- 1The First Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
- 2Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Sanming First Hospital, Sanming, China
- 3Department of Proctology, Yubei Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chongqing, China
Background: This investigation aimed to analyze the association between dietary vitamin E intake and constipation prevalence among United States adults.
Methods: Utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), this cross-sectional study assessed vitamin E intake through 24-h dietary recall and defined constipation based on the Bristol Stool Form Scale (BSFS). Logistic regression models were employed to evaluate the relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation, with results presented as odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Stratified analyses were conducted based on covariates such as age, and restricted cubic spline (RCS) models were generated to explore the potential linear or non-linear association.
Results: Individuals experiencing constipation exhibited lower vitamin E intake compared to those without constipation. Weighted multivariate logistic regression models demonstrated a negative correlation between vitamin E intake and constipation risk, even after adjusting for potential confounding variables. Further RCS analysis revealed a statistically significant non-linear inverse relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation risk (p-value for non-linearity = 0.0473).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest an independent inverse association between vitamin E intake and constipation prevalence in United States adults. Prospective research is needed to validate these observations.
1 Introduction
Constipation, a widespread chronic gastrointestinal issue, presents with a range of debilitating symptoms including difficulty passing stools, infrequent bowel movements, and a persistent feeling of incomplete evacuation. These symptoms significantly diminish patients’ quality of life (1). With a global prevalence estimated between 10.1 and 15.3% among adults (2), constipation disproportionately affects female individuals, exhibiting a higher incidence in women compared to men (3). The impact of constipation extends far beyond physical discomfort. Individuals struggling with constipation often experience psychological challenges, such as anxiety and depression, and may even exhibit cognitive impairments, further exacerbating their reduced quality of life (4). The Rome Criteria, a widely used diagnostic framework for functional gastrointestinal disorders, categorize constipation into distinct subtypes, such as functional constipation (FC), constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), defecation disorders (DDs), which involve difficulty with the process of defecation, and opioid-induced constipation (OIC), a common side effect of opioid medications (5). Seeking relief from constipation and its associated discomfort, patients often explore dietary interventions, especially when aiming to minimize the side effects of certain medications. Research suggests that certain dietary components, such as soluble fiber and essential trace elements such as selenium, magnesium, and phosphorus (6–8), may play a role in reducing the risk of chronic constipation. Conversely, diets high in saturated fats (1) or characterized by low energy intake (9) have been associated with an elevated risk of developing this condition. A cross-sectional study conducted in Turkey identified several risk factors contributing to constipation, including physical inactivity, insufficient dietary fiber and water intake, advancing age, female sex, and obesity. These findings underscore the multifactorial nature of constipation and the importance of considering various lifestyle and demographic factors when assessing individual risk (10).
While numerous studies have explored the impact of various nutritional factors on constipation, including the aforementioned fiber intake, fat consumption, and certain micronutrients, there remains a notable gap in our understanding of the potential role of specific vitamins in mitigating this condition. For instance, research has established a connection between vitamin D deficiency and an increased risk of constipation (11). However, the relationship between other fat-soluble vitamins, particularly vitamin E, and constipation has received limited attention in the scientific literature.
Vitamin E is a collective term for a group of fat-soluble compounds, initially discovered in 1922, with diverse biological functions and potential health benefits (12). Its primary role lies in its powerful antioxidant properties, effectively scavenging harmful peroxyl radicals and preventing the chain reaction of free radical propagation within tissues, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage (13). Moreover, vitamin E plays a crucial role in protecting cellular structures from the detrimental effects of oxidative stress and the damaging byproducts of lipid peroxidation, further contributing to overall cellular health and function (14).
The potential mechanisms linking vitamin E to constipation are multifaceted and warrant further investigation. First, vitamin E’s antioxidant properties may help maintain the integrity of the intestinal mucosa, potentially improving overall gut health and function (15). Second, vitamin E has been shown to modulate inflammatory responses in the gastrointestinal tract, which could influence bowel motility and stool consistency (16). In addition, some studies suggest that vitamin E may enhance the production of prostaglandins, which may play a role in regulating intestinal water and electrolyte absorption, potentially affecting stool softness and ease of passage (17, 18).
Given the potential benefits of vitamin E in gut health and its understudied relationship with constipation, there is a clear need for comprehensive research in this area. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database provides an excellent opportunity to investigate this relationship on a large scale. This extensive dataset allows for a thorough examination of the association between vitamin E intake and constipation while accounting for various confounding factors such as age, sex, dietary habits, and overall health status.
Therefore, this study leverages the comprehensive NHANES database to delve into the potential association between vitamin E intake and constipation. By utilizing this robust dataset, we aim to provide valuable insights into the role of vitamin E in gastrointestinal health and potentially identify new strategies for preventing and managing constipation through nutritional interventions.
2 Methods
2.1 Data source and study population
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) serves as a valuable resource for investigating the health and nutritional status of the United States population. As a publicly available research program conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (CDC), the NHANES offers a rich dataset representing a diverse cross-section of non-institutionalized individuals across the nation. Employing a rigorous sampling methodology, NHANES selects participants through a stratified, multi-stage, probability-cluster design, ensuring that the collected data accurately reflect the demographics and health characteristics of the broader United States population. To account for the complex sampling design, statistical analyses incorporate appropriate weighting adjustments (19). Adhering to strict ethical standards, the NHANES obtains informed consent from all participants, including parental consent for individuals under 18 years of age. The survey protocol has received ethics approval, and all data collection procedures are conducted in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. For the purpose of our investigation, we extracted relevant data from the NHANES cross-sectional study conducted between 2005 and 2010. This timeframe encompasses three 2-year cycles (2005–2006, 2007–2008, and 2009–2010), providing a substantial sample size and allowing for the assessment of potential trends over time.
The initial data extraction yielded a total of 31,034 participants. To ensure data quality and focus on the relevant adult population for our study, we applied a series of exclusion criteria. We excluded individuals under 20 years of age (n = 13,902), participants with missing information on key exposure or outcome variables (n = 2,666), and those with incomplete baseline or covariate data (n = 3,942), resulting in a remaining sample of 10,524 participants. To refine the study population and minimize potential confounding factors, we further excluded individuals who were pregnant or had a history of colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease (n = 479). In addition, to account for potential under- or over-nutrition, we excluded participants with extreme energy intake values based on sex-specific cutoffs (male participants: <500 or > 8,000 kcal/day; female participants: <500 or > 5,000 kcal/day) (n = 94) (20). This careful selection process resulted in a final study sample of 9,951 participants, ensuring a focused analysis of the relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation in the general adult population (Figure 1).
2.2 Definition of constipation
To assess participants’ bowel habits and identify potential cases of constipation, we utilized data from the common stool type questions included in the NHANES 2005–2010 bowel health questionnaire (21). This standardized questionnaire provides valuable insights into individuals’ bowel movement patterns and characteristics. Data collection for bowel habits during the three NHANES cycles between 2005 and 2010 employed the Bristol Stool Form Scale (BSFS). The BSFS is a widely recognized and validated tool for classifying stool consistency and form. Participants were presented with colored picture cards depicting seven distinct stool types, along with written descriptors, and were asked to identify the image that most closely resembled their usual stool consistency. This approach allowed for a standardized and visual assessment of bowel habits.
The BSFS categorizes stool into seven distinct types, ranging from Type 1 (characterized by separate hard lumps, resembling nuts) to Type 7 (entirely liquid stool with no solid pieces). Types 1 and 2 represent constipation, with stools that are hard, lumpy, and difficult to pass. Types 3 and 4 are considered normal or ideal stool forms, indicating healthy bowel function. Types 5 to 7 represent increasingly loose stools, potentially indicating diarrhea or other digestive issues. Following established criteria for identifying constipation based on stool form, participants who self-reported BSFS Type 1 or 2 stools were classified as experiencing constipation in our study (22, 23). This approach aligns with common clinical practice and allows for a clear distinction between individuals with and without constipation for the purpose of analysis.
