- 1Department of Family Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Neurology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Radiology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea
Background: Peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity (PSMD) is a novel marker of small vessel disease. This study aimed to investigate the presence of small vessel disease in patients with occipital lobe epilepsy (OLE) using PSMD.
Methods: We enrolled 27 patients newly diagnosed with OLE and included 29 healthy controls. The age and sex of the patients and controls were comparable. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) was performed using a 3 T MRI scanner. We measured the PSMD based on DTI in several steps, including preprocessing, skeletonization, application of a custom mask, and histogram analysis, using the FSL program. We compared PSMD between patients with OLE and healthy controls. Additionally, we performed a correlation analysis between PSMD and clinical factors in patients with OLE.
Results: Our findings revealed that the patients with OLE exhibited higher PSMD compared to healthy controls (2.459 vs. 2.079 × 10−4 mm2/s, p < 0.001). In addition, PSMD positively correlated with age (r = 0.412, p = 0.032). However, the PSMD of the patients with OLE was not associated with other clinical factors such as age at seizure onset and duration of epilepsy.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that patients with OLE had a higher PSMD than healthy controls, indicating evidence of small vessel disease in patients with OLE. This finding also highlights the potential of PSMD as a marker for detecting small vessel diseases in epileptic disorders.
1 Introduction
Occipital lobe epilepsy (OLE) is a relatively uncommon type of focal epilepsy, originating in the occipital lobe and accounting for approximately 2–8% of surgical cases (1). It can result from structural brain abnormalities, such as tumors, strokes, or hemorrhages. However, it also occurs as part of self-limited focal epilepsies in childhood, including self-limited epilepsy with autonomic seizures or childhood occipital visual epilepsy (2).
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequence that measures the diffusion of water molecules in tissues. Traditionally, DTI has been utilized in epilepsy surgery to define surgical margins using tractography (3). It also provides valuable insight into the microstructural integrity of white matter tracts, which cannot be visualized with conventional brain MRI (4, 5). DTI can facilitate calculations of fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) values, which serve as indicators of white matter microstructure. In patients with focal epilepsy, FA values generally increase, while MD values tend to decrease compared to healthy controls, with more pronounced changes observed on the ipsilateral side than the contralateral side (6). In addition, DTI can be used to investigate the structural connectivity of the brain. In patients with OLE, global integration is reduced, and alterations in local networks beyond the occipital lobe have been observed (7). Recently, DTI has been used to investigate the glymphatic system function of the brain, with dysfunction in this system identified in patients with OLE (8). Therefore, DTI is increasingly being used in both research and clinical practice, particularly for patients with epilepsy, including those with OLE.
Peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity (PSMD) is a recently proposed neuroimaging marker derived from DTI that serves as an objective index for quantifying white matter damage caused by small vessel disease (9, 10). PSMD can be fully automatically calculated in a short time and has shown a stronger correlation with cognitive impairment than conventional DTI measures such as FA or MD. As a result, active research using PSMD has been conducted in various neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, and dementia (11–15). However, white matter damage due to small vessel disease in patients with epilepsy, particularly OLE, has never been studied using PSMD.
Therefore, in this study, we aimed to investigate the degree of white matter damage due to small vessel disease in patients with OLE compared to healthy controls using PSMD. Additionally, we investigated the volumes of white matter hypointensities, which is another MRI marker for white matter damage based on T1-weighted imaging, in patients with OLE and compared them with healthy controls. We hypothesized that white matter damage in patients with OLE might be associated with small vessel disease than in the healthy control group.
2 Methods
2.1 Participants
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board, and informed consent was obtained from all participants. We enrolled 27 patients newly diagnosed with OLE according to the ILAE criteria (16, 17). Only patients whose ictal semiology clearly indicated OLE and whose electroencephalography showed ictal or interictal epileptiform discharges originating in the occipital lobe were included in this study. DTI and T1-weighted MRI was performed at the time of OLE diagnosis in the drug-naïve state. We excluded the following participants from this study: (1) those with structural lesions on brain MRI that could influence the results of imaging analysis, (2) those with any neurological diseases other than OLE, (3) those with risk factors for small vessel disease, such as diabetes, hypertension, or dyslipidemia, or (4) those who did not consent to participate in the study. We also enrolled 29 age- and sex-matched healthy controls who had not been diagnosed with any medical or neurological diseases. The healthy controls underwent DTI and T1-weighted MRI, and their brain MRI revealed no structural lesions. Like the patients, the healthy controls did not have the risk factors associated with small vessel disease.
