- 1School of Nursing, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
- 2Department of Nursing, Xiamen Medical College, Xiamen, China
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Fuzhou Second General Hospital, Fuzhou, China
- 4West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Objective: In this study, our objective was to provide practice recommendations by thoroughly examining lifestyle interventions for adults diagnosed with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). This was achieved through a systematic review of the literature, specifically focusing on lifestyle modification interventions in adults with MASLD.
Methods: The PIPOST (Population, Intervention, Professional, Outcome, Setting, and Type of evidence) framework was used to identify the questions for summarizing evidence. Utilizing the 6S model for the hierarchy of evidence, a computerized search was conducted to retrieve articles pertaining to lifestyle interventions for adults with MASLD from websites such as the UpToDate Clinical Advisor, BMJ Best Practice, JBI Library, Cochrane Library, International Guidelines Library, and PubMed, among others. The available research included clinical decisions, clinical practice guidelines, evidence summaries, systematic evaluation, expert consensus, and expert opinions. Two researchers independently evaluated the methodology of the studies, and evidence was subsequently extracted and grouped thematically. Our review encompassed publications from January 2018 to March 2023.
Results: A total of 26 publications were identified for the final review, consisting of seven guidelines, nine systematic evaluations, and 10 expert consensuses/opinions. From these sources, we derived six themes, 28 pieces of evidence: intervention modalities, diet management, exercise management, weight loss management, personalized management, and multidisciplinary collaboration.
Conclusion: In the management of adults with MASLD, healthcare professionals should embrace a multidisciplinary team approach, adhere to the best available evidence, and develop structured and personalized interventions based on the best evidence for lifestyle modifications.
1 Introduction
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) (1) is the updated term to describe steatotic liver disease associated with metabolic syndrome. This nomenclature was chosen to replace non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) (2, 3). MASLD stands as the most prevalent chronic liver condition globally, boasting a staggering 30% prevalence rate (4). This figure continues to rise annually, underscoring the urgency of addressing this disease as a significant public health concern (5). The escalating incidence of MASLD has been linked to unhealthy lifestyle factors, including sedentary behavior, high-calorie diet intake, and poor dietary balance (6). To date, there are no drugs that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of MASLD, and lifestyle interventions, such as diet and exercise are considered the cornerstone of treatment for patients with MASLD (7). Multiple dietary patterns such as hypocaloric diet (8), Mediterranean diet (9, 10), and intermittent fasting (11) are adopted in the treatment of patients with MASLD, and all of these dietary strategies have shown evidence of benefit in reducing liver fat and inflammation. Physical activity may also provide significant clinical benefits for patients with MASLD/NAFLD (12).
Literature on MASLD and NAFLD in both Chinese and global contexts includes treatment guidelines, systematic reviews, and expert consensuses. However, the existing evidence pertaining to lifestyle interventions is not concise, and the content is not suitable for widespread dissemination. “There is a notable absence of standardized specific measures, focused evidence extraction on the theme of lifestyle interventions, and concise, user-friendly lifestyle practice guidelines for medical professionals and patients dealing with MASLD. Therefore, in this review, we systematically retrieved, extracted, and summarized high-level evidence-based data from both Chinese and international sources. Our objective was to formulate practice recommendations specifically centered around lifestyle interventions for adults diagnosed with MASLD. This study is intended to inspire healthcare professionals to actively engage in lifestyle interventions for adults with MASLD, serving as a valuable evidence-based resource for researchers aiming to develop well-structured lifestyle intervention programs tailored to this population.
2 Materials and methods
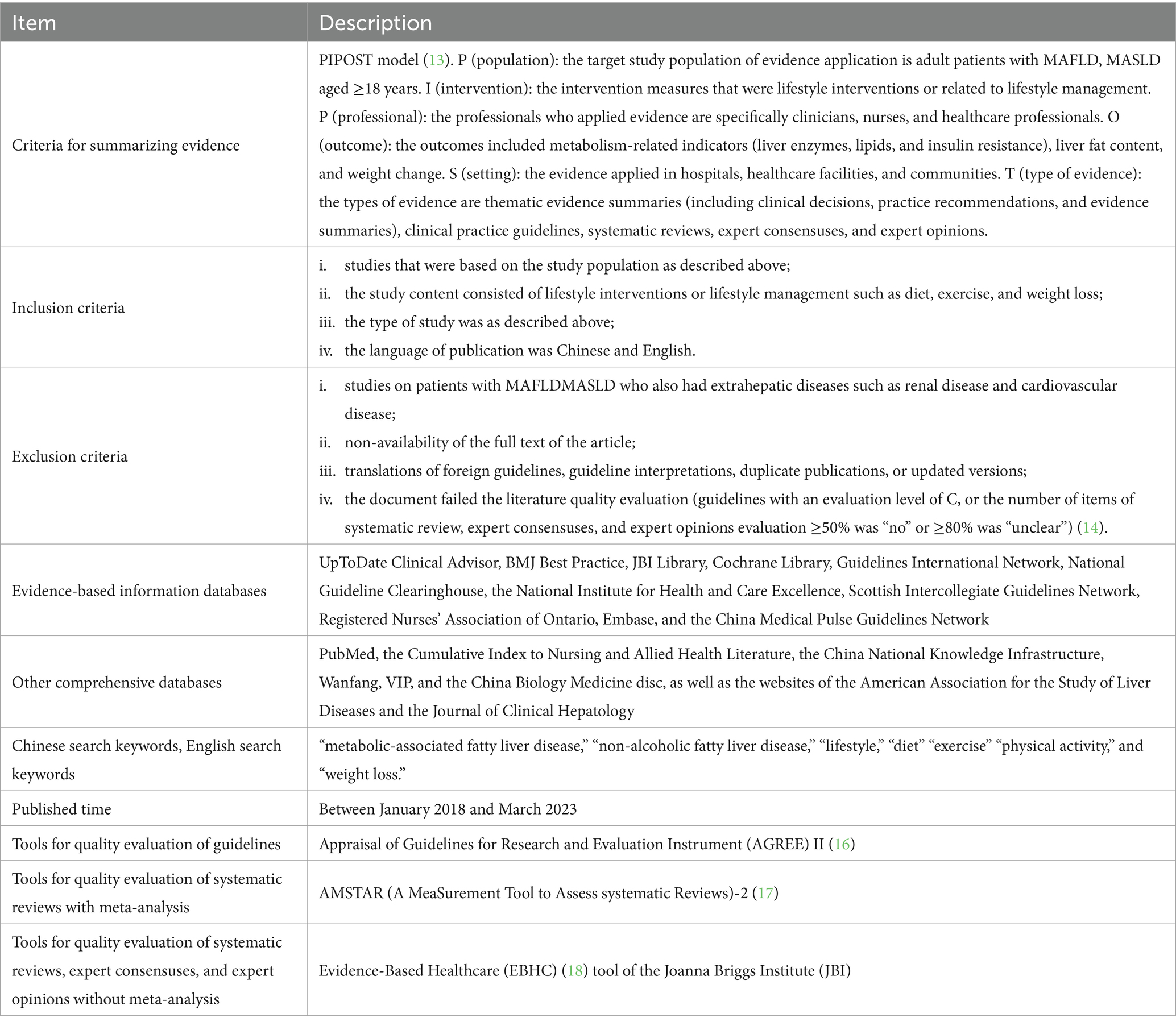
2.1 Criteria for summarizing evidence
We utilized the PIPOST (Table 1) model to identify specific questions for evidence summarization in this study (13).