2.3 Vitamin E intake assessment
The collection and processing of dietary intake data for NHANES participants involved a collaborative effort between NHANES, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), and the United States Department of Health & Human Services. This collaboration ensured the accuracy and reliability of the dietary information gathered from participants. To assess vitamin E intake, participants completed two 24-h dietary recall interviews. The first interview was conducted in person at a Mobile Exam Center (MEC), where trained interviewers used standardized protocols to collect detailed information about all foods and beverages consumed by participants during the previous 24-h period. A second interview, conducted by telephone 3 to 10 days later, aimed to capture additional dietary data and enhance the accuracy of intake estimates. It is important to note that NHANES participants did not receive standardized training in food portion size estimation. Given the potential for measurement errors and recall bias associated with 24-h dietary recall, particularly for the second interview conducted remotely, we opted to utilize dietary data solely from the first in-person interview for our analysis (24). This approach prioritized the accuracy and reliability of the dietary intake data used in our study. Our analysis focused specifically on dietary vitamin E intake obtained from food sources and did not account for any vitamin E intake from dietary supplements.
2.4 Covariates
To account for potential confounding variables and obtain more accurate estimates of the association between vitamin E intake and constipation, our study incorporated a comprehensive range of covariates reflecting demographic, socioeconomic, lifestyle, and health-related factors. These covariates included age, sex, race, marital status, body mass index (BMI), alcohol consumption, smoking status, education level, family poverty income ratio, and physical activity. Sex was categorized into two groups (male and female); race was classified as non-Hispanic white, Mexican American, non-Hispanic Black, other Hispanic, and other; marital status was divided into widowed/divorced/separated, never married, and married/living with a partner; education level included less than high school (completed grade 9 or less than 9–11 grades), high school or equivalent (high school graduate/GED or equivalent), and more than high school (some college or associate degree and college graduate or above). To assess the impact of socioeconomic status, we categorized the family poverty income ratio, a measure of household income relative to the federal poverty threshold, into three groups: less than 1.3, indicating greater financial hardship; between 1.3 and 3.5, representing moderate income; and greater than 3.5, signifying higher income levels (25). BMI was categorized into four groups: underweight (<18.5), normal (18.5 to <25), overweight (25 to <30), and obese (30+). Smoking status was classified as never, former, and current smokers based on whether they had smoked 100 cigarettes in their lifetime: “Never smokers” referred to individuals who had smoked less than 100 cigarettes in their lifetime, “current smokers” were those who currently smoke, and “former smokers” were those who had smoked more than 100 cigarettes in their lifetime but did not currently smoke (26). Alcohol consumption was categorized as follows: never, for individuals who had consumed less than 12 drinks in their lifetime; former, for those who had consumed at least 12 alcoholic drinks in their lifetime but less than 12 drinks in the past year; current, for those who had consumed more than 12 alcoholic drinks in the past year (27). The definition of vigorous physical activity underwent modifications across different survey cycles. During the 2005–2006 cycle, vigorous physical activity was characterized as engaging in any intense activities for a minimum of 10 min that resulted in heavy sweating, or large increases in breathing or heart rate within the preceding 30 days. For the 2007–2010 period, individuals were considered to have participated in vigorous physical activity if they responded ‘yes’ to the following query: ‘Work involves vigorous-intensity activities that cause significant increases in breathing or heart rate, such as carrying or lifting heavy loads, digging, or construction work for at least 10 min continuously’ (28). In addition, health risk factors, including diabetes, hypertension, and depression, were also considered. By including these health factors as covariates, we aimed to obtain a more precise estimation of the independent association between vitamin E intake and constipation.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Recognizing the complex sampling design employed by NHANES, we meticulously weighted the data to ensure accurate and representative results. Following NHANES guidelines, we applied appropriate weights, specifically one-third of the 2005–2010 weights, to account for the sampling methodology and obtain unbiased estimates. The normality of quantitative data was tested using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. For baseline characterization, continuous variables with normal distributions were expressed as means with standard deviations (SD), whereas continuous variables with skewed distributions were expressed as medians with interquartile ranges (IQRs). Categorical variables are presented as frequencies and percentages. For normally distributed continuous variables, we utilized Student’s t-test to compare group means and assess statistically significant differences between groups, and comparisons among the multiple groups were facilitated through the application of analysis of variance (ANOVA). For variables exhibiting skewed distributions, we employed the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, a non-parametric alternative to the t-test suitable for non-normal data. Categorical variables were analyzed using the chi-square test, allowing us to examine the association between different categories and identify potential statistically significant differences in proportions. Given the skewed distribution observed in vitamin E intake levels, we applied a natural log transformation to normalize the data. This transformation, resulting in the variable Log vitamin E, allowed for the application of parametric statistical methods that assume normality. For further analysis, we categorized Log vitamin E into quartiles, creating four groups based on intake levels. Prior to the multivariable analyses, we conducted weighted univariate logistic regression analyses for each covariate to assess its individual association with constipation. Weighted logistic regression analysis was applied to investigate the association between vitamin E intake and constipation. The results are presented as odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). In Model 1, no covariates were adjusted. Model 2 adjusted for age, sex, race, education level, marital status, and income level. Model 3 further adjusted for BMI, depression, diabetes, hypertension, and other confounding factors based on Model 2. In addition, a trend test (p for trend) was conducted by entering quartiles of vitamin E intake as a continuous variable and re-running the corresponding regression models. Subgroup analyses were performed stratified by all confounding factors. The p-value for interaction was used to determine whether the stratified effect was significant. Furthermore, restricted cubic spline (RCS) regression with four knots adjusted for all confounding variables was employed to examine the linear/non-linear relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation. If the association was non-linear, the inflection point of vitamin E intake, the value at which a change in the curve is observed, was sought. All statistical analyses and data processing were conducted using R version 4.3.1,1 a widely used statistical software package. Following conventional statistical practice, a two-tailed p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of participants
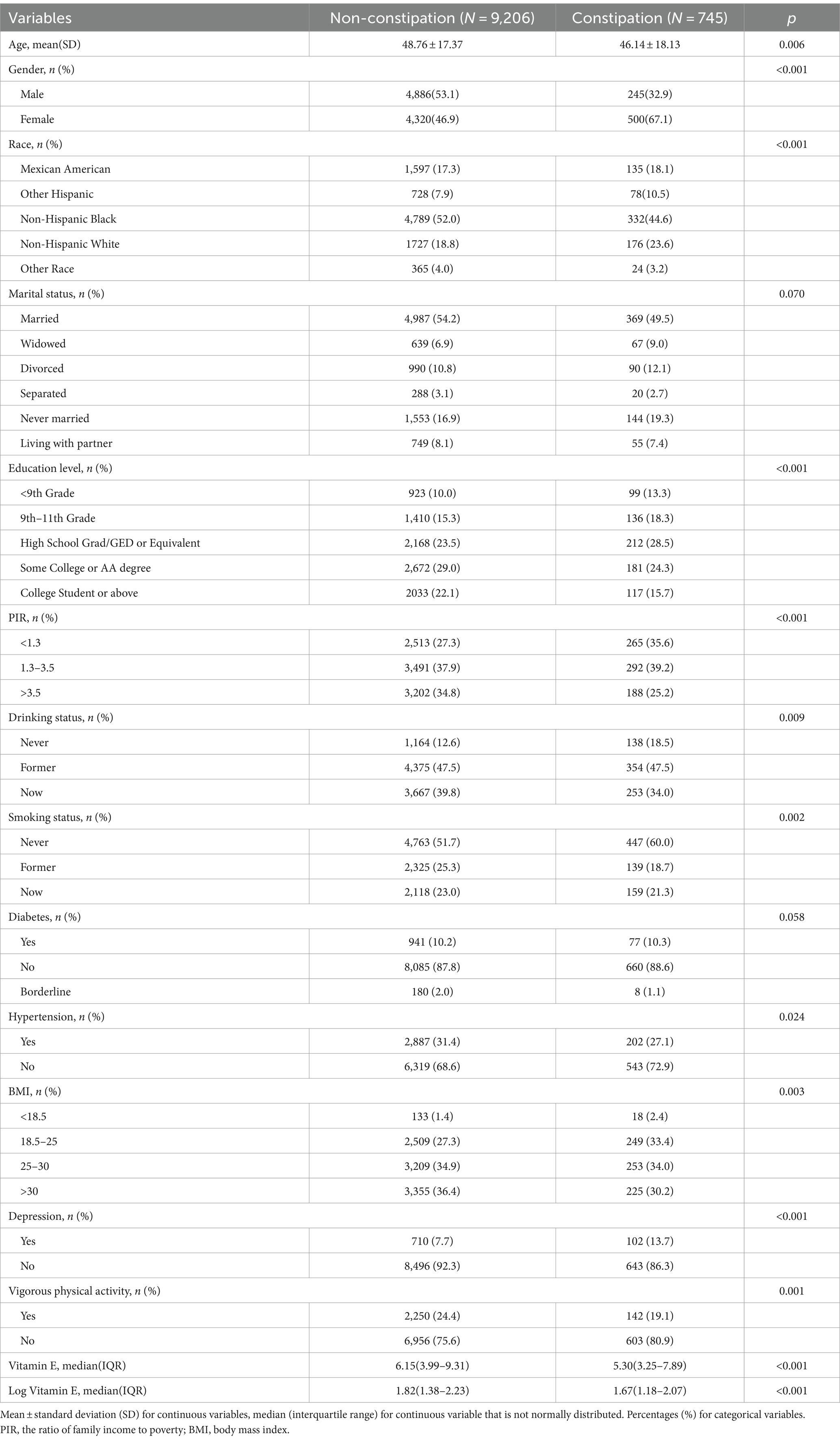
This study included a total of 9,951 individuals between the ages of 20 and 85 years. Table 1 presents the characteristics of the stratified study population based on quartiles of vitamin E intake from the 2005–2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The analysis revealed significant differences between vitamin E intake levels and various factors. Among demographic characteristics, gender and race were significantly correlated with vitamin E intake levels (p < 0.05). Vitamin E intake also showed significant differences across other variables including education level, marital status, poverty income ratio, smoking status, alcohol consumption status, diabetes, and depression (p < 0.05).