2.2 DTI scan
All DTI and T1-weighted MRI scans were performed using a 3.0 T MRI scanner (AchievaTx; Phillips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands) equipped with a 32-channel head coil for both patients with OLE and healthy controls. The DTI scans utilized spin-echo single-shot echo-planar pulse sequences with 32 different diffusion directions (repetition time/echo time, 8,620/85 ms; flip angle, 90°; slice thickness, 2.25 mm, acquisition matrix, 120 × 120; field of view, 240 × 240 mm2; and b-value, 1,000 s/mm2). The three-dimensional T1-weighted images were scanned using the following parameters: inversion time = 1,300 ms, repetition time/echo time = 8.6/3.96 ms, flip angle = 8°, and isotropic voxel size = 1 mm3.
2.3 Obtaining the PSMD
Figure 1 shows the process for obtaining PSMD from DTI using the FSL program installed on a Linux system, involving a total of four steps (9, 10). The first step preprocesses the DTI, which includes motion and eddy current correction, brain extraction, and tensor fitting. The second step is skeletonization, which involves tract-based spatial statistics obtained by registering an FA map to the common space and projecting it onto the skeleton. The same transformation matrices were used for MD data to obtain a skeletonized MD map. The third step was the application of a custom mask using the template thresholded at an FA value of 0.3 and a custom-made mask. The fourth step was histogram analysis, in which the width of the histogram (the difference between 95 and 5) derived from the MD values of all voxels included in the skeleton was obtained.
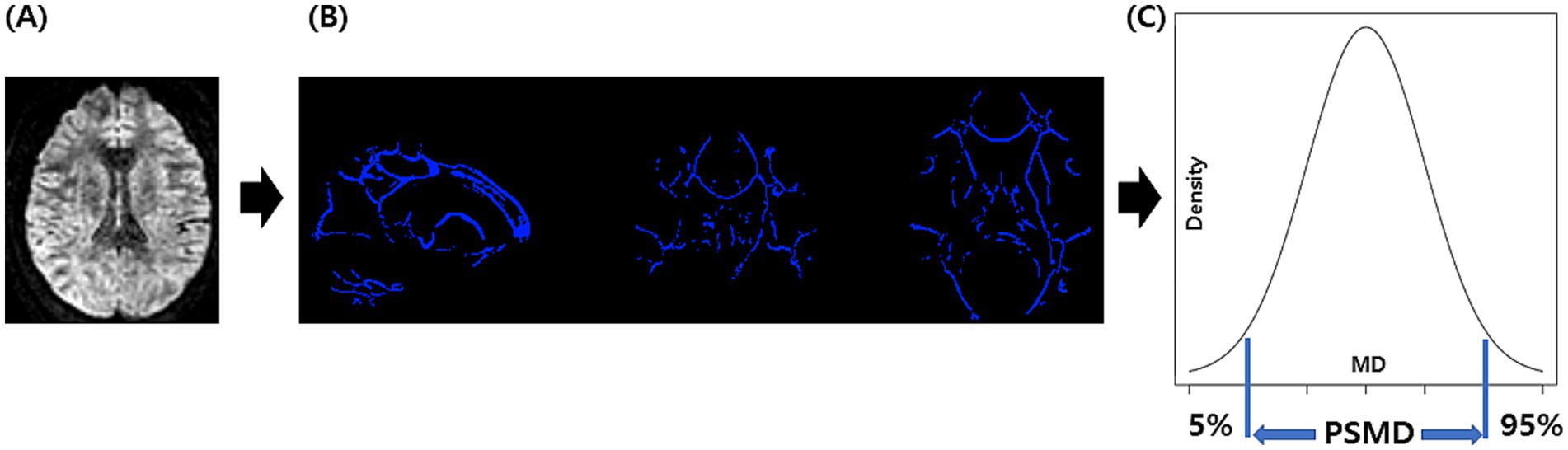
Figure 1. The process for obtaining PSMD: we perform DTI acquisition on the participants, followed by preprocessing steps including motion and eddy current correction, brain extraction, and tensor fitting (A). Subsequently, we conducted skeletonization, which included normalization, projection onto the skeleton template, and the application of a custom mask (B). Finally, we performed histogram analysis and calculated PSMD based on the difference between the 95th and 5th percentiles (C). PSMD, peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity.
2.4 White matter hypointensities segmentation
To segment white matter hypointensities from T1-weighted images and acquire the volumes of white matter hypointensities, we used WMH-SynthSeg (18), which provides segmentation for white matter hyper- or hypointensities from scans of any resolution and contrast without retraining, available as module in the development version of Freesurfer.