P (population): The target study population for evidence application consisted of adult patients with MASLD aged 18 years or older.
I (intervention): The intervention measures were focused on lifestyle interventions or those related to lifestyle management.
P (professional): The professionals who applied the evidence were primarily clinicians, nurses, and healthcare professionals.
O (outcome): The outcomes encompassed metabolism-related indicators (such as liver enzymes, lipids, and insulin resistance), liver fat content, and changes in weight.
S (setting): The evidence was applied in various settings, including hospitals, healthcare facilities, and communities.
T (type of evidence): The types of evidence encompassed thematic evidence summaries (comprising clinical decisions, practice recommendations, and evidence summaries), clinical practice guidelines, systematic reviews, expert consensuses, and expert opinions.
This project was registered with the Center for Evidence-Based Nursing, Fudan University (No. ES20231902).
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) studies that were based on the study population as described above; (ii) the study content consisted of lifestyle interventions or lifestyle management such as diet, exercise, and weight loss; (iii) the type of study was as described above; (iv) the language of publication was Chinese or English (Table 1).
The following were the exclusion criteria: (i) studies on patients with MASLD who also had extrahepatic diseases such as renal disease and cardiovascular disease; (ii) non-availability of the full text of the article; (iii) translations of guidelines that were originally not in English or Chinese, guideline interpretations, duplicate publications, or updated versions; (iv) the document failed the literature quality evaluation (guidelines with an evaluation level of C, or the number of items of systematic review, expert consensuses, and expert opinions evaluation ≥50% was “no” or ≥80% was “unclear”) (Table 1) (14).
2.3 Search strategies
Based on the “6S” model of evidence resources (15), we adopted a computerized top-down search of evidence-based information databases such as the UpToDate Clinical Advisor, BMJ Best Practice, JBI Library, Cochrane Library, Guidelines International Network, National Guideline Clearinghouse, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario, Embase, and the China Medical Pulse Guidelines Network. We also additionally searched other comprehensive databases, including PubMed, the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, the China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang, VIP, and the China Biology Medicine disc, as well as the websites of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Journal of Clinical Hepatology (Table 1).
The Chinese search keywords we used were “metabolic-associated fatty liver disease,” “non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,” “lifestyle,” “diet,” “exercise,” and “weight loss.” The English search keywords included “metabolic-associated fatty liver disease,” “non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,” “lifestyle,” “diet,” “exercise,” “physical activity,” and “weight loss.” The search strategy is shown in Appendix 1. We searched for articles published between January 2018 and March 2023 (Table 1).
2.4 Criteria and process for evidence quality evaluation
We used the appropriate tools for quality evaluation based on the type of evidence. (1) For quality evaluation of guidelines, we used the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation Instrument (AGREE) II (Table 1) (16), comprising six domains and 23 items. Each item was evaluated on a scale of 1–7, and the quality score for each domain was obtained. The overall score was then calculated by summing all the domains. The quality of the guidelines was classified into three levels: grade A when all six domain scores were ≥60%; grade B when scores of ≥3 domains were 30–60%; and grade C when scores of >3 domains were <30%.
(2) For evaluating the quality of systematic reviews with meta-analysis, we used the AMSTAR (A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews)-2 (Table 1) (17), which consists of 16 items, of which the responses to seven key items (items 2, 4, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13, and 15) were “yes,” “partially yes,” and “no.” The quality of the evaluation was classified as “high,” “moderate,” “low,” and “critically low.”
(3) We used the Evidence-Based Healthcare (EBHC) (18) tool of the Joanna Briggs Institute (Table 1) (JBI) to evaluate the quality of systematic reviews, expert consensuses, and expert opinions without meta-analysis. This tool for evaluating systematic reviews and expert consensuses consists of 11 and 6 items, respectively, with the responses being “yes,” “no,” “unclear,” and “not applicable.”