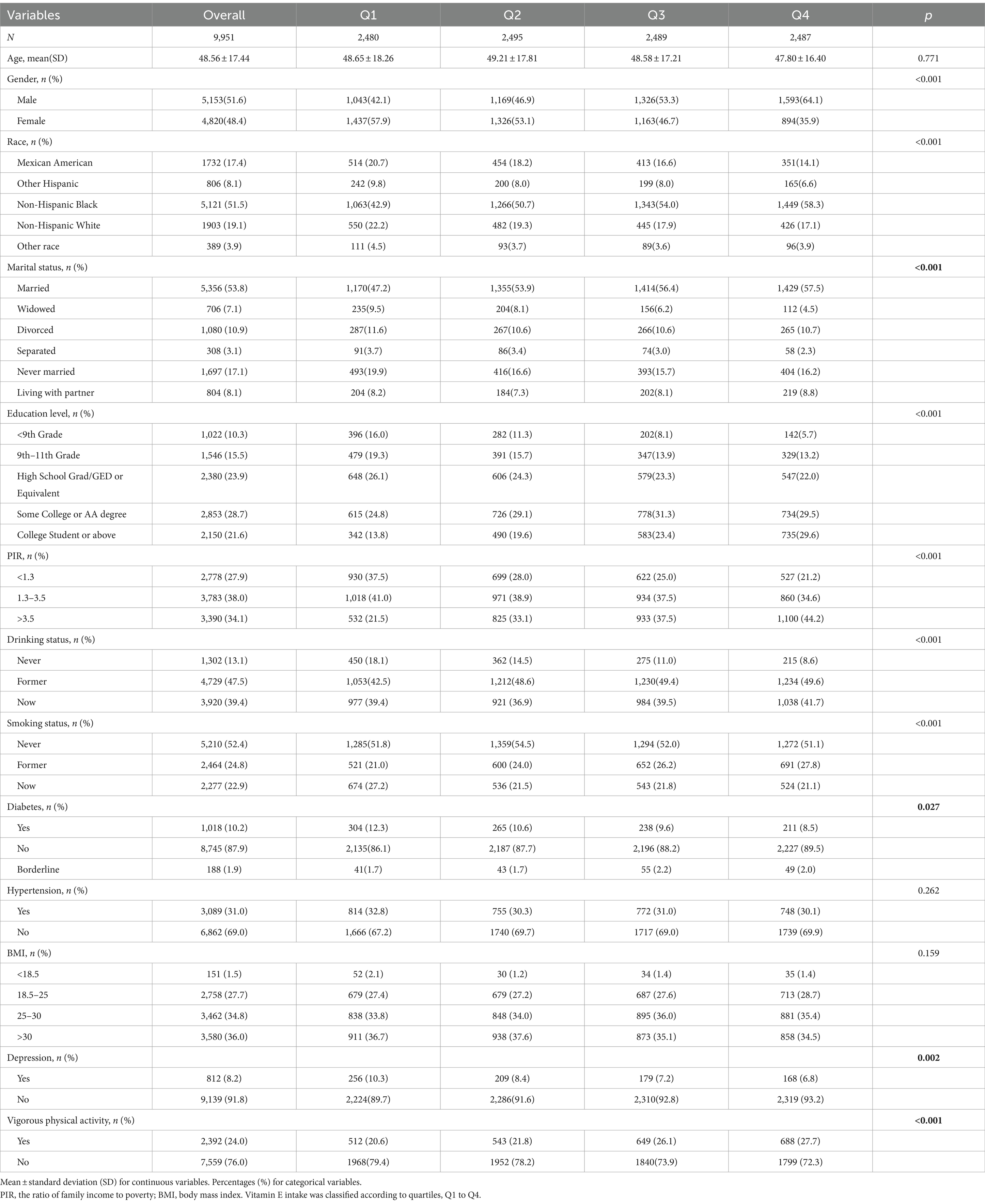
Table 1. Characteristics of the 99,51 participants from the NHANES 2005–2010 study were analyzed based on their serum vitamin E intake levels.
Table 2 displays the characteristics of the participants according to constipation status (constipated vs. non-constipated). Among them, 745 individuals were identified as having constipation. When comparing the characteristics of constipated and non-constipated individuals, we observed several notable differences. The proportion of female participants was significantly higher in the constipation group compared to the non-constipation group (p < 0.05). In addition, we observed a statistically significant difference in vitamin E intake between the two groups. Participants with constipation had significantly lower vitamin E intake compared to those without constipation symptoms (p < 0.05). The median vitamin E intake for participants with constipation symptoms was 5.30 mg/day (interquartile range: 3.25–7.89 mg/day), while for those without constipation symptoms, it was 6.15 mg/day (interquartile range: 3.99–9.31 mg/day). Due to the skewed distribution of vitamin E intake among participants, a natural log transformation was applied to vitamin E intake for better subsequent analysis. The results indicated that even after the log transformation, a significant difference in vitamin E intake persisted between individuals with and without constipation.
