
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Neurol. , 02 April 2025
Sec. Headache and Neurogenic Pain
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2025.1561000
Many migraine triggers, such as stress, sleep deprivation, fatigue, strenuous exercise, and fasting, are potentially linked to disturbances in brain energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, and oxidative stress. Alongside efforts to avoid modifiable factors, prophylactic migraine treatments that target brain energy metabolism have garnered increasing attention. However, the current evidence supporting the use of energy-modulating drugs in migraine treatment guidelines remains weak. This narrative review explores the relationship between energy metabolism and cortical spreading depression susceptibility, metabolic alterations in migraine (including glucose and insulin metabolism, insulin resistance, lipid metabolism, and energy metabolism imaging markers), oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses, mitochondrial dysfunction, and the role of energy metabolism-targeted medications in migraine management. Nutrients may help improve mitochondrial function, thereby alleviating brain energy metabolism deficits and oxidative stress in migraine.
Among 369 diseases analyzed across 204 countries, headache disorders ranked 14th in disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for the general population and were positioned as the second leading cause of DALYs in females aged 15–49 years (1). Migraine constitutes the second leading cause of health loss measured by years lived with disability (YLD) among all diseases in the general population, surpassing the aggregate burden of all other neurological disorders combined (2). Of note, migraine has been the leading cause of DALYs among youths and young adults in East Asia over the past 30 years (3). Numerous external environmental and internal factors are known to trigger migraine. External factors include temperature fluctuations, bright lights, loud noises, and strong odors, while internal triggers encompass anxiety, emotional stress, insomnia, specific foods, and inadequate blood glucose supply (4). A growing body of evidence points to a significant link between migraine and disruptions in brain energy metabolism (5). Many migraine triggers, such as stress, sleep deprivation, fatigue, strenuous exercise, and fasting, are potentially related to disturbances in brain energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, and oxidative stress (6). Clinical studies have also identified elevated levels of inflammatory markers and oxidative stress biomarkers in individuals with migraine (7). It has been suggested that the brain energy deficit-mitochondrial-oxidative stress axis may represent a key pathway in migraine pathogenesis (8). As a result, prophylactic treatments for migraine that target brain energy metabolism, including riboflavin, coenzyme Q10, alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), and ketogenic diet (KD), have gained increasing attention (Table 1).
Cortical spreading depression (CSD) is a neurophysiological phenomenon characterized by the strong depolarization of regional neurons or glial cells, spreading along the cortex to neighboring regions at a rate of 3–5 mm/min, ultimately leading to inhibition of neural activity (9). CSD is closely associated with migraine aura but is also observed in cerebral ischemia, epilepsy, and traumatic brain injury (10). The mechanisms underlying CSD involve an imbalance in the brain’s ionic homeostasis and disruptions in energy metabolism. Noninvasive detection of CSD in rats using near-infrared spectroscopy suggests that O₂ transport from blood to mitochondria is restricted, leading to reduced oxygen utilization during CSD (11). In addition to migraine-related CSD, brief needling of the frontal cortex has been shown to induce CSD, resulting in a sustained increase in cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen and a decrease in basal cerebral blood flow (12). CSD is associated with significant cerebral vasoconstriction (13), which triggers neuronal swelling and activation of meningeal trigeminal nerve endings and the trigeminal vascular system, ultimately contributing to migraine development (14–16). Cerebral glycogen deficiency or sleep deprivation leads to elevated extracellular potassium and glutamate concentrations (17), lowering the threshold for CSD. In summary, an inadequate energy supply increases susceptibility to CSD (18).
The brain relies on glucose as its primary energy substrate. Key pathways for energy production closely related to migraine include the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation (Figure 1). Investigating cerebral glucose uptake using 18FDG-positron emission tomography (PET) and visual evoked potentials between patients with interictal migraine without aura and healthy volunteers (19) has identified areas of increased neuronal activation-resting glucose uptake ratios in the optic cortex. Elevated plasma glucose levels have been observed in patients with migraine during attacks (20). Disruption of cerebral metabolic homeostasis is thought to be a cornerstone of migraine pathophysiology (19, 21). Migraine has been linked to glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and riboflavin metabolic pathways through proteomic and metabolomic study (22). Insulin resistance may be a critical metabolic link between migraine and its comorbidities (23), as insulin regulates mitochondrial signaling pathways (24). Chronic migraine has been associated with diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome (25). Case–control studies have demonstrated the presence of insulin resistance in individuals with migraine, a condition comparable to pre-diabetes (26, 27). Triglyceride-glucose, an index used to assess insulin resistance, has been shown to have a linear association with migraine (28). Furthermore, a recent study revealed significant genetic correlations between fasting insulin, glycosylated hemoglobin, and migraine (29), offering new insights into its pathogenesis at the genomic level. A blood biomarker study also found that triglyceride-glucose, C-reactive protein and phosphorus could guide treatment and preventive interventions for metabolic migraine (5).
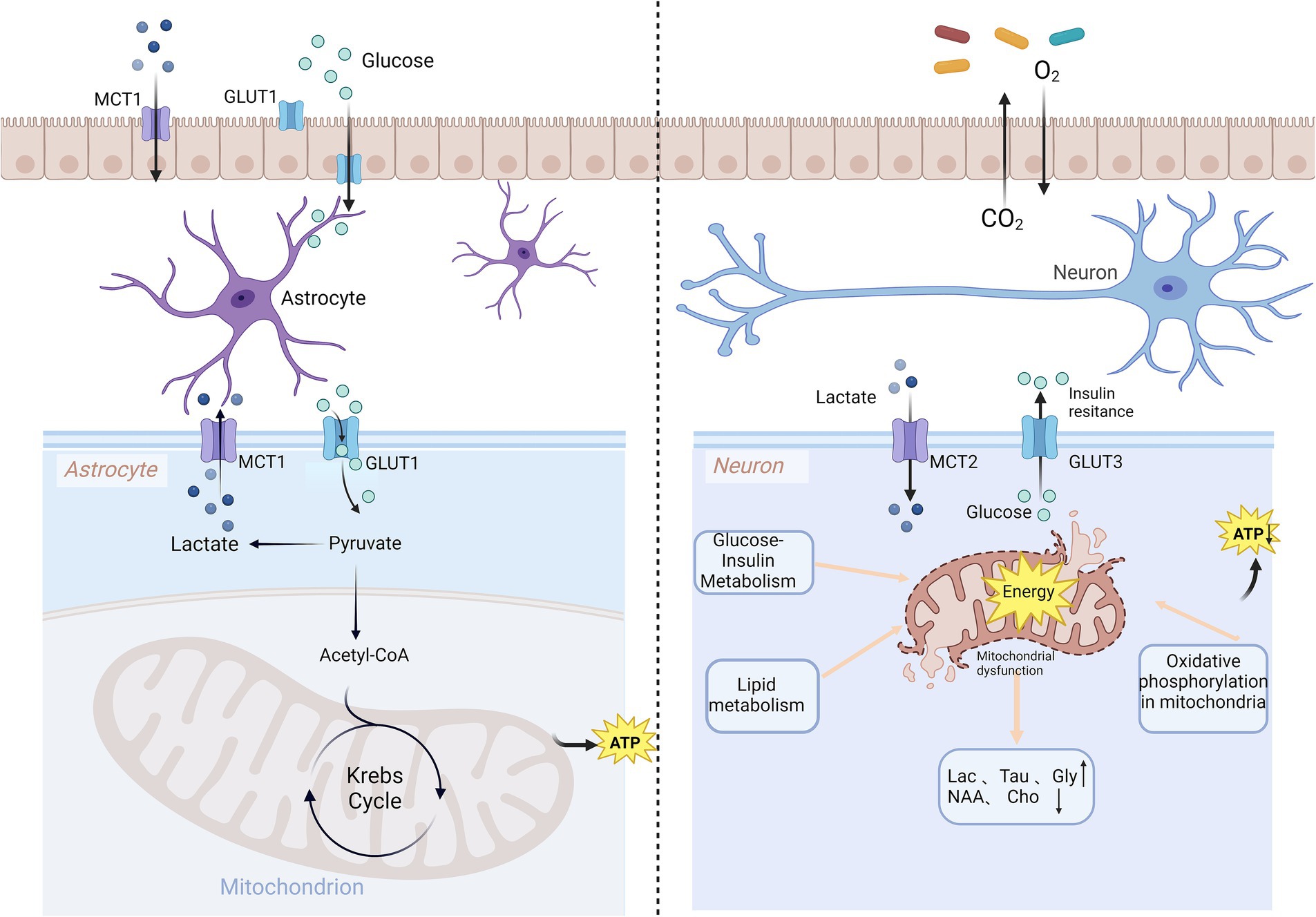
Figure 1. Brain metabolic disorders and migraine. ATP generation from glucose is the primary process of brain energy production and involves three key steps: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Disruptions in glucose-insulin metabolism, lipid metabolism, and oxidative phosphorylation impair mitochondrial function, leading to the development of migraine. MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; GLUT, glucose transporter; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Lac, lactate; Tau, taurine; Gly, glycine; NAA, N-acetylaspartate; Cho, choline.