Two researchers systematically trained in evidence-based methods separately evaluated the quality of the included literature, and in the case of conflicting evaluations, a third investigator participated in the discussion to arrive at a consensus.
2.5 Extraction, summary, and grading of evidence
Two researchers independently reviewed each article in the cited literature and collected evidence from it based on the theme. In cases where the conclusions and evidence of different sources were inconsistent, evidence was extracted following the criteria of priority of high-quality evidence, priority of recent evidence, and priority of evidence-based information. All the selected clinical practice guidelines, recommended practices, and evidence summaries were summarized with their original grading system (19). The evidence of the guidelines was graded using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE) system (20), and the levels of evidence were classified as “high (A),” “medium (B),” “low (C),” and “very low (D),” with the recommendation grade as “strong recommendation (1)” and “weak recommendation (2).” For evidence without a grading system, the 2014 version of the JBI evidence pre-grading and evidence recommendation level framework was used (21), and evidence was categorized into levels 1–5 and the recommendation was determined as grade A (strong recommendation) or grade B (weak recommendation) in combination with the JBI feasibility, appropriateness, meaningfulness, and effectiveness (FAME) approach and the JBI recommendation grades.
3 Results
3.1 Results of literature retrieval
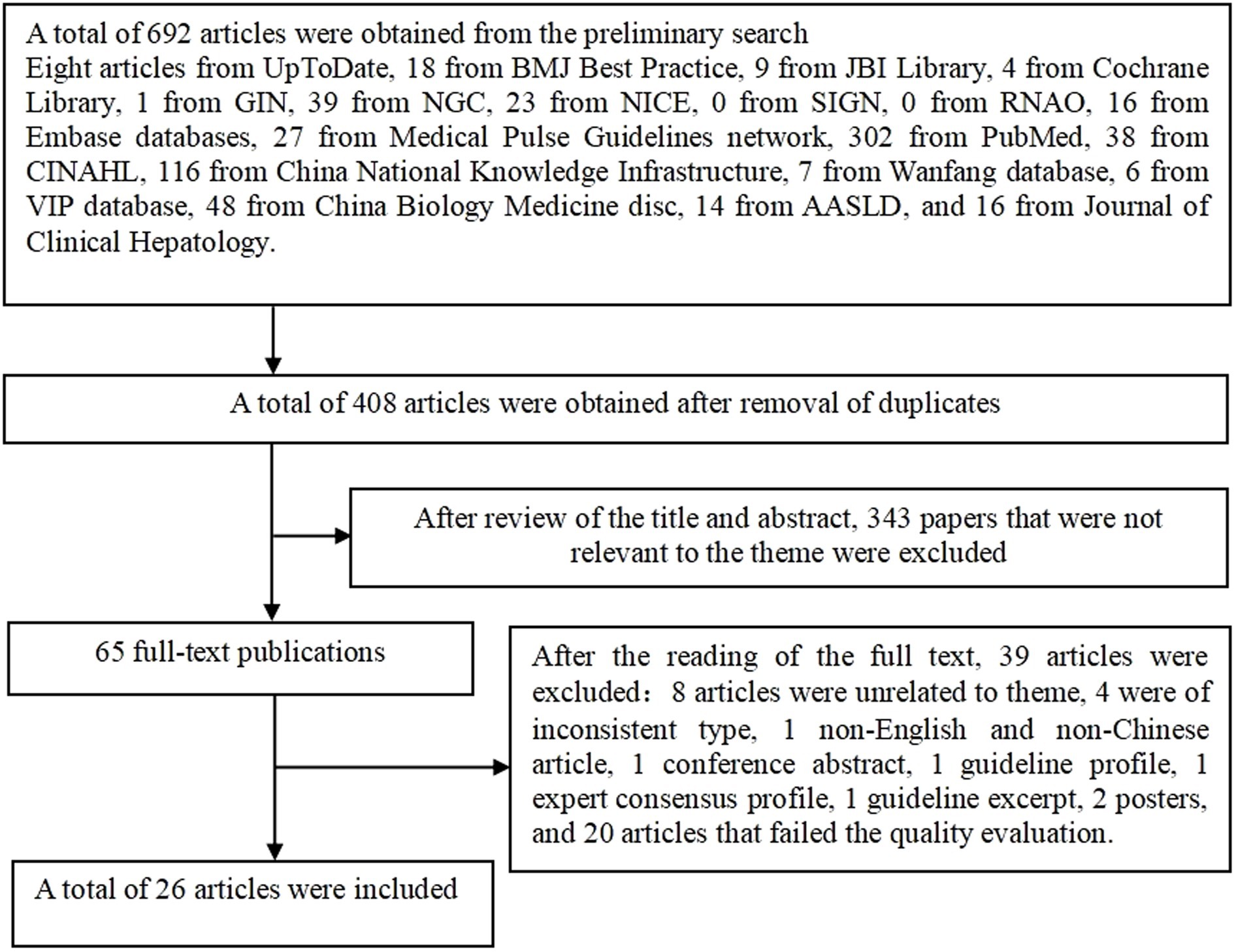
A total of 692 articles were retrieved and finally, 26 articles were included in the review after layer-by-layer screening. The literature screening process is shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Profile of the reviewed literature
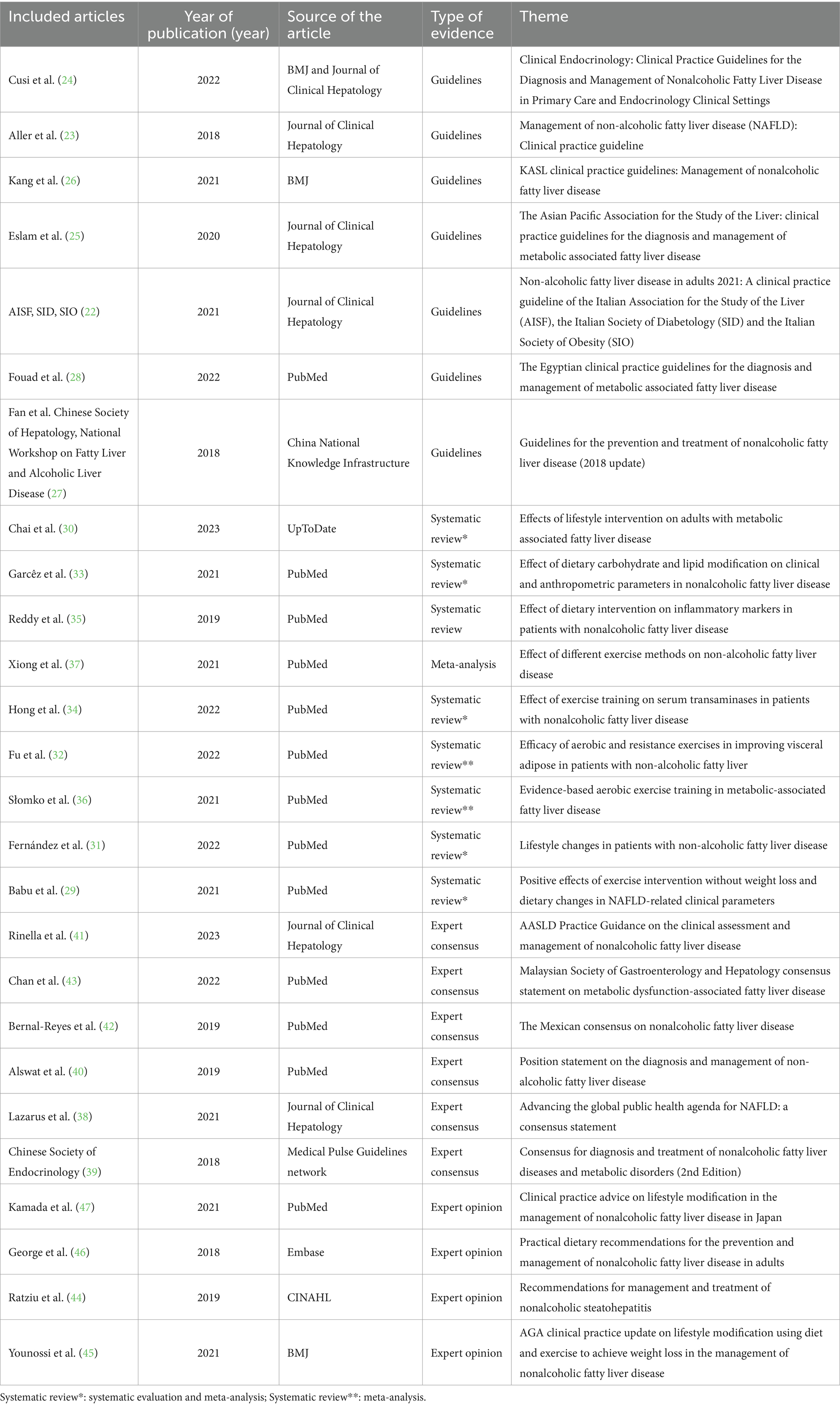
