- 1Liaocheng Research Institute of Donkey High-Efficiency Breeding and Ecological Feeding, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng, China
- 2Department of Theriogenology, Faculty of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Cholistan University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan
- 3Genome Analysis Laboratory of the Ministry of Agriculture, Agricultural Genomics Institute at Shenzhen, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shenzhen, China
Donkey milk has attracted attention due to its distinctive nutritional composition and potential health advantages, particularly because of its whey protein content, which includes lysozyme, α-lactalbumin, lactoferrin, and β-lactoglobulin and vitamin C, among other components. These elements contribute to immunoregulatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, positioning donkey milk as a possible therapeutic option. In addition, due to the low levels of caseins, the casein-to-whey protein ratio, and the β-lactoglobulin content in donkey milk, it presents an optimal alternative for infant formula for individuals with cow’s milk allergies. Moreover, research into donkey milk’s potential for cancer prevention, diabetes management, and as a treatment for various diseases is ongoing, thanks to its bioactive peptides and components. Nevertheless, challenges such as its low production yield and the not fully understood mechanisms behind its potential therapeutic role necessitate more thorough investigation. This review consolidates the existing knowledge on the therapeutic possibilities of donkey milk, emphasizing its importance for human health and the need for more detailed studies to confirm its health benefits.
1 Introduction
The therapeutic potential, similarities to human milk and high digestibility of donkey milk have captured the attention of researchers in this field (1–4). Donkey milk has low cholesterol, fat and protein level, however, consider a rich source of milk whey proteins (3, 5). In addition, donkey milk has a vitamin C level of 57 mg/L, which is closest to that of human milk (60 mg/L), and higher than cow milk (27 mg/L) (1, 6). The low level of casein and casein to whey protein ratio in donkey milk may contribute to its role in formula milk of infant (3, 7). Today, donkey milk is being marketed as a consumer product and is used by newborns (8, 9), people with cow’s milk protein allergies, and the elderly (10).
The growing interest in donkey milk is further justified by its multifaceted bioactivities, encompassing antimicrobial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative (2, 11–13) and antioxidant effects (3, 14). Additionally, its pronounced antibacterial activity against a spectrum of pathogenic bacteria (2) is linked to an extended shelf life of the milk. The immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral properties of donkey milk can largely be attributed to its constituent bioactive molecules, namely lactoferrin and lysozyme, as corroborated by extensive research (15, 16).
Lysozyme, a pivotal component of the innate immune system, is recognized for its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities against bacterial (15), fungal, and viral pathogens, thereby serving as a natural defense mechanism against infections. In the realm of pharmaceuticals, the application of milk-derived lysozyme spans the prophylaxis of diseases of bacterial, viral, fungal, and inflammatory etiologies, further supplemented by its immune-stimulatory (17, 18) and antihistaminic potentials (19, 20). The advancements in lysozyme modification open new avenues in clinical medicine (17, 21). The milk whey proteins were suggested to conduce to the destruction of tumors, as it modulates the synthesis of the tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) and also stimulates the production of Type I interferon (INFα, INFβ, INFγ), interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interleu-kin-6 (IL-6) by human lymphocytes (22).
Based on its abundance in the colostrum and milk, LF plays an essential immunomodulatory role that complements immature biological defense functions in neonates (23). Furthermore, LF enhances immune function, which declines with age (24). The previously reported physiological effects of LF include antimicrobial, antiviral, anti-aging, neuroprotective, regulation of iron metabolism, improvement of bone metabolism, and immunomodulatory effects (25).
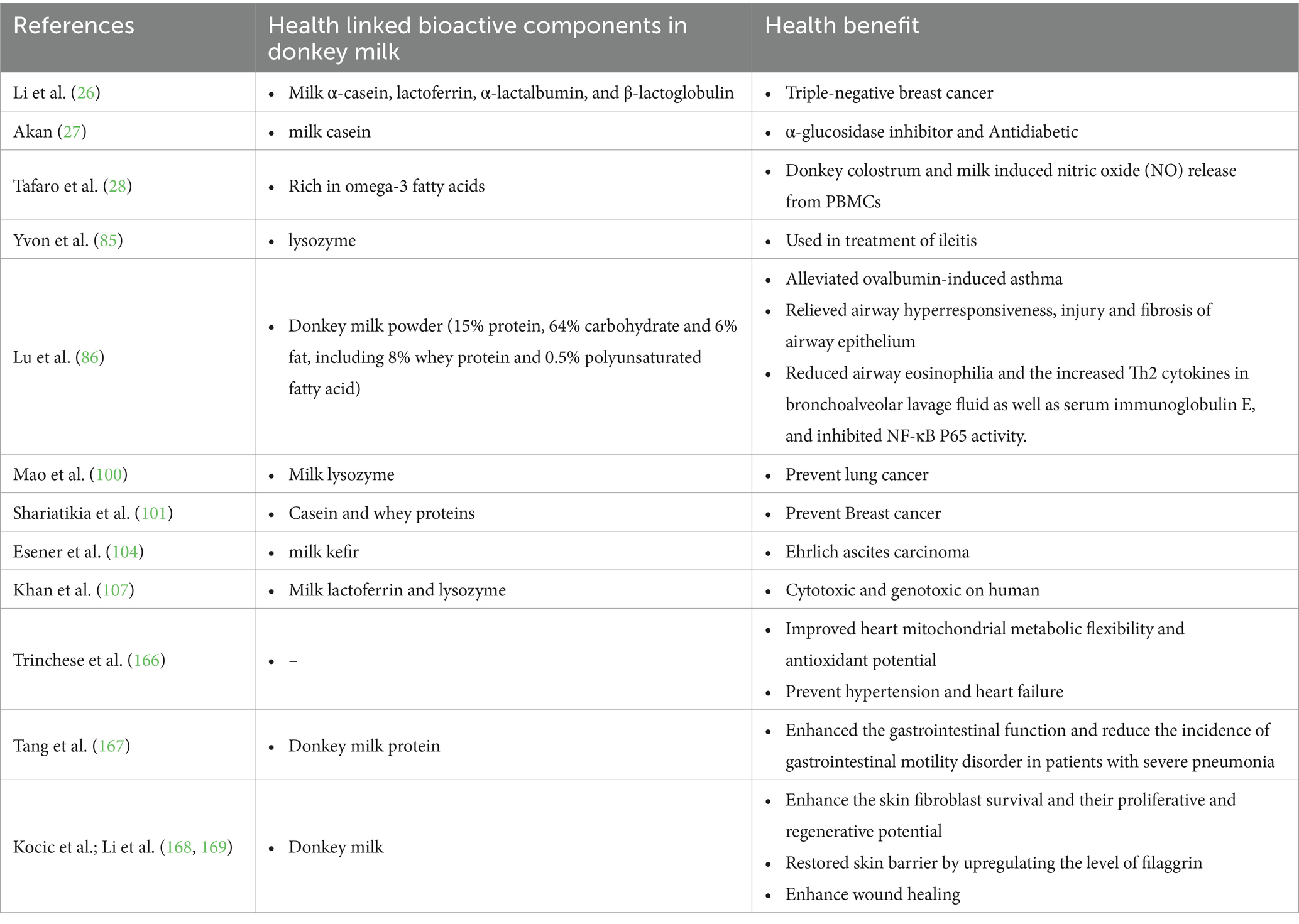
The use of donkey milk as a therapeutic agent to heal wounds and treat various diseases, such as bronchitis, asthma, joint pain, and gastritis, is being explored (10, 12). Consistently, the anti-cancer (26), antidiabetics (27), atherosclerosis (28) and anti-colitis (29) properties of donkey milk has also been reported. In the current pandemic of the coronavirus, some modified form of lysozyme can be used to stimulate the formation of interferon, an effective substance against coronavirus, and thus reduce the risk of the life-threatening form of COVID-19 up to 79% (30, 31).
This review aims to synthesize existing knowledge on the antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, immunoregulatory, and antioxidant attributes of donkey milk. In addition, we have highlighted the role of donkey milk as therapeutic agent in prevention of cancer, diabetes, and heart diseases. Furthermore, this review delineated the principal factors that detrimentally affect the milk characteristics of donkey.
2 Materials and methods
This review examines articles that discuss the composition and bioactive components of donkey milk, as well as studies highlighting its potential therapeutic uses. These therapeutic uses include its antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects. The data for this review was gathered from reputable platforms such as springerLink, Scopus, Web of Science, PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect. Various key terms were utilized in the search, including the composition of donkey milk, its bioactive elements, therapeutic benefits, and its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antioxidant properties. The selection criteria for the articles were rigorous, focusing only on studies published in reputable, peer-reviewed English language journals from 2010 onwards, with the exception of two earlier studies from 2007. Conference summaries, books, and book sections were not considered for this review.
3 Composition and bioactive components of donkey milk
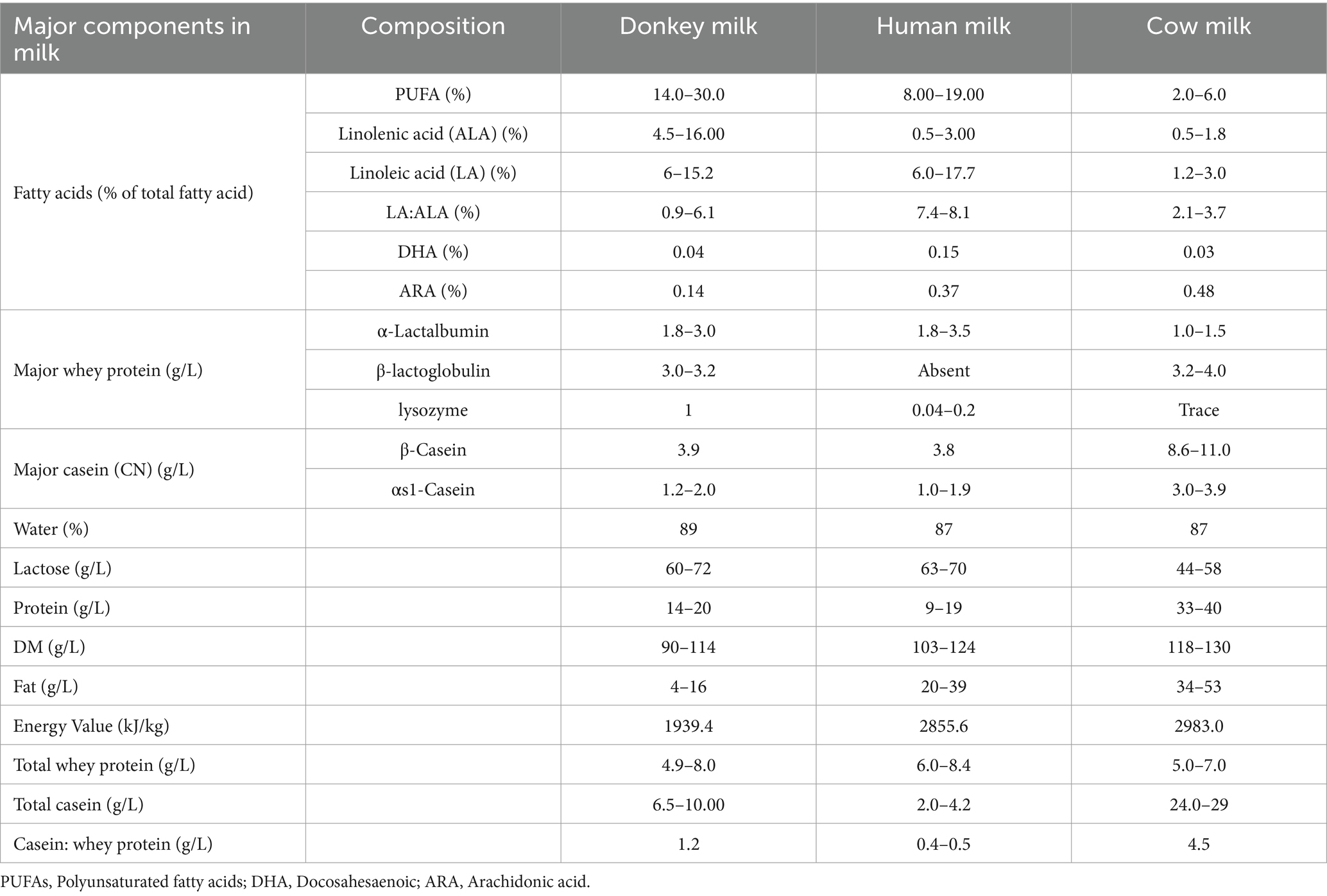
The nutritional composition and beneficial properties of donkey milk have been extensively explored in scientific literature, including in recent studies (32–36). The summary of donkey milk compositions has been provided in Table 1. Donkey milk is particularly valued for its close resemblance to human breast milk, both in terms of its nutritional profile and its health benefits. It is characterized by a balanced mix of essential nutrients, though it differs from cow’s milk in several key aspects.