3.2 Association between vitamin E intake and the risk of constipation
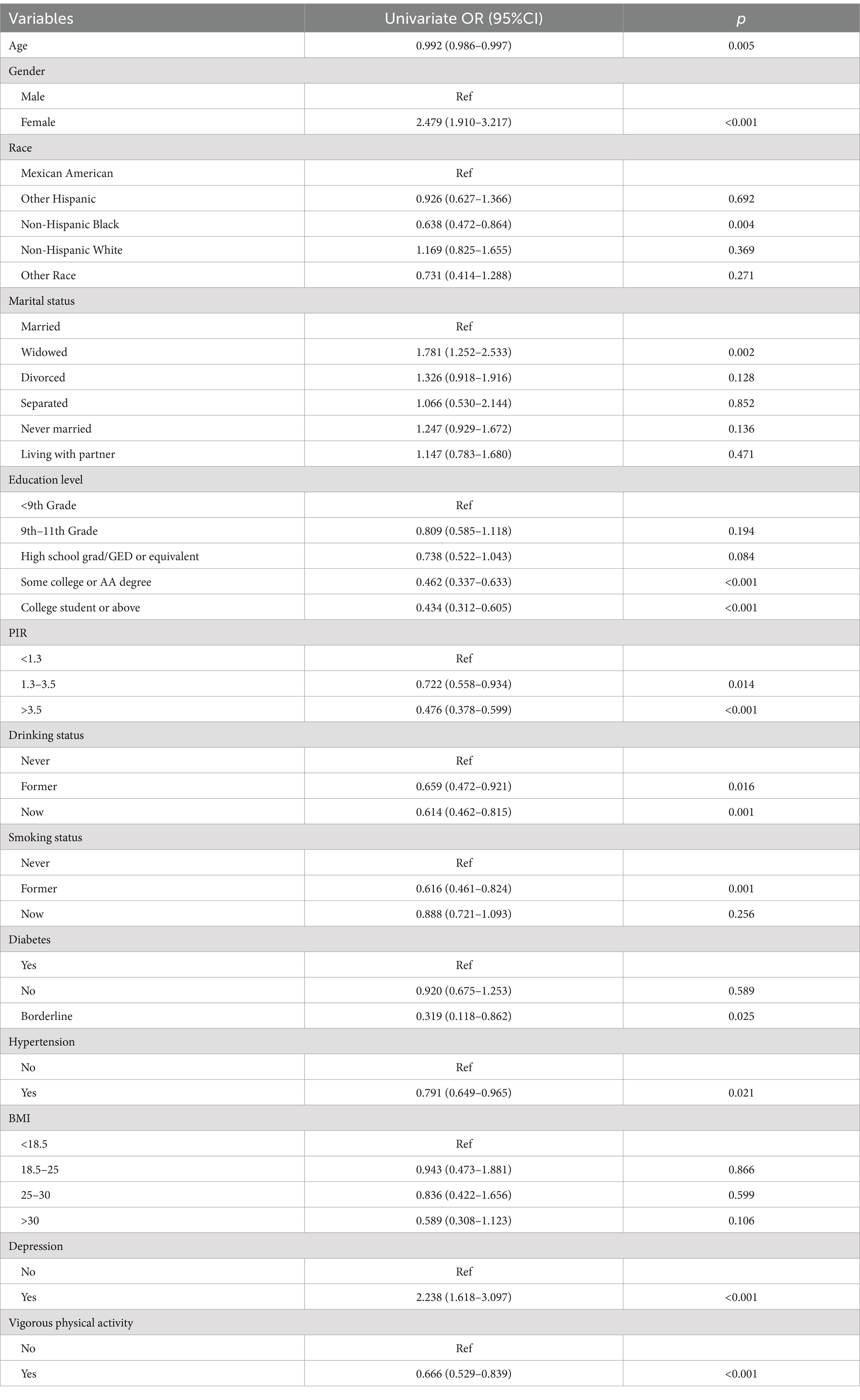
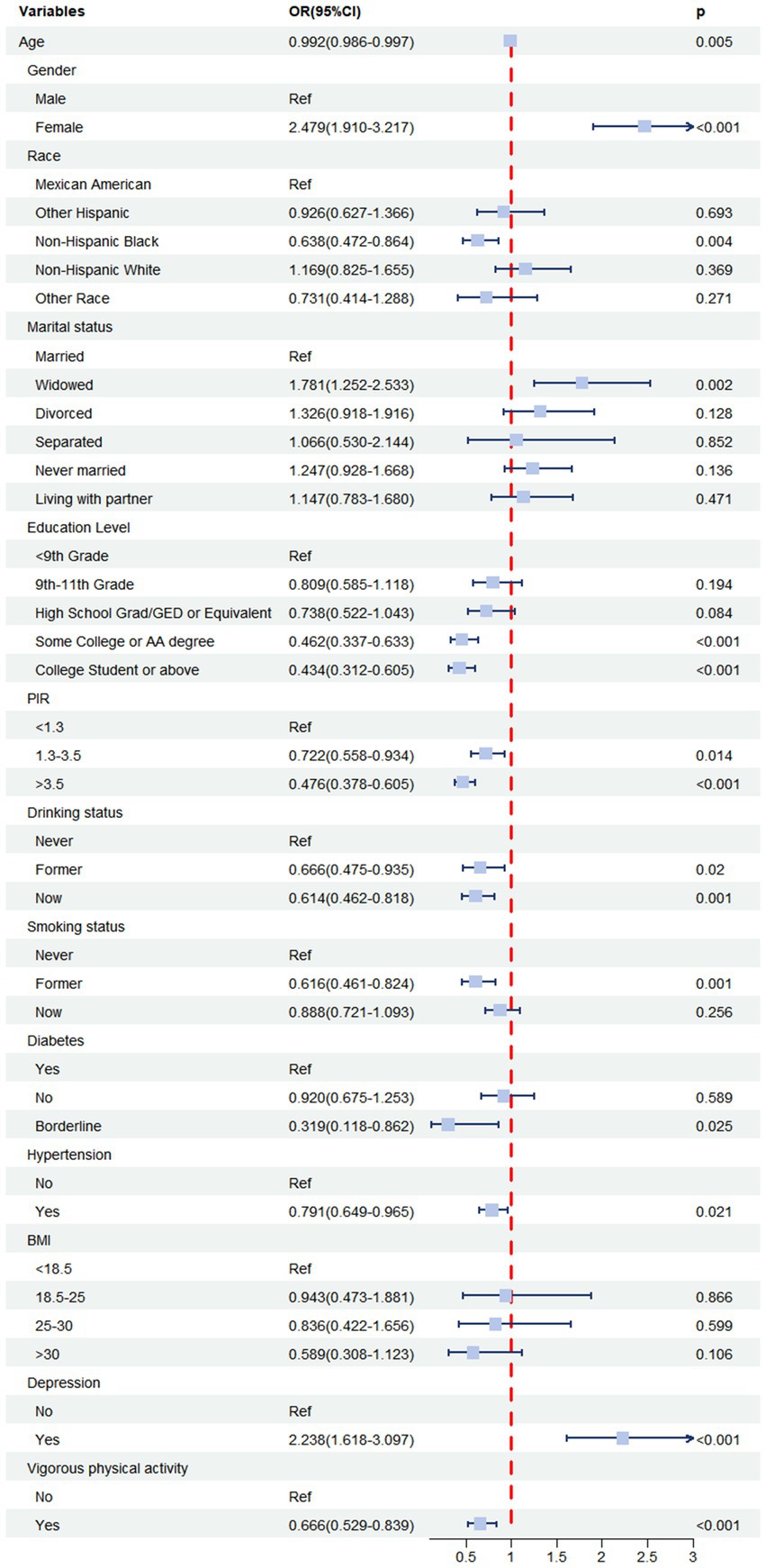
Prior to the multivariable analyses, we conducted weighted univariate logistic regression analyses for each covariate to assess its association with constipation (Table 3 and Figure 2). We found that female participants had a significantly higher risk of constipation compared to male participants (OR = 2.479, 95% CI: 1.910–3.217, p < 0.001), while individuals with higher education levels exhibited a lower risk of constipation compared to those with lower education levels. Similarly, higher income was associated with a lower risk of constipation compared to lower income. In addition, individuals with depression had a significantly higher risk of constipation compared to those without depression (OR = 2.238, 95% CI: 1.618–3.097, p < 0.001).