This review included 26 publications, comprising seven guidelines (22–28), nine systematic evaluations with meta-analyses (29–37), six expert consensuses (38–43), and four expert opinions (44–47). The details of the publications is shown in Table 2.
3.3 Results of the evaluation of the quality of literature
3.3.1 Quality evaluation of guidelines
This review included seven guidelines (22–28). The average percentage and recommended grade for each domain are listed in Table 3. One guideline (24) had a final score percentage of ≥60% on all six domains and a recommendation grade of A. The remaining guidelines (22, 23, 25–29) had a recommendation grade of B. Seven guidelines were of good overall quality and approved for inclusion in the review.
3.3.2 Quality evaluation of systematic reviews
A total of 9 systematic reviews (29–37) were evaluated using the AMSTAR 2 scale (16). One systematic review (34) had “yes” or “partially yes” responses for all seven key items and was evaluated with a grade of “medium.” Two systematic reviews had a response of “no” for 1 key item [item 13 for the study by Garcêz et al. (33) and item 7 for the study by Babu et al. (29)] and ≥1 non-key item, with an evaluation grade of “low.” The remaining six systematic reviews (30–32, 35–37) had a response of “no” for ≥1 key item and ≥1 non-key item, with an evaluation grade of “very low.” Nevertheless, since their “no” responses constituted less than 50% or “unclear” responses were less than 80% of the total evaluation items. Eventually, nine systematic reviews with relatively complete study designs were eventually analyzed.
3.3.3 Quality evaluation of expert consensus and expert opinions
A total of six expert consensuses (38–43) and four expert opinions (44–47) were included in this review. In the evaluation of one expert consensus (46), the response to the second item, “Is the opinion derived from an influential expert in the field,” was “unclear,” while the responses to the remaining items were “yes.” The remaining nine publications had a “yes” response to all items. All expert consensus and expert opinion literature were of high quality and, hence, were deemed eligible for inclusion.