Protein content in donkey milk ranges from 1.5–2.0%, which is less than that found in cow’s milk. The proteins in donkey milk include both caseins and whey proteins, such as α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin, but in smaller amounts compared to those in cow’s milk. Notably, donkey milk is richer in lactoferrin and lysozyme, two proteins known for their antimicrobial properties, than cow’s milk (37). Consistently, the fat content in donkey milk is relatively low, between 0.3–1.0%, and its fat includes a higher proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially linoleic acid, which contributes to its health benefits (38). Donkey milk is also higher in lactose than cow’s milk, with levels between 6.2 and 7.4%, lending it a slightly sweet taste (8).
Moreover, donkey milk is acknowledged for its healthful attributes, such as lower fat and cholesterol levels, and higher amounts of protein, casein, lactose, whey protein, calcium, selenium, and vitamin D3 (36). Consistently another study also reported that donkey milk has a lower cholesterol content, a lower casein to whey protein ratio, a higher calcium to phosphorus ratio, and a higher taurine content compared to bovine milk (39). The donkey milk also contains a variety of vitamins, including both water-soluble (B group and vitamin C) and fat-soluble (vitamins A, D, E, and K) types and minor components such as hormones (6). The vitamin content can fluctuate depending on the donkeys’ diet and environment. Donkey milk is a good source of essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium, though in amounts typically lower than in cow’s milk (40). Despite this, the bioavailability of these minerals is high, attributed to the low protein content of the milk.
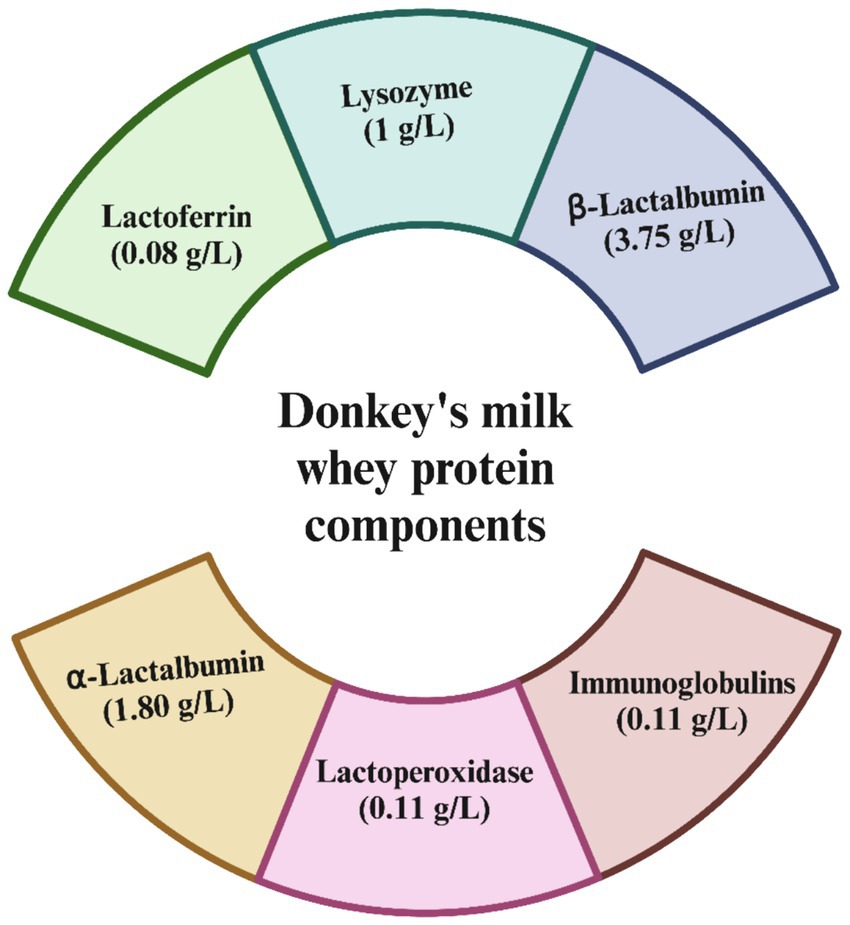
Donkey milk also features a range of bioactive components that support immunological health, such as immunoglobulins, lactoferrin, lysozyme, and cytokines, which may enhance its immune-boosting capabilities (41, 42). In terms of whey protein content, donkey milk contains about 4.9–9.6 g/L, which constitutes roughly 43–50% of its total protein. The whey protein is primarily composed of β-lactoglobulin, α-lactalbumin, immunoglobulins, lysozyme, serum albumin, and lactoferrin (Figure 1). These proteins not only provide energy but also play roles in antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor activities, contributing to the wide range of health benefits associated with donkey milk consumption (43). The whey protein fraction of donkey milk is predominantly constituted by β-lactoglobulin, with concentrations approximately at 3.75 g/L, and α-lactalbumin, measured around 1.80 g/L. Additionally, the composition includes immunoglobulins at roughly 1.30 g/L, lysozyme at about 1.00 g/L, serum albumin at nearly 0.40 g/L, and lactoferrin at approximately 0.08 g/L (38). After being consumed, proteins are broken down into smaller peptide fragments through enzymatic hydrolysis in the gastrointestinal tract. This process is essential for the efficient digestion and absorption of proteins and also results in the creation of bioactive peptides. These peptides have specific biological functions, often imitating or boosting the activities of the original proteins, thus enhancing their overall bioactivity. These proteins are not merely sources of energy but also play pivotal roles in various physiological processes. They exhibit a spectrum of bioactive functions, encompassing antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor properties, thereby underscoring the multifaceted health benefits conferred by whey protein constituents in donkey milk.
The contents for Table 1 are adopted from Baloš et al. (1); Zheleva, (2); Vincenzetti et al. (14); Derdak et al. (43); Cimmino et al. (44); Wang F et al. (45); Li M et al. (46); Claeys et al. (47);; Li Y et al. (48); Garhwal et al. (49); Parsad, (50); Altomonte et al. (51); Martemucci and D’Alessandro, (52).
4 Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effect of donkey milk
4.1 Antimicrobial regulatory properties of donkey milk
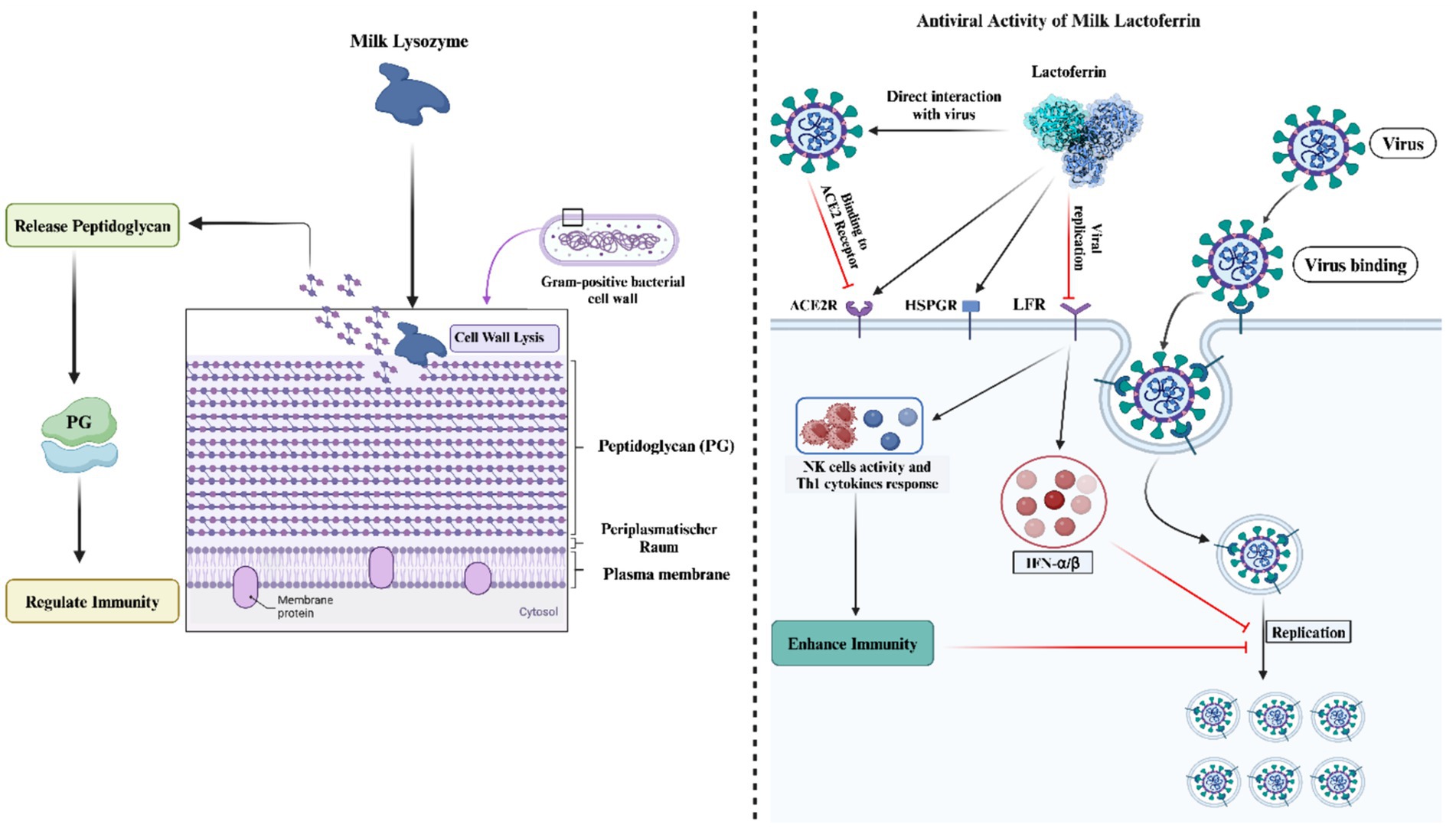
Recent in vitro investigations have elucidated the antibacterial properties of equid milk, attributing these characteristics to the elevated concentrations of lysozyme and lactoferrin (53–55). Furthermore, an association has been observed between the antibacterial activities of donkey milk and its high calcium content (56). The spectrum of anti-bacterial efficacy of donkey milk extends to pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus (57), S. haemolyticus, Listeria monocytogenes (58), Escherichia coli, and Salmonella enteritidis (12, 59, 60). The abundance of lysozyme in donkey milk is particularly noted for its capability to degrade the peptidoglycan layer of Gram-positive bacteria, thus facilitating bacterial lysis (61). Recent research by Saju et al. (36) has demonstrated that endosymbiotic bacteria isolated from donkey milk exhibit pronounced antibacterial activities against Escherichia coli, S. aureus, and Salmonella enterica. The comprehensive antimicrobial efficacy of donkey milk is likely due to the synergistic interactions among its bioactive components, namely lactoferrin, lysozyme, immunoglobulins, and fatty acids, in addition to anatomical factors related to the udder’s size and position (8, 62). However, a reduction in lysozyme levels during the later stages of lactation has been linked to the presence of pathogenic bacteria in donkey milk (63, 64).