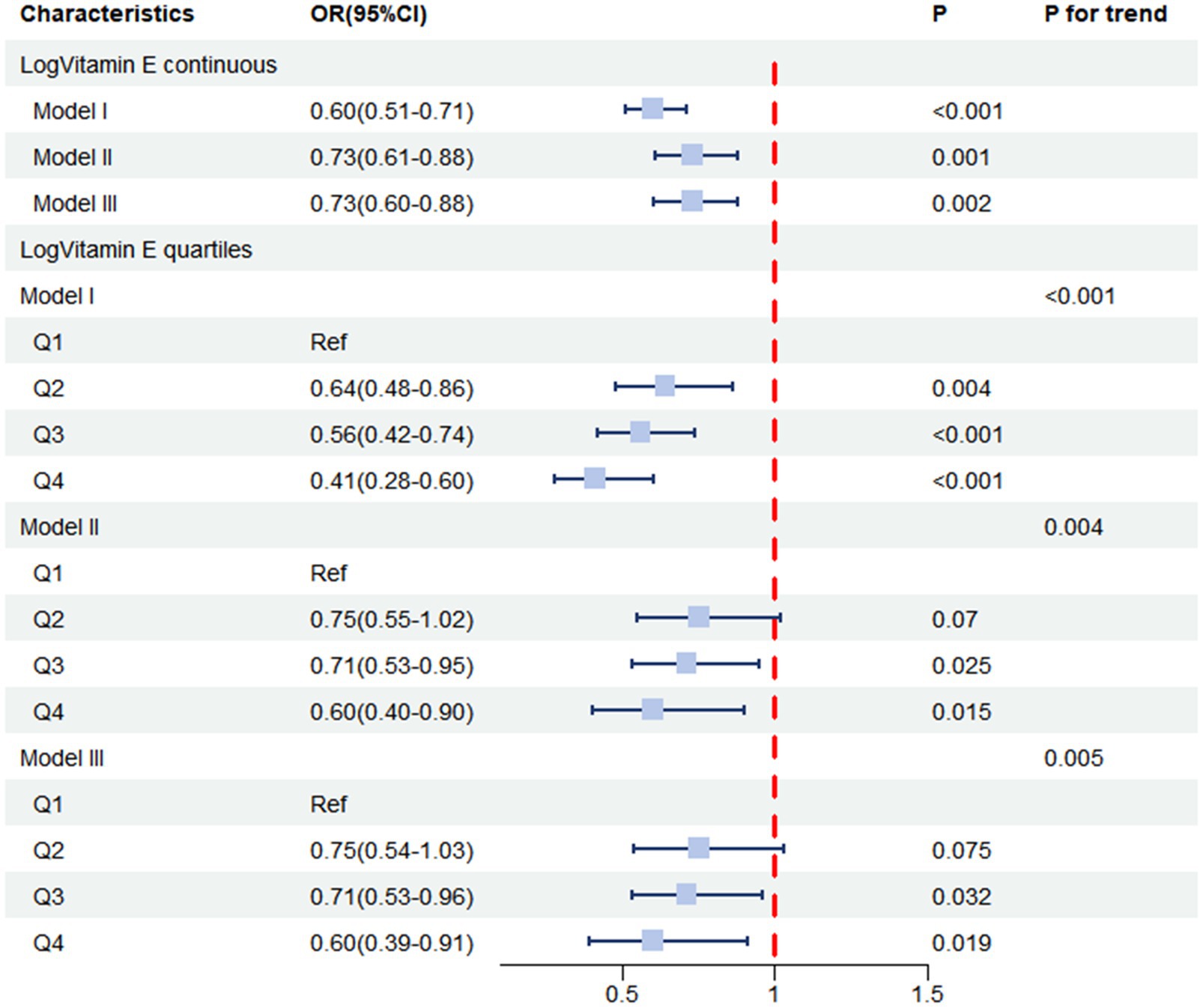
We then performed multivariable logistic regression analyses (Table 4 and Figure 3), where Model 1 was unadjusted for any factors, while Model II was adjusted for basic characteristics including age, race, sex, marital status, income level, and education level. Model III was further adjusted for all potential confounders. The results of the weighted logistic regression analyses indicated that higher vitamin E levels were associated with a lower risk of constipation. When examining the continuous form of Log Vitamin E, Model I, which did not adjust for any covariates, revealed a strong negative association between vitamin E intake and constipation risk (OR = 0.60, 95% CI: 0.51–0.71, p < 0.001). This association persisted even after adjusting for demographic and socioeconomic factors in Model II (OR = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.61–0.88, p = 0.001) and remained robust after further adjustment for all potential confounders in Model III (OR = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.60–0.88, p = 0.002). These findings highlight the independent nature of the association between vitamin E intake and constipation risk, suggesting that it is not solely explained by other factors considered in the analysis. Based on the results from Model III, we estimated that for each unit increase in Log Vitamin E intake, the odds of experiencing constipation decreased by 27%, providing a quantifiable measure of the protective effect associated with higher vitamin E intake.
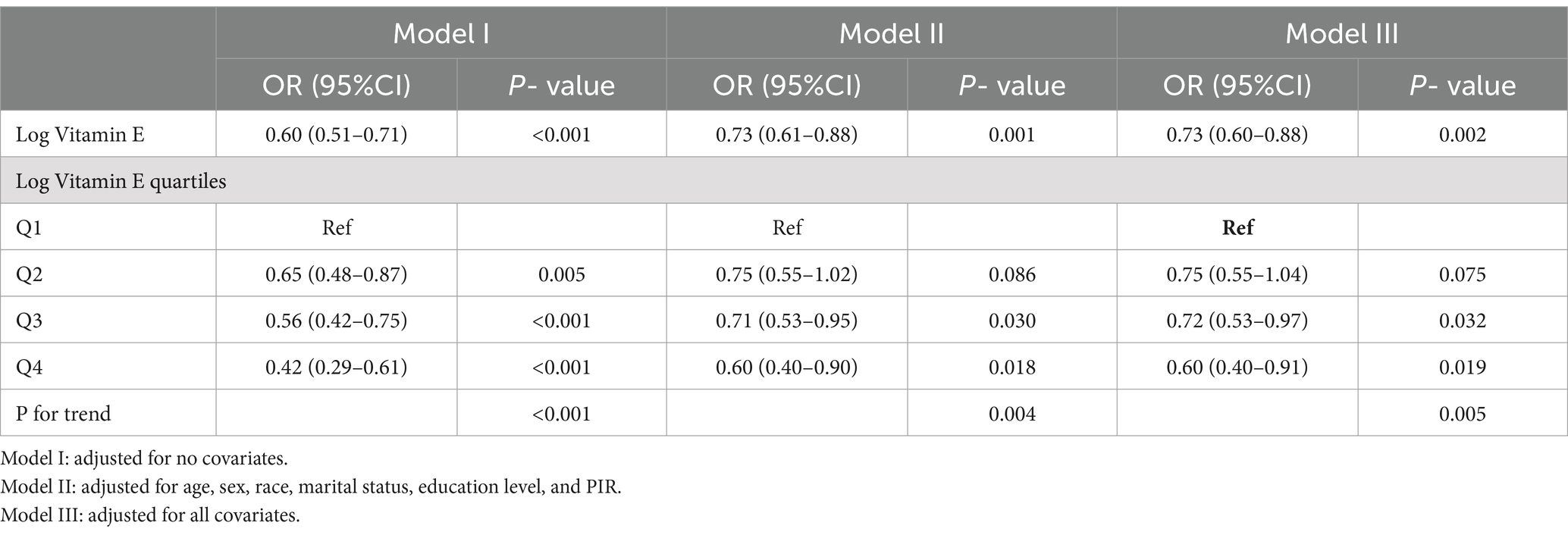
Table 4. Weighted logistic regression of the association between log Vitamin E intake and constipation.
For sensitivity analysis, we stratified Log vitamin E from continuous form into quartile form. From the fully adjusted model, the group in the highest quartile of Log vitamin E exhibited a lower risk of constipation compared to the group in the lowest quartile (OR = 0.60, 95% CI: 0.39–0.91, p = 0.019). Similar results were observed in the unadjusted model (Model I) and the partially adjusted model (Model II). Trend analysis revealed a decreasing trend in the association between Log vitamin E and constipation (P for trend <0.001 in the unadjusted model, P for trend = 0.004 in Model II, and P for trend = 0.005 in Model III).
3.3 Subgroup analysis
To assess the potential effect of modification of Log vitamin E intake on constipation, stratified analyses were conducted, including various subgroups. The results of these analyses are presented in the forest plot in Figure 4. The results revealed that the association between Log vitamin E intake and constipation risk was generally significant across multiple subgroups. In the interaction analysis, we examined potential differences in the association between Log vitamin E intake and constipation risk across various subgroups. Our comprehensive analysis did not reveal any statistically significant interactions (all p-values for interaction >0.05). This suggests that the relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation risk is relatively consistent across the different groups in our study population.