2.5 Statistical analysis
An independent sample t-test was used to compare age and PSMD values between patients with OLE and healthy controls. The Mann–Whitney test was used to compare the volumes of white matter hypointensities between the groups. The chi-square test was used to compare sex differences between the groups. Pearson’s correlation test was used for correlation analysis. The performance of the classification was evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Statistical significance was considered when the p-value was less at p < 0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using MedCalc® Statistical Software version 22.009 (MedCalc Software Ltd., Ostend, Belgium; https://www.medcalc.org; 2023).
3 Results
3.1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants
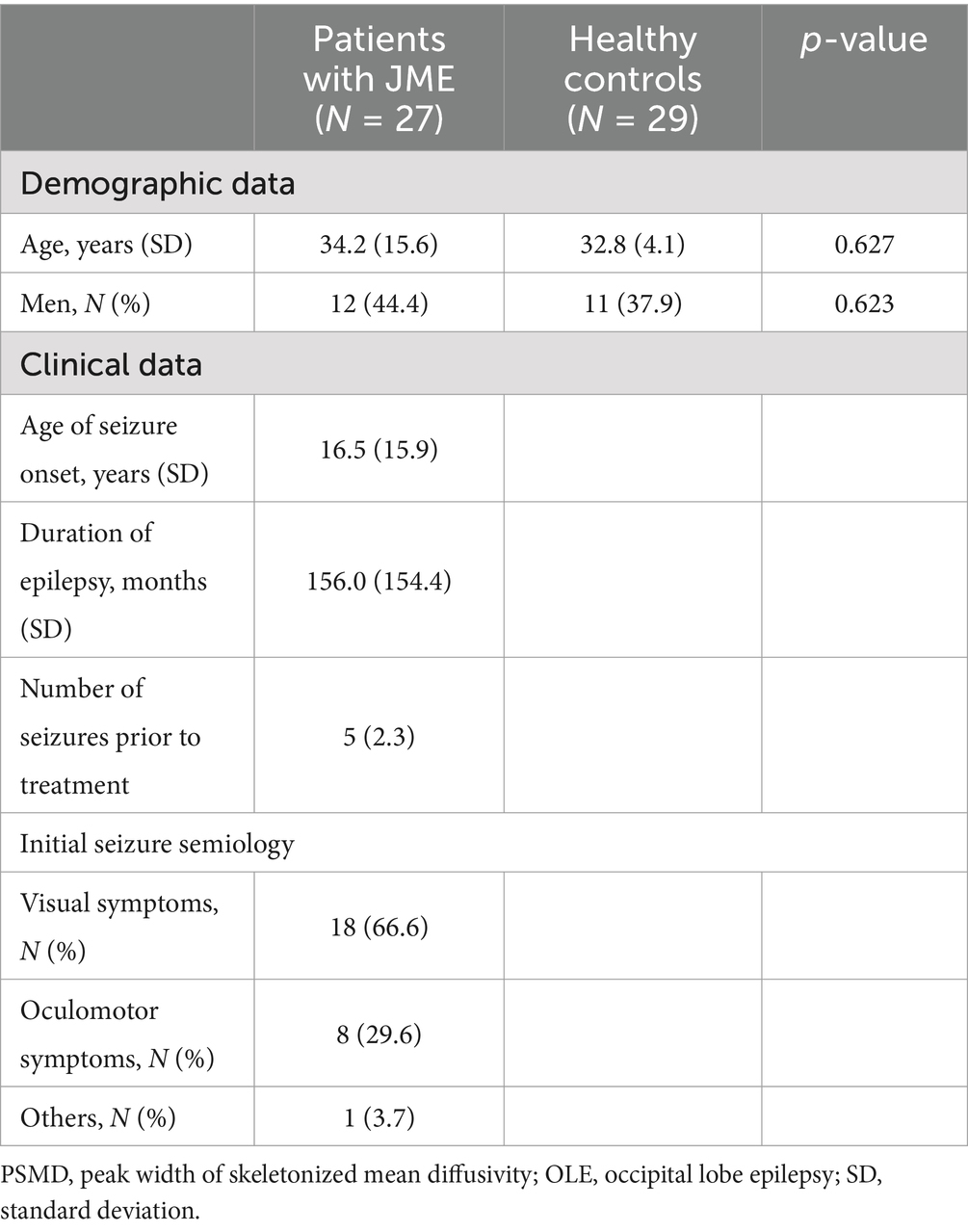
Table 1 shows the demographic data in the participants and clinical characteristics of patients with OLE. There were no significant differences in age or sex between the OLE patients and the healthy control group.
3.2 Difference in the PSMD between the groups
There was a significant difference in the PSMD between patients with OLE and healthy controls. The patients with OLE exhibited higher PSMD compared to healthy controls (2.459 vs. 2.079 × 10−4 mm2/s, p < 0.001) (Figure 2).