The antimicrobial efficacy of lactoferrin and lysozyme has been substantiated through a compendium of research efforts (18, 65–71). These studies collectively underscore the critical roles that these molecules play in the innate immune defense, particularly through their bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities. Lactoferrin, a multi-functional protein of the transferrin family, is renowned for its ability to sequester iron, thereby inhibiting the growth of iron-dependent bacteria in inflammatory sites. Con-currently, lysozyme, an enzyme that hydrolyzes the bonds in bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan, contributes to the bactericidal activity, particularly against gram-positive organisms. Further investigations have elucidated the synergistic antimicrobial potential when lysozyme and lactoferrin are combined with immunoglobulins and L-amino acid oxidase, as observed in donkey milk (72, 73). This synergism is attributed to the complementary mechanisms of action of these components, where lysozyme and lactoferrin disrupt bacterial cell walls and sequester essential growth nutrients, respectively, while immunoglobulins provide specific immunity and L-amino acid oxidase generates hydrogen peroxide, contributing to an antimicrobial environment.
The bactericidal mechanisms of lysozyme are multifaceted and can be delineated into three principal categories:
Direct bacteriolysis through peptidoglycan disruption: lysozyme exerts a direct bactericidal effect by cleaving the glycosidic bonds within the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls, a process that is lethal for certain susceptible bacteria. This disruption leads to osmotic imbalance and cell lysis, particularly in some nonpathogenic Gram-positive bacteria such as Micrococcus luteus and various Bacillus species. However, this mechanism is not universally effective across all bacterial species, as some exhibit inherent resistance or acquire resistance through structural modifications of peptidoglycan, such as O-acetylation of N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and de-N-acetylation of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG), which impede lysozyme’s enzymatic activity.
Indirect antimicrobial effects via enzymatic and non-enzymatic activities: beyond its enzymatic action, lysozyme can exhibit antimicrobial activity through non-enzymatic mechanisms, particularly at elevated concentrations. These activities are attributed to the highly cationic nature of lysozyme, facilitating interactions that can compromise bacterial membrane integrity or induce the release of autolytic enzymes, which are typically involved in bacterial cell wall remodeling. This aspect of lysozyme’s function is evidenced by the retention of antimicrobial activity even when the enzyme’s active site is altered by site-directed mutagenesis, suggesting a mechanism independent of its enzymatic cleavage of peptidoglycan.
Synergistic enhancement with host defense molecules: the bactericidal efficacy of lysozyme, particularly against pathogenic and gram-negative bacteria, is significantly augmented in the presence of other host defense molecules, such as lactoferrin, antibodies, complement proteins, hydrogen peroxide, and ascorbic acid. These cofactors are believed to facilitate the disruption of the outer bacterial membrane, thereby enhancing lysozyme’s access to the peptidoglycan layer. This synergistic interaction underscores the collaborative nature of the innate immune system in combating bacterial infections. Furthermore, recent studies have illuminated lysozyme’s role in modulating the host immune response. The enzymatic degradation and subsequent lysis of bacteria by lysozyme result in the release of bacterial components, including peptidoglycan fragments, which can activate pattern recognition receptors on host cells. This process not only contributes to the immediate defense against bacterial invasion but also plays a pivotal role in the activation and regulation of broader immune responses (18, 74–76). Thus, lysozyme’s contribution to antimicrobial defense extends beyond direct bactericidal activity, encompassing roles in immune modulation and synergy with other antimicrobial pathways.
Moreover, lactoferrin has demonstrated significant antiviral activity, inhibiting viral attachment to host cells and replication within them. This is achieved through the blockade of key viral receptors [Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE), Heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG)] and the induction of antiviral cytokines such as interferon (IFN)-α/β (77, 78). The administration of lactoferrin has also been shown to enhance natural killer (NK) cell activity and Th1 cytokine responses, thereby bolstering defenses against viral pathogens (79). The antimicrobial mechanism of donkey milk has been presented in Figure 2.
4.2 Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory role of donkey milk
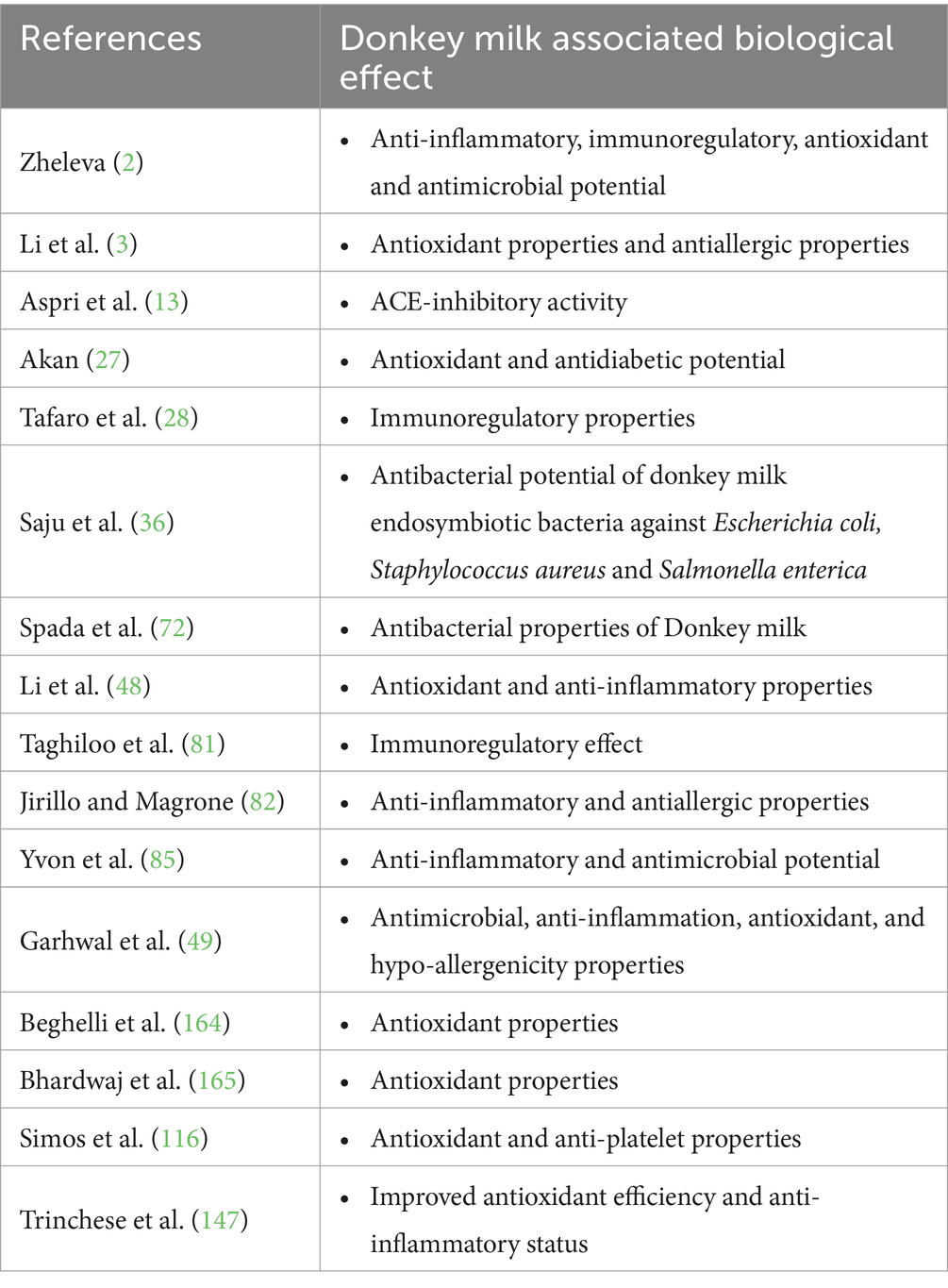
The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of donkey milk have garnered increasing scientific interest, as evidenced by recent studies (Table 2). Consistently, Kocyigit et al. (80) provided a foundational exploration into the anti-inflammatory properties of equid milk, setting a precedent for subsequent investigations in this domain. Our research team further substantiated these findings, demonstrating that the anti-inflammatory and antioxidative attributes of donkey milk contribute significantly to its regulatory effects on health (48). In a detailed study, Taghiloo et al. (81) elucidated the impact of donkey milk on immune cell function, revealing that treatment with donkey milk resulted in elevated levels of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). IL-8 serves as a chemotactic factor for neutrophils, while IL-6 plays a crucial role as an acute phase protein with protective functions. Furthermore, donkey milk was found to modestly enhance the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) from PBMCs, indicating a relatively low pro-inflammatory profile. The stimulation of normal human PBMCs with donkey milk also led to the release of interleukin-10 (IL-10) in supernatants, highlighting its potential to modulate immune responses and maintain immune homeostasis (81). These cytokines are instrumental in the maturation, differentiation, and regulation of immune cells, thereby facilitating the host’s defense mechanisms (82). Previous investigations have shown that donkey milk can induce the production of nitric oxide (NO) from PBMCs and promote adaptive immunity through cytokine production (83). In a mouse model of ileitis, donkey milk exhibited anti-inflammatory properties, which were associated with the normalization of antimicrobial peptides levels (lysozyme and α-defensin) in Paneth cells and a reduction in the dysbiosis typically associated with ileitis (84). Additionally, the impact of donkey milk on gut barrier function was observed in mice subjected to water-avoidance stress, further underscoring its therapeutic potential (85).
The anti-inflammatory capabilities of donkey milk have also been linked to the prevention of allergic asthma, showcasing its broad spectrum of health benefits (86). Moreover, a recent study by Farias et al. (87) demonstrated that asinine milk significantly downregulated salivary cortisol levels and the expression of the IL-1B gene in weaning piglets, thereby mitigating stress-induced inflammatory responses. Collectively, these studies highlight the multifaceted role of donkey milk in modulating inflammation and immune responses, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic agent in various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.
5 Unlocking the health benefits of donkey milk: in vitro insights
5.1 Anticancer activity of donkey milk
Donkey milk is recognized as a reservoir of numerous salutary components, including caseins, Omega-3 fatty acids, lactoferrin, lysozyme, α-lactalbumin, and β-lactoglobulin, which contribute to its potential therapeutic applications. The inclusion of long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) is of particular interest due to their documented role in the prophylaxis of various carcinomas, including but not limited to breast and colorectal cancers (88–97). Consistently, research delineates the inhibitory effects of α-casein on the activity of breast cancer stem cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts in MDA-MB-231 cells, mediated through the modulation of HIF-1α, STAT3, and STAT19 expression (98). Concurrently, Maurmayr et al. have elucidated the potent anti-tumorigenic properties of lactoferrin, α-lactalbumin, and β-lactoglobulin against a spectrum of human tumor cell lines, including A549, HT29, HepG2, and MDA231-LM2 (99).
Investigations into the bioactivity of donkey milk on A549 human lung cancer cells have revealed its capacity to augment the secretion of a cadre of cytokines, including IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β, thereby indicating a dual mechanism of action: direct antiproliferative effects on tumor cells and indirect tumoricidal effects mediated through the activation of lymphocytes and macrophages (100). This assertion is bolstered by Shariatikia et al. (101), who reported dose-dependent cytotoxic effects of donkey milk casein and whey proteins against MCF7 cells. The antiproliferative, antimutagenic, and antibacterial properties of donkey milk kefir have also been documented, with evidence suggesting its role in inducing apoptosis, inhibiting cell proliferation, and reducing the co-expression of iNOS and endothelial-NOS in the context of Ehrlich ascites carcinoma (EAC) in mice (102–105).
