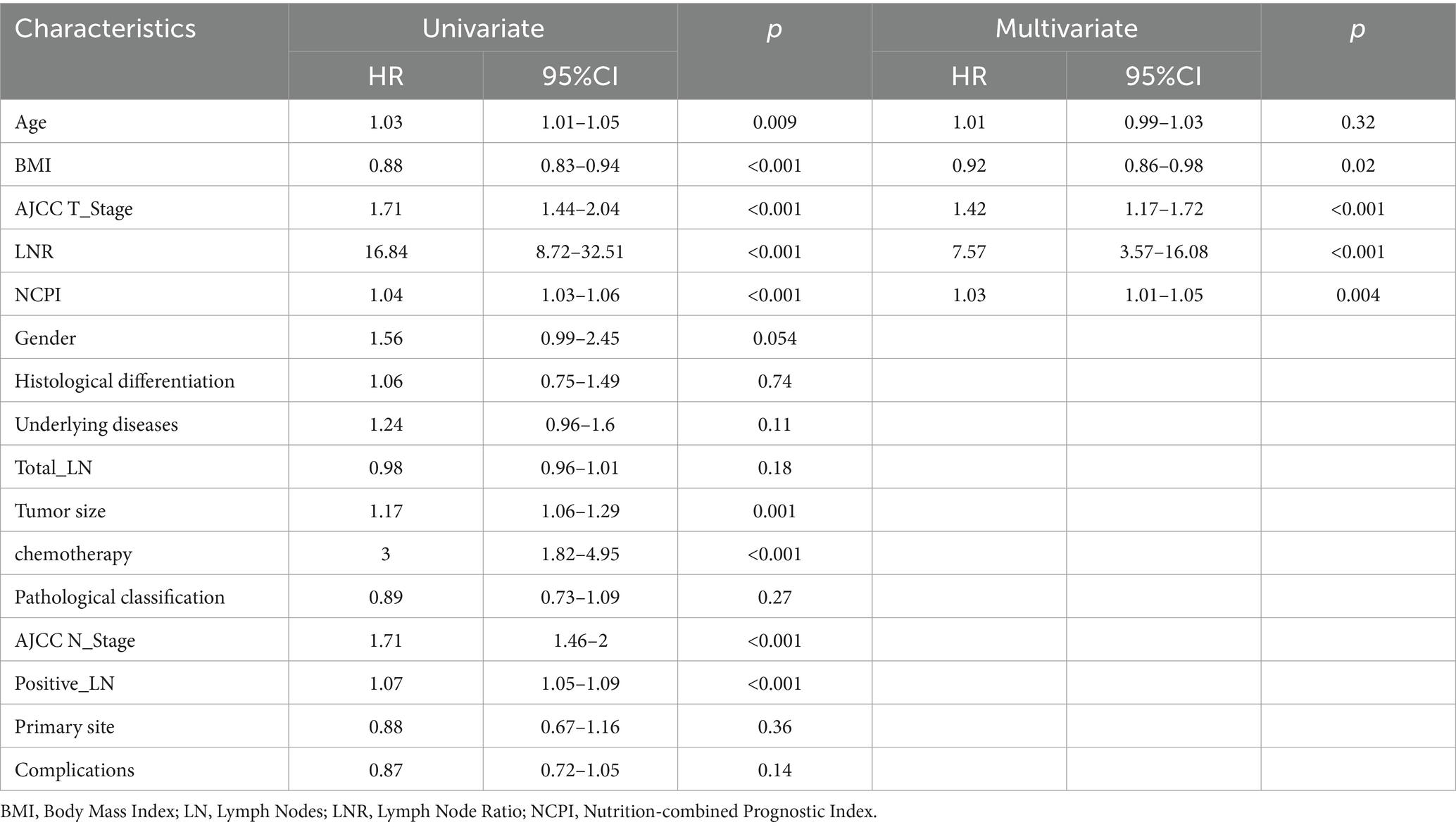
Table 3. Results of univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses to identify risk factors associated with overall survival in patients with gastric cancer.