Lipids serve as a major form of energy storage and as precursors for molecules involved in inflammation and pain signaling. However, the mechanisms through which lipid metabolism contributes to migraine pathology remain incomplete. Some findings suggest that migraine is associated with alterations in the metabolism of high-density lipoprotein isoforms rather than with general dyslipidemia (30). Changes in the activity of fatty acid elongation enzymes in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid may play an important role in the development of chronic migraine. Preliminary studies indicate that abnormal lipid metabolism in chronic migraine correlates with disruptions in energy homeostasis (31).
Neuroimaging studies suggest that patients with migraine exhibit abnormal brain energy metabolism and altered functional connectivity (32). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is a non-invasive method used to study in vivo tissue metabolism by measuring certain atomic nuclei, primarily hydrogen (1H). A study utilized 1H-MRS and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging to investigate metabolic changes throughout the migraine cycle and their relationship to functional connectivity. This study found that N-acetylaspartate (NAA)/total creatine (tCr) and choline (Cho)/tCr levels changed in a time-phase-dependent manner in migraine (33). PET studies suggest dysfunction in the thalamocortical pathways in patients with chronic migraine, potentially contributing to migraine chronicity (34). Patients with Migraine showed increased concentrations of lactate, taurine, tCr, and glycine, as well as decreased levels of NAA and total choline, as measured by 1H-MRS (35). Migraine attacks are associated with neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction and abnormal levels of glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The decrease in NAA may be a consequence of mitochondrial dysfunction and abnormal energy metabolism (36).
A study using a migraine rat model revealed increased malondialdehyde levels in the cortex and trigeminal ganglion, along with pro-injurious effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on the brain via transient receptor potential A1 (16). Clinical studies examining oxidative stress biomarkers in individuals with migraine have found that the number of monthly headache days was negatively correlated with serum concentrations of two antioxidant enzymes, catalase and superoxide dismutase, and total antioxidant capacity while being positively correlated with serum levels of glutathione peroxidase 1, nitric oxide, and malondialdehyde (37–39). Serum analysis of 32 patients with high-frequency migraine revealed abnormally low levels of alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) and lactate, along with abnormally high levels of peroxides in 46.9% of the patients, further supporting the role of oxidative stress and metabolic alterations in the pathophysiology of migraine (40).
Oxidative stress primarily refers to the process of oxidative damage resulting from an imbalance between oxidative and antioxidant systems in cells and tissues, leading to the accumulation of free radicals and ROS (41). Oxidative damage to lipids, amino acids, and proteins impairs mitochondrial function, triggering a vicious cycle of ROS generation and cellular damage (42). Clinical studies have shown elevated serum lipid peroxide levels in patients with migraine (43). Individuals with chronic migraine tend to have lower antioxidant capacity and higher oxidative stress levels (44). Pharmacological studies suggest that alleviating migraine nociceptive sensitization may be achieved through enhancing endogenous antioxidant defense systems and targeting anti-inflammatory pathways (45, 46).
The mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system is central to cellular metabolism. The respiratory chain within the inner mitochondrial membrane consists of enzyme complexes (I, II, III, IV, and V), which form a major structural and functional component of mitochondria (47). The electron transport chain catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Under abnormal metabolic conditions, such as hypoxia, ROS are primarily produced by complexes I and III. The generated ROS, in turn, induces mitochondrial DNA damage, contributing to oxidative stress (42, 48). 31P-MRS is a reliable, non-invasive tool for the in vivo assessment of mitochondrial function. Significantly lower levels of high-energy phosphates, such as ATP and PCr, as well as reduced oxidative phosphorylation, have been observed in patients with migraine and are closely linked to insufficient mitochondrial energy reserves (49, 50). Individuals with migraine exhibit significantly higher blood lactate levels and lower levels of NAA, along with decreased activities of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, and cytochrome c oxidase, suggesting a systemic impairment of mitochondrial function (51–53). Additionally, mitochondria are connected to the endoplasmic reticulum and co-regulate oxidative stress and mitochondrial autophagy (41). The PINK1/parkin pathway is a key mediator of mitophagy (54), effectively removing damaged mitochondria and avoiding excessive ROS production (55–58). Alterations in autophagic flux have been shown to modulate oxidative stress and ROS formation (57). Mitophagy plays a critical role in conditions such as stroke, cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury, and neurodegenerative diseases (59–62). Autophagy dysfunction has been linked to central sensitization in a nitroglycerin-induced chronic migraine model in mice (63). However, the relationship between mitophagy and migraine remains incompletely understood, and further investigation is needed to clarify how mitochondrial quality control interacts with oxidative stress in migraine.