Moreover, the comparative analysis of donkey colostrum (DC) and mature milk (DM) on 4 T1 triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) tumors in mice has yielded promising outcomes, with both DC and DM significantly attenuating the primary tumor volume and the relative organ weight of the liver and lungs in the 4 T1 mouse model, without adverse effects on body weight. This antitumor efficacy is attributed to the modulation of apoptotic and angiogenic markers, including an increase in cleaved-caspase-3 and Bax expression and a decrease in MMP2 and CD31 levels (26). Additionally, Akca et al. (106) have identified the anti-proliferative and genotoxic effects of donkey milk on lung cancer cells, with a specificity that spares normal lung cells, further underscoring the potential of donkey milk as a functional food with therapeutic implications in oncology.
5.2 Antidiabetics potential of donkey milk
Bioactive peptides, derived from a variety of protein sources with a notable emphasis on milk proteins, are increasingly recognized for their multifaceted biological functionalities. These include, but are not limited to, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-diabetic, antihypertensive, anticancer, and antitumor properties (107, 108). Type II diabetes mellitus, also referred to as non-insulin dependent diabetes, emerges as a pre-dominant metabolic disorder characterized by persistent hyperglycemia, with a significant global incidence annually (27, 109). The etiology of Type II diabetes is multi-factorial, with obesity, β-cell dysfunction, and insulin resistance in peripheral tissues being primary contributors (110–112).
A pivotal aspect of Type II diabetes management involves the modulation of di-peptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) and α-glucosidase activities, enzymes integral to the inactivation of incretins that are crucial for normoglycemic regulation (113, 114). The inhibition of these enzymes constitutes a strategic approach in the therapeutic management of this condition. Empirical evidence from in vivo investigations has under-scored the regulatory influence of food proteins on serum glucose concentrations (115). Corroborating these findings, in vitro studies have demonstrated that peptides derived from casein significantly attenuate the activity of DPP-IV and α-glucosidase, while concurrently enhancing antioxidant capacities, thereby contributing to the management of Type II diabetes (27).
Furthermore, the antidiabetic potential of donkey milk has been substantiated through various research endeavors (2, 42, 116, 117). Consequently, Li et al. (117) elucidated that donkey milk not only ameliorates the viability of compromised pancreatic β cells but also enhances insulin sensitivity in target organs without directly stimulating insulin secretion from the damaged β cells. This is attributed to the presence of α-lactalbumin in donkey milk. Additionally, donkey milk has been shown to decrease glycosylated hemoglobin levels and exert a therapeutic effect on diabetes by downregulating the expression of key hepatic gluconeogenesis enzymes, namely phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 and glucose-6-phosphatase (117). Collectively, these studies highlight the significant potential of bioactive peptides, particularly those derived from milk proteins, in the prevention and management of type II diabetes through various biochemical mechanisms. The key findings of studies reported the role of donkey milk in health improvement have been summarized in Table 3.
5.3 Use of donkey milk in cow’s milk protein allergy children
The research development on donkey milk as alternative for infants with cow milk allergy has been summarized in Figure 3. Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy (CMPA) delineates an aberrant immunologic response toward proteins presents in cow’s milk, manifesting in a subset of individuals. As a prevalent food allergy, particularly in developed nations, cow’s milk proteins often represent the initial exogenous proteins introduced to infants, with an incidence rate of 2–7% in children under 6 months, which notably diminishes to 0.1–0.5% in adults (118, 119). The allergic manifestations to cow’s milk can be attributed to diverse immunological pathways, including immediate IgE-mediated hypersensitivity, characterized by symptom onset within 30 min post-ingestion, and delayed non-IgE mediated reactions, where symptoms emerge hours to days subsequent to consumption (120, 121). The main allergens in cow’s milk are primarily the caseins (α-s1- and β-caseins). However, β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin are also involved to a lesser extent (118). It is worth noting that the lower allergenic potential of certain types of milk, such as that from non-ruminant animals like donkeys or horses, is not only due to their lower casein content but also to significant sequence differences between the proteins in their milk and those found in ruminants’ milk. Additionally, the reduced allergenicity observed in non-ruminant milk may largely be a result of substantial sequence differences between β-lactoglobulin in non-ruminants and its homologous protein in ruminants.
Figure 3. Research development of donkey milk as alternative in infants with milk cow allergy (1, 6, 7, 12–14, 38, 43, 50–52, 63, 82, 124, 147–163).
Addressing CMPA necessitates the comprehensive exclusion of cow’s milk from the diet. Given the critical role of milk as a nutritional mainstay up to the age of two, outright elimination is inadvisable; instead, alternative milk sources with appropriate nutritional profiles, low allergenic potential, palatability, and economic viability are recommended. While hypoallergenic formulas are preferred for managing CMPA, the incorporation of milk from other species warrants careful pediatric oversight. The diminished allergenicity of donkey milk is chiefly ascribed to its lower casein content (42, 122). Moreover, the high whey protein ratio in donkey milk facilitates easier digestion (123). Despite its lower fat and caloric density, the nutritional value of donkey milk can be enhanced through the addition of medium-chain triglycerides (8). This fat supplementation strategy is equally applicable to lyophilized donkey milk, which according to Vincenzetti et al. (42), retains its nutritional integrity in comparison to its raw counterpart.
6 Factors compromising the compositional properties and quality of donkey milk
The compositional properties and quality of donkey milk are influenced by a multifaceted array of factors, which include but are not limited to the method of preservation, the stage of lactation, and dietary considerations. These elements have been identified as pivotal in determining the nutritional and biochemical profile of donkey milk, with implications for both its quality and utility in various applications (124–126). The factors affecting quality and quantity of donkey milk are summarized in Table 4.
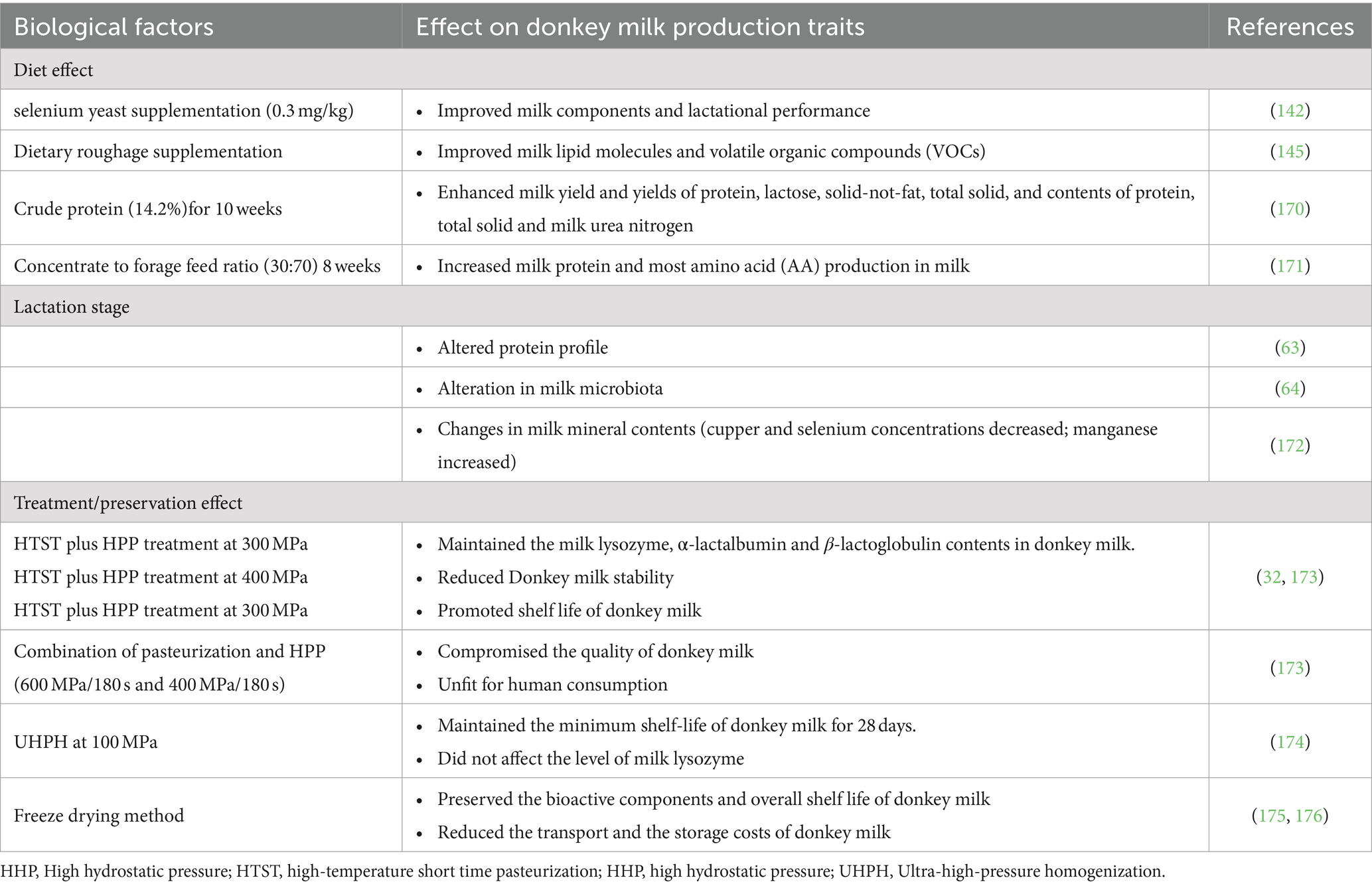
Table 4. Effect of lactation stage, diet and method of preservation/treatment on donkey milk production traits.
6.1 Lactation stage and its impact on donkey milk composition and quality
The stage of lactation has been observed to exert a significant influence on the compositional attributes of donkey milk, particularly with respect to its protein, lipids and volatiles contents (127). Research indicates a progressive decline in milk protein concentration as the lactation period extends (128, 129). This trend is corroborated by Malacarne et al. (40), who noted a discernible impact of the lactation phase on the protein and mineral content of donkey milk, albeit with caseins being an exception. Contrarily, Zhou et al. (63, 64) documented a fluctuating pattern in the relative expression levels of various casein proteins, which initially increased before diminishing as lactation progressed. Complementing these findings, dos Santos et al. (130) reported a decline in total solids and fats in correlation with advanced lactation stages, whereas Salgado et al. (131) observed an enhancement in total polyunsaturated and n − 3 fatty acids over time. Intriguingly, aging was linked with an elevation in protein and fat concentrations in milk, alongside a notable impact on the principal whey proteins, whose contents were also modulated by the lactation stage (130). The expression levels of lactoferrin and other whey proteins such as albumin, lysozyme, β-lactoglobulin, and α-lactalbumin exhibit-ed dynamic changes during the lactation period, with a significant portion of donkey milk protein being constituted by whey proteins (40). The lipid profile of donkey milk was also found to be significantly altered by lactation, with hormonal shifts, particularly in prolactin levels, being implicated in the observed reduction in lipid content (132, 133).
6.2 Dietary influences on donkey milk production traits
Nutritional strategies play a crucial role in optimizing the health and productive performance of livestock, including lactating donkeys. There is a substantial body of evidence underscoring the positive effects of nutrition on the overall well-being and output of livestock animals (134–141). Recent investigations have highlighted the potential of nutritional management during lactation to mitigate oxidative stress and enhance the health and lactational efficiency of donkeys (142–144). Specifically, dietary supplementation with selenium yeast (0.3 mg/kg) has been shown to significantly improve the composition and quality of donkey milk, as well as the overall lactational performance (142). Furthermore, the inclusion of dietary roughage has been associated with an upregulation of lipid molecules and volatile organic compounds in donkey milk, indicating the profound impact of diet on milk compositional traits (145).