3.4 Prognostic model establishment and validation
We next generated receiver operating characteristic curves for PNI, CONUT, NRI, and NCPI and calculated AUC values (Supplementary Figure 2; Supplementary Table 5). Despite NCPI exhibiting a higher AUC value than those generated using PNI, CONUT, and NRI, it fell short of expectations as a standalone predictor for GC prognosis. Thus, based on the results of the multivariate Cox analysis, we developed a nomogram for predicting 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS in patients with GC, incorporating four independent risk factors (Figure 4A). Assessment of model differentiation by calculating C-index values revealed favorable performance in both the training (C-index: 0.716, 95% CI: 0.677–0.752) and validation (C-index: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.731–0.806) datasets. Time-AUC curves illustrated stable predictive ability over 1-, 3-, and 5-years OS in both the training and validation datasets (Figures 4B,C). Calibration curves demonstrated close alignment between predicted and actual results (Figures 4D–I). Further, decision curve analysis highlighted the superior clinical utility of our prognostic model over conventional TNM stage (Figure 4J). Patient total scores categorized into high, medium, and low-risk groups using X-Tile software exhibited distinct survival curves (Supplementary Figure 3), with higher scores correlated with inferior prognosis (Figure 4K).
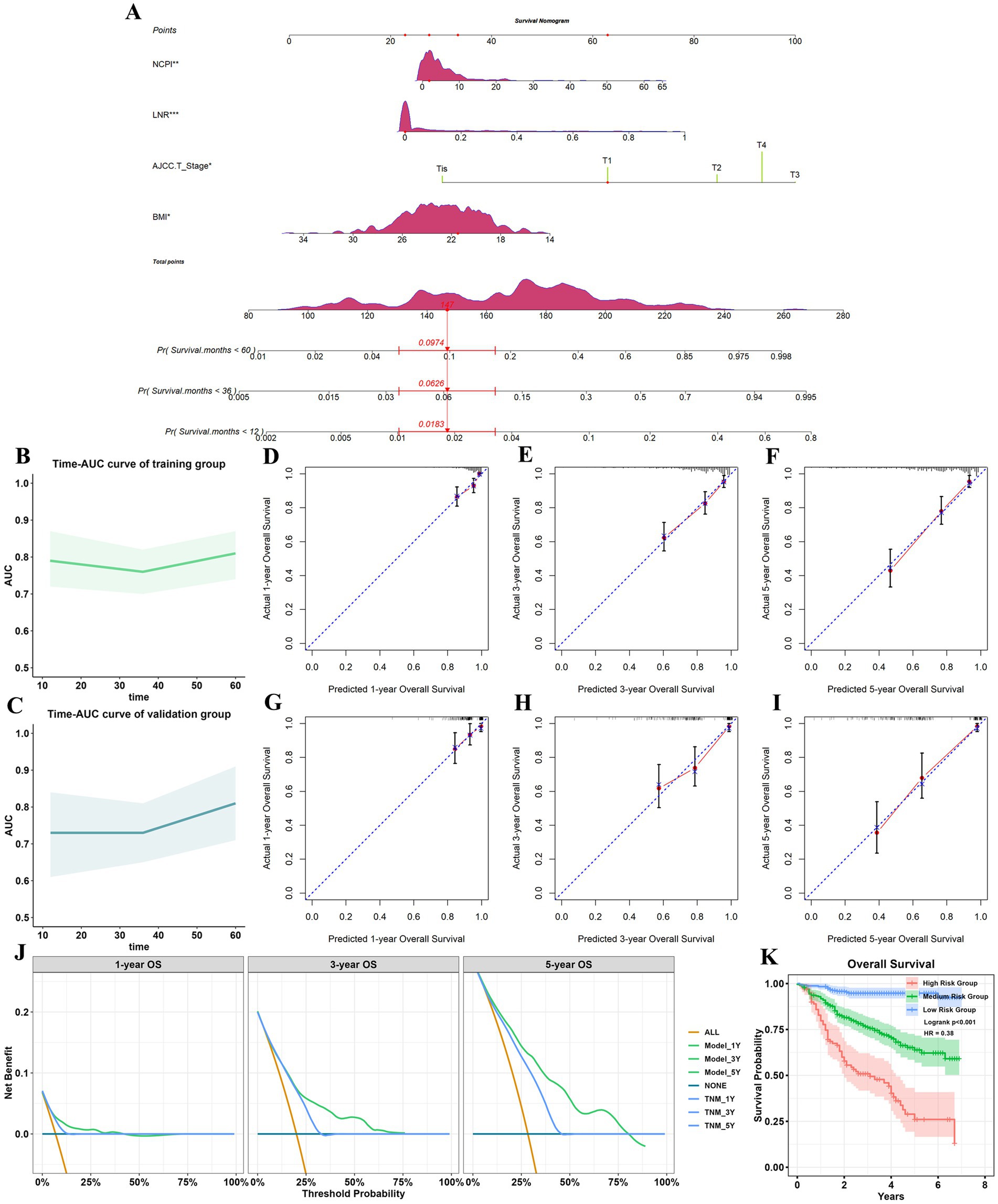
Figure 4. Establishment and validation of a prognostic model. (A) Nomogram for predicting 1-, 3-, and 5-year all-cause mortality rates in patients with GC. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Each parameter in the figure has a corresponding point value above it, and point values were summed corresponding to four patient parameters to obtain a total points value. Finally, the predicted probability corresponding to the total point value directly below it was identified. The figure shows an example of a patient with GC who had NCPI = 1.88, LNR = 0, AJCC T-stage T1, and BMI = 21.48, with a total points score of 147, corresponding to 1-, 3-, and 5-year all-cause mortality rates of 0.018, 0.063, and 0.097, respectively; and 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year OS of 0.982, 0.937, and 0.903. Time-AUC curves for the training group (B) and the validation group (C). (D–F) Calibration curves for 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS for the training group. (G–I) Calibration curves for 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS for the validation group. (J) Decision analysis curves. When the threshold was >10%, the net gain in 1-and 5-year OS for the predictive model was greater than that for the traditional TNM model; when the threshold is >24%, the 3-year net gain in OS of the prediction model was greater than that of the traditional TNM model. (K) Analysis of OS of patients with GC in different risk groups. GC, gastric cancer; NCPI, Nutrition-combined Prognostic Index.