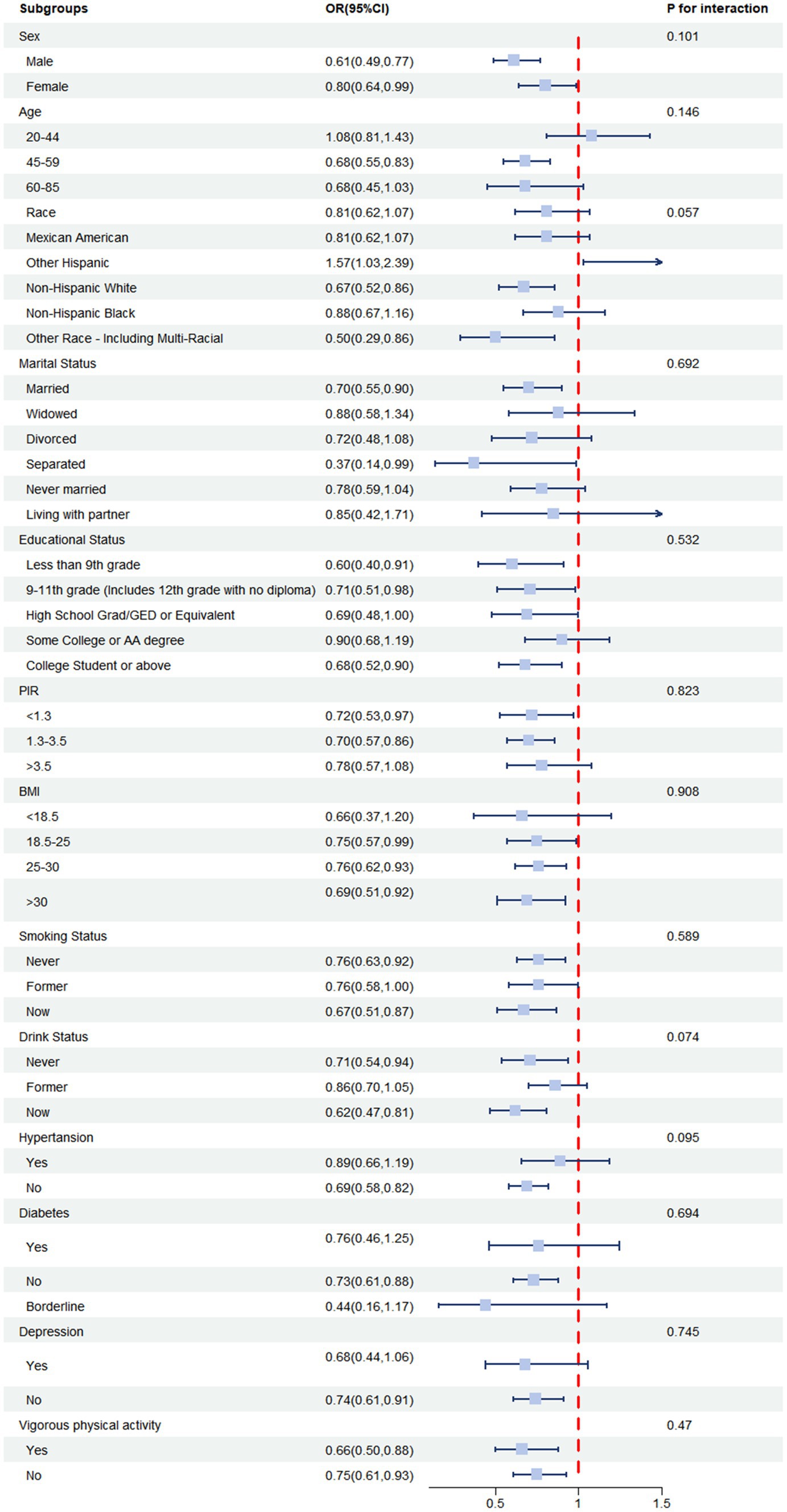
Figure 4. ORs (95% CI) from multiple logistic regression analysis models of associations between Log vitamin E intake and risk of constipation in different subgroups.
3.4 Dose–response relationship between log vitamin E intake and risk of constipation
To gain a deeper understanding of the nature of the association between Log vitamin E intake and constipation risk, we employed restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis. This flexible statistical technique allowed us to visually explore the potential for both linear and non-linear relationships while accounting for the influence of confounding variables. We utilized four knots in the RCS model, strategically placed to capture potential changes in the direction or magnitude of the association across the range of Log vitamin E intake values (Figure 5). The RCS curve visually depicted a clear and consistent pattern, demonstrating a steady decrease in constipation risk as Log vitamin E intake increased. In the unadjusted RCS model, the p-value for the non-linear relationship was less than 0.05, with an overall p-value <0.001, suggesting a non-linear relationship between Log vitamin E intake and constipation risk as statistically significant evidence of non-linearity was found. Similar conclusions were drawn in Model II, with partial adjustment for confounders, and Model III, with full adjustment for confounders, enhancing the robustness of the results.

Figure 5. (A) RCS plot adjusted for no covariates. (B) RCS plot adjusted for age, sex, race, marital status, education level, and PIR. (C) RCS plot adjusted for all covariates.
4 Discussion
To our knowledge, this investigation represents the pioneering exploration of the association between vitamin E intake and constipation within the adult population. We established inclusion and exclusion criteria and ultimately included a total of 9,951 United States adults to investigate the association between vitamin E intake and constipation. Participants with constipation had lower vitamin E intake levels compared to non-constipated participants. Lower vitamin E intake levels were associated with a higher risk of constipation. Subgroup analyses did not reveal any potential interactions between the variables of subgroups and the association between vitamin E intake and constipation risk. This may suggest that the relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation risk is relatively consistent across different demographic groups in our study population. In addition, RCS curve analysis indicated a non-linear relationship between Log vitamin E intake levels and constipation risk. Therefore, supplementation of vitamin E intake appears to significantly contribute to the prevention of constipation. In terms of demographic characteristics, our findings indicated that female participants (29), individuals with normal or lower BMI (30), and those with low-to-middle income levels (31) tend to have a higher prevalence of constipation. Our study also found that individuals engaging in vigorous physical activity had a lower incidence of constipation (28), which aligns with previous research findings.
Vitamin E plays a crucial role in human health, acting as an essential fat-soluble nutrient with diverse biological functions. As it cannot be synthesized by the human body, vitamin E must be obtained through dietary sources. Fortunately, vitamin E is abundant in various foods, including nuts, seeds, vegetable oils (such as coconut, maize, palm, and olive oils), green leafy vegetables, and fortified food products (32). Vitamin E deficiency is generally considered rare. According to the Office of Dietary Supplements of the National Institutes of Health (33), the recommended daily dietary intake for adults is 15 mg of α-tocopherol (equivalent to 22.4 or 33.3 IU of natural or synthetic α-tocopherol, respectively). The relationship between constipation and vitamin E is not yet fully understood. A case–control study conducted in Malaysia on the dietary patterns of IBS-C patients found that dietary vitamin E intake was significantly lower in IBS-C patients compared to healthy individuals (34). Zhou et al. conducted a randomized controlled trial with 70 children with chronic constipation and 70 age- and sex-matched healthy children, which included measuring plasma vitamin E levels. The results showed that plasma vitamin E levels in children with chronic constipation were significantly lower than those in healthy children (35). These findings are consistent with the conclusions of this article, further validating our research hypothesis.
However, the biological mechanisms underlying this potential association remain unclear. A review suggests that the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidative stress plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis and progression of many diseases, including intestinal diseases. Excessive ROS can lead to damage to cellular structures and molecules such as lipids, proteins, and DNA, ultimately resulting in intestinal diseases (36–38). Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) play a critical role in regulating intestinal motility by acting as pacemaker cells within the intestinal smooth muscle. Oxidative stress can disrupt ICC function and promote apoptosis (cell death), leading to impaired intestinal motility and potentially contributing to the development of constipation (39). In a mouse model of postoperative intestinal obstruction, surgical manipulation can lead to increased oxidative stress levels in intestinal tissues. Oxidative stress can damage intestinal tissues, including mucosa and muscularis, leading to intestinal motility dysfunction. Moreover, oxidative stress can activate inflammatory signaling pathways such as the MAPK signaling pathway, promoting the release of inflammatory mediators and infiltration of leukocytes, exacerbating intestinal inflammation and further aggravating intestinal obstruction (40). Several studies have shown that children with chronic constipation have underlying oxidative stress, manifested by decreased antioxidant levels and increased lipid peroxidation levels. This oxidative imbalance may be associated with intestinal dysfunction and increased toxin absorption and may exacerbate constipation symptoms (35, 41). As an important antioxidant, vitamin E plays a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative damage. It effectively scavenges harmful free radicals, neutralizing their damaging effects and preventing oxidative stress-induced cellular injury (42–44). Given the established role of oxidative stress in constipation and the antioxidant properties of vitamin E, we hypothesize that vitamin E may contribute to alleviating constipation symptoms by mitigating oxidative stress within intestinal tissues, thereby protecting the intestinal barrier and promoting healthy bowel motility. This potential mechanism warrants further investigation to fully elucidate the protective effects of vitamin E in the context of constipation.