6.3 Effect of breed on milk production traits in donkeys
The variability in donkey milk production and composition is closely linked to the specific breed of the animals involved. Studies have demonstrated that certain breeds exhibit markedly higher milk yields compared to others. For instance, Istrian donkeys have been shown to produce significantly more milk than Littoral Dinaric donkeys (146). Similarly, higher milk yields were observed in the Martina Franca and Ragusana breeds when compared with the Amiata jennies (129). Beyond yield, there are notable differences in the compositional traits of milk across various donkey breeds (40, 58, 144, 146). These findings underscore the critical influence of breed as a determining factor in both the quantity and quality of milk produced by donkeys. The breed-specific differences in milk composition likely reflect variations in genetics, physiology, and lactation dynamics, emphasizing the importance of considering breed as a primary factor in the selection of donkeys for milk production purposes. These findings collectively underscore the intricate interplay between lactation stage, dietary practices, and preservation/treatment methods in shaping the compositional quality of donkey milk. Understanding these dynamics is essential for devising strategies to optimize the nutritional value and functional properties of donkey milk for various applications.
7 Future perspectives and limitations
Future studies could focus on the in-depth analysis of the bioactive compounds present in donkey milk, such as lysozyme, lactoferrin, and immunoglobulins, which contribute to its antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities. The exploration of these components could lead to the development of functional foods or supplements aimed at enhancing immune function and overall health. Rigorous clinical trials are necessary to substantiate the health claims associated with donkey milk. This includes its purported benefits in managing allergies, improving gut health, and supporting the immune system. Establishing a strong evidence base will be crucial for gaining regulatory approval and consumer trust in donkey milk as a health-promoting food. As interest in donkey milk increases, sustainable and ethical farming practices must be developed to meet demand without compromising animal welfare or environmental integrity. This includes addressing the challenges of low milk yield and seasonal lactation in donkeys through advancements in animal husbandry and dairy technology. Efforts should be made to increase consumer awareness and acceptance of donkey milk as a nutritious and health-promoting food. This involves overcoming cultural and perceptual barriers, as well as establishing a premium market segment for donkey milk products, akin to those for other non-conventional dairy products like goat or sheep milk.
One of the primary limitations in the use of donkey milk is its low production yield. Donkeys produce significantly less milk than cows, goats, or sheep, and the milking process can be labor-intensive, contributing to higher production costs and limited availability. There is currently a lack of standardization in the production and processing of donkey milk, which can lead to variability in product quality and nutritional content. Establishing industry standards and regulatory guidelines will be essential for ensuring consistency and safety in donkey milk products. Despite promising preliminary research, there are still significant gaps in our understanding of the health benefits and nutritional properties of donkey milk. More comprehensive studies are needed to elucidate its mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications. The economic viability of donkey milk production on a large scale is questionable due to the aforementioned production challenges and market acceptance issues. Developing cost-effective production methods and creating value-added products could help mitigate these concerns.
8 Conclusion
In conclusion, donkey milk presents an intriguing option for health-promoting foods, with its unique nutritional profile and potential therapeutic properties. However, still need deep studies involving both invitro and in vivo experiments to establish the molecular mechanism through which donkey milk showed therapeutic effect against several diseases like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, asthma, hypoallergy and various types of cancers. In addition, realizing its potential will require overcoming significant challenges related to production, research, and market development. Future studies and innovations in dairy technology will play a critical role in addressing these limitations and unlocking the potential of donkey milk as a valuable addition to the functional food market.
Author contributions
MK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. WR: Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. BH: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XK: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. QU: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LW: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. TW: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AK: Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. CW: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ML: Conceptualization, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author (s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (grant no. 2022YFD1600103; 2023YFD1302004); the Shandong Province Modern Agricultural Technology System Donkey Industrial Innovation Team (grant no. SDAIT-27), Livestock and Poultry Breeding Industry Project of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (grant no. 19211162), The National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31671287), The Open Project of Liaocheng University Animal Husbandry Discipline (grant no. 319312101–14), The Open Project of Shandong Collaborative Innovation Center for Donkey Industry Technology (grant no. 3193308), Research on Donkey Pregnancy Improvement (grant no. K20LC0901), Key R&D Program Project of Shandong Province (2021TZXD012) and Liaocheng University scientific research fund (grant no. 318052025).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Baloš, MŽ, Pelić, DL, Jakšić, S, and Lazić, S. Donkey Milk: an overview of its chemical composition and Main nutritional properties or human health benefit properties. J Equine Vet. (2023) 121:104225. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2023.104225
2. Zheleva, NN. Bioactive components of donkey Milk. Food Sci Appl Biotechnol. (2022) 5:219–31. doi: 10.30721/fsab2022.v5.i2.212
3. Li, L, Liu, X, and Guo, H. The nutritional ingredients and antioxidant activity of donkey Milk and donkey Milk powder. Food Sci Biotechnol. (2018) 27:393–400. doi: 10.1007/s10068-017-0264-2
4. Murgia, A, Scano, P, Contu, M, Ibba, I, Altea, M, Bussu, M, et al. Characterization of donkey Milk and metabolite profile comparison with human Milk and formula Milk. LWT. (2016) 74:427–33. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.07.070
5. Albertos, I, Lopez, M, Jimenez, JM, Cao, MJ, Corell, A, and Castro-Alija, MJ. Characterisation of Zamorano-Leonese donkey Milk as an alternative sustainably produced protein food. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:872409. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.872409
6. Vincenzetti, S, Santini, G, Polzonetti, V, Pucciarelli, S, Klimanova, Y, and Polidori, P. Vitamins in human and donkey Milk: functional and nutritional role. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1509. doi: 10.3390/nu13051509
7. Souroullas, K, Aspri, M, and Papademas, P. Donkey Milk as a supplement in infant formula: benefits and technological challenges. Food Res Int. (2018) 109:416–25. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.04.051
8. Salimei, E, and Fantuz, F. Equid Milk for human consumption. Int Dairy J. (2012) 24:130–42. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2011.11.008
9. Mansueto, P, Iacono, G, Taormina, G, Seidita, AU, D’Alcamo, AL, Randazzo, GI, et al. Ass’s Milk in allergy to Cow’s Milk protein: a review. Acta Med Mediterr. (2013) 29:153.
10. Karami, Z, and Akbari-Adergani, B. Bioactive food derived peptides: a review on correlation between structure of bioactive peptides and their functional properties. J Food Sci Technol. (2019) 56:535–47. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3549-4
11. Hassan, ZM, Manyelo, TG, Nemukondeni, N, Sebola, AN, Selaledi, L, and Mabelebele, M. The possibility of including donkey meat and Milk in the food chain: a southern African scenario. Animals. (2022) 12:1073. doi: 10.3390/ani12091073
12. Martini, M, Altomonte, I, Licitra, R, and Salari, F. Nutritional and nutraceutical quality of donkey Milk. J Equine Vet. (2018) 65:33–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2017.10.020
13. Aspri, M, Economou, N, and Papademas, P. Donkey Milk: an overview on functionality, technology, and future prospects. Food Rev Int. (2017) 33:316–33. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2016.1175014
14. Vincenzetti, S, Pucciarelli, S, Polzonetti, V, and Polidori, P. Role of proteins and of some bioactive peptides on the nutritional quality of donkey Milk and their impact on human health. Beverages. (2017) 3:34. doi: 10.3390/beverages3030034
15. Nawaz, N, Wen, S, Wang, F, Nawaz, S, Raza, J, Iftikhar, M, et al. Lysozyme and its application as antibacterial agent in food industry. Molecules. (2022) 27:6305. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196305
16. Sienkiewicz, M, Jaśkiewicz, A, Tarasiuk, A, and Fichna, J. Lactoferrin: an overview of its Main functions, immunomodulatory and antimicrobial role, and clinical significance. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 62:6016–33. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1895063
17. Jiang, L, Li, Y, Wang, L, Guo, J, Liu, W, Meng, G, et al. Recent insights into the prognostic and therapeutic applications of lysozymes. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:767642. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.767642
18. Ferraboschi, P, Ciceri, S, and Grisenti, P. Applications of lysozyme, an innate immune defense factor, as an alternative antibiotic. Antibiotics. (2021) 10:1534. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121534
19. Tagashira, A, Nishi, K, Matsumoto, S, and Sugahara, T. Anti-inflammatory effect of lysozyme from hen egg white on mouse peritoneal macrophages. Cytotechnology. (2018) 70:929–38. doi: 10.1007/s10616-017-0184-2
20. Khan, MI, Dowarha, D, Katte, R, Chou, RH, Filipek, A, and Yu, C. Lysozyme as the anti-proliferative agent to Block the interaction between S100A6 and the RAGE V domain. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0216427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216427
21. Song, Y, Zhang, H, Zhu, Y, Zhao, X, Lei, Y, Zhou, W, et al. Lysozyme protects against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and inflammation in human corneal epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. (2022) 63:16. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.6.16
22. Liao, A-H, Hung, C-R, Lin, C-F, Lin, Y-C, and Chen, H-K. Treatment effects of lysozyme-shelled microbubbles and ultrasound in inflammatory skin disease. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:41325. doi: 10.1038/srep41325
23. Legrand, D. Overview of Lactoferrin as a natural immune modulator. J Pediatr. (2016) 173:S10–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.071
24. Kawakami, H, Park, H, Park, S, Kuwata, H, Shephard, RJ, and Aoyagi, Y. Effects of enteric-coated Lactoferrin supplementation on the immune function of elderly individuals: a randomised, double-blind. Placebo-controlled Trial Int Dairy J. (2015) 47:79–85. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2015.02.001
25. Kowalczyk, P, Kaczyńska, K, Kleczkowska, P, Bukowska-Ośko, I, Kramkowski, K, and Sulejczak, D. The Lactoferrin phenomenon—a miracle molecule. Molecules. (2022) 27:2941. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092941
26. Li, Q, Li, M, Zhang, J, Shi, X, Yang, M, Zheng, Y, et al. Donkey Milk inhibits triple-negative breast tumor progression and is associated with increased cleaved-caspase-3 expression. Food Funct. (2020) 11:3053–65. doi: 10.1039/C9FO02934F
27. Akan, E. An evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials of camel and donkey Milk peptides released from casein and whey proteins. J Food Sci Technol. (2021) 58:3743–51. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04832-5
28. Tafaro, A, Magrone, T, Jirillo, F, Martemucci, G, D’alessandro, AG, Amati, L, et al. Immunological properties of Donkey’s Milk: its potential use in the prevention of atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des. (2007) 13:3711–7. doi: 10.2174/138161207783018590