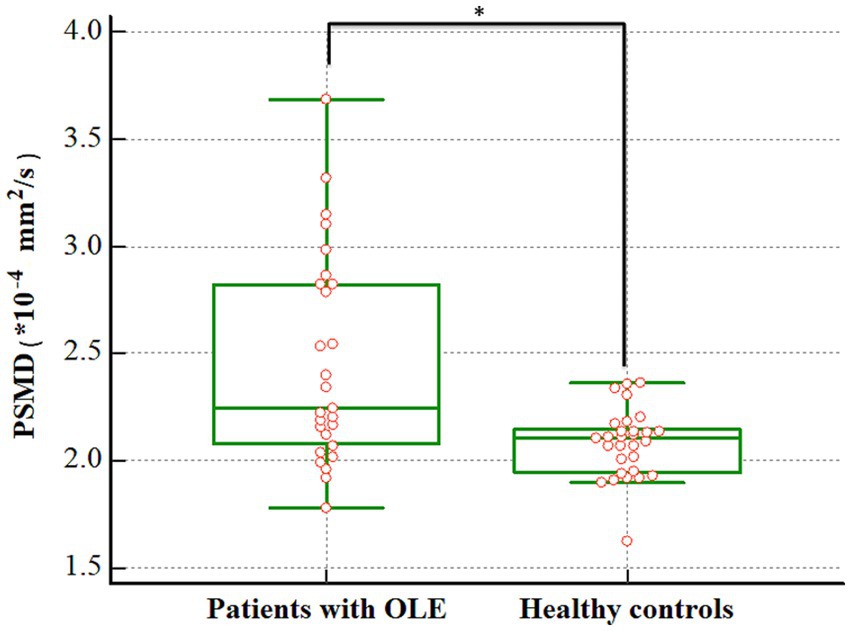
Figure 2. Difference in the PSMD between patients with OLE and healthy controls. The PSMD was higher in the OLE group than in the healthy control group (2.459 vs. 2.079 × 10−4 mm2/s, p < 0.001). PSMD, peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity; OLE, occipital lobe epilepsy. *p < 0.05.
3.3 Difference in the volumes of white matter hypointensities between the groups
The volumes of white matter hypointensities were higher in patients with OLE than that in the healthy controls [1309.6 (interquartile range, 1165.5–2793.2) vs. 1141.0 (interquartile range, 874.1–1298.9) mm3, p = 0.011].
3.4 ROC curve analysis
ROC curve analysis using PSMD showed an area under curve (AUC) of 0.747 in distinguishing the patients with OLE and healthy controls (p < 0.001). Additionally, ROC curve analysis using the volumes of white matter hypointensities revealed an AUC of 0.699 in distinguishing the groups (p = 0.005). Although the AUC using PSMD was higher than that of the volumes of white matter hypointensities, there were no significant difference in the comparison of AUC between PSMD and the volumes of white matter hypointensities in distinguishing the groups (p = 0.602) (Figure 3).
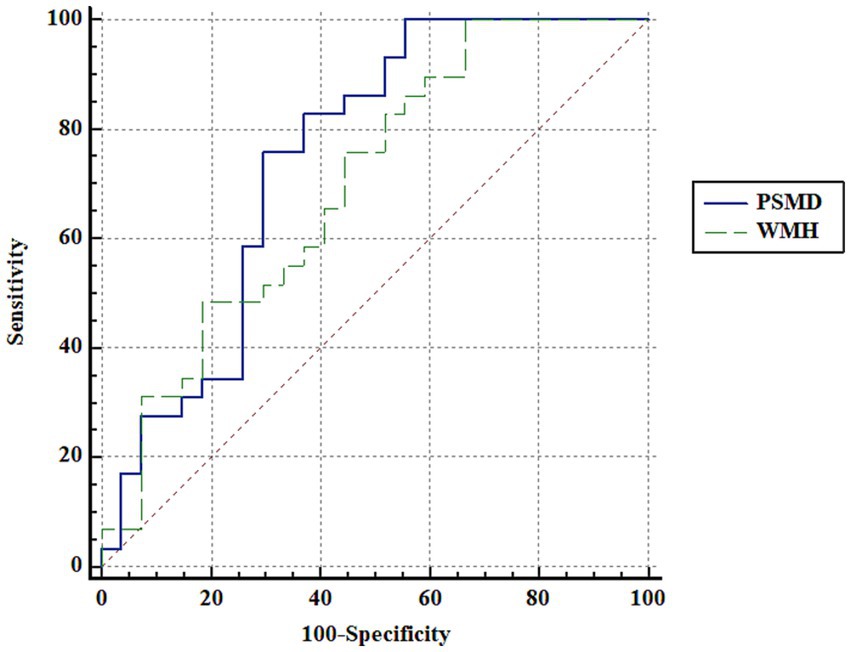
Figure 3. ROC curve analysis. ROC curve analysis using PSMD and the volumes of white matter hypointensities shows an area under curve (AUC) of 0.747 and 0.699, respectively, in distinguishing the patients with OLE and healthy controls. Although the AUC using PSMD is higher than that of the volumes of white matter hypointensities, there are no significant difference in the comparison of AUC between PSMD and the volumes of white matter hypointensities in distinguishing the groups (p = 0.602). PSMD, peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity; WMH, the volumes of white matter hypointensities.