3.4 Summary of evidence
Following extraction, summarization, and analysis of the evidence related to lifestyle interventions for adults with MASLD, a total of 28 articles were finally analyzed. The most compelling evidence across six key dimensions was synthesized. They were intervention modalities, diet management, exercise management, weight loss management, personalized management, and multidisciplinary collaboration (Table 4).
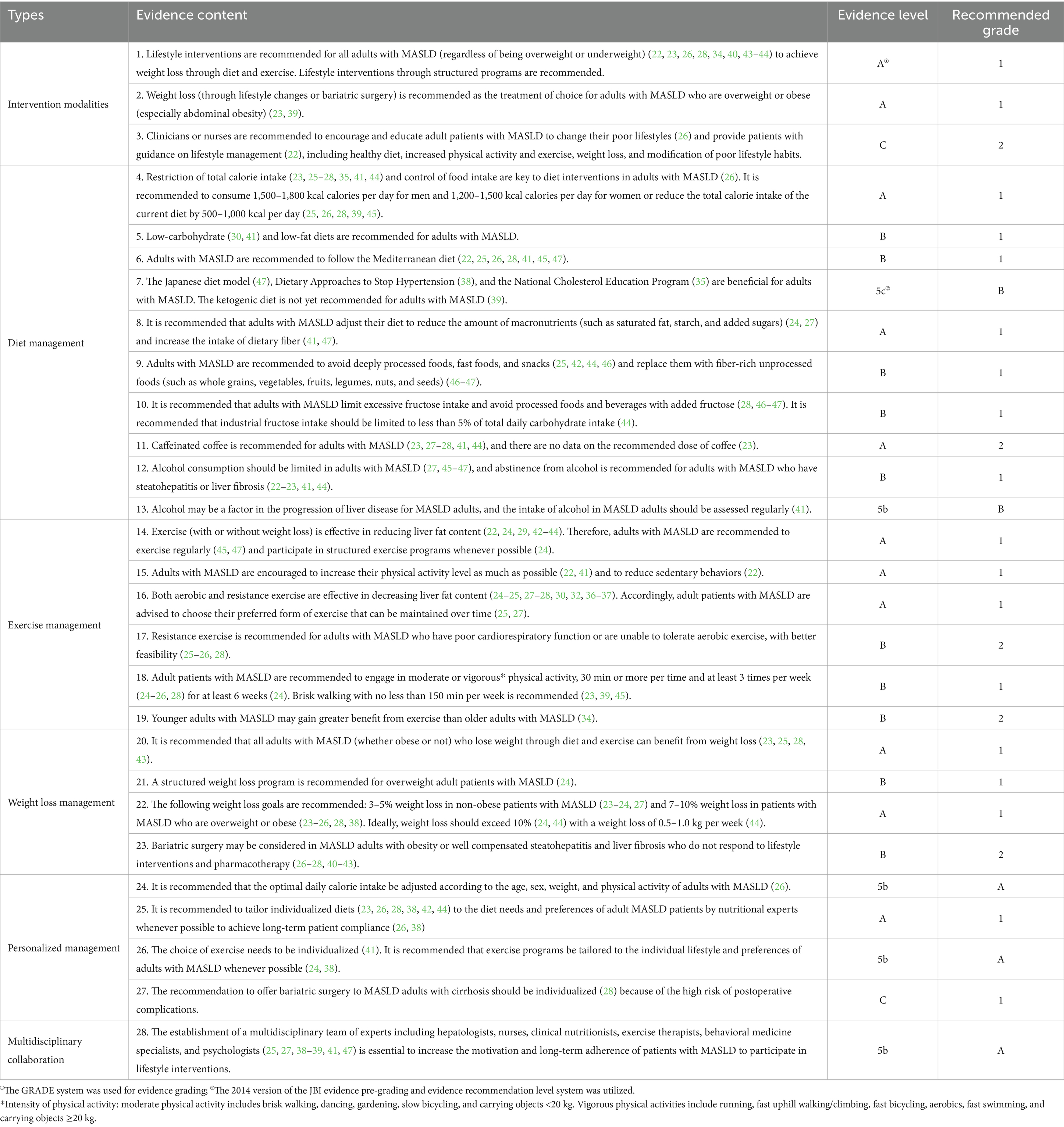
Table 4. Best evidence of lifestyle interventions in adult patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.
4 Discussion
4.1 Adults with MASLD can benefit from lifestyle modification interventions
The evidence summary revealed that lifestyle interventions (diet, exercise, and weight loss) were effective in reducing lipids, liver enzymes, intrahepatic fat content, and insulin resistance in patients (22, 26). Whilst there is emerging evidence for time-restricted eating, the impact of the time spent on diet and exercise is largely unknown. There is no clear consensus on the optimal diet regimen for adults with MASLD, such as calorie intake, diet pattern and structure, and the distribution of dietary components (ratio of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and ratio of saturated to unsaturated fats) (24, 44).
There is still debate about the frequency, intensity, duration, and type of exercise (25, 36). Furthermore, the protocols for aerobic exercise were consistent with the recommendations of the American College of Sports Medicine (36) in only 35% of studies. Therefore, large, multidisciplinary randomized controlled trials with adequate follow-up and robust documentation of diet and exercise adherence (49) are required to determine the optimal diet regimen and exercise prescription for adults with MASLD and to evaluate the health benefits of optimal diet and exercise doses for such patients (36).
All adults with MASLD can benefit from losing weight through changes in diet and exercise (45). However, the metabolic health of patients with MASLD benefits differently depending on the ratio of weight loss to the initial body weight. For instance, a weight loss of ≥5% can reduce hepatic steatosis, weight loss of ≥7% can contribute to the regression of steatohepatitis, and weight loss of ≥10% can lead to the regression or stabilization of liver fibrosis (5, 6, 13, 36, 37, 39). Furthermore, the type, safety, and efficacy of bariatric surgery for patients with MASLD are unclear and require careful benefit–risk assessment by a multidisciplinary team of experts, including hepatologists (41).