Animal studies have shown that migraine is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. ATP levels and basal oxygen consumption rates were reduced in the fasting group, and adenylate-activated protein kinase phosphorylation levels were decreased (64). Case studies suggest that 61% of patients with mitochondrial disease experience migraine-like headaches (65). Similarly, online questionnaires have found a high prevalence of migraine-like headaches among patients with mitochondrial disease (66). 31P-MRS has revealed defective energy metabolism in the brain and muscles of individuals with familial hemiplegic migraine, further suggesting mitochondrial dysfunction in this genetic group (67). In addition, muscle mitochondrial DNA deletions have been reported in patients with migraine, marking the first instance of mitochondrial DNA deletion linked to migraine. Most mitochondrial proteins are involved in ATP synthesis and the Krebs cycle. Mitochondrial proteomic analysis has demonstrated that the m.8296A > G variant results in differential expression of nuclear-encoded proteins involved in energy metabolism, suggesting a connection between mitochondrial dysfunction and energy metabolic diseases (68). Nutrients may help improve mitochondrial function, thereby alleviating brain energy metabolism deficits and oxidative stress in migraine (69). Mitochondrial DNA methylation plays a crucial role in the regulation of mitochondrial genes, and directed changes in the mitochondrial genome and DNA may influence cellular energy dynamics (24). A study using a migraine rat model revealed that alterations in mitochondrial dynamics inhibit mitochondrial biosynthetic signaling in trigeminal ganglion neurons (70). In a nitroglycerin-induced migraine rat model, sodium valproate demonstrated protective effects on mitochondrial energy metabolism and biosynthesis (71). A recent study found that mitochondrial damage occurs in the thalamus of mice with chronic migraine and may be implicated in central sensitization (72). Serum analysis of patients with high-frequency migraine demonstrated significant abnormalities in most markers of mitochondrial function (40). However, existing animal models of migraine primarily mimic secondary migraine-like headaches. Understanding the correlation between biomarkers of energy metabolism disorders and headache severity is critical for translating basic research into clinical practice.
Oxidative stress and brain energy metabolism disorders play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of migraine (73). Antioxidant drugs and nutrients hold promise as potential prophylactic treatments for migraine (44). Current migraine prophylaxis targeting mitochondrial function and energy metabolism includes riboflavin, coenzyme Q10, lipoic acid, and ketogenic ketones. However the level of evidence-based medicine supporting these treatments remains limited.
Riboflavin, a water-soluble member of the vitamin B family, plays an important role in combating oxidative stress and maintaining mitochondrial function (74). It is recommended by the Canadian Headache Society for migraine prophylaxis (75). High doses of riboflavin (400 mg) have demonstrated potential effectiveness for adult migraine prevention (76). Riboflavin promotes energy production, protects the brain from oxidative stress (77), and has been shown to be effective in clinical trials for migraine prevention (69). It is involved in key metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, and the metabolism of amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides (78, 79). Riboflavin transporters and flavin adenine dinucleotide-forming enzymes form a coordinated network to ensure cellular homeostasis (79). Riboflavin’s therapeutic potential has been demonstrated in both experimental and clinical migraine studies (80). A migraine rat model study found that selenium and riboflavin support the protective effects of the brain’s antioxidant system, and their combined use may offer enhanced protection (81). Studies on the efficacy of riboflavin in preventing migraine in children and adolescents indicate a reduction in migraine attacks; however, further research is needed to understand the relationship between dose, duration of administration, and the frequency and duration of migraine attacks (82–85). In adults, riboflavin’s efficacy in preventing migraine is classified as Level B evidence (86, 87). However, recent cross-sectional surveys have not established a clear relationship between riboflavin intake and the prevalence of migraine in adults (69, 88).
Coenzyme Q10, also known as ubiquinone, is involved in the electron transport chain and aerobic respiration in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells, playing an essential role in proton translocation and electron transport (89). Coenzyme Q10 acts as an activator of cellular respiratory metabolism, an antioxidant, and a non-specific immune enhancer. It is involved in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, indirectly regulates extra-mitochondrial metabolic pathways, and protects cells against excessive ROS generation (90). Coenzyme Q10 also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, reducing serum calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and tumor necrosis factor-α levels (91). Given its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and bioenergetic properties, coenzyme Q10 plays a key role in energy production pathways in the brain, and its deficiency can impair mitochondrial function (73). Coenzyme Q10 supplementation has been recommended as a safe and effective preventive therapy for migraine (74). Clinical trials have demonstrated that supplementation with coenzyme Q10 reduces the severity, frequency, and duration of migraine attacks, with effects typically observed within 4 weeks (92–94). It has shown favorable prophylactic effects in children aged 5–10 years with migraine and is well tolerated, with few side effects and no serious adverse events reported during long-term use (95, 96). However, while systematic reviews and meta-analyses affirm the role of coenzyme Q10 in reducing the frequency of migraine attacks, some controversy remains regarding its effects on headache severity and duration (97, 98). The combination of energy-modulating drugs is also of interest, with coenzyme Q10 combined with riboflavin or levocarnitine showing greater efficacy in alleviating migraine attacks (86, 99, 100). A prospective observational study suggested that the concomitant use of coenzyme Q10, magnesium, and feverfew may offer additional benefits for migraine management (101). These findings indicate that multi-targeted drug combinations focused on mitochondrial energy metabolism may be a promising direction for migraine prophylaxis.
ALA is an amphiphilic antioxidant that acts as a cofactor for pyruvate dehydrogenase and glycine decarboxylase. ALA directly or indirectly reduces oxidative stress in mitochondrial oxidative metabolism through its interaction with coenzymes such as triphenyl nitrate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (102). Abnormally low levels of lactate have been observed in the serum of patients with migraine, suggesting that lactate could serve as a potential migraine biomarker (40, 103). ALA supplementation significantly reduces serum lactate levels and vascular cell adhesion molecule in female patients with migraine, suggesting that prophylactic ALA treatment may be beneficial for managing migraine (103). Additionally, ALA possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. A clinical trial demonstrated that 3 months of ALA supplementation effectively improved oxidative, inflammatory, and emotional status in patients with migraine (104). A 6-month exploratory study also showed that ALA significantly reduced migraine days in patients with insulin resistance (99, 105). Beyond its effects in adult migraine, ALA was found to significantly reduce the frequency and severity of acute attacks in adolescent patients, along with lowering their serum CGRP levels (106). In conclusion, ALA supplementation may be considered a potential adjunctive treatment for patients with migraine (103, 107). Future clinical trials should further investigate its optimal dosage and administration schedule for migraine prophylaxis.
The ketogenic diet (KD) is a regimen that severely restricts carbohydrates and induces lipid metabolism and ketone body (KB) synthesis by mimicking a fasting state (108). KD has shown therapeutic potential in a variety of diseases, including obesity, epilepsy, metabolic syndrome, and Alzheimer’s disease (109). KBs serve as an alternative fuel source for the brain and may influence migraine pathophysiological mechanisms, such as mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, brain energy metabolism, and glutamate homeostasis (110–113). The effects of KBs on the central nervous system correlate with clinical improvements in migraine. KD has been found to improve migraine symptoms while significantly affecting cortical function-related potentials (114). KD plays an important role in reducing the frequency and severity of migraine attacks in both adolescents and adults (115), and it has also been shown to improve sleep disorders (116). As a result, KB supplementation may represent a potential prophylactic treatment strategy for migraine (117). A randomized controlled trial is currently investigating the safety and efficacy of exogenous KB salts, specifically 3-hydroxybutyric acid, for migraine prophylaxis (118). Additionally, recent studies suggest that both a 2:1 KD and a low-glycemic index diet may offer benefits for migraine treatment (119). However, future clinical studies are needed to monitor KB levels during KD and to explore the relationship between KB concentration and therapeutic efficacy.