3.5 Correlation between the PSMD and clinical characteristics
In patients with OLE, a positive correlation was observed between PSMD and age (r = 0.412, p = 0.032) (Figure 4). However, PSMD was not associated with other clinical factors, such as age at seizure onset (r = 0.082, p = 0.695), duration of epilepsy (r = −0.127, p = 0.545), and number of seizures prior to treatment (r = 0.058, p = 0.770).
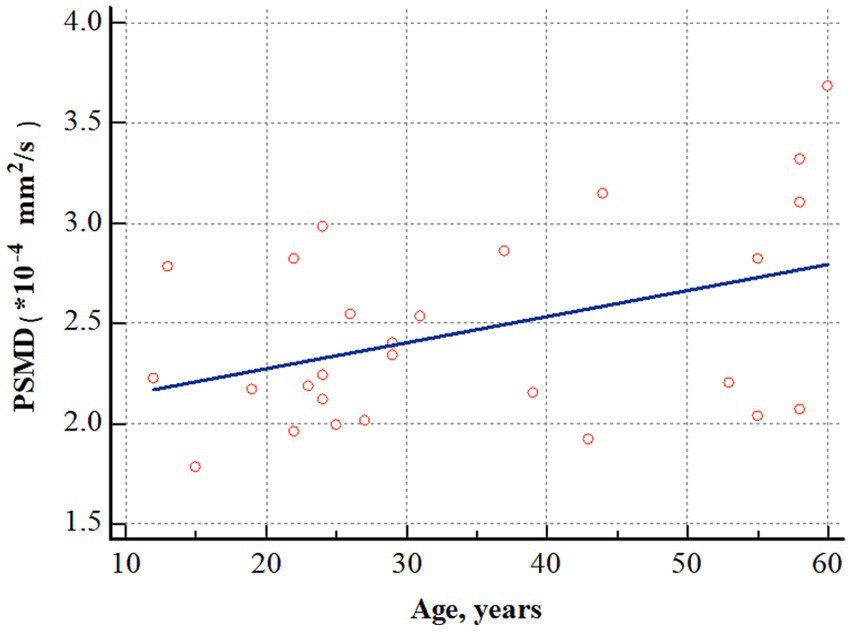
Figure 4. Correlation analysis between age and PSMD in patients with OLE. PSMD positively correlated with age (r = 0.412, p = 0.032). PSMD, peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity; OLE, occipital lobe epilepsy.
4 Discussion
This study is the first to demonstrate that PSMD is higher in patients with OLE than in healthy controls, indicating the presence of white matter damage due to small vessel disease in these patients. In addition, in patients with OLE, PSMD increases proportionally with age, confirming that small vessel disease progresses further with aging.
This study demonstrates the presence of white matter damage due to small vessel disease in patients with OLE, which aligns with previous studies. Maxwell et al. (19) investigated the presence of small vessel disease in 105 patients with epilepsy, particularly late-onset epilepsy, and 105 healthy controls. They used periventricular and subcortical white matter lesions as indicators of small vessel disease. They found that small vessel disease was present in 49.5% of patients with epilepsy, compared to 32.3% of the healthy controls, concluding that small vessel disease is more prevalent in individuals with epilepsy. Hanby et al. (19) analyzed white matter hyperintensities with automatic quantitation in patients with focal epilepsy and healthy controls, revealing higher white matter hyperintensities volume in patients with epilepsy (1,340 mm3) compared to controls (514 mm3) (20). Another study examined the correlation between the location of white matter lesions and the frequency of clinical symptoms such as stroke, seizure, vertigo, and gait apraxia. They reported that seizures were more frequent when lesions were located in the parieto-occipital lobe (21). This finding suggests an association between OLE and small vessel disease, similar to the present study. However, a previous study reported that epilepsy associated with leukoaraiosis was most closely related to the temporal lobe; therefore, further research is needed (22).