29. Li, M, Li, Q, Abdlla, R, Chen, J, Yue, X, and Quek, SY. Donkey whey proteins ameliorate dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by downregulating the S100A8-TRAF6-NF-κB Axis-mediated inflammatory response. Food Sci Human Wellness. (2023) 12:1809–19. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2023.02.045
30. Shalhoub, S. Interferon Beta-1b for COVID-19. Lancet. (2020) 395:1670–1. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31101-6
31. Acharya, D, Liu, G, and Gack, MU. Dysregulation of type I interferon responses in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:397–8. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0346-x
32. Gong, H, Wu, X, Du, J, and Mao, X. High hydrostatic pressure combined with high-temperature short time pasteurization improves the quality characteristics and extends the shelf life of donkey Milk. LWT. (2024) 196:115789. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2024.115789
33. Gonçalves, MS, Fidalgo, LG, Sousa, SG, Queirós, RP, Castro, SM, Pinto, CA, et al. Comparison of thermal and high-pressure pasteurization on immunoglobulins, lysozyme, and microbial quality of donkey colostrum. Appl Sci. (2024) 14:1592. doi: 10.3390/app14041592
34. Guan, B, Cao, X, Yang, M, Yue, X, and Liu, D. Comparative site-specific O-glycosylation analysis of the Milk fat globule membrane proteome in donkey colostrum and mature Milk. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:1405–17. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c07805
35. Natrella, G, Maggiolino, A, De Palo, P, Mefleh, M, and Faccia, M. Effect of ultrafiltration on the Cheesemaking properties of donkey Milk. Int Dairy J. (2024) 149:105830. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2023.105830
36. Saju, A, Ali, MM, Mehta, R, Dey, P, and Osborne, WJ. Endosymbiotic Bacteria from donkeys Milk in the inhibition of human pathogens. Food Biosci. (2023) 53:102821. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102821
37. Tidona, F, Sekse, C, Criscione, A, Jacobsen, M, Bordonaro, S, Marletta, D, et al. Antimicrobial effect of donkeys’ Milk digested in vitro with human gastrointestinal enzymes. Int Dairy J. (2011) 21:158–65. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2010.10.008
38. Coscia, A, Bertino, E, Tonetto, P, Peila, C, Cresi, F, Arslanoglu, S, et al. Nutritional adequacy of a novel human Milk fortifier from donkey Milk in feeding preterm infants: study protocol of a randomized controlled clinical trial. Nutr J. (2018) 17:1–7. doi: 10.1186/s12937-017-0308-8
39. Meena, S, Meena, GS, Gautam, PB, Rai, DC, and Kumari, S. A comprehensive review on donkey milk and its products: composition, functionality and processing aspects. Food Chem Adv. (2024) 100647:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2024.100647
40. Malacarne, M, Criscione, A, Franceschi, P, Bordonaro, S, Formaggioni, P, and Marletta, D. New insights into chemical and mineral composition of donkey milk throughout nine months of lactation. Animals. (2019) 9:1161. doi: 10.3390/ani9121161
41. Marino, VM, Schadt, I, La Terra, S, Caccamo, M, and Caggia, C. Lysozyme sources for disease prevention and health promotion—donkey milk in alternative to hen egg-white lysozyme. Future Foods. (2024) 9:100321. doi: 10.1016/j.fufo.2024.100321
42. Vincenzetti, S, Polidori, P, Mariani, P, Cammertoni, N, Fantuz, F, and Vita, A. Donkey’s milk protein fractions characterization. Food Chem. (2008) 106:640–9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.06.026
43. Derdak, R, Sakoui, S, Pop, OL, Muresan, CI, Vodnar, DC, Addoum, B, et al. Insights on health and food applications of Equus asinus (donkey) milk bioactive proteins and peptides—an overview. Food Secur. (2020) 9:1302. doi: 10.3390/foods9091302
44. Cimmino, F, Catapano, A, Villano, I, Di Maio, G, Petrella, L, Traina, G, et al. Invited review: human, cow, and donkey milk comparison: focus on metabolic effects. J Dairy Sci. (2023) 106:3072–85. doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-22465
45. Wang, F, Chen, M, Luo, R, Huang, G, Wu, X, Zheng, N, et al. Fatty acid profiles of milk from Holstein cows, Jersey cows, buffalos, yaks, humans, goats, camels, and donkeys based on gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Dairy Sci. (2022) 105:1687–700. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20750
46. Li, M, Liu, Y, Li, Q, Yang, M, Pi, Y, Yang, N, et al. Comparative exploration of free fatty acids in donkey colostrum and mature milk based on a metabolomics approach. J Dairy Sci. (2020) 103:6022–31. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17720
47. Claeys, WL, Verraes, C, Cardoen, S, De Block, J, Huyghebaert, A, Raes, K, et al. Consumption of raw or heated milk from different species: an evaluation of the nutritional and potential health benefits. Food Control. (2014) 42:188–201. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.01.045
48. Li, Y, Ma, Q, Liu, G, and Wang, C. Effects of donkey milk on oxidative stress and inflammatory response. J Food Biochem. (2022) 46:e13935. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13935
49. Garhwal, R, Sangwan, K, Mehra, R, Kumar, N, Bhardwaj, A, Pal, Y, et al. A systematic review of the bioactive components, nutritional qualities and potential therapeutic applications of donkey milk. J Equine Vet. (2022) 115:104006. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2022.104006
50. Prasad, B. Nutritional and health benefits of donkey milk. J Food Sci Nutr Ther. (2020) 6:022–5.
51. Altomonte, I, Salari, F, Licitra, R, and Martini, M. Donkey and human milk: insights into their compositional similarities. Int Dairy J. (2019) 89:111–8. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2018.09.005
52. Martemucci, G, and D’Alessandro, AG. Fat content, energy value and fatty acid profile of donkey milk during lactation and implications for human nutrition. Lipids Health Dis. (2012) 11:1–4. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-113
53. Šarić, L, Premović, T, Šarić, B, Čabarkapa, I, Todorić, O, Miljanić, J, et al. Microbiological quality of raw donkey milk from Serbia and its antibacterial properties at pre-cooling temperature. Animals. (2023) 13:327. doi: 10.3390/ani13030327
54. Brumini, D, Criscione, A, Bordonaro, S, Vegarud, GE, and Marletta, D. Whey proteins and their antimicrobial properties in donkey milk: a brief review. Dairy Sci Technol. (2016) 96:1–4. doi: 10.1007/s13594-015-0246-1
55. Šarić, L, Šarić, BM, Mandić, AI, Torbica, AM, Tomić, JM, and Cvetković, DD. Antibacterial properties of domestic Balkan donkeys’ milk. Int Dairy J. (2012) 25:142–6. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2012.03.007
56. Šarić, L, Šarić, B, Mandić, AN, Tomić, JE, Torbica, A, Nedeljković, NA, et al. Antibacterial activity of donkey milk against Salmonella. Agro Food Ind Hi Tech. (2014) 25:30–4.
57. Zhang, M, Li, S, Zhao, J, Shuang, Q, Xia, Y, and Zhang, F. A novel endogenous antimicrobial peptide MP-4 derived from koumiss of Inner Mongolia by peptidomics, and effects on Staphylococcus aureus. LWT. (2024) 191:115595. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.115595
58. Massouras, T, Bitsi, N, Paramithiotis, S, Manolopoulou, E, Drosinos, EH, and Triantaphyllopoulos, KA. Microbial profile, antibacterial properties and chemical composition of raw donkey milk. Animals. (2020) 10:2001. doi: 10.3390/ani10112001
59. Ren, S, Chen, A, Tian, Y, Bai, Z, and Wang, C. Lactobacillus paracasei from koumiss ameliorates diarrhea in mice via tight junctions’ modulation. Nutrition. (2022) 98:111584. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111584
60. Šarić, L, Šarić, BM, Mandić, AI, Kevrešan, ŽS, Ikonić, BB, Kravić, SŽ, et al. Role of calcium content in antibacterial activity of donkeys’ milk toward E. coli. Eur Food Res Technol. (2014) 239:1031–9. doi: 10.1007/s00217-014-2299-4
61. Martini, M, Salari, F, Licitra, R, La Motta, C, and Altomonte, I. Lysozyme activity in donkey milk. Int Dairy J. (2019) 96:98–101. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2019.04.009
62. Wang, X, Fei, Y, Shao, Y, Liao, Q, Meng, Q, Chen, R, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals immune function-related mRNA expression in donkey mammary glands during four developmental stages. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. (2024) 49:101169. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2023.101169
63. Zhou, M, Huang, F, Du, X, Wang, C, and Liu, G. Microbial quality of donkey milk during lactation stages. Food Secur. (2023) 12:4272. doi: 10.3390/foods12234272
64. Zhou, M, Huang, F, Du, X, Liu, G, and Wang, C. Analysis of the differentially expressed proteins in donkey milk in different lactation stages. Food Secur. (2023) 12:4466. doi: 10.3390/foods12244466
65. Abad, I, Pemán, L, Pérez, MD, Grasa, L, and Sánchez, L. Does lactoferrin, free, encapsulated or in dairy matrices, maintain its antibacterial activity after in vitro digestion? J Funct Foods. (2024) 112:105936. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2023.105936
66. Ostrówka, M, Duda-Madej, A, Pietluch, F, Mackiewicz, P, and Gagat, P. Testing antimicrobial properties of human lactoferrin-derived fragments. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:10529. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310529
67. Einerhand, AW, van Loo-Bouwman, CA, Weiss, GA, Wang, C, Ba, G, Fan, Q, et al. Can lactoferrin, a natural mammalian milk protein, assist in the battle against COVID-19? Nutrients. (2022) 14:5274. doi: 10.3390/nu14245274
68. Xu, Y, Wang, Y, He, J, and Zhu, W. Antibacterial properties of lactoferrin: a bibliometric analysis from 2000 to early 2022. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:947102. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.947102
69. Kell, DB, Heyden, EL, and Pretorius, E. The biology of lactoferrin, an iron-binding protein that can help defend against viruses and bacteria. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1221. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01221
70. Bielecka, M, Cichosz, G, and Czeczot, H. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticarcinogenic activities of bovine milk proteins and their hydrolysates—a review. Int Dairy J. (2022) 127:105208. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2021.105208
71. Kummer, N, Wu, T, De France, KJ, Zuber, F, Ren, Q, Fischer, P, et al. Self-assembly pathways and antimicrobial properties of lysozyme in different aggregation states. Biomacromolecules. (2021) 22:4327–36. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00870
72. Spada, V, Ferranti, P, Chianese, L, Salimei, E, Addeo, F, and Picariello, G. Antibacterial potential of donkey’s milk disclosed by untargeted proteomics. J Proteome. (2021) 231:104007. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2020.104007
73. Guo, HY, Pang, K, Zhang, XY, Zhao, L, Chen, SW, Dong, ML, et al. Composition, physicochemical properties, nitrogen fraction distribution, and amino acid profile of donkey milk. J Dairy Sci. (2007) 90:1635–43. doi: 10.3168/jds.2006-600
74. Ragland, SA, and Criss, AK. From bacterial killing to immune modulation: recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Pathog. (2017) 13:e1006512. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006512
75. Bersch, KL, DeMeester, KE, Zagani, R, Chen, S, Wodzanowski, KA, Liu, S, et al. Bacterial peptidoglycan fragments differentially regulate innate immune signaling. ACS Cent Sci. (2021) 7:688–96. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00200
76. Li, D, and Wu, M. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2021) 6:291. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00687-0
77. Wakabayashi, H, Oda, H, Yamauchi, K, and Abe, F. Lactoferrin for prevention of common viral infections. J Infect Chemother. (2014) 20:666–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2014.08.003
78. Andreu, S, Ripa, I, Bello-Morales, R, and López-Guerrero, JA. Liposomal lactoferrin exerts antiviral activity against HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses in vitro. Viruses. (2023) 15:972. doi: 10.3390/v15040972
79. Coccolini, C, Berselli, E, Blanco-Llamero, C, Fathi, F, Oliveira, MB, Krambeck, K, et al. Biomedical and nutritional applications of lactoferrin. Int J Pept Res Ther. (2023) 29:71. doi: 10.1007/s10989-023-10541-2
80. Kocyigit, E, Abdurakhmanov, R, and Kocyigit, BF. Potential role of camel, mare milk, and their products in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Int. (2024) 44:425–34. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05516-x
81. Taghiloo, S, Allahmoradi, E, Sadeghian-Kiadehi, SF, Omrani-Nava, V, Nazar, E, and Ebrahimzadeh, MA. Up-regulation of human immune system function by Donkey’s Milk. Braz. J Pharm Sci. (2021) 56:56. doi: 10.1590/s2175-97902019000418449