Many migraine triggers are related to brain energy metabolism disorders. Inadequate energy supply increases susceptibility to CSD, and the brain energy deficit-mitochondrial-oxidative stress axis may represent a key pathway in migraine pathogenesis (Figure 2). Conditions such as diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, high-density lipoprotein isoform alterations, fatty acid elongation enzyme activity, and metabolic syndrome have been associated with migraine. Additionally, metabolic changes in NAA/tCr, Cho/tCr, lactate, taurine, glutamate, GABA, and glycine levels have been observed in individuals with migraine. Patients with migraine also present with elevated oxidative stress and weakened antioxidant defenses. Nutrients may help improve mitochondrial function, thereby alleviating brain energy metabolism deficits and oxidative stress in migraine. Current prophylactic treatments targeting mitochondrial function and energy metabolism include riboflavin, coenzyme Q10, alpha-lipoic acid, and ketogenic ketones. However, the level of evidence supporting these treatments remains limited.
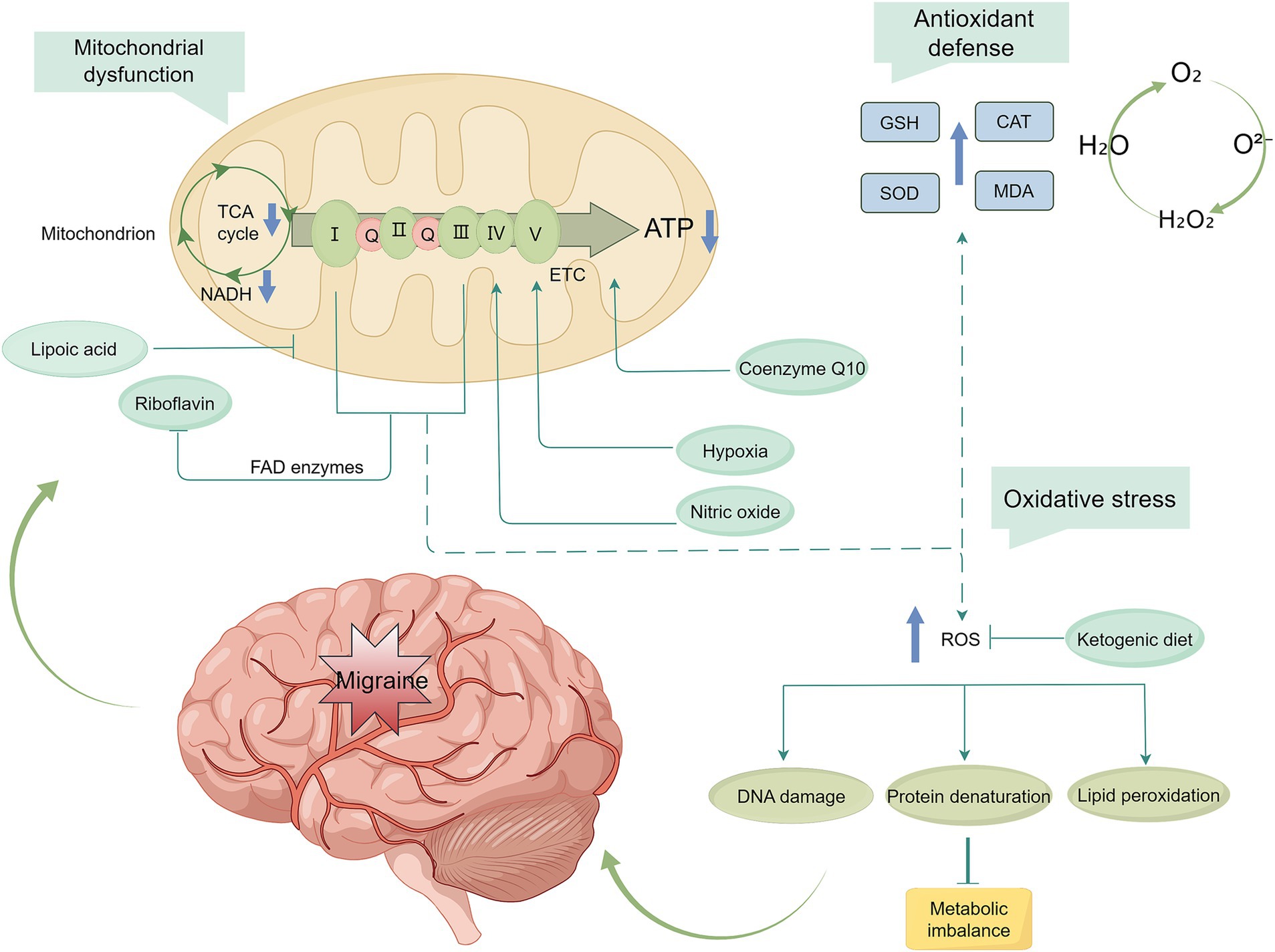
Figure 2. Migraine prophylactic targets for mitochondrial dysfunction. Nutrients play a protective role against migraine by modulating the mitochondria-energy production-oxidative stress pathway. These interventions help prevent excessive ROS production, thereby reducing oxidative stress and ameliorating energy deficits in the brain. TCA, tricarboxylic acid; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; ETC, electron transfer chain; GSH, glutathione; SOD, superoxide dismutase; CAT, catalase; MDA, malondialdehyde; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
W-xS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. T-yC: Methodology, Writing – original draft. M-mS: Methodology, Writing – original draft. Y-jG: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. S-yX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Shanxi Applied Basic Research Program (202303021221222).
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing. The images in this article were drawn by BioRender (www.biorender.com).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet. (2020) 396:1204–22.