The cross-sectional design of this study makes it challenging to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between small vessel disease and OLE. Thus, two primary hypotheses were considered. The first hypothesis for the small vessel disease-OLE relationship is that small vessel disease may cause OLE. Previous animal experiments demonstrated in hypertensive rats that small vessel disease induced focal epilepsy more often than generalized epilepsy (23). It was observed that early treatment with enalapril could reduce the incidence of epilepsy in these animals, suggesting a role for small vessel disease in epileptogenesis (23). Additionally, studies on humans have demonstrated that hypertension is an independent risk factor for epilepsy (24, 25). Patients with hypertension are approximately twice as likely to develop epilepsy compared to those without, with those having uncontrolled hypertension being up to 10 times more likely to develop epilepsy (24, 25). Small vessel disease can cause endothelial dysfunction and blood-brain barrier leakage, leading to extravasation of serum proteins and inflammation, which may contribute to epileptogenesis. Diffuse cerebral microangiopathy can impair cerebral perfusion, leading to epileptogenesis via neurovascular uncoupling (26, 27).
Another hypothesis is that small vessel disease is caused by seizures that occur in patients with OLE. Recurrent seizures have shown to cause depolarization of pericytic mitochondria and subsequent vasoconstriction, resulting in small vessel disease, which is associated with impaired neurovascular coupling and increased blood-brain barrier permeability (28). Arteriole vasoconstriction, mediated by cyclooxygenase-2 and L-type calcium channels, plays an important role in hypoperfusion/hypoxia resulting from recurrent seizures (29). Furthermore, while the cerebral cortex is primarily involved in epileptic seizures, secondary changes in the cerebral white matter, including major association, commissural, and projection fibers, are well-documented. These changes are correlated with age of seizure onset and duration of epilepsy (30–32) and maybe induced by multiple mechanisms, including excitotoxicity with excessive glutamate release, inflammation response by microglia and astrocytes, oxidative stress by reactive oxygen species, and blood-brain barrier disruption (30–32).
We also confirmed that white matter damage due to small vessel disease worsened with age in patients with OLE. Several factors contribute to this worsening with age: endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerosis, increased reactive oxygen species, and chronic low-grade inflammation. The endothelium is located inside the blood vessels, and with aging, its function declines, making it difficult to maintain the integrity of the blood vessels and reducing its ability to regulate blood flow (33). Atherosclerosis is caused by the development of plaques in both large and small blood vessels. This plaque buildup impedes blood flow, increases vessel rigidity, and reduces perfusion (34). The increase in reactive oxygen species with age causes injury to the blood vessel walls (35). Finally, as we age, chronic low-grade inflammation occurs, which increases vessel stiffness and plaque formation, resulting in the destruction of the vascular endothelium (36). Through this study, we confirmed that small vessel disease worsens with age in patients with OLE, even in the absence of vascular risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia.
This study is the first to demonstrate white matter damage due to small vessel disease in patients with OLE. However, it has some limitations. The sample size, i.e., the number of patients enrolled in this study, was relatively small due to the rarity of OLE and the exclusion of patients with structural lesions that could affect DTI analysis. Additionally, to exclude the influence of anti-seizure medications on DTI measurements, only patients with their first diagnosis of epilepsy at the time of DTI imaging were enrolled. Another limitation of this study is the cross-sectional design, which did not allow us to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between small vessel disease and OLE. The study was conducted at a center specializing in epilepsy disorders; hence, the results cannot be generalized to all patients with epilepsy. In addition, the results were limited to OLE; therefore, further research with a larger sample size is needed for other focal epilepsy or generalized epilepsy. Lastly, we could not analyze the volumes of white matter hyperintensities, since some datasets lacked fluid attenuated inversion recovery images. Instead of the volumes of white matter hyperintensities, we analyzed the volumes of white matter hypointensites, which is another MRI marker for white matter damage based on T1-weighted imaging. Although the volumes of white matter hyperintensities are more accurate and widely used to assess white matter damage, they have strong correlation with the volumes of white matter hypointensites.
5 Conclusion
We demonstrated that patients with OLE had a higher PSMD than healthy controls, indicating the presence of small vessel disease in patients with OLE. This finding also highlights the potential of PSMD as a marker for detecting small vessel disease in epilepsy.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Haeundai Paik Institutional Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation because the study is based solely on existing data.