Beyond its antioxidant capacity, vitamin E may also exert beneficial effects on gut health by influencing the composition and function of the gut microbiota. Studies suggest that vitamin E can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria within the gut, enhance the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and strengthen the intestinal barrier, collectively contributing to improved digestive health (45, 46). The gut microbiota plays a vital role in influencing intestinal motility. Some potential mechanisms include the following: the gut microbiota and its metabolites (such as short-chain fatty acids and tryptophan metabolites) influence enteric nervous system function through Toll-like receptors and serotonin signaling pathways, thereby regulating intestinal motility (47). Certain bacteria are involved in the deconjugation and dehydroxylation of primary bile acids, producing secondary bile acids. Secondary bile acids can activate TGR5 receptors, regulating intestinal motility and secretion (48). Dysbiosis, an imbalance in the gut microbiota composition, has been observed in individuals with constipation. Studies have reported a decrease in the abundance of Prevotella genus and an increase in certain Firmicutes genera within the gut microbiota of constipation patients compared to healthy controls (49).
Based on the collective evidence from our study and existing research, we propose that vitamin E may hold promise in alleviating constipation symptoms through its antioxidant properties and its ability to modulate the gut microbiota. To substantiate these hypotheses and establish a more definitive link between vitamin E and constipation management, further research, including well-designed intervention studies and mechanistic investigations, is warranted. These future studies will contribute valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of vitamin E for constipation and guide evidence-based recommendations for dietary and supplementation strategies.
In summary, to our knowledge, our study is the first to investigate the relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation in the entire adult population (from young adults to older adults). This study has several strengths. First, the study population came from the NHANES study, with a nationally representative sample, providing a sufficient basis for the research findings. Second, we considered various potential confounders to better estimate the association between vitamin E intake and constipation. However, it is crucial to acknowledge several important limitations of this study. First and foremost, the cross-sectional nature of this study precludes any causal inference regarding the relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation. While we observed an association, we cannot determine whether increased vitamin E intake leads to reduced constipation or if individuals with less constipation tend to have diets higher in vitamin E. This limitation is inherent to cross-sectional studies and highlights the need for longitudinal research to establish any potential causal relationship (50). Second, our reliance on dietary recalls may not accurately capture the participants’ usual vitamin E intake. While this method is commonly used in large-scale nutritional studies due to its feasibility, it has limitations in representing long-term dietary patterns. Day-to-day variations in diet and potential recall bias could lead to misclassification of vitamin E intake levels. This limitation may affect the precision of our estimates and potentially attenuate the observed associations. Future studies could benefit from using more comprehensive dietary assessment methods, such as food frequency questionnaires or multiple 24-h recalls over an extended period, to better represent habitual vitamin E intake.
Third, random measurement error is inevitable in dietary recall data and may bias the results. This measurement error could potentially lead to an underestimation of the true association between vitamin E intake and constipation. Finally, due to differences in genetic background, metabolism, and vitamin E intake levels, the United States findings may not be generalizable to other populations. This limits the external validity of our results and underscores the need for similar studies in diverse populations. Despite these limitations, our study provides valuable initial insights into the potential relationship between vitamin E intake and constipation. To address these limitations, future research should prioritize longitudinal study designs to establish causality, employ more comprehensive dietary assessment methods to accurately capture long-term vitamin E intake, and investigate this relationship in diverse populations.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we observed a negative association between vitamin E intake and constipation among United States adults. This may suggest a potential role for vitamin E in the prevention and management of constipation. Further research is warranted to confirm the potential benefits of adequate vitamin E intake in mitigating constipation and elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found at: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
JC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Resources, Investigation. DL: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RX: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft. XY: Supervision, Writing – original draft. YW: Supervision, Writing – original draft. FS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Chongqing City Science and Health Joint Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project (2024ZYYB026), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82074442).
Acknowledgments
We extend our sincere appreciation to the National Center for Health Statistics team within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and to every participant in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Camilleri, M, Ford, AC, Mawe, GM, Dinning, PG, Rao, SS, Chey, WD, et al. Chronic constipation. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2017) 3:17095. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.95
2. Salari, N, Ghasemianrad, M, Ammari-Allahyari, M, Rasoulpoor, S, Shohaimi, S, and Mohammadi, M. Global prevalence of constipation in older adults: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Wien Klin Wochenschr. (2023) 135:389–98. doi: 10.1007/s00508-023-02156-w
3. McCrea, GL, Miaskowski, C, Stotts, NA, Macera, L, and Varma, MG. A review of the literature on gender and age differences in the prevalence and characteristics of constipation in North America. J Pain Symptom Manag. (2009) 37:737–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2008.04.016
4. Wainwright, M, Russell, AJ, and Yiannakou, Y. Challenging the biopsychosocial model in a chronic constipation clinic. Qual Health Res. (2011) 21:1643–57. doi: 10.1177/1049732311416824
5. Mearin, F, Ciriza, C, Minguez, M, Rey, E, Mascort, JJ, Pena, E, et al. Clinical practice guideline: irritable bowel syndrome with constipation and functional constipation in the adult. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. (2016) 108:332–63. doi: 10.17235/reed.2016.4389/2016
6. Wang, C, Zhang, L, and Li, L. Association between selenium intake with chronic constipation and chronic diarrhea in adults: findings from the National Health and nutrition examination survey. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2021) 199:3205–12. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02451-x
7. Dupont, C, and Hebert, G. Magnesium sulfate-rich natural mineral waters in the treatment of functional constipation-a review. Nutrients. (2020) 12:52. doi: 10.3390/nu12072052
8. Zhao, X, Wang, L, and Quan, L. Association between dietary phosphorus intake and chronic constipation in adults: evidence from the National Health and nutrition examination survey. BMC Gastroenterol. (2023) 23:24. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02629-8
9. Rollet, M, Bohn, T, and Vahid, FOn Behalf of the Oriscav Working Group. Association between dietary factors and constipation in adults living in Luxembourg and taking part in the Oriscav-lux 2 survey. Nutrients. (2021) 14:10122. doi: 10.3390/nu14010122
10. Yurtdas, G, Acar-Tek, N, Akbulut, G, Cemali, O, Arslan, N, Beyaz Coskun, A, et al. Risk factors for constipation in adults: a cross-sectional study. J Am Coll Nutr. (2020) 39:713–9. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2020.1727380
11. Panarese, A, Pesce, F, Porcelli, P, Riezzo, G, Iacovazzi, PA, Leone, CM, et al. Chronic functional constipation is strongly linked to vitamin D deficiency. World J Gastroenterol. (2019) 25:1729–40. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i14.1729
12. Burton, GW. Vitamin E: Molecular and Biological Function. Proc Nutr Soc. (1994) 53:251–62. doi: 10.1079/pns19940030
13. Niki, E. Role of vitamin E as a lipid-soluble Peroxyl radical scavenger: in vitro and in vivo evidence. Free Radic Biol Med. (2014) 66:3–12. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.03.022
14. Wagner, BA, Buettner, GR, and Burns, CP. Vitamin E slows the rate of free radical-mediated lipid peroxidation in cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. (1996) 334:261–7. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1996.0454
15. Wu, Q, Luo, Y, Lu, H, Xie, T, Hu, Z, Chu, Z, et al. The potential role of vitamin E and the mechanism in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Food Secur. (2024) 13:898. doi: 10.3390/foods13060898