2. Ashina, M, Katsarava, Z, Do, TP, Buse, DC, Pozo-Rosich, P, Özge, A, et al. Migraine: epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet. (2021) 397:1485–95. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32160-7
3. Li, XY, Yang, CH, Lv, JJ, Liu, H, Zhang, LY, Yin, MY, et al. Global, regional, and national epidemiology of migraine and tension-type headache in youths and young adults aged 15-39 years from 1990 to 2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. J Headache Pain. (2023) 24:126. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01659-1
4. Gross, EC, Lisicki, M, Fischer, D, Sándor, PS, and Schoenen, J. The metabolic face of migraine —from pathophysiology to treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. (2019) 15:627–43. doi: 10.1038/s41582-019-0255-4
5. Gross, EC, Putananickal, N, Orsini, AL, Schoenen, J, Fischer, D, and Soto-Mota, A. Defining metabolic migraine with a distinct subgroup of patients with suboptimal inflammatory and metabolic markers. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:3787. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28499-y
6. Borkum, JM. Migraine triggers and oxidative stress: a narrative review and synthesis. Headache. (2016) 56:12–35. doi: 10.1111/head.12725
7. Puledda, F, Silva, EM, Suwanlaong, K, and Goadsby, PJ. Migraine: from pathophysiology to treatment. J Neurol. (2023) 270:3654–66. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11706-1
8. Borkum, JM. Brain energy deficit as a source of oxidative stress in migraine: a molecular basis for migraine susceptibility. Neuroch. Res. (2021) 46:1913–32. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03335-9
9. Zhao, J, and Levy, D. Dissociation between CSD-evoked metabolic perturbations and meningeal afferent activation and sensitization: implications for mechanisms of migraine headache onset. J Neurosci. (2018) 38:5053–66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0115-18.2018
10. Ghaemi, A, Alizadeh, L, Babaei, S, Jafarian, M, Khaleghi Ghadiri, M, Meuth, SG, et al. Astrocyte-mediated inflammation in cortical spreading depression. Cephalalgia. (2018) 38:626–38. doi: 10.1177/0333102417702132
11. Wolf, T, Lindauer, U, Obrig, H, Dreier, J, Back, T, Villringer, A, et al. Systemic nitric oxide Synthase inhibition does not affect brain oxygenation during cortical spreading depression in rats: a noninvasive near-infrared spectroscopy and laser-Doppler Flowmetry study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (1996) 16:1100–7. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199611000-00003
12. Piilgaard, H, and Lauritzen, M. Persistent increase in oxygen consumption and impaired neurovascular coupling after spreading depression in rat neocortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2009) 29:1517–27. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.73
13. Xu, S, Chang, JC, Chow, CC, Brennan, KC, and Huang, H. A mathematical model for persistent post-CSD vasoconstriction. PLoS Comput Biol. (2020) 16:e1007996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007996
14. Takano, T, Tian, GF, Peng, W, Lou, N, Lovatt, D, Hansen, AJ, et al. Cortical spreading depression causes and coincides with tissue hypoxia. Nat Neurosci. (2007) 10:754–62.
15. Yuzawa, I, Sakadžić, S, Srinivasan, VJ, Shin, HK, Eikermann-Haerter, K, Boas, DA, et al. Cortical spreading depression impairs oxygen delivery and metabolism in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2012) 32:376–86. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.148
16. Shatillo, A, Koroleva, K, Giniatullina, R, Naumenko, N, Slastnikova, AA, Aliev, RR, et al. Cortical spreading depression induces oxidative stress in the trigeminal nociceptive system. Neuroscience. (2013) 253:341–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.09.002
17. Auffenberg, E, Hedrich, UBS, Barbieri, R, Miely, D, Groschup, B, Wuttke, TV, et al. Hyperexcitable interneurons trigger cortical spreading depression in an Scn1a migraine model. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e142202. doi: 10.1172/JCI142202
18. Kilic, K, Karatas, H, Dönmez-Demir, B, Eren-Kocak, E, Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y, Can, A, et al. Inadequate brain glycogen or sleep increases spreading depression susceptibility. Ann Neurol. (2018) 83:61–73. doi: 10.1002/ana.25122
19. Lisicki, M, D’Ostilio, K, Coppola, G, Scholtes, F, Maertens de Noordhout, A, Parisi, V, et al. Evidence of an increased neuronal activation-to-resting glucose uptake ratio in the visual cortex of migraine patients: a study comparing 18FDG-PET and visual evoked potentials. J Headache Pain. (2018) 19:49. doi: 10.1186/s10194-018-0877-8
20. Zhang, DG, Amin, FM, Guo, S, Vestergaard, MB, Hougaard, A, and Ashina, M. Plasma glucose levels increase during spontaneous attacks of migraine with and without Aura. Headache. (2020) 60:655–64. doi: 10.1111/head.13760
21. Kim, JH, Kim, S, Suh, SI, Koh, SB, Park, KW, and Oh, K. Interictal metabolic changes in episodic migraine: a voxel-based FDG-PET study. Cephalalgia. (2010) 30:53–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01890.x
22. Liu, L, Li, W, Wang, L, Gong, P, Lyu, T, Liu, D, et al. Proteomic and metabolomic profiling of acupuncture for migraine reveals a correlative link via energy metabolism. Front Neurosci. (2022) 16:1013328. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1013328
23. Del Moro, L, Rota, E, Pirovano, E, and Rainero, I. Migraine, brain glucose metabolism and the “Neuroenergetic” hypothesis: a scoping review. J Pain. (2022) 23:1294–317. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2022.02.006
24. Gao, D, Zhu, B, Sun, H, and Wang, X. Mitochondrial DNA methylation and related disease. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. New York, NY: Springer New York LLC; (2017). p. 117–32.
25. Siva, ZO, Uluduz, D, Keskin, FE, Erenler, F, Balcı, H, Uygunoğlu, U, et al. Determinants of glucose metabolism and the role of NPY in the progression of insulin resistance in chronic migraine. Cephalalgia. (2018) 38:1773–81. doi: 10.1177/0333102417748928
26. Wang, X, Li, X, Diao, Y, Meng, S, Xing, Y, Zhou, H, et al. Are glucose and insulin metabolism and diabetes associated with migraine? A community-based, case-control study. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. (2017) 31:240–50. doi: 10.11607/ofph.1843
27. Fava, A, Pirritano, D, Consoli, D, Plastino, M, Casalinuovo, F, Cristofaro, S, et al. Chronic migraine in women is associated with insulin resistance: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Neurol. (2014) 21:267–72. doi: 10.1111/ene.12289
28. Liu, Y, Gao, X, Yuan, L, Li, Y, and Hong, P. The relationship between triglyceride glucose index and migraine: a cross-section study from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES). Curr Neurovasc Res. (2023) 20:230–6. doi: 10.2174/1567202620666230606100652
29. Islam, MR, and Nyholt, DR. Cross-trait analyses identify shared genetics between migraine, headache, and glycemic traits, and a causal relationship with fasting proinsulin. Hum Genet. (2023) 42:1149–72. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02532-6
30. Onderwater, GLJ, Ligthart, L, Bot, M, Demirkan, A, Fu, J, Van Der Kallen, CJH, et al. Large-scale plasma metabolome analysis reveals alterations in HDL metabolism in migraine. Neurology. (2019) 92:E1899–e1911. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007313
31. Castor, K, Dawlaty, J, Arakaki, X, Gross, N, Woldeamanuel, YW, Harrington, MG, et al. Plasma lipolysis and changes in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid signaling lipids reveal abnormal lipid metabolism in chronic migraine. Front Mol Neurosci. (2021) 14:691733. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.691733
32. Magistretti, PJ, and Pellerin, L. Cellular mechanisms of brain energy metabolism and their relevance to functional brain imaging. Philoso. Trans. Ro. Soc. B Biol. Sci. (1999) 354:1155–63.