Author contributions
JK: Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. H-JL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KP: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant No. HR21C1003).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Blume, WT, Whiting, SE, and Girvin, JP. Epilepsy surgery in the posterior cortex. Ann Neurol. (1991) 29:638–45. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290611
2. Specchio, N, Wirrell, EC, Scheffer, IE, Nabbout, R, Riney, K, Samia, P, et al. International League Against Epilepsy classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset in childhood: position paper by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia. (2022) 63:1398–442. doi: 10.1111/epi.17241
3. Lilja, Y, and Nilsson, DT. Strengths and limitations of tractography methods to identify the optic radiation for epilepsy surgery. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2015) 5:288–99. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2015.01.08
4. Szmuda, M, Szmuda, T, Springer, J, Rogowska, M, Sabisz, A, Dubaniewicz, M, et al. Diffusion tensor tractography imaging in pediatric epilepsy—a systematic review. Neurol Neurochir Pol. (2016) 50:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.pjnns.2015.10.003
5. Leon-Rojas, J, Cornell, I, Rojas-Garcia, A, D'Arco, F, Panovska-Griffiths, J, Cross, H, et al. The role of preoperative diffusion tensor imaging in predicting and improving functional outcome in pediatric patients undergoing epilepsy surgery: a systematic review. BJR Open. (2021) 3:20200002. doi: 10.1259/bjro.20200002
6. Hatton, SN, Huynh, KH, Bonilha, L, Abela, E, Alhusaini, S, Altmann, A, et al. White matter abnormalities across different epilepsy syndromes in adults: an ENIGMA-epilepsy study. Brain. (2020) 143:2454–73. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa200
7. Lee, DA, Lee, HJ, and Park, KM. Structural brain network analysis in occipital lobe epilepsy. BMC Neurol. (2023) 23:268. doi: 10.1186/s12883-023-03326-z
8. Kim, J, Lee, DA, Lee, HJ, and Park, KM. Glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with occipital lobe epilepsy. J Neuroimaging. (2023) 33:455–61. doi: 10.1111/jon.13083
9. Zanon Zotin, MC, Yilmaz, P, Sveikata, L, Schoemaker, D, van Veluw, SJ, Etherton, MR, et al. Peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity: a neuroimaging marker for white matter injury. Radiology. (2023) 306:e212780. doi: 10.1148/radiol.212780
10. Baykara, E, Gesierich, B, Adam, R, Tuladhar, AM, Biesbroek, JM, Koek, HL, et al. A novel imaging marker for small vessel disease based on skeletonization of white matter tracts and diffusion histograms. Ann Neurol. (2016) 80:581–92. doi: 10.1002/ana.24758
11. Vinciguerra, C, Giorgio, A, Zhang, J, Di Donato, I, Stromillo, ML, Tappa Brocci, R, et al. Peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity (PSMD) as marker of widespread white matter tissue damage in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. (2019) 27:294–7. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2018.11.011
12. Jochems, ACC, Muñoz Maniega, S, Clancy, U, Jaime Garcia, D, Arteaga, C, Hewins, W, et al. Associations of peak-width skeletonized mean diffusivity and post-stroke. Cognition Life. (2022) 12:1362. doi: 10.3390/life12091362
13. Zanon Zotin, MC, Schoemaker, D, Raposo, N, Perosa, V, Bretzner, M, Sveikata, L, et al. Peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity in cerebral amyloid angiopathy: spatial signature, cognitive, and neuroimaging associations. Front Neurosci. (2022) 16:1051038. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1051038
14. Low, A, Mak, E, Stefaniak, JD, Malpetti, M, Nicastro, N, Savulich, G, et al. Peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity as a marker of diffuse cerebrovascular damage. Front Neurosci. (2020) 14:238. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00238
15. Lam, BYK, Leung, KT, Yiu, B, Zhao, L, Biesbroek, JM, Au, L, et al. Peak width of skeletonized mean diffusivity and its association with age-related cognitive alterations and vascular risk factors. Alzheimers Dement. (2019) 11:721–9. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2019.09.003
16. Sveinbjornsdottir, S, and Duncan, JS. Parietal and occipital lobe epilepsy: a review. Epilepsia. (1993) 34:493–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1993.tb02590.x
17. Angus-Leppan, H, and Clay, TA. Adult occipital lobe epilepsy: 12-years on. J Neurol. (2021) 268:3926–34. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10557-y
18. Laso, P, Cerri, S, Sorby-Adams, A, Guo, J, Mateen, F, Goebl, P, et al. (2024). Quantifying white matter hyperintensity and brain volumes in heterogeneous clinical and low-field portable MRI. 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI): IEEE.