3.5 Web-based model calculator
We next created a web-based dynamic nomogram calculator, accessible.4 Clinicians can use this tool to promptly predict 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS for a patient by entering the relevant parameters as soon as test results are available in the clinic (Supplementary Figure 4).
4 Discussion
GC is a significant and ongoing health concern, ranking fifth and fourth in terms of incidence and mortality rates, respectively (1). The clinical importance of patient nutritional status in managing GC has gained recognition over time; nevertheless, clinicians have struggled to find a straightforward, objective, and accurate method to evaluate this parameter. In this study, we used PNI, CONUT, and NRI as simple, readily available, and objective indicators, to assess individual nutritional status from varying perspectives. Unfortunately, none of these separate indices emerged as independent risk factors for OS. Therefore, we amalgamated the PNI, CONUT, and NRI instruments to devise a novel index, NCPI, with the aim of providing a more comprehensive assessment of individual nutritional status. Our findings reveal that NCPI score correlates with patient prognosis and is an independent risk factor for OS in individuals with GC.
PNI combines data on serum albumin and peripheral lymphocyte counts, which are essential markers for assessing both nutritional and immune status, highlighting the crucial connection between nutrition and immunity. Serum albumin serves as a pivotal indicator of nutritional status, that is closely correlated with degree of malnutrition, and routinely applied in clinical settings to assess and monitor nutritional health. Studies, including those by Oñate-Ocaña et al. (28), have underscored the prognostic significance of serum albumin in the context of GC. Physiological dysregulation of cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 6, in patients with tumors may impede albumin synthesis by hepatocytes, influencing cancer progression and neoangiogenesis (29–32). Lymphocytes are pivotal in cellular immune surveillance and inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and migration, as well as having prognostic significance (33–35). Lower peripheral lymphocyte counts are often indicative of inferior patient prognosis (36). Nogueiro et al. reported positive correlations between higher PNI and improved OS and disease-free survival (37). Similarly, studies by Maejima et al. and Dai et al. reported that lower PNI levels were associated with shorter OS and progression-free survival (PFS), as well as inferior clinicopathological parameters (38, 39). Hirahara et al. identified PNI as an independent risk factor for postoperative complications in patients undergoing gastrectomy (40). Consistently, our findings demonstrate that patients in the low PNI group (≤ 44.9) had poorer OS and detrimental clinicopathological features, including advanced tumor stage, larger tumor size, and more positive lymph nodes.
