
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Nutr., 06 September 2022
Sec. Food Chemistry
Volume 9 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.953463
This article is a correction to:
Hsian-Tsao (Mesona chinensis Benth.) Extract Improves the Thermal Tolerance of Drosophila melanogaster
 Yan Huang1,2,3
Yan Huang1,2,3 Pumo Cai2
Pumo Cai2 Xinxin Su1,3
Xinxin Su1,3 Mingjing Zheng1,3,5
Mingjing Zheng1,3,5 Wenwen Chi1,3
Wenwen Chi1,3 Shaoling Lin1,3
Shaoling Lin1,3 Zhiwei Huang1,3
Zhiwei Huang1,3 Si Qin4
Si Qin4 Shaoxiao Zeng1,3*
Shaoxiao Zeng1,3*A corrigendum on
Hsian-Tsao (Mesona chinensis Benth.) extract improves the thermal tolerance of Drosophila melanogaster
by Huang, Y., Cai, P., Su, X., Zheng, M., Chi, W., Lin, S., Huang, Z., Qin, S., and Zeng, S. (2022). Front. Nutr. 9:819319. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.819319
In the published article, there was an error in Figures 5A, 6 as published. Figure 5A was not the latest version we uploaded, and Figure 6 was wrongly used. The corrected Figures 5A, 6 and their captions appear below.
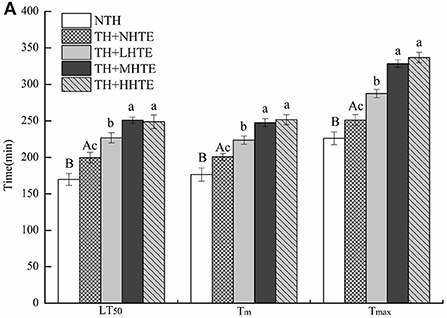
Figure 5. The lethal time of 50% (LT50), mean survival time (Tm), and maximum survival time (Tmax) (A) and survival curves (B) of female flies fed a diet containing hsian-tsao extract (HTE) of low, medium, or high concentrations (TH + LHTE, TH + MHTE, or TH + HHTE) with thermal hardening (TH) and a non-HTE control diet with or without TH (TH + NHTE, NTH) (150 female flies per group, 50 per replicate). Data show mean ± SD. Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences between NTH and TH + NHTE, while different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between groups with thermal hardening (LSD test after one-way ANOVA, P < 0.05).
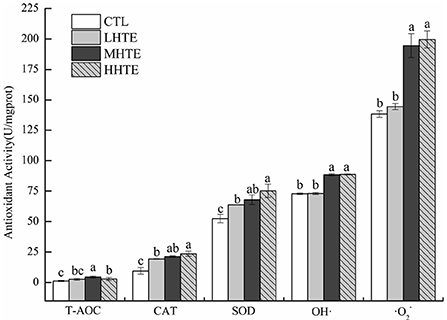
Figure 6. Total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), catalase (CAT) activity, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and the inhibition for hydroxyl radical (OH·) and superoxide anion (·) of female flies under thermal stress fed a diet containing hsian-tsao extract (HTE) of low, medium, or high concentrations (LHTE, MHTE, or HHTE) or a non-HTE control diet (CTL) (90 female flies per group, 30 per replicate). Data show mean ± SD. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between groups (LSD test after one-way ANOVA, P < 0.05).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Mesona chinensis Benth, Drosophila melanogaster, thermal tolerance, antioxidant activities, heat shock protein
Citation: Huang Y, Cai P, Su X, Zheng M, Chi W, Lin S, Huang Z, Qin S and Zeng S (2022) Corrigendum: Hsian-Tsao (Mesona chinensis Benth.) extract improves the thermal tolerance of Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Nutr. 9:953463. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.953463
Received: 26 May 2022; Accepted: 05 August 2022;
Published: 06 September 2022.
Edited and reviewed by: Michael Rychlik, Technical University of Munich, Germany
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Cai, Su, Zheng, Chi, Lin, Huang, Qin and Zeng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shaoxiao Zeng, enN4ZnN0QGZhZnUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.