33. Filippi, V, Steiger, R, Beliveau, V, Frank, F, Kaltseis, K, Gizewski, ER, et al. Investigating the migraine cycle over 21 consecutive days using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and resting-state fMRI: a pilot study. Brain Sci. (2022) 12:646. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12050646
34. Lin, YK, Tsai, CL, Lin, GY, Chou, CH, and Yang, FC. Pathophysiology of chronic migraine: Insights from recent neuroimaging research. Curr Pain Headache Rep. (2022) 26:843–54. doi: 10.1007/s11916-022-01087-x
35. Abad, N, Rosenberg, JT, Roussel, T, Grice, DC, Harrington, MG, and Grant, SC. Metabolic assessment of a migraine model using relaxation-enhanced 1H spectroscopy at ultrahigh field. Magn Reson Med. (2018) 79:1266–75. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26811
36. Younis, S, Hougaard, A, Vestergaard, MB, Larsson, HBW, and Ashina, M. Migraine and magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a systematic review. Curr Opin Neurol. (2017) 30:246–62. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000436
37. Mabrouk, DM, EMA, I, Ahmed, KA, Ramadan, MF, and Ibrahim, FM. Topiramate potential neurotoxicity and mitigating role of ginger oil in mice brain. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2022) 29:87184–99. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-21878-4
38. Talaie, A, Jafary, H, Faraji, F, and Malekirad, AA. The serum oxidative stress biomarkers and selenium levels in a Group of Migraine Patients Compared with healthy controls: a case-control study. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2022) 200:4250–5. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-03024-2
39. Shojaei, M, Sahebkar, A, Khorvash, F, Fallahpour, S, Askari, G, and Bagherniya, M. The effects of phytosomal curcumin supplementation on clinical symptoms, and inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers in patients with migraine: a protocol for a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Avicenna J Phytomed. (2023) 13:45–57. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2022.21242
40. Gross, EC, Putananickal, N, Orsini, AL, Vogt, DR, Sandor, PS, Schoenen, J, et al. Mitochondrial function and oxidative stress markers in higher-frequency episodic migraine. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:4543. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84102-2
41. Liu, X, Hussain, R, Mehmood, K, Tang, Z, Zhang, H, and Li, Y. Mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum communication-mediated oxidative stress and autophagy. Biomed Res Int. (2022) 2022:6459585. doi: 10.1155/2022/6459585
42. Bhat, AH, Dar, KB, Anees, S, Zargar, MA, Masood, A, Sofi, MA, et al. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight. Biomedi Pharmacother. (2015) 74:101–10. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.07.025
43. Borkum, JM. The migraine attack as a homeostatic, neuroprotective response to brain oxidative stress: preliminary evidence for a theory. Headache. (2018) 58:118–35. doi: 10.1111/head.13214
44. Togha, M, Razeghi Jahromi, S, Ghorbani, Z, Ghaemi, A, and Rafiee, P. An investigation of oxidant/antioxidant balance in patients with migraine: a case-control study. BMC Neurol. (2019) 19:323. doi: 10.1186/s12883-019-1555-4
45. Latif, K, Khan, AU, Izhar Ul Haque, M, and Naeem, K. Bergapten attenuates nitroglycerin-induced migraine headaches through inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2021) 12:3303–13. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00146
46. Casili, G, Lanza, M, Filippone, A, Campolo, M, Paterniti, I, Cuzzocrea, S, et al. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates the nitroglycerin (NTG)-induced migraine in mice. J Neuroinflammation. (2020) 17:59. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01736-1
47. Irene, V, and Leonid, AS. The assembly, regulation and function of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2022) 23:141–161.
48. Hollensworth, SB, Shen, C-C, Sim, JE, Spitz, DR, Wilson, GL, and Ledoux, SP. Glial cell type-specific responses to menadione-induced oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. (2000) 28:1161–74. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00214-8
49. Montagna, P, Cortelli, P, and Barbiroli, B. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in migraine. Neurobiol Pain. (2022) 12:100102. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2022.100102
50. Reyngoudt, H, Paemeleire, K, Descamps, B, De Deene, Y, and Achten, E. 31P-MRS demonstrates a reduction in high-energy phosphates in the occipital lobe of migraine without aura patients. Cephalalgia. (2011) 31:1243–53. doi: 10.1177/0333102410394675
51. Sangiorgi, S, Mochi, M, Riva, R, Cortelli, P, Monari, L, Pierangeli, G, et al. Abnormal platelet mitochondrial function in patients affected by migraine with and without aura. Cephalalgia. (1994) 14:21–3. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1994.1401021.x
52. Montagna, P, Sacquegna, T, Martinelli, P, Cortelli, P, Bresolin, N, Moggio, M, et al. Mitochondrial abnormalities in migraine. Preliminary findings. Headache J Head Face Pain. (1988) 28:477–80.
53. Alloush, R, Haroun, M, Shalash, A, El-Fawal, H, and Hamdy, M. Mitochondrial dysfunctions in patients with migraine. Neurosci Med. (2019) 10:339–53. doi: 10.4236/nm.2019.104025
54. Yun, HR, Jo, YH, Kim, J, Shin, Y, Kim, SS, and Choi, TG. Roles of autophagy in oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3289. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093289
55. Song, M, Zhou, Y, and Fan, X. Mitochondrial quality and quantity control: Mitophagy is a potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:3110–23. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02795-6
56. Cen, X, Zhang, M, Zhou, M, Ye, L, and Xia, H. Mitophagy regulates neurodegenerative diseases. Cells. (2021) 10:1876. doi: 10.3390/cells10081876
57. Garza-Lombó, C, Pappa, A, Panayiotidis, MI, and Franco, R. Redox homeostasis, oxidative stress and mitophagy. Mitochondrion. (2020) 51:105–17. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2020.01.002
58. De Gaetano, A, Gibellini, L, Zanini, G, Nasi, M, Cossarizza, A, and Pinti, M. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:794. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050794
59. Liu, H, Dai, C, Fan, Y, Guo, B, Ren, K, Sun, T, et al. From autophagy to mitophagy: the roles of P62 in neurodegenerative diseases. J Bioenerget Biomembr. (2017) 49:413–22. doi: 10.1007/s10863-017-9727-7
60. Shen, L, Gan, Q, Yang, Y, Reis, C, Zhang, Z, Xu, S, et al. Mitophagy in cerebral ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Aging Neurosci. (2021) 13:687246. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.687246
61. Zhong, WJ, Yang, XS, Zhou, H, Xie, BR, Liu, WW, and Li, Y. Role of Mitophagy in the pathogenesis of stroke: from mechanism to therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:6232902. doi: 10.1155/2022/6232902
62. Braun, RJ, Reddy, PH, Maa, SK, Huang, S-H, and Zhang, Z. Role of mitophagy in the neurodegenerative diseases and its pharmacological advances: a review. Front Mol Neurosci. 15:1014251. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1014251