CONUT was initially devised as a comprehensive scoring system to gage both nutritional and immunological status, and has been demonstrated to be correlated with hospitalization duration (41). The CONUT system integrates serum albumin, total cholesterol levels, and lymphocyte counts, encompassing various facets of nutrition to bolster its efficacy in accurately evaluating nutritional health. Research by Okuyama et al. highlighted associations between total cholesterol levels and the progression and prognosis of multiple types of cancer (42). Similarly, de Martino et al. reported a negative correlation between total cholesterol levels and the risk of cancer, including GC (43). One reason for these findings may be that cholesterol, as a major component of cell membranes, is involved in various signaling pathways that mediate tumor development (44). Further, Chen et al. found that patients with elevated CONUT scores experienced poorer PFS and OS (45), while Xiao et al. reported that individuals with high CONUT scores had shorter OS (p = 0.005) (15). Additionally, CONUT scores are significantly associated with postoperative complications in patients with GC (p < 0.001), particularly anastomotic fistula (p = 0.037). The findings of our study are consistent with these observations, in that individuals with high CONUT scores (> 1) had inferior OS and unfavorable clinicopathological characteristics.
NRI, which incorporates patient height, weight, and serum albumin, serves as a comprehensive indicator of nutritional status. A study of patients with esophageal cancer by Cox et al. highlighted the predictive value of baseline NRI < 100 for reduced OS (46). Interestingly, nutritional interventions at baseline improved survival outcomes, whereas interventions at later stages did not yield significant benefits. A retrospective analysis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma by Clavier et al. corroborated these findings, identifying NRI ≥ 97.5 as an independent prognostic factor (47). Further, research by Oh et al. underscored the significance of NRI in postoperative settings for patients with GC, particularly on the fifth day postoperatively, where lower NRI was associated with increased wound complications (48). In our study, we observed an association between NRI ≤ 91.3 and unfavorable patient clinicopathological characteristics, with lower NRI values indicating a higher risk of patient mortality, suggesting inferior prognosis.
Although we found that PNI, CONUT, and NRI were closely associated with clinicopathologic characteristics and OS in patients with GC, none of these indicators emerged as independent prognostic factors for OS following multivariate analysis. Therefore, we devised the novel nutritional parameter, NCPI, which integrates PNI, CONUT, and NRI. Through univariate, LASSO, and multivariate analyses, we identified NCPI, BMI, AJCC T-stage, and LNR as independent risk factors for OS following radical surgery for GC. NCPI >3.7 was indicative of detrimental clinicopathologic characteristics and inferior OS, where the risk of patient mortality escalated exponentially with increasing NCPI. Based on the results of multivariate analysis, we established a nomogram for predicting OS. C-index values of our model in the training and validation sets were 0.716 and 0.77, respectively, which surpassed the performance of the traditional TNM system. Additionally, calibration curves demonstrated close alignment between predicted and actual values. Furthermore, decision analysis curves indicated a greater net benefit of our predictive model relative to application of the traditional TNM system.
While our study provides valuable insights, it is important to acknowledge its limitations and exercise caution in interpreting the NCPI and nomogram. First, the retrospective nature of our study may have introduced selective bias. Second, our sample size was relatively small, and the follow-up period was relatively short, which could limit the generalizability of our findings. Third, as neoadjuvant therapy may affect some nutritional parameters, we did not include patients undergoing this type of treatment in our analysis. Fourth, while internal data validation was performed, external data validation is currently pending. Future endeavors should involve a multicenter prospective study, encompassing a sufficiently large sample size, with diverse population representation and an extended follow-up duration for validation purposes.