82. Jirillo, F, and Magrone, T. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties of donkey’s and goat’s milk. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. (2014) 14:27–37. doi: 10.2174/1871530314666140121143747
83. Jirillo, F, Jirillo, E, and Magrone, T. Donkey’s and goat’s milk consumption and benefits to human health with special reference to the inflammatory status. Curr Pharm Des. (2010) 16:859–63. doi: 10.2174/138161210790883688
84. Yvon, S, Olier, M, Leveque, M, Jard, G, Tormo, H, Haimoud-Lekhal, DA, et al. Donkey milk consumption exerts anti-inflammatory properties by normalizing antimicrobial peptides levels in Paneth’s cells in a model of ileitis in mice. Eur J Nutr. (2018) 57:155–66. doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1304-z
85. Yvon, S, Schwebel, L, Belahcen, L, Tormo, H, Peter, M, Haimoud-Lekhal, DA, et al. Effects of thermized donkey milk with lysozyme activity on altered gut barrier in mice exposed to water-avoidance stress. J Dairy Sci. (2019) 102:7697–706. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16642
86. Lu, Y, Zhou, Y, Lin, Y, Li, W, Tian, S, Hao, X, et al. Preventive effects of donkey milk powder on the ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice. J Funct Foods. (2021) 84:104603. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104603
87. Farias, SD, Dierings, AC, Mufalo, VC, Sabei, L, Parada Sarmiento, M, Silva, AN, et al. Asinine milk mitigates stress-mediated immune, cortisol and behavioral responses of piglets to weaning: a study to foster future interventions in humans. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1139249. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1139249
88. Guo, W, Liu, S, Khan, MZ, Wang, J, Chen, T, Alugongo, GM, et al. Bovine milk microbiota: key players, origins, and potential contributions to early-life gut development. J Adv Res. (2023) 59:49–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.06.016
89. Khadge, S, Thiele, GM, Sharp, JG, McGuire, TR, Klassen, LW, Black, PN, et al. Correction: long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease mammary tumor growth, multiorgan metastasis and enhance survival. Clin Exp Metastasis. (2023) 40:441. doi: 10.1007/s10585-023-10226-6
90. Liput, KP, Lepczyński, A, Ogłuszka, M, Nawrocka, A, Poławska, E, Grzesiak, A, et al. Effects of dietary n–3 and n–6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in inflammation and cancerogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:6965. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136965
91. Goupille, C, Frank, PG, Arbion, F, Jourdan, ML, Guimaraes, C, Pinault, M, et al. Low levels of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and bone metastasis in premenopausal women with breast cancer. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3832. doi: 10.3390/nu12123832
92. Khadge, S, Thiele, GM, Sharp, JG, McGuire, TR, Klassen, LW, Black, PN, et al. Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease mammary tumor growth, multiorgan metastasis and enhance survival. Clin Exp Metastasis. (2018) 35:797–818. doi: 10.1007/s10585-018-9941-7
93. Wang, W, Yang, J, Nimiya, Y, Lee, KS, Sanidad, K, Qi, W, et al. ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and their cytochrome P 450-derived metabolites suppress colorectal tumor development in mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2017) 48:29–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.06.006
94. Chung, H, Lee, YS, Mayoral, R, Oh, DY, Siu, JT, Webster, NJ, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce obesity-induced tumor progression independent of GPR120 in a mouse model of postmenopausal breast cancer. Oncogene. (2015) 34:3504–13. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.283
95. Wang, W, Zhu, J, Lyu, F, Panigrahy, D, Ferrara, KW, Hammock, B, et al. ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids-derived lipid metabolites on angiogenesis, inflammation and cancer. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. (2014) 113-115:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2014.07.002
96. Xu, Y, and Qian, SY. Anti-cancer activities of ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biom J. (2014) 37:112–9. doi: 10.4103/2319-4170.131378
97. Cockbain, AJ, Toogood, GJ, and Hull, MA. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids for the treatment and prevention of colorectal cancer. Gut. (2012) 61:135–49. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.233718
98. Bonuccelli, G, Castello-Cros, R, Capozza, F, Martinez-Outschoorn, UE, Lin, Z, Tsirigos, A, et al. The milk protein α-casein functions as a tumor suppressor via activation of STAT1 signaling, effectively preventing breast cancer tumor growth and metastasis. Cell Cycle. (2012) 11:3972–82. doi: 10.4161/cc.22227
99. Maurmayr, A, Cecchinato, A, Grigoletto, L, and Bittante, G. Detection and quantification of αS1-, αS2-, β-, κ-casein, α-lactalbumin, β-lactoglobulin, and lactoferrin in bovine milk by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Agric Conspec Sci. (2013) 78:201–5.
100. Mao, X, Gu, J, Sun, Y, Xu, S, Zhang, X, Yang, H, et al. Anti-proliferative and anti-tumour effect of active components in donkey milk on A549 human lung cancer cells. Int Dairy J. (2009) 19:703–8. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.05.007
101. Shariatikia, M, Behbahani, M, and Mohabatkar, H. Anticancer activity of cow, sheep, goat, mare, donkey, and camel milks and their caseins and whey proteins and in silico comparison of the caseins. Mol Biol Res Commun. (2017) 6:57–64.
102. Egea, MB, Santos, DC, Oliveira Filho, JG, Ores, JD, Takeuchi, KP, and Lemes, AC. A review of nondairy kefir products: their characteristics and potential human health benefits. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 62:1536–52. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1844140
103. Guzel-Seydim, ZB, Gökırmaklı, Ç, and Greene, AK. A comparison of milk kefir and water kefir: physical, chemical, microbiological and functional properties. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2021) 113:42–53. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.04.041
104. Esener, OB, Balkan, BM, Armutak, EI, Uvez, A, Yildiz, G, Hafizoglu, M, et al. Donkey milk kefir induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation of Ehrlich ascites carcinoma by decreasing iNOS in mice. Biotech Histochem. (2018) 93:424–31. doi: 10.1080/10520295.2018.1448112
105. Guzel-Seydim, ZB, Kok-Tas, T, Greene, AK, and Seydim, AC. Functional properties of kefir. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2011) 51:261–8. doi: 10.1080/10408390903579029
106. Akca, C, Vatan, O, Yilmaz, D, Huriyet, H, Cinkilic, N, and Cavas, T. In vitro cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of donkey milk on lung cancer and normal cells lines. Czech J Food Sci. (2019) 37:29–35. doi: 10.17221/221/2018-CJFS
107. Khan, MZ, Xiao, J, Ma, Y, Ma, J, Liu, S, Khan, A, et al. Research development on anti-microbial and antioxidant properties of camel milk and its role as an anti-cancer and anti-hepatitis agent. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:788. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050788
108. Ayyash, M, Al-Dhaheri, AS, Al Mahadin, S, Kizhakkayil, J, and Abushelaibi, A. In vitro investigation of anticancer, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, and antioxidant activities of camel milk fermented with camel milk probiotic: a comparative study with fermented bovine milk. J Dairy Sci. (2018) 101:900–11. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13400
109. Cho, NH, Shaw, JE, Karuranga, S, Huang, Y, da Rocha Fernandes, JD, Ohlrogge, AW, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2018) 138:271–81. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023
110. Dong, Q, Huang, J, Liu, S, Yang, L, Li, J, Li, B, et al. A survey on glycemic control rate of type 2 diabetes mellitus with different therapies and patients’ satisfaction in China. Patient Prefer Adherence. (2019) 13:1303–10. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S198908
111. Jia, W, Weng, J, Zhu, D, Ji, L, Lu, J, Zhou, Z, et al. Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2019) 35:e3158. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3158
112. Weng, J, Ji, L, Jia, W, Lu, J, Zhou, Z, Zou, D, et al. Standards of care for type 2 diabetes in China. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2016) 32:442–58. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2827
113. Kamal, H, Jafar, S, Mudgil, P, Murali, C, Amin, A, and Maqsood, S. Inhibitory properties of camel whey protein hydrolysates toward liver cancer cells, dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, and inflammation. J Dairy Sci. (2018) 101:8711–20. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-14586
114. Demuth, HU, McIntosh, CHS, and Pederson, RA. Type 2 diabetes therapy with dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta, Proteins Proteomics. (2005) 1751:33–44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.05.010
115. Lacroix, IME, and Li-Chan, ECY. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV and α-glucosidase activities by pepsin-treated whey proteins. J Agric Food Chem. (2013) 61:7500–6. doi: 10.1021/jf401000s
116. Simos, Y, Metsios, A, Verginadis, I, D’Alessandro, AG, Loiudice, P, Jirillo, E, et al. Antioxidant and anti-platelet properties of milk from goat, donkey and cow. Int Dairy J. (2011) 21:901–6. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2011.05.007
117. Li, Y, Fan, Y, Shaikh, AS, Wang, Z, Wang, D, and Tan, H. Dezhou donkey (Equus asinus) milk a potential treatment strategy for type 2 diabetes. J Ethnopharmacol. (2020) 246:112221. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112221
118. Host, A, and Halken, S. Cow’s milk allergy: where have we come from and where are we going? Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. (2014) 14:2–8. doi: 10.2174/1871530314666140121142900
119. Polidori, P, and Vincenzetti, S. Use of donkey milk in children with cow’s milk protein allergy. Food Secur. (2013) 2:151–9. doi: 10.3390/foods2020151
120. Caffarelli, C, Baldi, F, Bendandi, B, Calzone, L, Marani, M, and Pasquinelli, P. Cow’s milk protein allergy in children: a practical guide. Ital J Pediatr. (2010) 36:5–7. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-36-5
121. Muraro, MA, Giampietro, PG, and Galli, E. Soy formulas and nonbovine milk. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2002) 89:97–101. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62132-1
122. Vincenzetti, S, Savini, M, Cecchini, C, Micozzi, D, Carpi, F, Vita, A, et al. Effects of lyophilization and use of probiotics on donkey’s milk nutritional characteristics. Int J Food Eng. (2011) 7:1–14. doi: 10.2202/1556-3758.2032
123. Tidona, F, Criscione, A, Devold, TG, Bordonaro, S, Marletta, D, and Vegarud, GE. Protein composition and micelle size of donkey milk with different protein patterns: effects on digestibility. Int Dairy J. (2014) 35:57–62. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2013.10.018
124. Cunsolo, V, Saletti, R, Muccilli, V, Gallina, S, Di Francesco, A, and Foti, S. Proteins and bioactive peptides from donkey milk: the molecular basis for its reduced allergenic properties. Food Res Int. (2017) 99:41–57. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.002
125. Raspa, F, Cavallarin, L, McLean, AK, Bergero, D, and Valle, E. A review of the appropriate nutrition welfare criteria of dairy donkeys: nutritional requirements, farm management requirements and animal-based indicators. Animals. (2019) 9:315. doi: 10.3390/ani9060315
126. Valle, E, Pozzo, L, Giribaldi, M, Bergero, D, Gennero, MS, Dezzutto, D, et al. Effect of farming system on donkey milk composition. J Sci Food Agric. (2018) 98:2801–8. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8777
127. Li, M, Sun, L, Du, X, Zhao, Y, Ren, W, Man, L, et al. Characterization and discrimination of donkey milk lipids and volatiles across lactation stages. Food Chem X. (2024) 23:101740. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101740
128. Cosentino, C, Paolino, R, Freschi, P, and Calluso, AM. Short communication: Jenny milk production and qualitative characteristics. J Dairy Sci. (2012) 95:2910–5. doi: 10.3168/jds.2011-5232
129. Martini, M, Altomonte, I, Manica, E, and Salari, F. Changes in donkey Milk lipids in relation to season and lactation. J Food Compos Anal. (2015) 41:30–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2014.12.019
130. dos Santos, IC, Rangel, AHN, Ribeiro, CV, and de Araujo Oliveira, CA. Donkey Milk composition is altered by lactation stage and jennies age. J Food Compos Anal. (2023) 115:104971. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104971