4.2 Adults with MASLD can benefit from the development of structured lifestyle intervention programs
Several guidelines and consensus statements recommend lifestyle modification interventions through structured programs for adults with MASLD, especially for patients with advanced liver fibrosis and/or at high risk of rapid fibrosis progression (38). Syntheses of the available evidence revealed that there is no uniform, standardized, and structured lifestyle intervention program for adults with MASLD.
The purpose of this evidence summary was to provide a foundation for the development of standardized and structured lifestyle intervention programs for adults with MASLD by focusing on the evidence related to diet, exercise, and weight loss, thereby helping medical staff and healthcare professionals efficiently acquire and understand the evidence for such interventions. Future research should focus on the development and use of localized and structured lifestyle intervention programs based on the diet, exercise habits, and cultural norms of adults with MASLD.
4.3 Lifestyle intervention programs for adults with MASLD should be individualized as much as possible
Evidence shows that adults with MASLD have poor long-term compliance with lifestyle changes (44) and struggle to sustain healthy diet habits in the long-term (26). More than 80% of patients with MASLD do not complete a physical activity program of 30 min of moderate-intensity exercise per session and ≥3 times per week (36). It is equally challenging to achieve and maintain weight loss (28, 41). In a study of a 52-week structured weight loss intervention, only 30% (88/261 cases) of patients with MASLD achieved a weight loss of ≥5% (50). Only 32% of patients with MASLD who were overweight or obese achieved a weight loss of ≥5% during a 5-year follow-up, and among them, only 25% maintained their weight loss 5 years after the intervention (48). Therefore, several guidelines and consensus statements recommend that individualized lifestyle intervention programs be tailored to the culture, personal preferences, and needs of patients with MASLD to improve intervention outcomes and promote long-term adherence and compliance with the intervention program (38, 41).
4.4 A multidisciplinary team can increase the motivation of adults with MASLD to participate in and comply with lifestyle interventions
Although adherence to lifestyle changes can benefit patients with MASLD, research indicates that long-term compliance is poor in most patients during clinical implementation (44). To effectively design and implement structured lifestyle intervention programs for adults with MASLD, it is imperative to assemble a multidisciplinary team of experts. This team should ideally include hepatologists, nurses, clinical nutritionists, exercise therapists, behavioral medicine specialists, and psychologists. Additionally, studying the impact of various intervention models on long-term compliance and intervention outcomes is essential for the development of successful interventions. It is important that this team collaborate with patients and their support systems to develop structured and individualized lifestyle intervention programs incorporating different combinations of strategies (41). This method can be effective in managing lifestyle interventions for adults with MASLD as it increases their motivation and compliance (38).
5 Conclusion
Lifestyle intervention is a safe, low-cost, and highly effective method that is the foundation of treatment for MASLD. Nevertheless, the clinical application of lifestyle interventions remains suboptimal, and there is a significant issue with poor compliance in real-world clinical practice. In this review, we summarized the best evidence on lifestyle interventions for adults with MASLD by systematically identifying high-level evidence-based information from China and elsewhere and provided practice recommendations in six areas: intervention modalities, diet management, exercise management, weight loss management, personalized management, and multidisciplinary collaboration.
Through this review, we aimed to encourage clinical staff and healthcare professionals to follow the best evidence and guide adults with MASLD toward adopting standardized interventions for a healthy lifestyle. The use of evidence related to lifestyle interventions should be integrated with and tailored to suit the sociocultural situation of adults with MASLD, such as personal preferences, lifestyle norms, and behavioral habits, while keeping in mind the feasibility and applicability of the evidence. This can increase the compliance of patients and promote the translational application of the evidence. The evidence summary presented here requires continuous updates with the inclusion of newly published literature. Furthermore, there is a need for further studies to explore the utilization of the best available evidence in designing effective lifestyle modification interventions tailored for adults diagnosed with MASLD.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
M-jC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. YC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. J-qL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. RH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. DL: Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. J-yC: Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. KL: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. X-yJ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work financial was supported by grants from the Educational and Scientific Research Project (Science and Technology) for Young and Middle-aged Teachers from the Education Department of Fujian Province (grant number JAT22098) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (grant number 2023J011541).