63. Jiang, L, Zhang, Y, Jing, F, Long, T, Qin, G, Zhang, D, et al. P2X7R-mediated autophagic impairment contributes to central sensitization in a chronic migraine model with recurrent nitroglycerin stimulation in mice. J Neuroinflammation. (2021) 18:5. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-02056-0
64. Li, J, Ye, X, Zhou, Y, Peng, S, Zheng, P, Zhang, X, et al. Energy metabolic disorder of astrocytes may be an inducer of migraine attack. Brain Sci. (2022) 12:844. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12070844
65. Terrin, A, Bello, L, Valentino, ML, Caporali, L, Sorarù, G, Carelli, V, et al. The relevance of migraine in the clinical spectrum of mitochondrial disorders. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:4222. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08206-z
66. Tiehuis, LH, Koene, S, Saris, CGJ, and Janssen, MCH. Mitochondrial migraine; a prevalence, impact and treatment efficacy cohort study. Mitochondrion. (2020) 53:128–32. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2020.05.004
67. Uncini, A, Lodi, R, Muzio, AD, Silvestri, G, Servidei, S, Lugaresi, A, et al. Abnormal brain and muscle energy metabolism shown by 31P-MRS in familial hemiplegic migraine. J Neurol Sci. (1995) 129:214–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-510X(94)00283-T
68. Maraş Genç, H, Akpınar, G, Kasap, M, Uyur Yalçın, E, Üstek, D, Aslanger, AD, et al. Proteomic analysis of m.8296A>G variation in the mitochondrial tRNA (Lys) gene. Mol Syndromol. (2022) 13:305–17. doi: 10.1159/000519526
69. Fila, M, Chojnacki, C, Chojnacki, J, and Blasiak, J. Nutrients to improve mitochondrial function to reduce brain energy deficit and oxidative stress in migraine. Nutrients. (2021) 13:4433. doi: 10.3390/nu13124433
70. Dong, X, Guan, X, Chen, K, Jin, S, Wang, C, Yan, L, et al. Abnormal mitochondrial dynamics and impaired mitochondrial biogenesis in trigeminal ganglion neurons in a rat model of migraine. Neurosci Lett. (2017) 636:127–33. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.10.054
71. Li, R, Liu, Y, Chen, N, Zhang, Y, Song, G, and Zhang, Z. Valproate attenuates nitroglycerin-induced trigeminovascular activation by preserving mitochondrial function in a rat model of migraine. Med Sci Monit. (2016) 22:3229–37. doi: 10.12659/MSM.900185
72. Xie, W, Li, R, Tang, W, Ma, Z, Miao, S, Li, C, et al. Proteomics profiling reveals mitochondrial damage in the thalamus in a mouse model of chronic migraine. J Headache Pain. (2023) 24:122. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01646-6
73. Goschorska, M, Gutowska, I, Baranowska-bosiacka, I, Barczak, K, and Chlubek, D. The use of antioxidants in the treatment of migraine. Antioxidants. (2020) 9:116. doi: 10.3390/antiox9020116
74. Markley, HG. CoEnzyme Q10 and riboflavin: the mitochondrial connection. Headache. (2012) 52:81–7.
75. Pringsheim, T, Davenport, W, Mackie, G, Worthington, I, Aubé, M, Christie, SN, et al. Canadian headache society guideline for migraine prophylaxis. Can J Neurol Sci. (2012) 39:S1–S59. doi: 10.1017/S0317167100015109
76. Schoenen, J, Jacquy, J, and Lenaerts, M. Effectiveness of high-dose riboflavin in migraine prophylaxis. A randomized controlled trial. Neurology. (1998) 50:466–70.
77. Colombo, B, Saraceno, L, and Comi, G. Riboflavin and migraine: the bridge over troubled mitochondria. Neurol Sci. (2014) 35:141–4. doi: 10.1007/s10072-014-1755-z
79. Barile, M, Giancaspero, TA, Leone, P, Galluccio, M, and Indiveri, C. Riboflavin transport and metabolism in humans. J Inherit Metab Dis. (2016) 39:545–57. doi: 10.1007/s10545-016-9950-0
80. Yamanaka, G, Suzuki, S, Morishita, N, Takeshita, M, Kanou, K, Takamatsu, T, et al. Experimental and clinical evidence of the effectiveness of riboflavin on migraines. Nutrients. (2021) 13:2612. doi: 10.3390/nu13082612
81. Nazıroğlu, M, Çelik, Ö, Uğuz, AC, and Bütün, A. Protective effects of riboflavin and selenium on brain microsomal Ca2+-ATPase and oxidative damage caused by glyceryl Trinitrate in a rat headache model. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2015) 164:72–9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-014-0199-x
82. Das, R, and Qubty, W. Retrospective observational study on riboflavin prophylaxis in child and adolescent migraine. Pediatr Neurol. (2021) 114:5–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2020.09.009
83. Yamanaka, G, Suzuki, S, Takeshita, M, Go, S, Morishita, N, Takamatsu, T, et al. Effectiveness of low-dose riboflavin as a prophylactic agent in pediatric migraine. Brain Dev. (2020) 42:523–8. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2020.04.002
84. Bruijn, J, Duivenvoorden, H, Passchier, J, Locher, H, Dijkstra, N, and Arts, WF. Medium-dose riboflavin as a prophylactic agent in children with migraine: a preliminary placebo-controlled, randomised, double-blind, cross-over trial. Cephalalgia. (2010) 30:1426–34. doi: 10.1177/0333102410365106
85. O’Brien, HL, and Hershey, AD. Vitamins and paediatric migraine: riboflavin as a preventative medication. Cephalalgia. (2010) 30:1417–8. doi: 10.1177/0333102410378358
86. Gaul, C, Diener, HC, and Danesch, U. Improvement of migraine symptoms with a proprietary supplement containing riboflavin, magnesium and Q10: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter trial. J Headache Pain. (2015) 16:516. doi: 10.1186/s10194-015-0516-6
87. Boehnke, C, Reuter, U, Flach, U, Schuh-Hofer, S, Einhä, KM, and Arnold, G. High-dose riboflavin treatment is efficacious in migraine prophylaxis: an open study in a tertiary care centre. Eur J Neurol. (2004) 11:475–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2004.00813.x
88. Li, D, Guo, Y, Xia, M, Zhang, J, and Zang, W. Dietary intake of thiamine and riboflavin in relation to severe headache or migraine: a cross-sectional survey. Headache. (2022) 62:1133–42. doi: 10.1111/head.14384
89. Mantle, D, Heaton, RA, and Hargreaves, IP. Coenzyme q10 and immune function: an overview. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:759. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050759
90. Hidalgo-Gutiérrez, A, González-García, P, Díaz-Casado, ME, Barriocanal-Casado, E, López-Herrador, S, Quinzii, CM, et al. Metabolic targets of coenzyme q10 in mitochondria. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:520. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040520
91. Dahri, M, Tarighat-Esfanjani, A, Asghari-Jafarabadi, M, and Hashemilar, M. Oral coenzyme Q10 supplementation in patients with migraine: effects on clinical features and inflammatory markers. Nutr Neurosci. (2019) 22:607–15. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2017.1421039
92. Sándor, PS, Clemente Di, L, Fumal, CS, et al. Efficacy of coenzyme Q10 in migraine prophylaxis: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology. (2005) 64:713–5. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000151975.03598.ED
93. Rozen, TD, Oshinsky, ML, Gebeline, C, Bradley, KC, Young, WB, Shechter, A, et al. Open label trial of coenzyme Q10 as a migraine preventive. Cephalalgia. (2002) 22:137–41. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.2002.00335.x
94. Shoeibi, A, Olfati, N, Soltani Sabi, M, Salehi, M, Mali, S, and Akbari, OM. Effectiveness of coenzyme Q10 in prophylactic treatment of migraine headache: an open-label, add-on, controlled trial. Acta Neurol Belg. (2017) 117:103–9. doi: 10.1007/s13760-016-0697-z