5 Conclusion
The findings of this study underscore the significant link between nutritional status and OS in patients with GC. While we found that PNI, CONUT, and NRI were all associated with clinicopathologic features and OS in the context of GC, none were independent prognostic factors for OS. Therefore, we amalgamated PNI, CONUT, and NRI into a novel nutritional parameter, NCPI. Our data demonstrate that NCPI, BMI, AJCC T-stage, and LNR, are independent factors associated with OS following radical GC surgery. Leveraging these findings, we developed a nomogram and a web calculator to predict OS in patients with GC, which demonstrated superior predictive power and net benefit relative to traditional TNM stage-based predictions. Moving forward, it will be imperative to dynamically monitor patient nutritional status, implement interventions for those at nutritional risk, and further explore the nuanced relationship between nutritional risk and prognosis in the context of GC.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University (K2023-542) and the Ethics Committee of Chongqing University Fuling Hospital (2024CDFSFLYYEC-011). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from primarily isolated as part of your previous study for which ethical approval was obtained. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JX: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LW: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. KL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Fuling District Science Program of Chongqing Municipality (Grant No. 2023KWLH016).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2024.1438319/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. Sung, H, Ferlay, J, Siegel, RL, Laversanne, M, Soerjomataram, I, Jemal, A, et al. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Soerjomataram, I, Lortet-Tieulent, J, Parkin, DM, Ferlay, J, Mathers, C, Forman, D, et al. Global burden of cancer in 2008: a systematic analysis of disability-adjusted life-years in 12 world regions. Lancet. (2012) 380:1840–50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60919-2
3. Beyer, K. Surgery matters: Progress in surgical Management of Gastric Cancer. Curr Treat Options in Oncol. (2023) 24:108–29. doi: 10.1007/s11864-022-01042-3
4. Nguyen, LT, and Popovich, SM. Preoperative assessment and optimization of the cancer patient for onco-surgery. Textbook of onco-anesthesiology. (2021):69–80. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-0006-7_5
5. Islam, KM, Anggondowati, T, Deviany, PE, Ryan, JE, Fetrick, A, Bagenda, D, et al. Patient preferences of chemotherapy treatment options and tolerance of chemotherapy side effects in advanced stage lung cancer. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:835. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6054-x
6. Murphy, JL, Munir, F, Davey, F, Miller, L, Cutress, R, White, R, et al. The provision of nutritional advice and care for cancer patients: a UK national survey of healthcare professionals. Support Care Cancer. (2021) 29:2435–42. doi: 10.1007/s00520-020-05736-y
7. Mao, T, Yorke, J, Zhang, X, Shi, Y, Wang, J, Kong, X, et al. The relationship between nutritional status and prognosis in advanced gastrointestinal cancer patients in palliative care: a prospective cohort study. Support Care Cancer. (2024) 32:697. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08884-7
8. Weimann, A, Braga, M, Carli, F, Higashiguchi, T, Hübner, M, Klek, S, et al. ESPEN guideline: Clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin Nutr. (2017) 36:623–50. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2017.02.013
9. Schiesser, M, Kirchhoff, P, Müller, MK, Schäfer, M, and Clavien, PA. The correlation of nutrition risk index, nutrition risk score, and bioimpedance analysis with postoperative complications in patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. Surgery. (2009) 145:519–26. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2009.02.001
10. Henriksen, C, Paur, I, Pedersen, A, Kværner, AS, Ræder, H, Henriksen, HB, et al. Agreement between GLIM and PG-SGA for diagnosis of malnutrition depends on the screening tool used in GLIM. Clin Nutr. (2022) 41:329–36. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.12.024
11. Mueller, C, Compher, C, and Ellen, DM. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (a.S.P.E.N.) Board of Directors. A.S.P.E.N. Clinical guidelines: nutrition screening, assessment, and intervention in adults. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2011) 35:16–24. doi: 10.1177/0148607110389335
12. Guo, W, Ou, G, Li, X, Huang, J, Liu, J, and Wei, H. Screening of the nutritional risk of patients with gastric carcinoma before operation by NRS 2002 and its relationship with postoperative results. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2010) 25:800–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06198.x
13. Cederholm, T, Jensen, GL, Correia, MITD, Gonzalez, MC, Fukushima, R, Higashiguchi, T, et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition - a consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin Nutr. (2019) 38:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.002
14. Xu, YC, and Vincent, JI. Clinical measurement properties of malnutrition assessment tools for use with patients in hospitals: a systematic review. Nutr J. (2020) 19:106. doi: 10.1186/s12937-020-00613-0
15. Xiao, Q, Li, X, Duan, B, Li, X, Liu, S, Xu, B, et al. Clinical significance of controlling nutritional status score (CONUT) in evaluating outcome of postoperative patients with gastric cancer. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:93. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04128-4
16. Li, J, Xu, R, Hu, DM, Zhang, Y, Gong, TP, and Wu, XL. Prognostic nutritional index predicts outcomes of patients after gastrectomy for Cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of nonrandomized studies. Nutr Cancer. (2019) 71:557–68. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2019.1577986
17. Tong, YS, Tan, J, Zhou, XL, Song, YQ, and Song, YJ. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicting chemoradiation resistance and poor outcome in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. (2017) 15:221. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1326-1
18. Wang, Y, Battseren, B, Yin, W, Lin, Y, Zhou, L, Yang, F, et al. Predictive and prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index for locally advanced breast cancer. Gland Surg. (2019) 8:618–26. doi: 10.21037/gs.2019.10.08
19. Ignacio de Ulíbarri, J, González-Madroño, A, de Villar, NG, González, P, González, B, Mancha, A, et al. CONUT: a tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr Hosp. (2005) 20:38–45.