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the hard and dedicated work of all the staff that implemented the intervention and evaluation components of the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rinella, ME, Lazarus, JV, Ratziu, V, Francque, SM, Sanyal, AJ, Kanwal, F, et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:1542–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.06.003
2. Song, SJ, Lai, JC, Wong, GL, Wong, VW, and Yip, TC. Can we use old NAFLD data under the new MASLD definition? J Hepatol. (2023) 80:e54–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.07.021
3. Eslam, M, Sanyal, AJ, George, J, Sanyal, A, Neuschwander-Tetri, B, Tiribelli, C, et al. MAFLD: a consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:1999–2014.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312
4. Younossi, ZM, Golabi, P, Paik, JM, Henry, A, Van Dongen, C, and Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a systematic review. Hepatology. (2023) 77:1335–47. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000004
5. Lazarus, JV, Mark, HE, Villota-Rivas, M, Palayew, A, Carrieri, P, Colombo, M, et al. The global NAFLD policy review and preparedness index: are countries ready to address this silent public health challenge? J Hepatol. (2022) 76:771–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.10.025
6. Stefano, JT, Duarte, SMB, Ribeiro Leite Altikes, RG, and Oliveira, CP. Non-pharmacological management options for MASLD: a practical guide. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. (2023) 14:20420188231160394. doi: 10.1177/20420188231160394
7. Pathak, MP, Pathak, K, Saikia, R, Gogoi, U, Patowary, P, Chattopadhyay, P, et al. Therapeutic potential of bioactive phytoconstituents found in fruits in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a comprehensive review. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e15347. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15347
8. Guveli, H, Ozlu, T, Ersoy Tasar, B, Batuhan Kenger, E, and Kaya, E. Sustainability of diet-based moderate calorie restriction among obese patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol Forum. (2021) 2:97–101. doi: 10.14744/hf.2021.2021.0014
9. Barrea, L, Verde, L, Savastano, S, Colao, A, and Muscogiuri, G. Adherence to Mediterranean diet: any association with NAFLD? Antioxidants. (2023) 12:1318. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071318
10. Xiao, Y, Zhang, X, Yi, D, Qiu, F, Wu, L, Tang, Y, et al. Mediterranean diet affects the metabolic outcome of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1225946. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1225946
11. Wang, YY, Tian, F, Qian, XL, Ying, HM, and Zhou, ZF. Effect of 5:2 intermittent fasting diet versus daily calorie restriction eating on metabolic-associated fatty liver disease-a randomized controlled trial. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1439473. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1439473
12. von Loeffelholz, C, Roth, J, Coldewey, SM, and Birkenfeld, AL. The role of physical activity in nonalcoholic and metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:1853. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121853
13. Zhu, Z, Hu, Y, Zhou, Y, Gu, Y, Xing, W, Chen, Y, et al. Promoting the transformation of evidence to clinical practice: research topic selection and problem construction. J Nurses Train. (2020) 35:4. doi: 10.16821/j.cnki.hsjx.2020.09.008
14. Li, C, Fu, R, and Liang, L. Best evidence for lifestyle management in elderly patients with hypertension. Modern Clin Nurs. (2022) 6:21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8283.2022.06.011
15. Dicenso, A, Bayley, L, and Haynes, RB. Accessing pre-appraised evidence: fine-tuning the 5S model into a 6S model. Evid Based Nurs. (2009) 12:99.2–99.101. doi: 10.1136/ebn.12.4.99-b
16. Brouwers, MC, Kho, ME, Browman, GP, Burgers, JS, Cluzeau, F, Feder, G, et al. AGREE next steps consortium. AGREE II: advancing guideline development, reporting, and evaluation in health care. Prev Med. (2010) 51:421–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2010.08.005
17. Shea, BJ, Reeves, BC, Wells, G, Thuku, M, Hamel, C, Moran, J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. (2017) 358:j4008. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j4008
18. Zeng, X, Zhang, Y, Kwong, JS, Zhang, C, Li, S, Sun, F, et al. The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: a systematic review. J Evid Based Med. (2015) 8:2–10. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12141
19. Xing, W, Zhou, F, Wang, J, Zhang, J, Li, J, and Sheng, J. Evidence summary of safe infant sleeping environment for the prevention of sudden infant death syndrome. Chinese Nurs Manag. (2020) 20:7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2020.12.016
20. Atkins, D, Best, D, Briss, PA, Eccles, M, Falck-Ytter, Y, Flottorp, S, et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. (2004) 328:1490. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7454.1490
21. The Joanna Briggs Institute Levels of Evidence and Grades of Recommendation Working Party. Supporting document for the j oanna briggs institute levels of evidence and grades of recommendation[EB/OL]. (2014). Available at: http://Joannabriggs.org/jb-iapproach.Html#tabbed-nav=Levels-of-Evidence (Accessed May 18, 2018).
22. Associazione Italiana per lo Studio del Fegato (AISF), Società Italiana di Diabetologia (SID) and Società Italiana dell’Obesità (SIO). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults 2021: a clinical practice guideline of the Italian Association for the Study of the liver (AISF), the Italian Society of Diabetology (SID) and the Italian Society of Obesity (SIO). Eat Weight Disord. (2022 Jun) 27:1603–19. doi: 10.1007/s40519-021-01287-1
23. Aller, R, Fernández-Rodríguez, C, Lo Iacono, O, Bañares, R, Abad, J, Carrión, JA, et al. Consensus document. Management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Clinical practice guideline. Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 41:328–49. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2017.12.003
24. Cusi, K, Isaacs, S, Barb, D, Basu, R, Caprio, S, Garvey, WT, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in primary care and endocrinology clinical settings: co-sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Endocr Pract. (2022) 28:528–62. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2022.03.010
25. Eslam, M, Sarin, SK, Wong, VW, Fan, JG, Kawaguchi, T, Ahn, SH, et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol Int. (2020) 14:889–919. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10094-2
26. Kang, SH, Lee, HW, Yoo, JJ, Cho, Y, Kim, SU, Lee, TH, et al. KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2021) 27:363–401. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0178
27. Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease Group of Liver Disease Society of Chinese Medical Association, Expert Committee of Fat Liver Disease of Chinese Medical Doctor Association Fan, J, Wei, L, and Zhuang, H. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 2018 update. J Pract Hepatol. (2018) 21:30–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2018.02.007