131. Salgado, JG, Silva, AR, de Souza, CO, Lemos, PVF, Oliveira, RL, de Araujo Oliveira, CA, et al. Days in Milk alters the Milk fatty acid profile of grazing donkeys: a preliminary study. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. (2021) 105:1173–8. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13513
132. Li, M, Li, W, Wu, J, Zheng, Y, Shao, J, Li, Q, et al. Quantitative Lipidomics reveals alterations in donkey Milk lipids according to lactation. Food Chem. (2020) 310:125866. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125866
133. Martini, M, Altomonte, I, and Caroli, AM. Short communication: monitoring nutritional quality of Amiata donkey milk: effects of lactation and productive season. J Dairy Sci. (2014) 97:6819–22. doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-8544
134. Khan, MZ, Huang, B, Ullah, Q, Khan, IM, and Khan, A. Enhancing bovine immune, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory responses with vitamins, rumen-protected amino acids, and trace minerals to prevent Periparturient mastitis. Front Immunol. (2024) 14:1290044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1290044
135. Khan, MZ, Liu, S, Ma, Y, Ma, M, Ullah, Q, Khan, IM, et al. Overview of the effect of rumen-protected limiting amino acids (methionine and lysine) and choline on the immunity, Antioxidative, and inflammatory status of Periparturient ruminants. Front Immunol. (2023) 13:1042895. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1042895
136. Huang, B, Khan, MZ, Kou, X, Chen, Y, Liang, H, Ullah, Q, et al. Enhancing metabolism and Milk production performance in Periparturient dairy cattle through rumen-protected methionine and choline supplementation. Meta. (2023) 13:1080. doi: 10.3390/metabo13101080
137. Khan, MZ, Ma, Y, Xiao, J, Chen, T, Ma, J, Liu, S, et al. Role of selenium and vitamins E and B9 in the alleviation of bovine mastitis during the Periparturient period. Antioxidants. (2022) 11:657. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040657
138. Xiao, J, Khan, MZ, Ma, Y, Alugongo, GM, Ma, J, Chen, T, et al. The antioxidant properties of selenium and vitamin E; their role in Periparturient dairy cattle health regulation. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:1555. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101555
139. Khan, MZ, Liu, L, Zhang, Z, Khan, A, Wang, D, Mi, S, et al. Folic acid supplementation regulates Milk production variables, metabolic associated genes and pathways in perinatal Holsteins. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. (2020) 104:483–92. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13313
140. Khan, MZ, Khan, A, Xiao, J, Dou, J, Liu, L, and Yu, Y. Overview of folic acid supplementation alone or in combination with vitamin B12 in dairy cattle during Periparturient period. Meta. (2020) 10:263. doi: 10.3390/metabo10060263
141. Khan, MZ, Zhang, Z, Liu, L, Wang, D, Mi, S, Liu, X, et al. Folic acid supplementation regulates key immunity-associated genes and pathways during the Periparturient period in dairy cows. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2020) 33:1507–19. doi: 10.5713/ajas.18.0852
142. Tong, M, Li, S, Hui, F, Meng, F, Li, L, Shi, B, et al. Effects of dietary selenium yeast supplementation on lactation performance, antioxidant status, and immune responses in lactating donkeys. Antioxidants. (2024) 13:275. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030275
143. Huang, B, Khan, MZ, Wang, X, and Zhang, Z. Yeast polysaccharide supplementation: impact on lactation, growth, immunity, and gut microbiota in Dezhou donkeys. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1289371. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1289371
144. Salari, F, Licitra, R, Altomonte, I, and Martini, M. Donkey feeding during maintenance, pregnancy, and lactation: effects on Body weight, Milk production, and foal growth. J Equine Vet. (2020) 91:103131. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2020.103131
145. Ren, W, Sun, M, Shi, X, Wang, T, Wang, Y, Wang, X, et al. Effects of roughage on the lipid and volatile-organic-compound profiles of donkey Milk. Food Secur. (2023) 12:2231. doi: 10.3390/foods12112231
146. Ivanković, A, Šubara, G, Bittante, G, Šuran, E, Amalfitano, N, Aladrović, J, et al. Potential of endangered local donkey breeds in meat and milk production. Animals. (2023) 13:2146. doi: 10.3390/ani13132146
147. Trinchese, G, Cavaliere, G, De Filippo, C, Aceto, S, Prisco, M, Chun, JT, et al. Human milk and donkey milk, compared to cow milk, reduce inflammatory mediators and modulate glucose and lipid metabolism in rat skeletal muscle. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:32. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00032
148. Ji, Z, Dong, R, Du, Q, Jiang, H, Fan, R, Bu, D, et al. Insight into differences in whey proteome from human and eight dairy animal species for formula humanization. Food Chem. (2024) 430:137076. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137076
149. Lajnaf, R, Feki, S, Ameur, SB, Attia, H, Kammoun, T, Ayadi, MA, et al. Cows’ milk alternatives for children with cows’ milk protein allergy: review of health benefits and risks of allergic reaction. Int Dairy J. (2023) 141:105624. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2023.105624
150. Ning, J, Yang, M, Liu, W, Luo, X, and Yue, X. Proteomics and peptidomics as a tool to compare the proteins and endogenous peptides in human, cow, and donkey milk. J Agric Food Chem. (2023) 71:16435–51. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c04534
151. Salvo, ED, Conte, F, Casciaro, M, Gangemi, S, and Cicero, N. Bioactive natural products in donkey and camel milk: a perspective review. Nat Prod Res. (2023) 37:2098–112. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2022.2116706
152. Zhang, X, Jiang, G, Ji, C, Fan, Z, Ge, S, Li, H, et al. Comparative whey proteome profiling of donkey milk with human and cow milk. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:911454. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.911454
153. Zhang, X, Jiang, B, Ji, C, Li, H, Yang, L, Jiang, G, et al. Quantitative label-free proteomic analysis of milk fat globule membrane in donkey and human milk. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:670099. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.670099
154. Zhang, X, Li, H, Yang, L, Jiang, G, Ji, C, Zhang, Q, et al. Comparative lipidomics profiling of donkey milk with cow and human milk by UHPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J Food Compos Anal. (2021) 101:103988. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.103988
155. Martini, M, Altomonte, I, Tricò, D, Lapenta, R, and Salari, F. Current knowledge on functionality and potential therapeutic uses of donkey milk. Animals. (2021) 11:1382. doi: 10.3390/ani11051382
156. Bertino, E, Cavallarin, L, Cresi, F, Tonetto, P, Peila, C, Ansaldi, G, et al. A novel donkey milk–derived human milk fortifier in feeding preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2019) 68:116–23. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002168
157. Sarti, L, Martini, M, Brajon, G, Barni, S, Salari, F, Altomonte, I, et al. Donkey’s milk in the management of children with cow’s milk protein allergy: nutritional and hygienic aspects. Ital J Pediatr. (2019) 45:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s13052-019-0700-4
158. Barni, S, Sarti, L, Mori, F, Muscas, G, Belli, F, Pucci, N, et al. Tolerability and palatability of donkey’s milk in children with cow’s milk allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2018) 29:329–31. doi: 10.1111/pai.12871
159. Pastuszka, R, Barłowska, J, and Litwińczuk, Z. Allergenicity of milk of different animal species in relation to human milk. Adv Hyg Exp Med. (2016) 70:1451–9. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1227842
160. Ragona, G, Corrias, F, Benedetti, M, Paladini, M, Salari, F, and Martini, M. Amiata donkey milk chain: animal health evaluation and milk quality. Ital J Food Saf. (2016) 5:173–178. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2016.5951
161. Polidori, P, Ariani, A, and Vincenzetti, S. Use of donkey milk in cases of cow’s milk protein allergies. Int J. (2015) 4:174–9. doi: 10.6000/1929-4247.2015.04.03.6
162. Vincenzetti, S, Foghini, L, Pucciarelli, S, Polzonetti, V, Cammertoni, N, Beghelli, D, et al. Hypoallergenic properties of donkey’s milk: a preliminary study. Vet Ital. (2014) 50:99–107. doi: 10.12834/VetIt.219.125.5
163. Monti, G, Viola, S, Baro, C, Cresi, F, Tovo, PA, Moro, G, et al. Tolerability of donkey’s milk in 92 highly-problematic cow’s milk allergic children. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. (2012) 26:75–82.
164. Beghelli, D, Lupidi, G, Damiano, S, Cavallucci, C, Bistoni, O, De Cosmo, AM, et al. Rapid assay to evaluate the total antioxidant capacity in donkey milk and in more common animal milk for human consumption. Austin Food Sci. (2016) 1:1–4.
165. Bhardwaj, A, Kumari, P, Nayan, V, Legha, RA, Gautam, U, Pal, Y, et al. Estimation of antioxidant potential of indigenous Halari and French Poitu donkey milk. Asian J Dairy Food Res. (2019) 38:307–10. doi: 10.18805/ajdfr.DR-1501
166. Trinchese, G, Cimmino, F, Cavaliere, G, Rosati, L, Catapano, A, Sorriento, D, et al. Heart mitochondrial metabolic flexibility and redox status are improved by donkey and human milk intake. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:1807. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111807
167. Tang, W, Shao, X, Chen, Q, Zhu, L, He, Y, and Lu, E. Nutritional status of protein intake in severe pneumonia patients. J Infect Public Health. (2021) 14:66–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2019.07.016
168. Kocic, H, Langerholc, T, Kostic, M, Stojanovic, S, Najman, S, Krstic, M, et al. The regenerative potential of donkey and human milk on the redox-sensitive and proliferative signaling pathways of skin fibroblasts. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2020/5618127
169. Li, A, He, H, Chen, Y, Liao, F, Tang, J, Li, L, et al. Effects of donkey milk on UVB-induced skin barrier damage and melanin pigmentation. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1121498. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1121498
170. Yue, Y, Li, L, Tong, M, Li, S, Zhao, Y, Guo, X, et al. Effect of varying dietary crude protein level on Milk production, nutrient digestibility, and serum metabolites by lactating donkeys. Animals. (2022) 12:2066. doi: 10.3390/ani12162066
171. Liang, XS, Yue, YX, Zhao, YL, Guo, YM, Guo, XY, Shi, BL, et al. Effects of dietary concentrate to forage ratio on Milk performance, Milk amino acid composition and Milk protein synthesis of lactating donkeys. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2022) 292:115444. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2022.115444
172. Fantuz, F, Ferraro, S, Todini, L, Mariani, P, Piloni, R, and Salimei, E. Essential trace elements in Milk and blood serum of lactating donkeys as affected by lactation stage and dietary supplementation with trace elements. Animal. (2013) 7:1893–9. doi: 10.1017/S175173111300133X
173. Giacometti, F, Bardasi, L, Merialdi, G, Morbarigazzi, M, Federici, S, Piva, S, et al. Shelf life of donkey Milk subjected to different treatment and storage conditions. J Dairy Sci. (2016) 99:4291–9. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-10741
174. Addo, CN, and Ferragut, V. Evaluating the ultra-high pressure homogenization (UHPH) and pasteurization effects on the quality and shelf life of donkey Milk. Int J Food Stud. (2015) 4:4. doi: 10.7455/ijfs.v4i1.271
175. Vincenzetti, S, Cecchi, T, Perinelli, DR, Pucciarelli, S, Polzonetti, V, Bonacucina, G, et al. Effects of freeze-drying and spray-drying on donkey Milk volatile compounds and whey proteins stability. LWT. (2018) 88:189–95. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.10.019
Keywords: donkey milk, lysozyme, lactoferrin, antioxidant, antibacterial, immune regulator, therapeutic potential
Citation: Khan MZ, Chen W, Li M, Ren W, Huang B, Kou X, Ullah Q, Wei L, Wang T, Khan A, Zhang Z, Li L and Wang C (2024) Is there sufficient evidence to support the health benefits of including donkey milk in the diet? Front. Nutr. 11:1404998. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1404998
Edited by:
Weicheng Hu, Yangzhou University, ChinaReviewed by:
Gianluca Picariello, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyYaowei Liu, Jiangnan University, China
Copyright © 2024 Khan, Chen, Li, Ren, Huang, Kou, Ullah, Wei, Wang, Khan, Zhang, Li and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Changfa Wang, d2FuZ2NoYW5nZmFAbGN1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Muhammad Zahoor Khan
Muhammad Zahoor Khan Wenting Chen1†
Wenting Chen1† Qudrat Ullah
Qudrat Ullah Tongtong Wang
Tongtong Wang Adnan Khan
Adnan Khan Zhenwei Zhang
Zhenwei Zhang