95. Yaghini, O, Hoseini, N, Ghazavi, MR, Mansouri, V, Nasiri, J, Moosavian, T, et al. A comparative study on the efficacy of coenzyme Q10 and amitriptyline in the prophylactic treatment of migraine headaches in children: a randomized controlled trial. Advanced. Biomed Res. (2022) 11:43. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_235_20
96. Slater, SK, Nelson, TD, Kabbouche, MA, Lecates, SL, Horn, P, Segers, A, et al. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover, add-on study of CoEnzyme Q10 in the prevention of pediatric and adolescent migraine. Cephalalgia. (2011) 31:897–905. doi: 10.1177/0333102411406755
97. Sazali, S, Badrin, S, Norhayati, MN, and Idris, NS. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation for prophylaxis in adult patients with migraine - a meta-analysis. BMJ Open. (2021) 11:e039358. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039358
98. Parohan, M, Sarraf, P, Javanbakht, MH, Ranji-Burachaloo, S, and Djalali, M. Effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on clinical features of migraine: a systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Neurosci. (2020) 23:868–75. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2019.1572940
99. Hassan, SA, Farooque, U, Choudhry, AS, Pillai, B, and Sheikh, FN. Therapeutic implications of altered energy metabolism in migraine: a state-of-the-art review. Cureus. (2020) 12:e8571-e. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8571
100. Hajihashemi, P, Askari, G, Khorvash, F, Reza Maracy, M, and Nourian, M. The effects of concurrent coenzyme Q10, L-carnitine supplementation in migraine prophylaxis: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Cephalalgia. (2019) 39:648–54. doi: 10.1177/0333102418821661
101. Guilbot, A, Bangratz, M, Ait Abdellah, S, and Lucas, C. A combination of coenzyme Q10, feverfew and magnesium for migraine prophylaxis: a prospective observational study. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2017) 17:433. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1933-7
102. Solmonson, A, and DeBerardinis, RJ. Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation. J Biol Chem. (2018) 293:7522–30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM117.000259
103. Kelishadi, MR, Naeini, AA, Khorvash, F, Askari, G, and Heidari, Z. The beneficial effect of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation as a potential adjunct treatment in episodic migraines. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:271. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04397-z
104. Rezaei Kelishadi, M, Alavi Naeini, A, Askari, G, Khorvash, F, and Heidari, Z. The efficacy of alpha-lipoic acid in improving oxidative, inflammatory, and mood status in women with episodic migraine in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Int J Clin Pract. (2021) 75:e14455. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.14455
105. Cavestro, C, Bedogni, G, Molinari, F, Mandrino, S, Rota, E, and Frigeri, MC. Alpha-lipoic acid shows promise to improve migraine in patients with insulin resistance: a 6-month exploratory study. J Med Food. (2018) 21:269–73. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2017.0068
106. Puliappadamb, HM, Satpathy, AK, Mishra, BR, Maiti, R, and Jena, M. Evaluation of safety and efficacy of add-on alpha-lipoic acid on migraine prophylaxis in an adolescent population: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Pharmacol. (2023) 63:1398–407. doi: 10.1002/jcph.2331
107. Akbari, M, Ostadmohammadi, V, Tabrizi, R, Mobini, M, Lankarani, KB, Moosazadeh, M, et al. The effects of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation on inflammatory markers among patients with metabolic syndrome and related disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Metab. (2018) 15:39. doi: 10.1186/s12986-018-0274-y
108. McDonald, TJW, and Cervenka, MC. Ketogenic diets for adult neurological disorders. Neurotherapeutics. (2018) 15:1018–31. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-0666-8
109. Paoli, A, Bianco, A, Damiani, E, and Bosco, G. Ketogenic diet in neuromuscular and neurodegenerative diseases. Biomed Res Int. (2014) 2014:474296. doi: 10.1155/2014/474296
110. Gross, EC, Klement, RJ, Schoenen, J, D’Agostino, DP, and Fischer, D. Potential protective mechanisms of ketone bodies in migraine prevention. Nutrients. (2019) 11:811. doi: 10.3390/nu11040811
111. Di Lorenzo, C, Coppola, G, Sirianni, G, Di Lorenzo, G, Bracaglia, M, Di Lenola, D, et al. Migraine improvement during short lasting ketogenesis: a proof-of-concept study. Eur J Neurol. (2015) 22:170–7. doi: 10.1111/ene.12550
112. Danial, NN, Hartman, AL, Stafstrom, CE, and Thio, LL. How does the ketogenic diet work? Four potential mechanisms. J Child Neurol. (2013) 28:1027–33. doi: 10.1177/0883073813487598
113. Dyńka, D, Kowalcze, K, and Paziewska, A. The role of ketogenic diet in the treatment of neurological diseases. Nutrients. (2022) 14:5003. doi: 10.3390/nu14235003
114. Di Lorenzo, C, Coppola, G, Bracaglia, M, Di Lenola, D, Evangelista, M, Sirianni, G, et al. Cortical functional correlates of responsiveness to short-lasting preventive intervention with ketogenic diet in migraine: a multimodal evoked potentials study. J Headache Pain. (2016) 17:58. doi: 10.1186/s10194-016-0650-9
115. Caminha, MC, Moreira, AB, Matheus, FC, Rieger, DK, Moreira, JD, Dalmarco, EM, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of the ketogenic diet and its variations for preventing migraine in adolescents and adults: a systematic review. Nutr Rev. (2022) 80:1634–47. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuab080
116. Merlino, G, Tereshko, Y, Pez, S, Dal Bello, S, Pittino, A, Di Lorenzo, C, et al. Sleep of migraine patients is ameliorated by ketogenic diet, independently of pain control. Sleep Med. (2023) 107:196–201. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2023.05.006
117. Huynh, P, and Calabrese, P. Pathophysiological abnormalities in migraine ameliorated by ketosis: a proof-of-concept review. J Integr Neurosci. (2022) 21:167. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2106167
118. Gross, E, Putananickal, N, Orsini, AL, Schmidt, S, Vogt, DR, Cichon, S, et al. Efficacy and safety of exogenous ketone bodies for preventive treatment of migraine: a study protocol for a single-centred, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover trial. Trials. (2019) 20:61. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-3120-7
Keywords: insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, antioxidant defenses, oxidative stress, lipid metabolism
Citation: Sun W-x, Chen T-y, Song M-m, Gao Y-j and Xu S-y (2025) Energy metabolism disorders in migraine: triggers, pathways, and therapeutic repurposing. Front. Neurol. 16:1561000. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1561000
Received: 15 January 2025; Accepted: 17 March 2025;
Published: 02 April 2025.
Edited by:
Claudia Altamura, Fondazione Policlinico Campus Bio-Medico, ItalyReviewed by:
Emel Ur Ozcelik, Istanbul University, TürkiyeCopyright © 2025 Sun, Chen, Song, Gao and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sui-yi Xu, c3VpeWl4dUBzaW5hLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.