19. Maxwell, H, Hanby, M, Parkes, LM, Gibson, LM, Coutinho, C, and Emsley, HC. Prevalence and subtypes of radiological cerebrovascular disease in late-onset isolated seizures and epilepsy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2013) 115:591–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.07.009
20. Hanby, MF, Al-Bachari, S, Makin, F, Vidyasagar, R, Parkes, LM, and Emsley, HC. Structural and physiological MRI correlates of occult cerebrovascular disease in late-onset epilepsy. NeuroImage Clin. (2015) 9:128–33. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.07.016
21. Okroglic, S, Widmann, CN, Urbach, H, Scheltens, P, and Heneka, MT. Clinical symptoms and risk factors in cerebral microangiopathy patients. PLoS One. (2013) 8:e53455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053455
22. Gasparini, S, Ferlazzo, E, Beghi, E, Sofia, V, Mumoli, L, Labate, A, et al. Epilepsy associated with leukoaraiosis mainly affects temporal lobe: a casual or causal relationship? Epilepsy Res. (2015) 109:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.10.012
23. Russo, E, Leo, A, Scicchitano, F, Donato, A, Ferlazzo, E, Gasparini, S, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease predisposes to temporal lobe epilepsy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res Bull. (2017) 130:245–50. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.02.003
24. Ng, SK, Hauser, WA, Brust, JC, and Susser, M. Hypertension and the risk of new-onset unprovoked seizures. Neurology. (1993) 43:425–8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.2.425
25. Li, X, Breteler, MM, de Bruyne, MC, Meinardi, H, Hauser, WA, and Hofman, A. Vascular determinants of epilepsy: the Rotterdam Study. Epilepsia. (1997) 38:1216–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1997.tb01219.x
26. Gibson, LM, Allan, SM, Parkes, LM, and Emsley, HC. Occult cerebrovascular disease and late-onset epilepsy: could loss of neurovascular unit integrity be a viable model? Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol. (2011) 2011:130406:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2011/130406
27. de Souza, A, and Tasker, K. Inflammatory cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a broad clinical spectrum. J Clin Neurol. (2023) 19:230–41. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2022.0493
28. Prager, O, Kamintsky, L, Hasam-Henderson, LA, Schoknecht, K, Wuntke, V, Papageorgiou, I, et al. Seizure-induced microvascular injury is associated with impaired neurovascular coupling and blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Epilepsia. (2019) 60:322–36. doi: 10.1111/epi.14631
29. Farrell, JS, Colangeli, R, Wolff, MD, Wall, AK, Phillips, TJ, George, A, et al. Postictal hypoperfusion/hypoxia provides the foundation for a unified theory of seizure-induced brain abnormalities and behavioral dysfunction. Epilepsia. (2017) 58:1493–501. doi: 10.1111/epi.13827
30. Hogan, RE. Epilepsy as a disease of white matter. Epilepsy Curr. (2021) 21:27–9. doi: 10.1177/1535759720975744
31. Ran, H, Chen, G, Ran, C, He, Y, Xie, Y, Yu, Q, et al. Altered white-matter functional network in children with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Acad Radiol. (2024) 31:2930–41. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.12.043
32. Hou, XX, Feng, HX, Xu, B, Li, ZS, Lu, YL, Zhao, HM, et al. A tract-based spatial statistics study of white matter integrity in epilepsy. Am J Transl Res. (2022) 14:8980–90.
33. Cheng, X, Potenza, DM, Brenna, A, Ajalbert, G, Yang, Z, and Ming, XF. Aging increases hypoxia-induced endothelial permeability and blood-brain barrier dysfunction by upregulating arginase-II. Aging Dis. (2024) 15:2710. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1225
34. Ma, S, Xie, X, Yuan, R, Xin, Q, Miao, Y, Leng, SX, et al. Vascular aging and atherosclerosis: a perspective on aging. Aging Dis. (2024) 16:33–48. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0201-1
35. MohanKumar, SMJ, Murugan, A, Palaniyappan, A, and MohanKumar, PS. Role of cytokines and reactive oxygen species in brain aging. Mech Ageing Dev. (2023) 214:111855. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2023.111855
Keywords: epilepsy, diffusion tensor imaging, cerebral small vessel diseases, white matter, neuroimaging
Citation: Kim J, Lee DA, Lee H-J and Park KM (2025) Small-vessel-disease-induced white matter damage in occipital lobe epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 16:1538598. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1538598
Edited by:
Jieqiong Wang, Chinese Academy of Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Jin-Ming Zhang, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, United StatesHongmiao Yu, Nationwide Children’s Hospital, United States
Copyright © 2025 Kim, Lee, Lee and Park. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kang Min Park, c21pbGVwa21AaGFubWFpbC5uZXQ=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jinseung Kim
Jinseung Kim Dong Ah Lee
Dong Ah Lee Ho-Joon Lee
Ho-Joon Lee Kang Min Park
Kang Min Park