20. Lee, SC, Lee, JG, Lee, SH, Kim, EY, Chang, J, Kim, DJ, et al. Prediction of postoperative pulmonary complications using preoperative controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:12385. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68929-9
21. Buzby, GP, Williford, WO, Peterson, OL, Crosby, LO, Page, CP, Reinhardt, GF, et al. A randomized clinical trial of total parenteral nutrition in malnourished surgical patients: the rationale and impact of previous clinical trials and pilot study on protocol design. Am J Clin Nutr. (1988) 47:357–65. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/47.2.357
22. Naber, TH, de Bree, A, Schermer, TR, Bakkeren, J, Bär, B, de Wild, G, et al. Specificity of indexes of malnutrition when applied to apparently healthy people: the effect of age. Am J Clin Nutr. (1997) 65:1721–5. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/65.6.1721
23. Hasselmann, M, and Alix, E. Tools and procedures for screening for malnutrition and its associated in risks in hospital. Nutr Clin Metab. (2003) 17:218–26. doi: 10.1016/j.nupar.2003.09.004
24. Amin, MB, Greene, FL, Edge, SB, Compton, CC, Gershenwald, JE, Brookland, RK, et al. The eighth edition AJCC Cancer staging manual: continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more "personalized" approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin. (2017) 67:93–9. doi: 10.3322/caac.21388
25. Ajani, JA, D'Amico, TA, Bentrem, DJ, Chao, J, Cooke, D, Corvera, C, et al. Gastric Cancer, version 2.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. (2022) 20:167–92. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0008
26. Fang, T, Wang, Y, Yin, X, Zhai, Z, Zhang, Y, Yang, Y, et al. Diagnostic sensitivity of NLR and PLR in early diagnosis of gastric Cancer. J Immunol Res. (2020) 2020:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2020/9146042
27. Bouillanne, O, Morineau, G, Dupont, C, Coulombel, I, Vincent, JP, Nicolis, I, et al. Geriatric nutritional risk index: a new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am J Clin Nutr. (2005) 82:777–83. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/82.4.777
28. Oñate-Ocaña, LF, Aiello-Crocifoglio, V, Gallardo-Rincón, D, Herrera-Goepfert, R, Brom-Valladares, R, Carrillo, JF, et al. Serum albumin as a significant prognostic factor for patients with gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. (2007) 14:381–9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9093-x
29. Honda, H, Qureshi, AR, Heimbürger, O, Barany, P, Wang, K, Pecoits-Filho, R, et al. Serum albumin, C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and fetuin a as predictors of malnutrition, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in patients with ESRD. Am J Kidney Dis. (2006) 47:139–48. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2005.09.014
30. Peters, SJ, Vanhaecke, T, Papeleu, P, Rogiers, V, Haagsman, HP, and van Norren, K. Co-culture of primary rat hepatocytes with rat liver epithelial cells enhances interleukin-6-induced acute-phase protein response. Cell Tissue Res. (2010) 340:451–7. doi: 10.1007/s00441-010-0955-y
31. Liu, J, Dai, Y, Zhou, F, Long, Z, Li, Y, Liu, B, et al. The prognostic role of preoperative serum albumin/globulin ratio in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma undergoing radical cystectomy. Urol Oncol. (2016) 34:484.e1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.05.024
32. Balkwill, F. Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2009) 9:361–71. doi: 10.1038/nrc2628
33. Singh, S, Gupta, P, and Meena, A. A flavone with diverse therapeutic potential in cancer, inflammation, infections and other metabolic disorders. Food Chem Toxicol. (2020) 145:111708. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111708
34. Mantovani, A, Allavena, P, Sica, A, and Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. (2008) 454:436–44. doi: 10.1038/nature07205
35. Ray-Coquard, I, Cropet, C, Van Glabbeke, M, Sebban, C, Le Cesne, A, Judson, I, et al. Lymphopenia as a prognostic factor for overall survival in advanced carcinomas, sarcomas, and lymphomas. Cancer Res. (2009) 69:5383–91. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3845