28. Fouad, Y, Esmat, G, Elwakil, R, Zakaria, S, Yosry, A, Waked, I, et al. The Egyptian clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Saudi J Gastroenterol. (2022) 28:3–20. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_357_21
29. Babu, AF, Csader, S, Lok, J, Gómez-Gallego, C, Hanhineva, K, El-Nezami, H, et al. Positive effects of exercise intervention without weight loss and dietary changes in NAFLD-related clinical parameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3135. doi: 10.3390/nu13093135
30. Chai, XN, Zhou, BQ, Ning, N, Pan, T, Xu, F, He, SH, et al. Effects of lifestyle intervention on adults with metabolic associated fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1081096. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1081096
31. Fernández, T, Viñuela, M, Vidal, C, and Barrera, F. Lifestyle changes in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0263931. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263931
32. Fu, L, Zhang, W, Ao, Y, Zheng, Z, and Hu, H. Efficacy of aerobic and resistance exercises in improving visceral adipose in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Z Gastroenterol. (2022) 60:1644–58. doi: 10.1055/a-1742-4257
33. Garcêz, LS, Avelar, CR, Fonseca, NSS, Costa, PRF, Lyra, AC, Cunha, CM, et al. Effect of dietary carbohydrate and lipid modification on clinical and anthropometric parameters in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Rev. (2021) 79:1321–37. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuaa146
34. Hong, F, Liu, Y, Lebaka, VR, Mohammed, A, Ye, W, Chen, B, et al. Effect of exercise training on serum transaminases in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:894044. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.894044
35. Reddy, AJ, George, ES, Roberts, SK, and Tierney, AC. Effect of dietary intervention, with or without co-interventions, on inflammatory markers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic literature review. Nutr Rev. (2019) 77:765–86. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuz029
36. Słomko, J, Zalewska, M, Niemiro, W, Kujawski, S, Słupski, M, Januszko-Giergielewicz, B, et al. Evidence-based aerobic exercise training in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: systematic review with meta-analysis. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:1659. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081659
37. Xiong, Y, Peng, Q, Cao, C, Xu, Z, and Zhang, B. Effect of different exercise methods on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:3242. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18063242
38. Lazarus, JV, Mark, HE, Anstee, QM, Arab, JP, Batterham, RL, Castera, L, et al. Advancing the global public health agenda for NAFLD: a consensus statement. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 19:60–78. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00523-4
39. The Endocrinology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of non-alcoholic fat liver disease and related metabolic disorders (second edition). Chinese J Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 34:549–54. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2018.07.004
40. Alswat, KA, Fallatah, HI, Al-Judaibi, B, Elsiesy, HA, Al-Hamoudi, WK, Qutub, AN, et al. Position statement on the diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Saudi Med J. (2019) 40:531–40. doi: 10.15537/smj.2019.6.23980
41. Rinella, ME, Neuschwander-Tetri, BA, Siddiqui, MS, Abdelmalek, MF, Caldwell, S, Barb, D, et al. AASLD practice guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. (2023) 77:1797–835. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000323
42. Bernal-Reyes, R, Castro-Narro, G, Malé-Velázquez, R, Carmona-Sánchez, R, González-Huezo, MS, García-Juárez, I, et al. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. (2019) 84:69–99. doi: 10.1016/j.rgmx.2018.11.007
43. Chan, WK, Tan, SS, Chan, SP, Lee, YY, Tee, HP, Mahadeva, S, et al. Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology and Hepatology consensus statement on metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 37:795–811. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15787
44. Ratziu, V, Ghabril, M, Romero-Gomez, M, and Svegliati-Baroni, G. Recommendations for management and treatment of nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Transplantation. (2019) 103:28–38. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002483
45. Younossi, ZM, Corey, KE, and Lim, JK. AGA clinical practice update on lifestyle modification using diet and exercise to achieve weight loss in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: expert review. Gastroenterology. (2021) 160:912–8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.11.051
46. George, ES, Forsyth, A, Itsiopoulos, C, Nicoll, AJ, Ryan, M, Sood, S, et al. Practical dietary recommendations for the prevention and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. Adv Nutr. (2018) 9:30–40. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmx0007
47. Kamada, Y, Takahashi, H, Shimizu, M, Kawaguchi, T, Sumida, Y, Fujii, H, et al. Clinical practice advice on lifestyle modification in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Japan: an expert review. J Gastroenterol. (2021) 56:1045–61. doi: 10.1007/s00535-021-01833-9
48. Malespin, MH, Barritt, AS 4th, Watkins, SE, Schoen, C, Tincopa, MA, Corbin, KD, et al. Weight loss and weight regain in usual clinical practice: results from the TARGET-NASH observational cohort. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 20:2393–2395.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.023
49. Keating, SE, Chawla, Y, De, A, and George, ES. Lifestyle intervention for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a 24-h integrated behavior perspective. Hepatol Int. (2024) 18:959–76. doi: 10.1007/s12072-024-10663-9
50. Vilar-Gomez, E, Martinez-Perez, Y, Calzadilla-Bertot, L, Torres-Gonzalez, A, Gra-Oramas, B, Gonzalez-Fabian, L, et al. Weight loss through lifestyle modification significantly reduces features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. (2015) 149:367–378.e5; quiz e14-5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.005
Keywords: evidence-based nursing, evidence summary, lifestyle, intervention, metabolic dysfunction-associate fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Citation: Chen M-j, Chen Y, Lin J-q, Hu R, Liu D, Chen J-y, Li K and Jiang X-y (2025) Evidence summary of lifestyle interventions in adults with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Front. Nutr. 11:1421386. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1421386
Edited by:
Michele Barone, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyReviewed by:
Ludovica Verde, University of Naples Federico II, ItalySantiago Rodríguez Villafuerte, Hospital Vozandes, Ecuador
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Chen, Lin, Hu, Liu, Chen, Li and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiao-ying Jiang, eGlhb3lqMzIwQDEyNi5jb20=; Ka Li, bGlrYTEyN0AxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Mei-jing Chen1†
Mei-jing Chen1† Xiao-ying Jiang
Xiao-ying Jiang