16. Gothandapani, D, and Makpol, S. Effects of vitamin E on the gut microbiome in ageing and its relationship with age-related diseases: a review of the current literature. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:667. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914667
17. Stickel, F, Meydani, M, Wu, D, Bronson, R, Martin, A, Smith, D, et al. Effect of vitamin E supplementation on prostaglandin concentrations in aspirin-induced acute gastric injury in aged rats. Am J Clin Nutr. (1997) 66:1218–23. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/66.5.1218
18. Meydani, SN, Meydani, M, Verdon, CP, Shapiro, AA, Blumberg, JB, and Hayes, KC. Vitamin E supplementation suppresses prostaglandin E1(2) synthesis and enhances the immune response of aged mice. Mech Ageing Dev. (1986) 34:191–201. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(86)90034-5
19. Sarathy, H, Henriquez, G, Abramowitz, MK, Kramer, H, Rosas, SE, Johns, T, et al. Abdominal obesity, race and chronic kidney disease in young adults: results from Nhanes 1999-2010. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0153588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153588
20. Liu, Q, Kang, Y, and Yan, J. Association between overall dietary quality and constipation in American adults: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. (2022) 22:1971. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14360-w
21. Aziz, I, Whitehead, WE, Palsson, OS, Tornblom, H, and Simren, M. An approach to the diagnosis and Management of Rome iv Functional Disorders of chronic constipation. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 14:39–46. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2020.1708718
22. Barberio, B, Judge, C, Savarino, EV, and Ford, AC. Global prevalence of functional constipation according to the Rome criteria: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 6:638–48. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00111-4
23. Sommers, T, Mitsuhashi, S, Singh, P, Hirsch, W, Katon, J, Ballou, S, et al. Prevalence of chronic constipation and chronic diarrhea in diabetic individuals in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. (2019) 114:135–42. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0418-8
24. Zhang, Y, Tan, W, Xi, X, Yang, H, Zhang, K, Li, S, et al. Association between vitamin K intake and depressive symptoms in us adults: data from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (Nhanes) 2013-2018. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1102109. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1102109
25. Jackson, SL, Yang, EC, and Zhang, Z. Income disparities and cardiovascular risk factors among adolescents. Pediatrics. (2018) 142:1089. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-1089
26. Solberg, LI, Asche, SE, Boyle, R, McCarty, MC, and Thoele, MJ. Smoking and cessation behaviors among young adults of various educational backgrounds. Am J Public Health. (2007) 97:1421–6. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2006.098491
27. Tian, Y, Liu, J, Zhao, Y, Jiang, N, Liu, X, Zhao, G, et al. Alcohol consumption and all-cause and cause-specific mortality among us adults: prospective cohort study. BMC Med. (2023) 21:208. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02907-6
28. Wang, J, Kong, W, Liu, M, Wang, Y, Zheng, Y, and Zhou, Y. Association between dietary carotenoids intake and chronic constipation in American men and women adults: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:1597. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16367-3
29. Black, CJ, and Ford, AC. Chronic idiopathic constipation in adults: epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and clinical management. Med J Aust. (2018) 209:86–91. doi: 10.5694/mja18.00241
30. Silveira, EA, Santos, A, Ribeiro, JN, Noll, M, Dos Santos Rodrigues, AP, and de Oliveira, C. Prevalence of constipation in adults with obesity class ii and iii and associated factors. BMC Gastroenterol. (2021) 21:217. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01806-5
31. Johanson, JF, Sonnenberg, A, and Koch, TR. Clinical epidemiology of chronic constipation. J Clin Gastroenterol. (1989) 11:525–36. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198910000-00008
32. Zingg, JM. Vitamin E: an overview of major research directions. Mol Asp Med. (2007) 28:400–22. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2007.05.004
33. Vatassery, GT, Bauer, T, and Dysken, M. High doses of vitamin E in the treatment of disorders of the central nervous system in the aged. Am J Clin Nutr. (1999) 70:793–801. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/70.5.793
34. Shafiee, NH, Razalli, NH, Mokhtar, NM, Tan, E, and Ali, RAR. An evaluation of dietary adequacy among patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome in Malaysia. Intest Res. (2022) 20:124–33. doi: 10.5217/ir.2020.00050
35. Zhou, JF, Lou, JG, Zhou, SL, and Wang, JY. Potential oxidative stress in children with chronic constipation. World J Gastroenterol. (2005) 11:368–71. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i3.368
36. Vona, R, Pallotta, L, Cappelletti, M, Severi, C, and Matarrese, P. The impact of oxidative stress in human pathology: focus on gastrointestinal disorders. Antioxidants (Basel). (2021) 10:201. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020201
37. Peng, X, Yi, X, Deng, N, Liu, J, Tan, Z, and Cai, Y. Zhishi Daozhi decoction alleviates constipation induced by a high-fat and high-protein diet via regulating intestinal mucosal microbiota and oxidative stress. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1214577. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1214577
38. Felemovicius, I, Bonsack, ME, Baptista, ML, and Delaney, JP. Intestinal radioprotection by vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol). Ann Surg. (1995) 222:504–10; discussion 8-10. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199522240-00008
39. Yao, Z, Fu, S, Ren, B, Ma, L, and Sun, D. Based on network pharmacology and gut microbiota analysis to investigate the mechanism of the laxative effect of Pterostilbene on Loperamide-induced slow transit constipation in mice. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:913420. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.913420
40. De Backer, O, Elinck, E, Blanckaert, B, Leybaert, L, Motterlini, R, and Lefebvre, RA. Water-soluble co-releasing molecules reduce the development of postoperative ileus via modulation of Mapk/ho-1 Signalling and reduction of oxidative stress. Gut. (2009) 58:347–56. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.155481
41. Wang, JY, Wang, YL, Zhou, SL, and Zhou, JF. May chronic childhood constipation cause oxidative stress and potential free radical damage to children? Biomed Environ Sci. (2004) 17:266–72.
42. Sacheck, JM, and Blumberg, JB. Role of vitamin E and oxidative stress in exercise. Nutrition. (2001) 17:809–14. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(01)00639-6
43. Pazdro, R, and Burgess, JR. The role of vitamin E and oxidative stress in diabetes complications. Mech Ageing Dev. (2010) 131:276–86. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2010.03.005
44. Shirpoor, A, Barmaki, H, Khadem Ansari, M, Lkhanizadeh, B, and Barmaki, H. Protective effect of vitamin E against ethanol-induced small intestine damage in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. (2016) 78:150–5. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.01.015
45. Roberts, LJ 2nd, Oates, JA, Linton, MF, Fazio, S, Meador, BP, Gross, MD, et al. The relationship between dose of vitamin E and suppression of oxidative stress in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. (2007) 43:1388–93. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.06.019
46. Choi, Y, Lee, S, Kim, S, Lee, J, Ha, J, Oh, H, et al. Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) consumption influences gut microbiota composition. Int J Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 71:221–5. doi: 10.1080/09637486.2019.1639637
47. Pan, R, Wang, L, Xu, X, Chen, Y, Wang, H, Wang, G, et al. Crosstalk between the gut microbiome and colonic motility in chronic constipation: potential mechanisms and microbiota modulation. Nutrients. (2022) 14:704. doi: 10.3390/nu14183704
48. Kwiatkowska, M, and Krogulska, A. The significance of the gut microbiome in children with functional constipation. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2021) 30:471–80. doi: 10.17219/acem/131215
49. Zhu, L, Liu, W, Alkhouri, R, Baker, RD, Bard, JE, Quigley, EM, et al. Structural changes in the gut microbiome of constipated patients. Physiol Genomics. (2014) 46:679–86. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00082.2014
Keywords: Vitamin E, constipation, NHANES, dietary intake, population-based study
Citation: Cai J, Li D, Xie R, Yu X, Wu Y, Sun F and Zhang C (2024) Association between dietary vitamin E intake and constipation: NHANES 2005–2010. Front. Nutr. 11:1426280. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1426280
Edited by:
Mahdi Vajdi, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, IranReviewed by:
Sahar Golpour, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, IranMelika Darzi, Islamic Azad University, Iran
Copyright © 2024 Cai, Li, Xie, Yu, Wu, Sun and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chenxiong Zhang, cxiongzhang@126.com; Feng Sun, 458152220@qq.com
 Junfeng Cai
Junfeng Cai Danqing Li1
Danqing Li1 Chenxiong Zhang
Chenxiong Zhang