36. Liang, L, Zhu, J, Jia, H, Huang, L, Li, D, Li, Q, et al. Predictive value of pretreatment lymphocyte count in stage II colorectal cancer and in high-risk patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:1014–28. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5835
37. Nogueiro, J, Santos-Sousa, H, Pereira, A, Devezas, V, Fernandes, C, Sousa, F, et al. The impact of the prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in gastric cancer. Langenbeck's Arch Surg. (2022) 407:2703–14. doi: 10.1007/s00423-022-02627-0
38. Maejima, K, Taniai, N, and Yoshida, H. The prognostic nutritional index as a predictor of gastric Cancer progression and recurrence. J Nippon Med Sch. (2022) 89:487–93. doi: 10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-507
39. Dai, Y, Liu, M, Lei, L, and Lu, S. Prognostic significance of preoperative prognostic nutritional index in ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). (2020) 99:e21840. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021840
40. Hirahara, N, Matsubara, T, Kaji, S, Uchida, Y, Hyakudomi, R, Yamamoto, T, et al. Influence of nutrition on stage-stratified survival in gastric cancer patients with postoperative complications. Oncotarget. (2022) 13:183–97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28179
41. Cabré, M, Ferreiro, C, Arus, M, Roca, M, Palomera, E, and Serra-Prat, M. Evaluation of CONUT for clinical malnutrition detection and short-term prognostic assessment in hospitalized elderly people. J Nutr Health Aging. (2015) 19:729–33. doi: 10.1007/s12603-015-0536-6
42. Okuyama, H, Ichikawa, Y, Sun, Y, Hamazaki, T, and Lands, WE. Cancer and all-cause mortalities are lower in the higher total cholesterol groups among general populations. World Rev Nutr Diet. (2007) 96:37–54. doi: 10.1159/000097806
43. de Martino, M, Leitner, CV, Seemann, C, Hofbauer, SL, Lucca, I, Haitel, A, et al. Preoperative serum cholesterol is an independent prognostic factor for patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC). BJU Int. (2015) 115:397–404. doi: 10.1111/bju.12767
44. Haghikia, A, and Landmesser, U. High-density lipoproteins: effects on vascular function and role in the immune response. Cardiol Clin. (2018) 36:317–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2017.12.013
45. Chen, L, Sun, H, Zhao, R, Huang, R, Pan, H, Zuo, Y, et al. Controlling nutritional status (CONUT) predicts survival in gastric Cancer patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor (PD-1/PD-L1) outcomes. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:836958. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.836958
46. Cox, S, Powell, C, Carter, B, Hurt, C, Mukherjee, S, and Crosby, TD. Role of nutritional status and intervention in oesophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy: outcomes from SCOPE1. Br J Cancer. (2016) 115:172–7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.129
47. Clavier, JB, Antoni, D, Atlani, D, Ben Abdelghani, M, Schumacher, C, Dufour, P, et al. Baseline nutritional status is prognostic factor after definitive radiochemotherapy for esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. (2014) 27:560–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2012.01441.x
Keywords: gastric cancer, nutrition-combined prognostic index, nomogram, overall survival, nutrition
Citation: Li X, Fu Z, Zhang J, Xu J, Wang L and Li K (2024) A novel integrated nutrition-combined prognostic index for predicting overall survival after radical gastrectomy. Front. Nutr. 11:1438319. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1438319
Edited by:
Jean-Marc A. Lobaccaro, Université Clermont Auvergne, FranceReviewed by:
Akile Zengin, Eskişehir Osmangazi University, TürkiyeLi Chen, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Li, Fu, Zhang, Xu, Wang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ke Li, M2xpa2VAc2luYS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiang Li
Xiang Li Zhongxue Fu
Zhongxue Fu Jun Zhang
Jun Zhang Jinming Xu1
Jinming Xu1